User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
COVID-19 neurologic effects: Does the virus directly attack the brain?
A new review article summarizes what is known so far, and what clinicians need to look out for.
“We frequently see neurological conditions in people with COVID-19, but we understand very little about these effects. Is it the virus entering the brain/nerves or are they a result of a general inflammation or immune response – a bystander effect of people being severely ill. It is probably a combination of both,” said senior author Serena Spudich, MD, Gilbert H. Glaser Professor of Neurology; division chief of neurological infections & global neurology; and codirector of the Center for Neuroepidemiology and Clinical Neurological Research at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“Our message is that there are fairly frequent neurological sequelae of COVID-19 and we need to be alert to these, and to try to understand the potential long-term consequences,” she said.
The review was published online May 29 in JAMA Neurology.
Brain changes linked to loss of smell
In a separate article also published online in JAMA Neurology the same day, an Italian group describes a COVID-19 patient with anosmia (loss of sense of smell) who showed brain abnormalities on MRI in the areas associated with smell – the right gyrus rectus and the olfactory bulbs. These changes were resolved on later scan and the patient recovered her sense of smell.
“Based on the MRI findings, we can speculate that SARS-CoV-2 might invade the brain through the olfactory pathway,” conclude the researchers, led by first author Letterio S. Politi, MD, of the department of neuroradiology at IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas and Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
Can coronaviruses enter the CNS?
Dr. Spudich described this case report as “compelling evidence suggesting that loss of smell is a neurologic effect.”
“Loss of smell and/or taste is a common symptom in COVID-19, so this may suggest that an awful lot of people have some neurological involvement,” Dr. Spudich commented. “While a transient loss of smell or taste is not serious, if the virus has infected brain tissue the question is could this then spread to other parts of the brain and cause other more serious neurological effects,” she added.
In their review article, Dr. Spudich and colleagues present evidence showing that coronaviruses can enter the CNS.
“We know that SARS-1 and MERS have been shown to enter the nervous system and several coronaviruses have been shown to cause direct brain effects,” she said. “There is also some evidence that SARS-CoV-2 can do this too. As well as these latest MRI findings linked to loss of smell, there is a report of the virus being found in endothelial cells in the brain and a French autopsy study has also detected virus in the brain.”
Complications of other systemic effects?
Dr. Spudich is a neurologist specializing in neurologic consequences of infectious disease. “We don’t normally have such vast numbers of patients but in the last 3 months there has been an avalanche,” she says. From her personal experience, she believes the majority of neurologic symptoms in COVID-19 patients are most probably complications of other systemic effects, such as kidney, heart, or liver problems. But there is likely also a direct viral effect on the CNS in some patients.
“Reports from China suggested that serious neurologic effects were present in about one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. I would say in our experience the figure would be less than that – maybe around 10%,” she noted.
Some COVID-19 patients are presenting with primary neurologic symptoms. For example, an elderly person may first develop confusion rather than a cough or shortness of breath; others have had severe headache as an initial COVID-19 symptom, Dr. Spudich reported. “Medical staff need to be aware of this – a severe headache in a patient who doesn’t normally get headaches could be a sign of the virus.”
Some of the neurologic symptoms could be caused by autoimmunity. Dr. Spudich explained that, in acute HIV infection a small proportion of patients can first present with autoimmune neurologic effects such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune condition of the nerves which causes a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. “This is well described in HIV, but we are also now seeing this in COVID-19 patients too,” she said. “A panoply of conditions can be caused by autoimmunity.”
On the increase in strokes that has been reported in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Spudich said, “this could be due to direct effects of the virus (e.g., causing an increase in coagulation or infecting the endothelial cells in the brain) or it could just be the final trigger for patients who were at risk of stroke anyway.”
There have been some very high-profile reports of younger patients with major strokes, she said, “but we haven’t seen that in our hospital. For the most part in my experience, strokes are happening in older COVID-19 patients with stroke risk factors such as AF [atrial fibrillation], hypertension, and diabetes. We haven’t seen a preponderance of strokes in young, otherwise healthy people.”
Even in patients who have neurologic effects as the first sign of COVID-19 infection, it is not known whether these symptoms are caused directly by the virus.
“We know that flu can cause people to have headaches, but that is because of an increase in inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, patients with acute HIV infection often have headaches as a result of the virus getting into the brain. We don’t know where in this [cluster] COVID-19 virus falls,” Dr. Spudich said.
Much is still unknown
“The information we have is very sparse at this point. We need far more systematic information on this from CSF samples and imaging.” Dr. Spudich urged clinicians to try to collect such information in patients with neurologic symptoms.
Acknowledging that fewer such tests are being done at present because of concerns over infection risk, Dr. Spudich suggested that some changes in procedure may help. “In our hospital we have a portable MRI scanner which can be brought to the patient. This means the patient does not have to move across the hospital for a scan. This helps us to decide whether the patient has had a stroke, which can be missed when patients are on a ventilator.”
It is also unclear whether the neurologic effects seen during COVID-19 infection will last long term.
Dr. Spudich noted that there have been reports of COVID-19 patients discharged from intensive care having difficulty with higher cognitive function for some time thereafter. “This can happen after being in ICU but is it more pronounced in COVID-19 patients? An ongoing study is underway to look at this,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review article summarizes what is known so far, and what clinicians need to look out for.
“We frequently see neurological conditions in people with COVID-19, but we understand very little about these effects. Is it the virus entering the brain/nerves or are they a result of a general inflammation or immune response – a bystander effect of people being severely ill. It is probably a combination of both,” said senior author Serena Spudich, MD, Gilbert H. Glaser Professor of Neurology; division chief of neurological infections & global neurology; and codirector of the Center for Neuroepidemiology and Clinical Neurological Research at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“Our message is that there are fairly frequent neurological sequelae of COVID-19 and we need to be alert to these, and to try to understand the potential long-term consequences,” she said.
The review was published online May 29 in JAMA Neurology.
Brain changes linked to loss of smell
In a separate article also published online in JAMA Neurology the same day, an Italian group describes a COVID-19 patient with anosmia (loss of sense of smell) who showed brain abnormalities on MRI in the areas associated with smell – the right gyrus rectus and the olfactory bulbs. These changes were resolved on later scan and the patient recovered her sense of smell.
“Based on the MRI findings, we can speculate that SARS-CoV-2 might invade the brain through the olfactory pathway,” conclude the researchers, led by first author Letterio S. Politi, MD, of the department of neuroradiology at IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas and Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
Can coronaviruses enter the CNS?
Dr. Spudich described this case report as “compelling evidence suggesting that loss of smell is a neurologic effect.”
“Loss of smell and/or taste is a common symptom in COVID-19, so this may suggest that an awful lot of people have some neurological involvement,” Dr. Spudich commented. “While a transient loss of smell or taste is not serious, if the virus has infected brain tissue the question is could this then spread to other parts of the brain and cause other more serious neurological effects,” she added.
In their review article, Dr. Spudich and colleagues present evidence showing that coronaviruses can enter the CNS.
“We know that SARS-1 and MERS have been shown to enter the nervous system and several coronaviruses have been shown to cause direct brain effects,” she said. “There is also some evidence that SARS-CoV-2 can do this too. As well as these latest MRI findings linked to loss of smell, there is a report of the virus being found in endothelial cells in the brain and a French autopsy study has also detected virus in the brain.”
Complications of other systemic effects?
Dr. Spudich is a neurologist specializing in neurologic consequences of infectious disease. “We don’t normally have such vast numbers of patients but in the last 3 months there has been an avalanche,” she says. From her personal experience, she believes the majority of neurologic symptoms in COVID-19 patients are most probably complications of other systemic effects, such as kidney, heart, or liver problems. But there is likely also a direct viral effect on the CNS in some patients.
“Reports from China suggested that serious neurologic effects were present in about one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. I would say in our experience the figure would be less than that – maybe around 10%,” she noted.
Some COVID-19 patients are presenting with primary neurologic symptoms. For example, an elderly person may first develop confusion rather than a cough or shortness of breath; others have had severe headache as an initial COVID-19 symptom, Dr. Spudich reported. “Medical staff need to be aware of this – a severe headache in a patient who doesn’t normally get headaches could be a sign of the virus.”
Some of the neurologic symptoms could be caused by autoimmunity. Dr. Spudich explained that, in acute HIV infection a small proportion of patients can first present with autoimmune neurologic effects such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune condition of the nerves which causes a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. “This is well described in HIV, but we are also now seeing this in COVID-19 patients too,” she said. “A panoply of conditions can be caused by autoimmunity.”
On the increase in strokes that has been reported in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Spudich said, “this could be due to direct effects of the virus (e.g., causing an increase in coagulation or infecting the endothelial cells in the brain) or it could just be the final trigger for patients who were at risk of stroke anyway.”
There have been some very high-profile reports of younger patients with major strokes, she said, “but we haven’t seen that in our hospital. For the most part in my experience, strokes are happening in older COVID-19 patients with stroke risk factors such as AF [atrial fibrillation], hypertension, and diabetes. We haven’t seen a preponderance of strokes in young, otherwise healthy people.”
Even in patients who have neurologic effects as the first sign of COVID-19 infection, it is not known whether these symptoms are caused directly by the virus.
“We know that flu can cause people to have headaches, but that is because of an increase in inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, patients with acute HIV infection often have headaches as a result of the virus getting into the brain. We don’t know where in this [cluster] COVID-19 virus falls,” Dr. Spudich said.
Much is still unknown
“The information we have is very sparse at this point. We need far more systematic information on this from CSF samples and imaging.” Dr. Spudich urged clinicians to try to collect such information in patients with neurologic symptoms.
Acknowledging that fewer such tests are being done at present because of concerns over infection risk, Dr. Spudich suggested that some changes in procedure may help. “In our hospital we have a portable MRI scanner which can be brought to the patient. This means the patient does not have to move across the hospital for a scan. This helps us to decide whether the patient has had a stroke, which can be missed when patients are on a ventilator.”
It is also unclear whether the neurologic effects seen during COVID-19 infection will last long term.
Dr. Spudich noted that there have been reports of COVID-19 patients discharged from intensive care having difficulty with higher cognitive function for some time thereafter. “This can happen after being in ICU but is it more pronounced in COVID-19 patients? An ongoing study is underway to look at this,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review article summarizes what is known so far, and what clinicians need to look out for.
“We frequently see neurological conditions in people with COVID-19, but we understand very little about these effects. Is it the virus entering the brain/nerves or are they a result of a general inflammation or immune response – a bystander effect of people being severely ill. It is probably a combination of both,” said senior author Serena Spudich, MD, Gilbert H. Glaser Professor of Neurology; division chief of neurological infections & global neurology; and codirector of the Center for Neuroepidemiology and Clinical Neurological Research at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“Our message is that there are fairly frequent neurological sequelae of COVID-19 and we need to be alert to these, and to try to understand the potential long-term consequences,” she said.
The review was published online May 29 in JAMA Neurology.
Brain changes linked to loss of smell
In a separate article also published online in JAMA Neurology the same day, an Italian group describes a COVID-19 patient with anosmia (loss of sense of smell) who showed brain abnormalities on MRI in the areas associated with smell – the right gyrus rectus and the olfactory bulbs. These changes were resolved on later scan and the patient recovered her sense of smell.
“Based on the MRI findings, we can speculate that SARS-CoV-2 might invade the brain through the olfactory pathway,” conclude the researchers, led by first author Letterio S. Politi, MD, of the department of neuroradiology at IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas and Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
Can coronaviruses enter the CNS?
Dr. Spudich described this case report as “compelling evidence suggesting that loss of smell is a neurologic effect.”
“Loss of smell and/or taste is a common symptom in COVID-19, so this may suggest that an awful lot of people have some neurological involvement,” Dr. Spudich commented. “While a transient loss of smell or taste is not serious, if the virus has infected brain tissue the question is could this then spread to other parts of the brain and cause other more serious neurological effects,” she added.
In their review article, Dr. Spudich and colleagues present evidence showing that coronaviruses can enter the CNS.
“We know that SARS-1 and MERS have been shown to enter the nervous system and several coronaviruses have been shown to cause direct brain effects,” she said. “There is also some evidence that SARS-CoV-2 can do this too. As well as these latest MRI findings linked to loss of smell, there is a report of the virus being found in endothelial cells in the brain and a French autopsy study has also detected virus in the brain.”
Complications of other systemic effects?
Dr. Spudich is a neurologist specializing in neurologic consequences of infectious disease. “We don’t normally have such vast numbers of patients but in the last 3 months there has been an avalanche,” she says. From her personal experience, she believes the majority of neurologic symptoms in COVID-19 patients are most probably complications of other systemic effects, such as kidney, heart, or liver problems. But there is likely also a direct viral effect on the CNS in some patients.
“Reports from China suggested that serious neurologic effects were present in about one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. I would say in our experience the figure would be less than that – maybe around 10%,” she noted.
Some COVID-19 patients are presenting with primary neurologic symptoms. For example, an elderly person may first develop confusion rather than a cough or shortness of breath; others have had severe headache as an initial COVID-19 symptom, Dr. Spudich reported. “Medical staff need to be aware of this – a severe headache in a patient who doesn’t normally get headaches could be a sign of the virus.”
Some of the neurologic symptoms could be caused by autoimmunity. Dr. Spudich explained that, in acute HIV infection a small proportion of patients can first present with autoimmune neurologic effects such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune condition of the nerves which causes a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. “This is well described in HIV, but we are also now seeing this in COVID-19 patients too,” she said. “A panoply of conditions can be caused by autoimmunity.”
On the increase in strokes that has been reported in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Spudich said, “this could be due to direct effects of the virus (e.g., causing an increase in coagulation or infecting the endothelial cells in the brain) or it could just be the final trigger for patients who were at risk of stroke anyway.”
There have been some very high-profile reports of younger patients with major strokes, she said, “but we haven’t seen that in our hospital. For the most part in my experience, strokes are happening in older COVID-19 patients with stroke risk factors such as AF [atrial fibrillation], hypertension, and diabetes. We haven’t seen a preponderance of strokes in young, otherwise healthy people.”
Even in patients who have neurologic effects as the first sign of COVID-19 infection, it is not known whether these symptoms are caused directly by the virus.
“We know that flu can cause people to have headaches, but that is because of an increase in inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, patients with acute HIV infection often have headaches as a result of the virus getting into the brain. We don’t know where in this [cluster] COVID-19 virus falls,” Dr. Spudich said.
Much is still unknown
“The information we have is very sparse at this point. We need far more systematic information on this from CSF samples and imaging.” Dr. Spudich urged clinicians to try to collect such information in patients with neurologic symptoms.
Acknowledging that fewer such tests are being done at present because of concerns over infection risk, Dr. Spudich suggested that some changes in procedure may help. “In our hospital we have a portable MRI scanner which can be brought to the patient. This means the patient does not have to move across the hospital for a scan. This helps us to decide whether the patient has had a stroke, which can be missed when patients are on a ventilator.”
It is also unclear whether the neurologic effects seen during COVID-19 infection will last long term.
Dr. Spudich noted that there have been reports of COVID-19 patients discharged from intensive care having difficulty with higher cognitive function for some time thereafter. “This can happen after being in ICU but is it more pronounced in COVID-19 patients? An ongoing study is underway to look at this,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: Use these strategies to help parents with and without special needs children
Most people can cope, to some degree, with the multiple weeks of social distancing and stressors related to the pandemic. But what if those stressors became a way of life for a year – or longer? What sorts of skills would be essential not only to survive but to have a renewed sense of resilience?
I know of one group that has had experiences that mirror the challenges faced by the parents of children: the parents of special needs children. As I argued previously, those parents have faced many of the challenges presented by COVID-19. Among those challenges are social distancing and difficulty accessing everyday common experiences. These parents know that they have to manage more areas of their children’s rearing than do their counterparts.
In addition to having to plan for how to deal with acute urgent or emergent medical situations involving their special needs children, these parents also must prepare for the long-term effects of managing children who require ongoing daily care, attention, and dedication.
These strategies can help the parents of special needs kids find a sense of mastery and comfort. The hope is that, after practicing them for long periods of time, the strategies become second nature.
Here are several strategies that might help patients with children during this pandemic:
- Take time to reset: Sometimes it is helpful for parents to take a minute away from a difficult impasse with their kids to reset and take their own “time out.” A few seconds of mental time away from the “scene” provides space and a mental reminder that the minute that just happened is finite, and that a whole new one is coming up next. The break provides a sense of hope. This cognitive reframing could be practiced often.
- Re-enter the challenging scene with a warm voice: Parents model for their children, but they also are telling their own brains that they, too, can calm down. This approach also de-escalates the situation and allows children to get used to hearing directions from someone who is in control – without hostility or irritability.
- Keep a sense of humor; it might come in handy: This is especially the case when tension is in the home, or when facing a set of challenging bad news. As an example, consider how some situations are so repetitive that they border on the ridiculous – such as a grown child having a tantrum at a store. Encourage the children to give themselves permission to cry first so they can laugh second, and then move on.
- Establish a routine for children that is self-reinforcing, and allows for together and separate times: They can, as an example: A) Get ready for the day all by themselves, or as much as they can do independently, before they come down and then B) have breakfast. Then, the child can C) do homework, and then D) go play outside. The routine would then continue on its own without outside reinforcers.
- Tell the children that they can get to the reinforcing activity only after completing the previous one. Over time, they learn to take pride in completing the first activity and doing so more independently. Not having to wait to be told what to do all the time fosters a sense of independence.
- Plan for meals and fun tasks together, and separate for individual work. This creates a sense of change and gives the day a certain flow. Establish routines that are predictable for the children that can be easily documented for the whole family on a calendar. Establish a beginning and an end time to the work day. Mark the end of the day with a chalk line establishing when the family can engage in a certain activity, for example, going for a family bike ride. Let the routine honor healthy circadian rhythms for sleep/wakeful times, and be consistent.
- Feed the brain and body the “good stuff”: Limit negative news, and surround the children with people who bring them joy or provide hope. Listen to inspirational messages and uplifting music. Give the children food that nourishes and energizes their bodies. Take in the view outside, the greenery, or the sky if there is no green around. Connect with family/friends who are far away.
- Make time to replenish with something that is meaningful/productive/helpful: Parents have very little time for themselves when they are “on,” so when they can actually take a little time to recharge, the activity should check many boxes. For example, encourage them to go for a walk (exercise) while listening to music (relax), make a phone call to someone who can relate to their situation (socialize), pray with someone (be spiritual), or sit in their rooms to get some alone quiet time (meditate). Reach out to those who are lonely. Network. Mentor. Volunteer.
- Develop an eye for noticing the positive: Instead of hoping for things to go back to the way they were, tell your patients to practice embracing without judgment the new norm. Get them to notice the time they spend with their families. Break all tasks into many smaller tasks, so there is more possibility of observing progress, and it is evident for everyone to see. Learn to notice the small changes that they want to see in their children. Celebrate all that can be celebrated by stating the obvious: “You wiped your face after eating. You are observant; you are noticing when you have something on your face.”
- State when a child is forgiving, helpful, or puts forward some effort. Label the growth witnessed. The child will learn that that is who they are over time (“observant”). Verbalizing these behaviors also will provide patients with a sense of mastery over parenting, because they are driving the emotional and behavioral development of their children in a way that also complements their family values.
- Make everyone in the family a contributor and foster a sense of gratitude: Give everyone a reason to claim that their collaboration and effort are a big part of the plan’s success. Take turns to lessen everyone’s burden and to thank them for their contributions. Older children can take on leadership roles, even in small ways. Younger children can practice being good listeners, following directions, and helping. Reverse the roles when possible.
Special needs families sometimes have to work harder than others to overcome obstacles, grow, and learn to support one another. Since the pandemic, many parents have been just as challenged. Mastering the above skills might provide a sense of fulfillment and agency, as well as an appreciation for the unexpected gifts that special children – and all children – have to offer.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist with a private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. She has no disclosures.
Most people can cope, to some degree, with the multiple weeks of social distancing and stressors related to the pandemic. But what if those stressors became a way of life for a year – or longer? What sorts of skills would be essential not only to survive but to have a renewed sense of resilience?
I know of one group that has had experiences that mirror the challenges faced by the parents of children: the parents of special needs children. As I argued previously, those parents have faced many of the challenges presented by COVID-19. Among those challenges are social distancing and difficulty accessing everyday common experiences. These parents know that they have to manage more areas of their children’s rearing than do their counterparts.
In addition to having to plan for how to deal with acute urgent or emergent medical situations involving their special needs children, these parents also must prepare for the long-term effects of managing children who require ongoing daily care, attention, and dedication.
These strategies can help the parents of special needs kids find a sense of mastery and comfort. The hope is that, after practicing them for long periods of time, the strategies become second nature.
Here are several strategies that might help patients with children during this pandemic:
- Take time to reset: Sometimes it is helpful for parents to take a minute away from a difficult impasse with their kids to reset and take their own “time out.” A few seconds of mental time away from the “scene” provides space and a mental reminder that the minute that just happened is finite, and that a whole new one is coming up next. The break provides a sense of hope. This cognitive reframing could be practiced often.
- Re-enter the challenging scene with a warm voice: Parents model for their children, but they also are telling their own brains that they, too, can calm down. This approach also de-escalates the situation and allows children to get used to hearing directions from someone who is in control – without hostility or irritability.
- Keep a sense of humor; it might come in handy: This is especially the case when tension is in the home, or when facing a set of challenging bad news. As an example, consider how some situations are so repetitive that they border on the ridiculous – such as a grown child having a tantrum at a store. Encourage the children to give themselves permission to cry first so they can laugh second, and then move on.
- Establish a routine for children that is self-reinforcing, and allows for together and separate times: They can, as an example: A) Get ready for the day all by themselves, or as much as they can do independently, before they come down and then B) have breakfast. Then, the child can C) do homework, and then D) go play outside. The routine would then continue on its own without outside reinforcers.
- Tell the children that they can get to the reinforcing activity only after completing the previous one. Over time, they learn to take pride in completing the first activity and doing so more independently. Not having to wait to be told what to do all the time fosters a sense of independence.
- Plan for meals and fun tasks together, and separate for individual work. This creates a sense of change and gives the day a certain flow. Establish routines that are predictable for the children that can be easily documented for the whole family on a calendar. Establish a beginning and an end time to the work day. Mark the end of the day with a chalk line establishing when the family can engage in a certain activity, for example, going for a family bike ride. Let the routine honor healthy circadian rhythms for sleep/wakeful times, and be consistent.
- Feed the brain and body the “good stuff”: Limit negative news, and surround the children with people who bring them joy or provide hope. Listen to inspirational messages and uplifting music. Give the children food that nourishes and energizes their bodies. Take in the view outside, the greenery, or the sky if there is no green around. Connect with family/friends who are far away.
- Make time to replenish with something that is meaningful/productive/helpful: Parents have very little time for themselves when they are “on,” so when they can actually take a little time to recharge, the activity should check many boxes. For example, encourage them to go for a walk (exercise) while listening to music (relax), make a phone call to someone who can relate to their situation (socialize), pray with someone (be spiritual), or sit in their rooms to get some alone quiet time (meditate). Reach out to those who are lonely. Network. Mentor. Volunteer.
- Develop an eye for noticing the positive: Instead of hoping for things to go back to the way they were, tell your patients to practice embracing without judgment the new norm. Get them to notice the time they spend with their families. Break all tasks into many smaller tasks, so there is more possibility of observing progress, and it is evident for everyone to see. Learn to notice the small changes that they want to see in their children. Celebrate all that can be celebrated by stating the obvious: “You wiped your face after eating. You are observant; you are noticing when you have something on your face.”
- State when a child is forgiving, helpful, or puts forward some effort. Label the growth witnessed. The child will learn that that is who they are over time (“observant”). Verbalizing these behaviors also will provide patients with a sense of mastery over parenting, because they are driving the emotional and behavioral development of their children in a way that also complements their family values.
- Make everyone in the family a contributor and foster a sense of gratitude: Give everyone a reason to claim that their collaboration and effort are a big part of the plan’s success. Take turns to lessen everyone’s burden and to thank them for their contributions. Older children can take on leadership roles, even in small ways. Younger children can practice being good listeners, following directions, and helping. Reverse the roles when possible.
Special needs families sometimes have to work harder than others to overcome obstacles, grow, and learn to support one another. Since the pandemic, many parents have been just as challenged. Mastering the above skills might provide a sense of fulfillment and agency, as well as an appreciation for the unexpected gifts that special children – and all children – have to offer.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist with a private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. She has no disclosures.
Most people can cope, to some degree, with the multiple weeks of social distancing and stressors related to the pandemic. But what if those stressors became a way of life for a year – or longer? What sorts of skills would be essential not only to survive but to have a renewed sense of resilience?
I know of one group that has had experiences that mirror the challenges faced by the parents of children: the parents of special needs children. As I argued previously, those parents have faced many of the challenges presented by COVID-19. Among those challenges are social distancing and difficulty accessing everyday common experiences. These parents know that they have to manage more areas of their children’s rearing than do their counterparts.
In addition to having to plan for how to deal with acute urgent or emergent medical situations involving their special needs children, these parents also must prepare for the long-term effects of managing children who require ongoing daily care, attention, and dedication.
These strategies can help the parents of special needs kids find a sense of mastery and comfort. The hope is that, after practicing them for long periods of time, the strategies become second nature.
Here are several strategies that might help patients with children during this pandemic:
- Take time to reset: Sometimes it is helpful for parents to take a minute away from a difficult impasse with their kids to reset and take their own “time out.” A few seconds of mental time away from the “scene” provides space and a mental reminder that the minute that just happened is finite, and that a whole new one is coming up next. The break provides a sense of hope. This cognitive reframing could be practiced often.
- Re-enter the challenging scene with a warm voice: Parents model for their children, but they also are telling their own brains that they, too, can calm down. This approach also de-escalates the situation and allows children to get used to hearing directions from someone who is in control – without hostility or irritability.
- Keep a sense of humor; it might come in handy: This is especially the case when tension is in the home, or when facing a set of challenging bad news. As an example, consider how some situations are so repetitive that they border on the ridiculous – such as a grown child having a tantrum at a store. Encourage the children to give themselves permission to cry first so they can laugh second, and then move on.
- Establish a routine for children that is self-reinforcing, and allows for together and separate times: They can, as an example: A) Get ready for the day all by themselves, or as much as they can do independently, before they come down and then B) have breakfast. Then, the child can C) do homework, and then D) go play outside. The routine would then continue on its own without outside reinforcers.
- Tell the children that they can get to the reinforcing activity only after completing the previous one. Over time, they learn to take pride in completing the first activity and doing so more independently. Not having to wait to be told what to do all the time fosters a sense of independence.
- Plan for meals and fun tasks together, and separate for individual work. This creates a sense of change and gives the day a certain flow. Establish routines that are predictable for the children that can be easily documented for the whole family on a calendar. Establish a beginning and an end time to the work day. Mark the end of the day with a chalk line establishing when the family can engage in a certain activity, for example, going for a family bike ride. Let the routine honor healthy circadian rhythms for sleep/wakeful times, and be consistent.
- Feed the brain and body the “good stuff”: Limit negative news, and surround the children with people who bring them joy or provide hope. Listen to inspirational messages and uplifting music. Give the children food that nourishes and energizes their bodies. Take in the view outside, the greenery, or the sky if there is no green around. Connect with family/friends who are far away.
- Make time to replenish with something that is meaningful/productive/helpful: Parents have very little time for themselves when they are “on,” so when they can actually take a little time to recharge, the activity should check many boxes. For example, encourage them to go for a walk (exercise) while listening to music (relax), make a phone call to someone who can relate to their situation (socialize), pray with someone (be spiritual), or sit in their rooms to get some alone quiet time (meditate). Reach out to those who are lonely. Network. Mentor. Volunteer.
- Develop an eye for noticing the positive: Instead of hoping for things to go back to the way they were, tell your patients to practice embracing without judgment the new norm. Get them to notice the time they spend with their families. Break all tasks into many smaller tasks, so there is more possibility of observing progress, and it is evident for everyone to see. Learn to notice the small changes that they want to see in their children. Celebrate all that can be celebrated by stating the obvious: “You wiped your face after eating. You are observant; you are noticing when you have something on your face.”
- State when a child is forgiving, helpful, or puts forward some effort. Label the growth witnessed. The child will learn that that is who they are over time (“observant”). Verbalizing these behaviors also will provide patients with a sense of mastery over parenting, because they are driving the emotional and behavioral development of their children in a way that also complements their family values.
- Make everyone in the family a contributor and foster a sense of gratitude: Give everyone a reason to claim that their collaboration and effort are a big part of the plan’s success. Take turns to lessen everyone’s burden and to thank them for their contributions. Older children can take on leadership roles, even in small ways. Younger children can practice being good listeners, following directions, and helping. Reverse the roles when possible.
Special needs families sometimes have to work harder than others to overcome obstacles, grow, and learn to support one another. Since the pandemic, many parents have been just as challenged. Mastering the above skills might provide a sense of fulfillment and agency, as well as an appreciation for the unexpected gifts that special children – and all children – have to offer.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist with a private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. She has no disclosures.
Lancet, NEJM retract studies on hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19
The Lancet announced today that it has retracted a highly cited study that suggested hydroxychloroquine may cause more harm than benefit in patients with COVID-19. Hours later, the New England Journal of Medicine announced that it had retracted a second article by some of the same authors, also on heart disease and COVID-19.
The Lancet article, titled “Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19: A multinational registry analysis” was originally published online May 22. The NEJM article, “Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19” was initially published May 1.
Three authors of the Lancet article, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Frank Ruschitzka, MD, and Amit N. Patel, MD, wrote in a letter that the action came after concerns were raised about the integrity of the data, and about how the analysis was conducted by Chicago-based Surgisphere Corp and study coauthor Sapan Desai, MD, Surgisphere’s founder and CEO.
The authors asked for an independent third-party review of Surgisphere to evaluate the integrity of the trial elements and to replicate the analyses in the article.
“Our independent peer reviewers informed us that Surgisphere would not transfer the full dataset, client contracts, and the full ISO audit report to their servers for analysis, as such transfer would violate client agreements and confidentiality requirements,” the authors wrote.
Therefore, reviewers were not able to conduct the review and notified the authors they would withdraw from the peer-review process.
The Lancet said in a statement: “The Lancet takes issues of scientific integrity extremely seriously, and there are many outstanding questions about Surgisphere and the data that were allegedly included in this study. Following guidelines from the Committee on Publication Ethics and International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, institutional reviews of Surgisphere’s research collaborations are urgently needed.”
The authors wrote, “We can never forget the responsibility we have as researchers to scrupulously ensure that we rely on data sources that adhere to our high standards. Based on this development, we can no longer vouch for the veracity of the primary data sources. Due to this unfortunate development, the authors request that the paper be retracted.
“We all entered this collaboration to contribute in good faith and at a time of great need during the COVID-19 pandemic. We deeply apologize to you, the editors, and the journal readership for any embarrassment or inconvenience that this may have caused.”
In a similar, if briefer, note, the authors requested that the New England Journal of Medicine retract the earlier article as well. The retraction notice on the website reads: “Because all the authors were not granted access to the raw data and the raw data could not be made available to a third-party auditor, we are unable to validate the primary data sources underlying our article, ‘Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19.’ We therefore request that the article be retracted. We apologize to the editors and to readers of the Journal for the difficulties that this has caused.”
Both journals had already published “Expression of Concern” notices about the articles. The expression of concern followed an open letter, endorsed by more than 200 scientists, ethicists, and clinicians and posted on May 28, questioning the data and ethics of the study.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Lancet announced today that it has retracted a highly cited study that suggested hydroxychloroquine may cause more harm than benefit in patients with COVID-19. Hours later, the New England Journal of Medicine announced that it had retracted a second article by some of the same authors, also on heart disease and COVID-19.
The Lancet article, titled “Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19: A multinational registry analysis” was originally published online May 22. The NEJM article, “Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19” was initially published May 1.
Three authors of the Lancet article, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Frank Ruschitzka, MD, and Amit N. Patel, MD, wrote in a letter that the action came after concerns were raised about the integrity of the data, and about how the analysis was conducted by Chicago-based Surgisphere Corp and study coauthor Sapan Desai, MD, Surgisphere’s founder and CEO.
The authors asked for an independent third-party review of Surgisphere to evaluate the integrity of the trial elements and to replicate the analyses in the article.
“Our independent peer reviewers informed us that Surgisphere would not transfer the full dataset, client contracts, and the full ISO audit report to their servers for analysis, as such transfer would violate client agreements and confidentiality requirements,” the authors wrote.
Therefore, reviewers were not able to conduct the review and notified the authors they would withdraw from the peer-review process.
The Lancet said in a statement: “The Lancet takes issues of scientific integrity extremely seriously, and there are many outstanding questions about Surgisphere and the data that were allegedly included in this study. Following guidelines from the Committee on Publication Ethics and International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, institutional reviews of Surgisphere’s research collaborations are urgently needed.”
The authors wrote, “We can never forget the responsibility we have as researchers to scrupulously ensure that we rely on data sources that adhere to our high standards. Based on this development, we can no longer vouch for the veracity of the primary data sources. Due to this unfortunate development, the authors request that the paper be retracted.
“We all entered this collaboration to contribute in good faith and at a time of great need during the COVID-19 pandemic. We deeply apologize to you, the editors, and the journal readership for any embarrassment or inconvenience that this may have caused.”
In a similar, if briefer, note, the authors requested that the New England Journal of Medicine retract the earlier article as well. The retraction notice on the website reads: “Because all the authors were not granted access to the raw data and the raw data could not be made available to a third-party auditor, we are unable to validate the primary data sources underlying our article, ‘Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19.’ We therefore request that the article be retracted. We apologize to the editors and to readers of the Journal for the difficulties that this has caused.”
Both journals had already published “Expression of Concern” notices about the articles. The expression of concern followed an open letter, endorsed by more than 200 scientists, ethicists, and clinicians and posted on May 28, questioning the data and ethics of the study.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Lancet announced today that it has retracted a highly cited study that suggested hydroxychloroquine may cause more harm than benefit in patients with COVID-19. Hours later, the New England Journal of Medicine announced that it had retracted a second article by some of the same authors, also on heart disease and COVID-19.
The Lancet article, titled “Hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine with or without a macrolide for treatment of COVID-19: A multinational registry analysis” was originally published online May 22. The NEJM article, “Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19” was initially published May 1.
Three authors of the Lancet article, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Frank Ruschitzka, MD, and Amit N. Patel, MD, wrote in a letter that the action came after concerns were raised about the integrity of the data, and about how the analysis was conducted by Chicago-based Surgisphere Corp and study coauthor Sapan Desai, MD, Surgisphere’s founder and CEO.
The authors asked for an independent third-party review of Surgisphere to evaluate the integrity of the trial elements and to replicate the analyses in the article.
“Our independent peer reviewers informed us that Surgisphere would not transfer the full dataset, client contracts, and the full ISO audit report to their servers for analysis, as such transfer would violate client agreements and confidentiality requirements,” the authors wrote.
Therefore, reviewers were not able to conduct the review and notified the authors they would withdraw from the peer-review process.
The Lancet said in a statement: “The Lancet takes issues of scientific integrity extremely seriously, and there are many outstanding questions about Surgisphere and the data that were allegedly included in this study. Following guidelines from the Committee on Publication Ethics and International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, institutional reviews of Surgisphere’s research collaborations are urgently needed.”
The authors wrote, “We can never forget the responsibility we have as researchers to scrupulously ensure that we rely on data sources that adhere to our high standards. Based on this development, we can no longer vouch for the veracity of the primary data sources. Due to this unfortunate development, the authors request that the paper be retracted.
“We all entered this collaboration to contribute in good faith and at a time of great need during the COVID-19 pandemic. We deeply apologize to you, the editors, and the journal readership for any embarrassment or inconvenience that this may have caused.”
In a similar, if briefer, note, the authors requested that the New England Journal of Medicine retract the earlier article as well. The retraction notice on the website reads: “Because all the authors were not granted access to the raw data and the raw data could not be made available to a third-party auditor, we are unable to validate the primary data sources underlying our article, ‘Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19.’ We therefore request that the article be retracted. We apologize to the editors and to readers of the Journal for the difficulties that this has caused.”
Both journals had already published “Expression of Concern” notices about the articles. The expression of concern followed an open letter, endorsed by more than 200 scientists, ethicists, and clinicians and posted on May 28, questioning the data and ethics of the study.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Should healthcare workers wear masks at home?
Wearing a mask at home, even when everyone is feeling fine, might reduce the risk of frontline healthcare workers transmitting SARS-CoV-2 infection to their families, a recent study from China suggests. But the benefits might not outweigh the costs, according to several physicians interviewed.
“My gut reaction is that home mask use for healthcare workers would place an inordinately high burden on those healthcare workers and their families,” said Jeanne Noble, MD, an emergency care physician at the University of California, San Francisco. “Wearing a mask for a 10-hour shift already represents significant physical discomfort, causing sores across the nose and behind the ears. The emotional toll of the physical distance that comes with mask use, with limited facial expression, is also quite real.”
The suggested benefit of home mask use comes from research published online May 28 in BMJ Global Health. To assess predictors of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Yu Wang, MD, of the Beijing Center for Disease Prevention and Control and colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 124 families in Beijing in which there was a confirmed case of COVID-19 as of February 21. The researchers surveyed family members by telephone about household hygiene and behaviors during the pandemic to examine risk factors for transmission.
During the 2 weeks following onset of the primary case, secondary transmission occurred in 41 families. Overall, 77 of 335 family members developed COVID-19.
A multivariable logistic regression analysis found that in households in which family members wore masks at home before the first person became ill, there was less likelihood of transmission of disease to a family member, compared with families in which no one wore a mask prior to illness onset.
“Facemasks were 79% effective and disinfection was 77% effective in preventing transmission,” the researchers report, “whilst close frequent contact in the household increased the risk of transmission 18 times, and diarrhea in the index patient increased the risk by four times.
However, wearing masks after symptom onset was not protective, according to the analysis. The findings support “universal face mask use, and also provides guidance on risk reduction for families living with someone in quarantine or isolation, and families of health workers, who may face ongoing risk,” the authors write.
Still, other precautions may be more important, experts say.
“I think by far the best way for healthcare professionals to protect their families is to carefully employ appropriate infection prevention measures at work,” said Mark E. Rupp, MD, chief of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha. “The combination of administrative interventions, engineering improvements, and personal protective equipment is very effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 acquisition in the workplace.”
Many physicians already wear masks at home, and this study “only reemphasized the importance of doing so,” said Raghavendra Tirupathi, MD, medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, who recently reviewed studies about masks and COVID-19.
Home mask use provides “one more layer of protection that might help mitigate the risk of transmission to family members,” Tirupathi said. But it does not obviate the need to follow other preventive measures, such as social distancing and proper hygiene.
But Rupp, whose advice on how healthcare workers can protect their families was recently highlighted by the American Medical Association, isn’t convinced. He said he won’t be adding home mask use to his list of recommendations. “It would be intrusive, cumbersome, and impractical to wear a mask in the home setting,” Rupp said in an interview.
However, when out in the community, all family members must protect one another by practicing social distancing, wearing masks, and practicing proper hand hygiene. “I also think that it is a good idea to have some masks on hand in case anyone does develop symptoms in the household and to wear them if a family member falls ill ― at least until testing can confirm COVID-19,” Rupp said. “If a family member does fall ill, masks for the ill person as well as the well persons would be indicated along with other home quarantine measures.”
For her part, Noble, who has provided guidance about proper mask use, said that targeted use of masks at home, such as around older visiting relatives or other more vulnerable family members, may be more realistic than continuous in-home use.
When a household member becomes ill, recommendations for preventing disease spread include having a sick family member sleep in a separate bedroom, using a separate bathroom, and wearing a mask when within 6 feet of other household members. They also should avoid sharing meals. “For a household member who is a medical provider, to follow these self-isolation precautions while at home for months on end would have a significant emotional toll,” Noble said in an email. “With no end in sight for the pandemic, perpetual mask use in both the private and public sphere strikes me as overwhelming ― I write this near the end of my 10-hour shift wearing both an N95 and surgical mask and counting the minutes before I can take them off!”
A limitation of the study was its reliance on telephone interviews, which are subject to recall bias, the authors note.
The study was funded by the Beijing Science and Technology Planning Project. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Wearing a mask at home, even when everyone is feeling fine, might reduce the risk of frontline healthcare workers transmitting SARS-CoV-2 infection to their families, a recent study from China suggests. But the benefits might not outweigh the costs, according to several physicians interviewed.
“My gut reaction is that home mask use for healthcare workers would place an inordinately high burden on those healthcare workers and their families,” said Jeanne Noble, MD, an emergency care physician at the University of California, San Francisco. “Wearing a mask for a 10-hour shift already represents significant physical discomfort, causing sores across the nose and behind the ears. The emotional toll of the physical distance that comes with mask use, with limited facial expression, is also quite real.”
The suggested benefit of home mask use comes from research published online May 28 in BMJ Global Health. To assess predictors of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Yu Wang, MD, of the Beijing Center for Disease Prevention and Control and colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 124 families in Beijing in which there was a confirmed case of COVID-19 as of February 21. The researchers surveyed family members by telephone about household hygiene and behaviors during the pandemic to examine risk factors for transmission.
During the 2 weeks following onset of the primary case, secondary transmission occurred in 41 families. Overall, 77 of 335 family members developed COVID-19.
A multivariable logistic regression analysis found that in households in which family members wore masks at home before the first person became ill, there was less likelihood of transmission of disease to a family member, compared with families in which no one wore a mask prior to illness onset.
“Facemasks were 79% effective and disinfection was 77% effective in preventing transmission,” the researchers report, “whilst close frequent contact in the household increased the risk of transmission 18 times, and diarrhea in the index patient increased the risk by four times.
However, wearing masks after symptom onset was not protective, according to the analysis. The findings support “universal face mask use, and also provides guidance on risk reduction for families living with someone in quarantine or isolation, and families of health workers, who may face ongoing risk,” the authors write.
Still, other precautions may be more important, experts say.
“I think by far the best way for healthcare professionals to protect their families is to carefully employ appropriate infection prevention measures at work,” said Mark E. Rupp, MD, chief of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha. “The combination of administrative interventions, engineering improvements, and personal protective equipment is very effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 acquisition in the workplace.”
Many physicians already wear masks at home, and this study “only reemphasized the importance of doing so,” said Raghavendra Tirupathi, MD, medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, who recently reviewed studies about masks and COVID-19.
Home mask use provides “one more layer of protection that might help mitigate the risk of transmission to family members,” Tirupathi said. But it does not obviate the need to follow other preventive measures, such as social distancing and proper hygiene.
But Rupp, whose advice on how healthcare workers can protect their families was recently highlighted by the American Medical Association, isn’t convinced. He said he won’t be adding home mask use to his list of recommendations. “It would be intrusive, cumbersome, and impractical to wear a mask in the home setting,” Rupp said in an interview.
However, when out in the community, all family members must protect one another by practicing social distancing, wearing masks, and practicing proper hand hygiene. “I also think that it is a good idea to have some masks on hand in case anyone does develop symptoms in the household and to wear them if a family member falls ill ― at least until testing can confirm COVID-19,” Rupp said. “If a family member does fall ill, masks for the ill person as well as the well persons would be indicated along with other home quarantine measures.”
For her part, Noble, who has provided guidance about proper mask use, said that targeted use of masks at home, such as around older visiting relatives or other more vulnerable family members, may be more realistic than continuous in-home use.
When a household member becomes ill, recommendations for preventing disease spread include having a sick family member sleep in a separate bedroom, using a separate bathroom, and wearing a mask when within 6 feet of other household members. They also should avoid sharing meals. “For a household member who is a medical provider, to follow these self-isolation precautions while at home for months on end would have a significant emotional toll,” Noble said in an email. “With no end in sight for the pandemic, perpetual mask use in both the private and public sphere strikes me as overwhelming ― I write this near the end of my 10-hour shift wearing both an N95 and surgical mask and counting the minutes before I can take them off!”
A limitation of the study was its reliance on telephone interviews, which are subject to recall bias, the authors note.
The study was funded by the Beijing Science and Technology Planning Project. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Wearing a mask at home, even when everyone is feeling fine, might reduce the risk of frontline healthcare workers transmitting SARS-CoV-2 infection to their families, a recent study from China suggests. But the benefits might not outweigh the costs, according to several physicians interviewed.
“My gut reaction is that home mask use for healthcare workers would place an inordinately high burden on those healthcare workers and their families,” said Jeanne Noble, MD, an emergency care physician at the University of California, San Francisco. “Wearing a mask for a 10-hour shift already represents significant physical discomfort, causing sores across the nose and behind the ears. The emotional toll of the physical distance that comes with mask use, with limited facial expression, is also quite real.”
The suggested benefit of home mask use comes from research published online May 28 in BMJ Global Health. To assess predictors of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Yu Wang, MD, of the Beijing Center for Disease Prevention and Control and colleagues conducted a retrospective study of 124 families in Beijing in which there was a confirmed case of COVID-19 as of February 21. The researchers surveyed family members by telephone about household hygiene and behaviors during the pandemic to examine risk factors for transmission.
During the 2 weeks following onset of the primary case, secondary transmission occurred in 41 families. Overall, 77 of 335 family members developed COVID-19.
A multivariable logistic regression analysis found that in households in which family members wore masks at home before the first person became ill, there was less likelihood of transmission of disease to a family member, compared with families in which no one wore a mask prior to illness onset.
“Facemasks were 79% effective and disinfection was 77% effective in preventing transmission,” the researchers report, “whilst close frequent contact in the household increased the risk of transmission 18 times, and diarrhea in the index patient increased the risk by four times.
However, wearing masks after symptom onset was not protective, according to the analysis. The findings support “universal face mask use, and also provides guidance on risk reduction for families living with someone in quarantine or isolation, and families of health workers, who may face ongoing risk,” the authors write.
Still, other precautions may be more important, experts say.
“I think by far the best way for healthcare professionals to protect their families is to carefully employ appropriate infection prevention measures at work,” said Mark E. Rupp, MD, chief of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha. “The combination of administrative interventions, engineering improvements, and personal protective equipment is very effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 acquisition in the workplace.”
Many physicians already wear masks at home, and this study “only reemphasized the importance of doing so,” said Raghavendra Tirupathi, MD, medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, who recently reviewed studies about masks and COVID-19.
Home mask use provides “one more layer of protection that might help mitigate the risk of transmission to family members,” Tirupathi said. But it does not obviate the need to follow other preventive measures, such as social distancing and proper hygiene.
But Rupp, whose advice on how healthcare workers can protect their families was recently highlighted by the American Medical Association, isn’t convinced. He said he won’t be adding home mask use to his list of recommendations. “It would be intrusive, cumbersome, and impractical to wear a mask in the home setting,” Rupp said in an interview.
However, when out in the community, all family members must protect one another by practicing social distancing, wearing masks, and practicing proper hand hygiene. “I also think that it is a good idea to have some masks on hand in case anyone does develop symptoms in the household and to wear them if a family member falls ill ― at least until testing can confirm COVID-19,” Rupp said. “If a family member does fall ill, masks for the ill person as well as the well persons would be indicated along with other home quarantine measures.”
For her part, Noble, who has provided guidance about proper mask use, said that targeted use of masks at home, such as around older visiting relatives or other more vulnerable family members, may be more realistic than continuous in-home use.
When a household member becomes ill, recommendations for preventing disease spread include having a sick family member sleep in a separate bedroom, using a separate bathroom, and wearing a mask when within 6 feet of other household members. They also should avoid sharing meals. “For a household member who is a medical provider, to follow these self-isolation precautions while at home for months on end would have a significant emotional toll,” Noble said in an email. “With no end in sight for the pandemic, perpetual mask use in both the private and public sphere strikes me as overwhelming ― I write this near the end of my 10-hour shift wearing both an N95 and surgical mask and counting the minutes before I can take them off!”
A limitation of the study was its reliance on telephone interviews, which are subject to recall bias, the authors note.
The study was funded by the Beijing Science and Technology Planning Project. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today’s Top News Highlights: COVID-19 -- Heart transplant patients face greater mortality, rheumatology drugs look safe
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
More fatalities in heart transplant patients with COVID-19
COVID-19 infection appears to be associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant recipients. The conclusion is based on a case series with 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a heart transplant during March and April 2020. There was a case-fatality rate of 25%, according to the study published in JAMA Cardiology. “The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview. “These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection.” Read more.
High costs for type 1 diabetes patients: It’s not just insulin
For privately insured individuals with type 1 diabetes in the United States, out-of-pocket costs for insulin are typically lower than for other diabetes-related supplies. But overall out-of-pocket costs – taking into account everything that is needed to manage diabetes – are still very high. Two separate research letters recently published in JAMA Internal Medicine examined some of the drivers behind these high costs. The first research letter examined all costs for privately insured patients with type 1 diabetes, finding a mean out-of-pocket spend of approximately $2,500 a year. “Policymakers should improve the affordability of all care for type 1 diabetes,” said the lead author of the first research letter, Kao-Ping Chua, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatrics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Read more.
Most rheumatology drugs don’t up COVID-19 hospitalizations
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests. Researchers looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. Treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily – considered a moderate to high dose – was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization, however. “These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.” Read more.
A bumpy virtual #ASCO20
Some prominent oncologists gave up on the virtual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology after facing technical problems with online sessions. Despite those glitches, dozens of virtual meeting attendees praised the online effort, which was assembled in just a few months, and called out virtues such as the quick availability of video transcripts as well as the obvious benefits of low cost, zero travel, and overall convenience. But one sentiment was nearly universal: there’s nothing like the real thing. This year’s meeting, which involved 40,000-plus attendees, was shortened to 3 days and limited to scientific presentations because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Education sessions will be held online August 8-10. Read more.
Parenting special needs children: An unlikely model
As families adjust to daily life during a pandemic, the parents of special needs children may be able to offer them some lessons. The chronic struggles of many special needs parents – from staying home often to taking on roles in which they have not been trained – strongly resemble the challenges facing most families in the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Migdalia Miranda Sotir, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. “Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time,” she writes on MDedge. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
More fatalities in heart transplant patients with COVID-19
COVID-19 infection appears to be associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant recipients. The conclusion is based on a case series with 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a heart transplant during March and April 2020. There was a case-fatality rate of 25%, according to the study published in JAMA Cardiology. “The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview. “These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection.” Read more.
High costs for type 1 diabetes patients: It’s not just insulin
For privately insured individuals with type 1 diabetes in the United States, out-of-pocket costs for insulin are typically lower than for other diabetes-related supplies. But overall out-of-pocket costs – taking into account everything that is needed to manage diabetes – are still very high. Two separate research letters recently published in JAMA Internal Medicine examined some of the drivers behind these high costs. The first research letter examined all costs for privately insured patients with type 1 diabetes, finding a mean out-of-pocket spend of approximately $2,500 a year. “Policymakers should improve the affordability of all care for type 1 diabetes,” said the lead author of the first research letter, Kao-Ping Chua, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatrics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Read more.
Most rheumatology drugs don’t up COVID-19 hospitalizations
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests. Researchers looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. Treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily – considered a moderate to high dose – was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization, however. “These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.” Read more.
A bumpy virtual #ASCO20
Some prominent oncologists gave up on the virtual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology after facing technical problems with online sessions. Despite those glitches, dozens of virtual meeting attendees praised the online effort, which was assembled in just a few months, and called out virtues such as the quick availability of video transcripts as well as the obvious benefits of low cost, zero travel, and overall convenience. But one sentiment was nearly universal: there’s nothing like the real thing. This year’s meeting, which involved 40,000-plus attendees, was shortened to 3 days and limited to scientific presentations because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Education sessions will be held online August 8-10. Read more.
Parenting special needs children: An unlikely model
As families adjust to daily life during a pandemic, the parents of special needs children may be able to offer them some lessons. The chronic struggles of many special needs parents – from staying home often to taking on roles in which they have not been trained – strongly resemble the challenges facing most families in the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Migdalia Miranda Sotir, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. “Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time,” she writes on MDedge. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
More fatalities in heart transplant patients with COVID-19
COVID-19 infection appears to be associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant recipients. The conclusion is based on a case series with 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a heart transplant during March and April 2020. There was a case-fatality rate of 25%, according to the study published in JAMA Cardiology. “The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview. “These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection.” Read more.
High costs for type 1 diabetes patients: It’s not just insulin
For privately insured individuals with type 1 diabetes in the United States, out-of-pocket costs for insulin are typically lower than for other diabetes-related supplies. But overall out-of-pocket costs – taking into account everything that is needed to manage diabetes – are still very high. Two separate research letters recently published in JAMA Internal Medicine examined some of the drivers behind these high costs. The first research letter examined all costs for privately insured patients with type 1 diabetes, finding a mean out-of-pocket spend of approximately $2,500 a year. “Policymakers should improve the affordability of all care for type 1 diabetes,” said the lead author of the first research letter, Kao-Ping Chua, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatrics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Read more.
Most rheumatology drugs don’t up COVID-19 hospitalizations
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests. Researchers looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. Treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily – considered a moderate to high dose – was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization, however. “These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.” Read more.
A bumpy virtual #ASCO20
Some prominent oncologists gave up on the virtual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology after facing technical problems with online sessions. Despite those glitches, dozens of virtual meeting attendees praised the online effort, which was assembled in just a few months, and called out virtues such as the quick availability of video transcripts as well as the obvious benefits of low cost, zero travel, and overall convenience. But one sentiment was nearly universal: there’s nothing like the real thing. This year’s meeting, which involved 40,000-plus attendees, was shortened to 3 days and limited to scientific presentations because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Education sessions will be held online August 8-10. Read more.
Parenting special needs children: An unlikely model
As families adjust to daily life during a pandemic, the parents of special needs children may be able to offer them some lessons. The chronic struggles of many special needs parents – from staying home often to taking on roles in which they have not been trained – strongly resemble the challenges facing most families in the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Migdalia Miranda Sotir, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. “Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time,” she writes on MDedge. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Most rheumatology drugs don’t increase COVID-19 hospitalization risk
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Parenting special needs children: An unlikely model
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
More fatalities in heart transplant patients with COVID-19
COVID-19 infection is associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant (HT) recipients, a new case series suggests.
Investigators looked at data on 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a HT between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020 and found a case-fatality rate of 25%.
“The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, MSc, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection,” said Dr. Uriel, who is also a cardiologist at New York Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
The study was published online May 13 in JAMA Cardiology.
Similar presentation
HT recipients can have several comorbidities after the procedure, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiac allograft vasculopathy, and ongoing immunosuppression, all of which can place them at risk for infection and adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection, the authors wrote.
The researchers therefore embarked on a case series looking at 28 HT recipients with COVID-19 infection (median age, 64.0 years; interquartile range, 53.5-70.5; 79% male) to “describe the outcomes of recipients of HT who are chronically immunosuppressed and develop COVID-19 and raise important questions about the role of the immune system in the process.”
The median time from HT to study period was 8.6 (IQR, 4.2-14.5) years. Most patients had numerous comorbidities.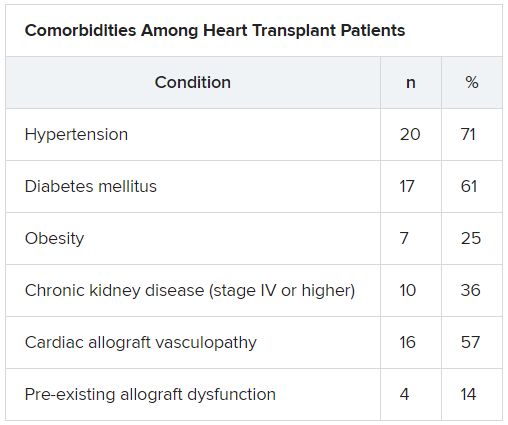
“The presentation of COVID-19 was similar to nontransplant patients with fever, dyspnea, cough, and GI symptoms,” Dr. Uriel reported.
No protective effect
Twenty-two patients (79%) required admission to the hospital, seven of whom (25%) required admission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation.
Despite the presence of immunosuppressive therapy, all patients had significant elevation of inflammatory biomarkers (median peak high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], 11.83 mg/dL; IQR, 7.44-19.26; median peak interleukin [IL]-6, 105 pg/mL; IQR, 38-296).
Three-quarters had myocardial injury, with a median high-sensitivity troponin T of 0.055 (0.0205 - 0.1345) ng/mL.
Treatments of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (18 patients; 78%), high-dose corticosteroids (eight patients; 47%), and IL-6 receptor antagonists (six patients; 26%).
Moreover, during hospitalization, mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in most (70%) patients, and one-quarter had a reduction in their calcineurin inhibitor dose.
“Heart transplant recipients generally require more intense immunosuppressive therapy than most other solid organ transplant recipients, and this high baseline immunosuppression increases their propensity to develop infections and their likelihood of experiencing severe manifestations of infections,” Dr. Uriel commented.
“With COVID-19, in which the body’s inflammatory reaction appears to play a role in disease severity, there has been a question of whether immunosuppression may offer a protective effect,” he continued.
“This case series suggests that this is not the case, although this would need to be confirmed in larger studies,” he said.
Low threshold
Among the 22 patients who were admitted to the hospital, half were discharged home and four (18%) were still hospitalized at the end of the study.
Of the seven patients who died, two died at the study center, and five died in an outside institution.
“In the HT population, social distancing (or isolation), strict use of masks when in public, proper handwashing, and sanitization of surfaces are of paramount importance in the prevention of COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Uriel stated.
“In addition, we have restricted these patients’ contact with the hospital as much as possible during the pandemic,” he said.
However, “there should be a low threshold to hospitalize heart transplant patients who develop infection with COVID-19. Furthermore, in our series, outcomes were better for patients hospitalized at the transplant center; therefore, strong consideration should be given to transferring HT patients when hospitalized at another hospital,” he added.
The authors emphasized that COVID-19 patients “will require ongoing monitoring in the recovery phase, as an immunosuppression regimen is reintroduced and the consequences to the allograft itself become apparent.”
Vulnerable population
Commenting on the study, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, MSc, William Harvey Distinguished Chair in Advanced Cardiovascular Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, suggested that “in epidemiological terms, [the findings] might not look as bad as the way they are reflected in the paper.”
Given that Columbia is “one of the larger heart transplant centers in the U.S., following probably 1,000 patients, having only 22 out of perhaps thousands whom they transplanted or are actively following would actually represent a low serious infection rate,” said Dr. Mehra, who is also the executive director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“We must not forget to emphasize that, when assessing these case fatality rates, we must look at the entire population at risk, not only the handful that we were able to observe,” explained Dr. Mehra, who was not involved with the study.
Moreover, the patients were “older and had comorbidities, with poor underlying kidney function and other complications, and underlying coronary artery disease in the transplanted heart,” so “it would not surprise me that they had such a high fatality rate, since they had a high degree of vulnerability,” he said.
Dr. Mehra, who is also the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, said that the journal has received manuscripts still in the review process that suggest different fatality rates than those found in the current case series.
However, he acknowledged that, because these are patients with serious vulnerability due to underlying heart disease, “you can’t be lackadaisical and need to do everything to decrease this vulnerability.”
The authors noted that, although their study did not show a protective effect from immunosuppression against COVID-19, further studies are needed to assess each individual immunosuppressive agent and provide a definitive answer.
The study was supported by a grant to one of the investigators from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Uriel reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the publication. Dr. Mehra reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 infection is associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant (HT) recipients, a new case series suggests.
Investigators looked at data on 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a HT between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020 and found a case-fatality rate of 25%.
“The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, MSc, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection,” said Dr. Uriel, who is also a cardiologist at New York Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
The study was published online May 13 in JAMA Cardiology.
Similar presentation
HT recipients can have several comorbidities after the procedure, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiac allograft vasculopathy, and ongoing immunosuppression, all of which can place them at risk for infection and adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection, the authors wrote.
The researchers therefore embarked on a case series looking at 28 HT recipients with COVID-19 infection (median age, 64.0 years; interquartile range, 53.5-70.5; 79% male) to “describe the outcomes of recipients of HT who are chronically immunosuppressed and develop COVID-19 and raise important questions about the role of the immune system in the process.”
The median time from HT to study period was 8.6 (IQR, 4.2-14.5) years. Most patients had numerous comorbidities.
“The presentation of COVID-19 was similar to nontransplant patients with fever, dyspnea, cough, and GI symptoms,” Dr. Uriel reported.
No protective effect
Twenty-two patients (79%) required admission to the hospital, seven of whom (25%) required admission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation.
Despite the presence of immunosuppressive therapy, all patients had significant elevation of inflammatory biomarkers (median peak high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], 11.83 mg/dL; IQR, 7.44-19.26; median peak interleukin [IL]-6, 105 pg/mL; IQR, 38-296).
Three-quarters had myocardial injury, with a median high-sensitivity troponin T of 0.055 (0.0205 - 0.1345) ng/mL.
Treatments of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (18 patients; 78%), high-dose corticosteroids (eight patients; 47%), and IL-6 receptor antagonists (six patients; 26%).
Moreover, during hospitalization, mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in most (70%) patients, and one-quarter had a reduction in their calcineurin inhibitor dose.
“Heart transplant recipients generally require more intense immunosuppressive therapy than most other solid organ transplant recipients, and this high baseline immunosuppression increases their propensity to develop infections and their likelihood of experiencing severe manifestations of infections,” Dr. Uriel commented.
“With COVID-19, in which the body’s inflammatory reaction appears to play a role in disease severity, there has been a question of whether immunosuppression may offer a protective effect,” he continued.
“This case series suggests that this is not the case, although this would need to be confirmed in larger studies,” he said.
Low threshold
Among the 22 patients who were admitted to the hospital, half were discharged home and four (18%) were still hospitalized at the end of the study.
Of the seven patients who died, two died at the study center, and five died in an outside institution.
“In the HT population, social distancing (or isolation), strict use of masks when in public, proper handwashing, and sanitization of surfaces are of paramount importance in the prevention of COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Uriel stated.
“In addition, we have restricted these patients’ contact with the hospital as much as possible during the pandemic,” he said.
However, “there should be a low threshold to hospitalize heart transplant patients who develop infection with COVID-19. Furthermore, in our series, outcomes were better for patients hospitalized at the transplant center; therefore, strong consideration should be given to transferring HT patients when hospitalized at another hospital,” he added.
The authors emphasized that COVID-19 patients “will require ongoing monitoring in the recovery phase, as an immunosuppression regimen is reintroduced and the consequences to the allograft itself become apparent.”
Vulnerable population
Commenting on the study, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, MSc, William Harvey Distinguished Chair in Advanced Cardiovascular Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, suggested that “in epidemiological terms, [the findings] might not look as bad as the way they are reflected in the paper.”
Given that Columbia is “one of the larger heart transplant centers in the U.S., following probably 1,000 patients, having only 22 out of perhaps thousands whom they transplanted or are actively following would actually represent a low serious infection rate,” said Dr. Mehra, who is also the executive director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“We must not forget to emphasize that, when assessing these case fatality rates, we must look at the entire population at risk, not only the handful that we were able to observe,” explained Dr. Mehra, who was not involved with the study.
Moreover, the patients were “older and had comorbidities, with poor underlying kidney function and other complications, and underlying coronary artery disease in the transplanted heart,” so “it would not surprise me that they had such a high fatality rate, since they had a high degree of vulnerability,” he said.
Dr. Mehra, who is also the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, said that the journal has received manuscripts still in the review process that suggest different fatality rates than those found in the current case series.
However, he acknowledged that, because these are patients with serious vulnerability due to underlying heart disease, “you can’t be lackadaisical and need to do everything to decrease this vulnerability.”
The authors noted that, although their study did not show a protective effect from immunosuppression against COVID-19, further studies are needed to assess each individual immunosuppressive agent and provide a definitive answer.
The study was supported by a grant to one of the investigators from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Uriel reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the publication. Dr. Mehra reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 infection is associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant (HT) recipients, a new case series suggests.
Investigators looked at data on 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a HT between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020 and found a case-fatality rate of 25%.
“The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, MSc, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection,” said Dr. Uriel, who is also a cardiologist at New York Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
The study was published online May 13 in JAMA Cardiology.
Similar presentation
HT recipients can have several comorbidities after the procedure, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiac allograft vasculopathy, and ongoing immunosuppression, all of which can place them at risk for infection and adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection, the authors wrote.
The researchers therefore embarked on a case series looking at 28 HT recipients with COVID-19 infection (median age, 64.0 years; interquartile range, 53.5-70.5; 79% male) to “describe the outcomes of recipients of HT who are chronically immunosuppressed and develop COVID-19 and raise important questions about the role of the immune system in the process.”
The median time from HT to study period was 8.6 (IQR, 4.2-14.5) years. Most patients had numerous comorbidities.
“The presentation of COVID-19 was similar to nontransplant patients with fever, dyspnea, cough, and GI symptoms,” Dr. Uriel reported.
No protective effect
Twenty-two patients (79%) required admission to the hospital, seven of whom (25%) required admission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation.
Despite the presence of immunosuppressive therapy, all patients had significant elevation of inflammatory biomarkers (median peak high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], 11.83 mg/dL; IQR, 7.44-19.26; median peak interleukin [IL]-6, 105 pg/mL; IQR, 38-296).
Three-quarters had myocardial injury, with a median high-sensitivity troponin T of 0.055 (0.0205 - 0.1345) ng/mL.
Treatments of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (18 patients; 78%), high-dose corticosteroids (eight patients; 47%), and IL-6 receptor antagonists (six patients; 26%).
Moreover, during hospitalization, mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in most (70%) patients, and one-quarter had a reduction in their calcineurin inhibitor dose.
“Heart transplant recipients generally require more intense immunosuppressive therapy than most other solid organ transplant recipients, and this high baseline immunosuppression increases their propensity to develop infections and their likelihood of experiencing severe manifestations of infections,” Dr. Uriel commented.
“With COVID-19, in which the body’s inflammatory reaction appears to play a role in disease severity, there has been a question of whether immunosuppression may offer a protective effect,” he continued.
“This case series suggests that this is not the case, although this would need to be confirmed in larger studies,” he said.
Low threshold
Among the 22 patients who were admitted to the hospital, half were discharged home and four (18%) were still hospitalized at the end of the study.
Of the seven patients who died, two died at the study center, and five died in an outside institution.
“In the HT population, social distancing (or isolation), strict use of masks when in public, proper handwashing, and sanitization of surfaces are of paramount importance in the prevention of COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Uriel stated.
“In addition, we have restricted these patients’ contact with the hospital as much as possible during the pandemic,” he said.
However, “there should be a low threshold to hospitalize heart transplant patients who develop infection with COVID-19. Furthermore, in our series, outcomes were better for patients hospitalized at the transplant center; therefore, strong consideration should be given to transferring HT patients when hospitalized at another hospital,” he added.
The authors emphasized that COVID-19 patients “will require ongoing monitoring in the recovery phase, as an immunosuppression regimen is reintroduced and the consequences to the allograft itself become apparent.”
Vulnerable population
Commenting on the study, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, MSc, William Harvey Distinguished Chair in Advanced Cardiovascular Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, suggested that “in epidemiological terms, [the findings] might not look as bad as the way they are reflected in the paper.”
Given that Columbia is “one of the larger heart transplant centers in the U.S., following probably 1,000 patients, having only 22 out of perhaps thousands whom they transplanted or are actively following would actually represent a low serious infection rate,” said Dr. Mehra, who is also the executive director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“We must not forget to emphasize that, when assessing these case fatality rates, we must look at the entire population at risk, not only the handful that we were able to observe,” explained Dr. Mehra, who was not involved with the study.
Moreover, the patients were “older and had comorbidities, with poor underlying kidney function and other complications, and underlying coronary artery disease in the transplanted heart,” so “it would not surprise me that they had such a high fatality rate, since they had a high degree of vulnerability,” he said.
Dr. Mehra, who is also the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, said that the journal has received manuscripts still in the review process that suggest different fatality rates than those found in the current case series.
However, he acknowledged that, because these are patients with serious vulnerability due to underlying heart disease, “you can’t be lackadaisical and need to do everything to decrease this vulnerability.”
The authors noted that, although their study did not show a protective effect from immunosuppression against COVID-19, further studies are needed to assess each individual immunosuppressive agent and provide a definitive answer.
The study was supported by a grant to one of the investigators from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Uriel reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the publication. Dr. Mehra reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Sex-based disparities in liver allocation driven by organ size mismatch, MELD score
Addressing local supply constraints may be insufficient to improve poorer outcomes among women who need a liver transplant, based on a large retrospective analysis.
Sex-based disparities in liver allocation were more strongly associated with liver size mismatch and MELD (Model for End-stage Liver Disease) score than geographic factors, reported lead author Jayme E. Locke, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues.
“Currently, the transplant community is considering geographic redistribution ... to redefine local organ supply by replacing donor service areas with fixed concentric circles around donor hospitals,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Surgery. “However, newly proposed geographic models rely on the same metric for medical urgency, the MELD score, and offer no solution for candidates with small body stature who may appear at the top of the match run yet are routinely skipped secondary to discrepancies in donor-recipient size.”
To further investigate the driving forces behind sex-based disparities, the investigators conducted the first national study of its kind, involving 81,357 adults who were wait-listed for liver transplant. Primary outcomes included deceased donor liver transplant and wait list mortality. Using multivariate regression models and inverse odds ratio weighting, the investigators determined proportions of disparity shared across MELD score, candidate anthropometric and liver measurements, and geographic location.
Compared with men, women were 14.4% less likely to receive a transplant, and 8.6% more likely to die on the wait list.
The only geographic factor significantly associated with the increased disparity between female sex and wait list mortality was organ procurement organization, which was associated with a 22% increase. The disparity between rates of transplant receipt was not linked with any geographic factors.
In contrast, MELD score accounted for increases in disparity of 10.3% and 50.1% for organ receipt and wait list mortality, respectively. Candidate anthropometric and liver measurements played an even greater role, raising disparity by 49.0% for organ receipt and 125.8% for wait list mortality.
“Size mismatch between the donor and intended recipient and incorrect assessments of liver disease severity were more strongly associated with the observed sex disparity in wait list mortality than local supply of organs,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Locke and colleagues noted that ongoing debates about geographic disparity hinge upon the assumption that the MELD score accurately measures disease severity, despite known shortcomings, including reliance upon serum creatinine level, which is influenced by muscle mass and therefore overestimates kidney function in women, and sex-based differences in size, which the MELD score does not incorporate whatsoever.
As such, the investigators suggested that addressing issues with the MELD score and organ size mismatch should be part of a more comprehensive approach to fixing sex-based disparities among candidates for liver transplant.
“Although geographic factors matter, examining geographic access alone may be insufficient,” they concluded.
James F. Markmann, MD, PhD, chief of the division of transplantation at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who has previously published research in support of geographic redistribution, said in an interview that the study by Dr. Locke and colleagues “highlights a well-known problem in the liver transplant field.”
“The cause of this disparity is nicely illustrated by Dr. Locke’s work, which shows multiple contributing factors,” Dr. Markmann said.
While Dr. Markmann agreed with Dr. Locke and colleagues’ proposal that estimated glomerular filtration rate, instead of creatinine, could be used to more accurately measure renal function across sexes, he suggested that the disparities uncovered by their analysis are more likely driven by body size than sex.
“A more impactful factor and one obvious to those performing transplants is that on average the smaller body habitus of females makes more organs unsuitable due to size mismatch,” Dr. Markmann said. “In general, it is technically much less of a barrier to put a small liver into a large patient, than a large liver in a small patient. But, the same disparity in access almost certainly applies to small males; unfortunately, the authors did not examine this point. If allocation changes are envisioned to gain greater fairness in organ access, at least for the recipient size issue, it should be a size issue and not a sex issue.”
Dr. Markmann went on to explain that steps are currently being taken to make liver access more equitable.
“As of February 4th of this year, a broader sharing program for deceased donor livers was implemented,” he said. “This will make more organs available to those in greatest need. It will also potentially increase the number of liver offers to sick patients with a small body habitus and will hopefully reduce the excess morbidity and mortality they suffer.”
According to Willscott E. Naugler, MD and Susan L. Orloff, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, novel clinical strategies need to be reinforced with a broader mindset in order to close the gap between men and women.
“A change in the MELD score is unlikely to fix this problem,” they wrote in an accompanying JAMA Surgery editorial, “but it is not hard to think of solutions; one could imagine, for example, allowing women of small stature to access pediatric livers while ramping up liver splits to increase contributions to the pediatric pool.”
Dr. Naugler and Dr. Orloff went on to suggest that barriers to equity may be culturally insidious.
“It is likely that the same unconscious biases that lead us to pay women surgeons less account for the lack of will to make these simple changes,” they wrote. “Not mentioned are multiple sociocultural elements that favor men over women in organ transplant. ... These realities cannot be fixed with changes to the MELD score, and we must be mindful not to let such notions distract from the essential hard work of creating long-lasting cultural changes that underpin a true path forward.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with Sanofi, Hansa Medical, Natera, and others.
SOURCE: Locke JE et al. JAMA Surg. 2020 May 20. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.1129.
Addressing local supply constraints may be insufficient to improve poorer outcomes among women who need a liver transplant, based on a large retrospective analysis.
Sex-based disparities in liver allocation were more strongly associated with liver size mismatch and MELD (Model for End-stage Liver Disease) score than geographic factors, reported lead author Jayme E. Locke, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues.
“Currently, the transplant community is considering geographic redistribution ... to redefine local organ supply by replacing donor service areas with fixed concentric circles around donor hospitals,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Surgery. “However, newly proposed geographic models rely on the same metric for medical urgency, the MELD score, and offer no solution for candidates with small body stature who may appear at the top of the match run yet are routinely skipped secondary to discrepancies in donor-recipient size.”
To further investigate the driving forces behind sex-based disparities, the investigators conducted the first national study of its kind, involving 81,357 adults who were wait-listed for liver transplant. Primary outcomes included deceased donor liver transplant and wait list mortality. Using multivariate regression models and inverse odds ratio weighting, the investigators determined proportions of disparity shared across MELD score, candidate anthropometric and liver measurements, and geographic location.
Compared with men, women were 14.4% less likely to receive a transplant, and 8.6% more likely to die on the wait list.
The only geographic factor significantly associated with the increased disparity between female sex and wait list mortality was organ procurement organization, which was associated with a 22% increase. The disparity between rates of transplant receipt was not linked with any geographic factors.
In contrast, MELD score accounted for increases in disparity of 10.3% and 50.1% for organ receipt and wait list mortality, respectively. Candidate anthropometric and liver measurements played an even greater role, raising disparity by 49.0% for organ receipt and 125.8% for wait list mortality.
“Size mismatch between the donor and intended recipient and incorrect assessments of liver disease severity were more strongly associated with the observed sex disparity in wait list mortality than local supply of organs,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Locke and colleagues noted that ongoing debates about geographic disparity hinge upon the assumption that the MELD score accurately measures disease severity, despite known shortcomings, including reliance upon serum creatinine level, which is influenced by muscle mass and therefore overestimates kidney function in women, and sex-based differences in size, which the MELD score does not incorporate whatsoever.
As such, the investigators suggested that addressing issues with the MELD score and organ size mismatch should be part of a more comprehensive approach to fixing sex-based disparities among candidates for liver transplant.
“Although geographic factors matter, examining geographic access alone may be insufficient,” they concluded.
James F. Markmann, MD, PhD, chief of the division of transplantation at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who has previously published research in support of geographic redistribution, said in an interview that the study by Dr. Locke and colleagues “highlights a well-known problem in the liver transplant field.”
“The cause of this disparity is nicely illustrated by Dr. Locke’s work, which shows multiple contributing factors,” Dr. Markmann said.
While Dr. Markmann agreed with Dr. Locke and colleagues’ proposal that estimated glomerular filtration rate, instead of creatinine, could be used to more accurately measure renal function across sexes, he suggested that the disparities uncovered by their analysis are more likely driven by body size than sex.
“A more impactful factor and one obvious to those performing transplants is that on average the smaller body habitus of females makes more organs unsuitable due to size mismatch,” Dr. Markmann said. “In general, it is technically much less of a barrier to put a small liver into a large patient, than a large liver in a small patient. But, the same disparity in access almost certainly applies to small males; unfortunately, the authors did not examine this point. If allocation changes are envisioned to gain greater fairness in organ access, at least for the recipient size issue, it should be a size issue and not a sex issue.”
Dr. Markmann went on to explain that steps are currently being taken to make liver access more equitable.
“As of February 4th of this year, a broader sharing program for deceased donor livers was implemented,” he said. “This will make more organs available to those in greatest need. It will also potentially increase the number of liver offers to sick patients with a small body habitus and will hopefully reduce the excess morbidity and mortality they suffer.”
According to Willscott E. Naugler, MD and Susan L. Orloff, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, novel clinical strategies need to be reinforced with a broader mindset in order to close the gap between men and women.
“A change in the MELD score is unlikely to fix this problem,” they wrote in an accompanying JAMA Surgery editorial, “but it is not hard to think of solutions; one could imagine, for example, allowing women of small stature to access pediatric livers while ramping up liver splits to increase contributions to the pediatric pool.”
Dr. Naugler and Dr. Orloff went on to suggest that barriers to equity may be culturally insidious.
“It is likely that the same unconscious biases that lead us to pay women surgeons less account for the lack of will to make these simple changes,” they wrote. “Not mentioned are multiple sociocultural elements that favor men over women in organ transplant. ... These realities cannot be fixed with changes to the MELD score, and we must be mindful not to let such notions distract from the essential hard work of creating long-lasting cultural changes that underpin a true path forward.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with Sanofi, Hansa Medical, Natera, and others.
SOURCE: Locke JE et al. JAMA Surg. 2020 May 20. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.1129.
Addressing local supply constraints may be insufficient to improve poorer outcomes among women who need a liver transplant, based on a large retrospective analysis.
Sex-based disparities in liver allocation were more strongly associated with liver size mismatch and MELD (Model for End-stage Liver Disease) score than geographic factors, reported lead author Jayme E. Locke, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues.
“Currently, the transplant community is considering geographic redistribution ... to redefine local organ supply by replacing donor service areas with fixed concentric circles around donor hospitals,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Surgery. “However, newly proposed geographic models rely on the same metric for medical urgency, the MELD score, and offer no solution for candidates with small body stature who may appear at the top of the match run yet are routinely skipped secondary to discrepancies in donor-recipient size.”
To further investigate the driving forces behind sex-based disparities, the investigators conducted the first national study of its kind, involving 81,357 adults who were wait-listed for liver transplant. Primary outcomes included deceased donor liver transplant and wait list mortality. Using multivariate regression models and inverse odds ratio weighting, the investigators determined proportions of disparity shared across MELD score, candidate anthropometric and liver measurements, and geographic location.
Compared with men, women were 14.4% less likely to receive a transplant, and 8.6% more likely to die on the wait list.
The only geographic factor significantly associated with the increased disparity between female sex and wait list mortality was organ procurement organization, which was associated with a 22% increase. The disparity between rates of transplant receipt was not linked with any geographic factors.
In contrast, MELD score accounted for increases in disparity of 10.3% and 50.1% for organ receipt and wait list mortality, respectively. Candidate anthropometric and liver measurements played an even greater role, raising disparity by 49.0% for organ receipt and 125.8% for wait list mortality.
“Size mismatch between the donor and intended recipient and incorrect assessments of liver disease severity were more strongly associated with the observed sex disparity in wait list mortality than local supply of organs,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Locke and colleagues noted that ongoing debates about geographic disparity hinge upon the assumption that the MELD score accurately measures disease severity, despite known shortcomings, including reliance upon serum creatinine level, which is influenced by muscle mass and therefore overestimates kidney function in women, and sex-based differences in size, which the MELD score does not incorporate whatsoever.
As such, the investigators suggested that addressing issues with the MELD score and organ size mismatch should be part of a more comprehensive approach to fixing sex-based disparities among candidates for liver transplant.
“Although geographic factors matter, examining geographic access alone may be insufficient,” they concluded.
James F. Markmann, MD, PhD, chief of the division of transplantation at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who has previously published research in support of geographic redistribution, said in an interview that the study by Dr. Locke and colleagues “highlights a well-known problem in the liver transplant field.”
“The cause of this disparity is nicely illustrated by Dr. Locke’s work, which shows multiple contributing factors,” Dr. Markmann said.
While Dr. Markmann agreed with Dr. Locke and colleagues’ proposal that estimated glomerular filtration rate, instead of creatinine, could be used to more accurately measure renal function across sexes, he suggested that the disparities uncovered by their analysis are more likely driven by body size than sex.
“A more impactful factor and one obvious to those performing transplants is that on average the smaller body habitus of females makes more organs unsuitable due to size mismatch,” Dr. Markmann said. “In general, it is technically much less of a barrier to put a small liver into a large patient, than a large liver in a small patient. But, the same disparity in access almost certainly applies to small males; unfortunately, the authors did not examine this point. If allocation changes are envisioned to gain greater fairness in organ access, at least for the recipient size issue, it should be a size issue and not a sex issue.”
Dr. Markmann went on to explain that steps are currently being taken to make liver access more equitable.
“As of February 4th of this year, a broader sharing program for deceased donor livers was implemented,” he said. “This will make more organs available to those in greatest need. It will also potentially increase the number of liver offers to sick patients with a small body habitus and will hopefully reduce the excess morbidity and mortality they suffer.”
According to Willscott E. Naugler, MD and Susan L. Orloff, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, novel clinical strategies need to be reinforced with a broader mindset in order to close the gap between men and women.
“A change in the MELD score is unlikely to fix this problem,” they wrote in an accompanying JAMA Surgery editorial, “but it is not hard to think of solutions; one could imagine, for example, allowing women of small stature to access pediatric livers while ramping up liver splits to increase contributions to the pediatric pool.”
Dr. Naugler and Dr. Orloff went on to suggest that barriers to equity may be culturally insidious.
“It is likely that the same unconscious biases that lead us to pay women surgeons less account for the lack of will to make these simple changes,” they wrote. “Not mentioned are multiple sociocultural elements that favor men over women in organ transplant. ... These realities cannot be fixed with changes to the MELD score, and we must be mindful not to let such notions distract from the essential hard work of creating long-lasting cultural changes that underpin a true path forward.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with Sanofi, Hansa Medical, Natera, and others.
SOURCE: Locke JE et al. JAMA Surg. 2020 May 20. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.1129.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Today’s top news highlights: COVID-19 could worsen gambling problems, food allergies less common than thought
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Could COVID-19 worsen gambling problems?
Take isolation, add excess available time and anxiety about illness or finances and you get the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. A call to action, recently published in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, says it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue. “People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said. Read more.
Food allergies in children are less frequent than expected
Food allergies appear to be less common than previously reported among 6- to 10-year-olds in Europe, according to a recent study. Prevalance ranged from a low of 1.4% to a high of 3.8%, both of which are “considerably lower” than the 16% rate based on parental reports of symptoms such as rash, itching, or diarrhea, Linus Grabenhenrich, MD, MPH, and colleagues reported in Allergy. The most commonly reported allergies were to peanuts and hazelnuts, with a prevalence of just over 5% for both. Previous research on pediatric food allergy prevalence has largely consisted of single-center studies with heterogeneous designs, the researchers noted. Read more.
The grocery store hug
William G. Wilkoff, MD, grew up in a family that didn’t embrace hugging, but as a small-town pediatrician he warmed up to the concept so much that he would frequently hug a passing acquaintance at the grocery store. That’s something he misses in the current environment and that he doesn’t expect will return. “[N]early every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship,” Dr. Wilkoff wrote in a column on MDedge. “Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child. I’m sure you have your own list of people who send off that we-need-to-hug spark.” Read more.
Identifying structural lesions of axial spondyloarthritis
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that show a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease. “Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19. “The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort.” Read more.
Making the world’s skin crawl
Clinicians should be aware of the skin manifestations of COVID-19, especially when triaging patients. In a commentary published on MDedge, Kathleen M. Coerdt and Amor Khachemoune, MD, describe the dermatologic implications of COVID-19, including the clinical manifestations of the disease, risk reduction techniques for patients and providers, personal protective equipment-associated adverse reactions, and the financial impact on dermatologists. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Could COVID-19 worsen gambling problems?
Take isolation, add excess available time and anxiety about illness or finances and you get the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. A call to action, recently published in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, says it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue. “People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said. Read more.
Food allergies in children are less frequent than expected
Food allergies appear to be less common than previously reported among 6- to 10-year-olds in Europe, according to a recent study. Prevalance ranged from a low of 1.4% to a high of 3.8%, both of which are “considerably lower” than the 16% rate based on parental reports of symptoms such as rash, itching, or diarrhea, Linus Grabenhenrich, MD, MPH, and colleagues reported in Allergy. The most commonly reported allergies were to peanuts and hazelnuts, with a prevalence of just over 5% for both. Previous research on pediatric food allergy prevalence has largely consisted of single-center studies with heterogeneous designs, the researchers noted. Read more.
The grocery store hug
William G. Wilkoff, MD, grew up in a family that didn’t embrace hugging, but as a small-town pediatrician he warmed up to the concept so much that he would frequently hug a passing acquaintance at the grocery store. That’s something he misses in the current environment and that he doesn’t expect will return. “[N]early every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship,” Dr. Wilkoff wrote in a column on MDedge. “Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child. I’m sure you have your own list of people who send off that we-need-to-hug spark.” Read more.
Identifying structural lesions of axial spondyloarthritis
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that show a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease. “Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19. “The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort.” Read more.
Making the world’s skin crawl
Clinicians should be aware of the skin manifestations of COVID-19, especially when triaging patients. In a commentary published on MDedge, Kathleen M. Coerdt and Amor Khachemoune, MD, describe the dermatologic implications of COVID-19, including the clinical manifestations of the disease, risk reduction techniques for patients and providers, personal protective equipment-associated adverse reactions, and the financial impact on dermatologists. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Could COVID-19 worsen gambling problems?
Take isolation, add excess available time and anxiety about illness or finances and you get the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. A call to action, recently published in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, says it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue. “People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said. Read more.
Food allergies in children are less frequent than expected
Food allergies appear to be less common than previously reported among 6- to 10-year-olds in Europe, according to a recent study. Prevalance ranged from a low of 1.4% to a high of 3.8%, both of which are “considerably lower” than the 16% rate based on parental reports of symptoms such as rash, itching, or diarrhea, Linus Grabenhenrich, MD, MPH, and colleagues reported in Allergy. The most commonly reported allergies were to peanuts and hazelnuts, with a prevalence of just over 5% for both. Previous research on pediatric food allergy prevalence has largely consisted of single-center studies with heterogeneous designs, the researchers noted. Read more.
The grocery store hug
William G. Wilkoff, MD, grew up in a family that didn’t embrace hugging, but as a small-town pediatrician he warmed up to the concept so much that he would frequently hug a passing acquaintance at the grocery store. That’s something he misses in the current environment and that he doesn’t expect will return. “[N]early every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship,” Dr. Wilkoff wrote in a column on MDedge. “Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child. I’m sure you have your own list of people who send off that we-need-to-hug spark.” Read more.
Identifying structural lesions of axial spondyloarthritis
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that show a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease. “Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19. “The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort.” Read more.
Making the world’s skin crawl
Clinicians should be aware of the skin manifestations of COVID-19, especially when triaging patients. In a commentary published on MDedge, Kathleen M. Coerdt and Amor Khachemoune, MD, describe the dermatologic implications of COVID-19, including the clinical manifestations of the disease, risk reduction techniques for patients and providers, personal protective equipment-associated adverse reactions, and the financial impact on dermatologists. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.








