User login
Efficacy of Subcutaneous Semaglutide Dose Escalation in Reducing Insulin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Efficacy of Subcutaneous Semaglutide Dose Escalation in Reducing Insulin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic disease becoming more prevalent each year and is the seventh-leading cause of death in the United States.1 The most common reason for hospitalization for patients with T2DM is uncontrolled glycemic levels.2 Nearly 25% of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patient population has T2DM.3 T2DM is the leading cause of blindness, end-stage renal disease, and amputation for VA patients.4
According to the 2023 American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines, treatment goals of T2DM include eliminating symptoms, preventing or delaying complications, and attaining glycemic goals. A typical hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) goal range is < 7%, but individual goals can vary up to < 9% due to a multitude of factors, including patient comorbidities and clinical status.5
Initial treatment recommendations are nonpharmacologic and include comprehensive lifestyle interventions such as optimizing nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral therapy. When pharmacologic therapy is required, metformin is the preferred first-line treatment for the majority of newly diagnosed patients with T2DM and should be added to continued lifestyle management.5 If HbA1c levels remains above goal, the 2023 ADA guidelines recommend adding a second medication, including but not limited to insulin, a glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), or a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor. Medication choice is largely based on the patient’s concomitant conditions (eg, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease). The 2023 ADA guidelines suggest initiating insulin therapy when a patient's blood glucose ≥ 300 mg/dL, HbA1c > 10%, or if the patient has symptoms of hyperglycemia, even at initial diagnosis. Initiating medications to minimize or avoid hypoglycemia is a priority, especially in high-risk individuals.5
Clinical evidence shows that GLP-1RAs may provide similar glycemic control to insulin with lower risk of hypoglycemia.6 Other reported benefits of GLP-1RAs include weight loss, blood pressure reduction, and improved lipid levels. The most common adverse events (AEs) with GLP-1RAs are gastrointestinal. Including GLP-1RAs in T2DM pharmacotherapy may lower the risk of hypoglycemia, especially in patients at high risk of hypoglycemia.
The 2023 ADA guidelines indicate that it is appropriate to initiate GLP-]1RAs in patients on insulin.5 However, while GLP-1RAs do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia independently, combination treatment with GLP-1RAs and insulin can still result in hypoglycemia.6 Insulin is the key suspect of this hypoglycemic risk.7 Thus, if insulin dosage can be reduced or discontinued, this might reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
The literature is limited on how the addition of a GLP-1RA to insulin treatment will affect the patient's daily insulin doses, particularly for the veteran population. The goal of this study is to examine this gap in current research by examining semaglutide, which is the current formulary preferred GLP-1RA at the VA.
Semaglutide is subcutaneously initiated at a dose of 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks to reduce gastrointestinal symptoms, then increased to 0.5 mg weekly. Additional increases to a maintenance dose of 1 mg or 2 mg weekly can occur to achieve glycemic goals. The SUSTAIN-FORTE randomized controlled trial sought to determine whether there was a difference in HbA1c level reduction and significant weight loss with the 2-mg vs 1-mg dose.8 Patients in the trial were taking metformin but needed additional medication to control their HbA1c. They were not using insulin and may or may not have been taking sulfonylureas prior to semaglutide initiation. Semaglutide 2 mg was found to significantly improve HbA1c control and promote weight loss compared with semaglutide 1 mg, while maintaining a similar safety profile.
Because this study involved patients who required additional HbA1c control, although semaglutide reduced HbA1c, not all patients were able to reduce their other diabetes medications, which depended on the baseline HbA1c level and the level upon completion of semaglutide titration. Dose reductions for the patients’ other T2DM medications were not reported at trial end. SUSTAIN-FORTE established titration up to semaglutide 2 mg as effective for HbA1c reduction, although it did not study patients also on insulin.8
Insulin is associated with hypoglycemic risk, weight gain, and other AEs.7,8 This study analyzed whether increasing semaglutide could reduce insulin doses and therefore reduce risk of AEs in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A retrospective, single-center, chart review was conducted at VA Sioux Falls Health Care System (VASFHCS). Data were collected through manual review of VASFHCS electronic medical records. Patients aged ≥ 18 years with active prescriptions for at least once-daily insulin who were initiated on 2-mg weekly dose of semaglutide at the VASFHCS clinical pharmacy practitioner medication management clinic between January 1, 2021, and September 1, 2023, were included. VASFHCS clinical pharmacy practitioners have a scope of practice that allows them to initiate, modify, or discontinue medication therapy within medication management clinics.
The most frequently used prandial insulin at VASFHCS is insulin aspart, and the most frequently used basal insulin is insulin glargine. Patients were retrospectively monitored as they progressed from baseline (the point in time where semaglutide 0.5 mg was initiated) to ≥ 3 months on semaglutide 2-mg therapy. Patients were excluded if they previously used a GLP-1RA or if they were on sliding scale insulin without an exact daily dosage.
The primary endpoint was the percent change in total daily insulin dose from baseline to each dose increase after receiving semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months. Secondary endpoints included changes in daily prandial insulin dose, daily basal insulin dose, HbA1c, and number of hypoglycemic events reported. Data collected included age, race, weight, body mass index, total daily prandial insulin dose, total daily basal insulin dose, HbA1c, and hypoglycemic events reported at the visit when semaglutide was initiated.
Statistical Analysis
The sample size was calculated prior to data collection, and it was determined that for α = .05, 47 patients were needed to achieve 95% power. The primary endpoint was assessed using a paired t test, as were each secondary endpoint. Results with P < .05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
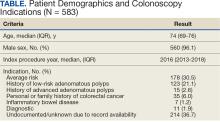
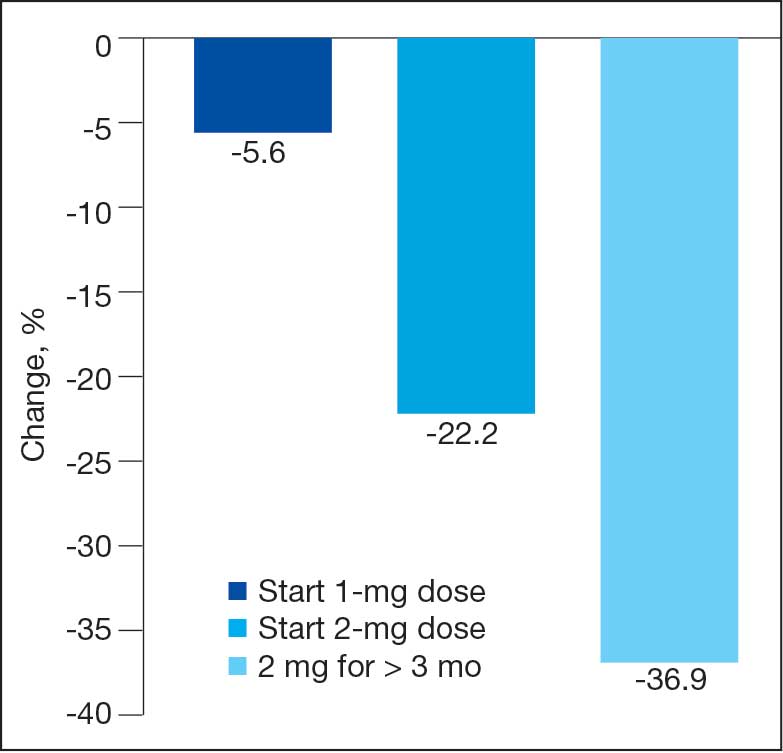
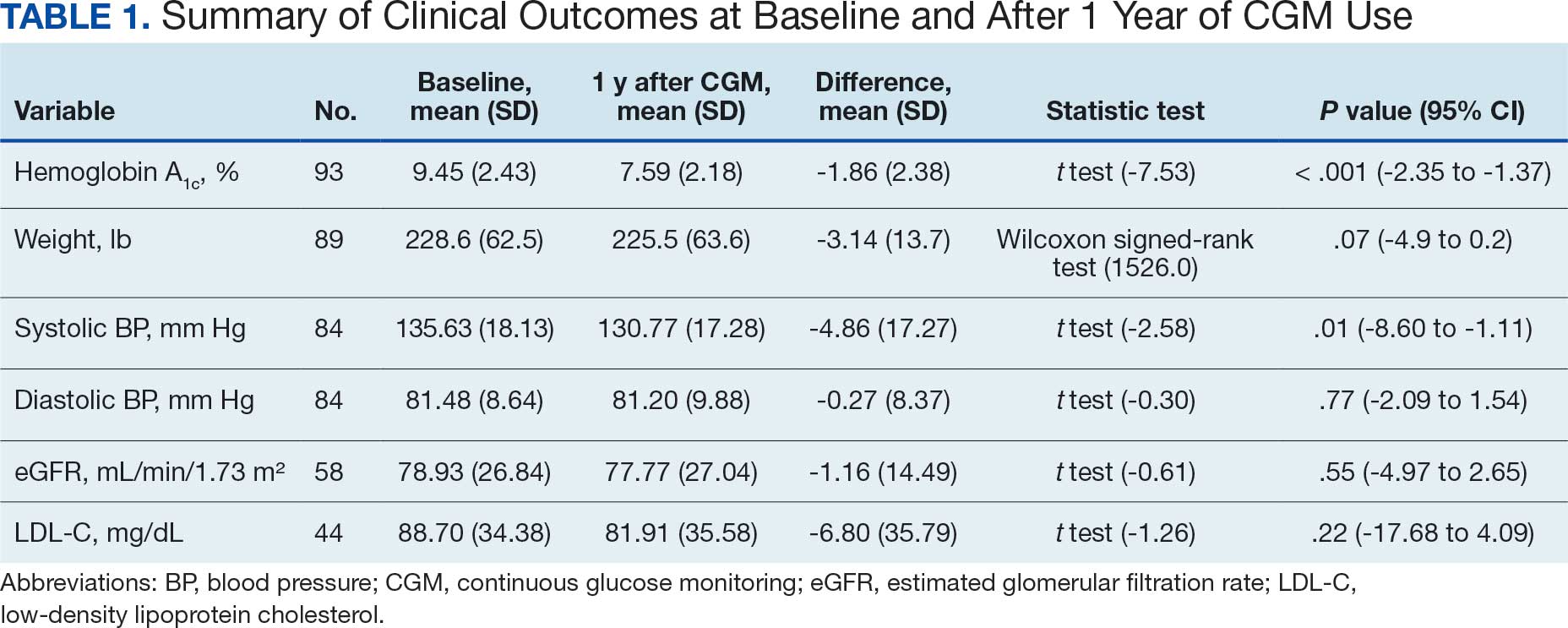
Sixty-two patients were included. The mean HbA1c level at baseline was 7.7%, the baseline mean prandial and insulin daily doses were 41.5 units and 85.1 units, respectively (Table 1) From baseline to initiation of a semaglutide 1-mg dose, the daily insulin dose changed –5.6% (95% CI, 2.2-14.0; P = .008). From baseline to 2-mg dose initiation daily insulin changed -22.2% (95% CI, 22.0-35.1; P < .001) and for patients receiving semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months it changed -36.9% (95% CI, 37.4-56.5; P < .001) (Figure).

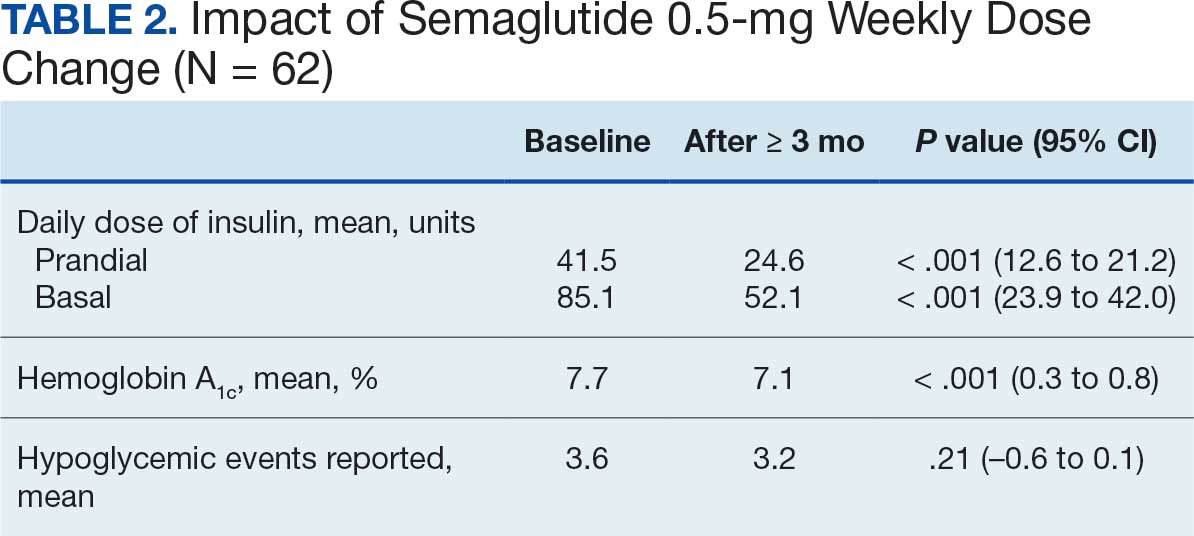
After receiving the 2-mg dose for ≥ 3 months, the mean daily dose of prandial insulin decreased from 41.5 units to 24.6 units (95% CI, 12.6-21.2; P < .001); mean daily dose of basal insulin decreased from 85.1 units to 52.1 units (95% CI, 23.9-42.0; P < .001); and mean HbA1c level decreased from 7.7% to 7.1% (95% CI, 0.3-0.8; P < .001). Mean number of hypoglycemic events reported was not statistically significant, changing from 3.6 to 3.2 (95% CI, –0.6 to 0.1; P = .21) (Table 2).
Discussion
This study investigated the effect of subcutaneous semaglutide dose escalation on total daily insulin dose for patients with T2DM. There was a statistically significant decrease in total daily insulin dose from baseline to 1 mg initiation; this decrease continued with further insulin dose reduction seen at the 2-mg dose initiation and additional insulin dose reduction at ≥ 3 months at this dose. It was hypothesized there would be a significant total daily insulin dose reduction at some point, especially when transitioning from the semaglutide 1-mg to the 2-mg dose, based on previous research. 9,10 The additional reduction in daily insulin dose when continuing on semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months was an unanticipated but added benefit, showing that if tolerated, maintaining the 2-mg dose will help patients reduce their insulin doses.
In terms of secondary endpoints, there was a statistically significant decrease in mean total daily dose individually for prandial and basal insulin from baseline to ≥ 3 months after semaglutide 2 mg initiation. The change in HbA1c level was also statistically significant and decreased from baseline, even as insulin doses were reduced. This change in HbA1c level was expected; previous literature has shown a significant link between improving HbA1c control when semaglutide doses are increased to 2 mg weekly.10 Due to having been shown in previous trials, it was expected that HbA1c levels would decrease even when the insulin doses were being reduced.10 Insulin dose reduction can potentially be added to the growing evidence of semaglutide benefits. The change in the number of hypoglycemic events was not statistically significant, which was unexpected since previous research show a trend in patients taking GLP-1RAs having fewer hypoglycemic events than those taking insulin.6 Further investigation with a larger sample size and prospective trial could determine whether this result is an outlier. In this study, there was no increase in HbA1c or hypoglycemic events reported with increasing semaglutide doses, which provides further evidence of the safety of semaglutide even at higher doses.
These data suggest that for a patient with T2DM who is already taking insulin, the recommended titration of semaglutide is to start with 0.5 mg and titrate up to a 2-mg subcutaneous weekly dose and to then continue at that dose. As long as the 2-mg dose is tolerated, it will provide patients with the most HbA1c control and lead to a reduction of their total daily insulin doses according to these results.
Strengths and Limitations
This study compared patient data at different points. This method did not require a second distinct control group, which would potentially introduce confounding factors, such as different baseline characteristics. Another strength is that documentation was available for all patients throughout the study so no one was lost to follow-up. This allowed comprehensive data collection and provided a stronger conclusion given the completeness of the data from baseline to follow-up.
Limitations include the retrospective design and small sample size. In addition, the study design did not allow for randomization. There is no documentation of adherence to medication regimen, which was difficult to determine due to the retrospective nature. Other changes to the patients’ medication regimen were not collected in aggregate and thus, it is possible the total daily insulin dose was impacted by other medication changes. There is also potential for inconsistent documentation of the patients’ true total daily insulin dose in the medical record, thus leading to inaccuracy of recorded data.
Conclusions
A small sample of veterans with T2DM had statistically significant reductions in total daily insulin dose when subcutaneous semaglutide was initiated, as well as after each dose increase. There was also a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c levels from baseline even as patient insulin doses were reduced. These results support the current practice of using semaglutide to treat T2DM, suggesting it may be safe and effective at reducing HbA1c levels as the dose is titrated up to 2 mg. There was no statistically significant change in the number of hypoglycemic events reported as semaglutide was titrated up. Thus, when semaglutide is increased to the maximum recommended dose of 2 mg for T2DM, patients may experience a reduction of their total daily dose of insulin and HbA1c levels. These benefits may reduce the risk of insulin-related AEs while maintaining appropriate glycemic control.
- Diabetes mellitus: in federal health care data trends 2017. Fed Pract. 2017:S20. Accessed August 6, 2025. https://www.fedprac-digital.com/federalpractitioner/data_trends_2017
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report. May 15, 2024. Accessed September 17, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on diabetes. Updated January 15, 2021. Accessed August 6, 2025. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/diabetes.cfm
- Liu Y, Sayam S, Shao X, et al. Prevalence of and trends in diabetes among veterans, United States, 2005-2014. Prev Chronic Dis. 2017;14:E135. doi:10.5888/pcd14.170230
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes. 2022;41:4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Zhao Z, Tang Y, Hu Y, Zhu H, Chen X, Zhao B. Hypoglycemia following the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a real-world analysis of post-marketing surveillance data. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9:1482. doi:10.21037/atm-21-4162
- Workgroup on Hypoglycemia, American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: a report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1245-1249. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.5.1245
- Frías JP, Auerbach P, Bajaj HS, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide 2.0 mg versus 1.0 mg in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN FORTE): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3B trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9:563-574. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00174-1
- Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm - 2020 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2020;26:107-139. doi:10.4158/CS-2019-0472
- Miles KE, Kerr JL. Semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pharm Technol. 2018;34:281-289. doi:10.1177/8755122518790925
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic disease becoming more prevalent each year and is the seventh-leading cause of death in the United States.1 The most common reason for hospitalization for patients with T2DM is uncontrolled glycemic levels.2 Nearly 25% of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patient population has T2DM.3 T2DM is the leading cause of blindness, end-stage renal disease, and amputation for VA patients.4
According to the 2023 American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines, treatment goals of T2DM include eliminating symptoms, preventing or delaying complications, and attaining glycemic goals. A typical hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) goal range is < 7%, but individual goals can vary up to < 9% due to a multitude of factors, including patient comorbidities and clinical status.5
Initial treatment recommendations are nonpharmacologic and include comprehensive lifestyle interventions such as optimizing nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral therapy. When pharmacologic therapy is required, metformin is the preferred first-line treatment for the majority of newly diagnosed patients with T2DM and should be added to continued lifestyle management.5 If HbA1c levels remains above goal, the 2023 ADA guidelines recommend adding a second medication, including but not limited to insulin, a glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), or a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor. Medication choice is largely based on the patient’s concomitant conditions (eg, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease). The 2023 ADA guidelines suggest initiating insulin therapy when a patient's blood glucose ≥ 300 mg/dL, HbA1c > 10%, or if the patient has symptoms of hyperglycemia, even at initial diagnosis. Initiating medications to minimize or avoid hypoglycemia is a priority, especially in high-risk individuals.5
Clinical evidence shows that GLP-1RAs may provide similar glycemic control to insulin with lower risk of hypoglycemia.6 Other reported benefits of GLP-1RAs include weight loss, blood pressure reduction, and improved lipid levels. The most common adverse events (AEs) with GLP-1RAs are gastrointestinal. Including GLP-1RAs in T2DM pharmacotherapy may lower the risk of hypoglycemia, especially in patients at high risk of hypoglycemia.
The 2023 ADA guidelines indicate that it is appropriate to initiate GLP-]1RAs in patients on insulin.5 However, while GLP-1RAs do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia independently, combination treatment with GLP-1RAs and insulin can still result in hypoglycemia.6 Insulin is the key suspect of this hypoglycemic risk.7 Thus, if insulin dosage can be reduced or discontinued, this might reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
The literature is limited on how the addition of a GLP-1RA to insulin treatment will affect the patient's daily insulin doses, particularly for the veteran population. The goal of this study is to examine this gap in current research by examining semaglutide, which is the current formulary preferred GLP-1RA at the VA.
Semaglutide is subcutaneously initiated at a dose of 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks to reduce gastrointestinal symptoms, then increased to 0.5 mg weekly. Additional increases to a maintenance dose of 1 mg or 2 mg weekly can occur to achieve glycemic goals. The SUSTAIN-FORTE randomized controlled trial sought to determine whether there was a difference in HbA1c level reduction and significant weight loss with the 2-mg vs 1-mg dose.8 Patients in the trial were taking metformin but needed additional medication to control their HbA1c. They were not using insulin and may or may not have been taking sulfonylureas prior to semaglutide initiation. Semaglutide 2 mg was found to significantly improve HbA1c control and promote weight loss compared with semaglutide 1 mg, while maintaining a similar safety profile.
Because this study involved patients who required additional HbA1c control, although semaglutide reduced HbA1c, not all patients were able to reduce their other diabetes medications, which depended on the baseline HbA1c level and the level upon completion of semaglutide titration. Dose reductions for the patients’ other T2DM medications were not reported at trial end. SUSTAIN-FORTE established titration up to semaglutide 2 mg as effective for HbA1c reduction, although it did not study patients also on insulin.8
Insulin is associated with hypoglycemic risk, weight gain, and other AEs.7,8 This study analyzed whether increasing semaglutide could reduce insulin doses and therefore reduce risk of AEs in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A retrospective, single-center, chart review was conducted at VA Sioux Falls Health Care System (VASFHCS). Data were collected through manual review of VASFHCS electronic medical records. Patients aged ≥ 18 years with active prescriptions for at least once-daily insulin who were initiated on 2-mg weekly dose of semaglutide at the VASFHCS clinical pharmacy practitioner medication management clinic between January 1, 2021, and September 1, 2023, were included. VASFHCS clinical pharmacy practitioners have a scope of practice that allows them to initiate, modify, or discontinue medication therapy within medication management clinics.
The most frequently used prandial insulin at VASFHCS is insulin aspart, and the most frequently used basal insulin is insulin glargine. Patients were retrospectively monitored as they progressed from baseline (the point in time where semaglutide 0.5 mg was initiated) to ≥ 3 months on semaglutide 2-mg therapy. Patients were excluded if they previously used a GLP-1RA or if they were on sliding scale insulin without an exact daily dosage.
The primary endpoint was the percent change in total daily insulin dose from baseline to each dose increase after receiving semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months. Secondary endpoints included changes in daily prandial insulin dose, daily basal insulin dose, HbA1c, and number of hypoglycemic events reported. Data collected included age, race, weight, body mass index, total daily prandial insulin dose, total daily basal insulin dose, HbA1c, and hypoglycemic events reported at the visit when semaglutide was initiated.
Statistical Analysis
The sample size was calculated prior to data collection, and it was determined that for α = .05, 47 patients were needed to achieve 95% power. The primary endpoint was assessed using a paired t test, as were each secondary endpoint. Results with P < .05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Sixty-two patients were included. The mean HbA1c level at baseline was 7.7%, the baseline mean prandial and insulin daily doses were 41.5 units and 85.1 units, respectively (Table 1) From baseline to initiation of a semaglutide 1-mg dose, the daily insulin dose changed –5.6% (95% CI, 2.2-14.0; P = .008). From baseline to 2-mg dose initiation daily insulin changed -22.2% (95% CI, 22.0-35.1; P < .001) and for patients receiving semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months it changed -36.9% (95% CI, 37.4-56.5; P < .001) (Figure).


After receiving the 2-mg dose for ≥ 3 months, the mean daily dose of prandial insulin decreased from 41.5 units to 24.6 units (95% CI, 12.6-21.2; P < .001); mean daily dose of basal insulin decreased from 85.1 units to 52.1 units (95% CI, 23.9-42.0; P < .001); and mean HbA1c level decreased from 7.7% to 7.1% (95% CI, 0.3-0.8; P < .001). Mean number of hypoglycemic events reported was not statistically significant, changing from 3.6 to 3.2 (95% CI, –0.6 to 0.1; P = .21) (Table 2).

Discussion
This study investigated the effect of subcutaneous semaglutide dose escalation on total daily insulin dose for patients with T2DM. There was a statistically significant decrease in total daily insulin dose from baseline to 1 mg initiation; this decrease continued with further insulin dose reduction seen at the 2-mg dose initiation and additional insulin dose reduction at ≥ 3 months at this dose. It was hypothesized there would be a significant total daily insulin dose reduction at some point, especially when transitioning from the semaglutide 1-mg to the 2-mg dose, based on previous research. 9,10 The additional reduction in daily insulin dose when continuing on semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months was an unanticipated but added benefit, showing that if tolerated, maintaining the 2-mg dose will help patients reduce their insulin doses.
In terms of secondary endpoints, there was a statistically significant decrease in mean total daily dose individually for prandial and basal insulin from baseline to ≥ 3 months after semaglutide 2 mg initiation. The change in HbA1c level was also statistically significant and decreased from baseline, even as insulin doses were reduced. This change in HbA1c level was expected; previous literature has shown a significant link between improving HbA1c control when semaglutide doses are increased to 2 mg weekly.10 Due to having been shown in previous trials, it was expected that HbA1c levels would decrease even when the insulin doses were being reduced.10 Insulin dose reduction can potentially be added to the growing evidence of semaglutide benefits. The change in the number of hypoglycemic events was not statistically significant, which was unexpected since previous research show a trend in patients taking GLP-1RAs having fewer hypoglycemic events than those taking insulin.6 Further investigation with a larger sample size and prospective trial could determine whether this result is an outlier. In this study, there was no increase in HbA1c or hypoglycemic events reported with increasing semaglutide doses, which provides further evidence of the safety of semaglutide even at higher doses.
These data suggest that for a patient with T2DM who is already taking insulin, the recommended titration of semaglutide is to start with 0.5 mg and titrate up to a 2-mg subcutaneous weekly dose and to then continue at that dose. As long as the 2-mg dose is tolerated, it will provide patients with the most HbA1c control and lead to a reduction of their total daily insulin doses according to these results.
Strengths and Limitations
This study compared patient data at different points. This method did not require a second distinct control group, which would potentially introduce confounding factors, such as different baseline characteristics. Another strength is that documentation was available for all patients throughout the study so no one was lost to follow-up. This allowed comprehensive data collection and provided a stronger conclusion given the completeness of the data from baseline to follow-up.
Limitations include the retrospective design and small sample size. In addition, the study design did not allow for randomization. There is no documentation of adherence to medication regimen, which was difficult to determine due to the retrospective nature. Other changes to the patients’ medication regimen were not collected in aggregate and thus, it is possible the total daily insulin dose was impacted by other medication changes. There is also potential for inconsistent documentation of the patients’ true total daily insulin dose in the medical record, thus leading to inaccuracy of recorded data.
Conclusions
A small sample of veterans with T2DM had statistically significant reductions in total daily insulin dose when subcutaneous semaglutide was initiated, as well as after each dose increase. There was also a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c levels from baseline even as patient insulin doses were reduced. These results support the current practice of using semaglutide to treat T2DM, suggesting it may be safe and effective at reducing HbA1c levels as the dose is titrated up to 2 mg. There was no statistically significant change in the number of hypoglycemic events reported as semaglutide was titrated up. Thus, when semaglutide is increased to the maximum recommended dose of 2 mg for T2DM, patients may experience a reduction of their total daily dose of insulin and HbA1c levels. These benefits may reduce the risk of insulin-related AEs while maintaining appropriate glycemic control.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic disease becoming more prevalent each year and is the seventh-leading cause of death in the United States.1 The most common reason for hospitalization for patients with T2DM is uncontrolled glycemic levels.2 Nearly 25% of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patient population has T2DM.3 T2DM is the leading cause of blindness, end-stage renal disease, and amputation for VA patients.4
According to the 2023 American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines, treatment goals of T2DM include eliminating symptoms, preventing or delaying complications, and attaining glycemic goals. A typical hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) goal range is < 7%, but individual goals can vary up to < 9% due to a multitude of factors, including patient comorbidities and clinical status.5
Initial treatment recommendations are nonpharmacologic and include comprehensive lifestyle interventions such as optimizing nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral therapy. When pharmacologic therapy is required, metformin is the preferred first-line treatment for the majority of newly diagnosed patients with T2DM and should be added to continued lifestyle management.5 If HbA1c levels remains above goal, the 2023 ADA guidelines recommend adding a second medication, including but not limited to insulin, a glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), or a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor. Medication choice is largely based on the patient’s concomitant conditions (eg, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease). The 2023 ADA guidelines suggest initiating insulin therapy when a patient's blood glucose ≥ 300 mg/dL, HbA1c > 10%, or if the patient has symptoms of hyperglycemia, even at initial diagnosis. Initiating medications to minimize or avoid hypoglycemia is a priority, especially in high-risk individuals.5
Clinical evidence shows that GLP-1RAs may provide similar glycemic control to insulin with lower risk of hypoglycemia.6 Other reported benefits of GLP-1RAs include weight loss, blood pressure reduction, and improved lipid levels. The most common adverse events (AEs) with GLP-1RAs are gastrointestinal. Including GLP-1RAs in T2DM pharmacotherapy may lower the risk of hypoglycemia, especially in patients at high risk of hypoglycemia.
The 2023 ADA guidelines indicate that it is appropriate to initiate GLP-]1RAs in patients on insulin.5 However, while GLP-1RAs do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia independently, combination treatment with GLP-1RAs and insulin can still result in hypoglycemia.6 Insulin is the key suspect of this hypoglycemic risk.7 Thus, if insulin dosage can be reduced or discontinued, this might reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
The literature is limited on how the addition of a GLP-1RA to insulin treatment will affect the patient's daily insulin doses, particularly for the veteran population. The goal of this study is to examine this gap in current research by examining semaglutide, which is the current formulary preferred GLP-1RA at the VA.
Semaglutide is subcutaneously initiated at a dose of 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks to reduce gastrointestinal symptoms, then increased to 0.5 mg weekly. Additional increases to a maintenance dose of 1 mg or 2 mg weekly can occur to achieve glycemic goals. The SUSTAIN-FORTE randomized controlled trial sought to determine whether there was a difference in HbA1c level reduction and significant weight loss with the 2-mg vs 1-mg dose.8 Patients in the trial were taking metformin but needed additional medication to control their HbA1c. They were not using insulin and may or may not have been taking sulfonylureas prior to semaglutide initiation. Semaglutide 2 mg was found to significantly improve HbA1c control and promote weight loss compared with semaglutide 1 mg, while maintaining a similar safety profile.
Because this study involved patients who required additional HbA1c control, although semaglutide reduced HbA1c, not all patients were able to reduce their other diabetes medications, which depended on the baseline HbA1c level and the level upon completion of semaglutide titration. Dose reductions for the patients’ other T2DM medications were not reported at trial end. SUSTAIN-FORTE established titration up to semaglutide 2 mg as effective for HbA1c reduction, although it did not study patients also on insulin.8
Insulin is associated with hypoglycemic risk, weight gain, and other AEs.7,8 This study analyzed whether increasing semaglutide could reduce insulin doses and therefore reduce risk of AEs in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A retrospective, single-center, chart review was conducted at VA Sioux Falls Health Care System (VASFHCS). Data were collected through manual review of VASFHCS electronic medical records. Patients aged ≥ 18 years with active prescriptions for at least once-daily insulin who were initiated on 2-mg weekly dose of semaglutide at the VASFHCS clinical pharmacy practitioner medication management clinic between January 1, 2021, and September 1, 2023, were included. VASFHCS clinical pharmacy practitioners have a scope of practice that allows them to initiate, modify, or discontinue medication therapy within medication management clinics.
The most frequently used prandial insulin at VASFHCS is insulin aspart, and the most frequently used basal insulin is insulin glargine. Patients were retrospectively monitored as they progressed from baseline (the point in time where semaglutide 0.5 mg was initiated) to ≥ 3 months on semaglutide 2-mg therapy. Patients were excluded if they previously used a GLP-1RA or if they were on sliding scale insulin without an exact daily dosage.
The primary endpoint was the percent change in total daily insulin dose from baseline to each dose increase after receiving semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months. Secondary endpoints included changes in daily prandial insulin dose, daily basal insulin dose, HbA1c, and number of hypoglycemic events reported. Data collected included age, race, weight, body mass index, total daily prandial insulin dose, total daily basal insulin dose, HbA1c, and hypoglycemic events reported at the visit when semaglutide was initiated.
Statistical Analysis
The sample size was calculated prior to data collection, and it was determined that for α = .05, 47 patients were needed to achieve 95% power. The primary endpoint was assessed using a paired t test, as were each secondary endpoint. Results with P < .05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Sixty-two patients were included. The mean HbA1c level at baseline was 7.7%, the baseline mean prandial and insulin daily doses were 41.5 units and 85.1 units, respectively (Table 1) From baseline to initiation of a semaglutide 1-mg dose, the daily insulin dose changed –5.6% (95% CI, 2.2-14.0; P = .008). From baseline to 2-mg dose initiation daily insulin changed -22.2% (95% CI, 22.0-35.1; P < .001) and for patients receiving semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months it changed -36.9% (95% CI, 37.4-56.5; P < .001) (Figure).


After receiving the 2-mg dose for ≥ 3 months, the mean daily dose of prandial insulin decreased from 41.5 units to 24.6 units (95% CI, 12.6-21.2; P < .001); mean daily dose of basal insulin decreased from 85.1 units to 52.1 units (95% CI, 23.9-42.0; P < .001); and mean HbA1c level decreased from 7.7% to 7.1% (95% CI, 0.3-0.8; P < .001). Mean number of hypoglycemic events reported was not statistically significant, changing from 3.6 to 3.2 (95% CI, –0.6 to 0.1; P = .21) (Table 2).

