User login
Passive income for the astute gastroenterologist
I don’t think I heard the term “passive income” until I was already an attending gastroenterologist.
That was no surprise. Why would I as a gastroenterologist with a focus in inflammatory bowel diseases be even remotely interested in that term?
Like most physicians, I went into medicine to take care of patients. That was my entire dream. It was a pleasant surprise to hear that gastroenterologists were relatively well paid compared to many other internal medicine specialties.
That was a bonus. I was not practicing medicine for the money. I was here to do good, only. Money was the evil one. It’s no surprise money remained a taboo topic amongst physicians.
This is reflected in the lack of financial education in our training.
I went through all my medical training without getting any financial education. In my last year of training, I wondered how I was going to not end up being a burned out, overworked physician mom. I knew I was going to work in a large hospital-based practice or academic center. I was already aware that employed physicians had a higher burnout rate compared to independent physicians. My desperation to avoid what looked like the natural history of most physicians in medicine was what led me to my financial awakening, as you could call it.
I became curious about where my money was going as it hit my bank account. Where was I investing? How was I going to ensure that I wasn’t putting all my financial eggs in one basket by relying solely on my clinical income? This road led me into a world that I didn’t know existed. It was the world of physician entrepreneurs.
I began thinking more critically of how I was spending my time outside of the hospital. As a busy physician mom, there already were a lot of competing needs and demands on the 24 hours that I was limited to within a day. How could I get things done and increase my earnability without needing to exchange more time for money in a one-to-one ratio?
Passive income!
First of all, what exactly is passive income?
It refers to money earned that does not require you to physically and actively pump in time in order to get money out. For instance, seeing patients clinically is not passive. Performing procedures is not passive.
What are some examples of passive income?
• Dividend paying stocks or funds
• Investing through retirement accounts
• Passive real estate investment through syndications, crowdfunding, REITs
• Book writing
• Business partnership or ownership such as surgery center co-ownership
• Peer-to-peer lending
• Affiliate marketing
• House hacking
• Rent out your car
• Rent out your backyard/ swimming pool
• Invention with royalty payment
• Podcasting
There are some myths about passive income that are worth exploring
1. Passive income is completely passive: This is relative passivity, meaning that for every investment, there is a phase of learning, acquiring knowledge, vetting, and possibly researching that is not passive. After the initial phase of set up, most passive sources of income may require some monitoring or checking in. However, what makes an investment passive is the absence of that one-to-one ratio of input to output that would normally exist in a more active income source.
2. Making passive income is lazy: If you are a physician, you are probably not lazy. Yes, we have a high standard of expectation for ourselves, but anyone that is able to withstand the rigors of medical training, residency, and fellowship is not lazy in my books. Burnout can present in various ways, including apathy. Let’s not confuse that as lazy because, if we do, that would qualify as gaslighting and self-splaining. As someone that teaches physicians how to have money, here is my opinion: In order to make money ethically, there has to be exchange in value. One person gives value, the other gives money as a thank you. Value can be physical as seen in clinical work. Value can also be monetary. For example, I could give $100,000 to a start-up company that needs that money to execute their brilliant idea, and, in return for my investment, they could give me a 15% return per year. Is that lazy? Without this, their brilliant idea may not see daylight. Value exchange is the key. Giving value comes in different ways.
3. Finding ideas for passive income is hard: Many of us are invested in the stock market, most commonly through retirement accounts. This would qualify as passive income. Typically, we have simply elected that the growth in our investment or dividends be reinvested as we are choosing to use this money long term. In other words, if you have a retirement account, you already have passive income. The question now is how you can find additional passive ways to invest.
What are the benefits to passive income as a gastroenterologist?
1. Changing landscape of medicine: Over the last few decades, we have seen a growing shift in the landscape of medicine. There has been an increase in administrations surpassing the increase in physicians. There seem to be more and more growing bodies that are wedging between physicians and patients. This has led to increasing dissatisfaction for patients and physicians alike. In order to respond to these changes and create lasting changes, there is a need for a change in the leadership. It is fair to say that when you have a more diversified source of income, there is less pressure on a single source of income to provide “food and shelter” for your family. Physician leaders that are liberated have to have a sense of financial liberation.
2. Not putting eggs in one basket: At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was significant fear of the unknown. Elective procedures were canceled, leading to financial strain for physicians. Gastroenterologists were not spared. When your income source is diverse, it provides more peace of mind.
3. Mental resourcefulness: This is an understated benefit of passive income and diversified income. As physicians, we went through a lot of hard work to get to where we are today. An average incoming medical student has had extensive demonstration of activity, volunteerism, and problem solving. Yet, as attending physicians, because of the burden of everyday clinical responsibilities and endless paperwork, as well as the platform and “warehouse” and “administrative-type involvement” in medicine, the average physician isn’t creating avenues to expend their cognitive abilities in a way that is diverse outside of the clinical setting. Having passive income opportunities creates a gym for mental resourcefulness that increases work satisfaction and may positively impact burnout.
4. Relationship building: As physicians, we tend to stick with our own. After working 60-80 hours per week, it is no surprise that most of your social network may end up being those that you work with. Passive income opportunities expose physicians to networking and social opportunities that may be critical for relationship building. This may improve mental wellness and overall sense of well-being.
5. Longevity in medicine: As more physicians elect to be employed by larger organizations outside of academics, sabbaticals are becoming less and less available. Having passive sources of income may permit a physician who would otherwise not be able to suffer loss of income the opportunity to take a leave of absence in the short term that may provide long-term longevity in medicine, while promoting wellness.
6. Wealth building: Wealth has had a negative reputation in the world. We seem to equate wealth as bad and being the source of evil. We forget that money is simply a tool that takes the shape of the container you place it in. If you are good, money becomes a tool for more good. Having passive income can help accelerate the journey to wealth building. This can be a great resource as physicians can support unique lifesaving, community-building, and environment-protecting initiatives, as well as support political candidates who will have a positive effect on patient care and the future of medicine.
I hope you are convinced that, Gastroenterologists have to do their due diligence to ensure that their finances are future proof to the best of their abilities.
Dr. Alli-Akintade, a gastroenterologist with Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento (Calif.) Medical Center, is founder of The MoneyFitMD and creator of The MoneyFitMD podcast (www.moneyfitmd.com).
I don’t think I heard the term “passive income” until I was already an attending gastroenterologist.
That was no surprise. Why would I as a gastroenterologist with a focus in inflammatory bowel diseases be even remotely interested in that term?
Like most physicians, I went into medicine to take care of patients. That was my entire dream. It was a pleasant surprise to hear that gastroenterologists were relatively well paid compared to many other internal medicine specialties.
That was a bonus. I was not practicing medicine for the money. I was here to do good, only. Money was the evil one. It’s no surprise money remained a taboo topic amongst physicians.
This is reflected in the lack of financial education in our training.
I went through all my medical training without getting any financial education. In my last year of training, I wondered how I was going to not end up being a burned out, overworked physician mom. I knew I was going to work in a large hospital-based practice or academic center. I was already aware that employed physicians had a higher burnout rate compared to independent physicians. My desperation to avoid what looked like the natural history of most physicians in medicine was what led me to my financial awakening, as you could call it.
I became curious about where my money was going as it hit my bank account. Where was I investing? How was I going to ensure that I wasn’t putting all my financial eggs in one basket by relying solely on my clinical income? This road led me into a world that I didn’t know existed. It was the world of physician entrepreneurs.
I began thinking more critically of how I was spending my time outside of the hospital. As a busy physician mom, there already were a lot of competing needs and demands on the 24 hours that I was limited to within a day. How could I get things done and increase my earnability without needing to exchange more time for money in a one-to-one ratio?
Passive income!
First of all, what exactly is passive income?
It refers to money earned that does not require you to physically and actively pump in time in order to get money out. For instance, seeing patients clinically is not passive. Performing procedures is not passive.
What are some examples of passive income?
• Dividend paying stocks or funds
• Investing through retirement accounts
• Passive real estate investment through syndications, crowdfunding, REITs
• Book writing
• Business partnership or ownership such as surgery center co-ownership
• Peer-to-peer lending
• Affiliate marketing
• House hacking
• Rent out your car
• Rent out your backyard/ swimming pool
• Invention with royalty payment
• Podcasting
There are some myths about passive income that are worth exploring
1. Passive income is completely passive: This is relative passivity, meaning that for every investment, there is a phase of learning, acquiring knowledge, vetting, and possibly researching that is not passive. After the initial phase of set up, most passive sources of income may require some monitoring or checking in. However, what makes an investment passive is the absence of that one-to-one ratio of input to output that would normally exist in a more active income source.
2. Making passive income is lazy: If you are a physician, you are probably not lazy. Yes, we have a high standard of expectation for ourselves, but anyone that is able to withstand the rigors of medical training, residency, and fellowship is not lazy in my books. Burnout can present in various ways, including apathy. Let’s not confuse that as lazy because, if we do, that would qualify as gaslighting and self-splaining. As someone that teaches physicians how to have money, here is my opinion: In order to make money ethically, there has to be exchange in value. One person gives value, the other gives money as a thank you. Value can be physical as seen in clinical work. Value can also be monetary. For example, I could give $100,000 to a start-up company that needs that money to execute their brilliant idea, and, in return for my investment, they could give me a 15% return per year. Is that lazy? Without this, their brilliant idea may not see daylight. Value exchange is the key. Giving value comes in different ways.
3. Finding ideas for passive income is hard: Many of us are invested in the stock market, most commonly through retirement accounts. This would qualify as passive income. Typically, we have simply elected that the growth in our investment or dividends be reinvested as we are choosing to use this money long term. In other words, if you have a retirement account, you already have passive income. The question now is how you can find additional passive ways to invest.
What are the benefits to passive income as a gastroenterologist?
1. Changing landscape of medicine: Over the last few decades, we have seen a growing shift in the landscape of medicine. There has been an increase in administrations surpassing the increase in physicians. There seem to be more and more growing bodies that are wedging between physicians and patients. This has led to increasing dissatisfaction for patients and physicians alike. In order to respond to these changes and create lasting changes, there is a need for a change in the leadership. It is fair to say that when you have a more diversified source of income, there is less pressure on a single source of income to provide “food and shelter” for your family. Physician leaders that are liberated have to have a sense of financial liberation.
2. Not putting eggs in one basket: At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was significant fear of the unknown. Elective procedures were canceled, leading to financial strain for physicians. Gastroenterologists were not spared. When your income source is diverse, it provides more peace of mind.
3. Mental resourcefulness: This is an understated benefit of passive income and diversified income. As physicians, we went through a lot of hard work to get to where we are today. An average incoming medical student has had extensive demonstration of activity, volunteerism, and problem solving. Yet, as attending physicians, because of the burden of everyday clinical responsibilities and endless paperwork, as well as the platform and “warehouse” and “administrative-type involvement” in medicine, the average physician isn’t creating avenues to expend their cognitive abilities in a way that is diverse outside of the clinical setting. Having passive income opportunities creates a gym for mental resourcefulness that increases work satisfaction and may positively impact burnout.
4. Relationship building: As physicians, we tend to stick with our own. After working 60-80 hours per week, it is no surprise that most of your social network may end up being those that you work with. Passive income opportunities expose physicians to networking and social opportunities that may be critical for relationship building. This may improve mental wellness and overall sense of well-being.
5. Longevity in medicine: As more physicians elect to be employed by larger organizations outside of academics, sabbaticals are becoming less and less available. Having passive sources of income may permit a physician who would otherwise not be able to suffer loss of income the opportunity to take a leave of absence in the short term that may provide long-term longevity in medicine, while promoting wellness.
6. Wealth building: Wealth has had a negative reputation in the world. We seem to equate wealth as bad and being the source of evil. We forget that money is simply a tool that takes the shape of the container you place it in. If you are good, money becomes a tool for more good. Having passive income can help accelerate the journey to wealth building. This can be a great resource as physicians can support unique lifesaving, community-building, and environment-protecting initiatives, as well as support political candidates who will have a positive effect on patient care and the future of medicine.
I hope you are convinced that, Gastroenterologists have to do their due diligence to ensure that their finances are future proof to the best of their abilities.
Dr. Alli-Akintade, a gastroenterologist with Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento (Calif.) Medical Center, is founder of The MoneyFitMD and creator of The MoneyFitMD podcast (www.moneyfitmd.com).
I don’t think I heard the term “passive income” until I was already an attending gastroenterologist.
That was no surprise. Why would I as a gastroenterologist with a focus in inflammatory bowel diseases be even remotely interested in that term?
Like most physicians, I went into medicine to take care of patients. That was my entire dream. It was a pleasant surprise to hear that gastroenterologists were relatively well paid compared to many other internal medicine specialties.
That was a bonus. I was not practicing medicine for the money. I was here to do good, only. Money was the evil one. It’s no surprise money remained a taboo topic amongst physicians.
This is reflected in the lack of financial education in our training.
I went through all my medical training without getting any financial education. In my last year of training, I wondered how I was going to not end up being a burned out, overworked physician mom. I knew I was going to work in a large hospital-based practice or academic center. I was already aware that employed physicians had a higher burnout rate compared to independent physicians. My desperation to avoid what looked like the natural history of most physicians in medicine was what led me to my financial awakening, as you could call it.
I became curious about where my money was going as it hit my bank account. Where was I investing? How was I going to ensure that I wasn’t putting all my financial eggs in one basket by relying solely on my clinical income? This road led me into a world that I didn’t know existed. It was the world of physician entrepreneurs.
I began thinking more critically of how I was spending my time outside of the hospital. As a busy physician mom, there already were a lot of competing needs and demands on the 24 hours that I was limited to within a day. How could I get things done and increase my earnability without needing to exchange more time for money in a one-to-one ratio?
Passive income!
First of all, what exactly is passive income?
It refers to money earned that does not require you to physically and actively pump in time in order to get money out. For instance, seeing patients clinically is not passive. Performing procedures is not passive.
What are some examples of passive income?
• Dividend paying stocks or funds
• Investing through retirement accounts
• Passive real estate investment through syndications, crowdfunding, REITs
• Book writing
• Business partnership or ownership such as surgery center co-ownership
• Peer-to-peer lending
• Affiliate marketing
• House hacking
• Rent out your car
• Rent out your backyard/ swimming pool
• Invention with royalty payment
• Podcasting
There are some myths about passive income that are worth exploring
1. Passive income is completely passive: This is relative passivity, meaning that for every investment, there is a phase of learning, acquiring knowledge, vetting, and possibly researching that is not passive. After the initial phase of set up, most passive sources of income may require some monitoring or checking in. However, what makes an investment passive is the absence of that one-to-one ratio of input to output that would normally exist in a more active income source.
2. Making passive income is lazy: If you are a physician, you are probably not lazy. Yes, we have a high standard of expectation for ourselves, but anyone that is able to withstand the rigors of medical training, residency, and fellowship is not lazy in my books. Burnout can present in various ways, including apathy. Let’s not confuse that as lazy because, if we do, that would qualify as gaslighting and self-splaining. As someone that teaches physicians how to have money, here is my opinion: In order to make money ethically, there has to be exchange in value. One person gives value, the other gives money as a thank you. Value can be physical as seen in clinical work. Value can also be monetary. For example, I could give $100,000 to a start-up company that needs that money to execute their brilliant idea, and, in return for my investment, they could give me a 15% return per year. Is that lazy? Without this, their brilliant idea may not see daylight. Value exchange is the key. Giving value comes in different ways.
3. Finding ideas for passive income is hard: Many of us are invested in the stock market, most commonly through retirement accounts. This would qualify as passive income. Typically, we have simply elected that the growth in our investment or dividends be reinvested as we are choosing to use this money long term. In other words, if you have a retirement account, you already have passive income. The question now is how you can find additional passive ways to invest.
What are the benefits to passive income as a gastroenterologist?
