User login
Dignity
Queen Elizabeth is everywhere. She was even on the last slide of a presentation on COVID, monkeypox, and influenza vaccines given by our physician in charge of quality. This was odd. The presenter wasn’t English. The Queen had nothing to do with vaccines. Nor apparently would she have said even if she did have an opinion about them. But there we were, an audience of physicians and staff pausing for a moment of remembrance of her.
I’m not a Monarchist – except perhaps for the Kennedys. I grew up in New England. I don’t have an opinion on whether or not the British Crown should endure. But I do marvel at the astounding effect Queen Elizabeth’s passing had on so many around the world. Her personal qualities, particularly her steadiness and humane sympathy, might explain why so many are sad hearing the news. But also I think there was something in her role that we all wished for: Not the owning of palaces and sceptres, but rather, the respect that was given to her.
She was a stateswoman of “unmatched dignity,” the White House wrote. That was true, but it seems being the Queen might have been the last job on earth where such dignity is still possible. Certainly in politics, education, and even health care, there doesn’t seem to be much left lately.
The same day of that presentation I walked into the room of a patient 22 minutes late, she held her arm forth tapping her watch to indicate the time and my tardiness. Unnecessary, if not impertinent. Covering for one of my female physician colleagues, I read an email from a patient which began, “Dear Julie, With all due respect …” Another patient submitted a photo for us to review that was clearly taken from her car while waiting at a stop light. Hardly the consideration a clinical encounter should be given.
Much has been lost for patients. too. There are patients trying to make appointments lately who are told: “There are none. Call back later.” . There is no dignified way to remove exam paper stuck to your backside before introducing yourself to the doctor. Maybe that last slide of Her Majesty was in fact for us to have a moment of silence for what we’ve all lost.
Walter Bagehot (pronounce it “Baj-et” if you tell this story to your Harlan wine friends) was a political writer and editor of The Economist in the 1860s. He famously said that the secret to the English government was having two kinds of institutions, the dignified and the efficient. The efficient, Parliament, was responsible for all the work. The dignified, the Crown, gives significance and holds everyone’s respect. If medicine ever once was both dignified and efficient, we aren’t lately. We push to reduce backlogs, offer same-time virtual care, work to reduce costs. We’ve driven medicine to the efficient and left little of the dignity it seems.
The Queen will be remembered for her lifelong dedication to the laborious service of others. Even though each of us in medicine pledges the same, we also mourn this week the loss of dignity that once came with it.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Queen Elizabeth is everywhere. She was even on the last slide of a presentation on COVID, monkeypox, and influenza vaccines given by our physician in charge of quality. This was odd. The presenter wasn’t English. The Queen had nothing to do with vaccines. Nor apparently would she have said even if she did have an opinion about them. But there we were, an audience of physicians and staff pausing for a moment of remembrance of her.
I’m not a Monarchist – except perhaps for the Kennedys. I grew up in New England. I don’t have an opinion on whether or not the British Crown should endure. But I do marvel at the astounding effect Queen Elizabeth’s passing had on so many around the world. Her personal qualities, particularly her steadiness and humane sympathy, might explain why so many are sad hearing the news. But also I think there was something in her role that we all wished for: Not the owning of palaces and sceptres, but rather, the respect that was given to her.
She was a stateswoman of “unmatched dignity,” the White House wrote. That was true, but it seems being the Queen might have been the last job on earth where such dignity is still possible. Certainly in politics, education, and even health care, there doesn’t seem to be much left lately.
The same day of that presentation I walked into the room of a patient 22 minutes late, she held her arm forth tapping her watch to indicate the time and my tardiness. Unnecessary, if not impertinent. Covering for one of my female physician colleagues, I read an email from a patient which began, “Dear Julie, With all due respect …” Another patient submitted a photo for us to review that was clearly taken from her car while waiting at a stop light. Hardly the consideration a clinical encounter should be given.
Much has been lost for patients. too. There are patients trying to make appointments lately who are told: “There are none. Call back later.” . There is no dignified way to remove exam paper stuck to your backside before introducing yourself to the doctor. Maybe that last slide of Her Majesty was in fact for us to have a moment of silence for what we’ve all lost.
Walter Bagehot (pronounce it “Baj-et” if you tell this story to your Harlan wine friends) was a political writer and editor of The Economist in the 1860s. He famously said that the secret to the English government was having two kinds of institutions, the dignified and the efficient. The efficient, Parliament, was responsible for all the work. The dignified, the Crown, gives significance and holds everyone’s respect. If medicine ever once was both dignified and efficient, we aren’t lately. We push to reduce backlogs, offer same-time virtual care, work to reduce costs. We’ve driven medicine to the efficient and left little of the dignity it seems.
The Queen will be remembered for her lifelong dedication to the laborious service of others. Even though each of us in medicine pledges the same, we also mourn this week the loss of dignity that once came with it.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Queen Elizabeth is everywhere. She was even on the last slide of a presentation on COVID, monkeypox, and influenza vaccines given by our physician in charge of quality. This was odd. The presenter wasn’t English. The Queen had nothing to do with vaccines. Nor apparently would she have said even if she did have an opinion about them. But there we were, an audience of physicians and staff pausing for a moment of remembrance of her.
I’m not a Monarchist – except perhaps for the Kennedys. I grew up in New England. I don’t have an opinion on whether or not the British Crown should endure. But I do marvel at the astounding effect Queen Elizabeth’s passing had on so many around the world. Her personal qualities, particularly her steadiness and humane sympathy, might explain why so many are sad hearing the news. But also I think there was something in her role that we all wished for: Not the owning of palaces and sceptres, but rather, the respect that was given to her.
She was a stateswoman of “unmatched dignity,” the White House wrote. That was true, but it seems being the Queen might have been the last job on earth where such dignity is still possible. Certainly in politics, education, and even health care, there doesn’t seem to be much left lately.
The same day of that presentation I walked into the room of a patient 22 minutes late, she held her arm forth tapping her watch to indicate the time and my tardiness. Unnecessary, if not impertinent. Covering for one of my female physician colleagues, I read an email from a patient which began, “Dear Julie, With all due respect …” Another patient submitted a photo for us to review that was clearly taken from her car while waiting at a stop light. Hardly the consideration a clinical encounter should be given.
Much has been lost for patients. too. There are patients trying to make appointments lately who are told: “There are none. Call back later.” . There is no dignified way to remove exam paper stuck to your backside before introducing yourself to the doctor. Maybe that last slide of Her Majesty was in fact for us to have a moment of silence for what we’ve all lost.
Walter Bagehot (pronounce it “Baj-et” if you tell this story to your Harlan wine friends) was a political writer and editor of The Economist in the 1860s. He famously said that the secret to the English government was having two kinds of institutions, the dignified and the efficient. The efficient, Parliament, was responsible for all the work. The dignified, the Crown, gives significance and holds everyone’s respect. If medicine ever once was both dignified and efficient, we aren’t lately. We push to reduce backlogs, offer same-time virtual care, work to reduce costs. We’ve driven medicine to the efficient and left little of the dignity it seems.
The Queen will be remembered for her lifelong dedication to the laborious service of others. Even though each of us in medicine pledges the same, we also mourn this week the loss of dignity that once came with it.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Employers’ self-funded health plans can leave rheumatology patients vulnerable
Health care costs are skyrocketing for everyone! For employers, the cost of health insurance is second only to their payroll expense. Per person spending in employer plans grew by 22% between 2015 and 2019. This outpaced inflation and economic growth. Affording health insurance for business owners has become more and more difficult, bordering on desperation for some. Consequently, they are looking for ways to be more efficient in their health care spending. One way is through self-funding their employees’ health care costs. This means that the employer directly pays for the care of their employees. While it has always been thought this was just for very large employers, it is becoming more common with smaller businesses. There is more flexibility and oversight with self-funded plans, and the employer can dictate exactly what benefits are covered within the bounds of the law. While this can make it easier to exclude certain therapies and even institute site-of-care restrictions, it also can make the employer vulnerable to health insurance companies, pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), and third-party administrators (TPAs) that promise large discounts in plan and drug spending at the expense of their employees’ health.
Recently enacted state laws often don’t apply
Because employers who self-fund the health care for their employees are increasingly desperate to save money, they will often agree to plans that are less expensive but offer suboptimal care, particularly for patients with chronic diseases requiring expensive medicines. Many employers are not fully informed of the ramifications of these policies, so the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations is creating an educational employer tool kit that not only highlights the importance of disease control for their employees with rheumatic conditions but also outlines the pitfalls and misinformation that may be given to them by the insurance companies, PBMs, and other third parties that administer their health plan.
Policies that sacrifice patient care of course are not exclusive to certain self-funded health plans. The CSRO’s Payer Issue Response Team (PIRT) receives complaints daily from rheumatologists around the country regarding both the Employee Retirement Income Security Act and non-ERISA health plan policies that are harmful to their patients. Our PIRT team assesses these complaints and researches solutions that can include writing letters to the health insurance companies, employers, and departments of insurance, as well as applying enacted state legislation that overrides some of the detrimental policies. (Utilization management legislation, which has passed in many states, can be easily found on CSRO’s map tool.) These state laws can help patients with everything from harmful step therapy and nonmedical switching policies to accumulator adjustment programs denying application of copay card value to their deductibles. Unfortunately, these laws do not apply to most self-funded employer health plans, which are preempted by ERISA. Consequently, those employees are not protected from harmful changes in formularies and other policies.
Forced ‘white bagging’ in self-funded plans
Mandated “white bagging” has become a favorite for health plans covered by large insurance companies, which say that the practice is less expensive than what the physician would charge for the medication. White bagging takes away the ability of the physician to “buy and bill” infusibles that are given in their office. While some rheumatologists may accept this, there are many who do not accept infusible medications coming from another source. Often the health plan will tell the rheumatologist they must accept the white bagging or transfer the patient to another rheumatologist who will. Clearly, many health plans and TPAs do not understand the bonds that are created over the years between rheumatologists and their patients. Ironically, the price of the white-bagged medication charged to the employer has been shown often to be higher than what the physician would have charged.
Some TPAs also convince employers to carve out specialty medications from their policy entirely, leaving the employee uninsured for these meds. These TPAs then attempt to obtain the medications from the manufacturers, foundations, compounding pharmacies, and even other countries for free or highly discounted prices. Even if obtained at no cost, the TPA will charge the employer a percentage of the list price or fee for obtaining it. On the surface, this may seem like a good idea, but there are a number of issues with this, including some that are legally suspect. First of all, uninsuring employees for certain medications to take advantage of patient assistance programs from manufacturers and foundations could be viewed as perfectly legal and perfectly unethical. The legality of this practice is questionable when these companies pretend to be the patient when applying for the assistance or present compounded medication as coming from the manufacturer, or if the TPA obtains the medication from outside the country. Additionally, many employers end up paying 20% of the list price of a medication for a service that physicians provide at no cost for uninsured patients.
Educating employers
CSRO’s employer tool kit hopes to educate employers with self-funded health plans about the pitfalls of some of these policies and offers suggestions on how to best navigate these issues for employees with rheumatic diseases. We are hoping to launch this tool kit to small to medium business groups in the near future.
Advocacy is more than just contacting health insurers and those who make our laws and regulations. Although that is important, reaching out to those who employ our patients can be integral to ensuring they get the best care.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
Health care costs are skyrocketing for everyone! For employers, the cost of health insurance is second only to their payroll expense. Per person spending in employer plans grew by 22% between 2015 and 2019. This outpaced inflation and economic growth. Affording health insurance for business owners has become more and more difficult, bordering on desperation for some. Consequently, they are looking for ways to be more efficient in their health care spending. One way is through self-funding their employees’ health care costs. This means that the employer directly pays for the care of their employees. While it has always been thought this was just for very large employers, it is becoming more common with smaller businesses. There is more flexibility and oversight with self-funded plans, and the employer can dictate exactly what benefits are covered within the bounds of the law. While this can make it easier to exclude certain therapies and even institute site-of-care restrictions, it also can make the employer vulnerable to health insurance companies, pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), and third-party administrators (TPAs) that promise large discounts in plan and drug spending at the expense of their employees’ health.
Recently enacted state laws often don’t apply
Because employers who self-fund the health care for their employees are increasingly desperate to save money, they will often agree to plans that are less expensive but offer suboptimal care, particularly for patients with chronic diseases requiring expensive medicines. Many employers are not fully informed of the ramifications of these policies, so the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations is creating an educational employer tool kit that not only highlights the importance of disease control for their employees with rheumatic conditions but also outlines the pitfalls and misinformation that may be given to them by the insurance companies, PBMs, and other third parties that administer their health plan.
Policies that sacrifice patient care of course are not exclusive to certain self-funded health plans. The CSRO’s Payer Issue Response Team (PIRT) receives complaints daily from rheumatologists around the country regarding both the Employee Retirement Income Security Act and non-ERISA health plan policies that are harmful to their patients. Our PIRT team assesses these complaints and researches solutions that can include writing letters to the health insurance companies, employers, and departments of insurance, as well as applying enacted state legislation that overrides some of the detrimental policies. (Utilization management legislation, which has passed in many states, can be easily found on CSRO’s map tool.) These state laws can help patients with everything from harmful step therapy and nonmedical switching policies to accumulator adjustment programs denying application of copay card value to their deductibles. Unfortunately, these laws do not apply to most self-funded employer health plans, which are preempted by ERISA. Consequently, those employees are not protected from harmful changes in formularies and other policies.
Forced ‘white bagging’ in self-funded plans
Mandated “white bagging” has become a favorite for health plans covered by large insurance companies, which say that the practice is less expensive than what the physician would charge for the medication. White bagging takes away the ability of the physician to “buy and bill” infusibles that are given in their office. While some rheumatologists may accept this, there are many who do not accept infusible medications coming from another source. Often the health plan will tell the rheumatologist they must accept the white bagging or transfer the patient to another rheumatologist who will. Clearly, many health plans and TPAs do not understand the bonds that are created over the years between rheumatologists and their patients. Ironically, the price of the white-bagged medication charged to the employer has been shown often to be higher than what the physician would have charged.
Some TPAs also convince employers to carve out specialty medications from their policy entirely, leaving the employee uninsured for these meds. These TPAs then attempt to obtain the medications from the manufacturers, foundations, compounding pharmacies, and even other countries for free or highly discounted prices. Even if obtained at no cost, the TPA will charge the employer a percentage of the list price or fee for obtaining it. On the surface, this may seem like a good idea, but there are a number of issues with this, including some that are legally suspect. First of all, uninsuring employees for certain medications to take advantage of patient assistance programs from manufacturers and foundations could be viewed as perfectly legal and perfectly unethical. The legality of this practice is questionable when these companies pretend to be the patient when applying for the assistance or present compounded medication as coming from the manufacturer, or if the TPA obtains the medication from outside the country. Additionally, many employers end up paying 20% of the list price of a medication for a service that physicians provide at no cost for uninsured patients.
Educating employers
CSRO’s employer tool kit hopes to educate employers with self-funded health plans about the pitfalls of some of these policies and offers suggestions on how to best navigate these issues for employees with rheumatic diseases. We are hoping to launch this tool kit to small to medium business groups in the near future.
Advocacy is more than just contacting health insurers and those who make our laws and regulations. Although that is important, reaching out to those who employ our patients can be integral to ensuring they get the best care.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
Health care costs are skyrocketing for everyone! For employers, the cost of health insurance is second only to their payroll expense. Per person spending in employer plans grew by 22% between 2015 and 2019. This outpaced inflation and economic growth. Affording health insurance for business owners has become more and more difficult, bordering on desperation for some. Consequently, they are looking for ways to be more efficient in their health care spending. One way is through self-funding their employees’ health care costs. This means that the employer directly pays for the care of their employees. While it has always been thought this was just for very large employers, it is becoming more common with smaller businesses. There is more flexibility and oversight with self-funded plans, and the employer can dictate exactly what benefits are covered within the bounds of the law. While this can make it easier to exclude certain therapies and even institute site-of-care restrictions, it also can make the employer vulnerable to health insurance companies, pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), and third-party administrators (TPAs) that promise large discounts in plan and drug spending at the expense of their employees’ health.
Recently enacted state laws often don’t apply
Because employers who self-fund the health care for their employees are increasingly desperate to save money, they will often agree to plans that are less expensive but offer suboptimal care, particularly for patients with chronic diseases requiring expensive medicines. Many employers are not fully informed of the ramifications of these policies, so the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations is creating an educational employer tool kit that not only highlights the importance of disease control for their employees with rheumatic conditions but also outlines the pitfalls and misinformation that may be given to them by the insurance companies, PBMs, and other third parties that administer their health plan.
Policies that sacrifice patient care of course are not exclusive to certain self-funded health plans. The CSRO’s Payer Issue Response Team (PIRT) receives complaints daily from rheumatologists around the country regarding both the Employee Retirement Income Security Act and non-ERISA health plan policies that are harmful to their patients. Our PIRT team assesses these complaints and researches solutions that can include writing letters to the health insurance companies, employers, and departments of insurance, as well as applying enacted state legislation that overrides some of the detrimental policies. (Utilization management legislation, which has passed in many states, can be easily found on CSRO’s map tool.) These state laws can help patients with everything from harmful step therapy and nonmedical switching policies to accumulator adjustment programs denying application of copay card value to their deductibles. Unfortunately, these laws do not apply to most self-funded employer health plans, which are preempted by ERISA. Consequently, those employees are not protected from harmful changes in formularies and other policies.
Forced ‘white bagging’ in self-funded plans
Mandated “white bagging” has become a favorite for health plans covered by large insurance companies, which say that the practice is less expensive than what the physician would charge for the medication. White bagging takes away the ability of the physician to “buy and bill” infusibles that are given in their office. While some rheumatologists may accept this, there are many who do not accept infusible medications coming from another source. Often the health plan will tell the rheumatologist they must accept the white bagging or transfer the patient to another rheumatologist who will. Clearly, many health plans and TPAs do not understand the bonds that are created over the years between rheumatologists and their patients. Ironically, the price of the white-bagged medication charged to the employer has been shown often to be higher than what the physician would have charged.