Discussion
This study investigated the effect of subcutaneous semaglutide dose escalation on total daily insulin dose for patients with T2DM. There was a statistically significant decrease in total daily insulin dose from baseline to 1 mg initiation; this decrease continued with further insulin dose reduction seen at the 2-mg dose initiation and additional insulin dose reduction at ≥ 3 months at this dose. It was hypothesized there would be a significant total daily insulin dose reduction at some point, especially when transitioning from the semaglutide 1-mg to the 2-mg dose, based on previous research. 9,10 The additional reduction in daily insulin dose when continuing on semaglutide 2 mg for ≥ 3 months was an unanticipated but added benefit, showing that if tolerated, maintaining the 2-mg dose will help patients reduce their insulin doses.
In terms of secondary endpoints, there was a statistically significant decrease in mean total daily dose individually for prandial and basal insulin from baseline to ≥ 3 months after semaglutide 2 mg initiation. The change in HbA1c level was also statistically significant and decreased from baseline, even as insulin doses were reduced. This change in HbA1c level was expected; previous literature has shown a significant link between improving HbA1c control when semaglutide doses are increased to 2 mg weekly.10 Due to having been shown in previous trials, it was expected that HbA1c levels would decrease even when the insulin doses were being reduced.10 Insulin dose reduction can potentially be added to the growing evidence of semaglutide benefits. The change in the number of hypoglycemic events was not statistically significant, which was unexpected since previous research show a trend in patients taking GLP-1RAs having fewer hypoglycemic events than those taking insulin.6 Further investigation with a larger sample size and prospective trial could determine whether this result is an outlier. In this study, there was no increase in HbA1c or hypoglycemic events reported with increasing semaglutide doses, which provides further evidence of the safety of semaglutide even at higher doses.
These data suggest that for a patient with T2DM who is already taking insulin, the recommended titration of semaglutide is to start with 0.5 mg and titrate up to a 2-mg subcutaneous weekly dose and to then continue at that dose. As long as the 2-mg dose is tolerated, it will provide patients with the most HbA1c control and lead to a reduction of their total daily insulin doses according to these results.
Strengths and Limitations
This study compared patient data at different points. This method did not require a second distinct control group, which would potentially introduce confounding factors, such as different baseline characteristics. Another strength is that documentation was available for all patients throughout the study so no one was lost to follow-up. This allowed comprehensive data collection and provided a stronger conclusion given the completeness of the data from baseline to follow-up.
Limitations include the retrospective design and small sample size. In addition, the study design did not allow for randomization. There is no documentation of adherence to medication regimen, which was difficult to determine due to the retrospective nature. Other changes to the patients’ medication regimen were not collected in aggregate and thus, it is possible the total daily insulin dose was impacted by other medication changes. There is also potential for inconsistent documentation of the patients’ true total daily insulin dose in the medical record, thus leading to inaccuracy of recorded data.
Conclusions
A small sample of veterans with T2DM had statistically significant reductions in total daily insulin dose when subcutaneous semaglutide was initiated, as well as after each dose increase. There was also a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c levels from baseline even as patient insulin doses were reduced. These results support the current practice of using semaglutide to treat T2DM, suggesting it may be safe and effective at reducing HbA1c levels as the dose is titrated up to 2 mg. There was no statistically significant change in the number of hypoglycemic events reported as semaglutide was titrated up. Thus, when semaglutide is increased to the maximum recommended dose of 2 mg for T2DM, patients may experience a reduction of their total daily dose of insulin and HbA1c levels. These benefits may reduce the risk of insulin-related AEs while maintaining appropriate glycemic control.
- Diabetes mellitus: in federal health care data trends 2017. Fed Pract. 2017:S20. Accessed August 6, 2025. https://www.fedprac-digital.com/federalpractitioner/data_trends_2017
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report. May 15, 2024. Accessed September 17, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on diabetes. Updated January 15, 2021. Accessed August 6, 2025. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/diabetes.cfm
- Liu Y, Sayam S, Shao X, et al. Prevalence of and trends in diabetes among veterans, United States, 2005-2014. Prev Chronic Dis. 2017;14:E135. doi:10.5888/pcd14.170230
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes. 2022;41:4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Zhao Z, Tang Y, Hu Y, Zhu H, Chen X, Zhao B. Hypoglycemia following the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a real-world analysis of post-marketing surveillance data. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9:1482. doi:10.21037/atm-21-4162
- Workgroup on Hypoglycemia, American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: a report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1245-1249. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.5.1245
- Frías JP, Auerbach P, Bajaj HS, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide 2.0 mg versus 1.0 mg in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN FORTE): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3B trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9:563-574. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00174-1
- Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm - 2020 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2020;26:107-139. doi:10.4158/CS-2019-0472
- Miles KE, Kerr JL. Semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pharm Technol. 2018;34:281-289. doi:10.1177/8755122518790925
- Diabetes mellitus: in federal health care data trends 2017. Fed Pract. 2017:S20. Accessed August 6, 2025. https://www.fedprac-digital.com/federalpractitioner/data_trends_2017
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report. May 15, 2024. Accessed September 17, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on diabetes. Updated January 15, 2021. Accessed August 6, 2025. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/diabetes.cfm
- Liu Y, Sayam S, Shao X, et al. Prevalence of and trends in diabetes among veterans, United States, 2005-2014. Prev Chronic Dis. 2017;14:E135. doi:10.5888/pcd14.170230
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes. 2022;41:4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Zhao Z, Tang Y, Hu Y, Zhu H, Chen X, Zhao B. Hypoglycemia following the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a real-world analysis of post-marketing surveillance data. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9:1482. doi:10.21037/atm-21-4162
- Workgroup on Hypoglycemia, American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: a report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1245-1249. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.5.1245
- Frías JP, Auerbach P, Bajaj HS, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide 2.0 mg versus 1.0 mg in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN FORTE): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3B trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9:563-574. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00174-1
- Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm - 2020 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2020;26:107-139. doi:10.4158/CS-2019-0472
- Miles KE, Kerr JL. Semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pharm Technol. 2018;34:281-289. doi:10.1177/8755122518790925
Efficacy of Subcutaneous Semaglutide Dose Escalation in Reducing Insulin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Efficacy of Subcutaneous Semaglutide Dose Escalation in Reducing Insulin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for American Indian/Alaska Native Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Not Using Insulin
Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for American Indian/Alaska Native Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Not Using Insulin
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a national health crisis affecting > 38 million people (11.6%) in the United States.1 American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults are disproportionately affected, with a prevalence of 14.5%—the highest among all racial and ethnic groups.1 Type 2 DM (T2DM) accounts for 90% to 95% of all DM cases and is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality due to its association with cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and other complications.2
Maintaining glycemic control is important for managing T2DM and preventing microvascular and macrovascular complications.3 The cornerstone of diabetes self-management has been patient self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) using finger-stick glucometers.4 However, SMBG provides measurements from a single point in time and requires frequent, painful, and inconvenient finger pricks, leading to decreased adherence.5,6 These limitations negatively affect patient engagement and overall glycemic control.7
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) offer real-time, continuous glucose readings and trends.8 CGMs improve glycemic control and reduce hypoglycemic episodes in patients who are insulin-dependent.9,10 Flash glucose monitors, a type of CGM that requires scanning to obtain glucose readings, provide similar benefits.11 Despite these demonstrated advantages, research has primarily focused on insulin-dependent populations, leaving a significant gap in understanding the effect of CGMs on patients with T2DM who are not insulin-dependent.12
Given the high prevalence of T2DM among AI/AN populations and the potential benefits of CGMs, this study sought to evaluate the effect of CGM use on glycemic control and other health metrics in patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM in an AI/AN population. This focus addresses a critical knowledge gap and may inform clinical practices and policies to improve diabetes management in this high-risk group.
Methods
A retrospective observational study was conducted using deidentified electronic health records (EHRs) from 2019 to 2024 at a federally operated outpatient Indian Health Service (IHS) clinic serving an AI/AN population in the IHS Portland Area (Oregon, Washington, Idaho). The study protocol was reviewed and deemed exempt by institutional review boards at Washington State University and the Portland Area IHS.
Study Population
This study included patients diagnosed with non–insulin-dependent T2DM, had used a CGM for ≥ 1 year, and had hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) measurements within 4 months prior to CGM initiation (baseline) and within ± 4 months after 1 year of CGM use. For other health metrics, including blood pressure (BP), weight, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), this study required measurements within 6 months before CGM initiation and within 6 months after 1 year of CGM use. The baseline HbA1c in the dataset ranged from 5.3% to > 14%.
Patients were excluded if they used insulin during the study period, had incomplete laboratory or clinical data for the required time frame, or had < 1 year of CGM use. The dataset did not include detailed information on oral DM medications; thus, we could not report or account for the type or number of oral hypoglycemic agents used by the patients. The IHS clinical applications coordinator compiled the dataset from the EHR, identifying patients who were prescribed and received a CGM at the clinic. All patients used the Abbott Freestyle Libre CGM, the only formulary CGM available at the clinic during the study period.
A 1-year follow-up endpoint was selected for several reasons: (1) to capture potential seasonal variations in diet and activity; (2) to align with the clinic’s standard practice of annual comprehensive diabetes evaluations; and (3) to allow sufficient time for patients to adapt to CGM use and reflect any meaningful changes in glycemic control.
All patients received standard DM care according to clinic protocols, which included DM self-management education and training. Patients met with the diabetes educator at least once, during which the educator emphasized making informed decisions using CGM data, such as adjusting dietary choices and physical activity levels to manage blood glucose concentrations effectively.
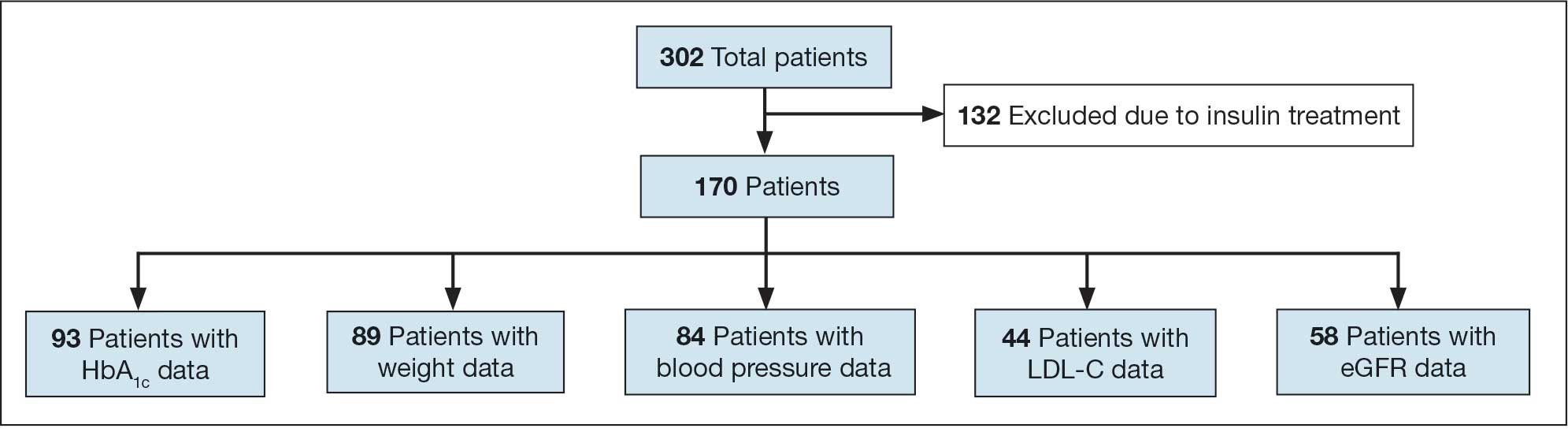
A total of 302 patients were initially identified. After applying exclusion criteria, 132 were excluded due to insulin use, and 77 were excluded due to incomplete HbA1c data within the specified time frames (Figure 1). The final sample included 93 patients.
Abbreviations: eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Measures
The primary outcome was the change in HbA1c levels from baseline to 1 year after CGM initiation. Secondary outcomes included changes in weight, systolic and diastolic BP, LDL-C concentrations, and eGFR. For the primary outcome, HbA1c values were collected within a grace period of ± 4 months from the baseline and 1-year time points. The laboratory’s upper reporting limit for HbA1c was 14%; values reported as “> 14%” were recorded as 14.1% for data analysis, although the actual values could have been higher.
For secondary outcomes, data were included if measurements were obtained within ± 6 months of the baseline and 1-year time points. Patients who did not have measurements within these time frames for specific metrics were excluded from secondary outcome analysis but remained in the overall study if they met the criteria for HbA1c and CGM use.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using R statistical software version 4.4.2. Paired t tests were conducted to compare baseline and 1-year follow- up measurements for variables with parametric distributions. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for nonparametric data. A linear regression analysis was conducted to examine the relationship between baseline HbA1c levels and the change in HbA1c after 1 year of CGM use. Differences were considered significant at P < .05 set a priori. To guide future research, a posthoc power analysis was performed using Cohen’s d to estimate the required sample sizes for detecting significant effects, assuming a similar population.
Results
The study included 93 patients, with a mean (SD) age of 55 (13) years (range, 29-83 years). Of the participants, 56 were female (60%) and 37 were male (40%). All participants were identified as AI/AN and had non–insulin-dependent T2DM.
Primary Outcomes
A significant reduction in HbA1c levels was observed after 1 year of CGM use. The mean (SD) baseline HbA1c was 9.5% (2.4%), which decreased to 7.6% (2.2%) at 1-year follow-up (Table 1). This difference represents a mean change of -1.86% (2.4%) (95% CI, -2.35 to -1.37; P < .001 [paired t test, -7.53]).
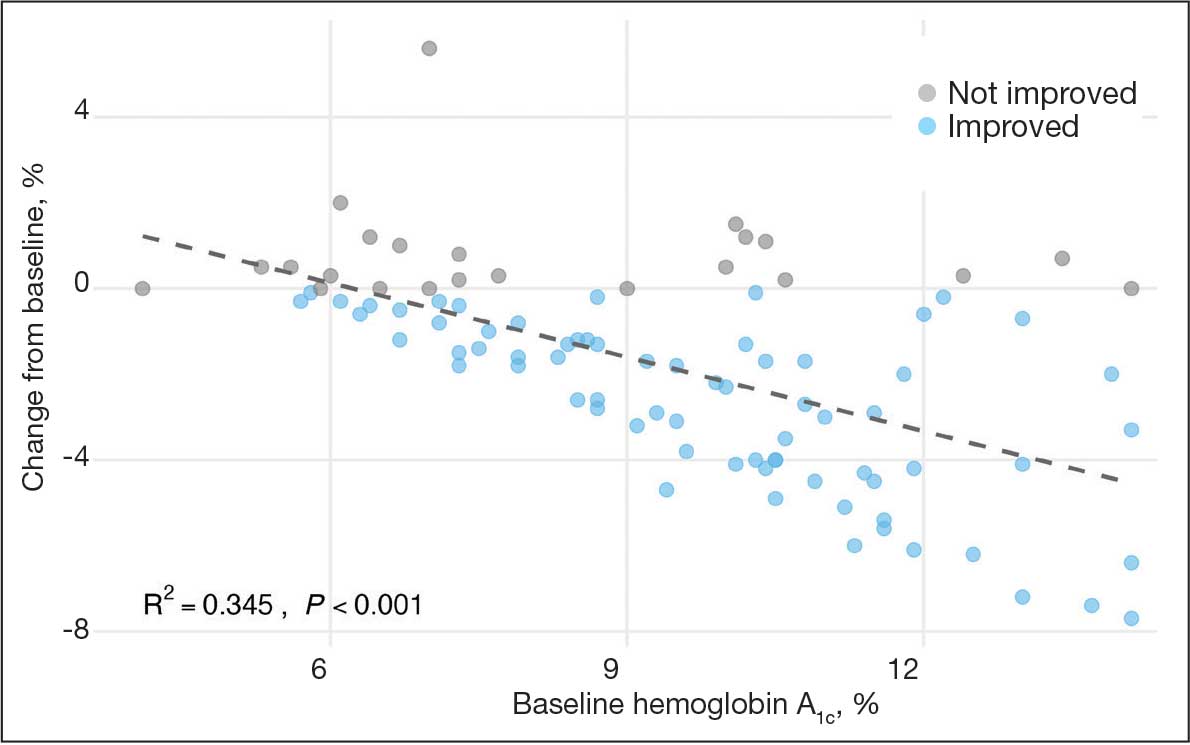
A linear regression model evaluated the relationship between baseline HbA1c (predictor) and the change in HbA1c after 1 year (outcome). The change in HbA1c was calculated as the difference between 1-year follow-up and baseline values. The regression model revealed a significant negative association between baseline HbA1c and the change in HbA1c (Β = -0.576; P < .001), indicating that higher baseline HbA1c values were associated with greater reductions in HbA1c over the year. The regression equation was: Change in HbA1c = 3.587 – 0.576 × Baseline HbA1c
The regression coefficient for baseline HbA1c was -0.576 (standard error, 0.083; t = -6.931; P < .001), indicating that for each 1% increase in baseline HbA1c, the reduction of HbA1c after 1 year increased by approximately 0.576% (Figure 2). The model explained 34.6% of the variance in HbA1c change (R2 = .345; adjusted R2 = .338).
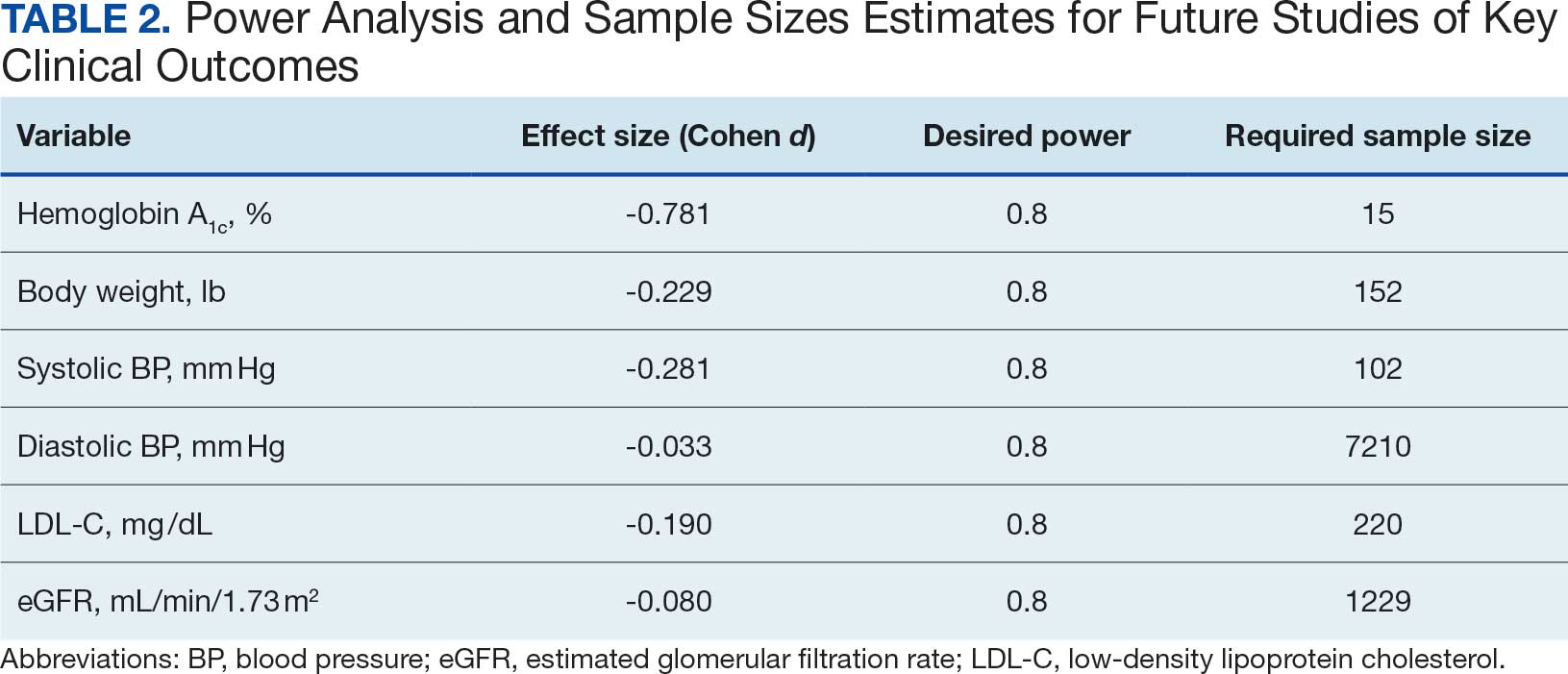
Secondary Outcomes
Systolic BP decreased by a mean (SD) -4.9 (17) mm Hg; 95% CI, -8.6 to -1.11; P = .01, paired t test). However, no significant change was observed for diastolic BP (P = .77, paired t test). Similarly, no significant changes were observed in weight, LDL-C concentrations, or eGFR after 1 year of CGM use. A posthoc power analysis indicated that the study was underpowered to detect smaller effect sizes in secondary outcomes. For example, sample size estimates indicated that detecting significant changes in weight and LDL-C concentrations would require sample sizes of 152 and 220 patients, respectively (Table 2).
Discussion
This study found a clinically significant reduction in HbA1c levels after 1 year among AI/AN patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM who used CGMs. The mean HbA1c decreased 1.9%, from 9.5% at baseline to 7.6% after 1 year. This reduction is not only statistically significant (P < .001), it is clinically meaningful—even a 1% decrease in HbA1c is associated with substantial reductions in the risk of microvascular complications.3 The magnitude of the HbA1c reduction observed suggests CGM use may be associated with improved glycemic control in this high-risk population. By achieving lower HbA1c levels, patients may experience improved long-term health outcomes and a reduced burden of DM-related complications.
Changes in oral DM medications during the study period may have contributed to the observed improvements in HbA1c levels. While the dataset lacked detailed information on types or dosages of oral hypoglycemic agents used, adjustments in medication regimens are common in DM management and could significantly affect glycemic control. The inability to account for these changes results in an inability to attribute the improvements in HbA1c solely to CGM use. Future studies should collect comprehensive medication data to better isolate the effects of CGM use from other treatment modifications.
Another factor that may have contributed to the improved glycemic control is the DM self-management education and training patients received as part of standard care. Patients met with diabetes educators at least once and learned how to use the CGM device and interpret the data for self-management decisions. This education may have enhanced patient engagement and empowerment, enabling them to make informed choices about diet, physical activity, and medication adherence. Studies have shown that DM self-management education can significantly improve glycemic control and patient outcomes.13 By combining the CGM technology with targeted education, patients may have been better equipped to manage their condition, contributing to the observed reduction in HbA1c levels. Future studies should consider synergistic effects of CGM use and DM education when evaluating interventions for glycemic control.
The significant reduction in HbA1c indicates CGM use is associated with improved glycemic control in non–insulin-dependent T2DM. The linear regression analysis suggests patients with poorer glycemic control at baseline experienced greater reductions in HbA1c over the course of 1 year. This finding aligns with previous studies that have shown greater HbA1c reductions in patients with higher initial levels when using CGMs. Yaron et al reported similar findings: higher baseline HbA1c levels predicted more substantial improvements with CGM use in patients with T2DM on insulin therapy.14
This study contributes to existing research by examining the association between CGM use and glycemic control in patients with non– insulin-dependent T2DM within an AI/AN population, a group that has been underreported in previous studies. Most prior research has focused on insulin-dependent patients or populations with different ethnic backgrounds.12 By focusing on patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM, this study highlights the broader applicability of CGMs beyond traditional use, showcasing their potential association with benefits in earlier stages of DM management. Targeting the AI/AN population addresses a critical knowledge gap, given the disproportionately high prevalence of T2DM and associated complications in this group. The findings of this study suggest integrating CGM technology into the standard care of AI/AN patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM may be associated with improved glycemic control and may help reduce health disparities.
The modest decrease in systolic BP observed in this study may indicate potential cardiovascular benefits associated with CGM use, possibly due to improved glycemic control and increased patient engagement in self-management. However, given the limited sample size and exclusion criteria, the study lacked sufficient power to detect significant associations between CGM use and other secondary outcomes such as BP, weight, LDL-C, and eGFR. Therefore, the significant finding with systolic BP should be interpreted with caution.
The lack of significant changes in secondary outcomes may be attributed to the study’s limited sample size and the relatively short duration for observing changes in these parameters. Larger studies are needed to assess the full impact of CGM on these variables. The required sample sizes for achieving adequate power in future studies were calculated, highlighting the utility of our study as a pilot, providing critical data for the design of larger, adequately powered studies.
Limitations
The retrospective design of this study limits causal inferences. Moreover, potential confounding variables were not controlled, such as changes in medication regimens (other than insulin use), dietary counseling, or physical activity. Additionally, we could not account for the type or number of oral DM medications prescribed to patients. The dataset included only information on insulin use, without detailed records of other antidiabetic medications. This limitation may have influenced the observed change in glycemic control, as variations in medication regimens could affect HbA1c levels.
Because this study lacked a comparator group, the effect of CGM use cannot be definitively isolated from other factors (eg, medication changes, dietary modifications, or physical activity). Moreover, CGM devices can be costly and are not universally covered by all insurance or IHS programs, potentially limiting widespread implementation. Policy-level restrictions and patient-specific barriers may also hinder feasibility in other settings.
The small sample size may limit the generalizability of the findings. Of the initial 302 patients, about 69% were excluded due to insulin use or incomplete laboratory data. A ± 4-month window was selected to balance data quality with real-world practices. Extending this window further (eg, ± 6 months) might have included more participants but risked diluting the 1-year endpoint consistency. The lack of statistical significance in secondary metrics may be due to insufficient power rather than the absence of an effect.
Exclusion of patients due to incomplete data may have introduced selection bias. However, patients were included in the overall analysis if they met the criteria for HbA1c and CGM use, even if they lacked data for secondary outcomes. Additionally, the laboratory’s upper reporting limit for HbA1c was 14%, with values above this reported as “> 14%.” For analysis, these were recorded as 14.1%, which may underestimate the true baseline HbA1c levels and impact of the assessment of change. This occurred for 4 of the 93 patients included.
All patients used the Freestyle Libre CGM, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other CGM brands or models. Differences in device features, accuracy, scanning frequency, and user experience may influence outcomes, and results might differ with other CGM technologies. The dataset did not include patients’ scanning frequency because this metric was not consistently included in the EHRs.
Conclusions
This study found that CGM use was significantly associated with improved glycemic control in patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM within an AI/AN population, particularly among patients with higher baseline HbA1c levels. The findings suggest that CGMs may be a valuable tool for managing T2DM beyond insulin-dependent populations.
Additional research with larger sample sizes, control groups, and extended follow-up periods is recommended to explore long-term benefits and impacts on other health metrics. The sample size estimates derived from this study serve as a valuable resource for researchers designing future studies aimed at addressing these gaps. Future research that expands on our findings by including larger, more diverse cohorts, accounting for medication use, and exploring different CGM technologies will enhance understanding and contribute to more effective diabetes management strategies for varied populations.
- National diabetes statistics report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. May 15, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html
- Elsayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:S19-S40. doi:10.2337/dc23-S002
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2011;29:116-122. doi:10.2337/diaclin.29.3.116
- Pleus S, Freckmann G, Schauer S, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose as an integral part in the management of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2022;13:829-846. doi:10.1007/s13300-022-01254-8
- Polonsky WH, Fisher L, Schikman CH, et al. Structured self-monitoring of blood glucose significantly reduces A1C levels in poorly controlled, noninsulin-treated type 2 diabetes: results from the Structured Testing Program study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:262-267. doi:10.2337/dc10-1732
- Tanaka N, Yabe D, Murotani K, et al. Mental distress and health-related quality of life among type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients using self-monitoring of blood glucose: a cross-sectional questionnaire study in Japan. J Diabetes Investig. 2018;9:1203-1211. doi:10.1111/jdi.12827
- Hortensius J, Kars MC, Wierenga WS, et al. Perspectives of patients with type 1 or insulin-treated type 2 diabetes on self-monitoring of blood glucose: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:167. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-12-167
- Didyuk O, Econom N, Guardia A, Livingston K, Klueh U. Continuous glucose monitoring devices: past, present, and future focus on the history and evolution of technological innovation. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2021;15:676-683. doi:10.1177/1932296819899394
- Beck RW, Riddlesworth TD, Ruedy K, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: the DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317:371-378. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19975
- Lind M, Polonsky W, Hirsch IB, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring vs conventional therapy for glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes treated with multiple daily insulin injections: the GOLD randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317:379-387. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19976
- Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, et al. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: a multicenter, non-masked, randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2254-2263. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31535-5
- Seidu S, Kunutsor SK, Ajjan RA, et al. Efficacy and safety of continuous glucose monitoring and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional evidence. Diabetes Care. 2024;47:169-179. doi:10.2337/dc23-1520
- ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. 5. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:S68-S96. doi:10.2337/dc23-S005
- Yaron M, Roitman E, Aharon-Hananel G, et al. Effect of flash glucose monitoring technology on glycemic control and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:1178-1184. doi:10.2337/dc18-0166
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a national health crisis affecting > 38 million people (11.6%) in the United States.1 American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults are disproportionately affected, with a prevalence of 14.5%—the highest among all racial and ethnic groups.1 Type 2 DM (T2DM) accounts for 90% to 95% of all DM cases and is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality due to its association with cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and other complications.2
Maintaining glycemic control is important for managing T2DM and preventing microvascular and macrovascular complications.3 The cornerstone of diabetes self-management has been patient self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) using finger-stick glucometers.4 However, SMBG provides measurements from a single point in time and requires frequent, painful, and inconvenient finger pricks, leading to decreased adherence.5,6 These limitations negatively affect patient engagement and overall glycemic control.7
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) offer real-time, continuous glucose readings and trends.8 CGMs improve glycemic control and reduce hypoglycemic episodes in patients who are insulin-dependent.9,10 Flash glucose monitors, a type of CGM that requires scanning to obtain glucose readings, provide similar benefits.11 Despite these demonstrated advantages, research has primarily focused on insulin-dependent populations, leaving a significant gap in understanding the effect of CGMs on patients with T2DM who are not insulin-dependent.12
Given the high prevalence of T2DM among AI/AN populations and the potential benefits of CGMs, this study sought to evaluate the effect of CGM use on glycemic control and other health metrics in patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM in an AI/AN population. This focus addresses a critical knowledge gap and may inform clinical practices and policies to improve diabetes management in this high-risk group.
Methods
A retrospective observational study was conducted using deidentified electronic health records (EHRs) from 2019 to 2024 at a federally operated outpatient Indian Health Service (IHS) clinic serving an AI/AN population in the IHS Portland Area (Oregon, Washington, Idaho). The study protocol was reviewed and deemed exempt by institutional review boards at Washington State University and the Portland Area IHS.
Study Population
This study included patients diagnosed with non–insulin-dependent T2DM, had used a CGM for ≥ 1 year, and had hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) measurements within 4 months prior to CGM initiation (baseline) and within ± 4 months after 1 year of CGM use. For other health metrics, including blood pressure (BP), weight, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), this study required measurements within 6 months before CGM initiation and within 6 months after 1 year of CGM use. The baseline HbA1c in the dataset ranged from 5.3% to > 14%.
Patients were excluded if they used insulin during the study period, had incomplete laboratory or clinical data for the required time frame, or had < 1 year of CGM use. The dataset did not include detailed information on oral DM medications; thus, we could not report or account for the type or number of oral hypoglycemic agents used by the patients. The IHS clinical applications coordinator compiled the dataset from the EHR, identifying patients who were prescribed and received a CGM at the clinic. All patients used the Abbott Freestyle Libre CGM, the only formulary CGM available at the clinic during the study period.
A 1-year follow-up endpoint was selected for several reasons: (1) to capture potential seasonal variations in diet and activity; (2) to align with the clinic’s standard practice of annual comprehensive diabetes evaluations; and (3) to allow sufficient time for patients to adapt to CGM use and reflect any meaningful changes in glycemic control.
All patients received standard DM care according to clinic protocols, which included DM self-management education and training. Patients met with the diabetes educator at least once, during which the educator emphasized making informed decisions using CGM data, such as adjusting dietary choices and physical activity levels to manage blood glucose concentrations effectively.
A total of 302 patients were initially identified. After applying exclusion criteria, 132 were excluded due to insulin use, and 77 were excluded due to incomplete HbA1c data within the specified time frames (Figure 1). The final sample included 93 patients.

Abbreviations: eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Measures
The primary outcome was the change in HbA1c levels from baseline to 1 year after CGM initiation. Secondary outcomes included changes in weight, systolic and diastolic BP, LDL-C concentrations, and eGFR. For the primary outcome, HbA1c values were collected within a grace period of ± 4 months from the baseline and 1-year time points. The laboratory’s upper reporting limit for HbA1c was 14%; values reported as “> 14%” were recorded as 14.1% for data analysis, although the actual values could have been higher.
For secondary outcomes, data were included if measurements were obtained within ± 6 months of the baseline and 1-year time points. Patients who did not have measurements within these time frames for specific metrics were excluded from secondary outcome analysis but remained in the overall study if they met the criteria for HbA1c and CGM use.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using R statistical software version 4.4.2. Paired t tests were conducted to compare baseline and 1-year follow- up measurements for variables with parametric distributions. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for nonparametric data. A linear regression analysis was conducted to examine the relationship between baseline HbA1c levels and the change in HbA1c after 1 year of CGM use. Differences were considered significant at P < .05 set a priori. To guide future research, a posthoc power analysis was performed using Cohen’s d to estimate the required sample sizes for detecting significant effects, assuming a similar population.
Results
The study included 93 patients, with a mean (SD) age of 55 (13) years (range, 29-83 years). Of the participants, 56 were female (60%) and 37 were male (40%). All participants were identified as AI/AN and had non–insulin-dependent T2DM.
Primary Outcomes
A significant reduction in HbA1c levels was observed after 1 year of CGM use. The mean (SD) baseline HbA1c was 9.5% (2.4%), which decreased to 7.6% (2.2%) at 1-year follow-up (Table 1). This difference represents a mean change of -1.86% (2.4%) (95% CI, -2.35 to -1.37; P < .001 [paired t test, -7.53]).

A linear regression model evaluated the relationship between baseline HbA1c (predictor) and the change in HbA1c after 1 year (outcome). The change in HbA1c was calculated as the difference between 1-year follow-up and baseline values. The regression model revealed a significant negative association between baseline HbA1c and the change in HbA1c (Β = -0.576; P < .001), indicating that higher baseline HbA1c values were associated with greater reductions in HbA1c over the year. The regression equation was: Change in HbA1c = 3.587 – 0.576 × Baseline HbA1c
The regression coefficient for baseline HbA1c was -0.576 (standard error, 0.083; t = -6.931; P < .001), indicating that for each 1% increase in baseline HbA1c, the reduction of HbA1c after 1 year increased by approximately 0.576% (Figure 2). The model explained 34.6% of the variance in HbA1c change (R2 = .345; adjusted R2 = .338).

Secondary Outcomes
Systolic BP decreased by a mean (SD) -4.9 (17) mm Hg; 95% CI, -8.6 to -1.11; P = .01, paired t test). However, no significant change was observed for diastolic BP (P = .77, paired t test). Similarly, no significant changes were observed in weight, LDL-C concentrations, or eGFR after 1 year of CGM use. A posthoc power analysis indicated that the study was underpowered to detect smaller effect sizes in secondary outcomes. For example, sample size estimates indicated that detecting significant changes in weight and LDL-C concentrations would require sample sizes of 152 and 220 patients, respectively (Table 2).

Discussion
This study found a clinically significant reduction in HbA1c levels after 1 year among AI/AN patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM who used CGMs. The mean HbA1c decreased 1.9%, from 9.5% at baseline to 7.6% after 1 year. This reduction is not only statistically significant (P < .001), it is clinically meaningful—even a 1% decrease in HbA1c is associated with substantial reductions in the risk of microvascular complications.3 The magnitude of the HbA1c reduction observed suggests CGM use may be associated with improved glycemic control in this high-risk population. By achieving lower HbA1c levels, patients may experience improved long-term health outcomes and a reduced burden of DM-related complications.
Changes in oral DM medications during the study period may have contributed to the observed improvements in HbA1c levels. While the dataset lacked detailed information on types or dosages of oral hypoglycemic agents used, adjustments in medication regimens are common in DM management and could significantly affect glycemic control. The inability to account for these changes results in an inability to attribute the improvements in HbA1c solely to CGM use. Future studies should collect comprehensive medication data to better isolate the effects of CGM use from other treatment modifications.
Another factor that may have contributed to the improved glycemic control is the DM self-management education and training patients received as part of standard care. Patients met with diabetes educators at least once and learned how to use the CGM device and interpret the data for self-management decisions. This education may have enhanced patient engagement and empowerment, enabling them to make informed choices about diet, physical activity, and medication adherence. Studies have shown that DM self-management education can significantly improve glycemic control and patient outcomes.13 By combining the CGM technology with targeted education, patients may have been better equipped to manage their condition, contributing to the observed reduction in HbA1c levels. Future studies should consider synergistic effects of CGM use and DM education when evaluating interventions for glycemic control.
The significant reduction in HbA1c indicates CGM use is associated with improved glycemic control in non–insulin-dependent T2DM. The linear regression analysis suggests patients with poorer glycemic control at baseline experienced greater reductions in HbA1c over the course of 1 year. This finding aligns with previous studies that have shown greater HbA1c reductions in patients with higher initial levels when using CGMs. Yaron et al reported similar findings: higher baseline HbA1c levels predicted more substantial improvements with CGM use in patients with T2DM on insulin therapy.14
This study contributes to existing research by examining the association between CGM use and glycemic control in patients with non– insulin-dependent T2DM within an AI/AN population, a group that has been underreported in previous studies. Most prior research has focused on insulin-dependent patients or populations with different ethnic backgrounds.12 By focusing on patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM, this study highlights the broader applicability of CGMs beyond traditional use, showcasing their potential association with benefits in earlier stages of DM management. Targeting the AI/AN population addresses a critical knowledge gap, given the disproportionately high prevalence of T2DM and associated complications in this group. The findings of this study suggest integrating CGM technology into the standard care of AI/AN patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM may be associated with improved glycemic control and may help reduce health disparities.
The modest decrease in systolic BP observed in this study may indicate potential cardiovascular benefits associated with CGM use, possibly due to improved glycemic control and increased patient engagement in self-management. However, given the limited sample size and exclusion criteria, the study lacked sufficient power to detect significant associations between CGM use and other secondary outcomes such as BP, weight, LDL-C, and eGFR. Therefore, the significant finding with systolic BP should be interpreted with caution.
The lack of significant changes in secondary outcomes may be attributed to the study’s limited sample size and the relatively short duration for observing changes in these parameters. Larger studies are needed to assess the full impact of CGM on these variables. The required sample sizes for achieving adequate power in future studies were calculated, highlighting the utility of our study as a pilot, providing critical data for the design of larger, adequately powered studies.
Limitations
The retrospective design of this study limits causal inferences. Moreover, potential confounding variables were not controlled, such as changes in medication regimens (other than insulin use), dietary counseling, or physical activity. Additionally, we could not account for the type or number of oral DM medications prescribed to patients. The dataset included only information on insulin use, without detailed records of other antidiabetic medications. This limitation may have influenced the observed change in glycemic control, as variations in medication regimens could affect HbA1c levels.
Because this study lacked a comparator group, the effect of CGM use cannot be definitively isolated from other factors (eg, medication changes, dietary modifications, or physical activity). Moreover, CGM devices can be costly and are not universally covered by all insurance or IHS programs, potentially limiting widespread implementation. Policy-level restrictions and patient-specific barriers may also hinder feasibility in other settings.
The small sample size may limit the generalizability of the findings. Of the initial 302 patients, about 69% were excluded due to insulin use or incomplete laboratory data. A ± 4-month window was selected to balance data quality with real-world practices. Extending this window further (eg, ± 6 months) might have included more participants but risked diluting the 1-year endpoint consistency. The lack of statistical significance in secondary metrics may be due to insufficient power rather than the absence of an effect.
Exclusion of patients due to incomplete data may have introduced selection bias. However, patients were included in the overall analysis if they met the criteria for HbA1c and CGM use, even if they lacked data for secondary outcomes. Additionally, the laboratory’s upper reporting limit for HbA1c was 14%, with values above this reported as “> 14%.” For analysis, these were recorded as 14.1%, which may underestimate the true baseline HbA1c levels and impact of the assessment of change. This occurred for 4 of the 93 patients included.
All patients used the Freestyle Libre CGM, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other CGM brands or models. Differences in device features, accuracy, scanning frequency, and user experience may influence outcomes, and results might differ with other CGM technologies. The dataset did not include patients’ scanning frequency because this metric was not consistently included in the EHRs.
Conclusions
This study found that CGM use was significantly associated with improved glycemic control in patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM within an AI/AN population, particularly among patients with higher baseline HbA1c levels. The findings suggest that CGMs may be a valuable tool for managing T2DM beyond insulin-dependent populations.
Additional research with larger sample sizes, control groups, and extended follow-up periods is recommended to explore long-term benefits and impacts on other health metrics. The sample size estimates derived from this study serve as a valuable resource for researchers designing future studies aimed at addressing these gaps. Future research that expands on our findings by including larger, more diverse cohorts, accounting for medication use, and exploring different CGM technologies will enhance understanding and contribute to more effective diabetes management strategies for varied populations.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a national health crisis affecting > 38 million people (11.6%) in the United States.1 American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults are disproportionately affected, with a prevalence of 14.5%—the highest among all racial and ethnic groups.1 Type 2 DM (T2DM) accounts for 90% to 95% of all DM cases and is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality due to its association with cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and other complications.2
Maintaining glycemic control is important for managing T2DM and preventing microvascular and macrovascular complications.3 The cornerstone of diabetes self-management has been patient self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) using finger-stick glucometers.4 However, SMBG provides measurements from a single point in time and requires frequent, painful, and inconvenient finger pricks, leading to decreased adherence.5,6 These limitations negatively affect patient engagement and overall glycemic control.7
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) offer real-time, continuous glucose readings and trends.8 CGMs improve glycemic control and reduce hypoglycemic episodes in patients who are insulin-dependent.9,10 Flash glucose monitors, a type of CGM that requires scanning to obtain glucose readings, provide similar benefits.11 Despite these demonstrated advantages, research has primarily focused on insulin-dependent populations, leaving a significant gap in understanding the effect of CGMs on patients with T2DM who are not insulin-dependent.12
Given the high prevalence of T2DM among AI/AN populations and the potential benefits of CGMs, this study sought to evaluate the effect of CGM use on glycemic control and other health metrics in patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM in an AI/AN population. This focus addresses a critical knowledge gap and may inform clinical practices and policies to improve diabetes management in this high-risk group.
Methods
A retrospective observational study was conducted using deidentified electronic health records (EHRs) from 2019 to 2024 at a federally operated outpatient Indian Health Service (IHS) clinic serving an AI/AN population in the IHS Portland Area (Oregon, Washington, Idaho). The study protocol was reviewed and deemed exempt by institutional review boards at Washington State University and the Portland Area IHS.
Study Population
This study included patients diagnosed with non–insulin-dependent T2DM, had used a CGM for ≥ 1 year, and had hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) measurements within 4 months prior to CGM initiation (baseline) and within ± 4 months after 1 year of CGM use. For other health metrics, including blood pressure (BP), weight, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), this study required measurements within 6 months before CGM initiation and within 6 months after 1 year of CGM use. The baseline HbA1c in the dataset ranged from 5.3% to > 14%.
Patients were excluded if they used insulin during the study period, had incomplete laboratory or clinical data for the required time frame, or had < 1 year of CGM use. The dataset did not include detailed information on oral DM medications; thus, we could not report or account for the type or number of oral hypoglycemic agents used by the patients. The IHS clinical applications coordinator compiled the dataset from the EHR, identifying patients who were prescribed and received a CGM at the clinic. All patients used the Abbott Freestyle Libre CGM, the only formulary CGM available at the clinic during the study period.
A 1-year follow-up endpoint was selected for several reasons: (1) to capture potential seasonal variations in diet and activity; (2) to align with the clinic’s standard practice of annual comprehensive diabetes evaluations; and (3) to allow sufficient time for patients to adapt to CGM use and reflect any meaningful changes in glycemic control.
All patients received standard DM care according to clinic protocols, which included DM self-management education and training. Patients met with the diabetes educator at least once, during which the educator emphasized making informed decisions using CGM data, such as adjusting dietary choices and physical activity levels to manage blood glucose concentrations effectively.
A total of 302 patients were initially identified. After applying exclusion criteria, 132 were excluded due to insulin use, and 77 were excluded due to incomplete HbA1c data within the specified time frames (Figure 1). The final sample included 93 patients.

Abbreviations: eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Measures
The primary outcome was the change in HbA1c levels from baseline to 1 year after CGM initiation. Secondary outcomes included changes in weight, systolic and diastolic BP, LDL-C concentrations, and eGFR. For the primary outcome, HbA1c values were collected within a grace period of ± 4 months from the baseline and 1-year time points. The laboratory’s upper reporting limit for HbA1c was 14%; values reported as “> 14%” were recorded as 14.1% for data analysis, although the actual values could have been higher.
For secondary outcomes, data were included if measurements were obtained within ± 6 months of the baseline and 1-year time points. Patients who did not have measurements within these time frames for specific metrics were excluded from secondary outcome analysis but remained in the overall study if they met the criteria for HbA1c and CGM use.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using R statistical software version 4.4.2. Paired t tests were conducted to compare baseline and 1-year follow- up measurements for variables with parametric distributions. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for nonparametric data. A linear regression analysis was conducted to examine the relationship between baseline HbA1c levels and the change in HbA1c after 1 year of CGM use. Differences were considered significant at P < .05 set a priori. To guide future research, a posthoc power analysis was performed using Cohen’s d to estimate the required sample sizes for detecting significant effects, assuming a similar population.
Results
The study included 93 patients, with a mean (SD) age of 55 (13) years (range, 29-83 years). Of the participants, 56 were female (60%) and 37 were male (40%). All participants were identified as AI/AN and had non–insulin-dependent T2DM.
Primary Outcomes
A significant reduction in HbA1c levels was observed after 1 year of CGM use. The mean (SD) baseline HbA1c was 9.5% (2.4%), which decreased to 7.6% (2.2%) at 1-year follow-up (Table 1). This difference represents a mean change of -1.86% (2.4%) (95% CI, -2.35 to -1.37; P < .001 [paired t test, -7.53]).

A linear regression model evaluated the relationship between baseline HbA1c (predictor) and the change in HbA1c after 1 year (outcome). The change in HbA1c was calculated as the difference between 1-year follow-up and baseline values. The regression model revealed a significant negative association between baseline HbA1c and the change in HbA1c (Β = -0.576; P < .001), indicating that higher baseline HbA1c values were associated with greater reductions in HbA1c over the year. The regression equation was: Change in HbA1c = 3.587 – 0.576 × Baseline HbA1c
The regression coefficient for baseline HbA1c was -0.576 (standard error, 0.083; t = -6.931; P < .001), indicating that for each 1% increase in baseline HbA1c, the reduction of HbA1c after 1 year increased by approximately 0.576% (Figure 2). The model explained 34.6% of the variance in HbA1c change (R2 = .345; adjusted R2 = .338).