1. Changing landscape of medicine: Over the last few decades, we have seen a growing shift in the landscape of medicine. There has been an increase in administrations surpassing the increase in physicians. There seem to be more and more growing bodies that are wedging between physicians and patients. This has led to increasing dissatisfaction for patients and physicians alike. In order to respond to these changes and create lasting changes, there is a need for a change in the leadership. It is fair to say that when you have a more diversified source of income, there is less pressure on a single source of income to provide “food and shelter” for your family. Physician leaders that are liberated have to have a sense of financial liberation.
2. Not putting eggs in one basket: At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was significant fear of the unknown. Elective procedures were canceled, leading to financial strain for physicians. Gastroenterologists were not spared. When your income source is diverse, it provides more peace of mind.
3. Mental resourcefulness: This is an understated benefit of passive income and diversified income. As physicians, we went through a lot of hard work to get to where we are today. An average incoming medical student has had extensive demonstration of activity, volunteerism, and problem solving. Yet, as attending physicians, because of the burden of everyday clinical responsibilities and endless paperwork, as well as the platform and “warehouse” and “administrative-type involvement” in medicine, the average physician isn’t creating avenues to expend their cognitive abilities in a way that is diverse outside of the clinical setting. Having passive income opportunities creates a gym for mental resourcefulness that increases work satisfaction and may positively impact burnout.
4. Relationship building: As physicians, we tend to stick with our own. After working 60-80 hours per week, it is no surprise that most of your social network may end up being those that you work with. Passive income opportunities expose physicians to networking and social opportunities that may be critical for relationship building. This may improve mental wellness and overall sense of well-being.
5. Longevity in medicine: As more physicians elect to be employed by larger organizations outside of academics, sabbaticals are becoming less and less available. Having passive sources of income may permit a physician who would otherwise not be able to suffer loss of income the opportunity to take a leave of absence in the short term that may provide long-term longevity in medicine, while promoting wellness.
6. Wealth building: Wealth has had a negative reputation in the world. We seem to equate wealth as bad and being the source of evil. We forget that money is simply a tool that takes the shape of the container you place it in. If you are good, money becomes a tool for more good. Having passive income can help accelerate the journey to wealth building. This can be a great resource as physicians can support unique lifesaving, community-building, and environment-protecting initiatives, as well as support political candidates who will have a positive effect on patient care and the future of medicine.
I hope you are convinced that, Gastroenterologists have to do their due diligence to ensure that their finances are future proof to the best of their abilities.
Dr. Alli-Akintade, a gastroenterologist with Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento (Calif.) Medical Center, is founder of The MoneyFitMD and creator of The MoneyFitMD podcast (www.moneyfitmd.com).
Children and COVID: Weekly cases drop to lowest level since April
A hefty decline in new COVID-19 cases among children resulted in the lowest weekly total since late April, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, making for 2 consecutive weeks of declines after almost 91,000 cases were recorded for the week ending Sept. 1, the AAP and CHA said in their latest COVID report of state-level data.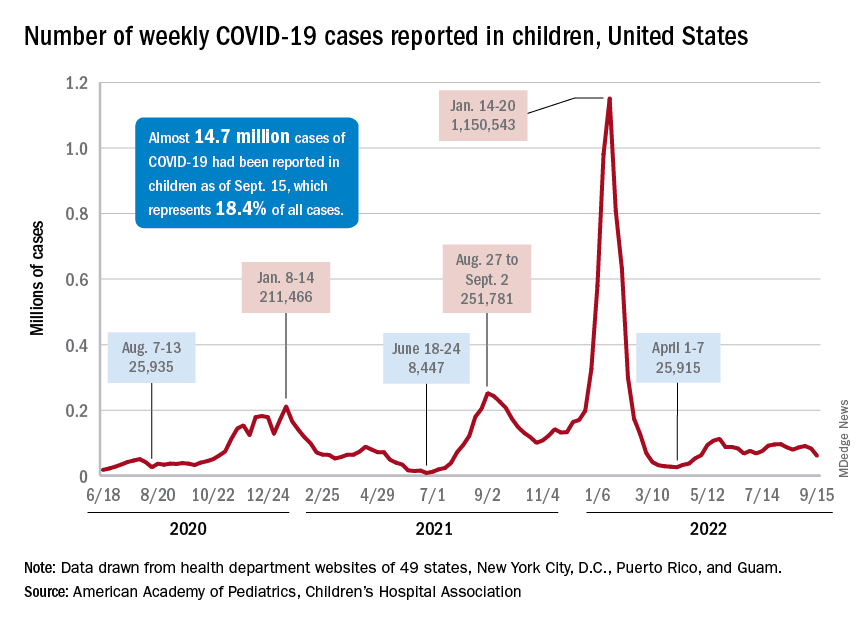
The last time the weekly count was under 60,000 came during the week of April 22-28, when 53,000 were reported by state and territorial health departments in the midst of a 7-week stretch of rising cases. Since that streak ended in mid-May, however, “reported weekly cases have plateaued, fluctuating between a low, now of 60,300 cases and a high of about 112,000,” the AAP noted.
Emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which showed less fluctuation over the summer and more steady rise and fall, have both dropped in recent weeks and are now approaching late May/early June rates, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
On Sept. 15, for example, ED visits for children under 12 years with diagnosed COVID were just 2.2% of all visits, lower than at any time since May 19 and down from a summer high of 6.8% in late July. Hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years also rose steadily through June and July, reaching 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30, but have since slipped to 0.29 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Vaccination continues to be a tough sell
Vaccination activity among the most recently eligible age group, in the meantime, remains tepid. Just 6.0% of children under age 5 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Sept. 13, about 3 months since its final approval in June, and 1.6% were fully vaccinated. For the two older groups of children with separate vaccine approvals, 31.5% of those aged 5-11 years and 43.3% of those aged 12-15 had received at least one dose 3 months after their vaccinations began, the CDC data show.
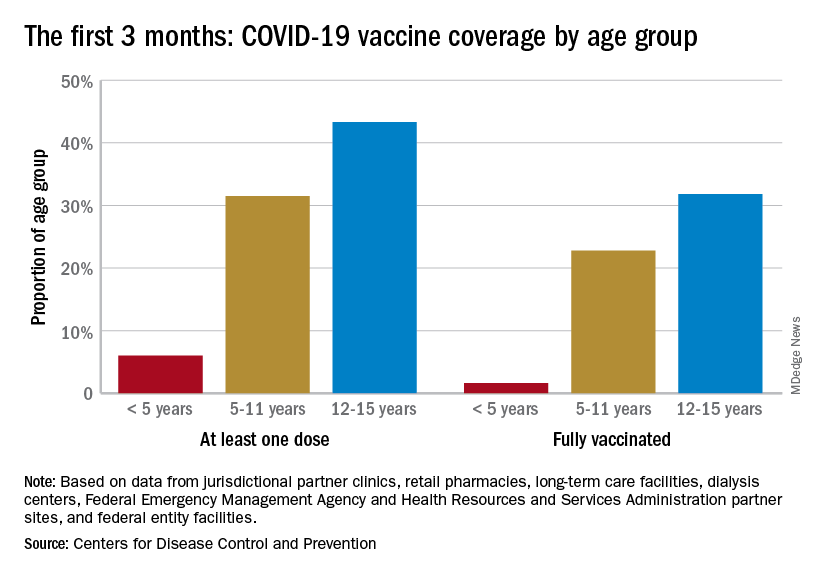
In the 2 weeks ending Sept. 14, almost 59,000 children under age 5 received their initial COVID-19 vaccine dose, as did 28,000 5- to 11-year-olds and 14,000 children aged 12-17. Children under age 5 years represented almost 20% of all Americans getting a first dose during Sept. 1-14, compared with 9.7% for those aged 5-11 and 4.8% for the 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
At the state level, children under age 5 years in the District of Columbia, where 28% have received at least one dose, and Vermont, at 24%, are the most likely to be vaccinated. The states with the lowest rates in this age group are Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, all of which are at 2%. Vermont and D.C. have the highest rates for ages 5-11 at 70% each, and Alabama (17%) is the lowest, while D.C. (100%), Rhode Island (99%), and Massachusetts (99%) are highest for children aged 12-17 years and Wyoming (41%) is the lowest, the AAP said in a separate report.
A hefty decline in new COVID-19 cases among children resulted in the lowest weekly total since late April, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, making for 2 consecutive weeks of declines after almost 91,000 cases were recorded for the week ending Sept. 1, the AAP and CHA said in their latest COVID report of state-level data.
The last time the weekly count was under 60,000 came during the week of April 22-28, when 53,000 were reported by state and territorial health departments in the midst of a 7-week stretch of rising cases. Since that streak ended in mid-May, however, “reported weekly cases have plateaued, fluctuating between a low, now of 60,300 cases and a high of about 112,000,” the AAP noted.
Emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which showed less fluctuation over the summer and more steady rise and fall, have both dropped in recent weeks and are now approaching late May/early June rates, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
On Sept. 15, for example, ED visits for children under 12 years with diagnosed COVID were just 2.2% of all visits, lower than at any time since May 19 and down from a summer high of 6.8% in late July. Hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years also rose steadily through June and July, reaching 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30, but have since slipped to 0.29 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Vaccination continues to be a tough sell
Vaccination activity among the most recently eligible age group, in the meantime, remains tepid. Just 6.0% of children under age 5 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Sept. 13, about 3 months since its final approval in June, and 1.6% were fully vaccinated. For the two older groups of children with separate vaccine approvals, 31.5% of those aged 5-11 years and 43.3% of those aged 12-15 had received at least one dose 3 months after their vaccinations began, the CDC data show.

In the 2 weeks ending Sept. 14, almost 59,000 children under age 5 received their initial COVID-19 vaccine dose, as did 28,000 5- to 11-year-olds and 14,000 children aged 12-17. Children under age 5 years represented almost 20% of all Americans getting a first dose during Sept. 1-14, compared with 9.7% for those aged 5-11 and 4.8% for the 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
At the state level, children under age 5 years in the District of Columbia, where 28% have received at least one dose, and Vermont, at 24%, are the most likely to be vaccinated. The states with the lowest rates in this age group are Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, all of which are at 2%. Vermont and D.C. have the highest rates for ages 5-11 at 70% each, and Alabama (17%) is the lowest, while D.C. (100%), Rhode Island (99%), and Massachusetts (99%) are highest for children aged 12-17 years and Wyoming (41%) is the lowest, the AAP said in a separate report.
A hefty decline in new COVID-19 cases among children resulted in the lowest weekly total since late April, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, making for 2 consecutive weeks of declines after almost 91,000 cases were recorded for the week ending Sept. 1, the AAP and CHA said in their latest COVID report of state-level data.
The last time the weekly count was under 60,000 came during the week of April 22-28, when 53,000 were reported by state and territorial health departments in the midst of a 7-week stretch of rising cases. Since that streak ended in mid-May, however, “reported weekly cases have plateaued, fluctuating between a low, now of 60,300 cases and a high of about 112,000,” the AAP noted.
Emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which showed less fluctuation over the summer and more steady rise and fall, have both dropped in recent weeks and are now approaching late May/early June rates, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
On Sept. 15, for example, ED visits for children under 12 years with diagnosed COVID were just 2.2% of all visits, lower than at any time since May 19 and down from a summer high of 6.8% in late July. Hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years also rose steadily through June and July, reaching 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30, but have since slipped to 0.29 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Vaccination continues to be a tough sell
Vaccination activity among the most recently eligible age group, in the meantime, remains tepid. Just 6.0% of children under age 5 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Sept. 13, about 3 months since its final approval in June, and 1.6% were fully vaccinated. For the two older groups of children with separate vaccine approvals, 31.5% of those aged 5-11 years and 43.3% of those aged 12-15 had received at least one dose 3 months after their vaccinations began, the CDC data show.

In the 2 weeks ending Sept. 14, almost 59,000 children under age 5 received their initial COVID-19 vaccine dose, as did 28,000 5- to 11-year-olds and 14,000 children aged 12-17. Children under age 5 years represented almost 20% of all Americans getting a first dose during Sept. 1-14, compared with 9.7% for those aged 5-11 and 4.8% for the 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
At the state level, children under age 5 years in the District of Columbia, where 28% have received at least one dose, and Vermont, at 24%, are the most likely to be vaccinated. The states with the lowest rates in this age group are Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, all of which are at 2%. Vermont and D.C. have the highest rates for ages 5-11 at 70% each, and Alabama (17%) is the lowest, while D.C. (100%), Rhode Island (99%), and Massachusetts (99%) are highest for children aged 12-17 years and Wyoming (41%) is the lowest, the AAP said in a separate report.
Eighty percent of U.S. maternal deaths are preventable: Study
More than 80% of U.S. maternal deaths across a 2-year period were due to preventable causes, according to a new CDC report.
Black mothers made up about a third of deaths, and more than 90% of deaths among Indigenous mothers were preventable.
“It’s significant. It’s staggering. It’s heartbreaking,” Allison Bryant, MD, a high-risk pregnancy specialist and senior medical director for health equity at Massachusetts General Hospital, told USA Today.
“It just means that we have so much work to do,” she said.
In the report, CDC researchers looked at pregnancy-related deaths between 2017 to 2019 based on numbers from maternal mortality review committees, which are multidisciplinary groups in 36 states that investigate the circumstances around maternal deaths.
Of the 1,018 deaths during the 2-year period, 839 occurred up to a year after delivery. About 22% of deaths happened during pregnancy, and 25% happened on the day of delivery or within a week after delivery. But 53% occurred more than 7 days after delivery.
Mental health conditions, such as overdoses and deaths by suicide, were the top underlying cause, followed by hemorrhage, or extreme bleeding. About a quarter of deaths were due to mental health conditions, followed by 14% due to hemorrhage and 13% due to heart problems. The rest were related to infection, embolism, cardiomyopathy, and high blood pressure-related disorders.
The analysis included a section on maternal deaths for American Indian and Alaska Native mothers, who are more than twice as likely as White mothers to die but are often undercounted in health data due to misclassification. More than 90% of their deaths were preventable between 2017 to 2019, with most due to mental health conditions and hemorrhage.
“It’s incredibly distressful,” Brian Thompson, MD, of the Oneida Nation and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Upstate Medical University, New York, told USA Today.
Dr. Thompson is working with the National Indian Health Board to create the first national tribal review committee for maternal deaths.
“It really needs to be looked at and examined why that is the case if essentially all of them are preventable,” he said.
Black mothers were also three times as likely as White mothers to die and more likely to die from heart problems. Hispanic mothers, who made up 14% of deaths, were more likely to die from mental health conditions.
Some of the deaths, such as hemorrhage, should be highly preventable. Existing toolkits for clinicians provide evidence-based guidelines to prevent and treat excessive bleeding.
“No pregnant person should be passing away from a hemorrhage,” Andrea Jackson, MD, division chief of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, San Francisco, told USA Today.
“We have the tools in the United States, and we know how to deal with it,” she said. “That was really disheartening to see.”
What’s more, the new CDC report highlights the need for more mental health resources during pregnancy and the postpartum period – up to a year or more after delivery – including improvements in access to care, diagnosis, and treatment.
“These are things that need to happen systemically,” LeThenia Baker, MD, an obstetrician and gynecologist at Wellstar Health, Georgia, told USA Today.
“It can’t just be a few practices here or there who are adopting best practices,” she said. “It has to be a systemic change.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More than 80% of U.S. maternal deaths across a 2-year period were due to preventable causes, according to a new CDC report.
Black mothers made up about a third of deaths, and more than 90% of deaths among Indigenous mothers were preventable.
“It’s significant. It’s staggering. It’s heartbreaking,” Allison Bryant, MD, a high-risk pregnancy specialist and senior medical director for health equity at Massachusetts General Hospital, told USA Today.
“It just means that we have so much work to do,” she said.
