User login
Resistance training tied to improvements in Parkinson’s disease symptoms
, new research suggests.
A meta-analysis, which included 18 randomized controlled trials and more than 1,000 patients with Parkinson’s disease, showed that those who underwent resistance training had significantly greater improvement in motor impairment, muscle strength, and mobility/balance than their peers who underwent passive or placebo interventions.
However, there was no significant difference between patients who participated in resistance training and those who participated in other active physical interventions, including yoga.
Overall, the results highlight the importance that these patients should participate in some type of physical exercise, said the study’s lead author, Romina Gollan, MSc, an assistant researcher in the division of medical psychology, University of Cologne, Germany. “Patients should definitely be doing exercises, including resistance training, if they want to. But the type of exercise is of secondary interest,” she said.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Positive but inconsistent
Previous reviews have suggested resistance training has positive effects on motor function in Parkinson’s disease. However, results from the included studies were inconsistent; and few reviews have examined nonmotor outcomes of resistance training in this population, the investigators noted.
After carrying out a literature search of studies that examined the effects of resistance training in Parkinson’s disease, the researchers included 18 randomized controlled trials in their current review. Among the 1,134 total participants, the mean age was 66 years, the mean Hoehn & Yahr stage was 2.3 (range 0-4), and the mean duration of Parkinson’s disease was 7.5 years.
The investigation was grouped into two meta-analysis groups: one examining resistance training versus a passive or placebo intervention and the other assessing resistance training versus active physical interventions, such as yoga.
During resistance training, participants use their full strength to do a repetition, working muscles to overcome a certain threshold, said Ms. Gollan. In contrast, a placebo intervention is “very low intensity” and involves a much lower threshold, she added.
Passive interventions include such things as stretching where the stimulus “is not high enough for muscles to adapt” and build strength, Ms. Gollan noted.
A passive intervention might also include “treatment as usual” or normal daily routines.
Patient preference important
The meta-analysis comparing resistance training groups with passive control groups showed significant large effects on muscle strength (standard mean difference, –0.84; 95% confidence interval, –1.29 to –0.39; P = .0003), motor impairment (SMD, –0.81; 95% CI, –1.34 to –0.27; P = .003), and mobility and balance (SMD, –1.80; 95% CI, –3.13 to –0.49; P = .007).
The review also showed significant but small effects on quality of life.
However, the meta-analysis that assessed resistance training versus other physical interventions showed no significant between-group differences.
Ms. Gollan noted that although there were some assessments of cognition and depression, the data were too limited to determine the impact of resistance training on these outcomes.
“We need more studies, especially randomized controlled trials, to investigate the effects of resistance training on nonmotor outcomes like depression and cognition,” she said.
Co-investigator Ann-Kristin Folkerts, PhD, who heads the University of Cologne medical psychology working group, noted that although exercise in general is beneficial for patients with Parkinson’s disease, the choice of activity should take patient preferences into consideration.
It is important that patients choose an exercise they enjoy “because otherwise they probably wouldn’t adhere to the treatment,” Dr. Folkerts said. “It’s important to have fun.”
Specific goals or objectives, such as improving quality of life or balance, should also be considered, she added.
Oversimplification?
Commenting on the research, Alice Nieuwboer, PhD, professor in the department of rehabilitation sciences and head of the neurorehabilitation research group at the University of Leuven, Belgium, disagreed that exercise type is of secondary importance in Parkinson’s disease.
“In my view, it’s of primary interest, especially at the mid- to later stages,” said Dr. Nieuwboer, who was not involved with the research.
She noted it is difficult to carry out meta-analyses of resistance training versus other interventions because studies comparing different exercise types “are rather scarce.”
“Another issue is that the dose may differ, so you’re comparing apples with pears,” said Dr. Nieuwboer.
She did agree that all patients should exercise, because it is “better than no exercise,” and they should be “free to choose a mode that interests them.”
However, she stressed that exercise requires significant effort on the part of patients with Parkinson’s disease, requires “sustained motivation,” and has to become habit-forming. This makes “exercise targeting” very important, with the target changing over the disease course, Dr. Nieuwboer said.
For example, for a patient at an early stage of the disease who can still move quite well, both resistance training and endurance training can improve fitness and health; but at a mid-stage, it is perhaps better for patients to work on balance and walking quality “to preempt the risk of falls and developing freezing,” she noted.
Later on, as movement becomes very difficult, “the exercise menu is even more restricted,” said Dr. Nieuwboer.
The bottom line is that a message saying “any movement counts” is an oversimplification, she added.
The study was funded by a grant from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. The investigators and Dr. Nieuwboer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
A meta-analysis, which included 18 randomized controlled trials and more than 1,000 patients with Parkinson’s disease, showed that those who underwent resistance training had significantly greater improvement in motor impairment, muscle strength, and mobility/balance than their peers who underwent passive or placebo interventions.
However, there was no significant difference between patients who participated in resistance training and those who participated in other active physical interventions, including yoga.
Overall, the results highlight the importance that these patients should participate in some type of physical exercise, said the study’s lead author, Romina Gollan, MSc, an assistant researcher in the division of medical psychology, University of Cologne, Germany. “Patients should definitely be doing exercises, including resistance training, if they want to. But the type of exercise is of secondary interest,” she said.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Positive but inconsistent
Previous reviews have suggested resistance training has positive effects on motor function in Parkinson’s disease. However, results from the included studies were inconsistent; and few reviews have examined nonmotor outcomes of resistance training in this population, the investigators noted.
After carrying out a literature search of studies that examined the effects of resistance training in Parkinson’s disease, the researchers included 18 randomized controlled trials in their current review. Among the 1,134 total participants, the mean age was 66 years, the mean Hoehn & Yahr stage was 2.3 (range 0-4), and the mean duration of Parkinson’s disease was 7.5 years.
The investigation was grouped into two meta-analysis groups: one examining resistance training versus a passive or placebo intervention and the other assessing resistance training versus active physical interventions, such as yoga.
During resistance training, participants use their full strength to do a repetition, working muscles to overcome a certain threshold, said Ms. Gollan. In contrast, a placebo intervention is “very low intensity” and involves a much lower threshold, she added.
Passive interventions include such things as stretching where the stimulus “is not high enough for muscles to adapt” and build strength, Ms. Gollan noted.
A passive intervention might also include “treatment as usual” or normal daily routines.
Patient preference important
The meta-analysis comparing resistance training groups with passive control groups showed significant large effects on muscle strength (standard mean difference, –0.84; 95% confidence interval, –1.29 to –0.39; P = .0003), motor impairment (SMD, –0.81; 95% CI, –1.34 to –0.27; P = .003), and mobility and balance (SMD, –1.80; 95% CI, –3.13 to –0.49; P = .007).
The review also showed significant but small effects on quality of life.
However, the meta-analysis that assessed resistance training versus other physical interventions showed no significant between-group differences.
Ms. Gollan noted that although there were some assessments of cognition and depression, the data were too limited to determine the impact of resistance training on these outcomes.
“We need more studies, especially randomized controlled trials, to investigate the effects of resistance training on nonmotor outcomes like depression and cognition,” she said.
Co-investigator Ann-Kristin Folkerts, PhD, who heads the University of Cologne medical psychology working group, noted that although exercise in general is beneficial for patients with Parkinson’s disease, the choice of activity should take patient preferences into consideration.
It is important that patients choose an exercise they enjoy “because otherwise they probably wouldn’t adhere to the treatment,” Dr. Folkerts said. “It’s important to have fun.”
Specific goals or objectives, such as improving quality of life or balance, should also be considered, she added.
Oversimplification?
Commenting on the research, Alice Nieuwboer, PhD, professor in the department of rehabilitation sciences and head of the neurorehabilitation research group at the University of Leuven, Belgium, disagreed that exercise type is of secondary importance in Parkinson’s disease.
“In my view, it’s of primary interest, especially at the mid- to later stages,” said Dr. Nieuwboer, who was not involved with the research.
She noted it is difficult to carry out meta-analyses of resistance training versus other interventions because studies comparing different exercise types “are rather scarce.”
“Another issue is that the dose may differ, so you’re comparing apples with pears,” said Dr. Nieuwboer.
She did agree that all patients should exercise, because it is “better than no exercise,” and they should be “free to choose a mode that interests them.”
However, she stressed that exercise requires significant effort on the part of patients with Parkinson’s disease, requires “sustained motivation,” and has to become habit-forming. This makes “exercise targeting” very important, with the target changing over the disease course, Dr. Nieuwboer said.
For example, for a patient at an early stage of the disease who can still move quite well, both resistance training and endurance training can improve fitness and health; but at a mid-stage, it is perhaps better for patients to work on balance and walking quality “to preempt the risk of falls and developing freezing,” she noted.
Later on, as movement becomes very difficult, “the exercise menu is even more restricted,” said Dr. Nieuwboer.
The bottom line is that a message saying “any movement counts” is an oversimplification, she added.
The study was funded by a grant from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. The investigators and Dr. Nieuwboer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
A meta-analysis, which included 18 randomized controlled trials and more than 1,000 patients with Parkinson’s disease, showed that those who underwent resistance training had significantly greater improvement in motor impairment, muscle strength, and mobility/balance than their peers who underwent passive or placebo interventions.
However, there was no significant difference between patients who participated in resistance training and those who participated in other active physical interventions, including yoga.
Overall, the results highlight the importance that these patients should participate in some type of physical exercise, said the study’s lead author, Romina Gollan, MSc, an assistant researcher in the division of medical psychology, University of Cologne, Germany. “Patients should definitely be doing exercises, including resistance training, if they want to. But the type of exercise is of secondary interest,” she said.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Positive but inconsistent
Previous reviews have suggested resistance training has positive effects on motor function in Parkinson’s disease. However, results from the included studies were inconsistent; and few reviews have examined nonmotor outcomes of resistance training in this population, the investigators noted.
After carrying out a literature search of studies that examined the effects of resistance training in Parkinson’s disease, the researchers included 18 randomized controlled trials in their current review. Among the 1,134 total participants, the mean age was 66 years, the mean Hoehn & Yahr stage was 2.3 (range 0-4), and the mean duration of Parkinson’s disease was 7.5 years.
The investigation was grouped into two meta-analysis groups: one examining resistance training versus a passive or placebo intervention and the other assessing resistance training versus active physical interventions, such as yoga.
During resistance training, participants use their full strength to do a repetition, working muscles to overcome a certain threshold, said Ms. Gollan. In contrast, a placebo intervention is “very low intensity” and involves a much lower threshold, she added.
Passive interventions include such things as stretching where the stimulus “is not high enough for muscles to adapt” and build strength, Ms. Gollan noted.
A passive intervention might also include “treatment as usual” or normal daily routines.
Patient preference important
The meta-analysis comparing resistance training groups with passive control groups showed significant large effects on muscle strength (standard mean difference, –0.84; 95% confidence interval, –1.29 to –0.39; P = .0003), motor impairment (SMD, –0.81; 95% CI, –1.34 to –0.27; P = .003), and mobility and balance (SMD, –1.80; 95% CI, –3.13 to –0.49; P = .007).
The review also showed significant but small effects on quality of life.
However, the meta-analysis that assessed resistance training versus other physical interventions showed no significant between-group differences.
Ms. Gollan noted that although there were some assessments of cognition and depression, the data were too limited to determine the impact of resistance training on these outcomes.
“We need more studies, especially randomized controlled trials, to investigate the effects of resistance training on nonmotor outcomes like depression and cognition,” she said.
Co-investigator Ann-Kristin Folkerts, PhD, who heads the University of Cologne medical psychology working group, noted that although exercise in general is beneficial for patients with Parkinson’s disease, the choice of activity should take patient preferences into consideration.
It is important that patients choose an exercise they enjoy “because otherwise they probably wouldn’t adhere to the treatment,” Dr. Folkerts said. “It’s important to have fun.”
Specific goals or objectives, such as improving quality of life or balance, should also be considered, she added.
Oversimplification?
Commenting on the research, Alice Nieuwboer, PhD, professor in the department of rehabilitation sciences and head of the neurorehabilitation research group at the University of Leuven, Belgium, disagreed that exercise type is of secondary importance in Parkinson’s disease.
“In my view, it’s of primary interest, especially at the mid- to later stages,” said Dr. Nieuwboer, who was not involved with the research.
She noted it is difficult to carry out meta-analyses of resistance training versus other interventions because studies comparing different exercise types “are rather scarce.”
“Another issue is that the dose may differ, so you’re comparing apples with pears,” said Dr. Nieuwboer.
She did agree that all patients should exercise, because it is “better than no exercise,” and they should be “free to choose a mode that interests them.”
However, she stressed that exercise requires significant effort on the part of patients with Parkinson’s disease, requires “sustained motivation,” and has to become habit-forming. This makes “exercise targeting” very important, with the target changing over the disease course, Dr. Nieuwboer said.
For example, for a patient at an early stage of the disease who can still move quite well, both resistance training and endurance training can improve fitness and health; but at a mid-stage, it is perhaps better for patients to work on balance and walking quality “to preempt the risk of falls and developing freezing,” she noted.
Later on, as movement becomes very difficult, “the exercise menu is even more restricted,” said Dr. Nieuwboer.
The bottom line is that a message saying “any movement counts” is an oversimplification, she added.
The study was funded by a grant from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. The investigators and Dr. Nieuwboer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MDS 2022
How do patients with chronic urticaria fare during pregnancy?
In addition, the rates of preterm births and medical problems of newborns in patients with CU are similar to those of the normal population and not linked to treatment used during pregnancy.
Those are the key findings from an analysis of new data from PREG-CU, an international, multicenter study of the Urticaria Centers of Reference and Excellence (UCARE) network. Results from the first PREG-CU analysis published in 2021 found that CU improved in about half of patients with CU during pregnancy. “However, two in five patients reported acute exacerbations of CU especially at the beginning and end of pregnancy,” investigators led by Emek Kocatürk, MD, of the department of dermatology and UCARE at Koç University School of Medicine, Istanbul, wrote in the new study, recently published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“In addition, 1 in 10 pregnant CU patients required urticaria emergency care and 1 of 6 had angioedema during pregnancy,” they said. Risk factors for worsening CU during pregnancy, they added, were “mild disease and no angioedema before pregnancy, not taking treatment before pregnancy, chronic inducible urticaria, CU worsening during a previous pregnancy, stress as a driver of exacerbations, and treatment during pregnancy.”