Secondary Outcomes
Systolic BP decreased by a mean (SD) -4.9 (17) mm Hg; 95% CI, -8.6 to -1.11; P = .01, paired t test). However, no significant change was observed for diastolic BP (P = .77, paired t test). Similarly, no significant changes were observed in weight, LDL-C concentrations, or eGFR after 1 year of CGM use. A posthoc power analysis indicated that the study was underpowered to detect smaller effect sizes in secondary outcomes. For example, sample size estimates indicated that detecting significant changes in weight and LDL-C concentrations would require sample sizes of 152 and 220 patients, respectively (Table 2).

Discussion
This study found a clinically significant reduction in HbA1c levels after 1 year among AI/AN patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM who used CGMs. The mean HbA1c decreased 1.9%, from 9.5% at baseline to 7.6% after 1 year. This reduction is not only statistically significant (P < .001), it is clinically meaningful—even a 1% decrease in HbA1c is associated with substantial reductions in the risk of microvascular complications.3 The magnitude of the HbA1c reduction observed suggests CGM use may be associated with improved glycemic control in this high-risk population. By achieving lower HbA1c levels, patients may experience improved long-term health outcomes and a reduced burden of DM-related complications.
Changes in oral DM medications during the study period may have contributed to the observed improvements in HbA1c levels. While the dataset lacked detailed information on types or dosages of oral hypoglycemic agents used, adjustments in medication regimens are common in DM management and could significantly affect glycemic control. The inability to account for these changes results in an inability to attribute the improvements in HbA1c solely to CGM use. Future studies should collect comprehensive medication data to better isolate the effects of CGM use from other treatment modifications.
Another factor that may have contributed to the improved glycemic control is the DM self-management education and training patients received as part of standard care. Patients met with diabetes educators at least once and learned how to use the CGM device and interpret the data for self-management decisions. This education may have enhanced patient engagement and empowerment, enabling them to make informed choices about diet, physical activity, and medication adherence. Studies have shown that DM self-management education can significantly improve glycemic control and patient outcomes.13 By combining the CGM technology with targeted education, patients may have been better equipped to manage their condition, contributing to the observed reduction in HbA1c levels. Future studies should consider synergistic effects of CGM use and DM education when evaluating interventions for glycemic control.
The significant reduction in HbA1c indicates CGM use is associated with improved glycemic control in non–insulin-dependent T2DM. The linear regression analysis suggests patients with poorer glycemic control at baseline experienced greater reductions in HbA1c over the course of 1 year. This finding aligns with previous studies that have shown greater HbA1c reductions in patients with higher initial levels when using CGMs. Yaron et al reported similar findings: higher baseline HbA1c levels predicted more substantial improvements with CGM use in patients with T2DM on insulin therapy.14
This study contributes to existing research by examining the association between CGM use and glycemic control in patients with non– insulin-dependent T2DM within an AI/AN population, a group that has been underreported in previous studies. Most prior research has focused on insulin-dependent patients or populations with different ethnic backgrounds.12 By focusing on patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM, this study highlights the broader applicability of CGMs beyond traditional use, showcasing their potential association with benefits in earlier stages of DM management. Targeting the AI/AN population addresses a critical knowledge gap, given the disproportionately high prevalence of T2DM and associated complications in this group. The findings of this study suggest integrating CGM technology into the standard care of AI/AN patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM may be associated with improved glycemic control and may help reduce health disparities.
The modest decrease in systolic BP observed in this study may indicate potential cardiovascular benefits associated with CGM use, possibly due to improved glycemic control and increased patient engagement in self-management. However, given the limited sample size and exclusion criteria, the study lacked sufficient power to detect significant associations between CGM use and other secondary outcomes such as BP, weight, LDL-C, and eGFR. Therefore, the significant finding with systolic BP should be interpreted with caution.
The lack of significant changes in secondary outcomes may be attributed to the study’s limited sample size and the relatively short duration for observing changes in these parameters. Larger studies are needed to assess the full impact of CGM on these variables. The required sample sizes for achieving adequate power in future studies were calculated, highlighting the utility of our study as a pilot, providing critical data for the design of larger, adequately powered studies.
Limitations
The retrospective design of this study limits causal inferences. Moreover, potential confounding variables were not controlled, such as changes in medication regimens (other than insulin use), dietary counseling, or physical activity. Additionally, we could not account for the type or number of oral DM medications prescribed to patients. The dataset included only information on insulin use, without detailed records of other antidiabetic medications. This limitation may have influenced the observed change in glycemic control, as variations in medication regimens could affect HbA1c levels.
Because this study lacked a comparator group, the effect of CGM use cannot be definitively isolated from other factors (eg, medication changes, dietary modifications, or physical activity). Moreover, CGM devices can be costly and are not universally covered by all insurance or IHS programs, potentially limiting widespread implementation. Policy-level restrictions and patient-specific barriers may also hinder feasibility in other settings.
The small sample size may limit the generalizability of the findings. Of the initial 302 patients, about 69% were excluded due to insulin use or incomplete laboratory data. A ± 4-month window was selected to balance data quality with real-world practices. Extending this window further (eg, ± 6 months) might have included more participants but risked diluting the 1-year endpoint consistency. The lack of statistical significance in secondary metrics may be due to insufficient power rather than the absence of an effect.
Exclusion of patients due to incomplete data may have introduced selection bias. However, patients were included in the overall analysis if they met the criteria for HbA1c and CGM use, even if they lacked data for secondary outcomes. Additionally, the laboratory’s upper reporting limit for HbA1c was 14%, with values above this reported as “> 14%.” For analysis, these were recorded as 14.1%, which may underestimate the true baseline HbA1c levels and impact of the assessment of change. This occurred for 4 of the 93 patients included.
All patients used the Freestyle Libre CGM, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other CGM brands or models. Differences in device features, accuracy, scanning frequency, and user experience may influence outcomes, and results might differ with other CGM technologies. The dataset did not include patients’ scanning frequency because this metric was not consistently included in the EHRs.
Conclusions
This study found that CGM use was significantly associated with improved glycemic control in patients with non–insulin-dependent T2DM within an AI/AN population, particularly among patients with higher baseline HbA1c levels. The findings suggest that CGMs may be a valuable tool for managing T2DM beyond insulin-dependent populations.
Additional research with larger sample sizes, control groups, and extended follow-up periods is recommended to explore long-term benefits and impacts on other health metrics. The sample size estimates derived from this study serve as a valuable resource for researchers designing future studies aimed at addressing these gaps. Future research that expands on our findings by including larger, more diverse cohorts, accounting for medication use, and exploring different CGM technologies will enhance understanding and contribute to more effective diabetes management strategies for varied populations.
- National diabetes statistics report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. May 15, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html
- Elsayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:S19-S40. doi:10.2337/dc23-S002
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2011;29:116-122. doi:10.2337/diaclin.29.3.116
- Pleus S, Freckmann G, Schauer S, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose as an integral part in the management of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2022;13:829-846. doi:10.1007/s13300-022-01254-8
- Polonsky WH, Fisher L, Schikman CH, et al. Structured self-monitoring of blood glucose significantly reduces A1C levels in poorly controlled, noninsulin-treated type 2 diabetes: results from the Structured Testing Program study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:262-267. doi:10.2337/dc10-1732
- Tanaka N, Yabe D, Murotani K, et al. Mental distress and health-related quality of life among type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients using self-monitoring of blood glucose: a cross-sectional questionnaire study in Japan. J Diabetes Investig. 2018;9:1203-1211. doi:10.1111/jdi.12827
- Hortensius J, Kars MC, Wierenga WS, et al. Perspectives of patients with type 1 or insulin-treated type 2 diabetes on self-monitoring of blood glucose: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:167. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-12-167
- Didyuk O, Econom N, Guardia A, Livingston K, Klueh U. Continuous glucose monitoring devices: past, present, and future focus on the history and evolution of technological innovation. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2021;15:676-683. doi:10.1177/1932296819899394
- Beck RW, Riddlesworth TD, Ruedy K, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: the DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317:371-378. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19975
- Lind M, Polonsky W, Hirsch IB, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring vs conventional therapy for glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes treated with multiple daily insulin injections: the GOLD randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317:379-387. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19976
- Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, et al. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: a multicenter, non-masked, randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2254-2263. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31535-5
- Seidu S, Kunutsor SK, Ajjan RA, et al. Efficacy and safety of continuous glucose monitoring and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional evidence. Diabetes Care. 2024;47:169-179. doi:10.2337/dc23-1520
- ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. 5. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:S68-S96. doi:10.2337/dc23-S005
- Yaron M, Roitman E, Aharon-Hananel G, et al. Effect of flash glucose monitoring technology on glycemic control and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:1178-1184. doi:10.2337/dc18-0166
- National diabetes statistics report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. May 15, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html
- Elsayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:S19-S40. doi:10.2337/dc23-S002
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2011;29:116-122. doi:10.2337/diaclin.29.3.116
- Pleus S, Freckmann G, Schauer S, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose as an integral part in the management of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2022;13:829-846. doi:10.1007/s13300-022-01254-8
- Polonsky WH, Fisher L, Schikman CH, et al. Structured self-monitoring of blood glucose significantly reduces A1C levels in poorly controlled, noninsulin-treated type 2 diabetes: results from the Structured Testing Program study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:262-267. doi:10.2337/dc10-1732
- Tanaka N, Yabe D, Murotani K, et al. Mental distress and health-related quality of life among type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients using self-monitoring of blood glucose: a cross-sectional questionnaire study in Japan. J Diabetes Investig. 2018;9:1203-1211. doi:10.1111/jdi.12827
- Hortensius J, Kars MC, Wierenga WS, et al. Perspectives of patients with type 1 or insulin-treated type 2 diabetes on self-monitoring of blood glucose: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:167. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-12-167
- Didyuk O, Econom N, Guardia A, Livingston K, Klueh U. Continuous glucose monitoring devices: past, present, and future focus on the history and evolution of technological innovation. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2021;15:676-683. doi:10.1177/1932296819899394
- Beck RW, Riddlesworth TD, Ruedy K, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: the DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317:371-378. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19975
- Lind M, Polonsky W, Hirsch IB, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring vs conventional therapy for glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes treated with multiple daily insulin injections: the GOLD randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317:379-387. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19976
- Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, et al. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: a multicenter, non-masked, randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2254-2263. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31535-5
- Seidu S, Kunutsor SK, Ajjan RA, et al. Efficacy and safety of continuous glucose monitoring and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional evidence. Diabetes Care. 2024;47:169-179. doi:10.2337/dc23-1520
- ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. 5. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:S68-S96. doi:10.2337/dc23-S005
- Yaron M, Roitman E, Aharon-Hananel G, et al. Effect of flash glucose monitoring technology on glycemic control and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:1178-1184. doi:10.2337/dc18-0166
Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for American Indian/Alaska Native Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Not Using Insulin
Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for American Indian/Alaska Native Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Not Using Insulin
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death among women in the United States.1 Most CVD is due to the buildup of plaque (ie, cholesterol, proteins, calcium, and inflammatory cells) in artery walls.2 The plaque may lead to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), which includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and aortic atherosclerotic disease.2,3 Control and reduction of ASCVD risk factors, including high cholesterol levels, elevated blood pressure, insulin resistance, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle, can contribute to a reduction in ASCVD morbidity and mortality.2 People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have an increased prevalence of lipid abnormalities, contributing to their high risk of ASCVD.4,5
The prescribing of statins (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzmye A reductase inhibitors) is the cornerstone of lipid-lowering therapy and cardiovascular risk reduction for primary and secondary prevention of ASCVD.6 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend moderate- to high-intensity statins for primary prevention in patients with T2DM and high-intensity statins for secondary prevention in those with or without diabetes when not contraindicated.4,5,7 Despite eligibility according to guideline recommendations, research predominantly shows that women are less likely to receive statin therapy; however, this trend is improving. [6,8-11] To explain the sex differences in statin use, Nanna et al found that there is a combination of women being offered statin therapy less frequently, declining therapy more frequently, and discontinuing treatment more frequently.11 One possibility for discontinuing treatment could be statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), which occur in about 10% of patients.12 The incidence of adverse effects (AEs) may be related to the way statins are metabolized.
Pharmacogenomic testing is free for veterans through the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) PHASER program, which offers information and recommendations for a panel of 11 gene variants. The panel includes genes related to common medication classes such as anticoagulants, antiplatelets, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, antidepressants, and statins. The VA PHASER panel includes the solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, which is predominantly expressed in the liver and facilitates the hepatic uptake of most statins.13,14 A reduced function of SLCO1B1 can lead to higher statin levels, resulting in increased concentrations that may potentially cause SAMS.13,14 Some alleles associated with reduced function include SLCO1B1*5, *15, *23, *31, and *46 to *49, whereas others are associated with increased function, such as SLCO1B1 *14 and *20 (Appendix).15 Supporting evidence shows the SLCO1B1*5 nucleotide polymorphism increases plasma levels of simvastatin and atorvastatin, affecting effectiveness or toxicity. 13 Females tend to have a lower body weight and higher percentage of body fat compared with males, which might lead to higher concentrations of lipophilic drugs, including atorvastatin and simvastatin, which may be exacerbated by decreased function of SLCO1B1*5.15 With pharmacogenomic testing, therapeutic recommendations can be made to improve the overall safety and efficacy of statins, thus improving adherence using a patient-specific approach.14,15
Methods
Carl Vinson VA Medical Center (CVVAMC) serves about 42,000 veterans in Central and South Georgia, of which about 15% are female. Of the female veterans enrolled in care, 63% identify as Black, 27% White, and 1.5% as Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, or Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander. The 2020 Veterans Chartbook report showed that female veterans and minority racial and ethnic groups had worse access to health care and higher mortality rates than their male and non-Hispanic White counterparts.16
The Primary Care Equity Dashboard (PCED) was developed to engage the VA health care workforce in the process of identifying and addressing inequities in local patient populations.17 Using electronic quality measure data, the PCED provides Veterans Integrated Service Network-level and facility-level performance on several metrics.18 The PCED had not been previously used at the CVVAMC, and few publications or quality improvement projects regarding its use have been reported by the VA Office of Health Equity. PCED helped identify disparities when comparing female to male patients in the prescribing of statin therapy for patients with CVD and statin therapy for patients with T2DM.
VA PHASER pharmacogenomic analyses provided an opportunity to expand this quality improvement project. Sanford Health and the VA collaborated on the PHASER program to offer free genetic testing for veterans. The program launched in 2019 and expanded to various VA sites, including CVVAMC in March 2023. This program has been extended to December 31, 2025.
The primary objective of this quality improvement project was to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk. Secondary outcomes included increased pharmacogenomic testing and the assessment of pharmacogenomic results related to statin therapy. This project was approved by the CVVAMC Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. The PCED was used to identify female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD without an active prescription for a statin between July and October 2023. A review of Computerized Patient Record System patient charts was completed to screen for prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria. Veterans were included if they were assigned female at birth, were enrolled in care at CVVAMC, and had a diagnosis of T2DM or CVD (history of myocardial infarction, coronary bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other revascularization in any setting).
Veterans were excluded if they were currently pregnant, trying to conceive, breastfeeding, had a T1DM diagnosis, had previously documented hypersensitivity to a statin, active liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis, previously documented statin-associated rhabdomyolysis or autoimmune myopathy, an active prescription for a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, or previously documented statin intolerance (defined as the inability to tolerate ≥ 3 statins, with ≥ 1 prescribed at low intensity or alternate-day dosing). The female veterans were compared to 2 comparators: the facility's male veterans and the VA national average, identified via the PCED.
Once a veteran was screened, they were telephoned between October 2023 and February 2024 and provided education on statin use and pharmacogenomic testing using a standardized note template. An order was placed for participants who provided verbal consent for pharmacogenomic testing. Those who agreed to statin initiation were referred to a clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) who contacted them at a later date to prescribe a statin following the recommendations of the 2019 ACC/AHA and 2023 ADA guidelines and pharmacogenomic testing, if applicable.4,5,7 Appropriate monitoring and follow-up occurred at the discretion of each CPP. Data collection included: age, race, diagnoses (T2DM, CVD, or both), baseline lipid panel (total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein), hepatic function, name and dose of statin, reasons for declining statin therapy, and pharmacogenomic testing results related to SLCO1B1.
Results
At baseline in July 2023, 77.8% of female veterans with T2DM were prescribed a statin, which exceeded the national VA average (77.0%), but was below the rate for male veterans (78.7%) in the facility comparator group.17 Additionally, 82.2% of females with CVD were prescribed a statin, which was below the national VA average of 86.0% and the 84.9% of male veterans in the facility comparator group.17 The PCED identified 189 female veterans from July 2023 to October 2023 who may benefit from statin therapy. Thirty-three females met the exclusion criteria. Of the 156 included veterans, 129 (82.7%) were successfully contacted and 27 (17.3%) could not be reached by telephone after 3 attempts (Figure 1). The 129 female veterans contacted had a mean age of 59 years and the majority were Black (82.9%) (Table 1).
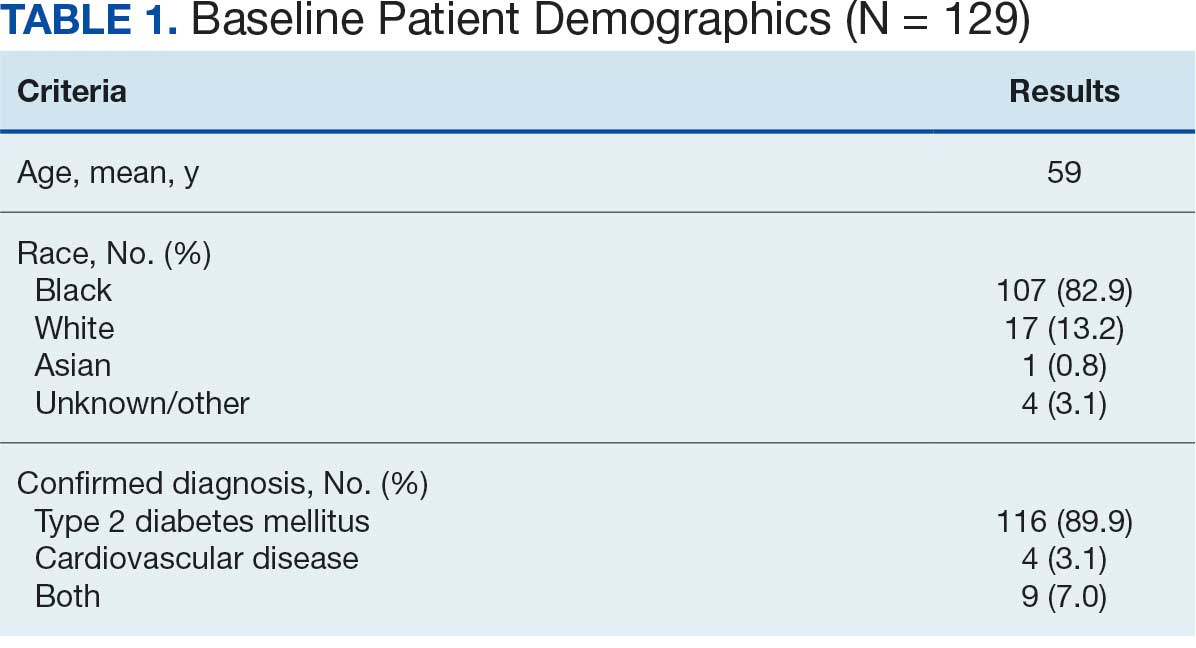
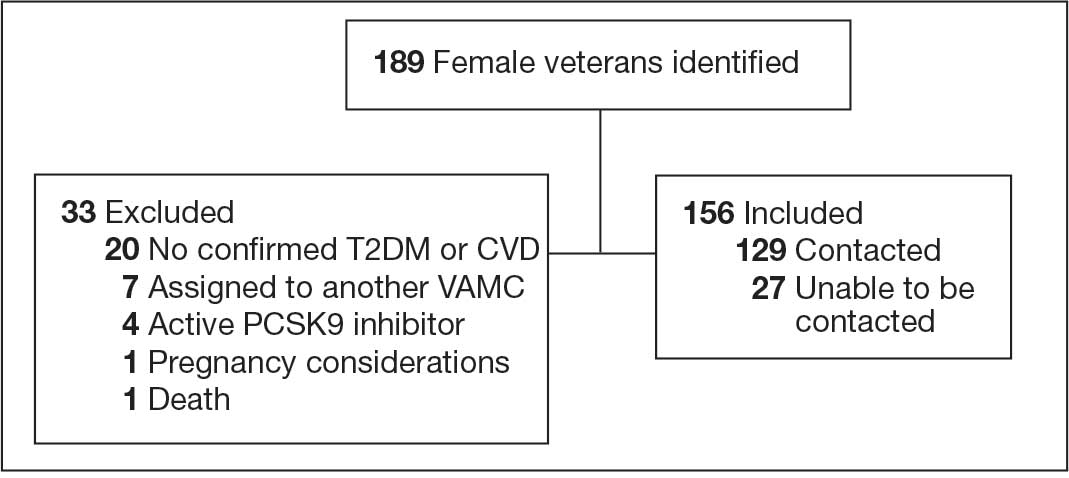
Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/
kexin type 9; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; VAMC, Veterans Affairs medical center.
Primary Outcomes
Of the 129 contacted veterans, 31 (24.0%) had a non-VA statin prescription, 13 (10.1%) had an active VA statin prescription, and 85 (65.9%) did not have a statin prescription, despite being eligible. Statin adherence was confirmed with participants, and the medication list was updated accordingly.
Of the 85 veterans with no active statin therapy, 37 (43.5%) accepted a new statin prescription and 48 (56.5%) declined. There were various reasons provided for declining statin therapy: 17 participants (35.4%) declined due to concern for AEs (Table 2).

From July 2023 to March 2024, the percentage of female veterans with active statin therapy with T2DM increased from 77.8% to 79.0%. For those with active statin therapy with CVD, usage increased from 82.2% to 90.2%, which exceeded the national VA average and facility male comparator group (Figures 2 and 3).17
Secondary Outcomes
Seventy-one of 129 veterans (55.0%) gave verbal consent, and 47 (66.2%) completed the pharmacogenomic testing; 58 (45.0%) declined. Five veterans (10.6%) had a known SLCO1B1 allele variant present. One veteran required a change in statin therapy based on the results (eAppendix).
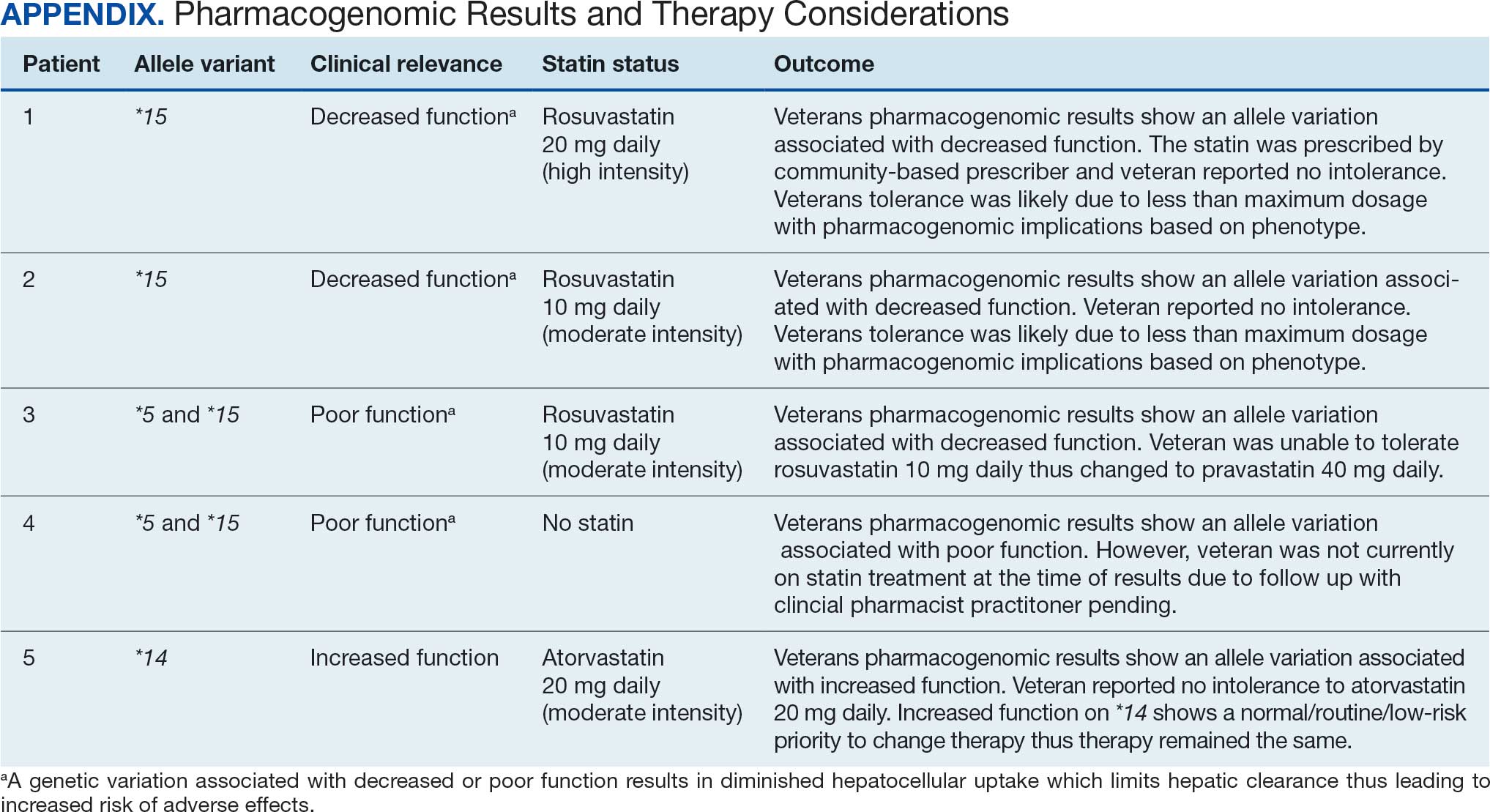
Discussion
This project aimed to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk and increase pharmacogenomic testing using the PCED and care managed by CPPs. The results of this quality improvement project illustrated that both metrics have improved at CVVAMC as a result of the intervention. The results in both metrics now exceed the PCED national VA average, and the CVD metric also exceeds that of the facility male comparator group. While there was only a 1.2% increase from July 2023 to March 2024 for patients with T2DM, there was an 8.0% increase for patients with CVD. Despite standardized education on statin use, more veterans declined therapy than accepted it, mostly due to concern for AEs. Recording the reasons for declining statin therapy offered valuable insight that can be used in additional discussions with veterans and clinicians.
Pharmacogenomics gives clinicians the unique opportunity to take a proactive approach to better predict drug responses, potentially allowing for less trial and error with medications, fewer AEs, greater trust in the clinician, and improved medication adherence. The CPPs incorporated pharmacogenomic testing into their practice, which led to identifying 5 SLCO1B1 gene abnormalities. The PCED served as a powerful tool for advancing equity-focused quality improvement initiatives on a local level and was crucial in prioritizing the detection of veterans potentially receiving suboptimal care.
Limitations
The nature of “cold calls” made it challenging to establish contact for inclusion in this study. An alternative to increase engagement could have been scheduled phone or face-to-face visits. While the use of the PCED was crucial, data did not account for statins listed in the non-VA medication list. All 31 patients with statins prescribed outside the VA had a start date added to provide the most accurate representation of the data moving forward.
Another limitation in this project was its small sample size and population. CVVAMC serves about 6200 female veterans, with roughly 63% identifying as Black. The preponderance of Black individuals (83%) in this project is typical for the female patient population at CVVAMC but may not reflect the demographics of other populations. Other limitations to this project consisted of scheduling conflicts. Appointments for laboratory draws at community-based outpatient clinics were subject to availability, which resulted in some delay in completion of pharmacogenomic testing.
Conclusions
CPPs can help reduce inequity in health care delivery. Increased incorporation of the PCED into regular practice within the VA is recommended to continue addressing sex disparities in statin use, diabetes control, blood pressure management, cancer screenings, and vaccination needs. CVVAMC plans to expand its use through another quality improvement project focused on reducing sex disparities in blood pressure management. Improving educational resources made available to veterans on the importance of statin therapy and potential to mitigate AEs through use of the VA PHASER program also would be helpful. This project successfully improved CVVAMC metrics for female veterans appropriately prescribed statin therapy and increased access to pharmacogenomic testing. Most importantly, it helped close the sex-based gap in CVD risk reduction care.
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2018. Nat Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-114.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical practice guideline for the management of dyslipidemia for cardiovascular risk reduction. Published June 2020. Accessed August 25, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/lipids/VADODDyslipidemiaCPG5087212020.pdf
- Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). American Heart Association. Accessed August 26, 2025. https:// www.heart.org/en/professional/quality-improvement/ascvd
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S144-S174. doi:10.2337/dc22-S010
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes. 2022;41(1):4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Buchanan CH, Brown EA, Bishu KG, et al. The magnitude and potential causes of gender disparities in statin therapy in veterans with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year nationwide longitudinal cohort study. Womens Health Issues. 2022;32:274-283. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2021.10.003
- Ahmed F, Lin J, Ahmed T, et al. Health disparities: statin prescribing patterns among patients with diabetes in a family medicine clinic. Health Equity. 2022;6:291-297. doi:10.1089/heq.2021.0144
- Metser G, Bradley C, Moise N, Liyanage-Don N, Kronish I, Ye S. Gaps and disparities in primary prevention statin prescription during outpatient care. Am J Cardiol. 2021;161:36-41. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.08.070
- Nanna MG, Wang TY, Xiang Q, et al. Sex differences in the use of statins in community practice. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(8):e005562. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.005562
- Kitzmiller JP, Mikulik EB, Dauki AM, Murkherjee C, Luzum JA. Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2016;9:97-106. doi:10.2147/PGPM.S86013
- Türkmen D, Masoli JAH, Kuo CL, Bowden J, Melzer D, Pilling LC. Statin treatment effectiveness and the SLCO1B1*5 reduced function genotype: long-term outcomes in women and men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88:3230-3240. doi:10.1111/bcp.15245
- Cooper-DeHoff RM, Niemi M, Ramsey LB, et al. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and statin-associated musculoskeletal symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;111:1007-1021. doi:10.1002/cpt.2557
- Ramsey LB, Gong L, Lee SB, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: SLCO1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023;113:782-793. doi:10.1002/cpt.2705
- National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report: Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); November 2020.
- Procario G. Primary Care Equity Dashboard [database online]. Power Bi. 2023. Accessed August 26, 2025. https://app.powerbigov.us
- Hausmann LRM, Lamorte C, Estock JL. Understanding the context for incorporating equity into quality improvement throughout a national health care system. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):312-320. doi:10.1089/heq.2023.0009
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death among women in the United States.1 Most CVD is due to the buildup of plaque (ie, cholesterol, proteins, calcium, and inflammatory cells) in artery walls.2 The plaque may lead to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), which includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and aortic atherosclerotic disease.2,3 Control and reduction of ASCVD risk factors, including high cholesterol levels, elevated blood pressure, insulin resistance, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle, can contribute to a reduction in ASCVD morbidity and mortality.2 People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have an increased prevalence of lipid abnormalities, contributing to their high risk of ASCVD.4,5
The prescribing of statins (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzmye A reductase inhibitors) is the cornerstone of lipid-lowering therapy and cardiovascular risk reduction for primary and secondary prevention of ASCVD.6 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend moderate- to high-intensity statins for primary prevention in patients with T2DM and high-intensity statins for secondary prevention in those with or without diabetes when not contraindicated.4,5,7 Despite eligibility according to guideline recommendations, research predominantly shows that women are less likely to receive statin therapy; however, this trend is improving. [6,8-11] To explain the sex differences in statin use, Nanna et al found that there is a combination of women being offered statin therapy less frequently, declining therapy more frequently, and discontinuing treatment more frequently.11 One possibility for discontinuing treatment could be statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), which occur in about 10% of patients.12 The incidence of adverse effects (AEs) may be related to the way statins are metabolized.
Pharmacogenomic testing is free for veterans through the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) PHASER program, which offers information and recommendations for a panel of 11 gene variants. The panel includes genes related to common medication classes such as anticoagulants, antiplatelets, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, antidepressants, and statins. The VA PHASER panel includes the solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, which is predominantly expressed in the liver and facilitates the hepatic uptake of most statins.13,14 A reduced function of SLCO1B1 can lead to higher statin levels, resulting in increased concentrations that may potentially cause SAMS.13,14 Some alleles associated with reduced function include SLCO1B1*5, *15, *23, *31, and *46 to *49, whereas others are associated with increased function, such as SLCO1B1 *14 and *20 (Appendix).15 Supporting evidence shows the SLCO1B1*5 nucleotide polymorphism increases plasma levels of simvastatin and atorvastatin, affecting effectiveness or toxicity. 13 Females tend to have a lower body weight and higher percentage of body fat compared with males, which might lead to higher concentrations of lipophilic drugs, including atorvastatin and simvastatin, which may be exacerbated by decreased function of SLCO1B1*5.15 With pharmacogenomic testing, therapeutic recommendations can be made to improve the overall safety and efficacy of statins, thus improving adherence using a patient-specific approach.14,15
Methods
Carl Vinson VA Medical Center (CVVAMC) serves about 42,000 veterans in Central and South Georgia, of which about 15% are female. Of the female veterans enrolled in care, 63% identify as Black, 27% White, and 1.5% as Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, or Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander. The 2020 Veterans Chartbook report showed that female veterans and minority racial and ethnic groups had worse access to health care and higher mortality rates than their male and non-Hispanic White counterparts.16
The Primary Care Equity Dashboard (PCED) was developed to engage the VA health care workforce in the process of identifying and addressing inequities in local patient populations.17 Using electronic quality measure data, the PCED provides Veterans Integrated Service Network-level and facility-level performance on several metrics.18 The PCED had not been previously used at the CVVAMC, and few publications or quality improvement projects regarding its use have been reported by the VA Office of Health Equity. PCED helped identify disparities when comparing female to male patients in the prescribing of statin therapy for patients with CVD and statin therapy for patients with T2DM.
VA PHASER pharmacogenomic analyses provided an opportunity to expand this quality improvement project. Sanford Health and the VA collaborated on the PHASER program to offer free genetic testing for veterans. The program launched in 2019 and expanded to various VA sites, including CVVAMC in March 2023. This program has been extended to December 31, 2025.
The primary objective of this quality improvement project was to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk. Secondary outcomes included increased pharmacogenomic testing and the assessment of pharmacogenomic results related to statin therapy. This project was approved by the CVVAMC Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. The PCED was used to identify female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD without an active prescription for a statin between July and October 2023. A review of Computerized Patient Record System patient charts was completed to screen for prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria. Veterans were included if they were assigned female at birth, were enrolled in care at CVVAMC, and had a diagnosis of T2DM or CVD (history of myocardial infarction, coronary bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other revascularization in any setting).
Veterans were excluded if they were currently pregnant, trying to conceive, breastfeeding, had a T1DM diagnosis, had previously documented hypersensitivity to a statin, active liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis, previously documented statin-associated rhabdomyolysis or autoimmune myopathy, an active prescription for a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, or previously documented statin intolerance (defined as the inability to tolerate ≥ 3 statins, with ≥ 1 prescribed at low intensity or alternate-day dosing). The female veterans were compared to 2 comparators: the facility's male veterans and the VA national average, identified via the PCED.
Once a veteran was screened, they were telephoned between October 2023 and February 2024 and provided education on statin use and pharmacogenomic testing using a standardized note template. An order was placed for participants who provided verbal consent for pharmacogenomic testing. Those who agreed to statin initiation were referred to a clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) who contacted them at a later date to prescribe a statin following the recommendations of the 2019 ACC/AHA and 2023 ADA guidelines and pharmacogenomic testing, if applicable.4,5,7 Appropriate monitoring and follow-up occurred at the discretion of each CPP. Data collection included: age, race, diagnoses (T2DM, CVD, or both), baseline lipid panel (total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein), hepatic function, name and dose of statin, reasons for declining statin therapy, and pharmacogenomic testing results related to SLCO1B1.
Results
At baseline in July 2023, 77.8% of female veterans with T2DM were prescribed a statin, which exceeded the national VA average (77.0%), but was below the rate for male veterans (78.7%) in the facility comparator group.17 Additionally, 82.2% of females with CVD were prescribed a statin, which was below the national VA average of 86.0% and the 84.9% of male veterans in the facility comparator group.17 The PCED identified 189 female veterans from July 2023 to October 2023 who may benefit from statin therapy. Thirty-three females met the exclusion criteria. Of the 156 included veterans, 129 (82.7%) were successfully contacted and 27 (17.3%) could not be reached by telephone after 3 attempts (Figure 1). The 129 female veterans contacted had a mean age of 59 years and the majority were Black (82.9%) (Table 1).


Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/
kexin type 9; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; VAMC, Veterans Affairs medical center.
Primary Outcomes
Of the 129 contacted veterans, 31 (24.0%) had a non-VA statin prescription, 13 (10.1%) had an active VA statin prescription, and 85 (65.9%) did not have a statin prescription, despite being eligible. Statin adherence was confirmed with participants, and the medication list was updated accordingly.
Of the 85 veterans with no active statin therapy, 37 (43.5%) accepted a new statin prescription and 48 (56.5%) declined. There were various reasons provided for declining statin therapy: 17 participants (35.4%) declined due to concern for AEs (Table 2).

From July 2023 to March 2024, the percentage of female veterans with active statin therapy with T2DM increased from 77.8% to 79.0%. For those with active statin therapy with CVD, usage increased from 82.2% to 90.2%, which exceeded the national VA average and facility male comparator group (Figures 2 and 3).17


Secondary Outcomes
Seventy-one of 129 veterans (55.0%) gave verbal consent, and 47 (66.2%) completed the pharmacogenomic testing; 58 (45.0%) declined. Five veterans (10.6%) had a known SLCO1B1 allele variant present. One veteran required a change in statin therapy based on the results (eAppendix).