In the report, CDC researchers looked at pregnancy-related deaths between 2017 to 2019 based on numbers from maternal mortality review committees, which are multidisciplinary groups in 36 states that investigate the circumstances around maternal deaths.
Of the 1,018 deaths during the 2-year period, 839 occurred up to a year after delivery. About 22% of deaths happened during pregnancy, and 25% happened on the day of delivery or within a week after delivery. But 53% occurred more than 7 days after delivery.
Mental health conditions, such as overdoses and deaths by suicide, were the top underlying cause, followed by hemorrhage, or extreme bleeding. About a quarter of deaths were due to mental health conditions, followed by 14% due to hemorrhage and 13% due to heart problems. The rest were related to infection, embolism, cardiomyopathy, and high blood pressure-related disorders.
The analysis included a section on maternal deaths for American Indian and Alaska Native mothers, who are more than twice as likely as White mothers to die but are often undercounted in health data due to misclassification. More than 90% of their deaths were preventable between 2017 to 2019, with most due to mental health conditions and hemorrhage.
“It’s incredibly distressful,” Brian Thompson, MD, of the Oneida Nation and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Upstate Medical University, New York, told USA Today.
Dr. Thompson is working with the National Indian Health Board to create the first national tribal review committee for maternal deaths.
“It really needs to be looked at and examined why that is the case if essentially all of them are preventable,” he said.
Black mothers were also three times as likely as White mothers to die and more likely to die from heart problems. Hispanic mothers, who made up 14% of deaths, were more likely to die from mental health conditions.
Some of the deaths, such as hemorrhage, should be highly preventable. Existing toolkits for clinicians provide evidence-based guidelines to prevent and treat excessive bleeding.
“No pregnant person should be passing away from a hemorrhage,” Andrea Jackson, MD, division chief of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, San Francisco, told USA Today.
“We have the tools in the United States, and we know how to deal with it,” she said. “That was really disheartening to see.”
What’s more, the new CDC report highlights the need for more mental health resources during pregnancy and the postpartum period – up to a year or more after delivery – including improvements in access to care, diagnosis, and treatment.
“These are things that need to happen systemically,” LeThenia Baker, MD, an obstetrician and gynecologist at Wellstar Health, Georgia, told USA Today.
“It can’t just be a few practices here or there who are adopting best practices,” she said. “It has to be a systemic change.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More than 80% of U.S. maternal deaths across a 2-year period were due to preventable causes, according to a new CDC report.
Black mothers made up about a third of deaths, and more than 90% of deaths among Indigenous mothers were preventable.
“It’s significant. It’s staggering. It’s heartbreaking,” Allison Bryant, MD, a high-risk pregnancy specialist and senior medical director for health equity at Massachusetts General Hospital, told USA Today.
“It just means that we have so much work to do,” she said.
In the report, CDC researchers looked at pregnancy-related deaths between 2017 to 2019 based on numbers from maternal mortality review committees, which are multidisciplinary groups in 36 states that investigate the circumstances around maternal deaths.
Of the 1,018 deaths during the 2-year period, 839 occurred up to a year after delivery. About 22% of deaths happened during pregnancy, and 25% happened on the day of delivery or within a week after delivery. But 53% occurred more than 7 days after delivery.
Mental health conditions, such as overdoses and deaths by suicide, were the top underlying cause, followed by hemorrhage, or extreme bleeding. About a quarter of deaths were due to mental health conditions, followed by 14% due to hemorrhage and 13% due to heart problems. The rest were related to infection, embolism, cardiomyopathy, and high blood pressure-related disorders.
The analysis included a section on maternal deaths for American Indian and Alaska Native mothers, who are more than twice as likely as White mothers to die but are often undercounted in health data due to misclassification. More than 90% of their deaths were preventable between 2017 to 2019, with most due to mental health conditions and hemorrhage.
“It’s incredibly distressful,” Brian Thompson, MD, of the Oneida Nation and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Upstate Medical University, New York, told USA Today.
Dr. Thompson is working with the National Indian Health Board to create the first national tribal review committee for maternal deaths.
“It really needs to be looked at and examined why that is the case if essentially all of them are preventable,” he said.
Black mothers were also three times as likely as White mothers to die and more likely to die from heart problems. Hispanic mothers, who made up 14% of deaths, were more likely to die from mental health conditions.
Some of the deaths, such as hemorrhage, should be highly preventable. Existing toolkits for clinicians provide evidence-based guidelines to prevent and treat excessive bleeding.
“No pregnant person should be passing away from a hemorrhage,” Andrea Jackson, MD, division chief of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, San Francisco, told USA Today.
“We have the tools in the United States, and we know how to deal with it,” she said. “That was really disheartening to see.”
What’s more, the new CDC report highlights the need for more mental health resources during pregnancy and the postpartum period – up to a year or more after delivery – including improvements in access to care, diagnosis, and treatment.
“These are things that need to happen systemically,” LeThenia Baker, MD, an obstetrician and gynecologist at Wellstar Health, Georgia, told USA Today.
“It can’t just be a few practices here or there who are adopting best practices,” she said. “It has to be a systemic change.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A week of anticoagulation halves post-PCI radial occlusion rate
Serious bleeding is not increased
BOSTON – Following transradial access for angiography or a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a low dose of the factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban for 7 days reduces the risk of an access-site occlusion by 50%, according to results of the randomized RIVARAD trial.
Of two multicenter, randomized trials to address this question it is the larger, according to Rania Hammami, MD, who presented the results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
In the open-label RIVARAD trial, 538 patients were randomized to 10 mg rivaroxaban or standard care alone. Standard care at the beginning of the procedure included unfractionated heparin in a dose of 50 IU/kg for angiography and up to 100 IU/kg for PCI. Manual compression was applied at the end of the procedure followed by an evaluation for complications, such as hematoma or aneurysm.
For the primary outcome of radial access occlusion at 30 days, the lower rate in the rivaroxaban arm (6.9% vs. 13.0%) translated into a statistically significant 50% reduction (odds ratio, 0.50; P = .011).
Rivaroxaban preserves radial pulse
Rivaroxaban was also favored for the endpoint of inability at 30 days to find a radial pulse (5.8% vs. 12.2%; P = .01). Interestingly, there was some disparity for this endpoint for clinical examination and ultrasound.
“In 12 patients, we were able to palpate a radial pulse, but the ultrasound showed an occlusion of the vessel, while in 7 patients we could not find a radial pulse even though the radial artery was patent on ultrasound,” Dr. Hammami, of the department of cardiology, Hedi Chaker Hospital, Sfax, Tunisia, said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The incidence of hemorrhagic complications was higher in the rivaroxaban group (2.7% vs. 1.9%), but the difference did not approach statistical significance (OR, 1.5; P = .54). Moreover, all of the bleeding complications were minor (Bleeding Academic Research Consortium level 1), and none of the bleeding complications were observed in patients receiving rivaroxaban alone. Rather, all patients with bleeding were taking one or more antiplatelet drugs along with rivaroxaban.
On univariate analysis, several baseline characteristics were associated with subsequent radial occlusion, including female sex (P = .02), current smoking (P = .03), renal failure (P = .004), and PCI for acute coronary syndrome (P = .02). On multivariate analysis, female sex (P = .001) and current smoking (P < .0001) became even stronger predictors of occlusion on a statistical basis, while a prior procedure involving radial access was also a significant predictor (P = .029).
“One woman out of two developed radial access occlusion if she had a history of smoking and had a history of a transradial puncture,” Dr. Hammami reported.
In a subgroup analysis, relative protection from radial artery occlusion from a 7-day course of rivaroxaban was particularly pronounced in those with diabetes, renal failure, or hypertension relative to those without these conditions, but the protective effect appeared to be about the same regardless of body mass index, age, sheath size, or current use of statins.
These findings are consistent with other studies evaluating the risk of radial access occlusion, according to Dr. Hammami. While different studies she cited reported incidences ranging from less than 1% to more than 30%, the risk has typically been highest in populations with increased susceptibility for thrombus formation, such as smokers and patients with diabetes.
Preventing radial artery occlusion has several benefits, not least of which is preserving this access point for future interventions, according to Dr. Hammami.
RIVARAD is the largest study to evaluate an anticoagulant for the prevention of radial artery occlusion, but it is not the first. Earlier in 2022, a Chinese trial called RESTORE was published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. In that placebo-controlled study of 382 patients, 7 days of 10 mg rivaroxaban was also linked to a significant reduction in radial artery occlusion at 30 days (3.8% vs. 11.5%; P = .011).
“We don’t know if a higher dose of rivaroxaban would be more effective and equally safe,” said Dr. Hammami, but added that a Canadian trial called CAPITAL RAPTOR will test this premise. In this trial, there is a planned enrollment of 1,800 patients who will be randomized to 15 mg rivaroxaban or standard treatment.
Occlusion risk appears underappreciated
The risk of radial artery occlusion might be underappreciated. According to data cited by Dr. Hammami, only about half of interventionalists in the United States and fewer than 10% outside of the United States routinely assess radial artery patency in conjunction with radial-access PCI. The data from this trial suggest that the risk can be substantially reduced, particularly in high-risk patients, with anticoagulant therapy.
Agreeing that this is a potentially avoidable complication, Roxanna Mehran, MD, director of interventional cardiovascular research and clinical trials, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, called the RIVARAD study “a clinically meaningful trial,” and valuable for identifying risk factors as well as for showing a treatment effect and acceptable safety from a short course of a factor Xa inhibitor.
“This is very important work,” said Dr. Mehran, who praised the quality of the study and the contribution it makes for considering how and when prophylaxis is needed.
Dr. Hammami reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehran has financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies but none with the sponsor of this trial, which was funded by Philadelphia Pharma, a drug company based in Tunisia.
Serious bleeding is not increased
Serious bleeding is not increased
BOSTON – Following transradial access for angiography or a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a low dose of the factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban for 7 days reduces the risk of an access-site occlusion by 50%, according to results of the randomized RIVARAD trial.
Of two multicenter, randomized trials to address this question it is the larger, according to Rania Hammami, MD, who presented the results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
In the open-label RIVARAD trial, 538 patients were randomized to 10 mg rivaroxaban or standard care alone. Standard care at the beginning of the procedure included unfractionated heparin in a dose of 50 IU/kg for angiography and up to 100 IU/kg for PCI. Manual compression was applied at the end of the procedure followed by an evaluation for complications, such as hematoma or aneurysm.
For the primary outcome of radial access occlusion at 30 days, the lower rate in the rivaroxaban arm (6.9% vs. 13.0%) translated into a statistically significant 50% reduction (odds ratio, 0.50; P = .011).
Rivaroxaban preserves radial pulse
Rivaroxaban was also favored for the endpoint of inability at 30 days to find a radial pulse (5.8% vs. 12.2%; P = .01). Interestingly, there was some disparity for this endpoint for clinical examination and ultrasound.
“In 12 patients, we were able to palpate a radial pulse, but the ultrasound showed an occlusion of the vessel, while in 7 patients we could not find a radial pulse even though the radial artery was patent on ultrasound,” Dr. Hammami, of the department of cardiology, Hedi Chaker Hospital, Sfax, Tunisia, said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The incidence of hemorrhagic complications was higher in the rivaroxaban group (2.7% vs. 1.9%), but the difference did not approach statistical significance (OR, 1.5; P = .54). Moreover, all of the bleeding complications were minor (Bleeding Academic Research Consortium level 1), and none of the bleeding complications were observed in patients receiving rivaroxaban alone. Rather, all patients with bleeding were taking one or more antiplatelet drugs along with rivaroxaban.
On univariate analysis, several baseline characteristics were associated with subsequent radial occlusion, including female sex (P = .02), current smoking (P = .03), renal failure (P = .004), and PCI for acute coronary syndrome (P = .02). On multivariate analysis, female sex (P = .001) and current smoking (P < .0001) became even stronger predictors of occlusion on a statistical basis, while a prior procedure involving radial access was also a significant predictor (P = .029).
“One woman out of two developed radial access occlusion if she had a history of smoking and had a history of a transradial puncture,” Dr. Hammami reported.
In a subgroup analysis, relative protection from radial artery occlusion from a 7-day course of rivaroxaban was particularly pronounced in those with diabetes, renal failure, or hypertension relative to those without these conditions, but the protective effect appeared to be about the same regardless of body mass index, age, sheath size, or current use of statins.
These findings are consistent with other studies evaluating the risk of radial access occlusion, according to Dr. Hammami. While different studies she cited reported incidences ranging from less than 1% to more than 30%, the risk has typically been highest in populations with increased susceptibility for thrombus formation, such as smokers and patients with diabetes.
Preventing radial artery occlusion has several benefits, not least of which is preserving this access point for future interventions, according to Dr. Hammami.
RIVARAD is the largest study to evaluate an anticoagulant for the prevention of radial artery occlusion, but it is not the first. Earlier in 2022, a Chinese trial called RESTORE was published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. In that placebo-controlled study of 382 patients, 7 days of 10 mg rivaroxaban was also linked to a significant reduction in radial artery occlusion at 30 days (3.8% vs. 11.5%; P = .011).
“We don’t know if a higher dose of rivaroxaban would be more effective and equally safe,” said Dr. Hammami, but added that a Canadian trial called CAPITAL RAPTOR will test this premise. In this trial, there is a planned enrollment of 1,800 patients who will be randomized to 15 mg rivaroxaban or standard treatment.
Occlusion risk appears underappreciated
The risk of radial artery occlusion might be underappreciated. According to data cited by Dr. Hammami, only about half of interventionalists in the United States and fewer than 10% outside of the United States routinely assess radial artery patency in conjunction with radial-access PCI. The data from this trial suggest that the risk can be substantially reduced, particularly in high-risk patients, with anticoagulant therapy.
Agreeing that this is a potentially avoidable complication, Roxanna Mehran, MD, director of interventional cardiovascular research and clinical trials, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, called the RIVARAD study “a clinically meaningful trial,” and valuable for identifying risk factors as well as for showing a treatment effect and acceptable safety from a short course of a factor Xa inhibitor.
“This is very important work,” said Dr. Mehran, who praised the quality of the study and the contribution it makes for considering how and when prophylaxis is needed.
Dr. Hammami reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehran has financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies but none with the sponsor of this trial, which was funded by Philadelphia Pharma, a drug company based in Tunisia.
BOSTON – Following transradial access for angiography or a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a low dose of the factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban for 7 days reduces the risk of an access-site occlusion by 50%, according to results of the randomized RIVARAD trial.
Of two multicenter, randomized trials to address this question it is the larger, according to Rania Hammami, MD, who presented the results at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
In the open-label RIVARAD trial, 538 patients were randomized to 10 mg rivaroxaban or standard care alone. Standard care at the beginning of the procedure included unfractionated heparin in a dose of 50 IU/kg for angiography and up to 100 IU/kg for PCI. Manual compression was applied at the end of the procedure followed by an evaluation for complications, such as hematoma or aneurysm.
For the primary outcome of radial access occlusion at 30 days, the lower rate in the rivaroxaban arm (6.9% vs. 13.0%) translated into a statistically significant 50% reduction (odds ratio, 0.50; P = .011).
Rivaroxaban preserves radial pulse
Rivaroxaban was also favored for the endpoint of inability at 30 days to find a radial pulse (5.8% vs. 12.2%; P = .01). Interestingly, there was some disparity for this endpoint for clinical examination and ultrasound.
“In 12 patients, we were able to palpate a radial pulse, but the ultrasound showed an occlusion of the vessel, while in 7 patients we could not find a radial pulse even though the radial artery was patent on ultrasound,” Dr. Hammami, of the department of cardiology, Hedi Chaker Hospital, Sfax, Tunisia, said at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
The incidence of hemorrhagic complications was higher in the rivaroxaban group (2.7% vs. 1.9%), but the difference did not approach statistical significance (OR, 1.5; P = .54). Moreover, all of the bleeding complications were minor (Bleeding Academic Research Consortium level 1), and none of the bleeding complications were observed in patients receiving rivaroxaban alone. Rather, all patients with bleeding were taking one or more antiplatelet drugs along with rivaroxaban.
