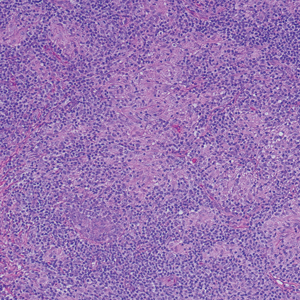
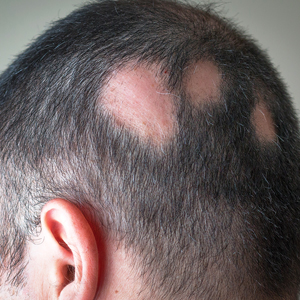
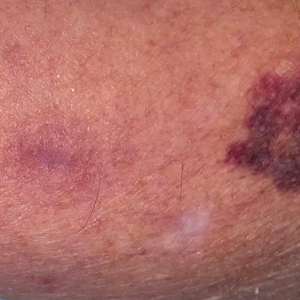
User login
A Counterintuitive Approach to Lowering Cholesterol in Children
With the flip of the calendar a few short weeks ago, gyms and fitness centers began ramping up their advertising campaigns in hopes of attracting the horde of resolution makers searching for a place where they can inject some exercise into their sedentary lives. A recent survey by C.S. Mott’s Children’s Hospital found that even young people are setting health-related goals with more than half of the parents of 11- to 18-year-olds reporting their children were setting personal goals for themselves. More than 40% of the young people listed more exercise as a target.
However, our personal and professional experiences have taught us that achieving goals, particularly when it comes to exercise, is far more difficult than setting the target. Finding an exercise buddy can be an important motivator on the days when just lacing up one’s sneakers is a stumbling block. Investing in a gym membership and sweating with a peer group can help. However, it is an investment that rarely pays a dividend. Exercise isn’t fun for everyone. For adults, showing up at a gym may be just one more reminder of how they have already lost their competitive edge over their leaner and fitter peers. If they aren’t lucky enough to find a sport or activity that they enjoy, the loneliness of the long-distance runner has little appeal.
A recent study on children in the United Kingdom suggests that at least when it comes to teens and young adults we as physicians may actually have been making things worse for our obese patients by urging them to accept unrealistic activity goals. While it is already known that sedentary time is responsible for 70% of the total increase in cholesterol as children advance to young adulthood an unqualified recommendation for more exercise may not be the best advice.
In an interview with the study author, Andre O. Agbaje MD, MPH, said that in his large study population “light physical activity outperforms moderate to vigorous physical activity by five to eight times in lowering lipids”. While we may be surprised by this counterintuitive finding, Dr. Agbaje points out that an increase in sedentariness from 6 to 9 hours per day translates into a loss of 3 hours of light physical activity. In other words if you’re not sedentary you must be standing at attention or engaged in some light activity.
In my experience, and I suspect yours, it is difficult to get adults to do something, particularly if that something involves exerting energy, even a small amount of energy. The general admonishment of “be more active” is often met with a blank stare and the sometimes unspoken question “Like what?”
You could fall into a bottomless trap with them by suggesting a long list of activities, many of which are probably ones you do or would enjoy but don’t happen to fit with any of their interests or capabilities. Your chances of hitting on a perfect activity that the patient will attempt, let alone adopt, is very slim. Those of you with more patience than I have may choose to persist with this strategy. You could argue that even if the patient only dabbles briefly in one of your recommended activities, this is a minor victory worth celebrating. Who knows? The brief jolt of energy they received from this activity may prompt them to seek and find something else that works.
My interpretation of Dr. Agbaje’s findings is this: If we are going to suggest more activity, aim low. Don’t even mention the heavily weighted words “sport” or “exercise,” which are likely to dredge up bad memories. For adults, “Go shopping” or “Visit a friend” may be sufficient to at least get the person off the couch and on their feet and moving, even if very briefly.
The second message from this study applies more to children and adolescents and is one of those unusual instances in which a negative intervention may be more effective than a positive approach. Acknowledging that we are likely to have difficulty finding even a light activity that the child enjoys, why not pivot to the other side of the equation? Make a list of the child’s primary sedentary “activities.” Then suggest the parents put the child on a couch potato diet by immediately cutting in half the time he or she spends being sedentary. By definition, this will automatically increase his or her light physical activity by 50%. According to Dr. Agbaje’s data, this should be more effective in lowering lipids than in the unlikely event of finding a moderate activity the child accepts.
You can argue that the child will hound his or her parents unmercifully asking to be entertained. This may be true and this persistent complaining will be more likely to come from the older the child and the longer that the child has been allowed to be sedentary. Although the child may appear to have lost the ability to self amuse, I contend this isn’t a permanent loss and, This is another example of how saying “No!” in the right circumstances is often the most effective remedy for an unhealthy situation. I would never claim saying “No” is easy and helping parents to learn how to say “No” is one of our most difficult challenges. But, nothing else seems to be working.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
With the flip of the calendar a few short weeks ago, gyms and fitness centers began ramping up their advertising campaigns in hopes of attracting the horde of resolution makers searching for a place where they can inject some exercise into their sedentary lives. A recent survey by C.S. Mott’s Children’s Hospital found that even young people are setting health-related goals with more than half of the parents of 11- to 18-year-olds reporting their children were setting personal goals for themselves. More than 40% of the young people listed more exercise as a target.
However, our personal and professional experiences have taught us that achieving goals, particularly when it comes to exercise, is far more difficult than setting the target. Finding an exercise buddy can be an important motivator on the days when just lacing up one’s sneakers is a stumbling block. Investing in a gym membership and sweating with a peer group can help. However, it is an investment that rarely pays a dividend. Exercise isn’t fun for everyone. For adults, showing up at a gym may be just one more reminder of how they have already lost their competitive edge over their leaner and fitter peers. If they aren’t lucky enough to find a sport or activity that they enjoy, the loneliness of the long-distance runner has little appeal.
A recent study on children in the United Kingdom suggests that at least when it comes to teens and young adults we as physicians may actually have been making things worse for our obese patients by urging them to accept unrealistic activity goals. While it is already known that sedentary time is responsible for 70% of the total increase in cholesterol as children advance to young adulthood an unqualified recommendation for more exercise may not be the best advice.
In an interview with the study author, Andre O. Agbaje MD, MPH, said that in his large study population “light physical activity outperforms moderate to vigorous physical activity by five to eight times in lowering lipids”. While we may be surprised by this counterintuitive finding, Dr. Agbaje points out that an increase in sedentariness from 6 to 9 hours per day translates into a loss of 3 hours of light physical activity. In other words if you’re not sedentary you must be standing at attention or engaged in some light activity.
In my experience, and I suspect yours, it is difficult to get adults to do something, particularly if that something involves exerting energy, even a small amount of energy. The general admonishment of “be more active” is often met with a blank stare and the sometimes unspoken question “Like what?”
You could fall into a bottomless trap with them by suggesting a long list of activities, many of which are probably ones you do or would enjoy but don’t happen to fit with any of their interests or capabilities. Your chances of hitting on a perfect activity that the patient will attempt, let alone adopt, is very slim. Those of you with more patience than I have may choose to persist with this strategy. You could argue that even if the patient only dabbles briefly in one of your recommended activities, this is a minor victory worth celebrating. Who knows? The brief jolt of energy they received from this activity may prompt them to seek and find something else that works.
My interpretation of Dr. Agbaje’s findings is this: If we are going to suggest more activity, aim low. Don’t even mention the heavily weighted words “sport” or “exercise,” which are likely to dredge up bad memories. For adults, “Go shopping” or “Visit a friend” may be sufficient to at least get the person off the couch and on their feet and moving, even if very briefly.
The second message from this study applies more to children and adolescents and is one of those unusual instances in which a negative intervention may be more effective than a positive approach. Acknowledging that we are likely to have difficulty finding even a light activity that the child enjoys, why not pivot to the other side of the equation? Make a list of the child’s primary sedentary “activities.” Then suggest the parents put the child on a couch potato diet by immediately cutting in half the time he or she spends being sedentary. By definition, this will automatically increase his or her light physical activity by 50%. According to Dr. Agbaje’s data, this should be more effective in lowering lipids than in the unlikely event of finding a moderate activity the child accepts.
You can argue that the child will hound his or her parents unmercifully asking to be entertained. This may be true and this persistent complaining will be more likely to come from the older the child and the longer that the child has been allowed to be sedentary. Although the child may appear to have lost the ability to self amuse, I contend this isn’t a permanent loss and, This is another example of how saying “No!” in the right circumstances is often the most effective remedy for an unhealthy situation. I would never claim saying “No” is easy and helping parents to learn how to say “No” is one of our most difficult challenges. But, nothing else seems to be working.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
With the flip of the calendar a few short weeks ago, gyms and fitness centers began ramping up their advertising campaigns in hopes of attracting the horde of resolution makers searching for a place where they can inject some exercise into their sedentary lives. A recent survey by C.S. Mott’s Children’s Hospital found that even young people are setting health-related goals with more than half of the parents of 11- to 18-year-olds reporting their children were setting personal goals for themselves. More than 40% of the young people listed more exercise as a target.
However, our personal and professional experiences have taught us that achieving goals, particularly when it comes to exercise, is far more difficult than setting the target. Finding an exercise buddy can be an important motivator on the days when just lacing up one’s sneakers is a stumbling block. Investing in a gym membership and sweating with a peer group can help. However, it is an investment that rarely pays a dividend. Exercise isn’t fun for everyone. For adults, showing up at a gym may be just one more reminder of how they have already lost their competitive edge over their leaner and fitter peers. If they aren’t lucky enough to find a sport or activity that they enjoy, the loneliness of the long-distance runner has little appeal.
A recent study on children in the United Kingdom suggests that at least when it comes to teens and young adults we as physicians may actually have been making things worse for our obese patients by urging them to accept unrealistic activity goals. While it is already known that sedentary time is responsible for 70% of the total increase in cholesterol as children advance to young adulthood an unqualified recommendation for more exercise may not be the best advice.
In an interview with the study author, Andre O. Agbaje MD, MPH, said that in his large study population “light physical activity outperforms moderate to vigorous physical activity by five to eight times in lowering lipids”. While we may be surprised by this counterintuitive finding, Dr. Agbaje points out that an increase in sedentariness from 6 to 9 hours per day translates into a loss of 3 hours of light physical activity. In other words if you’re not sedentary you must be standing at attention or engaged in some light activity.
In my experience, and I suspect yours, it is difficult to get adults to do something, particularly if that something involves exerting energy, even a small amount of energy. The general admonishment of “be more active” is often met with a blank stare and the sometimes unspoken question “Like what?”
You could fall into a bottomless trap with them by suggesting a long list of activities, many of which are probably ones you do or would enjoy but don’t happen to fit with any of their interests or capabilities. Your chances of hitting on a perfect activity that the patient will attempt, let alone adopt, is very slim. Those of you with more patience than I have may choose to persist with this strategy. You could argue that even if the patient only dabbles briefly in one of your recommended activities, this is a minor victory worth celebrating. Who knows? The brief jolt of energy they received from this activity may prompt them to seek and find something else that works.
My interpretation of Dr. Agbaje’s findings is this: If we are going to suggest more activity, aim low. Don’t even mention the heavily weighted words “sport” or “exercise,” which are likely to dredge up bad memories. For adults, “Go shopping” or “Visit a friend” may be sufficient to at least get the person off the couch and on their feet and moving, even if very briefly.
The second message from this study applies more to children and adolescents and is one of those unusual instances in which a negative intervention may be more effective than a positive approach. Acknowledging that we are likely to have difficulty finding even a light activity that the child enjoys, why not pivot to the other side of the equation? Make a list of the child’s primary sedentary “activities.” Then suggest the parents put the child on a couch potato diet by immediately cutting in half the time he or she spends being sedentary. By definition, this will automatically increase his or her light physical activity by 50%. According to Dr. Agbaje’s data, this should be more effective in lowering lipids than in the unlikely event of finding a moderate activity the child accepts.
You can argue that the child will hound his or her parents unmercifully asking to be entertained. This may be true and this persistent complaining will be more likely to come from the older the child and the longer that the child has been allowed to be sedentary. Although the child may appear to have lost the ability to self amuse, I contend this isn’t a permanent loss and, This is another example of how saying “No!” in the right circumstances is often the most effective remedy for an unhealthy situation. I would never claim saying “No” is easy and helping parents to learn how to say “No” is one of our most difficult challenges. But, nothing else seems to be working.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Healthcare Violence: Doctors and Nurses Are Bearing the Brunt of Business Pressures
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This month, I want to tackle the difficult subject of violence toward healthcare workers. There’s a reason this is top of mind for me in my practice, but I want to start by acknowledging that this has been a much larger issue for our profession and one that has been growing for a number of years now.
They also estimate that that rate doubled between 2011 and 2018. I think that range is important because it proves this was a problem, and a crescendoing problem, even before COVID.
Another thing I think is relevant is to look at where in the healthcare system are these attacks most likely. In the emergency room, ER staff have seen hostility toward them rise by at least 25% over the past several years. Some of the seeds of mistrust that were sown between the general public and the scientific and medical communities around the pandemic. I think there’s some explanation there for why that might be a particular crucible.
Perhaps most disturbingly of all, 60% of the victims of healthcare workplace violence are bedside nurses. There is something about the intensity of the inpatient setting that makes nerves particularly frayed and unfortunately makes patients and family members more likely to lash out. I think it’s actually the heightened sense of mortality.
I’m not excusing any of these behaviors, but maybe it’s akin to road rage. On the road, behind the wheel, tiny gestures can actually be, on some level, perceived as threats to our survival. Another driver swerving into your lane activates a fight-or-flight response, you feel threatened, and you might respond in the moment very rashly. I wonder if we’re not seeing that, quite unfairly, play out against bedside staff in our hospitals.
Here’s the thing. Those of us who practice in the outpatient setting — 95% of my work, for instance, happens in clinic — are not immune to this either. There are some very harrowing recent examples of physicians being killed, typically at gunpoint, often by patients, sometimes by aggrieved family members, in their offices. An orthopedist in Tennessee, a back surgeon in Tulsa, along with three of their colleagues. In the latter case, the assailant specifically blamed the surgeon for their pain.
This is where I think things get even more scary. We have to be the bearers of bad news in our profession. This has long been the task of the oncologist, in particular, to convey things that people don’t want to hear.
I think what brought this to my mind in terms of my reading was an incredible article in The ASCO Post and also in the Journal of Clinical Oncology by Dr. Noelle LoConte, who’s a medical oncologist in Wisconsin. The article is called, “I Want to Kill You,” and it recounts her telling a previously stage III colon cancer patient, with whom she thought she had good rapport, that the disease had recurred. The patient’s immediate reaction in the heat of that moment was to say, Dr LoConte, I want to kill you. I want to blow your face off.
Already, there’s clearly tension when we are telling people what they don’t want to hear. I think the final piece of the puzzle goes back to the intrusion of the business of healthcare on the practice of medicine. This is what I witnessed very recently. One of the things that’s interesting to think about is how what we do is now framed as customer service. I know there’s deriding of this model, but if perception is reality, we have a system where patients are set up to view themselves as consumers.
Let’s say, for instance, you’re in the unfortunate circumstance of being diagnosed with cancer and your insurer gives you the option to go to multiple oncologists. If you’re online browsing for oncologists, how do you differentiate me from some of my colleagues? The answer on these rating websites often has to do with domains that are about the overall experience — not just the patient-doctor interaction but also things like wait time, friendliness of staff, and promptness of care delivery.
That, I think, is the final piece of the puzzle, because what I really risk when I sit down with a patient and lay out a treatment plan is overpromising and underdelivering. I am long used to citing median overall survival for expectation of outcome. Of course, every patient wants to be an exceptional responder. Most patients want to be on the latter half of median survival. No one wants to be on the disappointingly shorter half.
My point is that I’ve long been able to mitigate that uncertainty for patients. What is getting harder and harder to explain away is the delay incurred between someone’s diagnosis, my meeting them and laying out a treatment plan, and their actual initiation of that therapy.
This finally brings me to my recent personal encounter. I have long taken care of a patient, much like Dr LoConte’s, with an extremely calm demeanor. I thought we had a great therapeutic alliance. I had to tell the patient that the disease had recurred, and then I laid out a treatment plan. It took weeks and then months for the insurer to approve this plan despite my providing my note in a timely fashion with a mountain of evidence behind the regimen that I’d selected.
This is where I think insurers — when they deny, deflect, and delay — are not taking adequate responsibility for the impact that has on the therapeutic alliance between a patient and their doctor. These people are trusting us with their lives. As an oncologist, I’ve already told them something they didn’t want to hear, and now I’m compounding that with the uncertainty of when we can actually begin treatment.
This gentleman — who, again, is normally extremely kind and affable — showed up at my office and was incredibly hostile toward me and my staff because of the delay that he was encountering. We literally couldn’t tell him when his insurer was going to approve his treatment, which would have been financially disastrous if he had tried to pay for it himself out of pocket. He needed his insurer’s approval before we could start, but we didn’t know when he could start. That uncertainty and not knowing was gnawing away at him until he was at the end of his rope.
What I’m here to say is that this has been a difficult couple of years in healthcare. I’m well aware that our ER staff are on the front lines, as are our bedside and inpatient teams. Even in the outpatient setting, I think we’re seeing this crucible and we’re seeing the pressure just grow, and grow, and grow. It’s like fracking. The more you increase the pressure, the more eventually you’re going to find out where the cracks are.
These patients are the ultimate stakeholders. It’s their lives on the line, and we should be concerned, but perhaps ultimately not surprised, that they’re lashing out to be heard. Given no other resort, they are taking out their frustration and their aggression on us. It›s not fair, but I am newly aware of it because, in a patient with whom I thought we had a superb rapport, I saw that vanish. As soon as he thought that his life was at risk, his fight-or-flight response kicked in. I was not dealing with the same man I knew. I was dealing with someone who was desperate and who just wanted to know when he could get the treatment.
I think this has taken the likelihood of workplace hostility to a whole other level for those of us in healthcare.
For any patients listening, I beg of you, please don’t shoot the messenger. We are here to serve you the best we can, but there are many external factors at play. We are doing our best to mitigate those for you so we can deliver the care that we promised in as timely a fashion as we can.
I hope everyone out there can stay safe. Thank you.
Dr. Lewis is director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, Utah. He has an interest in neuroendocrine tumors, hereditary cancer syndromes, and patient-physician communication. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This month, I want to tackle the difficult subject of violence toward healthcare workers. There’s a reason this is top of mind for me in my practice, but I want to start by acknowledging that this has been a much larger issue for our profession and one that has been growing for a number of years now.
They also estimate that that rate doubled between 2011 and 2018. I think that range is important because it proves this was a problem, and a crescendoing problem, even before COVID.
Another thing I think is relevant is to look at where in the healthcare system are these attacks most likely. In the emergency room, ER staff have seen hostility toward them rise by at least 25% over the past several years. Some of the seeds of mistrust that were sown between the general public and the scientific and medical communities around the pandemic. I think there’s some explanation there for why that might be a particular crucible.
Perhaps most disturbingly of all, 60% of the victims of healthcare workplace violence are bedside nurses. There is something about the intensity of the inpatient setting that makes nerves particularly frayed and unfortunately makes patients and family members more likely to lash out. I think it’s actually the heightened sense of mortality.
I’m not excusing any of these behaviors, but maybe it’s akin to road rage. On the road, behind the wheel, tiny gestures can actually be, on some level, perceived as threats to our survival. Another driver swerving into your lane activates a fight-or-flight response, you feel threatened, and you might respond in the moment very rashly. I wonder if we’re not seeing that, quite unfairly, play out against bedside staff in our hospitals.
Here’s the thing. Those of us who practice in the outpatient setting — 95% of my work, for instance, happens in clinic — are not immune to this either. There are some very harrowing recent examples of physicians being killed, typically at gunpoint, often by patients, sometimes by aggrieved family members, in their offices. An orthopedist in Tennessee, a back surgeon in Tulsa, along with three of their colleagues. In the latter case, the assailant specifically blamed the surgeon for their pain.
This is where I think things get even more scary. We have to be the bearers of bad news in our profession. This has long been the task of the oncologist, in particular, to convey things that people don’t want to hear.
I think what brought this to my mind in terms of my reading was an incredible article in The ASCO Post and also in the Journal of Clinical Oncology by Dr. Noelle LoConte, who’s a medical oncologist in Wisconsin. The article is called, “I Want to Kill You,” and it recounts her telling a previously stage III colon cancer patient, with whom she thought she had good rapport, that the disease had recurred. The patient’s immediate reaction in the heat of that moment was to say, Dr LoConte, I want to kill you. I want to blow your face off.
Already, there’s clearly tension when we are telling people what they don’t want to hear. I think the final piece of the puzzle goes back to the intrusion of the business of healthcare on the practice of medicine. This is what I witnessed very recently. One of the things that’s interesting to think about is how what we do is now framed as customer service. I know there’s deriding of this model, but if perception is reality, we have a system where patients are set up to view themselves as consumers.
Let’s say, for instance, you’re in the unfortunate circumstance of being diagnosed with cancer and your insurer gives you the option to go to multiple oncologists. If you’re online browsing for oncologists, how do you differentiate me from some of my colleagues? The answer on these rating websites often has to do with domains that are about the overall experience — not just the patient-doctor interaction but also things like wait time, friendliness of staff, and promptness of care delivery.
That, I think, is the final piece of the puzzle, because what I really risk when I sit down with a patient and lay out a treatment plan is overpromising and underdelivering. I am long used to citing median overall survival for expectation of outcome. Of course, every patient wants to be an exceptional responder. Most patients want to be on the latter half of median survival. No one wants to be on the disappointingly shorter half.
My point is that I’ve long been able to mitigate that uncertainty for patients. What is getting harder and harder to explain away is the delay incurred between someone’s diagnosis, my meeting them and laying out a treatment plan, and their actual initiation of that therapy.
This finally brings me to my recent personal encounter. I have long taken care of a patient, much like Dr LoConte’s, with an extremely calm demeanor. I thought we had a great therapeutic alliance. I had to tell the patient that the disease had recurred, and then I laid out a treatment plan. It took weeks and then months for the insurer to approve this plan despite my providing my note in a timely fashion with a mountain of evidence behind the regimen that I’d selected.
This is where I think insurers — when they deny, deflect, and delay — are not taking adequate responsibility for the impact that has on the therapeutic alliance between a patient and their doctor. These people are trusting us with their lives. As an oncologist, I’ve already told them something they didn’t want to hear, and now I’m compounding that with the uncertainty of when we can actually begin treatment.
This gentleman — who, again, is normally extremely kind and affable — showed up at my office and was incredibly hostile toward me and my staff because of the delay that he was encountering. We literally couldn’t tell him when his insurer was going to approve his treatment, which would have been financially disastrous if he had tried to pay for it himself out of pocket. He needed his insurer’s approval before we could start, but we didn’t know when he could start. That uncertainty and not knowing was gnawing away at him until he was at the end of his rope.
What I’m here to say is that this has been a difficult couple of years in healthcare. I’m well aware that our ER staff are on the front lines, as are our bedside and inpatient teams. Even in the outpatient setting, I think we’re seeing this crucible and we’re seeing the pressure just grow, and grow, and grow. It’s like fracking. The more you increase the pressure, the more eventually you’re going to find out where the cracks are.
These patients are the ultimate stakeholders. It’s their lives on the line, and we should be concerned, but perhaps ultimately not surprised, that they’re lashing out to be heard. Given no other resort, they are taking out their frustration and their aggression on us. It›s not fair, but I am newly aware of it because, in a patient with whom I thought we had a superb rapport, I saw that vanish. As soon as he thought that his life was at risk, his fight-or-flight response kicked in. I was not dealing with the same man I knew. I was dealing with someone who was desperate and who just wanted to know when he could get the treatment.
I think this has taken the likelihood of workplace hostility to a whole other level for those of us in healthcare.
For any patients listening, I beg of you, please don’t shoot the messenger. We are here to serve you the best we can, but there are many external factors at play. We are doing our best to mitigate those for you so we can deliver the care that we promised in as timely a fashion as we can.
I hope everyone out there can stay safe. Thank you.
Dr. Lewis is director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, Utah. He has an interest in neuroendocrine tumors, hereditary cancer syndromes, and patient-physician communication. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This month, I want to tackle the difficult subject of violence toward healthcare workers. There’s a reason this is top of mind for me in my practice, but I want to start by acknowledging that this has been a much larger issue for our profession and one that has been growing for a number of years now.
They also estimate that that rate doubled between 2011 and 2018. I think that range is important because it proves this was a problem, and a crescendoing problem, even before COVID.
Another thing I think is relevant is to look at where in the healthcare system are these attacks most likely. In the emergency room, ER staff have seen hostility toward them rise by at least 25% over the past several years. Some of the seeds of mistrust that were sown between the general public and the scientific and medical communities around the pandemic. I think there’s some explanation there for why that might be a particular crucible.
Perhaps most disturbingly of all, 60% of the victims of healthcare workplace violence are bedside nurses. There is something about the intensity of the inpatient setting that makes nerves particularly frayed and unfortunately makes patients and family members more likely to lash out. I think it’s actually the heightened sense of mortality.
I’m not excusing any of these behaviors, but maybe it’s akin to road rage. On the road, behind the wheel, tiny gestures can actually be, on some level, perceived as threats to our survival. Another driver swerving into your lane activates a fight-or-flight response, you feel threatened, and you might respond in the moment very rashly. I wonder if we’re not seeing that, quite unfairly, play out against bedside staff in our hospitals.
Here’s the thing. Those of us who practice in the outpatient setting — 95% of my work, for instance, happens in clinic — are not immune to this either. There are some very harrowing recent examples of physicians being killed, typically at gunpoint, often by patients, sometimes by aggrieved family members, in their offices. An orthopedist in Tennessee, a back surgeon in Tulsa, along with three of their colleagues. In the latter case, the assailant specifically blamed the surgeon for their pain.
This is where I think things get even more scary. We have to be the bearers of bad news in our profession. This has long been the task of the oncologist, in particular, to convey things that people don’t want to hear.
I think what brought this to my mind in terms of my reading was an incredible article in The ASCO Post and also in the Journal of Clinical Oncology by Dr. Noelle LoConte, who’s a medical oncologist in Wisconsin. The article is called, “I Want to Kill You,” and it recounts her telling a previously stage III colon cancer patient, with whom she thought she had good rapport, that the disease had recurred. The patient’s immediate reaction in the heat of that moment was to say, Dr LoConte, I want to kill you. I want to blow your face off.
Already, there’s clearly tension when we are telling people what they don’t want to hear. I think the final piece of the puzzle goes back to the intrusion of the business of healthcare on the practice of medicine. This is what I witnessed very recently. One of the things that’s interesting to think about is how what we do is now framed as customer service. I know there’s deriding of this model, but if perception is reality, we have a system where patients are set up to view themselves as consumers.
Let’s say, for instance, you’re in the unfortunate circumstance of being diagnosed with cancer and your insurer gives you the option to go to multiple oncologists. If you’re online browsing for oncologists, how do you differentiate me from some of my colleagues? The answer on these rating websites often has to do with domains that are about the overall experience — not just the patient-doctor interaction but also things like wait time, friendliness of staff, and promptness of care delivery.
That, I think, is the final piece of the puzzle, because what I really risk when I sit down with a patient and lay out a treatment plan is overpromising and underdelivering. I am long used to citing median overall survival for expectation of outcome. Of course, every patient wants to be an exceptional responder. Most patients want to be on the latter half of median survival. No one wants to be on the disappointingly shorter half.
My point is that I’ve long been able to mitigate that uncertainty for patients. What is getting harder and harder to explain away is the delay incurred between someone’s diagnosis, my meeting them and laying out a treatment plan, and their actual initiation of that therapy.
This finally brings me to my recent personal encounter. I have long taken care of a patient, much like Dr LoConte’s, with an extremely calm demeanor. I thought we had a great therapeutic alliance. I had to tell the patient that the disease had recurred, and then I laid out a treatment plan. It took weeks and then months for the insurer to approve this plan despite my providing my note in a timely fashion with a mountain of evidence behind the regimen that I’d selected.
This is where I think insurers — when they deny, deflect, and delay — are not taking adequate responsibility for the impact that has on the therapeutic alliance between a patient and their doctor. These people are trusting us with their lives. As an oncologist, I’ve already told them something they didn’t want to hear, and now I’m compounding that with the uncertainty of when we can actually begin treatment.
This gentleman — who, again, is normally extremely kind and affable — showed up at my office and was incredibly hostile toward me and my staff because of the delay that he was encountering. We literally couldn’t tell him when his insurer was going to approve his treatment, which would have been financially disastrous if he had tried to pay for it himself out of pocket. He needed his insurer’s approval before we could start, but we didn’t know when he could start. That uncertainty and not knowing was gnawing away at him until he was at the end of his rope.
What I’m here to say is that this has been a difficult couple of years in healthcare. I’m well aware that our ER staff are on the front lines, as are our bedside and inpatient teams. Even in the outpatient setting, I think we’re seeing this crucible and we’re seeing the pressure just grow, and grow, and grow. It’s like fracking. The more you increase the pressure, the more eventually you’re going to find out where the cracks are.
These patients are the ultimate stakeholders. It’s their lives on the line, and we should be concerned, but perhaps ultimately not surprised, that they’re lashing out to be heard. Given no other resort, they are taking out their frustration and their aggression on us. It›s not fair, but I am newly aware of it because, in a patient with whom I thought we had a superb rapport, I saw that vanish. As soon as he thought that his life was at risk, his fight-or-flight response kicked in. I was not dealing with the same man I knew. I was dealing with someone who was desperate and who just wanted to know when he could get the treatment.
I think this has taken the likelihood of workplace hostility to a whole other level for those of us in healthcare.
For any patients listening, I beg of you, please don’t shoot the messenger. We are here to serve you the best we can, but there are many external factors at play. We are doing our best to mitigate those for you so we can deliver the care that we promised in as timely a fashion as we can.
I hope everyone out there can stay safe. Thank you.
Dr. Lewis is director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, Utah. He has an interest in neuroendocrine tumors, hereditary cancer syndromes, and patient-physician communication. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Botanical Briefs: Neem Oil (Azadirachta indica)
Commonly known as neem or nimba, Azadirachta indica traditionally has been used as an oil or poultice to lighten skin pigment and reduce joint inflammation. Neem is a drought-resistant evergreen tree with thin serrated leaves, white fragrant flowers, and olivelike fruit (Figure 1). This plant is indigenous to India but also is readily found within tropical and semitropical environments throughout the Middle East, Southeast Asia, North Africa, and Australia.
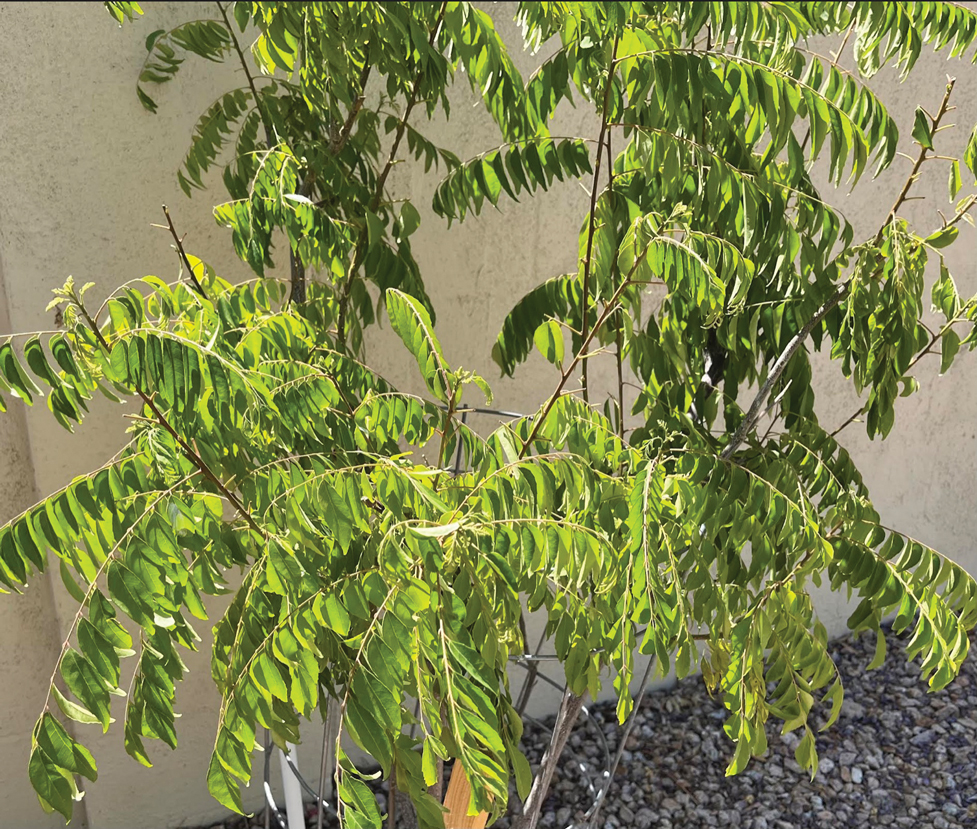