Analysis involved 288 pregnant women
To optimize treatment of CU during pregnancy and to better understand how treatment affects pregnancy outcomes, the researchers analyzed 288 pregnancies in 288 women with CU from 13 countries and 21 centers worldwide. Their mean age at pregnancy was 32.1 years, and their mean duration of CU was 84.9 months. Prior to pregnancy, 35.7% of patients rated the severity of their CU symptoms as mild, 34.2% rated it as moderate, and 29.7% rated it as severe.
The researchers found that during pregnancy, 60% of patients used urticaria medication, including standard-dose second-generation H1-antihistamines (35.1%), first-generation H1-antihistamines (7.6%), high-dose second-generation H1-antihistamines (5.6%), and omalizumab (5.6%). The preterm birth rate was 10.2%, which was similar between patients who did and did not receive treatment during pregnancy (11.6% vs. 8.7%, respectively; P = .59).
On multivariate logistic regression, two predictors for preterm birth emerged: giving birth to twins (a 13.3-fold increased risk; P = .016) and emergency referrals for CU (a 4.3-fold increased risk; P =.016). The cesarean delivery rate was 51.3%, and more than 90% of newborns were healthy at birth. There was no link between any patient or disease characteristics or treatments and medical problems at birth.
In other findings, 78.8% of women with CU breastfed their babies. Of the 58 patients who did not breastfeed, 20.7% indicated severe urticaria/angioedema and/or taking medications as the main reason for not breastfeeding.
“Most CU patients use treatment during pregnancy and such treatments, especially second generation H1 antihistamines, seem to be safe during pregnancy regardless of the trimester,” the researchers concluded. “Outcomes of pregnancy in patients with CU were similar compared to the general population and not linked to treatment used during pregnancy. Notably, emergency referral for CU was an independent risk factor for preterm birth,” and the high cesarean delivery rate was “probably linked to comorbidities associated with the disease,” they added. “Overall, these findings suggest that patients should continue their treatments using an individualized dose to provide optimal symptom control.”
International guidelines
The authors noted that international guidelines for the management of urticaria published in 2022 suggest that modern second-generation H1-antihistamines should be used for pregnant patients, preferably loratadine with a possible extrapolation to desloratadine, cetirizine, or levocetirizine.
“Similarly, in this population, we found that cetirizine and loratadine were the most commonly used antihistamines, followed by levocetirizine and fexofenadine,” Dr. Kocatürk and colleagues wrote.
“Guidelines also suggest that the use of first-generation H1-antihistamines should be avoided given their sedative effects; but if these are to be given, it would be wise to know that use of first-generation H1-antihistamines immediately before parturition could cause respiratory depression and other adverse effects in the neonate,” they added, noting that chlorpheniramine and diphenhydramine are the first-generation H1-antihistamines with the greatest evidence of safety in pregnancy.
They acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including its retrospective design and the fact that there were no data on low birth weight, small for gestational age, or miscarriage rates. In addition, disease activity or severity during pregnancy and after birth were not monitored.
Asked to comment on these results, Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who directs the center for eczema and itch in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, noted that despite a higher prevalence of CU among females compared with males, very little is known about how the condition is managed during pregnancy. “This retrospective study shows that most patients continue to utilize CU treatment during pregnancy (primarily second-generation antihistamines), with similar birth outcomes as the general population,” he said. “Interestingly, cesarean rates were higher among mothers with CU, and emergency CU referral was a risk factor for preterm birth. While additional prospective studies are needed, these results suggest that CU patients should be carefully managed, particularly during pregnancy, when treatment should be optimized.”
Dr. Kocatürk reported having received personal fees from Novartis, Ibrahim Etem-Menarini, and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Many coauthors reported having numerous financial disclosures. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
In addition, the rates of preterm births and medical problems of newborns in patients with CU are similar to those of the normal population and not linked to treatment used during pregnancy.
Those are the key findings from an analysis of new data from PREG-CU, an international, multicenter study of the Urticaria Centers of Reference and Excellence (UCARE) network. Results from the first PREG-CU analysis published in 2021 found that CU improved in about half of patients with CU during pregnancy. “However, two in five patients reported acute exacerbations of CU especially at the beginning and end of pregnancy,” investigators led by Emek Kocatürk, MD, of the department of dermatology and UCARE at Koç University School of Medicine, Istanbul, wrote in the new study, recently published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“In addition, 1 in 10 pregnant CU patients required urticaria emergency care and 1 of 6 had angioedema during pregnancy,” they said. Risk factors for worsening CU during pregnancy, they added, were “mild disease and no angioedema before pregnancy, not taking treatment before pregnancy, chronic inducible urticaria, CU worsening during a previous pregnancy, stress as a driver of exacerbations, and treatment during pregnancy.”
Analysis involved 288 pregnant women
To optimize treatment of CU during pregnancy and to better understand how treatment affects pregnancy outcomes, the researchers analyzed 288 pregnancies in 288 women with CU from 13 countries and 21 centers worldwide. Their mean age at pregnancy was 32.1 years, and their mean duration of CU was 84.9 months. Prior to pregnancy, 35.7% of patients rated the severity of their CU symptoms as mild, 34.2% rated it as moderate, and 29.7% rated it as severe.
The researchers found that during pregnancy, 60% of patients used urticaria medication, including standard-dose second-generation H1-antihistamines (35.1%), first-generation H1-antihistamines (7.6%), high-dose second-generation H1-antihistamines (5.6%), and omalizumab (5.6%). The preterm birth rate was 10.2%, which was similar between patients who did and did not receive treatment during pregnancy (11.6% vs. 8.7%, respectively; P = .59).
On multivariate logistic regression, two predictors for preterm birth emerged: giving birth to twins (a 13.3-fold increased risk; P = .016) and emergency referrals for CU (a 4.3-fold increased risk; P =.016). The cesarean delivery rate was 51.3%, and more than 90% of newborns were healthy at birth. There was no link between any patient or disease characteristics or treatments and medical problems at birth.
In other findings, 78.8% of women with CU breastfed their babies. Of the 58 patients who did not breastfeed, 20.7% indicated severe urticaria/angioedema and/or taking medications as the main reason for not breastfeeding.
“Most CU patients use treatment during pregnancy and such treatments, especially second generation H1 antihistamines, seem to be safe during pregnancy regardless of the trimester,” the researchers concluded. “Outcomes of pregnancy in patients with CU were similar compared to the general population and not linked to treatment used during pregnancy. Notably, emergency referral for CU was an independent risk factor for preterm birth,” and the high cesarean delivery rate was “probably linked to comorbidities associated with the disease,” they added. “Overall, these findings suggest that patients should continue their treatments using an individualized dose to provide optimal symptom control.”
International guidelines
The authors noted that international guidelines for the management of urticaria published in 2022 suggest that modern second-generation H1-antihistamines should be used for pregnant patients, preferably loratadine with a possible extrapolation to desloratadine, cetirizine, or levocetirizine.
“Similarly, in this population, we found that cetirizine and loratadine were the most commonly used antihistamines, followed by levocetirizine and fexofenadine,” Dr. Kocatürk and colleagues wrote.
“Guidelines also suggest that the use of first-generation H1-antihistamines should be avoided given their sedative effects; but if these are to be given, it would be wise to know that use of first-generation H1-antihistamines immediately before parturition could cause respiratory depression and other adverse effects in the neonate,” they added, noting that chlorpheniramine and diphenhydramine are the first-generation H1-antihistamines with the greatest evidence of safety in pregnancy.
They acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including its retrospective design and the fact that there were no data on low birth weight, small for gestational age, or miscarriage rates. In addition, disease activity or severity during pregnancy and after birth were not monitored.
Asked to comment on these results, Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who directs the center for eczema and itch in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, noted that despite a higher prevalence of CU among females compared with males, very little is known about how the condition is managed during pregnancy. “This retrospective study shows that most patients continue to utilize CU treatment during pregnancy (primarily second-generation antihistamines), with similar birth outcomes as the general population,” he said. “Interestingly, cesarean rates were higher among mothers with CU, and emergency CU referral was a risk factor for preterm birth. While additional prospective studies are needed, these results suggest that CU patients should be carefully managed, particularly during pregnancy, when treatment should be optimized.”
Dr. Kocatürk reported having received personal fees from Novartis, Ibrahim Etem-Menarini, and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Many coauthors reported having numerous financial disclosures. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
In addition, the rates of preterm births and medical problems of newborns in patients with CU are similar to those of the normal population and not linked to treatment used during pregnancy.
Those are the key findings from an analysis of new data from PREG-CU, an international, multicenter study of the Urticaria Centers of Reference and Excellence (UCARE) network. Results from the first PREG-CU analysis published in 2021 found that CU improved in about half of patients with CU during pregnancy. “However, two in five patients reported acute exacerbations of CU especially at the beginning and end of pregnancy,” investigators led by Emek Kocatürk, MD, of the department of dermatology and UCARE at Koç University School of Medicine, Istanbul, wrote in the new study, recently published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“In addition, 1 in 10 pregnant CU patients required urticaria emergency care and 1 of 6 had angioedema during pregnancy,” they said. Risk factors for worsening CU during pregnancy, they added, were “mild disease and no angioedema before pregnancy, not taking treatment before pregnancy, chronic inducible urticaria, CU worsening during a previous pregnancy, stress as a driver of exacerbations, and treatment during pregnancy.”
Analysis involved 288 pregnant women
To optimize treatment of CU during pregnancy and to better understand how treatment affects pregnancy outcomes, the researchers analyzed 288 pregnancies in 288 women with CU from 13 countries and 21 centers worldwide. Their mean age at pregnancy was 32.1 years, and their mean duration of CU was 84.9 months. Prior to pregnancy, 35.7% of patients rated the severity of their CU symptoms as mild, 34.2% rated it as moderate, and 29.7% rated it as severe.
The researchers found that during pregnancy, 60% of patients used urticaria medication, including standard-dose second-generation H1-antihistamines (35.1%), first-generation H1-antihistamines (7.6%), high-dose second-generation H1-antihistamines (5.6%), and omalizumab (5.6%). The preterm birth rate was 10.2%, which was similar between patients who did and did not receive treatment during pregnancy (11.6% vs. 8.7%, respectively; P = .59).
On multivariate logistic regression, two predictors for preterm birth emerged: giving birth to twins (a 13.3-fold increased risk; P = .016) and emergency referrals for CU (a 4.3-fold increased risk; P =.016). The cesarean delivery rate was 51.3%, and more than 90% of newborns were healthy at birth. There was no link between any patient or disease characteristics or treatments and medical problems at birth.
In other findings, 78.8% of women with CU breastfed their babies. Of the 58 patients who did not breastfeed, 20.7% indicated severe urticaria/angioedema and/or taking medications as the main reason for not breastfeeding.
“Most CU patients use treatment during pregnancy and such treatments, especially second generation H1 antihistamines, seem to be safe during pregnancy regardless of the trimester,” the researchers concluded. “Outcomes of pregnancy in patients with CU were similar compared to the general population and not linked to treatment used during pregnancy. Notably, emergency referral for CU was an independent risk factor for preterm birth,” and the high cesarean delivery rate was “probably linked to comorbidities associated with the disease,” they added. “Overall, these findings suggest that patients should continue their treatments using an individualized dose to provide optimal symptom control.”
International guidelines
The authors noted that international guidelines for the management of urticaria published in 2022 suggest that modern second-generation H1-antihistamines should be used for pregnant patients, preferably loratadine with a possible extrapolation to desloratadine, cetirizine, or levocetirizine.
“Similarly, in this population, we found that cetirizine and loratadine were the most commonly used antihistamines, followed by levocetirizine and fexofenadine,” Dr. Kocatürk and colleagues wrote.
“Guidelines also suggest that the use of first-generation H1-antihistamines should be avoided given their sedative effects; but if these are to be given, it would be wise to know that use of first-generation H1-antihistamines immediately before parturition could cause respiratory depression and other adverse effects in the neonate,” they added, noting that chlorpheniramine and diphenhydramine are the first-generation H1-antihistamines with the greatest evidence of safety in pregnancy.
They acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including its retrospective design and the fact that there were no data on low birth weight, small for gestational age, or miscarriage rates. In addition, disease activity or severity during pregnancy and after birth were not monitored.
Asked to comment on these results, Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who directs the center for eczema and itch in the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, noted that despite a higher prevalence of CU among females compared with males, very little is known about how the condition is managed during pregnancy. “This retrospective study shows that most patients continue to utilize CU treatment during pregnancy (primarily second-generation antihistamines), with similar birth outcomes as the general population,” he said. “Interestingly, cesarean rates were higher among mothers with CU, and emergency CU referral was a risk factor for preterm birth. While additional prospective studies are needed, these results suggest that CU patients should be carefully managed, particularly during pregnancy, when treatment should be optimized.”
Dr. Kocatürk reported having received personal fees from Novartis, Ibrahim Etem-Menarini, and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Many coauthors reported having numerous financial disclosures. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
FROM JEADV
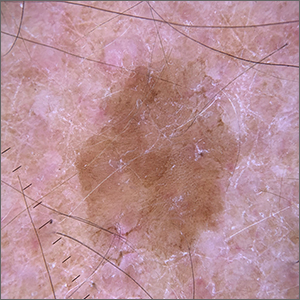
Velvety brown lesion
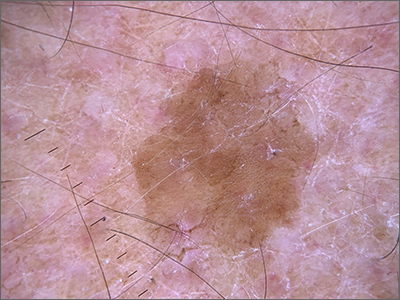
Dermoscopy revealed a uniform, sharply demarcated, slightly scaly lesion on a background of occasional scale and solar-damaged skin. This appearance, paired with the absence of abnormal blood vessels or suspicious, irregular pigmentation, pointed to a diagnosis of benign lichenoid keratosis also known as lichenoid keratosis (LK) or lichen planus-like keratosis. (It’s worth noting that in some cases, a dermoscopic evaluation will reveal blue-grey dots rather than the uniform, velvety brown pigmentation that was seen here.)