On univariate analysis, several baseline characteristics were associated with subsequent radial occlusion, including female sex (P = .02), current smoking (P = .03), renal failure (P = .004), and PCI for acute coronary syndrome (P = .02). On multivariate analysis, female sex (P = .001) and current smoking (P < .0001) became even stronger predictors of occlusion on a statistical basis, while a prior procedure involving radial access was also a significant predictor (P = .029).
“One woman out of two developed radial access occlusion if she had a history of smoking and had a history of a transradial puncture,” Dr. Hammami reported.
In a subgroup analysis, relative protection from radial artery occlusion from a 7-day course of rivaroxaban was particularly pronounced in those with diabetes, renal failure, or hypertension relative to those without these conditions, but the protective effect appeared to be about the same regardless of body mass index, age, sheath size, or current use of statins.
These findings are consistent with other studies evaluating the risk of radial access occlusion, according to Dr. Hammami. While different studies she cited reported incidences ranging from less than 1% to more than 30%, the risk has typically been highest in populations with increased susceptibility for thrombus formation, such as smokers and patients with diabetes.
Preventing radial artery occlusion has several benefits, not least of which is preserving this access point for future interventions, according to Dr. Hammami.
RIVARAD is the largest study to evaluate an anticoagulant for the prevention of radial artery occlusion, but it is not the first. Earlier in 2022, a Chinese trial called RESTORE was published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. In that placebo-controlled study of 382 patients, 7 days of 10 mg rivaroxaban was also linked to a significant reduction in radial artery occlusion at 30 days (3.8% vs. 11.5%; P = .011).
“We don’t know if a higher dose of rivaroxaban would be more effective and equally safe,” said Dr. Hammami, but added that a Canadian trial called CAPITAL RAPTOR will test this premise. In this trial, there is a planned enrollment of 1,800 patients who will be randomized to 15 mg rivaroxaban or standard treatment.
Occlusion risk appears underappreciated
The risk of radial artery occlusion might be underappreciated. According to data cited by Dr. Hammami, only about half of interventionalists in the United States and fewer than 10% outside of the United States routinely assess radial artery patency in conjunction with radial-access PCI. The data from this trial suggest that the risk can be substantially reduced, particularly in high-risk patients, with anticoagulant therapy.
Agreeing that this is a potentially avoidable complication, Roxanna Mehran, MD, director of interventional cardiovascular research and clinical trials, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, called the RIVARAD study “a clinically meaningful trial,” and valuable for identifying risk factors as well as for showing a treatment effect and acceptable safety from a short course of a factor Xa inhibitor.
“This is very important work,” said Dr. Mehran, who praised the quality of the study and the contribution it makes for considering how and when prophylaxis is needed.
Dr. Hammami reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehran has financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies but none with the sponsor of this trial, which was funded by Philadelphia Pharma, a drug company based in Tunisia.
AT TCT 2022
Experts debate infant chiropractic care on TikTok
Several chiropractors in the United States are posting TikTok videos of themselves working with newborns, babies, and toddlers, often promoting treatments that aren’t backed by science, according to The Washington Post.
The videos include various devices and treatments, such as vibrating handheld massagers, spinal adjustments, and body movements, which are meant to address colic, constipation, reflux, musculoskeletal problems, and even trauma that babies experience during childbirth.
Chiropractors say the treatments are safe and gentle for babies and are unlike the more strenuous movements associated with adult chiropractic care. However, some doctors have said the videos are concerning because babies have softer bones and looser joints.
“Ultimately, there is no way you’re going to get an improvement in a newborn from a manipulation,” Sean Tabaie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, told the newspaper.
Dr. Tabaie said his colleagues are shocked when he sends them Instagram or TikTok videos of chiropractic clinics treating infants.
“The only thing that you might possibly cause is harm,” he said.
Generally, chiropractors are licensed health professionals who use stretching, pressure, and joint manipulation on the spine to treat patients. Although chiropractic care is typically seen as an “alternative therapy,” some data in adults suggest that chiropractic treatments can help some conditions, such as low back pain.
“To my knowledge, there is little to no evidence that chiropractic care changes the natural history of any disease or condition,” Anthony Stans, MD, a pediatric orthopedic surgeon at Mayo Clinic Children’s Center, Rochester, Minn., told the newspaper. Stans said he would caution parents and recommend against chiropractic treatment for babies.
For some parents, the treatments and TikTok videos seem appealing because they promise relief for problems that traditional medicine can’t always address, especially colic, the newspaper reported. Colic, which features intense and prolonged crying in an otherwise healthy baby, tends to resolve over time without treatment.
Recent studies have attempted to study chiropractic care in infants. In a 2021 study, researchers in Denmark conducted a randomized controlled trial with 186 babies to test light pressure treatments. Although excessive crying was reduced by half an hour in the group that received treatment, the findings weren’t statistically significant in the end.
In a new study, researchers in Spain conducted a randomized trial with 58 babies to test “light touch manual therapy.” The babies who received treatment appeared to cry significantly less, but the parents weren’t “blinded” and were aware of the study’s treatment conditions, which can bias the results.
However, it can be challenging to “get that level of evidence” to support manual therapies such as chiropractic care, Joy Weydert, MD, director of pediatric integrative medicine at the University of Arizona, Tucson, told the newspaper. Certain treatments could help reduce the discomfort of colic or reflux, which can be difficult to measures in infants, she said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics told The Post that it doesn’t have an “official policy” on chiropractic care for infants or toddlers. At the same time, a 2017 report released by the organization concluded that “high-quality evidence” is lacking for spinal manipulation in children.
The American Chiropractic Association said chiropractic treatments are safe and effective for children, yet more research is needed to prove they work.
“We still haven’t been able to demonstrate in the research the effectiveness that we’ve seen clinically,” Jennifer Brocker, president of the group’s Council on Chiropractic Pediatrics, told the newspaper.
“We can’t really say for sure what’s happening,” she said. “It’s sort of like a black box. But what we do know is that, clinically, what we’re doing is effective because we see a change in the symptoms of the child.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Several chiropractors in the United States are posting TikTok videos of themselves working with newborns, babies, and toddlers, often promoting treatments that aren’t backed by science, according to The Washington Post.
The videos include various devices and treatments, such as vibrating handheld massagers, spinal adjustments, and body movements, which are meant to address colic, constipation, reflux, musculoskeletal problems, and even trauma that babies experience during childbirth.
Chiropractors say the treatments are safe and gentle for babies and are unlike the more strenuous movements associated with adult chiropractic care. However, some doctors have said the videos are concerning because babies have softer bones and looser joints.
“Ultimately, there is no way you’re going to get an improvement in a newborn from a manipulation,” Sean Tabaie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, told the newspaper.
Dr. Tabaie said his colleagues are shocked when he sends them Instagram or TikTok videos of chiropractic clinics treating infants.
“The only thing that you might possibly cause is harm,” he said.
Generally, chiropractors are licensed health professionals who use stretching, pressure, and joint manipulation on the spine to treat patients. Although chiropractic care is typically seen as an “alternative therapy,” some data in adults suggest that chiropractic treatments can help some conditions, such as low back pain.
“To my knowledge, there is little to no evidence that chiropractic care changes the natural history of any disease or condition,” Anthony Stans, MD, a pediatric orthopedic surgeon at Mayo Clinic Children’s Center, Rochester, Minn., told the newspaper. Stans said he would caution parents and recommend against chiropractic treatment for babies.
For some parents, the treatments and TikTok videos seem appealing because they promise relief for problems that traditional medicine can’t always address, especially colic, the newspaper reported. Colic, which features intense and prolonged crying in an otherwise healthy baby, tends to resolve over time without treatment.
Recent studies have attempted to study chiropractic care in infants. In a 2021 study, researchers in Denmark conducted a randomized controlled trial with 186 babies to test light pressure treatments. Although excessive crying was reduced by half an hour in the group that received treatment, the findings weren’t statistically significant in the end.
In a new study, researchers in Spain conducted a randomized trial with 58 babies to test “light touch manual therapy.” The babies who received treatment appeared to cry significantly less, but the parents weren’t “blinded” and were aware of the study’s treatment conditions, which can bias the results.
However, it can be challenging to “get that level of evidence” to support manual therapies such as chiropractic care, Joy Weydert, MD, director of pediatric integrative medicine at the University of Arizona, Tucson, told the newspaper. Certain treatments could help reduce the discomfort of colic or reflux, which can be difficult to measures in infants, she said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics told The Post that it doesn’t have an “official policy” on chiropractic care for infants or toddlers. At the same time, a 2017 report released by the organization concluded that “high-quality evidence” is lacking for spinal manipulation in children.
The American Chiropractic Association said chiropractic treatments are safe and effective for children, yet more research is needed to prove they work.
“We still haven’t been able to demonstrate in the research the effectiveness that we’ve seen clinically,” Jennifer Brocker, president of the group’s Council on Chiropractic Pediatrics, told the newspaper.
“We can’t really say for sure what’s happening,” she said. “It’s sort of like a black box. But what we do know is that, clinically, what we’re doing is effective because we see a change in the symptoms of the child.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Several chiropractors in the United States are posting TikTok videos of themselves working with newborns, babies, and toddlers, often promoting treatments that aren’t backed by science, according to The Washington Post.
The videos include various devices and treatments, such as vibrating handheld massagers, spinal adjustments, and body movements, which are meant to address colic, constipation, reflux, musculoskeletal problems, and even trauma that babies experience during childbirth.
Chiropractors say the treatments are safe and gentle for babies and are unlike the more strenuous movements associated with adult chiropractic care. However, some doctors have said the videos are concerning because babies have softer bones and looser joints.
“Ultimately, there is no way you’re going to get an improvement in a newborn from a manipulation,” Sean Tabaie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, told the newspaper.
Dr. Tabaie said his colleagues are shocked when he sends them Instagram or TikTok videos of chiropractic clinics treating infants.
“The only thing that you might possibly cause is harm,” he said.
Generally, chiropractors are licensed health professionals who use stretching, pressure, and joint manipulation on the spine to treat patients. Although chiropractic care is typically seen as an “alternative therapy,” some data in adults suggest that chiropractic treatments can help some conditions, such as low back pain.
“To my knowledge, there is little to no evidence that chiropractic care changes the natural history of any disease or condition,” Anthony Stans, MD, a pediatric orthopedic surgeon at Mayo Clinic Children’s Center, Rochester, Minn., told the newspaper. Stans said he would caution parents and recommend against chiropractic treatment for babies.
For some parents, the treatments and TikTok videos seem appealing because they promise relief for problems that traditional medicine can’t always address, especially colic, the newspaper reported. Colic, which features intense and prolonged crying in an otherwise healthy baby, tends to resolve over time without treatment.
Recent studies have attempted to study chiropractic care in infants. In a 2021 study, researchers in Denmark conducted a randomized controlled trial with 186 babies to test light pressure treatments. Although excessive crying was reduced by half an hour in the group that received treatment, the findings weren’t statistically significant in the end.
In a new study, researchers in Spain conducted a randomized trial with 58 babies to test “light touch manual therapy.” The babies who received treatment appeared to cry significantly less, but the parents weren’t “blinded” and were aware of the study’s treatment conditions, which can bias the results.
However, it can be challenging to “get that level of evidence” to support manual therapies such as chiropractic care, Joy Weydert, MD, director of pediatric integrative medicine at the University of Arizona, Tucson, told the newspaper. Certain treatments could help reduce the discomfort of colic or reflux, which can be difficult to measures in infants, she said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics told The Post that it doesn’t have an “official policy” on chiropractic care for infants or toddlers. At the same time, a 2017 report released by the organization concluded that “high-quality evidence” is lacking for spinal manipulation in children.
The American Chiropractic Association said chiropractic treatments are safe and effective for children, yet more research is needed to prove they work.
“We still haven’t been able to demonstrate in the research the effectiveness that we’ve seen clinically,” Jennifer Brocker, president of the group’s Council on Chiropractic Pediatrics, told the newspaper.
“We can’t really say for sure what’s happening,” she said. “It’s sort of like a black box. But what we do know is that, clinically, what we’re doing is effective because we see a change in the symptoms of the child.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Apremilast alleviates severe psoriasis in some children, data show
not controlled by topical therapy, according to the results of a phase 3 trial.
“Unfortunately, there are limited treatment options for pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis” who do not respond to or cannot use topical therapy, said study investigator Anna Belloni Fortina, MD, speaking at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“In this randomized, placebo-controlled trial, oral apremilast demonstrated effectiveness and was well tolerated,” added Dr. Belloni Fortina, of Azienda Ospedale Università Padova (Italy). “I underline oral because for children, oral administration is better than the injection treatment.”
Key findings
Dubbed the SPROUT study, the trial set a primary endpoint of the percentage of children with a Physician’s Global Assessment (sPGA) response after 16 weeks of treatment or placebo. The sPGA is a 5-point scale ranging from 0 (clear) to 4 (severe). The study enrolled children with an sPGA greater than or equal to 3. Response was defined as a sPGA score of 0 or 1, indicating clear or almost clear skin, with at least a 2-point reduction from baseline values.
At week 16, the primary endpoint was met by 33% of 163 children treated with apremilast versus 11% of 82 children who had been given a placebo, a treatment difference of 21.7% (95% confidence interval, 11.2%-32.1%).
A greater proportion of children treated with apremilast also achieved a major secondary endpoint, a 75% or greater reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI-75) (45.4% vs. 16.1%), a treatment difference of 29.4% (95% CI, 17.8%-40.9%).
Results unaffected by weight and age
Regarding apremilast, “it’s important to underline that patients were dosed according to their weight,” Dr. Belloni Fortina said.
A dose of 20 mg twice daily was given to children who weighed between 20 kg and less than 50 kg, and a 30-mg twice-daily dose was given to those who weighed greater than or equal to 50 kg.
When the data were analyzed according to weight, proportionately more children on apremilast saw a sPGA response: 47.4% versus 21.8% in the lower weight and dose range and 19.2% versus 1.6% in the higher weight and dose range.
As for PASI-75, a greater proportion of children on apremilast also responded in both the lower and upper weight ranges, a respective 52.4% and 38.7% of patients, compared with 21.4% and 11% of those treated with placebo.
Data were also evaluated according to age, with a younger (aged 6-11 years) and older (age 12-17 years) group. The mean age of children was 12 years overall. Results showed a similar pattern for weight: The psoriasis of more children treated with apremilast was reduced by both measures, sPGA response, and PASI-75.
Safety of apremilast in children
“The overall safety profile during the placebo-controlled phase was comparable with the known safety profile of apremilast,” Dr. Belloni Fontina reported. “No new safety signals were identified.”
The rate of any adverse event was substantially higher in children given the active treatment, however, at 65% versus 41.3% for placebo.
Rates of severe and serious adverse events were low, at around 1.3%, and similar between the groups.
There was also a low rate of withdrawal because of side effects, although this was higher in the apremilast group (3.1% vs. 1.3%).
The primary reason for withdrawal of apremilast treatment were the most commonly reported adverse events: gastrointestinal disorders, including diarrhea, nausea, upper and lower abdominal pain, and vomiting. Headache, pyrexia, and nasopharyngitis were also reported.
Despite being common, most treatment-related adverse effects resolved within 3 days, Dr. Belloni Fontina said.
Expect further data
Further data from the trial are to be expected, because only the 16-week primary endpoint results have been released so far. The trial also included a 36-week extension phase, during which all children who had originally been randomly assigned to placebo were now eligible to be treated with apremilast, and all those who were originally given the active treatment were able to continue. This extension treatment period means that data will be available for a full year of treatment, and there will also be a further 2-week observational follow-up at the end of the trial.
The study was funded by Amgen. Dr. Belloni Fontina reported acting as an investigator and advisory board member for and receiving honoraria from Amgen, Galderma, Leo Pharma, and Pfizer. She also reported speaking on behalf of Pierre-Fabre and Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
not controlled by topical therapy, according to the results of a phase 3 trial.
“Unfortunately, there are limited treatment options for pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis” who do not respond to or cannot use topical therapy, said study investigator Anna Belloni Fortina, MD, speaking at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“In this randomized, placebo-controlled trial, oral apremilast demonstrated effectiveness and was well tolerated,” added Dr. Belloni Fortina, of Azienda Ospedale Università Padova (Italy). “I underline oral because for children, oral administration is better than the injection treatment.”
Key findings
Dubbed the SPROUT study, the trial set a primary endpoint of the percentage of children with a Physician’s Global Assessment (sPGA) response after 16 weeks of treatment or placebo. The sPGA is a 5-point scale ranging from 0 (clear) to 4 (severe). The study enrolled children with an sPGA greater than or equal to 3. Response was defined as a sPGA score of 0 or 1, indicating clear or almost clear skin, with at least a 2-point reduction from baseline values.
At week 16, the primary endpoint was met by 33% of 163 children treated with apremilast versus 11% of 82 children who had been given a placebo, a treatment difference of 21.7% (95% confidence interval, 11.2%-32.1%).
A greater proportion of children treated with apremilast also achieved a major secondary endpoint, a 75% or greater reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI-75) (45.4% vs. 16.1%), a treatment difference of 29.4% (95% CI, 17.8%-40.9%).
Results unaffected by weight and age
Regarding apremilast, “it’s important to underline that patients were dosed according to their weight,” Dr. Belloni Fortina said.
A dose of 20 mg twice daily was given to children who weighed between 20 kg and less than 50 kg, and a 30-mg twice-daily dose was given to those who weighed greater than or equal to 50 kg.
When the data were analyzed according to weight, proportionately more children on apremilast saw a sPGA response: 47.4% versus 21.8% in the lower weight and dose range and 19.2% versus 1.6% in the higher weight and dose range.
As for PASI-75, a greater proportion of children on apremilast also responded in both the lower and upper weight ranges, a respective 52.4% and 38.7% of patients, compared with 21.4% and 11% of those treated with placebo.
Data were also evaluated according to age, with a younger (aged 6-11 years) and older (age 12-17 years) group. The mean age of children was 12 years overall. Results showed a similar pattern for weight: The psoriasis of more children treated with apremilast was reduced by both measures, sPGA response, and PASI-75.
Safety of apremilast in children
“The overall safety profile during the placebo-controlled phase was comparable with the known safety profile of apremilast,” Dr. Belloni Fontina reported. “No new safety signals were identified.”
The rate of any adverse event was substantially higher in children given the active treatment, however, at 65% versus 41.3% for placebo.
Rates of severe and serious adverse events were low, at around 1.3%, and similar between the groups.
There was also a low rate of withdrawal because of side effects, although this was higher in the apremilast group (3.1% vs. 1.3%).
The primary reason for withdrawal of apremilast treatment were the most commonly reported adverse events: gastrointestinal disorders, including diarrhea, nausea, upper and lower abdominal pain, and vomiting. Headache, pyrexia, and nasopharyngitis were also reported.
Despite being common, most treatment-related adverse effects resolved within 3 days, Dr. Belloni Fontina said.
Expect further data
Further data from the trial are to be expected, because only the 16-week primary endpoint results have been released so far. The trial also included a 36-week extension phase, during which all children who had originally been randomly assigned to placebo were now eligible to be treated with apremilast, and all those who were originally given the active treatment were able to continue. This extension treatment period means that data will be available for a full year of treatment, and there will also be a further 2-week observational follow-up at the end of the trial.
The study was funded by Amgen. Dr. Belloni Fontina reported acting as an investigator and advisory board member for and receiving honoraria from Amgen, Galderma, Leo Pharma, and Pfizer. She also reported speaking on behalf of Pierre-Fabre and Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
not controlled by topical therapy, according to the results of a phase 3 trial.
“Unfortunately, there are limited treatment options for pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis” who do not respond to or cannot use topical therapy, said study investigator Anna Belloni Fortina, MD, speaking at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“In this randomized, placebo-controlled trial, oral apremilast demonstrated effectiveness and was well tolerated,” added Dr. Belloni Fortina, of Azienda Ospedale Università Padova (Italy). “I underline oral because for children, oral administration is better than the injection treatment.”
Key findings
Dubbed the SPROUT study, the trial set a primary endpoint of the percentage of children with a Physician’s Global Assessment (sPGA) response after 16 weeks of treatment or placebo. The sPGA is a 5-point scale ranging from 0 (clear) to 4 (severe). The study enrolled children with an sPGA greater than or equal to 3. Response was defined as a sPGA score of 0 or 1, indicating clear or almost clear skin, with at least a 2-point reduction from baseline values.
At week 16, the primary endpoint was met by 33% of 163 children treated with apremilast versus 11% of 82 children who had been given a placebo, a treatment difference of 21.7% (95% confidence interval, 11.2%-32.1%).
A greater proportion of children treated with apremilast also achieved a major secondary endpoint, a 75% or greater reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI-75) (45.4% vs. 16.1%), a treatment difference of 29.4% (95% CI, 17.8%-40.9%).
Results unaffected by weight and age
Regarding apremilast, “it’s important to underline that patients were dosed according to their weight,” Dr. Belloni Fortina said.
A dose of 20 mg twice daily was given to children who weighed between 20 kg and less than 50 kg, and a 30-mg twice-daily dose was given to those who weighed greater than or equal to 50 kg.
When the data were analyzed according to weight, proportionately more children on apremilast saw a sPGA response: 47.4% versus 21.8% in the lower weight and dose range and 19.2% versus 1.6% in the higher weight and dose range.
As for PASI-75, a greater proportion of children on apremilast also responded in both the lower and upper weight ranges, a respective 52.4% and 38.7% of patients, compared with 21.4% and 11% of those treated with placebo.
Data were also evaluated according to age, with a younger (aged 6-11 years) and older (age 12-17 years) group. The mean age of children was 12 years overall. Results showed a similar pattern for weight: The psoriasis of more children treated with apremilast was reduced by both measures, sPGA response, and PASI-75.
Safety of apremilast in children
“The overall safety profile during the placebo-controlled phase was comparable with the known safety profile of apremilast,” Dr. Belloni Fontina reported. “No new safety signals were identified.”
The rate of any adverse event was substantially higher in children given the active treatment, however, at 65% versus 41.3% for placebo.
Rates of severe and serious adverse events were low, at around 1.3%, and similar between the groups.
There was also a low rate of withdrawal because of side effects, although this was higher in the apremilast group (3.1% vs. 1.3%).
The primary reason for withdrawal of apremilast treatment were the most commonly reported adverse events: gastrointestinal disorders, including diarrhea, nausea, upper and lower abdominal pain, and vomiting. Headache, pyrexia, and nasopharyngitis were also reported.
Despite being common, most treatment-related adverse effects resolved within 3 days, Dr. Belloni Fontina said.
Expect further data
Further data from the trial are to be expected, because only the 16-week primary endpoint results have been released so far. The trial also included a 36-week extension phase, during which all children who had originally been randomly assigned to placebo were now eligible to be treated with apremilast, and all those who were originally given the active treatment were able to continue. This extension treatment period means that data will be available for a full year of treatment, and there will also be a further 2-week observational follow-up at the end of the trial.
The study was funded by Amgen. Dr. Belloni Fontina reported acting as an investigator and advisory board member for and receiving honoraria from Amgen, Galderma, Leo Pharma, and Pfizer. She also reported speaking on behalf of Pierre-Fabre and Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2022
Uncombable hair syndrome: One gene, variants responsible for many cases
that manifests during infancy, investigators have reported.
The findings are from a cohort study published in JAMA Dermatology, which involved 107 unrelated children and adults suspected of having UHS, as well as family members, all of whom were recruited from January 2013 to December 2021. Genetic analyses were conducted in Germany from January 2014 to December 2021 with exome sequencing.
Study builds on prior research
Senior author Regina C. Betz, MD, professor of dermatogenetics at the Institute of Human Genetics, University Hospital Bonn, Germany, said that in 2016, she and her coinvestigators authored a study on the molecular genetics of UHS. That study, which involved 18 people with UHS, identified variants in three genes – PADI3, TCHH, and TGM3 – that encode proteins that play a role in the formation of the hair shaft. The investigators described how a deficiency in the shaping and mechanical strengthening of the hair shaft occurs in the UHS phenotype, which is characterized by dry, frizzy, and wiry hair that cannot be combed flat.
As a result of that previous work, “we base the assignment or confirmation of a clinical diagnosis of UHS on molecular genetic diagnostics,” the authors write in the new study, rather than on the clinical appearance of the hair and the physical examination of the patient, with confirmation on microscopical examination of the hair shaft.
Social media as instrument in finding study participants
Following the 2016 study, Dr. Betz and colleagues were contacted by many clinicians and by the public through Facebook and other social media platforms with details about possible cases of UHS, an autosomal recessive disorder. Through these contacts, blood samples, saliva, or DNA was sent to the investigators’ laboratory from 89 unrelated index patients (69 female patients, 20 male patients) suspected of having UHS. This resulted in the identification of pathogenic variants in 69 cases, the investigators write.
“In the first study, we had 18 patients, and then we tried to collect as many as possible” to determine the main mechanism behind UHS, Dr. Betz said. One question is whether there are additional genes responsible for UHS, she noted. “Even now, we are not sure, because in 25% [of cases in the new study], we didn’t find any mutation in the three known genes.”
The current study resulted in the discovery of eight novel pathogenic variants in PADI3, which are responsible for 71.0% (76) of the 107 cases. Of those, “6 were single observations and 2 were observed in 3 and 2 individuals, respectively,” the investigators write.
Children can grow out of this disorder, but it can also persist into adulthood, Dr. Betz noted. Communication that investigators had with parents of the children with UHS revealed that these children are often the targets of bullying by other children, she added.
She and her and colleagues will continue this research and are currently studying adults who have UHS.
Research leads to possible treatment pathways
Jeff Donovan, MD, FRCPC, FAAD, a dermatologist and medical director of the Donovan Hair Clinic in Whistler, British Columbia, described these findings as fundamental to understanding UHS and creating pathways to possible treatments.
The study “identifies more about the genetic basis of this challenging condition,” said Dr. Donovan, who is also clinical instructor in the department of dermatology at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and president of the Canadian Hair Loss Foundation. “We really need this type of information in order to have any sort of clue in terms of how to treat it,” he told this news organization.
“In the hair loss world, it’s pretty clear that if you can understand the genetic basis of things, or the basic science of a condition, whether it’s the basic genetics or the basic immunology, you give yourself the best chance to develop good treatments,” said Dr. Donovan.
The article provides advanced genetic information of the condition, such that geneticists can test for at least three markers if they are suspecting UHS, Dr. Donovan observed.
Condition can lead to bullying
Dr. Donovan also commented that UHS can have a detrimental impact on children with regard to socializing with their peers. “Having hair that sticks out and is very full like this is challenging because kids do get teased,” he said.
“It is often the parents who are the most affected” when a child aged 2-5 years has a hair condition such as UHS. But at age 5-9, “children are developing self-identity and an understanding of various aspects of self-esteem and what they look like and what others look like. And that’s where the teasing really starts. And that’s where it does become troublesome.”
Dr. Betz and Dr. Donovan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that manifests during infancy, investigators have reported.
The findings are from a cohort study published in JAMA Dermatology, which involved 107 unrelated children and adults suspected of having UHS, as well as family members, all of whom were recruited from January 2013 to December 2021. Genetic analyses were conducted in Germany from January 2014 to December 2021 with exome sequencing.
Study builds on prior research
Senior author Regina C. Betz, MD, professor of dermatogenetics at the Institute of Human Genetics, University Hospital Bonn, Germany, said that in 2016, she and her coinvestigators authored a study on the molecular genetics of UHS. That study, which involved 18 people with UHS, identified variants in three genes – PADI3, TCHH, and TGM3 – that encode proteins that play a role in the formation of the hair shaft. The investigators described how a deficiency in the shaping and mechanical strengthening of the hair shaft occurs in the UHS phenotype, which is characterized by dry, frizzy, and wiry hair that cannot be combed flat.
As a result of that previous work, “we base the assignment or confirmation of a clinical diagnosis of UHS on molecular genetic diagnostics,” the authors write in the new study, rather than on the clinical appearance of the hair and the physical examination of the patient, with confirmation on microscopical examination of the hair shaft.
Social media as instrument in finding study participants
Following the 2016 study, Dr. Betz and colleagues were contacted by many clinicians and by the public through Facebook and other social media platforms with details about possible cases of UHS, an autosomal recessive disorder. Through these contacts, blood samples, saliva, or DNA was sent to the investigators’ laboratory from 89 unrelated index patients (69 female patients, 20 male patients) suspected of having UHS. This resulted in the identification of pathogenic variants in 69 cases, the investigators write.
“In the first study, we had 18 patients, and then we tried to collect as many as possible” to determine the main mechanism behind UHS, Dr. Betz said. One question is whether there are additional genes responsible for UHS, she noted. “Even now, we are not sure, because in 25% [of cases in the new study], we didn’t find any mutation in the three known genes.”
The current study resulted in the discovery of eight novel pathogenic variants in PADI3, which are responsible for 71.0% (76) of the 107 cases. Of those, “6 were single observations and 2 were observed in 3 and 2 individuals, respectively,” the investigators write.
Children can grow out of this disorder, but it can also persist into adulthood, Dr. Betz noted. Communication that investigators had with parents of the children with UHS revealed that these children are often the targets of bullying by other children, she added.
She and her and colleagues will continue this research and are currently studying adults who have UHS.
Research leads to possible treatment pathways
Jeff Donovan, MD, FRCPC, FAAD, a dermatologist and medical director of the Donovan Hair Clinic in Whistler, British Columbia, described these findings as fundamental to understanding UHS and creating pathways to possible treatments.
The study “identifies more about the genetic basis of this challenging condition,” said Dr. Donovan, who is also clinical instructor in the department of dermatology at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and president of the Canadian Hair Loss Foundation. “We really need this type of information in order to have any sort of clue in terms of how to treat it,” he told this news organization.
“In the hair loss world, it’s pretty clear that if you can understand the genetic basis of things, or the basic science of a condition, whether it’s the basic genetics or the basic immunology, you give yourself the best chance to develop good treatments,” said Dr. Donovan.
The article provides advanced genetic information of the condition, such that geneticists can test for at least three markers if they are suspecting UHS, Dr. Donovan observed.
Condition can lead to bullying
Dr. Donovan also commented that UHS can have a detrimental impact on children with regard to socializing with their peers. “Having hair that sticks out and is very full like this is challenging because kids do get teased,” he said.
“It is often the parents who are the most affected” when a child aged 2-5 years has a hair condition such as UHS. But at age 5-9, “children are developing self-identity and an understanding of various aspects of self-esteem and what they look like and what others look like. And that’s where the teasing really starts. And that’s where it does become troublesome.”
Dr. Betz and Dr. Donovan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that manifests during infancy, investigators have reported.
The findings are from a cohort study published in JAMA Dermatology, which involved 107 unrelated children and adults suspected of having UHS, as well as family members, all of whom were recruited from January 2013 to December 2021. Genetic analyses were conducted in Germany from January 2014 to December 2021 with exome sequencing.
Study builds on prior research
Senior author Regina C. Betz, MD, professor of dermatogenetics at the Institute of Human Genetics, University Hospital Bonn, Germany, said that in 2016, she and her coinvestigators authored a study on the molecular genetics of UHS. That study, which involved 18 people with UHS, identified variants in three genes – PADI3, TCHH, and TGM3 – that encode proteins that play a role in the formation of the hair shaft. The investigators described how a deficiency in the shaping and mechanical strengthening of the hair shaft occurs in the UHS phenotype, which is characterized by dry, frizzy, and wiry hair that cannot be combed flat.
As a result of that previous work, “we base the assignment or confirmation of a clinical diagnosis of UHS on molecular genetic diagnostics,” the authors write in the new study, rather than on the clinical appearance of the hair and the physical examination of the patient, with confirmation on microscopical examination of the hair shaft.
Social media as instrument in finding study participants
Following the 2016 study, Dr. Betz and colleagues were contacted by many clinicians and by the public through Facebook and other social media platforms with details about possible cases of UHS, an autosomal recessive disorder. Through these contacts, blood samples, saliva, or DNA was sent to the investigators’ laboratory from 89 unrelated index patients (69 female patients, 20 male patients) suspected of having UHS. This resulted in the identification of pathogenic variants in 69 cases, the investigators write.
“In the first study, we had 18 patients, and then we tried to collect as many as possible” to determine the main mechanism behind UHS, Dr. Betz said. One question is whether there are additional genes responsible for UHS, she noted. “Even now, we are not sure, because in 25% [of cases in the new study], we didn’t find any mutation in the three known genes.”
The current study resulted in the discovery of eight novel pathogenic variants in PADI3, which are responsible for 71.0% (76) of the 107 cases. Of those, “6 were single observations and 2 were observed in 3 and 2 individuals, respectively,” the investigators write.
Children can grow out of this disorder, but it can also persist into adulthood, Dr. Betz noted. Communication that investigators had with parents of the children with UHS revealed that these children are often the targets of bullying by other children, she added.
She and her and colleagues will continue this research and are currently studying adults who have UHS.
Research leads to possible treatment pathways
Jeff Donovan, MD, FRCPC, FAAD, a dermatologist and medical director of the Donovan Hair Clinic in Whistler, British Columbia, described these findings as fundamental to understanding UHS and creating pathways to possible treatments.
The study “identifies more about the genetic basis of this challenging condition,” said Dr. Donovan, who is also clinical instructor in the department of dermatology at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and president of the Canadian Hair Loss Foundation. “We really need this type of information in order to have any sort of clue in terms of how to treat it,” he told this news organization.
“In the hair loss world, it’s pretty clear that if you can understand the genetic basis of things, or the basic science of a condition, whether it’s the basic genetics or the basic immunology, you give yourself the best chance to develop good treatments,” said Dr. Donovan.
The article provides advanced genetic information of the condition, such that geneticists can test for at least three markers if they are suspecting UHS, Dr. Donovan observed.
Condition can lead to bullying
Dr. Donovan also commented that UHS can have a detrimental impact on children with regard to socializing with their peers. “Having hair that sticks out and is very full like this is challenging because kids do get teased,” he said.
“It is often the parents who are the most affected” when a child aged 2-5 years has a hair condition such as UHS. But at age 5-9, “children are developing self-identity and an understanding of various aspects of self-esteem and what they look like and what others look like. And that’s where the teasing really starts. And that’s where it does become troublesome.”
Dr. Betz and Dr. Donovan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Lower BMI linked with better knee osteoarthritis outcomes
Losing weight and lowering body mass index may help people slow, delay, or even prevent the structural defects of knee osteoarthritis, especially on the medial side of the knee, results of a prospective multicohort study from Australia suggest.
“We showed that the more weight that is lost, the greater the apparent benefit for delaying or preventing knee joint degradation in osteoarthritis,” senior study author Amanda Sainsbury, PhD, professor of obesity research at the University of Western Australia, Perth, said in an interview. “For example, a person weighing 100 kilograms [220 pounds] who loses 10 kilograms [22 pounds] is likely to have double the benefit compared to losing 5 kilograms [11 pounds].”
“We showed evidence of association, not causality,” she and her colleagues wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “Future randomized, controlled trials are required to demonstrate causality.”
Dr. Sainsbury and colleagues analyzed radiographs of knees from three independent cohort studies from the United States and the Netherlands – the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI), the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study (MOST), and the Cohort Hip and Cohort Knee (CHECK) study – at baseline and again 4-5 years later.
The authors created two groups of knees at baseline: the “incidence cohort” of 9,683 knees from 5,774 participants without OA structural defects (Kellgren-Lawrence grade 0 or 1) and the “progression cohort” of 6,075 knees from 3,988 participants with OA structural defects (KL grade 2 or higher). After 4-5 years, they determined OA incidence (KL grade 2 or higher in participants without baseline knee OA) and progression (increase of one or more KL grades in those with baseline knee OA).At baseline, the mean patient age in both groups was around 60, and around 60% of participants were female. In the incidence and progression groups, respectively, White patients comprised 87.5% and 80.4% of participants; mean body mass index was 28.2 and 30.4 kg/m2; and 32.6% and 48.4% of participants were obese (BMI, 30 or higher). The authors combined data from the three studies and used logistic regression and generalized estimating equations, with clustering of both knees within individuals. On multivariable analysis, they found that change in BMI 4-5 years post baseline was positively linked with both incidence and progression of knee OA structural defects.
In the incidence group, BMI decreased 1 or more units in 1,101 patients and increased 1 or more units in 1,611. In the progression group, BMI decreased 1 or more units in 798 patients and increased in 1,008.
The adjusted odds ratio for overall structural defects in the incidence group was 1.05 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.09) and 1.05 (95% CI, 1.01-1.09) in the progression group was. A 1-unit decrease in BMI was linked with a nearly 5% drop in odds of incidence and progression of knee OA, and a 5-unit decrease was linked with a more than 21% drop in odds of incidence and progression.
In the incidence group, change in BMI was positively linked with medial, but not lateral, joint space degeneration (narrowing; OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.12) and with medial femoral surface degeneration indicated by osteophytes (OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
In the progression group, change in BMI was positively linked with overall structural defects (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 1.01-1.09) as well as medial, but not lateral, joint space degeneration (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
“Previous research showed that weight loss helps reduce symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, such as pain and impaired physical function,” said lead study author Zübeyir Salis, BEng, a PhD student in public health at the University of New South Wales, Kensington, Australia. “Weight loss is emerging as a suitable strategy for potentially delaying and preventing osteoarthritic knee joint degeneration.”
Two experts not involved in the study welcome its results
Kai Sun, MD, MS, assistant professor of medicine, rheumatology, and immunology at Duke University, Durham, N. C., said it makes mechanical sense that less weight bearing decreases knee damage over time, but she was somewhat surprised that even people who started with normal BMI improved their outcomes by decreasing BMI further.
“Knee osteoarthritis and obesity prevalence are both growing,” Dr. Sun said. “Knee osteoarthritis may one day be considered an obesity-related comorbidity like hypertension and diabetes and be used as additional justification for pharmacologic or nonpharmacologic interventions to treat obesity.”
She noted that the study’s major strengths include its large sample size, long follow-up, and separate inclusion of disease incidence and progression, but also noted some limitations.
“BMI data at only two time points does not consider BMI fluctuations between those times,” she added. “Limited data were presented on physical activity levels, and most participants being White and elderly limited the generalizability of the results.”
Eduardo Grunvald, MD, professor of medicine and medical director of the weight management program at the University of California, San Diego, agreed about the study’s strengths and pointed out its lack of information about the cause of BMI changes.
Dr. Grunvald would like to know whether the BMI changes contributed to the knee changes or vice versa. “An individual’s worsening knee pain could lead to less physical activity and possible increased BMI.
“Long-term weight-loss maintenance is extremely challenging, and for optimal outcomes, medical professionals who treat joint disease should partner with clinicians trained to treat obesity,” he advised.
The authors are planning further related research. “We’re looking forward to running a randomized, controlled clinical weight-loss trial,” Dr. Sainsbury said.The study was supported by scholarship and fellowship funds from the Australian government. Mr. Salis and Dr. Sainsbury each own 50% of shares in a company that provides educational resources and services in adult weight management. Dr. Sainsbury and one coauthor reported relevant financial relationships with various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Sun and Dr. Grunvald reported no relevant financial relationships.
Losing weight and lowering body mass index may help people slow, delay, or even prevent the structural defects of knee osteoarthritis, especially on the medial side of the knee, results of a prospective multicohort study from Australia suggest.
“We showed that the more weight that is lost, the greater the apparent benefit for delaying or preventing knee joint degradation in osteoarthritis,” senior study author Amanda Sainsbury, PhD, professor of obesity research at the University of Western Australia, Perth, said in an interview. “For example, a person weighing 100 kilograms [220 pounds] who loses 10 kilograms [22 pounds] is likely to have double the benefit compared to losing 5 kilograms [11 pounds].”
“We showed evidence of association, not causality,” she and her colleagues wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “Future randomized, controlled trials are required to demonstrate causality.”
Dr. Sainsbury and colleagues analyzed radiographs of knees from three independent cohort studies from the United States and the Netherlands – the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI), the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study (MOST), and the Cohort Hip and Cohort Knee (CHECK) study – at baseline and again 4-5 years later.
The authors created two groups of knees at baseline: the “incidence cohort” of 9,683 knees from 5,774 participants without OA structural defects (Kellgren-Lawrence grade 0 or 1) and the “progression cohort” of 6,075 knees from 3,988 participants with OA structural defects (KL grade 2 or higher). After 4-5 years, they determined OA incidence (KL grade 2 or higher in participants without baseline knee OA) and progression (increase of one or more KL grades in those with baseline knee OA).At baseline, the mean patient age in both groups was around 60, and around 60% of participants were female. In the incidence and progression groups, respectively, White patients comprised 87.5% and 80.4% of participants; mean body mass index was 28.2 and 30.4 kg/m2; and 32.6% and 48.4% of participants were obese (BMI, 30 or higher). The authors combined data from the three studies and used logistic regression and generalized estimating equations, with clustering of both knees within individuals. On multivariable analysis, they found that change in BMI 4-5 years post baseline was positively linked with both incidence and progression of knee OA structural defects.
In the incidence group, BMI decreased 1 or more units in 1,101 patients and increased 1 or more units in 1,611. In the progression group, BMI decreased 1 or more units in 798 patients and increased in 1,008.
The adjusted odds ratio for overall structural defects in the incidence group was 1.05 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.09) and 1.05 (95% CI, 1.01-1.09) in the progression group was. A 1-unit decrease in BMI was linked with a nearly 5% drop in odds of incidence and progression of knee OA, and a 5-unit decrease was linked with a more than 21% drop in odds of incidence and progression.
In the incidence group, change in BMI was positively linked with medial, but not lateral, joint space degeneration (narrowing; OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.12) and with medial femoral surface degeneration indicated by osteophytes (OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
In the progression group, change in BMI was positively linked with overall structural defects (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 1.01-1.09) as well as medial, but not lateral, joint space degeneration (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
“Previous research showed that weight loss helps reduce symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, such as pain and impaired physical function,” said lead study author Zübeyir Salis, BEng, a PhD student in public health at the University of New South Wales, Kensington, Australia. “Weight loss is emerging as a suitable strategy for potentially delaying and preventing osteoarthritic knee joint degeneration.”
Two experts not involved in the study welcome its results
Kai Sun, MD, MS, assistant professor of medicine, rheumatology, and immunology at Duke University, Durham, N. C., said it makes mechanical sense that less weight bearing decreases knee damage over time, but she was somewhat surprised that even people who started with normal BMI improved their outcomes by decreasing BMI further.
“Knee osteoarthritis and obesity prevalence are both growing,” Dr. Sun said. “Knee osteoarthritis may one day be considered an obesity-related comorbidity like hypertension and diabetes and be used as additional justification for pharmacologic or nonpharmacologic interventions to treat obesity.”
She noted that the study’s major strengths include its large sample size, long follow-up, and separate inclusion of disease incidence and progression, but also noted some limitations.
“BMI data at only two time points does not consider BMI fluctuations between those times,” she added. “Limited data were presented on physical activity levels, and most participants being White and elderly limited the generalizability of the results.”
Eduardo Grunvald, MD, professor of medicine and medical director of the weight management program at the University of California, San Diego, agreed about the study’s strengths and pointed out its lack of information about the cause of BMI changes.
Dr. Grunvald would like to know whether the BMI changes contributed to the knee changes or vice versa. “An individual’s worsening knee pain could lead to less physical activity and possible increased BMI.
“Long-term weight-loss maintenance is extremely challenging, and for optimal outcomes, medical professionals who treat joint disease should partner with clinicians trained to treat obesity,” he advised.
The authors are planning further related research. “We’re looking forward to running a randomized, controlled clinical weight-loss trial,” Dr. Sainsbury said.The study was supported by scholarship and fellowship funds from the Australian government. Mr. Salis and Dr. Sainsbury each own 50% of shares in a company that provides educational resources and services in adult weight management. Dr. Sainsbury and one coauthor reported relevant financial relationships with various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Sun and Dr. Grunvald reported no relevant financial relationships.
Losing weight and lowering body mass index may help people slow, delay, or even prevent the structural defects of knee osteoarthritis, especially on the medial side of the knee, results of a prospective multicohort study from Australia suggest.
“We showed that the more weight that is lost, the greater the apparent benefit for delaying or preventing knee joint degradation in osteoarthritis,” senior study author Amanda Sainsbury, PhD, professor of obesity research at the University of Western Australia, Perth, said in an interview. “For example, a person weighing 100 kilograms [220 pounds] who loses 10 kilograms [22 pounds] is likely to have double the benefit compared to losing 5 kilograms [11 pounds].”
“We showed evidence of association, not causality,” she and her colleagues wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “Future randomized, controlled trials are required to demonstrate causality.”
Dr. Sainsbury and colleagues analyzed radiographs of knees from three independent cohort studies from the United States and the Netherlands – the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI), the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study (MOST), and the Cohort Hip and Cohort Knee (CHECK) study – at baseline and again 4-5 years later.
The authors created two groups of knees at baseline: the “incidence cohort” of 9,683 knees from 5,774 participants without OA structural defects (Kellgren-Lawrence grade 0 or 1) and the “progression cohort” of 6,075 knees from 3,988 participants with OA structural defects (KL grade 2 or higher). After 4-5 years, they determined OA incidence (KL grade 2 or higher in participants without baseline knee OA) and progression (increase of one or more KL grades in those with baseline knee OA).At baseline, the mean patient age in both groups was around 60, and around 60% of participants were female. In the incidence and progression groups, respectively, White patients comprised 87.5% and 80.4% of participants; mean body mass index was 28.2 and 30.4 kg/m2; and 32.6% and 48.4% of participants were obese (BMI, 30 or higher). The authors combined data from the three studies and used logistic regression and generalized estimating equations, with clustering of both knees within individuals. On multivariable analysis, they found that change in BMI 4-5 years post baseline was positively linked with both incidence and progression of knee OA structural defects.
In the incidence group, BMI decreased 1 or more units in 1,101 patients and increased 1 or more units in 1,611. In the progression group, BMI decreased 1 or more units in 798 patients and increased in 1,008.
The adjusted odds ratio for overall structural defects in the incidence group was 1.05 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.09) and 1.05 (95% CI, 1.01-1.09) in the progression group was. A 1-unit decrease in BMI was linked with a nearly 5% drop in odds of incidence and progression of knee OA, and a 5-unit decrease was linked with a more than 21% drop in odds of incidence and progression.
In the incidence group, change in BMI was positively linked with medial, but not lateral, joint space degeneration (narrowing; OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.12) and with medial femoral surface degeneration indicated by osteophytes (OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
In the progression group, change in BMI was positively linked with overall structural defects (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 1.01-1.09) as well as medial, but not lateral, joint space degeneration (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
“Previous research showed that weight loss helps reduce symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, such as pain and impaired physical function,” said lead study author Zübeyir Salis, BEng, a PhD student in public health at the University of New South Wales, Kensington, Australia. “Weight loss is emerging as a suitable strategy for potentially delaying and preventing osteoarthritic knee joint degeneration.”
Two experts not involved in the study welcome its results
Kai Sun, MD, MS, assistant professor of medicine, rheumatology, and immunology at Duke University, Durham, N. C., said it makes mechanical sense that less weight bearing decreases knee damage over time, but she was somewhat surprised that even people who started with normal BMI improved their outcomes by decreasing BMI further.
“Knee osteoarthritis and obesity prevalence are both growing,” Dr. Sun said. “Knee osteoarthritis may one day be considered an obesity-related comorbidity like hypertension and diabetes and be used as additional justification for pharmacologic or nonpharmacologic interventions to treat obesity.”
She noted that the study’s major strengths include its large sample size, long follow-up, and separate inclusion of disease incidence and progression, but also noted some limitations.
“BMI data at only two time points does not consider BMI fluctuations between those times,” she added. “Limited data were presented on physical activity levels, and most participants being White and elderly limited the generalizability of the results.”
Eduardo Grunvald, MD, professor of medicine and medical director of the weight management program at the University of California, San Diego, agreed about the study’s strengths and pointed out its lack of information about the cause of BMI changes.
Dr. Grunvald would like to know whether the BMI changes contributed to the knee changes or vice versa. “An individual’s worsening knee pain could lead to less physical activity and possible increased BMI.
“Long-term weight-loss maintenance is extremely challenging, and for optimal outcomes, medical professionals who treat joint disease should partner with clinicians trained to treat obesity,” he advised.
The authors are planning further related research. “We’re looking forward to running a randomized, controlled clinical weight-loss trial,” Dr. Sainsbury said.The study was supported by scholarship and fellowship funds from the Australian government. Mr. Salis and Dr. Sainsbury each own 50% of shares in a company that provides educational resources and services in adult weight management. Dr. Sainsbury and one coauthor reported relevant financial relationships with various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Sun and Dr. Grunvald reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Ketamine linked to reduced suicidal thoughts, depression, anxiety
, new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective chart review analysis, which included more than 400 participants with TRD, illustrate that ketamine is a safe and rapid treatment in a real-world patient population, lead author Patrick A. Oliver, MD, founder and medical director, MindPeace Clinics, Richmond, Va., told this news organization.
The effect was perhaps most notable for reducing suicidal ideation, he said.
“In 2 weeks, we can take somebody from being suicidal to nonsuicidal. It’s a total game changer,” Dr. Oliver added.
Every year in the United States, about 12 million individuals think about suicide, 3.2 million make a plan to kill themselves, and more than 46,000 succeed, the investigators note.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Molecule mixture
Primarily used as an anesthetic in hospitals, ketamine is also taken illegally as a recreational drug. Users may aim for an intense high or feeling of dissociation, or an out-of-body–type experience.
Ketamine is a mixture of two mirror-image molecules. An intranasal version of one of these molecules (esketamine) is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for TRD. Both esketamine and ketamine are believed to increase neurotrophic signaling that affects synaptic function.
The study included 424 patients (mean age, 41.7 years) with major depressive disorder or another mood disorder and who received at least one ketamine infusion at a specialty clinic. Most participants had failed prior medication trials.
Patients in the study were typically started on 0.5 mg/kg of ketamine, with the dose titrated to achieve symptoms of partial dissociation. The median dose administered after titration was 0.93 mg/kg over 40 minutes.
The main treatment course of at least six infusions within 21 days was completed by 70% of the patients.
At each clinic visit, all participants completed the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7).
The primary outcome was PHQ-9 total scores, for which researchers looked at seven time periods: 1 week, 2-3 weeks, 4-6 weeks, 7-12 weeks, 13-24 weeks, 25-51 weeks, and 52+ weeks.
‘Blows it out of the water’
Results showed PHQ-9 total scores declined by 50% throughout the course of treatment, with much of the improvement gained within 4-6 weeks. There was a significant difference between week 1 and all later time periods (all P values < .001) and between weeks 2 and 3 and all later periods (all P values < .001).
Other measures included treatment response, defined as at least a 50% improvement on the PHQ-9, and depression remission, defined as a PHQ-9 score of less than 5. After three infusions, 14% of the patients responded and 7% were in remission. After 10 infusions, 72% responded and 38% were in remission.
These results compare favorably to other depression treatments, said Dr. Oliver. “Truthfully, with the exception of ECT [electroconvulsive therapy], this blows it all out of the water,” he added.
Dr. Oliver noted that the success rate for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is 40%-60% depending on the modality; and for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, the success rate “is somewhere between the mid-20s and low-30s percent range.”
Another outcome measure was the self-harm/suicidal ideation item of the PHQ-9 questionnaire, which asks about “thoughts that you would be better off dead, or of hurting yourself in some way.” About 22% of the study participants no longer reported suicidal ideation after 3 infusions, 50% by 6 infusions, and 75% by 10 infusions.
By 15 infusions, 85% no longer reported these thoughts. “Nothing else has shown that, ever,” said Dr. Oliver.
Symptoms of generalized anxiety were also substantially improved. There was about a 30% reduction in the GAD-7 score during treatment and, again, most of the response occurred by 4-6 weeks.
Study limitations
Sex, age, and other demographic characteristics did not predict response or remission, but suicide planning trended toward higher response rates (P = .083). This suggests that a more depressed subgroup can achieve greater benefit from the treatment than can less symptomatic patients, the investigators note.
A history of psychosis also trended toward better response to treatment (P = .086) but not remission.
The researchers note that study limitations include that it was retrospective, lacked a control group, and did not require patients to be hospitalized – so the study sample may have been less severely ill than in other studies.
In addition, most patients paid out of pocket for the treatment at $495 per infusion, and they self-reported their symptoms.
As well, the researchers did not assess adverse events, although nurses made follow-up calls to patients. Dr. Oliver noted the most common side effects of ketamine are nausea, vomiting, and anxiety.
Previous research has suggested that ketamine therapy is not linked to long-term side effects, such as sexual dysfunction, weight gain, lethargy, or cognitive issues, said Dr. Oliver.
The investigators point out another study limitation was lack of detailed demographic information, such as race, income, and education, which might affect its generalizability.
Concerns and questions
Pouya Movahed Rad, MD, PhD, senior consultant and researcher in psychiatry, Lund (Sweden) University, noted several concerns, including that the clinics treating the study participants with ketamine profited from it.
He also speculated about who can afford the treatment because only a few patients in the study were reimbursed through insurance.
Dr. Movahed Rad was not involved with the current research but was principal investigator for a recent study that compared intravenous ketamine to ECT.
He questioned whether the patient population in the new study really was “real world.” Well-designed randomized controlled trials have been carried out in a “naturalistic setting, [which] get closer to real-life patients,” he said.
He also noted that the median dose after clinician titration (0.93 mg/kg over 40 minutes) “may be considered very high.”
With regard to doses being titrated to achieve symptoms of partial dissociation, “there is no obvious evidence to my knowledge that patients need to develop dissociative symptoms in order to have antidepressant effect,” said Dr. Movahed Rad.
Finally, he noted that the finding that 28% of the participants were using illegal drugs “is worrying” and wondered what drugs they were taking; he also questioned why 81% of the study population needed to take antidepressants.
The study did not receive outside funding. Dr. Oliver is the founder of MindPeace Clinics, which specialize in ketamine therapeutics. Dr. Movahed Rad has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective chart review analysis, which included more than 400 participants with TRD, illustrate that ketamine is a safe and rapid treatment in a real-world patient population, lead author Patrick A. Oliver, MD, founder and medical director, MindPeace Clinics, Richmond, Va., told this news organization.
The effect was perhaps most notable for reducing suicidal ideation, he said.
“In 2 weeks, we can take somebody from being suicidal to nonsuicidal. It’s a total game changer,” Dr. Oliver added.
Every year in the United States, about 12 million individuals think about suicide, 3.2 million make a plan to kill themselves, and more than 46,000 succeed, the investigators note.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Molecule mixture
Primarily used as an anesthetic in hospitals, ketamine is also taken illegally as a recreational drug. Users may aim for an intense high or feeling of dissociation, or an out-of-body–type experience.
Ketamine is a mixture of two mirror-image molecules. An intranasal version of one of these molecules (esketamine) is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for TRD. Both esketamine and ketamine are believed to increase neurotrophic signaling that affects synaptic function.
The study included 424 patients (mean age, 41.7 years) with major depressive disorder or another mood disorder and who received at least one ketamine infusion at a specialty clinic. Most participants had failed prior medication trials.
Patients in the study were typically started on 0.5 mg/kg of ketamine, with the dose titrated to achieve symptoms of partial dissociation. The median dose administered after titration was 0.93 mg/kg over 40 minutes.
The main treatment course of at least six infusions within 21 days was completed by 70% of the patients.
At each clinic visit, all participants completed the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7).
The primary outcome was PHQ-9 total scores, for which researchers looked at seven time periods: 1 week, 2-3 weeks, 4-6 weeks, 7-12 weeks, 13-24 weeks, 25-51 weeks, and 52+ weeks.
‘Blows it out of the water’
Results showed PHQ-9 total scores declined by 50% throughout the course of treatment, with much of the improvement gained within 4-6 weeks. There was a significant difference between week 1 and all later time periods (all P values < .001) and between weeks 2 and 3 and all later periods (all P values < .001).
Other measures included treatment response, defined as at least a 50% improvement on the PHQ-9, and depression remission, defined as a PHQ-9 score of less than 5. After three infusions, 14% of the patients responded and 7% were in remission. After 10 infusions, 72% responded and 38% were in remission.
These results compare favorably to other depression treatments, said Dr. Oliver. “Truthfully, with the exception of ECT [electroconvulsive therapy], this blows it all out of the water,” he added.
Dr. Oliver noted that the success rate for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is 40%-60% depending on the modality; and for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, the success rate “is somewhere between the mid-20s and low-30s percent range.”
Another outcome measure was the self-harm/suicidal ideation item of the PHQ-9 questionnaire, which asks about “thoughts that you would be better off dead, or of hurting yourself in some way.” About 22% of the study participants no longer reported suicidal ideation after 3 infusions, 50% by 6 infusions, and 75% by 10 infusions.
By 15 infusions, 85% no longer reported these thoughts. “Nothing else has shown that, ever,” said Dr. Oliver.
Symptoms of generalized anxiety were also substantially improved. There was about a 30% reduction in the GAD-7 score during treatment and, again, most of the response occurred by 4-6 weeks.
Study limitations
Sex, age, and other demographic characteristics did not predict response or remission, but suicide planning trended toward higher response rates (P = .083). This suggests that a more depressed subgroup can achieve greater benefit from the treatment than can less symptomatic patients, the investigators note.
A history of psychosis also trended toward better response to treatment (P = .086) but not remission.
The researchers note that study limitations include that it was retrospective, lacked a control group, and did not require patients to be hospitalized – so the study sample may have been less severely ill than in other studies.
In addition, most patients paid out of pocket for the treatment at $495 per infusion, and they self-reported their symptoms.
As well, the researchers did not assess adverse events, although nurses made follow-up calls to patients. Dr. Oliver noted the most common side effects of ketamine are nausea, vomiting, and anxiety.
Previous research has suggested that ketamine therapy is not linked to long-term side effects, such as sexual dysfunction, weight gain, lethargy, or cognitive issues, said Dr. Oliver.
The investigators point out another study limitation was lack of detailed demographic information, such as race, income, and education, which might affect its generalizability.
Concerns and questions
Pouya Movahed Rad, MD, PhD, senior consultant and researcher in psychiatry, Lund (Sweden) University, noted several concerns, including that the clinics treating the study participants with ketamine profited from it.
He also speculated about who can afford the treatment because only a few patients in the study were reimbursed through insurance.
Dr. Movahed Rad was not involved with the current research but was principal investigator for a recent study that compared intravenous ketamine to ECT.
He questioned whether the patient population in the new study really was “real world.” Well-designed randomized controlled trials have been carried out in a “naturalistic setting, [which] get closer to real-life patients,” he said.
He also noted that the median dose after clinician titration (0.93 mg/kg over 40 minutes) “may be considered very high.”
With regard to doses being titrated to achieve symptoms of partial dissociation, “there is no obvious evidence to my knowledge that patients need to develop dissociative symptoms in order to have antidepressant effect,” said Dr. Movahed Rad.
Finally, he noted that the finding that 28% of the participants were using illegal drugs “is worrying” and wondered what drugs they were taking; he also questioned why 81% of the study population needed to take antidepressants.
The study did not receive outside funding. Dr. Oliver is the founder of MindPeace Clinics, which specialize in ketamine therapeutics. Dr. Movahed Rad has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective chart review analysis, which included more than 400 participants with TRD, illustrate that ketamine is a safe and rapid treatment in a real-world patient population, lead author Patrick A. Oliver, MD, founder and medical director, MindPeace Clinics, Richmond, Va., told this news organization.
The effect was perhaps most notable for reducing suicidal ideation, he said.
“In 2 weeks, we can take somebody from being suicidal to nonsuicidal. It’s a total game changer,” Dr. Oliver added.
Every year in the United States, about 12 million individuals think about suicide, 3.2 million make a plan to kill themselves, and more than 46,000 succeed, the investigators note.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Molecule mixture
Primarily used as an anesthetic in hospitals, ketamine is also taken illegally as a recreational drug. Users may aim for an intense high or feeling of dissociation, or an out-of-body–type experience.
Ketamine is a mixture of two mirror-image molecules. An intranasal version of one of these molecules (esketamine) is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for TRD. Both esketamine and ketamine are believed to increase neurotrophic signaling that affects synaptic function.
The study included 424 patients (mean age, 41.7 years) with major depressive disorder or another mood disorder and who received at least one ketamine infusion at a specialty clinic. Most participants had failed prior medication trials.
Patients in the study were typically started on 0.5 mg/kg of ketamine, with the dose titrated to achieve symptoms of partial dissociation. The median dose administered after titration was 0.93 mg/kg over 40 minutes.
The main treatment course of at least six infusions within 21 days was completed by 70% of the patients.
At each clinic visit, all participants completed the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7).
The primary outcome was PHQ-9 total scores, for which researchers looked at seven time periods: 1 week, 2-3 weeks, 4-6 weeks, 7-12 weeks, 13-24 weeks, 25-51 weeks, and 52+ weeks.
‘Blows it out of the water’
Results showed PHQ-9 total scores declined by 50% throughout the course of treatment, with much of the improvement gained within 4-6 weeks. There was a significant difference between week 1 and all later time periods (all P values < .001) and between weeks 2 and 3 and all later periods (all P values < .001).
Other measures included treatment response, defined as at least a 50% improvement on the PHQ-9, and depression remission, defined as a PHQ-9 score of less than 5. After three infusions, 14% of the patients responded and 7% were in remission. After 10 infusions, 72% responded and 38% were in remission.
These results compare favorably to other depression treatments, said Dr. Oliver. “Truthfully, with the exception of ECT [electroconvulsive therapy], this blows it all out of the water,” he added.
Dr. Oliver noted that the success rate for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is 40%-60% depending on the modality; and for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, the success rate “is somewhere between the mid-20s and low-30s percent range.”
Another outcome measure was the self-harm/suicidal ideation item of the PHQ-9 questionnaire, which asks about “thoughts that you would be better off dead, or of hurting yourself in some way.” About 22% of the study participants no longer reported suicidal ideation after 3 infusions, 50% by 6 infusions, and 75% by 10 infusions.
By 15 infusions, 85% no longer reported these thoughts. “Nothing else has shown that, ever,” said Dr. Oliver.
Symptoms of generalized anxiety were also substantially improved. There was about a 30% reduction in the GAD-7 score during treatment and, again, most of the response occurred by 4-6 weeks.