Traditional Uses
For more than 4000 years, neem leaves, bark, fruit, and seeds have been used in food, insecticide, and herbal medicine cross-culturally in Indian Ayurvedic medicine and across Southeast Asia, particularly in Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, and Vietnam.1-3 Because of its many essential nutrients—oleic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, linoleic acid, behenic acid, arachidic acid, and palmitoleic acid—and readily available nature, some ethnic groups include neem in their diet.4 Neem commonly is used as a seasoning in soups and rice, eaten as a cooked vegetable, infused into teas and tonics, and pickled with other spices.5
All parts of the neem tree—both externally and internally—have been utilized in traditional medicine for the treatment of various diseases and ailments. The flowers have been used to treat eye diseases and dyspepsia, the fruit has been employed as an anthelmintic, the seeds and leaves have been used for malaria treatment and insecticide, the stem bark has been used for the treatment of diarrhea, and the root bark has been used for skin diseases and inflammation.6 Neem oil is a yellow-brown bitter substance that often is utilized to treat skin diseases such as psoriasis, eczema, fungal infections, and abscesses.
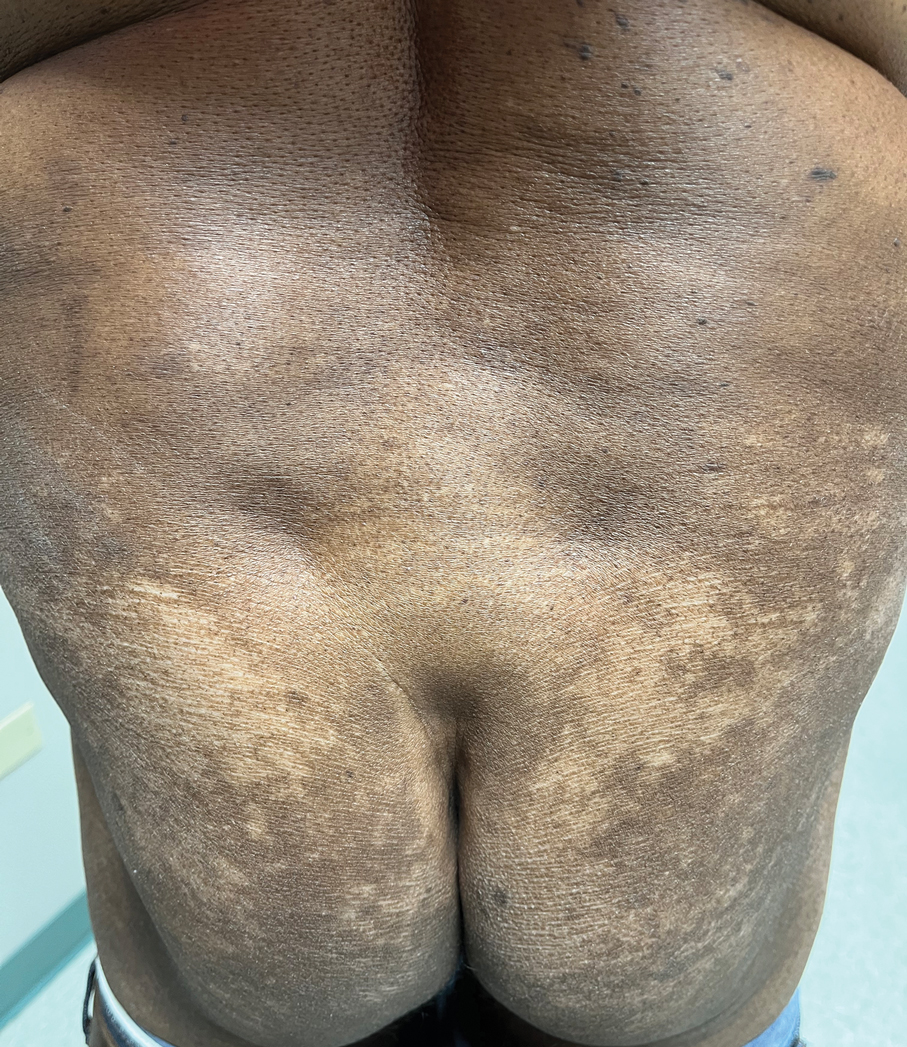
Case Report—A 77-year-old man presented with a diffuse rash across the lower back. He reported that he had been using topical neem oil to alleviate lower back pain and arthritis for the last 6 months with noted relief and improvement of back pain. After roughly 3 to 4 months of using neem oil, he noted a rash on the lower back, bilateral flanks, and buttocks (Figure 2). The rash was asymptomatic, and he denied any pruritus, scaling, pain, or burning. The patient was referred to dermatology and received a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma secondary to contact with A indica. The patient was advised to stop using the topical neem oil, and the rash was simply monitored, as it was asymptomatic.
Bioactivity
Research has elucidated multiple bioactivity mechanisms of neem, including melanogenesis-inhibitory activity, toxicity against pests, antimalarial activity, and antioxidant activity.1,7-9 Literature on the diverse phytochemical components of A indica indicate high levels of limonoids, flavonoids, and triterpenoids that are responsible for much of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and insecticide properties.1,10
Melanogenesis-Inhibitory Activity—To date, neem has been added to a number of cosmetic products used in Ayurvedic medicine. One study of isolated compounds in A indica showed superior inhibitory activities against melanogenesis with minimal toxicity to cells (86.5%–105.1% cell viability). Western blot analysis of samples extracted and isolated from neem root and bark showed melanogenesis-inhibitory activities in B16 melanoma cells through the inhibition of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor expression and decreased expression of tyrosinase, as well as tyrosinase-related proteins 1 and 2, which are largely responsible for melanin synthesis.11 In another study, A indica flowers and their extracted constituents—6-deacetylnimbin and kaempferide—suggest melanogenesis-inhibitory activities in B16 melanoma cells with little to no toxicity to the cells (81.0%–111.7% cell viability).1 In an evaluationof A indica seed extracts, some of the isolated limonoids and diterpenoids exhibited a marked melanogenesis-inhibitory effect (74%–91% reduction of melanin content) with no toxicity to the cell.5 All of these studies indicate that active compounds in neem root, bark, flowers, and seeds may be potential skin-lightening agents.
Toxicity Against Pests—Neem seeds have phytochemicals that convey some insecticidal properties. The seeds often are ground into a powder, combined with water, and sprayed onto crops to act as an insecticide. As a natural method of nonpesticidal management, A indica acts as an antifeedant, insect repellent, and egg-laying deterrent that protects crops from damage. Studies of A indica have noted effective nonpesticidal management against arthropod pests such as armyworm, termites, and the oriental fruit fly.7,12,13
Antimalarial Activity—One study indicated that nimbolide, a limonoid from the neem plant, demonstrated antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum. In separate cultures of asexual parasites and mature gametocytes, parasite numbers were less than 50% of the number in control cultures (8.0% vs 8.5% parasitemia, respectively).14 Thus, the lower parasite numbers indicated by this study highlight the antimalarial utility of nimbolide and neem oil.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activity—Neem bark has been reported to have considerable antioxidant activity due to its high phenolic content.1,15 One study showed that azadirachtin and nimbolide in neem exhibited concentration-dependent antiradical scavenging activity and antioxidant properties.16
The anti-inflammatory potential for neem may occur via the inhibition of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway, which is linked to cancer, inflammation, and apoptosis.17 It also has been observed that nimbidin within neem extracts—such as leaves, bark, and seed extract—suppresses the function of macrophages and neutrophils relevant to inflammation.16 Another study indicated neem’s anti-inflammatory activity due to the regulation of proinflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase.18
Safety, Toxicity, and Risks
Ingestion—Although neem is safe to use in the general population, neem oil poisoning has been reported, particularly in young children. Ingesting large quantities of neem has resulted in vomiting, hepatic toxicity, metabolic acidosis, late neurologic sequelae, and encephalopathy in young children.19 The diagnosis of neem oil poisoning is based on patient history, clinical examination, and imaging findings. Poisoning can manifest as drowsiness, tachypnea, and generalized seizures.20
Topical Application—Topical use of neem appears to be safe if the substance is diluted with other ingredients. However, direct application to the skin is not advised, as it may cause leukoderma and could induce allergic contact dermatitis and other allergic reactions.4
Final Thoughts
The use of neem extract for disease prevention and treatment has been prevalent around the world since ancient times. Neem has been documented to possess melanogenesis-inhibitory activity, toxicity against pests, antimalarial activity, and antioxidant activity by means of tyrosinase inhibition, phytochemical production, limonoid expression, and nuclear factor-κB regulation, respectively. However, topical use of neem may trigger a cutaneous response, highlighting the importance of considering a diagnosis of neem oil–induced chemical leukoderma when patients present with a hypopigmented rash and relevant history.
- Kitdamrongtham W, Ishii K, Ebina K, et al. Limonoids and flavonoids from the flowers of Azadirachta indica var. siamensis, and their melanogenesis-inhibitory and cytotoxic activities. Chem Biodivers. 2014;11:73-84. doi:10.1002/cbdv.201300266
- Singh A, Srivastava PS, Lakshmikumaran M. Comparison of AFLP and SAMPL markers for assessment of intra-population genetic variation in Azadirachta indica A. Juss. Plant Sci. 2002;162:17-25. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00503-9
- Pandey G, Verma K, Singh M. Evaluation of phytochemical, antibacterial and free radical scavenging properties of Azadirachta Indica (neem) leaves. Int J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2014;6:444-447.
- Romita P, Calogiuri G, Bellino M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by neem oil: an underrated allergen. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:133-134. doi:10.1111/cod. 13256
- Akihisa T, Noto T, Takahashi A, et al. Melanogenesis inhibitory, anti-inflammatory, and chemopreventive effects of limonoids from the seeds of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. (neem). J Oleo Sci. 2009;58:581-594.
- Subapriya R, Nagini S. Medicinal properties of neem leaves: a review. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005;5:149-156. doi:10.2174/1568011053174828
- Areekul S, Sinchaisri P, Tigvatananon S. Effect of Thai plant extracts on the Oriental fruit fly. I: toxicity test. Agriculture and Natural Resources. 1987;21:395-407.
- Rochanakij S, Thebtaranonth Y, Yenjai C, et al. Nimbolide, a constituent of Azadirachta indica, inhibits Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1985;16:66-72.
- Sithisarn P, Supabphol R, Gritsanapan W. Antioxidant activity of Siamese neem tree (VP1209). J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;99:109-112. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.02.008
- Yin F, Lei XX, Cheng L, et al. Isolation and structure identification of the compounds from the seeds and leaves of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. J China Pharmaceut University. 2005;36:10-12.
- Su S, Cheng J, Zhang C, et al. Melanogenesis-inhibitory activities of limonoids and tricyclic diterpenoids from Azadirachta indica. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2020;100:103941. doi:j.bioorg.2020.103941
- Tulashie SK, Adjei F, Abraham J, et al. Potential of neem extracts as natural insecticide against fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Case Stud Chem Environ Eng. 2021;4:100130. doi:10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100130
- Yashroy RC, Gupta PK. Neem-seed oil inhibits growth of termite surface-tunnels. Indian J Toxicol. 2000;7:49-50.
- Udeinya JI, Shu EN, Quakyi I, et al. An antimalarial neem leaf extract has both schizonticidal and gametocytocidal activities. Am J Therapeutics. 2008;15:108-110. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e31804c6d1d
- Bindurani R, Kumar K. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of hydro distilled extracts of leaf, heart wood and flower of Azadirachta indica. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013;20:222.
- Alzohairy MA. Therapeutics role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and their active constituents in diseases prevention and treatment [published online March 1, 2016]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1155/2016/7382506
- Schumacher M, Cerella C, Reuter S, et al. Anti-inflammatory, pro-apoptotic, and anti-proliferative effects of a methanolic neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf extract are mediated via modulation of the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Genes Nutr. 2011;6:149-160. doi:10.1007/s12263-010-0194-6
- Kaur G, Sarwar Alam M, Athar M. Nimbidin suppresses functions of macrophages and neutrophils: relevance to its anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Phytotherapy Res. 2004;18:419-424. doi:10.1002/ptr.1474
- Dhongade RK, Kavade SG, Damle RS. Neem oil poisoning. Indian Pediatr. 2008;45:56-57.
- Bhaskar MV, Pramod SJ, Jeevika MU, et al. MR imaging findings of neem oil poisoning. Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:E60-E61. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2146
Commonly known as neem or nimba, Azadirachta indica traditionally has been used as an oil or poultice to lighten skin pigment and reduce joint inflammation. Neem is a drought-resistant evergreen tree with thin serrated leaves, white fragrant flowers, and olivelike fruit (Figure 1). This plant is indigenous to India but also is readily found within tropical and semitropical environments throughout the Middle East, Southeast Asia, North Africa, and Australia.

Traditional Uses
For more than 4000 years, neem leaves, bark, fruit, and seeds have been used in food, insecticide, and herbal medicine cross-culturally in Indian Ayurvedic medicine and across Southeast Asia, particularly in Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, and Vietnam.1-3 Because of its many essential nutrients—oleic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, linoleic acid, behenic acid, arachidic acid, and palmitoleic acid—and readily available nature, some ethnic groups include neem in their diet.4 Neem commonly is used as a seasoning in soups and rice, eaten as a cooked vegetable, infused into teas and tonics, and pickled with other spices.5
All parts of the neem tree—both externally and internally—have been utilized in traditional medicine for the treatment of various diseases and ailments. The flowers have been used to treat eye diseases and dyspepsia, the fruit has been employed as an anthelmintic, the seeds and leaves have been used for malaria treatment and insecticide, the stem bark has been used for the treatment of diarrhea, and the root bark has been used for skin diseases and inflammation.6 Neem oil is a yellow-brown bitter substance that often is utilized to treat skin diseases such as psoriasis, eczema, fungal infections, and abscesses.
Case Report—A 77-year-old man presented with a diffuse rash across the lower back. He reported that he had been using topical neem oil to alleviate lower back pain and arthritis for the last 6 months with noted relief and improvement of back pain. After roughly 3 to 4 months of using neem oil, he noted a rash on the lower back, bilateral flanks, and buttocks (Figure 2). The rash was asymptomatic, and he denied any pruritus, scaling, pain, or burning. The patient was referred to dermatology and received a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma secondary to contact with A indica. The patient was advised to stop using the topical neem oil, and the rash was simply monitored, as it was asymptomatic.

Bioactivity
Research has elucidated multiple bioactivity mechanisms of neem, including melanogenesis-inhibitory activity, toxicity against pests, antimalarial activity, and antioxidant activity.1,7-9 Literature on the diverse phytochemical components of A indica indicate high levels of limonoids, flavonoids, and triterpenoids that are responsible for much of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and insecticide properties.1,10
Melanogenesis-Inhibitory Activity—To date, neem has been added to a number of cosmetic products used in Ayurvedic medicine. One study of isolated compounds in A indica showed superior inhibitory activities against melanogenesis with minimal toxicity to cells (86.5%–105.1% cell viability). Western blot analysis of samples extracted and isolated from neem root and bark showed melanogenesis-inhibitory activities in B16 melanoma cells through the inhibition of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor expression and decreased expression of tyrosinase, as well as tyrosinase-related proteins 1 and 2, which are largely responsible for melanin synthesis.11 In another study, A indica flowers and their extracted constituents—6-deacetylnimbin and kaempferide—suggest melanogenesis-inhibitory activities in B16 melanoma cells with little to no toxicity to the cells (81.0%–111.7% cell viability).1 In an evaluationof A indica seed extracts, some of the isolated limonoids and diterpenoids exhibited a marked melanogenesis-inhibitory effect (74%–91% reduction of melanin content) with no toxicity to the cell.5 All of these studies indicate that active compounds in neem root, bark, flowers, and seeds may be potential skin-lightening agents.
Toxicity Against Pests—Neem seeds have phytochemicals that convey some insecticidal properties. The seeds often are ground into a powder, combined with water, and sprayed onto crops to act as an insecticide. As a natural method of nonpesticidal management, A indica acts as an antifeedant, insect repellent, and egg-laying deterrent that protects crops from damage. Studies of A indica have noted effective nonpesticidal management against arthropod pests such as armyworm, termites, and the oriental fruit fly.7,12,13
Antimalarial Activity—One study indicated that nimbolide, a limonoid from the neem plant, demonstrated antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum. In separate cultures of asexual parasites and mature gametocytes, parasite numbers were less than 50% of the number in control cultures (8.0% vs 8.5% parasitemia, respectively).14 Thus, the lower parasite numbers indicated by this study highlight the antimalarial utility of nimbolide and neem oil.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activity—Neem bark has been reported to have considerable antioxidant activity due to its high phenolic content.1,15 One study showed that azadirachtin and nimbolide in neem exhibited concentration-dependent antiradical scavenging activity and antioxidant properties.16
The anti-inflammatory potential for neem may occur via the inhibition of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway, which is linked to cancer, inflammation, and apoptosis.17 It also has been observed that nimbidin within neem extracts—such as leaves, bark, and seed extract—suppresses the function of macrophages and neutrophils relevant to inflammation.16 Another study indicated neem’s anti-inflammatory activity due to the regulation of proinflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase.18
Safety, Toxicity, and Risks
Ingestion—Although neem is safe to use in the general population, neem oil poisoning has been reported, particularly in young children. Ingesting large quantities of neem has resulted in vomiting, hepatic toxicity, metabolic acidosis, late neurologic sequelae, and encephalopathy in young children.19 The diagnosis of neem oil poisoning is based on patient history, clinical examination, and imaging findings. Poisoning can manifest as drowsiness, tachypnea, and generalized seizures.20
Topical Application—Topical use of neem appears to be safe if the substance is diluted with other ingredients. However, direct application to the skin is not advised, as it may cause leukoderma and could induce allergic contact dermatitis and other allergic reactions.4
Final Thoughts
The use of neem extract for disease prevention and treatment has been prevalent around the world since ancient times. Neem has been documented to possess melanogenesis-inhibitory activity, toxicity against pests, antimalarial activity, and antioxidant activity by means of tyrosinase inhibition, phytochemical production, limonoid expression, and nuclear factor-κB regulation, respectively. However, topical use of neem may trigger a cutaneous response, highlighting the importance of considering a diagnosis of neem oil–induced chemical leukoderma when patients present with a hypopigmented rash and relevant history.
Commonly known as neem or nimba, Azadirachta indica traditionally has been used as an oil or poultice to lighten skin pigment and reduce joint inflammation. Neem is a drought-resistant evergreen tree with thin serrated leaves, white fragrant flowers, and olivelike fruit (Figure 1). This plant is indigenous to India but also is readily found within tropical and semitropical environments throughout the Middle East, Southeast Asia, North Africa, and Australia.

Traditional Uses
For more than 4000 years, neem leaves, bark, fruit, and seeds have been used in food, insecticide, and herbal medicine cross-culturally in Indian Ayurvedic medicine and across Southeast Asia, particularly in Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar, and Vietnam.1-3 Because of its many essential nutrients—oleic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, linoleic acid, behenic acid, arachidic acid, and palmitoleic acid—and readily available nature, some ethnic groups include neem in their diet.4 Neem commonly is used as a seasoning in soups and rice, eaten as a cooked vegetable, infused into teas and tonics, and pickled with other spices.5
All parts of the neem tree—both externally and internally—have been utilized in traditional medicine for the treatment of various diseases and ailments. The flowers have been used to treat eye diseases and dyspepsia, the fruit has been employed as an anthelmintic, the seeds and leaves have been used for malaria treatment and insecticide, the stem bark has been used for the treatment of diarrhea, and the root bark has been used for skin diseases and inflammation.6 Neem oil is a yellow-brown bitter substance that often is utilized to treat skin diseases such as psoriasis, eczema, fungal infections, and abscesses.
Case Report—A 77-year-old man presented with a diffuse rash across the lower back. He reported that he had been using topical neem oil to alleviate lower back pain and arthritis for the last 6 months with noted relief and improvement of back pain. After roughly 3 to 4 months of using neem oil, he noted a rash on the lower back, bilateral flanks, and buttocks (Figure 2). The rash was asymptomatic, and he denied any pruritus, scaling, pain, or burning. The patient was referred to dermatology and received a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma secondary to contact with A indica. The patient was advised to stop using the topical neem oil, and the rash was simply monitored, as it was asymptomatic.