Some TPAs also convince employers to carve out specialty medications from their policy entirely, leaving the employee uninsured for these meds. These TPAs then attempt to obtain the medications from the manufacturers, foundations, compounding pharmacies, and even other countries for free or highly discounted prices. Even if obtained at no cost, the TPA will charge the employer a percentage of the list price or fee for obtaining it. On the surface, this may seem like a good idea, but there are a number of issues with this, including some that are legally suspect. First of all, uninsuring employees for certain medications to take advantage of patient assistance programs from manufacturers and foundations could be viewed as perfectly legal and perfectly unethical. The legality of this practice is questionable when these companies pretend to be the patient when applying for the assistance or present compounded medication as coming from the manufacturer, or if the TPA obtains the medication from outside the country. Additionally, many employers end up paying 20% of the list price of a medication for a service that physicians provide at no cost for uninsured patients.
Educating employers
CSRO’s employer tool kit hopes to educate employers with self-funded health plans about the pitfalls of some of these policies and offers suggestions on how to best navigate these issues for employees with rheumatic diseases. We are hoping to launch this tool kit to small to medium business groups in the near future.
Advocacy is more than just contacting health insurers and those who make our laws and regulations. Although that is important, reaching out to those who employ our patients can be integral to ensuring they get the best care.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
Family affair: OncBrothers host oncology hangout online
It’s hard out there for a small-town cancer doctor. Just ask Wederson M. Claudino, MD, who serves the town of Paducah in far western Kentucky. The nearest cities with significant numbers of hematologist/oncologists are hours away in cities like St. Louis and Nashville, Tenn., too far to go to talk shop over coffee, drinks, or lunch.
“It’s very challenging in a rural or small community,” he said. “I miss the opportunity to elaborate on a case.”
Now Dr. Claudino and hundreds of colleagues have discovered that useful cancer conversations are just a click away.
Urban and rural oncologists gather there to discuss new research, compare notes about challenging cases, and get to know each other.
“Following their Twitter feed and the comments and discussions make me feel like part of a bigger community,” Dr. Claudino said. And @OncBrothers is indeed a bustling Internet destination: The account’s 4,300 followers include hundreds who participate in discussions and offer perspective.
For instance, the brothers recently posted a poll asking followers how they’d treat a 55-year-old patient with non–small cell lung cancer. Nearly 250 people responded with their preferred approaches, and the survey thread included comments from oncologists from the City of Hope National Medical Center, the University of Florida, UC San Diego, and elsewhere.
In an interview, the Gosain brothers said the Twitter account is an outgrowth of their phone conversations in recent years, as they trained and settled into their early careers as general medical oncologists in smaller communities.
“After our clinic days, we’ll jump on the phone for 30-45 minutes. We’d talk about patients, how he would treat a case, and what I would do,” Rahul said. “We realized that we were living in a bubble, but we also thought that there are a lot more people in the same boat. They might jump at being able to do the same thing.”
Rahul recently became medical director at the new Wilmot Webster Cancer Center in Rochester, N.Y., after working in Corning, a tiny New York town just north of the Pennsylvania border. His brother Rohit is chair of hematology and oncology at the University of Pittsburgh’s Hillman Cancer Center in Jamestown, a small town at the western edge of New York.
“When we initially kicked off the Twitter account in August 2021, we didn’t realize the traction it would get,” Rohit said. “Now we realize that there really is a need for this.”
On an ordinary day, the @OncBrothers account may highlight research presented at a oncology conference, retweet posts by other oncologists about new guidelines or FDA drug approvals, and ask followers to consider how they’d handle a difficult case.
The brothers are especially thrilled when posts spawn discussions that draw voices from leading medical institutions who normally don’t interact much with community oncologists. “You’ll have someone from Sloan Kettering or Dana-Farber saying ‘This is what would do,’ ” Rahul said. “You have the brightest minds pitching in, and we get to learn from them.”
The Gosain brothers were both born in India and immigrated as children to Toronto. They each went to medical school in the Caribbean – for Rohit, it was after a stint as a computer engineer – and they each embraced oncology. “For me, it was about having the right mentors while I was doing my clinical rotations as a medical student and as a resident,” Rahul said. In addition, he said, “this field was moving and is still moving so fast. It really intrigued and excited me and made me want to be at the forefront of it.”
The fast-moving nature of oncology, in fact, was one of the drivers behind the daily conversations between the brothers and the subsequent creation of the @OncBrothers account. “Just last year, in 2021, there were 40 new drugs that were indicated for hematology-oncology,” Rahul said. “To stay on top of that is very, very hard.”
It’s especially difficult to figure out treatment plans when multiple options exist. A 2022 thread on @OncBrothers revealed a wide divergence of opinions about triple therapy in prostate cancer: The 322 respondents to a Twitter poll were sharply divided about the best three-drug combination from these options – docetaxel, daratumumab, abiraterone, androgen deprivation therapy, and alpha-reductase inhibitors.
To make things more challenging, community oncologists often are generalists who treat patients with a wide variety of cancers from prostate and lung to breast and colon. As a result, these oncologists must keep up on developments across the entire cancer field. Rohit highlighted a 2022 thread that polled users about the approach they’d take to another patient with non–small cell lung cancer; 474 people responded. The accompanying discussion emphasized the need for the next-generation sequencing (NGS).
“A significant portion of community oncologists are not even doing NGS testing, which is FDA-approved,” Rohit said. “There’s a huge gap that still exists, and we weren’t even aware of it. We continue to learn from these conversations.”
The brothers contend that there’s a crucial need for education among community oncologists in light of evidence suggesting that some cancer outcomes are worse than those in urban areas.
In fact, Rohit led a 2019 study published in the journal Cancer that found that overall survival in rural patients with neuroendocrine tumors trended toward worse outcomes than in urban patients.
“There are many factors such as financial burden, lack of education, and rural patients not willing to travel to the city,” Rohit said. “We need to be more creative and ask, ‘How can we equip our medical oncologist in rural settings to continue to do better?’ ”
What’s next for the OncBrothers? The Gosains have created a website (www.oncbrothers.com) that highlights their social media work, and they’re exploring options such as podcasts and short videos. “Our goal is to focus on how to continue to keep general medical oncologists up to date, informed, and educated so patients can get the best care close to home,” Rahul said. “We need to do better.”
It’s hard out there for a small-town cancer doctor. Just ask Wederson M. Claudino, MD, who serves the town of Paducah in far western Kentucky. The nearest cities with significant numbers of hematologist/oncologists are hours away in cities like St. Louis and Nashville, Tenn., too far to go to talk shop over coffee, drinks, or lunch.
“It’s very challenging in a rural or small community,” he said. “I miss the opportunity to elaborate on a case.”
Now Dr. Claudino and hundreds of colleagues have discovered that useful cancer conversations are just a click away.
Urban and rural oncologists gather there to discuss new research, compare notes about challenging cases, and get to know each other.
“Following their Twitter feed and the comments and discussions make me feel like part of a bigger community,” Dr. Claudino said. And @OncBrothers is indeed a bustling Internet destination: The account’s 4,300 followers include hundreds who participate in discussions and offer perspective.
For instance, the brothers recently posted a poll asking followers how they’d treat a 55-year-old patient with non–small cell lung cancer. Nearly 250 people responded with their preferred approaches, and the survey thread included comments from oncologists from the City of Hope National Medical Center, the University of Florida, UC San Diego, and elsewhere.
In an interview, the Gosain brothers said the Twitter account is an outgrowth of their phone conversations in recent years, as they trained and settled into their early careers as general medical oncologists in smaller communities.
“After our clinic days, we’ll jump on the phone for 30-45 minutes. We’d talk about patients, how he would treat a case, and what I would do,” Rahul said. “We realized that we were living in a bubble, but we also thought that there are a lot more people in the same boat. They might jump at being able to do the same thing.”
Rahul recently became medical director at the new Wilmot Webster Cancer Center in Rochester, N.Y., after working in Corning, a tiny New York town just north of the Pennsylvania border. His brother Rohit is chair of hematology and oncology at the University of Pittsburgh’s Hillman Cancer Center in Jamestown, a small town at the western edge of New York.
“When we initially kicked off the Twitter account in August 2021, we didn’t realize the traction it would get,” Rohit said. “Now we realize that there really is a need for this.”
On an ordinary day, the @OncBrothers account may highlight research presented at a oncology conference, retweet posts by other oncologists about new guidelines or FDA drug approvals, and ask followers to consider how they’d handle a difficult case.
The brothers are especially thrilled when posts spawn discussions that draw voices from leading medical institutions who normally don’t interact much with community oncologists. “You’ll have someone from Sloan Kettering or Dana-Farber saying ‘This is what would do,’ ” Rahul said. “You have the brightest minds pitching in, and we get to learn from them.”
The Gosain brothers were both born in India and immigrated as children to Toronto. They each went to medical school in the Caribbean – for Rohit, it was after a stint as a computer engineer – and they each embraced oncology. “For me, it was about having the right mentors while I was doing my clinical rotations as a medical student and as a resident,” Rahul said. In addition, he said, “this field was moving and is still moving so fast. It really intrigued and excited me and made me want to be at the forefront of it.”
The fast-moving nature of oncology, in fact, was one of the drivers behind the daily conversations between the brothers and the subsequent creation of the @OncBrothers account. “Just last year, in 2021, there were 40 new drugs that were indicated for hematology-oncology,” Rahul said. “To stay on top of that is very, very hard.”
It’s especially difficult to figure out treatment plans when multiple options exist. A 2022 thread on @OncBrothers revealed a wide divergence of opinions about triple therapy in prostate cancer: The 322 respondents to a Twitter poll were sharply divided about the best three-drug combination from these options – docetaxel, daratumumab, abiraterone, androgen deprivation therapy, and alpha-reductase inhibitors.
To make things more challenging, community oncologists often are generalists who treat patients with a wide variety of cancers from prostate and lung to breast and colon. As a result, these oncologists must keep up on developments across the entire cancer field. Rohit highlighted a 2022 thread that polled users about the approach they’d take to another patient with non–small cell lung cancer; 474 people responded. The accompanying discussion emphasized the need for the next-generation sequencing (NGS).
“A significant portion of community oncologists are not even doing NGS testing, which is FDA-approved,” Rohit said. “There’s a huge gap that still exists, and we weren’t even aware of it. We continue to learn from these conversations.”
The brothers contend that there’s a crucial need for education among community oncologists in light of evidence suggesting that some cancer outcomes are worse than those in urban areas.
In fact, Rohit led a 2019 study published in the journal Cancer that found that overall survival in rural patients with neuroendocrine tumors trended toward worse outcomes than in urban patients.
“There are many factors such as financial burden, lack of education, and rural patients not willing to travel to the city,” Rohit said. “We need to be more creative and ask, ‘How can we equip our medical oncologist in rural settings to continue to do better?’ ”
What’s next for the OncBrothers? The Gosains have created a website (www.oncbrothers.com) that highlights their social media work, and they’re exploring options such as podcasts and short videos. “Our goal is to focus on how to continue to keep general medical oncologists up to date, informed, and educated so patients can get the best care close to home,” Rahul said. “We need to do better.”
It’s hard out there for a small-town cancer doctor. Just ask Wederson M. Claudino, MD, who serves the town of Paducah in far western Kentucky. The nearest cities with significant numbers of hematologist/oncologists are hours away in cities like St. Louis and Nashville, Tenn., too far to go to talk shop over coffee, drinks, or lunch.
“It’s very challenging in a rural or small community,” he said. “I miss the opportunity to elaborate on a case.”
Now Dr. Claudino and hundreds of colleagues have discovered that useful cancer conversations are just a click away.
Urban and rural oncologists gather there to discuss new research, compare notes about challenging cases, and get to know each other.
“Following their Twitter feed and the comments and discussions make me feel like part of a bigger community,” Dr. Claudino said. And @OncBrothers is indeed a bustling Internet destination: The account’s 4,300 followers include hundreds who participate in discussions and offer perspective.
For instance, the brothers recently posted a poll asking followers how they’d treat a 55-year-old patient with non–small cell lung cancer. Nearly 250 people responded with their preferred approaches, and the survey thread included comments from oncologists from the City of Hope National Medical Center, the University of Florida, UC San Diego, and elsewhere.
In an interview, the Gosain brothers said the Twitter account is an outgrowth of their phone conversations in recent years, as they trained and settled into their early careers as general medical oncologists in smaller communities.
“After our clinic days, we’ll jump on the phone for 30-45 minutes. We’d talk about patients, how he would treat a case, and what I would do,” Rahul said. “We realized that we were living in a bubble, but we also thought that there are a lot more people in the same boat. They might jump at being able to do the same thing.”
Rahul recently became medical director at the new Wilmot Webster Cancer Center in Rochester, N.Y., after working in Corning, a tiny New York town just north of the Pennsylvania border. His brother Rohit is chair of hematology and oncology at the University of Pittsburgh’s Hillman Cancer Center in Jamestown, a small town at the western edge of New York.
“When we initially kicked off the Twitter account in August 2021, we didn’t realize the traction it would get,” Rohit said. “Now we realize that there really is a need for this.”
On an ordinary day, the @OncBrothers account may highlight research presented at a oncology conference, retweet posts by other oncologists about new guidelines or FDA drug approvals, and ask followers to consider how they’d handle a difficult case.
The brothers are especially thrilled when posts spawn discussions that draw voices from leading medical institutions who normally don’t interact much with community oncologists. “You’ll have someone from Sloan Kettering or Dana-Farber saying ‘This is what would do,’ ” Rahul said. “You have the brightest minds pitching in, and we get to learn from them.”
The Gosain brothers were both born in India and immigrated as children to Toronto. They each went to medical school in the Caribbean – for Rohit, it was after a stint as a computer engineer – and they each embraced oncology. “For me, it was about having the right mentors while I was doing my clinical rotations as a medical student and as a resident,” Rahul said. In addition, he said, “this field was moving and is still moving so fast. It really intrigued and excited me and made me want to be at the forefront of it.”
The fast-moving nature of oncology, in fact, was one of the drivers behind the daily conversations between the brothers and the subsequent creation of the @OncBrothers account. “Just last year, in 2021, there were 40 new drugs that were indicated for hematology-oncology,” Rahul said. “To stay on top of that is very, very hard.”
It’s especially difficult to figure out treatment plans when multiple options exist. A 2022 thread on @OncBrothers revealed a wide divergence of opinions about triple therapy in prostate cancer: The 322 respondents to a Twitter poll were sharply divided about the best three-drug combination from these options – docetaxel, daratumumab, abiraterone, androgen deprivation therapy, and alpha-reductase inhibitors.
To make things more challenging, community oncologists often are generalists who treat patients with a wide variety of cancers from prostate and lung to breast and colon. As a result, these oncologists must keep up on developments across the entire cancer field. Rohit highlighted a 2022 thread that polled users about the approach they’d take to another patient with non–small cell lung cancer; 474 people responded. The accompanying discussion emphasized the need for the next-generation sequencing (NGS).
“A significant portion of community oncologists are not even doing NGS testing, which is FDA-approved,” Rohit said. “There’s a huge gap that still exists, and we weren’t even aware of it. We continue to learn from these conversations.”
The brothers contend that there’s a crucial need for education among community oncologists in light of evidence suggesting that some cancer outcomes are worse than those in urban areas.
In fact, Rohit led a 2019 study published in the journal Cancer that found that overall survival in rural patients with neuroendocrine tumors trended toward worse outcomes than in urban patients.
“There are many factors such as financial burden, lack of education, and rural patients not willing to travel to the city,” Rohit said. “We need to be more creative and ask, ‘How can we equip our medical oncologist in rural settings to continue to do better?’ ”
What’s next for the OncBrothers? The Gosains have created a website (www.oncbrothers.com) that highlights their social media work, and they’re exploring options such as podcasts and short videos. “Our goal is to focus on how to continue to keep general medical oncologists up to date, informed, and educated so patients can get the best care close to home,” Rahul said. “We need to do better.”
House passes prior authorization bill, Senate path unclear
The path through the U.S. Senate is not yet certain for a bill intended to speed the prior authorization process of insurer-run Medicare Advantage plans, despite the measure having breezed through the House.
House leaders opted to move the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act of 2021 (HR 3173) without requiring a roll-call vote. The measure was passed on Sept. 14 by a voice vote, an approach used in general with only uncontroversial measures that have broad support. The bill has 191 Democratic and 135 Republican sponsors, representing about three-quarters of the members of the House.
“There is no reason that patients should be waiting for medically appropriate care, especially when we know that this can lead to worse outcomes,” Rep. Earl Blumenauer (D-Ore.) said in a Sept. 14 speech on the House floor. “The fundamental promise of Medicare Advantage is undermined when people are delaying care, getting sicker, and ultimately costing Medicare more money.”
Rep. Greg Murphy, MD (R-N.C.), spoke on the House floor that day as well, bringing up cases he has seen in his own urology practice in which prior authorization delays disrupted medical care. One patient wound up in the hospital with abscess after an insurer denied an antibiotic prescription, Rep. Murphy said.
But the Senate appears unlikely at this time to move the prior authorization bill as a standalone measure. Instead, the bill may become part of a larger legislative package focused on health care that the Senate Finance Committee intends to prepare later this year.
The House-passed bill would require insurer-run Medicare plans to respond to expedited requests for prior authorization of services within 24 hours and to other requests within 7 days. This bill also would establish an electronic program for prior authorizations and mandate increased transparency as to how insurers use this tool.
CBO: Cost of change would be billions
In seeking to mandate changes in prior authorization, lawmakers likely will need to contend with the issue of a $16 billion cumulative cost estimate for the bill from the Congressional Budget Office. Members of Congress often seek to offset new spending by pairing bills that add to expected costs for the federal government with ones expected to produce savings.
Unlike Rep. Blumenauer, Rep. Murphy, and other backers of the prior authorization streamlining bill, CBO staff estimates that making the mandated changes would raise federal spending, inasmuch as there would be “a greater use of services.”
On Sept. 14, CBO issued a one-page report on the costs of the bill. The CBO report concerns only the bill in question, as is common practice with the office’s estimates.
Prior authorization changes would begin in fiscal 2025 and would add $899 million in spending, or outlays, that year, CBO said. The annual costs from the streamlined prior authorization practices through fiscal 2026 to 2032 range from $1.6 billion to $2.7 billion.
Looking at the CBO estimate against a backdrop of total Medicare Advantage costs, though, may provide important context.
The increases in spending estimated by CBO may suggest that there would be little change in federal spending as a result of streamlining prior authorization practices. These estimates of increased annual spending of $1.6 billion–$2.7 billion are only a small fraction of the current annual cost of insurer-run Medicare, and they represent an even smaller share of the projected expense.
The federal government last year spent about $350 billion on insurer-run plans, excluding Part D drug plan payments, according to the Medicare Advisory Payment Commission (MedPAC).
