User login
How can I keep from losing my mind?
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
Four commonly abused drugs linked with atrial fibrillation
Cocaine, methamphetamine, opioids, and cannabis may independently increase risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib), based on data from almost 24 million people.
While more work is needed to uncover causal links, physicians should be aware that these commonly abused substances could be driving new cases of AFib, reported investigators from the University of California, San Francisco.
“Though alcohol and tobacco smoking have each been associated with a heightened risk of [AFib], relationships between other drug use and [AFib] are poorly understood,” they wrote in European Heart Journal.
Some previous studies have ventured into this terrain, but most focused on fatal arrhythmias, or offered anecdotal evidence. This knowledge gap is particularly concerning for cannabis, the researchers noted, as medical and recreational use are on the rise.
The present analysis included data from 23.5 million adults in California who received care through a hospital, emergency department, or outpatient surgery center during 2005-2015. Based on ICD-9 diagnostic codes, 132,834 of these patients used cannabis, 98,271 used methamphetamines, 48,701 used cocaine, and 10,032 used opiates. Inclusion required lack of AFib at baseline.
Reliance on ICD-9 codes makes the data “quite specific,” but lacking sensitivity, according to principal author Gregory M. Marcus, MD, cardiologist and professor of medicine at UCSF.
“If they were designated as using these drugs, that is very likely true,” Dr. Marcus said in an interview. “But certainly, the absence of any mention of use of these drugs does not exclude the possibility that some people were still using them. That would not create spurious false-positive relationships; if anything, it attenuates existing relationships.”
In other words, using ICD-9 codes reduced the power to detect an association between each drug and AFib, meaning any relationship needed to be sufficiently strong enough to generate a significant result.
At the end of the decade-long study period, 998,747 patients (4.2%) had developed incident AFib. After adjusting for potential confounders and mediators, all four drugs showed significant, independent associations with AFib. Methamphetamines presented the greatest risk (hazard ratio, 1.86%), followed by opiates (HR, 1.74), cocaine (HR, 1.61), and cannabis (HR, 1.35).
“Our findings provide the first evidence utilizing a longitudinal cohort to demonstrate that cannabis use predicts the future onset of AFib,” Dr. Marcus and colleagues wrote.
Dose-response relationships were not detected for any of the substances; however, usage levels were also derived from ICD-9 codes, which may have been insufficient for this purpose, according to the investigators.
Causal mechanisms deserve a closer look
Causal links between AFib and each of the drugs remain unclear. Citing prior research, Dr. Marcus and colleagues explained how methamphetamines are capable of “significant cardiac electrical remodeling,” while cocaine may cause sodium channel dysregulation, and opioids can render atrial myocytes more susceptible to oxidative damage. Although cannabis has previously been linked with hospitalization for arrhythmia, a pharmacologic driver of this phenomenon remains largely unexamined.
“We don’t know for sure precisely what the constituents are that are responsible for our findings,” Dr. Marcus said. “It’s possible that there are some effects that are much more generic, such as inhaling a burned substance. There is good evidence that if you inhale pretty much any sort of particulate matter, that increases inflammation in the body. Inflammation is known to be a trigger for atrial fibrillation.”
Alternatively, all four drugs – whether stimulants or depressants – cause “quite dramatic and often rapid effects on the autonomic nervous system,” Dr. Marcus said, noting that these rapid swings are a known trigger for AFib.
Brian Olshansky, MD, emeritus professor of internal medicine-cardiovascular medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, suggested that nonpharmacologic factors are likely also playing a role.
“All these drugs have slightly different mechanisms of action, so there’s not one mechanism that would explain why all of them would cause atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Olshansky said in an interview. “That does suggest that there’s something else going on, besides just the drug itself. It would be potentially concerning if we were to lay the blame totally on these drugs.”
Dr. Olshansky, who recently coauthored a review of stimulant drugs and arrhythmias, suggested that lifestyle, comorbidities, and drug impurities may have added to the risk of AF.
“[The investigators] did try to correct for that kind of stuff, but it’s very hard to correct for a lot of the issues that may be ongoing with individuals who partake in these drugs,” Dr. Olshansky said in an interview. “They may not be a healthy lot, in general.”
Still, considering previous data linking drugs of abuse with arrhythmias, he said the detected risks were “intriguing,” and deserved a closer look.
“It’s a nice groundbreaking study, with regard to the fact that they showed unique relationships that we don’t completely understand,” Dr. Olshansky said. “It opens up a new opportunity for further investigation.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with InCarda, Baylis Medical, Johnson & Johnson, and others. Dr. Olshansky disclosed no relevant competing interests.
Cocaine, methamphetamine, opioids, and cannabis may independently increase risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib), based on data from almost 24 million people.
While more work is needed to uncover causal links, physicians should be aware that these commonly abused substances could be driving new cases of AFib, reported investigators from the University of California, San Francisco.
“Though alcohol and tobacco smoking have each been associated with a heightened risk of [AFib], relationships between other drug use and [AFib] are poorly understood,” they wrote in European Heart Journal.
Some previous studies have ventured into this terrain, but most focused on fatal arrhythmias, or offered anecdotal evidence. This knowledge gap is particularly concerning for cannabis, the researchers noted, as medical and recreational use are on the rise.
The present analysis included data from 23.5 million adults in California who received care through a hospital, emergency department, or outpatient surgery center during 2005-2015. Based on ICD-9 diagnostic codes, 132,834 of these patients used cannabis, 98,271 used methamphetamines, 48,701 used cocaine, and 10,032 used opiates. Inclusion required lack of AFib at baseline.
Reliance on ICD-9 codes makes the data “quite specific,” but lacking sensitivity, according to principal author Gregory M. Marcus, MD, cardiologist and professor of medicine at UCSF.
“If they were designated as using these drugs, that is very likely true,” Dr. Marcus said in an interview. “But certainly, the absence of any mention of use of these drugs does not exclude the possibility that some people were still using them. That would not create spurious false-positive relationships; if anything, it attenuates existing relationships.”
In other words, using ICD-9 codes reduced the power to detect an association between each drug and AFib, meaning any relationship needed to be sufficiently strong enough to generate a significant result.
At the end of the decade-long study period, 998,747 patients (4.2%) had developed incident AFib. After adjusting for potential confounders and mediators, all four drugs showed significant, independent associations with AFib. Methamphetamines presented the greatest risk (hazard ratio, 1.86%), followed by opiates (HR, 1.74), cocaine (HR, 1.61), and cannabis (HR, 1.35).
“Our findings provide the first evidence utilizing a longitudinal cohort to demonstrate that cannabis use predicts the future onset of AFib,” Dr. Marcus and colleagues wrote.
Dose-response relationships were not detected for any of the substances; however, usage levels were also derived from ICD-9 codes, which may have been insufficient for this purpose, according to the investigators.
Causal mechanisms deserve a closer look
Causal links between AFib and each of the drugs remain unclear. Citing prior research, Dr. Marcus and colleagues explained how methamphetamines are capable of “significant cardiac electrical remodeling,” while cocaine may cause sodium channel dysregulation, and opioids can render atrial myocytes more susceptible to oxidative damage. Although cannabis has previously been linked with hospitalization for arrhythmia, a pharmacologic driver of this phenomenon remains largely unexamined.
“We don’t know for sure precisely what the constituents are that are responsible for our findings,” Dr. Marcus said. “It’s possible that there are some effects that are much more generic, such as inhaling a burned substance. There is good evidence that if you inhale pretty much any sort of particulate matter, that increases inflammation in the body. Inflammation is known to be a trigger for atrial fibrillation.”
Alternatively, all four drugs – whether stimulants or depressants – cause “quite dramatic and often rapid effects on the autonomic nervous system,” Dr. Marcus said, noting that these rapid swings are a known trigger for AFib.
Brian Olshansky, MD, emeritus professor of internal medicine-cardiovascular medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, suggested that nonpharmacologic factors are likely also playing a role.
“All these drugs have slightly different mechanisms of action, so there’s not one mechanism that would explain why all of them would cause atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Olshansky said in an interview. “That does suggest that there’s something else going on, besides just the drug itself. It would be potentially concerning if we were to lay the blame totally on these drugs.”
Dr. Olshansky, who recently coauthored a review of stimulant drugs and arrhythmias, suggested that lifestyle, comorbidities, and drug impurities may have added to the risk of AF.
“[The investigators] did try to correct for that kind of stuff, but it’s very hard to correct for a lot of the issues that may be ongoing with individuals who partake in these drugs,” Dr. Olshansky said in an interview. “They may not be a healthy lot, in general.”
Still, considering previous data linking drugs of abuse with arrhythmias, he said the detected risks were “intriguing,” and deserved a closer look.
“It’s a nice groundbreaking study, with regard to the fact that they showed unique relationships that we don’t completely understand,” Dr. Olshansky said. “It opens up a new opportunity for further investigation.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with InCarda, Baylis Medical, Johnson & Johnson, and others. Dr. Olshansky disclosed no relevant competing interests.
Cocaine, methamphetamine, opioids, and cannabis may independently increase risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib), based on data from almost 24 million people.
While more work is needed to uncover causal links, physicians should be aware that these commonly abused substances could be driving new cases of AFib, reported investigators from the University of California, San Francisco.
“Though alcohol and tobacco smoking have each been associated with a heightened risk of [AFib], relationships between other drug use and [AFib] are poorly understood,” they wrote in European Heart Journal.
Some previous studies have ventured into this terrain, but most focused on fatal arrhythmias, or offered anecdotal evidence. This knowledge gap is particularly concerning for cannabis, the researchers noted, as medical and recreational use are on the rise.
The present analysis included data from 23.5 million adults in California who received care through a hospital, emergency department, or outpatient surgery center during 2005-2015. Based on ICD-9 diagnostic codes, 132,834 of these patients used cannabis, 98,271 used methamphetamines, 48,701 used cocaine, and 10,032 used opiates. Inclusion required lack of AFib at baseline.
Reliance on ICD-9 codes makes the data “quite specific,” but lacking sensitivity, according to principal author Gregory M. Marcus, MD, cardiologist and professor of medicine at UCSF.
“If they were designated as using these drugs, that is very likely true,” Dr. Marcus said in an interview. “But certainly, the absence of any mention of use of these drugs does not exclude the possibility that some people were still using them. That would not create spurious false-positive relationships; if anything, it attenuates existing relationships.”
In other words, using ICD-9 codes reduced the power to detect an association between each drug and AFib, meaning any relationship needed to be sufficiently strong enough to generate a significant result.
At the end of the decade-long study period, 998,747 patients (4.2%) had developed incident AFib. After adjusting for potential confounders and mediators, all four drugs showed significant, independent associations with AFib. Methamphetamines presented the greatest risk (hazard ratio, 1.86%), followed by opiates (HR, 1.74), cocaine (HR, 1.61), and cannabis (HR, 1.35).
“Our findings provide the first evidence utilizing a longitudinal cohort to demonstrate that cannabis use predicts the future onset of AFib,” Dr. Marcus and colleagues wrote.
Dose-response relationships were not detected for any of the substances; however, usage levels were also derived from ICD-9 codes, which may have been insufficient for this purpose, according to the investigators.
Causal mechanisms deserve a closer look
Causal links between AFib and each of the drugs remain unclear. Citing prior research, Dr. Marcus and colleagues explained how methamphetamines are capable of “significant cardiac electrical remodeling,” while cocaine may cause sodium channel dysregulation, and opioids can render atrial myocytes more susceptible to oxidative damage. Although cannabis has previously been linked with hospitalization for arrhythmia, a pharmacologic driver of this phenomenon remains largely unexamined.
“We don’t know for sure precisely what the constituents are that are responsible for our findings,” Dr. Marcus said. “It’s possible that there are some effects that are much more generic, such as inhaling a burned substance. There is good evidence that if you inhale pretty much any sort of particulate matter, that increases inflammation in the body. Inflammation is known to be a trigger for atrial fibrillation.”
Alternatively, all four drugs – whether stimulants or depressants – cause “quite dramatic and often rapid effects on the autonomic nervous system,” Dr. Marcus said, noting that these rapid swings are a known trigger for AFib.
Brian Olshansky, MD, emeritus professor of internal medicine-cardiovascular medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, suggested that nonpharmacologic factors are likely also playing a role.
“All these drugs have slightly different mechanisms of action, so there’s not one mechanism that would explain why all of them would cause atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Olshansky said in an interview. “That does suggest that there’s something else going on, besides just the drug itself. It would be potentially concerning if we were to lay the blame totally on these drugs.”
Dr. Olshansky, who recently coauthored a review of stimulant drugs and arrhythmias, suggested that lifestyle, comorbidities, and drug impurities may have added to the risk of AF.
“[The investigators] did try to correct for that kind of stuff, but it’s very hard to correct for a lot of the issues that may be ongoing with individuals who partake in these drugs,” Dr. Olshansky said in an interview. “They may not be a healthy lot, in general.”
Still, considering previous data linking drugs of abuse with arrhythmias, he said the detected risks were “intriguing,” and deserved a closer look.
“It’s a nice groundbreaking study, with regard to the fact that they showed unique relationships that we don’t completely understand,” Dr. Olshansky said. “It opens up a new opportunity for further investigation.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with InCarda, Baylis Medical, Johnson & Johnson, and others. Dr. Olshansky disclosed no relevant competing interests.
FROM EUROPEAN HEART JOURNAL
Asymptomatic Umbilical Nodule
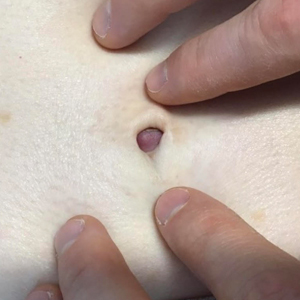
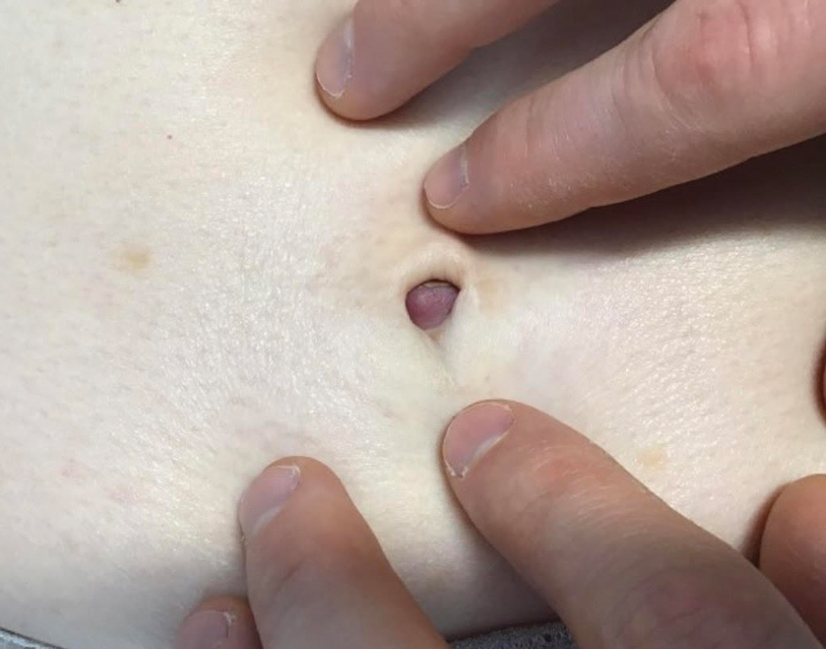
The Diagnosis: Sister Mary Joseph Nodule
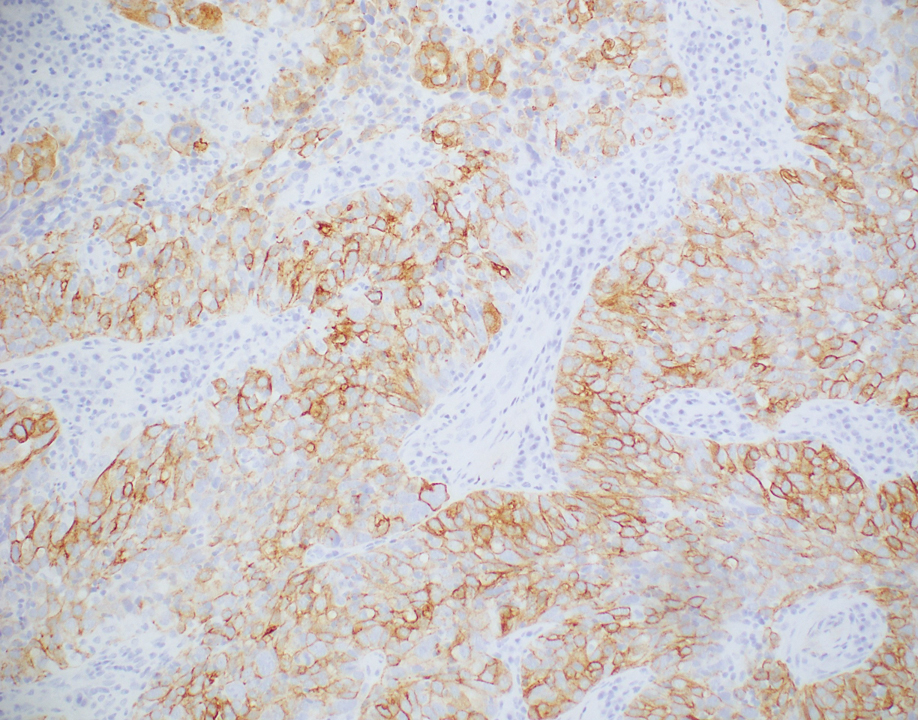
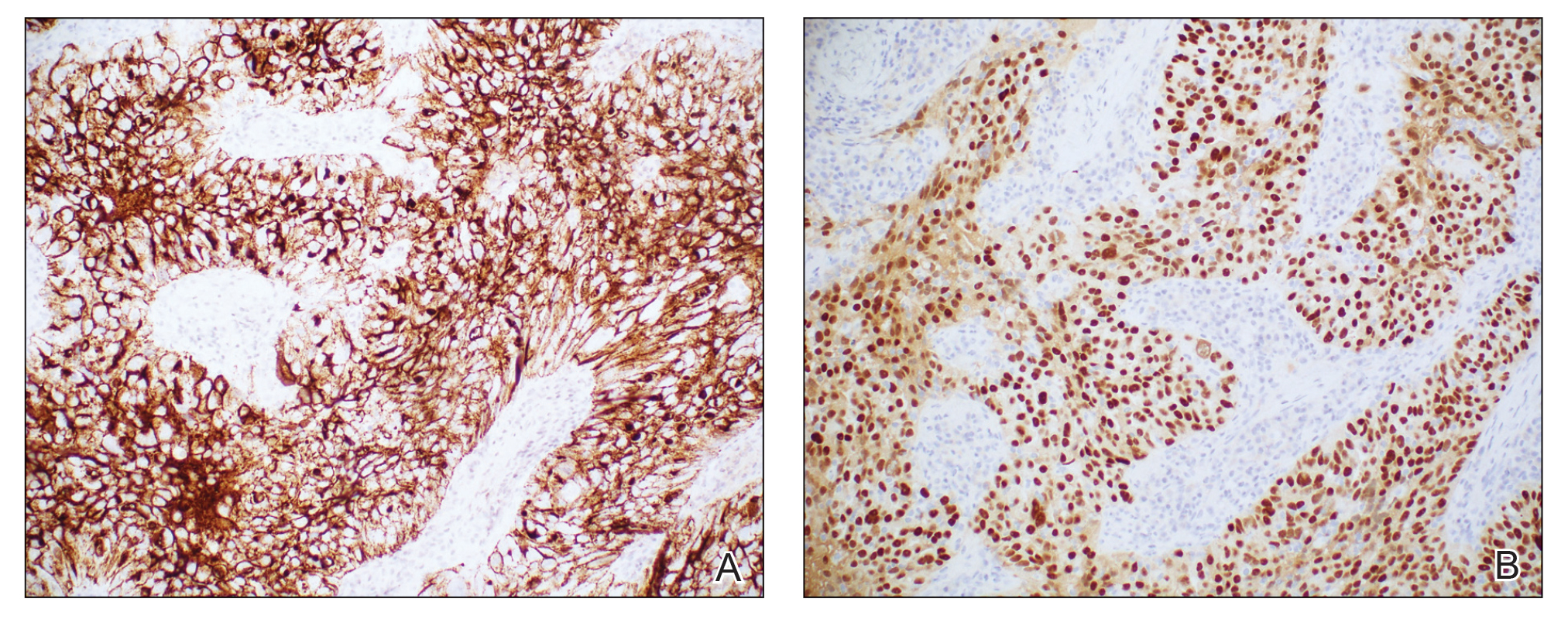
Histopathologic analysis of the biopsy specimen revealed a dense infiltrate of large, hyperchromatic, mucin-producing cells exhibiting varying degrees of nuclear pleomorphism (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was negative for cytokeratin (CK) 20; however, CK7 was found positive (Figure 2), which confirmed the presence of a metastatic adenocarcinoma, consistent with the clinical diagnosis of a Sister Mary Joseph nodule (SMJN). Subsequent IHC workup to determine the site of origin revealed densely positive expression of both cancer antigen 125 and paired homeobox gene 8 (PAX-8)(Figure 3), consistent with primary ovarian disease. Furthermore, expression of estrogen receptor and p53 both were positive within the nuclei, illustrating an aberrant expression pattern. On the other hand, cancer antigen 19-9, caudal-type homeobox 2, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and mammaglobin were all determined negative, thus leading to the pathologic diagnosis of a metastatic ovarian adenocarcinoma. Additional workup with computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis highlighted a large left ovarian mass with multiple omental nodules as well as enlarged retroperitoneal and pelvic lymph nodes.

The SMJN is a rare presentation of internal malignancy that appears as a nodule that metastasizes to the umbilicus. It may be ulcerated or necrotic and is seen in up to 10% of patients with cutaneous metastases from internal malignancy.1 These nodules are named after Sister Mary Joseph, the surgical assistant of Dr. William Mayo who first described the relationship between umbilical nodules seen in patients with gastrointestinal and genitourinary cancer. The most common underlying malignancies include primary gastrointestinal and gynecologic adenocarcinomas. In a retrospective study of 34 patients by Chalya et al,2 the stomach was found to be the most common primary site (41.1%). The presence of an SMJN affords a poor prognosis, with a mean overall survival of 11 months from the time of diagnosis.3 The mechanism of disease dissemination remains unknown but is thought to occur through lymphovascular invasion of tumor cells and spread via the umbilical ligament.1,4
Merkel cell carcinoma is a cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor that most commonly presents in elderly patients as red-violet nodules or plaques. Although Merkel cell carcinoma most frequently is encountered on sun-exposed skin, they also can arise on the trunk and abdomen. Positive IHC staining for CK20 would be expected; however, it was negative in our case.5
Cutaneous endometriosis is a rare disease presentation and most commonly occurs as a secondary process due to surgical inoculation of the abdominal wall. Primary cutaneous endometriosis in which there is no history of abdominal surgery less frequently is encountered. Patients typically will report pain and cyclical bleeding with menses. Pathology demonstrates ectopic endometrial tissue with glands and uterine myxoid stroma.6
Amelanotic melanoma is an uncommon subtype of malignant melanoma that presents as nonpigmented nodules that have a propensity to ulcerate and bleed. Furthermore, the umbilicus is an exceedingly rare location for primary melanoma. However, one report does exist, and amelanotic melanoma should be considered in the differential for patients with umbilical nodules.7
Dermoid cysts are benign congenital lesions that typically present as a painless, slow-growing, and wellcircumscribed nodule, as similarly experienced by our patient. They most commonly are found on the testicles and ovaries but also are known to arise in embryologic fusion planes, and reports of umbilical lesions exist.8 Dermoid cysts are diagnosed based on histopathology, supporting the need for a biopsy to distinguish a malignant process from benign lesions.9
- Gabriele R, Conte M, Egidi F, et al. Umbilical metastases: current viewpoint. World J Surg Oncol. 2005;3:13.
- Chalya PL, Mabula JB, Rambau PF, et al. Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule at a university teaching hospital in northwestern Tanzania: a retrospective review of 34 cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:151.
- Leyrat B, Bernadach M, Ginzac A, et al. Sister Mary Joseph nodules: a case report about a rare location of skin metastasis. Case Rep Oncol. 2021;14:664-670.
- Yendluri V, Centeno B, Springett GM. Pancreatic cancer presenting as a Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule: case report and update of the literature. Pancreas. 2007;34:161-164.
- Uchi H. Merkel cell carcinoma: an update and immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 2018;8:48.
- Bittar PG, Hryneewycz KT, Bryant EA. Primary cutaneous endometriosis presenting as an umbilical nodule. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1227.
- Kovitwanichkanont T, Joseph S, Yip L. Hidden in plain sight: umbilical melanoma [published online January 28, 2020]. Med J Aust. 2020;212:154-155.e1.
- Prior A, Anania P, Pacetti M, et al. Dermoid and epidermoid cysts of scalp: case series of 234 consecutive patients. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:119-124.
- Akinci O, Turker C, Erturk MS, et al. Umbilical dermoid cyst: a rare case. Cerrahpasa Med J. 2020;44:51-53.
The Diagnosis: Sister Mary Joseph Nodule
Histopathologic analysis of the biopsy specimen revealed a dense infiltrate of large, hyperchromatic, mucin-producing cells exhibiting varying degrees of nuclear pleomorphism (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was negative for cytokeratin (CK) 20; however, CK7 was found positive (Figure 2), which confirmed the presence of a metastatic adenocarcinoma, consistent with the clinical diagnosis of a Sister Mary Joseph nodule (SMJN). Subsequent IHC workup to determine the site of origin revealed densely positive expression of both cancer antigen 125 and paired homeobox gene 8 (PAX-8)(Figure 3), consistent with primary ovarian disease. Furthermore, expression of estrogen receptor and p53 both were positive within the nuclei, illustrating an aberrant expression pattern. On the other hand, cancer antigen 19-9, caudal-type homeobox 2, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and mammaglobin were all determined negative, thus leading to the pathologic diagnosis of a metastatic ovarian adenocarcinoma. Additional workup with computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis highlighted a large left ovarian mass with multiple omental nodules as well as enlarged retroperitoneal and pelvic lymph nodes.

The SMJN is a rare presentation of internal malignancy that appears as a nodule that metastasizes to the umbilicus. It may be ulcerated or necrotic and is seen in up to 10% of patients with cutaneous metastases from internal malignancy.1 These nodules are named after Sister Mary Joseph, the surgical assistant of Dr. William Mayo who first described the relationship between umbilical nodules seen in patients with gastrointestinal and genitourinary cancer. The most common underlying malignancies include primary gastrointestinal and gynecologic adenocarcinomas. In a retrospective study of 34 patients by Chalya et al,2 the stomach was found to be the most common primary site (41.1%). The presence of an SMJN affords a poor prognosis, with a mean overall survival of 11 months from the time of diagnosis.3 The mechanism of disease dissemination remains unknown but is thought to occur through lymphovascular invasion of tumor cells and spread via the umbilical ligament.1,4

Merkel cell carcinoma is a cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor that most commonly presents in elderly patients as red-violet nodules or plaques. Although Merkel cell carcinoma most frequently is encountered on sun-exposed skin, they also can arise on the trunk and abdomen. Positive IHC staining for CK20 would be expected; however, it was negative in our case.5

Cutaneous endometriosis is a rare disease presentation and most commonly occurs as a secondary process due to surgical inoculation of the abdominal wall. Primary cutaneous endometriosis in which there is no history of abdominal surgery less frequently is encountered. Patients typically will report pain and cyclical bleeding with menses. Pathology demonstrates ectopic endometrial tissue with glands and uterine myxoid stroma.6
Amelanotic melanoma is an uncommon subtype of malignant melanoma that presents as nonpigmented nodules that have a propensity to ulcerate and bleed. Furthermore, the umbilicus is an exceedingly rare location for primary melanoma. However, one report does exist, and amelanotic melanoma should be considered in the differential for patients with umbilical nodules.7
Dermoid cysts are benign congenital lesions that typically present as a painless, slow-growing, and wellcircumscribed nodule, as similarly experienced by our patient. They most commonly are found on the testicles and ovaries but also are known to arise in embryologic fusion planes, and reports of umbilical lesions exist.8 Dermoid cysts are diagnosed based on histopathology, supporting the need for a biopsy to distinguish a malignant process from benign lesions.9
The Diagnosis: Sister Mary Joseph Nodule
Histopathologic analysis of the biopsy specimen revealed a dense infiltrate of large, hyperchromatic, mucin-producing cells exhibiting varying degrees of nuclear pleomorphism (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was negative for cytokeratin (CK) 20; however, CK7 was found positive (Figure 2), which confirmed the presence of a metastatic adenocarcinoma, consistent with the clinical diagnosis of a Sister Mary Joseph nodule (SMJN). Subsequent IHC workup to determine the site of origin revealed densely positive expression of both cancer antigen 125 and paired homeobox gene 8 (PAX-8)(Figure 3), consistent with primary ovarian disease. Furthermore, expression of estrogen receptor and p53 both were positive within the nuclei, illustrating an aberrant expression pattern. On the other hand, cancer antigen 19-9, caudal-type homeobox 2, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and mammaglobin were all determined negative, thus leading to the pathologic diagnosis of a metastatic ovarian adenocarcinoma. Additional workup with computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis highlighted a large left ovarian mass with multiple omental nodules as well as enlarged retroperitoneal and pelvic lymph nodes.

The SMJN is a rare presentation of internal malignancy that appears as a nodule that metastasizes to the umbilicus. It may be ulcerated or necrotic and is seen in up to 10% of patients with cutaneous metastases from internal malignancy.1 These nodules are named after Sister Mary Joseph, the surgical assistant of Dr. William Mayo who first described the relationship between umbilical nodules seen in patients with gastrointestinal and genitourinary cancer. The most common underlying malignancies include primary gastrointestinal and gynecologic adenocarcinomas. In a retrospective study of 34 patients by Chalya et al,2 the stomach was found to be the most common primary site (41.1%). The presence of an SMJN affords a poor prognosis, with a mean overall survival of 11 months from the time of diagnosis.3 The mechanism of disease dissemination remains unknown but is thought to occur through lymphovascular invasion of tumor cells and spread via the umbilical ligament.1,4

Merkel cell carcinoma is a cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor that most commonly presents in elderly patients as red-violet nodules or plaques. Although Merkel cell carcinoma most frequently is encountered on sun-exposed skin, they also can arise on the trunk and abdomen. Positive IHC staining for CK20 would be expected; however, it was negative in our case.5

Cutaneous endometriosis is a rare disease presentation and most commonly occurs as a secondary process due to surgical inoculation of the abdominal wall. Primary cutaneous endometriosis in which there is no history of abdominal surgery less frequently is encountered. Patients typically will report pain and cyclical bleeding with menses. Pathology demonstrates ectopic endometrial tissue with glands and uterine myxoid stroma.6
Amelanotic melanoma is an uncommon subtype of malignant melanoma that presents as nonpigmented nodules that have a propensity to ulcerate and bleed. Furthermore, the umbilicus is an exceedingly rare location for primary melanoma. However, one report does exist, and amelanotic melanoma should be considered in the differential for patients with umbilical nodules.7
Dermoid cysts are benign congenital lesions that typically present as a painless, slow-growing, and wellcircumscribed nodule, as similarly experienced by our patient. They most commonly are found on the testicles and ovaries but also are known to arise in embryologic fusion planes, and reports of umbilical lesions exist.8 Dermoid cysts are diagnosed based on histopathology, supporting the need for a biopsy to distinguish a malignant process from benign lesions.9
- Gabriele R, Conte M, Egidi F, et al. Umbilical metastases: current viewpoint. World J Surg Oncol. 2005;3:13.
- Chalya PL, Mabula JB, Rambau PF, et al. Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule at a university teaching hospital in northwestern Tanzania: a retrospective review of 34 cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:151.
- Leyrat B, Bernadach M, Ginzac A, et al. Sister Mary Joseph nodules: a case report about a rare location of skin metastasis. Case Rep Oncol. 2021;14:664-670.
- Yendluri V, Centeno B, Springett GM. Pancreatic cancer presenting as a Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule: case report and update of the literature. Pancreas. 2007;34:161-164.
- Uchi H. Merkel cell carcinoma: an update and immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 2018;8:48.
- Bittar PG, Hryneewycz KT, Bryant EA. Primary cutaneous endometriosis presenting as an umbilical nodule. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1227.
- Kovitwanichkanont T, Joseph S, Yip L. Hidden in plain sight: umbilical melanoma [published online January 28, 2020]. Med J Aust. 2020;212:154-155.e1.
- Prior A, Anania P, Pacetti M, et al. Dermoid and epidermoid cysts of scalp: case series of 234 consecutive patients. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:119-124.
- Akinci O, Turker C, Erturk MS, et al. Umbilical dermoid cyst: a rare case. Cerrahpasa Med J. 2020;44:51-53.
- Gabriele R, Conte M, Egidi F, et al. Umbilical metastases: current viewpoint. World J Surg Oncol. 2005;3:13.
- Chalya PL, Mabula JB, Rambau PF, et al. Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule at a university teaching hospital in northwestern Tanzania: a retrospective review of 34 cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:151.
- Leyrat B, Bernadach M, Ginzac A, et al. Sister Mary Joseph nodules: a case report about a rare location of skin metastasis. Case Rep Oncol. 2021;14:664-670.
- Yendluri V, Centeno B, Springett GM. Pancreatic cancer presenting as a Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule: case report and update of the literature. Pancreas. 2007;34:161-164.
- Uchi H. Merkel cell carcinoma: an update and immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 2018;8:48.
- Bittar PG, Hryneewycz KT, Bryant EA. Primary cutaneous endometriosis presenting as an umbilical nodule. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1227.
- Kovitwanichkanont T, Joseph S, Yip L. Hidden in plain sight: umbilical melanoma [published online January 28, 2020]. Med J Aust. 2020;212:154-155.e1.
- Prior A, Anania P, Pacetti M, et al. Dermoid and epidermoid cysts of scalp: case series of 234 consecutive patients. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:119-124.
- Akinci O, Turker C, Erturk MS, et al. Umbilical dermoid cyst: a rare case. Cerrahpasa Med J. 2020;44:51-53.
A 64-year-old woman with no notable medical history was referred to our dermatology clinic with an intermittent eczematous rash around the eyelids of 3 months’ duration. While performing a total-body skin examination, a firm pink nodule with a smooth surface incidentally was discovered on the umbilicus. The patient was uncertain when the lesion first appeared and denied any associated symptoms including pain and bleeding. Additionally, a lymph node examination revealed right inguinal lymphadenopathy. Upon further questioning, she reported worsening muscle weakness, fatigue, night sweats, and an unintentional weight loss of 10 pounds. A 6-mm punch biopsy of the umbilical lesion was obtained for routine histopathology.
Preoperative D-dimer level is an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer after radical resection
Key clinical point: Preoperative elevated plasma D-dimer levels serve as an independent risk factor for poorer long-term survival outcomes in patients who have undergone curative surgery for gastric cancer.
Major finding: Multivariate analysis revealed elevated D-dimer levels to be independently associated with shorter overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.633; P = .003) and disease-free survival (aHR 1.58; P = .005).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study that included 903 patients with gastric cancer who underwent radical gastrectomy.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhang X et al. D-dimer, a predictor of bad outcome in gastric cancer patients undergoing radical resection. Sci Rep. 2022;12:16432 (Sep 30). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16582-9
Key clinical point: Preoperative elevated plasma D-dimer levels serve as an independent risk factor for poorer long-term survival outcomes in patients who have undergone curative surgery for gastric cancer.
Major finding: Multivariate analysis revealed elevated D-dimer levels to be independently associated with shorter overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.633; P = .003) and disease-free survival (aHR 1.58; P = .005).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study that included 903 patients with gastric cancer who underwent radical gastrectomy.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhang X et al. D-dimer, a predictor of bad outcome in gastric cancer patients undergoing radical resection. Sci Rep. 2022;12:16432 (Sep 30). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16582-9
Key clinical point: Preoperative elevated plasma D-dimer levels serve as an independent risk factor for poorer long-term survival outcomes in patients who have undergone curative surgery for gastric cancer.
Major finding: Multivariate analysis revealed elevated D-dimer levels to be independently associated with shorter overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.633; P = .003) and disease-free survival (aHR 1.58; P = .005).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study that included 903 patients with gastric cancer who underwent radical gastrectomy.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, among others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhang X et al. D-dimer, a predictor of bad outcome in gastric cancer patients undergoing radical resection. Sci Rep. 2022;12:16432 (Sep 30). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16582-9
Helicobacter pylori infection may predict a good response to immunotherapy in gastric cancer
Key clinical point: Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection is associated with the tumor expression of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in patients with gastric cancer.
Major finding: HP infection was significantly associated with the tumor expression of PD-L1 in patients with gastric cancer (odds ratio 1.90; P < .001), with the association not being significantly affected by the sample size, evaluation methods for PD-L1 expression, or quality score (all P > .05).
Study details: This meta-analysis of 10 observational studies investigated the association between HP infection and the tumor expression of PD-L1 in 1870 patients with gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of the Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China and others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhu Y et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2022:e13880 (Sep 27). Doi: 10.1111/eci.13880
Key clinical point: Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection is associated with the tumor expression of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in patients with gastric cancer.
Major finding: HP infection was significantly associated with the tumor expression of PD-L1 in patients with gastric cancer (odds ratio 1.90; P < .001), with the association not being significantly affected by the sample size, evaluation methods for PD-L1 expression, or quality score (all P > .05).
Study details: This meta-analysis of 10 observational studies investigated the association between HP infection and the tumor expression of PD-L1 in 1870 patients with gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of the Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China and others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhu Y et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2022:e13880 (Sep 27). Doi: 10.1111/eci.13880
Key clinical point: Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection is associated with the tumor expression of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in patients with gastric cancer.
Major finding: HP infection was significantly associated with the tumor expression of PD-L1 in patients with gastric cancer (odds ratio 1.90; P < .001), with the association not being significantly affected by the sample size, evaluation methods for PD-L1 expression, or quality score (all P > .05).
Study details: This meta-analysis of 10 observational studies investigated the association between HP infection and the tumor expression of PD-L1 in 1870 patients with gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of the Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China and others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Zhu Y et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2022:e13880 (Sep 27). Doi: 10.1111/eci.13880
Early gastric cancer: Outcomes of pylorus-preserving vs conventional distal gastrectomy
Key clinical point: In patients with early gastric cancer (EGC), pylorus-preserving gastrectomy (PPG) vs conventional distal gastrectomy (CDG) results in the harvest of fewer lymph nodes at stations 5, 6, 9, and 11p but similar survival outcomes.
Major finding: Patients who underwent PPG vs CDG had significantly lower numbers of lymph nodes harvested at stations 5, 6, 9, and 11p (weighted mean difference, −3.09; P < .001) but similar overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.63; P = .852) and recurrence-free survival (HR 0.29; P = .900).
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of 16 studies including 4500 patients with EGC who had undergone PPG or CDG with lymph node dissection.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Peking University People’s Hospital Research and Development Fund. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Hou S et al. Pathological and oncological outcomes of pylorus-preserving versus conventional distal gastrectomy in early gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20:308 (Sep 24). Doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02766-0
Key clinical point: In patients with early gastric cancer (EGC), pylorus-preserving gastrectomy (PPG) vs conventional distal gastrectomy (CDG) results in the harvest of fewer lymph nodes at stations 5, 6, 9, and 11p but similar survival outcomes.
Major finding: Patients who underwent PPG vs CDG had significantly lower numbers of lymph nodes harvested at stations 5, 6, 9, and 11p (weighted mean difference, −3.09; P < .001) but similar overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.63; P = .852) and recurrence-free survival (HR 0.29; P = .900).
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of 16 studies including 4500 patients with EGC who had undergone PPG or CDG with lymph node dissection.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Peking University People’s Hospital Research and Development Fund. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Hou S et al. Pathological and oncological outcomes of pylorus-preserving versus conventional distal gastrectomy in early gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20:308 (Sep 24). Doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02766-0
Key clinical point: In patients with early gastric cancer (EGC), pylorus-preserving gastrectomy (PPG) vs conventional distal gastrectomy (CDG) results in the harvest of fewer lymph nodes at stations 5, 6, 9, and 11p but similar survival outcomes.
Major finding: Patients who underwent PPG vs CDG had significantly lower numbers of lymph nodes harvested at stations 5, 6, 9, and 11p (weighted mean difference, −3.09; P < .001) but similar overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.63; P = .852) and recurrence-free survival (HR 0.29; P = .900).
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of 16 studies including 4500 patients with EGC who had undergone PPG or CDG with lymph node dissection.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Peking University People’s Hospital Research and Development Fund. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Hou S et al. Pathological and oncological outcomes of pylorus-preserving versus conventional distal gastrectomy in early gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20:308 (Sep 24). Doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02766-0
Risk factors for delayed gastric emptying following gastrectomy for gastric cancer
Key clinical point: The female sex, distal gastric tumors, and diabetes are risk factors for delayed gastric emptying (DGE) in patients who have undergone gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Major finding: Multivariate analysis revealed female sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.47; P = .037), diabetes (aOR 2.44; P = .041), and distal gastric tumors (aOR 2.59; P = .033) as independent risk factors for DGE.
Study details: This retrospective study included 412 patients with gastric cancer who underwent distal gastrectomy and thereafter did (n = 27) or did not (n = 385) experience DGE.
Disclosures: No information on funding sources was provided. The author declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Mukoyama T et al. Assessment of risk factors for delayed gastric emptying after distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2022;12:15903 (Sep 23). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20151-5
Key clinical point: The female sex, distal gastric tumors, and diabetes are risk factors for delayed gastric emptying (DGE) in patients who have undergone gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Major finding: Multivariate analysis revealed female sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.47; P = .037), diabetes (aOR 2.44; P = .041), and distal gastric tumors (aOR 2.59; P = .033) as independent risk factors for DGE.
Study details: This retrospective study included 412 patients with gastric cancer who underwent distal gastrectomy and thereafter did (n = 27) or did not (n = 385) experience DGE.
Disclosures: No information on funding sources was provided. The author declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Mukoyama T et al. Assessment of risk factors for delayed gastric emptying after distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2022;12:15903 (Sep 23). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20151-5
Key clinical point: The female sex, distal gastric tumors, and diabetes are risk factors for delayed gastric emptying (DGE) in patients who have undergone gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Major finding: Multivariate analysis revealed female sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 2.47; P = .037), diabetes (aOR 2.44; P = .041), and distal gastric tumors (aOR 2.59; P = .033) as independent risk factors for DGE.
Study details: This retrospective study included 412 patients with gastric cancer who underwent distal gastrectomy and thereafter did (n = 27) or did not (n = 385) experience DGE.
Disclosures: No information on funding sources was provided. The author declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Mukoyama T et al. Assessment of risk factors for delayed gastric emptying after distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2022;12:15903 (Sep 23). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20151-5
Laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: Postoperative NSAID use requires caution
Key clinical point: Postoperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use in intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (IV-PCA) is associated with an increased risk for anastomotic leakage, duodenal stump leakage, intra-abdominal bleeding, and intra-abdominal inflammation in patients who undergo laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Major finding: The NSAID vs non-NSAID group had a significantly higher incidence rate of anastomotic leakage (2.4% vs 0.7%; P = .002), duodenal stump leakage (1.8% vs 0.6%; P = .007), intra-abdominal bleeding (2.1% vs 0.7%; P = .005), and intra-abdominal abscess (1.5% vs 0.4%; P = .008).
Study details: This single-center retrospective study included 2150 patients with gastric cancer who underwent went laparoscopic gastrectomy and thereafter did (n = 935) or did not (n = 1,215) receive NSAID in IV-PCA.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Korean Gastric Cancer Association. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim SJ et al. Impact of postoperative NSAIDs (IV-PCA) use on short-term outcomes after laparoscopic gastrectomy for the patients of gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2022 (Sep 21). Doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09600-4
Key clinical point: Postoperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use in intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (IV-PCA) is associated with an increased risk for anastomotic leakage, duodenal stump leakage, intra-abdominal bleeding, and intra-abdominal inflammation in patients who undergo laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Major finding: The NSAID vs non-NSAID group had a significantly higher incidence rate of anastomotic leakage (2.4% vs 0.7%; P = .002), duodenal stump leakage (1.8% vs 0.6%; P = .007), intra-abdominal bleeding (2.1% vs 0.7%; P = .005), and intra-abdominal abscess (1.5% vs 0.4%; P = .008).
Study details: This single-center retrospective study included 2150 patients with gastric cancer who underwent went laparoscopic gastrectomy and thereafter did (n = 935) or did not (n = 1,215) receive NSAID in IV-PCA.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Korean Gastric Cancer Association. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim SJ et al. Impact of postoperative NSAIDs (IV-PCA) use on short-term outcomes after laparoscopic gastrectomy for the patients of gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2022 (Sep 21). Doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09600-4
Key clinical point: Postoperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use in intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (IV-PCA) is associated with an increased risk for anastomotic leakage, duodenal stump leakage, intra-abdominal bleeding, and intra-abdominal inflammation in patients who undergo laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Major finding: The NSAID vs non-NSAID group had a significantly higher incidence rate of anastomotic leakage (2.4% vs 0.7%; P = .002), duodenal stump leakage (1.8% vs 0.6%; P = .007), intra-abdominal bleeding (2.1% vs 0.7%; P = .005), and intra-abdominal abscess (1.5% vs 0.4%; P = .008).
Study details: This single-center retrospective study included 2150 patients with gastric cancer who underwent went laparoscopic gastrectomy and thereafter did (n = 935) or did not (n = 1,215) receive NSAID in IV-PCA.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Korean Gastric Cancer Association. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim SJ et al. Impact of postoperative NSAIDs (IV-PCA) use on short-term outcomes after laparoscopic gastrectomy for the patients of gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2022 (Sep 21). Doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09600-4
Early gastric cancer: Bleeding risk after ESD similar between patients with surgically altered and whole stomach
Key clinical point: The risk for bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for early gastric cancer (EGC) is not significantly different between patients with surgically altered stomach and whole stomach.
Major finding: Patients with surgically altered vs whole stomach did not have a significant difference in the risk for bleeding after ESD (adjusted odds ratio 1.37; 95% CI 0.87-2.17).
Study details: This subanalysis of a multicenter retrospective study included 10,765 patients who underwent ESD for EGC, of which 445 had surgically altered stomach and 10,320 had whole stomach.
Disclosures: This study was partially supported by the Japanese Foundation for Research and Promotion of Endoscopy Grant. M Fujishiro declared receiving lecture honoraria from various sources.
Source: Odagiri H et al. Bleeding following endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in surgically altered stomach. Digestion. 2022 (Oct 4). Doi: 10.1159/000526865
Key clinical point: The risk for bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for early gastric cancer (EGC) is not significantly different between patients with surgically altered stomach and whole stomach.
Major finding: Patients with surgically altered vs whole stomach did not have a significant difference in the risk for bleeding after ESD (adjusted odds ratio 1.37; 95% CI 0.87-2.17).
Study details: This subanalysis of a multicenter retrospective study included 10,765 patients who underwent ESD for EGC, of which 445 had surgically altered stomach and 10,320 had whole stomach.
Disclosures: This study was partially supported by the Japanese Foundation for Research and Promotion of Endoscopy Grant. M Fujishiro declared receiving lecture honoraria from various sources.
Source: Odagiri H et al. Bleeding following endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in surgically altered stomach. Digestion. 2022 (Oct 4). Doi: 10.1159/000526865
Key clinical point: The risk for bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for early gastric cancer (EGC) is not significantly different between patients with surgically altered stomach and whole stomach.
Major finding: Patients with surgically altered vs whole stomach did not have a significant difference in the risk for bleeding after ESD (adjusted odds ratio 1.37; 95% CI 0.87-2.17).
Study details: This subanalysis of a multicenter retrospective study included 10,765 patients who underwent ESD for EGC, of which 445 had surgically altered stomach and 10,320 had whole stomach.
Disclosures: This study was partially supported by the Japanese Foundation for Research and Promotion of Endoscopy Grant. M Fujishiro declared receiving lecture honoraria from various sources.
Source: Odagiri H et al. Bleeding following endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in surgically altered stomach. Digestion. 2022 (Oct 4). Doi: 10.1159/000526865
Gastric cancer: Neoadjuvant treatment status should not guide the extent of lymphadenectomy
Key clinical point: Routine D2-lymphadenectomy should be performed during total and distal gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer even after administering neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
Major finding: cT2, cT3, and cT4 stage tumors metastasized to all individual lymph node (LN) stations (1-9, 11, and 12a). Patients who did vs did not receive NAC had a numerically lower incidence of metastases in almost all stations (54% vs 63%) but a similar distribution of LN metastases over the different stations.
Study details: This side-study of the LOGICA trial included 212 patients with resectable gastric cancer who underwent total or distal D2-gastrectomy with en-bloc D2-lymphadenectomy combined with total omentectomy, of which 158 received NAC and 120 had LN metastases.
Disclosures: The LOGICA trial was sponsored by ZonMw (The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development); this side-study received no funding. Some authors declared serving as consultants or advisors for or receiving research funding and travel or accommodation fees and expenses from various sources.
Source: de Jongh C et al and the LOGICA Study Group. Pattern of lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: A side-study of the multicenter LOGICA-trial. Gastric Cancer. 2022 (Sep 14). Doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01329-2
Key clinical point: Routine D2-lymphadenectomy should be performed during total and distal gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer even after administering neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
Major finding: cT2, cT3, and cT4 stage tumors metastasized to all individual lymph node (LN) stations (1-9, 11, and 12a). Patients who did vs did not receive NAC had a numerically lower incidence of metastases in almost all stations (54% vs 63%) but a similar distribution of LN metastases over the different stations.
Study details: This side-study of the LOGICA trial included 212 patients with resectable gastric cancer who underwent total or distal D2-gastrectomy with en-bloc D2-lymphadenectomy combined with total omentectomy, of which 158 received NAC and 120 had LN metastases.
Disclosures: The LOGICA trial was sponsored by ZonMw (The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development); this side-study received no funding. Some authors declared serving as consultants or advisors for or receiving research funding and travel or accommodation fees and expenses from various sources.
Source: de Jongh C et al and the LOGICA Study Group. Pattern of lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: A side-study of the multicenter LOGICA-trial. Gastric Cancer. 2022 (Sep 14). Doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01329-2
Key clinical point: Routine D2-lymphadenectomy should be performed during total and distal gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer even after administering neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
Major finding: cT2, cT3, and cT4 stage tumors metastasized to all individual lymph node (LN) stations (1-9, 11, and 12a). Patients who did vs did not receive NAC had a numerically lower incidence of metastases in almost all stations (54% vs 63%) but a similar distribution of LN metastases over the different stations.
Study details: This side-study of the LOGICA trial included 212 patients with resectable gastric cancer who underwent total or distal D2-gastrectomy with en-bloc D2-lymphadenectomy combined with total omentectomy, of which 158 received NAC and 120 had LN metastases.
Disclosures: The LOGICA trial was sponsored by ZonMw (The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development); this side-study received no funding. Some authors declared serving as consultants or advisors for or receiving research funding and travel or accommodation fees and expenses from various sources.
Source: de Jongh C et al and the LOGICA Study Group. Pattern of lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: A side-study of the multicenter LOGICA-trial. Gastric Cancer. 2022 (Sep 14). Doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01329-2