Bioactivity
Research has elucidated multiple bioactivity mechanisms of neem, including melanogenesis-inhibitory activity, toxicity against pests, antimalarial activity, and antioxidant activity.1,7-9 Literature on the diverse phytochemical components of A indica indicate high levels of limonoids, flavonoids, and triterpenoids that are responsible for much of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and insecticide properties.1,10
Melanogenesis-Inhibitory Activity—To date, neem has been added to a number of cosmetic products used in Ayurvedic medicine. One study of isolated compounds in A indica showed superior inhibitory activities against melanogenesis with minimal toxicity to cells (86.5%–105.1% cell viability). Western blot analysis of samples extracted and isolated from neem root and bark showed melanogenesis-inhibitory activities in B16 melanoma cells through the inhibition of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor expression and decreased expression of tyrosinase, as well as tyrosinase-related proteins 1 and 2, which are largely responsible for melanin synthesis.11 In another study, A indica flowers and their extracted constituents—6-deacetylnimbin and kaempferide—suggest melanogenesis-inhibitory activities in B16 melanoma cells with little to no toxicity to the cells (81.0%–111.7% cell viability).1 In an evaluationof A indica seed extracts, some of the isolated limonoids and diterpenoids exhibited a marked melanogenesis-inhibitory effect (74%–91% reduction of melanin content) with no toxicity to the cell.5 All of these studies indicate that active compounds in neem root, bark, flowers, and seeds may be potential skin-lightening agents.
Toxicity Against Pests—Neem seeds have phytochemicals that convey some insecticidal properties. The seeds often are ground into a powder, combined with water, and sprayed onto crops to act as an insecticide. As a natural method of nonpesticidal management, A indica acts as an antifeedant, insect repellent, and egg-laying deterrent that protects crops from damage. Studies of A indica have noted effective nonpesticidal management against arthropod pests such as armyworm, termites, and the oriental fruit fly.7,12,13
Antimalarial Activity—One study indicated that nimbolide, a limonoid from the neem plant, demonstrated antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum. In separate cultures of asexual parasites and mature gametocytes, parasite numbers were less than 50% of the number in control cultures (8.0% vs 8.5% parasitemia, respectively).14 Thus, the lower parasite numbers indicated by this study highlight the antimalarial utility of nimbolide and neem oil.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activity—Neem bark has been reported to have considerable antioxidant activity due to its high phenolic content.1,15 One study showed that azadirachtin and nimbolide in neem exhibited concentration-dependent antiradical scavenging activity and antioxidant properties.16
The anti-inflammatory potential for neem may occur via the inhibition of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway, which is linked to cancer, inflammation, and apoptosis.17 It also has been observed that nimbidin within neem extracts—such as leaves, bark, and seed extract—suppresses the function of macrophages and neutrophils relevant to inflammation.16 Another study indicated neem’s anti-inflammatory activity due to the regulation of proinflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase.18
Safety, Toxicity, and Risks
Ingestion—Although neem is safe to use in the general population, neem oil poisoning has been reported, particularly in young children. Ingesting large quantities of neem has resulted in vomiting, hepatic toxicity, metabolic acidosis, late neurologic sequelae, and encephalopathy in young children.19 The diagnosis of neem oil poisoning is based on patient history, clinical examination, and imaging findings. Poisoning can manifest as drowsiness, tachypnea, and generalized seizures.20
Topical Application—Topical use of neem appears to be safe if the substance is diluted with other ingredients. However, direct application to the skin is not advised, as it may cause leukoderma and could induce allergic contact dermatitis and other allergic reactions.4
Final Thoughts
The use of neem extract for disease prevention and treatment has been prevalent around the world since ancient times. Neem has been documented to possess melanogenesis-inhibitory activity, toxicity against pests, antimalarial activity, and antioxidant activity by means of tyrosinase inhibition, phytochemical production, limonoid expression, and nuclear factor-κB regulation, respectively. However, topical use of neem may trigger a cutaneous response, highlighting the importance of considering a diagnosis of neem oil–induced chemical leukoderma when patients present with a hypopigmented rash and relevant history.
- Kitdamrongtham W, Ishii K, Ebina K, et al. Limonoids and flavonoids from the flowers of Azadirachta indica var. siamensis, and their melanogenesis-inhibitory and cytotoxic activities. Chem Biodivers. 2014;11:73-84. doi:10.1002/cbdv.201300266
- Singh A, Srivastava PS, Lakshmikumaran M. Comparison of AFLP and SAMPL markers for assessment of intra-population genetic variation in Azadirachta indica A. Juss. Plant Sci. 2002;162:17-25. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00503-9
- Pandey G, Verma K, Singh M. Evaluation of phytochemical, antibacterial and free radical scavenging properties of Azadirachta Indica (neem) leaves. Int J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2014;6:444-447.
- Romita P, Calogiuri G, Bellino M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by neem oil: an underrated allergen. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:133-134. doi:10.1111/cod. 13256
- Akihisa T, Noto T, Takahashi A, et al. Melanogenesis inhibitory, anti-inflammatory, and chemopreventive effects of limonoids from the seeds of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. (neem). J Oleo Sci. 2009;58:581-594.
- Subapriya R, Nagini S. Medicinal properties of neem leaves: a review. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005;5:149-156. doi:10.2174/1568011053174828
- Areekul S, Sinchaisri P, Tigvatananon S. Effect of Thai plant extracts on the Oriental fruit fly. I: toxicity test. Agriculture and Natural Resources. 1987;21:395-407.
- Rochanakij S, Thebtaranonth Y, Yenjai C, et al. Nimbolide, a constituent of Azadirachta indica, inhibits Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1985;16:66-72.
- Sithisarn P, Supabphol R, Gritsanapan W. Antioxidant activity of Siamese neem tree (VP1209). J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;99:109-112. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.02.008
- Yin F, Lei XX, Cheng L, et al. Isolation and structure identification of the compounds from the seeds and leaves of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. J China Pharmaceut University. 2005;36:10-12.
- Su S, Cheng J, Zhang C, et al. Melanogenesis-inhibitory activities of limonoids and tricyclic diterpenoids from Azadirachta indica. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2020;100:103941. doi:j.bioorg.2020.103941
- Tulashie SK, Adjei F, Abraham J, et al. Potential of neem extracts as natural insecticide against fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Case Stud Chem Environ Eng. 2021;4:100130. doi:10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100130
- Yashroy RC, Gupta PK. Neem-seed oil inhibits growth of termite surface-tunnels. Indian J Toxicol. 2000;7:49-50.
- Udeinya JI, Shu EN, Quakyi I, et al. An antimalarial neem leaf extract has both schizonticidal and gametocytocidal activities. Am J Therapeutics. 2008;15:108-110. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e31804c6d1d
- Bindurani R, Kumar K. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of hydro distilled extracts of leaf, heart wood and flower of Azadirachta indica. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013;20:222.
- Alzohairy MA. Therapeutics role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and their active constituents in diseases prevention and treatment [published online March 1, 2016]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1155/2016/7382506
- Schumacher M, Cerella C, Reuter S, et al. Anti-inflammatory, pro-apoptotic, and anti-proliferative effects of a methanolic neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf extract are mediated via modulation of the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Genes Nutr. 2011;6:149-160. doi:10.1007/s12263-010-0194-6
- Kaur G, Sarwar Alam M, Athar M. Nimbidin suppresses functions of macrophages and neutrophils: relevance to its anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Phytotherapy Res. 2004;18:419-424. doi:10.1002/ptr.1474
- Dhongade RK, Kavade SG, Damle RS. Neem oil poisoning. Indian Pediatr. 2008;45:56-57.
- Bhaskar MV, Pramod SJ, Jeevika MU, et al. MR imaging findings of neem oil poisoning. Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:E60-E61. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2146
- Kitdamrongtham W, Ishii K, Ebina K, et al. Limonoids and flavonoids from the flowers of Azadirachta indica var. siamensis, and their melanogenesis-inhibitory and cytotoxic activities. Chem Biodivers. 2014;11:73-84. doi:10.1002/cbdv.201300266
- Singh A, Srivastava PS, Lakshmikumaran M. Comparison of AFLP and SAMPL markers for assessment of intra-population genetic variation in Azadirachta indica A. Juss. Plant Sci. 2002;162:17-25. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00503-9
- Pandey G, Verma K, Singh M. Evaluation of phytochemical, antibacterial and free radical scavenging properties of Azadirachta Indica (neem) leaves. Int J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2014;6:444-447.
- Romita P, Calogiuri G, Bellino M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by neem oil: an underrated allergen. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:133-134. doi:10.1111/cod. 13256
- Akihisa T, Noto T, Takahashi A, et al. Melanogenesis inhibitory, anti-inflammatory, and chemopreventive effects of limonoids from the seeds of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. (neem). J Oleo Sci. 2009;58:581-594.
- Subapriya R, Nagini S. Medicinal properties of neem leaves: a review. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005;5:149-156. doi:10.2174/1568011053174828
- Areekul S, Sinchaisri P, Tigvatananon S. Effect of Thai plant extracts on the Oriental fruit fly. I: toxicity test. Agriculture and Natural Resources. 1987;21:395-407.
- Rochanakij S, Thebtaranonth Y, Yenjai C, et al. Nimbolide, a constituent of Azadirachta indica, inhibits Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1985;16:66-72.
- Sithisarn P, Supabphol R, Gritsanapan W. Antioxidant activity of Siamese neem tree (VP1209). J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;99:109-112. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.02.008
- Yin F, Lei XX, Cheng L, et al. Isolation and structure identification of the compounds from the seeds and leaves of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. J China Pharmaceut University. 2005;36:10-12.
- Su S, Cheng J, Zhang C, et al. Melanogenesis-inhibitory activities of limonoids and tricyclic diterpenoids from Azadirachta indica. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2020;100:103941. doi:j.bioorg.2020.103941
- Tulashie SK, Adjei F, Abraham J, et al. Potential of neem extracts as natural insecticide against fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Case Stud Chem Environ Eng. 2021;4:100130. doi:10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100130
- Yashroy RC, Gupta PK. Neem-seed oil inhibits growth of termite surface-tunnels. Indian J Toxicol. 2000;7:49-50.
- Udeinya JI, Shu EN, Quakyi I, et al. An antimalarial neem leaf extract has both schizonticidal and gametocytocidal activities. Am J Therapeutics. 2008;15:108-110. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e31804c6d1d
- Bindurani R, Kumar K. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of hydro distilled extracts of leaf, heart wood and flower of Azadirachta indica. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013;20:222.
- Alzohairy MA. Therapeutics role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and their active constituents in diseases prevention and treatment [published online March 1, 2016]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1155/2016/7382506
- Schumacher M, Cerella C, Reuter S, et al. Anti-inflammatory, pro-apoptotic, and anti-proliferative effects of a methanolic neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf extract are mediated via modulation of the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Genes Nutr. 2011;6:149-160. doi:10.1007/s12263-010-0194-6
- Kaur G, Sarwar Alam M, Athar M. Nimbidin suppresses functions of macrophages and neutrophils: relevance to its anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Phytotherapy Res. 2004;18:419-424. doi:10.1002/ptr.1474
- Dhongade RK, Kavade SG, Damle RS. Neem oil poisoning. Indian Pediatr. 2008;45:56-57.
- Bhaskar MV, Pramod SJ, Jeevika MU, et al. MR imaging findings of neem oil poisoning. Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:E60-E61. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2146
Practice Points
- Neem is a traditional herb with various bioactivities, such as melanogenesis-inhibitory activity, toxicity against pests, antimalarial activity, and antioxidant activity.
- Neem should be used with caution as a remedy because of its skin-lightening properties, which are attributed to melanogenesis-inhibitory activity via tyrosinase inhibition.
- Chemical leukoderma should be included in the differential diagnosis when a patient presents with a hypopigmented rash after topical use of neem products.
Analysis of Online Diet Recommendations for Vitiligo
Internet platforms have become a common source of medical information for individuals with a broad range of skin conditions including vitiligo. The prevalence of vitiligo among US adults ranges from 0.76% to 1.11%, with approximately 40% of adult cases of vitiligo in the United States remaining undiagnosed.1 The vitiligo community has become more inquisitive of the relationship between diet and vitiligo, turning to online sources for suggestions on diet modifications that may be beneficial for their condition. Although there is an abundance of online information, few diets or foods have been medically recognized to definitively improve or worsen vitiligo symptoms. We reviewed the top online web pages accessible to the public regarding diet suggestions that affect vitiligo symptoms. We then compared these online results to published peer-reviewed scientific literature.
Methods
Two independent online searches were performed by Researcher 1 (Y.A.) and Researcher 2 (I.M.) using Google Advanced Search. The independent searches were performed by the reviewers in neighboring areas of Chicago, Illinois, using the same Internet browser (Google Chrome). The primary search terms were diet and vitiligo along with the optional additional terms dietary supplement(s), food(s), nutrition, herb(s), or vitamin(s). Our search included any web pages published or updated from January 1, 2010, to December 31, 2021, and originally scribed in the English language. The domains “.com,” “.org,” “.edu,” and “.cc” were included.
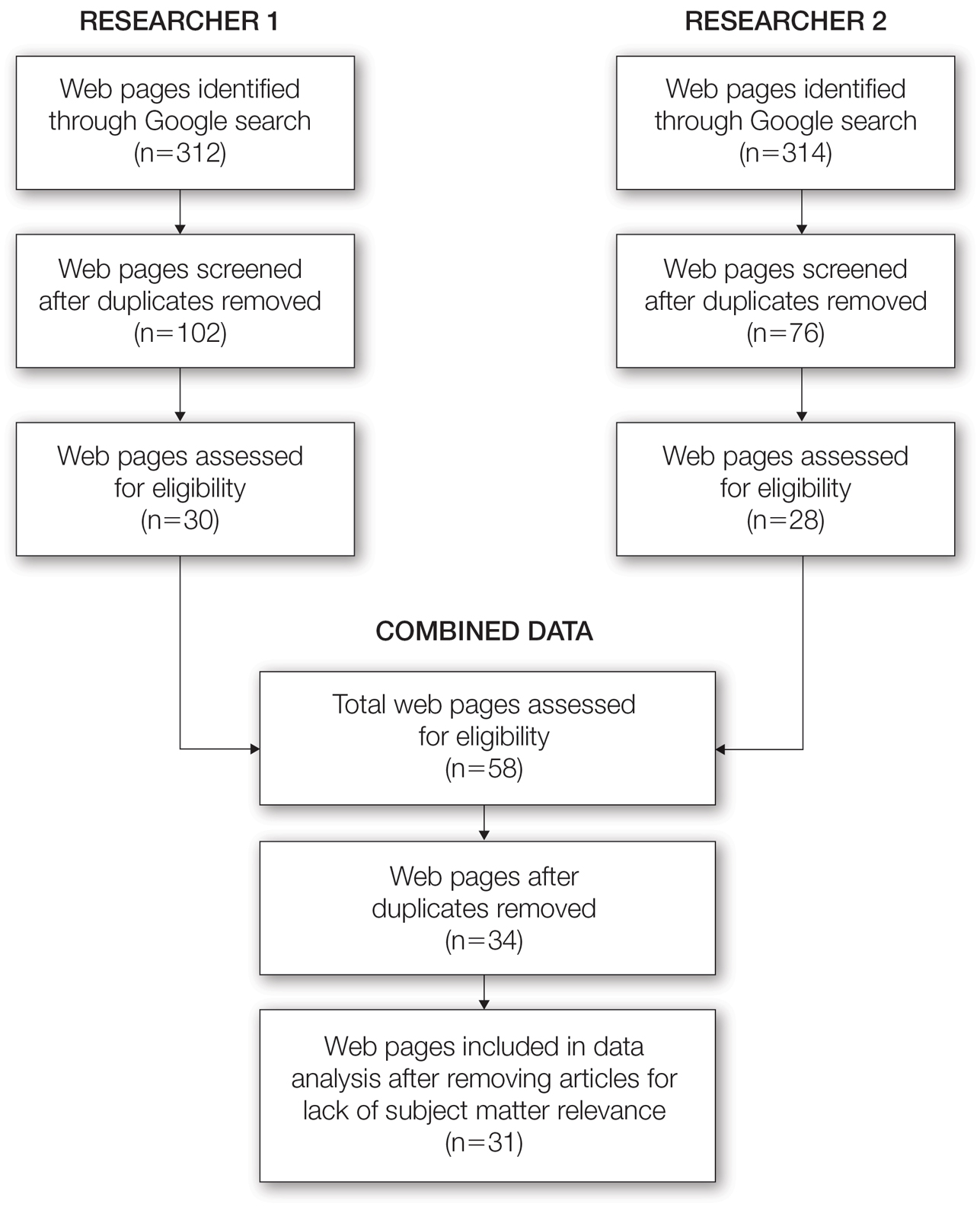
From this initial search, Researcher 1 identified 312 web pages and Researcher 2 identified 314 web pages. Each reviewer sorted their respective search results to identify the number of eligible records to be screened. Records were defined as unique web pages that met the search criteria. After removing duplicates, Researcher 1 screened 102 web pages and Researcher 2 screened 76 web pages. Of these records, web pages were excluded if they did not include any diet recommendations for vitiligo patients. Each reviewer independently created a list of eligible records, and the independent lists were then merged for a total of 58 web pages. Among these 58 web pages, there were 24 duplicate records and 3 records that were deemed ineligible for the study due to lack of subject matter relevance. A final total of 31 web pages were included in the data analysis (Figure). Of the 31 records selected, the reviewers jointly evaluated each web page and recorded the diet components that were recommended for individuals with vitiligo to either include or avoid (eTable).
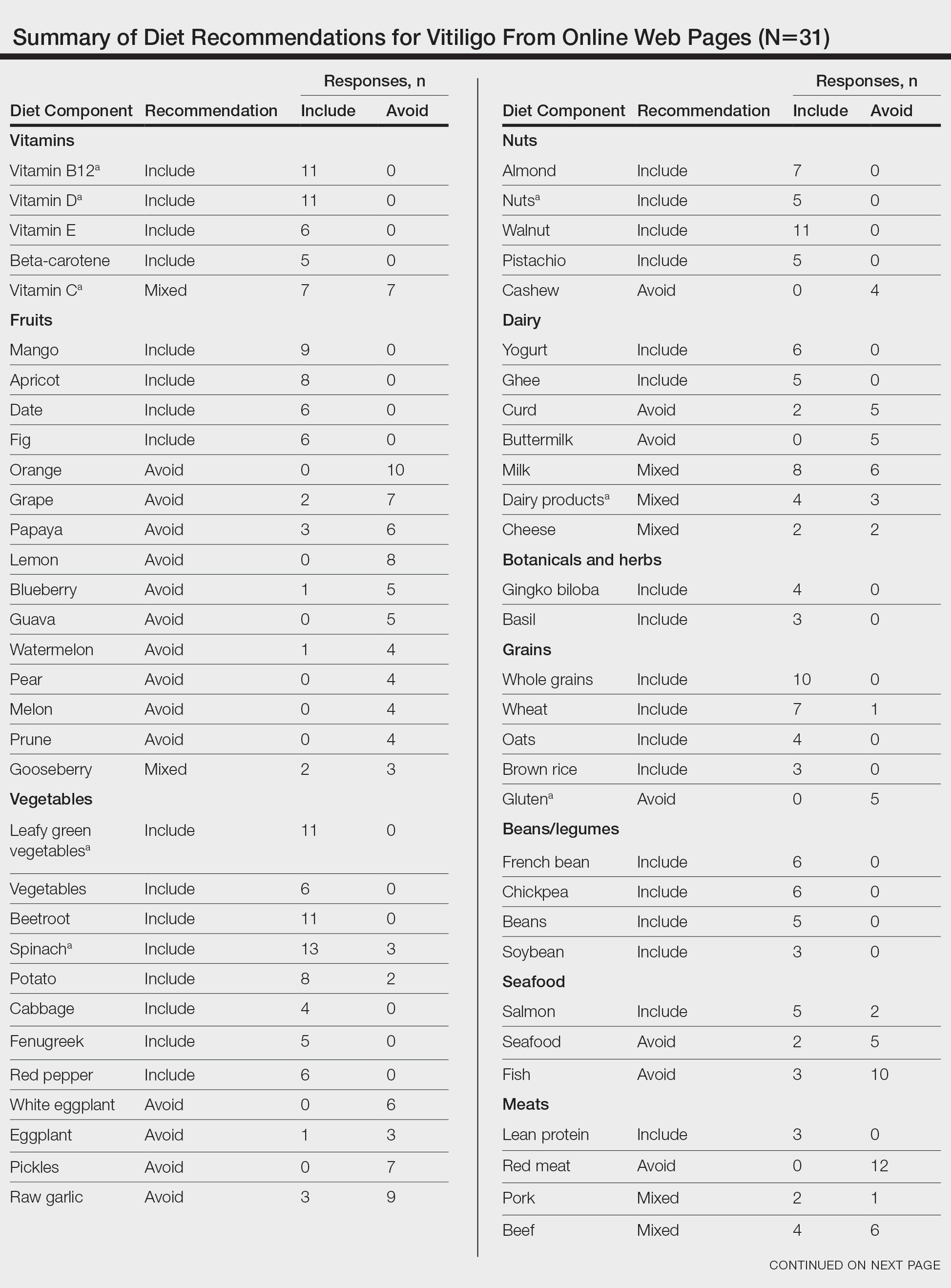
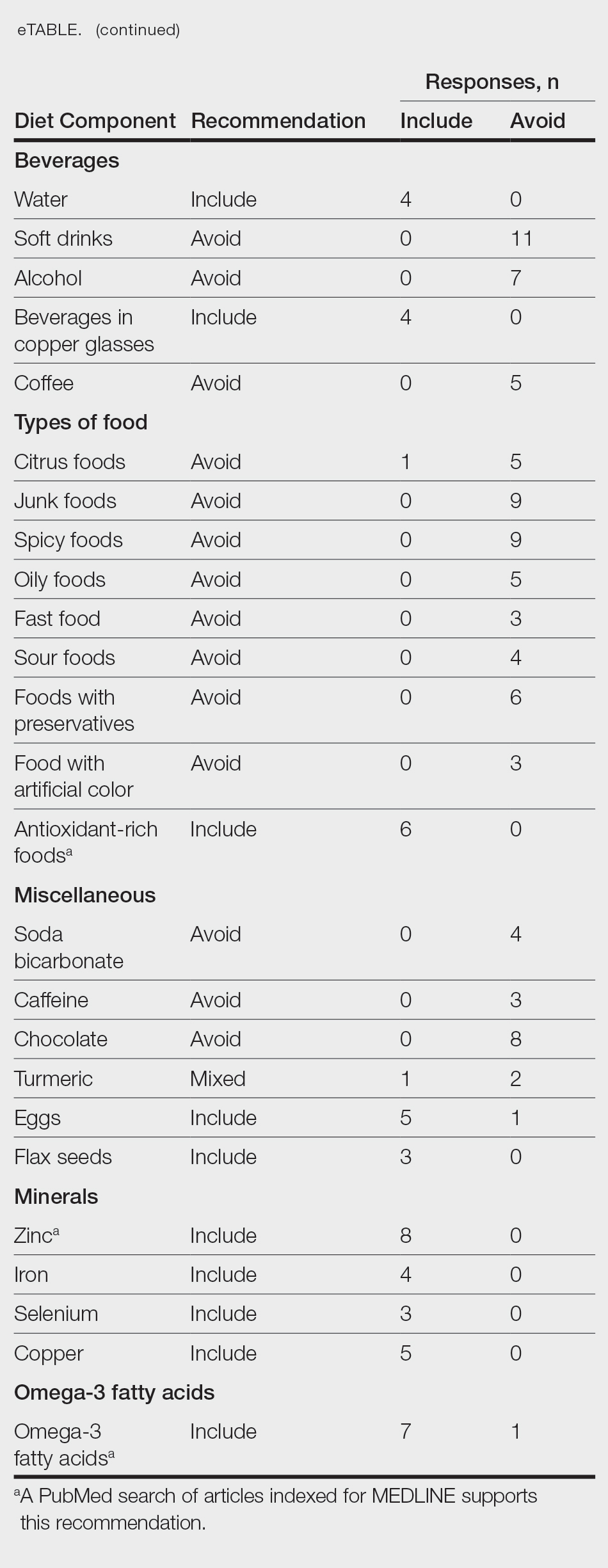
For comparison and support from published scientific literature, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the terms diet and vitiligo. Relevant human clinical studies published in the English-language literature were reviewed for content regarding the relationship between diet and vitiligo.
Results
Our online search revealed an abundance of information regarding various dietary modifications suggested to aid in the management of vitiligo symptoms. Most web pages (27/31 [87%]) were not authored by medical professionals or dermatologists. There were 27 diet components mentioned 8 or more times within the 31 total web pages. These diet components were selected for further review via PubMed. Each item was searched on PubMed using the term “[respective diet component] and vitiligo” among all published literature in the English language. Our study focused on summarizing the data on dietary components for which we were able to gather scientific support. These data have been organized into the following categories: vitamins, fruits, omega-3 fatty acids, grains, minerals, vegetables, and nuts.
Vitamins—The online literature recommended inclusion of vitamin supplements, in particular vitamins D and B12, which aligned with published scientific literature.2,3 Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended vitamin D in vitiligo. A 2010 study analyzing patients with vitiligo vulgaris (N=45) found that 68.9% of the cohort had insufficient (<30 ng/mL) 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.2 A prospective study of 30 individuals found that the use of tacrolimus ointment plus oral vitamin D supplementation was found to be more successful in repigmentation than topical tacrolimus alone.3 Vitamin D dosage ranged from 1500 IU/d if the patient’s serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were less than 20 ng/mL to 3000 IU/d if the serum levels were less than 10 ng/mL for 6 months.
Dairy products are a source of vitamin D.2,3 Of the web pages that mentioned dairy, a subtle majority (4/7 [57%]) recommended the inclusion of dairy products. Although many web pages did not specify whether oral vitamin D supplementation vs dietary food consumption is preferred, a 2013 controlled study of 16 vitiligo patients who received high doses of vitamin D supplementation with a low-calcium diet found that 4 patients showed 1% to 25% repigmentation, 5 patients showed 26% to 50% repigmentation, and 5 patients showed 51% to 75% repigmentation of the affected areas.4
Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended inclusion of vitamin B12 supplementation in vitiligo. A 2-year study with 100 participants showed that supplementation with folic acid and vitamin B12 along with sun exposure yielded more effective repigmentation than either vitamins or sun exposure alone.5 An additional hypothesis suggested vitamin B12 may aid in repigmentation through its role in the homocysteine pathway. Although the theory is unproven, it is proposed that inhibition of homocysteine via vitamin B12 or folic acid supplementation may play a role in reducing melanocyte destruction and restoring melanin synthesis.6
There were mixed recommendations regarding vitamin C via supplementation and/or eating citrus fruits such as oranges. Although there are limited clinical studies on the use of vitamin C and the treatment of vitiligo, a 6-year prospective study from Madagascar consisting of approximately 300 participants with vitiligo who were treated with a combination of topical corticosteroids, oral vitamin C, and oral vitamin B12 supplementation showed excellent repigmentation (defined by repigmentation of more than 76% of the originally affected area) in 50 participants.7
Fruits—Most web pages had mixed recommendations on whether to include or avoid certain fruits. Interestingly, inclusion of mangoes and apricots in the diet were highly recommended (9/31 [29%] and 8/31 [26%], respectively) while fruits such as oranges, lemons, papayas, and grapes were discouraged (10/31 [32%], 8/31 [26%], 6/31 [19%], and 7/31 [23%], respectively). Although some web pages suggested that vitamin C–rich produce including citrus and berries may help to increase melanin formation, others strongly suggested avoiding these fruits. There is limited information on the effects of citrus on vitiligo, but a 2022 study indicated that 5-demethylnobiletin, a flavonoid found in sweet citrus fruits, may stimulate melanin synthesis, which can possibly be beneficial for vitiligo.8
Omega-3 Fatty Acids—Seven of 31 (23%) web pages recommended the inclusion of omega-3 fatty acids for their role as antioxidants to improve vitiligo symptoms. Research has indicated a strong association between vitiligo and oxidative stress.9 A 2007 controlled clinical trial that included 28 vitiligo patients demonstrated that oral antioxidant supplementation in combination with narrowband UVB phototherapy can significantly decrease vitiligo-associated oxidative stress (P<.05); 8 of 17 (47%) patients in the treatment group saw greater than 75% repigmentation after antioxidant treatment.10
Grains—Five of 31 (16%) web pages suggested avoiding gluten—a protein naturally found in some grains including wheat, barley, and rye—to improve vitiligo symptoms. A 2021 review suggested that a gluten-free diet may be effective in managing celiac disease, and it is hypothesized that vitiligo may be managed with similar dietary adjustments.11 Studies have shown that celiac disease and vitiligo—both autoimmune conditions—involve IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, and IL-21 in their disease pathways.12,13 Their shared immunogenic mechanism may account for similar management options.
Upon review, 2 case reports were identified that discussed a relationship between a gluten-free diet and vitiligo symptom improvement. In one report, a 9-year-old child diagnosed with both celiac disease and vitiligo saw intense repigmentation of the skin after adhering to a gluten-free diet for 1 year.14 Another case study reported a 22-year-old woman with vitiligo whose symptoms improved after 1 month of a gluten-free diet following 2 years of failed treatment with a topical steroid and phototherapy.15
Seven of 31 (23%) web pages suggested that individuals with vitiligo should include wheat in their diet. There is no published literature discussing the relationship between vitiligo and wheat. Of the 31 web pages reviewed, 10 (32%) suggested including whole grain. There is no relevant scientific evidence or hypotheses describing how whole grains may be beneficial in vitiligo.
Minerals—Eight of 31 (26%) web pages suggested including zinc in the diet to improve vitiligo symptoms. A 2020 study evaluated how different serum levels of zinc in vitiligo patients might be affiliated with interleukin activity. Fifty patients diagnosed with active vitiligo were tested for serum levels of zinc, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-17.16 The results showed that mean serum levels of zinc were lower in vitiligo patients compared with patients without vitiligo. The study concluded that zinc could possibly be used as a supplement to improve vitiligo, though the dosage needs to be further studied and confirmed.16
Vegetables—Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended leafy green vegetables and 13 of 31 (42%) recommended spinach for patients with vitiligo. Spinach and other leafy green vegetables are known to be rich in antioxidants, which may have protective effects against reactive oxygen species that are thought to contribute to vitiligo progression.17,18
Nuts—Walnuts were recommended in 11 of 31 (35%) web pages. Nuts may be beneficial in reducing inflammation and providing protection against oxidative stress.9 However, there is no specific scientific literature that supports the inclusion of nuts in the diet to manage vitiligo symptoms.
Comment
With a growing amount of research suggesting that diet modifications may contribute to management of certain skin conditions, vitiligo patients often inquire about foods or supplements that may help improve their condition.19 Our review highlighted what information was available to the public regarding diet and vitiligo, with preliminary support of the following primary diet components: vitamin D, vitamin B12, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids. Our review showed no support in the literature for the items that were recommended to avoid. It is important to note that 27 of 31 (87%) web pages from our online search were not authored by medical professionals or dermatologists. Additionally, many web pages suggested conflicting information, making it difficult to draw concrete conclusions about what diet modifications will be beneficial to the vitiligo community. Further controlled clinical trials are warranted due to the lack of formal studies that assess the relationship between diet and vitiligo.
- Gandhi K, Ezzedine K, Anastassopoulos KP, et al. Prevalence of vitiligo among adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:43-50. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.4724
- Silverberg JI, Silverberg AI, Malka E, et al. A pilot study assessing the role of 25 hydroxy vitamin D levels in patients with vitiligo vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:937-941. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.11.024
- Karagüzel G, Sakarya NP, Bahadır S, et al. Vitamin D status and the effects of oral vitamin D treatment in children with vitiligo: a prospective study. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2016;15:28-31. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2016.05.006.
- Finamor DC, Sinigaglia-Coimbra R, Neves LC, et al. A pilot study assessing the effect of prolonged administration of high daily doses of vitamin D on the clinical course of vitiligo and psoriasis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2013;5:222-234. doi:10.4161/derm.24808
- Juhlin L, Olsson MJ. Improvement of vitiligo after oral treatment with vitamin B12 and folic acid and the importance of sun exposure. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997;77:460-462. doi:10.2340/000155555577460462
- Chen J, Zhuang T, Chen J, et al. Homocysteine induces melanocytes apoptosis via PERK-eIF2α-CHOP pathway in vitiligo. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020;134:1127-1141. doi:10.1042/CS20200218
- Sendrasoa FA, Ranaivo IM, Sata M, et al. Treatment responses in patients with vitiligo to very potent topical corticosteroids combined with vitamin therapy in Madagascar. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:908-911. doi:10.1111/ijd.14510
- Wang HM, Qu LQ, Ng JPL, et al. Natural citrus flavanone 5-demethylnobiletin stimulates melanogenesis through the activation of cAMP/CREB pathway in B16F10 cells. Phytomedicine. 2022;98:153941. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153941
- Ros E. Health benefits of nut consumption. Nutrients. 2010;2:652-682.
- Dell’Anna ML, Mastrofrancesco A, Sala R, et al. Antioxidants and narrow band-UVB in the treatment of vitiligo: a double-blind placebo controlled trial. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32:631-636.
- Gastrointestinal microbiome and gluten in celiac disease. Ann Med. 2021;53:1797-1805. doi:10.1080/07853890.2021.1990392
- Forabosco P, Neuhausen SL, Greco L, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide linkage studies in celiac disease. Hum Hered. 2009;68:223-230. doi:10.1159/000228920
- Akbulut UE, Çebi AH, Sag˘ E, et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-17 gene polymorphism association with celiac disease in children. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017;28:471-475. doi:10.5152/tjg.2017.17092
- Rodríguez-García C, González-Hernández S, Pérez-Robayna N, et al. Repigmentation of vitiligo lesions in a child with celiac disease after a gluten-free diet. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:209-210. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01388.x
- Khandalavala BN, Nirmalraj MC. Rapid partial repigmentation ofvitiligo in a young female adult with a gluten-free diet. Case Rep Dermatol. 2014;6:283-287.
- Sanad EM, El-Fallah AA, Al-Doori AR, et al. Serum zinc and inflammatory cytokines in vitiligo. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:(12 suppl 1):S29-S33.
- Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:7915-7922. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.17.7915
- Xian D, Guo M, Xu J, et al. Current evidence to support the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in oxidative stress-related dermatoses. Redox Rep. 2021;26:134-146. doi:10.1080 /13510002.2021.1962094
- Katta R, Kramer MJ. Skin and diet: an update on the role of dietary change as a treatment strategy for skin disease. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018;23:1-5.
Internet platforms have become a common source of medical information for individuals with a broad range of skin conditions including vitiligo. The prevalence of vitiligo among US adults ranges from 0.76% to 1.11%, with approximately 40% of adult cases of vitiligo in the United States remaining undiagnosed.1 The vitiligo community has become more inquisitive of the relationship between diet and vitiligo, turning to online sources for suggestions on diet modifications that may be beneficial for their condition. Although there is an abundance of online information, few diets or foods have been medically recognized to definitively improve or worsen vitiligo symptoms. We reviewed the top online web pages accessible to the public regarding diet suggestions that affect vitiligo symptoms. We then compared these online results to published peer-reviewed scientific literature.
Methods
Two independent online searches were performed by Researcher 1 (Y.A.) and Researcher 2 (I.M.) using Google Advanced Search. The independent searches were performed by the reviewers in neighboring areas of Chicago, Illinois, using the same Internet browser (Google Chrome). The primary search terms were diet and vitiligo along with the optional additional terms dietary supplement(s), food(s), nutrition, herb(s), or vitamin(s). Our search included any web pages published or updated from January 1, 2010, to December 31, 2021, and originally scribed in the English language. The domains “.com,” “.org,” “.edu,” and “.cc” were included.

From this initial search, Researcher 1 identified 312 web pages and Researcher 2 identified 314 web pages. Each reviewer sorted their respective search results to identify the number of eligible records to be screened. Records were defined as unique web pages that met the search criteria. After removing duplicates, Researcher 1 screened 102 web pages and Researcher 2 screened 76 web pages. Of these records, web pages were excluded if they did not include any diet recommendations for vitiligo patients. Each reviewer independently created a list of eligible records, and the independent lists were then merged for a total of 58 web pages. Among these 58 web pages, there were 24 duplicate records and 3 records that were deemed ineligible for the study due to lack of subject matter relevance. A final total of 31 web pages were included in the data analysis (Figure). Of the 31 records selected, the reviewers jointly evaluated each web page and recorded the diet components that were recommended for individuals with vitiligo to either include or avoid (eTable).


For comparison and support from published scientific literature, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the terms diet and vitiligo. Relevant human clinical studies published in the English-language literature were reviewed for content regarding the relationship between diet and vitiligo.
Results
Our online search revealed an abundance of information regarding various dietary modifications suggested to aid in the management of vitiligo symptoms. Most web pages (27/31 [87%]) were not authored by medical professionals or dermatologists. There were 27 diet components mentioned 8 or more times within the 31 total web pages. These diet components were selected for further review via PubMed. Each item was searched on PubMed using the term “[respective diet component] and vitiligo” among all published literature in the English language. Our study focused on summarizing the data on dietary components for which we were able to gather scientific support. These data have been organized into the following categories: vitamins, fruits, omega-3 fatty acids, grains, minerals, vegetables, and nuts.
Vitamins—The online literature recommended inclusion of vitamin supplements, in particular vitamins D and B12, which aligned with published scientific literature.2,3 Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended vitamin D in vitiligo. A 2010 study analyzing patients with vitiligo vulgaris (N=45) found that 68.9% of the cohort had insufficient (<30 ng/mL) 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.2 A prospective study of 30 individuals found that the use of tacrolimus ointment plus oral vitamin D supplementation was found to be more successful in repigmentation than topical tacrolimus alone.3 Vitamin D dosage ranged from 1500 IU/d if the patient’s serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were less than 20 ng/mL to 3000 IU/d if the serum levels were less than 10 ng/mL for 6 months.
Dairy products are a source of vitamin D.2,3 Of the web pages that mentioned dairy, a subtle majority (4/7 [57%]) recommended the inclusion of dairy products. Although many web pages did not specify whether oral vitamin D supplementation vs dietary food consumption is preferred, a 2013 controlled study of 16 vitiligo patients who received high doses of vitamin D supplementation with a low-calcium diet found that 4 patients showed 1% to 25% repigmentation, 5 patients showed 26% to 50% repigmentation, and 5 patients showed 51% to 75% repigmentation of the affected areas.4
Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended inclusion of vitamin B12 supplementation in vitiligo. A 2-year study with 100 participants showed that supplementation with folic acid and vitamin B12 along with sun exposure yielded more effective repigmentation than either vitamins or sun exposure alone.5 An additional hypothesis suggested vitamin B12 may aid in repigmentation through its role in the homocysteine pathway. Although the theory is unproven, it is proposed that inhibition of homocysteine via vitamin B12 or folic acid supplementation may play a role in reducing melanocyte destruction and restoring melanin synthesis.6
There were mixed recommendations regarding vitamin C via supplementation and/or eating citrus fruits such as oranges. Although there are limited clinical studies on the use of vitamin C and the treatment of vitiligo, a 6-year prospective study from Madagascar consisting of approximately 300 participants with vitiligo who were treated with a combination of topical corticosteroids, oral vitamin C, and oral vitamin B12 supplementation showed excellent repigmentation (defined by repigmentation of more than 76% of the originally affected area) in 50 participants.7
Fruits—Most web pages had mixed recommendations on whether to include or avoid certain fruits. Interestingly, inclusion of mangoes and apricots in the diet were highly recommended (9/31 [29%] and 8/31 [26%], respectively) while fruits such as oranges, lemons, papayas, and grapes were discouraged (10/31 [32%], 8/31 [26%], 6/31 [19%], and 7/31 [23%], respectively). Although some web pages suggested that vitamin C–rich produce including citrus and berries may help to increase melanin formation, others strongly suggested avoiding these fruits. There is limited information on the effects of citrus on vitiligo, but a 2022 study indicated that 5-demethylnobiletin, a flavonoid found in sweet citrus fruits, may stimulate melanin synthesis, which can possibly be beneficial for vitiligo.8
Omega-3 Fatty Acids—Seven of 31 (23%) web pages recommended the inclusion of omega-3 fatty acids for their role as antioxidants to improve vitiligo symptoms. Research has indicated a strong association between vitiligo and oxidative stress.9 A 2007 controlled clinical trial that included 28 vitiligo patients demonstrated that oral antioxidant supplementation in combination with narrowband UVB phototherapy can significantly decrease vitiligo-associated oxidative stress (P<.05); 8 of 17 (47%) patients in the treatment group saw greater than 75% repigmentation after antioxidant treatment.10
Grains—Five of 31 (16%) web pages suggested avoiding gluten—a protein naturally found in some grains including wheat, barley, and rye—to improve vitiligo symptoms. A 2021 review suggested that a gluten-free diet may be effective in managing celiac disease, and it is hypothesized that vitiligo may be managed with similar dietary adjustments.11 Studies have shown that celiac disease and vitiligo—both autoimmune conditions—involve IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, and IL-21 in their disease pathways.12,13 Their shared immunogenic mechanism may account for similar management options.
Upon review, 2 case reports were identified that discussed a relationship between a gluten-free diet and vitiligo symptom improvement. In one report, a 9-year-old child diagnosed with both celiac disease and vitiligo saw intense repigmentation of the skin after adhering to a gluten-free diet for 1 year.14 Another case study reported a 22-year-old woman with vitiligo whose symptoms improved after 1 month of a gluten-free diet following 2 years of failed treatment with a topical steroid and phototherapy.15
Seven of 31 (23%) web pages suggested that individuals with vitiligo should include wheat in their diet. There is no published literature discussing the relationship between vitiligo and wheat. Of the 31 web pages reviewed, 10 (32%) suggested including whole grain. There is no relevant scientific evidence or hypotheses describing how whole grains may be beneficial in vitiligo.
Minerals—Eight of 31 (26%) web pages suggested including zinc in the diet to improve vitiligo symptoms. A 2020 study evaluated how different serum levels of zinc in vitiligo patients might be affiliated with interleukin activity. Fifty patients diagnosed with active vitiligo were tested for serum levels of zinc, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-17.16 The results showed that mean serum levels of zinc were lower in vitiligo patients compared with patients without vitiligo. The study concluded that zinc could possibly be used as a supplement to improve vitiligo, though the dosage needs to be further studied and confirmed.16
Vegetables—Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended leafy green vegetables and 13 of 31 (42%) recommended spinach for patients with vitiligo. Spinach and other leafy green vegetables are known to be rich in antioxidants, which may have protective effects against reactive oxygen species that are thought to contribute to vitiligo progression.17,18
Nuts—Walnuts were recommended in 11 of 31 (35%) web pages. Nuts may be beneficial in reducing inflammation and providing protection against oxidative stress.9 However, there is no specific scientific literature that supports the inclusion of nuts in the diet to manage vitiligo symptoms.
Comment
With a growing amount of research suggesting that diet modifications may contribute to management of certain skin conditions, vitiligo patients often inquire about foods or supplements that may help improve their condition.19 Our review highlighted what information was available to the public regarding diet and vitiligo, with preliminary support of the following primary diet components: vitamin D, vitamin B12, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids. Our review showed no support in the literature for the items that were recommended to avoid. It is important to note that 27 of 31 (87%) web pages from our online search were not authored by medical professionals or dermatologists. Additionally, many web pages suggested conflicting information, making it difficult to draw concrete conclusions about what diet modifications will be beneficial to the vitiligo community. Further controlled clinical trials are warranted due to the lack of formal studies that assess the relationship between diet and vitiligo.
Internet platforms have become a common source of medical information for individuals with a broad range of skin conditions including vitiligo. The prevalence of vitiligo among US adults ranges from 0.76% to 1.11%, with approximately 40% of adult cases of vitiligo in the United States remaining undiagnosed.1 The vitiligo community has become more inquisitive of the relationship between diet and vitiligo, turning to online sources for suggestions on diet modifications that may be beneficial for their condition. Although there is an abundance of online information, few diets or foods have been medically recognized to definitively improve or worsen vitiligo symptoms. We reviewed the top online web pages accessible to the public regarding diet suggestions that affect vitiligo symptoms. We then compared these online results to published peer-reviewed scientific literature.
Methods
Two independent online searches were performed by Researcher 1 (Y.A.) and Researcher 2 (I.M.) using Google Advanced Search. The independent searches were performed by the reviewers in neighboring areas of Chicago, Illinois, using the same Internet browser (Google Chrome). The primary search terms were diet and vitiligo along with the optional additional terms dietary supplement(s), food(s), nutrition, herb(s), or vitamin(s). Our search included any web pages published or updated from January 1, 2010, to December 31, 2021, and originally scribed in the English language. The domains “.com,” “.org,” “.edu,” and “.cc” were included.

From this initial search, Researcher 1 identified 312 web pages and Researcher 2 identified 314 web pages. Each reviewer sorted their respective search results to identify the number of eligible records to be screened. Records were defined as unique web pages that met the search criteria. After removing duplicates, Researcher 1 screened 102 web pages and Researcher 2 screened 76 web pages. Of these records, web pages were excluded if they did not include any diet recommendations for vitiligo patients. Each reviewer independently created a list of eligible records, and the independent lists were then merged for a total of 58 web pages. Among these 58 web pages, there were 24 duplicate records and 3 records that were deemed ineligible for the study due to lack of subject matter relevance. A final total of 31 web pages were included in the data analysis (Figure). Of the 31 records selected, the reviewers jointly evaluated each web page and recorded the diet components that were recommended for individuals with vitiligo to either include or avoid (eTable).