As of 2021, about 27 million people were enrolled in these plans, accounting for about 46% of the total Medicare population. Enrollment has doubled since 2010, MedPAC said, and it is expected to continue to grow. By 2027, insurer-run Medicare could cover 50% of the program’s population, a figure that may reach 53% by 2031.
Federal payments to these plans will accelerate in the years ahead as insurers attract more people eligible for Medicare as customers. Payments to these private health plans could rise from an expected $418 billion this year to $940.6 billion by 2031, according to the most recent Medicare trustees report.
Good intentions, poor implementation?
Insurer-run Medicare has long enjoyed deep bipartisan support in Congress. That’s due in part to its potential for reducing spending on what are considered low-value treatments, or ones considered unlikely to provide a significant medical benefit, but Rep. Blumenauer is among the members of Congress who see insurer-run Medicare as a path for preserving the giant federal health program. Traditional Medicare has far fewer restrictions on services, which sometimes opens a path for tests and treatments that offer less value for patients.
“I believe that the way traditional fee-for-service Medicare operates is not sustainable and that Medicare Advantage is one of the tools we can use to demonstrate how we can incentivize value,” Rep. Blumenauer said on the House floor. “But this is only possible when the program operates as intended. I have been deeply concerned about the reports of delays in care” caused by the clunky prior authorization processes.
He highlighted a recent report from the internal watchdog group for the Department of Health & Human Services that raises concerns about denials of appropriate care. About 18% of a set of payment denials examined by the Office of Inspector General of HHS in April actually met Medicare coverage rules and plan billing rules.
“For patients and their families, being told that you need to wait longer for care that your doctor tells you that you need is incredibly frustrating and frightening,” Rep. Blumenauer said. “There’s no comfort to be found in the fact that your insurance company needs time to decide if your doctor is right.”
Trends in prior authorization
The CBO report does not provide detail on what kind of medical spending would increase under a streamlined prior authorization process in insurer-run Medicare plans.
From trends reported in prior authorization, though, two factors could be at play in what appear to be relatively small estimated increases in Medicare spending from streamlined prior authorization.
One is the work already underway to create less burdensome electronic systems for these requests, such as the Fast Prior Authorization Technology Highway initiative run by the trade association America’s Health Insurance Plans.
The other factor could be the number of cases in which prior authorization merely causes delays in treatments and tests and thus simply postpones spending while adding to clinicians’ administrative work.
An analysis of prior authorization requests for dermatologic practices affiliated with the University of Utah may represent an extreme example. In a report published in JAMA Dermatology in 2020, researchers described what happened with requests made during 1 month, September 2016.
The approval rate for procedures was 99.6% – 100% (95 of 95) for Mohs surgery, and 96% (130 of 131, with 4 additional cases pending) for excisions. These findings supported calls for simplifying prior authorization procedures, “perhaps first by eliminating unnecessary PAs [prior authorizations] and appeals,” Aaron M. Secrest, MD, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and coauthors wrote in the article.
Still, there is some evidence that insurer-run Medicare policies reduce the use of low-value care.
In a study published in JAMA Health Forum, Emily Boudreau, PhD, of insurer Humana Inc, and coauthors from Tufts University, Boston, and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia investigated whether insurer-run Medicare could do a better job in reducing the amount of low-value care delivered than the traditional program. They analyzed a set of claims data from 2017 to 2019 for people enrolled in insurer-run and traditional Medicare.
They reported a rate of 23.07 low-value services provided per 100 people in insurer-run Medicare, compared with 25.39 for those in traditional Medicare. Some of the biggest differences reported in the article were in cancer screenings for older people.
As an example, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that women older than 65 years not be screened for cervical cancer if they have undergone adequate screening in the past and are not at high risk for cervical cancer. There was an annual count of 1.76 screenings for cervical cancer per 100 women older than 65 in the insurer-run Medicare group versus 3.18 for those in traditional Medicare.
The Better Medicare Alliance issued a statement in favor of the House passage of the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act.
In it, the group said the measure would “modernize prior authorization while protecting its essential function in facilitating safe, high-value, evidence-based care.” The alliance promotes use of insurer-run Medicare. The board of the Better Medicare Alliance includes executives who serve with firms that run Advantage plans as well as medical organizations and universities.
“With studies showing that up to one-quarter of all health care expenditures are wasted on services with no benefit to the patient, we need a robust, next-generation prior authorization program to deter low-value, and even harmful, care while protecting access to needed treatment and effective therapies,” said A. Mark Fendrick, MD, director of the University of Michigan’s Center for Value-Based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor, in a statement issued by the Better Medicare Alliance. He is a member of the group’s council of scholars.
On the House floor on September 14, Rep. Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), said he has heard from former colleagues and his medical school classmates that they now spend as much as 40% of their time on administrative work. These distractions from patient care are helping drive physicians away from the practice of medicine.
Still, the internist defended the basic premise of prior authorization while strongly appealing for better systems of handling it.
“Yes, there is a role for prior authorization in limited cases. There is also a role to go back and retrospectively look at how care is being delivered,” Rep. Bera said. “But what is happening today is a travesty. It wasn’t the intention of prior authorization. It is a prior authorization process gone awry.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The path through the U.S. Senate is not yet certain for a bill intended to speed the prior authorization process of insurer-run Medicare Advantage plans, despite the measure having breezed through the House.
House leaders opted to move the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act of 2021 (HR 3173) without requiring a roll-call vote. The measure was passed on Sept. 14 by a voice vote, an approach used in general with only uncontroversial measures that have broad support. The bill has 191 Democratic and 135 Republican sponsors, representing about three-quarters of the members of the House.
“There is no reason that patients should be waiting for medically appropriate care, especially when we know that this can lead to worse outcomes,” Rep. Earl Blumenauer (D-Ore.) said in a Sept. 14 speech on the House floor. “The fundamental promise of Medicare Advantage is undermined when people are delaying care, getting sicker, and ultimately costing Medicare more money.”
Rep. Greg Murphy, MD (R-N.C.), spoke on the House floor that day as well, bringing up cases he has seen in his own urology practice in which prior authorization delays disrupted medical care. One patient wound up in the hospital with abscess after an insurer denied an antibiotic prescription, Rep. Murphy said.
But the Senate appears unlikely at this time to move the prior authorization bill as a standalone measure. Instead, the bill may become part of a larger legislative package focused on health care that the Senate Finance Committee intends to prepare later this year.
The House-passed bill would require insurer-run Medicare plans to respond to expedited requests for prior authorization of services within 24 hours and to other requests within 7 days. This bill also would establish an electronic program for prior authorizations and mandate increased transparency as to how insurers use this tool.
CBO: Cost of change would be billions
In seeking to mandate changes in prior authorization, lawmakers likely will need to contend with the issue of a $16 billion cumulative cost estimate for the bill from the Congressional Budget Office. Members of Congress often seek to offset new spending by pairing bills that add to expected costs for the federal government with ones expected to produce savings.
Unlike Rep. Blumenauer, Rep. Murphy, and other backers of the prior authorization streamlining bill, CBO staff estimates that making the mandated changes would raise federal spending, inasmuch as there would be “a greater use of services.”
On Sept. 14, CBO issued a one-page report on the costs of the bill. The CBO report concerns only the bill in question, as is common practice with the office’s estimates.
Prior authorization changes would begin in fiscal 2025 and would add $899 million in spending, or outlays, that year, CBO said. The annual costs from the streamlined prior authorization practices through fiscal 2026 to 2032 range from $1.6 billion to $2.7 billion.
Looking at the CBO estimate against a backdrop of total Medicare Advantage costs, though, may provide important context.
The increases in spending estimated by CBO may suggest that there would be little change in federal spending as a result of streamlining prior authorization practices. These estimates of increased annual spending of $1.6 billion–$2.7 billion are only a small fraction of the current annual cost of insurer-run Medicare, and they represent an even smaller share of the projected expense.
The federal government last year spent about $350 billion on insurer-run plans, excluding Part D drug plan payments, according to the Medicare Advisory Payment Commission (MedPAC).
As of 2021, about 27 million people were enrolled in these plans, accounting for about 46% of the total Medicare population. Enrollment has doubled since 2010, MedPAC said, and it is expected to continue to grow. By 2027, insurer-run Medicare could cover 50% of the program’s population, a figure that may reach 53% by 2031.
Federal payments to these plans will accelerate in the years ahead as insurers attract more people eligible for Medicare as customers. Payments to these private health plans could rise from an expected $418 billion this year to $940.6 billion by 2031, according to the most recent Medicare trustees report.
Good intentions, poor implementation?
Insurer-run Medicare has long enjoyed deep bipartisan support in Congress. That’s due in part to its potential for reducing spending on what are considered low-value treatments, or ones considered unlikely to provide a significant medical benefit, but Rep. Blumenauer is among the members of Congress who see insurer-run Medicare as a path for preserving the giant federal health program. Traditional Medicare has far fewer restrictions on services, which sometimes opens a path for tests and treatments that offer less value for patients.
“I believe that the way traditional fee-for-service Medicare operates is not sustainable and that Medicare Advantage is one of the tools we can use to demonstrate how we can incentivize value,” Rep. Blumenauer said on the House floor. “But this is only possible when the program operates as intended. I have been deeply concerned about the reports of delays in care” caused by the clunky prior authorization processes.
He highlighted a recent report from the internal watchdog group for the Department of Health & Human Services that raises concerns about denials of appropriate care. About 18% of a set of payment denials examined by the Office of Inspector General of HHS in April actually met Medicare coverage rules and plan billing rules.
“For patients and their families, being told that you need to wait longer for care that your doctor tells you that you need is incredibly frustrating and frightening,” Rep. Blumenauer said. “There’s no comfort to be found in the fact that your insurance company needs time to decide if your doctor is right.”
Trends in prior authorization
The CBO report does not provide detail on what kind of medical spending would increase under a streamlined prior authorization process in insurer-run Medicare plans.
From trends reported in prior authorization, though, two factors could be at play in what appear to be relatively small estimated increases in Medicare spending from streamlined prior authorization.
One is the work already underway to create less burdensome electronic systems for these requests, such as the Fast Prior Authorization Technology Highway initiative run by the trade association America’s Health Insurance Plans.
The other factor could be the number of cases in which prior authorization merely causes delays in treatments and tests and thus simply postpones spending while adding to clinicians’ administrative work.
An analysis of prior authorization requests for dermatologic practices affiliated with the University of Utah may represent an extreme example. In a report published in JAMA Dermatology in 2020, researchers described what happened with requests made during 1 month, September 2016.
The approval rate for procedures was 99.6% – 100% (95 of 95) for Mohs surgery, and 96% (130 of 131, with 4 additional cases pending) for excisions. These findings supported calls for simplifying prior authorization procedures, “perhaps first by eliminating unnecessary PAs [prior authorizations] and appeals,” Aaron M. Secrest, MD, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and coauthors wrote in the article.
Still, there is some evidence that insurer-run Medicare policies reduce the use of low-value care.
In a study published in JAMA Health Forum, Emily Boudreau, PhD, of insurer Humana Inc, and coauthors from Tufts University, Boston, and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia investigated whether insurer-run Medicare could do a better job in reducing the amount of low-value care delivered than the traditional program. They analyzed a set of claims data from 2017 to 2019 for people enrolled in insurer-run and traditional Medicare.
They reported a rate of 23.07 low-value services provided per 100 people in insurer-run Medicare, compared with 25.39 for those in traditional Medicare. Some of the biggest differences reported in the article were in cancer screenings for older people.
As an example, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that women older than 65 years not be screened for cervical cancer if they have undergone adequate screening in the past and are not at high risk for cervical cancer. There was an annual count of 1.76 screenings for cervical cancer per 100 women older than 65 in the insurer-run Medicare group versus 3.18 for those in traditional Medicare.
The Better Medicare Alliance issued a statement in favor of the House passage of the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act.
In it, the group said the measure would “modernize prior authorization while protecting its essential function in facilitating safe, high-value, evidence-based care.” The alliance promotes use of insurer-run Medicare. The board of the Better Medicare Alliance includes executives who serve with firms that run Advantage plans as well as medical organizations and universities.
“With studies showing that up to one-quarter of all health care expenditures are wasted on services with no benefit to the patient, we need a robust, next-generation prior authorization program to deter low-value, and even harmful, care while protecting access to needed treatment and effective therapies,” said A. Mark Fendrick, MD, director of the University of Michigan’s Center for Value-Based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor, in a statement issued by the Better Medicare Alliance. He is a member of the group’s council of scholars.
On the House floor on September 14, Rep. Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), said he has heard from former colleagues and his medical school classmates that they now spend as much as 40% of their time on administrative work. These distractions from patient care are helping drive physicians away from the practice of medicine.
Still, the internist defended the basic premise of prior authorization while strongly appealing for better systems of handling it.
“Yes, there is a role for prior authorization in limited cases. There is also a role to go back and retrospectively look at how care is being delivered,” Rep. Bera said. “But what is happening today is a travesty. It wasn’t the intention of prior authorization. It is a prior authorization process gone awry.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The path through the U.S. Senate is not yet certain for a bill intended to speed the prior authorization process of insurer-run Medicare Advantage plans, despite the measure having breezed through the House.
House leaders opted to move the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act of 2021 (HR 3173) without requiring a roll-call vote. The measure was passed on Sept. 14 by a voice vote, an approach used in general with only uncontroversial measures that have broad support. The bill has 191 Democratic and 135 Republican sponsors, representing about three-quarters of the members of the House.
“There is no reason that patients should be waiting for medically appropriate care, especially when we know that this can lead to worse outcomes,” Rep. Earl Blumenauer (D-Ore.) said in a Sept. 14 speech on the House floor. “The fundamental promise of Medicare Advantage is undermined when people are delaying care, getting sicker, and ultimately costing Medicare more money.”
Rep. Greg Murphy, MD (R-N.C.), spoke on the House floor that day as well, bringing up cases he has seen in his own urology practice in which prior authorization delays disrupted medical care. One patient wound up in the hospital with abscess after an insurer denied an antibiotic prescription, Rep. Murphy said.
But the Senate appears unlikely at this time to move the prior authorization bill as a standalone measure. Instead, the bill may become part of a larger legislative package focused on health care that the Senate Finance Committee intends to prepare later this year.
The House-passed bill would require insurer-run Medicare plans to respond to expedited requests for prior authorization of services within 24 hours and to other requests within 7 days. This bill also would establish an electronic program for prior authorizations and mandate increased transparency as to how insurers use this tool.
CBO: Cost of change would be billions
In seeking to mandate changes in prior authorization, lawmakers likely will need to contend with the issue of a $16 billion cumulative cost estimate for the bill from the Congressional Budget Office. Members of Congress often seek to offset new spending by pairing bills that add to expected costs for the federal government with ones expected to produce savings.
Unlike Rep. Blumenauer, Rep. Murphy, and other backers of the prior authorization streamlining bill, CBO staff estimates that making the mandated changes would raise federal spending, inasmuch as there would be “a greater use of services.”
On Sept. 14, CBO issued a one-page report on the costs of the bill. The CBO report concerns only the bill in question, as is common practice with the office’s estimates.
Prior authorization changes would begin in fiscal 2025 and would add $899 million in spending, or outlays, that year, CBO said. The annual costs from the streamlined prior authorization practices through fiscal 2026 to 2032 range from $1.6 billion to $2.7 billion.
Looking at the CBO estimate against a backdrop of total Medicare Advantage costs, though, may provide important context.
The increases in spending estimated by CBO may suggest that there would be little change in federal spending as a result of streamlining prior authorization practices. These estimates of increased annual spending of $1.6 billion–$2.7 billion are only a small fraction of the current annual cost of insurer-run Medicare, and they represent an even smaller share of the projected expense.
The federal government last year spent about $350 billion on insurer-run plans, excluding Part D drug plan payments, according to the Medicare Advisory Payment Commission (MedPAC).
As of 2021, about 27 million people were enrolled in these plans, accounting for about 46% of the total Medicare population. Enrollment has doubled since 2010, MedPAC said, and it is expected to continue to grow. By 2027, insurer-run Medicare could cover 50% of the program’s population, a figure that may reach 53% by 2031.
Federal payments to these plans will accelerate in the years ahead as insurers attract more people eligible for Medicare as customers. Payments to these private health plans could rise from an expected $418 billion this year to $940.6 billion by 2031, according to the most recent Medicare trustees report.
Good intentions, poor implementation?
Insurer-run Medicare has long enjoyed deep bipartisan support in Congress. That’s due in part to its potential for reducing spending on what are considered low-value treatments, or ones considered unlikely to provide a significant medical benefit, but Rep. Blumenauer is among the members of Congress who see insurer-run Medicare as a path for preserving the giant federal health program. Traditional Medicare has far fewer restrictions on services, which sometimes opens a path for tests and treatments that offer less value for patients.
“I believe that the way traditional fee-for-service Medicare operates is not sustainable and that Medicare Advantage is one of the tools we can use to demonstrate how we can incentivize value,” Rep. Blumenauer said on the House floor. “But this is only possible when the program operates as intended. I have been deeply concerned about the reports of delays in care” caused by the clunky prior authorization processes.
He highlighted a recent report from the internal watchdog group for the Department of Health & Human Services that raises concerns about denials of appropriate care. About 18% of a set of payment denials examined by the Office of Inspector General of HHS in April actually met Medicare coverage rules and plan billing rules.
“For patients and their families, being told that you need to wait longer for care that your doctor tells you that you need is incredibly frustrating and frightening,” Rep. Blumenauer said. “There’s no comfort to be found in the fact that your insurance company needs time to decide if your doctor is right.”
Trends in prior authorization
The CBO report does not provide detail on what kind of medical spending would increase under a streamlined prior authorization process in insurer-run Medicare plans.
From trends reported in prior authorization, though, two factors could be at play in what appear to be relatively small estimated increases in Medicare spending from streamlined prior authorization.
One is the work already underway to create less burdensome electronic systems for these requests, such as the Fast Prior Authorization Technology Highway initiative run by the trade association America’s Health Insurance Plans.
The other factor could be the number of cases in which prior authorization merely causes delays in treatments and tests and thus simply postpones spending while adding to clinicians’ administrative work.
An analysis of prior authorization requests for dermatologic practices affiliated with the University of Utah may represent an extreme example. In a report published in JAMA Dermatology in 2020, researchers described what happened with requests made during 1 month, September 2016.
