User login
ED visits for life-threatening conditions declined early in COVID-19 pandemic
ED visits for myocardial infarction, stroke, and hyperglycemic crisis dropped substantially in the 10 weeks after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
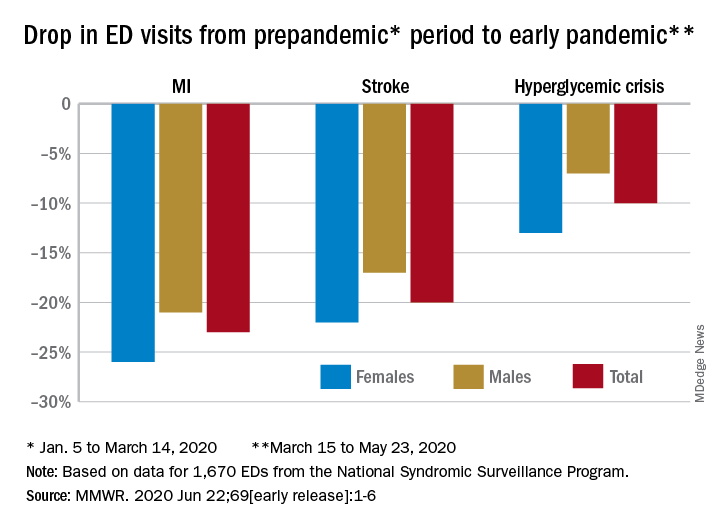
Compared with the 10-week period from Jan. 5 to March 14, ED visits were down by 23% for MI, 20% for stroke, and 10% for hyperglycemic crisis from March 15 to May 23, Samantha J. Lange, MPH, and associates at the CDC reported June 22 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“A short-term decline of this magnitude … is biologically implausible for MI and stroke, especially for older adults, and unlikely for hyperglycemic crisis, and the finding suggests that patients with these conditions either could not access care or were delaying or avoiding seeking care during the early pandemic period,” they wrote.
The largest decreases in the actual number of visits for MI occurred among both men (down by 2,114, –24%) and women (down by 1,459, –25%) aged 65-74 years. For stroke, men aged 65-74 years had 1,406 (–19%) fewer visits to the ED and women 75-84 years had 1,642 (–23%) fewer visits, the CDC researchers said.
For hypoglycemic crisis, the largest declines during the early pandemic period occurred among younger adults: ED visits for men and women aged 18-44 years were down, respectively, by 419 (–8%) and 775 (–16%), they reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
“Decreases in ED visits for hyperglycemic crisis might be less striking because patient recognition of this crisis is typically augmented by home glucose monitoring and not reliant upon symptoms alone, as is the case for MI and stroke,” Ms. Lange and her associates noted.
Charting weekly visit numbers showed that the drop for all three conditions actually started the week before the emergency was declared and reached its nadir the week after (March 22) for MI and 2 weeks later (March 29) for stroke and hypoglycemic crisis.
Visits for hypoglycemic crisis have largely returned to normal since those low points, but MI and stroke visits “remain below prepandemic levels” despite gradual increases through April and May, they said.
It has been reported that “deaths not associated with confirmed or probable COVID-19 might have been directly or indirectly attributed to the pandemic. The striking decline in ED visits for acute life-threatening conditions might partially explain observed excess mortality not associated with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote.
ED visits for myocardial infarction, stroke, and hyperglycemic crisis dropped substantially in the 10 weeks after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Compared with the 10-week period from Jan. 5 to March 14, ED visits were down by 23% for MI, 20% for stroke, and 10% for hyperglycemic crisis from March 15 to May 23, Samantha J. Lange, MPH, and associates at the CDC reported June 22 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“A short-term decline of this magnitude … is biologically implausible for MI and stroke, especially for older adults, and unlikely for hyperglycemic crisis, and the finding suggests that patients with these conditions either could not access care or were delaying or avoiding seeking care during the early pandemic period,” they wrote.
The largest decreases in the actual number of visits for MI occurred among both men (down by 2,114, –24%) and women (down by 1,459, –25%) aged 65-74 years. For stroke, men aged 65-74 years had 1,406 (–19%) fewer visits to the ED and women 75-84 years had 1,642 (–23%) fewer visits, the CDC researchers said.
For hypoglycemic crisis, the largest declines during the early pandemic period occurred among younger adults: ED visits for men and women aged 18-44 years were down, respectively, by 419 (–8%) and 775 (–16%), they reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
“Decreases in ED visits for hyperglycemic crisis might be less striking because patient recognition of this crisis is typically augmented by home glucose monitoring and not reliant upon symptoms alone, as is the case for MI and stroke,” Ms. Lange and her associates noted.
Charting weekly visit numbers showed that the drop for all three conditions actually started the week before the emergency was declared and reached its nadir the week after (March 22) for MI and 2 weeks later (March 29) for stroke and hypoglycemic crisis.
Visits for hypoglycemic crisis have largely returned to normal since those low points, but MI and stroke visits “remain below prepandemic levels” despite gradual increases through April and May, they said.
It has been reported that “deaths not associated with confirmed or probable COVID-19 might have been directly or indirectly attributed to the pandemic. The striking decline in ED visits for acute life-threatening conditions might partially explain observed excess mortality not associated with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote.
ED visits for myocardial infarction, stroke, and hyperglycemic crisis dropped substantially in the 10 weeks after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Compared with the 10-week period from Jan. 5 to March 14, ED visits were down by 23% for MI, 20% for stroke, and 10% for hyperglycemic crisis from March 15 to May 23, Samantha J. Lange, MPH, and associates at the CDC reported June 22 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“A short-term decline of this magnitude … is biologically implausible for MI and stroke, especially for older adults, and unlikely for hyperglycemic crisis, and the finding suggests that patients with these conditions either could not access care or were delaying or avoiding seeking care during the early pandemic period,” they wrote.
The largest decreases in the actual number of visits for MI occurred among both men (down by 2,114, –24%) and women (down by 1,459, –25%) aged 65-74 years. For stroke, men aged 65-74 years had 1,406 (–19%) fewer visits to the ED and women 75-84 years had 1,642 (–23%) fewer visits, the CDC researchers said.
For hypoglycemic crisis, the largest declines during the early pandemic period occurred among younger adults: ED visits for men and women aged 18-44 years were down, respectively, by 419 (–8%) and 775 (–16%), they reported based on data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
“Decreases in ED visits for hyperglycemic crisis might be less striking because patient recognition of this crisis is typically augmented by home glucose monitoring and not reliant upon symptoms alone, as is the case for MI and stroke,” Ms. Lange and her associates noted.
Charting weekly visit numbers showed that the drop for all three conditions actually started the week before the emergency was declared and reached its nadir the week after (March 22) for MI and 2 weeks later (March 29) for stroke and hypoglycemic crisis.
Visits for hypoglycemic crisis have largely returned to normal since those low points, but MI and stroke visits “remain below prepandemic levels” despite gradual increases through April and May, they said.
It has been reported that “deaths not associated with confirmed or probable COVID-19 might have been directly or indirectly attributed to the pandemic. The striking decline in ED visits for acute life-threatening conditions might partially explain observed excess mortality not associated with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote.
FROM MMWR
T2D plus heart failure packs a deadly punch
It’s bad news for patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes when they then develop heart failure during the next few years.
Patients with incident type 2 diabetes (T2D) who soon after also had heart failure appear faced a dramatically elevated mortality risk, higher than the incremental risk from any other cardiovascular or renal comorbidity that appeared following diabetes onset, in an analysis of more than 150,000 Danish patients with incident type 2 diabetes during 1998-2015.
The 5-year risk of death in patients who developed heart failure during the first 5 years following an initial diagnosis of T2D was about 48%, about threefold higher than in patients with newly diagnosed T2D who remained free of heart failure or any of the other studied comorbidities, Bochra Zareini, MD, and associates reported in a study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. The studied patients had no known cardiovascular or renal disease at the time of their first T2D diagnosis.
“Our study reports not only on the absolute 5-year risk” of mortality, “but also takes into consideration when patients developed” a comorbidity. “What is surprising and worrying is the very high risk of death following heart failure and the potential life years lost when compared to T2D patients who do not develop heart failure,” said Dr. Zareini, a cardiologist at Herlev and Gentofte University Hospital in Copenhagen. “The implications of our study are to create awareness and highlight the importance of early detection of heart failure development in patients with T2D.” The results also showed that “heart failure is a common cardiovascular disease” in patients with newly diagnosed T2D, she added in an interview.
The data she and her associates reported came from a retrospective analysis of 153,403 Danish citizens in national health records who received a prescription for an antidiabetes drug for the first time during 1998-2015, excluding patients with a prior diagnosis of heart failure, ischemic heart disease (IHD), stroke, peripheral artery disease (PAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), or gestational diabetes. They followed these patients for a median of just under 10 years, during which time 45% of the cohort had an incident diagnosis of at least one of these cardiovascular and renal conditions, based on medical-record entries from hospitalization discharges or ambulatory contacts.
Nearly two-thirds of the T2D patients with an incident comorbidity during follow-up had a single new diagnosis, a quarter had two new comorbidities appear during follow-up, and 13% developed at least three new comorbidities.
Heart failure, least common but deadliest comorbidity
The most common of the tracked comorbidities was IHD, which appeared in 8% of the T2D patients within 5 years and in 13% after 10 years. Next most common was stroke, affecting 3% of patients after 5 years and 5% after 10 years. CKD occurred in 2.2% after 5 years and in 4.0% after 10 years, PAD occurred in 2.1% after 5 years and in 3.0% at 10 years, and heart failure occurred in 1.6% at 5 years and in 2.2% after 10 years.
But despite being the least common of the studied comorbidities, heart failure was by far the most deadly, roughly tripling the 5-year mortality rate, compared with T2D patients with no comorbidities, regardless of exactly when it first appeared during the first 5 years after the initial T2D diagnosis. The next most deadly comorbidities were stroke and PAD, which each roughly doubled mortality, compared with the patients who remained free of any studied comorbidity. CKD boosted mortality by 70%-110%, depending on exactly when it appeared during the first 5 years of follow-up, and IHD, while the most frequent comorbidity was also the most benign, increasing mortality by about 30%.
The most deadly combinations of two comorbidities were when heart failure appeared with either CKD or with PAD; each of these combinations boosted mortality by 300%-400% when it occurred during the first few years after a T2D diagnosis.
The findings came from “a very big and unselected patient group of patients, making our results highly generalizable in terms of assessing the prognostic consequences of heart failure,” Dr. Zareini stressed.
Management implications
The dangerous combination of T2D and heart failure has been documented for several years, and prompted a focused statement in 2019 about best practices for managing these patients (Circulation. 2019 Aug 3;140[7]:e294-324). “Heart failure has been known for some time to predict poorer outcomes in patients with T2D. Not much surprising” in the new findings reported by Dr. Zareini and associates, commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, a cardiovascular endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Heart failure “rarely acts alone, but in combination with other forms of heart or renal disease,” he noted in an interview.
Earlier studies may have “overlooked” heart failure’s importance compared with other comorbidities because they often “only investigated one cardiovascular disease in patients with T2D,” Dr. Zareini noted. In recent years the importance of heart failure occurring in patients with T2D also gained heightened significance because of the growing role of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor drug class in treating patients with T2D and the documented ability of these drugs to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 28;75[16]:1956-74). Dr. Zareini and associates put it this way in their report: “Heart failure has in recent years been recognized as an important clinical endpoint ... in patients with T2D, in particular, after the results from randomized, controlled trials of SGLT2 inhibitors showed benefit on cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations.”
Despite this, the new findings “do not address treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2D, nor can we use our data to address which patients should not be treated,” with this drug class, which instead should rely on “current evidence and expert consensus,” she said.
“Guidelines favor SGLT2 inhibitors or [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists in patients with a history of or high risk for major adverse coronary events,” and SGLT2 inhibitors are also “preferable in patients with renal disease,” Dr. Eckel noted.
Other avenues also exist for minimizing the onset of heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases in patients with T2D, Dr. Zareini said, citing modifiable risks that lead to heart failure that include hypertension, “diabetic cardiomyopathy,” and ISD. “Clinicians must treat all modifiable risk factors in patients with T2D in order to improve prognosis and limit development of cardiovascular and renal disease.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Zareini and Dr. Eckel had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zareini B et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Jun 23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006260.
It’s bad news for patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes when they then develop heart failure during the next few years.
Patients with incident type 2 diabetes (T2D) who soon after also had heart failure appear faced a dramatically elevated mortality risk, higher than the incremental risk from any other cardiovascular or renal comorbidity that appeared following diabetes onset, in an analysis of more than 150,000 Danish patients with incident type 2 diabetes during 1998-2015.
The 5-year risk of death in patients who developed heart failure during the first 5 years following an initial diagnosis of T2D was about 48%, about threefold higher than in patients with newly diagnosed T2D who remained free of heart failure or any of the other studied comorbidities, Bochra Zareini, MD, and associates reported in a study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. The studied patients had no known cardiovascular or renal disease at the time of their first T2D diagnosis.
“Our study reports not only on the absolute 5-year risk” of mortality, “but also takes into consideration when patients developed” a comorbidity. “What is surprising and worrying is the very high risk of death following heart failure and the potential life years lost when compared to T2D patients who do not develop heart failure,” said Dr. Zareini, a cardiologist at Herlev and Gentofte University Hospital in Copenhagen. “The implications of our study are to create awareness and highlight the importance of early detection of heart failure development in patients with T2D.” The results also showed that “heart failure is a common cardiovascular disease” in patients with newly diagnosed T2D, she added in an interview.
The data she and her associates reported came from a retrospective analysis of 153,403 Danish citizens in national health records who received a prescription for an antidiabetes drug for the first time during 1998-2015, excluding patients with a prior diagnosis of heart failure, ischemic heart disease (IHD), stroke, peripheral artery disease (PAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), or gestational diabetes. They followed these patients for a median of just under 10 years, during which time 45% of the cohort had an incident diagnosis of at least one of these cardiovascular and renal conditions, based on medical-record entries from hospitalization discharges or ambulatory contacts.
Nearly two-thirds of the T2D patients with an incident comorbidity during follow-up had a single new diagnosis, a quarter had two new comorbidities appear during follow-up, and 13% developed at least three new comorbidities.
Heart failure, least common but deadliest comorbidity
The most common of the tracked comorbidities was IHD, which appeared in 8% of the T2D patients within 5 years and in 13% after 10 years. Next most common was stroke, affecting 3% of patients after 5 years and 5% after 10 years. CKD occurred in 2.2% after 5 years and in 4.0% after 10 years, PAD occurred in 2.1% after 5 years and in 3.0% at 10 years, and heart failure occurred in 1.6% at 5 years and in 2.2% after 10 years.
But despite being the least common of the studied comorbidities, heart failure was by far the most deadly, roughly tripling the 5-year mortality rate, compared with T2D patients with no comorbidities, regardless of exactly when it first appeared during the first 5 years after the initial T2D diagnosis. The next most deadly comorbidities were stroke and PAD, which each roughly doubled mortality, compared with the patients who remained free of any studied comorbidity. CKD boosted mortality by 70%-110%, depending on exactly when it appeared during the first 5 years of follow-up, and IHD, while the most frequent comorbidity was also the most benign, increasing mortality by about 30%.
The most deadly combinations of two comorbidities were when heart failure appeared with either CKD or with PAD; each of these combinations boosted mortality by 300%-400% when it occurred during the first few years after a T2D diagnosis.
The findings came from “a very big and unselected patient group of patients, making our results highly generalizable in terms of assessing the prognostic consequences of heart failure,” Dr. Zareini stressed.