For comparison and support from published scientific literature, a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the terms diet and vitiligo. Relevant human clinical studies published in the English-language literature were reviewed for content regarding the relationship between diet and vitiligo.
Results
Our online search revealed an abundance of information regarding various dietary modifications suggested to aid in the management of vitiligo symptoms. Most web pages (27/31 [87%]) were not authored by medical professionals or dermatologists. There were 27 diet components mentioned 8 or more times within the 31 total web pages. These diet components were selected for further review via PubMed. Each item was searched on PubMed using the term “[respective diet component] and vitiligo” among all published literature in the English language. Our study focused on summarizing the data on dietary components for which we were able to gather scientific support. These data have been organized into the following categories: vitamins, fruits, omega-3 fatty acids, grains, minerals, vegetables, and nuts.
Vitamins—The online literature recommended inclusion of vitamin supplements, in particular vitamins D and B12, which aligned with published scientific literature.2,3 Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended vitamin D in vitiligo. A 2010 study analyzing patients with vitiligo vulgaris (N=45) found that 68.9% of the cohort had insufficient (<30 ng/mL) 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.2 A prospective study of 30 individuals found that the use of tacrolimus ointment plus oral vitamin D supplementation was found to be more successful in repigmentation than topical tacrolimus alone.3 Vitamin D dosage ranged from 1500 IU/d if the patient’s serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were less than 20 ng/mL to 3000 IU/d if the serum levels were less than 10 ng/mL for 6 months.
Dairy products are a source of vitamin D.2,3 Of the web pages that mentioned dairy, a subtle majority (4/7 [57%]) recommended the inclusion of dairy products. Although many web pages did not specify whether oral vitamin D supplementation vs dietary food consumption is preferred, a 2013 controlled study of 16 vitiligo patients who received high doses of vitamin D supplementation with a low-calcium diet found that 4 patients showed 1% to 25% repigmentation, 5 patients showed 26% to 50% repigmentation, and 5 patients showed 51% to 75% repigmentation of the affected areas.4
Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended inclusion of vitamin B12 supplementation in vitiligo. A 2-year study with 100 participants showed that supplementation with folic acid and vitamin B12 along with sun exposure yielded more effective repigmentation than either vitamins or sun exposure alone.5 An additional hypothesis suggested vitamin B12 may aid in repigmentation through its role in the homocysteine pathway. Although the theory is unproven, it is proposed that inhibition of homocysteine via vitamin B12 or folic acid supplementation may play a role in reducing melanocyte destruction and restoring melanin synthesis.6
There were mixed recommendations regarding vitamin C via supplementation and/or eating citrus fruits such as oranges. Although there are limited clinical studies on the use of vitamin C and the treatment of vitiligo, a 6-year prospective study from Madagascar consisting of approximately 300 participants with vitiligo who were treated with a combination of topical corticosteroids, oral vitamin C, and oral vitamin B12 supplementation showed excellent repigmentation (defined by repigmentation of more than 76% of the originally affected area) in 50 participants.7
Fruits—Most web pages had mixed recommendations on whether to include or avoid certain fruits. Interestingly, inclusion of mangoes and apricots in the diet were highly recommended (9/31 [29%] and 8/31 [26%], respectively) while fruits such as oranges, lemons, papayas, and grapes were discouraged (10/31 [32%], 8/31 [26%], 6/31 [19%], and 7/31 [23%], respectively). Although some web pages suggested that vitamin C–rich produce including citrus and berries may help to increase melanin formation, others strongly suggested avoiding these fruits. There is limited information on the effects of citrus on vitiligo, but a 2022 study indicated that 5-demethylnobiletin, a flavonoid found in sweet citrus fruits, may stimulate melanin synthesis, which can possibly be beneficial for vitiligo.8
Omega-3 Fatty Acids—Seven of 31 (23%) web pages recommended the inclusion of omega-3 fatty acids for their role as antioxidants to improve vitiligo symptoms. Research has indicated a strong association between vitiligo and oxidative stress.9 A 2007 controlled clinical trial that included 28 vitiligo patients demonstrated that oral antioxidant supplementation in combination with narrowband UVB phototherapy can significantly decrease vitiligo-associated oxidative stress (P<.05); 8 of 17 (47%) patients in the treatment group saw greater than 75% repigmentation after antioxidant treatment.10
Grains—Five of 31 (16%) web pages suggested avoiding gluten—a protein naturally found in some grains including wheat, barley, and rye—to improve vitiligo symptoms. A 2021 review suggested that a gluten-free diet may be effective in managing celiac disease, and it is hypothesized that vitiligo may be managed with similar dietary adjustments.11 Studies have shown that celiac disease and vitiligo—both autoimmune conditions—involve IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, and IL-21 in their disease pathways.12,13 Their shared immunogenic mechanism may account for similar management options.
Upon review, 2 case reports were identified that discussed a relationship between a gluten-free diet and vitiligo symptom improvement. In one report, a 9-year-old child diagnosed with both celiac disease and vitiligo saw intense repigmentation of the skin after adhering to a gluten-free diet for 1 year.14 Another case study reported a 22-year-old woman with vitiligo whose symptoms improved after 1 month of a gluten-free diet following 2 years of failed treatment with a topical steroid and phototherapy.15
Seven of 31 (23%) web pages suggested that individuals with vitiligo should include wheat in their diet. There is no published literature discussing the relationship between vitiligo and wheat. Of the 31 web pages reviewed, 10 (32%) suggested including whole grain. There is no relevant scientific evidence or hypotheses describing how whole grains may be beneficial in vitiligo.
Minerals—Eight of 31 (26%) web pages suggested including zinc in the diet to improve vitiligo symptoms. A 2020 study evaluated how different serum levels of zinc in vitiligo patients might be affiliated with interleukin activity. Fifty patients diagnosed with active vitiligo were tested for serum levels of zinc, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-17.16 The results showed that mean serum levels of zinc were lower in vitiligo patients compared with patients without vitiligo. The study concluded that zinc could possibly be used as a supplement to improve vitiligo, though the dosage needs to be further studied and confirmed.16
Vegetables—Eleven of 31 (35%) web pages recommended leafy green vegetables and 13 of 31 (42%) recommended spinach for patients with vitiligo. Spinach and other leafy green vegetables are known to be rich in antioxidants, which may have protective effects against reactive oxygen species that are thought to contribute to vitiligo progression.17,18
Nuts—Walnuts were recommended in 11 of 31 (35%) web pages. Nuts may be beneficial in reducing inflammation and providing protection against oxidative stress.9 However, there is no specific scientific literature that supports the inclusion of nuts in the diet to manage vitiligo symptoms.
Comment
With a growing amount of research suggesting that diet modifications may contribute to management of certain skin conditions, vitiligo patients often inquire about foods or supplements that may help improve their condition.19 Our review highlighted what information was available to the public regarding diet and vitiligo, with preliminary support of the following primary diet components: vitamin D, vitamin B12, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids. Our review showed no support in the literature for the items that were recommended to avoid. It is important to note that 27 of 31 (87%) web pages from our online search were not authored by medical professionals or dermatologists. Additionally, many web pages suggested conflicting information, making it difficult to draw concrete conclusions about what diet modifications will be beneficial to the vitiligo community. Further controlled clinical trials are warranted due to the lack of formal studies that assess the relationship between diet and vitiligo.
- Gandhi K, Ezzedine K, Anastassopoulos KP, et al. Prevalence of vitiligo among adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:43-50. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.4724
- Silverberg JI, Silverberg AI, Malka E, et al. A pilot study assessing the role of 25 hydroxy vitamin D levels in patients with vitiligo vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:937-941. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.11.024
- Karagüzel G, Sakarya NP, Bahadır S, et al. Vitamin D status and the effects of oral vitamin D treatment in children with vitiligo: a prospective study. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2016;15:28-31. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2016.05.006.
- Finamor DC, Sinigaglia-Coimbra R, Neves LC, et al. A pilot study assessing the effect of prolonged administration of high daily doses of vitamin D on the clinical course of vitiligo and psoriasis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2013;5:222-234. doi:10.4161/derm.24808
- Juhlin L, Olsson MJ. Improvement of vitiligo after oral treatment with vitamin B12 and folic acid and the importance of sun exposure. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997;77:460-462. doi:10.2340/000155555577460462
- Chen J, Zhuang T, Chen J, et al. Homocysteine induces melanocytes apoptosis via PERK-eIF2α-CHOP pathway in vitiligo. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020;134:1127-1141. doi:10.1042/CS20200218
- Sendrasoa FA, Ranaivo IM, Sata M, et al. Treatment responses in patients with vitiligo to very potent topical corticosteroids combined with vitamin therapy in Madagascar. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:908-911. doi:10.1111/ijd.14510
- Wang HM, Qu LQ, Ng JPL, et al. Natural citrus flavanone 5-demethylnobiletin stimulates melanogenesis through the activation of cAMP/CREB pathway in B16F10 cells. Phytomedicine. 2022;98:153941. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153941
- Ros E. Health benefits of nut consumption. Nutrients. 2010;2:652-682.
- Dell’Anna ML, Mastrofrancesco A, Sala R, et al. Antioxidants and narrow band-UVB in the treatment of vitiligo: a double-blind placebo controlled trial. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32:631-636.
- Gastrointestinal microbiome and gluten in celiac disease. Ann Med. 2021;53:1797-1805. doi:10.1080/07853890.2021.1990392
- Forabosco P, Neuhausen SL, Greco L, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide linkage studies in celiac disease. Hum Hered. 2009;68:223-230. doi:10.1159/000228920
- Akbulut UE, Çebi AH, Sag˘ E, et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-17 gene polymorphism association with celiac disease in children. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017;28:471-475. doi:10.5152/tjg.2017.17092
- Rodríguez-García C, González-Hernández S, Pérez-Robayna N, et al. Repigmentation of vitiligo lesions in a child with celiac disease after a gluten-free diet. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:209-210. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01388.x
- Khandalavala BN, Nirmalraj MC. Rapid partial repigmentation ofvitiligo in a young female adult with a gluten-free diet. Case Rep Dermatol. 2014;6:283-287.
- Sanad EM, El-Fallah AA, Al-Doori AR, et al. Serum zinc and inflammatory cytokines in vitiligo. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:(12 suppl 1):S29-S33.
- Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:7915-7922. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.17.7915
- Xian D, Guo M, Xu J, et al. Current evidence to support the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in oxidative stress-related dermatoses. Redox Rep. 2021;26:134-146. doi:10.1080 /13510002.2021.1962094
- Katta R, Kramer MJ. Skin and diet: an update on the role of dietary change as a treatment strategy for skin disease. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018;23:1-5.
- Gandhi K, Ezzedine K, Anastassopoulos KP, et al. Prevalence of vitiligo among adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:43-50. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.4724
- Silverberg JI, Silverberg AI, Malka E, et al. A pilot study assessing the role of 25 hydroxy vitamin D levels in patients with vitiligo vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:937-941. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.11.024
- Karagüzel G, Sakarya NP, Bahadır S, et al. Vitamin D status and the effects of oral vitamin D treatment in children with vitiligo: a prospective study. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2016;15:28-31. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2016.05.006.
- Finamor DC, Sinigaglia-Coimbra R, Neves LC, et al. A pilot study assessing the effect of prolonged administration of high daily doses of vitamin D on the clinical course of vitiligo and psoriasis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2013;5:222-234. doi:10.4161/derm.24808
- Juhlin L, Olsson MJ. Improvement of vitiligo after oral treatment with vitamin B12 and folic acid and the importance of sun exposure. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997;77:460-462. doi:10.2340/000155555577460462
- Chen J, Zhuang T, Chen J, et al. Homocysteine induces melanocytes apoptosis via PERK-eIF2α-CHOP pathway in vitiligo. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020;134:1127-1141. doi:10.1042/CS20200218
- Sendrasoa FA, Ranaivo IM, Sata M, et al. Treatment responses in patients with vitiligo to very potent topical corticosteroids combined with vitamin therapy in Madagascar. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:908-911. doi:10.1111/ijd.14510
- Wang HM, Qu LQ, Ng JPL, et al. Natural citrus flavanone 5-demethylnobiletin stimulates melanogenesis through the activation of cAMP/CREB pathway in B16F10 cells. Phytomedicine. 2022;98:153941. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153941
- Ros E. Health benefits of nut consumption. Nutrients. 2010;2:652-682.
- Dell’Anna ML, Mastrofrancesco A, Sala R, et al. Antioxidants and narrow band-UVB in the treatment of vitiligo: a double-blind placebo controlled trial. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32:631-636.
- Gastrointestinal microbiome and gluten in celiac disease. Ann Med. 2021;53:1797-1805. doi:10.1080/07853890.2021.1990392
- Forabosco P, Neuhausen SL, Greco L, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide linkage studies in celiac disease. Hum Hered. 2009;68:223-230. doi:10.1159/000228920
- Akbulut UE, Çebi AH, Sag˘ E, et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-17 gene polymorphism association with celiac disease in children. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017;28:471-475. doi:10.5152/tjg.2017.17092
- Rodríguez-García C, González-Hernández S, Pérez-Robayna N, et al. Repigmentation of vitiligo lesions in a child with celiac disease after a gluten-free diet. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:209-210. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01388.x
- Khandalavala BN, Nirmalraj MC. Rapid partial repigmentation ofvitiligo in a young female adult with a gluten-free diet. Case Rep Dermatol. 2014;6:283-287.
- Sanad EM, El-Fallah AA, Al-Doori AR, et al. Serum zinc and inflammatory cytokines in vitiligo. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:(12 suppl 1):S29-S33.
- Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, Hagen TM. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:7915-7922. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.17.7915
- Xian D, Guo M, Xu J, et al. Current evidence to support the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in oxidative stress-related dermatoses. Redox Rep. 2021;26:134-146. doi:10.1080 /13510002.2021.1962094
- Katta R, Kramer MJ. Skin and diet: an update on the role of dietary change as a treatment strategy for skin disease. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018;23:1-5.
Practice Points
- There are numerous online dietary and supplement recommendations that claim to impact vitiligo but most are not authored by medical professionals or dermatologists.
- Scientific evidence supporting specific dietary and supplement recommendations for vitiligo is limited.
- Current preliminary data support the potential recommendation for dietary supplementation with vitamin D, vitamin B12, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Study: Early Tecovirimat Stops Mpox Progression in HIV Patients
A new analysis supports using the smallpox antiviral tecovirimat (TPOXX/ST-246) in HIV patients showing the first symptoms of the human smallpox disease mpox (monkeypox), caused by the variola virus.
In a small prospective matched cohort analysis, people with HIV (PWH) and mpox disease who received tecovirimat within 7 days of symptom onset were 13 times less likely to experience progression, compared with PWH not prescribed tecovirimat within that window. In a matched cohort of 112 PWH, mpox disease progression occurred in 5.4% in an early tecovirimat group and in 26.8% in a late- or no-tecovirimat group, for a paired odds ratio of 13.00 (95% CI, 1.71-99.40; P = .002).
“Results of the present study suggest that tecovirimat treatment should be started early at the time of suspected mpox diagnosis in all PWH, especially in those with nonsuppressed HIV viremia or mucosal site involvement,” wrote a team led by Bruce Aldred, MD, of the Division of Infectious Diseases in the Department of Medicine at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, in JAMA Internal Medicine. Early symptoms of mpox include skin rash and mucosal lesions, along with viral symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, low energy, and swollen lymph nodes.
As of March 1 of last year, the United States reported more than 30,000 cases, while cases numbered more than 86,000 worldwide.
Despite a lack of effectiveness data in humans, tecovirimat was widely prescribed to PWH with mpox during the 2022 epidemic, which disproportionately affected PWH, particularly those with low CD4+ T-cell counts or severe mpox clinical manifestations who needed urgent therapy. Developed to treat smallpox, tecovirimat has antiviral activity against other orthopoxviruses, and has reduced mpox-related morbidity and mortality in animals.
Based on the animal data, approval was granted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human mpox treatment. Dr. Aldred and colleagues undertook this cohort analysis in the absence of human data and with the postoutbreak decline in cases impeding recruitment to a full-scale clinical trial.
Study design
The preponderantly Black cohort included 112 PWH diagnosed with mpox at four Atlanta hospitals from June 1 to October 7, 2022. Patients were grouped in an early cohort receiving tecovirimat within 7 days of symptom onset or a no or late cohort (no tecovirimat or treatment more than 7 days after symptom onset. Multivariate logistic regression models identified factors associated with progression, defined as development of at least one severe CDC mpox criterion after symptom day 7.
The cohorts were then matched 1:1 using propensity scores based on the identified factors, and mpox disease progression was compared.
Of 112 PWH, 56 receive early tecovirimat and 56 received no or late treatment. In the early group, the median (interquartile range [IQR]) age was 35 (30-42) years; 54 individuals (96.4%) were cisgender men, 46 (82.1%) were Black, and 10 (17.9%) were, variously, White, American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, or of unknown race.
In the late- or no-tecovirimat group, the median (IQR) age was 36 (32-43) years; 54 (96.4%) were cisgender men, 49 (87.5%) were Black, and 7 (12.5%) were individuals of other or unknown race. Mpox disease progression occurred in 3 PWH in the early-tecovirimat group and 15 PWH (26.8%) in the late- or no-tecovirimat group.
Dr. Aldred and colleagues acknowledged that more research is needed to confirm the findings and cited several study limitations. These included the small sample size, the preponderance of Black participants, and the possibility that unmatched confounding variables could have led to the observation of fewer cases of severe disease in the early-tecovirimat cohort.
This study was supported by a grant from the Emory Center for AIDS Research. Coauthors reported grants from various institutes at the National Institutes of Health as well as from multiple pharmaceutical companies.
A new analysis supports using the smallpox antiviral tecovirimat (TPOXX/ST-246) in HIV patients showing the first symptoms of the human smallpox disease mpox (monkeypox), caused by the variola virus.
In a small prospective matched cohort analysis, people with HIV (PWH) and mpox disease who received tecovirimat within 7 days of symptom onset were 13 times less likely to experience progression, compared with PWH not prescribed tecovirimat within that window. In a matched cohort of 112 PWH, mpox disease progression occurred in 5.4% in an early tecovirimat group and in 26.8% in a late- or no-tecovirimat group, for a paired odds ratio of 13.00 (95% CI, 1.71-99.40; P = .002).
“Results of the present study suggest that tecovirimat treatment should be started early at the time of suspected mpox diagnosis in all PWH, especially in those with nonsuppressed HIV viremia or mucosal site involvement,” wrote a team led by Bruce Aldred, MD, of the Division of Infectious Diseases in the Department of Medicine at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, in JAMA Internal Medicine. Early symptoms of mpox include skin rash and mucosal lesions, along with viral symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, low energy, and swollen lymph nodes.
As of March 1 of last year, the United States reported more than 30,000 cases, while cases numbered more than 86,000 worldwide.
Despite a lack of effectiveness data in humans, tecovirimat was widely prescribed to PWH with mpox during the 2022 epidemic, which disproportionately affected PWH, particularly those with low CD4+ T-cell counts or severe mpox clinical manifestations who needed urgent therapy. Developed to treat smallpox, tecovirimat has antiviral activity against other orthopoxviruses, and has reduced mpox-related morbidity and mortality in animals.
Based on the animal data, approval was granted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human mpox treatment. Dr. Aldred and colleagues undertook this cohort analysis in the absence of human data and with the postoutbreak decline in cases impeding recruitment to a full-scale clinical trial.
Study design
The preponderantly Black cohort included 112 PWH diagnosed with mpox at four Atlanta hospitals from June 1 to October 7, 2022. Patients were grouped in an early cohort receiving tecovirimat within 7 days of symptom onset or a no or late cohort (no tecovirimat or treatment more than 7 days after symptom onset. Multivariate logistic regression models identified factors associated with progression, defined as development of at least one severe CDC mpox criterion after symptom day 7.
The cohorts were then matched 1:1 using propensity scores based on the identified factors, and mpox disease progression was compared.
Of 112 PWH, 56 receive early tecovirimat and 56 received no or late treatment. In the early group, the median (interquartile range [IQR]) age was 35 (30-42) years; 54 individuals (96.4%) were cisgender men, 46 (82.1%) were Black, and 10 (17.9%) were, variously, White, American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, or of unknown race.
In the late- or no-tecovirimat group, the median (IQR) age was 36 (32-43) years; 54 (96.4%) were cisgender men, 49 (87.5%) were Black, and 7 (12.5%) were individuals of other or unknown race. Mpox disease progression occurred in 3 PWH in the early-tecovirimat group and 15 PWH (26.8%) in the late- or no-tecovirimat group.
Dr. Aldred and colleagues acknowledged that more research is needed to confirm the findings and cited several study limitations. These included the small sample size, the preponderance of Black participants, and the possibility that unmatched confounding variables could have led to the observation of fewer cases of severe disease in the early-tecovirimat cohort.
This study was supported by a grant from the Emory Center for AIDS Research. Coauthors reported grants from various institutes at the National Institutes of Health as well as from multiple pharmaceutical companies.
A new analysis supports using the smallpox antiviral tecovirimat (TPOXX/ST-246) in HIV patients showing the first symptoms of the human smallpox disease mpox (monkeypox), caused by the variola virus.
In a small prospective matched cohort analysis, people with HIV (PWH) and mpox disease who received tecovirimat within 7 days of symptom onset were 13 times less likely to experience progression, compared with PWH not prescribed tecovirimat within that window. In a matched cohort of 112 PWH, mpox disease progression occurred in 5.4% in an early tecovirimat group and in 26.8% in a late- or no-tecovirimat group, for a paired odds ratio of 13.00 (95% CI, 1.71-99.40; P = .002).
“Results of the present study suggest that tecovirimat treatment should be started early at the time of suspected mpox diagnosis in all PWH, especially in those with nonsuppressed HIV viremia or mucosal site involvement,” wrote a team led by Bruce Aldred, MD, of the Division of Infectious Diseases in the Department of Medicine at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, in JAMA Internal Medicine. Early symptoms of mpox include skin rash and mucosal lesions, along with viral symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, low energy, and swollen lymph nodes.
As of March 1 of last year, the United States reported more than 30,000 cases, while cases numbered more than 86,000 worldwide.
Despite a lack of effectiveness data in humans, tecovirimat was widely prescribed to PWH with mpox during the 2022 epidemic, which disproportionately affected PWH, particularly those with low CD4+ T-cell counts or severe mpox clinical manifestations who needed urgent therapy. Developed to treat smallpox, tecovirimat has antiviral activity against other orthopoxviruses, and has reduced mpox-related morbidity and mortality in animals.
Based on the animal data, approval was granted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human mpox treatment. Dr. Aldred and colleagues undertook this cohort analysis in the absence of human data and with the postoutbreak decline in cases impeding recruitment to a full-scale clinical trial.
Study design
The preponderantly Black cohort included 112 PWH diagnosed with mpox at four Atlanta hospitals from June 1 to October 7, 2022. Patients were grouped in an early cohort receiving tecovirimat within 7 days of symptom onset or a no or late cohort (no tecovirimat or treatment more than 7 days after symptom onset. Multivariate logistic regression models identified factors associated with progression, defined as development of at least one severe CDC mpox criterion after symptom day 7.
The cohorts were then matched 1:1 using propensity scores based on the identified factors, and mpox disease progression was compared.
Of 112 PWH, 56 receive early tecovirimat and 56 received no or late treatment. In the early group, the median (interquartile range [IQR]) age was 35 (30-42) years; 54 individuals (96.4%) were cisgender men, 46 (82.1%) were Black, and 10 (17.9%) were, variously, White, American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, or of unknown race.
In the late- or no-tecovirimat group, the median (IQR) age was 36 (32-43) years; 54 (96.4%) were cisgender men, 49 (87.5%) were Black, and 7 (12.5%) were individuals of other or unknown race. Mpox disease progression occurred in 3 PWH in the early-tecovirimat group and 15 PWH (26.8%) in the late- or no-tecovirimat group.
Dr. Aldred and colleagues acknowledged that more research is needed to confirm the findings and cited several study limitations. These included the small sample size, the preponderance of Black participants, and the possibility that unmatched confounding variables could have led to the observation of fewer cases of severe disease in the early-tecovirimat cohort.
This study was supported by a grant from the Emory Center for AIDS Research. Coauthors reported grants from various institutes at the National Institutes of Health as well as from multiple pharmaceutical companies.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
Culprits of Medication-Induced Telogen Effluvium, Part 2
Medication-induced telogen effluvium (TE) is a nonscarring alopecia that typically is reversible. Appropriate management requires identification of the underlying trigger and cessation of potential culprit medications. In part 2 of this series, we review anticoagulant and antihypertensive medications as potential contributors to TE.
Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants target various parts of the coagulation cascade to prevent clot formation in patients with conditions that increase their risk for thromboembolic events. Common indications for initiating anticoagulant therapy include atrial fibrillation,1 venous thromboembolism,2 acute myocardial infarction,3 malignancy,4 and hypercoagulable states.5 Traditional anticoagulants include heparin and warfarin. Heparin is a glycosaminoglycan that exerts its anticoagulant effects through binding with antithrombin, greatly increasing its inactivation of thrombin and factor Xa of the coagulation cascade.6 Warfarin is a coumarin derivative that inhibits activation of vitamin K, subsequently limiting the function of vitamin K–dependent factors II, VII, IX, and X.7,8 Watras et al9 noted that heparin and warfarin were implicated in alopecia as their clinical use became widespread throughout the mid-20th century. Onset of alopecia following the use of heparin or warfarin was reported at 3 weeks to 3 months following medication initiation, with most cases clinically consistent with TE.9 Heparin and warfarin both have alopecia reported as a potential adverse effect in their structured product labeling documents.10,11
Heparin is further classified into unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH); the latter is a heterogeneous group of medications derived from chemical or enzymatic depolymerization of UFH.12 In contrast to UFH, LMWH exerts its anticoagulant effects through inactivation of factor Xa without the ability to bind thrombin.12 An animal study using anagen-induced mice demonstrated that intraperitoneal administration of heparin inhibited the development of anagen follicles, while in vitro studies showed that the addition of heparin inhibited mouse dermal papilla cell proliferation.13 Other animal and in vitro studies have examined the inhibitory effects of heparin on signaling pathways in tumor lymphangiogenesis, including the vascular endothelial growth factor C/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 axis.14,15 Clinically, it has been demonstrated that heparin, especially LMWHs, may be associated with a survival benefit among certain cancer patients,16,17 with the impact of LMWHs attributed to antimitotic and antimetastatic effects of heparin on tumor growth.14 It is hypothesized that such antiangiogenic and antimitotic effects also are involved in the pathomechanisms of heparin-induced alopecia.18
More recently, the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban has increased due to their more favorable adverse-effect profile and minimal monitoring requirements. Bonaldo et al19 conducted an analysis of reports submitted to the World Health Organization’s VigiBase database of alopecia associated with DOACs until May 2, 2018. They found 1316 nonduplicate DOAC-induced cases of alopecia, with rivaroxaban as the most reported drug associated with alopecia development (58.8% [774/1316]). Only 4 cases demonstrated alopecia with DOAC rechallenge, suggesting onset of alopecia may have been unrelated to DOAC use or caused by a different trigger. Among 243 cases with a documented time to onset of alopecia, the median was 28 days, with an interquartile range of 63 days. Because TE most commonly occurs 3 to 4 months after the inciting event or medication trigger, there is little evidence to suggest DOACs as the cause of TE, and the observed cases of alopecia may be attributable to another preceding medical event and/or medication exposure.19 More studies are needed to examine the impact of anticoagulant medications on the hair cycle.
Antihypertensives
Hypertension is a modifiable risk factor for several cardiovascular diseases.20 According to the 2019 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease,21 first-line medications include thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors exert their antihypertensive effects by reducing conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, thereby limiting the downstream effects of vasoconstriction as well as sodium and water retention. Given the proven mortality benefit of ACE inhibition in patients with congestive heart failure, ACE inhibitors are used as first-line therapy in these patients.22,23 Alopecia associated with ACE inhibitors is rare and limited to case reports following their introduction and approval in 1981.24-28 In one case, a woman in her 60s with congestive heart failure initiated captopril with development of an erythematous pruritic rash on the extremities and diffuse scalp hair loss 2 months later; spontaneous hair growth resumed 1 month following captopril discontinuation.25 In this case, the hair loss may be secondary to the drug eruption rather than true medication-induced TE. Initiation of enalapril in a woman in her 30s with hypertension was associated with diffuse scalp alopecia 4 weeks later that resolved with cessation of the suspected culprit, enalapril; rechallenge with enalapril several months later reproduced the hair loss.27 Given limited reports of ACE inhibitor–associated hair loss relative to their pervasive use, a direct causal role between ACE inhibition and TE is unlikely, or it has not been rigorously identified. The structured product labeling for captopril includes alopecia in its list of adverse effects reported in approximately 0.5% to 2% of patients but did not appear at increased frequency compared to placebo or other treatments used in controlled trials.29 Alternative inciting causes of alopecia in patients prescribed ACE inhibitors may include use of other medications, hospitalization, or metabolic derangements related to their underlying cardiac disease.
Although not indicated as a primary treatment for hypertension, β-blockers have US Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of certain arrhythmias, hypertension, heart failure, myocardial infarction, hyperthyroidism, and other conditions.30 β-Blockers are competitive antagonists of β-adrenergic receptors that limit the production of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate, but the mechanism of β-blockers as antihypertensives is unclear.31 Evidence supporting the role of β-adrenergic antagonists in TE is limited to case reports. Widespread alopecia across the scalp and arms was noted in a man in his 30s several months after starting propranolol.32 Biopsy of an affected area of the scalp demonstrated an increased number of telogen follicles with no other abnormalities. Near-complete resolution of alopecia was seen 4 months following cessation of propranolol, which recurred within 4 weeks of rechallenge.
Minoxidil—Oral minoxidil originally was approved for use in patients with resistant hypertension, defined as blood pressure elevated above goal despite concurrent use of the maximum dose of 3 classes of antihypertensives.36 Unlike other antihypertensive medications, minoxidil appears to cause reversible hypertrichosis that affects nearly all patients using oral minoxidil for longer than 1 month.37 This common adverse effect was a desired outcome in patients affected by hair loss, and a topical formulation of minoxidil was approved for androgenetic alopecia in men and women in 1988 and 1991, respectively.38 Since its approval, topical minoxidil has been commonly prescribed in the treatment of several types of alopecia, though evidence of its efficacy in the treatment of TE is limited.39,40 Low-dose oral minoxidil also has been reported to aid hair growth in androgenetic alopecia and TE.41 Taken orally, minoxidil is converted by sulfotransferases in the liver to minoxidil sulfate, which causes opening of plasma membrane adenosine triphosphate–sensitive potassium channels.42-44 The subsequent membrane hyperpolarization reduces calcium ion influx, which also reduces cell excitability, and inhibits contraction in vascular smooth muscle cells, which results in the arteriolar vasodilatory and antihypertensive effects of minoxidil.43,45 The potassium channel–opening effects of minoxidil may underly its hair growth stimulatory action. Unrelated potassium channel openers such as diazoxide and pinacidil also cause hypertrichosis.46-48 An animal study showed that topical minoxidil, cromakalim (potassium channel opener), and P1075 (pinacidil analog) applied daily to the scalps of balding stump-tailed macaques led to significant increases in hair weight over a 20-week treatment period compared with the vehicle control group (P<.05 for minoxidil 100 mM and 250 mM, cromakalim 100 mM, and P1075 100 mM and 250 mM).50 For minoxidil, this effect on hair growth appears to be dose dependent, as cumulative hair weights for the study period were significantly greater in the 250-mM concentration compared with 100-mM minoxidil (P<.05).49 The potassium channel–opening activity of minoxidil may induce stimulation of microcirculation around hair follicles conducive to hair growth.50 Other proposed mechanisms for hair growth with minoxidil include effects on keratinocyte and fibroblast cell proliferation,51-53 collagen synthesis,52,54 and prostaglandin activity.44,55
Final Thoughts
Medication-induced TE is an undesired adverse effect of many commonly used medications, including retinoids, azole antifungals, mood stabilizers, anticoagulants, and antihypertensives. In part 156 of this 2-part series, we reviewed the existing literature on hair loss from retinoids, antifungals, and psychotropic medications. Herein, we focused on anticoagulant and antihypertensive medications as potential culprits of TE. Heparin and its derivatives have been associated with development of diffuse alopecia weeks to months after the start of treatment. Alopecia associated with ACE inhibitors and β-blockers has been described only in case reports, suggesting that they may be unlikely causes of TE. In contrast, minoxidil is an antihypertensive that can result in hypertrichosis and is used in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. It should not be assumed that medications that share an indication or are part of the same medication class would similarly induce TE. The development of diffuse nonscarring alopecia should prompt suspicion for TE and thorough investigation of medications initiated 1 to 6 months prior to onset of clinically apparent alopecia. Suspected culprit medications should be carefully assessed for their likelihood of inducing TE.
- Angiolillo DJ, Bhatt DL, Cannon CP, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation treated with oral anticoagulation undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a North American perspective: 2021 update. Circulation. 2021;143:583-596. doi:10.1161 /circulationaha.120.050438
- Kearon C, Kahn SR. Long-term treatment of venous thromboembolism. Blood. 2020;135:317-325. doi:10.1182/blood.2019002364
- Frishman WH, Ribner HS. Anticoagulation in myocardial infarction: modern approach to an old problem. Am J Cardiol. 1979;43:1207-1213. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(79)90155-3
- Khorana AA, Mackman N, Falanga A, et al. Cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8:11. doi:10.1038 /s41572-022-00336-y
- Umerah CO, Momodu, II. Anticoagulation. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560651/
- Beurskens DMH, Huckriede JP, Schrijver R, et al. The anticoagulant and nonanticoagulant properties of heparin. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:1371-1383. doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715460
- Hirsh J, Dalen J, Anderson DR, et al. Oral anticoagulants: mechanism of action, clinical effectiveness, and optimal therapeutic range. Chest. 2001;119(1 suppl):8S-21S. doi:10.1378/chest.119.1_suppl.8s
- Holbrook AM, Pereira JA, Labiris R, et al. Systematic overview of warfarin and its drug and food interactions. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1095-1106. doi:10.1001/archinte.165.10.1095
- Watras MM, Patel JP, Arya R. Traditional anticoagulants and hair loss: a role for direct oral anticoagulants? a review of the literature. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2016;3:1-6. doi:10.1007/s40801-015-0056-z
- Heparin sodium. Product information. Hepalink USA Inc; January 2022. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/c4c6bc1f-e0c7-fd0d-e053-2995a90abdef/spl-doc?hl=heparin
- Warfarin sodium. Product information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; April 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/c41b7c23-8053-428a-ac1d-8395e714c2f1/spl-doc?hl=alopecia%7Cwarfarin#section-6
- Hirsh J. Low-molecular-weight heparin. Circulation. 1998;98:1575-1582. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.98.15.1575
- Paus R. Hair growth inhibition by heparin in mice: a model system for studying the modulation of epithelial cell growth by glycosaminoglycans? Br J Dermatol. 1991;124:415-422. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1991.tb00618.x
- Ma SN, Mao ZX, Wu Y, et al. The anti-cancer properties of heparin and its derivatives: a review and prospect. Cell Adh Migr. 2020;14:118-128. doi:10.1080/19336918.2020.1767489
- Choi JU, Chung SW, Al-Hilal TA, et al. A heparin conjugate, LHbisD4, inhibits lymphangiogenesis and attenuates lymph node metastasis by blocking VEGF-C signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 2017;139:56-66. doi:0.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.05.026
- Klerk CP, Smorenburg SM, Otten HM, et al. The effect of low molecular weight heparin on survival in patients with advanced malignancy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2130-2135. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.03.134
- Altinbas M, Coskun HS, Er O, et al. A randomized clinical trial of combination chemotherapy with and without low-molecular-weight heparin in small cell lung cancer. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:1266-1271. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2004.00871.x
- Weyand AC, Shavit JA. Agent specific effects of anticoagulant induced alopecia. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2017;1:90-92. doi:10.1002 /rth2.12001
- Bonaldo G, Vaccheri A, Motola D. Direct-acting oral anticoagulants and alopecia: the valuable support of postmarketing data. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;86:1654-1660. doi:10.1111/bcp.14221
- Fuchs FD, Whelton PK. High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension. 2020;75:285-292. doi:10.1161 /HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14240
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:E596-E646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:E240-E327. doi:10.1161 /CIR.0b013e31829e8776
- Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS). N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1429-1435. doi:10.1056 /nejm198706043162301
- Kataria V, Wang H, Wald JW, et al. Lisinopril-induced alopecia: a case report. J Pharm Pract. 2017;30:562-566. doi:10.1177/0897190016652554
- Motel PJ. Captopril and alopecia: a case report and review of known cutaneous reactions in captopril use. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:124-125. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81205-4
- Leaker B, Whitworth JA. Alopecia associated with captopril treatment. Aust N Z J Med. 1984;14:866. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.1984.tb03797.x
- Ahmad S. Enalapril and reversible alopecia. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151:404.
- Bicket DP. Using ACE inhibitors appropriately. Am Fam Physician. 2002;66:461-468.
- Captopril. Product information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; May 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/563737c5-4d63-4957-8022-e3bc3112dfac/spl-doc?hl=captopril
- Farzam K, Jan A. Beta blockers. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532906/
- Mason RP, Giles TD, Sowers JR. Evolving mechanisms of action of beta blockers: focus on nebivolol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009; 54:123-128.
- Martin CM, Southwick EG, Maibach HI. Propranolol induced alopecia. Am Heart J. 1973;86:236-237. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(73)90250-0
- Graeber CW, Lapkin RA. Metoprolol and alopecia. Cutis. 1981; 28:633-634.
- Hilder RJ. Propranolol and alopecia. Cutis. 1979;24:63-64.
- Coreg. Prescribing information. Woodward Pharma Services LLC; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/34aa881a-3df4-460b-acad-fb9975ca3a06/34aa881a-3df4-460b-acad-fb9975ca3a06.xml
- Carey RM, Calhoun DA, Bakris GL, et al. Resistant hypertension: detection, evaluation, and management: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2018;72:E53-E90. doi:10.1161/hyp.0000000000000084
- Campese VM. Minoxidil: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1981;22:257-278. doi:10.2165/00003495-198122040-00001
- Heymann WR. Coming full circle (almost): low dose oral minoxidil for alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:613-614. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2020.12.053
- Yin S, Zhang B, Lin J, et al. Development of purification process for dual-function recombinant human heavy-chain ferritin by the investigation of genetic modification impact on conformation. Eng Life Sci. 2021;21:630-642. doi:10.1002/elsc.202000105
- Mysore V, Parthasaradhi A, Kharkar RD, et al. Expert consensus on the management of telogen effluvium in India. Int J Trichology. 2019;11:107-112.
- Gupta AK, Talukder M, Shemar A, et al. Low-dose oral minoxidil for alopecia: a comprehensive review [published online September 27, 2023]. Skin Appendage Disord. doi:10.1159/000531890
- Meisheri KD, Cipkus LA, Taylor CJ. Mechanism of action of minoxidil sulfate-induced vasodilation: a role for increased K+ permeability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;245:751-760.
- Winquist RJ, Heaney LA, Wallace AA, et al. Glyburide blocks the relaxation response to BRL 34915 (cromakalim), minoxidil sulfate and diazoxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989;248:149-56.
- Messenger AG, Rundegren J. Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:186-194. doi:10.1111/j .1365-2133.2004.05785.x
- Alijotas-Reig J, García GV, Velthuis PJ, et al. Inflammatory immunemediated adverse reactions induced by COVID-19 vaccines in previously injected patients with soft tissue fillers: a case series of 20 patients. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21:3181-3187. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15117
- Boskabadi SJ, Ramezaninejad S, Sohrab M, et al. Diazoxideinduced hypertrichosis in a neonate with transient hyperinsulinism. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2023;16:11795476231151330. doi:10.1177/11795476231151330
- Burton JL, Schutt WH, Caldwell IW. Hypertrichosis due to diazoxide. Br J Dermatol. 1975;93:707-711. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb05123.x
- Goldberg MR. Clinical pharmacology of pinacidil, a prototype for drugs that affect potassium channels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 suppl 2:S41-S47. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198812002-00008
- Buhl AE, Waldon DJ, Conrad SJ, et al. Potassium channel conductance: a mechanism affecting hair growth both in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1992;98:315-319. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499788
- Patel P, Nessel TA, Kumar DD. Minoxidil. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482378/
- O’Keefe E, Payne RE Jr. Minoxidil: inhibition of proliferation of keratinocytes in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:534-536. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12481560
- Murad S, Pinnell SR. Suppression of fibroblast proliferation and lysyl hydroxylase activity by minoxidil. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:11973-11978.
- Baden HP, Kubilus J. Effect of minoxidil on cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1983;81:558-560. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12523220
- Murad S, Walker LC, Tajima S, et al. Minimum structural requirements for minoxidil inhibition of lysyl hydroxylase in cultured fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;308:42-47. doi:10.1006/abbi.1994.1006
- Kvedar JC, Baden HP, Levine L. Selective inhibition by minoxidil of prostacyclin production by cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988;37:867-874. doi:0.1016/0006-2952(88)90174-8
- Zhang D, LaSenna C, Shields BE. Culprits of medication-induced telogen effluvium, part 1. Cutis. 2023;112:267-271.
Medication-induced telogen effluvium (TE) is a nonscarring alopecia that typically is reversible. Appropriate management requires identification of the underlying trigger and cessation of potential culprit medications. In part 2 of this series, we review anticoagulant and antihypertensive medications as potential contributors to TE.
Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants target various parts of the coagulation cascade to prevent clot formation in patients with conditions that increase their risk for thromboembolic events. Common indications for initiating anticoagulant therapy include atrial fibrillation,1 venous thromboembolism,2 acute myocardial infarction,3 malignancy,4 and hypercoagulable states.5 Traditional anticoagulants include heparin and warfarin. Heparin is a glycosaminoglycan that exerts its anticoagulant effects through binding with antithrombin, greatly increasing its inactivation of thrombin and factor Xa of the coagulation cascade.6 Warfarin is a coumarin derivative that inhibits activation of vitamin K, subsequently limiting the function of vitamin K–dependent factors II, VII, IX, and X.7,8 Watras et al9 noted that heparin and warfarin were implicated in alopecia as their clinical use became widespread throughout the mid-20th century. Onset of alopecia following the use of heparin or warfarin was reported at 3 weeks to 3 months following medication initiation, with most cases clinically consistent with TE.9 Heparin and warfarin both have alopecia reported as a potential adverse effect in their structured product labeling documents.10,11
Heparin is further classified into unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH); the latter is a heterogeneous group of medications derived from chemical or enzymatic depolymerization of UFH.12 In contrast to UFH, LMWH exerts its anticoagulant effects through inactivation of factor Xa without the ability to bind thrombin.12 An animal study using anagen-induced mice demonstrated that intraperitoneal administration of heparin inhibited the development of anagen follicles, while in vitro studies showed that the addition of heparin inhibited mouse dermal papilla cell proliferation.13 Other animal and in vitro studies have examined the inhibitory effects of heparin on signaling pathways in tumor lymphangiogenesis, including the vascular endothelial growth factor C/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 axis.14,15 Clinically, it has been demonstrated that heparin, especially LMWHs, may be associated with a survival benefit among certain cancer patients,16,17 with the impact of LMWHs attributed to antimitotic and antimetastatic effects of heparin on tumor growth.14 It is hypothesized that such antiangiogenic and antimitotic effects also are involved in the pathomechanisms of heparin-induced alopecia.18