The approval rate for procedures was 99.6% – 100% (95 of 95) for Mohs surgery, and 96% (130 of 131, with 4 additional cases pending) for excisions. These findings supported calls for simplifying prior authorization procedures, “perhaps first by eliminating unnecessary PAs [prior authorizations] and appeals,” Aaron M. Secrest, MD, PhD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and coauthors wrote in the article.
Still, there is some evidence that insurer-run Medicare policies reduce the use of low-value care.
In a study published in JAMA Health Forum, Emily Boudreau, PhD, of insurer Humana Inc, and coauthors from Tufts University, Boston, and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia investigated whether insurer-run Medicare could do a better job in reducing the amount of low-value care delivered than the traditional program. They analyzed a set of claims data from 2017 to 2019 for people enrolled in insurer-run and traditional Medicare.
They reported a rate of 23.07 low-value services provided per 100 people in insurer-run Medicare, compared with 25.39 for those in traditional Medicare. Some of the biggest differences reported in the article were in cancer screenings for older people.
As an example, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that women older than 65 years not be screened for cervical cancer if they have undergone adequate screening in the past and are not at high risk for cervical cancer. There was an annual count of 1.76 screenings for cervical cancer per 100 women older than 65 in the insurer-run Medicare group versus 3.18 for those in traditional Medicare.
The Better Medicare Alliance issued a statement in favor of the House passage of the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act.
In it, the group said the measure would “modernize prior authorization while protecting its essential function in facilitating safe, high-value, evidence-based care.” The alliance promotes use of insurer-run Medicare. The board of the Better Medicare Alliance includes executives who serve with firms that run Advantage plans as well as medical organizations and universities.
“With studies showing that up to one-quarter of all health care expenditures are wasted on services with no benefit to the patient, we need a robust, next-generation prior authorization program to deter low-value, and even harmful, care while protecting access to needed treatment and effective therapies,” said A. Mark Fendrick, MD, director of the University of Michigan’s Center for Value-Based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor, in a statement issued by the Better Medicare Alliance. He is a member of the group’s council of scholars.
On the House floor on September 14, Rep. Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), said he has heard from former colleagues and his medical school classmates that they now spend as much as 40% of their time on administrative work. These distractions from patient care are helping drive physicians away from the practice of medicine.
Still, the internist defended the basic premise of prior authorization while strongly appealing for better systems of handling it.
“Yes, there is a role for prior authorization in limited cases. There is also a role to go back and retrospectively look at how care is being delivered,” Rep. Bera said. “But what is happening today is a travesty. It wasn’t the intention of prior authorization. It is a prior authorization process gone awry.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Horse hockey notwithstanding
He’s 24 years younger than I am, recently married, no kids. Just starting out as a neurologist. He also has a full head of hair, something I’m admittedly jealous of.
He’s always in a sweater, something that seems oddly out of place in Phoenix, Arizona.
He’s the picture on my hospital ID.
I don’t go to the hospital much anymore, but he still sits in my car, greeting me whenever I open the center console to get my sunglasses or phone charger. He looks very enthusiastic about starting his career. I clearly remember the day I had the picture taken, as a newly-minted attending getting his first hospital privileges.
Sometimes I talk to him. Usually it’s just silly advice (“bet on the ’16 Cubs”). Other times I wonder what he’d do in certain situations, with all his youthful enthusiasm. I’m sure he wonders the same about me, with my 24 years of experience.
To a large extent we are the same people we started out as, but time changes us, in ways besides the obvious (like my hairs jumping off like lemmings).
Looking back at him (or even the older pic on my medical school application) I have no complaints about where life and my career have taken me. Would there be a few things I might have changed if I could go back?
Realistically, maybe one or two, both involving my father, but neither of them would likely change where I am.
But as far as medicine goes? Not really. The things I liked then, that got me into the field? I still enjoy them. The horse hockey? Yeah, it’s always there, probably has gotten worse over time, and it still bothers me. But there isn’t a job that doesn’t have its share of cow patties. It’s just a matter of trying not to step in them more than necessary as you do the parts you enjoy.
Sometimes I look at my younger self, and wonder what I’d really say to him if we actually met.
Probably just “good luck, enjoy the ride, and ditch the sweater.”
We measure our gains out in luck and coincidence
Lanterns to turn back the night.
And put our defeats down to chance or experience
And try once again for the light.
– Al Stewart
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
He’s 24 years younger than I am, recently married, no kids. Just starting out as a neurologist. He also has a full head of hair, something I’m admittedly jealous of.
He’s always in a sweater, something that seems oddly out of place in Phoenix, Arizona.
He’s the picture on my hospital ID.
I don’t go to the hospital much anymore, but he still sits in my car, greeting me whenever I open the center console to get my sunglasses or phone charger. He looks very enthusiastic about starting his career. I clearly remember the day I had the picture taken, as a newly-minted attending getting his first hospital privileges.
Sometimes I talk to him. Usually it’s just silly advice (“bet on the ’16 Cubs”). Other times I wonder what he’d do in certain situations, with all his youthful enthusiasm. I’m sure he wonders the same about me, with my 24 years of experience.
To a large extent we are the same people we started out as, but time changes us, in ways besides the obvious (like my hairs jumping off like lemmings).
Looking back at him (or even the older pic on my medical school application) I have no complaints about where life and my career have taken me. Would there be a few things I might have changed if I could go back?
Realistically, maybe one or two, both involving my father, but neither of them would likely change where I am.
But as far as medicine goes? Not really. The things I liked then, that got me into the field? I still enjoy them. The horse hockey? Yeah, it’s always there, probably has gotten worse over time, and it still bothers me. But there isn’t a job that doesn’t have its share of cow patties. It’s just a matter of trying not to step in them more than necessary as you do the parts you enjoy.
Sometimes I look at my younger self, and wonder what I’d really say to him if we actually met.
Probably just “good luck, enjoy the ride, and ditch the sweater.”
We measure our gains out in luck and coincidence
Lanterns to turn back the night.
And put our defeats down to chance or experience
And try once again for the light.
– Al Stewart
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
He’s 24 years younger than I am, recently married, no kids. Just starting out as a neurologist. He also has a full head of hair, something I’m admittedly jealous of.
He’s always in a sweater, something that seems oddly out of place in Phoenix, Arizona.
He’s the picture on my hospital ID.
I don’t go to the hospital much anymore, but he still sits in my car, greeting me whenever I open the center console to get my sunglasses or phone charger. He looks very enthusiastic about starting his career. I clearly remember the day I had the picture taken, as a newly-minted attending getting his first hospital privileges.
Sometimes I talk to him. Usually it’s just silly advice (“bet on the ’16 Cubs”). Other times I wonder what he’d do in certain situations, with all his youthful enthusiasm. I’m sure he wonders the same about me, with my 24 years of experience.
To a large extent we are the same people we started out as, but time changes us, in ways besides the obvious (like my hairs jumping off like lemmings).
Looking back at him (or even the older pic on my medical school application) I have no complaints about where life and my career have taken me. Would there be a few things I might have changed if I could go back?
Realistically, maybe one or two, both involving my father, but neither of them would likely change where I am.
But as far as medicine goes? Not really. The things I liked then, that got me into the field? I still enjoy them. The horse hockey? Yeah, it’s always there, probably has gotten worse over time, and it still bothers me. But there isn’t a job that doesn’t have its share of cow patties. It’s just a matter of trying not to step in them more than necessary as you do the parts you enjoy.
Sometimes I look at my younger self, and wonder what I’d really say to him if we actually met.
Probably just “good luck, enjoy the ride, and ditch the sweater.”
We measure our gains out in luck and coincidence
Lanterns to turn back the night.
And put our defeats down to chance or experience
And try once again for the light.
– Al Stewart
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Physicians can’t be bystanders in ‘silent scourge’ of medical bullying
Maya Iyer, MD, MEd, experienced bullying as a faculty member, and she sensed that she wasn’t alone. “The best ideas for research often come from individual experiences, in both personal and the professional academic medicine setting,” she said in an interview.
“And I was correct. I was not the only one who experienced bullying. In fact, the most severe bullying experiences among ... women physician leaders occurred when they were in leadership positions,” said Dr. Iyer, a pediatric emergency medicine physician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
She is a coauthor of a study that was published in JAMA Network Open in which investigators surveyed the existence of antibullying policies for faculty at almost 100 U.S. medical schools.
The researchers defined bullying as “a severe form of mistreatment [that] occurs in the medical setting when a power differential allows offenders to consciously target individuals through persistent negative actions to impede the education or career of the target.”
The study included 91 medical schools, of which 4 schools had antibullying policies that included the reporting of procedures. Of the 87 medical schools without antibullying policies, 60 had antiharrassment policies; of those schools, 10 of the schools’ websites cited bullying and antiharassment policies. Five schools required a login to access policies, and one school’s website had a broken webpage link, per the study.
“We need to bring the silent scourge of bullying to the forefront because bullying is causing a brain drain on the medical profession,” said Dr. Iyer. “Bullying has numerous downstream negative effects, including depression, anxiety, burnout stress, decreased patient care satisfaction, increased medical errors, and job attrition.”
She added: “Through bullying, we are losing voices in medicine just at that point in time where we are trying to diversify the workforce to improve representation of all physicians.”
Dr. Iyer’s team sampled the top 25 schools for research and the top 25 schools for primary care. They also took a random sampling from 25 schools for research and a random sampling from top 25 schools for primary care. They assessed antibullying policies, antiharassment policies that mentioned bullying, antiharrassment policies that did not mention bullying, and the absence of policies addressing these issues.
Policy comprehensiveness was another focus for the researchers. They evaluated whether the relevant policies included faculty members and articulated the institution’s commitment to providing a safe and healthy workplace. Other factors included defining bullying and the roles and responsibilities of employees and procedures for reporting bullying.
Physicians can’t be bystanders to bullying
This means transitioning from being a bystander to an upstander.”
She doesn’t let medical schools off the hook, however. Instead, she advocated having institutions “provide safe spaces and opportunities for near-peer mentoring so that targets of bullying can share stories.”
Regarding who is responsible for addressing bullying, Dr. Iyer is emphatic. “I do want to be clear that the onus of disrupting does not fall on the targets. Rather, we need to fix the systems in which such behavior is tolerated.”
Her advice to leaders in academic medicine is to create comprehensive, zero-retaliation bullying policies that include detailed reporting procedures. Dr. Iyer advised leaders to partner with colleagues in human resources, offices of equity, and ombudspersons to develop, implement, and enforce these policies.
The study authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Maya Iyer, MD, MEd, experienced bullying as a faculty member, and she sensed that she wasn’t alone. “The best ideas for research often come from individual experiences, in both personal and the professional academic medicine setting,” she said in an interview.
“And I was correct. I was not the only one who experienced bullying. In fact, the most severe bullying experiences among ... women physician leaders occurred when they were in leadership positions,” said Dr. Iyer, a pediatric emergency medicine physician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
She is a coauthor of a study that was published in JAMA Network Open in which investigators surveyed the existence of antibullying policies for faculty at almost 100 U.S. medical schools.
The researchers defined bullying as “a severe form of mistreatment [that] occurs in the medical setting when a power differential allows offenders to consciously target individuals through persistent negative actions to impede the education or career of the target.”
The study included 91 medical schools, of which 4 schools had antibullying policies that included the reporting of procedures. Of the 87 medical schools without antibullying policies, 60 had antiharrassment policies; of those schools, 10 of the schools’ websites cited bullying and antiharassment policies. Five schools required a login to access policies, and one school’s website had a broken webpage link, per the study.
“We need to bring the silent scourge of bullying to the forefront because bullying is causing a brain drain on the medical profession,” said Dr. Iyer. “Bullying has numerous downstream negative effects, including depression, anxiety, burnout stress, decreased patient care satisfaction, increased medical errors, and job attrition.”
She added: “Through bullying, we are losing voices in medicine just at that point in time where we are trying to diversify the workforce to improve representation of all physicians.”
Dr. Iyer’s team sampled the top 25 schools for research and the top 25 schools for primary care. They also took a random sampling from 25 schools for research and a random sampling from top 25 schools for primary care. They assessed antibullying policies, antiharassment policies that mentioned bullying, antiharrassment policies that did not mention bullying, and the absence of policies addressing these issues.
Policy comprehensiveness was another focus for the researchers. They evaluated whether the relevant policies included faculty members and articulated the institution’s commitment to providing a safe and healthy workplace. Other factors included defining bullying and the roles and responsibilities of employees and procedures for reporting bullying.
Physicians can’t be bystanders to bullying
This means transitioning from being a bystander to an upstander.”
She doesn’t let medical schools off the hook, however. Instead, she advocated having institutions “provide safe spaces and opportunities for near-peer mentoring so that targets of bullying can share stories.”
Regarding who is responsible for addressing bullying, Dr. Iyer is emphatic. “I do want to be clear that the onus of disrupting does not fall on the targets. Rather, we need to fix the systems in which such behavior is tolerated.”
Her advice to leaders in academic medicine is to create comprehensive, zero-retaliation bullying policies that include detailed reporting procedures. Dr. Iyer advised leaders to partner with colleagues in human resources, offices of equity, and ombudspersons to develop, implement, and enforce these policies.
The study authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Maya Iyer, MD, MEd, experienced bullying as a faculty member, and she sensed that she wasn’t alone. “The best ideas for research often come from individual experiences, in both personal and the professional academic medicine setting,” she said in an interview.
“And I was correct. I was not the only one who experienced bullying. In fact, the most severe bullying experiences among ... women physician leaders occurred when they were in leadership positions,” said Dr. Iyer, a pediatric emergency medicine physician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
She is a coauthor of a study that was published in JAMA Network Open in which investigators surveyed the existence of antibullying policies for faculty at almost 100 U.S. medical schools.
The researchers defined bullying as “a severe form of mistreatment [that] occurs in the medical setting when a power differential allows offenders to consciously target individuals through persistent negative actions to impede the education or career of the target.”
The study included 91 medical schools, of which 4 schools had antibullying policies that included the reporting of procedures. Of the 87 medical schools without antibullying policies, 60 had antiharrassment policies; of those schools, 10 of the schools’ websites cited bullying and antiharassment policies. Five schools required a login to access policies, and one school’s website had a broken webpage link, per the study.
“We need to bring the silent scourge of bullying to the forefront because bullying is causing a brain drain on the medical profession,” said Dr. Iyer. “Bullying has numerous downstream negative effects, including depression, anxiety, burnout stress, decreased patient care satisfaction, increased medical errors, and job attrition.”
She added: “Through bullying, we are losing voices in medicine just at that point in time where we are trying to diversify the workforce to improve representation of all physicians.”
Dr. Iyer’s team sampled the top 25 schools for research and the top 25 schools for primary care. They also took a random sampling from 25 schools for research and a random sampling from top 25 schools for primary care. They assessed antibullying policies, antiharassment policies that mentioned bullying, antiharrassment policies that did not mention bullying, and the absence of policies addressing these issues.
Policy comprehensiveness was another focus for the researchers. They evaluated whether the relevant policies included faculty members and articulated the institution’s commitment to providing a safe and healthy workplace. Other factors included defining bullying and the roles and responsibilities of employees and procedures for reporting bullying.
Physicians can’t be bystanders to bullying
This means transitioning from being a bystander to an upstander.”
She doesn’t let medical schools off the hook, however. Instead, she advocated having institutions “provide safe spaces and opportunities for near-peer mentoring so that targets of bullying can share stories.”
Regarding who is responsible for addressing bullying, Dr. Iyer is emphatic. “I do want to be clear that the onus of disrupting does not fall on the targets. Rather, we need to fix the systems in which such behavior is tolerated.”
Her advice to leaders in academic medicine is to create comprehensive, zero-retaliation bullying policies that include detailed reporting procedures. Dr. Iyer advised leaders to partner with colleagues in human resources, offices of equity, and ombudspersons to develop, implement, and enforce these policies.
The study authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
EHR: A progress report
I wrote my first column on electronic health records in the mid-1990s. At the time, it seemed like an idea whose time had come. After all, in an era when just about every essential process in medicine had already been computerized, we physicians continued to process clinical data – our key asset – with pen and paper. Most of us were reluctant to make the switch, and for good reason:
Then, the government stepped in. Shortly after his inauguration in 2000, President George W. Bush outlined a plan to ensure that most Americans had electronic health records within 10 years. “By computerizing health records,” the president said, “we can avoid dangerous medical mistakes, reduce costs, and improve care.” The goal was to eliminate missing charts, duplication of lab testing, ineffective documentation, and inordinate amounts of time spent on paperwork, not to mention illegible handwriting, poor coordination of care between physicians, and many other problems. Studies were quoted, suggesting that EHR shortened inpatient stays, decreased risk of adverse drug interactions, improved the consistency and content of records, and improved continuity of care and follow-up.
The EHR Incentive Program (later renamed the Promoting Interoperability Program) was introduced to encourage physicians and hospitals “to adopt, implement, upgrade, and demonstrate meaningful use of certified electronic health record technology.”
Nearly a quarter-century later, implementation is well behind schedule. According to a 2019 federal study, while nearly all hospitals (96%) have adopted a certified EHR, only 72% of office-based physicians have done so.
There are multiple reasons for this. For one thing, EHR is still by and large slower than pen and paper, because direct data entry is still primarily done by keyboard. Voice recognition, hand-held and wireless devices have been developed, but most work only on specialized tasks. Even the best systems take more clinician time per encounter than the manual processes they replace.
Physicians have been slow to warm to a system that slows them down and forces them to change the way they think and work. In addition, paper systems never crash; the prospect of a server malfunction or Internet failure bringing an entire clinic to a grinding halt is not particularly inviting.
The special needs of dermatology – high patient volumes, multiple diagnoses and prescriptions per patient, the wide variety of procedures we perform, and digital image storage – present further hurdles.
Nevertheless, the march toward electronic record keeping continues, and I continue to receive many questions about choosing a good EHR system. As always, I cannot recommend any specific products since every office has unique needs and requirements.
The key phrase to keep in mind is caveat emptor. Several regulatory bodies exist to test vendor claims and certify system behaviors, but different agencies use different criteria that may or may not be relevant to your requirements. Vaporware is still as common as real software; beware the “feature in the next release” that might never appear, particularly if you need it right now.
Avoid the temptation to buy a flashy new system and then try to adapt it to your office; figure out your needs first, then find a system that meets them.
Unfortunately, there is no easy way around doing the work of comparing one system with another. The most important information a vendor can give you is the names and addresses of two or more offices where you can go watch their system in action. Site visits are time-consuming, but they are only way to pick the best EHR the first time around.
Don’t be the first office using a new system. Let the vendor work out the bugs somewhere else.