Management implications
The dangerous combination of T2D and heart failure has been documented for several years, and prompted a focused statement in 2019 about best practices for managing these patients (Circulation. 2019 Aug 3;140[7]:e294-324). “Heart failure has been known for some time to predict poorer outcomes in patients with T2D. Not much surprising” in the new findings reported by Dr. Zareini and associates, commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, a cardiovascular endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Heart failure “rarely acts alone, but in combination with other forms of heart or renal disease,” he noted in an interview.
Earlier studies may have “overlooked” heart failure’s importance compared with other comorbidities because they often “only investigated one cardiovascular disease in patients with T2D,” Dr. Zareini noted. In recent years the importance of heart failure occurring in patients with T2D also gained heightened significance because of the growing role of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor drug class in treating patients with T2D and the documented ability of these drugs to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 28;75[16]:1956-74). Dr. Zareini and associates put it this way in their report: “Heart failure has in recent years been recognized as an important clinical endpoint ... in patients with T2D, in particular, after the results from randomized, controlled trials of SGLT2 inhibitors showed benefit on cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations.”
Despite this, the new findings “do not address treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2D, nor can we use our data to address which patients should not be treated,” with this drug class, which instead should rely on “current evidence and expert consensus,” she said.
“Guidelines favor SGLT2 inhibitors or [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists in patients with a history of or high risk for major adverse coronary events,” and SGLT2 inhibitors are also “preferable in patients with renal disease,” Dr. Eckel noted.
Other avenues also exist for minimizing the onset of heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases in patients with T2D, Dr. Zareini said, citing modifiable risks that lead to heart failure that include hypertension, “diabetic cardiomyopathy,” and ISD. “Clinicians must treat all modifiable risk factors in patients with T2D in order to improve prognosis and limit development of cardiovascular and renal disease.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Zareini and Dr. Eckel had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zareini B et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Jun 23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006260.
It’s bad news for patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes when they then develop heart failure during the next few years.
Patients with incident type 2 diabetes (T2D) who soon after also had heart failure appear faced a dramatically elevated mortality risk, higher than the incremental risk from any other cardiovascular or renal comorbidity that appeared following diabetes onset, in an analysis of more than 150,000 Danish patients with incident type 2 diabetes during 1998-2015.
The 5-year risk of death in patients who developed heart failure during the first 5 years following an initial diagnosis of T2D was about 48%, about threefold higher than in patients with newly diagnosed T2D who remained free of heart failure or any of the other studied comorbidities, Bochra Zareini, MD, and associates reported in a study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. The studied patients had no known cardiovascular or renal disease at the time of their first T2D diagnosis.
“Our study reports not only on the absolute 5-year risk” of mortality, “but also takes into consideration when patients developed” a comorbidity. “What is surprising and worrying is the very high risk of death following heart failure and the potential life years lost when compared to T2D patients who do not develop heart failure,” said Dr. Zareini, a cardiologist at Herlev and Gentofte University Hospital in Copenhagen. “The implications of our study are to create awareness and highlight the importance of early detection of heart failure development in patients with T2D.” The results also showed that “heart failure is a common cardiovascular disease” in patients with newly diagnosed T2D, she added in an interview.
The data she and her associates reported came from a retrospective analysis of 153,403 Danish citizens in national health records who received a prescription for an antidiabetes drug for the first time during 1998-2015, excluding patients with a prior diagnosis of heart failure, ischemic heart disease (IHD), stroke, peripheral artery disease (PAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), or gestational diabetes. They followed these patients for a median of just under 10 years, during which time 45% of the cohort had an incident diagnosis of at least one of these cardiovascular and renal conditions, based on medical-record entries from hospitalization discharges or ambulatory contacts.
Nearly two-thirds of the T2D patients with an incident comorbidity during follow-up had a single new diagnosis, a quarter had two new comorbidities appear during follow-up, and 13% developed at least three new comorbidities.
Heart failure, least common but deadliest comorbidity
The most common of the tracked comorbidities was IHD, which appeared in 8% of the T2D patients within 5 years and in 13% after 10 years. Next most common was stroke, affecting 3% of patients after 5 years and 5% after 10 years. CKD occurred in 2.2% after 5 years and in 4.0% after 10 years, PAD occurred in 2.1% after 5 years and in 3.0% at 10 years, and heart failure occurred in 1.6% at 5 years and in 2.2% after 10 years.
But despite being the least common of the studied comorbidities, heart failure was by far the most deadly, roughly tripling the 5-year mortality rate, compared with T2D patients with no comorbidities, regardless of exactly when it first appeared during the first 5 years after the initial T2D diagnosis. The next most deadly comorbidities were stroke and PAD, which each roughly doubled mortality, compared with the patients who remained free of any studied comorbidity. CKD boosted mortality by 70%-110%, depending on exactly when it appeared during the first 5 years of follow-up, and IHD, while the most frequent comorbidity was also the most benign, increasing mortality by about 30%.
The most deadly combinations of two comorbidities were when heart failure appeared with either CKD or with PAD; each of these combinations boosted mortality by 300%-400% when it occurred during the first few years after a T2D diagnosis.
The findings came from “a very big and unselected patient group of patients, making our results highly generalizable in terms of assessing the prognostic consequences of heart failure,” Dr. Zareini stressed.
Management implications
The dangerous combination of T2D and heart failure has been documented for several years, and prompted a focused statement in 2019 about best practices for managing these patients (Circulation. 2019 Aug 3;140[7]:e294-324). “Heart failure has been known for some time to predict poorer outcomes in patients with T2D. Not much surprising” in the new findings reported by Dr. Zareini and associates, commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, a cardiovascular endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Heart failure “rarely acts alone, but in combination with other forms of heart or renal disease,” he noted in an interview.
Earlier studies may have “overlooked” heart failure’s importance compared with other comorbidities because they often “only investigated one cardiovascular disease in patients with T2D,” Dr. Zareini noted. In recent years the importance of heart failure occurring in patients with T2D also gained heightened significance because of the growing role of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor drug class in treating patients with T2D and the documented ability of these drugs to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 28;75[16]:1956-74). Dr. Zareini and associates put it this way in their report: “Heart failure has in recent years been recognized as an important clinical endpoint ... in patients with T2D, in particular, after the results from randomized, controlled trials of SGLT2 inhibitors showed benefit on cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations.”
Despite this, the new findings “do not address treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2D, nor can we use our data to address which patients should not be treated,” with this drug class, which instead should rely on “current evidence and expert consensus,” she said.
“Guidelines favor SGLT2 inhibitors or [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists in patients with a history of or high risk for major adverse coronary events,” and SGLT2 inhibitors are also “preferable in patients with renal disease,” Dr. Eckel noted.
Other avenues also exist for minimizing the onset of heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases in patients with T2D, Dr. Zareini said, citing modifiable risks that lead to heart failure that include hypertension, “diabetic cardiomyopathy,” and ISD. “Clinicians must treat all modifiable risk factors in patients with T2D in order to improve prognosis and limit development of cardiovascular and renal disease.”
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Zareini and Dr. Eckel had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zareini B et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Jun 23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006260.
FROM CIRCULATION: CARDIOVASCULAR QUALITY AND OUTCOMES
Cost of preventable adult hospital stays topped $33 billion in 2017
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
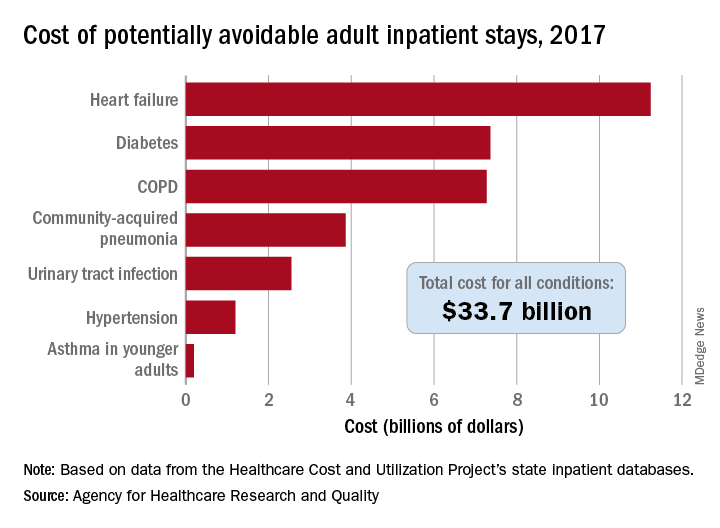
That year, there were 27.4 million inpatient visits by adults with a total cost of $380.1 billion, although obstetric stays were not included in the analysis. Of those inpatient admissions, 3.5 million (12.9%) were deemed to be “avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in a recent AHRQ statistical brief.
The charges for those 3.5 million visits came to $33.7 billion, or 8.9% of aggregate hospital costs in 2017, based on data from the AHRQ Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s state inpatient databases.
“Determining the volume and costs of potentially preventable inpatient stays can identify where potential cost savings might be found associated with reducing these hospitalizations overall and among specific subpopulations,” the investigators pointed out.
Of the seven conditions that are potentially avoidable, heart failure was the most expensive, producing more than 1.1 million inpatient admissions at a cost of $11.2 billion. Diabetes was next with a cost of almost $7.4 billion, followed by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at nearly $7.3 billion, they said.
Those three conditions, along with hypertension and asthma in younger adults, brought the total cost of the preventable-stay equation’s chronic side to $27.3 billion in 2017, versus $6.4 billion for the two acute conditions, community-acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections, said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ.
The rate of potentially avoidable stays for chronic conditions was higher for men (1,112/100,000 population) than for women (954/100,000), but women had a higher rate for acute conditions, 346 vs. 257, which made the overall rates similar (1,369 for men and 1,300 for women), they reported.
Differences by race/ethnicity were more striking. The rate of potentially avoidable stays for blacks was 2,573/100,000 in 2017, compared with 1,315 for Hispanics, 1,173 for whites, and 581 for Asians/Pacific Islanders. The considerable margins between those figures, however, were far eclipsed by the “other” category, which had 4,911 stays per 100,000, the researchers said.
Large disparities also can be seen when looking at community-level income. Communities with income in the lowest quartile had a preventable-hospitalization rate of 2,013/100,000, and the rate dropped with each successive quartile until it reached 878/100,000 for the highest-income communities, according to the report.
“High hospital admission rates for these conditions may indicate areas where changes to the healthcare delivery system could be implemented to improve patient outcomes and lower costs,” Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang wrote.
SOURCE: McDermott KW and Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

That year, there were 27.4 million inpatient visits by adults with a total cost of $380.1 billion, although obstetric stays were not included in the analysis. Of those inpatient admissions, 3.5 million (12.9%) were deemed to be “avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in a recent AHRQ statistical brief.
The charges for those 3.5 million visits came to $33.7 billion, or 8.9% of aggregate hospital costs in 2017, based on data from the AHRQ Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s state inpatient databases.
“Determining the volume and costs of potentially preventable inpatient stays can identify where potential cost savings might be found associated with reducing these hospitalizations overall and among specific subpopulations,” the investigators pointed out.
Of the seven conditions that are potentially avoidable, heart failure was the most expensive, producing more than 1.1 million inpatient admissions at a cost of $11.2 billion. Diabetes was next with a cost of almost $7.4 billion, followed by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at nearly $7.3 billion, they said.
Those three conditions, along with hypertension and asthma in younger adults, brought the total cost of the preventable-stay equation’s chronic side to $27.3 billion in 2017, versus $6.4 billion for the two acute conditions, community-acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections, said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ.
The rate of potentially avoidable stays for chronic conditions was higher for men (1,112/100,000 population) than for women (954/100,000), but women had a higher rate for acute conditions, 346 vs. 257, which made the overall rates similar (1,369 for men and 1,300 for women), they reported.
Differences by race/ethnicity were more striking. The rate of potentially avoidable stays for blacks was 2,573/100,000 in 2017, compared with 1,315 for Hispanics, 1,173 for whites, and 581 for Asians/Pacific Islanders. The considerable margins between those figures, however, were far eclipsed by the “other” category, which had 4,911 stays per 100,000, the researchers said.
Large disparities also can be seen when looking at community-level income. Communities with income in the lowest quartile had a preventable-hospitalization rate of 2,013/100,000, and the rate dropped with each successive quartile until it reached 878/100,000 for the highest-income communities, according to the report.
“High hospital admission rates for these conditions may indicate areas where changes to the healthcare delivery system could be implemented to improve patient outcomes and lower costs,” Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang wrote.
SOURCE: McDermott KW and Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

That year, there were 27.4 million inpatient visits by adults with a total cost of $380.1 billion, although obstetric stays were not included in the analysis. Of those inpatient admissions, 3.5 million (12.9%) were deemed to be “avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in a recent AHRQ statistical brief.
The charges for those 3.5 million visits came to $33.7 billion, or 8.9% of aggregate hospital costs in 2017, based on data from the AHRQ Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s state inpatient databases.
“Determining the volume and costs of potentially preventable inpatient stays can identify where potential cost savings might be found associated with reducing these hospitalizations overall and among specific subpopulations,” the investigators pointed out.
Of the seven conditions that are potentially avoidable, heart failure was the most expensive, producing more than 1.1 million inpatient admissions at a cost of $11.2 billion. Diabetes was next with a cost of almost $7.4 billion, followed by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at nearly $7.3 billion, they said.
Those three conditions, along with hypertension and asthma in younger adults, brought the total cost of the preventable-stay equation’s chronic side to $27.3 billion in 2017, versus $6.4 billion for the two acute conditions, community-acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections, said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ.
The rate of potentially avoidable stays for chronic conditions was higher for men (1,112/100,000 population) than for women (954/100,000), but women had a higher rate for acute conditions, 346 vs. 257, which made the overall rates similar (1,369 for men and 1,300 for women), they reported.
Differences by race/ethnicity were more striking. The rate of potentially avoidable stays for blacks was 2,573/100,000 in 2017, compared with 1,315 for Hispanics, 1,173 for whites, and 581 for Asians/Pacific Islanders. The considerable margins between those figures, however, were far eclipsed by the “other” category, which had 4,911 stays per 100,000, the researchers said.
Large disparities also can be seen when looking at community-level income. Communities with income in the lowest quartile had a preventable-hospitalization rate of 2,013/100,000, and the rate dropped with each successive quartile until it reached 878/100,000 for the highest-income communities, according to the report.
“High hospital admission rates for these conditions may indicate areas where changes to the healthcare delivery system could be implemented to improve patient outcomes and lower costs,” Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang wrote.
SOURCE: McDermott KW and Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
U.S. adults reach Healthy People 2020 cholesterol goal
Good news: High cholesterol is down in the United States. More good news: Low HDL cholesterol is down in the United States.
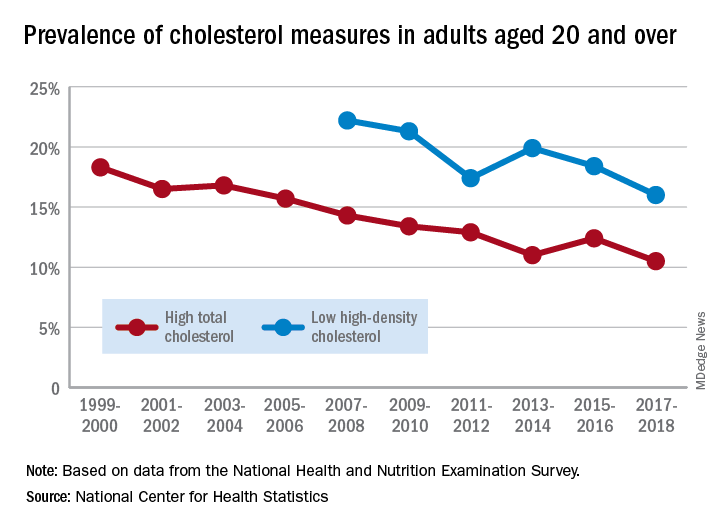
The prevalence of high total cholesterol in adults aged 20 years and older dropped from 18.3% in 1999-2000 to 10.5% in 2017-2018. And starting in 2007-2008, the prevalence of low HDL cholesterol declined from 22.2% to 16.0% in 2017-2018, the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
HDL cholesterol data before 2007 were not presented because of changes in laboratories and methods, but both trends are significant, and the decline in high total cholesterol means that the Healthy People 2020 goal of dropping prevalence to 13.5% has been met, said Margaret D. Carroll, MSPH, and Cheryl D. Fryar, MSPH, of the NCHS.
