User login
Time to positivity doesn’t predict mortality in bloodstream infections with enterococci
A short time to positivity (TTP), the period from incubation to blood culture positivity, may help predict mortality rates for patients with Enterococcus faecalis and vancomycin-sensitive E faecium (VSEfm) bloodstream infections (BSIs), but it is not an independent predictor of risk for death from bloodstream infections caused by enterococci, new research indicates.
Katharina Michelson, of the Institute of Microbiology, Jena University Hospital, Germany, and colleagues conducted a single-site study at Jena University Hospital that included 244 patients with monomicrobial BSIs to assess the value of TTP as a prognostic or diagnostic tool.
Death in the hospital was the primary endpoint considered in the study, which was conducted from January 2014 through December 2016. The shortest TTP of blood cultures was compared among groups.
Findings were published online in April in Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease.
Among the 244 patients with monomicrobial BSIs, 22.1% of cases were caused by E faecalis, 55.3% were caused by VSEfm, and 22.5% were caused by vancomycin-resistant E faecium (VREfm).
Average TTP of Enterococcus BSI (E-BSI) was 11.6 hours. The researchers found no significant association between risk for death and time to positivity with bloodstream infections with E faecalis, VSEfm, or VREfm, or its cutoffs.
The mortality rate of patients with bloodstream infections with E faecalis was 16.7%; for VSEfm, 26.7%; and for vancomycin-resistant E faecium, 38.2%. Cutoffs showed a significantly higher death rate when TTP was longer but were not risk factors in survival analysis.
The authors explain that “in literature, TTP has not always been proven to be a reliable parameter.”
Sam Aitken, PharmD, MPH, who is a pharmacy specialist for infectious diseases at Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, said in an interview that the main message from the article is that the TTP of E faecalis is quite different from that of E faecium and that “that’s in line with what we know about generally with how these organisms come about in patients.”
“This paper reinforces the differences that are sometimes underappreciated between these organisms because they are both enterococci,” he said.
The authors say appropriate antimicrobial therapy can lead to misinterpretation of TTP, so only patients who received inappropriate antimicrobial therapy on the day of positive blood culture were included in the study.
However, Dr. Aitken said that methodology doesn’t account for “immortal time bias.”
“They didn’t account for the fact that patients who tend to get active antibiotics are the ones who live longer. So unless you account for it, you’re not necessarily going to find that patients who get active antibiotics have improved survival,” he said.
The authors point out that finding new methods for quickly identifying patients with E-BSI is a high priority.
The mortality rates of E-BSI vary between 20% for E faecalis and 50% for E faecium.
Resistance to vancomycin is common in E faecium infections and is associated with high mortality, longer hospital stays, and increased costs. Vancomycin-resistant E faecium is part of a group of bacteria that is associated with multidrug resistance and nosocomial infections.
Dr. Aitken said that rather than TTP, “the best risk predictors are going to be in the microbiome studies we’re seeing. If there is a future for figuring out who’s going to get significant E faecium infections, at least, it’s going to be in the microbiome.”
Limitations of the study include its small size; the possibility of missing data, owing to the fact that the study was retrospective; potential delays to incubation; and the possibility of contamination of blood cultures.
The authors and Dr. Aitken have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A short time to positivity (TTP), the period from incubation to blood culture positivity, may help predict mortality rates for patients with Enterococcus faecalis and vancomycin-sensitive E faecium (VSEfm) bloodstream infections (BSIs), but it is not an independent predictor of risk for death from bloodstream infections caused by enterococci, new research indicates.
Katharina Michelson, of the Institute of Microbiology, Jena University Hospital, Germany, and colleagues conducted a single-site study at Jena University Hospital that included 244 patients with monomicrobial BSIs to assess the value of TTP as a prognostic or diagnostic tool.
Death in the hospital was the primary endpoint considered in the study, which was conducted from January 2014 through December 2016. The shortest TTP of blood cultures was compared among groups.
Findings were published online in April in Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease.
Among the 244 patients with monomicrobial BSIs, 22.1% of cases were caused by E faecalis, 55.3% were caused by VSEfm, and 22.5% were caused by vancomycin-resistant E faecium (VREfm).
Average TTP of Enterococcus BSI (E-BSI) was 11.6 hours. The researchers found no significant association between risk for death and time to positivity with bloodstream infections with E faecalis, VSEfm, or VREfm, or its cutoffs.
The mortality rate of patients with bloodstream infections with E faecalis was 16.7%; for VSEfm, 26.7%; and for vancomycin-resistant E faecium, 38.2%. Cutoffs showed a significantly higher death rate when TTP was longer but were not risk factors in survival analysis.
The authors explain that “in literature, TTP has not always been proven to be a reliable parameter.”
Sam Aitken, PharmD, MPH, who is a pharmacy specialist for infectious diseases at Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, said in an interview that the main message from the article is that the TTP of E faecalis is quite different from that of E faecium and that “that’s in line with what we know about generally with how these organisms come about in patients.”
“This paper reinforces the differences that are sometimes underappreciated between these organisms because they are both enterococci,” he said.
The authors say appropriate antimicrobial therapy can lead to misinterpretation of TTP, so only patients who received inappropriate antimicrobial therapy on the day of positive blood culture were included in the study.
However, Dr. Aitken said that methodology doesn’t account for “immortal time bias.”
“They didn’t account for the fact that patients who tend to get active antibiotics are the ones who live longer. So unless you account for it, you’re not necessarily going to find that patients who get active antibiotics have improved survival,” he said.
The authors point out that finding new methods for quickly identifying patients with E-BSI is a high priority.
The mortality rates of E-BSI vary between 20% for E faecalis and 50% for E faecium.
Resistance to vancomycin is common in E faecium infections and is associated with high mortality, longer hospital stays, and increased costs. Vancomycin-resistant E faecium is part of a group of bacteria that is associated with multidrug resistance and nosocomial infections.
Dr. Aitken said that rather than TTP, “the best risk predictors are going to be in the microbiome studies we’re seeing. If there is a future for figuring out who’s going to get significant E faecium infections, at least, it’s going to be in the microbiome.”
Limitations of the study include its small size; the possibility of missing data, owing to the fact that the study was retrospective; potential delays to incubation; and the possibility of contamination of blood cultures.
The authors and Dr. Aitken have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A short time to positivity (TTP), the period from incubation to blood culture positivity, may help predict mortality rates for patients with Enterococcus faecalis and vancomycin-sensitive E faecium (VSEfm) bloodstream infections (BSIs), but it is not an independent predictor of risk for death from bloodstream infections caused by enterococci, new research indicates.
Katharina Michelson, of the Institute of Microbiology, Jena University Hospital, Germany, and colleagues conducted a single-site study at Jena University Hospital that included 244 patients with monomicrobial BSIs to assess the value of TTP as a prognostic or diagnostic tool.
Death in the hospital was the primary endpoint considered in the study, which was conducted from January 2014 through December 2016. The shortest TTP of blood cultures was compared among groups.
Findings were published online in April in Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease.
Among the 244 patients with monomicrobial BSIs, 22.1% of cases were caused by E faecalis, 55.3% were caused by VSEfm, and 22.5% were caused by vancomycin-resistant E faecium (VREfm).
Average TTP of Enterococcus BSI (E-BSI) was 11.6 hours. The researchers found no significant association between risk for death and time to positivity with bloodstream infections with E faecalis, VSEfm, or VREfm, or its cutoffs.
The mortality rate of patients with bloodstream infections with E faecalis was 16.7%; for VSEfm, 26.7%; and for vancomycin-resistant E faecium, 38.2%. Cutoffs showed a significantly higher death rate when TTP was longer but were not risk factors in survival analysis.
The authors explain that “in literature, TTP has not always been proven to be a reliable parameter.”
Sam Aitken, PharmD, MPH, who is a pharmacy specialist for infectious diseases at Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, said in an interview that the main message from the article is that the TTP of E faecalis is quite different from that of E faecium and that “that’s in line with what we know about generally with how these organisms come about in patients.”
“This paper reinforces the differences that are sometimes underappreciated between these organisms because they are both enterococci,” he said.
The authors say appropriate antimicrobial therapy can lead to misinterpretation of TTP, so only patients who received inappropriate antimicrobial therapy on the day of positive blood culture were included in the study.
However, Dr. Aitken said that methodology doesn’t account for “immortal time bias.”
“They didn’t account for the fact that patients who tend to get active antibiotics are the ones who live longer. So unless you account for it, you’re not necessarily going to find that patients who get active antibiotics have improved survival,” he said.
The authors point out that finding new methods for quickly identifying patients with E-BSI is a high priority.
The mortality rates of E-BSI vary between 20% for E faecalis and 50% for E faecium.
Resistance to vancomycin is common in E faecium infections and is associated with high mortality, longer hospital stays, and increased costs. Vancomycin-resistant E faecium is part of a group of bacteria that is associated with multidrug resistance and nosocomial infections.
Dr. Aitken said that rather than TTP, “the best risk predictors are going to be in the microbiome studies we’re seeing. If there is a future for figuring out who’s going to get significant E faecium infections, at least, it’s going to be in the microbiome.”
Limitations of the study include its small size; the possibility of missing data, owing to the fact that the study was retrospective; potential delays to incubation; and the possibility of contamination of blood cultures.
The authors and Dr. Aitken have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nonmotor symptoms common in Parkinson’s
The hallmark of Parkinson’s disease is the accompanying motor symptoms, but the condition can bring other challenges. Among those are nonmotor symptoms, including depression, dementia, and even psychosis.
The culprit is Lewy bodies, which are also responsible for Lewy body dementia. “What we call Lewy body dementia and Parkinson’s disease are caused by the same pathological process – the formation of Lewy bodies in the brain,” Leslie Citrome, MD, MPH, said in an interview. Dr. Citrome discussed some of the psychiatric comorbidities associated with Parkinson’s disease at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
In fact, the association goes both ways. “Many people with Parkinson’s disease develop a dementia. Many people with Lewy body dementia develop motor symptoms that look just like Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Citrome, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at New York Medical College, Valhalla, and president of the American Society for Clinical Psychopharmacology.
The motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are generally attributable to loss of striatal dopaminergic neurons, while nonmotor symptoms can be traced to loss of neurons in nondopaminergic regions. Nonmotor symptoms – often including sleep disorders, depression, cognitive changes, and psychosis – may occur before motor symptoms. Other problems may include autonomic dysfunction, such as constipation, sexual dysfunction, sweating, or urinary retention.
Patients might not be aware that nonmotor symptoms can occur with Parkinson’s disease and may not even consider mentioning mood changes or hallucinations to their neurologist. Family members may also be unaware.
Sleep problems are common in Parkinson’s disease, including rapid eye-movement sleep behavior disorders, vivid dreams, restless legs syndrome, insomnia, and daytime somnolence. Dopamine agonists may also cause unintended sleep.
Depression is extremely common, affecting up to 90% of Parkinson’s disease patients, and this may be related to dopaminergic losses. Antidepressant medications can worsen Parkinson’s disease symptoms: Tricyclic antidepressants increase risk of adverse events from anticholinergic drugs. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can exacerbate tremor and may increase risk of serotonin syndrome when combined with MAO‐B inhibitors.
Dr. Citrome was not aware of any antidepressant drugs that have been tested specifically in Parkinson’s disease patients, though “I’d be surprised if there wasn’t,” he said during the Q&A session. “There’s no one perfect antidepressant for people with depression associated with Parkinson’s disease. I would make sure to select one that they would tolerate and be willing to take and that doesn’t interfere with their treatment of their movement disorder, and (I would make sure) that there’s no drug-drug interaction,” he said.
This can include reduced working memory, learning, and planning, and generally does not manifest until at least 1 year after motor symptoms have begun. Rivastigmine is Food and Drug Administration–approved for treatment of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease.
As many as 60% of Parkinson’s disease patients suffer from psychosis at some point, often visual hallucinations or delusions, which can include beliefs of spousal infidelity.
Many clinicians prescribe quetiapine off label, but there are not compelling data to support that it reduces intensity and frequency of hallucinations and delusions, according to Dr. Citrome. However, it is relatively easy to prescribe, requiring no preauthorizations, it is inexpensive, and it may improve sleep.
The FDA approved pimavanserin in 2016 for hallucinations and delusions in Parkinson’s disease, and it doesn’t worsen motor symptoms, Dr. Citrome said. That’s because pimavanserin is a highly selective antagonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, with no effect on dopaminergic, histaminergic, adrenergic, or muscarinic receptors.
The drug improves positive symptoms beginning at days 29 and 43, compared with placebo. An analysis by Dr. Citrome’s group found a number needed to treat (NNT) of 7 to gain a benefit over placebo if the metric is a ≥ 30% reduction in baseline symptom score. The drug had an NNT of 9 to achieve a ≥ 50% reduction, and an NNT of 5 to achieve a score of much improved or very much improved on the Clinical Global Impression–Improvement (CGI-I) scale. In general, an NNT less than 10 suggests that a drug is clinically useful.
In contrast, the number needed to harm (NNH) represents the number of patients who would need to receive a therapy to add one adverse event, compared with placebo. A number greater than 10 indicates that the therapy may be tolerable.
Using various measures, the NNH was well over 10 for pimavanserin. With respect to somnolence, the NNH over placebo was 138, and for a weight gain of 7% or more, the NNH was 594.
Overall, the study found that 4 patients would need to be treated to achieve a benefit over placebo with respect to a ≥ 3–point improvement in the Scale of Positive Symptoms–Parkinson’s Disease (SAPS-PD), while 21 would need to receive the drug to lead to one additional discontinuation because of an adverse event, compared to placebo.
When researchers compared pimavanserin to off-label use of quetiapine, olanzapine, and clozapine, they found a Cohen’s d value of 0.50, which was better than quetiapine and olanzapine, but lower than for clozapine. However, there is no requirement of blood monitoring, and clozapine can potentially worsen motor symptoms.
Dr. Citrome’s presentation should be a reminder to neurologists that psychiatric disorders are an important patient concern, said Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati, who moderated the session.
“I think this serves as a model to recognize that many neurological disorders actually present with numerous psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Nasrallah said during the meeting, presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Dr. Citrome has consulted for AbbVie, Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Angelini, Astellas, Avanir, Axsome, BioXcel, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Cadent Therapeutics, Eisai, Impel, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Karuna, Lundbeck, Lyndra, MedAvante-ProPhase, Merck, Neurocrine, Noven, Otsuka, Ovid, Relmada, Sage, Sunovion, and Teva. He has been a speaker for most of those companies, and he holds stock in Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, J&J, Merck, and Pfizer.
Dr. Nasrallah has consulted for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Indivior, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Neurocrine, Otsuka, Sunovion, and Teva. He has served on a speakers bureau for most of those companies, in addition to that of Noven.
The hallmark of Parkinson’s disease is the accompanying motor symptoms, but the condition can bring other challenges. Among those are nonmotor symptoms, including depression, dementia, and even psychosis.
The culprit is Lewy bodies, which are also responsible for Lewy body dementia. “What we call Lewy body dementia and Parkinson’s disease are caused by the same pathological process – the formation of Lewy bodies in the brain,” Leslie Citrome, MD, MPH, said in an interview. Dr. Citrome discussed some of the psychiatric comorbidities associated with Parkinson’s disease at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
In fact, the association goes both ways. “Many people with Parkinson’s disease develop a dementia. Many people with Lewy body dementia develop motor symptoms that look just like Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Citrome, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at New York Medical College, Valhalla, and president of the American Society for Clinical Psychopharmacology.
The motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are generally attributable to loss of striatal dopaminergic neurons, while nonmotor symptoms can be traced to loss of neurons in nondopaminergic regions. Nonmotor symptoms – often including sleep disorders, depression, cognitive changes, and psychosis – may occur before motor symptoms. Other problems may include autonomic dysfunction, such as constipation, sexual dysfunction, sweating, or urinary retention.
Patients might not be aware that nonmotor symptoms can occur with Parkinson’s disease and may not even consider mentioning mood changes or hallucinations to their neurologist. Family members may also be unaware.
Sleep problems are common in Parkinson’s disease, including rapid eye-movement sleep behavior disorders, vivid dreams, restless legs syndrome, insomnia, and daytime somnolence. Dopamine agonists may also cause unintended sleep.
Depression is extremely common, affecting up to 90% of Parkinson’s disease patients, and this may be related to dopaminergic losses. Antidepressant medications can worsen Parkinson’s disease symptoms: Tricyclic antidepressants increase risk of adverse events from anticholinergic drugs. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can exacerbate tremor and may increase risk of serotonin syndrome when combined with MAO‐B inhibitors.
Dr. Citrome was not aware of any antidepressant drugs that have been tested specifically in Parkinson’s disease patients, though “I’d be surprised if there wasn’t,” he said during the Q&A session. “There’s no one perfect antidepressant for people with depression associated with Parkinson’s disease. I would make sure to select one that they would tolerate and be willing to take and that doesn’t interfere with their treatment of their movement disorder, and (I would make sure) that there’s no drug-drug interaction,” he said.
This can include reduced working memory, learning, and planning, and generally does not manifest until at least 1 year after motor symptoms have begun. Rivastigmine is Food and Drug Administration–approved for treatment of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease.
As many as 60% of Parkinson’s disease patients suffer from psychosis at some point, often visual hallucinations or delusions, which can include beliefs of spousal infidelity.