More recently, the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban has increased due to their more favorable adverse-effect profile and minimal monitoring requirements. Bonaldo et al19 conducted an analysis of reports submitted to the World Health Organization’s VigiBase database of alopecia associated with DOACs until May 2, 2018. They found 1316 nonduplicate DOAC-induced cases of alopecia, with rivaroxaban as the most reported drug associated with alopecia development (58.8% [774/1316]). Only 4 cases demonstrated alopecia with DOAC rechallenge, suggesting onset of alopecia may have been unrelated to DOAC use or caused by a different trigger. Among 243 cases with a documented time to onset of alopecia, the median was 28 days, with an interquartile range of 63 days. Because TE most commonly occurs 3 to 4 months after the inciting event or medication trigger, there is little evidence to suggest DOACs as the cause of TE, and the observed cases of alopecia may be attributable to another preceding medical event and/or medication exposure.19 More studies are needed to examine the impact of anticoagulant medications on the hair cycle.
Antihypertensives
Hypertension is a modifiable risk factor for several cardiovascular diseases.20 According to the 2019 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease,21 first-line medications include thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors exert their antihypertensive effects by reducing conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, thereby limiting the downstream effects of vasoconstriction as well as sodium and water retention. Given the proven mortality benefit of ACE inhibition in patients with congestive heart failure, ACE inhibitors are used as first-line therapy in these patients.22,23 Alopecia associated with ACE inhibitors is rare and limited to case reports following their introduction and approval in 1981.24-28 In one case, a woman in her 60s with congestive heart failure initiated captopril with development of an erythematous pruritic rash on the extremities and diffuse scalp hair loss 2 months later; spontaneous hair growth resumed 1 month following captopril discontinuation.25 In this case, the hair loss may be secondary to the drug eruption rather than true medication-induced TE. Initiation of enalapril in a woman in her 30s with hypertension was associated with diffuse scalp alopecia 4 weeks later that resolved with cessation of the suspected culprit, enalapril; rechallenge with enalapril several months later reproduced the hair loss.27 Given limited reports of ACE inhibitor–associated hair loss relative to their pervasive use, a direct causal role between ACE inhibition and TE is unlikely, or it has not been rigorously identified. The structured product labeling for captopril includes alopecia in its list of adverse effects reported in approximately 0.5% to 2% of patients but did not appear at increased frequency compared to placebo or other treatments used in controlled trials.29 Alternative inciting causes of alopecia in patients prescribed ACE inhibitors may include use of other medications, hospitalization, or metabolic derangements related to their underlying cardiac disease.
Although not indicated as a primary treatment for hypertension, β-blockers have US Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of certain arrhythmias, hypertension, heart failure, myocardial infarction, hyperthyroidism, and other conditions.30 β-Blockers are competitive antagonists of β-adrenergic receptors that limit the production of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate, but the mechanism of β-blockers as antihypertensives is unclear.31 Evidence supporting the role of β-adrenergic antagonists in TE is limited to case reports. Widespread alopecia across the scalp and arms was noted in a man in his 30s several months after starting propranolol.32 Biopsy of an affected area of the scalp demonstrated an increased number of telogen follicles with no other abnormalities. Near-complete resolution of alopecia was seen 4 months following cessation of propranolol, which recurred within 4 weeks of rechallenge.
Minoxidil—Oral minoxidil originally was approved for use in patients with resistant hypertension, defined as blood pressure elevated above goal despite concurrent use of the maximum dose of 3 classes of antihypertensives.36 Unlike other antihypertensive medications, minoxidil appears to cause reversible hypertrichosis that affects nearly all patients using oral minoxidil for longer than 1 month.37 This common adverse effect was a desired outcome in patients affected by hair loss, and a topical formulation of minoxidil was approved for androgenetic alopecia in men and women in 1988 and 1991, respectively.38 Since its approval, topical minoxidil has been commonly prescribed in the treatment of several types of alopecia, though evidence of its efficacy in the treatment of TE is limited.39,40 Low-dose oral minoxidil also has been reported to aid hair growth in androgenetic alopecia and TE.41 Taken orally, minoxidil is converted by sulfotransferases in the liver to minoxidil sulfate, which causes opening of plasma membrane adenosine triphosphate–sensitive potassium channels.42-44 The subsequent membrane hyperpolarization reduces calcium ion influx, which also reduces cell excitability, and inhibits contraction in vascular smooth muscle cells, which results in the arteriolar vasodilatory and antihypertensive effects of minoxidil.43,45 The potassium channel–opening effects of minoxidil may underly its hair growth stimulatory action. Unrelated potassium channel openers such as diazoxide and pinacidil also cause hypertrichosis.46-48 An animal study showed that topical minoxidil, cromakalim (potassium channel opener), and P1075 (pinacidil analog) applied daily to the scalps of balding stump-tailed macaques led to significant increases in hair weight over a 20-week treatment period compared with the vehicle control group (P<.05 for minoxidil 100 mM and 250 mM, cromakalim 100 mM, and P1075 100 mM and 250 mM).50 For minoxidil, this effect on hair growth appears to be dose dependent, as cumulative hair weights for the study period were significantly greater in the 250-mM concentration compared with 100-mM minoxidil (P<.05).49 The potassium channel–opening activity of minoxidil may induce stimulation of microcirculation around hair follicles conducive to hair growth.50 Other proposed mechanisms for hair growth with minoxidil include effects on keratinocyte and fibroblast cell proliferation,51-53 collagen synthesis,52,54 and prostaglandin activity.44,55
Final Thoughts
Medication-induced TE is an undesired adverse effect of many commonly used medications, including retinoids, azole antifungals, mood stabilizers, anticoagulants, and antihypertensives. In part 156 of this 2-part series, we reviewed the existing literature on hair loss from retinoids, antifungals, and psychotropic medications. Herein, we focused on anticoagulant and antihypertensive medications as potential culprits of TE. Heparin and its derivatives have been associated with development of diffuse alopecia weeks to months after the start of treatment. Alopecia associated with ACE inhibitors and β-blockers has been described only in case reports, suggesting that they may be unlikely causes of TE. In contrast, minoxidil is an antihypertensive that can result in hypertrichosis and is used in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. It should not be assumed that medications that share an indication or are part of the same medication class would similarly induce TE. The development of diffuse nonscarring alopecia should prompt suspicion for TE and thorough investigation of medications initiated 1 to 6 months prior to onset of clinically apparent alopecia. Suspected culprit medications should be carefully assessed for their likelihood of inducing TE.
Medication-induced telogen effluvium (TE) is a nonscarring alopecia that typically is reversible. Appropriate management requires identification of the underlying trigger and cessation of potential culprit medications. In part 2 of this series, we review anticoagulant and antihypertensive medications as potential contributors to TE.
Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants target various parts of the coagulation cascade to prevent clot formation in patients with conditions that increase their risk for thromboembolic events. Common indications for initiating anticoagulant therapy include atrial fibrillation,1 venous thromboembolism,2 acute myocardial infarction,3 malignancy,4 and hypercoagulable states.5 Traditional anticoagulants include heparin and warfarin. Heparin is a glycosaminoglycan that exerts its anticoagulant effects through binding with antithrombin, greatly increasing its inactivation of thrombin and factor Xa of the coagulation cascade.6 Warfarin is a coumarin derivative that inhibits activation of vitamin K, subsequently limiting the function of vitamin K–dependent factors II, VII, IX, and X.7,8 Watras et al9 noted that heparin and warfarin were implicated in alopecia as their clinical use became widespread throughout the mid-20th century. Onset of alopecia following the use of heparin or warfarin was reported at 3 weeks to 3 months following medication initiation, with most cases clinically consistent with TE.9 Heparin and warfarin both have alopecia reported as a potential adverse effect in their structured product labeling documents.10,11
Heparin is further classified into unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH); the latter is a heterogeneous group of medications derived from chemical or enzymatic depolymerization of UFH.12 In contrast to UFH, LMWH exerts its anticoagulant effects through inactivation of factor Xa without the ability to bind thrombin.12 An animal study using anagen-induced mice demonstrated that intraperitoneal administration of heparin inhibited the development of anagen follicles, while in vitro studies showed that the addition of heparin inhibited mouse dermal papilla cell proliferation.13 Other animal and in vitro studies have examined the inhibitory effects of heparin on signaling pathways in tumor lymphangiogenesis, including the vascular endothelial growth factor C/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 axis.14,15 Clinically, it has been demonstrated that heparin, especially LMWHs, may be associated with a survival benefit among certain cancer patients,16,17 with the impact of LMWHs attributed to antimitotic and antimetastatic effects of heparin on tumor growth.14 It is hypothesized that such antiangiogenic and antimitotic effects also are involved in the pathomechanisms of heparin-induced alopecia.18
More recently, the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban has increased due to their more favorable adverse-effect profile and minimal monitoring requirements. Bonaldo et al19 conducted an analysis of reports submitted to the World Health Organization’s VigiBase database of alopecia associated with DOACs until May 2, 2018. They found 1316 nonduplicate DOAC-induced cases of alopecia, with rivaroxaban as the most reported drug associated with alopecia development (58.8% [774/1316]). Only 4 cases demonstrated alopecia with DOAC rechallenge, suggesting onset of alopecia may have been unrelated to DOAC use or caused by a different trigger. Among 243 cases with a documented time to onset of alopecia, the median was 28 days, with an interquartile range of 63 days. Because TE most commonly occurs 3 to 4 months after the inciting event or medication trigger, there is little evidence to suggest DOACs as the cause of TE, and the observed cases of alopecia may be attributable to another preceding medical event and/or medication exposure.19 More studies are needed to examine the impact of anticoagulant medications on the hair cycle.
Antihypertensives
Hypertension is a modifiable risk factor for several cardiovascular diseases.20 According to the 2019 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease,21 first-line medications include thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors exert their antihypertensive effects by reducing conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, thereby limiting the downstream effects of vasoconstriction as well as sodium and water retention. Given the proven mortality benefit of ACE inhibition in patients with congestive heart failure, ACE inhibitors are used as first-line therapy in these patients.22,23 Alopecia associated with ACE inhibitors is rare and limited to case reports following their introduction and approval in 1981.24-28 In one case, a woman in her 60s with congestive heart failure initiated captopril with development of an erythematous pruritic rash on the extremities and diffuse scalp hair loss 2 months later; spontaneous hair growth resumed 1 month following captopril discontinuation.25 In this case, the hair loss may be secondary to the drug eruption rather than true medication-induced TE. Initiation of enalapril in a woman in her 30s with hypertension was associated with diffuse scalp alopecia 4 weeks later that resolved with cessation of the suspected culprit, enalapril; rechallenge with enalapril several months later reproduced the hair loss.27 Given limited reports of ACE inhibitor–associated hair loss relative to their pervasive use, a direct causal role between ACE inhibition and TE is unlikely, or it has not been rigorously identified. The structured product labeling for captopril includes alopecia in its list of adverse effects reported in approximately 0.5% to 2% of patients but did not appear at increased frequency compared to placebo or other treatments used in controlled trials.29 Alternative inciting causes of alopecia in patients prescribed ACE inhibitors may include use of other medications, hospitalization, or metabolic derangements related to their underlying cardiac disease.
Although not indicated as a primary treatment for hypertension, β-blockers have US Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of certain arrhythmias, hypertension, heart failure, myocardial infarction, hyperthyroidism, and other conditions.30 β-Blockers are competitive antagonists of β-adrenergic receptors that limit the production of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate, but the mechanism of β-blockers as antihypertensives is unclear.31 Evidence supporting the role of β-adrenergic antagonists in TE is limited to case reports. Widespread alopecia across the scalp and arms was noted in a man in his 30s several months after starting propranolol.32 Biopsy of an affected area of the scalp demonstrated an increased number of telogen follicles with no other abnormalities. Near-complete resolution of alopecia was seen 4 months following cessation of propranolol, which recurred within 4 weeks of rechallenge.
Minoxidil—Oral minoxidil originally was approved for use in patients with resistant hypertension, defined as blood pressure elevated above goal despite concurrent use of the maximum dose of 3 classes of antihypertensives.36 Unlike other antihypertensive medications, minoxidil appears to cause reversible hypertrichosis that affects nearly all patients using oral minoxidil for longer than 1 month.37 This common adverse effect was a desired outcome in patients affected by hair loss, and a topical formulation of minoxidil was approved for androgenetic alopecia in men and women in 1988 and 1991, respectively.38 Since its approval, topical minoxidil has been commonly prescribed in the treatment of several types of alopecia, though evidence of its efficacy in the treatment of TE is limited.39,40 Low-dose oral minoxidil also has been reported to aid hair growth in androgenetic alopecia and TE.41 Taken orally, minoxidil is converted by sulfotransferases in the liver to minoxidil sulfate, which causes opening of plasma membrane adenosine triphosphate–sensitive potassium channels.42-44 The subsequent membrane hyperpolarization reduces calcium ion influx, which also reduces cell excitability, and inhibits contraction in vascular smooth muscle cells, which results in the arteriolar vasodilatory and antihypertensive effects of minoxidil.43,45 The potassium channel–opening effects of minoxidil may underly its hair growth stimulatory action. Unrelated potassium channel openers such as diazoxide and pinacidil also cause hypertrichosis.46-48 An animal study showed that topical minoxidil, cromakalim (potassium channel opener), and P1075 (pinacidil analog) applied daily to the scalps of balding stump-tailed macaques led to significant increases in hair weight over a 20-week treatment period compared with the vehicle control group (P<.05 for minoxidil 100 mM and 250 mM, cromakalim 100 mM, and P1075 100 mM and 250 mM).50 For minoxidil, this effect on hair growth appears to be dose dependent, as cumulative hair weights for the study period were significantly greater in the 250-mM concentration compared with 100-mM minoxidil (P<.05).49 The potassium channel–opening activity of minoxidil may induce stimulation of microcirculation around hair follicles conducive to hair growth.50 Other proposed mechanisms for hair growth with minoxidil include effects on keratinocyte and fibroblast cell proliferation,51-53 collagen synthesis,52,54 and prostaglandin activity.44,55
Final Thoughts
Medication-induced TE is an undesired adverse effect of many commonly used medications, including retinoids, azole antifungals, mood stabilizers, anticoagulants, and antihypertensives. In part 156 of this 2-part series, we reviewed the existing literature on hair loss from retinoids, antifungals, and psychotropic medications. Herein, we focused on anticoagulant and antihypertensive medications as potential culprits of TE. Heparin and its derivatives have been associated with development of diffuse alopecia weeks to months after the start of treatment. Alopecia associated with ACE inhibitors and β-blockers has been described only in case reports, suggesting that they may be unlikely causes of TE. In contrast, minoxidil is an antihypertensive that can result in hypertrichosis and is used in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. It should not be assumed that medications that share an indication or are part of the same medication class would similarly induce TE. The development of diffuse nonscarring alopecia should prompt suspicion for TE and thorough investigation of medications initiated 1 to 6 months prior to onset of clinically apparent alopecia. Suspected culprit medications should be carefully assessed for their likelihood of inducing TE.
- Angiolillo DJ, Bhatt DL, Cannon CP, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation treated with oral anticoagulation undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a North American perspective: 2021 update. Circulation. 2021;143:583-596. doi:10.1161 /circulationaha.120.050438
- Kearon C, Kahn SR. Long-term treatment of venous thromboembolism. Blood. 2020;135:317-325. doi:10.1182/blood.2019002364
- Frishman WH, Ribner HS. Anticoagulation in myocardial infarction: modern approach to an old problem. Am J Cardiol. 1979;43:1207-1213. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(79)90155-3
- Khorana AA, Mackman N, Falanga A, et al. Cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8:11. doi:10.1038 /s41572-022-00336-y
- Umerah CO, Momodu, II. Anticoagulation. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560651/
- Beurskens DMH, Huckriede JP, Schrijver R, et al. The anticoagulant and nonanticoagulant properties of heparin. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:1371-1383. doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715460
- Hirsh J, Dalen J, Anderson DR, et al. Oral anticoagulants: mechanism of action, clinical effectiveness, and optimal therapeutic range. Chest. 2001;119(1 suppl):8S-21S. doi:10.1378/chest.119.1_suppl.8s
- Holbrook AM, Pereira JA, Labiris R, et al. Systematic overview of warfarin and its drug and food interactions. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1095-1106. doi:10.1001/archinte.165.10.1095
- Watras MM, Patel JP, Arya R. Traditional anticoagulants and hair loss: a role for direct oral anticoagulants? a review of the literature. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2016;3:1-6. doi:10.1007/s40801-015-0056-z
- Heparin sodium. Product information. Hepalink USA Inc; January 2022. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/c4c6bc1f-e0c7-fd0d-e053-2995a90abdef/spl-doc?hl=heparin
- Warfarin sodium. Product information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; April 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/c41b7c23-8053-428a-ac1d-8395e714c2f1/spl-doc?hl=alopecia%7Cwarfarin#section-6
- Hirsh J. Low-molecular-weight heparin. Circulation. 1998;98:1575-1582. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.98.15.1575
- Paus R. Hair growth inhibition by heparin in mice: a model system for studying the modulation of epithelial cell growth by glycosaminoglycans? Br J Dermatol. 1991;124:415-422. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1991.tb00618.x
- Ma SN, Mao ZX, Wu Y, et al. The anti-cancer properties of heparin and its derivatives: a review and prospect. Cell Adh Migr. 2020;14:118-128. doi:10.1080/19336918.2020.1767489
- Choi JU, Chung SW, Al-Hilal TA, et al. A heparin conjugate, LHbisD4, inhibits lymphangiogenesis and attenuates lymph node metastasis by blocking VEGF-C signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 2017;139:56-66. doi:0.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.05.026
- Klerk CP, Smorenburg SM, Otten HM, et al. The effect of low molecular weight heparin on survival in patients with advanced malignancy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2130-2135. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.03.134
- Altinbas M, Coskun HS, Er O, et al. A randomized clinical trial of combination chemotherapy with and without low-molecular-weight heparin in small cell lung cancer. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:1266-1271. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2004.00871.x
- Weyand AC, Shavit JA. Agent specific effects of anticoagulant induced alopecia. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2017;1:90-92. doi:10.1002 /rth2.12001
- Bonaldo G, Vaccheri A, Motola D. Direct-acting oral anticoagulants and alopecia: the valuable support of postmarketing data. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;86:1654-1660. doi:10.1111/bcp.14221
- Fuchs FD, Whelton PK. High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension. 2020;75:285-292. doi:10.1161 /HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14240
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:E596-E646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:E240-E327. doi:10.1161 /CIR.0b013e31829e8776
- Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS). N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1429-1435. doi:10.1056 /nejm198706043162301
- Kataria V, Wang H, Wald JW, et al. Lisinopril-induced alopecia: a case report. J Pharm Pract. 2017;30:562-566. doi:10.1177/0897190016652554
- Motel PJ. Captopril and alopecia: a case report and review of known cutaneous reactions in captopril use. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:124-125. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81205-4
- Leaker B, Whitworth JA. Alopecia associated with captopril treatment. Aust N Z J Med. 1984;14:866. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.1984.tb03797.x
- Ahmad S. Enalapril and reversible alopecia. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151:404.
- Bicket DP. Using ACE inhibitors appropriately. Am Fam Physician. 2002;66:461-468.
- Captopril. Product information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; May 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/563737c5-4d63-4957-8022-e3bc3112dfac/spl-doc?hl=captopril
- Farzam K, Jan A. Beta blockers. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532906/
- Mason RP, Giles TD, Sowers JR. Evolving mechanisms of action of beta blockers: focus on nebivolol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009; 54:123-128.
- Martin CM, Southwick EG, Maibach HI. Propranolol induced alopecia. Am Heart J. 1973;86:236-237. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(73)90250-0
- Graeber CW, Lapkin RA. Metoprolol and alopecia. Cutis. 1981; 28:633-634.
- Hilder RJ. Propranolol and alopecia. Cutis. 1979;24:63-64.
- Coreg. Prescribing information. Woodward Pharma Services LLC; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/34aa881a-3df4-460b-acad-fb9975ca3a06/34aa881a-3df4-460b-acad-fb9975ca3a06.xml
- Carey RM, Calhoun DA, Bakris GL, et al. Resistant hypertension: detection, evaluation, and management: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2018;72:E53-E90. doi:10.1161/hyp.0000000000000084
- Campese VM. Minoxidil: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1981;22:257-278. doi:10.2165/00003495-198122040-00001
- Heymann WR. Coming full circle (almost): low dose oral minoxidil for alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:613-614. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2020.12.053
- Yin S, Zhang B, Lin J, et al. Development of purification process for dual-function recombinant human heavy-chain ferritin by the investigation of genetic modification impact on conformation. Eng Life Sci. 2021;21:630-642. doi:10.1002/elsc.202000105
- Mysore V, Parthasaradhi A, Kharkar RD, et al. Expert consensus on the management of telogen effluvium in India. Int J Trichology. 2019;11:107-112.
- Gupta AK, Talukder M, Shemar A, et al. Low-dose oral minoxidil for alopecia: a comprehensive review [published online September 27, 2023]. Skin Appendage Disord. doi:10.1159/000531890
- Meisheri KD, Cipkus LA, Taylor CJ. Mechanism of action of minoxidil sulfate-induced vasodilation: a role for increased K+ permeability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;245:751-760.
- Winquist RJ, Heaney LA, Wallace AA, et al. Glyburide blocks the relaxation response to BRL 34915 (cromakalim), minoxidil sulfate and diazoxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989;248:149-56.
- Messenger AG, Rundegren J. Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:186-194. doi:10.1111/j .1365-2133.2004.05785.x
- Alijotas-Reig J, García GV, Velthuis PJ, et al. Inflammatory immunemediated adverse reactions induced by COVID-19 vaccines in previously injected patients with soft tissue fillers: a case series of 20 patients. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21:3181-3187. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15117
- Boskabadi SJ, Ramezaninejad S, Sohrab M, et al. Diazoxideinduced hypertrichosis in a neonate with transient hyperinsulinism. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2023;16:11795476231151330. doi:10.1177/11795476231151330
- Burton JL, Schutt WH, Caldwell IW. Hypertrichosis due to diazoxide. Br J Dermatol. 1975;93:707-711. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb05123.x
- Goldberg MR. Clinical pharmacology of pinacidil, a prototype for drugs that affect potassium channels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 suppl 2:S41-S47. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198812002-00008
- Buhl AE, Waldon DJ, Conrad SJ, et al. Potassium channel conductance: a mechanism affecting hair growth both in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1992;98:315-319. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499788
- Patel P, Nessel TA, Kumar DD. Minoxidil. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482378/
- O’Keefe E, Payne RE Jr. Minoxidil: inhibition of proliferation of keratinocytes in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:534-536. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12481560
- Murad S, Pinnell SR. Suppression of fibroblast proliferation and lysyl hydroxylase activity by minoxidil. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:11973-11978.
- Baden HP, Kubilus J. Effect of minoxidil on cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1983;81:558-560. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12523220
- Murad S, Walker LC, Tajima S, et al. Minimum structural requirements for minoxidil inhibition of lysyl hydroxylase in cultured fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;308:42-47. doi:10.1006/abbi.1994.1006
- Kvedar JC, Baden HP, Levine L. Selective inhibition by minoxidil of prostacyclin production by cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988;37:867-874. doi:0.1016/0006-2952(88)90174-8
- Zhang D, LaSenna C, Shields BE. Culprits of medication-induced telogen effluvium, part 1. Cutis. 2023;112:267-271.
- Angiolillo DJ, Bhatt DL, Cannon CP, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation treated with oral anticoagulation undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a North American perspective: 2021 update. Circulation. 2021;143:583-596. doi:10.1161 /circulationaha.120.050438
- Kearon C, Kahn SR. Long-term treatment of venous thromboembolism. Blood. 2020;135:317-325. doi:10.1182/blood.2019002364
- Frishman WH, Ribner HS. Anticoagulation in myocardial infarction: modern approach to an old problem. Am J Cardiol. 1979;43:1207-1213. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(79)90155-3
- Khorana AA, Mackman N, Falanga A, et al. Cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8:11. doi:10.1038 /s41572-022-00336-y
- Umerah CO, Momodu, II. Anticoagulation. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560651/
- Beurskens DMH, Huckriede JP, Schrijver R, et al. The anticoagulant and nonanticoagulant properties of heparin. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:1371-1383. doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715460
- Hirsh J, Dalen J, Anderson DR, et al. Oral anticoagulants: mechanism of action, clinical effectiveness, and optimal therapeutic range. Chest. 2001;119(1 suppl):8S-21S. doi:10.1378/chest.119.1_suppl.8s
- Holbrook AM, Pereira JA, Labiris R, et al. Systematic overview of warfarin and its drug and food interactions. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1095-1106. doi:10.1001/archinte.165.10.1095
- Watras MM, Patel JP, Arya R. Traditional anticoagulants and hair loss: a role for direct oral anticoagulants? a review of the literature. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2016;3:1-6. doi:10.1007/s40801-015-0056-z
- Heparin sodium. Product information. Hepalink USA Inc; January 2022. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/c4c6bc1f-e0c7-fd0d-e053-2995a90abdef/spl-doc?hl=heparin
- Warfarin sodium. Product information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; April 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/c41b7c23-8053-428a-ac1d-8395e714c2f1/spl-doc?hl=alopecia%7Cwarfarin#section-6
- Hirsh J. Low-molecular-weight heparin. Circulation. 1998;98:1575-1582. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.98.15.1575
- Paus R. Hair growth inhibition by heparin in mice: a model system for studying the modulation of epithelial cell growth by glycosaminoglycans? Br J Dermatol. 1991;124:415-422. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1991.tb00618.x
- Ma SN, Mao ZX, Wu Y, et al. The anti-cancer properties of heparin and its derivatives: a review and prospect. Cell Adh Migr. 2020;14:118-128. doi:10.1080/19336918.2020.1767489
- Choi JU, Chung SW, Al-Hilal TA, et al. A heparin conjugate, LHbisD4, inhibits lymphangiogenesis and attenuates lymph node metastasis by blocking VEGF-C signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 2017;139:56-66. doi:0.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.05.026
- Klerk CP, Smorenburg SM, Otten HM, et al. The effect of low molecular weight heparin on survival in patients with advanced malignancy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2130-2135. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.03.134
- Altinbas M, Coskun HS, Er O, et al. A randomized clinical trial of combination chemotherapy with and without low-molecular-weight heparin in small cell lung cancer. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:1266-1271. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2004.00871.x
- Weyand AC, Shavit JA. Agent specific effects of anticoagulant induced alopecia. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2017;1:90-92. doi:10.1002 /rth2.12001
- Bonaldo G, Vaccheri A, Motola D. Direct-acting oral anticoagulants and alopecia: the valuable support of postmarketing data. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;86:1654-1660. doi:10.1111/bcp.14221
- Fuchs FD, Whelton PK. High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension. 2020;75:285-292. doi:10.1161 /HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14240
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:E596-E646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:E240-E327. doi:10.1161 /CIR.0b013e31829e8776
- Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS). N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1429-1435. doi:10.1056 /nejm198706043162301
- Kataria V, Wang H, Wald JW, et al. Lisinopril-induced alopecia: a case report. J Pharm Pract. 2017;30:562-566. doi:10.1177/0897190016652554
- Motel PJ. Captopril and alopecia: a case report and review of known cutaneous reactions in captopril use. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:124-125. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(08)81205-4
- Leaker B, Whitworth JA. Alopecia associated with captopril treatment. Aust N Z J Med. 1984;14:866. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.1984.tb03797.x
- Ahmad S. Enalapril and reversible alopecia. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151:404.
- Bicket DP. Using ACE inhibitors appropriately. Am Fam Physician. 2002;66:461-468.
- Captopril. Product information. Bryant Ranch Prepack; May 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://nctr-crs.fda.gov/fdalabel/services/spl/set-ids/563737c5-4d63-4957-8022-e3bc3112dfac/spl-doc?hl=captopril
- Farzam K, Jan A. Beta blockers. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532906/
- Mason RP, Giles TD, Sowers JR. Evolving mechanisms of action of beta blockers: focus on nebivolol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009; 54:123-128.
- Martin CM, Southwick EG, Maibach HI. Propranolol induced alopecia. Am Heart J. 1973;86:236-237. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(73)90250-0
- Graeber CW, Lapkin RA. Metoprolol and alopecia. Cutis. 1981; 28:633-634.
- Hilder RJ. Propranolol and alopecia. Cutis. 1979;24:63-64.
- Coreg. Prescribing information. Woodward Pharma Services LLC; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/34aa881a-3df4-460b-acad-fb9975ca3a06/34aa881a-3df4-460b-acad-fb9975ca3a06.xml
- Carey RM, Calhoun DA, Bakris GL, et al. Resistant hypertension: detection, evaluation, and management: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2018;72:E53-E90. doi:10.1161/hyp.0000000000000084
- Campese VM. Minoxidil: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1981;22:257-278. doi:10.2165/00003495-198122040-00001
- Heymann WR. Coming full circle (almost): low dose oral minoxidil for alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:613-614. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2020.12.053
- Yin S, Zhang B, Lin J, et al. Development of purification process for dual-function recombinant human heavy-chain ferritin by the investigation of genetic modification impact on conformation. Eng Life Sci. 2021;21:630-642. doi:10.1002/elsc.202000105
- Mysore V, Parthasaradhi A, Kharkar RD, et al. Expert consensus on the management of telogen effluvium in India. Int J Trichology. 2019;11:107-112.
- Gupta AK, Talukder M, Shemar A, et al. Low-dose oral minoxidil for alopecia: a comprehensive review [published online September 27, 2023]. Skin Appendage Disord. doi:10.1159/000531890
- Meisheri KD, Cipkus LA, Taylor CJ. Mechanism of action of minoxidil sulfate-induced vasodilation: a role for increased K+ permeability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;245:751-760.
- Winquist RJ, Heaney LA, Wallace AA, et al. Glyburide blocks the relaxation response to BRL 34915 (cromakalim), minoxidil sulfate and diazoxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989;248:149-56.
- Messenger AG, Rundegren J. Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:186-194. doi:10.1111/j .1365-2133.2004.05785.x
- Alijotas-Reig J, García GV, Velthuis PJ, et al. Inflammatory immunemediated adverse reactions induced by COVID-19 vaccines in previously injected patients with soft tissue fillers: a case series of 20 patients. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21:3181-3187. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15117
- Boskabadi SJ, Ramezaninejad S, Sohrab M, et al. Diazoxideinduced hypertrichosis in a neonate with transient hyperinsulinism. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2023;16:11795476231151330. doi:10.1177/11795476231151330
- Burton JL, Schutt WH, Caldwell IW. Hypertrichosis due to diazoxide. Br J Dermatol. 1975;93:707-711. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb05123.x
- Goldberg MR. Clinical pharmacology of pinacidil, a prototype for drugs that affect potassium channels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 suppl 2:S41-S47. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198812002-00008
- Buhl AE, Waldon DJ, Conrad SJ, et al. Potassium channel conductance: a mechanism affecting hair growth both in vitro and in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1992;98:315-319. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499788
- Patel P, Nessel TA, Kumar DD. Minoxidil. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed December 11, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482378/
- O’Keefe E, Payne RE Jr. Minoxidil: inhibition of proliferation of keratinocytes in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:534-536. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12481560
- Murad S, Pinnell SR. Suppression of fibroblast proliferation and lysyl hydroxylase activity by minoxidil. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:11973-11978.
- Baden HP, Kubilus J. Effect of minoxidil on cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1983;81:558-560. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12523220
- Murad S, Walker LC, Tajima S, et al. Minimum structural requirements for minoxidil inhibition of lysyl hydroxylase in cultured fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;308:42-47. doi:10.1006/abbi.1994.1006
- Kvedar JC, Baden HP, Levine L. Selective inhibition by minoxidil of prostacyclin production by cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988;37:867-874. doi:0.1016/0006-2952(88)90174-8
- Zhang D, LaSenna C, Shields BE. Culprits of medication-induced telogen effluvium, part 1. Cutis. 2023;112:267-271.
Practice Points
- Medications are a common culprit of telogen effluvium (TE), and medication-induced TE should be suspected in patients presenting with diffuse nonscarring alopecia who are taking systemic medication(s) such as heparin and its derivatives.
- Infection, illness, or hospitalization around the time of initiation of the suspected culprit medication may complicate identification of the inciting cause and may contribute to TE.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and β-blockers are unlikely culprits of medication-induced TE, and the benefits of discontinuing a suspected culprit medication should be weighed carefully against the risks of medication cessation.
Pink Papules on the Cheek
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare benign non- Langerhans cell histiocytopathy that can manifest initially with lymph node involvement—classically, massive painless cervical lymphadenopathy.1 Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease (CRDD) is a variant that can be associated with lymph node and internal involvement, but more than 80% of cases lack extracutaneous involvement.2,3 In cases with extracutaneous involvement, lymph node disease is most frequent.3 Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease unassociated with extracutaneous disease is a benign self-limiting histiocytopathy that manifests as painless red-brown, yellow, or fleshcolored nodules, plaques, or papules that may become tender or ulcerated.4
Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease represents a benign histiocytopathy of resident dendritic cell derivation.3 A characteristic immunohistochemical finding is S-100 positivity, which might suggest a Langerhans cell transdifferentiation phenotype, but other markers corroborative of a Langerhans cell phenotype—namely CD1a and langerin—will be negative. Biopsies typically show a mid to deep dermal histiocytic infiltration in a variably dense polymorphous inflammatory cell background comprised of a mixture of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils.3 At times the extent of lymphocytic infiltration can be to a magnitude that resembles a lymphoma on histopathology. In our patient, lymphoma was excluded based on clinical presentation, as this patient lacked the typical symptoms of lymphadenopathy or B symptoms that come with B-cell lymphoma.5
The histiocytes in CRDD are characteristically large mononuclear cells exhibiting a low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio reflective of the voluminous, nonvacuolated, watery cytoplasm. They have ill-defined cytoplasmic membranes resulting in a seemingly syncytial growth pattern. A hallmark of the histiocytes is emperipolesis characterized by intracytoplasmic localization of intact inflammatory cells including neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells.3
The differential diagnosis of CRDD includes Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), indeterminate cell histiocytosis, xanthogranuloma, and reticulohistiocytoma. All of these conditions can be differentiated by their unique histopathologic and phenotypic characteristics.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis is a distinct clonal histiocytopathy that has a varied presentation ranging from cutaneous confined cases manifesting as a solitary lesion to one of disseminated cutaneous disease with the potential for multiorgan involvement. Regardless of the variant of LCH, the hallmark cell is one showing an eccentrically disposed, reniform nucleus with an open chromatin and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 1).6 Both LCH and CRDD stain positive for S-100. However, unlike the histiocytes in CRDD, those seen in LCH stain positive for CD1a and langerin and would not express factor XIIIA. Additionally, the neoplastic cells would not exhibit the same extent of CD68 positivity seen in CRDD.6 Treatment of LCH depends on the extent of disease, especially for the presence or absence of extracutaneous disease.7
A variant of LCH is indeterminate cell histiocytosis, which can be seen in neonates or adults. It represents a neoplastic proliferation of Langerhans cells that are devoid of Birbeck granules, reflective of an immature early phase of differentiation in the skin prior to the cells acquiring the Birbeck granule (as would be seen in neonates) or a later phase of differentiation after the mature Langerhans cell has encountered antigen and is en route to the lymph node (typically seen in adults).8 The phenotypic profile is identical to conventional LCH except the cells do not express langerin. Microscopically, the infiltrates are composed of Langerhans cells that are morphologically indistinguishable from classic LCH but without epidermotropism and exhibit a dominant localization in the dermis typically unassociated with other inflammatory cell elements (Figure 2).9
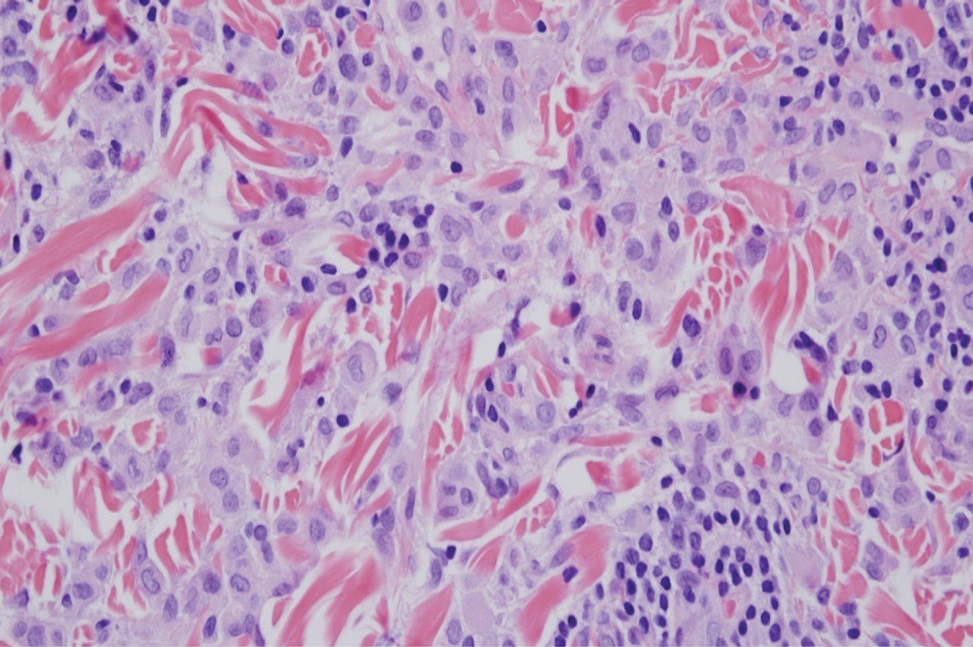
Xanthogranuloma is seen in young children (juvenile xanthogranuloma) as a solitary lesion, though a multifocal cutaneous variant and extracutaneous presentations have been described. Similar lesions can be seen in adults.10 These lesions are evolutionary in their morphology. In the inception of a juvenile xanthogranuloma, the lesions are highly cellular, and the histiocytes typically are poorly lipidized; there may be a dearth of other inflammatory cell elements. As the lesions mature, the histiocytes become lipidized, and characteristic Touton giant cells that exhibit a wreath of nuclei with peripheral lipidization may develop (Figure 3). In the later stages, there is considerable hyalinizing fibrosis, and the cells can acquire a spindled appearance. The absence of emperipolesis and the presence of notable lipidization are useful light microscopy features differentiating xanthogranuloma from CRDD.11 Treatment of xanthogranuloma can range from a conservative monitoring approach to an aggressive approach combining various antineoplastic therapies with immunosuppressive agents.12
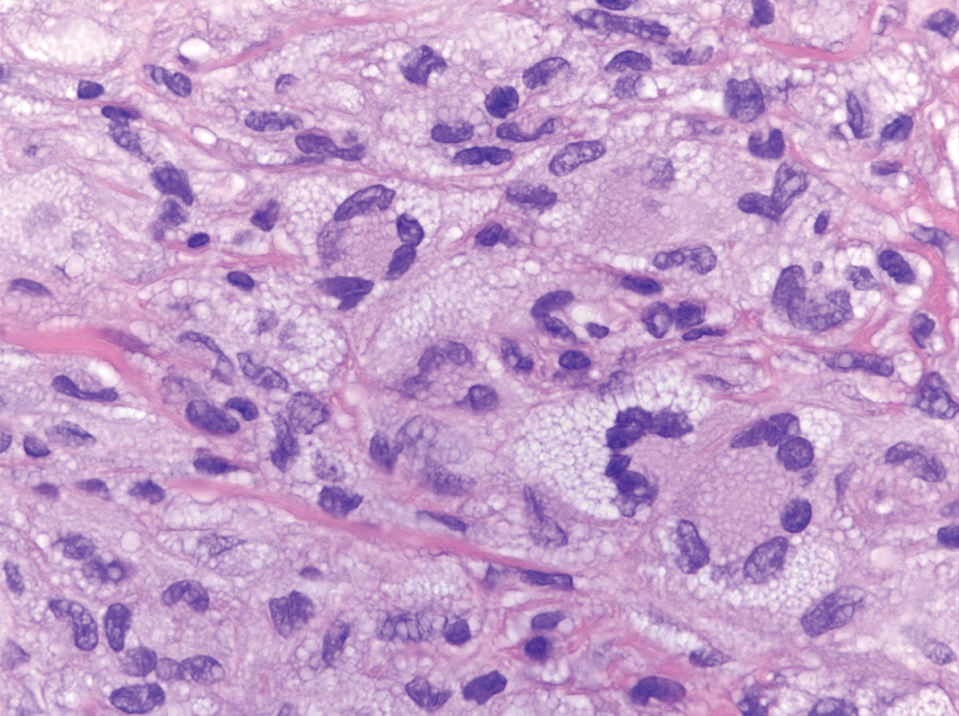
Solitary and multicentric reticulohistiocytoma is another form of resident dendritic cell histiocytopathy that can resemble Rosai-Dorfman disease. It is a dermal histiocytic infiltrate accompanied by a polymorphous inflammatory cell infiltrate (Figure 4) and can show variable fibrosis.13 One of the hallmarks is the distinct amphophilic cytoplasms, possibly attributable to nuclear DNA released into the cytoplasm from effete nuclei.13 The solitary form is unassociated with systemic disease, whereas the multicentric variant can be a paraneoplastic syndrome in the setting of solid and hematologic malignancies.14 In addition, in the multicentric variant, similar lesions can affect any organ but there can be a proclivity to involve the hand and knee joints, leading to a crippling arthritis.15 We presented a case of CRDD, a benign resident dendritic cell histiocytopathy that can manifest as a cutaneous confined process in the skin where the clinical course is characteristically benign. It potentially can be confused with LCH, indeterminate cell histiocytosis, xanthogranuloma, and reticulohistiocytoma. For a solitary lesion, intralesional triamcinolone injection and excision are options. Multifocal cutaneous disease or CRDD with notable extracutaneous disease may require systemic treatment.16 In our patient, one intralesional triamcinolone injection was performed with notable resolution.
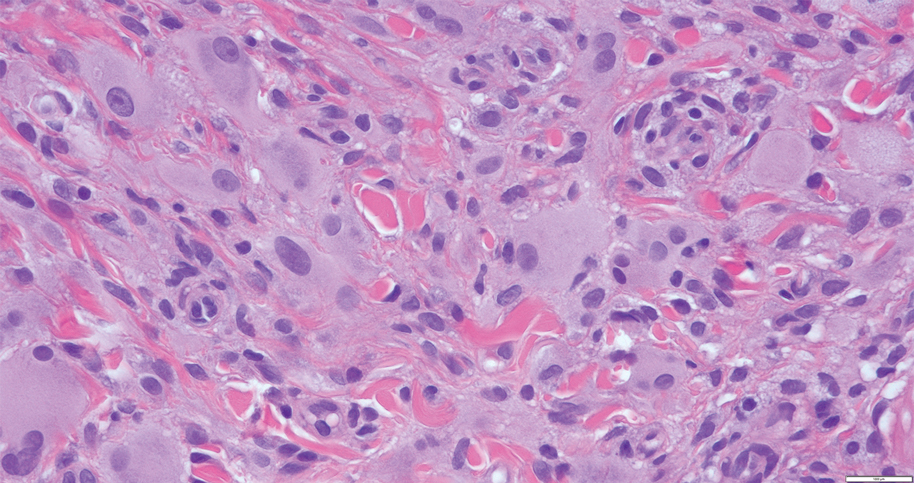
- Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: a newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969;87:63-70.
- Brenn T, Calonje E, Granter SR, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a distinct clinical entity. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:385.
- Ahmed A, Crowson N, Magro CM. A comprehensive assessment of cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2019;40:166-173.
- Frater JL, Maddox JS, Obadiah JM, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: comprehensive review of cases reported in the medical literature since 1990 and presentation of an illustrative case. J Cutan Med Surg. 2006;10:281-290.
- Friedberg JW, Fisher RI. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2008;22:941-952. Doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2008.07.002
- Allen CE, Merad M, McClain KL. Langerhans-cell histiocytosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:856-868.
- Board PPTE. Langerhans cell histiocytosis treatment (PDQ®). In: PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. National Cancer Institute (US); 2009.
- Chu A, Eisinger M, Lee JS, et al. Immunoelectron microscopic identification of Langerhans cells using a new antigenic marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982;78:177-180. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506352
- Berti E, Gianotti R, Alessi E. Unusual cutaneous histiocytosis expressing an intermediate immunophenotype between Langerhans’ cells and dermal macrophages. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:1250-1253. doi:10.1001/archderm.1988.01670080062020
- Cypel TKS, Zuker RM. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: case report and review of the literature. Can J Plast Surg. 2008;16:175-177.
- Rodriguez J, Ackerman AB. Xanthogranuloma in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:43-44.
- Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:486-492. doi:10.1016/j. clindermatol.2006.07.010
- Miettinen M, Fetsch JF. Reticulohistiocytoma (solitary epithelioid histiocytoma): a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 44 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:521.
- Gold RH, Metzger AL, Mirra JM, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (lipoid dermato-arthritis). An erosive polyarthritis with distinctive clinical, roentgenographic and pathologic features. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;124:610-624. doi:10.2214/ajr.124.4.610
- Dalia S, Sagatys E, Sokol L, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease: tumor biology, clinical features, pathology, and treatment. Cancer Control. 2014;21:322-327. doi:10.1177/107327481402100408
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare benign non- Langerhans cell histiocytopathy that can manifest initially with lymph node involvement—classically, massive painless cervical lymphadenopathy.1 Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease (CRDD) is a variant that can be associated with lymph node and internal involvement, but more than 80% of cases lack extracutaneous involvement.2,3 In cases with extracutaneous involvement, lymph node disease is most frequent.3 Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease unassociated with extracutaneous disease is a benign self-limiting histiocytopathy that manifests as painless red-brown, yellow, or fleshcolored nodules, plaques, or papules that may become tender or ulcerated.4
Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease represents a benign histiocytopathy of resident dendritic cell derivation.3 A characteristic immunohistochemical finding is S-100 positivity, which might suggest a Langerhans cell transdifferentiation phenotype, but other markers corroborative of a Langerhans cell phenotype—namely CD1a and langerin—will be negative. Biopsies typically show a mid to deep dermal histiocytic infiltration in a variably dense polymorphous inflammatory cell background comprised of a mixture of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils.3 At times the extent of lymphocytic infiltration can be to a magnitude that resembles a lymphoma on histopathology. In our patient, lymphoma was excluded based on clinical presentation, as this patient lacked the typical symptoms of lymphadenopathy or B symptoms that come with B-cell lymphoma.5
The histiocytes in CRDD are characteristically large mononuclear cells exhibiting a low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio reflective of the voluminous, nonvacuolated, watery cytoplasm. They have ill-defined cytoplasmic membranes resulting in a seemingly syncytial growth pattern. A hallmark of the histiocytes is emperipolesis characterized by intracytoplasmic localization of intact inflammatory cells including neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells.3
The differential diagnosis of CRDD includes Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), indeterminate cell histiocytosis, xanthogranuloma, and reticulohistiocytoma. All of these conditions can be differentiated by their unique histopathologic and phenotypic characteristics.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis is a distinct clonal histiocytopathy that has a varied presentation ranging from cutaneous confined cases manifesting as a solitary lesion to one of disseminated cutaneous disease with the potential for multiorgan involvement. Regardless of the variant of LCH, the hallmark cell is one showing an eccentrically disposed, reniform nucleus with an open chromatin and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 1).6 Both LCH and CRDD stain positive for S-100. However, unlike the histiocytes in CRDD, those seen in LCH stain positive for CD1a and langerin and would not express factor XIIIA. Additionally, the neoplastic cells would not exhibit the same extent of CD68 positivity seen in CRDD.6 Treatment of LCH depends on the extent of disease, especially for the presence or absence of extracutaneous disease.7