The demographic details, however, show some disparities hidden by the broader measures. The prevalence of low HDL cholesterol for women in 2015-2018 was 8.5%, but for men it was 26.6%, the NCHS investigators said.
And that Healthy People 2020 goal for total cholesterol? Age makes a difference: 7.5% of adults aged 20-39 years had high total cholesterol in 2015-2018, as did 11.4% of those aged 60 years and older, but those aged 40-59 years had a significantly higher prevalence of 15.7%, they reported.
Race/ethnicity was also a factor. Prevalence of low HDL was similar for white (16.6%) and Asian (15.8%) adults in 2015-2018, but black adults’ low HDL prevalence was significantly lower (11.9%) and Hispanics’ was significantly higher (21.9%), the researchers said.
The analysis was based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The investigators defined high total cholesterol as a level of 240 mg/dL or more, and low HDL cholesterol as less than 40 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol was not included in the analysis.
Good news: High cholesterol is down in the United States. More good news: Low HDL cholesterol is down in the United States.

The prevalence of high total cholesterol in adults aged 20 years and older dropped from 18.3% in 1999-2000 to 10.5% in 2017-2018. And starting in 2007-2008, the prevalence of low HDL cholesterol declined from 22.2% to 16.0% in 2017-2018, the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
HDL cholesterol data before 2007 were not presented because of changes in laboratories and methods, but both trends are significant, and the decline in high total cholesterol means that the Healthy People 2020 goal of dropping prevalence to 13.5% has been met, said Margaret D. Carroll, MSPH, and Cheryl D. Fryar, MSPH, of the NCHS.
The demographic details, however, show some disparities hidden by the broader measures. The prevalence of low HDL cholesterol for women in 2015-2018 was 8.5%, but for men it was 26.6%, the NCHS investigators said.
And that Healthy People 2020 goal for total cholesterol? Age makes a difference: 7.5% of adults aged 20-39 years had high total cholesterol in 2015-2018, as did 11.4% of those aged 60 years and older, but those aged 40-59 years had a significantly higher prevalence of 15.7%, they reported.
Race/ethnicity was also a factor. Prevalence of low HDL was similar for white (16.6%) and Asian (15.8%) adults in 2015-2018, but black adults’ low HDL prevalence was significantly lower (11.9%) and Hispanics’ was significantly higher (21.9%), the researchers said.
The analysis was based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The investigators defined high total cholesterol as a level of 240 mg/dL or more, and low HDL cholesterol as less than 40 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol was not included in the analysis.
Good news: High cholesterol is down in the United States. More good news: Low HDL cholesterol is down in the United States.

The prevalence of high total cholesterol in adults aged 20 years and older dropped from 18.3% in 1999-2000 to 10.5% in 2017-2018. And starting in 2007-2008, the prevalence of low HDL cholesterol declined from 22.2% to 16.0% in 2017-2018, the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
HDL cholesterol data before 2007 were not presented because of changes in laboratories and methods, but both trends are significant, and the decline in high total cholesterol means that the Healthy People 2020 goal of dropping prevalence to 13.5% has been met, said Margaret D. Carroll, MSPH, and Cheryl D. Fryar, MSPH, of the NCHS.
The demographic details, however, show some disparities hidden by the broader measures. The prevalence of low HDL cholesterol for women in 2015-2018 was 8.5%, but for men it was 26.6%, the NCHS investigators said.
And that Healthy People 2020 goal for total cholesterol? Age makes a difference: 7.5% of adults aged 20-39 years had high total cholesterol in 2015-2018, as did 11.4% of those aged 60 years and older, but those aged 40-59 years had a significantly higher prevalence of 15.7%, they reported.
Race/ethnicity was also a factor. Prevalence of low HDL was similar for white (16.6%) and Asian (15.8%) adults in 2015-2018, but black adults’ low HDL prevalence was significantly lower (11.9%) and Hispanics’ was significantly higher (21.9%), the researchers said.
The analysis was based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The investigators defined high total cholesterol as a level of 240 mg/dL or more, and low HDL cholesterol as less than 40 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol was not included in the analysis.
LAA Closure noninferior to DOACs to prevent AF-related events
Left atrial appendage closure was noninferior to use of direct oral anticoagulants for the prevention of atrial fibrillation (AFib)–related events in high-risk patients, based on data from 402 adults.
Given the limitations of vitamin K antagonists for preventing stroke in AFib, “a novel site-specific therapeutic alternative, mechanical left atrial appendage occlusion [LAAO], entered clinical practice,” but has not been compared with current safe and effective oral anticoagulants, wrote Pavel Osmancik, MD, of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady, Prague, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers randomized 201 moderate- or high-risk adults with nonvalvular AFib to LAAO and another 201 to direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Patients in the LAAO group underwent transesophageal echocardiography to exclude left atrial thrombi and underwent implantation with Boston Scientific’s Watchman, Watchman-FLX, or Abbott’s Amulet devices. Patients in the DOAC group received rivaroxaban, apixaban, or dabigatran at the manufacturer-recommended dose.
The primary outcome was a composite of complications related to procedures or devices, thromboembolic events (including stroke), and clinically significant bleeding. After an average of 20 months follow-up, 35 patients in the LAAO group and 41 in the DOAC group met the primary outcome (11% per 100 patient-years vs. 13% per 100 patient-years).
In addition, no differences appeared between the groups for the endpoint components of all-stroke/transient ischemic attack event (subdistribution hazard ratio, 1.00), clinically significantly bleeding (sHR, 0.81), or cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75).
Nine patients experienced major complications related to LAAO, including clinically significant bleeding (sHR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.44-1.52) and cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.34-1.62). Major LAAO-related complications occurred in nine (4.5%) patients, with a short-term (up to 7 days or hospital discharge) complication rate of 2.1% and a 2.7% late complication rate. The late complications included three pericardial effusions, one of which resulted in death, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to assess the differences among the components of the composite primary endpoint. For example, “Regarding the primary endpoint, stroke reduction may be more important than bleeding reduction,” the investigators wrote.
The results were strengthened, however, by the enrollment of a high-risk AF population and is the first known randomized trial to compare percutaneous LAAO and DOACs for stroke prevention in this group. But the late complication rate of 2.7% is “suboptimal” and safety issues reinforce the need for refinement of operator technique and device technology with LAAO, they concluded.
‘Important step forward,’ with caveats
“How LAAO might stack up against DOAC therapy has remained an open question: Compared with warfarin, DOACs are easier to use and are associated with a reduction in mortality, driven by a substantially lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage and fatal bleeding,” wrote Matthew J. Price, MD, of the Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, Calif., and Jacqueline Saw, MD, of Vancouver General Hospital, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous studies of LAAO have shown a reduced risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, but procedure hazards interfered with long-term benefits, they said. The current study findings of similar rates of stroke and lower bleeding rates with LAAO, compared with DOAC, “are provocative given the clinical consensus that DOACs are safer, well tolerated, and generally better than warfarin, which was an easy target for transcatheter LAAO, given warfarin’s extensive limitations,” the editorialists wrote. Although the findings lend support to the use of LAAO, clinicians should consider several caveats such as the inclusion of patients who were “not optimal candidates for long-term OAC but were selected because they were at high risk for bleeding or because OAC treatment had already failed.”
However, “despite its imperfections, PRAGUE-17 is an important step forward and reinforces the role of transcatheter LAAO as a stroke-prevention strategy for patients with [AFib] at high risk of bleeding or medical treatment failure, even in the modern era of the DOACs,” they concluded. “Going forward, successful enrollment in ongoing and planned clinical trials while avoiding off-label procedures will be critical to define the appropriate use of transcatheter LAAO in expanded patient populations.”
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot. Dr. Price’s financial disclosures included honoraria, speaker bureau fees, and/or research grants from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Chiesi USA, Daiichi Sankyo, and Medtronic. Dr. Saw disclosed receiving unrestricted research grant support several Canadian research institutes and fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and Servier, among other drug companies.
SOURCES: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
Left atrial appendage closure was noninferior to use of direct oral anticoagulants for the prevention of atrial fibrillation (AFib)–related events in high-risk patients, based on data from 402 adults.
Given the limitations of vitamin K antagonists for preventing stroke in AFib, “a novel site-specific therapeutic alternative, mechanical left atrial appendage occlusion [LAAO], entered clinical practice,” but has not been compared with current safe and effective oral anticoagulants, wrote Pavel Osmancik, MD, of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady, Prague, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers randomized 201 moderate- or high-risk adults with nonvalvular AFib to LAAO and another 201 to direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Patients in the LAAO group underwent transesophageal echocardiography to exclude left atrial thrombi and underwent implantation with Boston Scientific’s Watchman, Watchman-FLX, or Abbott’s Amulet devices. Patients in the DOAC group received rivaroxaban, apixaban, or dabigatran at the manufacturer-recommended dose.
The primary outcome was a composite of complications related to procedures or devices, thromboembolic events (including stroke), and clinically significant bleeding. After an average of 20 months follow-up, 35 patients in the LAAO group and 41 in the DOAC group met the primary outcome (11% per 100 patient-years vs. 13% per 100 patient-years).
In addition, no differences appeared between the groups for the endpoint components of all-stroke/transient ischemic attack event (subdistribution hazard ratio, 1.00), clinically significantly bleeding (sHR, 0.81), or cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75).
Nine patients experienced major complications related to LAAO, including clinically significant bleeding (sHR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.44-1.52) and cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.34-1.62). Major LAAO-related complications occurred in nine (4.5%) patients, with a short-term (up to 7 days or hospital discharge) complication rate of 2.1% and a 2.7% late complication rate. The late complications included three pericardial effusions, one of which resulted in death, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to assess the differences among the components of the composite primary endpoint. For example, “Regarding the primary endpoint, stroke reduction may be more important than bleeding reduction,” the investigators wrote.
The results were strengthened, however, by the enrollment of a high-risk AF population and is the first known randomized trial to compare percutaneous LAAO and DOACs for stroke prevention in this group. But the late complication rate of 2.7% is “suboptimal” and safety issues reinforce the need for refinement of operator technique and device technology with LAAO, they concluded.
‘Important step forward,’ with caveats
“How LAAO might stack up against DOAC therapy has remained an open question: Compared with warfarin, DOACs are easier to use and are associated with a reduction in mortality, driven by a substantially lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage and fatal bleeding,” wrote Matthew J. Price, MD, of the Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, Calif., and Jacqueline Saw, MD, of Vancouver General Hospital, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous studies of LAAO have shown a reduced risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, but procedure hazards interfered with long-term benefits, they said. The current study findings of similar rates of stroke and lower bleeding rates with LAAO, compared with DOAC, “are provocative given the clinical consensus that DOACs are safer, well tolerated, and generally better than warfarin, which was an easy target for transcatheter LAAO, given warfarin’s extensive limitations,” the editorialists wrote. Although the findings lend support to the use of LAAO, clinicians should consider several caveats such as the inclusion of patients who were “not optimal candidates for long-term OAC but were selected because they were at high risk for bleeding or because OAC treatment had already failed.”
However, “despite its imperfections, PRAGUE-17 is an important step forward and reinforces the role of transcatheter LAAO as a stroke-prevention strategy for patients with [AFib] at high risk of bleeding or medical treatment failure, even in the modern era of the DOACs,” they concluded. “Going forward, successful enrollment in ongoing and planned clinical trials while avoiding off-label procedures will be critical to define the appropriate use of transcatheter LAAO in expanded patient populations.”
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot. Dr. Price’s financial disclosures included honoraria, speaker bureau fees, and/or research grants from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Chiesi USA, Daiichi Sankyo, and Medtronic. Dr. Saw disclosed receiving unrestricted research grant support several Canadian research institutes and fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and Servier, among other drug companies.
SOURCES: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
Left atrial appendage closure was noninferior to use of direct oral anticoagulants for the prevention of atrial fibrillation (AFib)–related events in high-risk patients, based on data from 402 adults.
Given the limitations of vitamin K antagonists for preventing stroke in AFib, “a novel site-specific therapeutic alternative, mechanical left atrial appendage occlusion [LAAO], entered clinical practice,” but has not been compared with current safe and effective oral anticoagulants, wrote Pavel Osmancik, MD, of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady, Prague, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers randomized 201 moderate- or high-risk adults with nonvalvular AFib to LAAO and another 201 to direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Patients in the LAAO group underwent transesophageal echocardiography to exclude left atrial thrombi and underwent implantation with Boston Scientific’s Watchman, Watchman-FLX, or Abbott’s Amulet devices. Patients in the DOAC group received rivaroxaban, apixaban, or dabigatran at the manufacturer-recommended dose.
The primary outcome was a composite of complications related to procedures or devices, thromboembolic events (including stroke), and clinically significant bleeding. After an average of 20 months follow-up, 35 patients in the LAAO group and 41 in the DOAC group met the primary outcome (11% per 100 patient-years vs. 13% per 100 patient-years).
In addition, no differences appeared between the groups for the endpoint components of all-stroke/transient ischemic attack event (subdistribution hazard ratio, 1.00), clinically significantly bleeding (sHR, 0.81), or cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75).
Nine patients experienced major complications related to LAAO, including clinically significant bleeding (sHR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.44-1.52) and cardiovascular death (sHR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.34-1.62). Major LAAO-related complications occurred in nine (4.5%) patients, with a short-term (up to 7 days or hospital discharge) complication rate of 2.1% and a 2.7% late complication rate. The late complications included three pericardial effusions, one of which resulted in death, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to assess the differences among the components of the composite primary endpoint. For example, “Regarding the primary endpoint, stroke reduction may be more important than bleeding reduction,” the investigators wrote.
The results were strengthened, however, by the enrollment of a high-risk AF population and is the first known randomized trial to compare percutaneous LAAO and DOACs for stroke prevention in this group. But the late complication rate of 2.7% is “suboptimal” and safety issues reinforce the need for refinement of operator technique and device technology with LAAO, they concluded.
‘Important step forward,’ with caveats
“How LAAO might stack up against DOAC therapy has remained an open question: Compared with warfarin, DOACs are easier to use and are associated with a reduction in mortality, driven by a substantially lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage and fatal bleeding,” wrote Matthew J. Price, MD, of the Scripps Clinic in La Jolla, Calif., and Jacqueline Saw, MD, of Vancouver General Hospital, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous studies of LAAO have shown a reduced risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, but procedure hazards interfered with long-term benefits, they said. The current study findings of similar rates of stroke and lower bleeding rates with LAAO, compared with DOAC, “are provocative given the clinical consensus that DOACs are safer, well tolerated, and generally better than warfarin, which was an easy target for transcatheter LAAO, given warfarin’s extensive limitations,” the editorialists wrote. Although the findings lend support to the use of LAAO, clinicians should consider several caveats such as the inclusion of patients who were “not optimal candidates for long-term OAC but were selected because they were at high risk for bleeding or because OAC treatment had already failed.”
However, “despite its imperfections, PRAGUE-17 is an important step forward and reinforces the role of transcatheter LAAO as a stroke-prevention strategy for patients with [AFib] at high risk of bleeding or medical treatment failure, even in the modern era of the DOACs,” they concluded. “Going forward, successful enrollment in ongoing and planned clinical trials while avoiding off-label procedures will be critical to define the appropriate use of transcatheter LAAO in expanded patient populations.”