LK is a benign reactive inflammatory lesion that usually manifests as a solitary lesion in middle age. LKs can be found on the trunk or lower extremities. As the alternative name “lichen planus-like keratosis” implies, the lesions can be purple, polygonal, raised, and have stria. The etiology is unknown but thought to be a reaction to a lentigo or another lesion, resulting in an inflammatory infiltrate.1
If dermoscopic evaluation of the lesion is unclear, biopsy is warranted. Maor et al1 reported the pathology results of 263 consecutive patients with a histologic diagnosis of LK. Of those cases, 47% were clinically thought to be basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and 18% were submitted with a diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis.1 The high rate of concern for BCC and not listing a diagnosis of LK may have been the result of clinicians doing biopsies on the atypical lesions and clinically following the typical banal lesions.
At the patient’s request, he was given a written list of the diagnoses of his various skin lesions and advised that his LK was benign and did not require treatment. He was advised to continue coming in for serial skin examinations and report any concerning lesions in the interim.
Image and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Maor D, Ondhia C, Yu LL, et al. Lichenoid keratosis is frequently misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:663-666. doi: 10.1111/ced.13178

Dermoscopy revealed a uniform, sharply demarcated, slightly scaly lesion on a background of occasional scale and solar-damaged skin. This appearance, paired with the absence of abnormal blood vessels or suspicious, irregular pigmentation, pointed to a diagnosis of benign lichenoid keratosis also known as lichenoid keratosis (LK) or lichen planus-like keratosis. (It’s worth noting that in some cases, a dermoscopic evaluation will reveal blue-grey dots rather than the uniform, velvety brown pigmentation that was seen here.)
LK is a benign reactive inflammatory lesion that usually manifests as a solitary lesion in middle age. LKs can be found on the trunk or lower extremities. As the alternative name “lichen planus-like keratosis” implies, the lesions can be purple, polygonal, raised, and have stria. The etiology is unknown but thought to be a reaction to a lentigo or another lesion, resulting in an inflammatory infiltrate.1
If dermoscopic evaluation of the lesion is unclear, biopsy is warranted. Maor et al1 reported the pathology results of 263 consecutive patients with a histologic diagnosis of LK. Of those cases, 47% were clinically thought to be basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and 18% were submitted with a diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis.1 The high rate of concern for BCC and not listing a diagnosis of LK may have been the result of clinicians doing biopsies on the atypical lesions and clinically following the typical banal lesions.
At the patient’s request, he was given a written list of the diagnoses of his various skin lesions and advised that his LK was benign and did not require treatment. He was advised to continue coming in for serial skin examinations and report any concerning lesions in the interim.
Image and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

Dermoscopy revealed a uniform, sharply demarcated, slightly scaly lesion on a background of occasional scale and solar-damaged skin. This appearance, paired with the absence of abnormal blood vessels or suspicious, irregular pigmentation, pointed to a diagnosis of benign lichenoid keratosis also known as lichenoid keratosis (LK) or lichen planus-like keratosis. (It’s worth noting that in some cases, a dermoscopic evaluation will reveal blue-grey dots rather than the uniform, velvety brown pigmentation that was seen here.)
LK is a benign reactive inflammatory lesion that usually manifests as a solitary lesion in middle age. LKs can be found on the trunk or lower extremities. As the alternative name “lichen planus-like keratosis” implies, the lesions can be purple, polygonal, raised, and have stria. The etiology is unknown but thought to be a reaction to a lentigo or another lesion, resulting in an inflammatory infiltrate.1
If dermoscopic evaluation of the lesion is unclear, biopsy is warranted. Maor et al1 reported the pathology results of 263 consecutive patients with a histologic diagnosis of LK. Of those cases, 47% were clinically thought to be basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and 18% were submitted with a diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis.1 The high rate of concern for BCC and not listing a diagnosis of LK may have been the result of clinicians doing biopsies on the atypical lesions and clinically following the typical banal lesions.
At the patient’s request, he was given a written list of the diagnoses of his various skin lesions and advised that his LK was benign and did not require treatment. He was advised to continue coming in for serial skin examinations and report any concerning lesions in the interim.
Image and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Maor D, Ondhia C, Yu LL, et al. Lichenoid keratosis is frequently misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:663-666. doi: 10.1111/ced.13178
1. Maor D, Ondhia C, Yu LL, et al. Lichenoid keratosis is frequently misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:663-666. doi: 10.1111/ced.13178
Who are the patients with longstanding ankylosing spondylitis without syndesmophytes?
Syndesmophytes are not present in a subgroup of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and sacroiliac (SI) joint fusion who have had the disease for 20 years or longer, according to findings from a nested case-control study.
Syndesmophytes did not occur in only 23 (7%) of 354 patients, and these patients without spinal-fusing bone growths were less likely to be female but very likely to be HLA-B27 positive, Lauren K. Ridley, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, and colleagues reported in The Journal of Rheumatology.
“Women appear to have a different phenotype in AS; we found that they are less likely to form syndesmophytes despite fused SI joints with at least 20 years of disease duration. We do not understand the reasons behind these differences among the possibilities of genetic, hormonal, and bio-mechanical factors,” the authors wrote.
AS is a heterogenous disease that affects different people in various ways, Dr. Ridley noted. “Prior research has shown that and hasn’t really elucidated how different people manifest their disease. Previous research has shown that women tend to have more nonradiographic spondylitis,” Dr. Ridley said in an interview.
“This is still a very heterogenous disease. We don’t fully understand it, and we don’t know why some patients present with SI joint disease [and] no syndesmophytes, or some patients have the opposite. Truly, we do need to do more studies to find out why some patients behave differently and if there are ways we can try to alter that,” Dr. Ridley continued.
The researchers evaluated 354 patients from the Prospective Study of Outcomes in Ankylosing Spondylitis (PSOAS). Of these patients, 23 did not have syndesmophytes. Patients were selected if they had fused SI joints (bilateral grade 4 sacroiliac joint disease) and had a disease course lasting 20 years or more. The researchers identified risk factors for syndesmophytes using classification and regression trees (CART) analysis and then reassessed their validity with univariable logistic regression models.
All 23 patients who had no syndesmophytes were HLA-B27 positive, and all patients older than 45 years at symptom onset had syndesmophytes.
The results also highlighted age of disease onset as an important predictor of syndesmophytes in males. Syndesmophytes were less likely to be reported in males with a disease onset at 16 years or younger.
The presence of syndesmophytes was linked with an age older than 16 years at symptom onset (OR, 2.72; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-6.45), and syndesmophytes were less likely to occur among HLA-B27 positive individuals (P = .03).
Females were less likely than males to have syndesmophytes, as verified by univariable analysis (odds ratio, 0.17; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.41).
“There is likely a complex interplay of factors leading to differences in radiographic damage between the sacroiliac joints and the spine in AS, and it is interesting to consider if HLA-B27 may have more effect on sacroiliac joint damage than spinal damage,” the authors noted.
Some limitations of the study include the researchers’ choice to compare a subtype with overt spinal involvement and a subtype with limited spinal involvement when other criteria could have been used to separate cases, and their use of the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Scoring System (mSaSSS) to examine radiographic changes over time, as the mSaSSS does not take into account radiographic variation in the zygaphophyseal joints and thoracic spine (and were not part of the dataset). Another limitation was the relatively small cohort size, the researchers noted.
“This was a small study, and further studies are needed to elucidate why AS disease may behave differently in this and other subgroups,” Dr. Ridley and colleagues concluded.
Expert commentary
Researchers agree that spinal structural damage is a predictor of further damage in patients with radiographic AS, Marina Magrey, MD, the Roland W. Moskowitz Professor in Rheumatic Diseases at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. She pointed out that previous literature has shown that longer disease durations make it more likely that patients will have syndesmophytes.
Previous research has also shown that there was an association between structural damage in the SI joints and the function and mobility of the spine. This observation was independent of the disease activity and prior structural damage in the spine, Dr. Magrey noted.
“This is a very complex disease with very diverse manifestations. Traditionally, it was thought to be a disease of men, but now we believe it is equally common between men and women. The burden is equal between men and women, and they need to be treated equally. Both of them need to be treated early on to prevent this radiographic damage,” she said.
Looking ahead, there need to be more translational studies looking for answers as to why there are phenotypic differences between men and women, as well as why men have spinal fusion more often than women. Bed-to-the-bench studies are warranted to get more answers, she said.
The study was supported by an NIH Centers for Translational Science Award grant. The researchers declared having no conflicts of interest related to the study. One author is supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Intramural Research Program, and another by the Spondyloarthritis Association of America and the University of Texas Health Center for Clinical and Translational Sciences KL2 program. Another author is an adviser for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, and has grant support from Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
Dr. Magrey disclosed being a consultant for Novartis, UCB, Pfizer, AbbVie, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Eli Lilly.
Syndesmophytes are not present in a subgroup of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and sacroiliac (SI) joint fusion who have had the disease for 20 years or longer, according to findings from a nested case-control study.
Syndesmophytes did not occur in only 23 (7%) of 354 patients, and these patients without spinal-fusing bone growths were less likely to be female but very likely to be HLA-B27 positive, Lauren K. Ridley, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, and colleagues reported in The Journal of Rheumatology.
“Women appear to have a different phenotype in AS; we found that they are less likely to form syndesmophytes despite fused SI joints with at least 20 years of disease duration. We do not understand the reasons behind these differences among the possibilities of genetic, hormonal, and bio-mechanical factors,” the authors wrote.
AS is a heterogenous disease that affects different people in various ways, Dr. Ridley noted. “Prior research has shown that and hasn’t really elucidated how different people manifest their disease. Previous research has shown that women tend to have more nonradiographic spondylitis,” Dr. Ridley said in an interview.
“This is still a very heterogenous disease. We don’t fully understand it, and we don’t know why some patients present with SI joint disease [and] no syndesmophytes, or some patients have the opposite. Truly, we do need to do more studies to find out why some patients behave differently and if there are ways we can try to alter that,” Dr. Ridley continued.
The researchers evaluated 354 patients from the Prospective Study of Outcomes in Ankylosing Spondylitis (PSOAS). Of these patients, 23 did not have syndesmophytes. Patients were selected if they had fused SI joints (bilateral grade 4 sacroiliac joint disease) and had a disease course lasting 20 years or more. The researchers identified risk factors for syndesmophytes using classification and regression trees (CART) analysis and then reassessed their validity with univariable logistic regression models.
All 23 patients who had no syndesmophytes were HLA-B27 positive, and all patients older than 45 years at symptom onset had syndesmophytes.
The results also highlighted age of disease onset as an important predictor of syndesmophytes in males. Syndesmophytes were less likely to be reported in males with a disease onset at 16 years or younger.
The presence of syndesmophytes was linked with an age older than 16 years at symptom onset (OR, 2.72; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-6.45), and syndesmophytes were less likely to occur among HLA-B27 positive individuals (P = .03).
Females were less likely than males to have syndesmophytes, as verified by univariable analysis (odds ratio, 0.17; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.41).
“There is likely a complex interplay of factors leading to differences in radiographic damage between the sacroiliac joints and the spine in AS, and it is interesting to consider if HLA-B27 may have more effect on sacroiliac joint damage than spinal damage,” the authors noted.
Some limitations of the study include the researchers’ choice to compare a subtype with overt spinal involvement and a subtype with limited spinal involvement when other criteria could have been used to separate cases, and their use of the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Scoring System (mSaSSS) to examine radiographic changes over time, as the mSaSSS does not take into account radiographic variation in the zygaphophyseal joints and thoracic spine (and were not part of the dataset). Another limitation was the relatively small cohort size, the researchers noted.
“This was a small study, and further studies are needed to elucidate why AS disease may behave differently in this and other subgroups,” Dr. Ridley and colleagues concluded.
Expert commentary
Researchers agree that spinal structural damage is a predictor of further damage in patients with radiographic AS, Marina Magrey, MD, the Roland W. Moskowitz Professor in Rheumatic Diseases at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. She pointed out that previous literature has shown that longer disease durations make it more likely that patients will have syndesmophytes.
Previous research has also shown that there was an association between structural damage in the SI joints and the function and mobility of the spine. This observation was independent of the disease activity and prior structural damage in the spine, Dr. Magrey noted.
“This is a very complex disease with very diverse manifestations. Traditionally, it was thought to be a disease of men, but now we believe it is equally common between men and women. The burden is equal between men and women, and they need to be treated equally. Both of them need to be treated early on to prevent this radiographic damage,” she said.
Looking ahead, there need to be more translational studies looking for answers as to why there are phenotypic differences between men and women, as well as why men have spinal fusion more often than women. Bed-to-the-bench studies are warranted to get more answers, she said.
The study was supported by an NIH Centers for Translational Science Award grant. The researchers declared having no conflicts of interest related to the study. One author is supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Intramural Research Program, and another by the Spondyloarthritis Association of America and the University of Texas Health Center for Clinical and Translational Sciences KL2 program. Another author is an adviser for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, and has grant support from Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
Dr. Magrey disclosed being a consultant for Novartis, UCB, Pfizer, AbbVie, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Eli Lilly.
Syndesmophytes are not present in a subgroup of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and sacroiliac (SI) joint fusion who have had the disease for 20 years or longer, according to findings from a nested case-control study.
Syndesmophytes did not occur in only 23 (7%) of 354 patients, and these patients without spinal-fusing bone growths were less likely to be female but very likely to be HLA-B27 positive, Lauren K. Ridley, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, and colleagues reported in The Journal of Rheumatology.
“Women appear to have a different phenotype in AS; we found that they are less likely to form syndesmophytes despite fused SI joints with at least 20 years of disease duration. We do not understand the reasons behind these differences among the possibilities of genetic, hormonal, and bio-mechanical factors,” the authors wrote.
AS is a heterogenous disease that affects different people in various ways, Dr. Ridley noted. “Prior research has shown that and hasn’t really elucidated how different people manifest their disease. Previous research has shown that women tend to have more nonradiographic spondylitis,” Dr. Ridley said in an interview.
“This is still a very heterogenous disease. We don’t fully understand it, and we don’t know why some patients present with SI joint disease [and] no syndesmophytes, or some patients have the opposite. Truly, we do need to do more studies to find out why some patients behave differently and if there are ways we can try to alter that,” Dr. Ridley continued.
The researchers evaluated 354 patients from the Prospective Study of Outcomes in Ankylosing Spondylitis (PSOAS). Of these patients, 23 did not have syndesmophytes. Patients were selected if they had fused SI joints (bilateral grade 4 sacroiliac joint disease) and had a disease course lasting 20 years or more. The researchers identified risk factors for syndesmophytes using classification and regression trees (CART) analysis and then reassessed their validity with univariable logistic regression models.
All 23 patients who had no syndesmophytes were HLA-B27 positive, and all patients older than 45 years at symptom onset had syndesmophytes.
The results also highlighted age of disease onset as an important predictor of syndesmophytes in males. Syndesmophytes were less likely to be reported in males with a disease onset at 16 years or younger.
The presence of syndesmophytes was linked with an age older than 16 years at symptom onset (OR, 2.72; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-6.45), and syndesmophytes were less likely to occur among HLA-B27 positive individuals (P = .03).
Females were less likely than males to have syndesmophytes, as verified by univariable analysis (odds ratio, 0.17; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.41).
“There is likely a complex interplay of factors leading to differences in radiographic damage between the sacroiliac joints and the spine in AS, and it is interesting to consider if HLA-B27 may have more effect on sacroiliac joint damage than spinal damage,” the authors noted.
Some limitations of the study include the researchers’ choice to compare a subtype with overt spinal involvement and a subtype with limited spinal involvement when other criteria could have been used to separate cases, and their use of the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Scoring System (mSaSSS) to examine radiographic changes over time, as the mSaSSS does not take into account radiographic variation in the zygaphophyseal joints and thoracic spine (and were not part of the dataset). Another limitation was the relatively small cohort size, the researchers noted.
“This was a small study, and further studies are needed to elucidate why AS disease may behave differently in this and other subgroups,” Dr. Ridley and colleagues concluded.
Expert commentary
Researchers agree that spinal structural damage is a predictor of further damage in patients with radiographic AS, Marina Magrey, MD, the Roland W. Moskowitz Professor in Rheumatic Diseases at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. She pointed out that previous literature has shown that longer disease durations make it more likely that patients will have syndesmophytes.
Previous research has also shown that there was an association between structural damage in the SI joints and the function and mobility of the spine. This observation was independent of the disease activity and prior structural damage in the spine, Dr. Magrey noted.
“This is a very complex disease with very diverse manifestations. Traditionally, it was thought to be a disease of men, but now we believe it is equally common between men and women. The burden is equal between men and women, and they need to be treated equally. Both of them need to be treated early on to prevent this radiographic damage,” she said.
Looking ahead, there need to be more translational studies looking for answers as to why there are phenotypic differences between men and women, as well as why men have spinal fusion more often than women. Bed-to-the-bench studies are warranted to get more answers, she said.
The study was supported by an NIH Centers for Translational Science Award grant. The researchers declared having no conflicts of interest related to the study. One author is supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Intramural Research Program, and another by the Spondyloarthritis Association of America and the University of Texas Health Center for Clinical and Translational Sciences KL2 program. Another author is an adviser for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, and has grant support from Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
Dr. Magrey disclosed being a consultant for Novartis, UCB, Pfizer, AbbVie, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Eli Lilly.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF RHEUMATOLOGY
Mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 may be underestimated
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – The rate of mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection is likely higher than the current estimate of 2%-8%, suggests a recent study using cord blood serology to determine incidence. The study was presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“Cord blood screening is a potential tool to identify SARS-CoV-2 infected and/or exposed neonates who should then be followed for long-term consequences of mother-to-child transmission,” Amy Yeh, MD, an assistant professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, told attendees at the meeting.
Dr. Yeh and her colleagues collected cord blood from more than 500 mothers at LAC+USC Medical Center from October 2021 to April 2022 and tested them for IgG antibodies against three SARS-CoV-2 antigens: nucleoprotein (N), receptor-binding domain (RBD), and spike protein (S1). Results with an IgG mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) above 700 were considered positive for IgG antibodies. A positive result for N as well as RBD or S1 indicated a natural infection while a positive result for only RBD or S1 indicated a vaccine response or past infection.
The researchers also tested a subset of the IgG positive samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against N, S1, and RBD, with an IgM MFI greater than 24 and an IgA MFI greater than 102 used as the thresholds for positive results.
Among 384 cord blood samples analyzed, 85.4% were positive for IgG against RBD, indicating that the mother had SARS-CoV-2 immunity from either a past infection or vaccination. Of these anti-RBD positive samples, 60.7% were anti-N IgG negative, suggesting that N had waned since vaccination or the past infection.
Since the other 39.3% that were anti-N IgG positive suggest a past maternal infection, the researchers assessed these 129 samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against RBD. They found that 16 of them had high levels of anti-RBD IgA and/or IgM antibodies, pointing to a rate of mother-to-child-transmission of up to 12.4%.
Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, a professor and the chair of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the research, said most studies of placental transmission have focused on virologic testing, such as PCR. “Serologic tests for congenital infections are inherently challenged by the transfer of maternal IgG across the placenta and therefore must rely on non-IgG isotype response detection, which have inherently been more susceptible to false-positive results than IgG-based tests,” Dr. Permar said.
Also, “it is unclear if virologic testing was performed in the infants, which, if positive in the same infants for which cord blood IgM/IgA responses were identified, could further validate positive serologic findings,” added Dr. Permar, who is also pediatrician-in-chief at New York-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital.
Given these limitations, Dr. Permar reiterated that diagnostics for congenital SARS-CoV-2 continue to evolve, even if congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection currently appears rare. Dr. Permar said she agreed with Dr. Yeh that following those who do develop this infection is important.
“There have been initial reports of neurodevelopmental and other outcomes from long-term follow-up cohorts of infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection in utero with variable results and it should continue to be pursued using cohorts both enrolled early in the pandemic and those enrolled more recently after population-level immunity to SARS-CoV-2 was achieved,” said Dr. Permar.
Dr. Permar serves as a consultant to Moderna, Pfizer, Merck, Dynavax, and Hoopika on their CMV vaccine programs and has led sponsored research programs with Moderna and Merck. Information on study funding and on disclosures for Dr. Yeh was unavailable.
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – The rate of mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection is likely higher than the current estimate of 2%-8%, suggests a recent study using cord blood serology to determine incidence. The study was presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“Cord blood screening is a potential tool to identify SARS-CoV-2 infected and/or exposed neonates who should then be followed for long-term consequences of mother-to-child transmission,” Amy Yeh, MD, an assistant professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, told attendees at the meeting.
Dr. Yeh and her colleagues collected cord blood from more than 500 mothers at LAC+USC Medical Center from October 2021 to April 2022 and tested them for IgG antibodies against three SARS-CoV-2 antigens: nucleoprotein (N), receptor-binding domain (RBD), and spike protein (S1). Results with an IgG mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) above 700 were considered positive for IgG antibodies. A positive result for N as well as RBD or S1 indicated a natural infection while a positive result for only RBD or S1 indicated a vaccine response or past infection.
The researchers also tested a subset of the IgG positive samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against N, S1, and RBD, with an IgM MFI greater than 24 and an IgA MFI greater than 102 used as the thresholds for positive results.
Among 384 cord blood samples analyzed, 85.4% were positive for IgG against RBD, indicating that the mother had SARS-CoV-2 immunity from either a past infection or vaccination. Of these anti-RBD positive samples, 60.7% were anti-N IgG negative, suggesting that N had waned since vaccination or the past infection.
Since the other 39.3% that were anti-N IgG positive suggest a past maternal infection, the researchers assessed these 129 samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against RBD. They found that 16 of them had high levels of anti-RBD IgA and/or IgM antibodies, pointing to a rate of mother-to-child-transmission of up to 12.4%.
Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, a professor and the chair of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the research, said most studies of placental transmission have focused on virologic testing, such as PCR. “Serologic tests for congenital infections are inherently challenged by the transfer of maternal IgG across the placenta and therefore must rely on non-IgG isotype response detection, which have inherently been more susceptible to false-positive results than IgG-based tests,” Dr. Permar said.
Also, “it is unclear if virologic testing was performed in the infants, which, if positive in the same infants for which cord blood IgM/IgA responses were identified, could further validate positive serologic findings,” added Dr. Permar, who is also pediatrician-in-chief at New York-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital.
Given these limitations, Dr. Permar reiterated that diagnostics for congenital SARS-CoV-2 continue to evolve, even if congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection currently appears rare. Dr. Permar said she agreed with Dr. Yeh that following those who do develop this infection is important.
“There have been initial reports of neurodevelopmental and other outcomes from long-term follow-up cohorts of infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection in utero with variable results and it should continue to be pursued using cohorts both enrolled early in the pandemic and those enrolled more recently after population-level immunity to SARS-CoV-2 was achieved,” said Dr. Permar.
Dr. Permar serves as a consultant to Moderna, Pfizer, Merck, Dynavax, and Hoopika on their CMV vaccine programs and has led sponsored research programs with Moderna and Merck. Information on study funding and on disclosures for Dr. Yeh was unavailable.
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – The rate of mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection is likely higher than the current estimate of 2%-8%, suggests a recent study using cord blood serology to determine incidence. The study was presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“Cord blood screening is a potential tool to identify SARS-CoV-2 infected and/or exposed neonates who should then be followed for long-term consequences of mother-to-child transmission,” Amy Yeh, MD, an assistant professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, told attendees at the meeting.
Dr. Yeh and her colleagues collected cord blood from more than 500 mothers at LAC+USC Medical Center from October 2021 to April 2022 and tested them for IgG antibodies against three SARS-CoV-2 antigens: nucleoprotein (N), receptor-binding domain (RBD), and spike protein (S1). Results with an IgG mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) above 700 were considered positive for IgG antibodies. A positive result for N as well as RBD or S1 indicated a natural infection while a positive result for only RBD or S1 indicated a vaccine response or past infection.
The researchers also tested a subset of the IgG positive samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against N, S1, and RBD, with an IgM MFI greater than 24 and an IgA MFI greater than 102 used as the thresholds for positive results.
Among 384 cord blood samples analyzed, 85.4% were positive for IgG against RBD, indicating that the mother had SARS-CoV-2 immunity from either a past infection or vaccination. Of these anti-RBD positive samples, 60.7% were anti-N IgG negative, suggesting that N had waned since vaccination or the past infection.
Since the other 39.3% that were anti-N IgG positive suggest a past maternal infection, the researchers assessed these 129 samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against RBD. They found that 16 of them had high levels of anti-RBD IgA and/or IgM antibodies, pointing to a rate of mother-to-child-transmission of up to 12.4%.
Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, a professor and the chair of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the research, said most studies of placental transmission have focused on virologic testing, such as PCR. “Serologic tests for congenital infections are inherently challenged by the transfer of maternal IgG across the placenta and therefore must rely on non-IgG isotype response detection, which have inherently been more susceptible to false-positive results than IgG-based tests,” Dr. Permar said.
Also, “it is unclear if virologic testing was performed in the infants, which, if positive in the same infants for which cord blood IgM/IgA responses were identified, could further validate positive serologic findings,” added Dr. Permar, who is also pediatrician-in-chief at New York-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital.
Given these limitations, Dr. Permar reiterated that diagnostics for congenital SARS-CoV-2 continue to evolve, even if congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection currently appears rare. Dr. Permar said she agreed with Dr. Yeh that following those who do develop this infection is important.
“There have been initial reports of neurodevelopmental and other outcomes from long-term follow-up cohorts of infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection in utero with variable results and it should continue to be pursued using cohorts both enrolled early in the pandemic and those enrolled more recently after population-level immunity to SARS-CoV-2 was achieved,” said Dr. Permar.
Dr. Permar serves as a consultant to Moderna, Pfizer, Merck, Dynavax, and Hoopika on their CMV vaccine programs and has led sponsored research programs with Moderna and Merck. Information on study funding and on disclosures for Dr. Yeh was unavailable.
AT AAP 2022
Bariatric surgery prompts visceral fat reduction, cardiac changes
Weight loss after bariatric surgery was linked with visceral fat reduction as well as reduced blood pressure, fasting glucose, and left ventricular remodeling, based an imaging study in 213 patients.
“We found that ventricular function measured by strain imaging improved in both the left and right sides of the heart, but function measured in the traditional method using endocardial motion [in other words, ejection fraction] actually worsened,” senior investigator Barry A. Borlaug, MD, said in an interview.
Although previous studies have shown positive effects of weight loss on the heart after bariatric surgery, most have been short term and have not specifically examined the effects of visceral fat reduction, wrote the investigators.
“We are in the middle of an increasing epidemic of obesity worldwide, but particularly in the United States, where it is currently projected that one in two adults will be obese by 2030,” added Dr. Borlaug of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is growing in tandem, and numerous recent studies have shown that obesity is one of the strongest risk factors for developing HFpEF, and that the severity of HFpEF is intimately linked to excess body fat. This suggests that therapies to reduce body fat could improve the cardiac abnormalities that cause HFpEF, which was our focus in this study,” he explained.
In the study, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers reviewed echocardiography data from 213 obese patients before and more than 180 days after bariatric surgery. They also measured abdominal visceral adipose tissue (VAT) of 52 patients via computed tomography. The average age of the patients was 54 years, the average body mass index was 45 kg/m2, and 67% were women. Comorbidities included hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and obstructive sleep apnea.
The primary outcome was changes in cardiac structure and function.
After a median follow-up of 5.3 years, patients overall averaged a 23% reduction in body weight and a 22% reduction in BMI. In the 52 patients with abdominal scans, the VAT area decreased by 30% overall. Changes in left ventricular mass were significantly correlated to changes in the VAT.
Epicardial adipose thickness decreased by 14% overall. Left and right ventricular longitudinal strains improved at follow-up, but left atrial strain deteriorated, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the results suggest that left ventricular remodeling was associated with visceral adiposity rather than subcutaneous fat, the researchers wrote.
They also found that right ventricular strain was negatively correlated with VAT, but not with body weight or BMI.
“These findings suggest that weight loss, particularly reduction in visceral adiposity, benefits [right ventricular] structure and function in a manner akin to that observed in the [left ventricle],” the researchers noted.
Some surprises and limitations
Dr. Borlaug said he found some, but not all, of the results surprising. “Earlier studies had shown evidence for benefit from weight loss on cardiac structure and function, but had been limited by smaller sample sizes, shorter durations of evaluation, and variable methods used,” he said in an interview.
The findings that strain imaging showed both left and right ventricular function improved while EF declined “shows some of the problems with using EF, as it is affected by chamber size and geometry. We have previously shown that patients with HFpEF display an increase in fat around the heart, and this affects cardiac function and interaction between the left and right sides of the heart, so we expected to see that this fat depot would be reduced, and this was indeed the case,” Dr. Borlaug added.
In the current study, “visceral fat was most strongly tied to the heart remodeling in obesity, and changes in visceral fat were most strongly tied to improvements in cardiac structure following weight loss,” Dr. Borlaug told this news organization. “This further supports this concept that excess visceral fat plays a key role in HFpEF, especially in the abdomen and around the heart,” he said.
However, “The biggest surprise was the discordant effects in the left atrium,” Dr. Borlaug said. “Left atrial remodeling and dysfunction play a crucial role in HFpEF as well, and we expected that this would improve following weight loss, but in fact we observed that left atrial function deteriorated, and other indicators of atrial myopathy worsened, including higher estimates of left atrial pressures and increased prevalence of atrial fibrillation,” he said.
This difference emphasizes that weight loss may not address all abnormalities that lead to HFpEF, although a key limitation of the current study was the lack of a control group of patients with the same degree of obesity and no weight-loss intervention, and the deterioration in left atrial function might have been even greater in the absence of weight loss, Dr. Borlaug added.
Larger numbers support effects
Previous research shows that structural heart changes associated with obesity can be reversed through weight loss, but the current study fills a gap by providing long-term data in a larger sample than previously studied, wrote Paul Heidenreich, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University in an accompanying editorial).
“There has been uncertainty regarding the prolonged effect of weight loss on cardiac function; this study was larger than many prior studies and provided a longer follow-up,” Dr. Heidenreich said in an interview.
“One unusual finding was that, while weight loss led to left ventricle reverse remodeling (reduction in wall thickness), the same effect was not seen for the left atrium; the left atrial size continued to increase,” he said. “I would have expected the left atrial changes to mirror the changes in the left ventricle,” he noted.
The findings support the greater cardiac risk of visceral vs. subcutaneous adipose tissue, and although body mass index will retain prognostic value, measures of central obesity are more likely predictors of cardiac structural changes and events and should be reported in clinical studies, Dr. Heidenreich wrote.
However, “We need a better understanding of the factors that influence left atrial remodeling and reverse remodeling,” Dr. Heidenreich told this news organization. “While left ventricular compliance and pressure play a role, there are other factors that need to be elucidated,” he said.
Studies in progress may inform practice
The current data call for further study to test novel treatments to facilitate weight loss in patients with HFpEF and those at risk for HFpEF, and some of these studies with medicines are underway, Dr. Borlaug said in the interview.
“Until such studies are completed, we will not truly understand the effects of weight loss on the heart, but the present data certainly provide strong support that patients who have obesity and HFpEF or are at risk for HFpEF should try to lose weight through lifestyle interventions,” he said.
Whether the cardiac changes seen in the current study would be different with nonsurgical weight loss remains a key question because many obese patients are reluctant to undergo bariatric surgery, Dr. Borlaug said. “We cannot assess whether the effects would differ with nonsurgical weight loss, and this requires further study,” he added.
As for additional research, “Randomized, controlled trials of weight-loss interventions, with appropriate controls and comprehensive assessments of cardiac structure, function, and hemodynamics will be most informative,” said Dr. Borlaug. “Larger trials powered to evaluate cardiovascular outcomes such as heart failure hospitalization or cardiovascular death also are critically important to better understand the role of weight loss to treat and prevent HFpEF, the ultimate form of obesity-related heart disease,” he emphasized.
The study was supported in part by grants to lead author Dr. Hidemi Sorimachi of the Mayo Clinic from the Uehara Memorial Foundation, Japan, and to corresponding author Dr. Borlaug from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Borlaug also disclosed previous grants from National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, AstraZeneca, Corvia, Medtronic, GlaxoSmithKline, Mesoblast, Novartis, and Tenax Therapeutics; and consulting fees from Actelion, Amgen, Aria, Axon Therapies, Boehringer Ingelheim, Edwards Lifesciences, Eli Lilly, Imbria, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, and VADovations. Dr. Heidenreich had no financial disclosures.
Weight loss after bariatric surgery was linked with visceral fat reduction as well as reduced blood pressure, fasting glucose, and left ventricular remodeling, based an imaging study in 213 patients.
“We found that ventricular function measured by strain imaging improved in both the left and right sides of the heart, but function measured in the traditional method using endocardial motion [in other words, ejection fraction] actually worsened,” senior investigator Barry A. Borlaug, MD, said in an interview.
Although previous studies have shown positive effects of weight loss on the heart after bariatric surgery, most have been short term and have not specifically examined the effects of visceral fat reduction, wrote the investigators.
“We are in the middle of an increasing epidemic of obesity worldwide, but particularly in the United States, where it is currently projected that one in two adults will be obese by 2030,” added Dr. Borlaug of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is growing in tandem, and numerous recent studies have shown that obesity is one of the strongest risk factors for developing HFpEF, and that the severity of HFpEF is intimately linked to excess body fat. This suggests that therapies to reduce body fat could improve the cardiac abnormalities that cause HFpEF, which was our focus in this study,” he explained.
In the study, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers reviewed echocardiography data from 213 obese patients before and more than 180 days after bariatric surgery. They also measured abdominal visceral adipose tissue (VAT) of 52 patients via computed tomography. The average age of the patients was 54 years, the average body mass index was 45 kg/m2, and 67% were women. Comorbidities included hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and obstructive sleep apnea.
The primary outcome was changes in cardiac structure and function.
After a median follow-up of 5.3 years, patients overall averaged a 23% reduction in body weight and a 22% reduction in BMI. In the 52 patients with abdominal scans, the VAT area decreased by 30% overall. Changes in left ventricular mass were significantly correlated to changes in the VAT.
Epicardial adipose thickness decreased by 14% overall. Left and right ventricular longitudinal strains improved at follow-up, but left atrial strain deteriorated, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the results suggest that left ventricular remodeling was associated with visceral adiposity rather than subcutaneous fat, the researchers wrote.
They also found that right ventricular strain was negatively correlated with VAT, but not with body weight or BMI.
“These findings suggest that weight loss, particularly reduction in visceral adiposity, benefits [right ventricular] structure and function in a manner akin to that observed in the [left ventricle],” the researchers noted.
Some surprises and limitations
Dr. Borlaug said he found some, but not all, of the results surprising. “Earlier studies had shown evidence for benefit from weight loss on cardiac structure and function, but had been limited by smaller sample sizes, shorter durations of evaluation, and variable methods used,” he said in an interview.
The findings that strain imaging showed both left and right ventricular function improved while EF declined “shows some of the problems with using EF, as it is affected by chamber size and geometry. We have previously shown that patients with HFpEF display an increase in fat around the heart, and this affects cardiac function and interaction between the left and right sides of the heart, so we expected to see that this fat depot would be reduced, and this was indeed the case,” Dr. Borlaug added.
In the current study, “visceral fat was most strongly tied to the heart remodeling in obesity, and changes in visceral fat were most strongly tied to improvements in cardiac structure following weight loss,” Dr. Borlaug told this news organization. “This further supports this concept that excess visceral fat plays a key role in HFpEF, especially in the abdomen and around the heart,” he said.
However, “The biggest surprise was the discordant effects in the left atrium,” Dr. Borlaug said. “Left atrial remodeling and dysfunction play a crucial role in HFpEF as well, and we expected that this would improve following weight loss, but in fact we observed that left atrial function deteriorated, and other indicators of atrial myopathy worsened, including higher estimates of left atrial pressures and increased prevalence of atrial fibrillation,” he said.
This difference emphasizes that weight loss may not address all abnormalities that lead to HFpEF, although a key limitation of the current study was the lack of a control group of patients with the same degree of obesity and no weight-loss intervention, and the deterioration in left atrial function might have been even greater in the absence of weight loss, Dr. Borlaug added.
Larger numbers support effects
Previous research shows that structural heart changes associated with obesity can be reversed through weight loss, but the current study fills a gap by providing long-term data in a larger sample than previously studied, wrote Paul Heidenreich, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University in an accompanying editorial).
“There has been uncertainty regarding the prolonged effect of weight loss on cardiac function; this study was larger than many prior studies and provided a longer follow-up,” Dr. Heidenreich said in an interview.
“One unusual finding was that, while weight loss led to left ventricle reverse remodeling (reduction in wall thickness), the same effect was not seen for the left atrium; the left atrial size continued to increase,” he said. “I would have expected the left atrial changes to mirror the changes in the left ventricle,” he noted.
The findings support the greater cardiac risk of visceral vs. subcutaneous adipose tissue, and although body mass index will retain prognostic value, measures of central obesity are more likely predictors of cardiac structural changes and events and should be reported in clinical studies, Dr. Heidenreich wrote.
However, “We need a better understanding of the factors that influence left atrial remodeling and reverse remodeling,” Dr. Heidenreich told this news organization. “While left ventricular compliance and pressure play a role, there are other factors that need to be elucidated,” he said.
Studies in progress may inform practice
The current data call for further study to test novel treatments to facilitate weight loss in patients with HFpEF and those at risk for HFpEF, and some of these studies with medicines are underway, Dr. Borlaug said in the interview.
“Until such studies are completed, we will not truly understand the effects of weight loss on the heart, but the present data certainly provide strong support that patients who have obesity and HFpEF or are at risk for HFpEF should try to lose weight through lifestyle interventions,” he said.
Whether the cardiac changes seen in the current study would be different with nonsurgical weight loss remains a key question because many obese patients are reluctant to undergo bariatric surgery, Dr. Borlaug said. “We cannot assess whether the effects would differ with nonsurgical weight loss, and this requires further study,” he added.
As for additional research, “Randomized, controlled trials of weight-loss interventions, with appropriate controls and comprehensive assessments of cardiac structure, function, and hemodynamics will be most informative,” said Dr. Borlaug. “Larger trials powered to evaluate cardiovascular outcomes such as heart failure hospitalization or cardiovascular death also are critically important to better understand the role of weight loss to treat and prevent HFpEF, the ultimate form of obesity-related heart disease,” he emphasized.
The study was supported in part by grants to lead author Dr. Hidemi Sorimachi of the Mayo Clinic from the Uehara Memorial Foundation, Japan, and to corresponding author Dr. Borlaug from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Borlaug also disclosed previous grants from National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, AstraZeneca, Corvia, Medtronic, GlaxoSmithKline, Mesoblast, Novartis, and Tenax Therapeutics; and consulting fees from Actelion, Amgen, Aria, Axon Therapies, Boehringer Ingelheim, Edwards Lifesciences, Eli Lilly, Imbria, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, and VADovations. Dr. Heidenreich had no financial disclosures.
Weight loss after bariatric surgery was linked with visceral fat reduction as well as reduced blood pressure, fasting glucose, and left ventricular remodeling, based an imaging study in 213 patients.
“We found that ventricular function measured by strain imaging improved in both the left and right sides of the heart, but function measured in the traditional method using endocardial motion [in other words, ejection fraction] actually worsened,” senior investigator Barry A. Borlaug, MD, said in an interview.
Although previous studies have shown positive effects of weight loss on the heart after bariatric surgery, most have been short term and have not specifically examined the effects of visceral fat reduction, wrote the investigators.
“We are in the middle of an increasing epidemic of obesity worldwide, but particularly in the United States, where it is currently projected that one in two adults will be obese by 2030,” added Dr. Borlaug of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is growing in tandem, and numerous recent studies have shown that obesity is one of the strongest risk factors for developing HFpEF, and that the severity of HFpEF is intimately linked to excess body fat. This suggests that therapies to reduce body fat could improve the cardiac abnormalities that cause HFpEF, which was our focus in this study,” he explained.
In the study, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers reviewed echocardiography data from 213 obese patients before and more than 180 days after bariatric surgery. They also measured abdominal visceral adipose tissue (VAT) of 52 patients via computed tomography. The average age of the patients was 54 years, the average body mass index was 45 kg/m2, and 67% were women. Comorbidities included hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and obstructive sleep apnea.
The primary outcome was changes in cardiac structure and function.
After a median follow-up of 5.3 years, patients overall averaged a 23% reduction in body weight and a 22% reduction in BMI. In the 52 patients with abdominal scans, the VAT area decreased by 30% overall. Changes in left ventricular mass were significantly correlated to changes in the VAT.
Epicardial adipose thickness decreased by 14% overall. Left and right ventricular longitudinal strains improved at follow-up, but left atrial strain deteriorated, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the results suggest that left ventricular remodeling was associated with visceral adiposity rather than subcutaneous fat, the researchers wrote.
They also found that right ventricular strain was negatively correlated with VAT, but not with body weight or BMI.
“These findings suggest that weight loss, particularly reduction in visceral adiposity, benefits [right ventricular] structure and function in a manner akin to that observed in the [left ventricle],” the researchers noted.
Some surprises and limitations
Dr. Borlaug said he found some, but not all, of the results surprising. “Earlier studies had shown evidence for benefit from weight loss on cardiac structure and function, but had been limited by smaller sample sizes, shorter durations of evaluation, and variable methods used,” he said in an interview.
The findings that strain imaging showed both left and right ventricular function improved while EF declined “shows some of the problems with using EF, as it is affected by chamber size and geometry. We have previously shown that patients with HFpEF display an increase in fat around the heart, and this affects cardiac function and interaction between the left and right sides of the heart, so we expected to see that this fat depot would be reduced, and this was indeed the case,” Dr. Borlaug added.
In the current study, “visceral fat was most strongly tied to the heart remodeling in obesity, and changes in visceral fat were most strongly tied to improvements in cardiac structure following weight loss,” Dr. Borlaug told this news organization. “This further supports this concept that excess visceral fat plays a key role in HFpEF, especially in the abdomen and around the heart,” he said.
However, “The biggest surprise was the discordant effects in the left atrium,” Dr. Borlaug said. “Left atrial remodeling and dysfunction play a crucial role in HFpEF as well, and we expected that this would improve following weight loss, but in fact we observed that left atrial function deteriorated, and other indicators of atrial myopathy worsened, including higher estimates of left atrial pressures and increased prevalence of atrial fibrillation,” he said.
This difference emphasizes that weight loss may not address all abnormalities that lead to HFpEF, although a key limitation of the current study was the lack of a control group of patients with the same degree of obesity and no weight-loss intervention, and the deterioration in left atrial function might have been even greater in the absence of weight loss, Dr. Borlaug added.
Larger numbers support effects
Previous research shows that structural heart changes associated with obesity can be reversed through weight loss, but the current study fills a gap by providing long-term data in a larger sample than previously studied, wrote Paul Heidenreich, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University in an accompanying editorial).
“There has been uncertainty regarding the prolonged effect of weight loss on cardiac function; this study was larger than many prior studies and provided a longer follow-up,” Dr. Heidenreich said in an interview.
“One unusual finding was that, while weight loss led to left ventricle reverse remodeling (reduction in wall thickness), the same effect was not seen for the left atrium; the left atrial size continued to increase,” he said. “I would have expected the left atrial changes to mirror the changes in the left ventricle,” he noted.
The findings support the greater cardiac risk of visceral vs. subcutaneous adipose tissue, and although body mass index will retain prognostic value, measures of central obesity are more likely predictors of cardiac structural changes and events and should be reported in clinical studies, Dr. Heidenreich wrote.
However, “We need a better understanding of the factors that influence left atrial remodeling and reverse remodeling,” Dr. Heidenreich told this news organization. “While left ventricular compliance and pressure play a role, there are other factors that need to be elucidated,” he said.
Studies in progress may inform practice
The current data call for further study to test novel treatments to facilitate weight loss in patients with HFpEF and those at risk for HFpEF, and some of these studies with medicines are underway, Dr. Borlaug said in the interview.
“Until such studies are completed, we will not truly understand the effects of weight loss on the heart, but the present data certainly provide strong support that patients who have obesity and HFpEF or are at risk for HFpEF should try to lose weight through lifestyle interventions,” he said.
Whether the cardiac changes seen in the current study would be different with nonsurgical weight loss remains a key question because many obese patients are reluctant to undergo bariatric surgery, Dr. Borlaug said. “We cannot assess whether the effects would differ with nonsurgical weight loss, and this requires further study,” he added.
As for additional research, “Randomized, controlled trials of weight-loss interventions, with appropriate controls and comprehensive assessments of cardiac structure, function, and hemodynamics will be most informative,” said Dr. Borlaug. “Larger trials powered to evaluate cardiovascular outcomes such as heart failure hospitalization or cardiovascular death also are critically important to better understand the role of weight loss to treat and prevent HFpEF, the ultimate form of obesity-related heart disease,” he emphasized.
The study was supported in part by grants to lead author Dr. Hidemi Sorimachi of the Mayo Clinic from the Uehara Memorial Foundation, Japan, and to corresponding author Dr. Borlaug from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Borlaug also disclosed previous grants from National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, AstraZeneca, Corvia, Medtronic, GlaxoSmithKline, Mesoblast, Novartis, and Tenax Therapeutics; and consulting fees from Actelion, Amgen, Aria, Axon Therapies, Boehringer Ingelheim, Edwards Lifesciences, Eli Lilly, Imbria, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, and VADovations. Dr. Heidenreich had no financial disclosures.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Tinea Capitis
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.
Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) such as M canis. Microsporum canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations: • broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp • diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis • well-demarcated annular plaques • exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation • scalp pruritus • occipital scalp lymphadenopathy. Worth noting Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp; however, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to falsenegative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5 Health disparity highlight A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management [published online July 12, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi:10.1111/jdv.15088
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study [published online April 19, 2010]. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-2522
- Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
- Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
- Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015 [published online January 20, 2020]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi:10.1111 /pde.14092
- Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria [published online April 16, 2008]. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.

Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) such as M canis. Microsporum canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations: • broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp • diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis • well-demarcated annular plaques • exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation • scalp pruritus • occipital scalp lymphadenopathy. Worth noting Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp; however, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to falsenegative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5 Health disparity highlight A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
THE COMPARISON
A Areas of alopecia with erythema and scale in a young Black boy with tinea capitis. He also had an enlarged posterior cervical lymph node (arrow) from this fungal infection.
B White patches of scale from tinea capitis in a young Black boy with no obvious hair loss; however, a potassium hydroxide preparation from the scale was positive for fungus.
C A subtle area of tinea capitis on the scalp of a Latina girl showed comma hairs.

Tinea capitis is a common dermatophyte infection of the scalp in school-aged children. The infection is spread by close contact with infected people or with their personal items, including combs, brushes, pillowcases, and hats, as well as animals. It is uncommon in adults.
Epidemiology
Tinea capitis is the most common fungal infection among school-aged children worldwide.1 In a US-based study of more than 10,000 school-aged children, the prevalence of tinea capitis ranged from 0% to 19.4%, with Black children having the highest rates of infection at 12.9%.2 However, people of all races and ages may develop tinea capitis.3
Tinea capitis most commonly is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. Dermatophyte scalp infections caused by T tonsurans produce fungal spores that may occur within the hair shaft (endothrix) or with fungal elements external to the hair shaft (exothrix) such as M canis. Microsporum canis usually fluoresces an apple green color on Wood lamp examination because of the location of the spores.
Key clinical features
Tinea capitis has a variety of clinical presentations: • broken hairs that appear as black dots on the scalp • diffuse scale mimicking seborrheic dermatitis • well-demarcated annular plaques • exudate and tenderness caused by inflammation • scalp pruritus • occipital scalp lymphadenopathy. Worth noting Tinea capitis impacts all patient groups, not just Black patients. In the United States, Black and Hispanic children are most commonly affected.4 Due to a tendency to have dry hair and hair breakage, those with more tightly coiled, textured hair may routinely apply oil and/or grease to the scalp; however, the application of heavy emollients, oils, and grease to camouflage scale contributes to falsenegative fungal cultures of the scalp if applied within 1 week of the fungal culture, which may delay diagnosis. If tinea capitis is suspected, occipital lymphadenopathy on physical examination should prompt treatment for tinea capitis, even without a fungal culture.5 Health disparity highlight A risk factor for tinea capitis is crowded living environments. Some families may live in crowded environments due to economic and housing disparities. This close contact increases the risk for conditions such as tinea capitis.6 Treatment delays may occur due to some cultural practices of applying oils and grease to the hair and scalp, camouflaging the clinical signs of tinea capitis.
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management [published online July 12, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi:10.1111/jdv.15088
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study [published online April 19, 2010]. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-2522
- Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
- Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
- Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015 [published online January 20, 2020]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi:10.1111 /pde.14092
- Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria [published online April 16, 2008]. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Tinea capitis in children: a systematic review of management [published online July 12, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2264-2274. doi:10.1111/jdv.15088
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Farrand N, Schuenemann E, et al. The prevalence of infections with Trichophyton tonsurans in schoolchildren: the CAPITIS study [published online April 19, 2010]. Pediatrics. 2010;125:966-973. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-2522
- Silverberg NB, Weinberg JM, DeLeo VA. Tinea capitis: focus on African American women. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl understanding):S120-S124. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120793
- Alvarez MS, Silverberg NB. Tinea capitis. In: Kelly AP, Taylor SC, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. McGraw Hill Medical; 2009:246-255.
- Nguyen CV, Collier S, Merten AH, et al. Tinea capitis: a singleinstitution retrospective review from 2010 to 2015 [published online January 20, 2020]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:305-310. doi:10.1111 /pde.14092
- Emele FE, Oyeka CA. Tinea capitis among primary school children in Anambra state of Nigeria [published online April 16, 2008]. Mycoses. 2008;51:536-541. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01507.x
Burnout Is Rampant, But Oncologists Can Turn the Tide
SAN DIEGO—Before the pandemic, an estimated one-third of oncologists worldwide suffered a high level of burnout. Cancer physicians face many of the same risk factors as their colleagues—high workloads, lack of autonomy, and no support—along with the added pressure of working in a medical field where patients often die. Then COVID-19 hit, and the burnout crisis got even worse.
This tide can be reversed with a focus on best practices and resilience, a mental health researcher told cancer professionals at the September 2022 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. Assessments, long-term interventions, and communication are all key, said Fay J. Hlubocky, PhD, MA, a clinical health psychologist and ethicist at the University of Chicago.
Even simple actions like taking time for “mindful moments” and checking in with a colleague can make a difference, she said. But institutions must act, she said. “Long-term tailored strategies are incredibly important to promote well-being.”
Hlubocky, who led an American Society of Clinical Oncology committee on burnout prior to the pandemic, noted that statistics about burnout in American medicine and oncology specifically, are grim. In 2017, a systematic review and meta-analysis found that significant numbers of oncologists suffered from high burnout (32%), high psychiatric morbidity (27%), depression (at least 12%), and alcohol misuse (as many as 30%).
The pandemic piled on more stressors. In the second half of 2020, researchers interviewed 25 American oncologists in focus groups and found that their “underlying oncologist burnout exacerbated stressors associated with disruptions in care, education, research, financial practice health, and telemedicine. Many feared delays in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment [and] strongly considered working part-time or taking early retirement.”
As one participant put it, “everyone is seeing a lot of death and heartache and social isolation and anger that they’re not used to encountering and in very new and different ways.”
Major contributors to oncologist burnout, Hlubocky said, include moral distress, moral injury, and compassion fatigue. “Moral distress occurs when that individual believes he or she knows the right thing to do, but institutional constraints make it really difficult to do what is right,” Hlubocky said. “The individual is aware of the moral problem, acknowledges and takes moral responsibility, makes some moral judgments, but yet—as a result of these constraints — participates in perceived moral wrongdoing.”
Moral injury refers to the damage that can be caused by moral distress or by witnessing acts that violate morals, such as during military service. Compassion fatigue, meanwhile, is defined by the American Stress Institute as “a low level, chronic clouding of caring and concern for others in your life.”
What can be done? Hlubocky highlighted multiple interventions, such as adjustment of work patterns, cognitive behavioral therapy, and training in mindfulness, relaxation, and communication. One strategy is to adopt multiple in-person interventions simultaneously.
But first it’s crucial for administrators to understand the problem in a specific workplace: “You have to know what’s going on in your organization to intervene on it,” she said. “There are multiple tools that have been validated in other health care fields and can be used on a regular basis over time to measure burnout, satisfaction, and engagement.”
For individuals, other strategies include daily check-ins with colleagues to catch signs of stress, she said, as Toronto oncologists started doing amid the pandemic. The check-ins can include simple questions like: How are you doing? How are you feeling? Are you sleeping, eating and exercising? Do you need help?
As for resilience, Hlubocky said it must grow at the individual level. “We can't rely so much on the organization. We need to develop our personal resilience in order for professional resilience to flourish again, and we have to do a lot to protect ourselves. It’s about focusing on the strength of the individual—that empowerment to rise above adversity, that vitality, that engagement, that self-efficacy. It supports health and enhances coping, and it is the key element of physician and clinician well-being.”
Research into resilience offers guidance about how to achieve it, she said. A 2013 German study of 200 physicians found that the most resilient physicians change their attitudes and behaviors, take time off, set boundaries, spend time with family and friends, and ask colleagues for help. And they gained resilience, the study found, by getting older and becoming more experienced.
Hlubocky pointed to several useful resources for burned-out medical professionals, including mindfulness, cognitive behavioral therapy and breathing apps: She highlighted Breathe2Relax, Headspace, MoodGYM, Stress Gym, and guided audio files from the University of California at San Diego. And she said ASCO has resources on combatting burnout and promoting well-being.
Hlubocky has no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO—Before the pandemic, an estimated one-third of oncologists worldwide suffered a high level of burnout. Cancer physicians face many of the same risk factors as their colleagues—high workloads, lack of autonomy, and no support—along with the added pressure of working in a medical field where patients often die. Then COVID-19 hit, and the burnout crisis got even worse.
This tide can be reversed with a focus on best practices and resilience, a mental health researcher told cancer professionals at the September 2022 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. Assessments, long-term interventions, and communication are all key, said Fay J. Hlubocky, PhD, MA, a clinical health psychologist and ethicist at the University of Chicago.
Even simple actions like taking time for “mindful moments” and checking in with a colleague can make a difference, she said. But institutions must act, she said. “Long-term tailored strategies are incredibly important to promote well-being.”
Hlubocky, who led an American Society of Clinical Oncology committee on burnout prior to the pandemic, noted that statistics about burnout in American medicine and oncology specifically, are grim. In 2017, a systematic review and meta-analysis found that significant numbers of oncologists suffered from high burnout (32%), high psychiatric morbidity (27%), depression (at least 12%), and alcohol misuse (as many as 30%).
The pandemic piled on more stressors. In the second half of 2020, researchers interviewed 25 American oncologists in focus groups and found that their “underlying oncologist burnout exacerbated stressors associated with disruptions in care, education, research, financial practice health, and telemedicine. Many feared delays in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment [and] strongly considered working part-time or taking early retirement.”
As one participant put it, “everyone is seeing a lot of death and heartache and social isolation and anger that they’re not used to encountering and in very new and different ways.”
Major contributors to oncologist burnout, Hlubocky said, include moral distress, moral injury, and compassion fatigue. “Moral distress occurs when that individual believes he or she knows the right thing to do, but institutional constraints make it really difficult to do what is right,” Hlubocky said. “The individual is aware of the moral problem, acknowledges and takes moral responsibility, makes some moral judgments, but yet—as a result of these constraints — participates in perceived moral wrongdoing.”
Moral injury refers to the damage that can be caused by moral distress or by witnessing acts that violate morals, such as during military service. Compassion fatigue, meanwhile, is defined by the American Stress Institute as “a low level, chronic clouding of caring and concern for others in your life.”
What can be done? Hlubocky highlighted multiple interventions, such as adjustment of work patterns, cognitive behavioral therapy, and training in mindfulness, relaxation, and communication. One strategy is to adopt multiple in-person interventions simultaneously.
But first it’s crucial for administrators to understand the problem in a specific workplace: “You have to know what’s going on in your organization to intervene on it,” she said. “There are multiple tools that have been validated in other health care fields and can be used on a regular basis over time to measure burnout, satisfaction, and engagement.”
For individuals, other strategies include daily check-ins with colleagues to catch signs of stress, she said, as Toronto oncologists started doing amid the pandemic. The check-ins can include simple questions like: How are you doing? How are you feeling? Are you sleeping, eating and exercising? Do you need help?
As for resilience, Hlubocky said it must grow at the individual level. “We can't rely so much on the organization. We need to develop our personal resilience in order for professional resilience to flourish again, and we have to do a lot to protect ourselves. It’s about focusing on the strength of the individual—that empowerment to rise above adversity, that vitality, that engagement, that self-efficacy. It supports health and enhances coping, and it is the key element of physician and clinician well-being.”
Research into resilience offers guidance about how to achieve it, she said. A 2013 German study of 200 physicians found that the most resilient physicians change their attitudes and behaviors, take time off, set boundaries, spend time with family and friends, and ask colleagues for help. And they gained resilience, the study found, by getting older and becoming more experienced.
Hlubocky pointed to several useful resources for burned-out medical professionals, including mindfulness, cognitive behavioral therapy and breathing apps: She highlighted Breathe2Relax, Headspace, MoodGYM, Stress Gym, and guided audio files from the University of California at San Diego. And she said ASCO has resources on combatting burnout and promoting well-being.
Hlubocky has no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO—Before the pandemic, an estimated one-third of oncologists worldwide suffered a high level of burnout. Cancer physicians face many of the same risk factors as their colleagues—high workloads, lack of autonomy, and no support—along with the added pressure of working in a medical field where patients often die. Then COVID-19 hit, and the burnout crisis got even worse.
This tide can be reversed with a focus on best practices and resilience, a mental health researcher told cancer professionals at the September 2022 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. Assessments, long-term interventions, and communication are all key, said Fay J. Hlubocky, PhD, MA, a clinical health psychologist and ethicist at the University of Chicago.
Even simple actions like taking time for “mindful moments” and checking in with a colleague can make a difference, she said. But institutions must act, she said. “Long-term tailored strategies are incredibly important to promote well-being.”
Hlubocky, who led an American Society of Clinical Oncology committee on burnout prior to the pandemic, noted that statistics about burnout in American medicine and oncology specifically, are grim. In 2017, a systematic review and meta-analysis found that significant numbers of oncologists suffered from high burnout (32%), high psychiatric morbidity (27%), depression (at least 12%), and alcohol misuse (as many as 30%).
The pandemic piled on more stressors. In the second half of 2020, researchers interviewed 25 American oncologists in focus groups and found that their “underlying oncologist burnout exacerbated stressors associated with disruptions in care, education, research, financial practice health, and telemedicine. Many feared delays in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment [and] strongly considered working part-time or taking early retirement.”
As one participant put it, “everyone is seeing a lot of death and heartache and social isolation and anger that they’re not used to encountering and in very new and different ways.”
Major contributors to oncologist burnout, Hlubocky said, include moral distress, moral injury, and compassion fatigue. “Moral distress occurs when that individual believes he or she knows the right thing to do, but institutional constraints make it really difficult to do what is right,” Hlubocky said. “The individual is aware of the moral problem, acknowledges and takes moral responsibility, makes some moral judgments, but yet—as a result of these constraints — participates in perceived moral wrongdoing.”
Moral injury refers to the damage that can be caused by moral distress or by witnessing acts that violate morals, such as during military service. Compassion fatigue, meanwhile, is defined by the American Stress Institute as “a low level, chronic clouding of caring and concern for others in your life.”
What can be done? Hlubocky highlighted multiple interventions, such as adjustment of work patterns, cognitive behavioral therapy, and training in mindfulness, relaxation, and communication. One strategy is to adopt multiple in-person interventions simultaneously.
But first it’s crucial for administrators to understand the problem in a specific workplace: “You have to know what’s going on in your organization to intervene on it,” she said. “There are multiple tools that have been validated in other health care fields and can be used on a regular basis over time to measure burnout, satisfaction, and engagement.”
For individuals, other strategies include daily check-ins with colleagues to catch signs of stress, she said, as Toronto oncologists started doing amid the pandemic. The check-ins can include simple questions like: How are you doing? How are you feeling? Are you sleeping, eating and exercising? Do you need help?
As for resilience, Hlubocky said it must grow at the individual level. “We can't rely so much on the organization. We need to develop our personal resilience in order for professional resilience to flourish again, and we have to do a lot to protect ourselves. It’s about focusing on the strength of the individual—that empowerment to rise above adversity, that vitality, that engagement, that self-efficacy. It supports health and enhances coping, and it is the key element of physician and clinician well-being.”
Research into resilience offers guidance about how to achieve it, she said. A 2013 German study of 200 physicians found that the most resilient physicians change their attitudes and behaviors, take time off, set boundaries, spend time with family and friends, and ask colleagues for help. And they gained resilience, the study found, by getting older and becoming more experienced.
Hlubocky pointed to several useful resources for burned-out medical professionals, including mindfulness, cognitive behavioral therapy and breathing apps: She highlighted Breathe2Relax, Headspace, MoodGYM, Stress Gym, and guided audio files from the University of California at San Diego. And she said ASCO has resources on combatting burnout and promoting well-being.
Hlubocky has no relevant disclosures.
Roselyn Tso confirmed to head Indian Health Service
It took 609 days, but the US Senate has finally (unanimously) confirmed President Biden’s choice to head the Indian Health Service (IHS: Roselyn Tso.)
President Biden nominated Tso in March 2022, and she was formally sworn in on September 27, 2022. The long-awaited confirmation filled a space that hadn’t had a permanent director since Michael Weahkee, a Pueblo of Zuni citizen, stepped down in 2021. In the interim, Elizabeth Fowler, of the Comanche Nation, served as acting director.
Tso’s resume includes almost 40 years of professional experience working at all levels of the IHS. Before taking over as IHS director, she led the IHS Navajo area, the largest IHS regional area, managing more than 4000 employees and a budget of nearly $1 billion.
She also brings “decades of lived experience as a member of the Navajo Nation,” she said in a 40-minute Senate hearing with the US Senate Committee on Indian Affairs in May.
The first Navajo Nation citizen to head the IHS (and only the second woman to do so), Tso introduced herself in Navajo: Deeschii’nii (Start of the Red Streak People) and born for Hashk’aa hadzohi (Yucca Fruit Strung Out). “This is a historic achievement for all of our Navajo people and tribal nations across the country,” Navajo Nation President Jonathan Nez said. “To have one of our own Navajo members in the highest position with IHS is remarkable.”
Tso spoke of having to “navigate the services provided by the Agency for myself, family, and friends.” Her personal and professional backgrounds, she said, help her understand how patients experience the system and how that can be improved. “The health care provided at IHS is critical for those we serve. I understand this not just because I work there,” she said. “My family relies on IHS. My friends rely on IHS. I rely on the IHS.”
The long lacuna in confirming a permanent IHS director left the Native peoples particularly vulnerable—when the COVID-19 pandemic essentially worsened the existing problems they faced, such as diabetes mellitus and cancer. Life expectancy for Native people fell by more than 6 years between 2019 and 2021, to 65 years, compared with the US average of 76 years.
Without a full-time IHS leader, the National Council of Urban Indian Health said in a statement, tribal nations and other Native health care providers struggled to raise and address the issues they were facing amid the pandemic. “Since the resignation of Rear Admiral Weahkee, there have been countless requests from Indian Country calling on Congress and the Administration to nominate a new IHS director to address the growing health disparities experienced by AI/ANs.”
Tso laid out her priorities in her May testimony: creating a more unified health care system using the latest technology to develop centralized systems; improving accountability, transparency, and patient safety; addressing workforce needs and challenges, improving recruitment and retention.
Meeting her goals, she noted, would take “strong partnerships and communication with our Tribal partners…. Each tribe has unique needs, and those needs cannot be met if you do not understand them.”
Last year, President Joseph R. Biden asked Congress to significantly increase IHS funding, but his proposal was cut to $400 million. “For years, IHS has been funded at a rate that is far below its level of need, and the results of this historical neglect can be seen in the disparities in health outcomes for AI/AN people,” William Smith, Valdez Native Tribe, Chairman of the National Indian Health Board (NIHB), wrote to the Senate Committee on Indian Affairs, on the topic of the next IHS director. “Perhaps one of the greatest challenges facing the [Indian, tribal and urban] system is the chronic and severe underfunding and budgetary instability for health care and public health services infrastructure and delivery. Since its creation in 1955, IHS has been chronically underfunded, with annual appropriations never exceeding 50% of demonstrated need. This underfunding has contributed to substandard investment in health delivery systems, some of the worst health disparities among any US population and a severe lack of public health infrastructure and services for our people. At the start of the COVID-19 pandemic these vulnerabilities were starkly exposed and while Congress moved decisively to invest into Tribal health and public health, the new Director must work to maintain these one-time investments.”
Stacy Bohlen, NIHB chief executive, told The Oklahoman that tribal leaders will look to Tso to press Congress for more money and to secure mandatory full funding for IHS—in contrast with the current annual appropriations, where Congress includes IHS in much larger budget bills. “When those bills stall, so does the money tribal clinics need to pay employees and suppliers,” making it hard to recruit and retain employees. “In the Indian Health System,” Bohlen says, “we simply can’t afford that kind of vulnerability.”
Securing advance appropriations and, ultimately, full mandatory funding for IHS, Smith wrote in his letter to the Senate committee, “fulfills the commitment made to our people generations ago and breaks down the systemic healthcare funding inequities the federal government tolerates for Tribes.”
Tso emphasized her intent to “improve the physical, mental, social, and spiritual health and well-being of all American Indians and Alaskan Natives served by the Agency.” Tso “understands the healthcare needs that many first people of this country deal with,” President Nez said. “Her work ethic, value system and approach to problem solving demonstrates the resilience of Indigenous peoples and the commitment to combat the systemic inequities that impact tribal nations.”
It took 609 days, but the US Senate has finally (unanimously) confirmed President Biden’s choice to head the Indian Health Service (IHS: Roselyn Tso.)
President Biden nominated Tso in March 2022, and she was formally sworn in on September 27, 2022. The long-awaited confirmation filled a space that hadn’t had a permanent director since Michael Weahkee, a Pueblo of Zuni citizen, stepped down in 2021. In the interim, Elizabeth Fowler, of the Comanche Nation, served as acting director.
Tso’s resume includes almost 40 years of professional experience working at all levels of the IHS. Before taking over as IHS director, she led the IHS Navajo area, the largest IHS regional area, managing more than 4000 employees and a budget of nearly $1 billion.
She also brings “decades of lived experience as a member of the Navajo Nation,” she said in a 40-minute Senate hearing with the US Senate Committee on Indian Affairs in May.
The first Navajo Nation citizen to head the IHS (and only the second woman to do so), Tso introduced herself in Navajo: Deeschii’nii (Start of the Red Streak People) and born for Hashk’aa hadzohi (Yucca Fruit Strung Out). “This is a historic achievement for all of our Navajo people and tribal nations across the country,” Navajo Nation President Jonathan Nez said. “To have one of our own Navajo members in the highest position with IHS is remarkable.”
Tso spoke of having to “navigate the services provided by the Agency for myself, family, and friends.” Her personal and professional backgrounds, she said, help her understand how patients experience the system and how that can be improved. “The health care provided at IHS is critical for those we serve. I understand this not just because I work there,” she said. “My family relies on IHS. My friends rely on IHS. I rely on the IHS.”
The long lacuna in confirming a permanent IHS director left the Native peoples particularly vulnerable—when the COVID-19 pandemic essentially worsened the existing problems they faced, such as diabetes mellitus and cancer. Life expectancy for Native people fell by more than 6 years between 2019 and 2021, to 65 years, compared with the US average of 76 years.
Without a full-time IHS leader, the National Council of Urban Indian Health said in a statement, tribal nations and other Native health care providers struggled to raise and address the issues they were facing amid the pandemic. “Since the resignation of Rear Admiral Weahkee, there have been countless requests from Indian Country calling on Congress and the Administration to nominate a new IHS director to address the growing health disparities experienced by AI/ANs.”
Tso laid out her priorities in her May testimony: creating a more unified health care system using the latest technology to develop centralized systems; improving accountability, transparency, and patient safety; addressing workforce needs and challenges, improving recruitment and retention.
Meeting her goals, she noted, would take “strong partnerships and communication with our Tribal partners…. Each tribe has unique needs, and those needs cannot be met if you do not understand them.”
Last year, President Joseph R. Biden asked Congress to significantly increase IHS funding, but his proposal was cut to $400 million. “For years, IHS has been funded at a rate that is far below its level of need, and the results of this historical neglect can be seen in the disparities in health outcomes for AI/AN people,” William Smith, Valdez Native Tribe, Chairman of the National Indian Health Board (NIHB), wrote to the Senate Committee on Indian Affairs, on the topic of the next IHS director. “Perhaps one of the greatest challenges facing the [Indian, tribal and urban] system is the chronic and severe underfunding and budgetary instability for health care and public health services infrastructure and delivery. Since its creation in 1955, IHS has been chronically underfunded, with annual appropriations never exceeding 50% of demonstrated need. This underfunding has contributed to substandard investment in health delivery systems, some of the worst health disparities among any US population and a severe lack of public health infrastructure and services for our people. At the start of the COVID-19 pandemic these vulnerabilities were starkly exposed and while Congress moved decisively to invest into Tribal health and public health, the new Director must work to maintain these one-time investments.”
Stacy Bohlen, NIHB chief executive, told The Oklahoman that tribal leaders will look to Tso to press Congress for more money and to secure mandatory full funding for IHS—in contrast with the current annual appropriations, where Congress includes IHS in much larger budget bills. “When those bills stall, so does the money tribal clinics need to pay employees and suppliers,” making it hard to recruit and retain employees. “In the Indian Health System,” Bohlen says, “we simply can’t afford that kind of vulnerability.”
Securing advance appropriations and, ultimately, full mandatory funding for IHS, Smith wrote in his letter to the Senate committee, “fulfills the commitment made to our people generations ago and breaks down the systemic healthcare funding inequities the federal government tolerates for Tribes.”
Tso emphasized her intent to “improve the physical, mental, social, and spiritual health and well-being of all American Indians and Alaskan Natives served by the Agency.” Tso “understands the healthcare needs that many first people of this country deal with,” President Nez said. “Her work ethic, value system and approach to problem solving demonstrates the resilience of Indigenous peoples and the commitment to combat the systemic inequities that impact tribal nations.”
It took 609 days, but the US Senate has finally (unanimously) confirmed President Biden’s choice to head the Indian Health Service (IHS: Roselyn Tso.)
President Biden nominated Tso in March 2022, and she was formally sworn in on September 27, 2022. The long-awaited confirmation filled a space that hadn’t had a permanent director since Michael Weahkee, a Pueblo of Zuni citizen, stepped down in 2021. In the interim, Elizabeth Fowler, of the Comanche Nation, served as acting director.
Tso’s resume includes almost 40 years of professional experience working at all levels of the IHS. Before taking over as IHS director, she led the IHS Navajo area, the largest IHS regional area, managing more than 4000 employees and a budget of nearly $1 billion.
She also brings “decades of lived experience as a member of the Navajo Nation,” she said in a 40-minute Senate hearing with the US Senate Committee on Indian Affairs in May.
The first Navajo Nation citizen to head the IHS (and only the second woman to do so), Tso introduced herself in Navajo: Deeschii’nii (Start of the Red Streak People) and born for Hashk’aa hadzohi (Yucca Fruit Strung Out). “This is a historic achievement for all of our Navajo people and tribal nations across the country,” Navajo Nation President Jonathan Nez said. “To have one of our own Navajo members in the highest position with IHS is remarkable.”
Tso spoke of having to “navigate the services provided by the Agency for myself, family, and friends.” Her personal and professional backgrounds, she said, help her understand how patients experience the system and how that can be improved. “The health care provided at IHS is critical for those we serve. I understand this not just because I work there,” she said. “My family relies on IHS. My friends rely on IHS. I rely on the IHS.”
The long lacuna in confirming a permanent IHS director left the Native peoples particularly vulnerable—when the COVID-19 pandemic essentially worsened the existing problems they faced, such as diabetes mellitus and cancer. Life expectancy for Native people fell by more than 6 years between 2019 and 2021, to 65 years, compared with the US average of 76 years.
Without a full-time IHS leader, the National Council of Urban Indian Health said in a statement, tribal nations and other Native health care providers struggled to raise and address the issues they were facing amid the pandemic. “Since the resignation of Rear Admiral Weahkee, there have been countless requests from Indian Country calling on Congress and the Administration to nominate a new IHS director to address the growing health disparities experienced by AI/ANs.”
Tso laid out her priorities in her May testimony: creating a more unified health care system using the latest technology to develop centralized systems; improving accountability, transparency, and patient safety; addressing workforce needs and challenges, improving recruitment and retention.
Meeting her goals, she noted, would take “strong partnerships and communication with our Tribal partners…. Each tribe has unique needs, and those needs cannot be met if you do not understand them.”
Last year, President Joseph R. Biden asked Congress to significantly increase IHS funding, but his proposal was cut to $400 million. “For years, IHS has been funded at a rate that is far below its level of need, and the results of this historical neglect can be seen in the disparities in health outcomes for AI/AN people,” William Smith, Valdez Native Tribe, Chairman of the National Indian Health Board (NIHB), wrote to the Senate Committee on Indian Affairs, on the topic of the next IHS director. “Perhaps one of the greatest challenges facing the [Indian, tribal and urban] system is the chronic and severe underfunding and budgetary instability for health care and public health services infrastructure and delivery. Since its creation in 1955, IHS has been chronically underfunded, with annual appropriations never exceeding 50% of demonstrated need. This underfunding has contributed to substandard investment in health delivery systems, some of the worst health disparities among any US population and a severe lack of public health infrastructure and services for our people. At the start of the COVID-19 pandemic these vulnerabilities were starkly exposed and while Congress moved decisively to invest into Tribal health and public health, the new Director must work to maintain these one-time investments.”
Stacy Bohlen, NIHB chief executive, told The Oklahoman that tribal leaders will look to Tso to press Congress for more money and to secure mandatory full funding for IHS—in contrast with the current annual appropriations, where Congress includes IHS in much larger budget bills. “When those bills stall, so does the money tribal clinics need to pay employees and suppliers,” making it hard to recruit and retain employees. “In the Indian Health System,” Bohlen says, “we simply can’t afford that kind of vulnerability.”
Securing advance appropriations and, ultimately, full mandatory funding for IHS, Smith wrote in his letter to the Senate committee, “fulfills the commitment made to our people generations ago and breaks down the systemic healthcare funding inequities the federal government tolerates for Tribes.”
Tso emphasized her intent to “improve the physical, mental, social, and spiritual health and well-being of all American Indians and Alaskan Natives served by the Agency.” Tso “understands the healthcare needs that many first people of this country deal with,” President Nez said. “Her work ethic, value system and approach to problem solving demonstrates the resilience of Indigenous peoples and the commitment to combat the systemic inequities that impact tribal nations.”
Air pollution tied to stroke risk, subsequent CV events, and death
Results of a UK biobank study show high levels of air pollution were associated with an increased risk of transition from health to a first stroke and subsequent progression to cardiovascular (CV) events and death.
“These results indicate that understanding and reducing the effects of air pollutants on different transition stages in stroke will be beneficial in managing people’s health and preventing the occurrence and progression of stroke,” study investigator Hualiang Lin, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University School of Public Health, Guangzhou, China, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the journal Neurology.
A way to stop stroke progression?
The researchers assessed air pollution exposure in 318,752 people (mean age, 56) from the UK biobank database. None had a history of stroke or heart disease at the start of the study. Annual concentrations of air pollution near where people lived were estimated through land-use regressions.
During an average follow-up of 12 years, 5,967 people had a stroke, 2,985 developed post-stroke CVD, and 1,020 died.
After adjusting for confounding factors, every 5 µg/m3 increase in exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) was associated with a 24% increase in transition from healthy to first stroke (hazard ratio, 1.24; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.40) and a 30% increase in transition from being healthy to dying (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.21-1.40).
PM2.5 is less than 2.5 microns in diameter and includes fly ash from coal combustion. The World Health Organization recommends that annual PM2.5 exposure should not exceed 5 µg/m3.
Those who had a stroke during the study had an average exposure of 10.03 µg/m3 of PM2.5, compared with 9.97 µg/m3 for those who did not have a stroke.
The air pollutants nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide were also associated with an increased risk of stroke and death, but the associations were weaker.
“More research is needed, but it’s possible that decreasing exposure to heavy levels of air pollution could play a role in reducing the progression of stroke,” Dr. Lin said.
“People can reduce their exposure by staying indoors on heavy pollution days, reducing their outdoor exercise, wearing masks to filter out particulate matter, and using air purifiers,” Dr. Lin added.
Public policy implications
Reached for comment, Steffen E. Petersen, MD, MPH, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, said the study “elegantly confirms the increased risk of stroke due to air pollution in the UK Biobank population study but interestingly suggests that the impact of air pollution may continue to adversely impact cardiovascular health even after the stroke occurred.”
“This is further evidence to inform policymakers to tackle air pollution and get levels below the recommended levels,” Dr. Petersen said.
“On a personal level, everyone, including stroke patients, may wish to consider personal measures to reduce exposure to air pollution, such as avoiding walking along polluted streets and rather take a less polluted route away from the main roads,” Dr. Petersen added.
The study had no targeted funding. Dr. Lin and Dr. Petersen report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a UK biobank study show high levels of air pollution were associated with an increased risk of transition from health to a first stroke and subsequent progression to cardiovascular (CV) events and death.
“These results indicate that understanding and reducing the effects of air pollutants on different transition stages in stroke will be beneficial in managing people’s health and preventing the occurrence and progression of stroke,” study investigator Hualiang Lin, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University School of Public Health, Guangzhou, China, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the journal Neurology.
A way to stop stroke progression?
The researchers assessed air pollution exposure in 318,752 people (mean age, 56) from the UK biobank database. None had a history of stroke or heart disease at the start of the study. Annual concentrations of air pollution near where people lived were estimated through land-use regressions.
During an average follow-up of 12 years, 5,967 people had a stroke, 2,985 developed post-stroke CVD, and 1,020 died.
After adjusting for confounding factors, every 5 µg/m3 increase in exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) was associated with a 24% increase in transition from healthy to first stroke (hazard ratio, 1.24; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.40) and a 30% increase in transition from being healthy to dying (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.21-1.40).
PM2.5 is less than 2.5 microns in diameter and includes fly ash from coal combustion. The World Health Organization recommends that annual PM2.5 exposure should not exceed 5 µg/m3.
Those who had a stroke during the study had an average exposure of 10.03 µg/m3 of PM2.5, compared with 9.97 µg/m3 for those who did not have a stroke.
The air pollutants nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide were also associated with an increased risk of stroke and death, but the associations were weaker.
“More research is needed, but it’s possible that decreasing exposure to heavy levels of air pollution could play a role in reducing the progression of stroke,” Dr. Lin said.
“People can reduce their exposure by staying indoors on heavy pollution days, reducing their outdoor exercise, wearing masks to filter out particulate matter, and using air purifiers,” Dr. Lin added.
Public policy implications
Reached for comment, Steffen E. Petersen, MD, MPH, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, said the study “elegantly confirms the increased risk of stroke due to air pollution in the UK Biobank population study but interestingly suggests that the impact of air pollution may continue to adversely impact cardiovascular health even after the stroke occurred.”
“This is further evidence to inform policymakers to tackle air pollution and get levels below the recommended levels,” Dr. Petersen said.
“On a personal level, everyone, including stroke patients, may wish to consider personal measures to reduce exposure to air pollution, such as avoiding walking along polluted streets and rather take a less polluted route away from the main roads,” Dr. Petersen added.
The study had no targeted funding. Dr. Lin and Dr. Petersen report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a UK biobank study show high levels of air pollution were associated with an increased risk of transition from health to a first stroke and subsequent progression to cardiovascular (CV) events and death.
“These results indicate that understanding and reducing the effects of air pollutants on different transition stages in stroke will be beneficial in managing people’s health and preventing the occurrence and progression of stroke,” study investigator Hualiang Lin, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University School of Public Health, Guangzhou, China, said in a news release.
The study was published online in the journal Neurology.
A way to stop stroke progression?
The researchers assessed air pollution exposure in 318,752 people (mean age, 56) from the UK biobank database. None had a history of stroke or heart disease at the start of the study. Annual concentrations of air pollution near where people lived were estimated through land-use regressions.
During an average follow-up of 12 years, 5,967 people had a stroke, 2,985 developed post-stroke CVD, and 1,020 died.
After adjusting for confounding factors, every 5 µg/m3 increase in exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) was associated with a 24% increase in transition from healthy to first stroke (hazard ratio, 1.24; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.40) and a 30% increase in transition from being healthy to dying (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.21-1.40).
PM2.5 is less than 2.5 microns in diameter and includes fly ash from coal combustion. The World Health Organization recommends that annual PM2.5 exposure should not exceed 5 µg/m3.
Those who had a stroke during the study had an average exposure of 10.03 µg/m3 of PM2.5, compared with 9.97 µg/m3 for those who did not have a stroke.
The air pollutants nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide were also associated with an increased risk of stroke and death, but the associations were weaker.
“More research is needed, but it’s possible that decreasing exposure to heavy levels of air pollution could play a role in reducing the progression of stroke,” Dr. Lin said.
“People can reduce their exposure by staying indoors on heavy pollution days, reducing their outdoor exercise, wearing masks to filter out particulate matter, and using air purifiers,” Dr. Lin added.
Public policy implications
Reached for comment, Steffen E. Petersen, MD, MPH, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, said the study “elegantly confirms the increased risk of stroke due to air pollution in the UK Biobank population study but interestingly suggests that the impact of air pollution may continue to adversely impact cardiovascular health even after the stroke occurred.”
“This is further evidence to inform policymakers to tackle air pollution and get levels below the recommended levels,” Dr. Petersen said.
“On a personal level, everyone, including stroke patients, may wish to consider personal measures to reduce exposure to air pollution, such as avoiding walking along polluted streets and rather take a less polluted route away from the main roads,” Dr. Petersen added.
The study had no targeted funding. Dr. Lin and Dr. Petersen report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.