A variant of LCH is indeterminate cell histiocytosis, which can be seen in neonates or adults. It represents a neoplastic proliferation of Langerhans cells that are devoid of Birbeck granules, reflective of an immature early phase of differentiation in the skin prior to the cells acquiring the Birbeck granule (as would be seen in neonates) or a later phase of differentiation after the mature Langerhans cell has encountered antigen and is en route to the lymph node (typically seen in adults).8 The phenotypic profile is identical to conventional LCH except the cells do not express langerin. Microscopically, the infiltrates are composed of Langerhans cells that are morphologically indistinguishable from classic LCH but without epidermotropism and exhibit a dominant localization in the dermis typically unassociated with other inflammatory cell elements (Figure 2).9

Xanthogranuloma is seen in young children (juvenile xanthogranuloma) as a solitary lesion, though a multifocal cutaneous variant and extracutaneous presentations have been described. Similar lesions can be seen in adults.10 These lesions are evolutionary in their morphology. In the inception of a juvenile xanthogranuloma, the lesions are highly cellular, and the histiocytes typically are poorly lipidized; there may be a dearth of other inflammatory cell elements. As the lesions mature, the histiocytes become lipidized, and characteristic Touton giant cells that exhibit a wreath of nuclei with peripheral lipidization may develop (Figure 3). In the later stages, there is considerable hyalinizing fibrosis, and the cells can acquire a spindled appearance. The absence of emperipolesis and the presence of notable lipidization are useful light microscopy features differentiating xanthogranuloma from CRDD.11 Treatment of xanthogranuloma can range from a conservative monitoring approach to an aggressive approach combining various antineoplastic therapies with immunosuppressive agents.12

Solitary and multicentric reticulohistiocytoma is another form of resident dendritic cell histiocytopathy that can resemble Rosai-Dorfman disease. It is a dermal histiocytic infiltrate accompanied by a polymorphous inflammatory cell infiltrate (Figure 4) and can show variable fibrosis.13 One of the hallmarks is the distinct amphophilic cytoplasms, possibly attributable to nuclear DNA released into the cytoplasm from effete nuclei.13 The solitary form is unassociated with systemic disease, whereas the multicentric variant can be a paraneoplastic syndrome in the setting of solid and hematologic malignancies.14 In addition, in the multicentric variant, similar lesions can affect any organ but there can be a proclivity to involve the hand and knee joints, leading to a crippling arthritis.15 We presented a case of CRDD, a benign resident dendritic cell histiocytopathy that can manifest as a cutaneous confined process in the skin where the clinical course is characteristically benign. It potentially can be confused with LCH, indeterminate cell histiocytosis, xanthogranuloma, and reticulohistiocytoma. For a solitary lesion, intralesional triamcinolone injection and excision are options. Multifocal cutaneous disease or CRDD with notable extracutaneous disease may require systemic treatment.16 In our patient, one intralesional triamcinolone injection was performed with notable resolution.

The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare benign non- Langerhans cell histiocytopathy that can manifest initially with lymph node involvement—classically, massive painless cervical lymphadenopathy.1 Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease (CRDD) is a variant that can be associated with lymph node and internal involvement, but more than 80% of cases lack extracutaneous involvement.2,3 In cases with extracutaneous involvement, lymph node disease is most frequent.3 Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease unassociated with extracutaneous disease is a benign self-limiting histiocytopathy that manifests as painless red-brown, yellow, or fleshcolored nodules, plaques, or papules that may become tender or ulcerated.4
Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease represents a benign histiocytopathy of resident dendritic cell derivation.3 A characteristic immunohistochemical finding is S-100 positivity, which might suggest a Langerhans cell transdifferentiation phenotype, but other markers corroborative of a Langerhans cell phenotype—namely CD1a and langerin—will be negative. Biopsies typically show a mid to deep dermal histiocytic infiltration in a variably dense polymorphous inflammatory cell background comprised of a mixture of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils.3 At times the extent of lymphocytic infiltration can be to a magnitude that resembles a lymphoma on histopathology. In our patient, lymphoma was excluded based on clinical presentation, as this patient lacked the typical symptoms of lymphadenopathy or B symptoms that come with B-cell lymphoma.5
The histiocytes in CRDD are characteristically large mononuclear cells exhibiting a low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio reflective of the voluminous, nonvacuolated, watery cytoplasm. They have ill-defined cytoplasmic membranes resulting in a seemingly syncytial growth pattern. A hallmark of the histiocytes is emperipolesis characterized by intracytoplasmic localization of intact inflammatory cells including neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells.3
The differential diagnosis of CRDD includes Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), indeterminate cell histiocytosis, xanthogranuloma, and reticulohistiocytoma. All of these conditions can be differentiated by their unique histopathologic and phenotypic characteristics.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis is a distinct clonal histiocytopathy that has a varied presentation ranging from cutaneous confined cases manifesting as a solitary lesion to one of disseminated cutaneous disease with the potential for multiorgan involvement. Regardless of the variant of LCH, the hallmark cell is one showing an eccentrically disposed, reniform nucleus with an open chromatin and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 1).6 Both LCH and CRDD stain positive for S-100. However, unlike the histiocytes in CRDD, those seen in LCH stain positive for CD1a and langerin and would not express factor XIIIA. Additionally, the neoplastic cells would not exhibit the same extent of CD68 positivity seen in CRDD.6 Treatment of LCH depends on the extent of disease, especially for the presence or absence of extracutaneous disease.7

A variant of LCH is indeterminate cell histiocytosis, which can be seen in neonates or adults. It represents a neoplastic proliferation of Langerhans cells that are devoid of Birbeck granules, reflective of an immature early phase of differentiation in the skin prior to the cells acquiring the Birbeck granule (as would be seen in neonates) or a later phase of differentiation after the mature Langerhans cell has encountered antigen and is en route to the lymph node (typically seen in adults).8 The phenotypic profile is identical to conventional LCH except the cells do not express langerin. Microscopically, the infiltrates are composed of Langerhans cells that are morphologically indistinguishable from classic LCH but without epidermotropism and exhibit a dominant localization in the dermis typically unassociated with other inflammatory cell elements (Figure 2).9

Xanthogranuloma is seen in young children (juvenile xanthogranuloma) as a solitary lesion, though a multifocal cutaneous variant and extracutaneous presentations have been described. Similar lesions can be seen in adults.10 These lesions are evolutionary in their morphology. In the inception of a juvenile xanthogranuloma, the lesions are highly cellular, and the histiocytes typically are poorly lipidized; there may be a dearth of other inflammatory cell elements. As the lesions mature, the histiocytes become lipidized, and characteristic Touton giant cells that exhibit a wreath of nuclei with peripheral lipidization may develop (Figure 3). In the later stages, there is considerable hyalinizing fibrosis, and the cells can acquire a spindled appearance. The absence of emperipolesis and the presence of notable lipidization are useful light microscopy features differentiating xanthogranuloma from CRDD.11 Treatment of xanthogranuloma can range from a conservative monitoring approach to an aggressive approach combining various antineoplastic therapies with immunosuppressive agents.12

Solitary and multicentric reticulohistiocytoma is another form of resident dendritic cell histiocytopathy that can resemble Rosai-Dorfman disease. It is a dermal histiocytic infiltrate accompanied by a polymorphous inflammatory cell infiltrate (Figure 4) and can show variable fibrosis.13 One of the hallmarks is the distinct amphophilic cytoplasms, possibly attributable to nuclear DNA released into the cytoplasm from effete nuclei.13 The solitary form is unassociated with systemic disease, whereas the multicentric variant can be a paraneoplastic syndrome in the setting of solid and hematologic malignancies.14 In addition, in the multicentric variant, similar lesions can affect any organ but there can be a proclivity to involve the hand and knee joints, leading to a crippling arthritis.15 We presented a case of CRDD, a benign resident dendritic cell histiocytopathy that can manifest as a cutaneous confined process in the skin where the clinical course is characteristically benign. It potentially can be confused with LCH, indeterminate cell histiocytosis, xanthogranuloma, and reticulohistiocytoma. For a solitary lesion, intralesional triamcinolone injection and excision are options. Multifocal cutaneous disease or CRDD with notable extracutaneous disease may require systemic treatment.16 In our patient, one intralesional triamcinolone injection was performed with notable resolution.

- Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: a newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969;87:63-70.
- Brenn T, Calonje E, Granter SR, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a distinct clinical entity. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:385.
- Ahmed A, Crowson N, Magro CM. A comprehensive assessment of cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2019;40:166-173.
- Frater JL, Maddox JS, Obadiah JM, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: comprehensive review of cases reported in the medical literature since 1990 and presentation of an illustrative case. J Cutan Med Surg. 2006;10:281-290.
- Friedberg JW, Fisher RI. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2008;22:941-952. Doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2008.07.002
- Allen CE, Merad M, McClain KL. Langerhans-cell histiocytosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:856-868.
- Board PPTE. Langerhans cell histiocytosis treatment (PDQ®). In: PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. National Cancer Institute (US); 2009.
- Chu A, Eisinger M, Lee JS, et al. Immunoelectron microscopic identification of Langerhans cells using a new antigenic marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982;78:177-180. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506352
- Berti E, Gianotti R, Alessi E. Unusual cutaneous histiocytosis expressing an intermediate immunophenotype between Langerhans’ cells and dermal macrophages. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:1250-1253. doi:10.1001/archderm.1988.01670080062020
- Cypel TKS, Zuker RM. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: case report and review of the literature. Can J Plast Surg. 2008;16:175-177.
- Rodriguez J, Ackerman AB. Xanthogranuloma in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:43-44.
- Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:486-492. doi:10.1016/j. clindermatol.2006.07.010
- Miettinen M, Fetsch JF. Reticulohistiocytoma (solitary epithelioid histiocytoma): a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 44 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:521.
- Gold RH, Metzger AL, Mirra JM, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (lipoid dermato-arthritis). An erosive polyarthritis with distinctive clinical, roentgenographic and pathologic features. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;124:610-624. doi:10.2214/ajr.124.4.610
- Dalia S, Sagatys E, Sokol L, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease: tumor biology, clinical features, pathology, and treatment. Cancer Control. 2014;21:322-327. doi:10.1177/107327481402100408
- Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: a newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969;87:63-70.
- Brenn T, Calonje E, Granter SR, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a distinct clinical entity. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:385.
- Ahmed A, Crowson N, Magro CM. A comprehensive assessment of cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2019;40:166-173.
- Frater JL, Maddox JS, Obadiah JM, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: comprehensive review of cases reported in the medical literature since 1990 and presentation of an illustrative case. J Cutan Med Surg. 2006;10:281-290.
- Friedberg JW, Fisher RI. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2008;22:941-952. Doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2008.07.002
- Allen CE, Merad M, McClain KL. Langerhans-cell histiocytosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:856-868.
- Board PPTE. Langerhans cell histiocytosis treatment (PDQ®). In: PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. National Cancer Institute (US); 2009.
- Chu A, Eisinger M, Lee JS, et al. Immunoelectron microscopic identification of Langerhans cells using a new antigenic marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982;78:177-180. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506352
- Berti E, Gianotti R, Alessi E. Unusual cutaneous histiocytosis expressing an intermediate immunophenotype between Langerhans’ cells and dermal macrophages. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:1250-1253. doi:10.1001/archderm.1988.01670080062020
- Cypel TKS, Zuker RM. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: case report and review of the literature. Can J Plast Surg. 2008;16:175-177.
- Rodriguez J, Ackerman AB. Xanthogranuloma in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:43-44.
- Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:486-492. doi:10.1016/j. clindermatol.2006.07.010
- Miettinen M, Fetsch JF. Reticulohistiocytoma (solitary epithelioid histiocytoma): a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 44 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:521.
- Gold RH, Metzger AL, Mirra JM, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (lipoid dermato-arthritis). An erosive polyarthritis with distinctive clinical, roentgenographic and pathologic features. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;124:610-624. doi:10.2214/ajr.124.4.610
- Dalia S, Sagatys E, Sokol L, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease: tumor biology, clinical features, pathology, and treatment. Cancer Control. 2014;21:322-327. doi:10.1177/107327481402100408
A 31-year-old woman presented with a slow-growing, tender, pruritic lesion on the right cheek of 4 to 5 months’ duration. She had been applying petroleum jelly and hydrocortisone cream 2.5% without any improvement. Physical examination revealed a 1×5-mm, pearly pink, erythematous, crusted papule with arborizing vessels surrounded by scattered pink papules with white dots within. No cervical lymphadenopathy was appreciated on physical examination, and the patient denied any other systemic symptoms. Shave and punch biopsies of the lesion were performed; stains for microorganisms were negative. The biopsy showed a dense reticular mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate comprised of a mixture of histiocytes (top), lymphocytes, neutrophils, and plasma cells that assumed a diffuse growth pattern within the dermis. The histiocytes exhibited abundant watery cytoplasms with ill-defined cytoplasmic membranes; intact leukocytes were found within the cytoplasms. The histiocytes demonstrated a unique phenotype characterized by S-100 (bottom) and CD68 positivity.
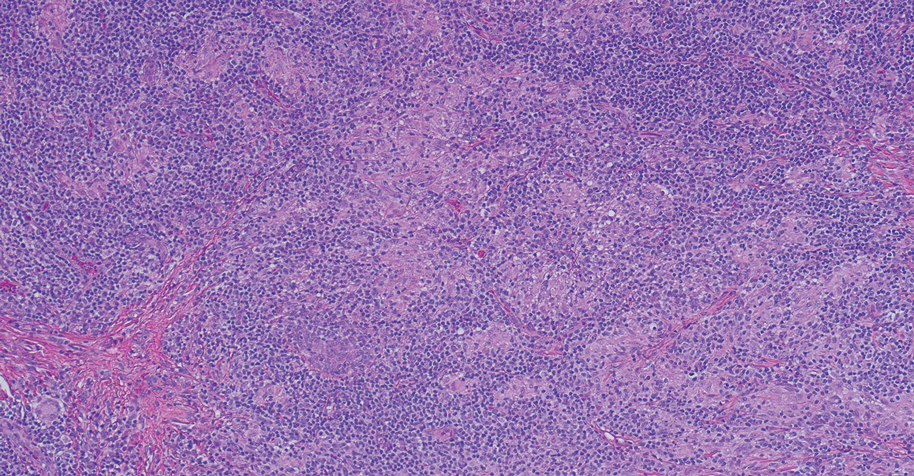
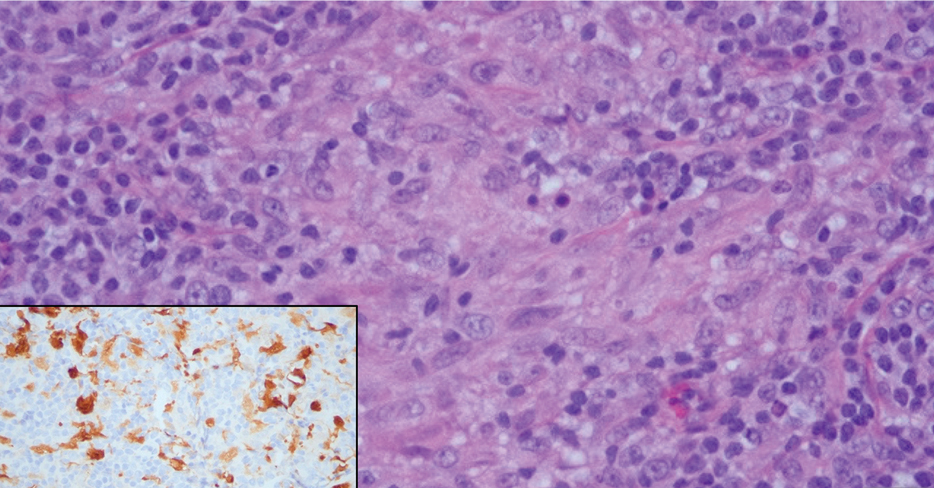
Androgenetic Alopecia: What Works?
When it comes to selecting medical treatments for androgenetic alopecia (AGA), patients and practitioners alike want to know, “What works?” The ideal AGA treatment is one that meets 4 criteria: highly effective, safe, affordable, and easy to use. To date, there is no known treatment for AGA that meets all these criteria. Some therapies are more effective than others, but there are no treatments at present that are able to completely and permanently reverse the condition. Some treatments are safer, some are less expensive, and some are easier to use than others. In the end, the treatment that the patient chooses is influenced not only by its known effectiveness but also by the value that the patient places on the other 3 categories—safety, affordability, and ease of use. Therefore, shared decision-making between patient and practitioner is central to the selection of specific AGA treatments.
Effectiveness: Some Treatments Work Better Than Others
Of the nearly 2 dozen medical treatments for AGA, some have been found to be more effective than others. Whether a given treatment should be considered a bona fide AGA therapy—and then whether to position it as a first-line, second-line, or third-line agent—depends on the answers to 3 fundamental questions:
- Does the treatment truly help patients with AGA?
- How effective is this treatment?
- How safe is it?
Does the Treatment Truly Help Patients?—Surprisingly, it is not always straightforward to confirm that a given treatment helps patients with AGA. Does oral finasteride help female AGA? Yes and no: Finasteride 1 mg is ineffective in the treatment of female AGA, but higher doses such as 2.5 or 5 mg likely have benefit.1,2 Does topical minoxidil help AGA? Yes and no: Minoxidil 5% is ineffective in the treatment of a male with Hamilton-Norwood stage VII AGA but often is helpful in earlier stages of the condition.
One of the best ways to determine if a treatment really helps AGA is to evaluate how it performs in the setting of a well-conducted, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. These types of clinical trials have been performed for many known AGA treatments and give us some of the best evidence that a treatment truly works. The AGA treatments with the highest-quality evidence (level 1) are topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and oral dutasteride for male AGA and topical minoxidil for female AGA.
How Effective Is This Treatment?—Patients are particularly interested to know whether a given treatment has the potential to notably restore hair density. It is one thing to know that use of the treatment might slightly improve hair density and another to know that it could potentially lead to dramatic improvement. In addition, patients want to know whether a specific treatment they are considering is more (or less) likely to improve their hair density compared to another treatment.
Advanced statistical methods such as the network meta-analysis are increasingly being used to understand how individual treatments from different studies compare. Two recent studies have provided us with powerful data on the relative efficacy of minoxidil and 5α-reductase inhibitors in the treatment of both male and female AGA.2,3 A 2022 network meta-analysis of male AGA ranked treatment efficacy from most to least effective: oral dutasteride 0.5 mg, oral finasteride 5 mg, oral minoxidil 5 mg, oral finasteride 1 mg, and topical minoxidil 5%.3 Similarly, a 2023 network meta-analysis of female AGA ranked treatment efficacy from most to least effective: oral 5 mg finasteride, minoxidil solution 5% twice daily, oral minoxidil 1 mg, and minoxidil foam 5% once daily.2 We are not yet able to rank all known treatments for AGA.
Things We Tend to Ignore: Quality of Data, Long-term Results, Nonresponders, and Study Populations—There are a few caveats for anyone treating AGA. First, the quality of published AGA studies is highly variable and many are of low quality. The highest-quality evidence (level 1) for male AGA comes from studies of minoxidil solution/foam 5% twice daily, oral finasteride 1 mg, and oral dutasteride 0.5 mg. For female AGA, the highest-quality evidence is for topical minoxidil—either 5% foam once daily or 2% solution twice daily. Lower-quality studies limit conclusions and the ability to properly compare treatments.
Second, long-term data are nonexistent for most of our AGA treatments. The exceptions include finasteride, dutasteride, and topical minoxidil, which have reasonably adequate long-term studies.4-6 However, most other treatments have been evaluated only through short-term studies. It is tempting to assume that results from a 24-week study can be used to infer how a patient might respond when using the same treatment over the course of many decades; however, making these assumptions would be unwise.
Third, most AGA treatments help improve hair density in only a proportion of patients who decide to use the given treatment. There usually is one subgroup of patients for whom the treatment does not seem to help much at all and one subgroup for whom the treatment halts further hair loss but does not regrow hair. For example, in the case of finasteride treatment of male AGA, approximately 10% of patients do not seem to respond to treatment at all, and another 50% seem to be able to halt further loss but never achieve hair regrowth.7 In an analysis of 12 studies with 3927 male patients, Mella et al8 showed that 5.6 patients needed to be treated short term and 3.4 patients needed to be treated long term for 1 patient to perceive an improvement in the hair. It is clear that many males who use finasteride will not see evidence of hair regrowth. This same general concept applies for all available treatments and is important to remember if a patient with AGA decides to start 2 new treatments simultaneously. Consider the 34-year-old man who starts oral minoxidil and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for AGA. At his follow-up appointment 9 months later, the patient reports improved hair density and wants to know what contributed to the improvement: the oral minoxidil, the PRP, or both? Many practitioners would believe that both treatments likely provided some degree of benefit—but in reality, that represents a flaw in logic. If 2 hair loss treatments are started at exactly the same time, it is impossible to know the relative benefit of each treatment and whether one might not be helping at all. Combination therapies are still common in my practice and highly encouraged, but my personal preference is to stagger start dates whenever possible so I can determine each treatment’s contribution to the patient’s final outcome.
Finally, when evaluating what works for AGA, we need to define the specific patient subpopulation, as the available data are less robust for some patient groups than others. We have limited data in children and adolescents with AGA, as well as limited comparative data across different racial backgrounds, body mass indices, and underlying health issues. For example, data on the most effective strategies to treat female AGA in the setting of polycystic ovary syndrome, premature menopause, and other endocrine disorders are lacking.
Which Treatments Also Have Good Safety?—The treatment that a patient ultimately selects also depends on its actual or perceived safety. Patients have vastly different levels of risk tolerance. Some patients would much rather start a less effective treatment if they believe that the chances of experiencing treatment-related adverse effects would be lower. In general, topical and injectable treatments tend to have fewer adverse effects than oral therapies. Long-term safety data generally are lacking for many hair-loss therapies. A limited number of studies of topical minoxidil include data up to 5 years,4 and some studies of oral finasteride and oral dutasteride include patients who used these medications for up to 10 years.5,6
So Then, What Works?
The Table shows treatments for AGA and how I prioritize starting them in my own clinic. First-line treatment options often include those with level 1 evidence but also may include those with less-robust evidence plus a good history (over many years) of safety, affordability, ease of use, and effectiveness (eg, spironolactone and finasteride for female-pattern hair loss).
• Male AGA: I consider topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and oral dutasteride as first-line agents, and low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and topical finasteride as second-line agents. Only topical minoxidil and oral finasteride are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for AGA in males; laser devices are FDA cleared.
• Premenopausal females with AGA: I use topical minoxidil and spironolactone as first-line agents. Low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and oral contraceptives are helpful second-line agents. Only topical minoxidil is FDA approved in women. I consider all treatments, with the exception of low-level laser, to be contraindicated in pregnancy.
• Postmenopausal females with AGA: I consider topical minoxidil, spironolactone, and oral finasteride as first-line agents. Low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and oral dutasteride are helpful second-line agents.
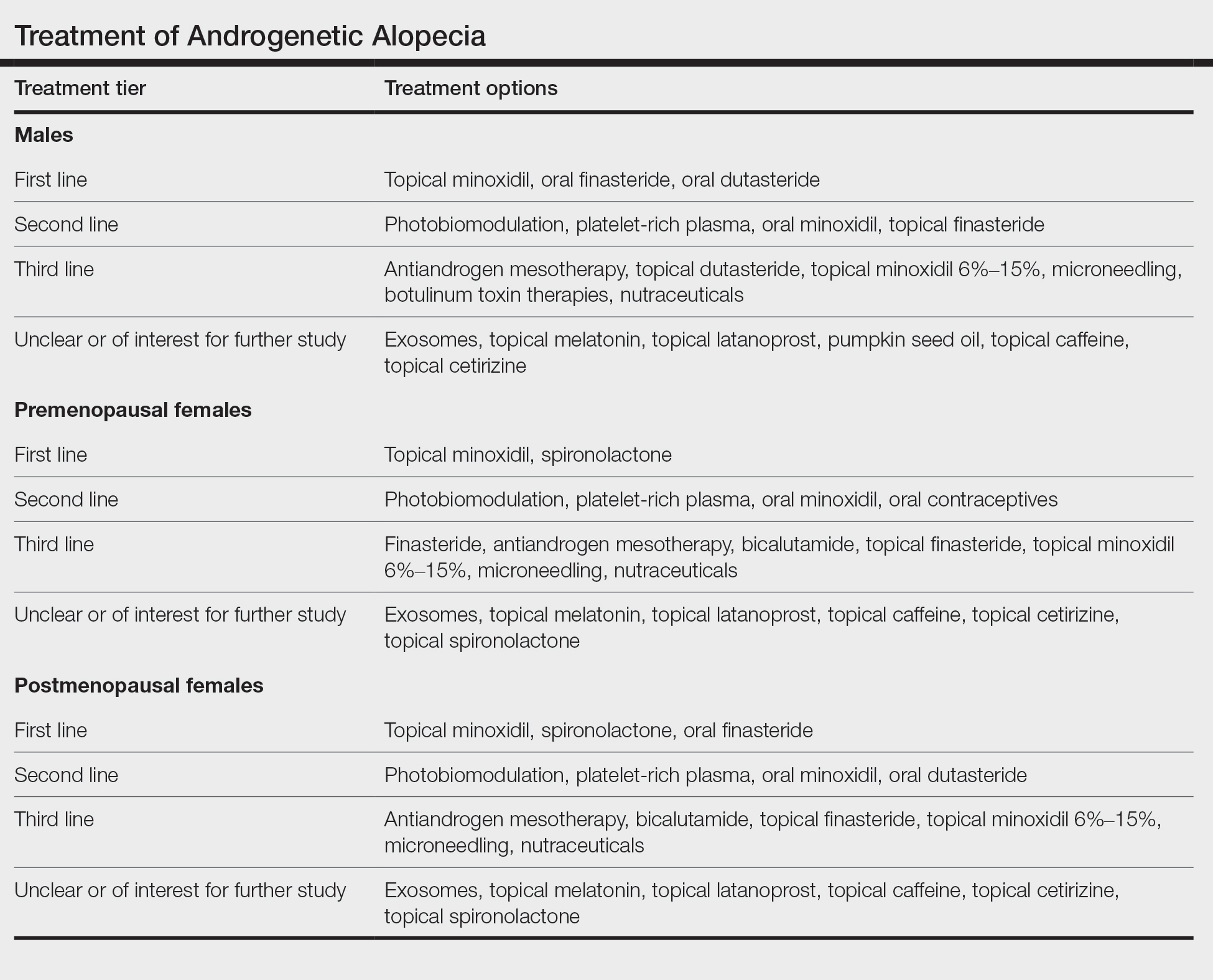
When choosing an initial treatment plan, I generally will start with one or more first-line options. I will then add or replace with remaining first-line options or a second-line option after 6 to 12 months depending on how well the patient responds to the first-line options. Patients who do not wish to use first-line options or have contraindications begin with second-line options. Third-line options are best reserved for patients who do not respond to or do not wish to use first- and second-line options.
Experts differ in opinion as to what constitutes a first-line treatment option and what constitutes a second- or third-line option. For example, some increasingly consider oral minoxidil to be a first-line option for AGA.9 In my opinion, the lack of high-quality comparative, randomized, controlled trials and long-term safety data keep oral minoxidil reserved as a respectable second-line option. Similarly, some experts reserve oral dutasteride as a second-line option for AGA.10 In my opinion, the data now are of the highest-quality evidence (level 1)9 to support placing oral dutasteride in the tier of first-line treatments.
Shared decision-making using an evidence-based approach is ultimately what connects patients with treatment plans that offer a good chance of helping to improve hair loss.
- Price VH, Roberts JL, Hordinsky M, et al. Lack of efficacy of finasteride in postmenopausal women with androgenetic alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43(5 pt 1):768-776. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.107953
- Gupta AK, Bamimore MA, Foley KA. Efficacy of non-surgical treatments for androgenetic alopecia in men and women: a systematic review with network meta-analyses, and an assessment of evidence quality. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:62-72. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1749547
- Gupta AK, Wang T, Bamimore MA, et al. The relative effect of monotherapy with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and minoxidil for female pattern hair loss: a network meta-analysis study [published online June 29, 2023]. J Cosmet Dermatol. doi:10.1111/jocd.15910
- Olsen EA, Weiner MS, Amara IA, et al. Five-year follow-up of men with androgenetic alopecia treated with topical minoxidil. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:64.
- Choi G-S, Sim W-Y, Kang H, et al. Long-term effectiveness and safety of dutasteride versus finasteride in patients with male androgenic alopecia in South Korea: a multicentre chart review study. Ann Dermatol. 2022;34:349-359. doi:10.5021/ad.22.027
- Rossi A, Cantisani C, Scarnò M, et al. Finasteride, 1 mg daily administration on male androgenetic alopecia in different age groups: 10-year follow-up. Dermatol Ther. 2011;24:455-461.
- Kaufman KD, Olsen EA, Whiting D, et al. Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. Finasteride Male Pattern Hair Loss Study Group. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(4 pt 1):578-89. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70007-6
- Mella JM, Perret MC, Manzotti M, et al. Efficacy and safety offinasteride therapy for androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1141-1150. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.256
- Vañó-Galván S, Fernandez-Crehuet P, Garnacho G, et al; Spanish Trichology Research Group. Recommendations on the clinical management of androgenetic alopecia: a consensus statement from the Spanish Trichology Group of the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venererology (AEDV). Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2023 Oct 25:S0001-7310(23)00844-X. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2023.10.013. Online ahead of print.
- Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men - short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:11-22. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14624
When it comes to selecting medical treatments for androgenetic alopecia (AGA), patients and practitioners alike want to know, “What works?” The ideal AGA treatment is one that meets 4 criteria: highly effective, safe, affordable, and easy to use. To date, there is no known treatment for AGA that meets all these criteria. Some therapies are more effective than others, but there are no treatments at present that are able to completely and permanently reverse the condition. Some treatments are safer, some are less expensive, and some are easier to use than others. In the end, the treatment that the patient chooses is influenced not only by its known effectiveness but also by the value that the patient places on the other 3 categories—safety, affordability, and ease of use. Therefore, shared decision-making between patient and practitioner is central to the selection of specific AGA treatments.
Effectiveness: Some Treatments Work Better Than Others
Of the nearly 2 dozen medical treatments for AGA, some have been found to be more effective than others. Whether a given treatment should be considered a bona fide AGA therapy—and then whether to position it as a first-line, second-line, or third-line agent—depends on the answers to 3 fundamental questions:
- Does the treatment truly help patients with AGA?
- How effective is this treatment?
- How safe is it?
Does the Treatment Truly Help Patients?—Surprisingly, it is not always straightforward to confirm that a given treatment helps patients with AGA. Does oral finasteride help female AGA? Yes and no: Finasteride 1 mg is ineffective in the treatment of female AGA, but higher doses such as 2.5 or 5 mg likely have benefit.1,2 Does topical minoxidil help AGA? Yes and no: Minoxidil 5% is ineffective in the treatment of a male with Hamilton-Norwood stage VII AGA but often is helpful in earlier stages of the condition.
One of the best ways to determine if a treatment really helps AGA is to evaluate how it performs in the setting of a well-conducted, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. These types of clinical trials have been performed for many known AGA treatments and give us some of the best evidence that a treatment truly works. The AGA treatments with the highest-quality evidence (level 1) are topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and oral dutasteride for male AGA and topical minoxidil for female AGA.
How Effective Is This Treatment?—Patients are particularly interested to know whether a given treatment has the potential to notably restore hair density. It is one thing to know that use of the treatment might slightly improve hair density and another to know that it could potentially lead to dramatic improvement. In addition, patients want to know whether a specific treatment they are considering is more (or less) likely to improve their hair density compared to another treatment.
Advanced statistical methods such as the network meta-analysis are increasingly being used to understand how individual treatments from different studies compare. Two recent studies have provided us with powerful data on the relative efficacy of minoxidil and 5α-reductase inhibitors in the treatment of both male and female AGA.2,3 A 2022 network meta-analysis of male AGA ranked treatment efficacy from most to least effective: oral dutasteride 0.5 mg, oral finasteride 5 mg, oral minoxidil 5 mg, oral finasteride 1 mg, and topical minoxidil 5%.3 Similarly, a 2023 network meta-analysis of female AGA ranked treatment efficacy from most to least effective: oral 5 mg finasteride, minoxidil solution 5% twice daily, oral minoxidil 1 mg, and minoxidil foam 5% once daily.2 We are not yet able to rank all known treatments for AGA.
Things We Tend to Ignore: Quality of Data, Long-term Results, Nonresponders, and Study Populations—There are a few caveats for anyone treating AGA. First, the quality of published AGA studies is highly variable and many are of low quality. The highest-quality evidence (level 1) for male AGA comes from studies of minoxidil solution/foam 5% twice daily, oral finasteride 1 mg, and oral dutasteride 0.5 mg. For female AGA, the highest-quality evidence is for topical minoxidil—either 5% foam once daily or 2% solution twice daily. Lower-quality studies limit conclusions and the ability to properly compare treatments.
Second, long-term data are nonexistent for most of our AGA treatments. The exceptions include finasteride, dutasteride, and topical minoxidil, which have reasonably adequate long-term studies.4-6 However, most other treatments have been evaluated only through short-term studies. It is tempting to assume that results from a 24-week study can be used to infer how a patient might respond when using the same treatment over the course of many decades; however, making these assumptions would be unwise.
Third, most AGA treatments help improve hair density in only a proportion of patients who decide to use the given treatment. There usually is one subgroup of patients for whom the treatment does not seem to help much at all and one subgroup for whom the treatment halts further hair loss but does not regrow hair. For example, in the case of finasteride treatment of male AGA, approximately 10% of patients do not seem to respond to treatment at all, and another 50% seem to be able to halt further loss but never achieve hair regrowth.7 In an analysis of 12 studies with 3927 male patients, Mella et al8 showed that 5.6 patients needed to be treated short term and 3.4 patients needed to be treated long term for 1 patient to perceive an improvement in the hair. It is clear that many males who use finasteride will not see evidence of hair regrowth. This same general concept applies for all available treatments and is important to remember if a patient with AGA decides to start 2 new treatments simultaneously. Consider the 34-year-old man who starts oral minoxidil and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for AGA. At his follow-up appointment 9 months later, the patient reports improved hair density and wants to know what contributed to the improvement: the oral minoxidil, the PRP, or both? Many practitioners would believe that both treatments likely provided some degree of benefit—but in reality, that represents a flaw in logic. If 2 hair loss treatments are started at exactly the same time, it is impossible to know the relative benefit of each treatment and whether one might not be helping at all. Combination therapies are still common in my practice and highly encouraged, but my personal preference is to stagger start dates whenever possible so I can determine each treatment’s contribution to the patient’s final outcome.
Finally, when evaluating what works for AGA, we need to define the specific patient subpopulation, as the available data are less robust for some patient groups than others. We have limited data in children and adolescents with AGA, as well as limited comparative data across different racial backgrounds, body mass indices, and underlying health issues. For example, data on the most effective strategies to treat female AGA in the setting of polycystic ovary syndrome, premature menopause, and other endocrine disorders are lacking.
Which Treatments Also Have Good Safety?—The treatment that a patient ultimately selects also depends on its actual or perceived safety. Patients have vastly different levels of risk tolerance. Some patients would much rather start a less effective treatment if they believe that the chances of experiencing treatment-related adverse effects would be lower. In general, topical and injectable treatments tend to have fewer adverse effects than oral therapies. Long-term safety data generally are lacking for many hair-loss therapies. A limited number of studies of topical minoxidil include data up to 5 years,4 and some studies of oral finasteride and oral dutasteride include patients who used these medications for up to 10 years.5,6
So Then, What Works?
The Table shows treatments for AGA and how I prioritize starting them in my own clinic. First-line treatment options often include those with level 1 evidence but also may include those with less-robust evidence plus a good history (over many years) of safety, affordability, ease of use, and effectiveness (eg, spironolactone and finasteride for female-pattern hair loss).
• Male AGA: I consider topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and oral dutasteride as first-line agents, and low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and topical finasteride as second-line agents. Only topical minoxidil and oral finasteride are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for AGA in males; laser devices are FDA cleared.
• Premenopausal females with AGA: I use topical minoxidil and spironolactone as first-line agents. Low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and oral contraceptives are helpful second-line agents. Only topical minoxidil is FDA approved in women. I consider all treatments, with the exception of low-level laser, to be contraindicated in pregnancy.
• Postmenopausal females with AGA: I consider topical minoxidil, spironolactone, and oral finasteride as first-line agents. Low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and oral dutasteride are helpful second-line agents.

When choosing an initial treatment plan, I generally will start with one or more first-line options. I will then add or replace with remaining first-line options or a second-line option after 6 to 12 months depending on how well the patient responds to the first-line options. Patients who do not wish to use first-line options or have contraindications begin with second-line options. Third-line options are best reserved for patients who do not respond to or do not wish to use first- and second-line options.
Experts differ in opinion as to what constitutes a first-line treatment option and what constitutes a second- or third-line option. For example, some increasingly consider oral minoxidil to be a first-line option for AGA.9 In my opinion, the lack of high-quality comparative, randomized, controlled trials and long-term safety data keep oral minoxidil reserved as a respectable second-line option. Similarly, some experts reserve oral dutasteride as a second-line option for AGA.10 In my opinion, the data now are of the highest-quality evidence (level 1)9 to support placing oral dutasteride in the tier of first-line treatments.
Shared decision-making using an evidence-based approach is ultimately what connects patients with treatment plans that offer a good chance of helping to improve hair loss.
When it comes to selecting medical treatments for androgenetic alopecia (AGA), patients and practitioners alike want to know, “What works?” The ideal AGA treatment is one that meets 4 criteria: highly effective, safe, affordable, and easy to use. To date, there is no known treatment for AGA that meets all these criteria. Some therapies are more effective than others, but there are no treatments at present that are able to completely and permanently reverse the condition. Some treatments are safer, some are less expensive, and some are easier to use than others. In the end, the treatment that the patient chooses is influenced not only by its known effectiveness but also by the value that the patient places on the other 3 categories—safety, affordability, and ease of use. Therefore, shared decision-making between patient and practitioner is central to the selection of specific AGA treatments.
Effectiveness: Some Treatments Work Better Than Others
Of the nearly 2 dozen medical treatments for AGA, some have been found to be more effective than others. Whether a given treatment should be considered a bona fide AGA therapy—and then whether to position it as a first-line, second-line, or third-line agent—depends on the answers to 3 fundamental questions:
- Does the treatment truly help patients with AGA?
- How effective is this treatment?
- How safe is it?
Does the Treatment Truly Help Patients?—Surprisingly, it is not always straightforward to confirm that a given treatment helps patients with AGA. Does oral finasteride help female AGA? Yes and no: Finasteride 1 mg is ineffective in the treatment of female AGA, but higher doses such as 2.5 or 5 mg likely have benefit.1,2 Does topical minoxidil help AGA? Yes and no: Minoxidil 5% is ineffective in the treatment of a male with Hamilton-Norwood stage VII AGA but often is helpful in earlier stages of the condition.
One of the best ways to determine if a treatment really helps AGA is to evaluate how it performs in the setting of a well-conducted, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. These types of clinical trials have been performed for many known AGA treatments and give us some of the best evidence that a treatment truly works. The AGA treatments with the highest-quality evidence (level 1) are topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and oral dutasteride for male AGA and topical minoxidil for female AGA.
How Effective Is This Treatment?—Patients are particularly interested to know whether a given treatment has the potential to notably restore hair density. It is one thing to know that use of the treatment might slightly improve hair density and another to know that it could potentially lead to dramatic improvement. In addition, patients want to know whether a specific treatment they are considering is more (or less) likely to improve their hair density compared to another treatment.
Advanced statistical methods such as the network meta-analysis are increasingly being used to understand how individual treatments from different studies compare. Two recent studies have provided us with powerful data on the relative efficacy of minoxidil and 5α-reductase inhibitors in the treatment of both male and female AGA.2,3 A 2022 network meta-analysis of male AGA ranked treatment efficacy from most to least effective: oral dutasteride 0.5 mg, oral finasteride 5 mg, oral minoxidil 5 mg, oral finasteride 1 mg, and topical minoxidil 5%.3 Similarly, a 2023 network meta-analysis of female AGA ranked treatment efficacy from most to least effective: oral 5 mg finasteride, minoxidil solution 5% twice daily, oral minoxidil 1 mg, and minoxidil foam 5% once daily.2 We are not yet able to rank all known treatments for AGA.
Things We Tend to Ignore: Quality of Data, Long-term Results, Nonresponders, and Study Populations—There are a few caveats for anyone treating AGA. First, the quality of published AGA studies is highly variable and many are of low quality. The highest-quality evidence (level 1) for male AGA comes from studies of minoxidil solution/foam 5% twice daily, oral finasteride 1 mg, and oral dutasteride 0.5 mg. For female AGA, the highest-quality evidence is for topical minoxidil—either 5% foam once daily or 2% solution twice daily. Lower-quality studies limit conclusions and the ability to properly compare treatments.
Second, long-term data are nonexistent for most of our AGA treatments. The exceptions include finasteride, dutasteride, and topical minoxidil, which have reasonably adequate long-term studies.4-6 However, most other treatments have been evaluated only through short-term studies. It is tempting to assume that results from a 24-week study can be used to infer how a patient might respond when using the same treatment over the course of many decades; however, making these assumptions would be unwise.
Third, most AGA treatments help improve hair density in only a proportion of patients who decide to use the given treatment. There usually is one subgroup of patients for whom the treatment does not seem to help much at all and one subgroup for whom the treatment halts further hair loss but does not regrow hair. For example, in the case of finasteride treatment of male AGA, approximately 10% of patients do not seem to respond to treatment at all, and another 50% seem to be able to halt further loss but never achieve hair regrowth.7 In an analysis of 12 studies with 3927 male patients, Mella et al8 showed that 5.6 patients needed to be treated short term and 3.4 patients needed to be treated long term for 1 patient to perceive an improvement in the hair. It is clear that many males who use finasteride will not see evidence of hair regrowth. This same general concept applies for all available treatments and is important to remember if a patient with AGA decides to start 2 new treatments simultaneously. Consider the 34-year-old man who starts oral minoxidil and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for AGA. At his follow-up appointment 9 months later, the patient reports improved hair density and wants to know what contributed to the improvement: the oral minoxidil, the PRP, or both? Many practitioners would believe that both treatments likely provided some degree of benefit—but in reality, that represents a flaw in logic. If 2 hair loss treatments are started at exactly the same time, it is impossible to know the relative benefit of each treatment and whether one might not be helping at all. Combination therapies are still common in my practice and highly encouraged, but my personal preference is to stagger start dates whenever possible so I can determine each treatment’s contribution to the patient’s final outcome.
Finally, when evaluating what works for AGA, we need to define the specific patient subpopulation, as the available data are less robust for some patient groups than others. We have limited data in children and adolescents with AGA, as well as limited comparative data across different racial backgrounds, body mass indices, and underlying health issues. For example, data on the most effective strategies to treat female AGA in the setting of polycystic ovary syndrome, premature menopause, and other endocrine disorders are lacking.
Which Treatments Also Have Good Safety?—The treatment that a patient ultimately selects also depends on its actual or perceived safety. Patients have vastly different levels of risk tolerance. Some patients would much rather start a less effective treatment if they believe that the chances of experiencing treatment-related adverse effects would be lower. In general, topical and injectable treatments tend to have fewer adverse effects than oral therapies. Long-term safety data generally are lacking for many hair-loss therapies. A limited number of studies of topical minoxidil include data up to 5 years,4 and some studies of oral finasteride and oral dutasteride include patients who used these medications for up to 10 years.5,6
So Then, What Works?
The Table shows treatments for AGA and how I prioritize starting them in my own clinic. First-line treatment options often include those with level 1 evidence but also may include those with less-robust evidence plus a good history (over many years) of safety, affordability, ease of use, and effectiveness (eg, spironolactone and finasteride for female-pattern hair loss).
• Male AGA: I consider topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and oral dutasteride as first-line agents, and low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and topical finasteride as second-line agents. Only topical minoxidil and oral finasteride are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for AGA in males; laser devices are FDA cleared.
• Premenopausal females with AGA: I use topical minoxidil and spironolactone as first-line agents. Low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and oral contraceptives are helpful second-line agents. Only topical minoxidil is FDA approved in women. I consider all treatments, with the exception of low-level laser, to be contraindicated in pregnancy.
• Postmenopausal females with AGA: I consider topical minoxidil, spironolactone, and oral finasteride as first-line agents. Low-level laser, PRP, oral minoxidil, and oral dutasteride are helpful second-line agents.