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot. Dr. Price’s financial disclosures included honoraria, speaker bureau fees, and/or research grants from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Chiesi USA, Daiichi Sankyo, and Medtronic. Dr. Saw disclosed receiving unrestricted research grant support several Canadian research institutes and fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and Servier, among other drug companies.
SOURCES: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: A composite primary outcome including stroke and death was not significantly different in high-risk patients randomized to left atrial appendage occlusion or direct oral anticoagulants at roughly 20 months’ follow-up (11% vs. 13%, respectively).
Study details: The data come from the PRAGUE-17 study, a randomized trial of 402 adults at increased risk for atrial fibrillation.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. Dr. Osmancik disclosed speaking honoraria from Bayer and Abbot.
Sources: Osmancik P et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3122-35; Price MJ, Saw J. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:3136-9.
CVD risk continues to fall down to systolic BP of 90 mm HG
The study analyzed data from a cohort of 1,457 participants (mean age, 58 years) who did not have any traditional cardiovascular risk factors and had a systolic blood pressure level between 90 and 129 mm Hg at baseline. Results showed that, during a mean follow-up of 14.5 years, there was an increase in traditional cardiovascular risk factors, coronary artery calcium, and incident cardiovascular events with increasing systolic blood pressure levels.
“We modeled systolic blood pressure on a continuous scale and saw the risk increasing in a linear fashion as blood pressure increased and this occurred right down to 90 mm Hg. We didn’t see any nadir or J-point where there may be an increased risk at lower pressures,” said lead author Seamus Whelton, MD.
Dr. Whelton is assistant professor of medicine at the division of cardiology at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore. He is the son of Paul Whelton, MD, chair of the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association hypertension guideline writing committee.
“From an individual level we can now say that in healthy individuals, a systolic pressure in the 90s is not too low. It is a positive thing. And it is recommended to try and keep systolic pressure at these levels if possible by maintaining a healthy lifestyle,” Dr. Whelton said in an interview. “At a population level this finding could lead to stronger recommendations on interventions to prevent increasing blood pressure such as healthier diets, reducing sodium intake, and increasing exercise. Small changes in blood pressure on a population level will lead to large changes in cardiovascular risk on a population a level.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on June 10.
The researchers noted that populations in nonindustrialized countries have little to no increase in systolic blood pressure levels with age, while systolic blood pressure levels typically increase with age in countries with industrialized diets and lifestyles. This has important implications, because atherosclerosis is a slowly progressive disease and the lower an individual’s lifetime exposure to cardiovascular risk factors, such as increased systolic blood pressure, the lower their probable risk for a future cardiovascular event, they wrote.
While the association between systolic blood pressure level, coronary artery calcium, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is well established at higher blood pressure levels, optimal systolic pressure levels for a healthy adult and whether there is a J-shaped relationship or lower limit of systolic pressure necessary to maintain adequate organ perfusion has been uncertain, they explained.
In addition, prior studies have typically used a reference systolic pressure of less than 115-120 mm Hg to define a normal level, and it is uncertain whether there is a lower level at which the risk for incident cardiovascular disease plateaus or increases.
To investigate this, they analyzed data from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, a community-based, multiethnic cohort free from known cardiovascular disease at enrollment. The current analysis included individuals with a systolic blood pressure between 90 and 129 mm Hg without other traditional cardiovascular risk factors including dyslipidemia (LDL cholesterol >160 mg/dL or HDL cholesterol <40 mg/dL), diabetes, or current tobacco use.
Results showed an adjusted hazard ratio for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease was 1.53 for every 10 mm Hg increase in systolic blood pressure levels.
Compared with people with systolic pressures of 90-99 mm Hg, the adjusted hazard ratio for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk was 3.00 for those with 100-109 mm Hg, 3.10 for those with 110-119 mm Hg, and 4.58 for those with 120-129 mm Hg.
There was also a graded increase in the prevalence of coronary artery calcium starting from systolic blood pressure levels as low as 90 mm Hg.
“Previous research on the J-shaped curve for blood pressure has primarily focused on diastolic pressure. We did control for diastolic pressure in this analysis but that was not the focus,” Dr. Whelton said. “Obviously, there will be a minimum optimum value for both diastolic and systolic pressure. But from this study we can say that for systolic pressure, that minimum recommended value is below 90 mm Hg.”
In terms of implications, the researchers wrote: “Among individuals at low or intermediate atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk, it may be more efficacious to focus on a life-course approach for preventing an increase in systolic blood pressure levels rather than treatment of established hypertension to lower systolic blood pressure levels.”
What is a normal blood pressure?
In an accompanying commentary, Daniel Jones, MD, of the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, said these new findings support the position that risk imposed by blood pressure level begins well below the current 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension and guideline-recommended goal.
The study is “a reminder that even a good execution of treatment of hypertension is far from an ideal way to prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” he said.
“A systolic of 130 is not the number we should focus on for patients who are not yet hypertensive, as 130 is not a normal blood pressure,” Dr. Jones added in an audio interview on the JAMA website.
“The findings also suggest that the disease process for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease begins early in life and support the importance of primordial prevention through a healthy lifestyle, including a healthy diet and levels of physical activity. In addition, the findings highlight the need for a population-based strategy focusing on primordial prevention to reduce the age-related increase in BP reported in all industrialized societies,” Dr. Jones wrote.
He recommended that clinicians encourage a healthy lifestyle in patients and families of patients with cardiovascular disease. “This intervention requires no sophisticated genetic testing or clinical trials to credibly inform a family that the children and grandchildren of a patient with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or risk factors will benefit from a healthy lifestyle beginning at the earliest age.
“Clinicians often lose sight of the big picture with regard to blood pressure because they have the patient in front of them. But that patient has children and grandchildren who may share the risk and may be in a better position with regard to prevention of future [coronary artery disease], stroke, and kidney disease,” he said.
Conducting the JAMA audio interview, Clyde Yancy, MD, chief of cardiology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that “this is very stimulating research. It is not asking the question of what is the target blood pressure for patients with hypertension, but rather: What is the goal blood pressure if you actually want to avoid atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk altogether?
“These data have made us understand that there is a difference between the goal blood pressure reduction and treatment thresholds that we respect, the normative blood pressure values we see in a clinical setting, and what is truly normal blood pressure,” Dr. Yancy concluded. “That is a very important nuance, especially when we’re talking about population health. Families and communities need to understand what the true normal is.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The study analyzed data from a cohort of 1,457 participants (mean age, 58 years) who did not have any traditional cardiovascular risk factors and had a systolic blood pressure level between 90 and 129 mm Hg at baseline. Results showed that, during a mean follow-up of 14.5 years, there was an increase in traditional cardiovascular risk factors, coronary artery calcium, and incident cardiovascular events with increasing systolic blood pressure levels.
“We modeled systolic blood pressure on a continuous scale and saw the risk increasing in a linear fashion as blood pressure increased and this occurred right down to 90 mm Hg. We didn’t see any nadir or J-point where there may be an increased risk at lower pressures,” said lead author Seamus Whelton, MD.
Dr. Whelton is assistant professor of medicine at the division of cardiology at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore. He is the son of Paul Whelton, MD, chair of the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association hypertension guideline writing committee.
“From an individual level we can now say that in healthy individuals, a systolic pressure in the 90s is not too low. It is a positive thing. And it is recommended to try and keep systolic pressure at these levels if possible by maintaining a healthy lifestyle,” Dr. Whelton said in an interview. “At a population level this finding could lead to stronger recommendations on interventions to prevent increasing blood pressure such as healthier diets, reducing sodium intake, and increasing exercise. Small changes in blood pressure on a population level will lead to large changes in cardiovascular risk on a population a level.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on June 10.
The researchers noted that populations in nonindustrialized countries have little to no increase in systolic blood pressure levels with age, while systolic blood pressure levels typically increase with age in countries with industrialized diets and lifestyles. This has important implications, because atherosclerosis is a slowly progressive disease and the lower an individual’s lifetime exposure to cardiovascular risk factors, such as increased systolic blood pressure, the lower their probable risk for a future cardiovascular event, they wrote.
While the association between systolic blood pressure level, coronary artery calcium, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is well established at higher blood pressure levels, optimal systolic pressure levels for a healthy adult and whether there is a J-shaped relationship or lower limit of systolic pressure necessary to maintain adequate organ perfusion has been uncertain, they explained.
In addition, prior studies have typically used a reference systolic pressure of less than 115-120 mm Hg to define a normal level, and it is uncertain whether there is a lower level at which the risk for incident cardiovascular disease plateaus or increases.
To investigate this, they analyzed data from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, a community-based, multiethnic cohort free from known cardiovascular disease at enrollment. The current analysis included individuals with a systolic blood pressure between 90 and 129 mm Hg without other traditional cardiovascular risk factors including dyslipidemia (LDL cholesterol >160 mg/dL or HDL cholesterol <40 mg/dL), diabetes, or current tobacco use.
Results showed an adjusted hazard ratio for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease was 1.53 for every 10 mm Hg increase in systolic blood pressure levels.
Compared with people with systolic pressures of 90-99 mm Hg, the adjusted hazard ratio for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk was 3.00 for those with 100-109 mm Hg, 3.10 for those with 110-119 mm Hg, and 4.58 for those with 120-129 mm Hg.
There was also a graded increase in the prevalence of coronary artery calcium starting from systolic blood pressure levels as low as 90 mm Hg.
“Previous research on the J-shaped curve for blood pressure has primarily focused on diastolic pressure. We did control for diastolic pressure in this analysis but that was not the focus,” Dr. Whelton said. “Obviously, there will be a minimum optimum value for both diastolic and systolic pressure. But from this study we can say that for systolic pressure, that minimum recommended value is below 90 mm Hg.”
In terms of implications, the researchers wrote: “Among individuals at low or intermediate atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk, it may be more efficacious to focus on a life-course approach for preventing an increase in systolic blood pressure levels rather than treatment of established hypertension to lower systolic blood pressure levels.”
What is a normal blood pressure?
In an accompanying commentary, Daniel Jones, MD, of the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, said these new findings support the position that risk imposed by blood pressure level begins well below the current 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension and guideline-recommended goal.
The study is “a reminder that even a good execution of treatment of hypertension is far from an ideal way to prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” he said.
“A systolic of 130 is not the number we should focus on for patients who are not yet hypertensive, as 130 is not a normal blood pressure,” Dr. Jones added in an audio interview on the JAMA website.
“The findings also suggest that the disease process for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease begins early in life and support the importance of primordial prevention through a healthy lifestyle, including a healthy diet and levels of physical activity. In addition, the findings highlight the need for a population-based strategy focusing on primordial prevention to reduce the age-related increase in BP reported in all industrialized societies,” Dr. Jones wrote.
He recommended that clinicians encourage a healthy lifestyle in patients and families of patients with cardiovascular disease. “This intervention requires no sophisticated genetic testing or clinical trials to credibly inform a family that the children and grandchildren of a patient with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or risk factors will benefit from a healthy lifestyle beginning at the earliest age.
“Clinicians often lose sight of the big picture with regard to blood pressure because they have the patient in front of them. But that patient has children and grandchildren who may share the risk and may be in a better position with regard to prevention of future [coronary artery disease], stroke, and kidney disease,” he said.
Conducting the JAMA audio interview, Clyde Yancy, MD, chief of cardiology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that “this is very stimulating research. It is not asking the question of what is the target blood pressure for patients with hypertension, but rather: What is the goal blood pressure if you actually want to avoid atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk altogether?
“These data have made us understand that there is a difference between the goal blood pressure reduction and treatment thresholds that we respect, the normative blood pressure values we see in a clinical setting, and what is truly normal blood pressure,” Dr. Yancy concluded. “That is a very important nuance, especially when we’re talking about population health. Families and communities need to understand what the true normal is.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The study analyzed data from a cohort of 1,457 participants (mean age, 58 years) who did not have any traditional cardiovascular risk factors and had a systolic blood pressure level between 90 and 129 mm Hg at baseline. Results showed that, during a mean follow-up of 14.5 years, there was an increase in traditional cardiovascular risk factors, coronary artery calcium, and incident cardiovascular events with increasing systolic blood pressure levels.
“We modeled systolic blood pressure on a continuous scale and saw the risk increasing in a linear fashion as blood pressure increased and this occurred right down to 90 mm Hg. We didn’t see any nadir or J-point where there may be an increased risk at lower pressures,” said lead author Seamus Whelton, MD.
Dr. Whelton is assistant professor of medicine at the division of cardiology at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore. He is the son of Paul Whelton, MD, chair of the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association hypertension guideline writing committee.
“From an individual level we can now say that in healthy individuals, a systolic pressure in the 90s is not too low. It is a positive thing. And it is recommended to try and keep systolic pressure at these levels if possible by maintaining a healthy lifestyle,” Dr. Whelton said in an interview. “At a population level this finding could lead to stronger recommendations on interventions to prevent increasing blood pressure such as healthier diets, reducing sodium intake, and increasing exercise. Small changes in blood pressure on a population level will lead to large changes in cardiovascular risk on a population a level.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on June 10.
The researchers noted that populations in nonindustrialized countries have little to no increase in systolic blood pressure levels with age, while systolic blood pressure levels typically increase with age in countries with industrialized diets and lifestyles. This has important implications, because atherosclerosis is a slowly progressive disease and the lower an individual’s lifetime exposure to cardiovascular risk factors, such as increased systolic blood pressure, the lower their probable risk for a future cardiovascular event, they wrote.
While the association between systolic blood pressure level, coronary artery calcium, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is well established at higher blood pressure levels, optimal systolic pressure levels for a healthy adult and whether there is a J-shaped relationship or lower limit of systolic pressure necessary to maintain adequate organ perfusion has been uncertain, they explained.
In addition, prior studies have typically used a reference systolic pressure of less than 115-120 mm Hg to define a normal level, and it is uncertain whether there is a lower level at which the risk for incident cardiovascular disease plateaus or increases.
To investigate this, they analyzed data from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, a community-based, multiethnic cohort free from known cardiovascular disease at enrollment. The current analysis included individuals with a systolic blood pressure between 90 and 129 mm Hg without other traditional cardiovascular risk factors including dyslipidemia (LDL cholesterol >160 mg/dL or HDL cholesterol <40 mg/dL), diabetes, or current tobacco use.
Results showed an adjusted hazard ratio for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease was 1.53 for every 10 mm Hg increase in systolic blood pressure levels.
Compared with people with systolic pressures of 90-99 mm Hg, the adjusted hazard ratio for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk was 3.00 for those with 100-109 mm Hg, 3.10 for those with 110-119 mm Hg, and 4.58 for those with 120-129 mm Hg.
There was also a graded increase in the prevalence of coronary artery calcium starting from systolic blood pressure levels as low as 90 mm Hg.
“Previous research on the J-shaped curve for blood pressure has primarily focused on diastolic pressure. We did control for diastolic pressure in this analysis but that was not the focus,” Dr. Whelton said. “Obviously, there will be a minimum optimum value for both diastolic and systolic pressure. But from this study we can say that for systolic pressure, that minimum recommended value is below 90 mm Hg.”
In terms of implications, the researchers wrote: “Among individuals at low or intermediate atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk, it may be more efficacious to focus on a life-course approach for preventing an increase in systolic blood pressure levels rather than treatment of established hypertension to lower systolic blood pressure levels.”
What is a normal blood pressure?
In an accompanying commentary, Daniel Jones, MD, of the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, said these new findings support the position that risk imposed by blood pressure level begins well below the current 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension and guideline-recommended goal.
The study is “a reminder that even a good execution of treatment of hypertension is far from an ideal way to prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” he said.