Many clinicians prescribe quetiapine off label, but there are not compelling data to support that it reduces intensity and frequency of hallucinations and delusions, according to Dr. Citrome. However, it is relatively easy to prescribe, requiring no preauthorizations, it is inexpensive, and it may improve sleep.
The FDA approved pimavanserin in 2016 for hallucinations and delusions in Parkinson’s disease, and it doesn’t worsen motor symptoms, Dr. Citrome said. That’s because pimavanserin is a highly selective antagonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, with no effect on dopaminergic, histaminergic, adrenergic, or muscarinic receptors.
The drug improves positive symptoms beginning at days 29 and 43, compared with placebo. An analysis by Dr. Citrome’s group found a number needed to treat (NNT) of 7 to gain a benefit over placebo if the metric is a ≥ 30% reduction in baseline symptom score. The drug had an NNT of 9 to achieve a ≥ 50% reduction, and an NNT of 5 to achieve a score of much improved or very much improved on the Clinical Global Impression–Improvement (CGI-I) scale. In general, an NNT less than 10 suggests that a drug is clinically useful.
In contrast, the number needed to harm (NNH) represents the number of patients who would need to receive a therapy to add one adverse event, compared with placebo. A number greater than 10 indicates that the therapy may be tolerable.
Using various measures, the NNH was well over 10 for pimavanserin. With respect to somnolence, the NNH over placebo was 138, and for a weight gain of 7% or more, the NNH was 594.
Overall, the study found that 4 patients would need to be treated to achieve a benefit over placebo with respect to a ≥ 3–point improvement in the Scale of Positive Symptoms–Parkinson’s Disease (SAPS-PD), while 21 would need to receive the drug to lead to one additional discontinuation because of an adverse event, compared to placebo.
When researchers compared pimavanserin to off-label use of quetiapine, olanzapine, and clozapine, they found a Cohen’s d value of 0.50, which was better than quetiapine and olanzapine, but lower than for clozapine. However, there is no requirement of blood monitoring, and clozapine can potentially worsen motor symptoms.
Dr. Citrome’s presentation should be a reminder to neurologists that psychiatric disorders are an important patient concern, said Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati, who moderated the session.
“I think this serves as a model to recognize that many neurological disorders actually present with numerous psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Nasrallah said during the meeting, presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Dr. Citrome has consulted for AbbVie, Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Angelini, Astellas, Avanir, Axsome, BioXcel, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Cadent Therapeutics, Eisai, Impel, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Karuna, Lundbeck, Lyndra, MedAvante-ProPhase, Merck, Neurocrine, Noven, Otsuka, Ovid, Relmada, Sage, Sunovion, and Teva. He has been a speaker for most of those companies, and he holds stock in Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, J&J, Merck, and Pfizer.
Dr. Nasrallah has consulted for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Indivior, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Neurocrine, Otsuka, Sunovion, and Teva. He has served on a speakers bureau for most of those companies, in addition to that of Noven.
The hallmark of Parkinson’s disease is the accompanying motor symptoms, but the condition can bring other challenges. Among those are nonmotor symptoms, including depression, dementia, and even psychosis.
The culprit is Lewy bodies, which are also responsible for Lewy body dementia. “What we call Lewy body dementia and Parkinson’s disease are caused by the same pathological process – the formation of Lewy bodies in the brain,” Leslie Citrome, MD, MPH, said in an interview. Dr. Citrome discussed some of the psychiatric comorbidities associated with Parkinson’s disease at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
In fact, the association goes both ways. “Many people with Parkinson’s disease develop a dementia. Many people with Lewy body dementia develop motor symptoms that look just like Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Citrome, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at New York Medical College, Valhalla, and president of the American Society for Clinical Psychopharmacology.
The motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are generally attributable to loss of striatal dopaminergic neurons, while nonmotor symptoms can be traced to loss of neurons in nondopaminergic regions. Nonmotor symptoms – often including sleep disorders, depression, cognitive changes, and psychosis – may occur before motor symptoms. Other problems may include autonomic dysfunction, such as constipation, sexual dysfunction, sweating, or urinary retention.
Patients might not be aware that nonmotor symptoms can occur with Parkinson’s disease and may not even consider mentioning mood changes or hallucinations to their neurologist. Family members may also be unaware.
Sleep problems are common in Parkinson’s disease, including rapid eye-movement sleep behavior disorders, vivid dreams, restless legs syndrome, insomnia, and daytime somnolence. Dopamine agonists may also cause unintended sleep.
Depression is extremely common, affecting up to 90% of Parkinson’s disease patients, and this may be related to dopaminergic losses. Antidepressant medications can worsen Parkinson’s disease symptoms: Tricyclic antidepressants increase risk of adverse events from anticholinergic drugs. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can exacerbate tremor and may increase risk of serotonin syndrome when combined with MAO‐B inhibitors.
Dr. Citrome was not aware of any antidepressant drugs that have been tested specifically in Parkinson’s disease patients, though “I’d be surprised if there wasn’t,” he said during the Q&A session. “There’s no one perfect antidepressant for people with depression associated with Parkinson’s disease. I would make sure to select one that they would tolerate and be willing to take and that doesn’t interfere with their treatment of their movement disorder, and (I would make sure) that there’s no drug-drug interaction,” he said.
This can include reduced working memory, learning, and planning, and generally does not manifest until at least 1 year after motor symptoms have begun. Rivastigmine is Food and Drug Administration–approved for treatment of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease.
As many as 60% of Parkinson’s disease patients suffer from psychosis at some point, often visual hallucinations or delusions, which can include beliefs of spousal infidelity.
Many clinicians prescribe quetiapine off label, but there are not compelling data to support that it reduces intensity and frequency of hallucinations and delusions, according to Dr. Citrome. However, it is relatively easy to prescribe, requiring no preauthorizations, it is inexpensive, and it may improve sleep.
The FDA approved pimavanserin in 2016 for hallucinations and delusions in Parkinson’s disease, and it doesn’t worsen motor symptoms, Dr. Citrome said. That’s because pimavanserin is a highly selective antagonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, with no effect on dopaminergic, histaminergic, adrenergic, or muscarinic receptors.
The drug improves positive symptoms beginning at days 29 and 43, compared with placebo. An analysis by Dr. Citrome’s group found a number needed to treat (NNT) of 7 to gain a benefit over placebo if the metric is a ≥ 30% reduction in baseline symptom score. The drug had an NNT of 9 to achieve a ≥ 50% reduction, and an NNT of 5 to achieve a score of much improved or very much improved on the Clinical Global Impression–Improvement (CGI-I) scale. In general, an NNT less than 10 suggests that a drug is clinically useful.
In contrast, the number needed to harm (NNH) represents the number of patients who would need to receive a therapy to add one adverse event, compared with placebo. A number greater than 10 indicates that the therapy may be tolerable.
Using various measures, the NNH was well over 10 for pimavanserin. With respect to somnolence, the NNH over placebo was 138, and for a weight gain of 7% or more, the NNH was 594.
Overall, the study found that 4 patients would need to be treated to achieve a benefit over placebo with respect to a ≥ 3–point improvement in the Scale of Positive Symptoms–Parkinson’s Disease (SAPS-PD), while 21 would need to receive the drug to lead to one additional discontinuation because of an adverse event, compared to placebo.
When researchers compared pimavanserin to off-label use of quetiapine, olanzapine, and clozapine, they found a Cohen’s d value of 0.50, which was better than quetiapine and olanzapine, but lower than for clozapine. However, there is no requirement of blood monitoring, and clozapine can potentially worsen motor symptoms.
Dr. Citrome’s presentation should be a reminder to neurologists that psychiatric disorders are an important patient concern, said Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati, who moderated the session.
“I think this serves as a model to recognize that many neurological disorders actually present with numerous psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Nasrallah said during the meeting, presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Dr. Citrome has consulted for AbbVie, Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Angelini, Astellas, Avanir, Axsome, BioXcel, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Cadent Therapeutics, Eisai, Impel, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Karuna, Lundbeck, Lyndra, MedAvante-ProPhase, Merck, Neurocrine, Noven, Otsuka, Ovid, Relmada, Sage, Sunovion, and Teva. He has been a speaker for most of those companies, and he holds stock in Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, J&J, Merck, and Pfizer.
Dr. Nasrallah has consulted for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Indivior, Intra-Cellular, Janssen, Neurocrine, Otsuka, Sunovion, and Teva. He has served on a speakers bureau for most of those companies, in addition to that of Noven.
FROM FOCUS ON NEUROPSYCHIATRY 2021
Nivolumab gets additional adjuvant indication for bladder cancer
The new indication builds on the PD-1 inhibitor’s prior approvals for advanced or metastatic UC that’s progressed during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy or that’s progressed within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new indication is based results from the CheckMate-274 trial, which found an almost doubling of median disease-free survival (DFS) with nivolumab compared with placebo.
BMS noted that the new approval makes nivolumab “the first and only PD-1 inhibitor approved for urothelial carcinoma in the adjuvant setting,” regardless of prior neoadjuvant chemotherapy, nodal involvement, or PD-L1 status.
It “has the potential to become a new standard-of-care option in this setting,” said CheckMate-274’s primary investigator, Matthew Galsky, MD, a genitourinary medical oncologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, in the company press release.
Rival PD-1 blocker pembrolizumab (Keytruda), from Merck, carries several UC indications of its own for locally advanced or metastatic disease in patients who are ineligible for platinum-containing chemotherapy or that has progressed despite it, as well as for high-risk, non–muscle invasive bladder cancer that has not responded to bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment in cases in which patients are ineligible for or opt out of cystectomy, according to labeling.
In the CheckMate-274 trial, 353 patients with UC were randomly assigned to receive nivolumab after radical resection, and 356 others were assigned to receive placebo. Nivolumab was adminstered at 240 mg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks until recurrence or unacceptable toxicity for a maximum duration of 1 year. Neoadjuvant cisplatin chemotherapy was allowed.
Median DFS was 20.8 months with nivolumab versus 10.8 months in the placebo arm. Among patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or more, median DFS was 8.4 months in the placebo group; it was not reached with nivolumab.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients who received nivolumab. The most frequent was urinary tract infection. Fatal reactions, including pneumonitis, occurred in 1%. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, the labeling notes.
The trial was funded by BMS and Ono Pharmaceutical. Dr. Galsky has been a paid consultant for BMS.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new indication builds on the PD-1 inhibitor’s prior approvals for advanced or metastatic UC that’s progressed during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy or that’s progressed within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new indication is based results from the CheckMate-274 trial, which found an almost doubling of median disease-free survival (DFS) with nivolumab compared with placebo.
BMS noted that the new approval makes nivolumab “the first and only PD-1 inhibitor approved for urothelial carcinoma in the adjuvant setting,” regardless of prior neoadjuvant chemotherapy, nodal involvement, or PD-L1 status.
It “has the potential to become a new standard-of-care option in this setting,” said CheckMate-274’s primary investigator, Matthew Galsky, MD, a genitourinary medical oncologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, in the company press release.
Rival PD-1 blocker pembrolizumab (Keytruda), from Merck, carries several UC indications of its own for locally advanced or metastatic disease in patients who are ineligible for platinum-containing chemotherapy or that has progressed despite it, as well as for high-risk, non–muscle invasive bladder cancer that has not responded to bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment in cases in which patients are ineligible for or opt out of cystectomy, according to labeling.
In the CheckMate-274 trial, 353 patients with UC were randomly assigned to receive nivolumab after radical resection, and 356 others were assigned to receive placebo. Nivolumab was adminstered at 240 mg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks until recurrence or unacceptable toxicity for a maximum duration of 1 year. Neoadjuvant cisplatin chemotherapy was allowed.
Median DFS was 20.8 months with nivolumab versus 10.8 months in the placebo arm. Among patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or more, median DFS was 8.4 months in the placebo group; it was not reached with nivolumab.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients who received nivolumab. The most frequent was urinary tract infection. Fatal reactions, including pneumonitis, occurred in 1%. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, the labeling notes.
The trial was funded by BMS and Ono Pharmaceutical. Dr. Galsky has been a paid consultant for BMS.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new indication builds on the PD-1 inhibitor’s prior approvals for advanced or metastatic UC that’s progressed during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy or that’s progressed within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new indication is based results from the CheckMate-274 trial, which found an almost doubling of median disease-free survival (DFS) with nivolumab compared with placebo.
BMS noted that the new approval makes nivolumab “the first and only PD-1 inhibitor approved for urothelial carcinoma in the adjuvant setting,” regardless of prior neoadjuvant chemotherapy, nodal involvement, or PD-L1 status.
It “has the potential to become a new standard-of-care option in this setting,” said CheckMate-274’s primary investigator, Matthew Galsky, MD, a genitourinary medical oncologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, in the company press release.
Rival PD-1 blocker pembrolizumab (Keytruda), from Merck, carries several UC indications of its own for locally advanced or metastatic disease in patients who are ineligible for platinum-containing chemotherapy or that has progressed despite it, as well as for high-risk, non–muscle invasive bladder cancer that has not responded to bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment in cases in which patients are ineligible for or opt out of cystectomy, according to labeling.
In the CheckMate-274 trial, 353 patients with UC were randomly assigned to receive nivolumab after radical resection, and 356 others were assigned to receive placebo. Nivolumab was adminstered at 240 mg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks until recurrence or unacceptable toxicity for a maximum duration of 1 year. Neoadjuvant cisplatin chemotherapy was allowed.
Median DFS was 20.8 months with nivolumab versus 10.8 months in the placebo arm. Among patients with PD-L1 expression of 1% or more, median DFS was 8.4 months in the placebo group; it was not reached with nivolumab.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients who received nivolumab. The most frequent was urinary tract infection. Fatal reactions, including pneumonitis, occurred in 1%. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, the labeling notes.
The trial was funded by BMS and Ono Pharmaceutical. Dr. Galsky has been a paid consultant for BMS.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists’ income and net worth rise despite pandemic
Overall, oncologists’ average annual income rose from $377,000 in 2020 to $403,000 this year.
Although many offices closed for periods during 2020, some physicians used the Paycheck Protection Program. Others found other methods to keep their earnings relatively stable, such as switching to telehealth, cutting staff, and renegotiating leases.
The overall net worth of oncologists also increased. This year, 55% reported a net worth of $1.5 million, compared to 42% last year. A contributing factor is the rise in home prices, suggested Joel Greenwald, MD, CFP, a wealth management advisor for physicians.
The rise in the stock market also played a role, he noted. “And I’ve seen clients accumulate cash, which has added to their net worth. They cut back on spending because they were worried about big declines in income and also because there was simply less to spend money on.”
The percentage of oncologists (16%) with a net worth of more than $5 million stayed pretty much the same. Oncology remained in the upper half of the list of wealthy specialties. Topping that list are dermatology (28%), orthopedics and orthopedic surgery (25%), and plastic surgery (24%).
On the flip side, the percentage of oncologists on the lower end of the net worth scale declined from last year. Oncology was the specialty with the lowest percentage of practitioners (16%) reporting a net worth of under $500,000.
Expenses and debts
Similar to reports from previous years, this latest survey found that more than half of oncologists (56%) said they are paying off a mortgage on a primary residence. About a third (32%) are paying off a car loan. Credit card debt (19%), college or medical school loans (17%), childcare (14%), and medical expenses for themselves or a loved one (12%) were also reported.
When it comes to paying off school loans, oncology was near the bottom of the list of 29 medical specialties, along with nephrology, gastroenterology, and diabetes and endocrinology. Emergency medicine topped that list, followed by family medicine, pediatrics, physical medicine, and rehabilitation (all 31%).
Although the vast majority of oncologists (94%) were able to keep up with their bills, the pandemic did take a toll on some. Six percent said that they were unable to keep up with their bills, and 3% could not meet their mortgage. This is far superior to the American population at large – a quarter of adults missed a mortgage payment or rent payment because of challenges associated with the pandemic.
Saving and losses
Most oncologists did not take any extra steps to curtail spending – 77% reported that they had not done anything to reduce major expenses. About a quarter of respondents took significant steps to lower their expenses, such as deferring or refinancing loans (11%), switching to a different type of car (6%), or moving to a different home (5%).
Savings for tax deferred accounts this year was a mixed bag. More than half (56%) of oncologists said that they put aside the same amount every month, give or take; 11% do not regularly put money into a 401(k) retirement account or tax-deferred savings account. Compared to last year, 32% put less money into their savings accounts. Having fewer patients or working fewer hours during the pandemic may have resulted in oncologists needing more of their income, or even their full income, to pay their bills.
Similar results were seen with taxable savings. Half of oncologists were putting the same amount into bank accounts; 20% reported that they do not regularly put money into this type of account. Compared to last year, 29% put less money into taxable savings.
Most oncologists (75%) reported that they did not experience any significant financial losses during the past year. This was similar to last year (77%). The percentage of those who had losses related to their practice rose from 3% to 8%. Much of this increase was due to COVID-19.
Living within their means
The vast majority of oncologists live within or below their means (94%). “There are certainly folks who believe that as long as they pay their credit card every month and contribute to their 401(k) enough to get their employer match, they’re doing okay,” said Dr. Greenwald. “I would say living within one’s means is having a 3 to 6 months’ emergency fund and saving at least 20% of gross income toward retirement.”
Although most oncologists live within their means, they also have a higher than average number of credit cards. More than half (54%) have at least five; the average American has four. Nineteen percent of oncologists reported having seven or more credit cards, and none said they had no credit cards.
Mortgage payments varied considerably among respondents, from less than $100,000 (16%) to more than half a million (21%). More than a third (37%) reported having no mortgage at all. According to the Mortgage Bankers Association, the overall average size of a home mortgage loan was $344,556 in March 2020.
For household finances, 57% reported that they pool incomes to pay the bills, regardless of how much each person earns. A quarter said that they do not have joint finances with a spouse or partner, and for 13%, the person with the higher income paid a larger share.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, oncologists’ average annual income rose from $377,000 in 2020 to $403,000 this year.
Although many offices closed for periods during 2020, some physicians used the Paycheck Protection Program. Others found other methods to keep their earnings relatively stable, such as switching to telehealth, cutting staff, and renegotiating leases.
The overall net worth of oncologists also increased. This year, 55% reported a net worth of $1.5 million, compared to 42% last year. A contributing factor is the rise in home prices, suggested Joel Greenwald, MD, CFP, a wealth management advisor for physicians.
The rise in the stock market also played a role, he noted. “And I’ve seen clients accumulate cash, which has added to their net worth. They cut back on spending because they were worried about big declines in income and also because there was simply less to spend money on.”
The percentage of oncologists (16%) with a net worth of more than $5 million stayed pretty much the same. Oncology remained in the upper half of the list of wealthy specialties. Topping that list are dermatology (28%), orthopedics and orthopedic surgery (25%), and plastic surgery (24%).
On the flip side, the percentage of oncologists on the lower end of the net worth scale declined from last year. Oncology was the specialty with the lowest percentage of practitioners (16%) reporting a net worth of under $500,000.
Expenses and debts
Similar to reports from previous years, this latest survey found that more than half of oncologists (56%) said they are paying off a mortgage on a primary residence. About a third (32%) are paying off a car loan. Credit card debt (19%), college or medical school loans (17%), childcare (14%), and medical expenses for themselves or a loved one (12%) were also reported.
When it comes to paying off school loans, oncology was near the bottom of the list of 29 medical specialties, along with nephrology, gastroenterology, and diabetes and endocrinology. Emergency medicine topped that list, followed by family medicine, pediatrics, physical medicine, and rehabilitation (all 31%).
Although the vast majority of oncologists (94%) were able to keep up with their bills, the pandemic did take a toll on some. Six percent said that they were unable to keep up with their bills, and 3% could not meet their mortgage. This is far superior to the American population at large – a quarter of adults missed a mortgage payment or rent payment because of challenges associated with the pandemic.
Saving and losses
Most oncologists did not take any extra steps to curtail spending – 77% reported that they had not done anything to reduce major expenses. About a quarter of respondents took significant steps to lower their expenses, such as deferring or refinancing loans (11%), switching to a different type of car (6%), or moving to a different home (5%).
Savings for tax deferred accounts this year was a mixed bag. More than half (56%) of oncologists said that they put aside the same amount every month, give or take; 11% do not regularly put money into a 401(k) retirement account or tax-deferred savings account. Compared to last year, 32% put less money into their savings accounts. Having fewer patients or working fewer hours during the pandemic may have resulted in oncologists needing more of their income, or even their full income, to pay their bills.
Similar results were seen with taxable savings. Half of oncologists were putting the same amount into bank accounts; 20% reported that they do not regularly put money into this type of account. Compared to last year, 29% put less money into taxable savings.
Most oncologists (75%) reported that they did not experience any significant financial losses during the past year. This was similar to last year (77%). The percentage of those who had losses related to their practice rose from 3% to 8%. Much of this increase was due to COVID-19.
Living within their means
The vast majority of oncologists live within or below their means (94%). “There are certainly folks who believe that as long as they pay their credit card every month and contribute to their 401(k) enough to get their employer match, they’re doing okay,” said Dr. Greenwald. “I would say living within one’s means is having a 3 to 6 months’ emergency fund and saving at least 20% of gross income toward retirement.”
Although most oncologists live within their means, they also have a higher than average number of credit cards. More than half (54%) have at least five; the average American has four. Nineteen percent of oncologists reported having seven or more credit cards, and none said they had no credit cards.
Mortgage payments varied considerably among respondents, from less than $100,000 (16%) to more than half a million (21%). More than a third (37%) reported having no mortgage at all. According to the Mortgage Bankers Association, the overall average size of a home mortgage loan was $344,556 in March 2020.
For household finances, 57% reported that they pool incomes to pay the bills, regardless of how much each person earns. A quarter said that they do not have joint finances with a spouse or partner, and for 13%, the person with the higher income paid a larger share.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, oncologists’ average annual income rose from $377,000 in 2020 to $403,000 this year.
Although many offices closed for periods during 2020, some physicians used the Paycheck Protection Program. Others found other methods to keep their earnings relatively stable, such as switching to telehealth, cutting staff, and renegotiating leases.
The overall net worth of oncologists also increased. This year, 55% reported a net worth of $1.5 million, compared to 42% last year. A contributing factor is the rise in home prices, suggested Joel Greenwald, MD, CFP, a wealth management advisor for physicians.
The rise in the stock market also played a role, he noted. “And I’ve seen clients accumulate cash, which has added to their net worth. They cut back on spending because they were worried about big declines in income and also because there was simply less to spend money on.”
The percentage of oncologists (16%) with a net worth of more than $5 million stayed pretty much the same. Oncology remained in the upper half of the list of wealthy specialties. Topping that list are dermatology (28%), orthopedics and orthopedic surgery (25%), and plastic surgery (24%).
On the flip side, the percentage of oncologists on the lower end of the net worth scale declined from last year. Oncology was the specialty with the lowest percentage of practitioners (16%) reporting a net worth of under $500,000.
Expenses and debts
Similar to reports from previous years, this latest survey found that more than half of oncologists (56%) said they are paying off a mortgage on a primary residence. About a third (32%) are paying off a car loan. Credit card debt (19%), college or medical school loans (17%), childcare (14%), and medical expenses for themselves or a loved one (12%) were also reported.
When it comes to paying off school loans, oncology was near the bottom of the list of 29 medical specialties, along with nephrology, gastroenterology, and diabetes and endocrinology. Emergency medicine topped that list, followed by family medicine, pediatrics, physical medicine, and rehabilitation (all 31%).
Although the vast majority of oncologists (94%) were able to keep up with their bills, the pandemic did take a toll on some. Six percent said that they were unable to keep up with their bills, and 3% could not meet their mortgage. This is far superior to the American population at large – a quarter of adults missed a mortgage payment or rent payment because of challenges associated with the pandemic.
Saving and losses
Most oncologists did not take any extra steps to curtail spending – 77% reported that they had not done anything to reduce major expenses. About a quarter of respondents took significant steps to lower their expenses, such as deferring or refinancing loans (11%), switching to a different type of car (6%), or moving to a different home (5%).
Savings for tax deferred accounts this year was a mixed bag. More than half (56%) of oncologists said that they put aside the same amount every month, give or take; 11% do not regularly put money into a 401(k) retirement account or tax-deferred savings account. Compared to last year, 32% put less money into their savings accounts. Having fewer patients or working fewer hours during the pandemic may have resulted in oncologists needing more of their income, or even their full income, to pay their bills.
Similar results were seen with taxable savings. Half of oncologists were putting the same amount into bank accounts; 20% reported that they do not regularly put money into this type of account. Compared to last year, 29% put less money into taxable savings.
Most oncologists (75%) reported that they did not experience any significant financial losses during the past year. This was similar to last year (77%). The percentage of those who had losses related to their practice rose from 3% to 8%. Much of this increase was due to COVID-19.
Living within their means
The vast majority of oncologists live within or below their means (94%). “There are certainly folks who believe that as long as they pay their credit card every month and contribute to their 401(k) enough to get their employer match, they’re doing okay,” said Dr. Greenwald. “I would say living within one’s means is having a 3 to 6 months’ emergency fund and saving at least 20% of gross income toward retirement.”
Although most oncologists live within their means, they also have a higher than average number of credit cards. More than half (54%) have at least five; the average American has four. Nineteen percent of oncologists reported having seven or more credit cards, and none said they had no credit cards.
Mortgage payments varied considerably among respondents, from less than $100,000 (16%) to more than half a million (21%). More than a third (37%) reported having no mortgage at all. According to the Mortgage Bankers Association, the overall average size of a home mortgage loan was $344,556 in March 2020.
For household finances, 57% reported that they pool incomes to pay the bills, regardless of how much each person earns. A quarter said that they do not have joint finances with a spouse or partner, and for 13%, the person with the higher income paid a larger share.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth abortions are 95% effective, similar to in-person care
Telehealth abortion may be just as safe and effective as in-person care, according to a small study published online in JAMA Network Open.
Of the 110 women from whom researchers collected remote abortion outcome data, 95% had a complete abortion without additional medical interventions, such as aspiration or surgery, and none experienced adverse events. Researchers said this efficacy rate is similar to in-person visits.
“There was no reason to expect that the medications prescribed [via telemedicine] and delivered through the mail would have different outcomes from when a patient traveled to a clinic,” study author Ushma D. Upadhyay, PhD, MPH, associate professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
Medication abortion, which usually involves taking mifepristone (Mifeprex) followed by misoprostol (Cytotec) during the first 10 weeks of pregnancy, has been available in the United States since 2000. The Food and Drug Administration’s Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy requires that mifepristone be dispensed in a medical office, clinic, or hospital, prohibiting dispensing from pharmacies in an effort to reduce potential risk for complications.
In April 2021, the FDA lifted the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, Dr. Upadhyay hopes the findings of her current study will make this suspension permanent.
For the study, Dr. Upadhyay and colleagues examined the safety and efficacy of fully remote, medication abortion care. Eligibility for the medication was assessed using an online form that relies on patient history, or patients recalling their last period, to assess pregnancy duration and screen for ectopic pregnancy risks. Nurse practitioners reviewed the form and referred patients with unknown last menstrual period date or ectopic pregnancy risk factors for ultrasonography. A mail-order pharmacy delivered medications to eligible patients. The protocol involved three follow-up contacts: confirmation of medication administration, a 3-day assessment of symptoms, and a home pregnancy test after 4 weeks. Follow-up interactions were conducted by text, secure messaging, or telephone.
Researchers found that in addition to the 95% of the patients having a complete abortion without intervention, 5% (five) of patients required addition medical care to complete the abortion. Two of those patients were treated in EDs.
Gillian Burkhardt, MD, who was not involved in the study, said Dr. Upadhyay’s study proves what has been known all along, that medication is super safe and that women “can help to determine their own eligibility as well as in conjunction with the provider.”
“I hope that this will be one more study that the FDA can use when thinking about changing the risk evaluation administration strategy so that it’s removing the requirement that a person be in the dispensing medical office,” Dr. Burkhardt, assistant professor of family planning in the department of obstetrics & gynecology at the University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “I hope it also makes providers feel more comfortable as well, because I think there’s some hesitancy among providers to provide abortion without doing an ultrasound or without seeing the patient typically in front of them.”
This isn’t the first study to suggest the safety of telemedicine abortion. A 2019 study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, which analyzed records from nearly 6,000 patients receiving medication abortion either through telemedicine or in person at 26 Planned Parenthood health centers in four states found that ongoing pregnancy and aspiration procedures were less common among telemedicine patients. Another 2017 study published in BMJ found that women who used an online consultation service and self-sourced medical abortion during a 3-year period were able to successfully end their pregnancies with few adverse events.
Dr. Upadhyay said one limitation of the current study is its sample size, so more studies should be conducted to prove telemedicine abortion’s safety.
“I think that we need continued research on this model of care just so we have more multiple studies that contribute to the evidence that can convince providers as well that they don’t need a lot of tests and that they can mail,” Dr. Upadhyay said.
Neither Dr. Upadhyay nor Dr. Burkhardt reported conflicts of interests.
Telehealth abortion may be just as safe and effective as in-person care, according to a small study published online in JAMA Network Open.
Of the 110 women from whom researchers collected remote abortion outcome data, 95% had a complete abortion without additional medical interventions, such as aspiration or surgery, and none experienced adverse events. Researchers said this efficacy rate is similar to in-person visits.
“There was no reason to expect that the medications prescribed [via telemedicine] and delivered through the mail would have different outcomes from when a patient traveled to a clinic,” study author Ushma D. Upadhyay, PhD, MPH, associate professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
Medication abortion, which usually involves taking mifepristone (Mifeprex) followed by misoprostol (Cytotec) during the first 10 weeks of pregnancy, has been available in the United States since 2000. The Food and Drug Administration’s Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy requires that mifepristone be dispensed in a medical office, clinic, or hospital, prohibiting dispensing from pharmacies in an effort to reduce potential risk for complications.
In April 2021, the FDA lifted the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, Dr. Upadhyay hopes the findings of her current study will make this suspension permanent.
For the study, Dr. Upadhyay and colleagues examined the safety and efficacy of fully remote, medication abortion care. Eligibility for the medication was assessed using an online form that relies on patient history, or patients recalling their last period, to assess pregnancy duration and screen for ectopic pregnancy risks. Nurse practitioners reviewed the form and referred patients with unknown last menstrual period date or ectopic pregnancy risk factors for ultrasonography. A mail-order pharmacy delivered medications to eligible patients. The protocol involved three follow-up contacts: confirmation of medication administration, a 3-day assessment of symptoms, and a home pregnancy test after 4 weeks. Follow-up interactions were conducted by text, secure messaging, or telephone.
Researchers found that in addition to the 95% of the patients having a complete abortion without intervention, 5% (five) of patients required addition medical care to complete the abortion. Two of those patients were treated in EDs.
Gillian Burkhardt, MD, who was not involved in the study, said Dr. Upadhyay’s study proves what has been known all along, that medication is super safe and that women “can help to determine their own eligibility as well as in conjunction with the provider.”
“I hope that this will be one more study that the FDA can use when thinking about changing the risk evaluation administration strategy so that it’s removing the requirement that a person be in the dispensing medical office,” Dr. Burkhardt, assistant professor of family planning in the department of obstetrics & gynecology at the University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “I hope it also makes providers feel more comfortable as well, because I think there’s some hesitancy among providers to provide abortion without doing an ultrasound or without seeing the patient typically in front of them.”
This isn’t the first study to suggest the safety of telemedicine abortion. A 2019 study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, which analyzed records from nearly 6,000 patients receiving medication abortion either through telemedicine or in person at 26 Planned Parenthood health centers in four states found that ongoing pregnancy and aspiration procedures were less common among telemedicine patients. Another 2017 study published in BMJ found that women who used an online consultation service and self-sourced medical abortion during a 3-year period were able to successfully end their pregnancies with few adverse events.
Dr. Upadhyay said one limitation of the current study is its sample size, so more studies should be conducted to prove telemedicine abortion’s safety.
“I think that we need continued research on this model of care just so we have more multiple studies that contribute to the evidence that can convince providers as well that they don’t need a lot of tests and that they can mail,” Dr. Upadhyay said.
Neither Dr. Upadhyay nor Dr. Burkhardt reported conflicts of interests.
Telehealth abortion may be just as safe and effective as in-person care, according to a small study published online in JAMA Network Open.
Of the 110 women from whom researchers collected remote abortion outcome data, 95% had a complete abortion without additional medical interventions, such as aspiration or surgery, and none experienced adverse events. Researchers said this efficacy rate is similar to in-person visits.
“There was no reason to expect that the medications prescribed [via telemedicine] and delivered through the mail would have different outcomes from when a patient traveled to a clinic,” study author Ushma D. Upadhyay, PhD, MPH, associate professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
Medication abortion, which usually involves taking mifepristone (Mifeprex) followed by misoprostol (Cytotec) during the first 10 weeks of pregnancy, has been available in the United States since 2000. The Food and Drug Administration’s Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy requires that mifepristone be dispensed in a medical office, clinic, or hospital, prohibiting dispensing from pharmacies in an effort to reduce potential risk for complications.
In April 2021, the FDA lifted the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, Dr. Upadhyay hopes the findings of her current study will make this suspension permanent.
For the study, Dr. Upadhyay and colleagues examined the safety and efficacy of fully remote, medication abortion care. Eligibility for the medication was assessed using an online form that relies on patient history, or patients recalling their last period, to assess pregnancy duration and screen for ectopic pregnancy risks. Nurse practitioners reviewed the form and referred patients with unknown last menstrual period date or ectopic pregnancy risk factors for ultrasonography. A mail-order pharmacy delivered medications to eligible patients. The protocol involved three follow-up contacts: confirmation of medication administration, a 3-day assessment of symptoms, and a home pregnancy test after 4 weeks. Follow-up interactions were conducted by text, secure messaging, or telephone.
Researchers found that in addition to the 95% of the patients having a complete abortion without intervention, 5% (five) of patients required addition medical care to complete the abortion. Two of those patients were treated in EDs.
Gillian Burkhardt, MD, who was not involved in the study, said Dr. Upadhyay’s study proves what has been known all along, that medication is super safe and that women “can help to determine their own eligibility as well as in conjunction with the provider.”
“I hope that this will be one more study that the FDA can use when thinking about changing the risk evaluation administration strategy so that it’s removing the requirement that a person be in the dispensing medical office,” Dr. Burkhardt, assistant professor of family planning in the department of obstetrics & gynecology at the University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “I hope it also makes providers feel more comfortable as well, because I think there’s some hesitancy among providers to provide abortion without doing an ultrasound or without seeing the patient typically in front of them.”
This isn’t the first study to suggest the safety of telemedicine abortion. A 2019 study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, which analyzed records from nearly 6,000 patients receiving medication abortion either through telemedicine or in person at 26 Planned Parenthood health centers in four states found that ongoing pregnancy and aspiration procedures were less common among telemedicine patients. Another 2017 study published in BMJ found that women who used an online consultation service and self-sourced medical abortion during a 3-year period were able to successfully end their pregnancies with few adverse events.
Dr. Upadhyay said one limitation of the current study is its sample size, so more studies should be conducted to prove telemedicine abortion’s safety.
“I think that we need continued research on this model of care just so we have more multiple studies that contribute to the evidence that can convince providers as well that they don’t need a lot of tests and that they can mail,” Dr. Upadhyay said.
Neither Dr. Upadhyay nor Dr. Burkhardt reported conflicts of interests.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
How is a woman determined to have dense breast tissue?
Breasts that are heterogeneously dense or extremely dense on mammography are considered “dense breasts.” Breast density matters for 2 reasons: Dense tissue can mask cancer on a mammogram, and having dense breasts increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
Breast density measurement
A woman’s breast density is usually determined during her breast cancer screening with mammography by her radiologist through visual evaluation of the images taken. Breast density also can be measured from individual mammograms by computer software, and it can be estimated on computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In the United States, information about breast density is usually included in a report sent from the radiologist to the referring clinician after a mammogram is taken, and may also be included in the patient letter following up screening mammography. In Europe, national reporting guidelines for physicians vary.
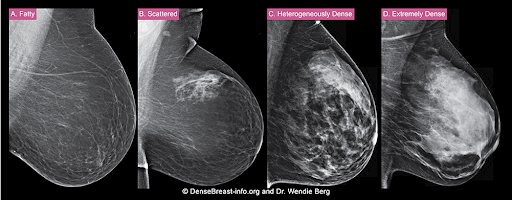
The density of a woman’s breast tissue is described using one of four BI-RADS® breast composition categories1 as shown in the FIGURE.
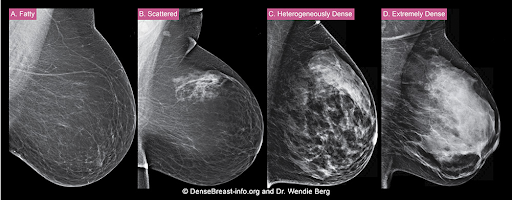
A. ALMOST ENTIRELY FATTY – On a mammogram, most of the tissue appears dark gray or black, while small amounts of dense (or fibroglandular) tissue display as light gray or white. About 13% of women aged 40 to 74 have breasts considered to be “fatty.”2
B. SCATTERED FIBROGLANDULAR DENSITY – There are scattered areas of dense (fibroglandular) tissue mixed with fat. Even in breasts with scattered areas of breast tissue, cancers can sometimes be missed when they look like areas of normal tissue or are within an area of denser tissue. About 43% of women aged 40 to 74 have breasts with scattered fibroglandular tissue.2
C. HETEROGENEOUSLY DENSE – There are large portions of the breast where dense (fibroglandular) tissue could hide small masses. About 36% of all women aged 40 to 74 have heterogeneously dense breasts.2
D. EXTREMELY DENSE – Most of the breast appears to consist of dense (fibroglandular) tissue, creating a “white out” situation and making it extremely difficult to see through and lowering the sensitivity of mammography. About 7% of all women aged 40 to 74 have extremely dense breasts.2
Factors that may impact breast density
Age. Breasts tend to become less dense as women get older, especially after menopause (as the glandular tissue atrophies and the breasts may appear more fatty-replaced).
Postmenopausal hormone therapy. An increase in mammographic density is more common among women taking continuous combined hormonal therapy than for those using oral low-dose estrogen or transdermal estrogen therapy.
Lactation. Breast density increases with lactation.
Weight changes. Weight gain can increase the amount of fat relative to dense tissue, resulting in slightly lower density as a proportion of breast tissue overall. Similarly, weight loss can decrease the amount of fat in the breasts, making breast density appear greater overall. Importantly, there is no change in the amount of glandular tissue; only the relative proportions change.
Tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors. These medications can slightly reduce breast density.
Because breast density may change with age and other factors, it should be assessed every year.
For more information, visit medically sourced DenseBreast-info.org.
Comprehensive resources include a free CME opportunity, Dense Breasts and Supplemental Screening.
1. Sickles EA, D’Orsi CJ, Bassett LW, et al. ACR BI-RADS Mammography. ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology; 2013.
2. Sprague BL, Gangnon RE, Burt V, et al. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju255. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju255.
Breasts that are heterogeneously dense or extremely dense on mammography are considered “dense breasts.” Breast density matters for 2 reasons: Dense tissue can mask cancer on a mammogram, and having dense breasts increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
Breast density measurement
A woman’s breast density is usually determined during her breast cancer screening with mammography by her radiologist through visual evaluation of the images taken. Breast density also can be measured from individual mammograms by computer software, and it can be estimated on computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In the United States, information about breast density is usually included in a report sent from the radiologist to the referring clinician after a mammogram is taken, and may also be included in the patient letter following up screening mammography. In Europe, national reporting guidelines for physicians vary.
The density of a woman’s breast tissue is described using one of four BI-RADS® breast composition categories1 as shown in the FIGURE.

A. ALMOST ENTIRELY FATTY – On a mammogram, most of the tissue appears dark gray or black, while small amounts of dense (or fibroglandular) tissue display as light gray or white. About 13% of women aged 40 to 74 have breasts considered to be “fatty.”2
B. SCATTERED FIBROGLANDULAR DENSITY – There are scattered areas of dense (fibroglandular) tissue mixed with fat. Even in breasts with scattered areas of breast tissue, cancers can sometimes be missed when they look like areas of normal tissue or are within an area of denser tissue. About 43% of women aged 40 to 74 have breasts with scattered fibroglandular tissue.2
C. HETEROGENEOUSLY DENSE – There are large portions of the breast where dense (fibroglandular) tissue could hide small masses. About 36% of all women aged 40 to 74 have heterogeneously dense breasts.2
D. EXTREMELY DENSE – Most of the breast appears to consist of dense (fibroglandular) tissue, creating a “white out” situation and making it extremely difficult to see through and lowering the sensitivity of mammography. About 7% of all women aged 40 to 74 have extremely dense breasts.2
Factors that may impact breast density
Age. Breasts tend to become less dense as women get older, especially after menopause (as the glandular tissue atrophies and the breasts may appear more fatty-replaced).
Postmenopausal hormone therapy. An increase in mammographic density is more common among women taking continuous combined hormonal therapy than for those using oral low-dose estrogen or transdermal estrogen therapy.
Lactation. Breast density increases with lactation.
Weight changes. Weight gain can increase the amount of fat relative to dense tissue, resulting in slightly lower density as a proportion of breast tissue overall. Similarly, weight loss can decrease the amount of fat in the breasts, making breast density appear greater overall. Importantly, there is no change in the amount of glandular tissue; only the relative proportions change.
Tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors. These medications can slightly reduce breast density.
Because breast density may change with age and other factors, it should be assessed every year.
For more information, visit medically sourced DenseBreast-info.org.
Comprehensive resources include a free CME opportunity, Dense Breasts and Supplemental Screening.
Breasts that are heterogeneously dense or extremely dense on mammography are considered “dense breasts.” Breast density matters for 2 reasons: Dense tissue can mask cancer on a mammogram, and having dense breasts increases the risk of developing breast cancer.
Breast density measurement
A woman’s breast density is usually determined during her breast cancer screening with mammography by her radiologist through visual evaluation of the images taken. Breast density also can be measured from individual mammograms by computer software, and it can be estimated on computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In the United States, information about breast density is usually included in a report sent from the radiologist to the referring clinician after a mammogram is taken, and may also be included in the patient letter following up screening mammography. In Europe, national reporting guidelines for physicians vary.
The density of a woman’s breast tissue is described using one of four BI-RADS® breast composition categories1 as shown in the FIGURE.

A. ALMOST ENTIRELY FATTY – On a mammogram, most of the tissue appears dark gray or black, while small amounts of dense (or fibroglandular) tissue display as light gray or white. About 13% of women aged 40 to 74 have breasts considered to be “fatty.”2
B. SCATTERED FIBROGLANDULAR DENSITY – There are scattered areas of dense (fibroglandular) tissue mixed with fat. Even in breasts with scattered areas of breast tissue, cancers can sometimes be missed when they look like areas of normal tissue or are within an area of denser tissue. About 43% of women aged 40 to 74 have breasts with scattered fibroglandular tissue.2
C. HETEROGENEOUSLY DENSE – There are large portions of the breast where dense (fibroglandular) tissue could hide small masses. About 36% of all women aged 40 to 74 have heterogeneously dense breasts.2
D. EXTREMELY DENSE – Most of the breast appears to consist of dense (fibroglandular) tissue, creating a “white out” situation and making it extremely difficult to see through and lowering the sensitivity of mammography. About 7% of all women aged 40 to 74 have extremely dense breasts.2
Factors that may impact breast density
Age. Breasts tend to become less dense as women get older, especially after menopause (as the glandular tissue atrophies and the breasts may appear more fatty-replaced).
Postmenopausal hormone therapy. An increase in mammographic density is more common among women taking continuous combined hormonal therapy than for those using oral low-dose estrogen or transdermal estrogen therapy.
Lactation. Breast density increases with lactation.
Weight changes. Weight gain can increase the amount of fat relative to dense tissue, resulting in slightly lower density as a proportion of breast tissue overall. Similarly, weight loss can decrease the amount of fat in the breasts, making breast density appear greater overall. Importantly, there is no change in the amount of glandular tissue; only the relative proportions change.
Tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors. These medications can slightly reduce breast density.
Because breast density may change with age and other factors, it should be assessed every year.
For more information, visit medically sourced DenseBreast-info.org.
Comprehensive resources include a free CME opportunity, Dense Breasts and Supplemental Screening.
1. Sickles EA, D’Orsi CJ, Bassett LW, et al. ACR BI-RADS Mammography. ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology; 2013.
2. Sprague BL, Gangnon RE, Burt V, et al. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju255. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju255.
1. Sickles EA, D’Orsi CJ, Bassett LW, et al. ACR BI-RADS Mammography. ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology; 2013.
2. Sprague BL, Gangnon RE, Burt V, et al. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju255. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju255.
Pandemic unveils growing suicide crisis for communities of color
This story is a collaboration between KHN and “Science Friday.”
Rafiah Maxie has been a licensed clinical social worker in the Chicago area for a decade. Throughout that time, she’d viewed suicide as a problem most prevalent among middle-aged white men.
Until May 27, 2020.
That day, Maxie’s 19-year-old son, Jamal Clay – who loved playing the trumpet and participating in theater, who would help her unload groceries from the car and raise funds for the March of the Dimes – killed himself in their garage.
“Now I cannot blink without seeing my son hanging,” said Maxie, who is Black.
Clay’s death, along with the suicides of more than 100 other Black residents in Illinois last year, has led locals to call for new prevention efforts focused on Black communities. In 2020, during the pandemic’s first year, suicides among White residents decreased compared with previous years, while they increased among Black residents, according to state data.
But this is not a local problem. Nor is it limited to the pandemic.
Interviews with a dozen suicide researchers, data collected from states across the country, and a review of decades of research revealed that suicide is a growing crisis for communities of color – one that plagued them well before the pandemic and has only been exacerbated since.
Overall suicide rates in the U.S. decreased in 2019 and 2020. National and local studies attribute the trend to a drop among White Americans, who make up the majority of suicide deaths. Meanwhile, rates for Black, Hispanic, and Asian Americans – though lower than those of their white peers – continued to climb in many states. (Suicide rates have been consistently high for Native Americans.)
“COVID created more transparency regarding what we already knew was happening,” said Sonyia Richardson, a licensed clinical social worker who focuses on serving people of color, and assistant professor at the University of North Carolina–Charlotte, where she researches suicide. When you put the suicide rates of all communities in one bucket, “that bucket says it’s getting better and what we’re doing is working,” she said. “But that’s not the case for communities of color.”
Losing generations
Although the suicide rate is highest among middle-aged White men, young people of color are emerging as particularly at risk.
Research shows Black kids younger than 13 die by suicide at nearly twice the rate of White kids and, over time, their suicide rates have grown even as rates have decreased for White children. Among teenagers and young adults, suicide deaths have increased more than 45% for Black Americans and about 40% for Asian Americans in the 7 years ending in 2019. Other concerning trends in suicide attempts date to the ’90s.
“We have to pay attention now because if you’re out of the first decade of life and think life is not worth pursuing, that’s a signal to say something is going really wrong.”
These statistics also refute traditional ideas that suicide doesn’t happen in certain ethnic or minority populations because they’re “protected” and “resilient” or the “model minority,” said Kiara Alvarez, a researcher and psychologist at Massachusetts General Hospital who focuses on suicide among Hispanic and immigrant populations.
Although these groups may have had low suicide rates historically, that’s changing, she said.
Paul Chin lost his 17-year-old brother, Chris, to suicide in 2009. A poem Chris wrote in high school about his heritage has left Chin, 8 years his senior, wondering if his brother struggled to feel accepted in the U.S., despite being born and raised in New York.
Growing up, Asian Americans weren’t represented in lessons at school or in pop culture, said Chin, now 37. Even in clinical research on suicide as well as other health topics, kids like Chris are underrepresented, with less than 1% of federal research funding focused on Asian Americans.
It wasn’t until the pandemic, and the concurrent rise in hate crimes against Asian Americans, that Chin saw national attention on the community’s mental health. He hopes the interest is not short-lived.
Suicide is the leading cause of death for Asian Americans ages 15 to 24, yet “that doesn’t get enough attention,” Chin said. “It’s important to continue to share these stories.”
Kathy Williams, who is Black, has been on a similar mission since her 15-year-old son, Torian Graves, died by suicide in 1996. People didn’t talk about suicide in the Black community then, she said. So she started raising the topic at her church in Durham, N.C., and in local schools. She wanted Black families to know the warning signs and society at large to recognize the seriousness of the problem.
The pandemic may have highlighted this, Williams said, but “it has always happened. Always.”
Pandemic sheds light on the triggers
Pinpointing the root causes of rising suicide within communities of color has proved difficult. How much stems from mental illness? How much from socioeconomic changes like job losses or social isolation? Now, COVID-19 may offer some clues.
Recent decades have been marked by growing economic instability, a widening racial wealth gap, and more public attention on police killings of unarmed Black and Brown people, said Michael Lindsey, executive director of the New York University McSilver Institute for Poverty Policy and Research.
With social media, youths face racism on more fronts than their parents did, said Leslie Adams, assistant professor in the department of mental health at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Each of these factors has been shown to affect suicide risk. For example, experiencing racism and sexism together is linked to a threefold increase in suicidal thoughts for Asian American women, said Brian Keum, assistant professor at UCLA, based on preliminary research findings.
COVID-19 intensified these hardships among communities of color, with disproportionate numbers of lost loved ones, lost jobs, and lost housing. The murder of George Floyd prompted widespread racial unrest, and Asian Americans saw an increase in hate crimes.
At the same time, studies in Connecticut and Maryland found that suicide rates rose within these populations and dropped for their White counterparts.
“It’s not just a problem within the person, but societal issues that need to be addressed,” said Shari Jager-Hyman, assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania.
Lessons from Texas
In Texas, COVID-19 hit Hispanics especially hard. As of July 2021, they accounted for 45% of all COVID-19 deaths and disproportionately lost jobs. Individuals living in the U.S. without authorization were generally not eligible for unemployment benefits or federal stimulus checks.
During this time, suicide deaths among Hispanic Texans climbed from 847 deaths in 2019 to 962 deaths in 2020, according to preliminary state data. Suicide deaths rose for Black Texans and residents classified as “other” races or ethnicities, but decreased for White Texans.
The numbers didn’t surprise Marc Mendiola. The 20-year-old grew up in a majority-Hispanic community on the south side of San Antonio. Even before the pandemic, he often heard classmates say they were suicidal. Many faced dire finances at home, sometimes living without electricity, food, or water. Those who sought mental health treatment often found services prohibitively expensive or inaccessible because they weren’t offered in Spanish.
“These are conditions the community has always been in,” Mendiola said. “But with the pandemic, it’s even worse.”
Four years ago, Mendiola and his classmates at South San High School began advocating for mental health services. In late 2019, just months before COVID-19 struck, their vision became reality. Six community agencies partnered to offer free services to students and their families across three school districts.
Richard Davidson, chief operating officer of Family Service, one of the groups in the collaborative, said the number of students discussing economic stressors has been on the rise since April 2020. More than 90% of the students who received services in the first half of 2021 were Hispanic, and nearly 10% reported thoughts of suicide or self-harm, program data show. None died by suicide.
Many students are so worried about what’s for dinner the next day that they’re not able to see a future beyond that, Davidson said. That’s when suicide can feel like a viable option.
“One of the things we do is help them see … that despite this situation now, you can create a vision for your future,” Davidson said.
A good future
Researchers say the promise of a good future is often overlooked in suicide prevention, perhaps because achieving it is so challenging. It requires economic and social growth and breaking systemic barriers.
Tevis Simon works to address all those fronts. As a child in West Baltimore, Simon, who is Black, faced poverty and trauma. As an adult, she attempted suicide three times. But now she shares her story with youths across the city to inspire them to overcome challenges. She also talks to politicians, law enforcement agencies, and public policy officials about their responsibilities.
“We can’t not talk about race,” said Simon, 43. “We can’t not talk about systematic oppression. We cannot not talk about these conditions that affect our mental well-being and our feeling and desire to live.”
For Jamal Clay in Illinois, the systemic barriers started early. Before his suicide last year, he had tried to harm himself when he was 12 and the victim of bullies. At that time, he was hospitalized for a few days and told to follow up with outpatient therapy, said his mother, Maxie.
But it was difficult to find therapists who accepted Medicaid, she said. When Maxie finally found one, there was a 60-day wait. Other therapists canceled appointments, she said.
“So we worked on our own,” Maxie said, relying on church and community. Her son seemed to improve. “We thought we closed that chapter in our lives.”
But when the pandemic hit, everything got worse, she said. Clay came home from college and worked at an Amazon warehouse. On drives to and from work, he was frequently pulled over by police. He stopped wearing hats so officers would consider him less intimidating, Maxie said.
“He felt uncomfortable being out in the street,” she said.
Maxie is still trying to make sense of what happened the day Clay died. But she’s found meaning in starting a nonprofit called Soul Survivors of Chicago. Through the organization, she provides education, scholarships and shoes – including Jamal’s old ones – to those impacted by violence, suicide, and trauma.
“My son won’t be able to have a first interview in [those] shoes. He won’t be able to have a nice jump shot or go to church or even meet his wife,” Maxie said.
But she hopes his shoes will carry someone else to a good future.
[Editor’s note: For the purposes of this story, “people of color” or “communities of color” refers to any racial or ethnic populations whose members do not identify as White, including those who are multiracial. Hispanics can be of any race or combination of races.]
KHN senior correspondent JoNel Aleccia contributed to this report. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
This story is a collaboration between KHN and “Science Friday.”
Rafiah Maxie has been a licensed clinical social worker in the Chicago area for a decade. Throughout that time, she’d viewed suicide as a problem most prevalent among middle-aged white men.
Until May 27, 2020.
That day, Maxie’s 19-year-old son, Jamal Clay – who loved playing the trumpet and participating in theater, who would help her unload groceries from the car and raise funds for the March of the Dimes – killed himself in their garage.
“Now I cannot blink without seeing my son hanging,” said Maxie, who is Black.
Clay’s death, along with the suicides of more than 100 other Black residents in Illinois last year, has led locals to call for new prevention efforts focused on Black communities. In 2020, during the pandemic’s first year, suicides among White residents decreased compared with previous years, while they increased among Black residents, according to state data.
But this is not a local problem. Nor is it limited to the pandemic.
Interviews with a dozen suicide researchers, data collected from states across the country, and a review of decades of research revealed that suicide is a growing crisis for communities of color – one that plagued them well before the pandemic and has only been exacerbated since.
Overall suicide rates in the U.S. decreased in 2019 and 2020. National and local studies attribute the trend to a drop among White Americans, who make up the majority of suicide deaths. Meanwhile, rates for Black, Hispanic, and Asian Americans – though lower than those of their white peers – continued to climb in many states. (Suicide rates have been consistently high for Native Americans.)
“COVID created more transparency regarding what we already knew was happening,” said Sonyia Richardson, a licensed clinical social worker who focuses on serving people of color, and assistant professor at the University of North Carolina–Charlotte, where she researches suicide. When you put the suicide rates of all communities in one bucket, “that bucket says it’s getting better and what we’re doing is working,” she said. “But that’s not the case for communities of color.”
Losing generations
Although the suicide rate is highest among middle-aged White men, young people of color are emerging as particularly at risk.
Research shows Black kids younger than 13 die by suicide at nearly twice the rate of White kids and, over time, their suicide rates have grown even as rates have decreased for White children. Among teenagers and young adults, suicide deaths have increased more than 45% for Black Americans and about 40% for Asian Americans in the 7 years ending in 2019. Other concerning trends in suicide attempts date to the ’90s.
“We have to pay attention now because if you’re out of the first decade of life and think life is not worth pursuing, that’s a signal to say something is going really wrong.”
These statistics also refute traditional ideas that suicide doesn’t happen in certain ethnic or minority populations because they’re “protected” and “resilient” or the “model minority,” said Kiara Alvarez, a researcher and psychologist at Massachusetts General Hospital who focuses on suicide among Hispanic and immigrant populations.
Although these groups may have had low suicide rates historically, that’s changing, she said.
Paul Chin lost his 17-year-old brother, Chris, to suicide in 2009. A poem Chris wrote in high school about his heritage has left Chin, 8 years his senior, wondering if his brother struggled to feel accepted in the U.S., despite being born and raised in New York.
Growing up, Asian Americans weren’t represented in lessons at school or in pop culture, said Chin, now 37. Even in clinical research on suicide as well as other health topics, kids like Chris are underrepresented, with less than 1% of federal research funding focused on Asian Americans.
It wasn’t until the pandemic, and the concurrent rise in hate crimes against Asian Americans, that Chin saw national attention on the community’s mental health. He hopes the interest is not short-lived.
Suicide is the leading cause of death for Asian Americans ages 15 to 24, yet “that doesn’t get enough attention,” Chin said. “It’s important to continue to share these stories.”
Kathy Williams, who is Black, has been on a similar mission since her 15-year-old son, Torian Graves, died by suicide in 1996. People didn’t talk about suicide in the Black community then, she said. So she started raising the topic at her church in Durham, N.C., and in local schools. She wanted Black families to know the warning signs and society at large to recognize the seriousness of the problem.
The pandemic may have highlighted this, Williams said, but “it has always happened. Always.”
Pandemic sheds light on the triggers
Pinpointing the root causes of rising suicide within communities of color has proved difficult. How much stems from mental illness? How much from socioeconomic changes like job losses or social isolation? Now, COVID-19 may offer some clues.
Recent decades have been marked by growing economic instability, a widening racial wealth gap, and more public attention on police killings of unarmed Black and Brown people, said Michael Lindsey, executive director of the New York University McSilver Institute for Poverty Policy and Research.
With social media, youths face racism on more fronts than their parents did, said Leslie Adams, assistant professor in the department of mental health at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Each of these factors has been shown to affect suicide risk. For example, experiencing racism and sexism together is linked to a threefold increase in suicidal thoughts for Asian American women, said Brian Keum, assistant professor at UCLA, based on preliminary research findings.
COVID-19 intensified these hardships among communities of color, with disproportionate numbers of lost loved ones, lost jobs, and lost housing. The murder of George Floyd prompted widespread racial unrest, and Asian Americans saw an increase in hate crimes.
At the same time, studies in Connecticut and Maryland found that suicide rates rose within these populations and dropped for their White counterparts.
“It’s not just a problem within the person, but societal issues that need to be addressed,” said Shari Jager-Hyman, assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania.
Lessons from Texas
In Texas, COVID-19 hit Hispanics especially hard. As of July 2021, they accounted for 45% of all COVID-19 deaths and disproportionately lost jobs. Individuals living in the U.S. without authorization were generally not eligible for unemployment benefits or federal stimulus checks.
During this time, suicide deaths among Hispanic Texans climbed from 847 deaths in 2019 to 962 deaths in 2020, according to preliminary state data. Suicide deaths rose for Black Texans and residents classified as “other” races or ethnicities, but decreased for White Texans.
The numbers didn’t surprise Marc Mendiola. The 20-year-old grew up in a majority-Hispanic community on the south side of San Antonio. Even before the pandemic, he often heard classmates say they were suicidal. Many faced dire finances at home, sometimes living without electricity, food, or water. Those who sought mental health treatment often found services prohibitively expensive or inaccessible because they weren’t offered in Spanish.
“These are conditions the community has always been in,” Mendiola said. “But with the pandemic, it’s even worse.”
Four years ago, Mendiola and his classmates at South San High School began advocating for mental health services. In late 2019, just months before COVID-19 struck, their vision became reality. Six community agencies partnered to offer free services to students and their families across three school districts.
Richard Davidson, chief operating officer of Family Service, one of the groups in the collaborative, said the number of students discussing economic stressors has been on the rise since April 2020. More than 90% of the students who received services in the first half of 2021 were Hispanic, and nearly 10% reported thoughts of suicide or self-harm, program data show. None died by suicide.
Many students are so worried about what’s for dinner the next day that they’re not able to see a future beyond that, Davidson said. That’s when suicide can feel like a viable option.
“One of the things we do is help them see … that despite this situation now, you can create a vision for your future,” Davidson said.
A good future
Researchers say the promise of a good future is often overlooked in suicide prevention, perhaps because achieving it is so challenging. It requires economic and social growth and breaking systemic barriers.
Tevis Simon works to address all those fronts. As a child in West Baltimore, Simon, who is Black, faced poverty and trauma. As an adult, she attempted suicide three times. But now she shares her story with youths across the city to inspire them to overcome challenges. She also talks to politicians, law enforcement agencies, and public policy officials about their responsibilities.
“We can’t not talk about race,” said Simon, 43. “We can’t not talk about systematic oppression. We cannot not talk about these conditions that affect our mental well-being and our feeling and desire to live.”
For Jamal Clay in Illinois, the systemic barriers started early. Before his suicide last year, he had tried to harm himself when he was 12 and the victim of bullies. At that time, he was hospitalized for a few days and told to follow up with outpatient therapy, said his mother, Maxie.
But it was difficult to find therapists who accepted Medicaid, she said. When Maxie finally found one, there was a 60-day wait. Other therapists canceled appointments, she said.
“So we worked on our own,” Maxie said, relying on church and community. Her son seemed to improve. “We thought we closed that chapter in our lives.”
But when the pandemic hit, everything got worse, she said. Clay came home from college and worked at an Amazon warehouse. On drives to and from work, he was frequently pulled over by police. He stopped wearing hats so officers would consider him less intimidating, Maxie said.
“He felt uncomfortable being out in the street,” she said.
Maxie is still trying to make sense of what happened the day Clay died. But she’s found meaning in starting a nonprofit called Soul Survivors of Chicago. Through the organization, she provides education, scholarships and shoes – including Jamal’s old ones – to those impacted by violence, suicide, and trauma.
“My son won’t be able to have a first interview in [those] shoes. He won’t be able to have a nice jump shot or go to church or even meet his wife,” Maxie said.
But she hopes his shoes will carry someone else to a good future.
[Editor’s note: For the purposes of this story, “people of color” or “communities of color” refers to any racial or ethnic populations whose members do not identify as White, including those who are multiracial. Hispanics can be of any race or combination of races.]
KHN senior correspondent JoNel Aleccia contributed to this report. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
This story is a collaboration between KHN and “Science Friday.”
Rafiah Maxie has been a licensed clinical social worker in the Chicago area for a decade. Throughout that time, she’d viewed suicide as a problem most prevalent among middle-aged white men.
Until May 27, 2020.
That day, Maxie’s 19-year-old son, Jamal Clay – who loved playing the trumpet and participating in theater, who would help her unload groceries from the car and raise funds for the March of the Dimes – killed himself in their garage.
“Now I cannot blink without seeing my son hanging,” said Maxie, who is Black.
Clay’s death, along with the suicides of more than 100 other Black residents in Illinois last year, has led locals to call for new prevention efforts focused on Black communities. In 2020, during the pandemic’s first year, suicides among White residents decreased compared with previous years, while they increased among Black residents, according to state data.
But this is not a local problem. Nor is it limited to the pandemic.
Interviews with a dozen suicide researchers, data collected from states across the country, and a review of decades of research revealed that suicide is a growing crisis for communities of color – one that plagued them well before the pandemic and has only been exacerbated since.
Overall suicide rates in the U.S. decreased in 2019 and 2020. National and local studies attribute the trend to a drop among White Americans, who make up the majority of suicide deaths. Meanwhile, rates for Black, Hispanic, and Asian Americans – though lower than those of their white peers – continued to climb in many states. (Suicide rates have been consistently high for Native Americans.)
“COVID created more transparency regarding what we already knew was happening,” said Sonyia Richardson, a licensed clinical social worker who focuses on serving people of color, and assistant professor at the University of North Carolina–Charlotte, where she researches suicide. When you put the suicide rates of all communities in one bucket, “that bucket says it’s getting better and what we’re doing is working,” she said. “But that’s not the case for communities of color.”
Losing generations
Although the suicide rate is highest among middle-aged White men, young people of color are emerging as particularly at risk.
Research shows Black kids younger than 13 die by suicide at nearly twice the rate of White kids and, over time, their suicide rates have grown even as rates have decreased for White children. Among teenagers and young adults, suicide deaths have increased more than 45% for Black Americans and about 40% for Asian Americans in the 7 years ending in 2019. Other concerning trends in suicide attempts date to the ’90s.
“We have to pay attention now because if you’re out of the first decade of life and think life is not worth pursuing, that’s a signal to say something is going really wrong.”
These statistics also refute traditional ideas that suicide doesn’t happen in certain ethnic or minority populations because they’re “protected” and “resilient” or the “model minority,” said Kiara Alvarez, a researcher and psychologist at Massachusetts General Hospital who focuses on suicide among Hispanic and immigrant populations.
Although these groups may have had low suicide rates historically, that’s changing, she said.
Paul Chin lost his 17-year-old brother, Chris, to suicide in 2009. A poem Chris wrote in high school about his heritage has left Chin, 8 years his senior, wondering if his brother struggled to feel accepted in the U.S., despite being born and raised in New York.
Growing up, Asian Americans weren’t represented in lessons at school or in pop culture, said Chin, now 37. Even in clinical research on suicide as well as other health topics, kids like Chris are underrepresented, with less than 1% of federal research funding focused on Asian Americans.
It wasn’t until the pandemic, and the concurrent rise in hate crimes against Asian Americans, that Chin saw national attention on the community’s mental health. He hopes the interest is not short-lived.
Suicide is the leading cause of death for Asian Americans ages 15 to 24, yet “that doesn’t get enough attention,” Chin said. “It’s important to continue to share these stories.”
Kathy Williams, who is Black, has been on a similar mission since her 15-year-old son, Torian Graves, died by suicide in 1996. People didn’t talk about suicide in the Black community then, she said. So she started raising the topic at her church in Durham, N.C., and in local schools. She wanted Black families to know the warning signs and society at large to recognize the seriousness of the problem.
The pandemic may have highlighted this, Williams said, but “it has always happened. Always.”
Pandemic sheds light on the triggers
Pinpointing the root causes of rising suicide within communities of color has proved difficult. How much stems from mental illness? How much from socioeconomic changes like job losses or social isolation? Now, COVID-19 may offer some clues.
Recent decades have been marked by growing economic instability, a widening racial wealth gap, and more public attention on police killings of unarmed Black and Brown people, said Michael Lindsey, executive director of the New York University McSilver Institute for Poverty Policy and Research.
With social media, youths face racism on more fronts than their parents did, said Leslie Adams, assistant professor in the department of mental health at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Each of these factors has been shown to affect suicide risk. For example, experiencing racism and sexism together is linked to a threefold increase in suicidal thoughts for Asian American women, said Brian Keum, assistant professor at UCLA, based on preliminary research findings.
COVID-19 intensified these hardships among communities of color, with disproportionate numbers of lost loved ones, lost jobs, and lost housing. The murder of George Floyd prompted widespread racial unrest, and Asian Americans saw an increase in hate crimes.
At the same time, studies in Connecticut and Maryland found that suicide rates rose within these populations and dropped for their White counterparts.
“It’s not just a problem within the person, but societal issues that need to be addressed,” said Shari Jager-Hyman, assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania.
Lessons from Texas
In Texas, COVID-19 hit Hispanics especially hard. As of July 2021, they accounted for 45% of all COVID-19 deaths and disproportionately lost jobs. Individuals living in the U.S. without authorization were generally not eligible for unemployment benefits or federal stimulus checks.
During this time, suicide deaths among Hispanic Texans climbed from 847 deaths in 2019 to 962 deaths in 2020, according to preliminary state data. Suicide deaths rose for Black Texans and residents classified as “other” races or ethnicities, but decreased for White Texans.
The numbers didn’t surprise Marc Mendiola. The 20-year-old grew up in a majority-Hispanic community on the south side of San Antonio. Even before the pandemic, he often heard classmates say they were suicidal. Many faced dire finances at home, sometimes living without electricity, food, or water. Those who sought mental health treatment often found services prohibitively expensive or inaccessible because they weren’t offered in Spanish.
“These are conditions the community has always been in,” Mendiola said. “But with the pandemic, it’s even worse.”
Four years ago, Mendiola and his classmates at South San High School began advocating for mental health services. In late 2019, just months before COVID-19 struck, their vision became reality. Six community agencies partnered to offer free services to students and their families across three school districts.
Richard Davidson, chief operating officer of Family Service, one of the groups in the collaborative, said the number of students discussing economic stressors has been on the rise since April 2020. More than 90% of the students who received services in the first half of 2021 were Hispanic, and nearly 10% reported thoughts of suicide or self-harm, program data show. None died by suicide.
Many students are so worried about what’s for dinner the next day that they’re not able to see a future beyond that, Davidson said. That’s when suicide can feel like a viable option.
“One of the things we do is help them see … that despite this situation now, you can create a vision for your future,” Davidson said.
A good future
Researchers say the promise of a good future is often overlooked in suicide prevention, perhaps because achieving it is so challenging. It requires economic and social growth and breaking systemic barriers.
Tevis Simon works to address all those fronts. As a child in West Baltimore, Simon, who is Black, faced poverty and trauma. As an adult, she attempted suicide three times. But now she shares her story with youths across the city to inspire them to overcome challenges. She also talks to politicians, law enforcement agencies, and public policy officials about their responsibilities.
“We can’t not talk about race,” said Simon, 43. “We can’t not talk about systematic oppression. We cannot not talk about these conditions that affect our mental well-being and our feeling and desire to live.”
For Jamal Clay in Illinois, the systemic barriers started early. Before his suicide last year, he had tried to harm himself when he was 12 and the victim of bullies. At that time, he was hospitalized for a few days and told to follow up with outpatient therapy, said his mother, Maxie.
But it was difficult to find therapists who accepted Medicaid, she said. When Maxie finally found one, there was a 60-day wait. Other therapists canceled appointments, she said.
“So we worked on our own,” Maxie said, relying on church and community. Her son seemed to improve. “We thought we closed that chapter in our lives.”
But when the pandemic hit, everything got worse, she said. Clay came home from college and worked at an Amazon warehouse. On drives to and from work, he was frequently pulled over by police. He stopped wearing hats so officers would consider him less intimidating, Maxie said.
“He felt uncomfortable being out in the street,” she said.
Maxie is still trying to make sense of what happened the day Clay died. But she’s found meaning in starting a nonprofit called Soul Survivors of Chicago. Through the organization, she provides education, scholarships and shoes – including Jamal’s old ones – to those impacted by violence, suicide, and trauma.
“My son won’t be able to have a first interview in [those] shoes. He won’t be able to have a nice jump shot or go to church or even meet his wife,” Maxie said.
But she hopes his shoes will carry someone else to a good future.
[Editor’s note: For the purposes of this story, “people of color” or “communities of color” refers to any racial or ethnic populations whose members do not identify as White, including those who are multiracial. Hispanics can be of any race or combination of races.]
KHN senior correspondent JoNel Aleccia contributed to this report. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Most stent misdeployments in EUS-GE are manageable
Most instances of stent misdeployment in cases of endoscopic ultrasound–guided gastroenterostomy (EUS-GE) can be managed endoscopically, based on data from 16 tertiary care centers in the United States and Europe.
EUS-GE provides a viable alternative to traditional surgical gastroenterostomy and stent placement for patients with gastric outlet obstruction (GOO), but the potential for stent misdeployment has limited adoption of the procedure because it remains the most common cause of technical failures and adverse events, Bachir Ghandour, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
However, data on outcomes and management of stent misdeployment during EUS-GE are limited, and the researchers hypothesized that most stent misdeployments could be managed endoscopically.
In a retrospective study published in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the researchers reviewed data from 467 EUS-GE procedures performed for gastric outlet obstruction between March 2015 and December 2020 at eight centers in the United States and eight in Europe. The primary outcome was the rate and severity of stent misdeployment.
Stent misdeployment occurred in 46 patients (9.9%). Of these, 73.2% occurred during the operators’ first 13 cases.
The researchers created a classification system of stent misdeployment according to type, depending on which flange was misdeployed.
Type I was the most common, and occurred in 29 patients; this type was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the peritoneum and proximal flange in the stomach without evidence of a resulting enterotomy”; type II (14 patients) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the peritoneum and proximal flange in the stomach despite an enterotomy (i.e., visual confirmation of stent having penetrated targeted small bowel, under EUS or fluoroscopy, but migrated out on deployment)”; type III (1 patient) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the small bowel and proximal flange in the peritoneum”; and type IV (2 patients) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the colon and proximal flange in the stomach resulting in a gastrocolic anastomosis,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also classified the stent misdeployment in terms of severity as mild (28 patients), moderate (11 patients), severe (6 cases) or fatal (1 case) based on the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy lexicon.
Overall, type I was significantly more likely to be mild in severity, compared with type II (75.9% vs. 42.9%; P = .04), although the rate of surgical repair was similar between these two types (10.3% vs. 7.1%). Rates of ICU admission were approximately 7% in patients with type I and type II stent misdeployments, and the median postprocedural stay was 4 days for these two groups.
Same-session salvage management of GOO was achieved by EUS/endoscopic-GE in 24 patients, duodenal stent placement in 6 patients, duodenal dilation in 1 patient, and gastroenterostomy with natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in 3 patients. Of the remaining 12 patients, GOO was managed with subsequent EUS-GE in 6 patients and surgical GI in 6 patients.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and inclusion of a time period that encompassed changes and improvements in the EUS-GE, the researchers noted. The small sample size of type III and IV stent misdeployments prohibited comparison with other types.
However, the cohort size was relatively large, compared with previous studies, and included a range of centers and countries with different strategies for managing stent misdeployments. Given the steep learning curve for EUS-GE, the study findings may help endoscopists better understand the implications and potential consequences of stent misdeployment by classifying the misdeployments into types. “We believe that such a classification or categorization of the different types is important because patient outcomes vary depending on the specific [stent misdeployment] subtype and site of injury. Such a classification will also be very helpful for future research by standardizing the terminology,” the researchers said.
“Although [stent misdeployment] is not infrequent during EUS-GE, with a rate of approximately 10%, the majority of cases are mild in severity and can be managed or repaired endoscopically without ill consequences,” they concluded. “Surgical intervention is required in less than 11% of the cases.”
Data support safe stent use in GI disease
“The lines continue to be blurred between surgical and endoscopic management of gastrointestinal disease, especially with a rise in therapeutic EUS,” Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview.
“Stent misdeployment has been commonly reported during EUS-GE and may limit uptake of this more technically challenging procedure,” Dr. Ketwaroo said. “A comprehensive assessment of stent misdeployment, with suggestions for management and a classification system that predicts outcomes, can help practitioners to more confidently perform this procedure.”
Risks associated with misdeployed stents include “inability to perform the endoscopic management of gastric outlet obstruction, as well as adverse events such as peritonitis,” said Dr. Ketwaroo. He noted that, in most cases, the defect was closed and same-session salvage was performed, primarily by repeat EUS-GE.
Dr. Ketwaroo highlighted one challenge to endoscopic management of stent misdeployment. “If the proximal flange is deployed/slips into peritoneum (type III by currently proposed classification system), it can be more difficult to retrieve the stent,” but “this complication was treated with surgery, and it was very rare – only one case of this in the study,” he explained. “This is a large retrospective multicenter study, which adds validity to the generalizability of the study.” However, prospective studies will be needed as EUS-GE is more widely adopted, he added.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Ghandour had no financial conflicts to disclose. Other authors disclosed industry relationships, such as consulting for Boston Scientific, Apollo, Olympus America, Medtronic, and GI Supply. Dr. Ketwaroo had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News editorial advisory board.
Most instances of stent misdeployment in cases of endoscopic ultrasound–guided gastroenterostomy (EUS-GE) can be managed endoscopically, based on data from 16 tertiary care centers in the United States and Europe.
EUS-GE provides a viable alternative to traditional surgical gastroenterostomy and stent placement for patients with gastric outlet obstruction (GOO), but the potential for stent misdeployment has limited adoption of the procedure because it remains the most common cause of technical failures and adverse events, Bachir Ghandour, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
However, data on outcomes and management of stent misdeployment during EUS-GE are limited, and the researchers hypothesized that most stent misdeployments could be managed endoscopically.
In a retrospective study published in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the researchers reviewed data from 467 EUS-GE procedures performed for gastric outlet obstruction between March 2015 and December 2020 at eight centers in the United States and eight in Europe. The primary outcome was the rate and severity of stent misdeployment.
Stent misdeployment occurred in 46 patients (9.9%). Of these, 73.2% occurred during the operators’ first 13 cases.
The researchers created a classification system of stent misdeployment according to type, depending on which flange was misdeployed.
Type I was the most common, and occurred in 29 patients; this type was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the peritoneum and proximal flange in the stomach without evidence of a resulting enterotomy”; type II (14 patients) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the peritoneum and proximal flange in the stomach despite an enterotomy (i.e., visual confirmation of stent having penetrated targeted small bowel, under EUS or fluoroscopy, but migrated out on deployment)”; type III (1 patient) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the small bowel and proximal flange in the peritoneum”; and type IV (2 patients) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the colon and proximal flange in the stomach resulting in a gastrocolic anastomosis,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also classified the stent misdeployment in terms of severity as mild (28 patients), moderate (11 patients), severe (6 cases) or fatal (1 case) based on the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy lexicon.
Overall, type I was significantly more likely to be mild in severity, compared with type II (75.9% vs. 42.9%; P = .04), although the rate of surgical repair was similar between these two types (10.3% vs. 7.1%). Rates of ICU admission were approximately 7% in patients with type I and type II stent misdeployments, and the median postprocedural stay was 4 days for these two groups.
Same-session salvage management of GOO was achieved by EUS/endoscopic-GE in 24 patients, duodenal stent placement in 6 patients, duodenal dilation in 1 patient, and gastroenterostomy with natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in 3 patients. Of the remaining 12 patients, GOO was managed with subsequent EUS-GE in 6 patients and surgical GI in 6 patients.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and inclusion of a time period that encompassed changes and improvements in the EUS-GE, the researchers noted. The small sample size of type III and IV stent misdeployments prohibited comparison with other types.
However, the cohort size was relatively large, compared with previous studies, and included a range of centers and countries with different strategies for managing stent misdeployments. Given the steep learning curve for EUS-GE, the study findings may help endoscopists better understand the implications and potential consequences of stent misdeployment by classifying the misdeployments into types. “We believe that such a classification or categorization of the different types is important because patient outcomes vary depending on the specific [stent misdeployment] subtype and site of injury. Such a classification will also be very helpful for future research by standardizing the terminology,” the researchers said.
“Although [stent misdeployment] is not infrequent during EUS-GE, with a rate of approximately 10%, the majority of cases are mild in severity and can be managed or repaired endoscopically without ill consequences,” they concluded. “Surgical intervention is required in less than 11% of the cases.”
Data support safe stent use in GI disease
“The lines continue to be blurred between surgical and endoscopic management of gastrointestinal disease, especially with a rise in therapeutic EUS,” Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview.
“Stent misdeployment has been commonly reported during EUS-GE and may limit uptake of this more technically challenging procedure,” Dr. Ketwaroo said. “A comprehensive assessment of stent misdeployment, with suggestions for management and a classification system that predicts outcomes, can help practitioners to more confidently perform this procedure.”
Risks associated with misdeployed stents include “inability to perform the endoscopic management of gastric outlet obstruction, as well as adverse events such as peritonitis,” said Dr. Ketwaroo. He noted that, in most cases, the defect was closed and same-session salvage was performed, primarily by repeat EUS-GE.
Dr. Ketwaroo highlighted one challenge to endoscopic management of stent misdeployment. “If the proximal flange is deployed/slips into peritoneum (type III by currently proposed classification system), it can be more difficult to retrieve the stent,” but “this complication was treated with surgery, and it was very rare – only one case of this in the study,” he explained. “This is a large retrospective multicenter study, which adds validity to the generalizability of the study.” However, prospective studies will be needed as EUS-GE is more widely adopted, he added.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Ghandour had no financial conflicts to disclose. Other authors disclosed industry relationships, such as consulting for Boston Scientific, Apollo, Olympus America, Medtronic, and GI Supply. Dr. Ketwaroo had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News editorial advisory board.
Most instances of stent misdeployment in cases of endoscopic ultrasound–guided gastroenterostomy (EUS-GE) can be managed endoscopically, based on data from 16 tertiary care centers in the United States and Europe.
EUS-GE provides a viable alternative to traditional surgical gastroenterostomy and stent placement for patients with gastric outlet obstruction (GOO), but the potential for stent misdeployment has limited adoption of the procedure because it remains the most common cause of technical failures and adverse events, Bachir Ghandour, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
However, data on outcomes and management of stent misdeployment during EUS-GE are limited, and the researchers hypothesized that most stent misdeployments could be managed endoscopically.
In a retrospective study published in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the researchers reviewed data from 467 EUS-GE procedures performed for gastric outlet obstruction between March 2015 and December 2020 at eight centers in the United States and eight in Europe. The primary outcome was the rate and severity of stent misdeployment.
Stent misdeployment occurred in 46 patients (9.9%). Of these, 73.2% occurred during the operators’ first 13 cases.
The researchers created a classification system of stent misdeployment according to type, depending on which flange was misdeployed.
Type I was the most common, and occurred in 29 patients; this type was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the peritoneum and proximal flange in the stomach without evidence of a resulting enterotomy”; type II (14 patients) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the peritoneum and proximal flange in the stomach despite an enterotomy (i.e., visual confirmation of stent having penetrated targeted small bowel, under EUS or fluoroscopy, but migrated out on deployment)”; type III (1 patient) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the small bowel and proximal flange in the peritoneum”; and type IV (2 patients) was defined as “the deployment of the distal flange in the colon and proximal flange in the stomach resulting in a gastrocolic anastomosis,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also classified the stent misdeployment in terms of severity as mild (28 patients), moderate (11 patients), severe (6 cases) or fatal (1 case) based on the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy lexicon.
Overall, type I was significantly more likely to be mild in severity, compared with type II (75.9% vs. 42.9%; P = .04), although the rate of surgical repair was similar between these two types (10.3% vs. 7.1%). Rates of ICU admission were approximately 7% in patients with type I and type II stent misdeployments, and the median postprocedural stay was 4 days for these two groups.
Same-session salvage management of GOO was achieved by EUS/endoscopic-GE in 24 patients, duodenal stent placement in 6 patients, duodenal dilation in 1 patient, and gastroenterostomy with natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in 3 patients. Of the remaining 12 patients, GOO was managed with subsequent EUS-GE in 6 patients and surgical GI in 6 patients.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and inclusion of a time period that encompassed changes and improvements in the EUS-GE, the researchers noted. The small sample size of type III and IV stent misdeployments prohibited comparison with other types.
However, the cohort size was relatively large, compared with previous studies, and included a range of centers and countries with different strategies for managing stent misdeployments. Given the steep learning curve for EUS-GE, the study findings may help endoscopists better understand the implications and potential consequences of stent misdeployment by classifying the misdeployments into types. “We believe that such a classification or categorization of the different types is important because patient outcomes vary depending on the specific [stent misdeployment] subtype and site of injury. Such a classification will also be very helpful for future research by standardizing the terminology,” the researchers said.
“Although [stent misdeployment] is not infrequent during EUS-GE, with a rate of approximately 10%, the majority of cases are mild in severity and can be managed or repaired endoscopically without ill consequences,” they concluded. “Surgical intervention is required in less than 11% of the cases.”
Data support safe stent use in GI disease
“The lines continue to be blurred between surgical and endoscopic management of gastrointestinal disease, especially with a rise in therapeutic EUS,” Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview.
“Stent misdeployment has been commonly reported during EUS-GE and may limit uptake of this more technically challenging procedure,” Dr. Ketwaroo said. “A comprehensive assessment of stent misdeployment, with suggestions for management and a classification system that predicts outcomes, can help practitioners to more confidently perform this procedure.”
Risks associated with misdeployed stents include “inability to perform the endoscopic management of gastric outlet obstruction, as well as adverse events such as peritonitis,” said Dr. Ketwaroo. He noted that, in most cases, the defect was closed and same-session salvage was performed, primarily by repeat EUS-GE.
Dr. Ketwaroo highlighted one challenge to endoscopic management of stent misdeployment. “If the proximal flange is deployed/slips into peritoneum (type III by currently proposed classification system), it can be more difficult to retrieve the stent,” but “this complication was treated with surgery, and it was very rare – only one case of this in the study,” he explained. “This is a large retrospective multicenter study, which adds validity to the generalizability of the study.” However, prospective studies will be needed as EUS-GE is more widely adopted, he added.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Ghandour had no financial conflicts to disclose. Other authors disclosed industry relationships, such as consulting for Boston Scientific, Apollo, Olympus America, Medtronic, and GI Supply. Dr. Ketwaroo had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News editorial advisory board.
FROM GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
Peanut allergy patients reap continuing benefits past first year, Palforzia study shows
A recent analysis of 142 peanut-allergic children treated for 1.5 to 2 years with a licensed oral immunotherapy (OIT) product confirms what various smaller studies have shown: Maintaining treatment for longer periods improves protection and reduces adverse effects. The findings offer some reassurance regarding the controversial approach, which has become available at a small number of clinics yet faces an uncertain future.
The new study, published July 28 in Allergy, included a subset of patients who chose to complete an extension of the phase 3 PALISADE trial of Palforzia, a proprietary set of premeasured peanut flour capsules developed by Aimmune Therapeutics.
Palforzia was approved last year for children aged 4 to 17 years with peanut allergy – one of the most common food allergies, affecting around 2% of children in the United States and Europe. The treatment is not a cure – patients must still watch what they eat and carry epinephrine for emergency reactions – but it helps build protection through daily ingestion of gradually increasing amounts of the allergen over a period of months.
In the 1-year PALISADE trial, which enrolled 496 peanut-allergic children at 66 sites in North America and Europe, participants received daily doses of study drug or placebo. The dose of the drug was escalated from 3 mg to 300 mg over 6 months; the 300-mg dose was then maintained for another 6 months. By the end of the study, about two-thirds of the children who underwent treatment could safely consume at least 600 mg of peanut protein, about the equivalent of two peanuts.
Could protection be increased with further treatment, and what would be required to sustain it? To address these questions, PALISADE patients who successfully reached the 600-mg threshold, along with those from the placebo group, were invited to participate in Aimmune’s open-label follow-on study. The extension study also explored whether protection could be maintained with less frequent dosing.
Among the 358 eligible participants who opted into the 1-year extension study, 256 came from the PALISADE treatment arm. These children were assigned to five cohorts to continue for 6 months or 12 months with daily or less frequent doses. Within the 6-month group, all started with the 300-mg daily dose. A subset received two doses a week. Within the 12-month group, some patients maintained daily dosing throughout; others received doses every other day, twice weekly, or once every 2 weeks.
The children who continued daily maintenance dosing the longest gained the most protection. Those in less-frequent dosing groups experienced more adverse events than those who received doses every day, the company reported last December in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
More than a quarter (97 of 358, or 27.1%) of participants failed to complete the extension. Families could withdraw any time for any reason. Participating in an OIT trial is demanding – it requires office visits for dosing adjustments and blood tests, rest periods, keeping symptom logs in which daily doses are recorded, and possible allergic reactions from the treatment itself. “A common reason for ‘withdrawal of consent’ in clinical studies is the inconvenience of remaining in a long-term study,” Mohamed Yassine, MD, Aimmune’s senior vice present of medical affairs, said via email.
Attrition was concentrated within certain subgroups. Most participants in (88.7%; 102 of 115) PALISADE who received placebo elected to enter the open-label extension; nearly half did not finish. Dropout rates were also high (29.2%) for non-daily dosing participants who had come from the PALISADE treatment arm.
The authors did not report on those high-dropout groups. Instead, they focused their analysis on the 142 treated PALISADE participants who continued daily dosing through the extension – 110 patients for a total of about 1.5 years and 32 patients for about 2 years. In a subgroup analysis, 48.1% of children in the 1.5-year group upped their tolerance to 2,000 mg peanut protein, and even more (80.8%) in the 2-year group reached that threshold – all while taking a 300-mg maintenance dose.
Those who remained on treatment longer also had fewer adverse events. At the exit food challenge, 24% of the 1.5-year participants had reactions that required epinephrine, but among 2-year participants, only 3.8% needed the rescue medication.
Continuing therapy past the first year seemed to have additional benefits, Sandra Hong, MD, director of the Cleveland Clinic Food Allergy Center of Excellence, said in an interview. Dr. Hong was not involved in the new research and has no financial ties with Aimmune or other food allergy companies. “Not only can you ingest more, but your reaction when you do react is going to be less,” she says.
Palforzia is only available through a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program, which educates patients, health care professionals, and pharmacies about immunotherapy risks and precautionary measures. As of last summer, before Aimmune was acquired by Nestlé Health Science, about 100 allergists in the United States had enrolled patients in the REMS program. Families can find allergists who are certified to prescribe Palforzia using the website’s Certified Participant Locator.
Although the field at large remains apprehensive about OIT and other forms of immunotherapy, an estimated 200 or more U.S. clinics are administering home-grown OIT using commercial food products, says Richard Wasserman, an OIT pioneer whose clinic in Dallas has treated allergies to about 20 foods since the practice started offering the therapy in 2008. OIT practitioners have treated more than 15,000 food allergy patients nationwide, Dr. Wasserman said via email, yet they make up just a tiny fraction of the more than 6,000 board-certified allergists in the United States.
Whether using Palforzia or nonproprietary food products, oral immunotherapy requires a lot of time and effort – not just for patients but also practitioners. “You need more space. You need more staffing. Patients doing oral challenges stay in your office for 4 to 5 hours, and we have one-to-one nursing care for them,” said Dr. Hong. “So it’s a lot of resources.”
Her team has treated about 20 children with Palforzia since the Cleveland Clinic began offering the therapy last summer. Dr. Hong and coworkers have administered OIT using commercial peanut flour and peanut butter to some 80 peanut-allergic toddlers younger than 4 years who are too young to receive for the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment. Their early data, which were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology in February, suggest that toddlers get complete OIT more quickly with fewer side effects than older children, Dr. Hong says. A recent study of preschoolers in Canada also found that nonproprietary OIT is very safe and effective in this younger set and could be cost-saving in the long run.
By comparison, Palforzia, which has a list price of $890 per month, was judged to be less cost-effective in analyses by academic allergists and by the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review. But through a copay savings program, depending on their insurance coverage, some eligible families can pay as little as $20 per month for the FDA-approved treatment.
Because the therapy is time consuming for families and is resource intensive for practices, questions remain as to how long and how frequently patients need to remain on treatment to sustain protection. Do they need to keep taking Palforzia, or “can we switch them to an equivalent amount of food and not bother with the study drug?” said Edwin Kim, director of the UNC Food Allergy Initiative, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, and study investigator for several Palforzia trials, in an interview.
The Food Allergy Support Team, a nonprofit group started by Dr. Wasserman and colleagues, publishes best practices and meets annually to discuss research and protocols. However, the best maintenance dose, the best dosing frequency, and the duration of daily dosing that yields the best outcomes are not known, Dr. Wasserman says.
“We think the best way to answer that question is with a regulated, pharmaceutical-grade form of peanut protein,” Dr. Yassine said.
The field’s experience with Palforzia raises a dilemma: Does its approval legitimize oral immunotherapy in general, or will rigorous, multi-million dollar trials be needed to approve products for each food or combination of foods? About 32 million people in the United States have food allergies – about 1 in 10 adults and 1 in 13 children.
“I think the field has always grappled with that, honestly,” said Stacie Jones, MD, professor of pediatrics and chief of allergy and immunology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, in an interview. Home-grown OIT is “easier to do when you have high control of your small patient volumes or you’re in a clinical trial,” said Dr. Jones, who has served as an investigator on Palforzia trials and last year received more than $30,000 in consulting fees from Aimmune. “It becomes a very different situation when it becomes a national or an international recommended therapy.”
The Canadian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology has published clinical practice guidelines and provides practical information on its website on how to implement OIT – including protocols for dozens of foods and diary sheets for patients to log doses and symptoms.
However, U.S. professional societies still consider OIT investigational and suggest that it will not be approved by the FDA. “As a field, are we willing to wait 4 to 5 more years for an egg product? Should we? Are we willing?” said Dr. Kim. “These are tough questions.”
Stacie M. Jones reports advisory board fees, Aimmune Therapeutics, FARE; personal fees, DBV Technologies; clinical trials grants, Aimmune Therapeutics, DBV Technologies, Astellas, Sanofi, Regeneron, FARE, Genentech, and NIH-NIAID. Edwin Kim reports consultancy with Aimmune Therapeutics, Allako, AllerGenis, Belhaven Pharma, DBV Technologies, Duke Clinical Research Institute, and Nutricia; advisory board membership with ALK, DBV Technologies, Kenota Health, and Ukko; grant support from the NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health and Immune Tolerance Network; Food Allergy Research and Education, and the Wallace Research Foundation. Richard Wasserman receives consulting fees from Aimmune Therapeutics and DBV Technologies. Mohamed Yassine is employed by Aimmune Therapeutics. Sandra Hong has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent analysis of 142 peanut-allergic children treated for 1.5 to 2 years with a licensed oral immunotherapy (OIT) product confirms what various smaller studies have shown: Maintaining treatment for longer periods improves protection and reduces adverse effects. The findings offer some reassurance regarding the controversial approach, which has become available at a small number of clinics yet faces an uncertain future.
The new study, published July 28 in Allergy, included a subset of patients who chose to complete an extension of the phase 3 PALISADE trial of Palforzia, a proprietary set of premeasured peanut flour capsules developed by Aimmune Therapeutics.
Palforzia was approved last year for children aged 4 to 17 years with peanut allergy – one of the most common food allergies, affecting around 2% of children in the United States and Europe. The treatment is not a cure – patients must still watch what they eat and carry epinephrine for emergency reactions – but it helps build protection through daily ingestion of gradually increasing amounts of the allergen over a period of months.
In the 1-year PALISADE trial, which enrolled 496 peanut-allergic children at 66 sites in North America and Europe, participants received daily doses of study drug or placebo. The dose of the drug was escalated from 3 mg to 300 mg over 6 months; the 300-mg dose was then maintained for another 6 months. By the end of the study, about two-thirds of the children who underwent treatment could safely consume at least 600 mg of peanut protein, about the equivalent of two peanuts.
Could protection be increased with further treatment, and what would be required to sustain it? To address these questions, PALISADE patients who successfully reached the 600-mg threshold, along with those from the placebo group, were invited to participate in Aimmune’s open-label follow-on study. The extension study also explored whether protection could be maintained with less frequent dosing.
Among the 358 eligible participants who opted into the 1-year extension study, 256 came from the PALISADE treatment arm. These children were assigned to five cohorts to continue for 6 months or 12 months with daily or less frequent doses. Within the 6-month group, all started with the 300-mg daily dose. A subset received two doses a week. Within the 12-month group, some patients maintained daily dosing throughout; others received doses every other day, twice weekly, or once every 2 weeks.
The children who continued daily maintenance dosing the longest gained the most protection. Those in less-frequent dosing groups experienced more adverse events than those who received doses every day, the company reported last December in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
More than a quarter (97 of 358, or 27.1%) of participants failed to complete the extension. Families could withdraw any time for any reason. Participating in an OIT trial is demanding – it requires office visits for dosing adjustments and blood tests, rest periods, keeping symptom logs in which daily doses are recorded, and possible allergic reactions from the treatment itself. “A common reason for ‘withdrawal of consent’ in clinical studies is the inconvenience of remaining in a long-term study,” Mohamed Yassine, MD, Aimmune’s senior vice present of medical affairs, said via email.
Attrition was concentrated within certain subgroups. Most participants in (88.7%; 102 of 115) PALISADE who received placebo elected to enter the open-label extension; nearly half did not finish. Dropout rates were also high (29.2%) for non-daily dosing participants who had come from the PALISADE treatment arm.
The authors did not report on those high-dropout groups. Instead, they focused their analysis on the 142 treated PALISADE participants who continued daily dosing through the extension – 110 patients for a total of about 1.5 years and 32 patients for about 2 years. In a subgroup analysis, 48.1% of children in the 1.5-year group upped their tolerance to 2,000 mg peanut protein, and even more (80.8%) in the 2-year group reached that threshold – all while taking a 300-mg maintenance dose.
Those who remained on treatment longer also had fewer adverse events. At the exit food challenge, 24% of the 1.5-year participants had reactions that required epinephrine, but among 2-year participants, only 3.8% needed the rescue medication.
Continuing therapy past the first year seemed to have additional benefits, Sandra Hong, MD, director of the Cleveland Clinic Food Allergy Center of Excellence, said in an interview. Dr. Hong was not involved in the new research and has no financial ties with Aimmune or other food allergy companies. “Not only can you ingest more, but your reaction when you do react is going to be less,” she says.
Palforzia is only available through a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program, which educates patients, health care professionals, and pharmacies about immunotherapy risks and precautionary measures. As of last summer, before Aimmune was acquired by Nestlé Health Science, about 100 allergists in the United States had enrolled patients in the REMS program. Families can find allergists who are certified to prescribe Palforzia using the website’s Certified Participant Locator.
Although the field at large remains apprehensive about OIT and other forms of immunotherapy, an estimated 200 or more U.S. clinics are administering home-grown OIT using commercial food products, says Richard Wasserman, an OIT pioneer whose clinic in Dallas has treated allergies to about 20 foods since the practice started offering the therapy in 2008. OIT practitioners have treated more than 15,000 food allergy patients nationwide, Dr. Wasserman said via email, yet they make up just a tiny fraction of the more than 6,000 board-certified allergists in the United States.
Whether using Palforzia or nonproprietary food products, oral immunotherapy requires a lot of time and effort – not just for patients but also practitioners. “You need more space. You need more staffing. Patients doing oral challenges stay in your office for 4 to 5 hours, and we have one-to-one nursing care for them,” said Dr. Hong. “So it’s a lot of resources.”
Her team has treated about 20 children with Palforzia since the Cleveland Clinic began offering the therapy last summer. Dr. Hong and coworkers have administered OIT using commercial peanut flour and peanut butter to some 80 peanut-allergic toddlers younger than 4 years who are too young to receive for the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment. Their early data, which were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology in February, suggest that toddlers get complete OIT more quickly with fewer side effects than older children, Dr. Hong says. A recent study of preschoolers in Canada also found that nonproprietary OIT is very safe and effective in this younger set and could be cost-saving in the long run.
By comparison, Palforzia, which has a list price of $890 per month, was judged to be less cost-effective in analyses by academic allergists and by the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review. But through a copay savings program, depending on their insurance coverage, some eligible families can pay as little as $20 per month for the FDA-approved treatment.
Because the therapy is time consuming for families and is resource intensive for practices, questions remain as to how long and how frequently patients need to remain on treatment to sustain protection. Do they need to keep taking Palforzia, or “can we switch them to an equivalent amount of food and not bother with the study drug?” said Edwin Kim, director of the UNC Food Allergy Initiative, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, and study investigator for several Palforzia trials, in an interview.
The Food Allergy Support Team, a nonprofit group started by Dr. Wasserman and colleagues, publishes best practices and meets annually to discuss research and protocols. However, the best maintenance dose, the best dosing frequency, and the duration of daily dosing that yields the best outcomes are not known, Dr. Wasserman says.
“We think the best way to answer that question is with a regulated, pharmaceutical-grade form of peanut protein,” Dr. Yassine said.
The field’s experience with Palforzia raises a dilemma: Does its approval legitimize oral immunotherapy in general, or will rigorous, multi-million dollar trials be needed to approve products for each food or combination of foods? About 32 million people in the United States have food allergies – about 1 in 10 adults and 1 in 13 children.
“I think the field has always grappled with that, honestly,” said Stacie Jones, MD, professor of pediatrics and chief of allergy and immunology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, in an interview. Home-grown OIT is “easier to do when you have high control of your small patient volumes or you’re in a clinical trial,” said Dr. Jones, who has served as an investigator on Palforzia trials and last year received more than $30,000 in consulting fees from Aimmune. “It becomes a very different situation when it becomes a national or an international recommended therapy.”
The Canadian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology has published clinical practice guidelines and provides practical information on its website on how to implement OIT – including protocols for dozens of foods and diary sheets for patients to log doses and symptoms.
However, U.S. professional societies still consider OIT investigational and suggest that it will not be approved by the FDA. “As a field, are we willing to wait 4 to 5 more years for an egg product? Should we? Are we willing?” said Dr. Kim. “These are tough questions.”
Stacie M. Jones reports advisory board fees, Aimmune Therapeutics, FARE; personal fees, DBV Technologies; clinical trials grants, Aimmune Therapeutics, DBV Technologies, Astellas, Sanofi, Regeneron, FARE, Genentech, and NIH-NIAID. Edwin Kim reports consultancy with Aimmune Therapeutics, Allako, AllerGenis, Belhaven Pharma, DBV Technologies, Duke Clinical Research Institute, and Nutricia; advisory board membership with ALK, DBV Technologies, Kenota Health, and Ukko; grant support from the NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health and Immune Tolerance Network; Food Allergy Research and Education, and the Wallace Research Foundation. Richard Wasserman receives consulting fees from Aimmune Therapeutics and DBV Technologies. Mohamed Yassine is employed by Aimmune Therapeutics. Sandra Hong has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent analysis of 142 peanut-allergic children treated for 1.5 to 2 years with a licensed oral immunotherapy (OIT) product confirms what various smaller studies have shown: Maintaining treatment for longer periods improves protection and reduces adverse effects. The findings offer some reassurance regarding the controversial approach, which has become available at a small number of clinics yet faces an uncertain future.
The new study, published July 28 in Allergy, included a subset of patients who chose to complete an extension of the phase 3 PALISADE trial of Palforzia, a proprietary set of premeasured peanut flour capsules developed by Aimmune Therapeutics.
Palforzia was approved last year for children aged 4 to 17 years with peanut allergy – one of the most common food allergies, affecting around 2% of children in the United States and Europe. The treatment is not a cure – patients must still watch what they eat and carry epinephrine for emergency reactions – but it helps build protection through daily ingestion of gradually increasing amounts of the allergen over a period of months.
In the 1-year PALISADE trial, which enrolled 496 peanut-allergic children at 66 sites in North America and Europe, participants received daily doses of study drug or placebo. The dose of the drug was escalated from 3 mg to 300 mg over 6 months; the 300-mg dose was then maintained for another 6 months. By the end of the study, about two-thirds of the children who underwent treatment could safely consume at least 600 mg of peanut protein, about the equivalent of two peanuts.
Could protection be increased with further treatment, and what would be required to sustain it? To address these questions, PALISADE patients who successfully reached the 600-mg threshold, along with those from the placebo group, were invited to participate in Aimmune’s open-label follow-on study. The extension study also explored whether protection could be maintained with less frequent dosing.
Among the 358 eligible participants who opted into the 1-year extension study, 256 came from the PALISADE treatment arm. These children were assigned to five cohorts to continue for 6 months or 12 months with daily or less frequent doses. Within the 6-month group, all started with the 300-mg daily dose. A subset received two doses a week. Within the 12-month group, some patients maintained daily dosing throughout; others received doses every other day, twice weekly, or once every 2 weeks.
The children who continued daily maintenance dosing the longest gained the most protection. Those in less-frequent dosing groups experienced more adverse events than those who received doses every day, the company reported last December in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
More than a quarter (97 of 358, or 27.1%) of participants failed to complete the extension. Families could withdraw any time for any reason. Participating in an OIT trial is demanding – it requires office visits for dosing adjustments and blood tests, rest periods, keeping symptom logs in which daily doses are recorded, and possible allergic reactions from the treatment itself. “A common reason for ‘withdrawal of consent’ in clinical studies is the inconvenience of remaining in a long-term study,” Mohamed Yassine, MD, Aimmune’s senior vice present of medical affairs, said via email.
Attrition was concentrated within certain subgroups. Most participants in (88.7%; 102 of 115) PALISADE who received placebo elected to enter the open-label extension; nearly half did not finish. Dropout rates were also high (29.2%) for non-daily dosing participants who had come from the PALISADE treatment arm.
The authors did not report on those high-dropout groups. Instead, they focused their analysis on the 142 treated PALISADE participants who continued daily dosing through the extension – 110 patients for a total of about 1.5 years and 32 patients for about 2 years. In a subgroup analysis, 48.1% of children in the 1.5-year group upped their tolerance to 2,000 mg peanut protein, and even more (80.8%) in the 2-year group reached that threshold – all while taking a 300-mg maintenance dose.
Those who remained on treatment longer also had fewer adverse events. At the exit food challenge, 24% of the 1.5-year participants had reactions that required epinephrine, but among 2-year participants, only 3.8% needed the rescue medication.
Continuing therapy past the first year seemed to have additional benefits, Sandra Hong, MD, director of the Cleveland Clinic Food Allergy Center of Excellence, said in an interview. Dr. Hong was not involved in the new research and has no financial ties with Aimmune or other food allergy companies. “Not only can you ingest more, but your reaction when you do react is going to be less,” she says.
Palforzia is only available through a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program, which educates patients, health care professionals, and pharmacies about immunotherapy risks and precautionary measures. As of last summer, before Aimmune was acquired by Nestlé Health Science, about 100 allergists in the United States had enrolled patients in the REMS program. Families can find allergists who are certified to prescribe Palforzia using the website’s Certified Participant Locator.
Although the field at large remains apprehensive about OIT and other forms of immunotherapy, an estimated 200 or more U.S. clinics are administering home-grown OIT using commercial food products, says Richard Wasserman, an OIT pioneer whose clinic in Dallas has treated allergies to about 20 foods since the practice started offering the therapy in 2008. OIT practitioners have treated more than 15,000 food allergy patients nationwide, Dr. Wasserman said via email, yet they make up just a tiny fraction of the more than 6,000 board-certified allergists in the United States.
Whether using Palforzia or nonproprietary food products, oral immunotherapy requires a lot of time and effort – not just for patients but also practitioners. “You need more space. You need more staffing. Patients doing oral challenges stay in your office for 4 to 5 hours, and we have one-to-one nursing care for them,” said Dr. Hong. “So it’s a lot of resources.”
Her team has treated about 20 children with Palforzia since the Cleveland Clinic began offering the therapy last summer. Dr. Hong and coworkers have administered OIT using commercial peanut flour and peanut butter to some 80 peanut-allergic toddlers younger than 4 years who are too young to receive for the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment. Their early data, which were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology in February, suggest that toddlers get complete OIT more quickly with fewer side effects than older children, Dr. Hong says. A recent study of preschoolers in Canada also found that nonproprietary OIT is very safe and effective in this younger set and could be cost-saving in the long run.
By comparison, Palforzia, which has a list price of $890 per month, was judged to be less cost-effective in analyses by academic allergists and by the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review. But through a copay savings program, depending on their insurance coverage, some eligible families can pay as little as $20 per month for the FDA-approved treatment.
Because the therapy is time consuming for families and is resource intensive for practices, questions remain as to how long and how frequently patients need to remain on treatment to sustain protection. Do they need to keep taking Palforzia, or “can we switch them to an equivalent amount of food and not bother with the study drug?” said Edwin Kim, director of the UNC Food Allergy Initiative, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, and study investigator for several Palforzia trials, in an interview.
The Food Allergy Support Team, a nonprofit group started by Dr. Wasserman and colleagues, publishes best practices and meets annually to discuss research and protocols. However, the best maintenance dose, the best dosing frequency, and the duration of daily dosing that yields the best outcomes are not known, Dr. Wasserman says.
“We think the best way to answer that question is with a regulated, pharmaceutical-grade form of peanut protein,” Dr. Yassine said.
The field’s experience with Palforzia raises a dilemma: Does its approval legitimize oral immunotherapy in general, or will rigorous, multi-million dollar trials be needed to approve products for each food or combination of foods? About 32 million people in the United States have food allergies – about 1 in 10 adults and 1 in 13 children.
“I think the field has always grappled with that, honestly,” said Stacie Jones, MD, professor of pediatrics and chief of allergy and immunology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, in an interview. Home-grown OIT is “easier to do when you have high control of your small patient volumes or you’re in a clinical trial,” said Dr. Jones, who has served as an investigator on Palforzia trials and last year received more than $30,000 in consulting fees from Aimmune. “It becomes a very different situation when it becomes a national or an international recommended therapy.”
The Canadian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology has published clinical practice guidelines and provides practical information on its website on how to implement OIT – including protocols for dozens of foods and diary sheets for patients to log doses and symptoms.
However, U.S. professional societies still consider OIT investigational and suggest that it will not be approved by the FDA. “As a field, are we willing to wait 4 to 5 more years for an egg product? Should we? Are we willing?” said Dr. Kim. “These are tough questions.”
Stacie M. Jones reports advisory board fees, Aimmune Therapeutics, FARE; personal fees, DBV Technologies; clinical trials grants, Aimmune Therapeutics, DBV Technologies, Astellas, Sanofi, Regeneron, FARE, Genentech, and NIH-NIAID. Edwin Kim reports consultancy with Aimmune Therapeutics, Allako, AllerGenis, Belhaven Pharma, DBV Technologies, Duke Clinical Research Institute, and Nutricia; advisory board membership with ALK, DBV Technologies, Kenota Health, and Ukko; grant support from the NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health and Immune Tolerance Network; Food Allergy Research and Education, and the Wallace Research Foundation. Richard Wasserman receives consulting fees from Aimmune Therapeutics and DBV Technologies. Mohamed Yassine is employed by Aimmune Therapeutics. Sandra Hong has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel mutation may be unrecognized cause of sudden infant death
A previously healthy infant who survived sudden cardiac arrest at home was later found to have a de novo likely pathogenic genetic mutation in the SOS1 gene, which might be an unrecognized cause of sudden infant death, report clinicians from Missouri.
SOS1 gene variants are associated with Noonan syndrome, a genetic disorder that affects the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway. However, on presentation, the infant had none of the usual structural cardiac findings typical of Noonan syndrome, such as valvular disease or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
“To date, this is the first case reported of a ventricular fibrillation arrest in a patient with a RASopathy-related variant prior to development of the typically associated structural cardiac phenotype and may represent a previously unrecognized etiology of sudden death during infancy,” write Christopher W. Follansbee, MD, and Lindsey Malloy-Walton, DO, from the Ward Family Heart Center, Children’s Mercy Kansas City, and the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
“Genetic testing in cases of unexplained aborted or sudden cardiac deaths, even in previously healthy children, can be valuable in establishing a diagnosis, determining the prognosis, and assessing risk to family members,” they add in a news release.
Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton describe the case in a report published in the August issue of HeartRhythm Case Reports.
Case details
The case involved a 2-month-old girl who did not wake up as usual for her morning feeding. Her mother found her limp, pale, and having difficulty breathing.
When emergency medical services arrived, the infant had no pulse. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was initiated and an external defibrillator revealed coarse ventricular fibrillation. An initial shock of 10 J was given with conversion to an atrial rhythm with aberrant ventricular conduction.
The infant developed increasing frequency of ectopy before degenerating to ventricular fibrillation. A second shock with 20 J was unsuccessful, but a third shock of 20 J successfully converted the rhythm to sinus with aberrant ventricular conduction and atrial ectopy with return of spontaneous circulation.
In the ICU, the infant displayed incessant, nonsustained ectopic atrial tachycardia, with rapid episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia with ventricular rates up to 300 beats per minute in the setting of seizure activity, they report.
With intravenous lorazepam, seizure activity resolved and treatment with amiodarone boluses led to transient establishment of sinus rhythm.
The QTc was noted to be above 500 ms and Brugada positioning of leads was unrevealing, the authors note.
Transthoracic echocardiogram showed a structurally normal heart with normal valve morphology and a patent foramen ovale with left-to-right flow. The initial ejection fraction was 49%. There was no evidence of ventricular hypertrophy, dilation, or noncompaction.
The infant was started on an esmolol infusion titrated to 225 μg/kg per min with frequent, nonsustained breakthrough of ectopic atrial tachycardia. Over the next 24 hours, the QTc interval normalized with normal T-wave morphology.
A procainamide challenge was negative. Cardiac MRI revealed normalization of ventricular function.
The genetics team was called in and a standard three-generation family history was obtained. An older sibling, 2 years of age, had no known medical conditions. The child’s paternal grandfather had died of a presumed myocardial infarction in his 50s, but no autopsy had been performed.
There was no family history of congenital heart disease, arrhythmia, sudden death, cardiomyopathy, recurrent syncope, congenital deafness, seizure, miscarriage, or developmental delay. Electrocardiograms obtained on the parents were normal.
Genetic testing using a comprehensive arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy next-generation sequencing panel revealed a de novo likely pathogenetic variant of the SOS1 gene associated with Noonan syndrome.
Given the aborted sudden cardiac death, the patient underwent dual-chamber epicardial implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation prior to discharge.
Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton say a limitation to the case report is the lack of definitive association of the SOS1 variant with the presentation.
However, knowing the infant has the SOS1 variant and a history of aborted sudden death will allow for “monitoring and early intervention on typical manifestations of Noonan syndrome as the patient grows,” they say.
This research had no specific funding. Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A previously healthy infant who survived sudden cardiac arrest at home was later found to have a de novo likely pathogenic genetic mutation in the SOS1 gene, which might be an unrecognized cause of sudden infant death, report clinicians from Missouri.
SOS1 gene variants are associated with Noonan syndrome, a genetic disorder that affects the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway. However, on presentation, the infant had none of the usual structural cardiac findings typical of Noonan syndrome, such as valvular disease or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
“To date, this is the first case reported of a ventricular fibrillation arrest in a patient with a RASopathy-related variant prior to development of the typically associated structural cardiac phenotype and may represent a previously unrecognized etiology of sudden death during infancy,” write Christopher W. Follansbee, MD, and Lindsey Malloy-Walton, DO, from the Ward Family Heart Center, Children’s Mercy Kansas City, and the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
“Genetic testing in cases of unexplained aborted or sudden cardiac deaths, even in previously healthy children, can be valuable in establishing a diagnosis, determining the prognosis, and assessing risk to family members,” they add in a news release.
Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton describe the case in a report published in the August issue of HeartRhythm Case Reports.
Case details
The case involved a 2-month-old girl who did not wake up as usual for her morning feeding. Her mother found her limp, pale, and having difficulty breathing.
When emergency medical services arrived, the infant had no pulse. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was initiated and an external defibrillator revealed coarse ventricular fibrillation. An initial shock of 10 J was given with conversion to an atrial rhythm with aberrant ventricular conduction.
The infant developed increasing frequency of ectopy before degenerating to ventricular fibrillation. A second shock with 20 J was unsuccessful, but a third shock of 20 J successfully converted the rhythm to sinus with aberrant ventricular conduction and atrial ectopy with return of spontaneous circulation.
In the ICU, the infant displayed incessant, nonsustained ectopic atrial tachycardia, with rapid episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia with ventricular rates up to 300 beats per minute in the setting of seizure activity, they report.
With intravenous lorazepam, seizure activity resolved and treatment with amiodarone boluses led to transient establishment of sinus rhythm.
The QTc was noted to be above 500 ms and Brugada positioning of leads was unrevealing, the authors note.
Transthoracic echocardiogram showed a structurally normal heart with normal valve morphology and a patent foramen ovale with left-to-right flow. The initial ejection fraction was 49%. There was no evidence of ventricular hypertrophy, dilation, or noncompaction.
The infant was started on an esmolol infusion titrated to 225 μg/kg per min with frequent, nonsustained breakthrough of ectopic atrial tachycardia. Over the next 24 hours, the QTc interval normalized with normal T-wave morphology.
A procainamide challenge was negative. Cardiac MRI revealed normalization of ventricular function.
The genetics team was called in and a standard three-generation family history was obtained. An older sibling, 2 years of age, had no known medical conditions. The child’s paternal grandfather had died of a presumed myocardial infarction in his 50s, but no autopsy had been performed.
There was no family history of congenital heart disease, arrhythmia, sudden death, cardiomyopathy, recurrent syncope, congenital deafness, seizure, miscarriage, or developmental delay. Electrocardiograms obtained on the parents were normal.
Genetic testing using a comprehensive arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy next-generation sequencing panel revealed a de novo likely pathogenetic variant of the SOS1 gene associated with Noonan syndrome.
Given the aborted sudden cardiac death, the patient underwent dual-chamber epicardial implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation prior to discharge.
Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton say a limitation to the case report is the lack of definitive association of the SOS1 variant with the presentation.
However, knowing the infant has the SOS1 variant and a history of aborted sudden death will allow for “monitoring and early intervention on typical manifestations of Noonan syndrome as the patient grows,” they say.
This research had no specific funding. Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A previously healthy infant who survived sudden cardiac arrest at home was later found to have a de novo likely pathogenic genetic mutation in the SOS1 gene, which might be an unrecognized cause of sudden infant death, report clinicians from Missouri.
SOS1 gene variants are associated with Noonan syndrome, a genetic disorder that affects the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway. However, on presentation, the infant had none of the usual structural cardiac findings typical of Noonan syndrome, such as valvular disease or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
“To date, this is the first case reported of a ventricular fibrillation arrest in a patient with a RASopathy-related variant prior to development of the typically associated structural cardiac phenotype and may represent a previously unrecognized etiology of sudden death during infancy,” write Christopher W. Follansbee, MD, and Lindsey Malloy-Walton, DO, from the Ward Family Heart Center, Children’s Mercy Kansas City, and the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
“Genetic testing in cases of unexplained aborted or sudden cardiac deaths, even in previously healthy children, can be valuable in establishing a diagnosis, determining the prognosis, and assessing risk to family members,” they add in a news release.
Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton describe the case in a report published in the August issue of HeartRhythm Case Reports.
Case details
The case involved a 2-month-old girl who did not wake up as usual for her morning feeding. Her mother found her limp, pale, and having difficulty breathing.
When emergency medical services arrived, the infant had no pulse. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was initiated and an external defibrillator revealed coarse ventricular fibrillation. An initial shock of 10 J was given with conversion to an atrial rhythm with aberrant ventricular conduction.
The infant developed increasing frequency of ectopy before degenerating to ventricular fibrillation. A second shock with 20 J was unsuccessful, but a third shock of 20 J successfully converted the rhythm to sinus with aberrant ventricular conduction and atrial ectopy with return of spontaneous circulation.
In the ICU, the infant displayed incessant, nonsustained ectopic atrial tachycardia, with rapid episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia with ventricular rates up to 300 beats per minute in the setting of seizure activity, they report.
With intravenous lorazepam, seizure activity resolved and treatment with amiodarone boluses led to transient establishment of sinus rhythm.
The QTc was noted to be above 500 ms and Brugada positioning of leads was unrevealing, the authors note.
Transthoracic echocardiogram showed a structurally normal heart with normal valve morphology and a patent foramen ovale with left-to-right flow. The initial ejection fraction was 49%. There was no evidence of ventricular hypertrophy, dilation, or noncompaction.
The infant was started on an esmolol infusion titrated to 225 μg/kg per min with frequent, nonsustained breakthrough of ectopic atrial tachycardia. Over the next 24 hours, the QTc interval normalized with normal T-wave morphology.
A procainamide challenge was negative. Cardiac MRI revealed normalization of ventricular function.
The genetics team was called in and a standard three-generation family history was obtained. An older sibling, 2 years of age, had no known medical conditions. The child’s paternal grandfather had died of a presumed myocardial infarction in his 50s, but no autopsy had been performed.
There was no family history of congenital heart disease, arrhythmia, sudden death, cardiomyopathy, recurrent syncope, congenital deafness, seizure, miscarriage, or developmental delay. Electrocardiograms obtained on the parents were normal.
Genetic testing using a comprehensive arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy next-generation sequencing panel revealed a de novo likely pathogenetic variant of the SOS1 gene associated with Noonan syndrome.
Given the aborted sudden cardiac death, the patient underwent dual-chamber epicardial implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation prior to discharge.
Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton say a limitation to the case report is the lack of definitive association of the SOS1 variant with the presentation.
However, knowing the infant has the SOS1 variant and a history of aborted sudden death will allow for “monitoring and early intervention on typical manifestations of Noonan syndrome as the patient grows,” they say.
This research had no specific funding. Dr. Follansbee and Dr. Malloy-Walton have disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.