Study limitations
Sex, age, and other demographic characteristics did not predict response or remission, but suicide planning trended toward higher response rates (P = .083). This suggests that a more depressed subgroup can achieve greater benefit from the treatment than can less symptomatic patients, the investigators note.
A history of psychosis also trended toward better response to treatment (P = .086) but not remission.
The researchers note that study limitations include that it was retrospective, lacked a control group, and did not require patients to be hospitalized – so the study sample may have been less severely ill than in other studies.
In addition, most patients paid out of pocket for the treatment at $495 per infusion, and they self-reported their symptoms.
As well, the researchers did not assess adverse events, although nurses made follow-up calls to patients. Dr. Oliver noted the most common side effects of ketamine are nausea, vomiting, and anxiety.
Previous research has suggested that ketamine therapy is not linked to long-term side effects, such as sexual dysfunction, weight gain, lethargy, or cognitive issues, said Dr. Oliver.
The investigators point out another study limitation was lack of detailed demographic information, such as race, income, and education, which might affect its generalizability.
Concerns and questions
Pouya Movahed Rad, MD, PhD, senior consultant and researcher in psychiatry, Lund (Sweden) University, noted several concerns, including that the clinics treating the study participants with ketamine profited from it.
He also speculated about who can afford the treatment because only a few patients in the study were reimbursed through insurance.
Dr. Movahed Rad was not involved with the current research but was principal investigator for a recent study that compared intravenous ketamine to ECT.
He questioned whether the patient population in the new study really was “real world.” Well-designed randomized controlled trials have been carried out in a “naturalistic setting, [which] get closer to real-life patients,” he said.
He also noted that the median dose after clinician titration (0.93 mg/kg over 40 minutes) “may be considered very high.”
With regard to doses being titrated to achieve symptoms of partial dissociation, “there is no obvious evidence to my knowledge that patients need to develop dissociative symptoms in order to have antidepressant effect,” said Dr. Movahed Rad.
Finally, he noted that the finding that 28% of the participants were using illegal drugs “is worrying” and wondered what drugs they were taking; he also questioned why 81% of the study population needed to take antidepressants.
The study did not receive outside funding. Dr. Oliver is the founder of MindPeace Clinics, which specialize in ketamine therapeutics. Dr. Movahed Rad has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
A history of head trauma may predict Parkinson’s disease progression
, new research suggests.
In a longitudinal online study, among patients with Parkinson’s disease who had a history of head injury, motor impairment developed 25% faster and cognitive impairment developed 45% faster than among those without such a history.
In addition, severe head injuries were associated with an even more rapid onset of impairment. The results give weight to the idea that “it’s head injuries themselves” prior to the development of Parkinson’s disease that might exacerbate motor and cognitive symptoms, said study investigator Ethan Brown, MD, assistant professor, Weill Institute of Neurosciences, department of neurology, University of California, San Francisco.
The findings emphasize the importance of “doing everything we can” to prevent falls and head injuries for patients with Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Brown said.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Reverse causality concerns
Head injury is a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease, but its relationship to Parkinson’s disease progression is not well established. “There has always been this concern in Parkinson’s disease that maybe it’s problems with motor impairment that lead to head injuries, so reverse causality is an issue,” said Dr. Brown. “We wanted to look at whether risk factors we know relate to the development of Parkinson’s disease can also have a bearing on its progression,” he added.
The analysis was part of the online Fox Insight study that is evaluating motor and nonmotor symptoms in individuals with and those without Parkinson’s disease. The study included participants who had completed questionnaires on such things as head trauma.
The study included 1,065 patients (47% women; mean age, 63 years) with Parkinson’s disease who reported having had a head injury at least 5 years prior to their diagnosis. Among the participants, the mean duration of Parkinson’s disease was 7.5 years.
The investigators employed a 5-year lag time in their study to exclude head injuries caused by early motor dysfunction, they noted. “We wanted to look at people who had these head injuries we think might be part of the cause of Parkinson’s disease as opposed to a result of them,” Dr. Brown said.
In this head injury group, 51% had received one head injury, 28% had received two injuries, and 22% had received more than two injuries.
The study also included 1,457 participants (56% women; mean age, 65 years) with Parkinson’s disease who had not had a head injury prior to their diagnosis. Of these patients, the mean time with a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis was 8 years.
Dr. Brown noted that the age and sex distribution of the study group was “probably representative” of the general Parkinson’s disease population. However, because the participants had to be able to go online and complete questionnaires, it is unlikely that, among these patients, Parkinson’s disease was far advanced, he said.
The investigators adjusted for age, sex, years of education, and Parkinson’s disease duration.
Two-hit hypothesis?
The researchers compared time from diagnosis to the development of significant motor impairment, such as the need for assistance with walking, and cognitive impairment, such as having a score of less than 43 on the Penn Daily Activities Questionnaire.
They also examined the role of more severe head injuries. In the head injury group, over half (54%) had had a severe head injury, including 543 who had lost consciousness and others who had suffered a fracture or had had a seizure.
Results showed that the adjusted hazard ratio for developing motor impairment among those with a head injury, compared with those who had not had a head injury was 1.24 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.53; P = .037). For severe injuries, the aHR for motor impairment was 1.44 (95% CI, 1.13-1.83; P = .003).
For cognitive impairment, the aHR for those with versus without head injuries was 1.45 (95% CI, 1.14-1.86; P = .003); and for severe injuries, the aHR was 1.49 (95% CI, 1.11-2.0; P = .008).
Aside from severity, the researchers did not examine subgroups. However, Dr. Brown reported that his team would like to stratify results by sex and other variables in the future.
He noted that various mechanisms may explain why Parkinson’s disease progression is faster for patients who have a history of head injury, compared with others. Chronic inflammation due to the injury and “co-pathology” might play some role, he said. He noted that head injuries are associated with cognitive impairment in other conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease.
There is also the “two hit” hypothesis, Dr. Brown said. “A head injury could cause such broad damage that once people develop Parkinson’s disease, it’s harder for them to compensate.”
Dr. Brown also noted there might have been a “higher magnitude” of a difference between groups had the study captured participants with more severe symptoms.
‘Provocative’ findings
Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor at the Parkinson’s Foundation and professor and director at the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida, Gainesville, said the new data are “provocative.”
“The idea that a head injury may be important in predicting how quickly and how severely deficits will manifest could be important to the treating clinician,” said Dr. Okun, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that the results suggest clinicians should elicit more information from patients about head trauma. “They should be seeking more than a binary ‘yes or no’ answer to head injury when questioning patients,” he added.
Dr. Okun reiterated that head injury is a “known and important risk factor” not only for Parkinson’s disease but also for other neurodegenerative diseases. “It’s important to counsel patients about the association,” he said.
The study was supported by the Michael J. Fox Foundation. Dr. Brown reports having received grant support from the Michael J. Fox Foundation. Dr. Okun has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a longitudinal online study, among patients with Parkinson’s disease who had a history of head injury, motor impairment developed 25% faster and cognitive impairment developed 45% faster than among those without such a history.
In addition, severe head injuries were associated with an even more rapid onset of impairment. The results give weight to the idea that “it’s head injuries themselves” prior to the development of Parkinson’s disease that might exacerbate motor and cognitive symptoms, said study investigator Ethan Brown, MD, assistant professor, Weill Institute of Neurosciences, department of neurology, University of California, San Francisco.
The findings emphasize the importance of “doing everything we can” to prevent falls and head injuries for patients with Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Brown said.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Reverse causality concerns
Head injury is a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease, but its relationship to Parkinson’s disease progression is not well established. “There has always been this concern in Parkinson’s disease that maybe it’s problems with motor impairment that lead to head injuries, so reverse causality is an issue,” said Dr. Brown. “We wanted to look at whether risk factors we know relate to the development of Parkinson’s disease can also have a bearing on its progression,” he added.
The analysis was part of the online Fox Insight study that is evaluating motor and nonmotor symptoms in individuals with and those without Parkinson’s disease. The study included participants who had completed questionnaires on such things as head trauma.
The study included 1,065 patients (47% women; mean age, 63 years) with Parkinson’s disease who reported having had a head injury at least 5 years prior to their diagnosis. Among the participants, the mean duration of Parkinson’s disease was 7.5 years.
The investigators employed a 5-year lag time in their study to exclude head injuries caused by early motor dysfunction, they noted. “We wanted to look at people who had these head injuries we think might be part of the cause of Parkinson’s disease as opposed to a result of them,” Dr. Brown said.
In this head injury group, 51% had received one head injury, 28% had received two injuries, and 22% had received more than two injuries.
The study also included 1,457 participants (56% women; mean age, 65 years) with Parkinson’s disease who had not had a head injury prior to their diagnosis. Of these patients, the mean time with a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis was 8 years.
Dr. Brown noted that the age and sex distribution of the study group was “probably representative” of the general Parkinson’s disease population. However, because the participants had to be able to go online and complete questionnaires, it is unlikely that, among these patients, Parkinson’s disease was far advanced, he said.
The investigators adjusted for age, sex, years of education, and Parkinson’s disease duration.
Two-hit hypothesis?
The researchers compared time from diagnosis to the development of significant motor impairment, such as the need for assistance with walking, and cognitive impairment, such as having a score of less than 43 on the Penn Daily Activities Questionnaire.
They also examined the role of more severe head injuries. In the head injury group, over half (54%) had had a severe head injury, including 543 who had lost consciousness and others who had suffered a fracture or had had a seizure.
Results showed that the adjusted hazard ratio for developing motor impairment among those with a head injury, compared with those who had not had a head injury was 1.24 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.53; P = .037). For severe injuries, the aHR for motor impairment was 1.44 (95% CI, 1.13-1.83; P = .003).
For cognitive impairment, the aHR for those with versus without head injuries was 1.45 (95% CI, 1.14-1.86; P = .003); and for severe injuries, the aHR was 1.49 (95% CI, 1.11-2.0; P = .008).
Aside from severity, the researchers did not examine subgroups. However, Dr. Brown reported that his team would like to stratify results by sex and other variables in the future.
He noted that various mechanisms may explain why Parkinson’s disease progression is faster for patients who have a history of head injury, compared with others. Chronic inflammation due to the injury and “co-pathology” might play some role, he said. He noted that head injuries are associated with cognitive impairment in other conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease.
There is also the “two hit” hypothesis, Dr. Brown said. “A head injury could cause such broad damage that once people develop Parkinson’s disease, it’s harder for them to compensate.”
Dr. Brown also noted there might have been a “higher magnitude” of a difference between groups had the study captured participants with more severe symptoms.
‘Provocative’ findings
Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor at the Parkinson’s Foundation and professor and director at the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida, Gainesville, said the new data are “provocative.”
“The idea that a head injury may be important in predicting how quickly and how severely deficits will manifest could be important to the treating clinician,” said Dr. Okun, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that the results suggest clinicians should elicit more information from patients about head trauma. “They should be seeking more than a binary ‘yes or no’ answer to head injury when questioning patients,” he added.
Dr. Okun reiterated that head injury is a “known and important risk factor” not only for Parkinson’s disease but also for other neurodegenerative diseases. “It’s important to counsel patients about the association,” he said.
The study was supported by the Michael J. Fox Foundation. Dr. Brown reports having received grant support from the Michael J. Fox Foundation. Dr. Okun has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a longitudinal online study, among patients with Parkinson’s disease who had a history of head injury, motor impairment developed 25% faster and cognitive impairment developed 45% faster than among those without such a history.
In addition, severe head injuries were associated with an even more rapid onset of impairment. The results give weight to the idea that “it’s head injuries themselves” prior to the development of Parkinson’s disease that might exacerbate motor and cognitive symptoms, said study investigator Ethan Brown, MD, assistant professor, Weill Institute of Neurosciences, department of neurology, University of California, San Francisco.
The findings emphasize the importance of “doing everything we can” to prevent falls and head injuries for patients with Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Brown said.
The findings were presented at the International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders.
Reverse causality concerns
Head injury is a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease, but its relationship to Parkinson’s disease progression is not well established. “There has always been this concern in Parkinson’s disease that maybe it’s problems with motor impairment that lead to head injuries, so reverse causality is an issue,” said Dr. Brown. “We wanted to look at whether risk factors we know relate to the development of Parkinson’s disease can also have a bearing on its progression,” he added.
The analysis was part of the online Fox Insight study that is evaluating motor and nonmotor symptoms in individuals with and those without Parkinson’s disease. The study included participants who had completed questionnaires on such things as head trauma.
The study included 1,065 patients (47% women; mean age, 63 years) with Parkinson’s disease who reported having had a head injury at least 5 years prior to their diagnosis. Among the participants, the mean duration of Parkinson’s disease was 7.5 years.
The investigators employed a 5-year lag time in their study to exclude head injuries caused by early motor dysfunction, they noted. “We wanted to look at people who had these head injuries we think might be part of the cause of Parkinson’s disease as opposed to a result of them,” Dr. Brown said.
In this head injury group, 51% had received one head injury, 28% had received two injuries, and 22% had received more than two injuries.
The study also included 1,457 participants (56% women; mean age, 65 years) with Parkinson’s disease who had not had a head injury prior to their diagnosis. Of these patients, the mean time with a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis was 8 years.
Dr. Brown noted that the age and sex distribution of the study group was “probably representative” of the general Parkinson’s disease population. However, because the participants had to be able to go online and complete questionnaires, it is unlikely that, among these patients, Parkinson’s disease was far advanced, he said.
The investigators adjusted for age, sex, years of education, and Parkinson’s disease duration.
Two-hit hypothesis?
The researchers compared time from diagnosis to the development of significant motor impairment, such as the need for assistance with walking, and cognitive impairment, such as having a score of less than 43 on the Penn Daily Activities Questionnaire.
They also examined the role of more severe head injuries. In the head injury group, over half (54%) had had a severe head injury, including 543 who had lost consciousness and others who had suffered a fracture or had had a seizure.
Results showed that the adjusted hazard ratio for developing motor impairment among those with a head injury, compared with those who had not had a head injury was 1.24 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.53; P = .037). For severe injuries, the aHR for motor impairment was 1.44 (95% CI, 1.13-1.83; P = .003).
For cognitive impairment, the aHR for those with versus without head injuries was 1.45 (95% CI, 1.14-1.86; P = .003); and for severe injuries, the aHR was 1.49 (95% CI, 1.11-2.0; P = .008).
Aside from severity, the researchers did not examine subgroups. However, Dr. Brown reported that his team would like to stratify results by sex and other variables in the future.
He noted that various mechanisms may explain why Parkinson’s disease progression is faster for patients who have a history of head injury, compared with others. Chronic inflammation due to the injury and “co-pathology” might play some role, he said. He noted that head injuries are associated with cognitive impairment in other conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease.
There is also the “two hit” hypothesis, Dr. Brown said. “A head injury could cause such broad damage that once people develop Parkinson’s disease, it’s harder for them to compensate.”
Dr. Brown also noted there might have been a “higher magnitude” of a difference between groups had the study captured participants with more severe symptoms.
‘Provocative’ findings
Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor at the Parkinson’s Foundation and professor and director at the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida, Gainesville, said the new data are “provocative.”
“The idea that a head injury may be important in predicting how quickly and how severely deficits will manifest could be important to the treating clinician,” said Dr. Okun, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that the results suggest clinicians should elicit more information from patients about head trauma. “They should be seeking more than a binary ‘yes or no’ answer to head injury when questioning patients,” he added.
Dr. Okun reiterated that head injury is a “known and important risk factor” not only for Parkinson’s disease but also for other neurodegenerative diseases. “It’s important to counsel patients about the association,” he said.
The study was supported by the Michael J. Fox Foundation. Dr. Brown reports having received grant support from the Michael J. Fox Foundation. Dr. Okun has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From MDS 2022