“A systolic of 130 is not the number we should focus on for patients who are not yet hypertensive, as 130 is not a normal blood pressure,” Dr. Jones added in an audio interview on the JAMA website.
“The findings also suggest that the disease process for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease begins early in life and support the importance of primordial prevention through a healthy lifestyle, including a healthy diet and levels of physical activity. In addition, the findings highlight the need for a population-based strategy focusing on primordial prevention to reduce the age-related increase in BP reported in all industrialized societies,” Dr. Jones wrote.
He recommended that clinicians encourage a healthy lifestyle in patients and families of patients with cardiovascular disease. “This intervention requires no sophisticated genetic testing or clinical trials to credibly inform a family that the children and grandchildren of a patient with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or risk factors will benefit from a healthy lifestyle beginning at the earliest age.
“Clinicians often lose sight of the big picture with regard to blood pressure because they have the patient in front of them. But that patient has children and grandchildren who may share the risk and may be in a better position with regard to prevention of future [coronary artery disease], stroke, and kidney disease,” he said.
Conducting the JAMA audio interview, Clyde Yancy, MD, chief of cardiology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said that “this is very stimulating research. It is not asking the question of what is the target blood pressure for patients with hypertension, but rather: What is the goal blood pressure if you actually want to avoid atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk altogether?
“These data have made us understand that there is a difference between the goal blood pressure reduction and treatment thresholds that we respect, the normative blood pressure values we see in a clinical setting, and what is truly normal blood pressure,” Dr. Yancy concluded. “That is a very important nuance, especially when we’re talking about population health. Families and communities need to understand what the true normal is.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
VERTIS-CV: Ertugliflozin’s CV outcomes trial confirms SGLT2i benefits
The cardiovascular outcome trial results for a fourth sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, ertugliflozin, were most notable for their consistency with the four prior, similar trials run on the three other drugs from this class on the U.S. market, canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin, further solidifying the important role this drug class has recently taken on for patients with type 2 diabetes.
But the ertugliflozin results, which showed statistically significant superiority to placebo for just one endpoint, hospitalization for heart failure, made it unclear whether clinicians will regard ertugliflozin as the top agent from this class to prescribe.
“Our big takeaway is that the findings are consistent with what’s been seen in the other studies” of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME study of empagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28 ), the CANVAS (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[7]:644-57) and CREDENCE (N Engl J Med. 2019 June 13;380[24]:2295-306 ) studies of canagliflozin, and the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial with dapagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380[4]:347-57), Christopher P. Cannon, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs), mandated in 2008 by Food and Drug Administration guidance for type 2 diabetes drugs that is now in the process of undergoing an update, have had the main goal of proving safety, and the primary endpoint of the new ertugliflozin trial, VERTIS-CV, was noninferiority to placebo when used on top of standard type 2 diabetes medications for the combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke.
Key findings
Both of the tested dosages of ertugliflozin, 5 mg and 15 mg daily, met this endpoint, with event rates over a median 3.0 years of follow-up that ran very close to the placebo rate, clearly proving noninferiority. But the results showed no suggestion of superiority in a study that randomized 5,499 patients to either of the ertugliflozin regimens and 2,747 to placebo, reported Dr. Cannon, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The primary outcome also showed similar event rates for each component of the composite endpoint, and subgroup analysis showed consistent results from ertugliflozin, compared with placebo, regardless of study-cohort subdivision by demographic, clinical, or treatment factors.
The trial design called for a hierarchical sequence of secondary-outcome superiority analyses, starting with the impact of ertugliflozin on cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization, and for this outcome ertugliflozin showed a point estimate of a 12% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients, but this difference was not statistically significant. This meant that all subsequent superiority analyses in this trial could only be hypothesis generating and not definitive.
This negated the statistical validity of the only statistically significant treatment difference between ertugliflozin and placebo seen in VERTIS-CV, for the outcome of hospitalization for heart failure, where ertugliflozin treatment cut this outcome by 30%, compared with placebo patients. The rate of cardiovascular death alone, as well as a renal composite endpoint each showed no statistically significant benefit of ertugliflozin, compared with placebo, although the renal endpoint came close, with ertugliflozin reducing the combined rate of renal death, need for dialysis, need for renal transplant, or a doubling of serum creatinine from baseline by 19%, compared with placebo (P = .08).
How results compare with prior CVOTs
In some ways, these results seemed to contrast with outcomes from the CVOTs for the other SGLT2 inhibitors, which all showed at least two statistically significant benefits for major endpoints when compared with placebo.
As summarized in a new meta-analysis of all the CVOTs by Darren K. McGuire, MD, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at the University of Texas, Dallas, both empagliflozin and canagliflozin showed statistically significant superiority compared with placebo for their trial’s primary, combined major cardiovascular adverse event endpoint, but dapagliflozin and ertugliflozin did not. Empagliflozin was the sole SGLT2 inhibitor to show a statistically significant cut in cardiovascular deaths, compared with placebo.
The primary, composite renal efficacy endpoints used in these trials were hardest to compare because they differed from study to study, but unlike ertugliflozin, all the other three drugs in the class showed a statistically significant improvement, compared with placebo, for their respective renal outcomes. On the other hand, the pattern of estimated glomerular filtration rates measured at multiple times during the various trials showed a high level of consistency across the CVOTs.
The greatest consistently among the major endpoints across the trials was for heart failure hospitalization. All four agents showed statistically significant improvements, compared with placebo, and all four had roughly equal magnitudes of effect, a cut in event rates by about one-third.
“The greatest magnitude of benefit is for reductions in heart failure hospitalizations and for renal outcomes,” with the heart failure outcomes the “most consistent” across the studies and the renal outcomes “largely consistent,” concluded Dr. McGuire. All together, the five CVOTs for these four SGLT2 inhibitors involved more than 46,000 patients.
“A lot of data suggest these are all class effects,” that are roughly similar across all four of these SGLT2 inhibitors, commented Mark E. Cooper, MBBS, a professor and head of the department of diabetes at Monash University, Melbourne, and designated discussant for the study.
There was “clear homogeneity” between the VERTIS-CV results for hospitalization for heart failure and the other CVOTs, he noted. “I think there is a difference” in the cardiovascular death outcomes, specifically the sole statistically significant, 38% relative risk reduction with empagliflozin that stood out from the other CVOTs, but this difference is “totally unexplained,” added Dr. Cooper. “To really determine differences you’d need head-to-head studies that are unlikely to happen.”
The results of new SGLT2 inhibitor meta-analysis appeared to also “support contemporary society recommendations to prioritize the use of SGLT2 inhibitors independent of glucose-control considerations in patients with type 2 diabetes with or at high risk for cardiovascular and renal complications,” said Dr. McGuire.
“The guidelines have it right. Now it’s on us to implement these treatments to appropriate patients,” concluded Dr. Cannon.
Study details
VERTIS-CV (Cardiovascular Outcomes Following Ertugliflozin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Participants With Vascular Disease) enrolled and followed patients with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease at 531 centers in 34 countries during December 2013–December 2019. Other effects from ertugliflozin recorded during the trial were consistent with prior studies of the drug, which is already FDA approved for glycemic control: Compared with placebo, ertugliflozin treatment reduced hemoglobin A1c by an average of 0.5% after 1 year, cut average body weight by about 2.5 kg after 1 year with additional modest weight loss, during subsequent years on the drug, and reduced systolic blood pressure by about 3 mm Hg after 1 year.
The drug’s safety profile was generally reassuring and consistent with prior studies of this drug and others in the class, with overall no increase in total adverse events or serious adverse events, compared with placebo, and modestly increased rates of urinary tract and mycotic genital infections.
VERTIS-CV was sponsored by Merck and Pfizer, the companies that market ertugliflozin (Steglatro). Dr. Cannon has received research funding and fees from Merck and Pfizer and from several other companies. Dr. McGuire has received honoraria from Merck, has been a consultant to Pfizer, and has had similar relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cooper has been an advisor to and received honoraria from Merck. He has also received honoraria from or been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, MundiPharma, Novartis, Reata, and Servier, and he has received research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Novo Nordisk.
The cardiovascular outcome trial results for a fourth sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, ertugliflozin, were most notable for their consistency with the four prior, similar trials run on the three other drugs from this class on the U.S. market, canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin, further solidifying the important role this drug class has recently taken on for patients with type 2 diabetes.
But the ertugliflozin results, which showed statistically significant superiority to placebo for just one endpoint, hospitalization for heart failure, made it unclear whether clinicians will regard ertugliflozin as the top agent from this class to prescribe.
“Our big takeaway is that the findings are consistent with what’s been seen in the other studies” of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME study of empagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28 ), the CANVAS (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[7]:644-57) and CREDENCE (N Engl J Med. 2019 June 13;380[24]:2295-306 ) studies of canagliflozin, and the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial with dapagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380[4]:347-57), Christopher P. Cannon, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs), mandated in 2008 by Food and Drug Administration guidance for type 2 diabetes drugs that is now in the process of undergoing an update, have had the main goal of proving safety, and the primary endpoint of the new ertugliflozin trial, VERTIS-CV, was noninferiority to placebo when used on top of standard type 2 diabetes medications for the combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke.
Key findings
Both of the tested dosages of ertugliflozin, 5 mg and 15 mg daily, met this endpoint, with event rates over a median 3.0 years of follow-up that ran very close to the placebo rate, clearly proving noninferiority. But the results showed no suggestion of superiority in a study that randomized 5,499 patients to either of the ertugliflozin regimens and 2,747 to placebo, reported Dr. Cannon, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The primary outcome also showed similar event rates for each component of the composite endpoint, and subgroup analysis showed consistent results from ertugliflozin, compared with placebo, regardless of study-cohort subdivision by demographic, clinical, or treatment factors.
The trial design called for a hierarchical sequence of secondary-outcome superiority analyses, starting with the impact of ertugliflozin on cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization, and for this outcome ertugliflozin showed a point estimate of a 12% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients, but this difference was not statistically significant. This meant that all subsequent superiority analyses in this trial could only be hypothesis generating and not definitive.
This negated the statistical validity of the only statistically significant treatment difference between ertugliflozin and placebo seen in VERTIS-CV, for the outcome of hospitalization for heart failure, where ertugliflozin treatment cut this outcome by 30%, compared with placebo patients. The rate of cardiovascular death alone, as well as a renal composite endpoint each showed no statistically significant benefit of ertugliflozin, compared with placebo, although the renal endpoint came close, with ertugliflozin reducing the combined rate of renal death, need for dialysis, need for renal transplant, or a doubling of serum creatinine from baseline by 19%, compared with placebo (P = .08).
How results compare with prior CVOTs
In some ways, these results seemed to contrast with outcomes from the CVOTs for the other SGLT2 inhibitors, which all showed at least two statistically significant benefits for major endpoints when compared with placebo.
As summarized in a new meta-analysis of all the CVOTs by Darren K. McGuire, MD, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at the University of Texas, Dallas, both empagliflozin and canagliflozin showed statistically significant superiority compared with placebo for their trial’s primary, combined major cardiovascular adverse event endpoint, but dapagliflozin and ertugliflozin did not. Empagliflozin was the sole SGLT2 inhibitor to show a statistically significant cut in cardiovascular deaths, compared with placebo.
The primary, composite renal efficacy endpoints used in these trials were hardest to compare because they differed from study to study, but unlike ertugliflozin, all the other three drugs in the class showed a statistically significant improvement, compared with placebo, for their respective renal outcomes. On the other hand, the pattern of estimated glomerular filtration rates measured at multiple times during the various trials showed a high level of consistency across the CVOTs.
The greatest consistently among the major endpoints across the trials was for heart failure hospitalization. All four agents showed statistically significant improvements, compared with placebo, and all four had roughly equal magnitudes of effect, a cut in event rates by about one-third.
“The greatest magnitude of benefit is for reductions in heart failure hospitalizations and for renal outcomes,” with the heart failure outcomes the “most consistent” across the studies and the renal outcomes “largely consistent,” concluded Dr. McGuire. All together, the five CVOTs for these four SGLT2 inhibitors involved more than 46,000 patients.
“A lot of data suggest these are all class effects,” that are roughly similar across all four of these SGLT2 inhibitors, commented Mark E. Cooper, MBBS, a professor and head of the department of diabetes at Monash University, Melbourne, and designated discussant for the study.
There was “clear homogeneity” between the VERTIS-CV results for hospitalization for heart failure and the other CVOTs, he noted. “I think there is a difference” in the cardiovascular death outcomes, specifically the sole statistically significant, 38% relative risk reduction with empagliflozin that stood out from the other CVOTs, but this difference is “totally unexplained,” added Dr. Cooper. “To really determine differences you’d need head-to-head studies that are unlikely to happen.”
The results of new SGLT2 inhibitor meta-analysis appeared to also “support contemporary society recommendations to prioritize the use of SGLT2 inhibitors independent of glucose-control considerations in patients with type 2 diabetes with or at high risk for cardiovascular and renal complications,” said Dr. McGuire.
“The guidelines have it right. Now it’s on us to implement these treatments to appropriate patients,” concluded Dr. Cannon.
Study details
VERTIS-CV (Cardiovascular Outcomes Following Ertugliflozin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Participants With Vascular Disease) enrolled and followed patients with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease at 531 centers in 34 countries during December 2013–December 2019. Other effects from ertugliflozin recorded during the trial were consistent with prior studies of the drug, which is already FDA approved for glycemic control: Compared with placebo, ertugliflozin treatment reduced hemoglobin A1c by an average of 0.5% after 1 year, cut average body weight by about 2.5 kg after 1 year with additional modest weight loss, during subsequent years on the drug, and reduced systolic blood pressure by about 3 mm Hg after 1 year.
The drug’s safety profile was generally reassuring and consistent with prior studies of this drug and others in the class, with overall no increase in total adverse events or serious adverse events, compared with placebo, and modestly increased rates of urinary tract and mycotic genital infections.
VERTIS-CV was sponsored by Merck and Pfizer, the companies that market ertugliflozin (Steglatro). Dr. Cannon has received research funding and fees from Merck and Pfizer and from several other companies. Dr. McGuire has received honoraria from Merck, has been a consultant to Pfizer, and has had similar relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cooper has been an advisor to and received honoraria from Merck. He has also received honoraria from or been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, MundiPharma, Novartis, Reata, and Servier, and he has received research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Novo Nordisk.
The cardiovascular outcome trial results for a fourth sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, ertugliflozin, were most notable for their consistency with the four prior, similar trials run on the three other drugs from this class on the U.S. market, canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin, further solidifying the important role this drug class has recently taken on for patients with type 2 diabetes.
But the ertugliflozin results, which showed statistically significant superiority to placebo for just one endpoint, hospitalization for heart failure, made it unclear whether clinicians will regard ertugliflozin as the top agent from this class to prescribe.
“Our big takeaway is that the findings are consistent with what’s been seen in the other studies” of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME study of empagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28 ), the CANVAS (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[7]:644-57) and CREDENCE (N Engl J Med. 2019 June 13;380[24]:2295-306 ) studies of canagliflozin, and the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial with dapagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380[4]:347-57), Christopher P. Cannon, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs), mandated in 2008 by Food and Drug Administration guidance for type 2 diabetes drugs that is now in the process of undergoing an update, have had the main goal of proving safety, and the primary endpoint of the new ertugliflozin trial, VERTIS-CV, was noninferiority to placebo when used on top of standard type 2 diabetes medications for the combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke.
Key findings
Both of the tested dosages of ertugliflozin, 5 mg and 15 mg daily, met this endpoint, with event rates over a median 3.0 years of follow-up that ran very close to the placebo rate, clearly proving noninferiority. But the results showed no suggestion of superiority in a study that randomized 5,499 patients to either of the ertugliflozin regimens and 2,747 to placebo, reported Dr. Cannon, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The primary outcome also showed similar event rates for each component of the composite endpoint, and subgroup analysis showed consistent results from ertugliflozin, compared with placebo, regardless of study-cohort subdivision by demographic, clinical, or treatment factors.
The trial design called for a hierarchical sequence of secondary-outcome superiority analyses, starting with the impact of ertugliflozin on cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization, and for this outcome ertugliflozin showed a point estimate of a 12% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients, but this difference was not statistically significant. This meant that all subsequent superiority analyses in this trial could only be hypothesis generating and not definitive.
This negated the statistical validity of the only statistically significant treatment difference between ertugliflozin and placebo seen in VERTIS-CV, for the outcome of hospitalization for heart failure, where ertugliflozin treatment cut this outcome by 30%, compared with placebo patients. The rate of cardiovascular death alone, as well as a renal composite endpoint each showed no statistically significant benefit of ertugliflozin, compared with placebo, although the renal endpoint came close, with ertugliflozin reducing the combined rate of renal death, need for dialysis, need for renal transplant, or a doubling of serum creatinine from baseline by 19%, compared with placebo (P = .08).
How results compare with prior CVOTs
In some ways, these results seemed to contrast with outcomes from the CVOTs for the other SGLT2 inhibitors, which all showed at least two statistically significant benefits for major endpoints when compared with placebo.
As summarized in a new meta-analysis of all the CVOTs by Darren K. McGuire, MD, a cardiologist and professor of medicine at the University of Texas, Dallas, both empagliflozin and canagliflozin showed statistically significant superiority compared with placebo for their trial’s primary, combined major cardiovascular adverse event endpoint, but dapagliflozin and ertugliflozin did not. Empagliflozin was the sole SGLT2 inhibitor to show a statistically significant cut in cardiovascular deaths, compared with placebo.
The primary, composite renal efficacy endpoints used in these trials were hardest to compare because they differed from study to study, but unlike ertugliflozin, all the other three drugs in the class showed a statistically significant improvement, compared with placebo, for their respective renal outcomes. On the other hand, the pattern of estimated glomerular filtration rates measured at multiple times during the various trials showed a high level of consistency across the CVOTs.
The greatest consistently among the major endpoints across the trials was for heart failure hospitalization. All four agents showed statistically significant improvements, compared with placebo, and all four had roughly equal magnitudes of effect, a cut in event rates by about one-third.
“The greatest magnitude of benefit is for reductions in heart failure hospitalizations and for renal outcomes,” with the heart failure outcomes the “most consistent” across the studies and the renal outcomes “largely consistent,” concluded Dr. McGuire. All together, the five CVOTs for these four SGLT2 inhibitors involved more than 46,000 patients.
“A lot of data suggest these are all class effects,” that are roughly similar across all four of these SGLT2 inhibitors, commented Mark E. Cooper, MBBS, a professor and head of the department of diabetes at Monash University, Melbourne, and designated discussant for the study.
There was “clear homogeneity” between the VERTIS-CV results for hospitalization for heart failure and the other CVOTs, he noted. “I think there is a difference” in the cardiovascular death outcomes, specifically the sole statistically significant, 38% relative risk reduction with empagliflozin that stood out from the other CVOTs, but this difference is “totally unexplained,” added Dr. Cooper. “To really determine differences you’d need head-to-head studies that are unlikely to happen.”
The results of new SGLT2 inhibitor meta-analysis appeared to also “support contemporary society recommendations to prioritize the use of SGLT2 inhibitors independent of glucose-control considerations in patients with type 2 diabetes with or at high risk for cardiovascular and renal complications,” said Dr. McGuire.
“The guidelines have it right. Now it’s on us to implement these treatments to appropriate patients,” concluded Dr. Cannon.
Study details
VERTIS-CV (Cardiovascular Outcomes Following Ertugliflozin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Participants With Vascular Disease) enrolled and followed patients with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease at 531 centers in 34 countries during December 2013–December 2019. Other effects from ertugliflozin recorded during the trial were consistent with prior studies of the drug, which is already FDA approved for glycemic control: Compared with placebo, ertugliflozin treatment reduced hemoglobin A1c by an average of 0.5% after 1 year, cut average body weight by about 2.5 kg after 1 year with additional modest weight loss, during subsequent years on the drug, and reduced systolic blood pressure by about 3 mm Hg after 1 year.
The drug’s safety profile was generally reassuring and consistent with prior studies of this drug and others in the class, with overall no increase in total adverse events or serious adverse events, compared with placebo, and modestly increased rates of urinary tract and mycotic genital infections.
VERTIS-CV was sponsored by Merck and Pfizer, the companies that market ertugliflozin (Steglatro). Dr. Cannon has received research funding and fees from Merck and Pfizer and from several other companies. Dr. McGuire has received honoraria from Merck, has been a consultant to Pfizer, and has had similar relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cooper has been an advisor to and received honoraria from Merck. He has also received honoraria from or been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, MundiPharma, Novartis, Reata, and Servier, and he has received research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Novo Nordisk.
FROM ADA 2020
Preventing arrhythmias and QTc prolongation in COVID-19 patients on psychotropics
Over the last few weeks, several conflicting reports about the efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 treatments have emerged, including high-profile papers that were placed in the limelight and groundbreaking retractions that were issued by the Lancet and New England Journal of Medicine, involving the potential dangers of COVID therapy with findings derived from the Surgisphere database. Hydroxychloroquine has garnered considerable media attention and was touted earlier by President Trump for its therapeutic effects.1 Naturally, there are political connotations associated with the agent, and it is unlikely that hydroxychloroquine will be supplanted in the near future as ongoing clinical trials have demonstrated mixed results amid the controversy.
As clinicians navigating unchartered territory within the hospital setting, we have to come to terms with these new challenges, tailoring treatment protocols accordingly with the best clinical practices in mind. Patients with preexisting mental health conditions and who are being treated for COVID-19 are particularly susceptible to clinical deterioration. Recent studies have indicated that psychiatric patients are more prone to feelings of isolation and/or estrangement as well as exacerbation of symptoms such as paranoia.2 Even more concerning is the medication regimen, namely, the novel combination therapies that arise when agents such as hydroxychloroquine are used in tandem with certain antipsychotics or antidepressants.
What’s at stake for COVID-19–positive mental health care patients?
Although the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine is currently being investigated,3 the antimalarial is usually prescribed in tandem with azithromycin for people with COVID-19. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has advised against that particular combination therapy because of ongoing concerns about toxicities.3,4
In another study, azithromycin was effectively substituted with doxycycline to help minimize systemic effects for patients with cardiac and/or pulmonary issues.5 Azithromycin is notorious in the literature for influencing the electrical activity of the heart with the potential for fatal arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease.5,6,7 It should be noted that both of these commonly prescribed COVID-19 medications (for example, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin) could lead to QT interval prolongation especially within the context of combination therapy. This is largely concerning for psychiatrists and various other mental health practitioners for the following reasons: (1) higher rates of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases among psychiatric patients8 and/or (2) effects of certain antipsychotics (for example, IV haloperidol, thioridazine, and ziprasidone) and antidepressants (for example, citalopram and escitalopram) on the QT interval.9
SARS-CoV-2 and clinical judgment: Evaluating patients at higher risk
Although COVID-19 medication guidelines are still being actively developed, hydroxychloroquine appears to be commonly prescribed by physicians. The medication is known myriad untoward effects, including potential behavioral dysfunction (for example, irritability, agitation, suicidal ideation)10 as well as the aforementioned issues concerning arrhythmia (for example, torsades de pointes). Health care professionals might not have much control over the choice of COVID-19 agents because of a lack of available resources or limited options, but they can exercise clinical judgment with respect to selecting the appropriate psychotropic medications.
Treatment recommendations
1. Establish a baseline EKG
A baseline 12-lead EKG is the standard of care for patients currently being screened for COVID-19. It is necessary to rule out the presence of an underlying cardiovascular disease or a rhythm irregularity. A prolonged QTc interval is generally regarded as being around greater than 450-470 msecs with variations attributable to gender;11 numerous studies have affirmed that the risk of acquiring torsades de pointes is substantial when the QTc interval exceeds 500 msecs.12
2. Medical management and risk assessment
Commonly prescribed antipsychotics such as IV haloperidol and ziprasidone are known for exerting a negative effect on the interval and should readily be substituted with other agents in patients who are being treated for COVID-19; the combination of these antipsychotics alongside some COVID-19 medication regimens (for example, hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin) might prove to be fatal. The same logic applies to COVID-19 patients previously on antidepressant therapeutics such as citalopram and escitalopram.
3. Embrace an individually tailored approach to therapeutics
While American Psychiatric Association guidelines historically supported a cessation or reduction in the offending agent under normal circumstances,12 our team is recommending that the psychotropics associated with QTc interval prolongation are discontinued altogether (or substituted with a low-risk agent) in the event that a patient presents with suspected COVID-19. However, after the patients tests negative with COVID-19, they may resume therapy as indicated under the discretion of the mental health practitioner.
References
1. Offard C. “Lancet, NEJM Retract Surgisphere Studies on COVID-19 Patients.” The Scientist Magazine. 2020 Jun 4.
2. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020 Apr;74(4):281-2.
3. Keshtkar-Jahromi M and Bavari S. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):932-3.
4. Palca J. “NIH panel recommends against drug combination promoted by Trump for COVID-19.” NPR. 2020 Apr 21.
5. Mongelli L. “Long Island doctor tries new twist on hydroxychloroquine for elderly COVID-19 patients.” New York Post. 2020 Apr 4.
6. Hancox JC et al. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013 Oct;(5):155-65.
7. Giudicessi JR and Ackerman MJ. Cleve Clin J Med. 2013 Sep;80(9):539-44.
8. Casey DE. Am J Med. 2005 Apr 1;118(Suppl 2):15S-22S.
9. Beach SR et al. Psychosomatics. 2013 Jan 1;54(1):1-3.
10. Bogaczewicz A and Sobów T. Psychiatria i Psychologia Kliniczna. 2017;17(2):111-4.
11. Chohan PS et al. Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Sep-Oct;31(5):1269-71.
12. Lieberman JA et al. APA guidance on the use of antipsychotic drugs and cardiac sudden death. NYS Office of Mental Health. 2012.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Faisal Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Mohammed Islam is affiliated with the department of psychiatry at the Interfaith Medical Center, New York. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Over the last few weeks, several conflicting reports about the efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 treatments have emerged, including high-profile papers that were placed in the limelight and groundbreaking retractions that were issued by the Lancet and New England Journal of Medicine, involving the potential dangers of COVID therapy with findings derived from the Surgisphere database. Hydroxychloroquine has garnered considerable media attention and was touted earlier by President Trump for its therapeutic effects.1 Naturally, there are political connotations associated with the agent, and it is unlikely that hydroxychloroquine will be supplanted in the near future as ongoing clinical trials have demonstrated mixed results amid the controversy.
As clinicians navigating unchartered territory within the hospital setting, we have to come to terms with these new challenges, tailoring treatment protocols accordingly with the best clinical practices in mind. Patients with preexisting mental health conditions and who are being treated for COVID-19 are particularly susceptible to clinical deterioration. Recent studies have indicated that psychiatric patients are more prone to feelings of isolation and/or estrangement as well as exacerbation of symptoms such as paranoia.2 Even more concerning is the medication regimen, namely, the novel combination therapies that arise when agents such as hydroxychloroquine are used in tandem with certain antipsychotics or antidepressants.
What’s at stake for COVID-19–positive mental health care patients?
Although the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine is currently being investigated,3 the antimalarial is usually prescribed in tandem with azithromycin for people with COVID-19. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has advised against that particular combination therapy because of ongoing concerns about toxicities.3,4
In another study, azithromycin was effectively substituted with doxycycline to help minimize systemic effects for patients with cardiac and/or pulmonary issues.5 Azithromycin is notorious in the literature for influencing the electrical activity of the heart with the potential for fatal arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease.5,6,7 It should be noted that both of these commonly prescribed COVID-19 medications (for example, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin) could lead to QT interval prolongation especially within the context of combination therapy. This is largely concerning for psychiatrists and various other mental health practitioners for the following reasons: (1) higher rates of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases among psychiatric patients8 and/or (2) effects of certain antipsychotics (for example, IV haloperidol, thioridazine, and ziprasidone) and antidepressants (for example, citalopram and escitalopram) on the QT interval.9
SARS-CoV-2 and clinical judgment: Evaluating patients at higher risk
Although COVID-19 medication guidelines are still being actively developed, hydroxychloroquine appears to be commonly prescribed by physicians. The medication is known myriad untoward effects, including potential behavioral dysfunction (for example, irritability, agitation, suicidal ideation)10 as well as the aforementioned issues concerning arrhythmia (for example, torsades de pointes). Health care professionals might not have much control over the choice of COVID-19 agents because of a lack of available resources or limited options, but they can exercise clinical judgment with respect to selecting the appropriate psychotropic medications.
Treatment recommendations
1. Establish a baseline EKG
A baseline 12-lead EKG is the standard of care for patients currently being screened for COVID-19. It is necessary to rule out the presence of an underlying cardiovascular disease or a rhythm irregularity. A prolonged QTc interval is generally regarded as being around greater than 450-470 msecs with variations attributable to gender;11 numerous studies have affirmed that the risk of acquiring torsades de pointes is substantial when the QTc interval exceeds 500 msecs.12
2. Medical management and risk assessment
Commonly prescribed antipsychotics such as IV haloperidol and ziprasidone are known for exerting a negative effect on the interval and should readily be substituted with other agents in patients who are being treated for COVID-19; the combination of these antipsychotics alongside some COVID-19 medication regimens (for example, hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin) might prove to be fatal. The same logic applies to COVID-19 patients previously on antidepressant therapeutics such as citalopram and escitalopram.
3. Embrace an individually tailored approach to therapeutics
While American Psychiatric Association guidelines historically supported a cessation or reduction in the offending agent under normal circumstances,12 our team is recommending that the psychotropics associated with QTc interval prolongation are discontinued altogether (or substituted with a low-risk agent) in the event that a patient presents with suspected COVID-19. However, after the patients tests negative with COVID-19, they may resume therapy as indicated under the discretion of the mental health practitioner.
References
1. Offard C. “Lancet, NEJM Retract Surgisphere Studies on COVID-19 Patients.” The Scientist Magazine. 2020 Jun 4.
2. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020 Apr;74(4):281-2.
3. Keshtkar-Jahromi M and Bavari S. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):932-3.
4. Palca J. “NIH panel recommends against drug combination promoted by Trump for COVID-19.” NPR. 2020 Apr 21.
5. Mongelli L. “Long Island doctor tries new twist on hydroxychloroquine for elderly COVID-19 patients.” New York Post. 2020 Apr 4.
6. Hancox JC et al. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013 Oct;(5):155-65.
7. Giudicessi JR and Ackerman MJ. Cleve Clin J Med. 2013 Sep;80(9):539-44.
8. Casey DE. Am J Med. 2005 Apr 1;118(Suppl 2):15S-22S.
9. Beach SR et al. Psychosomatics. 2013 Jan 1;54(1):1-3.
10. Bogaczewicz A and Sobów T. Psychiatria i Psychologia Kliniczna. 2017;17(2):111-4.
11. Chohan PS et al. Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Sep-Oct;31(5):1269-71.
12. Lieberman JA et al. APA guidance on the use of antipsychotic drugs and cardiac sudden death. NYS Office of Mental Health. 2012.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Faisal Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Mohammed Islam is affiliated with the department of psychiatry at the Interfaith Medical Center, New York. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Over the last few weeks, several conflicting reports about the efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 treatments have emerged, including high-profile papers that were placed in the limelight and groundbreaking retractions that were issued by the Lancet and New England Journal of Medicine, involving the potential dangers of COVID therapy with findings derived from the Surgisphere database. Hydroxychloroquine has garnered considerable media attention and was touted earlier by President Trump for its therapeutic effects.1 Naturally, there are political connotations associated with the agent, and it is unlikely that hydroxychloroquine will be supplanted in the near future as ongoing clinical trials have demonstrated mixed results amid the controversy.
As clinicians navigating unchartered territory within the hospital setting, we have to come to terms with these new challenges, tailoring treatment protocols accordingly with the best clinical practices in mind. Patients with preexisting mental health conditions and who are being treated for COVID-19 are particularly susceptible to clinical deterioration. Recent studies have indicated that psychiatric patients are more prone to feelings of isolation and/or estrangement as well as exacerbation of symptoms such as paranoia.2 Even more concerning is the medication regimen, namely, the novel combination therapies that arise when agents such as hydroxychloroquine are used in tandem with certain antipsychotics or antidepressants.
What’s at stake for COVID-19–positive mental health care patients?
Although the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine is currently being investigated,3 the antimalarial is usually prescribed in tandem with azithromycin for people with COVID-19. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has advised against that particular combination therapy because of ongoing concerns about toxicities.3,4
In another study, azithromycin was effectively substituted with doxycycline to help minimize systemic effects for patients with cardiac and/or pulmonary issues.5 Azithromycin is notorious in the literature for influencing the electrical activity of the heart with the potential for fatal arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease.5,6,7 It should be noted that both of these commonly prescribed COVID-19 medications (for example, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin) could lead to QT interval prolongation especially within the context of combination therapy. This is largely concerning for psychiatrists and various other mental health practitioners for the following reasons: (1) higher rates of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases among psychiatric patients8 and/or (2) effects of certain antipsychotics (for example, IV haloperidol, thioridazine, and ziprasidone) and antidepressants (for example, citalopram and escitalopram) on the QT interval.9
SARS-CoV-2 and clinical judgment: Evaluating patients at higher risk
Although COVID-19 medication guidelines are still being actively developed, hydroxychloroquine appears to be commonly prescribed by physicians. The medication is known myriad untoward effects, including potential behavioral dysfunction (for example, irritability, agitation, suicidal ideation)10 as well as the aforementioned issues concerning arrhythmia (for example, torsades de pointes). Health care professionals might not have much control over the choice of COVID-19 agents because of a lack of available resources or limited options, but they can exercise clinical judgment with respect to selecting the appropriate psychotropic medications.
Treatment recommendations
1. Establish a baseline EKG
A baseline 12-lead EKG is the standard of care for patients currently being screened for COVID-19. It is necessary to rule out the presence of an underlying cardiovascular disease or a rhythm irregularity. A prolonged QTc interval is generally regarded as being around greater than 450-470 msecs with variations attributable to gender;11 numerous studies have affirmed that the risk of acquiring torsades de pointes is substantial when the QTc interval exceeds 500 msecs.12
2. Medical management and risk assessment
Commonly prescribed antipsychotics such as IV haloperidol and ziprasidone are known for exerting a negative effect on the interval and should readily be substituted with other agents in patients who are being treated for COVID-19; the combination of these antipsychotics alongside some COVID-19 medication regimens (for example, hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin) might prove to be fatal. The same logic applies to COVID-19 patients previously on antidepressant therapeutics such as citalopram and escitalopram.
3. Embrace an individually tailored approach to therapeutics
While American Psychiatric Association guidelines historically supported a cessation or reduction in the offending agent under normal circumstances,12 our team is recommending that the psychotropics associated with QTc interval prolongation are discontinued altogether (or substituted with a low-risk agent) in the event that a patient presents with suspected COVID-19. However, after the patients tests negative with COVID-19, they may resume therapy as indicated under the discretion of the mental health practitioner.
References
1. Offard C. “Lancet, NEJM Retract Surgisphere Studies on COVID-19 Patients.” The Scientist Magazine. 2020 Jun 4.
2. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020 Apr;74(4):281-2.
3. Keshtkar-Jahromi M and Bavari S. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):932-3.
4. Palca J. “NIH panel recommends against drug combination promoted by Trump for COVID-19.” NPR. 2020 Apr 21.
5. Mongelli L. “Long Island doctor tries new twist on hydroxychloroquine for elderly COVID-19 patients.” New York Post. 2020 Apr 4.
6. Hancox JC et al. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013 Oct;(5):155-65.
7. Giudicessi JR and Ackerman MJ. Cleve Clin J Med. 2013 Sep;80(9):539-44.
8. Casey DE. Am J Med. 2005 Apr 1;118(Suppl 2):15S-22S.
9. Beach SR et al. Psychosomatics. 2013 Jan 1;54(1):1-3.
10. Bogaczewicz A and Sobów T. Psychiatria i Psychologia Kliniczna. 2017;17(2):111-4.
11. Chohan PS et al. Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Sep-Oct;31(5):1269-71.
12. Lieberman JA et al. APA guidance on the use of antipsychotic drugs and cardiac sudden death. NYS Office of Mental Health. 2012.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Faisal Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Mohammed Islam is affiliated with the department of psychiatry at the Interfaith Medical Center, New York. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Frequent hypoglycemic episodes raise cardiac event risk
Frequent hypoglycemic episodes were linked to a raised incidence of cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes in a recent retrospective study, suggesting certain hypoglycemia-associated diabetes drugs should be avoided, an investigator said.
Patients who had more than five hypoglycemic episodes per year had a 61% greater risk of cardiovascular (CV) events, compared with patients with less frequent episodes, according to results of the study.
Although there were fewer strokes among younger patients, the overall increase in cardiovascular event risk held up regardless of age group, according to investigator Aman Rajpal, MD, of Louis Stokes Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University, both in Cleveland.
On the basis of these and earlier studies tying hypoglycemia to CV risk, health care providers need to “pay close attention” to low blood sugar and personalize glycemic control targets for each patient based on risk of hypoglycemia, Dr. Rajpal said in a presentation of the study at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
“Also, this suggests that avoidance of drugs associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia – namely insulin, sulfonylureas, or others – is essential to avoid and minimize the risk of cardiovascular events in this patient population with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Rajpal. “Let us remember part of our Hippocratic oath: ‘Above all, do no harm.’ ”
Tailoring treatment to mitigate risk
Mark Schutta, MD, medical director of Penn Rodebaugh Diabetes Center in Philadelphia, said that results of this study suggest a need to carefully select medical therapy for each individual patient with diabetes in order to mitigate CV risk.
“It’s really about tailoring their drugs to their personal situation,” Dr. Schutta said in an interview.
Although newer diabetes drug classes are associated with low to no risk of hypoglycemia, Dr. Schutta said that there is still a place for drugs such as sulfonylureas in certain situations.
Among sulfonylureas, glyburide comes with a much higher incidence of hypoglycemia, compared with glipizide and glimepiride, according to Dr. Schutta. “I think there’s a role for both drugs, but you have to be very careful, and you have to get the data from your patients.”
Hypoglycemia frequency and outcomes
Speculation that hypoglycemia could be linked to adverse CV outcomes was sparked years ago by trials such as ADVANCE. Severe hypoglycemia in that study was associated with a 168% increased risk of death from a CV cause (N Engl J Med. 2010 Oct 7;363:1410-8).
At the time, ADVANCE investigators said they were unable to find evidence that multiple severe hypoglycemia episodes conferred a greater risk of CV events versus a single hypoglycemia episode, though they added that few patients had recurrent events.
“In other words, the association between the number of hypoglycemia events, and adverse CV outcomes is still unclear,” said Dr. Rajpal in his virtual ADA presentation.
Potential elevated risks with more than five episodes
To evaluate the association between frequent hypoglycemic episodes (i.e., more than five per year, compared with one to five episodes) and CV events, Dr. Rajpal and colleagues evaluated outcomes data for 4.9 million adults with type 2 diabetes found in a large commercial database including information on patients in 27 U.S. health care networks.
Database records indicated that about 182,000 patients, or nearly 4%, had episodes of hyperglycemia, which Dr. Rajpal said was presumed to mean a plasma glucose level of less than 70 mg/dL.
Characteristics of the patients with more than five hypoglycemic episodes were similar to those with one to five episodes, although they were more likely to be 65 years or older, and were “slightly more likely” to be on insulin, which could possibly precipitate more hypoglycemic episodes in that group, Dr. Rajpal said.
Key findings
In the main analysis, Dr. Rajpal said, risk of CV events was significantly increased in those with more than five hypoglycemic episodes, compared with those with one to five episodes, with an odds ratio of 1.61 (95% confidence interval, 1.56-1.66). The incidence of cardiovascular events was 33.1% in those with more than five episodes and 23.5% in those with one to five episodes, according to the data presented.
Risks were also significantly increased specifically for cardiac arrhythmias, cerebrovascular accidents, and MI, Dr. Rajpal said, with ORs of 1.65 (95% CI, 1.9-1.71), 1.38 (95% CI, 1.22-1.56), and 1.43 (95% CI, 1.36-1.50), respectively.
Because individuals in the group with more than five hypoglycemic episodes were more likely to be elderly, Dr. Rajpal said that he and coinvestigators decided to perform an age-specific stratified analysis.
Although cerebral vascular incidence was low in younger patients, risk of CV events overall was nevertheless significantly elevated for those aged 65 years or older, 45-64 years, and 18-44 years, with ORs of 1.69 (95% CI, 1.61-1.7), 1.58 (95% CI, 1.48-1.69), and 1.62 (95% CI, 1.33-1.97).
“The results were still valid in stratified analysis based on different age groups,” Dr. Rajpal said.
Dr. Rajpal and coauthors reported that he had no conflicts of interest related to the research.
SOURCE: Rajpal A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 161-OR.
Frequent hypoglycemic episodes were linked to a raised incidence of cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes in a recent retrospective study, suggesting certain hypoglycemia-associated diabetes drugs should be avoided, an investigator said.
Patients who had more than five hypoglycemic episodes per year had a 61% greater risk of cardiovascular (CV) events, compared with patients with less frequent episodes, according to results of the study.
Although there were fewer strokes among younger patients, the overall increase in cardiovascular event risk held up regardless of age group, according to investigator Aman Rajpal, MD, of Louis Stokes Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University, both in Cleveland.
On the basis of these and earlier studies tying hypoglycemia to CV risk, health care providers need to “pay close attention” to low blood sugar and personalize glycemic control targets for each patient based on risk of hypoglycemia, Dr. Rajpal said in a presentation of the study at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
“Also, this suggests that avoidance of drugs associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia – namely insulin, sulfonylureas, or others – is essential to avoid and minimize the risk of cardiovascular events in this patient population with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Rajpal. “Let us remember part of our Hippocratic oath: ‘Above all, do no harm.’ ”
Tailoring treatment to mitigate risk
Mark Schutta, MD, medical director of Penn Rodebaugh Diabetes Center in Philadelphia, said that results of this study suggest a need to carefully select medical therapy for each individual patient with diabetes in order to mitigate CV risk.
“It’s really about tailoring their drugs to their personal situation,” Dr. Schutta said in an interview.
Although newer diabetes drug classes are associated with low to no risk of hypoglycemia, Dr. Schutta said that there is still a place for drugs such as sulfonylureas in certain situations.
Among sulfonylureas, glyburide comes with a much higher incidence of hypoglycemia, compared with glipizide and glimepiride, according to Dr. Schutta. “I think there’s a role for both drugs, but you have to be very careful, and you have to get the data from your patients.”
Hypoglycemia frequency and outcomes
Speculation that hypoglycemia could be linked to adverse CV outcomes was sparked years ago by trials such as ADVANCE. Severe hypoglycemia in that study was associated with a 168% increased risk of death from a CV cause (N Engl J Med. 2010 Oct 7;363:1410-8).
At the time, ADVANCE investigators said they were unable to find evidence that multiple severe hypoglycemia episodes conferred a greater risk of CV events versus a single hypoglycemia episode, though they added that few patients had recurrent events.
“In other words, the association between the number of hypoglycemia events, and adverse CV outcomes is still unclear,” said Dr. Rajpal in his virtual ADA presentation.
Potential elevated risks with more than five episodes
To evaluate the association between frequent hypoglycemic episodes (i.e., more than five per year, compared with one to five episodes) and CV events, Dr. Rajpal and colleagues evaluated outcomes data for 4.9 million adults with type 2 diabetes found in a large commercial database including information on patients in 27 U.S. health care networks.
Database records indicated that about 182,000 patients, or nearly 4%, had episodes of hyperglycemia, which Dr. Rajpal said was presumed to mean a plasma glucose level of less than 70 mg/dL.
Characteristics of the patients with more than five hypoglycemic episodes were similar to those with one to five episodes, although they were more likely to be 65 years or older, and were “slightly more likely” to be on insulin, which could possibly precipitate more hypoglycemic episodes in that group, Dr. Rajpal said.
Key findings
In the main analysis, Dr. Rajpal said, risk of CV events was significantly increased in those with more than five hypoglycemic episodes, compared with those with one to five episodes, with an odds ratio of 1.61 (95% confidence interval, 1.56-1.66). The incidence of cardiovascular events was 33.1% in those with more than five episodes and 23.5% in those with one to five episodes, according to the data presented.
Risks were also significantly increased specifically for cardiac arrhythmias, cerebrovascular accidents, and MI, Dr. Rajpal said, with ORs of 1.65 (95% CI, 1.9-1.71), 1.38 (95% CI, 1.22-1.56), and 1.43 (95% CI, 1.36-1.50), respectively.
Because individuals in the group with more than five hypoglycemic episodes were more likely to be elderly, Dr. Rajpal said that he and coinvestigators decided to perform an age-specific stratified analysis.
Although cerebral vascular incidence was low in younger patients, risk of CV events overall was nevertheless significantly elevated for those aged 65 years or older, 45-64 years, and 18-44 years, with ORs of 1.69 (95% CI, 1.61-1.7), 1.58 (95% CI, 1.48-1.69), and 1.62 (95% CI, 1.33-1.97).
“The results were still valid in stratified analysis based on different age groups,” Dr. Rajpal said.
Dr. Rajpal and coauthors reported that he had no conflicts of interest related to the research.
SOURCE: Rajpal A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 161-OR.
Frequent hypoglycemic episodes were linked to a raised incidence of cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes in a recent retrospective study, suggesting certain hypoglycemia-associated diabetes drugs should be avoided, an investigator said.
Patients who had more than five hypoglycemic episodes per year had a 61% greater risk of cardiovascular (CV) events, compared with patients with less frequent episodes, according to results of the study.
Although there were fewer strokes among younger patients, the overall increase in cardiovascular event risk held up regardless of age group, according to investigator Aman Rajpal, MD, of Louis Stokes Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University, both in Cleveland.
On the basis of these and earlier studies tying hypoglycemia to CV risk, health care providers need to “pay close attention” to low blood sugar and personalize glycemic control targets for each patient based on risk of hypoglycemia, Dr. Rajpal said in a presentation of the study at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
“Also, this suggests that avoidance of drugs associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia – namely insulin, sulfonylureas, or others – is essential to avoid and minimize the risk of cardiovascular events in this patient population with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Rajpal. “Let us remember part of our Hippocratic oath: ‘Above all, do no harm.’ ”
Tailoring treatment to mitigate risk
Mark Schutta, MD, medical director of Penn Rodebaugh Diabetes Center in Philadelphia, said that results of this study suggest a need to carefully select medical therapy for each individual patient with diabetes in order to mitigate CV risk.
“It’s really about tailoring their drugs to their personal situation,” Dr. Schutta said in an interview.
Although newer diabetes drug classes are associated with low to no risk of hypoglycemia, Dr. Schutta said that there is still a place for drugs such as sulfonylureas in certain situations.
Among sulfonylureas, glyburide comes with a much higher incidence of hypoglycemia, compared with glipizide and glimepiride, according to Dr. Schutta. “I think there’s a role for both drugs, but you have to be very careful, and you have to get the data from your patients.”
Hypoglycemia frequency and outcomes
Speculation that hypoglycemia could be linked to adverse CV outcomes was sparked years ago by trials such as ADVANCE. Severe hypoglycemia in that study was associated with a 168% increased risk of death from a CV cause (N Engl J Med. 2010 Oct 7;363:1410-8).
At the time, ADVANCE investigators said they were unable to find evidence that multiple severe hypoglycemia episodes conferred a greater risk of CV events versus a single hypoglycemia episode, though they added that few patients had recurrent events.
“In other words, the association between the number of hypoglycemia events, and adverse CV outcomes is still unclear,” said Dr. Rajpal in his virtual ADA presentation.
Potential elevated risks with more than five episodes
To evaluate the association between frequent hypoglycemic episodes (i.e., more than five per year, compared with one to five episodes) and CV events, Dr. Rajpal and colleagues evaluated outcomes data for 4.9 million adults with type 2 diabetes found in a large commercial database including information on patients in 27 U.S. health care networks.
Database records indicated that about 182,000 patients, or nearly 4%, had episodes of hyperglycemia, which Dr. Rajpal said was presumed to mean a plasma glucose level of less than 70 mg/dL.
Characteristics of the patients with more than five hypoglycemic episodes were similar to those with one to five episodes, although they were more likely to be 65 years or older, and were “slightly more likely” to be on insulin, which could possibly precipitate more hypoglycemic episodes in that group, Dr. Rajpal said.
Key findings
In the main analysis, Dr. Rajpal said, risk of CV events was significantly increased in those with more than five hypoglycemic episodes, compared with those with one to five episodes, with an odds ratio of 1.61 (95% confidence interval, 1.56-1.66). The incidence of cardiovascular events was 33.1% in those with more than five episodes and 23.5% in those with one to five episodes, according to the data presented.
Risks were also significantly increased specifically for cardiac arrhythmias, cerebrovascular accidents, and MI, Dr. Rajpal said, with ORs of 1.65 (95% CI, 1.9-1.71), 1.38 (95% CI, 1.22-1.56), and 1.43 (95% CI, 1.36-1.50), respectively.
Because individuals in the group with more than five hypoglycemic episodes were more likely to be elderly, Dr. Rajpal said that he and coinvestigators decided to perform an age-specific stratified analysis.
Although cerebral vascular incidence was low in younger patients, risk of CV events overall was nevertheless significantly elevated for those aged 65 years or older, 45-64 years, and 18-44 years, with ORs of 1.69 (95% CI, 1.61-1.7), 1.58 (95% CI, 1.48-1.69), and 1.62 (95% CI, 1.33-1.97).
“The results were still valid in stratified analysis based on different age groups,” Dr. Rajpal said.
Dr. Rajpal and coauthors reported that he had no conflicts of interest related to the research.
SOURCE: Rajpal A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 161-OR.
FROM ADA 2020
CAC scoring pinpoints stenoses in asymptomatic diabetes patients
For diabetes patients with no cardiovascular symptoms despite certain risk factors, incorporating coronary calcium scoring into a silent myocardial ischemia screening algorithm may be an effective and cost-conscious strategy that avoids missed coronary stenoses suitable for revascularization, results of a recent study suggest.
Zero patients in need of revascularization were missed in a risk stratification model in which screening for silent myocardial ischemia (SMI) was done only for patients with peripheral artery disease, severe nephropathy, or a high coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, according to investigator Paul Valensi, MD.
In practical terms, that means stress myocardial scintigraphy to detect SMI could be reserved for patients with evidence of target organ damage or a CAC score of 100 or higher, according to Dr. Valensi, head of the department of endocrinology, diabetology, and nutrition at Jean Verdier Hospital in Bondy, France.
“The strategy appears to be a good compromise, and the most cost effective strategy,” Dr. Valensi said in a presentation of the results at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Utility of CAC scoring in diabetes
This algorithm proposed by Dr. Valenti and colleagues is a “reasonable” approach to guide risk stratification in asymptomatic diabetes patients, said Matthew J. Budoff, MD, professor of medicine and director of cardiac CT at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center in Torrance, Calif.
“Calcium scoring could certainly help you identify those patients (at increased risk) as a first-line test, because if their calcium score is zero, their chance of having obstructive disease is probably either zero or very close to zero,” Dr. Budoff said in an interview.
Using CAC scores to assess cardiovascular risk in asymptomatic adults with diabetes was supported by 2010 guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, Dr. Budoff said, while 2019 guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) describe CAC score combined with CT as a potential risk modifier in the evaluation of certain asymptomatic patients with diabetes.
“We are starting to see that we might be able to understand diabetes better and the cardiovascular implications by understanding how much plaque (patients) have at the time that we see them,” Dr. Budoff said in a presentation on use of CAC scans he gave earlier at the virtual ADA meeting.
In the interview, Dr. Budoff also noted that CAC scores may be particularly useful for guiding use of statins, PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9) inhibitors, or other treatments in patients with diabetes: “There are a lot of therapies that we can apply, if we knew somebody was at higher risk, that would potentially help them avoid a heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death,” he said.
CAC scoring and coronary artery stenoses
Although about 20% of patients with type 2 diabetes have SMI, screening for it is “debated,” according to Dr. Valensi.
The recent ESC guidelines state that while routine screening for coronary artery disease in asymptomatic diabetics is not recommended, stress testing or coronary angiography “may be indicated” in asymptomatic diabetics in the very-high cardiovascular risk category.
That position is based on a lack of benefit seen with a broad screening strategy, the guidelines say, possibly due in part to low event rates in randomized controlled trials that have studied the approach.
Using CAC scoring could change the equation by helping to identify a greater proportion of type 2 diabetics with SMI, according to Dr. Valensi.
“The role of the CAC score in the strategy of detection of SMI needs to be defined, and this role may depend on the a priori cardiovascular risk,” he said.
Dr. Valensi and colleagues accordingly tested several different approaches to selecting asymptomatic diabetic patients for SMI screening to see how they would perform in finding patients with coronary stenoses eligible for revascularization.
Their study included 416 diabetes patients with diabetes at very high cardiovascular risk but with no cardiac history or symptoms. A total of 40 patients (9.6%) had SMI, including 15 patients in which coronary stenoses were found; of those, 11 (73.5%) underwent a revascularization procedure.
They found that, by performing myocardial scintigraphy only in those patients with peripheral artery disease or severe nephropathy, they would have missed 6 patients with coronary stenosis suitable for revascularization among the 275 patients who did not meet those target organ damage criteria.
By contrast, zero patients would have been missed by performing myocardial scintigraphy in patients who either met those target organ damage criteria, or who had an elevated CAC score.
“We suggest screening for SMI, using stress myocardial CT scanning and coronary stenosis screening, only the patients with peripheral artery disease or severe nephropathy or with a high CAC score over 100 Agatston units,” said Dr. Valensi.
Dr. Valensi reported disclosures related to Merck Sharp Dohme, Novo Nordisk, Pierre Fabre, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, and others. Coauthors provided no disclosures related to the research. Dr. Budoff reported that he has served as a paid consultant to GE.
SOURCE: Berkane N et al. ADA 2020. Abstract 8-OR.
For diabetes patients with no cardiovascular symptoms despite certain risk factors, incorporating coronary calcium scoring into a silent myocardial ischemia screening algorithm may be an effective and cost-conscious strategy that avoids missed coronary stenoses suitable for revascularization, results of a recent study suggest.
Zero patients in need of revascularization were missed in a risk stratification model in which screening for silent myocardial ischemia (SMI) was done only for patients with peripheral artery disease, severe nephropathy, or a high coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, according to investigator Paul Valensi, MD.
In practical terms, that means stress myocardial scintigraphy to detect SMI could be reserved for patients with evidence of target organ damage or a CAC score of 100 or higher, according to Dr. Valensi, head of the department of endocrinology, diabetology, and nutrition at Jean Verdier Hospital in Bondy, France.
“The strategy appears to be a good compromise, and the most cost effective strategy,” Dr. Valensi said in a presentation of the results at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Utility of CAC scoring in diabetes
This algorithm proposed by Dr. Valenti and colleagues is a “reasonable” approach to guide risk stratification in asymptomatic diabetes patients, said Matthew J. Budoff, MD, professor of medicine and director of cardiac CT at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center in Torrance, Calif.
“Calcium scoring could certainly help you identify those patients (at increased risk) as a first-line test, because if their calcium score is zero, their chance of having obstructive disease is probably either zero or very close to zero,” Dr. Budoff said in an interview.
Using CAC scores to assess cardiovascular risk in asymptomatic adults with diabetes was supported by 2010 guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, Dr. Budoff said, while 2019 guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) describe CAC score combined with CT as a potential risk modifier in the evaluation of certain asymptomatic patients with diabetes.
“We are starting to see that we might be able to understand diabetes better and the cardiovascular implications by understanding how much plaque (patients) have at the time that we see them,” Dr. Budoff said in a presentation on use of CAC scans he gave earlier at the virtual ADA meeting.
In the interview, Dr. Budoff also noted that CAC scores may be particularly useful for guiding use of statins, PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9) inhibitors, or other treatments in patients with diabetes: “There are a lot of therapies that we can apply, if we knew somebody was at higher risk, that would potentially help them avoid a heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death,” he said.
CAC scoring and coronary artery stenoses
Although about 20% of patients with type 2 diabetes have SMI, screening for it is “debated,” according to Dr. Valensi.
The recent ESC guidelines state that while routine screening for coronary artery disease in asymptomatic diabetics is not recommended, stress testing or coronary angiography “may be indicated” in asymptomatic diabetics in the very-high cardiovascular risk category.
That position is based on a lack of benefit seen with a broad screening strategy, the guidelines say, possibly due in part to low event rates in randomized controlled trials that have studied the approach.
Using CAC scoring could change the equation by helping to identify a greater proportion of type 2 diabetics with SMI, according to Dr. Valensi.
“The role of the CAC score in the strategy of detection of SMI needs to be defined, and this role may depend on the a priori cardiovascular risk,” he said.
Dr. Valensi and colleagues accordingly tested several different approaches to selecting asymptomatic diabetic patients for SMI screening to see how they would perform in finding patients with coronary stenoses eligible for revascularization.
Their study included 416 diabetes patients with diabetes at very high cardiovascular risk but with no cardiac history or symptoms. A total of 40 patients (9.6%) had SMI, including 15 patients in which coronary stenoses were found; of those, 11 (73.5%) underwent a revascularization procedure.
They found that, by performing myocardial scintigraphy only in those patients with peripheral artery disease or severe nephropathy, they would have missed 6 patients with coronary stenosis suitable for revascularization among the 275 patients who did not meet those target organ damage criteria.
By contrast, zero patients would have been missed by performing myocardial scintigraphy in patients who either met those target organ damage criteria, or who had an elevated CAC score.
“We suggest screening for SMI, using stress myocardial CT scanning and coronary stenosis screening, only the patients with peripheral artery disease or severe nephropathy or with a high CAC score over 100 Agatston units,” said Dr. Valensi.
Dr. Valensi reported disclosures related to Merck Sharp Dohme, Novo Nordisk, Pierre Fabre, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, and others. Coauthors provided no disclosures related to the research. Dr. Budoff reported that he has served as a paid consultant to GE.
SOURCE: Berkane N et al. ADA 2020. Abstract 8-OR.
For diabetes patients with no cardiovascular symptoms despite certain risk factors, incorporating coronary calcium scoring into a silent myocardial ischemia screening algorithm may be an effective and cost-conscious strategy that avoids missed coronary stenoses suitable for revascularization, results of a recent study suggest.
Zero patients in need of revascularization were missed in a risk stratification model in which screening for silent myocardial ischemia (SMI) was done only for patients with peripheral artery disease, severe nephropathy, or a high coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, according to investigator Paul Valensi, MD.
In practical terms, that means stress myocardial scintigraphy to detect SMI could be reserved for patients with evidence of target organ damage or a CAC score of 100 or higher, according to Dr. Valensi, head of the department of endocrinology, diabetology, and nutrition at Jean Verdier Hospital in Bondy, France.
“The strategy appears to be a good compromise, and the most cost effective strategy,” Dr. Valensi said in a presentation of the results at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Utility of CAC scoring in diabetes
This algorithm proposed by Dr. Valenti and colleagues is a “reasonable” approach to guide risk stratification in asymptomatic diabetes patients, said Matthew J. Budoff, MD, professor of medicine and director of cardiac CT at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center in Torrance, Calif.
“Calcium scoring could certainly help you identify those patients (at increased risk) as a first-line test, because if their calcium score is zero, their chance of having obstructive disease is probably either zero or very close to zero,” Dr. Budoff said in an interview.
Using CAC scores to assess cardiovascular risk in asymptomatic adults with diabetes was supported by 2010 guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, Dr. Budoff said, while 2019 guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) describe CAC score combined with CT as a potential risk modifier in the evaluation of certain asymptomatic patients with diabetes.
“We are starting to see that we might be able to understand diabetes better and the cardiovascular implications by understanding how much plaque (patients) have at the time that we see them,” Dr. Budoff said in a presentation on use of CAC scans he gave earlier at the virtual ADA meeting.
In the interview, Dr. Budoff also noted that CAC scores may be particularly useful for guiding use of statins, PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9) inhibitors, or other treatments in patients with diabetes: “There are a lot of therapies that we can apply, if we knew somebody was at higher risk, that would potentially help them avoid a heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death,” he said.
CAC scoring and coronary artery stenoses
Although about 20% of patients with type 2 diabetes have SMI, screening for it is “debated,” according to Dr. Valensi.
The recent ESC guidelines state that while routine screening for coronary artery disease in asymptomatic diabetics is not recommended, stress testing or coronary angiography “may be indicated” in asymptomatic diabetics in the very-high cardiovascular risk category.
That position is based on a lack of benefit seen with a broad screening strategy, the guidelines say, possibly due in part to low event rates in randomized controlled trials that have studied the approach.
Using CAC scoring could change the equation by helping to identify a greater proportion of type 2 diabetics with SMI, according to Dr. Valensi.
“The role of the CAC score in the strategy of detection of SMI needs to be defined, and this role may depend on the a priori cardiovascular risk,” he said.
Dr. Valensi and colleagues accordingly tested several different approaches to selecting asymptomatic diabetic patients for SMI screening to see how they would perform in finding patients with coronary stenoses eligible for revascularization.
Their study included 416 diabetes patients with diabetes at very high cardiovascular risk but with no cardiac history or symptoms. A total of 40 patients (9.6%) had SMI, including 15 patients in which coronary stenoses were found; of those, 11 (73.5%) underwent a revascularization procedure.
They found that, by performing myocardial scintigraphy only in those patients with peripheral artery disease or severe nephropathy, they would have missed 6 patients with coronary stenosis suitable for revascularization among the 275 patients who did not meet those target organ damage criteria.
By contrast, zero patients would have been missed by performing myocardial scintigraphy in patients who either met those target organ damage criteria, or who had an elevated CAC score.
“We suggest screening for SMI, using stress myocardial CT scanning and coronary stenosis screening, only the patients with peripheral artery disease or severe nephropathy or with a high CAC score over 100 Agatston units,” said Dr. Valensi.
Dr. Valensi reported disclosures related to Merck Sharp Dohme, Novo Nordisk, Pierre Fabre, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, and others. Coauthors provided no disclosures related to the research. Dr. Budoff reported that he has served as a paid consultant to GE.
SOURCE: Berkane N et al. ADA 2020. Abstract 8-OR.
FROM ADA 2020