Above all, if you have disorganized paper records, don’t count on EHR to automatically solve your problems. Well-designed paper systems usually lend themselves to effective automation, but automating a poorly designed system just increases the chaos. If your paper system is in disarray, solve that problem before considering EHR.
With all of its problems and hurdles, EHRs will inevitably be a part of most of our lives. And for those who take the time to do it right, it will ultimately be an improvement.
Think of information technologies as power tools: They can help you to do things better, but they can also amplify your errors. So choose carefully.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
I wrote my first column on electronic health records in the mid-1990s. At the time, it seemed like an idea whose time had come. After all, in an era when just about every essential process in medicine had already been computerized, we physicians continued to process clinical data – our key asset – with pen and paper. Most of us were reluctant to make the switch, and for good reason:
Then, the government stepped in. Shortly after his inauguration in 2000, President George W. Bush outlined a plan to ensure that most Americans had electronic health records within 10 years. “By computerizing health records,” the president said, “we can avoid dangerous medical mistakes, reduce costs, and improve care.” The goal was to eliminate missing charts, duplication of lab testing, ineffective documentation, and inordinate amounts of time spent on paperwork, not to mention illegible handwriting, poor coordination of care between physicians, and many other problems. Studies were quoted, suggesting that EHR shortened inpatient stays, decreased risk of adverse drug interactions, improved the consistency and content of records, and improved continuity of care and follow-up.
The EHR Incentive Program (later renamed the Promoting Interoperability Program) was introduced to encourage physicians and hospitals “to adopt, implement, upgrade, and demonstrate meaningful use of certified electronic health record technology.”
Nearly a quarter-century later, implementation is well behind schedule. According to a 2019 federal study, while nearly all hospitals (96%) have adopted a certified EHR, only 72% of office-based physicians have done so.
There are multiple reasons for this. For one thing, EHR is still by and large slower than pen and paper, because direct data entry is still primarily done by keyboard. Voice recognition, hand-held and wireless devices have been developed, but most work only on specialized tasks. Even the best systems take more clinician time per encounter than the manual processes they replace.
Physicians have been slow to warm to a system that slows them down and forces them to change the way they think and work. In addition, paper systems never crash; the prospect of a server malfunction or Internet failure bringing an entire clinic to a grinding halt is not particularly inviting.
The special needs of dermatology – high patient volumes, multiple diagnoses and prescriptions per patient, the wide variety of procedures we perform, and digital image storage – present further hurdles.
Nevertheless, the march toward electronic record keeping continues, and I continue to receive many questions about choosing a good EHR system. As always, I cannot recommend any specific products since every office has unique needs and requirements.
The key phrase to keep in mind is caveat emptor. Several regulatory bodies exist to test vendor claims and certify system behaviors, but different agencies use different criteria that may or may not be relevant to your requirements. Vaporware is still as common as real software; beware the “feature in the next release” that might never appear, particularly if you need it right now.
Avoid the temptation to buy a flashy new system and then try to adapt it to your office; figure out your needs first, then find a system that meets them.
Unfortunately, there is no easy way around doing the work of comparing one system with another. The most important information a vendor can give you is the names and addresses of two or more offices where you can go watch their system in action. Site visits are time-consuming, but they are only way to pick the best EHR the first time around.
Don’t be the first office using a new system. Let the vendor work out the bugs somewhere else.
Above all, if you have disorganized paper records, don’t count on EHR to automatically solve your problems. Well-designed paper systems usually lend themselves to effective automation, but automating a poorly designed system just increases the chaos. If your paper system is in disarray, solve that problem before considering EHR.
With all of its problems and hurdles, EHRs will inevitably be a part of most of our lives. And for those who take the time to do it right, it will ultimately be an improvement.
Think of information technologies as power tools: They can help you to do things better, but they can also amplify your errors. So choose carefully.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
I wrote my first column on electronic health records in the mid-1990s. At the time, it seemed like an idea whose time had come. After all, in an era when just about every essential process in medicine had already been computerized, we physicians continued to process clinical data – our key asset – with pen and paper. Most of us were reluctant to make the switch, and for good reason:
Then, the government stepped in. Shortly after his inauguration in 2000, President George W. Bush outlined a plan to ensure that most Americans had electronic health records within 10 years. “By computerizing health records,” the president said, “we can avoid dangerous medical mistakes, reduce costs, and improve care.” The goal was to eliminate missing charts, duplication of lab testing, ineffective documentation, and inordinate amounts of time spent on paperwork, not to mention illegible handwriting, poor coordination of care between physicians, and many other problems. Studies were quoted, suggesting that EHR shortened inpatient stays, decreased risk of adverse drug interactions, improved the consistency and content of records, and improved continuity of care and follow-up.
The EHR Incentive Program (later renamed the Promoting Interoperability Program) was introduced to encourage physicians and hospitals “to adopt, implement, upgrade, and demonstrate meaningful use of certified electronic health record technology.”
Nearly a quarter-century later, implementation is well behind schedule. According to a 2019 federal study, while nearly all hospitals (96%) have adopted a certified EHR, only 72% of office-based physicians have done so.
There are multiple reasons for this. For one thing, EHR is still by and large slower than pen and paper, because direct data entry is still primarily done by keyboard. Voice recognition, hand-held and wireless devices have been developed, but most work only on specialized tasks. Even the best systems take more clinician time per encounter than the manual processes they replace.
Physicians have been slow to warm to a system that slows them down and forces them to change the way they think and work. In addition, paper systems never crash; the prospect of a server malfunction or Internet failure bringing an entire clinic to a grinding halt is not particularly inviting.
The special needs of dermatology – high patient volumes, multiple diagnoses and prescriptions per patient, the wide variety of procedures we perform, and digital image storage – present further hurdles.
Nevertheless, the march toward electronic record keeping continues, and I continue to receive many questions about choosing a good EHR system. As always, I cannot recommend any specific products since every office has unique needs and requirements.
The key phrase to keep in mind is caveat emptor. Several regulatory bodies exist to test vendor claims and certify system behaviors, but different agencies use different criteria that may or may not be relevant to your requirements. Vaporware is still as common as real software; beware the “feature in the next release” that might never appear, particularly if you need it right now.
Avoid the temptation to buy a flashy new system and then try to adapt it to your office; figure out your needs first, then find a system that meets them.
Unfortunately, there is no easy way around doing the work of comparing one system with another. The most important information a vendor can give you is the names and addresses of two or more offices where you can go watch their system in action. Site visits are time-consuming, but they are only way to pick the best EHR the first time around.
Don’t be the first office using a new system. Let the vendor work out the bugs somewhere else.
Above all, if you have disorganized paper records, don’t count on EHR to automatically solve your problems. Well-designed paper systems usually lend themselves to effective automation, but automating a poorly designed system just increases the chaos. If your paper system is in disarray, solve that problem before considering EHR.
With all of its problems and hurdles, EHRs will inevitably be a part of most of our lives. And for those who take the time to do it right, it will ultimately be an improvement.
Think of information technologies as power tools: They can help you to do things better, but they can also amplify your errors. So choose carefully.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Anesthesiologist arrested, implicated in death of colleague
at Baylor Scott & White Surgicare, a North Dallas surgical center. Raynaldo Rivera Ortiz Jr., MD, 59, is accused of injecting nerve-blocking and bronchodilating drugs into patient IV bags, resulting in at least one death and multiple cardiac emergencies.
In June, an anesthesiologist identified by Dallas ABC affiliate WFAA as Melanie Kaspar, MD, a colleague of Dr. Ortiz’s at the outpatient center, was ill and treated herself for dehydration using an IV bag of saline she had taken home from work. She died immediately after injecting the contents of the bag. According to the autopsy report, she died from a lethal dose of bupivacaine, a nerve-blocking agent often used during the administration of anesthesia. According to WFAA, Dr. Kaspar’s death was initially ruled accidental, but the Dallas County Medical Examiner has since reopened the case.
Then in August, an 18-year-old male patient, identified in court documents as J.A., experienced a cardiac emergency during a scheduled surgery at the clinic. The teen, who according to local press coverage was undergoing nose surgery after a dirt bike accident, was transferred to a local ICU. A chemical analysis of the fluid from the saline bag that was used during his surgery found epinephrine (a stimulant that could have caused his symptoms), bupivacaine, and lidocaine.
According to court documents, an investigation by the surgical center identified about 10 additional unexpected cardiac emergencies that occurred during what should have been unremarkable surgeries, an exceptionally high rate of complications, suggesting a pattern of intentional adulteration of IV bags. These surgeries were performed between May and August.
In addition, the complaint alleges that none of the cardiac incidents occurred during Dr. Ortiz’s surgeries; however, all of the incidents occurred around the time Dr. Ortiz performed services at the facility, and no incidents occurred while he was on vacation. The incidents began 2 days after Dr. Ortiz had been notified that he was the subject of a disciplinary inquiry stemming from an incident in which he allegedly “deviated from the standard of care” during an anesthesia procedure when a patient experienced a medical emergency, according to federal officials.
The complaint also alleges that Dr. Ortiz had a history of disciplinary actions against him, including at the facility, and he complained that the center was trying to “crucify” him.
Surveillance video from the hallway of the center’s operating room shows Dr. Ortiz placing IV bags in the stainless-steel bag warmer shortly before other doctors’ patients experienced cardiac emergencies, according to the complaint. In the description of one instance captured on video, Dr. Ortiz was observed walking quickly from an operating room to the bag warmer, placing a single IV bag inside, visually scanning the empty hallway, and quickly walking away. Just over an hour later, according to the complaint, a 56-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
The complaint alleges that in another instance, Dr. Ortiz was observed exiting his operating room carrying an IV bag concealed in what appeared to be a paper folder, swapping the bag with another bag from the warmer, and walking away. Roughly 30 minutes later, a 54-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
“Our complaint alleges this defendant surreptitiously injected heart-stopping drugs into patient IV bags, decimating the Hippocratic Oath,” said Chad E. Meacham, U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Texas. “A single incident of seemingly intentional patient harm would be disconcerting; multiple incidents are truly disturbing. At this point, however, we believe that the problem is limited to one individual, who is currently behind bars. We will work tirelessly to hold him accountable.”
Dr. Ortiz is charged with tampering with a consumer product and with intentionally adulterating drugs. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of life in prison. Dr. Ortiz will make his initial appearance before U.S. Magistrate Judge Renee Toliver in Dallas Sept. 16.
On Sept. 9, the Texas Medical Board suspended Dr. Ortiz’s license in connection with this investigation, noting that the panel found “an imminent peril to the public health, safety, or welfare” and that Dr. Ortiz’s “continuation in the practice of medicine poses a continuing threat to public welfare.”
“It is astounding, stunning [for the victims] to think that anyone did this intentionally,” said Bruce W. Steckler, an attorney for some of the victims, in an interview with WFAA.
Baylor Scott & White Health, which operates the surgical center, said in a statement that the North Dallas facility will remain closed as the investigation continues.
“We actively assisted authorities in their investigation and will continue to do so. We also remain focused on communicating with patients,” the health system said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
at Baylor Scott & White Surgicare, a North Dallas surgical center. Raynaldo Rivera Ortiz Jr., MD, 59, is accused of injecting nerve-blocking and bronchodilating drugs into patient IV bags, resulting in at least one death and multiple cardiac emergencies.
In June, an anesthesiologist identified by Dallas ABC affiliate WFAA as Melanie Kaspar, MD, a colleague of Dr. Ortiz’s at the outpatient center, was ill and treated herself for dehydration using an IV bag of saline she had taken home from work. She died immediately after injecting the contents of the bag. According to the autopsy report, she died from a lethal dose of bupivacaine, a nerve-blocking agent often used during the administration of anesthesia. According to WFAA, Dr. Kaspar’s death was initially ruled accidental, but the Dallas County Medical Examiner has since reopened the case.
Then in August, an 18-year-old male patient, identified in court documents as J.A., experienced a cardiac emergency during a scheduled surgery at the clinic. The teen, who according to local press coverage was undergoing nose surgery after a dirt bike accident, was transferred to a local ICU. A chemical analysis of the fluid from the saline bag that was used during his surgery found epinephrine (a stimulant that could have caused his symptoms), bupivacaine, and lidocaine.
According to court documents, an investigation by the surgical center identified about 10 additional unexpected cardiac emergencies that occurred during what should have been unremarkable surgeries, an exceptionally high rate of complications, suggesting a pattern of intentional adulteration of IV bags. These surgeries were performed between May and August.
In addition, the complaint alleges that none of the cardiac incidents occurred during Dr. Ortiz’s surgeries; however, all of the incidents occurred around the time Dr. Ortiz performed services at the facility, and no incidents occurred while he was on vacation. The incidents began 2 days after Dr. Ortiz had been notified that he was the subject of a disciplinary inquiry stemming from an incident in which he allegedly “deviated from the standard of care” during an anesthesia procedure when a patient experienced a medical emergency, according to federal officials.
The complaint also alleges that Dr. Ortiz had a history of disciplinary actions against him, including at the facility, and he complained that the center was trying to “crucify” him.
Surveillance video from the hallway of the center’s operating room shows Dr. Ortiz placing IV bags in the stainless-steel bag warmer shortly before other doctors’ patients experienced cardiac emergencies, according to the complaint. In the description of one instance captured on video, Dr. Ortiz was observed walking quickly from an operating room to the bag warmer, placing a single IV bag inside, visually scanning the empty hallway, and quickly walking away. Just over an hour later, according to the complaint, a 56-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
The complaint alleges that in another instance, Dr. Ortiz was observed exiting his operating room carrying an IV bag concealed in what appeared to be a paper folder, swapping the bag with another bag from the warmer, and walking away. Roughly 30 minutes later, a 54-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
“Our complaint alleges this defendant surreptitiously injected heart-stopping drugs into patient IV bags, decimating the Hippocratic Oath,” said Chad E. Meacham, U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Texas. “A single incident of seemingly intentional patient harm would be disconcerting; multiple incidents are truly disturbing. At this point, however, we believe that the problem is limited to one individual, who is currently behind bars. We will work tirelessly to hold him accountable.”
Dr. Ortiz is charged with tampering with a consumer product and with intentionally adulterating drugs. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of life in prison. Dr. Ortiz will make his initial appearance before U.S. Magistrate Judge Renee Toliver in Dallas Sept. 16.
On Sept. 9, the Texas Medical Board suspended Dr. Ortiz’s license in connection with this investigation, noting that the panel found “an imminent peril to the public health, safety, or welfare” and that Dr. Ortiz’s “continuation in the practice of medicine poses a continuing threat to public welfare.”
“It is astounding, stunning [for the victims] to think that anyone did this intentionally,” said Bruce W. Steckler, an attorney for some of the victims, in an interview with WFAA.
Baylor Scott & White Health, which operates the surgical center, said in a statement that the North Dallas facility will remain closed as the investigation continues.
“We actively assisted authorities in their investigation and will continue to do so. We also remain focused on communicating with patients,” the health system said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
at Baylor Scott & White Surgicare, a North Dallas surgical center. Raynaldo Rivera Ortiz Jr., MD, 59, is accused of injecting nerve-blocking and bronchodilating drugs into patient IV bags, resulting in at least one death and multiple cardiac emergencies.
In June, an anesthesiologist identified by Dallas ABC affiliate WFAA as Melanie Kaspar, MD, a colleague of Dr. Ortiz’s at the outpatient center, was ill and treated herself for dehydration using an IV bag of saline she had taken home from work. She died immediately after injecting the contents of the bag. According to the autopsy report, she died from a lethal dose of bupivacaine, a nerve-blocking agent often used during the administration of anesthesia. According to WFAA, Dr. Kaspar’s death was initially ruled accidental, but the Dallas County Medical Examiner has since reopened the case.
Then in August, an 18-year-old male patient, identified in court documents as J.A., experienced a cardiac emergency during a scheduled surgery at the clinic. The teen, who according to local press coverage was undergoing nose surgery after a dirt bike accident, was transferred to a local ICU. A chemical analysis of the fluid from the saline bag that was used during his surgery found epinephrine (a stimulant that could have caused his symptoms), bupivacaine, and lidocaine.
According to court documents, an investigation by the surgical center identified about 10 additional unexpected cardiac emergencies that occurred during what should have been unremarkable surgeries, an exceptionally high rate of complications, suggesting a pattern of intentional adulteration of IV bags. These surgeries were performed between May and August.
In addition, the complaint alleges that none of the cardiac incidents occurred during Dr. Ortiz’s surgeries; however, all of the incidents occurred around the time Dr. Ortiz performed services at the facility, and no incidents occurred while he was on vacation. The incidents began 2 days after Dr. Ortiz had been notified that he was the subject of a disciplinary inquiry stemming from an incident in which he allegedly “deviated from the standard of care” during an anesthesia procedure when a patient experienced a medical emergency, according to federal officials.
The complaint also alleges that Dr. Ortiz had a history of disciplinary actions against him, including at the facility, and he complained that the center was trying to “crucify” him.
Surveillance video from the hallway of the center’s operating room shows Dr. Ortiz placing IV bags in the stainless-steel bag warmer shortly before other doctors’ patients experienced cardiac emergencies, according to the complaint. In the description of one instance captured on video, Dr. Ortiz was observed walking quickly from an operating room to the bag warmer, placing a single IV bag inside, visually scanning the empty hallway, and quickly walking away. Just over an hour later, according to the complaint, a 56-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
The complaint alleges that in another instance, Dr. Ortiz was observed exiting his operating room carrying an IV bag concealed in what appeared to be a paper folder, swapping the bag with another bag from the warmer, and walking away. Roughly 30 minutes later, a 54-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
“Our complaint alleges this defendant surreptitiously injected heart-stopping drugs into patient IV bags, decimating the Hippocratic Oath,” said Chad E. Meacham, U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Texas. “A single incident of seemingly intentional patient harm would be disconcerting; multiple incidents are truly disturbing. At this point, however, we believe that the problem is limited to one individual, who is currently behind bars. We will work tirelessly to hold him accountable.”
Dr. Ortiz is charged with tampering with a consumer product and with intentionally adulterating drugs. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of life in prison. Dr. Ortiz will make his initial appearance before U.S. Magistrate Judge Renee Toliver in Dallas Sept. 16.
On Sept. 9, the Texas Medical Board suspended Dr. Ortiz’s license in connection with this investigation, noting that the panel found “an imminent peril to the public health, safety, or welfare” and that Dr. Ortiz’s “continuation in the practice of medicine poses a continuing threat to public welfare.”
“It is astounding, stunning [for the victims] to think that anyone did this intentionally,” said Bruce W. Steckler, an attorney for some of the victims, in an interview with WFAA.
Baylor Scott & White Health, which operates the surgical center, said in a statement that the North Dallas facility will remain closed as the investigation continues.
“We actively assisted authorities in their investigation and will continue to do so. We also remain focused on communicating with patients,” the health system said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical coding creates barriers to care for transgender patients
In 2021, Tim Chevalier received the first of many coverage denials from his insurance company for the hair-removal procedure he needed as part of a phalloplasty, the creation of a penis.
Electrolysis is a common procedure among transgender people like Mr. Chevalier, a software developer in Oakland, Calif.. In some cases, it’s used to remove unwanted hair from the face or body. But it’s also required for a phalloplasty or a vaginoplasty, the creation of a vagina, because all hair must be removed from the tissue that will be relocated during surgery.
Mr. Chevalier’s insurer, Anthem Blue Cross, told him he needed what’s known as a prior authorization for the procedure. Even after Mr. Chevalier received the authorization, he said, his reimbursement claims kept getting denied. According to Mr. Chevalier, Anthem said the procedure was considered cosmetic.
Many trans patients have trouble getting their insurers to cover gender-affirming care. One reason is transphobia within the U.S. health care system, but another involves how medical diagnoses and procedures are coded for insurance companies. Nationwide, health care providers use a list of diagnostic codes provided by the ICD-10. And many of those, advocates for transgender people say, haven’t caught up to the needs of patients. Such diagnostic codes provide the basis for determining which procedures, such as electrolysis or surgery, insurance will cover.
“It’s widely regarded that the codes are very limited in ICD-10,” said Johanna Olson-Kennedy, MD, medical director of the Center for Transyouth Health and Development at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles.
She advocates for a move to the 11th edition of the coding system, which was endorsed by the World Health Organization in 2019 and began to be adopted around the globe in February. Today, more than 34 countries use ICD-11.
The new edition has replaced outdated terms like “transsexualism” and “gender identity disorder” with “gender incongruence,” which is no longer classified as a mental health condition, but as a sexual health one. This is crucial in reducing the stigmatization of trans people in health care, said Dr. Olson-Kennedy.
A move away from the mental health classification may also mean more coverage of gender-affirming care by insurance companies, which sometimes question mental health claims more rigorously than those for physical illnesses. WHO officials have said they hope that adding gender incongruence to a sexual health chapter will “help increase access to care for health interventions” and “destigmatize the condition,” according to the WHO website.
However, history suggests that ICD-11 likely won’t be implemented in the United States for years. The WHO first endorsed ICD-10 in 1990, but the United States didn’t implement it for 25 years.
Meanwhile, patients who identify as transgender and their doctors are spending hours trying to get coverage – or using crowdfunding to cover big out-of-pocket bills. Mr. Chevalier estimated he has received 78 hours of electrolysis at $140 per hour, costing $10,920.
Anthem spokesperson Michael Bowman wrote in an email that “there has been no medical denials or denial of coverage” because Anthem “preapproved coverage for these services.”
However, even after the preapproval was given, Anthem responded to Mr. Chevalier’s claims by stating the electrolysis would not be reimbursed because the procedure is considered cosmetic, rather than medically necessary. This is regardless of Mr. Chevalier’s diagnosis of gender dysphoria – the psychological distress felt when someone’s biological sex and gender identity don’t match – which many doctors consider a medically legitimate reason for hair removal.
Bowman wrote that “once this issue was identified, Anthem implemented an internal process which included a manual override in the billing system.”
Still, Mr. Chevalier filed a complaint with the California Department of Managed Health Care, and the state declared Anthem Blue Cross out of compliance. Additionally, after KHN started asking Anthem questions about Chevalier’s bills, two claims that had not been addressed since April were resolved in July. So far, Anthem has reimbursed Chevalier around $8,000.
Some procedures that trans patients receive can also be excluded from coverage because insurance companies consider them “sex specific.” For example, a transgender man’s gynecological visit may not be covered because his insurance plan covers those visits only for people enrolled as women.
“There is always this question of: What gender should you tell the insurance company?” said Nick Gorton, MD, an emergency medicine physician in Davis, Calif. Dr. Gorton, who is trans, recommends his patients with insurance plans that exclude trans care calculate the out-of-pocket costs that would be required for certain procedures based on whether the patient lists themselves as male or female on their insurance paperwork. For example, Dr. Gorton said, the question for a trans man becomes “what’s more expensive – paying for testosterone or paying for a Pap smear?” – since insurance likely won’t cover both.
For years, some physicians helped trans patients get coverage by finding other medical reasons for their trans-related care. Dr. Gorton said that if, for instance, a transgender man wanted a hysterectomy but his insurance didn’t cover gender-affirming care, Dr. Gorton would enter the ICD-10 code for pelvic pain, as opposed to gender dysphoria, into the patient’s billing record. Pelvic pain is a legitimate reason for the surgery and is commonly accepted by insurance providers, Dr. Gorton said. But some insurance companies pushed back, and he had to find other ways to help his patients.
In 2005, California passed a first-of-its-kind law that prohibits discrimination by health insurance on the basis of gender or gender identity. Now, 24 states and Washington, D.C., forbid private insurance from excluding transgender-related health care benefits.
Consequently, Dr. Gorton no longer needs to use different codes for patients seeking gender-affirming care at his practice in California. But physicians in other states are still struggling.
When Eric Meininger, MD, MPH, an internist and pediatrician at Indiana University Health’s gender health program in Indianapolis, treats a trans kid seeking hormone therapy, he commonly uses the ICD-10 code for “medication management” as the primary reason for the patient’s visit. That’s because Indiana has no law providing insurance protections for LGBTQ+ people, and when gender dysphoria is listed as the primary reason, insurance companies have denied coverage.
“It’s frustrating,” Dr. Meininger said. In a patient’s billing record, he sometimes provides multiple diagnoses, including gender dysphoria, to increase the likelihood that a procedure will be covered. “It’s not hard usually to come up with five or seven or eight diagnoses for someone because there’s lots of vague ones out there.”
Implementing ICD-11 won’t fix all the coding problems, as insurance companies may still refuse to cover procedures related to gender incongruence even though it is listed as a sexual health condition. It also won’t change the fact that many states still allow insurance to exclude gender-affirming care. But in terms of reducing stigma, it’s a step forward, Dr. Olson-Kennedy said.
One reason the United States took so long to switch to ICD-10 is that the American Medical Association strongly opposed the move. It argued the new system would put an incredible burden on doctors. Physicians would have to “contend with 68,000 diagnosis codes – a fivefold increase from the approximately 13,000 diagnosis codes in use today,” the AMA wrote in a 2014 letter. Implementing software to update providers’ coding systems would also be costly, dealing a financial blow to small medical practices, the association argued.
Unlike past coding systems, ICD-11 is fully electronic, with no physical manual of codes, and can be incorporated into a medical facility’s current coding system without requiring a new rollout, said Christian Lindmeier, a WHO spokesperson.
Whether these changes will make the adoption of the new edition easier in the United States is yet to be seen. For now, many trans patients in need of gender-affirming care must pay their bills out of pocket, fight their insurance company for coverage, or rely on the generosity of others.
“Even though I did get reimbursed eventually, the reimbursements were delayed, and it burned up a lot of my time,” Mr. Chevalier said. “Most people would have just given up.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
In 2021, Tim Chevalier received the first of many coverage denials from his insurance company for the hair-removal procedure he needed as part of a phalloplasty, the creation of a penis.
Electrolysis is a common procedure among transgender people like Mr. Chevalier, a software developer in Oakland, Calif.. In some cases, it’s used to remove unwanted hair from the face or body. But it’s also required for a phalloplasty or a vaginoplasty, the creation of a vagina, because all hair must be removed from the tissue that will be relocated during surgery.
Mr. Chevalier’s insurer, Anthem Blue Cross, told him he needed what’s known as a prior authorization for the procedure. Even after Mr. Chevalier received the authorization, he said, his reimbursement claims kept getting denied. According to Mr. Chevalier, Anthem said the procedure was considered cosmetic.
Many trans patients have trouble getting their insurers to cover gender-affirming care. One reason is transphobia within the U.S. health care system, but another involves how medical diagnoses and procedures are coded for insurance companies. Nationwide, health care providers use a list of diagnostic codes provided by the ICD-10. And many of those, advocates for transgender people say, haven’t caught up to the needs of patients. Such diagnostic codes provide the basis for determining which procedures, such as electrolysis or surgery, insurance will cover.
“It’s widely regarded that the codes are very limited in ICD-10,” said Johanna Olson-Kennedy, MD, medical director of the Center for Transyouth Health and Development at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles.
She advocates for a move to the 11th edition of the coding system, which was endorsed by the World Health Organization in 2019 and began to be adopted around the globe in February. Today, more than 34 countries use ICD-11.
The new edition has replaced outdated terms like “transsexualism” and “gender identity disorder” with “gender incongruence,” which is no longer classified as a mental health condition, but as a sexual health one. This is crucial in reducing the stigmatization of trans people in health care, said Dr. Olson-Kennedy.
A move away from the mental health classification may also mean more coverage of gender-affirming care by insurance companies, which sometimes question mental health claims more rigorously than those for physical illnesses. WHO officials have said they hope that adding gender incongruence to a sexual health chapter will “help increase access to care for health interventions” and “destigmatize the condition,” according to the WHO website.
However, history suggests that ICD-11 likely won’t be implemented in the United States for years. The WHO first endorsed ICD-10 in 1990, but the United States didn’t implement it for 25 years.
Meanwhile, patients who identify as transgender and their doctors are spending hours trying to get coverage – or using crowdfunding to cover big out-of-pocket bills. Mr. Chevalier estimated he has received 78 hours of electrolysis at $140 per hour, costing $10,920.
Anthem spokesperson Michael Bowman wrote in an email that “there has been no medical denials or denial of coverage” because Anthem “preapproved coverage for these services.”
However, even after the preapproval was given, Anthem responded to Mr. Chevalier’s claims by stating the electrolysis would not be reimbursed because the procedure is considered cosmetic, rather than medically necessary. This is regardless of Mr. Chevalier’s diagnosis of gender dysphoria – the psychological distress felt when someone’s biological sex and gender identity don’t match – which many doctors consider a medically legitimate reason for hair removal.
Bowman wrote that “once this issue was identified, Anthem implemented an internal process which included a manual override in the billing system.”
Still, Mr. Chevalier filed a complaint with the California Department of Managed Health Care, and the state declared Anthem Blue Cross out of compliance. Additionally, after KHN started asking Anthem questions about Chevalier’s bills, two claims that had not been addressed since April were resolved in July. So far, Anthem has reimbursed Chevalier around $8,000.
Some procedures that trans patients receive can also be excluded from coverage because insurance companies consider them “sex specific.” For example, a transgender man’s gynecological visit may not be covered because his insurance plan covers those visits only for people enrolled as women.
“There is always this question of: What gender should you tell the insurance company?” said Nick Gorton, MD, an emergency medicine physician in Davis, Calif. Dr. Gorton, who is trans, recommends his patients with insurance plans that exclude trans care calculate the out-of-pocket costs that would be required for certain procedures based on whether the patient lists themselves as male or female on their insurance paperwork. For example, Dr. Gorton said, the question for a trans man becomes “what’s more expensive – paying for testosterone or paying for a Pap smear?” – since insurance likely won’t cover both.
For years, some physicians helped trans patients get coverage by finding other medical reasons for their trans-related care. Dr. Gorton said that if, for instance, a transgender man wanted a hysterectomy but his insurance didn’t cover gender-affirming care, Dr. Gorton would enter the ICD-10 code for pelvic pain, as opposed to gender dysphoria, into the patient’s billing record. Pelvic pain is a legitimate reason for the surgery and is commonly accepted by insurance providers, Dr. Gorton said. But some insurance companies pushed back, and he had to find other ways to help his patients.
In 2005, California passed a first-of-its-kind law that prohibits discrimination by health insurance on the basis of gender or gender identity. Now, 24 states and Washington, D.C., forbid private insurance from excluding transgender-related health care benefits.
Consequently, Dr. Gorton no longer needs to use different codes for patients seeking gender-affirming care at his practice in California. But physicians in other states are still struggling.
When Eric Meininger, MD, MPH, an internist and pediatrician at Indiana University Health’s gender health program in Indianapolis, treats a trans kid seeking hormone therapy, he commonly uses the ICD-10 code for “medication management” as the primary reason for the patient’s visit. That’s because Indiana has no law providing insurance protections for LGBTQ+ people, and when gender dysphoria is listed as the primary reason, insurance companies have denied coverage.
“It’s frustrating,” Dr. Meininger said. In a patient’s billing record, he sometimes provides multiple diagnoses, including gender dysphoria, to increase the likelihood that a procedure will be covered. “It’s not hard usually to come up with five or seven or eight diagnoses for someone because there’s lots of vague ones out there.”
Implementing ICD-11 won’t fix all the coding problems, as insurance companies may still refuse to cover procedures related to gender incongruence even though it is listed as a sexual health condition. It also won’t change the fact that many states still allow insurance to exclude gender-affirming care. But in terms of reducing stigma, it’s a step forward, Dr. Olson-Kennedy said.
One reason the United States took so long to switch to ICD-10 is that the American Medical Association strongly opposed the move. It argued the new system would put an incredible burden on doctors. Physicians would have to “contend with 68,000 diagnosis codes – a fivefold increase from the approximately 13,000 diagnosis codes in use today,” the AMA wrote in a 2014 letter. Implementing software to update providers’ coding systems would also be costly, dealing a financial blow to small medical practices, the association argued.
Unlike past coding systems, ICD-11 is fully electronic, with no physical manual of codes, and can be incorporated into a medical facility’s current coding system without requiring a new rollout, said Christian Lindmeier, a WHO spokesperson.
Whether these changes will make the adoption of the new edition easier in the United States is yet to be seen. For now, many trans patients in need of gender-affirming care must pay their bills out of pocket, fight their insurance company for coverage, or rely on the generosity of others.
“Even though I did get reimbursed eventually, the reimbursements were delayed, and it burned up a lot of my time,” Mr. Chevalier said. “Most people would have just given up.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
In 2021, Tim Chevalier received the first of many coverage denials from his insurance company for the hair-removal procedure he needed as part of a phalloplasty, the creation of a penis.
Electrolysis is a common procedure among transgender people like Mr. Chevalier, a software developer in Oakland, Calif.. In some cases, it’s used to remove unwanted hair from the face or body. But it’s also required for a phalloplasty or a vaginoplasty, the creation of a vagina, because all hair must be removed from the tissue that will be relocated during surgery.
Mr. Chevalier’s insurer, Anthem Blue Cross, told him he needed what’s known as a prior authorization for the procedure. Even after Mr. Chevalier received the authorization, he said, his reimbursement claims kept getting denied. According to Mr. Chevalier, Anthem said the procedure was considered cosmetic.
Many trans patients have trouble getting their insurers to cover gender-affirming care. One reason is transphobia within the U.S. health care system, but another involves how medical diagnoses and procedures are coded for insurance companies. Nationwide, health care providers use a list of diagnostic codes provided by the ICD-10. And many of those, advocates for transgender people say, haven’t caught up to the needs of patients. Such diagnostic codes provide the basis for determining which procedures, such as electrolysis or surgery, insurance will cover.
“It’s widely regarded that the codes are very limited in ICD-10,” said Johanna Olson-Kennedy, MD, medical director of the Center for Transyouth Health and Development at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles.
She advocates for a move to the 11th edition of the coding system, which was endorsed by the World Health Organization in 2019 and began to be adopted around the globe in February. Today, more than 34 countries use ICD-11.
The new edition has replaced outdated terms like “transsexualism” and “gender identity disorder” with “gender incongruence,” which is no longer classified as a mental health condition, but as a sexual health one. This is crucial in reducing the stigmatization of trans people in health care, said Dr. Olson-Kennedy.
A move away from the mental health classification may also mean more coverage of gender-affirming care by insurance companies, which sometimes question mental health claims more rigorously than those for physical illnesses. WHO officials have said they hope that adding gender incongruence to a sexual health chapter will “help increase access to care for health interventions” and “destigmatize the condition,” according to the WHO website.
However, history suggests that ICD-11 likely won’t be implemented in the United States for years. The WHO first endorsed ICD-10 in 1990, but the United States didn’t implement it for 25 years.
Meanwhile, patients who identify as transgender and their doctors are spending hours trying to get coverage – or using crowdfunding to cover big out-of-pocket bills. Mr. Chevalier estimated he has received 78 hours of electrolysis at $140 per hour, costing $10,920.
Anthem spokesperson Michael Bowman wrote in an email that “there has been no medical denials or denial of coverage” because Anthem “preapproved coverage for these services.”
However, even after the preapproval was given, Anthem responded to Mr. Chevalier’s claims by stating the electrolysis would not be reimbursed because the procedure is considered cosmetic, rather than medically necessary. This is regardless of Mr. Chevalier’s diagnosis of gender dysphoria – the psychological distress felt when someone’s biological sex and gender identity don’t match – which many doctors consider a medically legitimate reason for hair removal.
Bowman wrote that “once this issue was identified, Anthem implemented an internal process which included a manual override in the billing system.”
Still, Mr. Chevalier filed a complaint with the California Department of Managed Health Care, and the state declared Anthem Blue Cross out of compliance. Additionally, after KHN started asking Anthem questions about Chevalier’s bills, two claims that had not been addressed since April were resolved in July. So far, Anthem has reimbursed Chevalier around $8,000.
Some procedures that trans patients receive can also be excluded from coverage because insurance companies consider them “sex specific.” For example, a transgender man’s gynecological visit may not be covered because his insurance plan covers those visits only for people enrolled as women.
“There is always this question of: What gender should you tell the insurance company?” said Nick Gorton, MD, an emergency medicine physician in Davis, Calif. Dr. Gorton, who is trans, recommends his patients with insurance plans that exclude trans care calculate the out-of-pocket costs that would be required for certain procedures based on whether the patient lists themselves as male or female on their insurance paperwork. For example, Dr. Gorton said, the question for a trans man becomes “what’s more expensive – paying for testosterone or paying for a Pap smear?” – since insurance likely won’t cover both.
For years, some physicians helped trans patients get coverage by finding other medical reasons for their trans-related care. Dr. Gorton said that if, for instance, a transgender man wanted a hysterectomy but his insurance didn’t cover gender-affirming care, Dr. Gorton would enter the ICD-10 code for pelvic pain, as opposed to gender dysphoria, into the patient’s billing record. Pelvic pain is a legitimate reason for the surgery and is commonly accepted by insurance providers, Dr. Gorton said. But some insurance companies pushed back, and he had to find other ways to help his patients.
In 2005, California passed a first-of-its-kind law that prohibits discrimination by health insurance on the basis of gender or gender identity. Now, 24 states and Washington, D.C., forbid private insurance from excluding transgender-related health care benefits.
Consequently, Dr. Gorton no longer needs to use different codes for patients seeking gender-affirming care at his practice in California. But physicians in other states are still struggling.
When Eric Meininger, MD, MPH, an internist and pediatrician at Indiana University Health’s gender health program in Indianapolis, treats a trans kid seeking hormone therapy, he commonly uses the ICD-10 code for “medication management” as the primary reason for the patient’s visit. That’s because Indiana has no law providing insurance protections for LGBTQ+ people, and when gender dysphoria is listed as the primary reason, insurance companies have denied coverage.
“It’s frustrating,” Dr. Meininger said. In a patient’s billing record, he sometimes provides multiple diagnoses, including gender dysphoria, to increase the likelihood that a procedure will be covered. “It’s not hard usually to come up with five or seven or eight diagnoses for someone because there’s lots of vague ones out there.”
Implementing ICD-11 won’t fix all the coding problems, as insurance companies may still refuse to cover procedures related to gender incongruence even though it is listed as a sexual health condition. It also won’t change the fact that many states still allow insurance to exclude gender-affirming care. But in terms of reducing stigma, it’s a step forward, Dr. Olson-Kennedy said.
One reason the United States took so long to switch to ICD-10 is that the American Medical Association strongly opposed the move. It argued the new system would put an incredible burden on doctors. Physicians would have to “contend with 68,000 diagnosis codes – a fivefold increase from the approximately 13,000 diagnosis codes in use today,” the AMA wrote in a 2014 letter. Implementing software to update providers’ coding systems would also be costly, dealing a financial blow to small medical practices, the association argued.
Unlike past coding systems, ICD-11 is fully electronic, with no physical manual of codes, and can be incorporated into a medical facility’s current coding system without requiring a new rollout, said Christian Lindmeier, a WHO spokesperson.
Whether these changes will make the adoption of the new edition easier in the United States is yet to be seen. For now, many trans patients in need of gender-affirming care must pay their bills out of pocket, fight their insurance company for coverage, or rely on the generosity of others.
“Even though I did get reimbursed eventually, the reimbursements were delayed, and it burned up a lot of my time,” Mr. Chevalier said. “Most people would have just given up.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Improving Inpatient COVID-19 Vaccination Rates Among Adult Patients at a Tertiary Academic Medical Center
From the Department of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
Abstract
Objective: Inpatient vaccination initiatives are well described in the literature. During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals began administering COVID-19 vaccines to hospitalized patients. Although vaccination rates increased, there remained many unvaccinated patients despite community efforts. This quality improvement project aimed to increase the COVID-19 vaccination rates of hospitalized patients on the medicine service at the George Washington University Hospital (GWUH).
Methods: From November 2021 through February 2022, we conducted a Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle with 3 phases. Initial steps included gathering baseline data from the electronic health record and consulting stakeholders. The first 2 phases focused on educating housestaff on the availability, ordering process, and administration of the Pfizer vaccine. The third phase consisted of developing educational pamphlets for patients to be included in their admission packets.
Results: The baseline mean COVID-19 vaccination rate (August to October 2021) of eligible patients on the medicine service was 10.7%. In the months after we implemented the PDSA cycle (November 2021 to February 2022), the mean vaccination rate increased to 15.4%.
Conclusion: This quality improvement project implemented measures to increase administration of the Pfizer vaccine to eligible patients admitted to the medicine service at GWUH. The mean vaccination rate increased from 10.7% in the 3 months prior to implementation to 15.4% during the 4 months post implementation. Other measures to consider in the future include increasing the availability of other COVID-19 vaccines at our hospital and incorporating the vaccine into the admission order set to help facilitate vaccination early in the hospital course.
Keywords: housestaff, quality improvement, PDSA, COVID-19, BNT162b2 vaccine, patient education
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, case rates in the United States have fluctuated considerably, corresponding to epidemic waves. In 2021, US daily cases of COVID-19 peaked at nearly 300,000 in early January and reached a nadir of 8000 cases in mid-June.1 In September 2021, new cases had increased to 200,000 per day due to the prevalence of the Delta variant.1 Particularly with the emergence of new variants of SARS-CoV-2, vaccination efforts to limit the spread of infection and severity of illness are critical. Data have shown that 2 doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech) were largely protective against severe infection for approximately 6 months.2,3 When we began this quality improvement (QI) project in September 2021, only 179 million Americans had been fully vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is just over half of the US population.4 An electronic survey conducted in the United States with more than 5 million responses found that, of those who were hesitant about receiving the vaccine, 49% reported a fear of adverse effects and 48% reported a lack of trust in the vaccine.5
This QI project sought to target unvaccinated individuals admitted to the internal medicine inpatient service. Vaccinating hospitalized patients is especially important since they are sicker than the general population and at higher risk of having poor outcomes from COVID-19. Inpatient vaccine initiatives, such as administering influenza vaccine prior to discharge, have been successfully implemented in the past.6 One large COVID-19 vaccination program featured an admission order set to increase the rates of vaccination among hospitalized patients.7 Our QI project piloted a multidisciplinary approach involving the nursing staff, pharmacy, information technology (IT) department, and internal medicine housestaff to increase COVID-19 vaccination rates among hospitalized patients on the medical service. This project aimed to increase inpatient vaccination rates through interventions targeting both primary providers as well as the patients themselves.
Methods
Setting and Interventions
This project was conducted at the George Washington University Hospital (GWUH) in Washington, DC. The clinicians involved in the study were the internal medicine housestaff, and the patients included were adults admitted to the resident medicine ward teams. The project was exempt by the institutional review board and did not require informed consent.
The quality improvement initiative had 3 phases, each featuring a different intervention (Table 1). The first phase involved sending a weekly announcement (via email and a secure health care messaging app) to current residents rotating on the inpatient medicine service. The announcement contained information regarding COVID-19 vaccine availability at the hospital, instructions on ordering the vaccine, and the process of coordinating with pharmacy to facilitate vaccine administration. Thereafter, residents were educated on the process of giving a COVID-19 vaccine to a patient from start to finish. Due to the nature of the residency schedule, different housestaff members rotated in and out of the medicine wards during the intervention periods. The weekly email was sent to the entire internal medicine housestaff, informing all residents about the QI project, while the weekly secure messages served as reminders and were only sent to residents currently on the medicine wards.
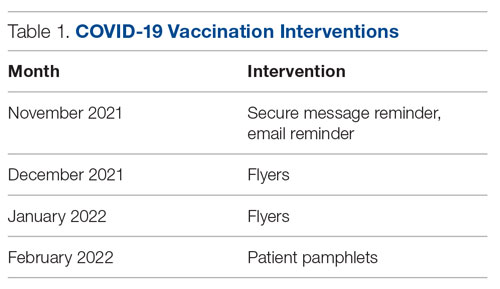
In the second phase, we posted paper flyers throughout the hospital to remind housestaff to give the vaccine and again educate them on the process of ordering the vaccine. For the third intervention, a COVID-19 vaccine educational pamphlet was developed for distribution to inpatients at GWUH. The pamphlet included information on vaccine efficacy, safety, side effects, and eligibility. The pamphlet was incorporated in the admission packet that every patient receives upon admission to the hospital. The patients reviewed the pamphlets with nursing staff, who would answer any questions, with residents available to discuss any outstanding concerns.
Measures and Data Gathering
The primary endpoint of the study was inpatient vaccination rate, defined as the number of COVID-19 vaccines administered divided by the number of patients eligible to receive a vaccine (not fully vaccinated). During initial triage, nursing staff documented vaccination status in the electronic health record (EHR), checking a box in a data entry form if a patient had received 0, 1, or 2 doses of the COVID-19 vaccine. The GWUH IT department generated data from this form to determine the number of patients eligible to receive a COVID-19 vaccine. Data were extracted from the medication administration record in the EHR to determine the number of vaccines that were administered to patients during their hospitalization on the inpatient medical service. Each month, the IT department extracted data for the number of eligible patients and the number of vaccines administered. This yielded the monthly vaccination rates. The monthly vaccination rates in the period prior to starting the QI initiative were compared to the rates in the period after the interventions were implemented.
Of note, during the course of this project, patients became eligible for a third COVID-19 vaccine (booster). We decided to continue with the original aim of vaccinating adults who had only received 0 or 1 dose of the vaccine. Therefore, the eligibility criteria remained the same throughout the study. We obtained retrospective data to ensure that the vaccines being counted toward the vaccination rate were vaccines given to patients not yet fully vaccinated and not vaccines given as boosters.
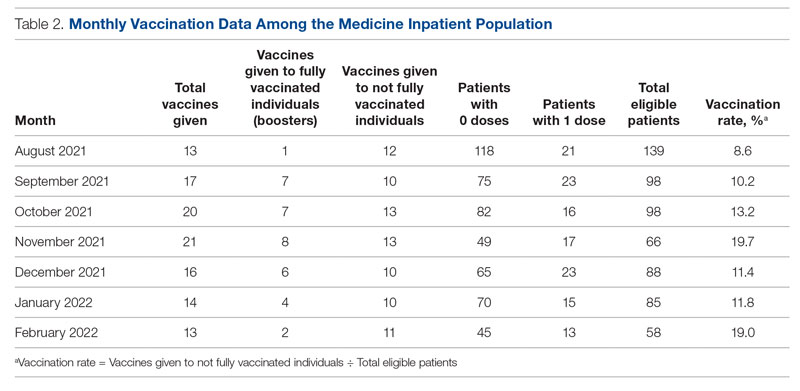
Results
From August to October 2021, the baseline average monthly vaccination rate of patients on the medicine service who were eligible to receive a COVID-19 vaccine was 10.7%. After the first intervention, the vaccination rate increased to 19.7% in November 2021 (Table 2). The second intervention yielded vaccination rates of 11.4% and 11.8% in December 2021 and January 2022, respectively. During the final phase in February 2022, the vaccination rate was 19.0%. At the conclusion of the study, the mean vaccination rate for the intervention months was 15.4% (Figure 1). Process stability and variation are demonstrated with a statistical process control chart (Figure 2).
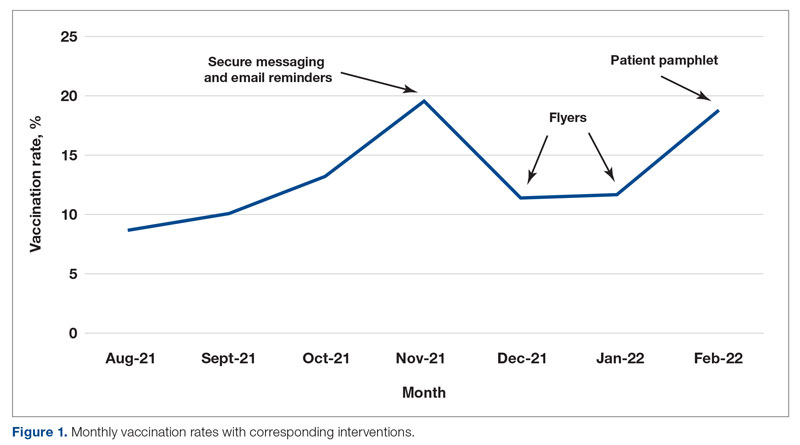
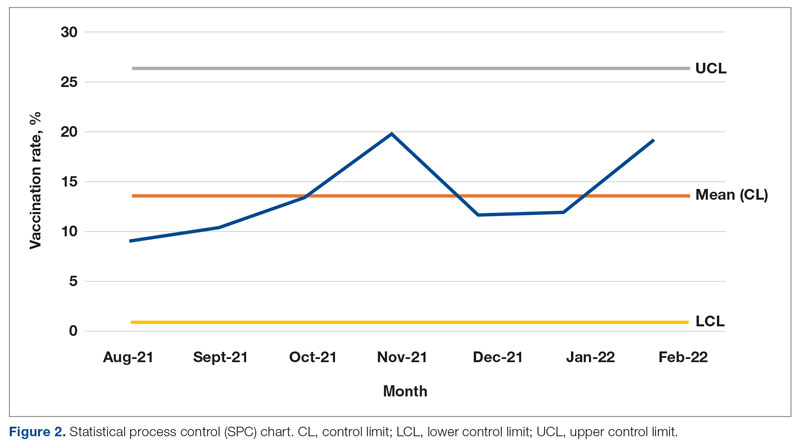
Discussion
For this housestaff-driven QI project, we implemented an inpatient COVID-19 vaccination campaign consisting of 3 phases that targeted both providers and patients. During the intervention period, we observed an increased vaccination rate compared to the period just prior to implementation of the QI project. While our interventions may certainly have boosted vaccination rates, we understand other variables could have contributed to increased rates as well. The emergence of variants in the United States, such as omicron in December 2021,8 could have precipitated a demand for vaccinations among patients. Holidays in November and December may also have increased patients’ desire to get vaccinated before travel.
We encountered a number of roadblocks that challenged our project, including difficulty identifying patients who were eligible for the vaccine, logistical vaccine administration challenges, and hesitancy among the inpatient population. Accurately identifying patients who were eligible for a vaccine in the EHR was especially challenging in the setting of rapidly changing guidelines regarding COVID-19 vaccination. In September 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration authorized the Pfizer booster for certain populations and later, in November 2021, for all adults. This meant that some fully vaccinated hospitalized patients (those with 2 doses) then qualified for an additional dose of the vaccine and received a dose during hospitalization. To determine the true vaccination rate, we obtained retrospective data that allowed us to track each vaccine administered. If a patient had already received 2 doses of the COVID-19 vaccine, the vaccine administered was counted as a booster and excluded from the calculation of the vaccination rate. Future PDSA cycles could include updating the EHR to capture the whole range of COVID-19 vaccination status (unvaccinated, partially vaccinated, fully vaccinated, fully vaccinated with 1 booster, fully vaccinated with 2 boosters).
We also encountered logistical challenges with the administration of the COVID-19 vaccine to hospitalized patients. During the intervention period, our pharmacy department required 5 COVID-19 vaccination orders before opening a vial and administering the vaccine doses in order to reduce waste. This policy may have limited our ability to vaccinate eligible inpatients because we were not always able to identify 5 patients simultaneously on the service who were eligible and consented to the vaccine.
The majority of patients who were interested in receiving COVID-19 vaccination had already been vaccinated in the outpatient setting. This fact made the inpatient internal medicine subset of patients a particularly challenging population to target, given their possible hesitancy regarding vaccination. By utilizing a multidisciplinary team and increasing communication of providers and nursing staff, we helped to increase the COVID-19 vaccination rates at our hospital from 10.7% to 15.4%.
Future Directions
Future interventions to consider include increasing the availability of other approved COVID-19 vaccines at our hospital besides the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Furthermore, incorporating the vaccine into the admission order set would help initiate the vaccination process early in the hospital course. We encourage other institutions to utilize similar approaches to not only remind providers about inpatient vaccination, but also educate and encourage patients to receive the vaccine. These measures will help institutions increase inpatient COVID-19 vaccination rates in a high-risk population.
Corresponding author: Anna Rubin, MD, Department of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; arubin@mfa.gwu.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Trends in number of COVID-19 cases and deaths in the US reported to CDC, by state/territory. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_dailycases
2. Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162B2 MRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(27):2603-2615. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2034577
3. Hall V, Foulkes S, Insalata F, et al. Protection against SARS-COV-2 after covid-19 vaccination and previous infection. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(13):1207-1220. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2118691
4. Trends in number of COVID-19 vaccinations in the US. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccination-trends_vacctrends-fully-cum
5. King WC, Rubinstein M, Reinhart A, Mejia R. Time trends, factors associated with, and reasons for covid-19 vaccine hesitancy: A massive online survey of US adults from January-May 2021. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(12). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0260731
6. Cohen ES, Ogrinc G, Taylor T, et al. Influenza vaccination rates for hospitalised patients: A multiyear quality improvement effort. BMJ Qual Saf. 2015;24(3):221-227. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2014-003556
7. Berger RE, Diaz DC, Chacko S, et al. Implementation of an inpatient covid-19 vaccination program. NEJM Catalyst. 2021;2(10). doi:10.1056/cat.21.0235
8. CDC COVID-19 Response Team. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant - United States, December 1-8, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(50):1731-1734. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7050e1
From the Department of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
Abstract
Objective: Inpatient vaccination initiatives are well described in the literature. During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals began administering COVID-19 vaccines to hospitalized patients. Although vaccination rates increased, there remained many unvaccinated patients despite community efforts. This quality improvement project aimed to increase the COVID-19 vaccination rates of hospitalized patients on the medicine service at the George Washington University Hospital (GWUH).
Methods: From November 2021 through February 2022, we conducted a Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle with 3 phases. Initial steps included gathering baseline data from the electronic health record and consulting stakeholders. The first 2 phases focused on educating housestaff on the availability, ordering process, and administration of the Pfizer vaccine. The third phase consisted of developing educational pamphlets for patients to be included in their admission packets.
Results: The baseline mean COVID-19 vaccination rate (August to October 2021) of eligible patients on the medicine service was 10.7%. In the months after we implemented the PDSA cycle (November 2021 to February 2022), the mean vaccination rate increased to 15.4%.
Conclusion: This quality improvement project implemented measures to increase administration of the Pfizer vaccine to eligible patients admitted to the medicine service at GWUH. The mean vaccination rate increased from 10.7% in the 3 months prior to implementation to 15.4% during the 4 months post implementation. Other measures to consider in the future include increasing the availability of other COVID-19 vaccines at our hospital and incorporating the vaccine into the admission order set to help facilitate vaccination early in the hospital course.
Keywords: housestaff, quality improvement, PDSA, COVID-19, BNT162b2 vaccine, patient education
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, case rates in the United States have fluctuated considerably, corresponding to epidemic waves. In 2021, US daily cases of COVID-19 peaked at nearly 300,000 in early January and reached a nadir of 8000 cases in mid-June.1 In September 2021, new cases had increased to 200,000 per day due to the prevalence of the Delta variant.1 Particularly with the emergence of new variants of SARS-CoV-2, vaccination efforts to limit the spread of infection and severity of illness are critical. Data have shown that 2 doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech) were largely protective against severe infection for approximately 6 months.2,3 When we began this quality improvement (QI) project in September 2021, only 179 million Americans had been fully vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is just over half of the US population.4 An electronic survey conducted in the United States with more than 5 million responses found that, of those who were hesitant about receiving the vaccine, 49% reported a fear of adverse effects and 48% reported a lack of trust in the vaccine.5
This QI project sought to target unvaccinated individuals admitted to the internal medicine inpatient service. Vaccinating hospitalized patients is especially important since they are sicker than the general population and at higher risk of having poor outcomes from COVID-19. Inpatient vaccine initiatives, such as administering influenza vaccine prior to discharge, have been successfully implemented in the past.6 One large COVID-19 vaccination program featured an admission order set to increase the rates of vaccination among hospitalized patients.7 Our QI project piloted a multidisciplinary approach involving the nursing staff, pharmacy, information technology (IT) department, and internal medicine housestaff to increase COVID-19 vaccination rates among hospitalized patients on the medical service. This project aimed to increase inpatient vaccination rates through interventions targeting both primary providers as well as the patients themselves.
Methods
Setting and Interventions
This project was conducted at the George Washington University Hospital (GWUH) in Washington, DC. The clinicians involved in the study were the internal medicine housestaff, and the patients included were adults admitted to the resident medicine ward teams. The project was exempt by the institutional review board and did not require informed consent.
The quality improvement initiative had 3 phases, each featuring a different intervention (Table 1). The first phase involved sending a weekly announcement (via email and a secure health care messaging app) to current residents rotating on the inpatient medicine service. The announcement contained information regarding COVID-19 vaccine availability at the hospital, instructions on ordering the vaccine, and the process of coordinating with pharmacy to facilitate vaccine administration. Thereafter, residents were educated on the process of giving a COVID-19 vaccine to a patient from start to finish. Due to the nature of the residency schedule, different housestaff members rotated in and out of the medicine wards during the intervention periods. The weekly email was sent to the entire internal medicine housestaff, informing all residents about the QI project, while the weekly secure messages served as reminders and were only sent to residents currently on the medicine wards.

In the second phase, we posted paper flyers throughout the hospital to remind housestaff to give the vaccine and again educate them on the process of ordering the vaccine. For the third intervention, a COVID-19 vaccine educational pamphlet was developed for distribution to inpatients at GWUH. The pamphlet included information on vaccine efficacy, safety, side effects, and eligibility. The pamphlet was incorporated in the admission packet that every patient receives upon admission to the hospital. The patients reviewed the pamphlets with nursing staff, who would answer any questions, with residents available to discuss any outstanding concerns.
Measures and Data Gathering
The primary endpoint of the study was inpatient vaccination rate, defined as the number of COVID-19 vaccines administered divided by the number of patients eligible to receive a vaccine (not fully vaccinated). During initial triage, nursing staff documented vaccination status in the electronic health record (EHR), checking a box in a data entry form if a patient had received 0, 1, or 2 doses of the COVID-19 vaccine. The GWUH IT department generated data from this form to determine the number of patients eligible to receive a COVID-19 vaccine. Data were extracted from the medication administration record in the EHR to determine the number of vaccines that were administered to patients during their hospitalization on the inpatient medical service. Each month, the IT department extracted data for the number of eligible patients and the number of vaccines administered. This yielded the monthly vaccination rates. The monthly vaccination rates in the period prior to starting the QI initiative were compared to the rates in the period after the interventions were implemented.
Of note, during the course of this project, patients became eligible for a third COVID-19 vaccine (booster). We decided to continue with the original aim of vaccinating adults who had only received 0 or 1 dose of the vaccine. Therefore, the eligibility criteria remained the same throughout the study. We obtained retrospective data to ensure that the vaccines being counted toward the vaccination rate were vaccines given to patients not yet fully vaccinated and not vaccines given as boosters.

Results
From August to October 2021, the baseline average monthly vaccination rate of patients on the medicine service who were eligible to receive a COVID-19 vaccine was 10.7%. After the first intervention, the vaccination rate increased to 19.7% in November 2021 (Table 2). The second intervention yielded vaccination rates of 11.4% and 11.8% in December 2021 and January 2022, respectively. During the final phase in February 2022, the vaccination rate was 19.0%. At the conclusion of the study, the mean vaccination rate for the intervention months was 15.4% (Figure 1). Process stability and variation are demonstrated with a statistical process control chart (Figure 2).


Discussion
For this housestaff-driven QI project, we implemented an inpatient COVID-19 vaccination campaign consisting of 3 phases that targeted both providers and patients. During the intervention period, we observed an increased vaccination rate compared to the period just prior to implementation of the QI project. While our interventions may certainly have boosted vaccination rates, we understand other variables could have contributed to increased rates as well. The emergence of variants in the United States, such as omicron in December 2021,8 could have precipitated a demand for vaccinations among patients. Holidays in November and December may also have increased patients’ desire to get vaccinated before travel.
We encountered a number of roadblocks that challenged our project, including difficulty identifying patients who were eligible for the vaccine, logistical vaccine administration challenges, and hesitancy among the inpatient population. Accurately identifying patients who were eligible for a vaccine in the EHR was especially challenging in the setting of rapidly changing guidelines regarding COVID-19 vaccination. In September 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration authorized the Pfizer booster for certain populations and later, in November 2021, for all adults. This meant that some fully vaccinated hospitalized patients (those with 2 doses) then qualified for an additional dose of the vaccine and received a dose during hospitalization. To determine the true vaccination rate, we obtained retrospective data that allowed us to track each vaccine administered. If a patient had already received 2 doses of the COVID-19 vaccine, the vaccine administered was counted as a booster and excluded from the calculation of the vaccination rate. Future PDSA cycles could include updating the EHR to capture the whole range of COVID-19 vaccination status (unvaccinated, partially vaccinated, fully vaccinated, fully vaccinated with 1 booster, fully vaccinated with 2 boosters).
We also encountered logistical challenges with the administration of the COVID-19 vaccine to hospitalized patients. During the intervention period, our pharmacy department required 5 COVID-19 vaccination orders before opening a vial and administering the vaccine doses in order to reduce waste. This policy may have limited our ability to vaccinate eligible inpatients because we were not always able to identify 5 patients simultaneously on the service who were eligible and consented to the vaccine.
The majority of patients who were interested in receiving COVID-19 vaccination had already been vaccinated in the outpatient setting. This fact made the inpatient internal medicine subset of patients a particularly challenging population to target, given their possible hesitancy regarding vaccination. By utilizing a multidisciplinary team and increasing communication of providers and nursing staff, we helped to increase the COVID-19 vaccination rates at our hospital from 10.7% to 15.4%.
Future Directions
Future interventions to consider include increasing the availability of other approved COVID-19 vaccines at our hospital besides the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Furthermore, incorporating the vaccine into the admission order set would help initiate the vaccination process early in the hospital course. We encourage other institutions to utilize similar approaches to not only remind providers about inpatient vaccination, but also educate and encourage patients to receive the vaccine. These measures will help institutions increase inpatient COVID-19 vaccination rates in a high-risk population.
Corresponding author: Anna Rubin, MD, Department of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; arubin@mfa.gwu.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
From the Department of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
Abstract
Objective: Inpatient vaccination initiatives are well described in the literature. During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals began administering COVID-19 vaccines to hospitalized patients. Although vaccination rates increased, there remained many unvaccinated patients despite community efforts. This quality improvement project aimed to increase the COVID-19 vaccination rates of hospitalized patients on the medicine service at the George Washington University Hospital (GWUH).
Methods: From November 2021 through February 2022, we conducted a Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle with 3 phases. Initial steps included gathering baseline data from the electronic health record and consulting stakeholders. The first 2 phases focused on educating housestaff on the availability, ordering process, and administration of the Pfizer vaccine. The third phase consisted of developing educational pamphlets for patients to be included in their admission packets.
Results: The baseline mean COVID-19 vaccination rate (August to October 2021) of eligible patients on the medicine service was 10.7%. In the months after we implemented the PDSA cycle (November 2021 to February 2022), the mean vaccination rate increased to 15.4%.
Conclusion: This quality improvement project implemented measures to increase administration of the Pfizer vaccine to eligible patients admitted to the medicine service at GWUH. The mean vaccination rate increased from 10.7% in the 3 months prior to implementation to 15.4% during the 4 months post implementation. Other measures to consider in the future include increasing the availability of other COVID-19 vaccines at our hospital and incorporating the vaccine into the admission order set to help facilitate vaccination early in the hospital course.
Keywords: housestaff, quality improvement, PDSA, COVID-19, BNT162b2 vaccine, patient education
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, case rates in the United States have fluctuated considerably, corresponding to epidemic waves. In 2021, US daily cases of COVID-19 peaked at nearly 300,000 in early January and reached a nadir of 8000 cases in mid-June.1 In September 2021, new cases had increased to 200,000 per day due to the prevalence of the Delta variant.1 Particularly with the emergence of new variants of SARS-CoV-2, vaccination efforts to limit the spread of infection and severity of illness are critical. Data have shown that 2 doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech) were largely protective against severe infection for approximately 6 months.2,3 When we began this quality improvement (QI) project in September 2021, only 179 million Americans had been fully vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is just over half of the US population.4 An electronic survey conducted in the United States with more than 5 million responses found that, of those who were hesitant about receiving the vaccine, 49% reported a fear of adverse effects and 48% reported a lack of trust in the vaccine.5
This QI project sought to target unvaccinated individuals admitted to the internal medicine inpatient service. Vaccinating hospitalized patients is especially important since they are sicker than the general population and at higher risk of having poor outcomes from COVID-19. Inpatient vaccine initiatives, such as administering influenza vaccine prior to discharge, have been successfully implemented in the past.6 One large COVID-19 vaccination program featured an admission order set to increase the rates of vaccination among hospitalized patients.7 Our QI project piloted a multidisciplinary approach involving the nursing staff, pharmacy, information technology (IT) department, and internal medicine housestaff to increase COVID-19 vaccination rates among hospitalized patients on the medical service. This project aimed to increase inpatient vaccination rates through interventions targeting both primary providers as well as the patients themselves.
Methods
Setting and Interventions
This project was conducted at the George Washington University Hospital (GWUH) in Washington, DC. The clinicians involved in the study were the internal medicine housestaff, and the patients included were adults admitted to the resident medicine ward teams. The project was exempt by the institutional review board and did not require informed consent.
The quality improvement initiative had 3 phases, each featuring a different intervention (Table 1). The first phase involved sending a weekly announcement (via email and a secure health care messaging app) to current residents rotating on the inpatient medicine service. The announcement contained information regarding COVID-19 vaccine availability at the hospital, instructions on ordering the vaccine, and the process of coordinating with pharmacy to facilitate vaccine administration. Thereafter, residents were educated on the process of giving a COVID-19 vaccine to a patient from start to finish. Due to the nature of the residency schedule, different housestaff members rotated in and out of the medicine wards during the intervention periods. The weekly email was sent to the entire internal medicine housestaff, informing all residents about the QI project, while the weekly secure messages served as reminders and were only sent to residents currently on the medicine wards.

In the second phase, we posted paper flyers throughout the hospital to remind housestaff to give the vaccine and again educate them on the process of ordering the vaccine. For the third intervention, a COVID-19 vaccine educational pamphlet was developed for distribution to inpatients at GWUH. The pamphlet included information on vaccine efficacy, safety, side effects, and eligibility. The pamphlet was incorporated in the admission packet that every patient receives upon admission to the hospital. The patients reviewed the pamphlets with nursing staff, who would answer any questions, with residents available to discuss any outstanding concerns.
Measures and Data Gathering
The primary endpoint of the study was inpatient vaccination rate, defined as the number of COVID-19 vaccines administered divided by the number of patients eligible to receive a vaccine (not fully vaccinated). During initial triage, nursing staff documented vaccination status in the electronic health record (EHR), checking a box in a data entry form if a patient had received 0, 1, or 2 doses of the COVID-19 vaccine. The GWUH IT department generated data from this form to determine the number of patients eligible to receive a COVID-19 vaccine. Data were extracted from the medication administration record in the EHR to determine the number of vaccines that were administered to patients during their hospitalization on the inpatient medical service. Each month, the IT department extracted data for the number of eligible patients and the number of vaccines administered. This yielded the monthly vaccination rates. The monthly vaccination rates in the period prior to starting the QI initiative were compared to the rates in the period after the interventions were implemented.
Of note, during the course of this project, patients became eligible for a third COVID-19 vaccine (booster). We decided to continue with the original aim of vaccinating adults who had only received 0 or 1 dose of the vaccine. Therefore, the eligibility criteria remained the same throughout the study. We obtained retrospective data to ensure that the vaccines being counted toward the vaccination rate were vaccines given to patients not yet fully vaccinated and not vaccines given as boosters.

Results
From August to October 2021, the baseline average monthly vaccination rate of patients on the medicine service who were eligible to receive a COVID-19 vaccine was 10.7%. After the first intervention, the vaccination rate increased to 19.7% in November 2021 (Table 2). The second intervention yielded vaccination rates of 11.4% and 11.8% in December 2021 and January 2022, respectively. During the final phase in February 2022, the vaccination rate was 19.0%. At the conclusion of the study, the mean vaccination rate for the intervention months was 15.4% (Figure 1). Process stability and variation are demonstrated with a statistical process control chart (Figure 2).


Discussion
For this housestaff-driven QI project, we implemented an inpatient COVID-19 vaccination campaign consisting of 3 phases that targeted both providers and patients. During the intervention period, we observed an increased vaccination rate compared to the period just prior to implementation of the QI project. While our interventions may certainly have boosted vaccination rates, we understand other variables could have contributed to increased rates as well. The emergence of variants in the United States, such as omicron in December 2021,8 could have precipitated a demand for vaccinations among patients. Holidays in November and December may also have increased patients’ desire to get vaccinated before travel.
We encountered a number of roadblocks that challenged our project, including difficulty identifying patients who were eligible for the vaccine, logistical vaccine administration challenges, and hesitancy among the inpatient population. Accurately identifying patients who were eligible for a vaccine in the EHR was especially challenging in the setting of rapidly changing guidelines regarding COVID-19 vaccination. In September 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration authorized the Pfizer booster for certain populations and later, in November 2021, for all adults. This meant that some fully vaccinated hospitalized patients (those with 2 doses) then qualified for an additional dose of the vaccine and received a dose during hospitalization. To determine the true vaccination rate, we obtained retrospective data that allowed us to track each vaccine administered. If a patient had already received 2 doses of the COVID-19 vaccine, the vaccine administered was counted as a booster and excluded from the calculation of the vaccination rate. Future PDSA cycles could include updating the EHR to capture the whole range of COVID-19 vaccination status (unvaccinated, partially vaccinated, fully vaccinated, fully vaccinated with 1 booster, fully vaccinated with 2 boosters).
We also encountered logistical challenges with the administration of the COVID-19 vaccine to hospitalized patients. During the intervention period, our pharmacy department required 5 COVID-19 vaccination orders before opening a vial and administering the vaccine doses in order to reduce waste. This policy may have limited our ability to vaccinate eligible inpatients because we were not always able to identify 5 patients simultaneously on the service who were eligible and consented to the vaccine.
The majority of patients who were interested in receiving COVID-19 vaccination had already been vaccinated in the outpatient setting. This fact made the inpatient internal medicine subset of patients a particularly challenging population to target, given their possible hesitancy regarding vaccination. By utilizing a multidisciplinary team and increasing communication of providers and nursing staff, we helped to increase the COVID-19 vaccination rates at our hospital from 10.7% to 15.4%.
Future Directions
Future interventions to consider include increasing the availability of other approved COVID-19 vaccines at our hospital besides the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Furthermore, incorporating the vaccine into the admission order set would help initiate the vaccination process early in the hospital course. We encourage other institutions to utilize similar approaches to not only remind providers about inpatient vaccination, but also educate and encourage patients to receive the vaccine. These measures will help institutions increase inpatient COVID-19 vaccination rates in a high-risk population.
Corresponding author: Anna Rubin, MD, Department of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; arubin@mfa.gwu.edu
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Trends in number of COVID-19 cases and deaths in the US reported to CDC, by state/territory. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_dailycases
2. Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162B2 MRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(27):2603-2615. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2034577
3. Hall V, Foulkes S, Insalata F, et al. Protection against SARS-COV-2 after covid-19 vaccination and previous infection. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(13):1207-1220. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2118691
4. Trends in number of COVID-19 vaccinations in the US. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccination-trends_vacctrends-fully-cum
5. King WC, Rubinstein M, Reinhart A, Mejia R. Time trends, factors associated with, and reasons for covid-19 vaccine hesitancy: A massive online survey of US adults from January-May 2021. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(12). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0260731
6. Cohen ES, Ogrinc G, Taylor T, et al. Influenza vaccination rates for hospitalised patients: A multiyear quality improvement effort. BMJ Qual Saf. 2015;24(3):221-227. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2014-003556
7. Berger RE, Diaz DC, Chacko S, et al. Implementation of an inpatient covid-19 vaccination program. NEJM Catalyst. 2021;2(10). doi:10.1056/cat.21.0235
8. CDC COVID-19 Response Team. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant - United States, December 1-8, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(50):1731-1734. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7050e1
1. Trends in number of COVID-19 cases and deaths in the US reported to CDC, by state/territory. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_dailycases
2. Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162B2 MRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(27):2603-2615. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2034577
3. Hall V, Foulkes S, Insalata F, et al. Protection against SARS-COV-2 after covid-19 vaccination and previous infection. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(13):1207-1220. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2118691
4. Trends in number of COVID-19 vaccinations in the US. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccination-trends_vacctrends-fully-cum
5. King WC, Rubinstein M, Reinhart A, Mejia R. Time trends, factors associated with, and reasons for covid-19 vaccine hesitancy: A massive online survey of US adults from January-May 2021. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(12). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0260731
6. Cohen ES, Ogrinc G, Taylor T, et al. Influenza vaccination rates for hospitalised patients: A multiyear quality improvement effort. BMJ Qual Saf. 2015;24(3):221-227. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2014-003556
7. Berger RE, Diaz DC, Chacko S, et al. Implementation of an inpatient covid-19 vaccination program. NEJM Catalyst. 2021;2(10). doi:10.1056/cat.21.0235
8. CDC COVID-19 Response Team. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant - United States, December 1-8, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(50):1731-1734. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7050e1