Discussion
This project aimed to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk and increase pharmacogenomic testing using the PCED and care managed by CPPs. The results of this quality improvement project illustrated that both metrics have improved at CVVAMC as a result of the intervention. The results in both metrics now exceed the PCED national VA average, and the CVD metric also exceeds that of the facility male comparator group. While there was only a 1.2% increase from July 2023 to March 2024 for patients with T2DM, there was an 8.0% increase for patients with CVD. Despite standardized education on statin use, more veterans declined therapy than accepted it, mostly due to concern for AEs. Recording the reasons for declining statin therapy offered valuable insight that can be used in additional discussions with veterans and clinicians.
Pharmacogenomics gives clinicians the unique opportunity to take a proactive approach to better predict drug responses, potentially allowing for less trial and error with medications, fewer AEs, greater trust in the clinician, and improved medication adherence. The CPPs incorporated pharmacogenomic testing into their practice, which led to identifying 5 SLCO1B1 gene abnormalities. The PCED served as a powerful tool for advancing equity-focused quality improvement initiatives on a local level and was crucial in prioritizing the detection of veterans potentially receiving suboptimal care.
Limitations
The nature of “cold calls” made it challenging to establish contact for inclusion in this study. An alternative to increase engagement could have been scheduled phone or face-to-face visits. While the use of the PCED was crucial, data did not account for statins listed in the non-VA medication list. All 31 patients with statins prescribed outside the VA had a start date added to provide the most accurate representation of the data moving forward.
Another limitation in this project was its small sample size and population. CVVAMC serves about 6200 female veterans, with roughly 63% identifying as Black. The preponderance of Black individuals (83%) in this project is typical for the female patient population at CVVAMC but may not reflect the demographics of other populations. Other limitations to this project consisted of scheduling conflicts. Appointments for laboratory draws at community-based outpatient clinics were subject to availability, which resulted in some delay in completion of pharmacogenomic testing.
Conclusions
CPPs can help reduce inequity in health care delivery. Increased incorporation of the PCED into regular practice within the VA is recommended to continue addressing sex disparities in statin use, diabetes control, blood pressure management, cancer screenings, and vaccination needs. CVVAMC plans to expand its use through another quality improvement project focused on reducing sex disparities in blood pressure management. Improving educational resources made available to veterans on the importance of statin therapy and potential to mitigate AEs through use of the VA PHASER program also would be helpful. This project successfully improved CVVAMC metrics for female veterans appropriately prescribed statin therapy and increased access to pharmacogenomic testing. Most importantly, it helped close the sex-based gap in CVD risk reduction care.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death among women in the United States.1 Most CVD is due to the buildup of plaque (ie, cholesterol, proteins, calcium, and inflammatory cells) in artery walls.2 The plaque may lead to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), which includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and aortic atherosclerotic disease.2,3 Control and reduction of ASCVD risk factors, including high cholesterol levels, elevated blood pressure, insulin resistance, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle, can contribute to a reduction in ASCVD morbidity and mortality.2 People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have an increased prevalence of lipid abnormalities, contributing to their high risk of ASCVD.4,5
The prescribing of statins (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzmye A reductase inhibitors) is the cornerstone of lipid-lowering therapy and cardiovascular risk reduction for primary and secondary prevention of ASCVD.6 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend moderate- to high-intensity statins for primary prevention in patients with T2DM and high-intensity statins for secondary prevention in those with or without diabetes when not contraindicated.4,5,7 Despite eligibility according to guideline recommendations, research predominantly shows that women are less likely to receive statin therapy; however, this trend is improving. [6,8-11] To explain the sex differences in statin use, Nanna et al found that there is a combination of women being offered statin therapy less frequently, declining therapy more frequently, and discontinuing treatment more frequently.11 One possibility for discontinuing treatment could be statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), which occur in about 10% of patients.12 The incidence of adverse effects (AEs) may be related to the way statins are metabolized.
Pharmacogenomic testing is free for veterans through the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) PHASER program, which offers information and recommendations for a panel of 11 gene variants. The panel includes genes related to common medication classes such as anticoagulants, antiplatelets, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, antidepressants, and statins. The VA PHASER panel includes the solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, which is predominantly expressed in the liver and facilitates the hepatic uptake of most statins.13,14 A reduced function of SLCO1B1 can lead to higher statin levels, resulting in increased concentrations that may potentially cause SAMS.13,14 Some alleles associated with reduced function include SLCO1B1*5, *15, *23, *31, and *46 to *49, whereas others are associated with increased function, such as SLCO1B1 *14 and *20 (Appendix).15 Supporting evidence shows the SLCO1B1*5 nucleotide polymorphism increases plasma levels of simvastatin and atorvastatin, affecting effectiveness or toxicity. 13 Females tend to have a lower body weight and higher percentage of body fat compared with males, which might lead to higher concentrations of lipophilic drugs, including atorvastatin and simvastatin, which may be exacerbated by decreased function of SLCO1B1*5.15 With pharmacogenomic testing, therapeutic recommendations can be made to improve the overall safety and efficacy of statins, thus improving adherence using a patient-specific approach.14,15
Methods
Carl Vinson VA Medical Center (CVVAMC) serves about 42,000 veterans in Central and South Georgia, of which about 15% are female. Of the female veterans enrolled in care, 63% identify as Black, 27% White, and 1.5% as Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, or Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander. The 2020 Veterans Chartbook report showed that female veterans and minority racial and ethnic groups had worse access to health care and higher mortality rates than their male and non-Hispanic White counterparts.16
The Primary Care Equity Dashboard (PCED) was developed to engage the VA health care workforce in the process of identifying and addressing inequities in local patient populations.17 Using electronic quality measure data, the PCED provides Veterans Integrated Service Network-level and facility-level performance on several metrics.18 The PCED had not been previously used at the CVVAMC, and few publications or quality improvement projects regarding its use have been reported by the VA Office of Health Equity. PCED helped identify disparities when comparing female to male patients in the prescribing of statin therapy for patients with CVD and statin therapy for patients with T2DM.
VA PHASER pharmacogenomic analyses provided an opportunity to expand this quality improvement project. Sanford Health and the VA collaborated on the PHASER program to offer free genetic testing for veterans. The program launched in 2019 and expanded to various VA sites, including CVVAMC in March 2023. This program has been extended to December 31, 2025.
The primary objective of this quality improvement project was to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk. Secondary outcomes included increased pharmacogenomic testing and the assessment of pharmacogenomic results related to statin therapy. This project was approved by the CVVAMC Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. The PCED was used to identify female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD without an active prescription for a statin between July and October 2023. A review of Computerized Patient Record System patient charts was completed to screen for prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria. Veterans were included if they were assigned female at birth, were enrolled in care at CVVAMC, and had a diagnosis of T2DM or CVD (history of myocardial infarction, coronary bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other revascularization in any setting).
Veterans were excluded if they were currently pregnant, trying to conceive, breastfeeding, had a T1DM diagnosis, had previously documented hypersensitivity to a statin, active liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis, previously documented statin-associated rhabdomyolysis or autoimmune myopathy, an active prescription for a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, or previously documented statin intolerance (defined as the inability to tolerate ≥ 3 statins, with ≥ 1 prescribed at low intensity or alternate-day dosing). The female veterans were compared to 2 comparators: the facility's male veterans and the VA national average, identified via the PCED.
Once a veteran was screened, they were telephoned between October 2023 and February 2024 and provided education on statin use and pharmacogenomic testing using a standardized note template. An order was placed for participants who provided verbal consent for pharmacogenomic testing. Those who agreed to statin initiation were referred to a clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) who contacted them at a later date to prescribe a statin following the recommendations of the 2019 ACC/AHA and 2023 ADA guidelines and pharmacogenomic testing, if applicable.4,5,7 Appropriate monitoring and follow-up occurred at the discretion of each CPP. Data collection included: age, race, diagnoses (T2DM, CVD, or both), baseline lipid panel (total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein), hepatic function, name and dose of statin, reasons for declining statin therapy, and pharmacogenomic testing results related to SLCO1B1.
Results
At baseline in July 2023, 77.8% of female veterans with T2DM were prescribed a statin, which exceeded the national VA average (77.0%), but was below the rate for male veterans (78.7%) in the facility comparator group.17 Additionally, 82.2% of females with CVD were prescribed a statin, which was below the national VA average of 86.0% and the 84.9% of male veterans in the facility comparator group.17 The PCED identified 189 female veterans from July 2023 to October 2023 who may benefit from statin therapy. Thirty-three females met the exclusion criteria. Of the 156 included veterans, 129 (82.7%) were successfully contacted and 27 (17.3%) could not be reached by telephone after 3 attempts (Figure 1). The 129 female veterans contacted had a mean age of 59 years and the majority were Black (82.9%) (Table 1).


Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/
kexin type 9; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; VAMC, Veterans Affairs medical center.
Primary Outcomes
Of the 129 contacted veterans, 31 (24.0%) had a non-VA statin prescription, 13 (10.1%) had an active VA statin prescription, and 85 (65.9%) did not have a statin prescription, despite being eligible. Statin adherence was confirmed with participants, and the medication list was updated accordingly.
Of the 85 veterans with no active statin therapy, 37 (43.5%) accepted a new statin prescription and 48 (56.5%) declined. There were various reasons provided for declining statin therapy: 17 participants (35.4%) declined due to concern for AEs (Table 2).

From July 2023 to March 2024, the percentage of female veterans with active statin therapy with T2DM increased from 77.8% to 79.0%. For those with active statin therapy with CVD, usage increased from 82.2% to 90.2%, which exceeded the national VA average and facility male comparator group (Figures 2 and 3).17


Secondary Outcomes
Seventy-one of 129 veterans (55.0%) gave verbal consent, and 47 (66.2%) completed the pharmacogenomic testing; 58 (45.0%) declined. Five veterans (10.6%) had a known SLCO1B1 allele variant present. One veteran required a change in statin therapy based on the results (eAppendix).

Discussion
This project aimed to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk and increase pharmacogenomic testing using the PCED and care managed by CPPs. The results of this quality improvement project illustrated that both metrics have improved at CVVAMC as a result of the intervention. The results in both metrics now exceed the PCED national VA average, and the CVD metric also exceeds that of the facility male comparator group. While there was only a 1.2% increase from July 2023 to March 2024 for patients with T2DM, there was an 8.0% increase for patients with CVD. Despite standardized education on statin use, more veterans declined therapy than accepted it, mostly due to concern for AEs. Recording the reasons for declining statin therapy offered valuable insight that can be used in additional discussions with veterans and clinicians.
Pharmacogenomics gives clinicians the unique opportunity to take a proactive approach to better predict drug responses, potentially allowing for less trial and error with medications, fewer AEs, greater trust in the clinician, and improved medication adherence. The CPPs incorporated pharmacogenomic testing into their practice, which led to identifying 5 SLCO1B1 gene abnormalities. The PCED served as a powerful tool for advancing equity-focused quality improvement initiatives on a local level and was crucial in prioritizing the detection of veterans potentially receiving suboptimal care.
Limitations
The nature of “cold calls” made it challenging to establish contact for inclusion in this study. An alternative to increase engagement could have been scheduled phone or face-to-face visits. While the use of the PCED was crucial, data did not account for statins listed in the non-VA medication list. All 31 patients with statins prescribed outside the VA had a start date added to provide the most accurate representation of the data moving forward.
Another limitation in this project was its small sample size and population. CVVAMC serves about 6200 female veterans, with roughly 63% identifying as Black. The preponderance of Black individuals (83%) in this project is typical for the female patient population at CVVAMC but may not reflect the demographics of other populations. Other limitations to this project consisted of scheduling conflicts. Appointments for laboratory draws at community-based outpatient clinics were subject to availability, which resulted in some delay in completion of pharmacogenomic testing.
Conclusions
CPPs can help reduce inequity in health care delivery. Increased incorporation of the PCED into regular practice within the VA is recommended to continue addressing sex disparities in statin use, diabetes control, blood pressure management, cancer screenings, and vaccination needs. CVVAMC plans to expand its use through another quality improvement project focused on reducing sex disparities in blood pressure management. Improving educational resources made available to veterans on the importance of statin therapy and potential to mitigate AEs through use of the VA PHASER program also would be helpful. This project successfully improved CVVAMC metrics for female veterans appropriately prescribed statin therapy and increased access to pharmacogenomic testing. Most importantly, it helped close the sex-based gap in CVD risk reduction care.
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2018. Nat Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-114.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical practice guideline for the management of dyslipidemia for cardiovascular risk reduction. Published June 2020. Accessed August 25, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/lipids/VADODDyslipidemiaCPG5087212020.pdf
- Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). American Heart Association. Accessed August 26, 2025. https:// www.heart.org/en/professional/quality-improvement/ascvd
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S144-S174. doi:10.2337/dc22-S010
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes. 2022;41(1):4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Buchanan CH, Brown EA, Bishu KG, et al. The magnitude and potential causes of gender disparities in statin therapy in veterans with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year nationwide longitudinal cohort study. Womens Health Issues. 2022;32:274-283. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2021.10.003
- Ahmed F, Lin J, Ahmed T, et al. Health disparities: statin prescribing patterns among patients with diabetes in a family medicine clinic. Health Equity. 2022;6:291-297. doi:10.1089/heq.2021.0144
- Metser G, Bradley C, Moise N, Liyanage-Don N, Kronish I, Ye S. Gaps and disparities in primary prevention statin prescription during outpatient care. Am J Cardiol. 2021;161:36-41. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.08.070
- Nanna MG, Wang TY, Xiang Q, et al. Sex differences in the use of statins in community practice. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(8):e005562. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.005562
- Kitzmiller JP, Mikulik EB, Dauki AM, Murkherjee C, Luzum JA. Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2016;9:97-106. doi:10.2147/PGPM.S86013
- Türkmen D, Masoli JAH, Kuo CL, Bowden J, Melzer D, Pilling LC. Statin treatment effectiveness and the SLCO1B1*5 reduced function genotype: long-term outcomes in women and men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88:3230-3240. doi:10.1111/bcp.15245
- Cooper-DeHoff RM, Niemi M, Ramsey LB, et al. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and statin-associated musculoskeletal symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;111:1007-1021. doi:10.1002/cpt.2557
- Ramsey LB, Gong L, Lee SB, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: SLCO1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023;113:782-793. doi:10.1002/cpt.2705
- National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report: Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); November 2020.
- Procario G. Primary Care Equity Dashboard [database online]. Power Bi. 2023. Accessed August 26, 2025. https://app.powerbigov.us
- Hausmann LRM, Lamorte C, Estock JL. Understanding the context for incorporating equity into quality improvement throughout a national health care system. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):312-320. doi:10.1089/heq.2023.0009
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2018. Nat Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-114.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical practice guideline for the management of dyslipidemia for cardiovascular risk reduction. Published June 2020. Accessed August 25, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/lipids/VADODDyslipidemiaCPG5087212020.pdf
- Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). American Heart Association. Accessed August 26, 2025. https:// www.heart.org/en/professional/quality-improvement/ascvd
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S144-S174. doi:10.2337/dc22-S010
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes. 2022;41(1):4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Buchanan CH, Brown EA, Bishu KG, et al. The magnitude and potential causes of gender disparities in statin therapy in veterans with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year nationwide longitudinal cohort study. Womens Health Issues. 2022;32:274-283. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2021.10.003
- Ahmed F, Lin J, Ahmed T, et al. Health disparities: statin prescribing patterns among patients with diabetes in a family medicine clinic. Health Equity. 2022;6:291-297. doi:10.1089/heq.2021.0144
- Metser G, Bradley C, Moise N, Liyanage-Don N, Kronish I, Ye S. Gaps and disparities in primary prevention statin prescription during outpatient care. Am J Cardiol. 2021;161:36-41. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.08.070
- Nanna MG, Wang TY, Xiang Q, et al. Sex differences in the use of statins in community practice. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(8):e005562. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.005562
- Kitzmiller JP, Mikulik EB, Dauki AM, Murkherjee C, Luzum JA. Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2016;9:97-106. doi:10.2147/PGPM.S86013
- Türkmen D, Masoli JAH, Kuo CL, Bowden J, Melzer D, Pilling LC. Statin treatment effectiveness and the SLCO1B1*5 reduced function genotype: long-term outcomes in women and men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88:3230-3240. doi:10.1111/bcp.15245
- Cooper-DeHoff RM, Niemi M, Ramsey LB, et al. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and statin-associated musculoskeletal symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;111:1007-1021. doi:10.1002/cpt.2557
- Ramsey LB, Gong L, Lee SB, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: SLCO1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023;113:782-793. doi:10.1002/cpt.2705
- National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report: Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); November 2020.
- Procario G. Primary Care Equity Dashboard [database online]. Power Bi. 2023. Accessed August 26, 2025. https://app.powerbigov.us
- Hausmann LRM, Lamorte C, Estock JL. Understanding the context for incorporating equity into quality improvement throughout a national health care system. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):312-320. doi:10.1089/heq.2023.0009
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
In 2020, the US Multi-Society Task Force (USMSTF) on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) increased the recommended colon polyp surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas from 5 to 10 years to 7 to 10 years.1 This change was prompted by emerging research indicating that rates of CRC and advanced neoplasia among patients with a history of only 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas are lower than initially estimated.2,3 This extension provides an opportunity to increase endoscopy capacity and improve access to colonoscopies by retroactively applying the 2020 guidelines to surveillance interval recommendations made before their introduction. For example, based on the updated guidelines, patients previously recommended to undergo colon polyp surveillance colonoscopy 5 years after an index colonoscopy could extend their surveillance interval by 2 to 5 years. Increasing endoscopic capacity could address the growing demand for colonoscopies from new screening guidelines that reduced the age of initial CRC screening from 50 years to 45 years and the backlog of procedures due to COVID-19 restrictions.4
As part of a project to increase endoscopic capacity at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS), this study assessed the potential impact of retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity. These results may be informative for other VA and private-sector health care systems seeking to identify strategies to improve endoscopy capacity.
Methods
VAPHS is an integrated health care system in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) serving 85,000 patients across 8 health care institutions in Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. VAPHS manages colorectal screening recommendations for patients receiving medical care in the health care system regardless of whether their prior colonoscopy was performed at VAPHS or external facilities. The VA maintains a national CRC screening and surveillance electronic medical record reminder that prompts health care practitioners to order colon polyp surveillance based on interval recommendations from the index colonoscopy. This study reviewed all patients from the VAPHS panel with a reminder to undergo colonoscopy for screening for CRC or surveillance of colon polyps within 12 months from September 1, 2022.
Among patients with a reminder, 3 investigators reviewed index colonoscopy and pathology reports to identify CRC risk category, colonoscopy indication, procedural quality, and recommended repeat colonoscopy interval. Per the USMSTF guidelines, patients with incomplete colonoscopy or pathology records, high-risk indications (ie, personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, personal history of CRC, or family history of CRC), or inadequate bowel preparation (Boston Bowel Preparation Score < 6) were excluded. Additionally, patients who had CRC screening or surveillance discontinued due to age or comorbidities, had completed a subsequent follow-up colonoscopy, or were deceased at the time of review were excluded.
Retroactive Interval Reclassification
Among eligible patients, this study compared the repeat colonoscopy interval recommended by the prior endoscopist with those from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines. In cases where the interval was documented as a range of years, the lower end was considered the recommendation. Similarly, the lower end of the range from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was used for the reclassified surveillance interval. Years extended per patient were quantified relative to September 1, 2023 (ie, 1 year after the review date). For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2016, the initial surveillance recommendation was 5 years, and the reclassified recommendation was 7 years, the interval extension beyond September 1, 2023, was 0 years.
Furthermore, because index surveillance recommendations are not always guideline concordant, the years extended per patient were calculated by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s recommendations with the guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy.5 For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2018, and the endoscopist recommended a 5-year follow-up for a patient with average risk for CRC, adequate bowel preparation, and no colorectal polyps, that patient is eligible to extend their colonoscopy to September 1, 2028, based on guideline recommendations at the time of index endoscopy recommending that the next colonoscopy occur in 10 years. In this analysis the 2012 USMSTF guidelines were applied to all index colonoscopies completed in 2021 or earlier to allow time for adoption of the 2020 guidelines.
This project fulfilled a facility mandate to increase capacity to conduct endoscopic procedures. Institutional review board approval was not required by VAPHS policy relating to clinical operations projects. Approval for publication of clinical operations activity was obtained from the VAPHS facility director.
Results
Within 1 year of the September 1, 2022, review date, 637 patients receiving care at VAPHS had clinical reminders for an upcoming colonoscopy. Of these, 54 (8.4%) were already up to date or were deceased at the time of review. Of the 583 eligible patients, 96% were male, the median age was 74 years, the median index colonoscopy year was 2016, and 178 (30.5%) had an average-risk CRC screening indication at the index colonoscopy (Table).
Of the 583 patients due for colonoscopy, 331 (56.7%) had both colonoscopy and pathology reports available. The majority of those with incomplete records had the index colonoscopy completed outside VAPHS. Among these patients, 222 (67.0%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of those with adequate bowel preparation, 43 were not eligible for interval extension because of high-risk conditions and 13 were not eligible because there was no index surveillance interval recommendation from the index endoscopist. Of the patients due for colonoscopy, 166 (28.4%) were potentially eligible for surveillance interval extension (Figure).
Sixty-five (39.2%) of the 166 patients had 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas on their index colonoscopy. Sixty-two patients were eligible for interval extension to 7 years, but this only resulted in ≥ 1 year of extension beyond the review date for 36 (6% of all 583 patients due for colonoscopy). The 36 patients were extended 63 years. By harmonizing the index endoscopists’ surveillance interval recommendation with the guideline at the time of the index colonoscopy, 29 additional patients could have their colonoscopy extended by ≥ 1 year. Harmonization extended colonoscopy intervals by 93 years. Retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines and harmonizing recommendations to guidelines extended the time of index colonoscopy by 153 years.
Discussion
With retroactive application of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines, 6% of patients due for an upcoming colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year by extending the surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas to 7 years. An additional 5% of patients could extend their interval by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s interval recommendation with polyp surveillance guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy. These findings are consistent with the results of 2 studies that demonstrated that about 14% of patients due for colonoscopy could have their interval extended.6,7 The current study enhances those insights by separating the contribution of 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines from the contribution of harmonizing surveillance intervals with guidelines for other polyp histologies. This study found that there is an opportunity to improve endoscopic capacity by harmonizing recommendations with guidelines. This complements a 2023 study showing that even when knowledgeable about guidelines, clinicians do not necessarily follow recommendations.8 While this and previous research have identified that 11% to 14% of patients are eligible for extension, these individuals would also have to be willing to have their polyp surveillance intervals extended for there to be a real-world impact on endoscopic capacity. A 2024 study found that only 19% to 37% of patients with 1 to 2 small tubular adenomas were willing to have polyps surveillance interval extension.9 This suggests the actual effect on capacity may be even lower than reported.
Limitations
The overall impact of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity was blunted by the high prevalence of incomplete index colonoscopy records among the study population. Without data on bowel preparation quality or procedure indications, this study could not assess whether 43% of patients were eligible for surveillance interval extension. Most index colonoscopies with incomplete documentation were completed at community-care gastroenterology facilities. This high rate of incomplete documentation is likely generalizable to other VA health care systems—especially in the era of the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, which increased veteran access to non-VA community care.10 Veterans due for colon polyp surveillance colonoscopies are more likely to have had their prior colonoscopy in community care compared with prior eras.11 Furthermore, because the VHA is among the most established integrated health care systems offering primary and subspecialty care in the US, private sector health care systems may have even greater rates of care fragmentation for longitudinal CRC screening and colon polyp surveillance, as these systems have only begun to regionally integrate recently.12,13
Another limitation is that nearly one-third of the individuals with documentation had inadequate bowel preparation for surveillance recommendations. This results in shorter surveillance follow-up colonoscopies and increases downstream demand for future colonoscopies. The low yield of extending colon polyp surveillance interval in this study emphasizes that improved efforts to obtain colonoscopy and pathology reports from community care, right-sizing the colon polyp surveillance intervals recommended by endoscopists, and improving quality of bowel preparation could have downstream health care system benefits in the future. These efforts could increase colonoscopy capacity at VA health care systems, thereby shortening colonoscopy wait times, decreasing fragmentation of care, and increasing the number of veterans who receive high-quality colonoscopies at VA health care systems.14
Conclusions
Eleven percent of patients in this study due for a colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year. About half of these extensions were directly due to the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance interval extension for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas. The rest resulted from harmonizing recommendations with guidelines at the time of the procedure. To determine whether retroactively applying polyp surveillance guidelines to follow-up interval recommendations will result in improved endoscopic capacity, health care system administrators should consider the degree of CRC screening care fragmentation in their patient population. Greater long-term gains in endoscopic capacity may be achieved by proactively supporting endoscopists in making guideline-concordant screening recommendations at the time of colonoscopy.
Gupta S, Lieberman D, Anderson JC, et al. Recommendations for follow-up after colonoscopy and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:463-485. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.01.014
Dubé C, Yakubu M, McCurdy BR, et al. Risk of advanced adenoma, colorectal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality in people with low-risk adenomas at baseline colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1790-1801. doi:10.1038/ajg.2017.360
Click B, Pinsky PF, Hickey T, Doroudi M, Shoen RE. Association of colonoscopy adenoma findings with long-term colorectal cancer incidence. JAMA. 2018;319:2021-2031. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.5809
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
Djinbachian R, Dubé AJ, Durand M, et al. Adherence to post-polypectomy surveillance guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2019;51:673-683. doi:10.1055/a-0865-2082
Gawron AJ, Kaltenbach T, Dominitz JA. The impact of the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic on access to endoscopy procedures in the VA healthcare system. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1216-1220.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.033
Xiao AH, Chang SY, Stevoff CG, Komanduri S, Pandolfino JE, Keswani RN. Adoption of multi-society guidelines facilitates value-based reduction in screening and surveillance colonoscopy volume during COVID-19 pandemic. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:2578-2584. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06539-1
Dong J, Wang LF, Ardolino E, Feuerstein JD. Real-world compliance with the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer polypectomy surveillance guidelines: an observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023;97:350-356.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.020
Lee JK, Koripella PC, Jensen CD, et al. Randomized trial of patient outreach approaches to de-implement outdated colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22:1315-1322.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.027
Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, HR 3230, 113th Cong (2014). Accessed September 8, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/113th-congress/house-bill/3230
Dueker JM, Khalid A. Performance of the Veterans Choice Program for improving access to colonoscopy at a tertiary VA facility. Fed Pract. 2020;37:224-228.
Oliver A. The Veterans Health Administration: an American success story? Milbank Q. 2007;85:5-35. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0009.2007.00475.x
Furukawa MF, Machta RM, Barrett KA, et al. Landscape of health systems in the United States. Med Care Res Rev. 2020;77:357-366. doi:10.1177/1077558718823130
Petros V, Tsambikos E, Madhoun M, Tierney WM. Impact of community referral on colonoscopy quality metrics in a Veterans Affairs Medical Center. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13:e00460. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000460
In 2020, the US Multi-Society Task Force (USMSTF) on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) increased the recommended colon polyp surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas from 5 to 10 years to 7 to 10 years.1 This change was prompted by emerging research indicating that rates of CRC and advanced neoplasia among patients with a history of only 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas are lower than initially estimated.2,3 This extension provides an opportunity to increase endoscopy capacity and improve access to colonoscopies by retroactively applying the 2020 guidelines to surveillance interval recommendations made before their introduction. For example, based on the updated guidelines, patients previously recommended to undergo colon polyp surveillance colonoscopy 5 years after an index colonoscopy could extend their surveillance interval by 2 to 5 years. Increasing endoscopic capacity could address the growing demand for colonoscopies from new screening guidelines that reduced the age of initial CRC screening from 50 years to 45 years and the backlog of procedures due to COVID-19 restrictions.4
As part of a project to increase endoscopic capacity at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS), this study assessed the potential impact of retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity. These results may be informative for other VA and private-sector health care systems seeking to identify strategies to improve endoscopy capacity.
Methods
VAPHS is an integrated health care system in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) serving 85,000 patients across 8 health care institutions in Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. VAPHS manages colorectal screening recommendations for patients receiving medical care in the health care system regardless of whether their prior colonoscopy was performed at VAPHS or external facilities. The VA maintains a national CRC screening and surveillance electronic medical record reminder that prompts health care practitioners to order colon polyp surveillance based on interval recommendations from the index colonoscopy. This study reviewed all patients from the VAPHS panel with a reminder to undergo colonoscopy for screening for CRC or surveillance of colon polyps within 12 months from September 1, 2022.
Among patients with a reminder, 3 investigators reviewed index colonoscopy and pathology reports to identify CRC risk category, colonoscopy indication, procedural quality, and recommended repeat colonoscopy interval. Per the USMSTF guidelines, patients with incomplete colonoscopy or pathology records, high-risk indications (ie, personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, personal history of CRC, or family history of CRC), or inadequate bowel preparation (Boston Bowel Preparation Score < 6) were excluded. Additionally, patients who had CRC screening or surveillance discontinued due to age or comorbidities, had completed a subsequent follow-up colonoscopy, or were deceased at the time of review were excluded.
Retroactive Interval Reclassification
Among eligible patients, this study compared the repeat colonoscopy interval recommended by the prior endoscopist with those from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines. In cases where the interval was documented as a range of years, the lower end was considered the recommendation. Similarly, the lower end of the range from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was used for the reclassified surveillance interval. Years extended per patient were quantified relative to September 1, 2023 (ie, 1 year after the review date). For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2016, the initial surveillance recommendation was 5 years, and the reclassified recommendation was 7 years, the interval extension beyond September 1, 2023, was 0 years.
Furthermore, because index surveillance recommendations are not always guideline concordant, the years extended per patient were calculated by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s recommendations with the guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy.5 For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2018, and the endoscopist recommended a 5-year follow-up for a patient with average risk for CRC, adequate bowel preparation, and no colorectal polyps, that patient is eligible to extend their colonoscopy to September 1, 2028, based on guideline recommendations at the time of index endoscopy recommending that the next colonoscopy occur in 10 years. In this analysis the 2012 USMSTF guidelines were applied to all index colonoscopies completed in 2021 or earlier to allow time for adoption of the 2020 guidelines.
This project fulfilled a facility mandate to increase capacity to conduct endoscopic procedures. Institutional review board approval was not required by VAPHS policy relating to clinical operations projects. Approval for publication of clinical operations activity was obtained from the VAPHS facility director.
Results
Within 1 year of the September 1, 2022, review date, 637 patients receiving care at VAPHS had clinical reminders for an upcoming colonoscopy. Of these, 54 (8.4%) were already up to date or were deceased at the time of review. Of the 583 eligible patients, 96% were male, the median age was 74 years, the median index colonoscopy year was 2016, and 178 (30.5%) had an average-risk CRC screening indication at the index colonoscopy (Table).
Of the 583 patients due for colonoscopy, 331 (56.7%) had both colonoscopy and pathology reports available. The majority of those with incomplete records had the index colonoscopy completed outside VAPHS. Among these patients, 222 (67.0%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of those with adequate bowel preparation, 43 were not eligible for interval extension because of high-risk conditions and 13 were not eligible because there was no index surveillance interval recommendation from the index endoscopist. Of the patients due for colonoscopy, 166 (28.4%) were potentially eligible for surveillance interval extension (Figure).
Sixty-five (39.2%) of the 166 patients had 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas on their index colonoscopy. Sixty-two patients were eligible for interval extension to 7 years, but this only resulted in ≥ 1 year of extension beyond the review date for 36 (6% of all 583 patients due for colonoscopy). The 36 patients were extended 63 years. By harmonizing the index endoscopists’ surveillance interval recommendation with the guideline at the time of the index colonoscopy, 29 additional patients could have their colonoscopy extended by ≥ 1 year. Harmonization extended colonoscopy intervals by 93 years. Retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines and harmonizing recommendations to guidelines extended the time of index colonoscopy by 153 years.
Discussion
With retroactive application of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines, 6% of patients due for an upcoming colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year by extending the surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas to 7 years. An additional 5% of patients could extend their interval by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s interval recommendation with polyp surveillance guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy. These findings are consistent with the results of 2 studies that demonstrated that about 14% of patients due for colonoscopy could have their interval extended.6,7 The current study enhances those insights by separating the contribution of 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines from the contribution of harmonizing surveillance intervals with guidelines for other polyp histologies. This study found that there is an opportunity to improve endoscopic capacity by harmonizing recommendations with guidelines. This complements a 2023 study showing that even when knowledgeable about guidelines, clinicians do not necessarily follow recommendations.8 While this and previous research have identified that 11% to 14% of patients are eligible for extension, these individuals would also have to be willing to have their polyp surveillance intervals extended for there to be a real-world impact on endoscopic capacity. A 2024 study found that only 19% to 37% of patients with 1 to 2 small tubular adenomas were willing to have polyps surveillance interval extension.9 This suggests the actual effect on capacity may be even lower than reported.
Limitations
The overall impact of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity was blunted by the high prevalence of incomplete index colonoscopy records among the study population. Without data on bowel preparation quality or procedure indications, this study could not assess whether 43% of patients were eligible for surveillance interval extension. Most index colonoscopies with incomplete documentation were completed at community-care gastroenterology facilities. This high rate of incomplete documentation is likely generalizable to other VA health care systems—especially in the era of the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, which increased veteran access to non-VA community care.10 Veterans due for colon polyp surveillance colonoscopies are more likely to have had their prior colonoscopy in community care compared with prior eras.11 Furthermore, because the VHA is among the most established integrated health care systems offering primary and subspecialty care in the US, private sector health care systems may have even greater rates of care fragmentation for longitudinal CRC screening and colon polyp surveillance, as these systems have only begun to regionally integrate recently.12,13
Another limitation is that nearly one-third of the individuals with documentation had inadequate bowel preparation for surveillance recommendations. This results in shorter surveillance follow-up colonoscopies and increases downstream demand for future colonoscopies. The low yield of extending colon polyp surveillance interval in this study emphasizes that improved efforts to obtain colonoscopy and pathology reports from community care, right-sizing the colon polyp surveillance intervals recommended by endoscopists, and improving quality of bowel preparation could have downstream health care system benefits in the future. These efforts could increase colonoscopy capacity at VA health care systems, thereby shortening colonoscopy wait times, decreasing fragmentation of care, and increasing the number of veterans who receive high-quality colonoscopies at VA health care systems.14
Conclusions
Eleven percent of patients in this study due for a colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year. About half of these extensions were directly due to the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance interval extension for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas. The rest resulted from harmonizing recommendations with guidelines at the time of the procedure. To determine whether retroactively applying polyp surveillance guidelines to follow-up interval recommendations will result in improved endoscopic capacity, health care system administrators should consider the degree of CRC screening care fragmentation in their patient population. Greater long-term gains in endoscopic capacity may be achieved by proactively supporting endoscopists in making guideline-concordant screening recommendations at the time of colonoscopy.
In 2020, the US Multi-Society Task Force (USMSTF) on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) increased the recommended colon polyp surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas from 5 to 10 years to 7 to 10 years.1 This change was prompted by emerging research indicating that rates of CRC and advanced neoplasia among patients with a history of only 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas are lower than initially estimated.2,3 This extension provides an opportunity to increase endoscopy capacity and improve access to colonoscopies by retroactively applying the 2020 guidelines to surveillance interval recommendations made before their introduction. For example, based on the updated guidelines, patients previously recommended to undergo colon polyp surveillance colonoscopy 5 years after an index colonoscopy could extend their surveillance interval by 2 to 5 years. Increasing endoscopic capacity could address the growing demand for colonoscopies from new screening guidelines that reduced the age of initial CRC screening from 50 years to 45 years and the backlog of procedures due to COVID-19 restrictions.4
As part of a project to increase endoscopic capacity at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS), this study assessed the potential impact of retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity. These results may be informative for other VA and private-sector health care systems seeking to identify strategies to improve endoscopy capacity.
Methods
VAPHS is an integrated health care system in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) serving 85,000 patients across 8 health care institutions in Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. VAPHS manages colorectal screening recommendations for patients receiving medical care in the health care system regardless of whether their prior colonoscopy was performed at VAPHS or external facilities. The VA maintains a national CRC screening and surveillance electronic medical record reminder that prompts health care practitioners to order colon polyp surveillance based on interval recommendations from the index colonoscopy. This study reviewed all patients from the VAPHS panel with a reminder to undergo colonoscopy for screening for CRC or surveillance of colon polyps within 12 months from September 1, 2022.
Among patients with a reminder, 3 investigators reviewed index colonoscopy and pathology reports to identify CRC risk category, colonoscopy indication, procedural quality, and recommended repeat colonoscopy interval. Per the USMSTF guidelines, patients with incomplete colonoscopy or pathology records, high-risk indications (ie, personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, personal history of CRC, or family history of CRC), or inadequate bowel preparation (Boston Bowel Preparation Score < 6) were excluded. Additionally, patients who had CRC screening or surveillance discontinued due to age or comorbidities, had completed a subsequent follow-up colonoscopy, or were deceased at the time of review were excluded.
Retroactive Interval Reclassification
Among eligible patients, this study compared the repeat colonoscopy interval recommended by the prior endoscopist with those from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines. In cases where the interval was documented as a range of years, the lower end was considered the recommendation. Similarly, the lower end of the range from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was used for the reclassified surveillance interval. Years extended per patient were quantified relative to September 1, 2023 (ie, 1 year after the review date). For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2016, the initial surveillance recommendation was 5 years, and the reclassified recommendation was 7 years, the interval extension beyond September 1, 2023, was 0 years.
Furthermore, because index surveillance recommendations are not always guideline concordant, the years extended per patient were calculated by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s recommendations with the guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy.5 For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2018, and the endoscopist recommended a 5-year follow-up for a patient with average risk for CRC, adequate bowel preparation, and no colorectal polyps, that patient is eligible to extend their colonoscopy to September 1, 2028, based on guideline recommendations at the time of index endoscopy recommending that the next colonoscopy occur in 10 years. In this analysis the 2012 USMSTF guidelines were applied to all index colonoscopies completed in 2021 or earlier to allow time for adoption of the 2020 guidelines.
This project fulfilled a facility mandate to increase capacity to conduct endoscopic procedures. Institutional review board approval was not required by VAPHS policy relating to clinical operations projects. Approval for publication of clinical operations activity was obtained from the VAPHS facility director.
Results
Within 1 year of the September 1, 2022, review date, 637 patients receiving care at VAPHS had clinical reminders for an upcoming colonoscopy. Of these, 54 (8.4%) were already up to date or were deceased at the time of review. Of the 583 eligible patients, 96% were male, the median age was 74 years, the median index colonoscopy year was 2016, and 178 (30.5%) had an average-risk CRC screening indication at the index colonoscopy (Table).
Of the 583 patients due for colonoscopy, 331 (56.7%) had both colonoscopy and pathology reports available. The majority of those with incomplete records had the index colonoscopy completed outside VAPHS. Among these patients, 222 (67.0%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of those with adequate bowel preparation, 43 were not eligible for interval extension because of high-risk conditions and 13 were not eligible because there was no index surveillance interval recommendation from the index endoscopist. Of the patients due for colonoscopy, 166 (28.4%) were potentially eligible for surveillance interval extension (Figure).
Sixty-five (39.2%) of the 166 patients had 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas on their index colonoscopy. Sixty-two patients were eligible for interval extension to 7 years, but this only resulted in ≥ 1 year of extension beyond the review date for 36 (6% of all 583 patients due for colonoscopy). The 36 patients were extended 63 years. By harmonizing the index endoscopists’ surveillance interval recommendation with the guideline at the time of the index colonoscopy, 29 additional patients could have their colonoscopy extended by ≥ 1 year. Harmonization extended colonoscopy intervals by 93 years. Retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines and harmonizing recommendations to guidelines extended the time of index colonoscopy by 153 years.
Discussion
With retroactive application of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines, 6% of patients due for an upcoming colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year by extending the surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas to 7 years. An additional 5% of patients could extend their interval by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s interval recommendation with polyp surveillance guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy. These findings are consistent with the results of 2 studies that demonstrated that about 14% of patients due for colonoscopy could have their interval extended.6,7 The current study enhances those insights by separating the contribution of 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines from the contribution of harmonizing surveillance intervals with guidelines for other polyp histologies. This study found that there is an opportunity to improve endoscopic capacity by harmonizing recommendations with guidelines. This complements a 2023 study showing that even when knowledgeable about guidelines, clinicians do not necessarily follow recommendations.8 While this and previous research have identified that 11% to 14% of patients are eligible for extension, these individuals would also have to be willing to have their polyp surveillance intervals extended for there to be a real-world impact on endoscopic capacity. A 2024 study found that only 19% to 37% of patients with 1 to 2 small tubular adenomas were willing to have polyps surveillance interval extension.9 This suggests the actual effect on capacity may be even lower than reported.
Limitations
The overall impact of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity was blunted by the high prevalence of incomplete index colonoscopy records among the study population. Without data on bowel preparation quality or procedure indications, this study could not assess whether 43% of patients were eligible for surveillance interval extension. Most index colonoscopies with incomplete documentation were completed at community-care gastroenterology facilities. This high rate of incomplete documentation is likely generalizable to other VA health care systems—especially in the era of the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, which increased veteran access to non-VA community care.10 Veterans due for colon polyp surveillance colonoscopies are more likely to have had their prior colonoscopy in community care compared with prior eras.11 Furthermore, because the VHA is among the most established integrated health care systems offering primary and subspecialty care in the US, private sector health care systems may have even greater rates of care fragmentation for longitudinal CRC screening and colon polyp surveillance, as these systems have only begun to regionally integrate recently.12,13
Another limitation is that nearly one-third of the individuals with documentation had inadequate bowel preparation for surveillance recommendations. This results in shorter surveillance follow-up colonoscopies and increases downstream demand for future colonoscopies. The low yield of extending colon polyp surveillance interval in this study emphasizes that improved efforts to obtain colonoscopy and pathology reports from community care, right-sizing the colon polyp surveillance intervals recommended by endoscopists, and improving quality of bowel preparation could have downstream health care system benefits in the future. These efforts could increase colonoscopy capacity at VA health care systems, thereby shortening colonoscopy wait times, decreasing fragmentation of care, and increasing the number of veterans who receive high-quality colonoscopies at VA health care systems.14
Conclusions
Eleven percent of patients in this study due for a colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year. About half of these extensions were directly due to the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance interval extension for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas. The rest resulted from harmonizing recommendations with guidelines at the time of the procedure. To determine whether retroactively applying polyp surveillance guidelines to follow-up interval recommendations will result in improved endoscopic capacity, health care system administrators should consider the degree of CRC screening care fragmentation in their patient population. Greater long-term gains in endoscopic capacity may be achieved by proactively supporting endoscopists in making guideline-concordant screening recommendations at the time of colonoscopy.
Gupta S, Lieberman D, Anderson JC, et al. Recommendations for follow-up after colonoscopy and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:463-485. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.01.014
Dubé C, Yakubu M, McCurdy BR, et al. Risk of advanced adenoma, colorectal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality in people with low-risk adenomas at baseline colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1790-1801. doi:10.1038/ajg.2017.360
Click B, Pinsky PF, Hickey T, Doroudi M, Shoen RE. Association of colonoscopy adenoma findings with long-term colorectal cancer incidence. JAMA. 2018;319:2021-2031. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.5809
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
Djinbachian R, Dubé AJ, Durand M, et al. Adherence to post-polypectomy surveillance guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2019;51:673-683. doi:10.1055/a-0865-2082
Gawron AJ, Kaltenbach T, Dominitz JA. The impact of the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic on access to endoscopy procedures in the VA healthcare system. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1216-1220.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.033
Xiao AH, Chang SY, Stevoff CG, Komanduri S, Pandolfino JE, Keswani RN. Adoption of multi-society guidelines facilitates value-based reduction in screening and surveillance colonoscopy volume during COVID-19 pandemic. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:2578-2584. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06539-1
Dong J, Wang LF, Ardolino E, Feuerstein JD. Real-world compliance with the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer polypectomy surveillance guidelines: an observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023;97:350-356.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.020
Lee JK, Koripella PC, Jensen CD, et al. Randomized trial of patient outreach approaches to de-implement outdated colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22:1315-1322.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.027
Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, HR 3230, 113th Cong (2014). Accessed September 8, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/113th-congress/house-bill/3230
Dueker JM, Khalid A. Performance of the Veterans Choice Program for improving access to colonoscopy at a tertiary VA facility. Fed Pract. 2020;37:224-228.
Oliver A. The Veterans Health Administration: an American success story? Milbank Q. 2007;85:5-35. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0009.2007.00475.x
Furukawa MF, Machta RM, Barrett KA, et al. Landscape of health systems in the United States. Med Care Res Rev. 2020;77:357-366. doi:10.1177/1077558718823130
Petros V, Tsambikos E, Madhoun M, Tierney WM. Impact of community referral on colonoscopy quality metrics in a Veterans Affairs Medical Center. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13:e00460. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000460
Gupta S, Lieberman D, Anderson JC, et al. Recommendations for follow-up after colonoscopy and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:463-485. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.01.014
Dubé C, Yakubu M, McCurdy BR, et al. Risk of advanced adenoma, colorectal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality in people with low-risk adenomas at baseline colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1790-1801. doi:10.1038/ajg.2017.360
Click B, Pinsky PF, Hickey T, Doroudi M, Shoen RE. Association of colonoscopy adenoma findings with long-term colorectal cancer incidence. JAMA. 2018;319:2021-2031. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.5809
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
Djinbachian R, Dubé AJ, Durand M, et al. Adherence to post-polypectomy surveillance guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2019;51:673-683. doi:10.1055/a-0865-2082
Gawron AJ, Kaltenbach T, Dominitz JA. The impact of the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic on access to endoscopy procedures in the VA healthcare system. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1216-1220.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.033
Xiao AH, Chang SY, Stevoff CG, Komanduri S, Pandolfino JE, Keswani RN. Adoption of multi-society guidelines facilitates value-based reduction in screening and surveillance colonoscopy volume during COVID-19 pandemic. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:2578-2584. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06539-1
Dong J, Wang LF, Ardolino E, Feuerstein JD. Real-world compliance with the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer polypectomy surveillance guidelines: an observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023;97:350-356.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.020
Lee JK, Koripella PC, Jensen CD, et al. Randomized trial of patient outreach approaches to de-implement outdated colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22:1315-1322.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.027
Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, HR 3230, 113th Cong (2014). Accessed September 8, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/113th-congress/house-bill/3230
Dueker JM, Khalid A. Performance of the Veterans Choice Program for improving access to colonoscopy at a tertiary VA facility. Fed Pract. 2020;37:224-228.
Oliver A. The Veterans Health Administration: an American success story? Milbank Q. 2007;85:5-35. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0009.2007.00475.x
Furukawa MF, Machta RM, Barrett KA, et al. Landscape of health systems in the United States. Med Care Res Rev. 2020;77:357-366. doi:10.1177/1077558718823130
Petros V, Tsambikos E, Madhoun M, Tierney WM. Impact of community referral on colonoscopy quality metrics in a Veterans Affairs Medical Center. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13:e00460. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000460
Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
Streamlined Testosterone Order Template to Improve the Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hypogonadism in Veterans
Streamlined Testosterone Order Template to Improve the Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hypogonadism in Veterans
Testosterone therapy is administered following pragmatic diagnostic evaluation and workup to assess whether an adult male is hypogonadal, based on symptoms consistent with androgen deficiency and low morning serum testosterone concentrations on ≥ 2 occasions. Effects of testosterone administration include the development or maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics and increases in libido, muscle strength, fat-free mass, and bone density.
Testosterone prescriptions have markedly increased in the past 20 years, including within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system.1-3 This trend may be influenced by various factors, including patient perceptions of benefit, an increase in marketing, and the availability of more user-friendly formulations.
Since 2006, evidence-based clinical practice guidelines have recommended specific clinical and laboratory evaluation and counseling prior to starting testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).4-8 However, research has shown poor adherence to these recommendations, including at the VA, which raises concerns about inappropriate TRT initiation without proper diagnostic evaluation.9,10 Observational research has suggested a possible link between testosterone therapy and increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) events. The US Food and Drug Administration prescribing information includes boxed warnings about potential risks of high blood pressure, myocardial infarction, stroke, and CV-related mortality with testosterone treatment, contact transfer of transdermal testosterone, and pulmonary oil microembolism with testosterone undecanoate injections.11-15
A VA Office of Inspector General (OIG) review of VA clinician adherence to clinical and laboratory evaluation guidelines for testosterone deficiency found poor adherence among VA practitioners and made recommendations for improvement.4,15 These focused on establishing clinical signs and symptoms consistent with testosterone deficiency, confirming hypogonadism by repeated testosterone testing, determining the etiology of hypogonadism by measuring gonadotropins, initiating a discussion of risks and benefits of TRT, and assessing clinical improvement and obtaining an updated hematocrit test within 3 to 6 months of initiation.
The VA Puget Sound Health Care System (VAPSHCS) developed a local prior authorization template to assist health care practitioners (HCPs) to address the OIG recommendations. This testosterone order template (TOT) aimed to improve the diagnosis, evaluation, and monitoring of TRT in males with hypogonadism, combined with existing VA pharmacy criteria for the use of testosterone based on Endocrine Society guidelines. A version of the VAPSHCS TOT was approved as the national VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) template.
Preliminary evaluation of the TOT suggested improved short-term adherence to guideline recommendations following implementation.16 This quality improvement study sought to assess the long-term effectiveness of the TOT with respect to clinical practice guideline adherence. The OIG did not address prostate-specific antigen (PSA) monitoring because understanding of the relationship between TRT and the risks of elevated PSA levels remains incomplete.6,17 This project hypothesized that implementation of a pharmacy-managed TOT incorporated into CPRS would result in higher adherence rates to guideline-recommended clinical and laboratory evaluation, in addition to counseling of men with hypogonadism prior to initiation of TRT.
Methods
Eligible participants were cisgender males who received a new testosterone prescription, had ≥ 2 clinic visits at VAPSHCS, and no previous testosterone prescription in the previous 2 years. Individuals were excluded if they had testosterone administered at VAPSHCS; were prescribed testosterone at another facility (VA or community-based); pilot tested an initial version of the TOT prior to November 30, 2019; or had an International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes for hypopituitarism, gender identity disorder, history of sexual assignment, or Klinefelter syndrome for which testosterone therapy was already approved. Patients who met the inclusion criteria were identified by an algorithm developed by the VAPSHCS pharmacoeconomist.
This quality improvement project used a retrospective, pre-post experimental design. Electronic chart review and systematic manual review of all eligible patient charts were performed for the pretemplate period (December 1, 2018, to November 30, 2019) and after the template implementation, (December 1, 2021, to November 30, 2022).
An initial version of the TOT was implemented on July 1, 2019, but was not fully integrated into CPRS until early 2020; individuals in whom the TOT was used prior to November 30, 2019, were excluded. Data from the initial period of the COVID-19 pandemic were avoided because of alterations in clinic and prescribing practices. As a quality improvement project, the TOT evaluation was exempt from formal review by the VAPSHCS Institutional Review Board, as determined by the Director of the Office of Transformation/Quality/Safety/Value.
Interventions
Testosterone is a Schedule III controlled substance with potential risks and a propensity for varied prescribing practices. It was designated as a restricted drug requiring a prior authorization drug request (PADR) for which a specific TOT was developed, approved by the VAPSHCS Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee, and incorporated into CPRS. A team of pharmacists, primary care physicians, geriatricians, endocrinologists, and health informatics experts created and developed the TOT. Pharmacists managed and monitored its completion.
The process for prescribing testosterone via the TOT is outlined in the eAppendix. When an HCP orders testosterone in CPRS, reminders prompt them to use the TOT and indicate required laboratory measurements (an order set is provided). Completion of TOT is not necessary to order testosterone for patients with an existing diagnosis of an organic cause of hypogonadism (eg, Klinefelter syndrome or hypopituitarism) or transgender women (assigned male at birth). In the TOT, the prescriber must also indicate signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency; required laboratory tests; and counseling regarding potential risks and benefits of TRT. A pharmacist reviews the TOT and either approves or rejects the testosterone prescription and provides follow-up guidance to the prescriber. The completed TOT serves as documentation of guideline adherence in CPRS. The TOT also includes sections for first renewal testosterone prescriptions, addressing guideline recommendations for follow-up laboratory evaluation and clinical response to TRT. Due to limited completion of this section in the posttemplate period, evaluating adherence to follow-up recommendations was not feasible.
Measures
This project assessed the percentage of patients in the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period with an approved PADR. Documentation of specific guideline-recommended measures was assessed: signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency; ≥ 2 serum testosterone measurements (≥ 2 total, free and total, or 2 free testosterone levels, and ≥ 1 testosterone level before 10
The project also assessed the proportion of patients in the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period who had all hormone tests (≥ 2 serum testosterone and LH and FSH concentrations), all laboratory tests (hormone tests and hematocrit), and all 5 guideline-recommended measures.
Analysis
Statistical comparisons between the proportions of patients in the pretemplate and posttemplate periods for each measure were performed using a χ2 test, without correction for multiple comparisons. All analyses were conducted using Stata version 10.0. A P value < .05 was considered significant for all comparisons.
Results
Chart review identified 189 patients in the pretemplate period and 113 patients in the posttemplate period with a new testosterone prescription (Figure). After exclusions, 91 and 49 patients, respectively, met eligibility criteria (Table 1). Fifty-six patients (62%) pretemplate and 40 patients (82%) posttemplate (P = .015) had approved PADRs and comprised the groups that were analyzed (Table 2).
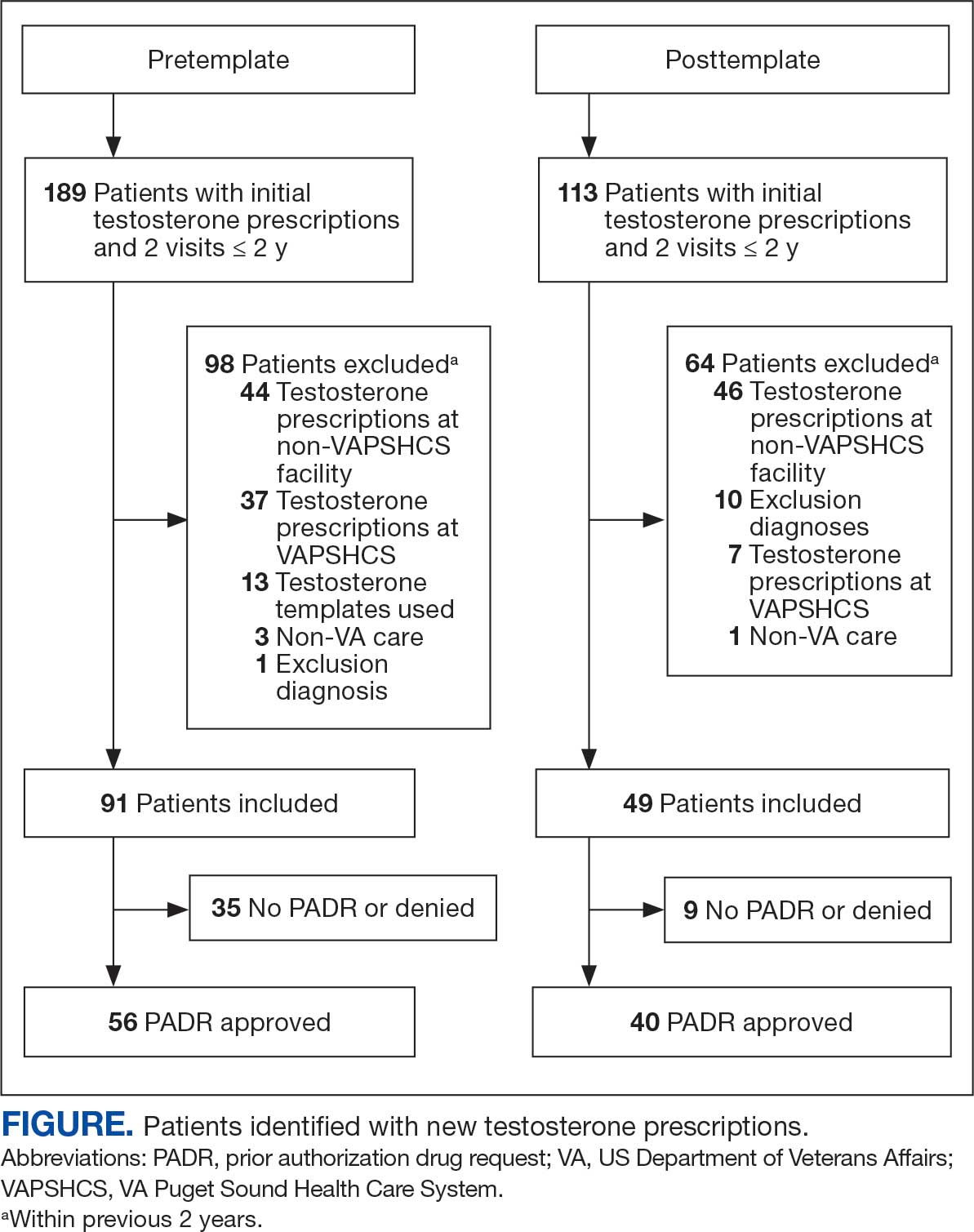
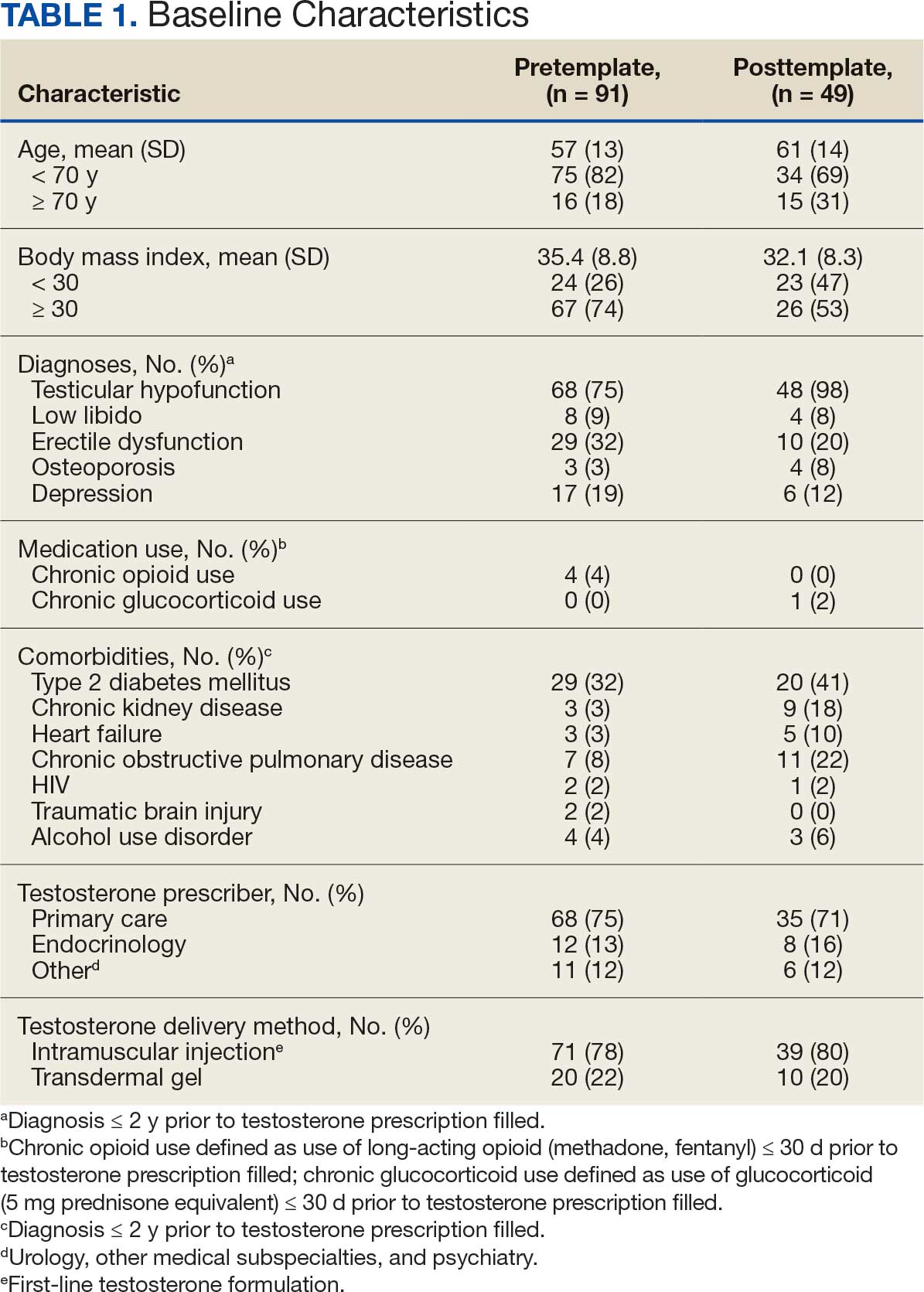

The mean age and body mass index were similar in the pretemplate and posttemplate periods, but there was variation in the proportions of patients aged < 70 years and those with a body mass index < 30 between the groups. The most common diagnosis in both groups was testicular hypofunction, and the most common comorbidity was type 2 diabetes mellitus. Concomitant use of opioids or glucocorticoids that can lower testosterone levels was rare. Most testosterone prescriptions originated from primary care clinics in both periods: 68 (75%) in the pretemplate period and 35 (71%) in the posttemplate period. Most testosterone treatment was delivered by intramuscular injection.
In the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period, the proportion of patients with an approved PADR (82% vs 62%, P = .02), and documentation of signs and symptoms of hypogonadism (93% vs 71%, P = .002) prior to starting TRT were higher, while the percentage of patients having ≥ 2 testosterone measurements (85% vs 89%, P = .53), ≥ 1 testosterone level before 10 AM (78% vs 75%, P = .70), and hematocrit measured (95% vs 91%, P = .47) were similar. Rates of LH and FSH testing were higher in the posttemplate period (80%) vs the pretemplate period (63%) but did not achieve statistical significance (P = .07), and discussion of the risks and benefits of TRT was higher in the posttemplate period (58%) vs the pretemplate period (34%) (P = .02). The percentage of patients who had all hormone measurements (total and/or free testosterone, LH, and FSH) was higher in the posttemplate period (78%) vs the pretemplate period (59%) but did not achieve statistical significance (P = .06). The rates of all guideline-recommended laboratory test orders were higher in the posttemplate period (78%) vs the pretemplate period (55%) (P = .03), and all 5 guideline-recommended clinical and laboratory measures were higher in the posttemplate period (45%) vs the pretemplate period (18%) (P = .004).
Discussion
The implementation of a pharmacy-managed TOT in CPRS demonstrated higher adherence to evidence-based guidelines for diagnosing and evaluating hypogonadism before TRT. After TOT implementation, a higher proportion of patients had documented signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency, underwent all recommended laboratory tests, and had discussions about the risks and benefits of TRT. Adherence to 5 clinical and laboratory measures recommended by Endocrine Society guidelines was higher after TOT implementation, indicating improved prescribing practices.4
The requirement for TOT completion before testosterone prescription and its management by trained pharmacists likely contributed to higher adherence to guideline recommendations than previously reported. Integration of the TOT into CPRS with pharmacy oversight may have enhanced adherence by summarizing and codifying evidence-based guideline recommendations for clinical and biochemical evaluation prior to TRT initiation, offering relevant education to clinicians and pharmacists, automatically importing pertinent clinical information and laboratory results, and generating CPRS documentation to reduce clinician burden during patient care.
The proportion of patients with documented signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency before TRT increased from the pretemplate period (71%) to the posttemplate period (93%), indicating that most patients receiving TRT had clinical manifestations of hypogonadism. This aligns with Endocrine Society guidelines, which define hypogonadism as a clinical disorder characterized by clinical manifestations of testosterone deficiency and persistently low serum testosterone levels on ≥ 2 separate occasions.4,6 However, recent trends in direct-to-consumer advertising for testosterone and the rise of “low T” clinics may contribute to increased testing, varied practices, and inappropriate testosterone therapy initiation (eg, in men with low testosterone levels who lack symptoms of hypogonadism).18 Improved adherence in documenting clinical hypogonadism with implementation of the TOT reinforces the value of incorporating educational material, as previously reported.11
Adherence to guideline recommendations following implementation of the TOT in this project was higher than those previously reported. In a study of 111,631 outpatient veterans prescribed testosterone from 2009 to 2012, only 18.3% had ≥ 2 testosterone prescriptions, and 3.5% had ≥ 2 testosterone, LH, and FSH levels measured prior to the initiation of a TRT.9 In a report of 63,534 insured patients who received TRT from 2010 to 2012, 40.3% had ≥ 2 testosterone prescriptions, and 12% had LH and/or FSH measured prior to the initiation.8
Low rates of guideline-recommended laboratory tests prior to initiation of testosterone treatment were reported in prior non-VA studies.19,20 Poor guideline adherence reinforces the need for clinician education or other methods to improve TRT and ensure appropriate prescribing practices across health care systems. The TOT described in this project is a sustainable clinical tool with the potential to improve testosterone prescribing practices.
The high rates of adherence to guideline recommendations at VAPSHCS likely stem from local endocrine expertise and ongoing educational initiatives, as well as the requirement for template completion before testosterone prescription. However, most testosterone prescriptions were initiated by primary care and monitored by pharmacists with varying degrees of training and clinical experience in hypogonadism and TRT.
However, adherence to guideline recommendations was modest, suggesting there is still an opportunity for improvement. The decision to initiate therapy should be made only after appropriate counseling with patients regarding its potential benefits and risks. Reports on the CV risk of TRT have been mixed. The 2023 TRAVERSE study found no increase in major adverse CV events among older men with hypogonadism and pre-existing CV risks undergoing TRT, but noted higher instances of pulmonary embolism, atrial fibrillation, and acute kidney injury.21 This highlights the need for clinicians to continue to engage in informed decision-making with patients. Effective pretreatment counseling is important but time-consuming; future TOT monitoring and modifications could consider mandatory checkboxes to document counseling on TRT risks and benefits.
The TOT described in this study could be adapted and incorporated into the prescribing process and electronic health record of larger health care systems. Use of an electronic template allows for automatic real-time dashboard monitoring of organization performance. The TOT described could be modified or simplified for specialty or primary care clinics or individual practitioners to improve adherence to evidence-based guideline recommendations and quality of care.
Strengths
A strength of this study is the multidisciplinary team (composed of stakeholders with experience in VA health care system and subject matter experts in hypogonadism) that developed and incorporated a user-friendly template for testosterone prescriptions; the use of evidence-based guideline recommendations; and the use of a structured chart review permitted accurate assessment of adherence to recommendations to document signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency and a discussion of potential risks and benefits prior to TRT. To our knowledge, these recommendations have not been assessed in previous reports.
Limitations
The retrospective pre-post design of this study precludes a conclusion that implementation of the TOT caused the increase in adherence to guideline recommendations. Improved adherence could have resulted from the ongoing development of the preauthorization process for testosterone prescriptions or other changes over time. However, the preauthorization process had already been established for many years prior to template implementation. Forty-nine patients had new prescriptions for testosterone in the posttemplate period compared to 91 in the pretemplate period, but TRT was initiated in accordance with guideline recommendations more appropriately in the posttemplate period. The study’s sample size was small, and many eligible patients were excluded; however, exclusions were necessary to evaluate men who had new testosterone prescriptions for which the template was designed. Most men excluded were already taking testosterone.
Conclusions
The implementation of a CPRS-based TOT improved adherence to evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis, evaluation, and counseling of patients with hypogonadism before starting TRT. While there were improvements in adherence with the TOT, the relatively low proportion of patients with documentation of TRT risks and benefits and all guideline recommendations highlights the need for additional efforts to further strengthen adherence to guideline recommendations and ensure appropriate evaluation, counseling, and prescribing practices before initiating TRT.
- Layton JB, Li D, Meier CR, et al. Testosterone lab testing and initiation in the United Kingdom and the United States, 2000 to 2011. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:835-842. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-3570
- Baillargeon J, Kuo YF, Westra JR, et al. Testosterone prescribing in the United States, 2002-2016. JAMA. 2018;320:200-202. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7999
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Rose AJ. Patterns of testosterone prescription overuse. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2017;24:240-245. doi:10.1097/MED.0000000000000336
- Bhasin S, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, et al. Testosterone therapy in adult men with androgen deficiency syndromes: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1995-2010. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2847
- Bhasin S, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with androgen deficiency syndromes: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:2536-2559. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2354
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:1715-1744. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00229
- Mulhall JP, Trost LW, Brannigan RE, et al. Evaluation and management of testosterone deficiency: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2018;200:423-432. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.115
- Muram D, Zhang X, Cui Z, et al. Use of hormone testing for the diagnosis and evaluation of male hypogonadism and monitoring of testosterone therapy: application of hormone testing guideline recommendations in clinical practice. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1886-1894. doi:10.1111/jsm.12968
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Ascertainment of testosterone prescribing practices in the VA. Med Care. 2015;53:746-752. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000398?
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Who gets testosterone? Patient characteristics associated with testosterone prescribing in the Veteran Affairs system: a cross-sectional study. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:304-311. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3940-7
- Basaria S, Coviello AD, Travison TG, et al. Adverse events associated with testosterone administration. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:109-122. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1000485
- Vigen R, O’Donnell CI, Barón AE, et al. Association of testosterone therapy with mortality, myocardial infarction, and stroke in men with low testosterone levels. JAMA. 2013;310:1829-1836. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.280386
- Finkle WD, Greenland S, Ridgeway GK, et al. Increased risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction following testosterone therapy prescription in men. PLoS One. 2014;9:e85805. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085805
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions about using testosterone products for low testosterone due to aging; requires labeling change to inform of possible increased risk of heart attack and stroke with use. FDA.gov. March 3, 2015. Updated February 28, 2025. Accessed July 8, 2025. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm436259.htm
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Inspector General. Healthcare inspection – testosterone replacement therapy initiation and follow-up evaluation in VA male patients. April 11, 2018. Accessed July 8, 2025. https://www.vaoig.gov/reports/national-healthcare-review/healthcare-inspection-testosterone-replacement-therapy
- Narla R, Mobley D, Nguyen EHK, et al. Preliminary evaluation of an order template to improve diagnosis and testosterone therapy of hypogonadism in veterans. Fed Pract. 2021;38:121-127. doi:10.12788/fp.0103
- Bhasin S, Travison TG, Pencina KM, et al. Prostate safety events during testosterone replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2348692. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.48692
- Dubin JM, Jesse E, Fantus RJ, et al. Guideline-discordant care among direct-to-consumer testosterone therapy platforms. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182:1321-1323. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.4928
- Baillargeon J, Urban RJ, Ottenbacher KJ, et al. Trends in androgen prescribing in the United States, 2001 to 2011. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1465-1466. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.6895
- Locke JA, Flannigan R, Günther OP, et al. Testosterone therapy: prescribing and monitoring patterns of practice in British Columbia. Can Urol Assoc J. 2021;15:e110-e117. doi:10.5489/cuaj.6586
- Lincoff AM, Bhasin S, Flevaris P, et al. Cardiovascular safety of testosterone-replacement therapy. N Engl J Med. 2023;389:107-117. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2215025
Testosterone therapy is administered following pragmatic diagnostic evaluation and workup to assess whether an adult male is hypogonadal, based on symptoms consistent with androgen deficiency and low morning serum testosterone concentrations on ≥ 2 occasions. Effects of testosterone administration include the development or maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics and increases in libido, muscle strength, fat-free mass, and bone density.
Testosterone prescriptions have markedly increased in the past 20 years, including within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system.1-3 This trend may be influenced by various factors, including patient perceptions of benefit, an increase in marketing, and the availability of more user-friendly formulations.
Since 2006, evidence-based clinical practice guidelines have recommended specific clinical and laboratory evaluation and counseling prior to starting testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).4-8 However, research has shown poor adherence to these recommendations, including at the VA, which raises concerns about inappropriate TRT initiation without proper diagnostic evaluation.9,10 Observational research has suggested a possible link between testosterone therapy and increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) events. The US Food and Drug Administration prescribing information includes boxed warnings about potential risks of high blood pressure, myocardial infarction, stroke, and CV-related mortality with testosterone treatment, contact transfer of transdermal testosterone, and pulmonary oil microembolism with testosterone undecanoate injections.11-15
A VA Office of Inspector General (OIG) review of VA clinician adherence to clinical and laboratory evaluation guidelines for testosterone deficiency found poor adherence among VA practitioners and made recommendations for improvement.4,15 These focused on establishing clinical signs and symptoms consistent with testosterone deficiency, confirming hypogonadism by repeated testosterone testing, determining the etiology of hypogonadism by measuring gonadotropins, initiating a discussion of risks and benefits of TRT, and assessing clinical improvement and obtaining an updated hematocrit test within 3 to 6 months of initiation.
The VA Puget Sound Health Care System (VAPSHCS) developed a local prior authorization template to assist health care practitioners (HCPs) to address the OIG recommendations. This testosterone order template (TOT) aimed to improve the diagnosis, evaluation, and monitoring of TRT in males with hypogonadism, combined with existing VA pharmacy criteria for the use of testosterone based on Endocrine Society guidelines. A version of the VAPSHCS TOT was approved as the national VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) template.
Preliminary evaluation of the TOT suggested improved short-term adherence to guideline recommendations following implementation.16 This quality improvement study sought to assess the long-term effectiveness of the TOT with respect to clinical practice guideline adherence. The OIG did not address prostate-specific antigen (PSA) monitoring because understanding of the relationship between TRT and the risks of elevated PSA levels remains incomplete.6,17 This project hypothesized that implementation of a pharmacy-managed TOT incorporated into CPRS would result in higher adherence rates to guideline-recommended clinical and laboratory evaluation, in addition to counseling of men with hypogonadism prior to initiation of TRT.
Methods
Eligible participants were cisgender males who received a new testosterone prescription, had ≥ 2 clinic visits at VAPSHCS, and no previous testosterone prescription in the previous 2 years. Individuals were excluded if they had testosterone administered at VAPSHCS; were prescribed testosterone at another facility (VA or community-based); pilot tested an initial version of the TOT prior to November 30, 2019; or had an International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes for hypopituitarism, gender identity disorder, history of sexual assignment, or Klinefelter syndrome for which testosterone therapy was already approved. Patients who met the inclusion criteria were identified by an algorithm developed by the VAPSHCS pharmacoeconomist.
This quality improvement project used a retrospective, pre-post experimental design. Electronic chart review and systematic manual review of all eligible patient charts were performed for the pretemplate period (December 1, 2018, to November 30, 2019) and after the template implementation, (December 1, 2021, to November 30, 2022).
An initial version of the TOT was implemented on July 1, 2019, but was not fully integrated into CPRS until early 2020; individuals in whom the TOT was used prior to November 30, 2019, were excluded. Data from the initial period of the COVID-19 pandemic were avoided because of alterations in clinic and prescribing practices. As a quality improvement project, the TOT evaluation was exempt from formal review by the VAPSHCS Institutional Review Board, as determined by the Director of the Office of Transformation/Quality/Safety/Value.
Interventions
Testosterone is a Schedule III controlled substance with potential risks and a propensity for varied prescribing practices. It was designated as a restricted drug requiring a prior authorization drug request (PADR) for which a specific TOT was developed, approved by the VAPSHCS Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee, and incorporated into CPRS. A team of pharmacists, primary care physicians, geriatricians, endocrinologists, and health informatics experts created and developed the TOT. Pharmacists managed and monitored its completion.
The process for prescribing testosterone via the TOT is outlined in the eAppendix. When an HCP orders testosterone in CPRS, reminders prompt them to use the TOT and indicate required laboratory measurements (an order set is provided). Completion of TOT is not necessary to order testosterone for patients with an existing diagnosis of an organic cause of hypogonadism (eg, Klinefelter syndrome or hypopituitarism) or transgender women (assigned male at birth). In the TOT, the prescriber must also indicate signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency; required laboratory tests; and counseling regarding potential risks and benefits of TRT. A pharmacist reviews the TOT and either approves or rejects the testosterone prescription and provides follow-up guidance to the prescriber. The completed TOT serves as documentation of guideline adherence in CPRS. The TOT also includes sections for first renewal testosterone prescriptions, addressing guideline recommendations for follow-up laboratory evaluation and clinical response to TRT. Due to limited completion of this section in the posttemplate period, evaluating adherence to follow-up recommendations was not feasible.
Measures
This project assessed the percentage of patients in the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period with an approved PADR. Documentation of specific guideline-recommended measures was assessed: signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency; ≥ 2 serum testosterone measurements (≥ 2 total, free and total, or 2 free testosterone levels, and ≥ 1 testosterone level before 10
The project also assessed the proportion of patients in the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period who had all hormone tests (≥ 2 serum testosterone and LH and FSH concentrations), all laboratory tests (hormone tests and hematocrit), and all 5 guideline-recommended measures.
Analysis
Statistical comparisons between the proportions of patients in the pretemplate and posttemplate periods for each measure were performed using a χ2 test, without correction for multiple comparisons. All analyses were conducted using Stata version 10.0. A P value < .05 was considered significant for all comparisons.
Results
Chart review identified 189 patients in the pretemplate period and 113 patients in the posttemplate period with a new testosterone prescription (Figure). After exclusions, 91 and 49 patients, respectively, met eligibility criteria (Table 1). Fifty-six patients (62%) pretemplate and 40 patients (82%) posttemplate (P = .015) had approved PADRs and comprised the groups that were analyzed (Table 2).



The mean age and body mass index were similar in the pretemplate and posttemplate periods, but there was variation in the proportions of patients aged < 70 years and those with a body mass index < 30 between the groups. The most common diagnosis in both groups was testicular hypofunction, and the most common comorbidity was type 2 diabetes mellitus. Concomitant use of opioids or glucocorticoids that can lower testosterone levels was rare. Most testosterone prescriptions originated from primary care clinics in both periods: 68 (75%) in the pretemplate period and 35 (71%) in the posttemplate period. Most testosterone treatment was delivered by intramuscular injection.
In the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period, the proportion of patients with an approved PADR (82% vs 62%, P = .02), and documentation of signs and symptoms of hypogonadism (93% vs 71%, P = .002) prior to starting TRT were higher, while the percentage of patients having ≥ 2 testosterone measurements (85% vs 89%, P = .53), ≥ 1 testosterone level before 10 AM (78% vs 75%, P = .70), and hematocrit measured (95% vs 91%, P = .47) were similar. Rates of LH and FSH testing were higher in the posttemplate period (80%) vs the pretemplate period (63%) but did not achieve statistical significance (P = .07), and discussion of the risks and benefits of TRT was higher in the posttemplate period (58%) vs the pretemplate period (34%) (P = .02). The percentage of patients who had all hormone measurements (total and/or free testosterone, LH, and FSH) was higher in the posttemplate period (78%) vs the pretemplate period (59%) but did not achieve statistical significance (P = .06). The rates of all guideline-recommended laboratory test orders were higher in the posttemplate period (78%) vs the pretemplate period (55%) (P = .03), and all 5 guideline-recommended clinical and laboratory measures were higher in the posttemplate period (45%) vs the pretemplate period (18%) (P = .004).
Discussion
The implementation of a pharmacy-managed TOT in CPRS demonstrated higher adherence to evidence-based guidelines for diagnosing and evaluating hypogonadism before TRT. After TOT implementation, a higher proportion of patients had documented signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency, underwent all recommended laboratory tests, and had discussions about the risks and benefits of TRT. Adherence to 5 clinical and laboratory measures recommended by Endocrine Society guidelines was higher after TOT implementation, indicating improved prescribing practices.4
The requirement for TOT completion before testosterone prescription and its management by trained pharmacists likely contributed to higher adherence to guideline recommendations than previously reported. Integration of the TOT into CPRS with pharmacy oversight may have enhanced adherence by summarizing and codifying evidence-based guideline recommendations for clinical and biochemical evaluation prior to TRT initiation, offering relevant education to clinicians and pharmacists, automatically importing pertinent clinical information and laboratory results, and generating CPRS documentation to reduce clinician burden during patient care.
The proportion of patients with documented signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency before TRT increased from the pretemplate period (71%) to the posttemplate period (93%), indicating that most patients receiving TRT had clinical manifestations of hypogonadism. This aligns with Endocrine Society guidelines, which define hypogonadism as a clinical disorder characterized by clinical manifestations of testosterone deficiency and persistently low serum testosterone levels on ≥ 2 separate occasions.4,6 However, recent trends in direct-to-consumer advertising for testosterone and the rise of “low T” clinics may contribute to increased testing, varied practices, and inappropriate testosterone therapy initiation (eg, in men with low testosterone levels who lack symptoms of hypogonadism).18 Improved adherence in documenting clinical hypogonadism with implementation of the TOT reinforces the value of incorporating educational material, as previously reported.11
Adherence to guideline recommendations following implementation of the TOT in this project was higher than those previously reported. In a study of 111,631 outpatient veterans prescribed testosterone from 2009 to 2012, only 18.3% had ≥ 2 testosterone prescriptions, and 3.5% had ≥ 2 testosterone, LH, and FSH levels measured prior to the initiation of a TRT.9 In a report of 63,534 insured patients who received TRT from 2010 to 2012, 40.3% had ≥ 2 testosterone prescriptions, and 12% had LH and/or FSH measured prior to the initiation.8
Low rates of guideline-recommended laboratory tests prior to initiation of testosterone treatment were reported in prior non-VA studies.19,20 Poor guideline adherence reinforces the need for clinician education or other methods to improve TRT and ensure appropriate prescribing practices across health care systems. The TOT described in this project is a sustainable clinical tool with the potential to improve testosterone prescribing practices.
The high rates of adherence to guideline recommendations at VAPSHCS likely stem from local endocrine expertise and ongoing educational initiatives, as well as the requirement for template completion before testosterone prescription. However, most testosterone prescriptions were initiated by primary care and monitored by pharmacists with varying degrees of training and clinical experience in hypogonadism and TRT.
However, adherence to guideline recommendations was modest, suggesting there is still an opportunity for improvement. The decision to initiate therapy should be made only after appropriate counseling with patients regarding its potential benefits and risks. Reports on the CV risk of TRT have been mixed. The 2023 TRAVERSE study found no increase in major adverse CV events among older men with hypogonadism and pre-existing CV risks undergoing TRT, but noted higher instances of pulmonary embolism, atrial fibrillation, and acute kidney injury.21 This highlights the need for clinicians to continue to engage in informed decision-making with patients. Effective pretreatment counseling is important but time-consuming; future TOT monitoring and modifications could consider mandatory checkboxes to document counseling on TRT risks and benefits.
The TOT described in this study could be adapted and incorporated into the prescribing process and electronic health record of larger health care systems. Use of an electronic template allows for automatic real-time dashboard monitoring of organization performance. The TOT described could be modified or simplified for specialty or primary care clinics or individual practitioners to improve adherence to evidence-based guideline recommendations and quality of care.
Strengths
A strength of this study is the multidisciplinary team (composed of stakeholders with experience in VA health care system and subject matter experts in hypogonadism) that developed and incorporated a user-friendly template for testosterone prescriptions; the use of evidence-based guideline recommendations; and the use of a structured chart review permitted accurate assessment of adherence to recommendations to document signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency and a discussion of potential risks and benefits prior to TRT. To our knowledge, these recommendations have not been assessed in previous reports.
Limitations
The retrospective pre-post design of this study precludes a conclusion that implementation of the TOT caused the increase in adherence to guideline recommendations. Improved adherence could have resulted from the ongoing development of the preauthorization process for testosterone prescriptions or other changes over time. However, the preauthorization process had already been established for many years prior to template implementation. Forty-nine patients had new prescriptions for testosterone in the posttemplate period compared to 91 in the pretemplate period, but TRT was initiated in accordance with guideline recommendations more appropriately in the posttemplate period. The study’s sample size was small, and many eligible patients were excluded; however, exclusions were necessary to evaluate men who had new testosterone prescriptions for which the template was designed. Most men excluded were already taking testosterone.
Conclusions
The implementation of a CPRS-based TOT improved adherence to evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis, evaluation, and counseling of patients with hypogonadism before starting TRT. While there were improvements in adherence with the TOT, the relatively low proportion of patients with documentation of TRT risks and benefits and all guideline recommendations highlights the need for additional efforts to further strengthen adherence to guideline recommendations and ensure appropriate evaluation, counseling, and prescribing practices before initiating TRT.
Testosterone therapy is administered following pragmatic diagnostic evaluation and workup to assess whether an adult male is hypogonadal, based on symptoms consistent with androgen deficiency and low morning serum testosterone concentrations on ≥ 2 occasions. Effects of testosterone administration include the development or maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics and increases in libido, muscle strength, fat-free mass, and bone density.
Testosterone prescriptions have markedly increased in the past 20 years, including within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system.1-3 This trend may be influenced by various factors, including patient perceptions of benefit, an increase in marketing, and the availability of more user-friendly formulations.
Since 2006, evidence-based clinical practice guidelines have recommended specific clinical and laboratory evaluation and counseling prior to starting testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).4-8 However, research has shown poor adherence to these recommendations, including at the VA, which raises concerns about inappropriate TRT initiation without proper diagnostic evaluation.9,10 Observational research has suggested a possible link between testosterone therapy and increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) events. The US Food and Drug Administration prescribing information includes boxed warnings about potential risks of high blood pressure, myocardial infarction, stroke, and CV-related mortality with testosterone treatment, contact transfer of transdermal testosterone, and pulmonary oil microembolism with testosterone undecanoate injections.11-15
A VA Office of Inspector General (OIG) review of VA clinician adherence to clinical and laboratory evaluation guidelines for testosterone deficiency found poor adherence among VA practitioners and made recommendations for improvement.4,15 These focused on establishing clinical signs and symptoms consistent with testosterone deficiency, confirming hypogonadism by repeated testosterone testing, determining the etiology of hypogonadism by measuring gonadotropins, initiating a discussion of risks and benefits of TRT, and assessing clinical improvement and obtaining an updated hematocrit test within 3 to 6 months of initiation.
The VA Puget Sound Health Care System (VAPSHCS) developed a local prior authorization template to assist health care practitioners (HCPs) to address the OIG recommendations. This testosterone order template (TOT) aimed to improve the diagnosis, evaluation, and monitoring of TRT in males with hypogonadism, combined with existing VA pharmacy criteria for the use of testosterone based on Endocrine Society guidelines. A version of the VAPSHCS TOT was approved as the national VA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) template.
Preliminary evaluation of the TOT suggested improved short-term adherence to guideline recommendations following implementation.16 This quality improvement study sought to assess the long-term effectiveness of the TOT with respect to clinical practice guideline adherence. The OIG did not address prostate-specific antigen (PSA) monitoring because understanding of the relationship between TRT and the risks of elevated PSA levels remains incomplete.6,17 This project hypothesized that implementation of a pharmacy-managed TOT incorporated into CPRS would result in higher adherence rates to guideline-recommended clinical and laboratory evaluation, in addition to counseling of men with hypogonadism prior to initiation of TRT.
Methods
Eligible participants were cisgender males who received a new testosterone prescription, had ≥ 2 clinic visits at VAPSHCS, and no previous testosterone prescription in the previous 2 years. Individuals were excluded if they had testosterone administered at VAPSHCS; were prescribed testosterone at another facility (VA or community-based); pilot tested an initial version of the TOT prior to November 30, 2019; or had an International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes for hypopituitarism, gender identity disorder, history of sexual assignment, or Klinefelter syndrome for which testosterone therapy was already approved. Patients who met the inclusion criteria were identified by an algorithm developed by the VAPSHCS pharmacoeconomist.
This quality improvement project used a retrospective, pre-post experimental design. Electronic chart review and systematic manual review of all eligible patient charts were performed for the pretemplate period (December 1, 2018, to November 30, 2019) and after the template implementation, (December 1, 2021, to November 30, 2022).
An initial version of the TOT was implemented on July 1, 2019, but was not fully integrated into CPRS until early 2020; individuals in whom the TOT was used prior to November 30, 2019, were excluded. Data from the initial period of the COVID-19 pandemic were avoided because of alterations in clinic and prescribing practices. As a quality improvement project, the TOT evaluation was exempt from formal review by the VAPSHCS Institutional Review Board, as determined by the Director of the Office of Transformation/Quality/Safety/Value.
Interventions
Testosterone is a Schedule III controlled substance with potential risks and a propensity for varied prescribing practices. It was designated as a restricted drug requiring a prior authorization drug request (PADR) for which a specific TOT was developed, approved by the VAPSHCS Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee, and incorporated into CPRS. A team of pharmacists, primary care physicians, geriatricians, endocrinologists, and health informatics experts created and developed the TOT. Pharmacists managed and monitored its completion.
The process for prescribing testosterone via the TOT is outlined in the eAppendix. When an HCP orders testosterone in CPRS, reminders prompt them to use the TOT and indicate required laboratory measurements (an order set is provided). Completion of TOT is not necessary to order testosterone for patients with an existing diagnosis of an organic cause of hypogonadism (eg, Klinefelter syndrome or hypopituitarism) or transgender women (assigned male at birth). In the TOT, the prescriber must also indicate signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency; required laboratory tests; and counseling regarding potential risks and benefits of TRT. A pharmacist reviews the TOT and either approves or rejects the testosterone prescription and provides follow-up guidance to the prescriber. The completed TOT serves as documentation of guideline adherence in CPRS. The TOT also includes sections for first renewal testosterone prescriptions, addressing guideline recommendations for follow-up laboratory evaluation and clinical response to TRT. Due to limited completion of this section in the posttemplate period, evaluating adherence to follow-up recommendations was not feasible.
Measures
This project assessed the percentage of patients in the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period with an approved PADR. Documentation of specific guideline-recommended measures was assessed: signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency; ≥ 2 serum testosterone measurements (≥ 2 total, free and total, or 2 free testosterone levels, and ≥ 1 testosterone level before 10
The project also assessed the proportion of patients in the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period who had all hormone tests (≥ 2 serum testosterone and LH and FSH concentrations), all laboratory tests (hormone tests and hematocrit), and all 5 guideline-recommended measures.
Analysis
Statistical comparisons between the proportions of patients in the pretemplate and posttemplate periods for each measure were performed using a χ2 test, without correction for multiple comparisons. All analyses were conducted using Stata version 10.0. A P value < .05 was considered significant for all comparisons.
Results
Chart review identified 189 patients in the pretemplate period and 113 patients in the posttemplate period with a new testosterone prescription (Figure). After exclusions, 91 and 49 patients, respectively, met eligibility criteria (Table 1). Fifty-six patients (62%) pretemplate and 40 patients (82%) posttemplate (P = .015) had approved PADRs and comprised the groups that were analyzed (Table 2).



The mean age and body mass index were similar in the pretemplate and posttemplate periods, but there was variation in the proportions of patients aged < 70 years and those with a body mass index < 30 between the groups. The most common diagnosis in both groups was testicular hypofunction, and the most common comorbidity was type 2 diabetes mellitus. Concomitant use of opioids or glucocorticoids that can lower testosterone levels was rare. Most testosterone prescriptions originated from primary care clinics in both periods: 68 (75%) in the pretemplate period and 35 (71%) in the posttemplate period. Most testosterone treatment was delivered by intramuscular injection.
In the posttemplate period vs pretemplate period, the proportion of patients with an approved PADR (82% vs 62%, P = .02), and documentation of signs and symptoms of hypogonadism (93% vs 71%, P = .002) prior to starting TRT were higher, while the percentage of patients having ≥ 2 testosterone measurements (85% vs 89%, P = .53), ≥ 1 testosterone level before 10 AM (78% vs 75%, P = .70), and hematocrit measured (95% vs 91%, P = .47) were similar. Rates of LH and FSH testing were higher in the posttemplate period (80%) vs the pretemplate period (63%) but did not achieve statistical significance (P = .07), and discussion of the risks and benefits of TRT was higher in the posttemplate period (58%) vs the pretemplate period (34%) (P = .02). The percentage of patients who had all hormone measurements (total and/or free testosterone, LH, and FSH) was higher in the posttemplate period (78%) vs the pretemplate period (59%) but did not achieve statistical significance (P = .06). The rates of all guideline-recommended laboratory test orders were higher in the posttemplate period (78%) vs the pretemplate period (55%) (P = .03), and all 5 guideline-recommended clinical and laboratory measures were higher in the posttemplate period (45%) vs the pretemplate period (18%) (P = .004).
Discussion
The implementation of a pharmacy-managed TOT in CPRS demonstrated higher adherence to evidence-based guidelines for diagnosing and evaluating hypogonadism before TRT. After TOT implementation, a higher proportion of patients had documented signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency, underwent all recommended laboratory tests, and had discussions about the risks and benefits of TRT. Adherence to 5 clinical and laboratory measures recommended by Endocrine Society guidelines was higher after TOT implementation, indicating improved prescribing practices.4
The requirement for TOT completion before testosterone prescription and its management by trained pharmacists likely contributed to higher adherence to guideline recommendations than previously reported. Integration of the TOT into CPRS with pharmacy oversight may have enhanced adherence by summarizing and codifying evidence-based guideline recommendations for clinical and biochemical evaluation prior to TRT initiation, offering relevant education to clinicians and pharmacists, automatically importing pertinent clinical information and laboratory results, and generating CPRS documentation to reduce clinician burden during patient care.
The proportion of patients with documented signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency before TRT increased from the pretemplate period (71%) to the posttemplate period (93%), indicating that most patients receiving TRT had clinical manifestations of hypogonadism. This aligns with Endocrine Society guidelines, which define hypogonadism as a clinical disorder characterized by clinical manifestations of testosterone deficiency and persistently low serum testosterone levels on ≥ 2 separate occasions.4,6 However, recent trends in direct-to-consumer advertising for testosterone and the rise of “low T” clinics may contribute to increased testing, varied practices, and inappropriate testosterone therapy initiation (eg, in men with low testosterone levels who lack symptoms of hypogonadism).18 Improved adherence in documenting clinical hypogonadism with implementation of the TOT reinforces the value of incorporating educational material, as previously reported.11
Adherence to guideline recommendations following implementation of the TOT in this project was higher than those previously reported. In a study of 111,631 outpatient veterans prescribed testosterone from 2009 to 2012, only 18.3% had ≥ 2 testosterone prescriptions, and 3.5% had ≥ 2 testosterone, LH, and FSH levels measured prior to the initiation of a TRT.9 In a report of 63,534 insured patients who received TRT from 2010 to 2012, 40.3% had ≥ 2 testosterone prescriptions, and 12% had LH and/or FSH measured prior to the initiation.8
Low rates of guideline-recommended laboratory tests prior to initiation of testosterone treatment were reported in prior non-VA studies.19,20 Poor guideline adherence reinforces the need for clinician education or other methods to improve TRT and ensure appropriate prescribing practices across health care systems. The TOT described in this project is a sustainable clinical tool with the potential to improve testosterone prescribing practices.
The high rates of adherence to guideline recommendations at VAPSHCS likely stem from local endocrine expertise and ongoing educational initiatives, as well as the requirement for template completion before testosterone prescription. However, most testosterone prescriptions were initiated by primary care and monitored by pharmacists with varying degrees of training and clinical experience in hypogonadism and TRT.
However, adherence to guideline recommendations was modest, suggesting there is still an opportunity for improvement. The decision to initiate therapy should be made only after appropriate counseling with patients regarding its potential benefits and risks. Reports on the CV risk of TRT have been mixed. The 2023 TRAVERSE study found no increase in major adverse CV events among older men with hypogonadism and pre-existing CV risks undergoing TRT, but noted higher instances of pulmonary embolism, atrial fibrillation, and acute kidney injury.21 This highlights the need for clinicians to continue to engage in informed decision-making with patients. Effective pretreatment counseling is important but time-consuming; future TOT monitoring and modifications could consider mandatory checkboxes to document counseling on TRT risks and benefits.
The TOT described in this study could be adapted and incorporated into the prescribing process and electronic health record of larger health care systems. Use of an electronic template allows for automatic real-time dashboard monitoring of organization performance. The TOT described could be modified or simplified for specialty or primary care clinics or individual practitioners to improve adherence to evidence-based guideline recommendations and quality of care.
Strengths
A strength of this study is the multidisciplinary team (composed of stakeholders with experience in VA health care system and subject matter experts in hypogonadism) that developed and incorporated a user-friendly template for testosterone prescriptions; the use of evidence-based guideline recommendations; and the use of a structured chart review permitted accurate assessment of adherence to recommendations to document signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency and a discussion of potential risks and benefits prior to TRT. To our knowledge, these recommendations have not been assessed in previous reports.
Limitations
The retrospective pre-post design of this study precludes a conclusion that implementation of the TOT caused the increase in adherence to guideline recommendations. Improved adherence could have resulted from the ongoing development of the preauthorization process for testosterone prescriptions or other changes over time. However, the preauthorization process had already been established for many years prior to template implementation. Forty-nine patients had new prescriptions for testosterone in the posttemplate period compared to 91 in the pretemplate period, but TRT was initiated in accordance with guideline recommendations more appropriately in the posttemplate period. The study’s sample size was small, and many eligible patients were excluded; however, exclusions were necessary to evaluate men who had new testosterone prescriptions for which the template was designed. Most men excluded were already taking testosterone.
Conclusions
The implementation of a CPRS-based TOT improved adherence to evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis, evaluation, and counseling of patients with hypogonadism before starting TRT. While there were improvements in adherence with the TOT, the relatively low proportion of patients with documentation of TRT risks and benefits and all guideline recommendations highlights the need for additional efforts to further strengthen adherence to guideline recommendations and ensure appropriate evaluation, counseling, and prescribing practices before initiating TRT.
- Layton JB, Li D, Meier CR, et al. Testosterone lab testing and initiation in the United Kingdom and the United States, 2000 to 2011. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:835-842. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-3570
- Baillargeon J, Kuo YF, Westra JR, et al. Testosterone prescribing in the United States, 2002-2016. JAMA. 2018;320:200-202. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7999
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Rose AJ. Patterns of testosterone prescription overuse. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2017;24:240-245. doi:10.1097/MED.0000000000000336
- Bhasin S, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, et al. Testosterone therapy in adult men with androgen deficiency syndromes: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1995-2010. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2847
- Bhasin S, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with androgen deficiency syndromes: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:2536-2559. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2354
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:1715-1744. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00229
- Mulhall JP, Trost LW, Brannigan RE, et al. Evaluation and management of testosterone deficiency: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2018;200:423-432. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.115
- Muram D, Zhang X, Cui Z, et al. Use of hormone testing for the diagnosis and evaluation of male hypogonadism and monitoring of testosterone therapy: application of hormone testing guideline recommendations in clinical practice. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1886-1894. doi:10.1111/jsm.12968
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Ascertainment of testosterone prescribing practices in the VA. Med Care. 2015;53:746-752. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000398?
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Who gets testosterone? Patient characteristics associated with testosterone prescribing in the Veteran Affairs system: a cross-sectional study. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:304-311. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3940-7
- Basaria S, Coviello AD, Travison TG, et al. Adverse events associated with testosterone administration. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:109-122. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1000485
- Vigen R, O’Donnell CI, Barón AE, et al. Association of testosterone therapy with mortality, myocardial infarction, and stroke in men with low testosterone levels. JAMA. 2013;310:1829-1836. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.280386
- Finkle WD, Greenland S, Ridgeway GK, et al. Increased risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction following testosterone therapy prescription in men. PLoS One. 2014;9:e85805. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085805
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions about using testosterone products for low testosterone due to aging; requires labeling change to inform of possible increased risk of heart attack and stroke with use. FDA.gov. March 3, 2015. Updated February 28, 2025. Accessed July 8, 2025. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm436259.htm
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Inspector General. Healthcare inspection – testosterone replacement therapy initiation and follow-up evaluation in VA male patients. April 11, 2018. Accessed July 8, 2025. https://www.vaoig.gov/reports/national-healthcare-review/healthcare-inspection-testosterone-replacement-therapy
- Narla R, Mobley D, Nguyen EHK, et al. Preliminary evaluation of an order template to improve diagnosis and testosterone therapy of hypogonadism in veterans. Fed Pract. 2021;38:121-127. doi:10.12788/fp.0103
- Bhasin S, Travison TG, Pencina KM, et al. Prostate safety events during testosterone replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2348692. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.48692
- Dubin JM, Jesse E, Fantus RJ, et al. Guideline-discordant care among direct-to-consumer testosterone therapy platforms. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182:1321-1323. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.4928
- Baillargeon J, Urban RJ, Ottenbacher KJ, et al. Trends in androgen prescribing in the United States, 2001 to 2011. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1465-1466. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.6895
- Locke JA, Flannigan R, Günther OP, et al. Testosterone therapy: prescribing and monitoring patterns of practice in British Columbia. Can Urol Assoc J. 2021;15:e110-e117. doi:10.5489/cuaj.6586
- Lincoff AM, Bhasin S, Flevaris P, et al. Cardiovascular safety of testosterone-replacement therapy. N Engl J Med. 2023;389:107-117. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2215025
- Layton JB, Li D, Meier CR, et al. Testosterone lab testing and initiation in the United Kingdom and the United States, 2000 to 2011. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:835-842. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-3570
- Baillargeon J, Kuo YF, Westra JR, et al. Testosterone prescribing in the United States, 2002-2016. JAMA. 2018;320:200-202. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7999
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Rose AJ. Patterns of testosterone prescription overuse. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2017;24:240-245. doi:10.1097/MED.0000000000000336
- Bhasin S, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, et al. Testosterone therapy in adult men with androgen deficiency syndromes: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1995-2010. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2847
- Bhasin S, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with androgen deficiency syndromes: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:2536-2559. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2354
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:1715-1744. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00229
- Mulhall JP, Trost LW, Brannigan RE, et al. Evaluation and management of testosterone deficiency: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2018;200:423-432. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.115
- Muram D, Zhang X, Cui Z, et al. Use of hormone testing for the diagnosis and evaluation of male hypogonadism and monitoring of testosterone therapy: application of hormone testing guideline recommendations in clinical practice. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1886-1894. doi:10.1111/jsm.12968
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Ascertainment of testosterone prescribing practices in the VA. Med Care. 2015;53:746-752. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000398?
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Who gets testosterone? Patient characteristics associated with testosterone prescribing in the Veteran Affairs system: a cross-sectional study. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:304-311. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3940-7
- Basaria S, Coviello AD, Travison TG, et al. Adverse events associated with testosterone administration. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:109-122. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1000485
- Vigen R, O’Donnell CI, Barón AE, et al. Association of testosterone therapy with mortality, myocardial infarction, and stroke in men with low testosterone levels. JAMA. 2013;310:1829-1836. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.280386
- Finkle WD, Greenland S, Ridgeway GK, et al. Increased risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction following testosterone therapy prescription in men. PLoS One. 2014;9:e85805. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085805
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions about using testosterone products for low testosterone due to aging; requires labeling change to inform of possible increased risk of heart attack and stroke with use. FDA.gov. March 3, 2015. Updated February 28, 2025. Accessed July 8, 2025. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm436259.htm
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Inspector General. Healthcare inspection – testosterone replacement therapy initiation and follow-up evaluation in VA male patients. April 11, 2018. Accessed July 8, 2025. https://www.vaoig.gov/reports/national-healthcare-review/healthcare-inspection-testosterone-replacement-therapy
- Narla R, Mobley D, Nguyen EHK, et al. Preliminary evaluation of an order template to improve diagnosis and testosterone therapy of hypogonadism in veterans. Fed Pract. 2021;38:121-127. doi:10.12788/fp.0103
- Bhasin S, Travison TG, Pencina KM, et al. Prostate safety events during testosterone replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2348692. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.48692
- Dubin JM, Jesse E, Fantus RJ, et al. Guideline-discordant care among direct-to-consumer testosterone therapy platforms. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182:1321-1323. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.4928
- Baillargeon J, Urban RJ, Ottenbacher KJ, et al. Trends in androgen prescribing in the United States, 2001 to 2011. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1465-1466. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.6895
- Locke JA, Flannigan R, Günther OP, et al. Testosterone therapy: prescribing and monitoring patterns of practice in British Columbia. Can Urol Assoc J. 2021;15:e110-e117. doi:10.5489/cuaj.6586
- Lincoff AM, Bhasin S, Flevaris P, et al. Cardiovascular safety of testosterone-replacement therapy. N Engl J Med. 2023;389:107-117. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2215025
Streamlined Testosterone Order Template to Improve the Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hypogonadism in Veterans
Streamlined Testosterone Order Template to Improve the Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hypogonadism in Veterans
Diagnostic Value of Deep Punch Biopsies in Intravascular Large B-cell Lymphoma
Diagnostic Value of Deep Punch Biopsies in Intravascular Large B-cell Lymphoma
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVBCL) is an exceedingly rare aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma with tumor cells growing selectively in vascular lumina.1 The annual incidence of IVBCL is fewer than 0.5 cases per 1,000,000 individuals worldwide.2 Only about 500 known cases of IVBCL have been recorded in the literature,3 and it accounts for less than 1% of all lymphomas. It generally affects middle-aged to elderly individuals, with an average age at diagnosis of 70 years.2 It has a predilection for men and commonly develops in individuals who are immunosuppressed.3,4
Multiple variants of IVBCL have been described in the literature, with central nervous system and cutaneous involvement being the most classic findings.5 Bone marrow involvement with hepatosplenomegaly also has been noted in the literature.6,7 Diagnosis of IVBCL and its variants requires a high index of suspicion, as the clinical manifestations and tissues involved typically are nonspecific and highly variable. Even in the classic variant of IVBCL, skin involvement is only reported in approximately half of cases.3 When present, cutaneous manifestations can range from nodules and violaceous plaques to induration and telangiectasias.3 Lymphadenopathy and lymphoma (leukemic) cells are not seen on a peripheral blood smear.2,8,9
The lack of lymphadenopathy or identifiable leukemic cells in the peripheral blood presents a diagnostic dilemma, as sufficient information for accurate diagnosis must be obtained while minimizing invasive procedures and resource expenditure. Because IVBCL cells can reside in the vascular lumina of various organs, numerous biopsy sites have been proposed for diagnosis of lymphoma, including the bone marrow, skin, prostate, adrenal gland, brain, liver, and kidneys.10 While some studies have reported that the optimal diagnostic site is the bone marrow, skin biopsies are more routinely carried out, as they represent a convenient and cost-effective alternative to other more invasive techniques.6,7,10 Studies have shown biopsy sensitivity values ranging from 77.8% to 83.3% for detection of IVBCL in normal-appearing skin, which is comparable to the sensitivities of a bone marrow biopsy.7,8 Although skin biopsy of random sites has shown diagnostic efficacy, some studies have proposed that biopsies taken from hemangiomas and other hypervascular lesions can further improve diagnostic yield, as lymphoma cells often are present in capillaries of subcutaneous adipose tissue.6,10,11 However, no obvious clinicopathologic differences were observed between IVBCL with and without involvement of a cutaneous hemangioma.11
The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic efficacy of skin biopsies for detecting IVBCL at various body sites and to establish whether biopsies from hemangiomas yield higher diagnostic value.
Methods
A 66-year-old man recently died at our institution secondary to IVBCL. His disease course was characterized by multiple hospital admissions in a 6-month period for fever of unknown origin and tachycardia unresponsive to broad-spectrum antibiotics and systemic steroids. The patient declined over the course of 3 to 4 weeks with findings suggestive of lymphoma and tumor lysis syndrome, and he eventually developed shock, hypoxic respiratory failure, and acute renal failure. As imaging studies and examinations had not shown lymphadenopathy, bone marrow biopsy was performed, and dermatology was consulted to perform skin biopsies to evaluate for IVBCL. Both bone marrow biopsies and random skin biopsies from the abdomen showed large and atypical CD20+ B cells within select vascular lumina (Figure). No extravascular lymphoma cells were seen. Based on the bone marrow and skin biopsies, a diagnosis of IVBCL was made. Unfortunately, no progress was made clinically, and the patient was transitioned to comfort measures. Upon the patient’s death, his family expressed interest in participating in IVBCL research and agreed to a limited autopsy consisting of numerous skin biopsies to evaluate different body sites and biopsy types (normal skin vs hemangiomas) to ascertain whether diagnostic yield could be increased by performing selective biopsies of hemangiomas if IVBCL was suspected.
Twenty-four postmortem 4-mm punch biopsies containing subcutaneous adipose tissue were taken within 24 hours of the death of the patient before embalming. The biopsies were taken from all regions of the body except the head and neck for cosmetic preservation of the decedent. Eighteen of the biopsies were taken from random sites of normal-appearing skin; the remaining 6 were taken from clinically identifiable cherry hemangiomas (5 on the trunk and 1 on the thigh). There was a variable degree of livor mortis in the dependent areas of the body, which was included in the random biopsies from the back to ensure any pooling of dependent blood would not alter the findings.
A histopathologic examination by a board-certified dermatopathologist (M.P.) on a single hematoxylin-eosin–stained level was performed to evaluate each biopsy for superficial involvement and deep involvement by IVBCL. Superficial involvement was defined as dermal involvement at or above the level of the eccrine sweat glands; deep involvement was defined as dermal involvement beneath the eccrine sweat glands and all subcutaneous fat present. Skin and bone marrow biopsies used to make the original diagnosis prior to the patient’s death were reviewed, including CD20 immunohistochemistry for morphologic comparison to the study slides. Involvement was graded as 0 to 3+ (eTable).
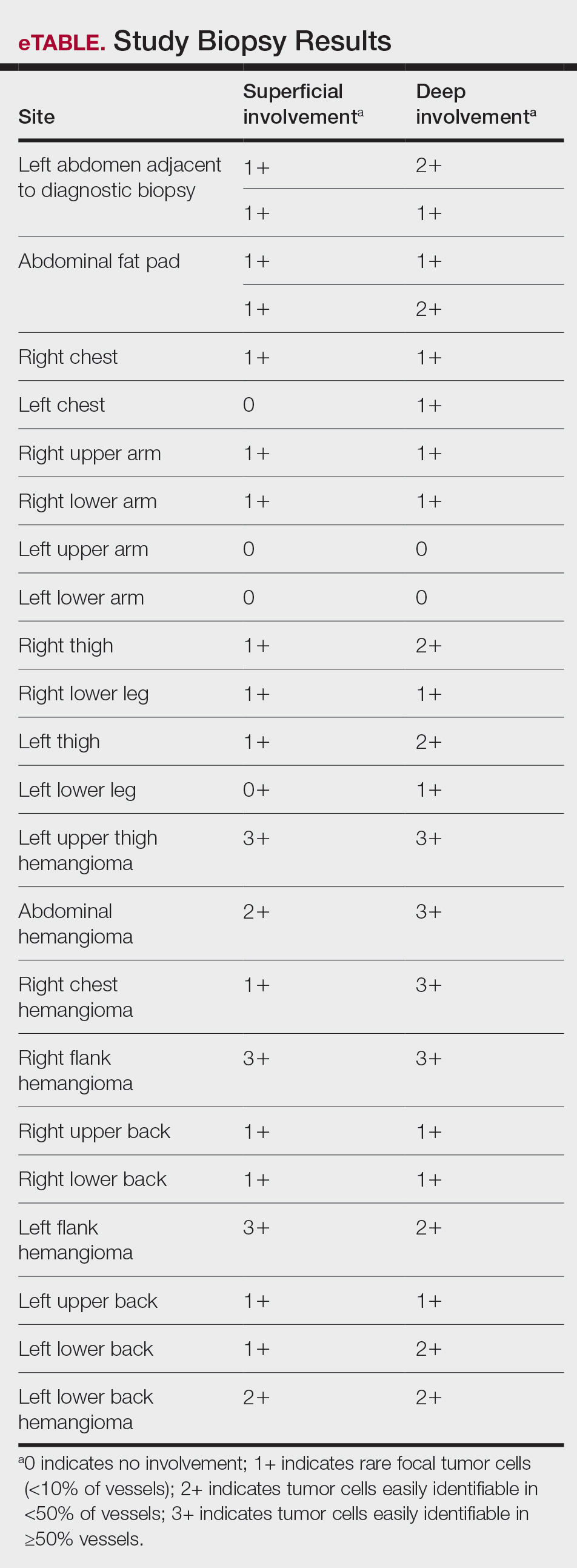
Results
Results from all 24 biopsies are shown in the eTable. Twenty-two (91.7%) biopsies showed at least focal involvement by IVBCL. Nine (37.5%) biopsies showed more deep vs superficial involvement of the same site. On average, the 6 biopsies from clinically detected hemangiomas showed more involvement by IVBCL than the random biopsies (eFigures 1 and 2A). The superficial involvement of skin with a hemangioma showed an average score of 2.33 v 0.78 when compared with the superficial aspect of the random biopsies; the deep involvement of skin with a hemangioma showed an average score of 2.67 vs 1.16 when compared with the deep aspect of the random biopsies (eFigure 2B).
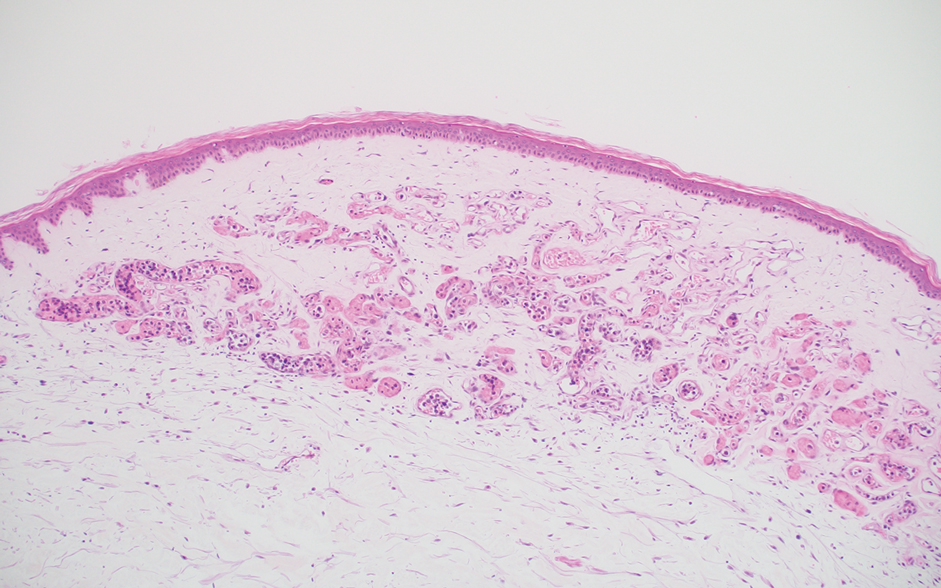
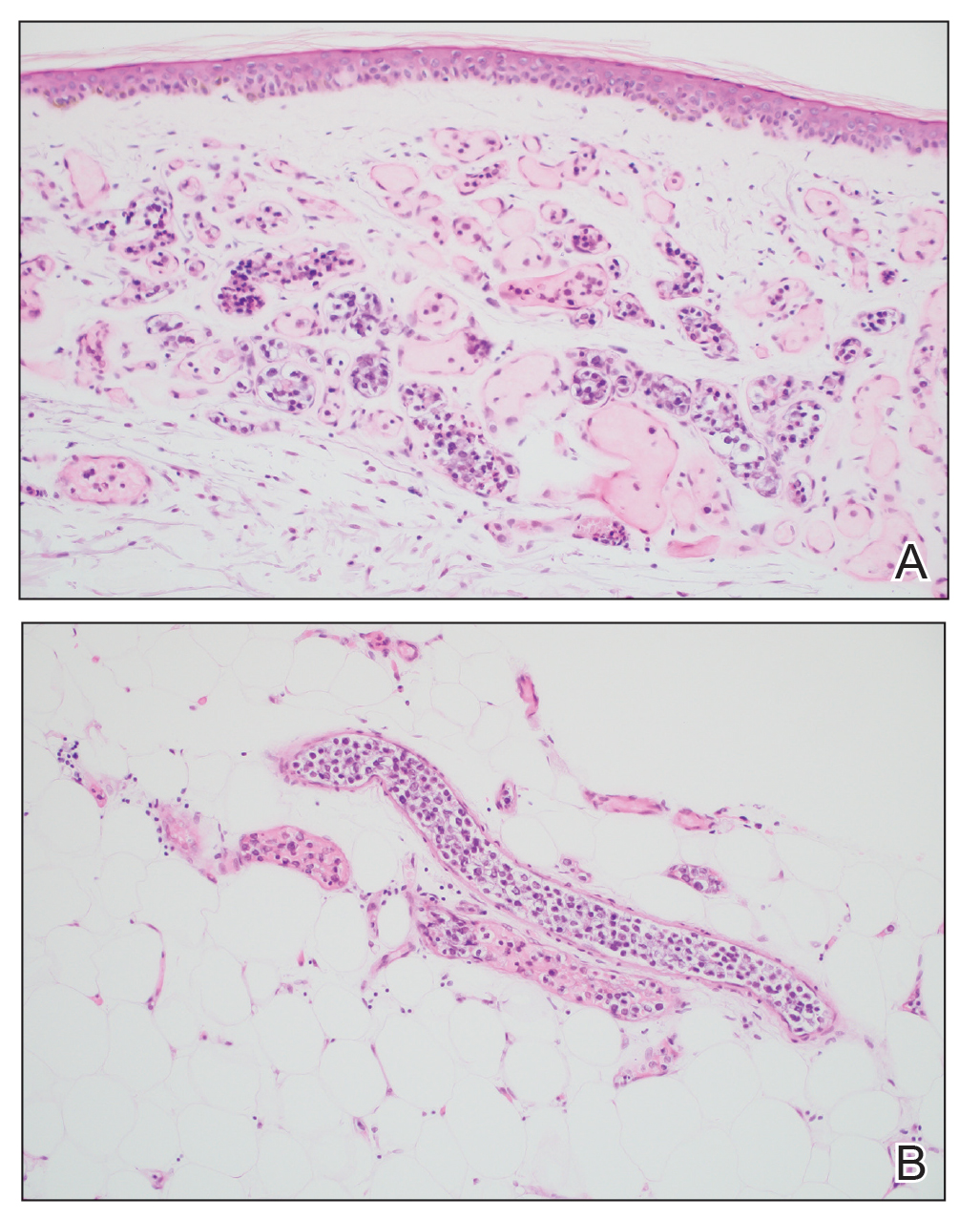
Comment
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma is an aggressive malignancy that traditionally is difficult to diagnose. Many efforts have been made to improve detection and early diagnosis. As cutaneous involvement is common and sometimes the only sign of disease, dermatologists may be called upon to evaluate and biopsy patients with this suspected diagnosis. The purpose of our study was to improve diagnostic efficacy by methodically performing numerous biopsies and assessing the level of involvement of the superficial and deep skin as well as involvement of hemangiomas. The goal of this meticulous approach was to identify the highest-yield areas for biopsy with minimal impact on the patient. Our results showed that random skin biopsies are an effective way to identify IVBCL. Twenty-two (91.7%) biopsies contained at least focal lymphoma cells. Although the 2 biopsies that showed no tumor cells at all happened to both be from the left arm, this is believed to be coincidental. No discernable pattern was identified regarding involvement and anatomic region. Even though 20 (83.3%) biopsies showed superficial involvement, deep biopsy is essential, as 9 (37.5%) biopsies showed increased deep involvement compared to superficial involvement. Therefore, a deep punch biopsy is essential for maximum sensitivity.
Hemangiomas provide a potential target that could increase the sensitivity of a biopsy in the absence of clinical findings, when the disease in question is exclusively intravascular. The data gathered in this study support this idea, as biopsies from hemangiomas showed increased involvement compared to random biopsies, both superficially and deep (2.33 vs 0.78 and 2.67 vs 1.16, respectively). Interestingly, the hemangioma biopsy sites showed increased deep and superficial involvement, despite these typical cherry hemangiomas only involving the superficial dermis. One possible explanation for this is that the hemangiomas have larger-caliber feeder vessels with increased blood flow beneath them. It would then follow that this increased vasculature would increase the chances of identifying intravascular lymphoma cells. This finding further accentuates the need for a deep punch biopsy containing subcutaneous fat.
Completing the study in the setting of an autopsy provided the advantage of being able to take numerous biopsies without increased harm to the patient. This extensive set of biopsies would not be reasonable to complete on a living patient. This study also has limitations. Although this patient did fall within the typical demographics for patients with IVBCL, the data were still limited to 1 patient. This autopsy format (on a patient whose cause of death was indeed IVBCL) also implies terminal disease, which may mean the patient had a larger disease burden than a living patient who would typically be biopsied. Although this increased disease burden may have increased the sensitivity of finding IVBCL in the biopsies of this study, this further emphasizes the importance of trying to determine any factors that could increase sensitivity in a living patient with a lower disease burden.
Conclusion
Skin biopsies can provide a sensitive, low-cost, and low-morbidity method to assess a patient for IVBCL. Though random skin biopsies can yield valuable information, deep, 4-mm punch biopsies of clinically identifiable hemangiomas may provide the highest sensitivity for IVBCL.
- Ponzoni M, Campo E, Nakamura S. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a chameleon with multiple faces and many masks. Blood. 2018;132:1561-1567. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-04-737445
- Roy AM, Pandey Y, Middleton D, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a diagnostic dilemma. Cureus. 2021;13:e16459. doi:10.7759/cureus.16459
- Bayçelebi D, Yildiz L, S?entürk N. A case report and literature review of cutaneous intravascular large B-cell lymphoma presenting clinically as panniculitis: a difficult diagnosis, but a good prognosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:72-75. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.08.004
- Orwat DE, Batalis NI. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136:333-338. doi:10.5858/arpa.2010-0747-RS
- Breakell T, Waibel H, Schliep S, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a review with a focus on the prognostic value of skininvolvement. Curr Oncol. 2022;29:2909-2919. doi:10.3390/curroncol29050237
- Oppegard L, O’Donnell M, Piro K, et al. Going skin deep: excavating a diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:3368-3371. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06141-1
- Barker JL, Swarup O, Puliyayil A. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: representative cases and approach to diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021;14:e244069. doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-244069
- Matsue K, Asada N, Odawara J, et al. Random skin biopsy and bone marrow biopsy for diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2011;90:417-421. doi:10.1007/s00277-010-1101-3
- Shimada K, Kinoshita T, Naoe T, et al. Presentation and management of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:895-902. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70140-8
- Adachi Y, Kosami K, Mizuta N, et al. Benefits of skin biopsy of senile hemangioma in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:2003-2006. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2017
- Ishida M, Hodohara K, Yoshida T, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma colonizing in senile hemangioma: a case report and proposal of possible diagnostic strategy for intravascular lymphoma. Pathol Int. 2011;61:555-557. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02697.x
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVBCL) is an exceedingly rare aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma with tumor cells growing selectively in vascular lumina.1 The annual incidence of IVBCL is fewer than 0.5 cases per 1,000,000 individuals worldwide.2 Only about 500 known cases of IVBCL have been recorded in the literature,3 and it accounts for less than 1% of all lymphomas. It generally affects middle-aged to elderly individuals, with an average age at diagnosis of 70 years.2 It has a predilection for men and commonly develops in individuals who are immunosuppressed.3,4
Multiple variants of IVBCL have been described in the literature, with central nervous system and cutaneous involvement being the most classic findings.5 Bone marrow involvement with hepatosplenomegaly also has been noted in the literature.6,7 Diagnosis of IVBCL and its variants requires a high index of suspicion, as the clinical manifestations and tissues involved typically are nonspecific and highly variable. Even in the classic variant of IVBCL, skin involvement is only reported in approximately half of cases.3 When present, cutaneous manifestations can range from nodules and violaceous plaques to induration and telangiectasias.3 Lymphadenopathy and lymphoma (leukemic) cells are not seen on a peripheral blood smear.2,8,9
The lack of lymphadenopathy or identifiable leukemic cells in the peripheral blood presents a diagnostic dilemma, as sufficient information for accurate diagnosis must be obtained while minimizing invasive procedures and resource expenditure. Because IVBCL cells can reside in the vascular lumina of various organs, numerous biopsy sites have been proposed for diagnosis of lymphoma, including the bone marrow, skin, prostate, adrenal gland, brain, liver, and kidneys.10 While some studies have reported that the optimal diagnostic site is the bone marrow, skin biopsies are more routinely carried out, as they represent a convenient and cost-effective alternative to other more invasive techniques.6,7,10 Studies have shown biopsy sensitivity values ranging from 77.8% to 83.3% for detection of IVBCL in normal-appearing skin, which is comparable to the sensitivities of a bone marrow biopsy.7,8 Although skin biopsy of random sites has shown diagnostic efficacy, some studies have proposed that biopsies taken from hemangiomas and other hypervascular lesions can further improve diagnostic yield, as lymphoma cells often are present in capillaries of subcutaneous adipose tissue.6,10,11 However, no obvious clinicopathologic differences were observed between IVBCL with and without involvement of a cutaneous hemangioma.11
The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic efficacy of skin biopsies for detecting IVBCL at various body sites and to establish whether biopsies from hemangiomas yield higher diagnostic value.
Methods
A 66-year-old man recently died at our institution secondary to IVBCL. His disease course was characterized by multiple hospital admissions in a 6-month period for fever of unknown origin and tachycardia unresponsive to broad-spectrum antibiotics and systemic steroids. The patient declined over the course of 3 to 4 weeks with findings suggestive of lymphoma and tumor lysis syndrome, and he eventually developed shock, hypoxic respiratory failure, and acute renal failure. As imaging studies and examinations had not shown lymphadenopathy, bone marrow biopsy was performed, and dermatology was consulted to perform skin biopsies to evaluate for IVBCL. Both bone marrow biopsies and random skin biopsies from the abdomen showed large and atypical CD20+ B cells within select vascular lumina (Figure). No extravascular lymphoma cells were seen. Based on the bone marrow and skin biopsies, a diagnosis of IVBCL was made. Unfortunately, no progress was made clinically, and the patient was transitioned to comfort measures. Upon the patient’s death, his family expressed interest in participating in IVBCL research and agreed to a limited autopsy consisting of numerous skin biopsies to evaluate different body sites and biopsy types (normal skin vs hemangiomas) to ascertain whether diagnostic yield could be increased by performing selective biopsies of hemangiomas if IVBCL was suspected.

Twenty-four postmortem 4-mm punch biopsies containing subcutaneous adipose tissue were taken within 24 hours of the death of the patient before embalming. The biopsies were taken from all regions of the body except the head and neck for cosmetic preservation of the decedent. Eighteen of the biopsies were taken from random sites of normal-appearing skin; the remaining 6 were taken from clinically identifiable cherry hemangiomas (5 on the trunk and 1 on the thigh). There was a variable degree of livor mortis in the dependent areas of the body, which was included in the random biopsies from the back to ensure any pooling of dependent blood would not alter the findings.
A histopathologic examination by a board-certified dermatopathologist (M.P.) on a single hematoxylin-eosin–stained level was performed to evaluate each biopsy for superficial involvement and deep involvement by IVBCL. Superficial involvement was defined as dermal involvement at or above the level of the eccrine sweat glands; deep involvement was defined as dermal involvement beneath the eccrine sweat glands and all subcutaneous fat present. Skin and bone marrow biopsies used to make the original diagnosis prior to the patient’s death were reviewed, including CD20 immunohistochemistry for morphologic comparison to the study slides. Involvement was graded as 0 to 3+ (eTable).

Results
Results from all 24 biopsies are shown in the eTable. Twenty-two (91.7%) biopsies showed at least focal involvement by IVBCL. Nine (37.5%) biopsies showed more deep vs superficial involvement of the same site. On average, the 6 biopsies from clinically detected hemangiomas showed more involvement by IVBCL than the random biopsies (eFigures 1 and 2A). The superficial involvement of skin with a hemangioma showed an average score of 2.33 v 0.78 when compared with the superficial aspect of the random biopsies; the deep involvement of skin with a hemangioma showed an average score of 2.67 vs 1.16 when compared with the deep aspect of the random biopsies (eFigure 2B).


Comment
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma is an aggressive malignancy that traditionally is difficult to diagnose. Many efforts have been made to improve detection and early diagnosis. As cutaneous involvement is common and sometimes the only sign of disease, dermatologists may be called upon to evaluate and biopsy patients with this suspected diagnosis. The purpose of our study was to improve diagnostic efficacy by methodically performing numerous biopsies and assessing the level of involvement of the superficial and deep skin as well as involvement of hemangiomas. The goal of this meticulous approach was to identify the highest-yield areas for biopsy with minimal impact on the patient. Our results showed that random skin biopsies are an effective way to identify IVBCL. Twenty-two (91.7%) biopsies contained at least focal lymphoma cells. Although the 2 biopsies that showed no tumor cells at all happened to both be from the left arm, this is believed to be coincidental. No discernable pattern was identified regarding involvement and anatomic region. Even though 20 (83.3%) biopsies showed superficial involvement, deep biopsy is essential, as 9 (37.5%) biopsies showed increased deep involvement compared to superficial involvement. Therefore, a deep punch biopsy is essential for maximum sensitivity.
Hemangiomas provide a potential target that could increase the sensitivity of a biopsy in the absence of clinical findings, when the disease in question is exclusively intravascular. The data gathered in this study support this idea, as biopsies from hemangiomas showed increased involvement compared to random biopsies, both superficially and deep (2.33 vs 0.78 and 2.67 vs 1.16, respectively). Interestingly, the hemangioma biopsy sites showed increased deep and superficial involvement, despite these typical cherry hemangiomas only involving the superficial dermis. One possible explanation for this is that the hemangiomas have larger-caliber feeder vessels with increased blood flow beneath them. It would then follow that this increased vasculature would increase the chances of identifying intravascular lymphoma cells. This finding further accentuates the need for a deep punch biopsy containing subcutaneous fat.
Completing the study in the setting of an autopsy provided the advantage of being able to take numerous biopsies without increased harm to the patient. This extensive set of biopsies would not be reasonable to complete on a living patient. This study also has limitations. Although this patient did fall within the typical demographics for patients with IVBCL, the data were still limited to 1 patient. This autopsy format (on a patient whose cause of death was indeed IVBCL) also implies terminal disease, which may mean the patient had a larger disease burden than a living patient who would typically be biopsied. Although this increased disease burden may have increased the sensitivity of finding IVBCL in the biopsies of this study, this further emphasizes the importance of trying to determine any factors that could increase sensitivity in a living patient with a lower disease burden.
Conclusion
Skin biopsies can provide a sensitive, low-cost, and low-morbidity method to assess a patient for IVBCL. Though random skin biopsies can yield valuable information, deep, 4-mm punch biopsies of clinically identifiable hemangiomas may provide the highest sensitivity for IVBCL.
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVBCL) is an exceedingly rare aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma with tumor cells growing selectively in vascular lumina.1 The annual incidence of IVBCL is fewer than 0.5 cases per 1,000,000 individuals worldwide.2 Only about 500 known cases of IVBCL have been recorded in the literature,3 and it accounts for less than 1% of all lymphomas. It generally affects middle-aged to elderly individuals, with an average age at diagnosis of 70 years.2 It has a predilection for men and commonly develops in individuals who are immunosuppressed.3,4
Multiple variants of IVBCL have been described in the literature, with central nervous system and cutaneous involvement being the most classic findings.5 Bone marrow involvement with hepatosplenomegaly also has been noted in the literature.6,7 Diagnosis of IVBCL and its variants requires a high index of suspicion, as the clinical manifestations and tissues involved typically are nonspecific and highly variable. Even in the classic variant of IVBCL, skin involvement is only reported in approximately half of cases.3 When present, cutaneous manifestations can range from nodules and violaceous plaques to induration and telangiectasias.3 Lymphadenopathy and lymphoma (leukemic) cells are not seen on a peripheral blood smear.2,8,9
The lack of lymphadenopathy or identifiable leukemic cells in the peripheral blood presents a diagnostic dilemma, as sufficient information for accurate diagnosis must be obtained while minimizing invasive procedures and resource expenditure. Because IVBCL cells can reside in the vascular lumina of various organs, numerous biopsy sites have been proposed for diagnosis of lymphoma, including the bone marrow, skin, prostate, adrenal gland, brain, liver, and kidneys.10 While some studies have reported that the optimal diagnostic site is the bone marrow, skin biopsies are more routinely carried out, as they represent a convenient and cost-effective alternative to other more invasive techniques.6,7,10 Studies have shown biopsy sensitivity values ranging from 77.8% to 83.3% for detection of IVBCL in normal-appearing skin, which is comparable to the sensitivities of a bone marrow biopsy.7,8 Although skin biopsy of random sites has shown diagnostic efficacy, some studies have proposed that biopsies taken from hemangiomas and other hypervascular lesions can further improve diagnostic yield, as lymphoma cells often are present in capillaries of subcutaneous adipose tissue.6,10,11 However, no obvious clinicopathologic differences were observed between IVBCL with and without involvement of a cutaneous hemangioma.11
The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic efficacy of skin biopsies for detecting IVBCL at various body sites and to establish whether biopsies from hemangiomas yield higher diagnostic value.
Methods
A 66-year-old man recently died at our institution secondary to IVBCL. His disease course was characterized by multiple hospital admissions in a 6-month period for fever of unknown origin and tachycardia unresponsive to broad-spectrum antibiotics and systemic steroids. The patient declined over the course of 3 to 4 weeks with findings suggestive of lymphoma and tumor lysis syndrome, and he eventually developed shock, hypoxic respiratory failure, and acute renal failure. As imaging studies and examinations had not shown lymphadenopathy, bone marrow biopsy was performed, and dermatology was consulted to perform skin biopsies to evaluate for IVBCL. Both bone marrow biopsies and random skin biopsies from the abdomen showed large and atypical CD20+ B cells within select vascular lumina (Figure). No extravascular lymphoma cells were seen. Based on the bone marrow and skin biopsies, a diagnosis of IVBCL was made. Unfortunately, no progress was made clinically, and the patient was transitioned to comfort measures. Upon the patient’s death, his family expressed interest in participating in IVBCL research and agreed to a limited autopsy consisting of numerous skin biopsies to evaluate different body sites and biopsy types (normal skin vs hemangiomas) to ascertain whether diagnostic yield could be increased by performing selective biopsies of hemangiomas if IVBCL was suspected.

Twenty-four postmortem 4-mm punch biopsies containing subcutaneous adipose tissue were taken within 24 hours of the death of the patient before embalming. The biopsies were taken from all regions of the body except the head and neck for cosmetic preservation of the decedent. Eighteen of the biopsies were taken from random sites of normal-appearing skin; the remaining 6 were taken from clinically identifiable cherry hemangiomas (5 on the trunk and 1 on the thigh). There was a variable degree of livor mortis in the dependent areas of the body, which was included in the random biopsies from the back to ensure any pooling of dependent blood would not alter the findings.
A histopathologic examination by a board-certified dermatopathologist (M.P.) on a single hematoxylin-eosin–stained level was performed to evaluate each biopsy for superficial involvement and deep involvement by IVBCL. Superficial involvement was defined as dermal involvement at or above the level of the eccrine sweat glands; deep involvement was defined as dermal involvement beneath the eccrine sweat glands and all subcutaneous fat present. Skin and bone marrow biopsies used to make the original diagnosis prior to the patient’s death were reviewed, including CD20 immunohistochemistry for morphologic comparison to the study slides. Involvement was graded as 0 to 3+ (eTable).

Results
Results from all 24 biopsies are shown in the eTable. Twenty-two (91.7%) biopsies showed at least focal involvement by IVBCL. Nine (37.5%) biopsies showed more deep vs superficial involvement of the same site. On average, the 6 biopsies from clinically detected hemangiomas showed more involvement by IVBCL than the random biopsies (eFigures 1 and 2A). The superficial involvement of skin with a hemangioma showed an average score of 2.33 v 0.78 when compared with the superficial aspect of the random biopsies; the deep involvement of skin with a hemangioma showed an average score of 2.67 vs 1.16 when compared with the deep aspect of the random biopsies (eFigure 2B).


Comment
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma is an aggressive malignancy that traditionally is difficult to diagnose. Many efforts have been made to improve detection and early diagnosis. As cutaneous involvement is common and sometimes the only sign of disease, dermatologists may be called upon to evaluate and biopsy patients with this suspected diagnosis. The purpose of our study was to improve diagnostic efficacy by methodically performing numerous biopsies and assessing the level of involvement of the superficial and deep skin as well as involvement of hemangiomas. The goal of this meticulous approach was to identify the highest-yield areas for biopsy with minimal impact on the patient. Our results showed that random skin biopsies are an effective way to identify IVBCL. Twenty-two (91.7%) biopsies contained at least focal lymphoma cells. Although the 2 biopsies that showed no tumor cells at all happened to both be from the left arm, this is believed to be coincidental. No discernable pattern was identified regarding involvement and anatomic region. Even though 20 (83.3%) biopsies showed superficial involvement, deep biopsy is essential, as 9 (37.5%) biopsies showed increased deep involvement compared to superficial involvement. Therefore, a deep punch biopsy is essential for maximum sensitivity.
Hemangiomas provide a potential target that could increase the sensitivity of a biopsy in the absence of clinical findings, when the disease in question is exclusively intravascular. The data gathered in this study support this idea, as biopsies from hemangiomas showed increased involvement compared to random biopsies, both superficially and deep (2.33 vs 0.78 and 2.67 vs 1.16, respectively). Interestingly, the hemangioma biopsy sites showed increased deep and superficial involvement, despite these typical cherry hemangiomas only involving the superficial dermis. One possible explanation for this is that the hemangiomas have larger-caliber feeder vessels with increased blood flow beneath them. It would then follow that this increased vasculature would increase the chances of identifying intravascular lymphoma cells. This finding further accentuates the need for a deep punch biopsy containing subcutaneous fat.
Completing the study in the setting of an autopsy provided the advantage of being able to take numerous biopsies without increased harm to the patient. This extensive set of biopsies would not be reasonable to complete on a living patient. This study also has limitations. Although this patient did fall within the typical demographics for patients with IVBCL, the data were still limited to 1 patient. This autopsy format (on a patient whose cause of death was indeed IVBCL) also implies terminal disease, which may mean the patient had a larger disease burden than a living patient who would typically be biopsied. Although this increased disease burden may have increased the sensitivity of finding IVBCL in the biopsies of this study, this further emphasizes the importance of trying to determine any factors that could increase sensitivity in a living patient with a lower disease burden.
Conclusion
Skin biopsies can provide a sensitive, low-cost, and low-morbidity method to assess a patient for IVBCL. Though random skin biopsies can yield valuable information, deep, 4-mm punch biopsies of clinically identifiable hemangiomas may provide the highest sensitivity for IVBCL.
- Ponzoni M, Campo E, Nakamura S. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a chameleon with multiple faces and many masks. Blood. 2018;132:1561-1567. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-04-737445
- Roy AM, Pandey Y, Middleton D, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a diagnostic dilemma. Cureus. 2021;13:e16459. doi:10.7759/cureus.16459
- Bayçelebi D, Yildiz L, S?entürk N. A case report and literature review of cutaneous intravascular large B-cell lymphoma presenting clinically as panniculitis: a difficult diagnosis, but a good prognosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:72-75. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.08.004
- Orwat DE, Batalis NI. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136:333-338. doi:10.5858/arpa.2010-0747-RS
- Breakell T, Waibel H, Schliep S, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a review with a focus on the prognostic value of skininvolvement. Curr Oncol. 2022;29:2909-2919. doi:10.3390/curroncol29050237
- Oppegard L, O’Donnell M, Piro K, et al. Going skin deep: excavating a diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:3368-3371. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06141-1
- Barker JL, Swarup O, Puliyayil A. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: representative cases and approach to diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021;14:e244069. doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-244069
- Matsue K, Asada N, Odawara J, et al. Random skin biopsy and bone marrow biopsy for diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2011;90:417-421. doi:10.1007/s00277-010-1101-3
- Shimada K, Kinoshita T, Naoe T, et al. Presentation and management of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:895-902. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70140-8
- Adachi Y, Kosami K, Mizuta N, et al. Benefits of skin biopsy of senile hemangioma in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:2003-2006. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2017
- Ishida M, Hodohara K, Yoshida T, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma colonizing in senile hemangioma: a case report and proposal of possible diagnostic strategy for intravascular lymphoma. Pathol Int. 2011;61:555-557. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02697.x
- Ponzoni M, Campo E, Nakamura S. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a chameleon with multiple faces and many masks. Blood. 2018;132:1561-1567. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-04-737445
- Roy AM, Pandey Y, Middleton D, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a diagnostic dilemma. Cureus. 2021;13:e16459. doi:10.7759/cureus.16459
- Bayçelebi D, Yildiz L, S?entürk N. A case report and literature review of cutaneous intravascular large B-cell lymphoma presenting clinically as panniculitis: a difficult diagnosis, but a good prognosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:72-75. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.08.004
- Orwat DE, Batalis NI. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136:333-338. doi:10.5858/arpa.2010-0747-RS
- Breakell T, Waibel H, Schliep S, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a review with a focus on the prognostic value of skininvolvement. Curr Oncol. 2022;29:2909-2919. doi:10.3390/curroncol29050237
- Oppegard L, O’Donnell M, Piro K, et al. Going skin deep: excavating a diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:3368-3371. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06141-1
- Barker JL, Swarup O, Puliyayil A. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: representative cases and approach to diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021;14:e244069. doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-244069
- Matsue K, Asada N, Odawara J, et al. Random skin biopsy and bone marrow biopsy for diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2011;90:417-421. doi:10.1007/s00277-010-1101-3
- Shimada K, Kinoshita T, Naoe T, et al. Presentation and management of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:895-902. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70140-8
- Adachi Y, Kosami K, Mizuta N, et al. Benefits of skin biopsy of senile hemangioma in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:2003-2006. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2017
- Ishida M, Hodohara K, Yoshida T, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma colonizing in senile hemangioma: a case report and proposal of possible diagnostic strategy for intravascular lymphoma. Pathol Int. 2011;61:555-557. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02697.x
Diagnostic Value of Deep Punch Biopsies in Intravascular Large B-cell Lymphoma
Diagnostic Value of Deep Punch Biopsies in Intravascular Large B-cell Lymphoma
Practice Points
- Skin biopsy is an effective method for identifying intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVBCL).
- Deep punch biopsies of sites involving hemangiomas may further heighten sensitivity for detection of IVBCL, as these lesions may harbor increased numbers of intravascular lymphoma cells.
- Deep and strategically placed skin biopsies offer potential improvements in timely diagnosis and outcomes of patients with IVBCL.
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a public health threat, with a global prevalence of 4.8% and a prevalence in males that increases with age, from 1.3% between ages 45 and 54 years to 12.5% between ages 75 and 84 years.1 AAA is often asymptomatic until it ruptures and can become life-threatening, with mortality rates near 90% in the event of rupture with survival rates of about 50% to 70% for individuals with rupture who require urgent surgical intervention.2,3 Males experience AAA at 4 times the rate of females.4
Previous research has found that the awareness of having an AAA causes anxiety that some have described as “living with a ticking time bomb.”5 Others reported worries and concerns about life’s fragility and mortality due to an AAA diagnosis.6 However, the psychological impact on the individuals’ quality of life (QoL) remains unclear, especially for individuals with a small AAA (< 5.5 cm).7 Factors such as age, male sex, smoking, family history, hypertension, carotid artery disease, and hypercholesterolemia have been strongly associated with increased growth rate and the risk of small AAA ruptures.8,9
Most patients with a small AAA enter surveillance awaiting future repair and not only have the anxiety of living with an AAA despite the low risk of rupture, but also a worse QoL than those who have undergone repair.10,11 However, data are sparse regarding the effects on QoL of knowing they have an AAA, whether repaired or not. This study sought to examine the impact an AAA diagnosis had on male QoL at the initial investigation and after 12 months.
Methods
This prospective study was examined and approved by the Veterans Affairs Northern California Health Care System (NCHCS) Institutional Review Board. It was conducted at the Sacramento US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center from January 1, 2019, to February 28, 2022. Patients were identified through the vascular clinic. One hundred sixteen patients with AAA were eligible and agreed to participate. Of these, 91 (78%) completed the survey at baseline and 12 months later. Participation was voluntary; written informed consent was obtained from every patient before completing the survey. This study included only male patients due to their higher prevalence than female patients.4 Patients were also eligible if they were aged > 18 years and had a previously known AAA that was being followed with a recorded clinical imaging study in the NCHCS vascular clinic. Patients were excluded if they were unable to return for their 12-month follow-up investigation, were incapable of giving informed consent, were unable to complete the 12-item short form health survey version 2 (SF-12v2), had a documented history of psychiatric illness, or refused to participate. The SF-12v2, an abbreviated version of the 36-item short form health survey (SF-36), is a generic health-related quality-of-life survey that measures 8 domains of general health status: general health (GH), physical functioning (PF), role limitations due to physical problems (RP), bodily pain (BP), vitality (VT), social functioning (SF), role emotional (RE), and mental health (MH). A higher number on the QoL scale indicates better QoL. The GH, PF, RP, and BP scales yield a physical component score (PCS), and the VT, SF, RE, and MH scales generate a mental component score (MCS). Although SF-12v2 has not been validated for patients with AAA, it has been widely used and validated to measure health-related QoL in cohorts of healthy and chronically ill individuals.12,13
Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including means, SDs, frequency, percentages, 95% CIs, and correlations were calculated. The t test was used to analyze differences in mean scores. For continuous variables, such as SF-12v2 domains, PCS, and MCS, mean, SD, 95% CI, and range were determined. Comparisons were performed using X2 or t test. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Clinical risk factors, including age, race, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and smoking status, were also recorded.
Results
Between January 1, 2019, and February 28, 2022, 91 patients were diagnosed with an AAA and completed the survey at the initial and 12-month investigations. Patients had a mean (SD) age of 76.0 (5.6) years (range, 64-93) and BMI of 29.7 (6.4). Comorbid diabetes was present in 31% of patients, hypertension in 75%, hyperlipidemia 66%, and coronary artery disease in 12% (Table 1). Most patients smoked tobacco: 71% indicated previous use and 22% were current users.
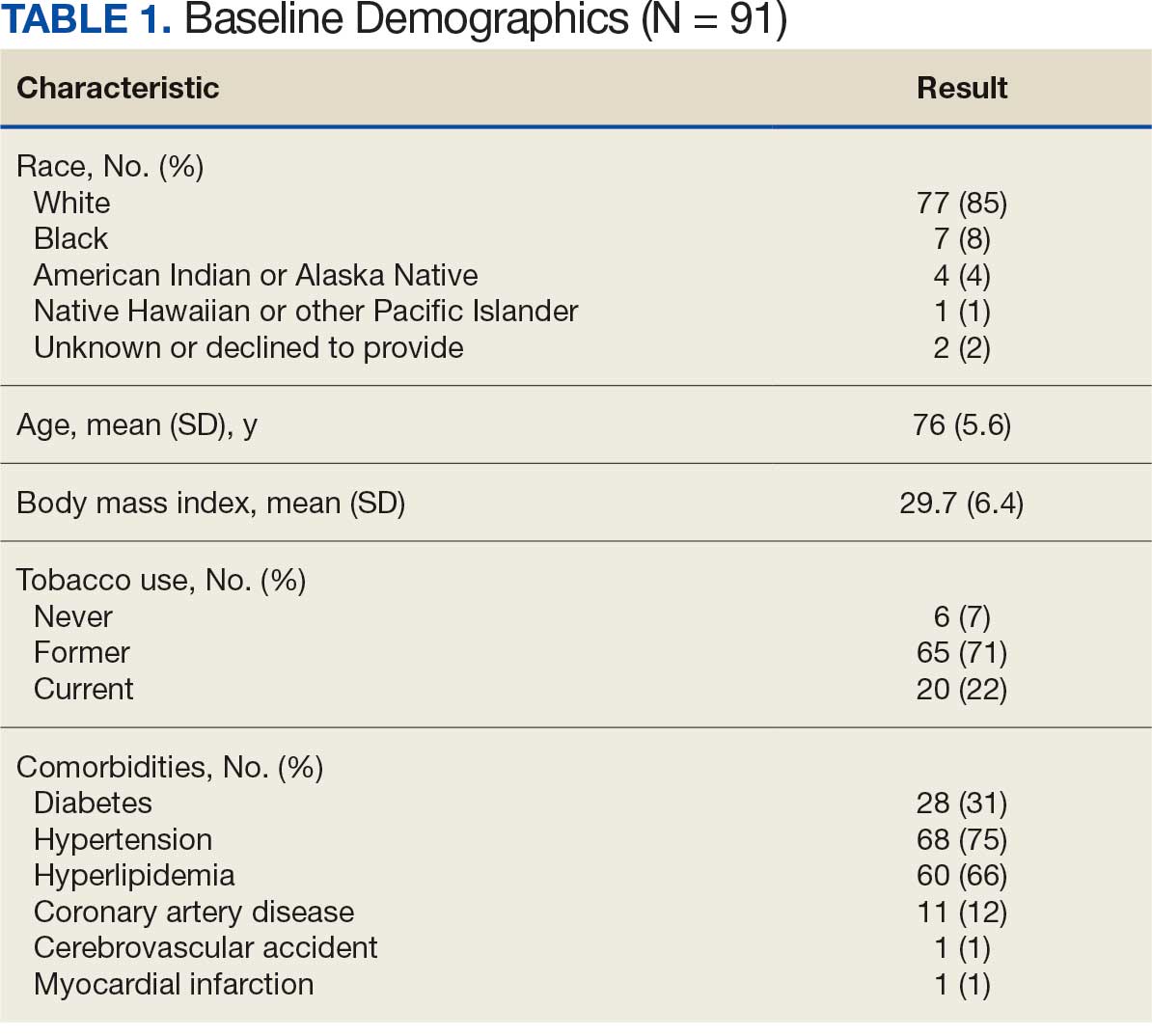
When comparing baseline vs 12-month follow-up, patients indicated a higher QoL in GH (3.2 vs 3.5, respectively; P < .05) and BP (3.1 vs 3.6, respectively; P < .05). No statistically significant difference was seen PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, MH, as well as PCS and MCS between baseline and follow-up with respect to QoL (P < .05). However, the 5 domains of SF-12v2: PF, RP, SF, RE, MH, and PCS had lower QoL scores at the 12-month follow-up when compared with baseline, but with no statistically significant difference between both investigations (Table 2).
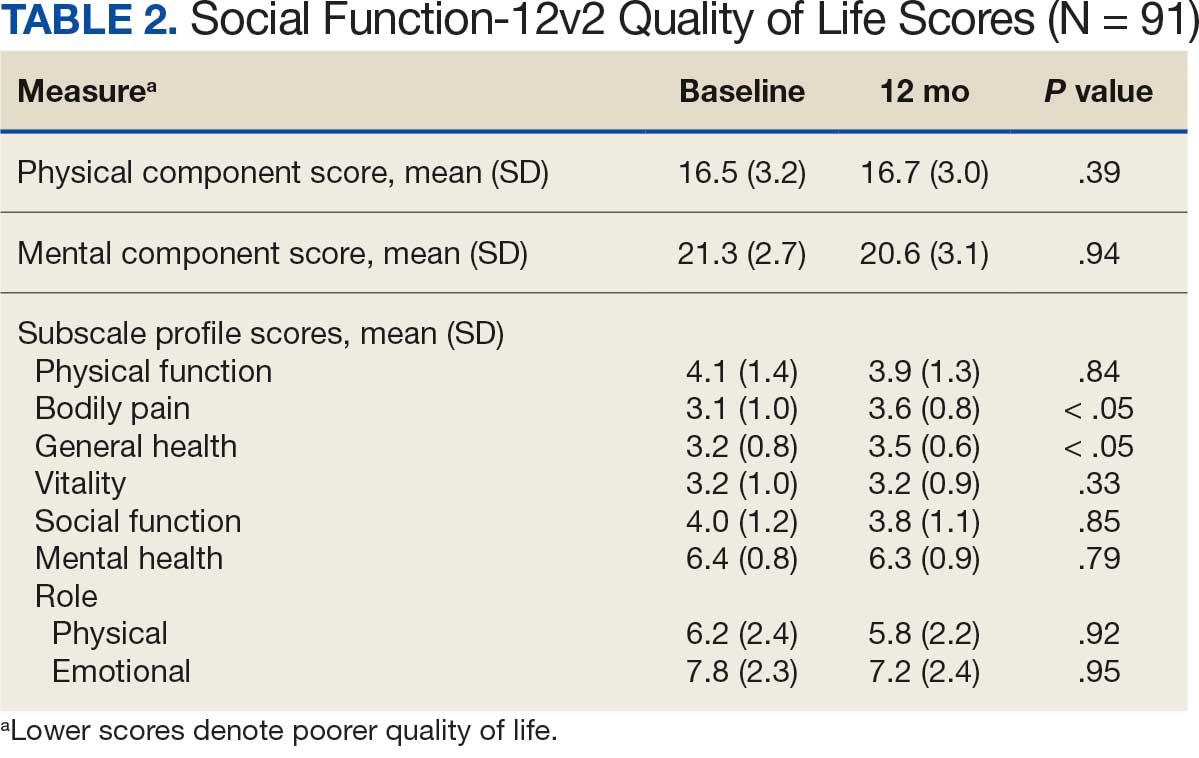
Discussion
Previous studies have characterized the results of QoL measures as subjective because they are based on patient perceptions of their physical and psychological condition.14,15 However, SF-36 and SF-12v2 responses provide a multifaceted account that encompasses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of QoL. Despite being the most widely used generic instrument in many fields of medicine, SF-36 is time consuming for clinicians who may prefer simpler and more time-efficient instruments.16-18 The SF-12v2 not only imposes less burden on respondents but also generates accurate summary scores for patients physical and mental health.19
The replicability of SF-12v2 PCS and MCS scores has been demonstrated. In the United Kingdom, Jenkinson and Layte constructed SF-12v2 summary measures from a large scale dataset by sending the SF-36 and other questions on health and lifestyles to 9332 individuals and compared the results of the SF-36 and SF-12v2 across diverse patient groups (eg, Parkinson disease, congestive heart failure, sleep apnea, benign prostatic hypertrophy). Results from SF-36 PCS, SF-36 MCS, and PCS-12v2 (ρ, 0.94; P < .001) and SF-12v2 MCS (ρ, 0.96; P < .001) were found to be highly correlated, and also produced similar results, both in the community sample and across a variety of disease-specific groups.20
The aim of this longitudinal observational study was to measure the QoL of males with an AAA ≥ 3.0 cm at baseline and 12 months later. The mean age of participants was 76 years, which aligns with previous research that found the prevalence of AAAs increased with age.1 Study participants had a mean BMI of 29.7, which also supports previous research that indicated that obesity is independently associated with an AAA.21 Patients with an AAA and a history of smoking (former or current), hypertension, or hyperlipidemia had lower mean scores for 3 of 8 SF-12v2 domains at the 12-month follow-up.
These findings support previous research that indicated smoking is not only a very strong risk factor for the presence of an AAA but also associated with increased rates of expansion and the risk of rupture in patients with an AAA.22 Bath et al found that patients with an AAA compared to patients without an AAA were older (age 72.6 vs 69.8 years; P < .001), had a higher BMI (28.1 vs 27.0; P < .001), were more likely to be a current smoker (15.1% vs 5.2%; P < .001), and were more likely to have diabetes (18.8% vs 10.0%; P < .001), ischemic heart disease (12.2% vs 4.4%; P < .001), high cholesterol (53.2% vs 30.8%; P <. 001), previous stroke (6.1% vs 2.9%; P < .001), and a previous myocardial infarction (21.1% vs 5.8%; P < .001).23 Lesjak et al found that men with AAA reported significantly lower scores in the domains of social functioning, pain, and general health 6 months after ultrasound compared with men without AAA.24
Previous research indicates that patients with an AAA have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and comorbidities that may impact their perceived QoL. In a study assessing cardiovascular risk in 2323 patients with a small AAA, Bath et al found a high prevalence of coronary artery disease (44.9%), myocardial infarction (26.8%), heart failure (4.4%) and cerebrovascular accident (14.0%) which may have contributed to the decreased level of self-perceived QoL in these patients.25
This aligned with a study by Golledge et al, who found that participants diagnosed with an AAA and peripheral artery disease not only had significantly poorer QoL scores in 5 SF-36 domains (PF, RP, GH, VT, and PCS)when compared with participants diagnosed with an AAA alone. They also had significantly poorer QoL scores in 7 domains of the SF-36 (PF, RP, GH, VT, SF, RE, and PCS) when compared with controls without an AAA.26
Our analysis found that males with an AAA had a rise in SF-12v2 QoL scores from baseline to 12-month follow-up in the GH and BP domains. There was no statistically significant difference in QoL in the other 6 domains (PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, and MH) between the initial and 12-month investigations. Bath et al also found that men with an AAA had a transient reduction in mental QoL during the first year after the initial screening but returned to baseline.23
Strengths and Limitations
This study is notable for its sample of patients who previously had a diagnosed AAA that were followed with a recorded clinical imaging study and the use of a validated QoL measure (SF-12v2) that provided virtually identical summary scores (PCS and MCS) as the SF-36.27 However, this study was limited by the brevity of the SF-12v2 instrument which made it difficult to extract sufficient reliable information for the 8 domains.28 Subjective perception of patients is another limitation inherent to any QoL study. QoL scores were not available before the initial investigation. Measuring QoL at baseline and 12 months later does not capture the potential fluctuations and changes in QoL that the patient may experience some months later. Another limitation arises from the fact that the AAA patient population in the study included patients under surveillance and patients who had undergone repair.
Fourteen patients (15%) had received AAA repair: 10 had endovascular reconstruction and 4 had open surgical repair. Including patients with a previous AAA repair may have influenced reported QoL levels. Suckow et al performed a 2-phase study on 1008 patients, 351 (35%) were under surveillance and 657 (65%) had undergone repair. In that study, patients under AAA surveillance had worse emotional impact scores compared with patients with repair (22 vs 13; P < .001).11 Additionally, the size of the abdominal aorta at the time of survey was not addressed in the study, which could constitute explanatory variables.
Conclusions
This study found higher QoL at 12-month follow-up compared to baseline in both the GH and BP domains of the SF-12v2 health survey for male veterans with an AAA. Periodic QoL assessments for patients with an AAA may be helpful in tracking QoL course, minimizing their physical and psychological concerns, and improving overall care and support. However, further research is necessary to assess the QoL of patients with an AAA who are under surveillance compared with those who had an aneurysm repair to accurately measure the impact of an AAA on QoL.
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Profeta VF, et al. Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in population- based studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:2805. doi:10.3390/ijerph15122805
- Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The society for vascular surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
- Kent KC. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
- Harthun NL. Current issues in the treatment of women with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Gend Med. 2008;5:36-43.
- Aoki H. Taking control of the time bomb in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ J. 2016;80:314-315. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-15-1350
- Damhus CS, Siersma V, Hansson A, Bang CW, Brodersen J. Psychosocial consequences of screeningdetected abdominal aortic aneurisms: a cross-sectional study. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2021;39:459-465. doi:10.1080/02813432.2021.2004713
- Ericsson A, Kumlien C, Ching S, Carlson E, Molassiotis A. Impact on quality of life of men with screening-detected abdominal aortic aneurysms attending regular follow ups: a narrative literature review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:589-596. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.10.012
- Galyfos G, Voulalas G, Stamatatos I, et al. Small abdominal aortic aneurysms: should we wait? Vasc Dis Manag. 2015;12:E152-E159.
- Kristensen KL, Dahl M, Rasmussen LM, et al. Glycated hemoglobin is associated with the growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37:730-736. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308874
- Xiao-Yan L, Yu-Kui M, Li-Hui L. Risk factors for preoperative anxiety and depression in patients scheduled for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Chine Med J. 2018;131:1951-1957. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.238154
- Suckow BD, Schanzer AS, Hoel AW, et al. A novel quality of life instrument for patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:809-815. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.01.018
- Flatz A, Casillas A, Stringhini S, et al. Association between education and quality of diabetes care in Switzerland. Int J Gen Med. 2015;8:87-92. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S77139
- Christensen AV, Bjorner JB, Ekholm O, et al. Increased risk of mortality and readmission associated with lower SF-12 scores in cardiac patients: Results from the national DenHeart study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19:330-338. doi:10.1177/1474515119885480
- Hamming JF, De Vries J. Measuring quality of life. Br J Surg. 2007;94:923-924. doi:10.1002/bjs.5948
- Urbach DR. Measuring quality of life after surgery. Surg Innov. 2005;12:161-165. doi:10.1177/ 155335060501200216
- Gandek B, Sinclair SJ, Kosinski M, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the SF-36® health survey in medicare managed care. Health Care Financ Rev. 2004;25:5.
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short form health survey (SF-36). Med Care. 1992;30:473-483. doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
- Takayoshi K, Mototsugu T, Tomohiro T, et al. Health-related quality of life prospectively evaluated by the 8-item short form after endovascular repair versus open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Heart Vessels. 2017;32:960- 968. doi:10.1007/s00380-017-0956-9
- Pickard AS, Johnson JA, Penn A, et al. Replicability of SF-36 summary scores by the SF-12 in stroke patients. Stroke. 1999;30:1213-1217. doi:10.1161/01.str.30.6.1213
- Jenkinson C, Layte R. The development and testing of the UK SF-12. J Health Serv Res Policy. 1997;2:14-18. doi:10.1177/135581969700200105
- Golledge J, Clancy P, Jamrozik K, et al. Obesity, adipokines, and abdominal aortic aneurysm: Health in Men study. Circulation. 2007;116:2275-2279. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.717926
- Norman PE, Curci JA. Understanding the effects of tobacco smoke on the pathogenesis of aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:1473-1477. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300158
- Bath MF, Sidloff D, Saratzis A, et al. Impact of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening on quality of life. BJS. 2018;105:203-208. doi:10.1002/bjs.10721
- Lesjak M, Boreland F, Lyle D, Sidford J, Flecknoe-Brown S, Fletcher J. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: does it affect men’s quality of life? Aust J Prim Health. 2012;18:284-288. doi:10.1071/PY11131
- Bath MF, Gokani VJ, Sidloff DA, et al. Systematic review of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular death in patients with a small abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015;102:866-872. doi:10.1002/bjs.9837
- Golledge J, Pinchbeck J, Rowbotham SE, et al. Health-related quality of life amongst people diagnosed with abdominal aortic aneurysm and peripheral artery disease and the effect of fenofibrate. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14583. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71454-4
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D. A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? J Public Health Med. 1997;19:179- 186. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubmed.a024606
- White MK, Maher SM, Rizio AA, et al. A meta-analytic review of measurement equivalence study findings of the SF-36® and SF-12® Health Surveys across electronic modes compared to paper administration. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1757-1767. doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1851-2
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a public health threat, with a global prevalence of 4.8% and a prevalence in males that increases with age, from 1.3% between ages 45 and 54 years to 12.5% between ages 75 and 84 years.1 AAA is often asymptomatic until it ruptures and can become life-threatening, with mortality rates near 90% in the event of rupture with survival rates of about 50% to 70% for individuals with rupture who require urgent surgical intervention.2,3 Males experience AAA at 4 times the rate of females.4
Previous research has found that the awareness of having an AAA causes anxiety that some have described as “living with a ticking time bomb.”5 Others reported worries and concerns about life’s fragility and mortality due to an AAA diagnosis.6 However, the psychological impact on the individuals’ quality of life (QoL) remains unclear, especially for individuals with a small AAA (< 5.5 cm).7 Factors such as age, male sex, smoking, family history, hypertension, carotid artery disease, and hypercholesterolemia have been strongly associated with increased growth rate and the risk of small AAA ruptures.8,9
Most patients with a small AAA enter surveillance awaiting future repair and not only have the anxiety of living with an AAA despite the low risk of rupture, but also a worse QoL than those who have undergone repair.10,11 However, data are sparse regarding the effects on QoL of knowing they have an AAA, whether repaired or not. This study sought to examine the impact an AAA diagnosis had on male QoL at the initial investigation and after 12 months.
Methods
This prospective study was examined and approved by the Veterans Affairs Northern California Health Care System (NCHCS) Institutional Review Board. It was conducted at the Sacramento US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center from January 1, 2019, to February 28, 2022. Patients were identified through the vascular clinic. One hundred sixteen patients with AAA were eligible and agreed to participate. Of these, 91 (78%) completed the survey at baseline and 12 months later. Participation was voluntary; written informed consent was obtained from every patient before completing the survey. This study included only male patients due to their higher prevalence than female patients.4 Patients were also eligible if they were aged > 18 years and had a previously known AAA that was being followed with a recorded clinical imaging study in the NCHCS vascular clinic. Patients were excluded if they were unable to return for their 12-month follow-up investigation, were incapable of giving informed consent, were unable to complete the 12-item short form health survey version 2 (SF-12v2), had a documented history of psychiatric illness, or refused to participate. The SF-12v2, an abbreviated version of the 36-item short form health survey (SF-36), is a generic health-related quality-of-life survey that measures 8 domains of general health status: general health (GH), physical functioning (PF), role limitations due to physical problems (RP), bodily pain (BP), vitality (VT), social functioning (SF), role emotional (RE), and mental health (MH). A higher number on the QoL scale indicates better QoL. The GH, PF, RP, and BP scales yield a physical component score (PCS), and the VT, SF, RE, and MH scales generate a mental component score (MCS). Although SF-12v2 has not been validated for patients with AAA, it has been widely used and validated to measure health-related QoL in cohorts of healthy and chronically ill individuals.12,13
Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including means, SDs, frequency, percentages, 95% CIs, and correlations were calculated. The t test was used to analyze differences in mean scores. For continuous variables, such as SF-12v2 domains, PCS, and MCS, mean, SD, 95% CI, and range were determined. Comparisons were performed using X2 or t test. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Clinical risk factors, including age, race, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and smoking status, were also recorded.
Results
Between January 1, 2019, and February 28, 2022, 91 patients were diagnosed with an AAA and completed the survey at the initial and 12-month investigations. Patients had a mean (SD) age of 76.0 (5.6) years (range, 64-93) and BMI of 29.7 (6.4). Comorbid diabetes was present in 31% of patients, hypertension in 75%, hyperlipidemia 66%, and coronary artery disease in 12% (Table 1). Most patients smoked tobacco: 71% indicated previous use and 22% were current users.

When comparing baseline vs 12-month follow-up, patients indicated a higher QoL in GH (3.2 vs 3.5, respectively; P < .05) and BP (3.1 vs 3.6, respectively; P < .05). No statistically significant difference was seen PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, MH, as well as PCS and MCS between baseline and follow-up with respect to QoL (P < .05). However, the 5 domains of SF-12v2: PF, RP, SF, RE, MH, and PCS had lower QoL scores at the 12-month follow-up when compared with baseline, but with no statistically significant difference between both investigations (Table 2).

Discussion
Previous studies have characterized the results of QoL measures as subjective because they are based on patient perceptions of their physical and psychological condition.14,15 However, SF-36 and SF-12v2 responses provide a multifaceted account that encompasses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of QoL. Despite being the most widely used generic instrument in many fields of medicine, SF-36 is time consuming for clinicians who may prefer simpler and more time-efficient instruments.16-18 The SF-12v2 not only imposes less burden on respondents but also generates accurate summary scores for patients physical and mental health.19
The replicability of SF-12v2 PCS and MCS scores has been demonstrated. In the United Kingdom, Jenkinson and Layte constructed SF-12v2 summary measures from a large scale dataset by sending the SF-36 and other questions on health and lifestyles to 9332 individuals and compared the results of the SF-36 and SF-12v2 across diverse patient groups (eg, Parkinson disease, congestive heart failure, sleep apnea, benign prostatic hypertrophy). Results from SF-36 PCS, SF-36 MCS, and PCS-12v2 (ρ, 0.94; P < .001) and SF-12v2 MCS (ρ, 0.96; P < .001) were found to be highly correlated, and also produced similar results, both in the community sample and across a variety of disease-specific groups.20
The aim of this longitudinal observational study was to measure the QoL of males with an AAA ≥ 3.0 cm at baseline and 12 months later. The mean age of participants was 76 years, which aligns with previous research that found the prevalence of AAAs increased with age.1 Study participants had a mean BMI of 29.7, which also supports previous research that indicated that obesity is independently associated with an AAA.21 Patients with an AAA and a history of smoking (former or current), hypertension, or hyperlipidemia had lower mean scores for 3 of 8 SF-12v2 domains at the 12-month follow-up.
These findings support previous research that indicated smoking is not only a very strong risk factor for the presence of an AAA but also associated with increased rates of expansion and the risk of rupture in patients with an AAA.22 Bath et al found that patients with an AAA compared to patients without an AAA were older (age 72.6 vs 69.8 years; P < .001), had a higher BMI (28.1 vs 27.0; P < .001), were more likely to be a current smoker (15.1% vs 5.2%; P < .001), and were more likely to have diabetes (18.8% vs 10.0%; P < .001), ischemic heart disease (12.2% vs 4.4%; P < .001), high cholesterol (53.2% vs 30.8%; P <. 001), previous stroke (6.1% vs 2.9%; P < .001), and a previous myocardial infarction (21.1% vs 5.8%; P < .001).23 Lesjak et al found that men with AAA reported significantly lower scores in the domains of social functioning, pain, and general health 6 months after ultrasound compared with men without AAA.24
Previous research indicates that patients with an AAA have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and comorbidities that may impact their perceived QoL. In a study assessing cardiovascular risk in 2323 patients with a small AAA, Bath et al found a high prevalence of coronary artery disease (44.9%), myocardial infarction (26.8%), heart failure (4.4%) and cerebrovascular accident (14.0%) which may have contributed to the decreased level of self-perceived QoL in these patients.25
This aligned with a study by Golledge et al, who found that participants diagnosed with an AAA and peripheral artery disease not only had significantly poorer QoL scores in 5 SF-36 domains (PF, RP, GH, VT, and PCS)when compared with participants diagnosed with an AAA alone. They also had significantly poorer QoL scores in 7 domains of the SF-36 (PF, RP, GH, VT, SF, RE, and PCS) when compared with controls without an AAA.26
Our analysis found that males with an AAA had a rise in SF-12v2 QoL scores from baseline to 12-month follow-up in the GH and BP domains. There was no statistically significant difference in QoL in the other 6 domains (PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, and MH) between the initial and 12-month investigations. Bath et al also found that men with an AAA had a transient reduction in mental QoL during the first year after the initial screening but returned to baseline.23
Strengths and Limitations
This study is notable for its sample of patients who previously had a diagnosed AAA that were followed with a recorded clinical imaging study and the use of a validated QoL measure (SF-12v2) that provided virtually identical summary scores (PCS and MCS) as the SF-36.27 However, this study was limited by the brevity of the SF-12v2 instrument which made it difficult to extract sufficient reliable information for the 8 domains.28 Subjective perception of patients is another limitation inherent to any QoL study. QoL scores were not available before the initial investigation. Measuring QoL at baseline and 12 months later does not capture the potential fluctuations and changes in QoL that the patient may experience some months later. Another limitation arises from the fact that the AAA patient population in the study included patients under surveillance and patients who had undergone repair.
Fourteen patients (15%) had received AAA repair: 10 had endovascular reconstruction and 4 had open surgical repair. Including patients with a previous AAA repair may have influenced reported QoL levels. Suckow et al performed a 2-phase study on 1008 patients, 351 (35%) were under surveillance and 657 (65%) had undergone repair. In that study, patients under AAA surveillance had worse emotional impact scores compared with patients with repair (22 vs 13; P < .001).11 Additionally, the size of the abdominal aorta at the time of survey was not addressed in the study, which could constitute explanatory variables.
Conclusions
This study found higher QoL at 12-month follow-up compared to baseline in both the GH and BP domains of the SF-12v2 health survey for male veterans with an AAA. Periodic QoL assessments for patients with an AAA may be helpful in tracking QoL course, minimizing their physical and psychological concerns, and improving overall care and support. However, further research is necessary to assess the QoL of patients with an AAA who are under surveillance compared with those who had an aneurysm repair to accurately measure the impact of an AAA on QoL.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a public health threat, with a global prevalence of 4.8% and a prevalence in males that increases with age, from 1.3% between ages 45 and 54 years to 12.5% between ages 75 and 84 years.1 AAA is often asymptomatic until it ruptures and can become life-threatening, with mortality rates near 90% in the event of rupture with survival rates of about 50% to 70% for individuals with rupture who require urgent surgical intervention.2,3 Males experience AAA at 4 times the rate of females.4
Previous research has found that the awareness of having an AAA causes anxiety that some have described as “living with a ticking time bomb.”5 Others reported worries and concerns about life’s fragility and mortality due to an AAA diagnosis.6 However, the psychological impact on the individuals’ quality of life (QoL) remains unclear, especially for individuals with a small AAA (< 5.5 cm).7 Factors such as age, male sex, smoking, family history, hypertension, carotid artery disease, and hypercholesterolemia have been strongly associated with increased growth rate and the risk of small AAA ruptures.8,9
Most patients with a small AAA enter surveillance awaiting future repair and not only have the anxiety of living with an AAA despite the low risk of rupture, but also a worse QoL than those who have undergone repair.10,11 However, data are sparse regarding the effects on QoL of knowing they have an AAA, whether repaired or not. This study sought to examine the impact an AAA diagnosis had on male QoL at the initial investigation and after 12 months.
Methods
This prospective study was examined and approved by the Veterans Affairs Northern California Health Care System (NCHCS) Institutional Review Board. It was conducted at the Sacramento US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center from January 1, 2019, to February 28, 2022. Patients were identified through the vascular clinic. One hundred sixteen patients with AAA were eligible and agreed to participate. Of these, 91 (78%) completed the survey at baseline and 12 months later. Participation was voluntary; written informed consent was obtained from every patient before completing the survey. This study included only male patients due to their higher prevalence than female patients.4 Patients were also eligible if they were aged > 18 years and had a previously known AAA that was being followed with a recorded clinical imaging study in the NCHCS vascular clinic. Patients were excluded if they were unable to return for their 12-month follow-up investigation, were incapable of giving informed consent, were unable to complete the 12-item short form health survey version 2 (SF-12v2), had a documented history of psychiatric illness, or refused to participate. The SF-12v2, an abbreviated version of the 36-item short form health survey (SF-36), is a generic health-related quality-of-life survey that measures 8 domains of general health status: general health (GH), physical functioning (PF), role limitations due to physical problems (RP), bodily pain (BP), vitality (VT), social functioning (SF), role emotional (RE), and mental health (MH). A higher number on the QoL scale indicates better QoL. The GH, PF, RP, and BP scales yield a physical component score (PCS), and the VT, SF, RE, and MH scales generate a mental component score (MCS). Although SF-12v2 has not been validated for patients with AAA, it has been widely used and validated to measure health-related QoL in cohorts of healthy and chronically ill individuals.12,13
Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including means, SDs, frequency, percentages, 95% CIs, and correlations were calculated. The t test was used to analyze differences in mean scores. For continuous variables, such as SF-12v2 domains, PCS, and MCS, mean, SD, 95% CI, and range were determined. Comparisons were performed using X2 or t test. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Clinical risk factors, including age, race, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and smoking status, were also recorded.
Results
Between January 1, 2019, and February 28, 2022, 91 patients were diagnosed with an AAA and completed the survey at the initial and 12-month investigations. Patients had a mean (SD) age of 76.0 (5.6) years (range, 64-93) and BMI of 29.7 (6.4). Comorbid diabetes was present in 31% of patients, hypertension in 75%, hyperlipidemia 66%, and coronary artery disease in 12% (Table 1). Most patients smoked tobacco: 71% indicated previous use and 22% were current users.

When comparing baseline vs 12-month follow-up, patients indicated a higher QoL in GH (3.2 vs 3.5, respectively; P < .05) and BP (3.1 vs 3.6, respectively; P < .05). No statistically significant difference was seen PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, MH, as well as PCS and MCS between baseline and follow-up with respect to QoL (P < .05). However, the 5 domains of SF-12v2: PF, RP, SF, RE, MH, and PCS had lower QoL scores at the 12-month follow-up when compared with baseline, but with no statistically significant difference between both investigations (Table 2).

Discussion
Previous studies have characterized the results of QoL measures as subjective because they are based on patient perceptions of their physical and psychological condition.14,15 However, SF-36 and SF-12v2 responses provide a multifaceted account that encompasses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of QoL. Despite being the most widely used generic instrument in many fields of medicine, SF-36 is time consuming for clinicians who may prefer simpler and more time-efficient instruments.16-18 The SF-12v2 not only imposes less burden on respondents but also generates accurate summary scores for patients physical and mental health.19
The replicability of SF-12v2 PCS and MCS scores has been demonstrated. In the United Kingdom, Jenkinson and Layte constructed SF-12v2 summary measures from a large scale dataset by sending the SF-36 and other questions on health and lifestyles to 9332 individuals and compared the results of the SF-36 and SF-12v2 across diverse patient groups (eg, Parkinson disease, congestive heart failure, sleep apnea, benign prostatic hypertrophy). Results from SF-36 PCS, SF-36 MCS, and PCS-12v2 (ρ, 0.94; P < .001) and SF-12v2 MCS (ρ, 0.96; P < .001) were found to be highly correlated, and also produced similar results, both in the community sample and across a variety of disease-specific groups.20
The aim of this longitudinal observational study was to measure the QoL of males with an AAA ≥ 3.0 cm at baseline and 12 months later. The mean age of participants was 76 years, which aligns with previous research that found the prevalence of AAAs increased with age.1 Study participants had a mean BMI of 29.7, which also supports previous research that indicated that obesity is independently associated with an AAA.21 Patients with an AAA and a history of smoking (former or current), hypertension, or hyperlipidemia had lower mean scores for 3 of 8 SF-12v2 domains at the 12-month follow-up.
These findings support previous research that indicated smoking is not only a very strong risk factor for the presence of an AAA but also associated with increased rates of expansion and the risk of rupture in patients with an AAA.22 Bath et al found that patients with an AAA compared to patients without an AAA were older (age 72.6 vs 69.8 years; P < .001), had a higher BMI (28.1 vs 27.0; P < .001), were more likely to be a current smoker (15.1% vs 5.2%; P < .001), and were more likely to have diabetes (18.8% vs 10.0%; P < .001), ischemic heart disease (12.2% vs 4.4%; P < .001), high cholesterol (53.2% vs 30.8%; P <. 001), previous stroke (6.1% vs 2.9%; P < .001), and a previous myocardial infarction (21.1% vs 5.8%; P < .001).23 Lesjak et al found that men with AAA reported significantly lower scores in the domains of social functioning, pain, and general health 6 months after ultrasound compared with men without AAA.24
Previous research indicates that patients with an AAA have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and comorbidities that may impact their perceived QoL. In a study assessing cardiovascular risk in 2323 patients with a small AAA, Bath et al found a high prevalence of coronary artery disease (44.9%), myocardial infarction (26.8%), heart failure (4.4%) and cerebrovascular accident (14.0%) which may have contributed to the decreased level of self-perceived QoL in these patients.25
This aligned with a study by Golledge et al, who found that participants diagnosed with an AAA and peripheral artery disease not only had significantly poorer QoL scores in 5 SF-36 domains (PF, RP, GH, VT, and PCS)when compared with participants diagnosed with an AAA alone. They also had significantly poorer QoL scores in 7 domains of the SF-36 (PF, RP, GH, VT, SF, RE, and PCS) when compared with controls without an AAA.26
Our analysis found that males with an AAA had a rise in SF-12v2 QoL scores from baseline to 12-month follow-up in the GH and BP domains. There was no statistically significant difference in QoL in the other 6 domains (PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, and MH) between the initial and 12-month investigations. Bath et al also found that men with an AAA had a transient reduction in mental QoL during the first year after the initial screening but returned to baseline.23
Strengths and Limitations
This study is notable for its sample of patients who previously had a diagnosed AAA that were followed with a recorded clinical imaging study and the use of a validated QoL measure (SF-12v2) that provided virtually identical summary scores (PCS and MCS) as the SF-36.27 However, this study was limited by the brevity of the SF-12v2 instrument which made it difficult to extract sufficient reliable information for the 8 domains.28 Subjective perception of patients is another limitation inherent to any QoL study. QoL scores were not available before the initial investigation. Measuring QoL at baseline and 12 months later does not capture the potential fluctuations and changes in QoL that the patient may experience some months later. Another limitation arises from the fact that the AAA patient population in the study included patients under surveillance and patients who had undergone repair.
Fourteen patients (15%) had received AAA repair: 10 had endovascular reconstruction and 4 had open surgical repair. Including patients with a previous AAA repair may have influenced reported QoL levels. Suckow et al performed a 2-phase study on 1008 patients, 351 (35%) were under surveillance and 657 (65%) had undergone repair. In that study, patients under AAA surveillance had worse emotional impact scores compared with patients with repair (22 vs 13; P < .001).11 Additionally, the size of the abdominal aorta at the time of survey was not addressed in the study, which could constitute explanatory variables.
Conclusions
This study found higher QoL at 12-month follow-up compared to baseline in both the GH and BP domains of the SF-12v2 health survey for male veterans with an AAA. Periodic QoL assessments for patients with an AAA may be helpful in tracking QoL course, minimizing their physical and psychological concerns, and improving overall care and support. However, further research is necessary to assess the QoL of patients with an AAA who are under surveillance compared with those who had an aneurysm repair to accurately measure the impact of an AAA on QoL.
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Profeta VF, et al. Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in population- based studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:2805. doi:10.3390/ijerph15122805
- Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The society for vascular surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
- Kent KC. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
- Harthun NL. Current issues in the treatment of women with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Gend Med. 2008;5:36-43.
- Aoki H. Taking control of the time bomb in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ J. 2016;80:314-315. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-15-1350
- Damhus CS, Siersma V, Hansson A, Bang CW, Brodersen J. Psychosocial consequences of screeningdetected abdominal aortic aneurisms: a cross-sectional study. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2021;39:459-465. doi:10.1080/02813432.2021.2004713
- Ericsson A, Kumlien C, Ching S, Carlson E, Molassiotis A. Impact on quality of life of men with screening-detected abdominal aortic aneurysms attending regular follow ups: a narrative literature review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:589-596. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.10.012
- Galyfos G, Voulalas G, Stamatatos I, et al. Small abdominal aortic aneurysms: should we wait? Vasc Dis Manag. 2015;12:E152-E159.
- Kristensen KL, Dahl M, Rasmussen LM, et al. Glycated hemoglobin is associated with the growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37:730-736. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308874
- Xiao-Yan L, Yu-Kui M, Li-Hui L. Risk factors for preoperative anxiety and depression in patients scheduled for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Chine Med J. 2018;131:1951-1957. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.238154
- Suckow BD, Schanzer AS, Hoel AW, et al. A novel quality of life instrument for patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:809-815. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.01.018
- Flatz A, Casillas A, Stringhini S, et al. Association between education and quality of diabetes care in Switzerland. Int J Gen Med. 2015;8:87-92. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S77139
- Christensen AV, Bjorner JB, Ekholm O, et al. Increased risk of mortality and readmission associated with lower SF-12 scores in cardiac patients: Results from the national DenHeart study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19:330-338. doi:10.1177/1474515119885480
- Hamming JF, De Vries J. Measuring quality of life. Br J Surg. 2007;94:923-924. doi:10.1002/bjs.5948
- Urbach DR. Measuring quality of life after surgery. Surg Innov. 2005;12:161-165. doi:10.1177/ 155335060501200216
- Gandek B, Sinclair SJ, Kosinski M, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the SF-36® health survey in medicare managed care. Health Care Financ Rev. 2004;25:5.
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short form health survey (SF-36). Med Care. 1992;30:473-483. doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
- Takayoshi K, Mototsugu T, Tomohiro T, et al. Health-related quality of life prospectively evaluated by the 8-item short form after endovascular repair versus open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Heart Vessels. 2017;32:960- 968. doi:10.1007/s00380-017-0956-9
- Pickard AS, Johnson JA, Penn A, et al. Replicability of SF-36 summary scores by the SF-12 in stroke patients. Stroke. 1999;30:1213-1217. doi:10.1161/01.str.30.6.1213
- Jenkinson C, Layte R. The development and testing of the UK SF-12. J Health Serv Res Policy. 1997;2:14-18. doi:10.1177/135581969700200105
- Golledge J, Clancy P, Jamrozik K, et al. Obesity, adipokines, and abdominal aortic aneurysm: Health in Men study. Circulation. 2007;116:2275-2279. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.717926
- Norman PE, Curci JA. Understanding the effects of tobacco smoke on the pathogenesis of aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:1473-1477. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300158
- Bath MF, Sidloff D, Saratzis A, et al. Impact of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening on quality of life. BJS. 2018;105:203-208. doi:10.1002/bjs.10721
- Lesjak M, Boreland F, Lyle D, Sidford J, Flecknoe-Brown S, Fletcher J. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: does it affect men’s quality of life? Aust J Prim Health. 2012;18:284-288. doi:10.1071/PY11131
- Bath MF, Gokani VJ, Sidloff DA, et al. Systematic review of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular death in patients with a small abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015;102:866-872. doi:10.1002/bjs.9837
- Golledge J, Pinchbeck J, Rowbotham SE, et al. Health-related quality of life amongst people diagnosed with abdominal aortic aneurysm and peripheral artery disease and the effect of fenofibrate. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14583. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71454-4
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D. A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? J Public Health Med. 1997;19:179- 186. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubmed.a024606
- White MK, Maher SM, Rizio AA, et al. A meta-analytic review of measurement equivalence study findings of the SF-36® and SF-12® Health Surveys across electronic modes compared to paper administration. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1757-1767. doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1851-2
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Profeta VF, et al. Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in population- based studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:2805. doi:10.3390/ijerph15122805
- Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The society for vascular surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
- Kent KC. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
- Harthun NL. Current issues in the treatment of women with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Gend Med. 2008;5:36-43.
- Aoki H. Taking control of the time bomb in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ J. 2016;80:314-315. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-15-1350
- Damhus CS, Siersma V, Hansson A, Bang CW, Brodersen J. Psychosocial consequences of screeningdetected abdominal aortic aneurisms: a cross-sectional study. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2021;39:459-465. doi:10.1080/02813432.2021.2004713
- Ericsson A, Kumlien C, Ching S, Carlson E, Molassiotis A. Impact on quality of life of men with screening-detected abdominal aortic aneurysms attending regular follow ups: a narrative literature review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:589-596. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.10.012
- Galyfos G, Voulalas G, Stamatatos I, et al. Small abdominal aortic aneurysms: should we wait? Vasc Dis Manag. 2015;12:E152-E159.
- Kristensen KL, Dahl M, Rasmussen LM, et al. Glycated hemoglobin is associated with the growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37:730-736. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308874
- Xiao-Yan L, Yu-Kui M, Li-Hui L. Risk factors for preoperative anxiety and depression in patients scheduled for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Chine Med J. 2018;131:1951-1957. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.238154
- Suckow BD, Schanzer AS, Hoel AW, et al. A novel quality of life instrument for patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:809-815. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.01.018
- Flatz A, Casillas A, Stringhini S, et al. Association between education and quality of diabetes care in Switzerland. Int J Gen Med. 2015;8:87-92. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S77139
- Christensen AV, Bjorner JB, Ekholm O, et al. Increased risk of mortality and readmission associated with lower SF-12 scores in cardiac patients: Results from the national DenHeart study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19:330-338. doi:10.1177/1474515119885480
- Hamming JF, De Vries J. Measuring quality of life. Br J Surg. 2007;94:923-924. doi:10.1002/bjs.5948
- Urbach DR. Measuring quality of life after surgery. Surg Innov. 2005;12:161-165. doi:10.1177/ 155335060501200216
- Gandek B, Sinclair SJ, Kosinski M, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the SF-36® health survey in medicare managed care. Health Care Financ Rev. 2004;25:5.
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short form health survey (SF-36). Med Care. 1992;30:473-483. doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
- Takayoshi K, Mototsugu T, Tomohiro T, et al. Health-related quality of life prospectively evaluated by the 8-item short form after endovascular repair versus open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Heart Vessels. 2017;32:960- 968. doi:10.1007/s00380-017-0956-9
- Pickard AS, Johnson JA, Penn A, et al. Replicability of SF-36 summary scores by the SF-12 in stroke patients. Stroke. 1999;30:1213-1217. doi:10.1161/01.str.30.6.1213
- Jenkinson C, Layte R. The development and testing of the UK SF-12. J Health Serv Res Policy. 1997;2:14-18. doi:10.1177/135581969700200105
- Golledge J, Clancy P, Jamrozik K, et al. Obesity, adipokines, and abdominal aortic aneurysm: Health in Men study. Circulation. 2007;116:2275-2279. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.717926
- Norman PE, Curci JA. Understanding the effects of tobacco smoke on the pathogenesis of aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:1473-1477. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300158
- Bath MF, Sidloff D, Saratzis A, et al. Impact of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening on quality of life. BJS. 2018;105:203-208. doi:10.1002/bjs.10721
- Lesjak M, Boreland F, Lyle D, Sidford J, Flecknoe-Brown S, Fletcher J. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: does it affect men’s quality of life? Aust J Prim Health. 2012;18:284-288. doi:10.1071/PY11131
- Bath MF, Gokani VJ, Sidloff DA, et al. Systematic review of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular death in patients with a small abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015;102:866-872. doi:10.1002/bjs.9837
- Golledge J, Pinchbeck J, Rowbotham SE, et al. Health-related quality of life amongst people diagnosed with abdominal aortic aneurysm and peripheral artery disease and the effect of fenofibrate. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14583. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71454-4
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D. A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? J Public Health Med. 1997;19:179- 186. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubmed.a024606
- White MK, Maher SM, Rizio AA, et al. A meta-analytic review of measurement equivalence study findings of the SF-36® and SF-12® Health Surveys across electronic modes compared to paper administration. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1757-1767. doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1851-2
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Tall Cell Carcinoma with Reversed Polarity
Background
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) is a rare and distinct subtype of invasive breast carcinoma, defined by tall columnar cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and reversed nuclear polarity. TCCRP remains poorly characterized in the literature, with limited population-level evidence to guide management and prognostication. This study uses the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to examine the epidemiology, clinical features, and outcomes of this neoplasm.
Methods
A retrospective cohort analysis included 951 patients diagnosed with TCCRP (ICD-O-3 code 8509) from 2018–2020 using the NCDB. Demographic and treatment variables were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Incidence trends were assessed using linear regression, and overall survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results
Most patients were female (98.1%) with a mean age of 69.1 years. The majority were White (82.0%), followed by Black (9.0%) and Hispanic (8.7%). Primary tumor sites included overlapping breast lesions (28.5%) and the upper-inner quadrant (27.0%). Incidence remained stable (R2 = 0.0). Most patients were diagnosed at Stage I (58.4%) and had a Charlson-Deyo score of 0 (76.2%). Socioeconomically, 41.8% lived in the highest income quartile (≥$74,063), and most had Medicare (64.7%). The most common treatment settings were comprehensive community cancer programs (40.3%). Surgery was performed in 95.6% of cases, with negative margins in 91.1%. Radiation therapy (46.6%) and hormone therapy (44.3%) were frequently used. Mortality was 1.1% at 30 days and 1.7% at 90 days. Survival was 98.9% at 2 years, 97.3% at 5 years, and 94.5% at 10 years, with a mean survival of 46.4 months.
Conclusions
This is the first NCDB-based study of TCCRP, highlighting favorable outcomes and distinct clinicodemographic features. Patients were predominantly older, White, and Medicare-insured, often receiving care at community cancer programs. These findings suggest that socioeconomic factors may influence access and treatment. Results may inform strategies to promote equitable care delivery across health systems and guide further research on clinical management and survivorship in TCCRP, particularly for rare cancers within community-based settings such as the VHA.
Background
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) is a rare and distinct subtype of invasive breast carcinoma, defined by tall columnar cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and reversed nuclear polarity. TCCRP remains poorly characterized in the literature, with limited population-level evidence to guide management and prognostication. This study uses the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to examine the epidemiology, clinical features, and outcomes of this neoplasm.
Methods
A retrospective cohort analysis included 951 patients diagnosed with TCCRP (ICD-O-3 code 8509) from 2018–2020 using the NCDB. Demographic and treatment variables were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Incidence trends were assessed using linear regression, and overall survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results
Most patients were female (98.1%) with a mean age of 69.1 years. The majority were White (82.0%), followed by Black (9.0%) and Hispanic (8.7%). Primary tumor sites included overlapping breast lesions (28.5%) and the upper-inner quadrant (27.0%). Incidence remained stable (R2 = 0.0). Most patients were diagnosed at Stage I (58.4%) and had a Charlson-Deyo score of 0 (76.2%). Socioeconomically, 41.8% lived in the highest income quartile (≥$74,063), and most had Medicare (64.7%). The most common treatment settings were comprehensive community cancer programs (40.3%). Surgery was performed in 95.6% of cases, with negative margins in 91.1%. Radiation therapy (46.6%) and hormone therapy (44.3%) were frequently used. Mortality was 1.1% at 30 days and 1.7% at 90 days. Survival was 98.9% at 2 years, 97.3% at 5 years, and 94.5% at 10 years, with a mean survival of 46.4 months.
Conclusions
This is the first NCDB-based study of TCCRP, highlighting favorable outcomes and distinct clinicodemographic features. Patients were predominantly older, White, and Medicare-insured, often receiving care at community cancer programs. These findings suggest that socioeconomic factors may influence access and treatment. Results may inform strategies to promote equitable care delivery across health systems and guide further research on clinical management and survivorship in TCCRP, particularly for rare cancers within community-based settings such as the VHA.
Background
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) is a rare and distinct subtype of invasive breast carcinoma, defined by tall columnar cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and reversed nuclear polarity. TCCRP remains poorly characterized in the literature, with limited population-level evidence to guide management and prognostication. This study uses the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to examine the epidemiology, clinical features, and outcomes of this neoplasm.
Methods
A retrospective cohort analysis included 951 patients diagnosed with TCCRP (ICD-O-3 code 8509) from 2018–2020 using the NCDB. Demographic and treatment variables were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Incidence trends were assessed using linear regression, and overall survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results
Most patients were female (98.1%) with a mean age of 69.1 years. The majority were White (82.0%), followed by Black (9.0%) and Hispanic (8.7%). Primary tumor sites included overlapping breast lesions (28.5%) and the upper-inner quadrant (27.0%). Incidence remained stable (R2 = 0.0). Most patients were diagnosed at Stage I (58.4%) and had a Charlson-Deyo score of 0 (76.2%). Socioeconomically, 41.8% lived in the highest income quartile (≥$74,063), and most had Medicare (64.7%). The most common treatment settings were comprehensive community cancer programs (40.3%). Surgery was performed in 95.6% of cases, with negative margins in 91.1%. Radiation therapy (46.6%) and hormone therapy (44.3%) were frequently used. Mortality was 1.1% at 30 days and 1.7% at 90 days. Survival was 98.9% at 2 years, 97.3% at 5 years, and 94.5% at 10 years, with a mean survival of 46.4 months.
Conclusions
This is the first NCDB-based study of TCCRP, highlighting favorable outcomes and distinct clinicodemographic features. Patients were predominantly older, White, and Medicare-insured, often receiving care at community cancer programs. These findings suggest that socioeconomic factors may influence access and treatment. Results may inform strategies to promote equitable care delivery across health systems and guide further research on clinical management and survivorship in TCCRP, particularly for rare cancers within community-based settings such as the VHA.
ERCC2, KDM6A, and TERT as Key Prognostic Factors in Bladder Cancer: Insights from the AACR Project GENIE Database
Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is among the top 10 frequently diagnosed cancers in the world. Mutations in FGFR3, ARID1A, and TP53 are well documented as being some of the most frequent mutations found in UC. Despite advances in treatment, survival outcomes remain poor, especially in advanced stages. To promote future pharmacotherapeutic development, the molecular understanding of UC needs to be continually updated using more recently available databases.
Methods
This study utilizes the AACR Project GENIE database from the American Association for Cancer Research to explore the mutational profiles of patients with UC. Gene mutation frequencies were calculated, and two Kaplan-Meier curves were drawn for each gene, showing one curve for patients with the mutation and one for those without. Log-Rank tests were calculated with subsequent FDR (Benjamini–Hochberg) correction applied to account for multiple hypothesis testing. Data was analyzed using R 4.4.2 and statistical significance was set at α = 0.05.
Results
In this study, 4525 patients had histology consistent with UC. The 5 most common mutations were TERT (n = 1714, 37.9%), TP53 (n = 1689, 37.3%), KDM6A (n = 1091, 24.1%), ARID1A (n = 872, 19.3%), and FGFR3 (n = 762, 16.8%). Mutations associated with differential survival outcomes included ERCC2 (mutated n = 387, wild type n = 3751, p < 0.0001), KDM6A (mutated n = 1091, wild type n = 3047, p < 0.0001), TERT (mutated n = 1714, wild type n = 2424), and TP53 (mutated n = 1689, wild type n = 2449, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Interestingly, while mutations in TP53 and ERCC2 were associated with shorter median survival, mutations in KDM6A and TERT were associated with longer median survival.
Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is among the top 10 frequently diagnosed cancers in the world. Mutations in FGFR3, ARID1A, and TP53 are well documented as being some of the most frequent mutations found in UC. Despite advances in treatment, survival outcomes remain poor, especially in advanced stages. To promote future pharmacotherapeutic development, the molecular understanding of UC needs to be continually updated using more recently available databases.
Methods
This study utilizes the AACR Project GENIE database from the American Association for Cancer Research to explore the mutational profiles of patients with UC. Gene mutation frequencies were calculated, and two Kaplan-Meier curves were drawn for each gene, showing one curve for patients with the mutation and one for those without. Log-Rank tests were calculated with subsequent FDR (Benjamini–Hochberg) correction applied to account for multiple hypothesis testing. Data was analyzed using R 4.4.2 and statistical significance was set at α = 0.05.
Results
In this study, 4525 patients had histology consistent with UC. The 5 most common mutations were TERT (n = 1714, 37.9%), TP53 (n = 1689, 37.3%), KDM6A (n = 1091, 24.1%), ARID1A (n = 872, 19.3%), and FGFR3 (n = 762, 16.8%). Mutations associated with differential survival outcomes included ERCC2 (mutated n = 387, wild type n = 3751, p < 0.0001), KDM6A (mutated n = 1091, wild type n = 3047, p < 0.0001), TERT (mutated n = 1714, wild type n = 2424), and TP53 (mutated n = 1689, wild type n = 2449, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Interestingly, while mutations in TP53 and ERCC2 were associated with shorter median survival, mutations in KDM6A and TERT were associated with longer median survival.
Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is among the top 10 frequently diagnosed cancers in the world. Mutations in FGFR3, ARID1A, and TP53 are well documented as being some of the most frequent mutations found in UC. Despite advances in treatment, survival outcomes remain poor, especially in advanced stages. To promote future pharmacotherapeutic development, the molecular understanding of UC needs to be continually updated using more recently available databases.
Methods
This study utilizes the AACR Project GENIE database from the American Association for Cancer Research to explore the mutational profiles of patients with UC. Gene mutation frequencies were calculated, and two Kaplan-Meier curves were drawn for each gene, showing one curve for patients with the mutation and one for those without. Log-Rank tests were calculated with subsequent FDR (Benjamini–Hochberg) correction applied to account for multiple hypothesis testing. Data was analyzed using R 4.4.2 and statistical significance was set at α = 0.05.
Results
In this study, 4525 patients had histology consistent with UC. The 5 most common mutations were TERT (n = 1714, 37.9%), TP53 (n = 1689, 37.3%), KDM6A (n = 1091, 24.1%), ARID1A (n = 872, 19.3%), and FGFR3 (n = 762, 16.8%). Mutations associated with differential survival outcomes included ERCC2 (mutated n = 387, wild type n = 3751, p < 0.0001), KDM6A (mutated n = 1091, wild type n = 3047, p < 0.0001), TERT (mutated n = 1714, wild type n = 2424), and TP53 (mutated n = 1689, wild type n = 2449, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Interestingly, while mutations in TP53 and ERCC2 were associated with shorter median survival, mutations in KDM6A and TERT were associated with longer median survival.
Communication Modality (CM) Among Veterans Using National TeleOncology (NTO) Services
Background
We examined characteristics of Veterans receiving care through NTO and their CM (e.g., telephone only [T], video only [V], or both [TV]). Relevant background: In-person VA cancer care can be challenging for many Veterans due to rurality, transportation, finances, and distance to subspecialists. Such factors may impact care modality preferences.
Methods
We linked a list of all Veterans who received NTO care with Corporate Data Warehouse data to confirm an ICD-10 diagnostic code for malignancy, and to define the number of NTO interactions, latency of days between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, and demographics. The Office of Rural Health categories for rurality and NIH categories for race were used.
Data analysis
We report descriptive statistics for CM. To compare differences between Veterans by CM, we report chi-squared tests for categorical variables and ANOVAs for continuous variables.
Results
Among 13,902 NTO Veterans with CM data, most were V (9,998, 72%), few were T 2% (n= 295), and some were TV 26% (n= 3,609). There were statistically significant differences between CM in number of interactions, latency between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, age at first NTO interaction, sex, race, rurality, and cancer type. Veterans diagnosed with lung cancer were more likely to exclusively use T. Veterans with breast cancer were more likely to exclusively use V. Specifically, T were oldest (mean age = 74.3), followed by TV (69.0) and V (61.6; p < .001). Women were most represented in V (28.3%) and Rural or highly rural residence was most common among T users (54.6%), compared to V (36.8%) and TV (43.0%; p < .001). Urban users were more prevalent in the TV group (61.9%) than in the T only group (45.4%).
Implications
We identified differences in communication modality based on Veteran characteristics. This could suggest differences in Veteran or provider preference, feasibility, or acceptability, based on CM.
Significance
While V communications appear to be achievable for many Veterans, more work is needed to determine preference, feasibility, and acceptability among Veterans and their care teams regarding V and T only cancer care.
Background
We examined characteristics of Veterans receiving care through NTO and their CM (e.g., telephone only [T], video only [V], or both [TV]). Relevant background: In-person VA cancer care can be challenging for many Veterans due to rurality, transportation, finances, and distance to subspecialists. Such factors may impact care modality preferences.
Methods
We linked a list of all Veterans who received NTO care with Corporate Data Warehouse data to confirm an ICD-10 diagnostic code for malignancy, and to define the number of NTO interactions, latency of days between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, and demographics. The Office of Rural Health categories for rurality and NIH categories for race were used.
Data analysis
We report descriptive statistics for CM. To compare differences between Veterans by CM, we report chi-squared tests for categorical variables and ANOVAs for continuous variables.
Results
Among 13,902 NTO Veterans with CM data, most were V (9,998, 72%), few were T 2% (n= 295), and some were TV 26% (n= 3,609). There were statistically significant differences between CM in number of interactions, latency between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, age at first NTO interaction, sex, race, rurality, and cancer type. Veterans diagnosed with lung cancer were more likely to exclusively use T. Veterans with breast cancer were more likely to exclusively use V. Specifically, T were oldest (mean age = 74.3), followed by TV (69.0) and V (61.6; p < .001). Women were most represented in V (28.3%) and Rural or highly rural residence was most common among T users (54.6%), compared to V (36.8%) and TV (43.0%; p < .001). Urban users were more prevalent in the TV group (61.9%) than in the T only group (45.4%).
Implications
We identified differences in communication modality based on Veteran characteristics. This could suggest differences in Veteran or provider preference, feasibility, or acceptability, based on CM.
Significance
While V communications appear to be achievable for many Veterans, more work is needed to determine preference, feasibility, and acceptability among Veterans and their care teams regarding V and T only cancer care.
Background
We examined characteristics of Veterans receiving care through NTO and their CM (e.g., telephone only [T], video only [V], or both [TV]). Relevant background: In-person VA cancer care can be challenging for many Veterans due to rurality, transportation, finances, and distance to subspecialists. Such factors may impact care modality preferences.
Methods
We linked a list of all Veterans who received NTO care with Corporate Data Warehouse data to confirm an ICD-10 diagnostic code for malignancy, and to define the number of NTO interactions, latency of days between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, and demographics. The Office of Rural Health categories for rurality and NIH categories for race were used.
Data analysis
We report descriptive statistics for CM. To compare differences between Veterans by CM, we report chi-squared tests for categorical variables and ANOVAs for continuous variables.
Results
Among 13,902 NTO Veterans with CM data, most were V (9,998, 72%), few were T 2% (n= 295), and some were TV 26% (n= 3,609). There were statistically significant differences between CM in number of interactions, latency between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, age at first NTO interaction, sex, race, rurality, and cancer type. Veterans diagnosed with lung cancer were more likely to exclusively use T. Veterans with breast cancer were more likely to exclusively use V. Specifically, T were oldest (mean age = 74.3), followed by TV (69.0) and V (61.6; p < .001). Women were most represented in V (28.3%) and Rural or highly rural residence was most common among T users (54.6%), compared to V (36.8%) and TV (43.0%; p < .001). Urban users were more prevalent in the TV group (61.9%) than in the T only group (45.4%).
Implications
We identified differences in communication modality based on Veteran characteristics. This could suggest differences in Veteran or provider preference, feasibility, or acceptability, based on CM.
Significance
While V communications appear to be achievable for many Veterans, more work is needed to determine preference, feasibility, and acceptability among Veterans and their care teams regarding V and T only cancer care.