When choosing an initial treatment plan, I generally will start with one or more first-line options. I will then add or replace with remaining first-line options or a second-line option after 6 to 12 months depending on how well the patient responds to the first-line options. Patients who do not wish to use first-line options or have contraindications begin with second-line options. Third-line options are best reserved for patients who do not respond to or do not wish to use first- and second-line options.
Experts differ in opinion as to what constitutes a first-line treatment option and what constitutes a second- or third-line option. For example, some increasingly consider oral minoxidil to be a first-line option for AGA.9 In my opinion, the lack of high-quality comparative, randomized, controlled trials and long-term safety data keep oral minoxidil reserved as a respectable second-line option. Similarly, some experts reserve oral dutasteride as a second-line option for AGA.10 In my opinion, the data now are of the highest-quality evidence (level 1)9 to support placing oral dutasteride in the tier of first-line treatments.
Shared decision-making using an evidence-based approach is ultimately what connects patients with treatment plans that offer a good chance of helping to improve hair loss.
- Price VH, Roberts JL, Hordinsky M, et al. Lack of efficacy of finasteride in postmenopausal women with androgenetic alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43(5 pt 1):768-776. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.107953
- Gupta AK, Bamimore MA, Foley KA. Efficacy of non-surgical treatments for androgenetic alopecia in men and women: a systematic review with network meta-analyses, and an assessment of evidence quality. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:62-72. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1749547
- Gupta AK, Wang T, Bamimore MA, et al. The relative effect of monotherapy with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and minoxidil for female pattern hair loss: a network meta-analysis study [published online June 29, 2023]. J Cosmet Dermatol. doi:10.1111/jocd.15910
- Olsen EA, Weiner MS, Amara IA, et al. Five-year follow-up of men with androgenetic alopecia treated with topical minoxidil. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:64.
- Choi G-S, Sim W-Y, Kang H, et al. Long-term effectiveness and safety of dutasteride versus finasteride in patients with male androgenic alopecia in South Korea: a multicentre chart review study. Ann Dermatol. 2022;34:349-359. doi:10.5021/ad.22.027
- Rossi A, Cantisani C, Scarnò M, et al. Finasteride, 1 mg daily administration on male androgenetic alopecia in different age groups: 10-year follow-up. Dermatol Ther. 2011;24:455-461.
- Kaufman KD, Olsen EA, Whiting D, et al. Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. Finasteride Male Pattern Hair Loss Study Group. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(4 pt 1):578-89. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70007-6
- Mella JM, Perret MC, Manzotti M, et al. Efficacy and safety offinasteride therapy for androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1141-1150. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.256
- Vañó-Galván S, Fernandez-Crehuet P, Garnacho G, et al; Spanish Trichology Research Group. Recommendations on the clinical management of androgenetic alopecia: a consensus statement from the Spanish Trichology Group of the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venererology (AEDV). Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2023 Oct 25:S0001-7310(23)00844-X. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2023.10.013. Online ahead of print.
- Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men - short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:11-22. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14624
- Price VH, Roberts JL, Hordinsky M, et al. Lack of efficacy of finasteride in postmenopausal women with androgenetic alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43(5 pt 1):768-776. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.107953
- Gupta AK, Bamimore MA, Foley KA. Efficacy of non-surgical treatments for androgenetic alopecia in men and women: a systematic review with network meta-analyses, and an assessment of evidence quality. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:62-72. doi:10.1080/09546634.2020.1749547
- Gupta AK, Wang T, Bamimore MA, et al. The relative effect of monotherapy with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and minoxidil for female pattern hair loss: a network meta-analysis study [published online June 29, 2023]. J Cosmet Dermatol. doi:10.1111/jocd.15910
- Olsen EA, Weiner MS, Amara IA, et al. Five-year follow-up of men with androgenetic alopecia treated with topical minoxidil. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:64.
- Choi G-S, Sim W-Y, Kang H, et al. Long-term effectiveness and safety of dutasteride versus finasteride in patients with male androgenic alopecia in South Korea: a multicentre chart review study. Ann Dermatol. 2022;34:349-359. doi:10.5021/ad.22.027
- Rossi A, Cantisani C, Scarnò M, et al. Finasteride, 1 mg daily administration on male androgenetic alopecia in different age groups: 10-year follow-up. Dermatol Ther. 2011;24:455-461.
- Kaufman KD, Olsen EA, Whiting D, et al. Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. Finasteride Male Pattern Hair Loss Study Group. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(4 pt 1):578-89. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70007-6
- Mella JM, Perret MC, Manzotti M, et al. Efficacy and safety offinasteride therapy for androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1141-1150. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.256
- Vañó-Galván S, Fernandez-Crehuet P, Garnacho G, et al; Spanish Trichology Research Group. Recommendations on the clinical management of androgenetic alopecia: a consensus statement from the Spanish Trichology Group of the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venererology (AEDV). Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2023 Oct 25:S0001-7310(23)00844-X. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2023.10.013. Online ahead of print.
- Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men - short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:11-22. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14624
The Struggle to Provide Gender-Affirming Care to Youth
Pediatrician Michelle Collins-Ogle, MD, already has a busy practice helping young people address questions about their gender identity. She has treated more than 230 patients over the past 2 years at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore in the Bronx, New York.
Dr. Collins-Ogle specializes in adolescent medicine in New York, a state without the restrictions on such care that have been enacted in roughly half the country.
On December 13, 2023, Ohio lawmakers passed a bill banning gender-affirming medical care to minors which Gov. Mike DeWine vetoed on December 29. Another 26 states have similar restrictions in place, according to a tally provided to this news organization by the Human Rights Campaign, which tracks this issue.
Clinicians like Dr. Collins-Ogle are feeling the impact. In her practice, Dr. Collins-Ogle met a couple that moved from Texas to New York to allow their child to access gender-affirming medical care.
“They wanted their child to be able to receive medical care, but they also were afraid for their own safety, of having their child taken from them, and being locked up,” Dr. Collins-Ogle told this news organization.
With patients have also come protestors and harassment. In fact, many physicians are reluctant to speak on this topic amid a recent spate of threats. Psychiatric News reported that conservative pundits and high-profile social media accounts have targeted physicians who provide gender-affirming medical care, spurring harassment campaigns against clinics in cities such as Akron, Boston, and Nashville. “The attackers asserted that the clinics were mutilating children and giving them ‘chemical castration drugs,’ among other claims,” the Psychiatric News reported.
This news organization contacted more than a half dozen organizations that provide gender-affirming care for adolescents and teens seeking interviews about the effects of these restrictions.
All but Montefiore’s Dr. Collins-Ogle turned down the request.
“If my kids are brave enough to come see me, I can’t cower,” Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
But Dr. Collins-Ogle emphasized she understands why many fellow physicians are concerned about speaking publicly about gender-affirming medical care.
Dissenters Spread Misinformation and Threats
Recent years have seen increasing politicization of this issue, often due to inaccurate depictions of gender-affirming medical care circulating on social media.
In 2022, the American Medical Association (AMA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Children’s Hospital Association asked the Justice Department to investigate what they called “increasing threats of violence against physicians, hospitals, and families of children for providing and seeking evidence-based gender-affirming care.”
The three organizations also called on X (formerly known as Twitter), TikTok, and Meta, which owns Facebook and Instagram, to do more to address coordinated campaigns of disinformation.
“We cannot stand by as threats of violence against our members and their patients proliferate with little consequence,” said Moira Szilagyi, MD, PhD, then AAP president in a statement.
Medical Groups Defend Care to Prevent Suicide
The AAP, AMA, and other influential medical associations are banding together to fight new legal restrictions on gender-affirming medical care for teens and adolescents. (These briefs do not discuss surgeries typically available for adults.)
Since 2022, these medical organizations have filed amicus briefs in cases challenging new restrictions put in place in Arkansas, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Kentucky, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Texas.
Other signers to the amicus briefs:
- Academic Pediatric Association
- American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry
- American Academy of Family Physicians
- American Academy of Nursing
- GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
- American College of Osteopathic Pediatricians
- The American College of Physicians
- American Pediatric Society
- Association of Medical School Pediatric Department Chairs, Inc.
- Endocrine Society
- National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners
- The Pediatric Endocrine Society, Societies for Pediatric Urology
- Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine
- Society for Pediatric Research
- The Society of Pediatric Nurses
- World Professional Association for Transgender Health
In these amicus briefs, the medical groups argue that evidence-based guidelines support the use of medication in treating gender dysphoria. The amicus briefs in particular cite an Endocrine Society guideline and the standards of care developed by the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH).
Research shows that adolescents with gender dysphoria who receive puberty blockers and other medications experience less depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation, the groups have said.
“In light of this evidence supporting the connection between lack of access to gender-affirming care and lifetime suicide risk, banning such care can put patients’ lives at risk,” the AAP and other groups said.
Debate Over Source of Gender Identity Concerns
Having doubts and concerns about one’s gender remains a relatively rare phenomena, although it appears more common among younger people.
Among US adults, 0.5% or about 1.3 million people identify as transgender whereas about 1.4% or about 300,000 people in the 13-17–year-old group do so, according to a report issued in 2022 by the Williams Institute of the UCLA School of Law.
Questionable Diagnosis Drives Bans on Care
The term “rapid-onset gender dysphoria,” referring to young people who suddenly question their gender as part of peer group dynamics, persists in political debates. The conservative Heritage Foundation has used the term as well as “social contagion” in its effort to seek restrictions on gender-affirming care for young people.
Ohio Rep. Gary Click, a Republican, said at an April 2023 hearing that his Save Adolescents from Experimentation (SAFE) bill would prevent teens from being harmed due to “social contagion” or “ rapid-onset gender dysphoria.”
The bill, which the Ohio legislature cleared in December, would block physicians from starting new patients on puberty blockers. (It also bars surgeries as part of gender-affirming medical care, although hospital officials and physicians told lawmakers these are not done in Ohio.)
Among the groups opposing Click’s bill were the Ohio chapter of the AAP, the Ohio State Medical Association and several hospitals and hospital groups as well as physicians speaking independently.
Gender-Affirming Care ‘Buys Time’ to Avoid Impulsive Decisions
Kate Krueck, MD, a pediatrician with a practice in the Columbus area, testified about her experience as the mother of a transgender child who once attempted suicide.
“It wasn’t always easy to reconstruct my vision of a baby with a vagina into the adolescent before me with a new name and changed pronouns, but they were still the same incredible person,” Krueck said.
She urged lawmakers to understand how puberty blockers can “buy time” for teens to cope with a body at odds with their vision of themselves, noting that many of the effects of these medications are largely reversible. The side effects that are not reversible, such as facial hair growth and the growth of Adam’s Apple, are certainly outweighed by the risks of withholding treatment, she said.
Bad Patient Experience Drives Detractor Activist
Arguing against that point was Chloe Cole, a detransitioner activist who had returned to a female identity. At the Ohio legislative hearings, Ms. Cole spoke of her experience in California as a teen treated for gender dysphoria.
“I was fast-tracked by medical butchers starting at 13 when I was given cross sex hormones, and they took my breasts away from me at 15 years old,” she said.
Ms. Cole appears frequently to testify in favor of bans on gender-affirming medical care. In 2022, she told the Ohio lawmakers about her experience of attending a class with about a dozen other young people in the midst of female-to-male transitions. She now sees that class as having inadvertently helped reinforce her decision to have her breasts removed.
“Despite all these consultations and classes, I don’t feel like I understood all the ramifications that came with any of the medical decisions I was making,” Ms. Cole said. “I didn’t realize how traumatic the recovery would be, and it wasn’t until I was almost a year post-op that I realized I may want to breastfeed my future children; I will never be able to do that.”
Ms. Cole also spoke in July before the US House subcommittee on the Constitution and Limited Government.
“I look in the mirror sometimes, and I feel like a monster,” Ms. Cole said at the House hearing, which was titled “ The Dangers and Due Process Violations of ‘Gender-Affirming Care’.”
During the hearing, Shannon Minter, legal director of the National Center for Lesbian Rights (NCLR), who also made a gender transition, thanked Ms. Cole but noted that her case is an exception.
A 2022 Lancet Child and Adolescent Health article reported that 704 (98%) people in the Netherlands who had started gender-affirming medical treatment in adolescence continued to use gender-affirming hormones at follow-up. Ms. Minter credits this high rate of continuation to clinicians taking their duties to adolescents seriously.
State legislatures and medical boards oversee the regulation of medical practice in the US. But a few Republicans in both chambers of the US Congress have shown an interest in enacting a federal ban restricting physicians’ ability to provide gender-affirming medical care.
They include Rep. Mike Johnson of Louisiana, who in October 2023 became Speaker of the House. He chaired the July hearing at which Ms. Cole spoke. He’s also a sponsor of a House bill introduced by Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA).
This measure, which has the support of 45 House Republicans, would make it a felony to perform any gender-affirming care on a minor, and it permits a minor on whom such care is performed to bring a civil action against each individual who provided the care. Sen. JD Vance (R-OH) introduced the companion Senate measure.
Reality of Gender-Affirming Care
The drive to pass laws like those in Ohio and Arkansas stem from a lack of knowledge about gender-affirming treatments, including a false idea that doctors prescribe medications at teens’ requests, Montefiore’s Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
“There’s a misperception that young people will say ‘I’m transgender’ and that those of us who provide care are just giving them hormones or whatever they want. It’s not true, and it doesn’t happen that way,” Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
At the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, Dr. Collins-Ogle said her work with patients wrestling with gender identity issues begins with questions.
“What’s your understanding of dysphoria? Where’s the incongruence between the gender you were assigned at birth and what you’re feeling now? You have to be able to verbalize that” before the treatment proceeds, she said.
Sometimes teens leave after an initial conversation and then return later when they have a more clearly defined sense of what dysphoria means.
“There are other kids who clearly, clearly understand that the gender they were assigned at birth is not who they are,” she said.
Children now wrestle with added concerns that their parents could be put at risk for trying to help them, she said.
“These kids go through so much. And we have these people in powerful positions telling them that they don’t matter and telling them, ‘We’re going to cut off your access to healthcare, Medicaid; if your parents tried to seek out this care for you, we’re going to put them in jail,’” she said.
“It’s the biggest factor in fear mongering,” she said.
Dr. Collins-Ogle said she wonders why legislators who lack medical training are trying to dictate how physicians can practice.
“I took a Hippocratic oath to do no harm. I have a medical board that I answer to,” she said. “I don’t understand how legislators can get away with legislating about something they know nothing about.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatrician Michelle Collins-Ogle, MD, already has a busy practice helping young people address questions about their gender identity. She has treated more than 230 patients over the past 2 years at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore in the Bronx, New York.
Dr. Collins-Ogle specializes in adolescent medicine in New York, a state without the restrictions on such care that have been enacted in roughly half the country.
On December 13, 2023, Ohio lawmakers passed a bill banning gender-affirming medical care to minors which Gov. Mike DeWine vetoed on December 29. Another 26 states have similar restrictions in place, according to a tally provided to this news organization by the Human Rights Campaign, which tracks this issue.
Clinicians like Dr. Collins-Ogle are feeling the impact. In her practice, Dr. Collins-Ogle met a couple that moved from Texas to New York to allow their child to access gender-affirming medical care.
“They wanted their child to be able to receive medical care, but they also were afraid for their own safety, of having their child taken from them, and being locked up,” Dr. Collins-Ogle told this news organization.
With patients have also come protestors and harassment. In fact, many physicians are reluctant to speak on this topic amid a recent spate of threats. Psychiatric News reported that conservative pundits and high-profile social media accounts have targeted physicians who provide gender-affirming medical care, spurring harassment campaigns against clinics in cities such as Akron, Boston, and Nashville. “The attackers asserted that the clinics were mutilating children and giving them ‘chemical castration drugs,’ among other claims,” the Psychiatric News reported.
This news organization contacted more than a half dozen organizations that provide gender-affirming care for adolescents and teens seeking interviews about the effects of these restrictions.
All but Montefiore’s Dr. Collins-Ogle turned down the request.
“If my kids are brave enough to come see me, I can’t cower,” Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
But Dr. Collins-Ogle emphasized she understands why many fellow physicians are concerned about speaking publicly about gender-affirming medical care.
Dissenters Spread Misinformation and Threats
Recent years have seen increasing politicization of this issue, often due to inaccurate depictions of gender-affirming medical care circulating on social media.
In 2022, the American Medical Association (AMA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Children’s Hospital Association asked the Justice Department to investigate what they called “increasing threats of violence against physicians, hospitals, and families of children for providing and seeking evidence-based gender-affirming care.”
The three organizations also called on X (formerly known as Twitter), TikTok, and Meta, which owns Facebook and Instagram, to do more to address coordinated campaigns of disinformation.
“We cannot stand by as threats of violence against our members and their patients proliferate with little consequence,” said Moira Szilagyi, MD, PhD, then AAP president in a statement.
Medical Groups Defend Care to Prevent Suicide
The AAP, AMA, and other influential medical associations are banding together to fight new legal restrictions on gender-affirming medical care for teens and adolescents. (These briefs do not discuss surgeries typically available for adults.)
Since 2022, these medical organizations have filed amicus briefs in cases challenging new restrictions put in place in Arkansas, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Kentucky, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Texas.
Other signers to the amicus briefs:
- Academic Pediatric Association
- American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry
- American Academy of Family Physicians
- American Academy of Nursing
- GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
- American College of Osteopathic Pediatricians
- The American College of Physicians
- American Pediatric Society
- Association of Medical School Pediatric Department Chairs, Inc.
- Endocrine Society
- National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners
- The Pediatric Endocrine Society, Societies for Pediatric Urology
- Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine
- Society for Pediatric Research
- The Society of Pediatric Nurses
- World Professional Association for Transgender Health
In these amicus briefs, the medical groups argue that evidence-based guidelines support the use of medication in treating gender dysphoria. The amicus briefs in particular cite an Endocrine Society guideline and the standards of care developed by the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH).
Research shows that adolescents with gender dysphoria who receive puberty blockers and other medications experience less depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation, the groups have said.
“In light of this evidence supporting the connection between lack of access to gender-affirming care and lifetime suicide risk, banning such care can put patients’ lives at risk,” the AAP and other groups said.
Debate Over Source of Gender Identity Concerns
Having doubts and concerns about one’s gender remains a relatively rare phenomena, although it appears more common among younger people.
Among US adults, 0.5% or about 1.3 million people identify as transgender whereas about 1.4% or about 300,000 people in the 13-17–year-old group do so, according to a report issued in 2022 by the Williams Institute of the UCLA School of Law.
Questionable Diagnosis Drives Bans on Care
The term “rapid-onset gender dysphoria,” referring to young people who suddenly question their gender as part of peer group dynamics, persists in political debates. The conservative Heritage Foundation has used the term as well as “social contagion” in its effort to seek restrictions on gender-affirming care for young people.
Ohio Rep. Gary Click, a Republican, said at an April 2023 hearing that his Save Adolescents from Experimentation (SAFE) bill would prevent teens from being harmed due to “social contagion” or “ rapid-onset gender dysphoria.”
The bill, which the Ohio legislature cleared in December, would block physicians from starting new patients on puberty blockers. (It also bars surgeries as part of gender-affirming medical care, although hospital officials and physicians told lawmakers these are not done in Ohio.)
Among the groups opposing Click’s bill were the Ohio chapter of the AAP, the Ohio State Medical Association and several hospitals and hospital groups as well as physicians speaking independently.
Gender-Affirming Care ‘Buys Time’ to Avoid Impulsive Decisions
Kate Krueck, MD, a pediatrician with a practice in the Columbus area, testified about her experience as the mother of a transgender child who once attempted suicide.
“It wasn’t always easy to reconstruct my vision of a baby with a vagina into the adolescent before me with a new name and changed pronouns, but they were still the same incredible person,” Krueck said.
She urged lawmakers to understand how puberty blockers can “buy time” for teens to cope with a body at odds with their vision of themselves, noting that many of the effects of these medications are largely reversible. The side effects that are not reversible, such as facial hair growth and the growth of Adam’s Apple, are certainly outweighed by the risks of withholding treatment, she said.
Bad Patient Experience Drives Detractor Activist
Arguing against that point was Chloe Cole, a detransitioner activist who had returned to a female identity. At the Ohio legislative hearings, Ms. Cole spoke of her experience in California as a teen treated for gender dysphoria.
“I was fast-tracked by medical butchers starting at 13 when I was given cross sex hormones, and they took my breasts away from me at 15 years old,” she said.
Ms. Cole appears frequently to testify in favor of bans on gender-affirming medical care. In 2022, she told the Ohio lawmakers about her experience of attending a class with about a dozen other young people in the midst of female-to-male transitions. She now sees that class as having inadvertently helped reinforce her decision to have her breasts removed.
“Despite all these consultations and classes, I don’t feel like I understood all the ramifications that came with any of the medical decisions I was making,” Ms. Cole said. “I didn’t realize how traumatic the recovery would be, and it wasn’t until I was almost a year post-op that I realized I may want to breastfeed my future children; I will never be able to do that.”
Ms. Cole also spoke in July before the US House subcommittee on the Constitution and Limited Government.
“I look in the mirror sometimes, and I feel like a monster,” Ms. Cole said at the House hearing, which was titled “ The Dangers and Due Process Violations of ‘Gender-Affirming Care’.”
During the hearing, Shannon Minter, legal director of the National Center for Lesbian Rights (NCLR), who also made a gender transition, thanked Ms. Cole but noted that her case is an exception.
A 2022 Lancet Child and Adolescent Health article reported that 704 (98%) people in the Netherlands who had started gender-affirming medical treatment in adolescence continued to use gender-affirming hormones at follow-up. Ms. Minter credits this high rate of continuation to clinicians taking their duties to adolescents seriously.
State legislatures and medical boards oversee the regulation of medical practice in the US. But a few Republicans in both chambers of the US Congress have shown an interest in enacting a federal ban restricting physicians’ ability to provide gender-affirming medical care.
They include Rep. Mike Johnson of Louisiana, who in October 2023 became Speaker of the House. He chaired the July hearing at which Ms. Cole spoke. He’s also a sponsor of a House bill introduced by Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA).
This measure, which has the support of 45 House Republicans, would make it a felony to perform any gender-affirming care on a minor, and it permits a minor on whom such care is performed to bring a civil action against each individual who provided the care. Sen. JD Vance (R-OH) introduced the companion Senate measure.
Reality of Gender-Affirming Care
The drive to pass laws like those in Ohio and Arkansas stem from a lack of knowledge about gender-affirming treatments, including a false idea that doctors prescribe medications at teens’ requests, Montefiore’s Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
“There’s a misperception that young people will say ‘I’m transgender’ and that those of us who provide care are just giving them hormones or whatever they want. It’s not true, and it doesn’t happen that way,” Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
At the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, Dr. Collins-Ogle said her work with patients wrestling with gender identity issues begins with questions.
“What’s your understanding of dysphoria? Where’s the incongruence between the gender you were assigned at birth and what you’re feeling now? You have to be able to verbalize that” before the treatment proceeds, she said.
Sometimes teens leave after an initial conversation and then return later when they have a more clearly defined sense of what dysphoria means.
“There are other kids who clearly, clearly understand that the gender they were assigned at birth is not who they are,” she said.
Children now wrestle with added concerns that their parents could be put at risk for trying to help them, she said.
“These kids go through so much. And we have these people in powerful positions telling them that they don’t matter and telling them, ‘We’re going to cut off your access to healthcare, Medicaid; if your parents tried to seek out this care for you, we’re going to put them in jail,’” she said.
“It’s the biggest factor in fear mongering,” she said.
Dr. Collins-Ogle said she wonders why legislators who lack medical training are trying to dictate how physicians can practice.
“I took a Hippocratic oath to do no harm. I have a medical board that I answer to,” she said. “I don’t understand how legislators can get away with legislating about something they know nothing about.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatrician Michelle Collins-Ogle, MD, already has a busy practice helping young people address questions about their gender identity. She has treated more than 230 patients over the past 2 years at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore in the Bronx, New York.
Dr. Collins-Ogle specializes in adolescent medicine in New York, a state without the restrictions on such care that have been enacted in roughly half the country.
On December 13, 2023, Ohio lawmakers passed a bill banning gender-affirming medical care to minors which Gov. Mike DeWine vetoed on December 29. Another 26 states have similar restrictions in place, according to a tally provided to this news organization by the Human Rights Campaign, which tracks this issue.
Clinicians like Dr. Collins-Ogle are feeling the impact. In her practice, Dr. Collins-Ogle met a couple that moved from Texas to New York to allow their child to access gender-affirming medical care.
“They wanted their child to be able to receive medical care, but they also were afraid for their own safety, of having their child taken from them, and being locked up,” Dr. Collins-Ogle told this news organization.
With patients have also come protestors and harassment. In fact, many physicians are reluctant to speak on this topic amid a recent spate of threats. Psychiatric News reported that conservative pundits and high-profile social media accounts have targeted physicians who provide gender-affirming medical care, spurring harassment campaigns against clinics in cities such as Akron, Boston, and Nashville. “The attackers asserted that the clinics were mutilating children and giving them ‘chemical castration drugs,’ among other claims,” the Psychiatric News reported.
This news organization contacted more than a half dozen organizations that provide gender-affirming care for adolescents and teens seeking interviews about the effects of these restrictions.
All but Montefiore’s Dr. Collins-Ogle turned down the request.
“If my kids are brave enough to come see me, I can’t cower,” Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
But Dr. Collins-Ogle emphasized she understands why many fellow physicians are concerned about speaking publicly about gender-affirming medical care.
Dissenters Spread Misinformation and Threats
Recent years have seen increasing politicization of this issue, often due to inaccurate depictions of gender-affirming medical care circulating on social media.
In 2022, the American Medical Association (AMA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Children’s Hospital Association asked the Justice Department to investigate what they called “increasing threats of violence against physicians, hospitals, and families of children for providing and seeking evidence-based gender-affirming care.”
The three organizations also called on X (formerly known as Twitter), TikTok, and Meta, which owns Facebook and Instagram, to do more to address coordinated campaigns of disinformation.
“We cannot stand by as threats of violence against our members and their patients proliferate with little consequence,” said Moira Szilagyi, MD, PhD, then AAP president in a statement.
Medical Groups Defend Care to Prevent Suicide
The AAP, AMA, and other influential medical associations are banding together to fight new legal restrictions on gender-affirming medical care for teens and adolescents. (These briefs do not discuss surgeries typically available for adults.)
Since 2022, these medical organizations have filed amicus briefs in cases challenging new restrictions put in place in Arkansas, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Kentucky, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Texas.
Other signers to the amicus briefs:
- Academic Pediatric Association
- American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry
- American Academy of Family Physicians
- American Academy of Nursing
- GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ+ Equality
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
- American College of Osteopathic Pediatricians
- The American College of Physicians
- American Pediatric Society
- Association of Medical School Pediatric Department Chairs, Inc.
- Endocrine Society
- National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners
- The Pediatric Endocrine Society, Societies for Pediatric Urology
- Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine
- Society for Pediatric Research
- The Society of Pediatric Nurses
- World Professional Association for Transgender Health
In these amicus briefs, the medical groups argue that evidence-based guidelines support the use of medication in treating gender dysphoria. The amicus briefs in particular cite an Endocrine Society guideline and the standards of care developed by the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH).
Research shows that adolescents with gender dysphoria who receive puberty blockers and other medications experience less depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation, the groups have said.
“In light of this evidence supporting the connection between lack of access to gender-affirming care and lifetime suicide risk, banning such care can put patients’ lives at risk,” the AAP and other groups said.
Debate Over Source of Gender Identity Concerns
Having doubts and concerns about one’s gender remains a relatively rare phenomena, although it appears more common among younger people.
Among US adults, 0.5% or about 1.3 million people identify as transgender whereas about 1.4% or about 300,000 people in the 13-17–year-old group do so, according to a report issued in 2022 by the Williams Institute of the UCLA School of Law.
Questionable Diagnosis Drives Bans on Care
The term “rapid-onset gender dysphoria,” referring to young people who suddenly question their gender as part of peer group dynamics, persists in political debates. The conservative Heritage Foundation has used the term as well as “social contagion” in its effort to seek restrictions on gender-affirming care for young people.
Ohio Rep. Gary Click, a Republican, said at an April 2023 hearing that his Save Adolescents from Experimentation (SAFE) bill would prevent teens from being harmed due to “social contagion” or “ rapid-onset gender dysphoria.”
The bill, which the Ohio legislature cleared in December, would block physicians from starting new patients on puberty blockers. (It also bars surgeries as part of gender-affirming medical care, although hospital officials and physicians told lawmakers these are not done in Ohio.)
Among the groups opposing Click’s bill were the Ohio chapter of the AAP, the Ohio State Medical Association and several hospitals and hospital groups as well as physicians speaking independently.
Gender-Affirming Care ‘Buys Time’ to Avoid Impulsive Decisions
Kate Krueck, MD, a pediatrician with a practice in the Columbus area, testified about her experience as the mother of a transgender child who once attempted suicide.
“It wasn’t always easy to reconstruct my vision of a baby with a vagina into the adolescent before me with a new name and changed pronouns, but they were still the same incredible person,” Krueck said.
She urged lawmakers to understand how puberty blockers can “buy time” for teens to cope with a body at odds with their vision of themselves, noting that many of the effects of these medications are largely reversible. The side effects that are not reversible, such as facial hair growth and the growth of Adam’s Apple, are certainly outweighed by the risks of withholding treatment, she said.
Bad Patient Experience Drives Detractor Activist
Arguing against that point was Chloe Cole, a detransitioner activist who had returned to a female identity. At the Ohio legislative hearings, Ms. Cole spoke of her experience in California as a teen treated for gender dysphoria.
“I was fast-tracked by medical butchers starting at 13 when I was given cross sex hormones, and they took my breasts away from me at 15 years old,” she said.
Ms. Cole appears frequently to testify in favor of bans on gender-affirming medical care. In 2022, she told the Ohio lawmakers about her experience of attending a class with about a dozen other young people in the midst of female-to-male transitions. She now sees that class as having inadvertently helped reinforce her decision to have her breasts removed.
“Despite all these consultations and classes, I don’t feel like I understood all the ramifications that came with any of the medical decisions I was making,” Ms. Cole said. “I didn’t realize how traumatic the recovery would be, and it wasn’t until I was almost a year post-op that I realized I may want to breastfeed my future children; I will never be able to do that.”
Ms. Cole also spoke in July before the US House subcommittee on the Constitution and Limited Government.
“I look in the mirror sometimes, and I feel like a monster,” Ms. Cole said at the House hearing, which was titled “ The Dangers and Due Process Violations of ‘Gender-Affirming Care’.”
During the hearing, Shannon Minter, legal director of the National Center for Lesbian Rights (NCLR), who also made a gender transition, thanked Ms. Cole but noted that her case is an exception.
A 2022 Lancet Child and Adolescent Health article reported that 704 (98%) people in the Netherlands who had started gender-affirming medical treatment in adolescence continued to use gender-affirming hormones at follow-up. Ms. Minter credits this high rate of continuation to clinicians taking their duties to adolescents seriously.
State legislatures and medical boards oversee the regulation of medical practice in the US. But a few Republicans in both chambers of the US Congress have shown an interest in enacting a federal ban restricting physicians’ ability to provide gender-affirming medical care.
They include Rep. Mike Johnson of Louisiana, who in October 2023 became Speaker of the House. He chaired the July hearing at which Ms. Cole spoke. He’s also a sponsor of a House bill introduced by Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA).
This measure, which has the support of 45 House Republicans, would make it a felony to perform any gender-affirming care on a minor, and it permits a minor on whom such care is performed to bring a civil action against each individual who provided the care. Sen. JD Vance (R-OH) introduced the companion Senate measure.
Reality of Gender-Affirming Care
The drive to pass laws like those in Ohio and Arkansas stem from a lack of knowledge about gender-affirming treatments, including a false idea that doctors prescribe medications at teens’ requests, Montefiore’s Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
“There’s a misperception that young people will say ‘I’m transgender’ and that those of us who provide care are just giving them hormones or whatever they want. It’s not true, and it doesn’t happen that way,” Dr. Collins-Ogle said.
At the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, Dr. Collins-Ogle said her work with patients wrestling with gender identity issues begins with questions.
“What’s your understanding of dysphoria? Where’s the incongruence between the gender you were assigned at birth and what you’re feeling now? You have to be able to verbalize that” before the treatment proceeds, she said.
Sometimes teens leave after an initial conversation and then return later when they have a more clearly defined sense of what dysphoria means.
“There are other kids who clearly, clearly understand that the gender they were assigned at birth is not who they are,” she said.
Children now wrestle with added concerns that their parents could be put at risk for trying to help them, she said.
“These kids go through so much. And we have these people in powerful positions telling them that they don’t matter and telling them, ‘We’re going to cut off your access to healthcare, Medicaid; if your parents tried to seek out this care for you, we’re going to put them in jail,’” she said.
“It’s the biggest factor in fear mongering,” she said.
Dr. Collins-Ogle said she wonders why legislators who lack medical training are trying to dictate how physicians can practice.
“I took a Hippocratic oath to do no harm. I have a medical board that I answer to,” she said. “I don’t understand how legislators can get away with legislating about something they know nothing about.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Many Uses of the Humble Alcohol Swab
Practice Gap
In light of inflation, rising costs of procedures, and decreased reimbursements,1 there is an increased need to identify and utilize inexpensive multitasking tools that can serve the dermatologic surgeon from preoperative to postoperative care. The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab may be the dermatologist’s most cost-effective and versatile surgical tool.
The Technique
When assessing a lesion, alcohol swabs can remove scale, crust, or residue from personal care products to help reveal primary morphology. They aid in the diagnosis of porokeratosis by highlighting the cornoid lamella when used following application of gentian violet.2 The alcohol swab also can lay down a liquid interface to facilitate contact dermoscopy and improve visualization while also reducing the transmission of pathogens by the dermatoscope.3 Rubbing an area with an alcohol swab can induce vasodilation of scar tissue, which also may help localize a prior biopsy or surgical site (Figure).
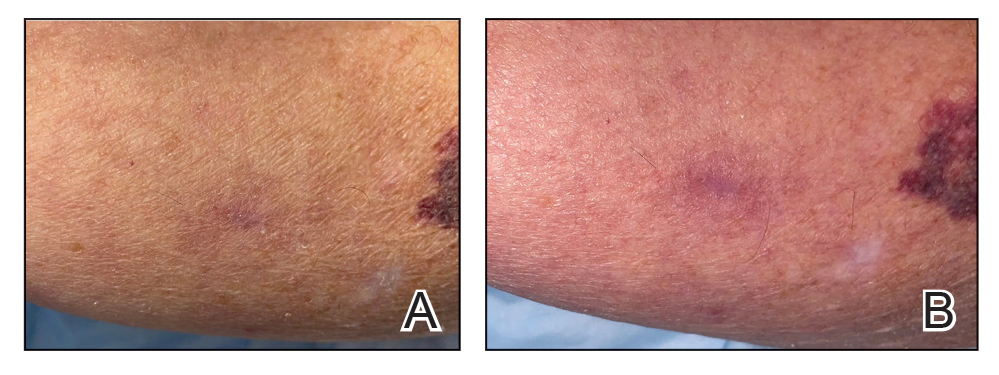
Before a surgical site is marked, an initial cleanse with an alcohol swab serves to both remove debris and provide antisepsis ahead of the procedure. Additionally, the swab may improve adherence of skin markers by clearing excess lipid from the skin surface. Assessing the amount of debris and oil removed in the process can help determine a patient’s baseline level of hygiene, which can aid postoperative wound care planning. In extreme cases, use of an alcohol swab may help diagnose dermatitis neglecta or terra firma-forme dermatosis by completely removing any pigmentation.4
After surgery, the alcohol swab can remove skin marker(s) and blood and prepare the site for the surgical dressing. There also is some evidence to suggest that cleansing the surgical site with an alcohol swab as part of routine postoperative wound care may decrease incidence of surgical-site infection.5 At follow-up, the swab can remove crust and clean the skin before suture removal. If infection is suspected, the swab can cleanse skin before a wound culture is obtained to remove skin commensals and flora on the outer surface of the wound.
Practice Implications
The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab can assist the dermatologist in numerous tasks related to everyday procedures. It is readily available in every clinic and costs only a few cents.
- Pollock JR, Chen JY, Dorius DA, et al. Decreasing physician Medicare reimbursement for dermatology services. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1154-1156.
- Thomas CJ, Elston DM. Medical pearl: Gentian violet to highlight the cornoid lamella in disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(3 pt 1):513-514.
- Kelly SC, Purcell SM. Prevention of nosocomial infection during dermoscopy? Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:552-555.
- Blattner CM, Perry B, Snider K, et al. Clinical pearl: increasing utility of isopropyl alcohol for cutaneous dyschromia. Cutis. 2016;97:287;301.
- Vogt KN, Chadi S, Parry N, et al. Daily incision cleansing with alcohol reduces the rate of surgical site infections: a pilot study. Am Surg. 2015;81:1182-1186.
Practice Gap
In light of inflation, rising costs of procedures, and decreased reimbursements,1 there is an increased need to identify and utilize inexpensive multitasking tools that can serve the dermatologic surgeon from preoperative to postoperative care. The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab may be the dermatologist’s most cost-effective and versatile surgical tool.
The Technique
When assessing a lesion, alcohol swabs can remove scale, crust, or residue from personal care products to help reveal primary morphology. They aid in the diagnosis of porokeratosis by highlighting the cornoid lamella when used following application of gentian violet.2 The alcohol swab also can lay down a liquid interface to facilitate contact dermoscopy and improve visualization while also reducing the transmission of pathogens by the dermatoscope.3 Rubbing an area with an alcohol swab can induce vasodilation of scar tissue, which also may help localize a prior biopsy or surgical site (Figure).

Before a surgical site is marked, an initial cleanse with an alcohol swab serves to both remove debris and provide antisepsis ahead of the procedure. Additionally, the swab may improve adherence of skin markers by clearing excess lipid from the skin surface. Assessing the amount of debris and oil removed in the process can help determine a patient’s baseline level of hygiene, which can aid postoperative wound care planning. In extreme cases, use of an alcohol swab may help diagnose dermatitis neglecta or terra firma-forme dermatosis by completely removing any pigmentation.4
After surgery, the alcohol swab can remove skin marker(s) and blood and prepare the site for the surgical dressing. There also is some evidence to suggest that cleansing the surgical site with an alcohol swab as part of routine postoperative wound care may decrease incidence of surgical-site infection.5 At follow-up, the swab can remove crust and clean the skin before suture removal. If infection is suspected, the swab can cleanse skin before a wound culture is obtained to remove skin commensals and flora on the outer surface of the wound.
Practice Implications
The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab can assist the dermatologist in numerous tasks related to everyday procedures. It is readily available in every clinic and costs only a few cents.
Practice Gap
In light of inflation, rising costs of procedures, and decreased reimbursements,1 there is an increased need to identify and utilize inexpensive multitasking tools that can serve the dermatologic surgeon from preoperative to postoperative care. The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab may be the dermatologist’s most cost-effective and versatile surgical tool.
The Technique
When assessing a lesion, alcohol swabs can remove scale, crust, or residue from personal care products to help reveal primary morphology. They aid in the diagnosis of porokeratosis by highlighting the cornoid lamella when used following application of gentian violet.2 The alcohol swab also can lay down a liquid interface to facilitate contact dermoscopy and improve visualization while also reducing the transmission of pathogens by the dermatoscope.3 Rubbing an area with an alcohol swab can induce vasodilation of scar tissue, which also may help localize a prior biopsy or surgical site (Figure).

Before a surgical site is marked, an initial cleanse with an alcohol swab serves to both remove debris and provide antisepsis ahead of the procedure. Additionally, the swab may improve adherence of skin markers by clearing excess lipid from the skin surface. Assessing the amount of debris and oil removed in the process can help determine a patient’s baseline level of hygiene, which can aid postoperative wound care planning. In extreme cases, use of an alcohol swab may help diagnose dermatitis neglecta or terra firma-forme dermatosis by completely removing any pigmentation.4
After surgery, the alcohol swab can remove skin marker(s) and blood and prepare the site for the surgical dressing. There also is some evidence to suggest that cleansing the surgical site with an alcohol swab as part of routine postoperative wound care may decrease incidence of surgical-site infection.5 At follow-up, the swab can remove crust and clean the skin before suture removal. If infection is suspected, the swab can cleanse skin before a wound culture is obtained to remove skin commensals and flora on the outer surface of the wound.
Practice Implications
The 70% isopropyl alcohol swab can assist the dermatologist in numerous tasks related to everyday procedures. It is readily available in every clinic and costs only a few cents.
- Pollock JR, Chen JY, Dorius DA, et al. Decreasing physician Medicare reimbursement for dermatology services. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1154-1156.
- Thomas CJ, Elston DM. Medical pearl: Gentian violet to highlight the cornoid lamella in disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(3 pt 1):513-514.
- Kelly SC, Purcell SM. Prevention of nosocomial infection during dermoscopy? Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:552-555.
- Blattner CM, Perry B, Snider K, et al. Clinical pearl: increasing utility of isopropyl alcohol for cutaneous dyschromia. Cutis. 2016;97:287;301.
- Vogt KN, Chadi S, Parry N, et al. Daily incision cleansing with alcohol reduces the rate of surgical site infections: a pilot study. Am Surg. 2015;81:1182-1186.
- Pollock JR, Chen JY, Dorius DA, et al. Decreasing physician Medicare reimbursement for dermatology services. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1154-1156.
- Thomas CJ, Elston DM. