User login
Measles outbreaks: Protecting your patients during international travel
The U.S. immunization program is one of the best public health success stories. Physicians who provide care for children are familiar with the routine childhood immunization schedule and administer a measles-containing vaccine at age-appropriate times. Thanks to its rigorous implementation and acceptance, endemic measles (absence of continuous virus transmission for > 1 year) was eliminated in the U.S. in 2000. Loss of this status was in jeopardy in 2019 when 22 measles outbreaks occurred in 17 states (7 were multistate outbreaks). That year, 1,163 cases were reported.1 Most cases occurred in unvaccinated persons (89%) and 81 cases were imported of which 54 were in U.S. citizens returning from international travel. All outbreaks were linked to travel. Fortunately, the outbreaks were controlled prior to the elimination deadline, or the United States would have lost its measles elimination status. Restrictions on travel because of COVID-19 have relaxed significantly since the introduction of COVID-19 vaccines, resulting in increased regional and international travel. Multiple countries, including the United States noted a decline in routine immunizations rates during the last 2 years. Recent U.S. data for the 2020-2021 school year indicates that MMR immunizations rates (two doses) for kindergarteners declined to 93.9% (range 78.9% to > 98.9%), while the overall percentage of those students with an exemption remained low at 2.2%. Vaccine coverage greater than 95% was reported in only 16 states. Coverage of less than 90% was reported in seven states and the District of Columbia (Georgia, Idaho, Kentucky, Maryland, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin).2 Vaccine coverage should be 95% or higher to maintain herd immunity and control outbreaks.
Why is measles prevention so important? Many physicians practicing in the United States today have never seen a case or know its potential complications. I saw my first case as a resident in an immigrant child. It took our training director to point out the subtle signs and symptoms. It was the first time I saw Kolpik spots. Measles is transmitted person to person via large respiratory droplets and less often by airborne spread. It is highly contagious for susceptible individuals with an attack rate of 90%. In this case, a medical student on the team developed symptoms about 10 days later. Six years would pass before I diagnosed my next case of measles. An HIV patient acquired it after close contact with someone who was in the prodromal stage. He presented with the 3 C’s: Cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, in addition to fever and an erythematous rash. He did not recover from complications of the disease.
Prior to the routine administration of a measles vaccine, 3-4 million cases with almost 500 deaths occurred annually in the United States. Worldwide, 35 million cases and more than 6 million deaths occurred each year. Here, most patients recover completely; however, complications including otitis media, pneumonia, croup, and encephalitis can develop. Complications commonly occur in immunocompromised individuals and young children. Groups with the highest fatality rates include children aged less than 5 years, immunocompromised persons, and pregnant women. Worldwide, fatality rates are dependent on the patients underlying nutritional and health status in addition to the quality of health care available.3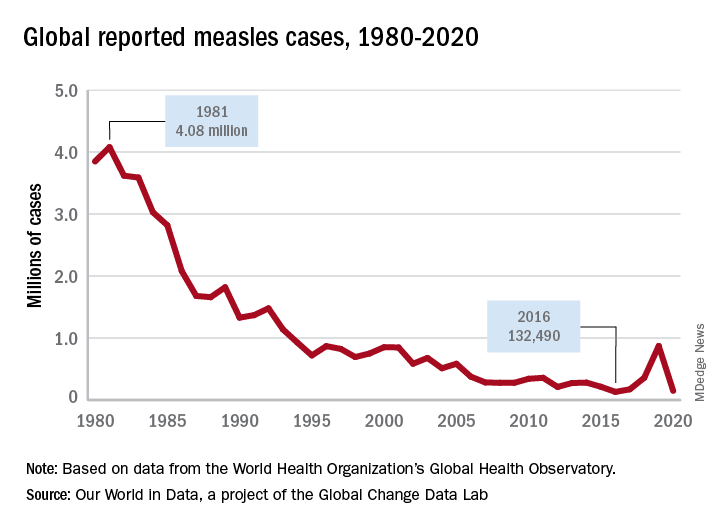
Measles vaccine was licensed in 1963 and cases began to decline (Figure 1). There was a resurgence in 1989 but it was not limited to the United States. The cause of the U.S. resurgence was multifactorial: Widespread viral transmission among unvaccinated preschool-age children residing in inner cities, outbreaks in vaccinated school-age children, outbreaks in students and personnel on college campuses, and primary vaccine failure (2%-5% of recipients failed to have an adequate response). In 1989, to help prevent future outbreaks, the United States recommended a two-dose schedule for measles and in 1993, the Vaccines for Children Program, a federally funded program, was established to improve access to vaccines for all children.
What is going on internationally?
Figure 2 lists the top 10 countries with current measles outbreaks.

Most countries on the list may not be typical travel destinations for tourists; however, they are common destinations for individuals visiting friends and relatives after immigrating to the United States. In contrast to the United States, most countries with limited resources and infrastructure have mass-vaccination campaigns to ensure vaccine administration to large segments of the population. They too have been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. By report, at least 41 countries delayed implementation of their measles campaign in 2020 and 2021, thus, leading to the potential for even larger outbreaks.4
Progress toward the global elimination of measles is evidenced by the following: All 194 countries now include one dose of measles in their routine schedules; between 2000 and 2019 coverage of one dose of measles increased from 72% to 85% and countries with more than 90% coverage increased from 45% to 63%. Finally, the number of countries offering two doses of measles increased from 50% to 91% and vaccine coverage increased from 18% to 71% over the same time period.3
What can you do for your patients and their parents before they travel abroad?
- Inform all staff that the MMR vaccine can be administered to children as young as 6 months and at times other than those listed on the routine immunization schedule. This will help avoid parents seeking vaccine being denied an appointment.
- Children 6-11 months need 1 dose of MMR. Two additional doses will still need to be administered at the routine time.
- Children 12 months or older need 2 doses of MMR at least 4 weeks apart.
- If yellow fever vaccine is needed, coordinate administration with a travel medicine clinic since both are live vaccines and must be given on the same day.
- Any person born after 1956 should have 2 doses of MMR at least 4 weeks apart if they have no evidence of immunity.
- Encourage parents to always inform you and your staff of any international travel plans.
Moving forward, remember this increased global activity and the presence of inadequately vaccinated individuals/communities keeps the United States at continued risk for measles outbreaks. The source of the next outbreak may only be one plane ride away.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was updated 6/29/22.
References
1. Patel M et al. MMWR. 2019 Oct 11; 68(40):893-6.
2. Seither R et al. MMWR. 2022 Apr 22;71(16):561-8.
3. Gastañaduy PA et al. J Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 30;224(12 Suppl 2):S420-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa793.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles (Rubeola). http://www.CDC.gov/Measles.
The U.S. immunization program is one of the best public health success stories. Physicians who provide care for children are familiar with the routine childhood immunization schedule and administer a measles-containing vaccine at age-appropriate times. Thanks to its rigorous implementation and acceptance, endemic measles (absence of continuous virus transmission for > 1 year) was eliminated in the U.S. in 2000. Loss of this status was in jeopardy in 2019 when 22 measles outbreaks occurred in 17 states (7 were multistate outbreaks). That year, 1,163 cases were reported.1 Most cases occurred in unvaccinated persons (89%) and 81 cases were imported of which 54 were in U.S. citizens returning from international travel. All outbreaks were linked to travel. Fortunately, the outbreaks were controlled prior to the elimination deadline, or the United States would have lost its measles elimination status. Restrictions on travel because of COVID-19 have relaxed significantly since the introduction of COVID-19 vaccines, resulting in increased regional and international travel. Multiple countries, including the United States noted a decline in routine immunizations rates during the last 2 years. Recent U.S. data for the 2020-2021 school year indicates that MMR immunizations rates (two doses) for kindergarteners declined to 93.9% (range 78.9% to > 98.9%), while the overall percentage of those students with an exemption remained low at 2.2%. Vaccine coverage greater than 95% was reported in only 16 states. Coverage of less than 90% was reported in seven states and the District of Columbia (Georgia, Idaho, Kentucky, Maryland, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin).2 Vaccine coverage should be 95% or higher to maintain herd immunity and control outbreaks.
Why is measles prevention so important? Many physicians practicing in the United States today have never seen a case or know its potential complications. I saw my first case as a resident in an immigrant child. It took our training director to point out the subtle signs and symptoms. It was the first time I saw Kolpik spots. Measles is transmitted person to person via large respiratory droplets and less often by airborne spread. It is highly contagious for susceptible individuals with an attack rate of 90%. In this case, a medical student on the team developed symptoms about 10 days later. Six years would pass before I diagnosed my next case of measles. An HIV patient acquired it after close contact with someone who was in the prodromal stage. He presented with the 3 C’s: Cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, in addition to fever and an erythematous rash. He did not recover from complications of the disease.
Prior to the routine administration of a measles vaccine, 3-4 million cases with almost 500 deaths occurred annually in the United States. Worldwide, 35 million cases and more than 6 million deaths occurred each year. Here, most patients recover completely; however, complications including otitis media, pneumonia, croup, and encephalitis can develop. Complications commonly occur in immunocompromised individuals and young children. Groups with the highest fatality rates include children aged less than 5 years, immunocompromised persons, and pregnant women. Worldwide, fatality rates are dependent on the patients underlying nutritional and health status in addition to the quality of health care available.3
Measles vaccine was licensed in 1963 and cases began to decline (Figure 1). There was a resurgence in 1989 but it was not limited to the United States. The cause of the U.S. resurgence was multifactorial: Widespread viral transmission among unvaccinated preschool-age children residing in inner cities, outbreaks in vaccinated school-age children, outbreaks in students and personnel on college campuses, and primary vaccine failure (2%-5% of recipients failed to have an adequate response). In 1989, to help prevent future outbreaks, the United States recommended a two-dose schedule for measles and in 1993, the Vaccines for Children Program, a federally funded program, was established to improve access to vaccines for all children.
What is going on internationally?
Figure 2 lists the top 10 countries with current measles outbreaks.

Most countries on the list may not be typical travel destinations for tourists; however, they are common destinations for individuals visiting friends and relatives after immigrating to the United States. In contrast to the United States, most countries with limited resources and infrastructure have mass-vaccination campaigns to ensure vaccine administration to large segments of the population. They too have been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. By report, at least 41 countries delayed implementation of their measles campaign in 2020 and 2021, thus, leading to the potential for even larger outbreaks.4
Progress toward the global elimination of measles is evidenced by the following: All 194 countries now include one dose of measles in their routine schedules; between 2000 and 2019 coverage of one dose of measles increased from 72% to 85% and countries with more than 90% coverage increased from 45% to 63%. Finally, the number of countries offering two doses of measles increased from 50% to 91% and vaccine coverage increased from 18% to 71% over the same time period.3
What can you do for your patients and their parents before they travel abroad?
- Inform all staff that the MMR vaccine can be administered to children as young as 6 months and at times other than those listed on the routine immunization schedule. This will help avoid parents seeking vaccine being denied an appointment.
- Children 6-11 months need 1 dose of MMR. Two additional doses will still need to be administered at the routine time.
- Children 12 months or older need 2 doses of MMR at least 4 weeks apart.
- If yellow fever vaccine is needed, coordinate administration with a travel medicine clinic since both are live vaccines and must be given on the same day.
- Any person born after 1956 should have 2 doses of MMR at least 4 weeks apart if they have no evidence of immunity.
- Encourage parents to always inform you and your staff of any international travel plans.
Moving forward, remember this increased global activity and the presence of inadequately vaccinated individuals/communities keeps the United States at continued risk for measles outbreaks. The source of the next outbreak may only be one plane ride away.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was updated 6/29/22.
References
1. Patel M et al. MMWR. 2019 Oct 11; 68(40):893-6.
2. Seither R et al. MMWR. 2022 Apr 22;71(16):561-8.
3. Gastañaduy PA et al. J Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 30;224(12 Suppl 2):S420-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa793.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles (Rubeola). http://www.CDC.gov/Measles.
The U.S. immunization program is one of the best public health success stories. Physicians who provide care for children are familiar with the routine childhood immunization schedule and administer a measles-containing vaccine at age-appropriate times. Thanks to its rigorous implementation and acceptance, endemic measles (absence of continuous virus transmission for > 1 year) was eliminated in the U.S. in 2000. Loss of this status was in jeopardy in 2019 when 22 measles outbreaks occurred in 17 states (7 were multistate outbreaks). That year, 1,163 cases were reported.1 Most cases occurred in unvaccinated persons (89%) and 81 cases were imported of which 54 were in U.S. citizens returning from international travel. All outbreaks were linked to travel. Fortunately, the outbreaks were controlled prior to the elimination deadline, or the United States would have lost its measles elimination status. Restrictions on travel because of COVID-19 have relaxed significantly since the introduction of COVID-19 vaccines, resulting in increased regional and international travel. Multiple countries, including the United States noted a decline in routine immunizations rates during the last 2 years. Recent U.S. data for the 2020-2021 school year indicates that MMR immunizations rates (two doses) for kindergarteners declined to 93.9% (range 78.9% to > 98.9%), while the overall percentage of those students with an exemption remained low at 2.2%. Vaccine coverage greater than 95% was reported in only 16 states. Coverage of less than 90% was reported in seven states and the District of Columbia (Georgia, Idaho, Kentucky, Maryland, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin).2 Vaccine coverage should be 95% or higher to maintain herd immunity and control outbreaks.
Why is measles prevention so important? Many physicians practicing in the United States today have never seen a case or know its potential complications. I saw my first case as a resident in an immigrant child. It took our training director to point out the subtle signs and symptoms. It was the first time I saw Kolpik spots. Measles is transmitted person to person via large respiratory droplets and less often by airborne spread. It is highly contagious for susceptible individuals with an attack rate of 90%. In this case, a medical student on the team developed symptoms about 10 days later. Six years would pass before I diagnosed my next case of measles. An HIV patient acquired it after close contact with someone who was in the prodromal stage. He presented with the 3 C’s: Cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, in addition to fever and an erythematous rash. He did not recover from complications of the disease.
Prior to the routine administration of a measles vaccine, 3-4 million cases with almost 500 deaths occurred annually in the United States. Worldwide, 35 million cases and more than 6 million deaths occurred each year. Here, most patients recover completely; however, complications including otitis media, pneumonia, croup, and encephalitis can develop. Complications commonly occur in immunocompromised individuals and young children. Groups with the highest fatality rates include children aged less than 5 years, immunocompromised persons, and pregnant women. Worldwide, fatality rates are dependent on the patients underlying nutritional and health status in addition to the quality of health care available.3
Measles vaccine was licensed in 1963 and cases began to decline (Figure 1). There was a resurgence in 1989 but it was not limited to the United States. The cause of the U.S. resurgence was multifactorial: Widespread viral transmission among unvaccinated preschool-age children residing in inner cities, outbreaks in vaccinated school-age children, outbreaks in students and personnel on college campuses, and primary vaccine failure (2%-5% of recipients failed to have an adequate response). In 1989, to help prevent future outbreaks, the United States recommended a two-dose schedule for measles and in 1993, the Vaccines for Children Program, a federally funded program, was established to improve access to vaccines for all children.
What is going on internationally?
Figure 2 lists the top 10 countries with current measles outbreaks.

Most countries on the list may not be typical travel destinations for tourists; however, they are common destinations for individuals visiting friends and relatives after immigrating to the United States. In contrast to the United States, most countries with limited resources and infrastructure have mass-vaccination campaigns to ensure vaccine administration to large segments of the population. They too have been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. By report, at least 41 countries delayed implementation of their measles campaign in 2020 and 2021, thus, leading to the potential for even larger outbreaks.4
Progress toward the global elimination of measles is evidenced by the following: All 194 countries now include one dose of measles in their routine schedules; between 2000 and 2019 coverage of one dose of measles increased from 72% to 85% and countries with more than 90% coverage increased from 45% to 63%. Finally, the number of countries offering two doses of measles increased from 50% to 91% and vaccine coverage increased from 18% to 71% over the same time period.3
What can you do for your patients and their parents before they travel abroad?
- Inform all staff that the MMR vaccine can be administered to children as young as 6 months and at times other than those listed on the routine immunization schedule. This will help avoid parents seeking vaccine being denied an appointment.
- Children 6-11 months need 1 dose of MMR. Two additional doses will still need to be administered at the routine time.
- Children 12 months or older need 2 doses of MMR at least 4 weeks apart.
- If yellow fever vaccine is needed, coordinate administration with a travel medicine clinic since both are live vaccines and must be given on the same day.
- Any person born after 1956 should have 2 doses of MMR at least 4 weeks apart if they have no evidence of immunity.
- Encourage parents to always inform you and your staff of any international travel plans.
Moving forward, remember this increased global activity and the presence of inadequately vaccinated individuals/communities keeps the United States at continued risk for measles outbreaks. The source of the next outbreak may only be one plane ride away.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was updated 6/29/22.
References
1. Patel M et al. MMWR. 2019 Oct 11; 68(40):893-6.
2. Seither R et al. MMWR. 2022 Apr 22;71(16):561-8.
3. Gastañaduy PA et al. J Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 30;224(12 Suppl 2):S420-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa793.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles (Rubeola). http://www.CDC.gov/Measles.
How to make visits run more smoothly and be more productive
We all feel pressure from not having enough time to care for our patients the way we want to.
Organ recital
Some of our patients need to share an update on all their symptoms each visit, old and new, including those that are minor or possibly concerning. I have learned over the years that, for many patients, this allows them to release the worry about symptoms.
Some symptoms are so distressing and severe that symptomatic treatment is needed, but most aren’t.
I am very honest with patients when I have no idea what is causing their symptoms. I tell them, we will watch for other clues to see if the symptom needs a workup.
One thing I don’t do, and I strongly recommend against, is doing a review of systems. This leads a patient to believe you are concerned about exploring each possible symptom, ones that they didn’t even bring up! The yield is very low, and the time commitment is great.
The angry patient
Imagine a scenario when you are running 15 minutes behind and, when you step into the room, your patient is angry. You are already behind, and helping the patient navigate their anger will be part of your clinic visit.
In these situations, I always address the patient’s anger immediately. Problems with getting appointments with specialists, delays in diagnostic tests, or a broken entry to the parking garage have all been sources of my patients’ frustrations.
When we have limited time, using much of the clinic visit to process frustration leads to empty clinic visits. I listen and work to empathize with the patient, often agreeing that there are so many messed up aspects of the health care system. I do not like to use the corporate “I am sad you feel that way” response, because I feel it is not helpful. Instead, I tell them how much I want to help them today in any way I can at this visit.
The Internet sleuth
When our patients have new symptoms, some of them will go to the Internet to try to self-diagnose. Sometimes they make a correct diagnosis, but other times consider scary diagnoses we would not consider based on their symptoms and risk factors.
In these scenarios, I always ask the patient why they think their diagnosis is accurate. Their response to this question gives me insight into where their beliefs come from and helps me understand what information I need to provide.
McMullan said physicians can be defensive, collaborative, and informative when they interact with patients about information they have found on the Internet. In the first model, the physician is authoritative. The second involves working with the patient and obtaining and analyzing information. In the third model, the physician provides reputable internet sites to patients for obtaining information.
‘Oh, by the way’
Patients frequently bring up sensitive topics or complicated requests after the visit has wrapped up. Topics such as insomnia, erectile dysfunction, and anxiety are often brought up with the assumption that a quick prescription is the answer. For many years, I would add time to the appointment and try to address these issues as quickly as I could. But I invariably did a poor job at helping with these problems. Now, I offer to see the patient back soon to spend an entire visit discussing the newly brought up concern. I tell them that the problem is too important to not have my full attention and focus.
Pearls
- Empathetically listen to descriptions of symptoms, but don’t focus on fixing them.
- Empathize with the angry patient, and move on to taking care of their medical problems.
- Avoid the urge to address newly raised problems at the end of the visit.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose.
We all feel pressure from not having enough time to care for our patients the way we want to.
Organ recital
Some of our patients need to share an update on all their symptoms each visit, old and new, including those that are minor or possibly concerning. I have learned over the years that, for many patients, this allows them to release the worry about symptoms.
Some symptoms are so distressing and severe that symptomatic treatment is needed, but most aren’t.
I am very honest with patients when I have no idea what is causing their symptoms. I tell them, we will watch for other clues to see if the symptom needs a workup.
One thing I don’t do, and I strongly recommend against, is doing a review of systems. This leads a patient to believe you are concerned about exploring each possible symptom, ones that they didn’t even bring up! The yield is very low, and the time commitment is great.
The angry patient
Imagine a scenario when you are running 15 minutes behind and, when you step into the room, your patient is angry. You are already behind, and helping the patient navigate their anger will be part of your clinic visit.
In these situations, I always address the patient’s anger immediately. Problems with getting appointments with specialists, delays in diagnostic tests, or a broken entry to the parking garage have all been sources of my patients’ frustrations.
When we have limited time, using much of the clinic visit to process frustration leads to empty clinic visits. I listen and work to empathize with the patient, often agreeing that there are so many messed up aspects of the health care system. I do not like to use the corporate “I am sad you feel that way” response, because I feel it is not helpful. Instead, I tell them how much I want to help them today in any way I can at this visit.
The Internet sleuth
When our patients have new symptoms, some of them will go to the Internet to try to self-diagnose. Sometimes they make a correct diagnosis, but other times consider scary diagnoses we would not consider based on their symptoms and risk factors.
In these scenarios, I always ask the patient why they think their diagnosis is accurate. Their response to this question gives me insight into where their beliefs come from and helps me understand what information I need to provide.
McMullan said physicians can be defensive, collaborative, and informative when they interact with patients about information they have found on the Internet. In the first model, the physician is authoritative. The second involves working with the patient and obtaining and analyzing information. In the third model, the physician provides reputable internet sites to patients for obtaining information.
‘Oh, by the way’
Patients frequently bring up sensitive topics or complicated requests after the visit has wrapped up. Topics such as insomnia, erectile dysfunction, and anxiety are often brought up with the assumption that a quick prescription is the answer. For many years, I would add time to the appointment and try to address these issues as quickly as I could. But I invariably did a poor job at helping with these problems. Now, I offer to see the patient back soon to spend an entire visit discussing the newly brought up concern. I tell them that the problem is too important to not have my full attention and focus.
Pearls
- Empathetically listen to descriptions of symptoms, but don’t focus on fixing them.
- Empathize with the angry patient, and move on to taking care of their medical problems.
- Avoid the urge to address newly raised problems at the end of the visit.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose.
We all feel pressure from not having enough time to care for our patients the way we want to.
Organ recital
Some of our patients need to share an update on all their symptoms each visit, old and new, including those that are minor or possibly concerning. I have learned over the years that, for many patients, this allows them to release the worry about symptoms.
Some symptoms are so distressing and severe that symptomatic treatment is needed, but most aren’t.
I am very honest with patients when I have no idea what is causing their symptoms. I tell them, we will watch for other clues to see if the symptom needs a workup.
One thing I don’t do, and I strongly recommend against, is doing a review of systems. This leads a patient to believe you are concerned about exploring each possible symptom, ones that they didn’t even bring up! The yield is very low, and the time commitment is great.
The angry patient
Imagine a scenario when you are running 15 minutes behind and, when you step into the room, your patient is angry. You are already behind, and helping the patient navigate their anger will be part of your clinic visit.
In these situations, I always address the patient’s anger immediately. Problems with getting appointments with specialists, delays in diagnostic tests, or a broken entry to the parking garage have all been sources of my patients’ frustrations.
When we have limited time, using much of the clinic visit to process frustration leads to empty clinic visits. I listen and work to empathize with the patient, often agreeing that there are so many messed up aspects of the health care system. I do not like to use the corporate “I am sad you feel that way” response, because I feel it is not helpful. Instead, I tell them how much I want to help them today in any way I can at this visit.
The Internet sleuth
When our patients have new symptoms, some of them will go to the Internet to try to self-diagnose. Sometimes they make a correct diagnosis, but other times consider scary diagnoses we would not consider based on their symptoms and risk factors.
In these scenarios, I always ask the patient why they think their diagnosis is accurate. Their response to this question gives me insight into where their beliefs come from and helps me understand what information I need to provide.
McMullan said physicians can be defensive, collaborative, and informative when they interact with patients about information they have found on the Internet. In the first model, the physician is authoritative. The second involves working with the patient and obtaining and analyzing information. In the third model, the physician provides reputable internet sites to patients for obtaining information.
‘Oh, by the way’
Patients frequently bring up sensitive topics or complicated requests after the visit has wrapped up. Topics such as insomnia, erectile dysfunction, and anxiety are often brought up with the assumption that a quick prescription is the answer. For many years, I would add time to the appointment and try to address these issues as quickly as I could. But I invariably did a poor job at helping with these problems. Now, I offer to see the patient back soon to spend an entire visit discussing the newly brought up concern. I tell them that the problem is too important to not have my full attention and focus.
Pearls
- Empathetically listen to descriptions of symptoms, but don’t focus on fixing them.
- Empathize with the angry patient, and move on to taking care of their medical problems.
- Avoid the urge to address newly raised problems at the end of the visit.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose.
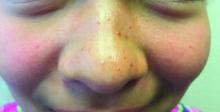
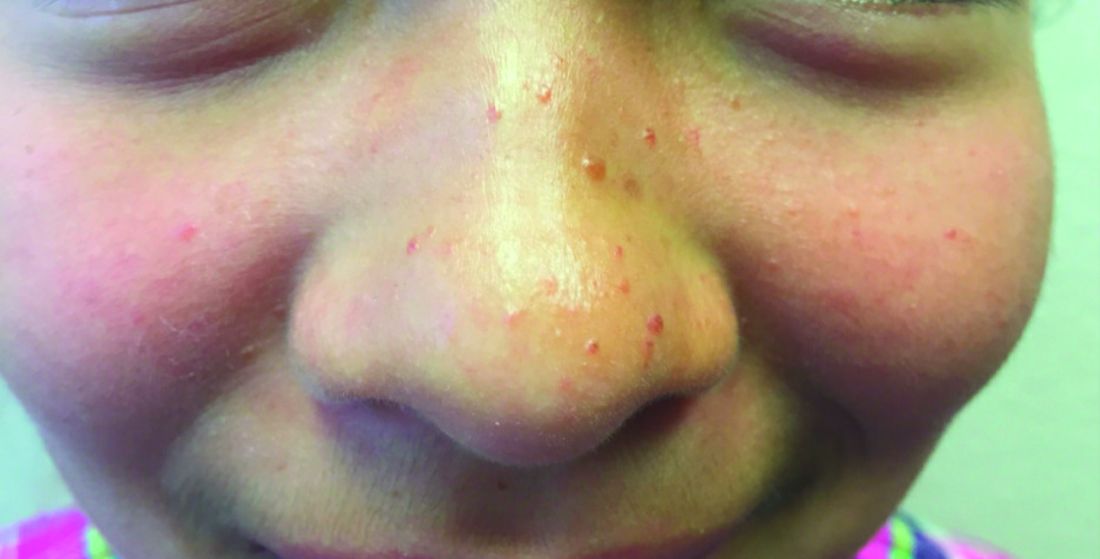
A 7-year-old with red bumps on her nose
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
A 7-year-old female presented with a bump on the bridge of her nose that was present for 10 months, with subsequent development of multiple papules on the nose and cheeks.
A 7-year-old, previously healthy female presented with a bump on the bridge of her nose that was present for 10 months, with subsequent development of multiple papules on the nose and cheeks. She has no significant medical history aside from a wart on her hand that was recently frozen with liquid nitrogen and resolved. She denied pruritus, bumps, or skin changes elsewhere on the body. The patient was prescribed tretinoin 0.1% cream applied nightly for several months without response.
Anorexia nervosa in adolescent patients: What pediatricians need to know
Eating disorders are among the most prevalent, disabling, and potentially fatal psychiatric illnesses, and the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated their burden, with a 15.3% increase in incidence in 2020 compared with previous years.1 This increase was almost solely among adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa (AN), which is often insidious in onset and more difficult to treat as it advances. Adolescents with AN are most likely to present to their pediatricians, so awareness and early recognition of the symptoms is critical. Pediatricians are also an integral part of the treatment team in AN and can offer monitoring for serious complications, alongside valuable guidance to parents, who are central to treatment and the reestablishment of healthy eating habits in their children. Here we will review the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of anorexia, with an emphasis on what pediatricians need to know to screen and to facilitate treatment.
Epidemiology
AN is marked by a fear of gaining weight or behaviors that interfere with weight gain and a self-evaluation unduly influenced by weight and body shape. Youth with AN often deny the seriousness of their malnutrition, although that is not required for diagnosis. AN can be of a restrictive or binge-purge subtype, and amenorrhea is no longer a requirement for diagnosis. There is not a specific weight or body mass index cutoff for the diagnosis, but the severity of AN is determined by the BMI percentile normed to age and sex. The average age of onset is 18, and the prepandemic prevalence of AN was about 1% of the population. It affects about 10 times as many females as males. It is quite rare prior to puberty, affecting about 0.01% of that age group. There is a heritable component, with a fivefold relative risk in youth with a parent with AN, and twin studies suggest heritability rates as high as 75%. Youth with rigid cognitive styles appear more vulnerable, as do those who participate in activities such as ballet, gymnastics, modeling, and wrestling because of the role of appearance and weight in performance. More than half of patients with AN will have another psychiatric illness, most commonly anxiety disorders, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. AN becomes chronic in up to 15% of sufferers and the mortality rate is close to 10%, with approximately half dying from medical complications and half dying by suicide.
Screening
Parents and pediatricians are usually the first to notice that a child has started to lose weight or is falling off the growth curve. But weight changes usually emerge after feelings of preoccupation with weight, body shape, and body satisfaction. If parents report escalating pickiness around food, increased or compulsive exercise, persistent self-consciousness and self-criticism around weight and body shape, it is worth starting with screening questions.
If you notice preoccupation or anxiety around being weighed, even if the weight or growth curve are still normal, it is worthwhile to screen. Screening questions, such as the SCOFF questionnaire with five simple questions, can be very sensitive for both AN and bulimia nervosa.2 There are also many validated screening instruments, such as the Eating Disorder Inventory or Eating Attitudes Test (for adolescents) and the Kids Eating Disorder Survey and the Child Eating Attitudes Test (for younger children), that are short self-reports that you can have your patients fill out when you have a higher index of suspicion. Weight loss or growth failure without a preoccupation around weight or appearance needs a thorough a medical workup, and could be a function of other psychiatric problems, such as depression.
If a child screens positive for an eating disorder, your full physical examination, growth curves, and longitudinal growth charts are critical for diagnosis. Percentile BMIs must be used, given the inaccuracy of standard BMI calculations in this age group. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age and sex growth charts include methods for this calculation). Laboratory assessment, including metabolic, kidney, pancreatic, and thyroid function, and an EKG can illuminate if there are consequences of restricting or purging. Of course, you want to evaluate for significant medical symptoms, including bradycardia, orthostasis, and hypokalemia. These medical symptoms are not limited to the severely underweight and merit referral to an emergency department and possible medical admission.
Then, a referral to a clinician who is expert in the assessment and treatment of eating disorders is needed. This may be a child psychiatrist, psychologist, or a colleague pediatrician with this specialization. It is also very important to begin the conversation with the family to introduce your concerns, describe what you have noticed, and discuss the need for further assessment and possibly treatment.
Be mindful that discussing this in front of your patient may heighten the patient’s anxiety or distress. Be prepared to offer support and understanding for your patient’s anxiety, while steadfastly providing absolute clarity for the parents about the necessity of further evaluation and treatment. Many parents will be concerned and ready to do whatever is needed to get their child’s eating and growth back on track. But some parents may have more difficulty. They may have their own history with an eating disorder. They may be avoiding a sense of shame or alarm. They may be eager to avoid adding to their child’s stress. They may be tired of engaging in power struggles with the child. They may be proud of their ambitious, accomplished young athlete. Their trust in you makes you uniquely positioned to complicate their thinking. And treatment will hinge on them, so this is a critical bridge to care.
Beyond telling parents that they will need to bring more structure and supervision to mealtimes to begin addressing their child’s nutrition, you might offer guidance on other strategies. Empower parents to limit their child’s use of social media sites such as Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok, where they may be immersed in comparing themselves to idealized (and airbrushed) influencers. Empower them to make their child’s participation in beloved sports contingent on eating meals together and completely or on a stabilized weight (as will be common in treatment). Remind them that there are no bad foods, that the goal is health, and that they are not in a power struggle with their child, but instead allied with their child to treat AN. Remind them to also look for chances to have fun with their child, to help everyone remember what matters.
Treatment
Family-based therapy (FBT) is the first-line treatment of shorter-duration AN in children and adolescents. It focuses on the parents, helping them to calmly and effectively manage their child’s eating behaviors until their weight and behaviors have normalized. As a patient’s nutritional status improves, so does cognitive function, emotional flexibility, and mood. Individual therapy and psychopharmacologic treatment can be very effective for comorbid anxiety, mood, attentional, and thought disorders. Family-based work does include the child and is often done in group-based settings with clinicians from multiple disciplines. Dietitians provide education and guidance about healthy nutrition to the child and parents. Therapists may work with the child, parents, or full family to focus on behavior modification and managing distress. Most academic medical centers provide access to FBT, but there are many regions with no providers of this evidence-based treatment. One of the silver linings of the COVID-19 pandemic is that several online services have emerged offering FBT, working with families to manage mealtimes and treatment entirely at home.3 Pediatricians provide regular medical checks to measure progress and help with decisions about when it is safe to permit exercise or advance privileges and independence around eating. Some pediatricians have discovered a deep interest in this area of pediatrics and built their practices on it. Given the surge in prevalence of AN and the needs for adolescent mental health services, we hope more will do so.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Taquet M et al. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220:262-4.
2. Morgan JF et al. West J Med. 2000 Mar;172(3):164-5.
3. Matheson BE et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2020 Jul;53(7):1142-54.
Eating disorders are among the most prevalent, disabling, and potentially fatal psychiatric illnesses, and the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated their burden, with a 15.3% increase in incidence in 2020 compared with previous years.1 This increase was almost solely among adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa (AN), which is often insidious in onset and more difficult to treat as it advances. Adolescents with AN are most likely to present to their pediatricians, so awareness and early recognition of the symptoms is critical. Pediatricians are also an integral part of the treatment team in AN and can offer monitoring for serious complications, alongside valuable guidance to parents, who are central to treatment and the reestablishment of healthy eating habits in their children. Here we will review the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of anorexia, with an emphasis on what pediatricians need to know to screen and to facilitate treatment.
Epidemiology
AN is marked by a fear of gaining weight or behaviors that interfere with weight gain and a self-evaluation unduly influenced by weight and body shape. Youth with AN often deny the seriousness of their malnutrition, although that is not required for diagnosis. AN can be of a restrictive or binge-purge subtype, and amenorrhea is no longer a requirement for diagnosis. There is not a specific weight or body mass index cutoff for the diagnosis, but the severity of AN is determined by the BMI percentile normed to age and sex. The average age of onset is 18, and the prepandemic prevalence of AN was about 1% of the population. It affects about 10 times as many females as males. It is quite rare prior to puberty, affecting about 0.01% of that age group. There is a heritable component, with a fivefold relative risk in youth with a parent with AN, and twin studies suggest heritability rates as high as 75%. Youth with rigid cognitive styles appear more vulnerable, as do those who participate in activities such as ballet, gymnastics, modeling, and wrestling because of the role of appearance and weight in performance. More than half of patients with AN will have another psychiatric illness, most commonly anxiety disorders, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. AN becomes chronic in up to 15% of sufferers and the mortality rate is close to 10%, with approximately half dying from medical complications and half dying by suicide.
Screening
Parents and pediatricians are usually the first to notice that a child has started to lose weight or is falling off the growth curve. But weight changes usually emerge after feelings of preoccupation with weight, body shape, and body satisfaction. If parents report escalating pickiness around food, increased or compulsive exercise, persistent self-consciousness and self-criticism around weight and body shape, it is worth starting with screening questions.
If you notice preoccupation or anxiety around being weighed, even if the weight or growth curve are still normal, it is worthwhile to screen. Screening questions, such as the SCOFF questionnaire with five simple questions, can be very sensitive for both AN and bulimia nervosa.2 There are also many validated screening instruments, such as the Eating Disorder Inventory or Eating Attitudes Test (for adolescents) and the Kids Eating Disorder Survey and the Child Eating Attitudes Test (for younger children), that are short self-reports that you can have your patients fill out when you have a higher index of suspicion. Weight loss or growth failure without a preoccupation around weight or appearance needs a thorough a medical workup, and could be a function of other psychiatric problems, such as depression.
If a child screens positive for an eating disorder, your full physical examination, growth curves, and longitudinal growth charts are critical for diagnosis. Percentile BMIs must be used, given the inaccuracy of standard BMI calculations in this age group. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age and sex growth charts include methods for this calculation). Laboratory assessment, including metabolic, kidney, pancreatic, and thyroid function, and an EKG can illuminate if there are consequences of restricting or purging. Of course, you want to evaluate for significant medical symptoms, including bradycardia, orthostasis, and hypokalemia. These medical symptoms are not limited to the severely underweight and merit referral to an emergency department and possible medical admission.
Then, a referral to a clinician who is expert in the assessment and treatment of eating disorders is needed. This may be a child psychiatrist, psychologist, or a colleague pediatrician with this specialization. It is also very important to begin the conversation with the family to introduce your concerns, describe what you have noticed, and discuss the need for further assessment and possibly treatment.
Be mindful that discussing this in front of your patient may heighten the patient’s anxiety or distress. Be prepared to offer support and understanding for your patient’s anxiety, while steadfastly providing absolute clarity for the parents about the necessity of further evaluation and treatment. Many parents will be concerned and ready to do whatever is needed to get their child’s eating and growth back on track. But some parents may have more difficulty. They may have their own history with an eating disorder. They may be avoiding a sense of shame or alarm. They may be eager to avoid adding to their child’s stress. They may be tired of engaging in power struggles with the child. They may be proud of their ambitious, accomplished young athlete. Their trust in you makes you uniquely positioned to complicate their thinking. And treatment will hinge on them, so this is a critical bridge to care.
Beyond telling parents that they will need to bring more structure and supervision to mealtimes to begin addressing their child’s nutrition, you might offer guidance on other strategies. Empower parents to limit their child’s use of social media sites such as Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok, where they may be immersed in comparing themselves to idealized (and airbrushed) influencers. Empower them to make their child’s participation in beloved sports contingent on eating meals together and completely or on a stabilized weight (as will be common in treatment). Remind them that there are no bad foods, that the goal is health, and that they are not in a power struggle with their child, but instead allied with their child to treat AN. Remind them to also look for chances to have fun with their child, to help everyone remember what matters.
Treatment
Family-based therapy (FBT) is the first-line treatment of shorter-duration AN in children and adolescents. It focuses on the parents, helping them to calmly and effectively manage their child’s eating behaviors until their weight and behaviors have normalized. As a patient’s nutritional status improves, so does cognitive function, emotional flexibility, and mood. Individual therapy and psychopharmacologic treatment can be very effective for comorbid anxiety, mood, attentional, and thought disorders. Family-based work does include the child and is often done in group-based settings with clinicians from multiple disciplines. Dietitians provide education and guidance about healthy nutrition to the child and parents. Therapists may work with the child, parents, or full family to focus on behavior modification and managing distress. Most academic medical centers provide access to FBT, but there are many regions with no providers of this evidence-based treatment. One of the silver linings of the COVID-19 pandemic is that several online services have emerged offering FBT, working with families to manage mealtimes and treatment entirely at home.3 Pediatricians provide regular medical checks to measure progress and help with decisions about when it is safe to permit exercise or advance privileges and independence around eating. Some pediatricians have discovered a deep interest in this area of pediatrics and built their practices on it. Given the surge in prevalence of AN and the needs for adolescent mental health services, we hope more will do so.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Taquet M et al. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220:262-4.
2. Morgan JF et al. West J Med. 2000 Mar;172(3):164-5.
3. Matheson BE et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2020 Jul;53(7):1142-54.
Eating disorders are among the most prevalent, disabling, and potentially fatal psychiatric illnesses, and the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated their burden, with a 15.3% increase in incidence in 2020 compared with previous years.1 This increase was almost solely among adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa (AN), which is often insidious in onset and more difficult to treat as it advances. Adolescents with AN are most likely to present to their pediatricians, so awareness and early recognition of the symptoms is critical. Pediatricians are also an integral part of the treatment team in AN and can offer monitoring for serious complications, alongside valuable guidance to parents, who are central to treatment and the reestablishment of healthy eating habits in their children. Here we will review the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of anorexia, with an emphasis on what pediatricians need to know to screen and to facilitate treatment.
Epidemiology
AN is marked by a fear of gaining weight or behaviors that interfere with weight gain and a self-evaluation unduly influenced by weight and body shape. Youth with AN often deny the seriousness of their malnutrition, although that is not required for diagnosis. AN can be of a restrictive or binge-purge subtype, and amenorrhea is no longer a requirement for diagnosis. There is not a specific weight or body mass index cutoff for the diagnosis, but the severity of AN is determined by the BMI percentile normed to age and sex. The average age of onset is 18, and the prepandemic prevalence of AN was about 1% of the population. It affects about 10 times as many females as males. It is quite rare prior to puberty, affecting about 0.01% of that age group. There is a heritable component, with a fivefold relative risk in youth with a parent with AN, and twin studies suggest heritability rates as high as 75%. Youth with rigid cognitive styles appear more vulnerable, as do those who participate in activities such as ballet, gymnastics, modeling, and wrestling because of the role of appearance and weight in performance. More than half of patients with AN will have another psychiatric illness, most commonly anxiety disorders, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. AN becomes chronic in up to 15% of sufferers and the mortality rate is close to 10%, with approximately half dying from medical complications and half dying by suicide.
Screening
Parents and pediatricians are usually the first to notice that a child has started to lose weight or is falling off the growth curve. But weight changes usually emerge after feelings of preoccupation with weight, body shape, and body satisfaction. If parents report escalating pickiness around food, increased or compulsive exercise, persistent self-consciousness and self-criticism around weight and body shape, it is worth starting with screening questions.
If you notice preoccupation or anxiety around being weighed, even if the weight or growth curve are still normal, it is worthwhile to screen. Screening questions, such as the SCOFF questionnaire with five simple questions, can be very sensitive for both AN and bulimia nervosa.2 There are also many validated screening instruments, such as the Eating Disorder Inventory or Eating Attitudes Test (for adolescents) and the Kids Eating Disorder Survey and the Child Eating Attitudes Test (for younger children), that are short self-reports that you can have your patients fill out when you have a higher index of suspicion. Weight loss or growth failure without a preoccupation around weight or appearance needs a thorough a medical workup, and could be a function of other psychiatric problems, such as depression.
If a child screens positive for an eating disorder, your full physical examination, growth curves, and longitudinal growth charts are critical for diagnosis. Percentile BMIs must be used, given the inaccuracy of standard BMI calculations in this age group. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age and sex growth charts include methods for this calculation). Laboratory assessment, including metabolic, kidney, pancreatic, and thyroid function, and an EKG can illuminate if there are consequences of restricting or purging. Of course, you want to evaluate for significant medical symptoms, including bradycardia, orthostasis, and hypokalemia. These medical symptoms are not limited to the severely underweight and merit referral to an emergency department and possible medical admission.
Then, a referral to a clinician who is expert in the assessment and treatment of eating disorders is needed. This may be a child psychiatrist, psychologist, or a colleague pediatrician with this specialization. It is also very important to begin the conversation with the family to introduce your concerns, describe what you have noticed, and discuss the need for further assessment and possibly treatment.
Be mindful that discussing this in front of your patient may heighten the patient’s anxiety or distress. Be prepared to offer support and understanding for your patient’s anxiety, while steadfastly providing absolute clarity for the parents about the necessity of further evaluation and treatment. Many parents will be concerned and ready to do whatever is needed to get their child’s eating and growth back on track. But some parents may have more difficulty. They may have their own history with an eating disorder. They may be avoiding a sense of shame or alarm. They may be eager to avoid adding to their child’s stress. They may be tired of engaging in power struggles with the child. They may be proud of their ambitious, accomplished young athlete. Their trust in you makes you uniquely positioned to complicate their thinking. And treatment will hinge on them, so this is a critical bridge to care.
Beyond telling parents that they will need to bring more structure and supervision to mealtimes to begin addressing their child’s nutrition, you might offer guidance on other strategies. Empower parents to limit their child’s use of social media sites such as Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok, where they may be immersed in comparing themselves to idealized (and airbrushed) influencers. Empower them to make their child’s participation in beloved sports contingent on eating meals together and completely or on a stabilized weight (as will be common in treatment). Remind them that there are no bad foods, that the goal is health, and that they are not in a power struggle with their child, but instead allied with their child to treat AN. Remind them to also look for chances to have fun with their child, to help everyone remember what matters.
Treatment
Family-based therapy (FBT) is the first-line treatment of shorter-duration AN in children and adolescents. It focuses on the parents, helping them to calmly and effectively manage their child’s eating behaviors until their weight and behaviors have normalized. As a patient’s nutritional status improves, so does cognitive function, emotional flexibility, and mood. Individual therapy and psychopharmacologic treatment can be very effective for comorbid anxiety, mood, attentional, and thought disorders. Family-based work does include the child and is often done in group-based settings with clinicians from multiple disciplines. Dietitians provide education and guidance about healthy nutrition to the child and parents. Therapists may work with the child, parents, or full family to focus on behavior modification and managing distress. Most academic medical centers provide access to FBT, but there are many regions with no providers of this evidence-based treatment. One of the silver linings of the COVID-19 pandemic is that several online services have emerged offering FBT, working with families to manage mealtimes and treatment entirely at home.3 Pediatricians provide regular medical checks to measure progress and help with decisions about when it is safe to permit exercise or advance privileges and independence around eating. Some pediatricians have discovered a deep interest in this area of pediatrics and built their practices on it. Given the surge in prevalence of AN and the needs for adolescent mental health services, we hope more will do so.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Taquet M et al. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220:262-4.
2. Morgan JF et al. West J Med. 2000 Mar;172(3):164-5.
3. Matheson BE et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2020 Jul;53(7):1142-54.
When coping skills and parenting behavioral interventions ‘don’t work’
You have an appointment with a 14-year-old youth you last saw for an annual camp physical. He had screened positive for depression, and you had referred him to a local therapist. He did not have an appointment until after camp, and you have only met a few times, but since you had spoken with him about his depression, he set up an appointment with you to ask about medications. When you meet him you ask about what he had been doing in therapy and he says, “I’m learning ‘coping skills,’ but they don’t work.”
From breathing exercises and sticker charts to mindfulness and grounding exercise, coping skills can be crucial for learning how to manage distress, regulate emotions, become more effective interpersonally, and function better. Similarly, parenting interventions, which change the way parents and youth interact, are a central family intervention for behavioral problems in youth.
It is very common, however, to hear that they “don’t work” or have a parent say, “We tried that, it doesn’t work.”
When kids and parents reject coping skills and behavioral interventions by saying they do not work, the consequences can be substantial. It can mean the rejection of coping skills and strategies that actually would have helped, given time and support; that kids and families bounce between services with increasing frustration; that they search for a magic bullet (which also won’t work); and, particularly concerning for physicians, a belief that the youth have not received the right medication, resulting in potentially unhelpful concoctions of medication.
One of the biggest challenges in helping youth and parents overcome their difficulties – whether these difficulties are depression and anxiety or being better parents to struggling kids – is helping them understand that despite the fact that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not seem to work, they work.
We just have to do a better job explaining what that “work” is.
There are five points you can make.
- First, the coping skill or behavioral intervention is not supposed to work if that means solving the underlying problem. Coping skills and behavioral interventions do not immediately cure anxiety, mend broken hearts, correct disruptive behaviors, disentangle power struggles, or alleviate depression. That is not what their job is. Coping skills and behavioral interventions are there to help us get better at handling complex situations and feelings. In particular, they are good at helping us manage our thoughts (“I can’t do it,” “He should behave better”) and our affect (anger, frustration, rage, anxiety, sadness), so that over time we get better at solving the problems, and break out of the patterns that perpetuate these problems.
- Second, kids and parents do not give skills credit for when they do work. That time you were spiraling out of control and told your mom you needed a break and watched some YouTube videos and then joined the family for dinner? Your coping skills worked, but nobody noticed because they worked. We need to help our young patients and families identify those times that coping skills and behavioral interventions worked.
- Third, let’s face it: Nothing works all the time. It is no wonder kids and families are disappointed by coping skills and behavioral interventions if they think they magically work once and forever. We need to manage expectations.
- Fourth, we know they are supposed to fail, and we should discuss this openly up front. This may sound surprising, but challenging behaviors often get worse when we begin to work on them. “Extinction bursts” is probably the easiest explanation, but for psychodynamically oriented youth and families we could talk about “resistance.” No matter what, things tend to get worse before they get better. We should let people know this ahead of time.
- Fifth, and this is the one that forces youth and parents to ask how hard they actually tried, these skills need to be practiced. You can’t be in the middle of a panic attack and for the first time start trying to pace your breathing with a technique a therapist told you about 3 weeks ago. This makes about as much sense as not training for a marathon. You need to practice and build up the skills, recognizing that as you become more familiar with them, they will help you manage during stressful situations. Every skill should be practiced, preferably several times or more in sessions, maybe every session, and definitely outside of sessions when not in distress.
We cannot blame children and parents for thinking that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not work. They are struggling, suffering, fighting, frightened, angry, anxious, frustrated, and often desperate for something to make everything better. Helping them recognize this desire for things to be better while managing expectations is an essential complement to supporting the use of coping skills and behavioral interventions, and a fairly easy conversation to have with youth.
So when you are talking about coping skills and parental behavioral interventions, it is important to be prepared for the “it didn’t work” conversation, and even to address these issues up front. After all, these strategies may not solve all the problems in the world, but can be lifelong ways of coping with life’s challenges.
Dr. Henderson is associate professor of clinical psychiatry at New York University and deputy director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
You have an appointment with a 14-year-old youth you last saw for an annual camp physical. He had screened positive for depression, and you had referred him to a local therapist. He did not have an appointment until after camp, and you have only met a few times, but since you had spoken with him about his depression, he set up an appointment with you to ask about medications. When you meet him you ask about what he had been doing in therapy and he says, “I’m learning ‘coping skills,’ but they don’t work.”
From breathing exercises and sticker charts to mindfulness and grounding exercise, coping skills can be crucial for learning how to manage distress, regulate emotions, become more effective interpersonally, and function better. Similarly, parenting interventions, which change the way parents and youth interact, are a central family intervention for behavioral problems in youth.
It is very common, however, to hear that they “don’t work” or have a parent say, “We tried that, it doesn’t work.”
When kids and parents reject coping skills and behavioral interventions by saying they do not work, the consequences can be substantial. It can mean the rejection of coping skills and strategies that actually would have helped, given time and support; that kids and families bounce between services with increasing frustration; that they search for a magic bullet (which also won’t work); and, particularly concerning for physicians, a belief that the youth have not received the right medication, resulting in potentially unhelpful concoctions of medication.
One of the biggest challenges in helping youth and parents overcome their difficulties – whether these difficulties are depression and anxiety or being better parents to struggling kids – is helping them understand that despite the fact that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not seem to work, they work.
We just have to do a better job explaining what that “work” is.
There are five points you can make.
- First, the coping skill or behavioral intervention is not supposed to work if that means solving the underlying problem. Coping skills and behavioral interventions do not immediately cure anxiety, mend broken hearts, correct disruptive behaviors, disentangle power struggles, or alleviate depression. That is not what their job is. Coping skills and behavioral interventions are there to help us get better at handling complex situations and feelings. In particular, they are good at helping us manage our thoughts (“I can’t do it,” “He should behave better”) and our affect (anger, frustration, rage, anxiety, sadness), so that over time we get better at solving the problems, and break out of the patterns that perpetuate these problems.
- Second, kids and parents do not give skills credit for when they do work. That time you were spiraling out of control and told your mom you needed a break and watched some YouTube videos and then joined the family for dinner? Your coping skills worked, but nobody noticed because they worked. We need to help our young patients and families identify those times that coping skills and behavioral interventions worked.
- Third, let’s face it: Nothing works all the time. It is no wonder kids and families are disappointed by coping skills and behavioral interventions if they think they magically work once and forever. We need to manage expectations.
- Fourth, we know they are supposed to fail, and we should discuss this openly up front. This may sound surprising, but challenging behaviors often get worse when we begin to work on them. “Extinction bursts” is probably the easiest explanation, but for psychodynamically oriented youth and families we could talk about “resistance.” No matter what, things tend to get worse before they get better. We should let people know this ahead of time.
- Fifth, and this is the one that forces youth and parents to ask how hard they actually tried, these skills need to be practiced. You can’t be in the middle of a panic attack and for the first time start trying to pace your breathing with a technique a therapist told you about 3 weeks ago. This makes about as much sense as not training for a marathon. You need to practice and build up the skills, recognizing that as you become more familiar with them, they will help you manage during stressful situations. Every skill should be practiced, preferably several times or more in sessions, maybe every session, and definitely outside of sessions when not in distress.
We cannot blame children and parents for thinking that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not work. They are struggling, suffering, fighting, frightened, angry, anxious, frustrated, and often desperate for something to make everything better. Helping them recognize this desire for things to be better while managing expectations is an essential complement to supporting the use of coping skills and behavioral interventions, and a fairly easy conversation to have with youth.
So when you are talking about coping skills and parental behavioral interventions, it is important to be prepared for the “it didn’t work” conversation, and even to address these issues up front. After all, these strategies may not solve all the problems in the world, but can be lifelong ways of coping with life’s challenges.
Dr. Henderson is associate professor of clinical psychiatry at New York University and deputy director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
You have an appointment with a 14-year-old youth you last saw for an annual camp physical. He had screened positive for depression, and you had referred him to a local therapist. He did not have an appointment until after camp, and you have only met a few times, but since you had spoken with him about his depression, he set up an appointment with you to ask about medications. When you meet him you ask about what he had been doing in therapy and he says, “I’m learning ‘coping skills,’ but they don’t work.”
From breathing exercises and sticker charts to mindfulness and grounding exercise, coping skills can be crucial for learning how to manage distress, regulate emotions, become more effective interpersonally, and function better. Similarly, parenting interventions, which change the way parents and youth interact, are a central family intervention for behavioral problems in youth.
It is very common, however, to hear that they “don’t work” or have a parent say, “We tried that, it doesn’t work.”
When kids and parents reject coping skills and behavioral interventions by saying they do not work, the consequences can be substantial. It can mean the rejection of coping skills and strategies that actually would have helped, given time and support; that kids and families bounce between services with increasing frustration; that they search for a magic bullet (which also won’t work); and, particularly concerning for physicians, a belief that the youth have not received the right medication, resulting in potentially unhelpful concoctions of medication.
One of the biggest challenges in helping youth and parents overcome their difficulties – whether these difficulties are depression and anxiety or being better parents to struggling kids – is helping them understand that despite the fact that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not seem to work, they work.
We just have to do a better job explaining what that “work” is.
There are five points you can make.
- First, the coping skill or behavioral intervention is not supposed to work if that means solving the underlying problem. Coping skills and behavioral interventions do not immediately cure anxiety, mend broken hearts, correct disruptive behaviors, disentangle power struggles, or alleviate depression. That is not what their job is. Coping skills and behavioral interventions are there to help us get better at handling complex situations and feelings. In particular, they are good at helping us manage our thoughts (“I can’t do it,” “He should behave better”) and our affect (anger, frustration, rage, anxiety, sadness), so that over time we get better at solving the problems, and break out of the patterns that perpetuate these problems.
- Second, kids and parents do not give skills credit for when they do work. That time you were spiraling out of control and told your mom you needed a break and watched some YouTube videos and then joined the family for dinner? Your coping skills worked, but nobody noticed because they worked. We need to help our young patients and families identify those times that coping skills and behavioral interventions worked.
- Third, let’s face it: Nothing works all the time. It is no wonder kids and families are disappointed by coping skills and behavioral interventions if they think they magically work once and forever. We need to manage expectations.
- Fourth, we know they are supposed to fail, and we should discuss this openly up front. This may sound surprising, but challenging behaviors often get worse when we begin to work on them. “Extinction bursts” is probably the easiest explanation, but for psychodynamically oriented youth and families we could talk about “resistance.” No matter what, things tend to get worse before they get better. We should let people know this ahead of time.
- Fifth, and this is the one that forces youth and parents to ask how hard they actually tried, these skills need to be practiced. You can’t be in the middle of a panic attack and for the first time start trying to pace your breathing with a technique a therapist told you about 3 weeks ago. This makes about as much sense as not training for a marathon. You need to practice and build up the skills, recognizing that as you become more familiar with them, they will help you manage during stressful situations. Every skill should be practiced, preferably several times or more in sessions, maybe every session, and definitely outside of sessions when not in distress.
We cannot blame children and parents for thinking that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not work. They are struggling, suffering, fighting, frightened, angry, anxious, frustrated, and often desperate for something to make everything better. Helping them recognize this desire for things to be better while managing expectations is an essential complement to supporting the use of coping skills and behavioral interventions, and a fairly easy conversation to have with youth.
So when you are talking about coping skills and parental behavioral interventions, it is important to be prepared for the “it didn’t work” conversation, and even to address these issues up front. After all, these strategies may not solve all the problems in the world, but can be lifelong ways of coping with life’s challenges.
Dr. Henderson is associate professor of clinical psychiatry at New York University and deputy director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
Tactile stimulation for inadequate neonatal respiration at birth
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Dodging potholes from cancer care to hospice transitions
I’m often in the position of caring for patients after they’ve stopped active cancer treatments, but before they’ve made the decision to enroll in hospice. They remain under my care until they feel emotionally ready, or until their care needs have escalated to the point in which hospice is unavoidable.
Jenny, a mom in her 50s with metastatic pancreatic cancer, stopped coming to the clinic. She lived about 40 minutes away from the clinic and was no longer receiving treatment. The car rides were painful and difficult for her. I held weekly video visits with her for 2 months before she eventually went to hospice and passed away. Before she died, she shared with me her sadness that her oncologist – who had taken care of her for 3 years – had “washed his hands of [me].” She rarely heard from him after their final conversation in the clinic when he informed her that she was no longer a candidate for further therapy. The sense of abandonment Jenny described was visceral and devastating. With her permission, I let her oncology team know how she felt and they reached out to her just 1 week before her death. After she died, her husband told me how meaningful it had been for the whole family to hear from Jenny’s oncologist who told them that she had done everything possible to fight her cancer and that “no stone was left unturned.” Her husband felt this final conversation provided Jenny with the closure she needed to pass away peacefully.
Transitioning from active therapy to symptom management
Switching gears from an all-out pursuit of active therapy to focusing on cancer symptoms is often a scary transition for patients and their families. The transition is often viewed as a movement away from hope and optimism to “giving up the fight.” Whether you agree with the warrior language or not, many patients still describe their journey in these terms and thus, experience enrollment in hospice as a sense of having failed.
The sense of failure can be compounded by feelings of abandonment by oncology providers when they are referred without much guidance or continuity through the hospice enrollment process. Unfortunately, the consequences of suboptimal hospice transitions can be damaging, especially for the mental health and well-being of the patient and their surviving loved ones.
When managed poorly, hospice transitions can easily lead to patient and family harm, which is a claim supported by research. A qualitative study published in 2019 included 92 caregivers of patients with terminal cancer. The authors found three common pathways for end-of-life transitions – a frictionless transition in which the patient and family are well prepared in advance by their oncologist; a more turbulent transition in which patient and family had direct conversations with their oncologist about the incurability of the disease and the lack of efficacy of further treatments, but were given no guidance on prognosis; and a third type of transition marked by abrupt shifts toward end-of-life care occurring in extremis and typically in the hospital.
In the latter two groups, caregivers felt their loved ones died very quickly after stopping treatment, taking them by surprise and leaving them rushing to put end-of-life care plans in place without much support from their oncologists. In the last group, caregivers shared they received their first prognostic information from the hospital or ICU doctor caring for their actively dying loved one, leaving them with a sense of anger and betrayal toward their oncologist for allowing them to be so ill-prepared.
A Japanese survey published in 2018 in The Oncologist of families of cancer patients who had passed away under hospice care over a 2-year period (2012-2014), found that about one-quarter felt abandoned by oncologists. Several factors that were associated with feeling either more or less abandonment. Spouses of patients, patients aged less than 60 years, and patients whose oncologists informed them that there was “nothing more to do” felt more abandoned by oncologists; whereas families for whom the oncologist provided reassurance about the trajectory of care, recommended hospice, and engaged with a palliative care team felt less abandoned by oncologists. Families who felt more abandoned had higher levels of depression and grief when measured with standardized instruments.
‘Don’t just put in the hospice order and walk away’
Fortunately, there are a few low-resource interventions that can improve the quality of care-to-hospice transitions and prevent the sense of abandonment felt by many patients and families.
First, don’t just put in the hospice order and walk away. Designate a staffer in your office to contact hospice directly, ensure all medical records are faxed and received, and update the patient and family on this progress throughout the transition. Taking care of details like these ensures the patient enrolls in hospice in a timely manner and reduces the chance the patient, who is likely to be quite sick at this point, will end up in the hospital despite your best efforts to get hospice involved.
Make sure the patient and family understand that you are still their oncologist and still available to them. If they want to continue care with you, have them name you as the “non–hospice-attending physician” so that you can continue to bill for telemedicine and office visits using the terminal diagnosis (with a billing modifier). This does not mean that you will be expected to manage the patient’s hospice problem list or respond to hospice nurse calls at 2 a.m. – the hospice doctor will still do this. It just ensures that patients do not receive a bill if you continue to see them.
If ongoing office or video visits are too much for the patient and family, consider assigning a member of your team to call the patient and family on a weekly basis to check in and offer support. A small 2018 pilot study aimed at improving communication found that when caregivers of advanced cancer patients transitioning to hospice received weekly supportive phone calls by a member of their oncology team (typically a nurse or nurse practitioner), they felt emotionally supported, had good continuity of care throughout the hospice enrollment, and appreciated the ability to have closure with their oncology team. In other words, a sense of abandonment was prevented and the patient-provider relationship was actually deepened through the transition.
These suggestions are not rocket science – they are simple, obvious ways to try to restore patient-centeredness to a transition that for providers can seem routine, but for patients and families is often the first time they have confronted the reality that death is approaching. That reality is terrifying and overwhelming. Patients and caregivers need our support more during hospice transitions than at any other point during their cancer journey – except perhaps at diagnosis.
As with Jenny, my patient who felt abandoned, all it took was a single call by her oncology team to restore the trust and heal the sense of feeling forsaken by the people who cared for her for years. Sometimes, even just one more phone call can feel like a lot to a chronically overburdened provider – but what a difference a simple call can make.
Ms. D’Ambruoso is a hospice and palliative care nurse practitioner for UCLA Health Cancer Care, Santa Monica, Calif.
I’m often in the position of caring for patients after they’ve stopped active cancer treatments, but before they’ve made the decision to enroll in hospice. They remain under my care until they feel emotionally ready, or until their care needs have escalated to the point in which hospice is unavoidable.
Jenny, a mom in her 50s with metastatic pancreatic cancer, stopped coming to the clinic. She lived about 40 minutes away from the clinic and was no longer receiving treatment. The car rides were painful and difficult for her. I held weekly video visits with her for 2 months before she eventually went to hospice and passed away. Before she died, she shared with me her sadness that her oncologist – who had taken care of her for 3 years – had “washed his hands of [me].” She rarely heard from him after their final conversation in the clinic when he informed her that she was no longer a candidate for further therapy. The sense of abandonment Jenny described was visceral and devastating. With her permission, I let her oncology team know how she felt and they reached out to her just 1 week before her death. After she died, her husband told me how meaningful it had been for the whole family to hear from Jenny’s oncologist who told them that she had done everything possible to fight her cancer and that “no stone was left unturned.” Her husband felt this final conversation provided Jenny with the closure she needed to pass away peacefully.
Transitioning from active therapy to symptom management
Switching gears from an all-out pursuit of active therapy to focusing on cancer symptoms is often a scary transition for patients and their families. The transition is often viewed as a movement away from hope and optimism to “giving up the fight.” Whether you agree with the warrior language or not, many patients still describe their journey in these terms and thus, experience enrollment in hospice as a sense of having failed.
The sense of failure can be compounded by feelings of abandonment by oncology providers when they are referred without much guidance or continuity through the hospice enrollment process. Unfortunately, the consequences of suboptimal hospice transitions can be damaging, especially for the mental health and well-being of the patient and their surviving loved ones.
When managed poorly, hospice transitions can easily lead to patient and family harm, which is a claim supported by research. A qualitative study published in 2019 included 92 caregivers of patients with terminal cancer. The authors found three common pathways for end-of-life transitions – a frictionless transition in which the patient and family are well prepared in advance by their oncologist; a more turbulent transition in which patient and family had direct conversations with their oncologist about the incurability of the disease and the lack of efficacy of further treatments, but were given no guidance on prognosis; and a third type of transition marked by abrupt shifts toward end-of-life care occurring in extremis and typically in the hospital.
In the latter two groups, caregivers felt their loved ones died very quickly after stopping treatment, taking them by surprise and leaving them rushing to put end-of-life care plans in place without much support from their oncologists. In the last group, caregivers shared they received their first prognostic information from the hospital or ICU doctor caring for their actively dying loved one, leaving them with a sense of anger and betrayal toward their oncologist for allowing them to be so ill-prepared.
A Japanese survey published in 2018 in The Oncologist of families of cancer patients who had passed away under hospice care over a 2-year period (2012-2014), found that about one-quarter felt abandoned by oncologists. Several factors that were associated with feeling either more or less abandonment. Spouses of patients, patients aged less than 60 years, and patients whose oncologists informed them that there was “nothing more to do” felt more abandoned by oncologists; whereas families for whom the oncologist provided reassurance about the trajectory of care, recommended hospice, and engaged with a palliative care team felt less abandoned by oncologists. Families who felt more abandoned had higher levels of depression and grief when measured with standardized instruments.
‘Don’t just put in the hospice order and walk away’
Fortunately, there are a few low-resource interventions that can improve the quality of care-to-hospice transitions and prevent the sense of abandonment felt by many patients and families.
First, don’t just put in the hospice order and walk away. Designate a staffer in your office to contact hospice directly, ensure all medical records are faxed and received, and update the patient and family on this progress throughout the transition. Taking care of details like these ensures the patient enrolls in hospice in a timely manner and reduces the chance the patient, who is likely to be quite sick at this point, will end up in the hospital despite your best efforts to get hospice involved.
Make sure the patient and family understand that you are still their oncologist and still available to them. If they want to continue care with you, have them name you as the “non–hospice-attending physician” so that you can continue to bill for telemedicine and office visits using the terminal diagnosis (with a billing modifier). This does not mean that you will be expected to manage the patient’s hospice problem list or respond to hospice nurse calls at 2 a.m. – the hospice doctor will still do this. It just ensures that patients do not receive a bill if you continue to see them.
If ongoing office or video visits are too much for the patient and family, consider assigning a member of your team to call the patient and family on a weekly basis to check in and offer support. A small 2018 pilot study aimed at improving communication found that when caregivers of advanced cancer patients transitioning to hospice received weekly supportive phone calls by a member of their oncology team (typically a nurse or nurse practitioner), they felt emotionally supported, had good continuity of care throughout the hospice enrollment, and appreciated the ability to have closure with their oncology team. In other words, a sense of abandonment was prevented and the patient-provider relationship was actually deepened through the transition.
These suggestions are not rocket science – they are simple, obvious ways to try to restore patient-centeredness to a transition that for providers can seem routine, but for patients and families is often the first time they have confronted the reality that death is approaching. That reality is terrifying and overwhelming. Patients and caregivers need our support more during hospice transitions than at any other point during their cancer journey – except perhaps at diagnosis.
As with Jenny, my patient who felt abandoned, all it took was a single call by her oncology team to restore the trust and heal the sense of feeling forsaken by the people who cared for her for years. Sometimes, even just one more phone call can feel like a lot to a chronically overburdened provider – but what a difference a simple call can make.
Ms. D’Ambruoso is a hospice and palliative care nurse practitioner for UCLA Health Cancer Care, Santa Monica, Calif.
I’m often in the position of caring for patients after they’ve stopped active cancer treatments, but before they’ve made the decision to enroll in hospice. They remain under my care until they feel emotionally ready, or until their care needs have escalated to the point in which hospice is unavoidable.
Jenny, a mom in her 50s with metastatic pancreatic cancer, stopped coming to the clinic. She lived about 40 minutes away from the clinic and was no longer receiving treatment. The car rides were painful and difficult for her. I held weekly video visits with her for 2 months before she eventually went to hospice and passed away. Before she died, she shared with me her sadness that her oncologist – who had taken care of her for 3 years – had “washed his hands of [me].” She rarely heard from him after their final conversation in the clinic when he informed her that she was no longer a candidate for further therapy. The sense of abandonment Jenny described was visceral and devastating. With her permission, I let her oncology team know how she felt and they reached out to her just 1 week before her death. After she died, her husband told me how meaningful it had been for the whole family to hear from Jenny’s oncologist who told them that she had done everything possible to fight her cancer and that “no stone was left unturned.” Her husband felt this final conversation provided Jenny with the closure she needed to pass away peacefully.
Transitioning from active therapy to symptom management
Switching gears from an all-out pursuit of active therapy to focusing on cancer symptoms is often a scary transition for patients and their families. The transition is often viewed as a movement away from hope and optimism to “giving up the fight.” Whether you agree with the warrior language or not, many patients still describe their journey in these terms and thus, experience enrollment in hospice as a sense of having failed.
The sense of failure can be compounded by feelings of abandonment by oncology providers when they are referred without much guidance or continuity through the hospice enrollment process. Unfortunately, the consequences of suboptimal hospice transitions can be damaging, especially for the mental health and well-being of the patient and their surviving loved ones.
When managed poorly, hospice transitions can easily lead to patient and family harm, which is a claim supported by research. A qualitative study published in 2019 included 92 caregivers of patients with terminal cancer. The authors found three common pathways for end-of-life transitions – a frictionless transition in which the patient and family are well prepared in advance by their oncologist; a more turbulent transition in which patient and family had direct conversations with their oncologist about the incurability of the disease and the lack of efficacy of further treatments, but were given no guidance on prognosis; and a third type of transition marked by abrupt shifts toward end-of-life care occurring in extremis and typically in the hospital.
In the latter two groups, caregivers felt their loved ones died very quickly after stopping treatment, taking them by surprise and leaving them rushing to put end-of-life care plans in place without much support from their oncologists. In the last group, caregivers shared they received their first prognostic information from the hospital or ICU doctor caring for their actively dying loved one, leaving them with a sense of anger and betrayal toward their oncologist for allowing them to be so ill-prepared.
A Japanese survey published in 2018 in The Oncologist of families of cancer patients who had passed away under hospice care over a 2-year period (2012-2014), found that about one-quarter felt abandoned by oncologists. Several factors that were associated with feeling either more or less abandonment. Spouses of patients, patients aged less than 60 years, and patients whose oncologists informed them that there was “nothing more to do” felt more abandoned by oncologists; whereas families for whom the oncologist provided reassurance about the trajectory of care, recommended hospice, and engaged with a palliative care team felt less abandoned by oncologists. Families who felt more abandoned had higher levels of depression and grief when measured with standardized instruments.
‘Don’t just put in the hospice order and walk away’
Fortunately, there are a few low-resource interventions that can improve the quality of care-to-hospice transitions and prevent the sense of abandonment felt by many patients and families.
First, don’t just put in the hospice order and walk away. Designate a staffer in your office to contact hospice directly, ensure all medical records are faxed and received, and update the patient and family on this progress throughout the transition. Taking care of details like these ensures the patient enrolls in hospice in a timely manner and reduces the chance the patient, who is likely to be quite sick at this point, will end up in the hospital despite your best efforts to get hospice involved.
Make sure the patient and family understand that you are still their oncologist and still available to them. If they want to continue care with you, have them name you as the “non–hospice-attending physician” so that you can continue to bill for telemedicine and office visits using the terminal diagnosis (with a billing modifier). This does not mean that you will be expected to manage the patient’s hospice problem list or respond to hospice nurse calls at 2 a.m. – the hospice doctor will still do this. It just ensures that patients do not receive a bill if you continue to see them.
If ongoing office or video visits are too much for the patient and family, consider assigning a member of your team to call the patient and family on a weekly basis to check in and offer support. A small 2018 pilot study aimed at improving communication found that when caregivers of advanced cancer patients transitioning to hospice received weekly supportive phone calls by a member of their oncology team (typically a nurse or nurse practitioner), they felt emotionally supported, had good continuity of care throughout the hospice enrollment, and appreciated the ability to have closure with their oncology team. In other words, a sense of abandonment was prevented and the patient-provider relationship was actually deepened through the transition.
These suggestions are not rocket science – they are simple, obvious ways to try to restore patient-centeredness to a transition that for providers can seem routine, but for patients and families is often the first time they have confronted the reality that death is approaching. That reality is terrifying and overwhelming. Patients and caregivers need our support more during hospice transitions than at any other point during their cancer journey – except perhaps at diagnosis.
As with Jenny, my patient who felt abandoned, all it took was a single call by her oncology team to restore the trust and heal the sense of feeling forsaken by the people who cared for her for years. Sometimes, even just one more phone call can feel like a lot to a chronically overburdened provider – but what a difference a simple call can make.
Ms. D’Ambruoso is a hospice and palliative care nurse practitioner for UCLA Health Cancer Care, Santa Monica, Calif.
Could a common cold virus be causing severe hepatitis in kids?
This is a transcript of a video that first appeared on Medscape.com. It has been edited for clarity.
On April 21, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a Health Alert Network advisory regarding a cluster of nine cases of acute hepatitis in children in Alabama over a 5-month period from October 2021 to February 2022 – a rate substantially higher than what would be expected, given the relative rarity of hepatitis in children.
Standard workup was negative for the common causative agents – hepatitis A, B, and C – and no toxic exposures were identified. But there was one common thread among all these kids: They all tested positive for adenovirus.
And that is really strange.
There are about 100 circulating adenoviruses in the world that we know of, and around 50 of them infect humans. If you are an adult, it’s a virtual certainty that you have been infected with an adenovirus in the past. Most strains cause symptoms we would describe as the common cold: runny nose, sore throat. Some strains cause conjunctivitis (pink eye). Some cause gastrointestinal illness – the stomach bugs that kids get.
It’s the banality of adenovirus that makes this hepatitis finding so surprising.
The United States is not alone in reporting this new hepatitis syndrome. As of April 21, 169 cases have been reported across the world, including 114 in the United Kingdom.
Of the 169 cases reported worldwide, 74 had evidence of adenovirus infection. On molecular testing, 18 of those were adenovirus 41.
What I wanted to do today was go through the various hypotheses for what could be going on with these hepatitis cases, one by one, and highlight the evidence supporting them. We won’t reach a conclusion, but hopefully by the end, the path forward will be more clear. OK, let’s get started.
Hypothesis 1: Nothing is happening.
It’s worth noting that “clusters” of disease occur all the time, even when no relevant epidemiologic process has occurred. If there is some baseline rate of hepatitis, every once in a while, through bad luck alone, you’d see a group of cases all at once. This is known as the clustering illusion. And I’m quite confident in saying that this is not the case here.
For one, this phenomenon is worldwide, as we know from the World Health Organization report. In fact, the CDC didn’t provide the most detailed data about the nine (now 12) cases in the United States. This study from Scotland is the first to give a detailed accounting of cases, reporting on 13 cases of acute hepatitis of unknown cause in kids at a single hospital from January to April. Typically, the hospital sees fewer than four cases of hepatitis per year. Five of these 13 kids tested positive for adenovirus. So let’s take the clustering illusion off the list.
Hypothesis 2: It’s adenovirus.
The major evidence supporting adenovirus as the causative agent here is that a lot of these kids had adenovirus, and adenovirus 41 – a gut-tropic strain – in particular. This is important, because stool testing might be necessary for diagnosis and lots of kids with this condition didn’t get that. In other words, we have hard evidence of adenovirus infection in about 40% of the cases so far, but the true number might be substantially higher.
That said, adenovirus is seasonal, and we are in adenovirus season. Granted, 40% seems quite a bit higher than the background infection rate, but we have to be careful not to assume that correlation means causation.
The evidence against adenovirus, even adenovirus 41, is that this acute hepatitis syndrome is new, and adenovirus 41 is not. To be fair, we know adenoviruses can cause acute hepatitis, but the vast majority of reports are in immunocompromised individuals – organ transplant recipients and those with HIV. I was able to find just a handful of cases of immunocompetent kids developing hepatitis from adenovirus prior to this current outbreak.
The current outbreak would exceed the published literature by nearly two orders of magnitude. It feels like something else has to be going on.
Hypothesis 3: It’s coronavirus.
SARS-CoV-2 is a strange virus, both in its acute presentation and its long-term outcomes. It was clear early in the pandemic that some children infected by the coronavirus would develop MIS-C – multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. MIS-C is associated with hepatitis in about 10% of children, according to this New England Journal of Medicine
But the presentation of these kids is quite different from MIS-C; fever is rare, for example. The WHO reports that of the 169 identified cases so far, 20 had active COVID infection. The Scotland cohort suggests that a similar proportion had past COVID infections. In other times, we might consider this a smoking gun, but at this point a history of COVID is not remarkable – after the Omicron wave, it’s about as common to have a history of COVID as it is not to have a history of COVID.
A brief aside here. This is not because of coronavirus vaccination. Of the more than 100 cases reported in the United Kingdom, none of these kids were vaccinated. So let’s put aside the possibility that this is a vaccine effect – there’s no real evidence to support that.
Which brings us to …
Hypothesis 4: It’s coronavirus and adenovirus.
This is sort of intriguing and can work a few different ways, via a direct and indirect path.
In the direct path, we posit that COVID infection does something to kids’ immune systems – something we don’t yet understand that limits their ability to fight off adenovirus. There is some support for this idea. This study in Immunity found that COVID infection can functionally impair dendritic cells and T-cells, including natural killer cells. These cells are important components of our innate antiviral immunity.
There’s an indirect path as well. COVID has led to lockdowns, distancing, masking – stuff that prevents kids from being exposed to germs from other kids. Could a lack of exposure to adenovirus or other viruses because of distancing increase the risk for severe disease when restrictions are lifted? Also possible – the severity of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections this year is substantially higher than what we’ve seen in the past, for example.
And finally, hypothesis 5: This is something new.
We can’t ignore the possibility that this is simply a new disease-causing agent. Toxicology studies so far have been negative, and we wouldn’t expect hepatitis from a chemical toxin to appear in multiple countries around the world; this is almost certainly a biological phenomenon. It is possible that this is a new strain of adenovirus 41, or that adenovirus is a red herring altogether. Remember, we knew about “non-A/non-B viral hepatitis” for more than 2 decades before hepatitis C was discovered.
The pace of science is faster now, fortunately, and information is coming out quickly. As we learn more, we’ll share it with you.
Dr. Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and hosts a repository of his communication work at www.methodsman.com. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This is a transcript of a video that first appeared on Medscape.com. It has been edited for clarity.
On April 21, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a Health Alert Network advisory regarding a cluster of nine cases of acute hepatitis in children in Alabama over a 5-month period from October 2021 to February 2022 – a rate substantially higher than what would be expected, given the relative rarity of hepatitis in children.
Standard workup was negative for the common causative agents – hepatitis A, B, and C – and no toxic exposures were identified. But there was one common thread among all these kids: They all tested positive for adenovirus.
And that is really strange.
There are about 100 circulating adenoviruses in the world that we know of, and around 50 of them infect humans. If you are an adult, it’s a virtual certainty that you have been infected with an adenovirus in the past. Most strains cause symptoms we would describe as the common cold: runny nose, sore throat. Some strains cause conjunctivitis (pink eye). Some cause gastrointestinal illness – the stomach bugs that kids get.
It’s the banality of adenovirus that makes this hepatitis finding so surprising.
The United States is not alone in reporting this new hepatitis syndrome. As of April 21, 169 cases have been reported across the world, including 114 in the United Kingdom.
Of the 169 cases reported worldwide, 74 had evidence of adenovirus infection. On molecular testing, 18 of those were adenovirus 41.
What I wanted to do today was go through the various hypotheses for what could be going on with these hepatitis cases, one by one, and highlight the evidence supporting them. We won’t reach a conclusion, but hopefully by the end, the path forward will be more clear. OK, let’s get started.
Hypothesis 1: Nothing is happening.
It’s worth noting that “clusters” of disease occur all the time, even when no relevant epidemiologic process has occurred. If there is some baseline rate of hepatitis, every once in a while, through bad luck alone, you’d see a group of cases all at once. This is known as the clustering illusion. And I’m quite confident in saying that this is not the case here.
For one, this phenomenon is worldwide, as we know from the World Health Organization report. In fact, the CDC didn’t provide the most detailed data about the nine (now 12) cases in the United States. This study from Scotland is the first to give a detailed accounting of cases, reporting on 13 cases of acute hepatitis of unknown cause in kids at a single hospital from January to April. Typically, the hospital sees fewer than four cases of hepatitis per year. Five of these 13 kids tested positive for adenovirus. So let’s take the clustering illusion off the list.
Hypothesis 2: It’s adenovirus.
The major evidence supporting adenovirus as the causative agent here is that a lot of these kids had adenovirus, and adenovirus 41 – a gut-tropic strain – in particular. This is important, because stool testing might be necessary for diagnosis and lots of kids with this condition didn’t get that. In other words, we have hard evidence of adenovirus infection in about 40% of the cases so far, but the true number might be substantially higher.
That said, adenovirus is seasonal, and we are in adenovirus season. Granted, 40% seems quite a bit higher than the background infection rate, but we have to be careful not to assume that correlation means causation.
The evidence against adenovirus, even adenovirus 41, is that this acute hepatitis syndrome is new, and adenovirus 41 is not. To be fair, we know adenoviruses can cause acute hepatitis, but the vast majority of reports are in immunocompromised individuals – organ transplant recipients and those with HIV. I was able to find just a handful of cases of immunocompetent kids developing hepatitis from adenovirus prior to this current outbreak.
The current outbreak would exceed the published literature by nearly two orders of magnitude. It feels like something else has to be going on.
Hypothesis 3: It’s coronavirus.
SARS-CoV-2 is a strange virus, both in its acute presentation and its long-term outcomes. It was clear early in the pandemic that some children infected by the coronavirus would develop MIS-C – multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. MIS-C is associated with hepatitis in about 10% of children, according to this New England Journal of Medicine
But the presentation of these kids is quite different from MIS-C; fever is rare, for example. The WHO reports that of the 169 identified cases so far, 20 had active COVID infection. The Scotland cohort suggests that a similar proportion had past COVID infections. In other times, we might consider this a smoking gun, but at this point a history of COVID is not remarkable – after the Omicron wave, it’s about as common to have a history of COVID as it is not to have a history of COVID.
A brief aside here. This is not because of coronavirus vaccination. Of the more than 100 cases reported in the United Kingdom, none of these kids were vaccinated. So let’s put aside the possibility that this is a vaccine effect – there’s no real evidence to support that.
Which brings us to …
Hypothesis 4: It’s coronavirus and adenovirus.
This is sort of intriguing and can work a few different ways, via a direct and indirect path.
In the direct path, we posit that COVID infection does something to kids’ immune systems – something we don’t yet understand that limits their ability to fight off adenovirus. There is some support for this idea. This study in Immunity found that COVID infection can functionally impair dendritic cells and T-cells, including natural killer cells. These cells are important components of our innate antiviral immunity.
There’s an indirect path as well. COVID has led to lockdowns, distancing, masking – stuff that prevents kids from being exposed to germs from other kids. Could a lack of exposure to adenovirus or other viruses because of distancing increase the risk for severe disease when restrictions are lifted? Also possible – the severity of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections this year is substantially higher than what we’ve seen in the past, for example.
And finally, hypothesis 5: This is something new.
We can’t ignore the possibility that this is simply a new disease-causing agent. Toxicology studies so far have been negative, and we wouldn’t expect hepatitis from a chemical toxin to appear in multiple countries around the world; this is almost certainly a biological phenomenon. It is possible that this is a new strain of adenovirus 41, or that adenovirus is a red herring altogether. Remember, we knew about “non-A/non-B viral hepatitis” for more than 2 decades before hepatitis C was discovered.
The pace of science is faster now, fortunately, and information is coming out quickly. As we learn more, we’ll share it with you.
Dr. Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and hosts a repository of his communication work at www.methodsman.com. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This is a transcript of a video that first appeared on Medscape.com. It has been edited for clarity.
On April 21, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a Health Alert Network advisory regarding a cluster of nine cases of acute hepatitis in children in Alabama over a 5-month period from October 2021 to February 2022 – a rate substantially higher than what would be expected, given the relative rarity of hepatitis in children.
Standard workup was negative for the common causative agents – hepatitis A, B, and C – and no toxic exposures were identified. But there was one common thread among all these kids: They all tested positive for adenovirus.
And that is really strange.
There are about 100 circulating adenoviruses in the world that we know of, and around 50 of them infect humans. If you are an adult, it’s a virtual certainty that you have been infected with an adenovirus in the past. Most strains cause symptoms we would describe as the common cold: runny nose, sore throat. Some strains cause conjunctivitis (pink eye). Some cause gastrointestinal illness – the stomach bugs that kids get.
It’s the banality of adenovirus that makes this hepatitis finding so surprising.
The United States is not alone in reporting this new hepatitis syndrome. As of April 21, 169 cases have been reported across the world, including 114 in the United Kingdom.
Of the 169 cases reported worldwide, 74 had evidence of adenovirus infection. On molecular testing, 18 of those were adenovirus 41.
What I wanted to do today was go through the various hypotheses for what could be going on with these hepatitis cases, one by one, and highlight the evidence supporting them. We won’t reach a conclusion, but hopefully by the end, the path forward will be more clear. OK, let’s get started.
Hypothesis 1: Nothing is happening.
It’s worth noting that “clusters” of disease occur all the time, even when no relevant epidemiologic process has occurred. If there is some baseline rate of hepatitis, every once in a while, through bad luck alone, you’d see a group of cases all at once. This is known as the clustering illusion. And I’m quite confident in saying that this is not the case here.
For one, this phenomenon is worldwide, as we know from the World Health Organization report. In fact, the CDC didn’t provide the most detailed data about the nine (now 12) cases in the United States. This study from Scotland is the first to give a detailed accounting of cases, reporting on 13 cases of acute hepatitis of unknown cause in kids at a single hospital from January to April. Typically, the hospital sees fewer than four cases of hepatitis per year. Five of these 13 kids tested positive for adenovirus. So let’s take the clustering illusion off the list.
Hypothesis 2: It’s adenovirus.
The major evidence supporting adenovirus as the causative agent here is that a lot of these kids had adenovirus, and adenovirus 41 – a gut-tropic strain – in particular. This is important, because stool testing might be necessary for diagnosis and lots of kids with this condition didn’t get that. In other words, we have hard evidence of adenovirus infection in about 40% of the cases so far, but the true number might be substantially higher.
That said, adenovirus is seasonal, and we are in adenovirus season. Granted, 40% seems quite a bit higher than the background infection rate, but we have to be careful not to assume that correlation means causation.
The evidence against adenovirus, even adenovirus 41, is that this acute hepatitis syndrome is new, and adenovirus 41 is not. To be fair, we know adenoviruses can cause acute hepatitis, but the vast majority of reports are in immunocompromised individuals – organ transplant recipients and those with HIV. I was able to find just a handful of cases of immunocompetent kids developing hepatitis from adenovirus prior to this current outbreak.
The current outbreak would exceed the published literature by nearly two orders of magnitude. It feels like something else has to be going on.
Hypothesis 3: It’s coronavirus.
SARS-CoV-2 is a strange virus, both in its acute presentation and its long-term outcomes. It was clear early in the pandemic that some children infected by the coronavirus would develop MIS-C – multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. MIS-C is associated with hepatitis in about 10% of children, according to this New England Journal of Medicine
But the presentation of these kids is quite different from MIS-C; fever is rare, for example. The WHO reports that of the 169 identified cases so far, 20 had active COVID infection. The Scotland cohort suggests that a similar proportion had past COVID infections. In other times, we might consider this a smoking gun, but at this point a history of COVID is not remarkable – after the Omicron wave, it’s about as common to have a history of COVID as it is not to have a history of COVID.
A brief aside here. This is not because of coronavirus vaccination. Of the more than 100 cases reported in the United Kingdom, none of these kids were vaccinated. So let’s put aside the possibility that this is a vaccine effect – there’s no real evidence to support that.
Which brings us to …
Hypothesis 4: It’s coronavirus and adenovirus.
This is sort of intriguing and can work a few different ways, via a direct and indirect path.
In the direct path, we posit that COVID infection does something to kids’ immune systems – something we don’t yet understand that limits their ability to fight off adenovirus. There is some support for this idea. This study in Immunity found that COVID infection can functionally impair dendritic cells and T-cells, including natural killer cells. These cells are important components of our innate antiviral immunity.
There’s an indirect path as well. COVID has led to lockdowns, distancing, masking – stuff that prevents kids from being exposed to germs from other kids. Could a lack of exposure to adenovirus or other viruses because of distancing increase the risk for severe disease when restrictions are lifted? Also possible – the severity of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections this year is substantially higher than what we’ve seen in the past, for example.
And finally, hypothesis 5: This is something new.
We can’t ignore the possibility that this is simply a new disease-causing agent. Toxicology studies so far have been negative, and we wouldn’t expect hepatitis from a chemical toxin to appear in multiple countries around the world; this is almost certainly a biological phenomenon. It is possible that this is a new strain of adenovirus 41, or that adenovirus is a red herring altogether. Remember, we knew about “non-A/non-B viral hepatitis” for more than 2 decades before hepatitis C was discovered.
The pace of science is faster now, fortunately, and information is coming out quickly. As we learn more, we’ll share it with you.
Dr. Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and hosts a repository of his communication work at www.methodsman.com. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Mood instability in childhood as a precursor to bipolar disorder
Mood instability, or sudden, unpredictable, and frequent shifts in emotional states, characterizes many types of psychiatric disorder, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), personality disorders, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder. To say that individuals with bipolar disorder (BD) have mood instability sounds like a tautology. Nonetheless, mood instability has particular relevance to BD: Many patients have irregular or labile moods even when they are between major episodes of mania and depression.1
Children of parents with BD who have high levels of mood instability are at particularly high risk for developing BD (types I or II) in late adolescence or early adulthood.2 The following case provides an illustration:
Patrick, age 14, entered treatment with diagnoses of ADHD and other specified bipolar disorder. His mother felt that his behavior resembled that of his father, who had been treated for manic episodes. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Patrick had become increasingly difficult at home, with significant oppositionality, impulsive behavior, and difficulty following through on school assignments or household tasks. His mother’s most significant complaints concerned Patrick’s sudden outbursts of anger and abrupt verbal abuse when she asked him to stop playing video games. When interrupted, he cursed loudly and sometimes turned violent; he had broken a window and a door at home and had on one occasion physically attacked his younger brother. Patrick agreed that he became angry at times, but felt that others provoked him. When queried about depression, he described anxiety and worry. He was unable to describe a particular trigger for his anxiety except for being interrupted in online games with his friends, which made him “feel like a total loser.”
His mother reported that Patrick had multiple 1- to 2-day intervals in which he became “really silly, laughing at nothing,” talking rapidly, jumping from one topic to another, and becoming annoyed when others didn’t share his enthusiasm. In these activated intervals, he slept little and seemed to be full of energy; his mother would hear him talking loudly into his phone throughout the night. During one such interval he had become verbally aggressive with a peer, which had ruined their friendship. Both Patrick and his mother reported that they had been fighting constantly and, in her words, “our house has become a war zone.”
In our recent article in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry,3 my coauthors and I examined the association between parents’ ratings of mood instability and clinicians’ longitudinal ratings of symptoms and functioning among youth (ages 9-17 years) who were at high risk for BD. The participants met DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder or other specified BD, defined as recurrent and brief periods of elevation and activation that did not meet syndromal mania or hypomania criteria. All participants had at least one first- or second-degree family member with a history of BD I or II. Following a period of evaluation, participants were randomly assigned to one of two 4-month psychological therapies: Family-focused therapy (12 sessions of psychoeducation, communication training, and problem-solving skills training) or enhanced usual care (6 sessions of family and individual psychoeducation and support). They also received pharmacological management from study-affiliated psychiatrists when warranted.
We measured mood instability at intake and every 4-6 months over an average of 2 years (range 0-255 weeks). We used a brief parent questionnaire – the Children’s Affective Lability Scale4 – which enables measurement of lability on the dimensions of elevation or activation (e.g., bursts of silliness or hilarity, excessive familiarity with others), irritability (e.g., temper outbursts), or anxious-depression (e.g., sudden bouts of crying).
Over the 1- to 4-year period of follow-up, mood instability was associated with poor prognosis indicators in high-risk youth: Being younger, having younger ages at first symptom onset, being diagnosed with other specified BD (vs. major depression), and having more complex patterns of comorbid disorders. Mood instability tracked closely with levels of mania, depression, and global functioning over the follow-up. There was a temporal pathway between a diagnosis of other specified bipolar disorder at intake and higher levels of mood instability at follow-up, which in turn predicted higher levels of parent/child conflict. High levels of mood lability may lead to isolation from peers and tension within family relationships, which may fuel further children’s expressions of frustration, rage, depression, or impulsive behavior.
Youth with higher levels of mood instability required more complex medication regimens over 1 year than did those with lower instability. There was an overall reduction in mood instability as children aged (or spent more time in treatment). Over the 1- to 4-year follow-up, family-focused therapy was associated with longer intervals prior to new mood episodes than was enhanced usual care, but reductions in mood instability were independent of the type of psychosocial treatment assigned to children.
The participants in this study could not be followed long enough to determine whether levels of mood instability were associated with the later development of syndromal BD. Other studies, however, have documented this relationship. Large-scale longitudinal studies of high-risk children find that measures of mood lability – along with early onset manic symptoms, depression, anxiety, and a family history of mania or hypomania – can be combined to calculate the risk that any individual child will develop BD I or II over the next 5-8 years.2,5
Clinicians should include measurement of the severity and psychosocial determinants of persistent mood shifts in youth under their care, particularly those with a family history of BD. Mood instability is associated with more severe symptom trajectories, more social isolation, and greater distress and conflict within the family. It may require a greater intensity of both pharmacological and psychosocial treatments to treat existing symptoms and functional impairments, and to prevent further mood deterioration.
Dr. Miklowitz is Distinguished Professor of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior. He is the author of “The Bipolar Disorder Survival Guide, 3rd Ed.” (New York: Guilford Press, 2019) and “Bipolar Disorder: A Family-Focused Treatment Approach, 2nd Ed” (New York: Guilford Press, 2010). He has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Contact Dr. Miklowitz at dmiklowitz@mednet.ucla.edu.
References
1. Bonsall MB, et al. Nonlinear time-series approaches in characterizing mood stability and mood instability in bipolar disorder. Proc Biol Sci. Mar 7 2012;279(1730):916-24. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2011.1246.
2. Hafeman DM, et al. Toward the definition of a bipolar prodrome: Dimensional predictors of bipolar spectrum disorders in at-risk youths. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(7):695-704. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15040414.
3. Miklowitz DJ, et al. Mood instability in youth at high risk for bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adol Psychiatry. 2022 Mar 17;S0890-8567(22)00118-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2022.03.009.
4. Gerson AC, et al. The Children’s Affective Lability Scale: a psychometric evaluation of reliability. Psychiatry Res. Dec 20 1996;65(3):189-98. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1781(96)02851-x.
5. Birmaher B, et al. A risk calculator to predict the individual risk of conversion from subthreshold bipolar symptoms to bipolar disorder I or II in youth. J Am Acad Child Adol Psychiatry. 2018;57(10):755-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2018.05.023.
Mood instability, or sudden, unpredictable, and frequent shifts in emotional states, characterizes many types of psychiatric disorder, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), personality disorders, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder. To say that individuals with bipolar disorder (BD) have mood instability sounds like a tautology. Nonetheless, mood instability has particular relevance to BD: Many patients have irregular or labile moods even when they are between major episodes of mania and depression.1
Children of parents with BD who have high levels of mood instability are at particularly high risk for developing BD (types I or II) in late adolescence or early adulthood.2 The following case provides an illustration:
Patrick, age 14, entered treatment with diagnoses of ADHD and other specified bipolar disorder. His mother felt that his behavior resembled that of his father, who had been treated for manic episodes. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Patrick had become increasingly difficult at home, with significant oppositionality, impulsive behavior, and difficulty following through on school assignments or household tasks. His mother’s most significant complaints concerned Patrick’s sudden outbursts of anger and abrupt verbal abuse when she asked him to stop playing video games. When interrupted, he cursed loudly and sometimes turned violent; he had broken a window and a door at home and had on one occasion physically attacked his younger brother. Patrick agreed that he became angry at times, but felt that others provoked him. When queried about depression, he described anxiety and worry. He was unable to describe a particular trigger for his anxiety except for being interrupted in online games with his friends, which made him “feel like a total loser.”
His mother reported that Patrick had multiple 1- to 2-day intervals in which he became “really silly, laughing at nothing,” talking rapidly, jumping from one topic to another, and becoming annoyed when others didn’t share his enthusiasm. In these activated intervals, he slept little and seemed to be full of energy; his mother would hear him talking loudly into his phone throughout the night. During one such interval he had become verbally aggressive with a peer, which had ruined their friendship. Both Patrick and his mother reported that they had been fighting constantly and, in her words, “our house has become a war zone.”
In our recent article in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry,3 my coauthors and I examined the association between parents’ ratings of mood instability and clinicians’ longitudinal ratings of symptoms and functioning among youth (ages 9-17 years) who were at high risk for BD. The participants met DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder or other specified BD, defined as recurrent and brief periods of elevation and activation that did not meet syndromal mania or hypomania criteria. All participants had at least one first- or second-degree family member with a history of BD I or II. Following a period of evaluation, participants were randomly assigned to one of two 4-month psychological therapies: Family-focused therapy (12 sessions of psychoeducation, communication training, and problem-solving skills training) or enhanced usual care (6 sessions of family and individual psychoeducation and support). They also received pharmacological management from study-affiliated psychiatrists when warranted.
We measured mood instability at intake and every 4-6 months over an average of 2 years (range 0-255 weeks). We used a brief parent questionnaire – the Children’s Affective Lability Scale4 – which enables measurement of lability on the dimensions of elevation or activation (e.g., bursts of silliness or hilarity, excessive familiarity with others), irritability (e.g., temper outbursts), or anxious-depression (e.g., sudden bouts of crying).
Over the 1- to 4-year period of follow-up, mood instability was associated with poor prognosis indicators in high-risk youth: Being younger, having younger ages at first symptom onset, being diagnosed with other specified BD (vs. major depression), and having more complex patterns of comorbid disorders. Mood instability tracked closely with levels of mania, depression, and global functioning over the follow-up. There was a temporal pathway between a diagnosis of other specified bipolar disorder at intake and higher levels of mood instability at follow-up, which in turn predicted higher levels of parent/child conflict. High levels of mood lability may lead to isolation from peers and tension within family relationships, which may fuel further children’s expressions of frustration, rage, depression, or impulsive behavior.
Youth with higher levels of mood instability required more complex medication regimens over 1 year than did those with lower instability. There was an overall reduction in mood instability as children aged (or spent more time in treatment). Over the 1- to 4-year follow-up, family-focused therapy was associated with longer intervals prior to new mood episodes than was enhanced usual care, but reductions in mood instability were independent of the type of psychosocial treatment assigned to children.
The participants in this study could not be followed long enough to determine whether levels of mood instability were associated with the later development of syndromal BD. Other studies, however, have documented this relationship. Large-scale longitudinal studies of high-risk children find that measures of mood lability – along with early onset manic symptoms, depression, anxiety, and a family history of mania or hypomania – can be combined to calculate the risk that any individual child will develop BD I or II over the next 5-8 years.2,5
Clinicians should include measurement of the severity and psychosocial determinants of persistent mood shifts in youth under their care, particularly those with a family history of BD. Mood instability is associated with more severe symptom trajectories, more social isolation, and greater distress and conflict within the family. It may require a greater intensity of both pharmacological and psychosocial treatments to treat existing symptoms and functional impairments, and to prevent further mood deterioration.
Dr. Miklowitz is Distinguished Professor of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior. He is the author of “The Bipolar Disorder Survival Guide, 3rd Ed.” (New York: Guilford Press, 2019) and “Bipolar Disorder: A Family-Focused Treatment Approach, 2nd Ed” (New York: Guilford Press, 2010). He has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Contact Dr. Miklowitz at dmiklowitz@mednet.ucla.edu.
References
1. Bonsall MB, et al. Nonlinear time-series approaches in characterizing mood stability and mood instability in bipolar disorder. Proc Biol Sci. Mar 7 2012;279(1730):916-24. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2011.1246.
2. Hafeman DM, et al. Toward the definition of a bipolar prodrome: Dimensional predictors of bipolar spectrum disorders in at-risk youths. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(7):695-704. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15040414.
3. Miklowitz DJ, et al. Mood instability in youth at high risk for bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adol Psychiatry. 2022 Mar 17;S0890-8567(22)00118-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2022.03.009.
4. Gerson AC, et al. The Children’s Affective Lability Scale: a psychometric evaluation of reliability. Psychiatry Res. Dec 20 1996;65(3):189-98. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1781(96)02851-x.
5. Birmaher B, et al. A risk calculator to predict the individual risk of conversion from subthreshold bipolar symptoms to bipolar disorder I or II in youth. J Am Acad Child Adol Psychiatry. 2018;57(10):755-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2018.05.023.
Mood instability, or sudden, unpredictable, and frequent shifts in emotional states, characterizes many types of psychiatric disorder, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), personality disorders, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder. To say that individuals with bipolar disorder (BD) have mood instability sounds like a tautology. Nonetheless, mood instability has particular relevance to BD: Many patients have irregular or labile moods even when they are between major episodes of mania and depression.1
Children of parents with BD who have high levels of mood instability are at particularly high risk for developing BD (types I or II) in late adolescence or early adulthood.2 The following case provides an illustration:
Patrick, age 14, entered treatment with diagnoses of ADHD and other specified bipolar disorder. His mother felt that his behavior resembled that of his father, who had been treated for manic episodes. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Patrick had become increasingly difficult at home, with significant oppositionality, impulsive behavior, and difficulty following through on school assignments or household tasks. His mother’s most significant complaints concerned Patrick’s sudden outbursts of anger and abrupt verbal abuse when she asked him to stop playing video games. When interrupted, he cursed loudly and sometimes turned violent; he had broken a window and a door at home and had on one occasion physically attacked his younger brother. Patrick agreed that he became angry at times, but felt that others provoked him. When queried about depression, he described anxiety and worry. He was unable to describe a particular trigger for his anxiety except for being interrupted in online games with his friends, which made him “feel like a total loser.”
His mother reported that Patrick had multiple 1- to 2-day intervals in which he became “really silly, laughing at nothing,” talking rapidly, jumping from one topic to another, and becoming annoyed when others didn’t share his enthusiasm. In these activated intervals, he slept little and seemed to be full of energy; his mother would hear him talking loudly into his phone throughout the night. During one such interval he had become verbally aggressive with a peer, which had ruined their friendship. Both Patrick and his mother reported that they had been fighting constantly and, in her words, “our house has become a war zone.”
In our recent article in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry,3 my coauthors and I examined the association between parents’ ratings of mood instability and clinicians’ longitudinal ratings of symptoms and functioning among youth (ages 9-17 years) who were at high risk for BD. The participants met DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder or other specified BD, defined as recurrent and brief periods of elevation and activation that did not meet syndromal mania or hypomania criteria. All participants had at least one first- or second-degree family member with a history of BD I or II. Following a period of evaluation, participants were randomly assigned to one of two 4-month psychological therapies: Family-focused therapy (12 sessions of psychoeducation, communication training, and problem-solving skills training) or enhanced usual care (6 sessions of family and individual psychoeducation and support). They also received pharmacological management from study-affiliated psychiatrists when warranted.
We measured mood instability at intake and every 4-6 months over an average of 2 years (range 0-255 weeks). We used a brief parent questionnaire – the Children’s Affective Lability Scale4 – which enables measurement of lability on the dimensions of elevation or activation (e.g., bursts of silliness or hilarity, excessive familiarity with others), irritability (e.g., temper outbursts), or anxious-depression (e.g., sudden bouts of crying).
Over the 1- to 4-year period of follow-up, mood instability was associated with poor prognosis indicators in high-risk youth: Being younger, having younger ages at first symptom onset, being diagnosed with other specified BD (vs. major depression), and having more complex patterns of comorbid disorders. Mood instability tracked closely with levels of mania, depression, and global functioning over the follow-up. There was a temporal pathway between a diagnosis of other specified bipolar disorder at intake and higher levels of mood instability at follow-up, which in turn predicted higher levels of parent/child conflict. High levels of mood lability may lead to isolation from peers and tension within family relationships, which may fuel further children’s expressions of frustration, rage, depression, or impulsive behavior.
Youth with higher levels of mood instability required more complex medication regimens over 1 year than did those with lower instability. There was an overall reduction in mood instability as children aged (or spent more time in treatment). Over the 1- to 4-year follow-up, family-focused therapy was associated with longer intervals prior to new mood episodes than was enhanced usual care, but reductions in mood instability were independent of the type of psychosocial treatment assigned to children.
The participants in this study could not be followed long enough to determine whether levels of mood instability were associated with the later development of syndromal BD. Other studies, however, have documented this relationship. Large-scale longitudinal studies of high-risk children find that measures of mood lability – along with early onset manic symptoms, depression, anxiety, and a family history of mania or hypomania – can be combined to calculate the risk that any individual child will develop BD I or II over the next 5-8 years.2,5
Clinicians should include measurement of the severity and psychosocial determinants of persistent mood shifts in youth under their care, particularly those with a family history of BD. Mood instability is associated with more severe symptom trajectories, more social isolation, and greater distress and conflict within the family. It may require a greater intensity of both pharmacological and psychosocial treatments to treat existing symptoms and functional impairments, and to prevent further mood deterioration.
Dr. Miklowitz is Distinguished Professor of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior. He is the author of “The Bipolar Disorder Survival Guide, 3rd Ed.” (New York: Guilford Press, 2019) and “Bipolar Disorder: A Family-Focused Treatment Approach, 2nd Ed” (New York: Guilford Press, 2010). He has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Contact Dr. Miklowitz at dmiklowitz@mednet.ucla.edu.
References
1. Bonsall MB, et al. Nonlinear time-series approaches in characterizing mood stability and mood instability in bipolar disorder. Proc Biol Sci. Mar 7 2012;279(1730):916-24. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2011.1246.
2. Hafeman DM, et al. Toward the definition of a bipolar prodrome: Dimensional predictors of bipolar spectrum disorders in at-risk youths. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(7):695-704. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15040414.
3. Miklowitz DJ, et al. Mood instability in youth at high risk for bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adol Psychiatry. 2022 Mar 17;S0890-8567(22)00118-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2022.03.009.
4. Gerson AC, et al. The Children’s Affective Lability Scale: a psychometric evaluation of reliability. Psychiatry Res. Dec 20 1996;65(3):189-98. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1781(96)02851-x.
5. Birmaher B, et al. A risk calculator to predict the individual risk of conversion from subthreshold bipolar symptoms to bipolar disorder I or II in youth. J Am Acad Child Adol Psychiatry. 2018;57(10):755-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2018.05.023.
The neurobiology of Jeopardy! champions
As a regular viewer of Jeopardy! I find it both interesting and educational. But the psychiatric neuroscientist in me marvels at the splendid cerebral attributes embedded in the brains of Jeopardy! champions.
Back in my college days, I participated in what were then called “general knowledge contests” and won a couple of trophies, the most gratifying of which was when our team of medical students beat the faculty team! Later, when my wife and I had children, Trivial Pursuit was a game frequently played in our household. So it is no wonder I have often thought of the remarkable, sometimes stunning intellectual performances of Jeopardy! champions.
What does it take to excel at Jeopardy!?
Watching contestants successfully answer a bewildering array of questions across an extensive spectrum of topics is simply dazzling and prompts me to ask: Which neurologic structures play a central role in the brains of Jeopardy! champions? So I channeled my inner neurobiologist and came up with the following prerequisites to excel at Jeopardy!:
- A hippocampus on steroids! Memory is obviously a core ingredient for responding to Jeopardy! questions. Unlike ordinary mortals, Jeopardy! champions appear to retain and instantaneously, accurately recall everything they have read, saw, or heard.
- A sublime network of dendritic spines, where learning is immediately transduced to biological memories, thanks to the wonders of experiential neuroplasticity in homo sapiens.
- A superlative frontal lobe, which provides the champion with an ultra-rapid abstraction ability in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, along with razor-sharp concentration and attention.
- An extremely well-myelinated network of the 137,000 miles of white matter fibers in the human brain. This is what leads to fabulous processing speed. Rapid neurotransmission is impossible without very well-myelinated axons and dendrites. It is not enough for a Jeopardy! champion to know the answer and retrieve it from the hippocampus—they also must transmit the answer at lightning speed to the speech area, and then activate the motor area to enunciate the answer. Processing speed is the foundation of overall cognitive functioning.
- A first-rate Broca’s area, referred to as “the brain’s scriptwriter,” which shapes human speech. It receives the flow of sensory information from the temporal cortex, devises a plan for speaking, and passes that plan seamlessly to the motor cortex, which controls the movements of the mouth.
- Blistering speed reflexes to click the handheld response buzzer within a fraction of a millisecond after the host finishes reading the clue (not before, or a penalty is incurred). Jeopardy! champions always click the buzzer faster than their competitors, who may know the answer but have ordinary motor reflexes (also related to the degree of myelination and a motoric component of processing speed).
- A thick corpus callosum, the largest interhemispheric commissure, a bundle of 200 million white matter fibers connecting analogous regions in the right and left hemispheres, is vital for the rapid bidirectional transfer of bits of information from the intuitive/nonverbal right hemisphere to the mathematical/verbal left hemisphere, when the answer requires right hemispheric input.
- A bright occipital cortex and exceptional optic nerve and retina, so that champions can recognize faces or locations and read the questions before the host finishes reading them, which gives them an awesome edge on other contestants.
Obviously, the brains of Jeopardy! champions are a breed of their own, with exceptional performances by multiple regions converging to produce a winning performance. But during their childhood and youthful years, such brains also generate motivation, curiosity, and interest in a wide range of topics, from cultures, regions, music genres, and word games to history, geography, sports, science, medicine, astronomy, and Greek mythology.
Jeopardy! champions may appear to have regular jobs and ordinary lives, but they have resplendent “renaissance” brains. I wonder how they spent their childhood, who mentored them, what type of family lives they had, and what they dream of accomplishing other than winning on Jeopardy!. Will their awe-inspiring performance in Jeopardy! translate to overall success in life? That’s a story that remains to be told.
As a regular viewer of Jeopardy! I find it both interesting and educational. But the psychiatric neuroscientist in me marvels at the splendid cerebral attributes embedded in the brains of Jeopardy! champions.
Back in my college days, I participated in what were then called “general knowledge contests” and won a couple of trophies, the most gratifying of which was when our team of medical students beat the faculty team! Later, when my wife and I had children, Trivial Pursuit was a game frequently played in our household. So it is no wonder I have often thought of the remarkable, sometimes stunning intellectual performances of Jeopardy! champions.
What does it take to excel at Jeopardy!?
Watching contestants successfully answer a bewildering array of questions across an extensive spectrum of topics is simply dazzling and prompts me to ask: Which neurologic structures play a central role in the brains of Jeopardy! champions? So I channeled my inner neurobiologist and came up with the following prerequisites to excel at Jeopardy!:
- A hippocampus on steroids! Memory is obviously a core ingredient for responding to Jeopardy! questions. Unlike ordinary mortals, Jeopardy! champions appear to retain and instantaneously, accurately recall everything they have read, saw, or heard.
- A sublime network of dendritic spines, where learning is immediately transduced to biological memories, thanks to the wonders of experiential neuroplasticity in homo sapiens.
- A superlative frontal lobe, which provides the champion with an ultra-rapid abstraction ability in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, along with razor-sharp concentration and attention.
- An extremely well-myelinated network of the 137,000 miles of white matter fibers in the human brain. This is what leads to fabulous processing speed. Rapid neurotransmission is impossible without very well-myelinated axons and dendrites. It is not enough for a Jeopardy! champion to know the answer and retrieve it from the hippocampus—they also must transmit the answer at lightning speed to the speech area, and then activate the motor area to enunciate the answer. Processing speed is the foundation of overall cognitive functioning.
- A first-rate Broca’s area, referred to as “the brain’s scriptwriter,” which shapes human speech. It receives the flow of sensory information from the temporal cortex, devises a plan for speaking, and passes that plan seamlessly to the motor cortex, which controls the movements of the mouth.
- Blistering speed reflexes to click the handheld response buzzer within a fraction of a millisecond after the host finishes reading the clue (not before, or a penalty is incurred). Jeopardy! champions always click the buzzer faster than their competitors, who may know the answer but have ordinary motor reflexes (also related to the degree of myelination and a motoric component of processing speed).
- A thick corpus callosum, the largest interhemispheric commissure, a bundle of 200 million white matter fibers connecting analogous regions in the right and left hemispheres, is vital for the rapid bidirectional transfer of bits of information from the intuitive/nonverbal right hemisphere to the mathematical/verbal left hemisphere, when the answer requires right hemispheric input.
- A bright occipital cortex and exceptional optic nerve and retina, so that champions can recognize faces or locations and read the questions before the host finishes reading them, which gives them an awesome edge on other contestants.
Obviously, the brains of Jeopardy! champions are a breed of their own, with exceptional performances by multiple regions converging to produce a winning performance. But during their childhood and youthful years, such brains also generate motivation, curiosity, and interest in a wide range of topics, from cultures, regions, music genres, and word games to history, geography, sports, science, medicine, astronomy, and Greek mythology.
Jeopardy! champions may appear to have regular jobs and ordinary lives, but they have resplendent “renaissance” brains. I wonder how they spent their childhood, who mentored them, what type of family lives they had, and what they dream of accomplishing other than winning on Jeopardy!. Will their awe-inspiring performance in Jeopardy! translate to overall success in life? That’s a story that remains to be told.
As a regular viewer of Jeopardy! I find it both interesting and educational. But the psychiatric neuroscientist in me marvels at the splendid cerebral attributes embedded in the brains of Jeopardy! champions.
Back in my college days, I participated in what were then called “general knowledge contests” and won a couple of trophies, the most gratifying of which was when our team of medical students beat the faculty team! Later, when my wife and I had children, Trivial Pursuit was a game frequently played in our household. So it is no wonder I have often thought of the remarkable, sometimes stunning intellectual performances of Jeopardy! champions.
What does it take to excel at Jeopardy!?
Watching contestants successfully answer a bewildering array of questions across an extensive spectrum of topics is simply dazzling and prompts me to ask: Which neurologic structures play a central role in the brains of Jeopardy! champions? So I channeled my inner neurobiologist and came up with the following prerequisites to excel at Jeopardy!:
- A hippocampus on steroids! Memory is obviously a core ingredient for responding to Jeopardy! questions. Unlike ordinary mortals, Jeopardy! champions appear to retain and instantaneously, accurately recall everything they have read, saw, or heard.
- A sublime network of dendritic spines, where learning is immediately transduced to biological memories, thanks to the wonders of experiential neuroplasticity in homo sapiens.
- A superlative frontal lobe, which provides the champion with an ultra-rapid abstraction ability in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, along with razor-sharp concentration and attention.
- An extremely well-myelinated network of the 137,000 miles of white matter fibers in the human brain. This is what leads to fabulous processing speed. Rapid neurotransmission is impossible without very well-myelinated axons and dendrites. It is not enough for a Jeopardy! champion to know the answer and retrieve it from the hippocampus—they also must transmit the answer at lightning speed to the speech area, and then activate the motor area to enunciate the answer. Processing speed is the foundation of overall cognitive functioning.
- A first-rate Broca’s area, referred to as “the brain’s scriptwriter,” which shapes human speech. It receives the flow of sensory information from the temporal cortex, devises a plan for speaking, and passes that plan seamlessly to the motor cortex, which controls the movements of the mouth.
- Blistering speed reflexes to click the handheld response buzzer within a fraction of a millisecond after the host finishes reading the clue (not before, or a penalty is incurred). Jeopardy! champions always click the buzzer faster than their competitors, who may know the answer but have ordinary motor reflexes (also related to the degree of myelination and a motoric component of processing speed).
- A thick corpus callosum, the largest interhemispheric commissure, a bundle of 200 million white matter fibers connecting analogous regions in the right and left hemispheres, is vital for the rapid bidirectional transfer of bits of information from the intuitive/nonverbal right hemisphere to the mathematical/verbal left hemisphere, when the answer requires right hemispheric input.
- A bright occipital cortex and exceptional optic nerve and retina, so that champions can recognize faces or locations and read the questions before the host finishes reading them, which gives them an awesome edge on other contestants.
Obviously, the brains of Jeopardy! champions are a breed of their own, with exceptional performances by multiple regions converging to produce a winning performance. But during their childhood and youthful years, such brains also generate motivation, curiosity, and interest in a wide range of topics, from cultures, regions, music genres, and word games to history, geography, sports, science, medicine, astronomy, and Greek mythology.
Jeopardy! champions may appear to have regular jobs and ordinary lives, but they have resplendent “renaissance” brains. I wonder how they spent their childhood, who mentored them, what type of family lives they had, and what they dream of accomplishing other than winning on Jeopardy!. Will their awe-inspiring performance in Jeopardy! translate to overall success in life? That’s a story that remains to be told.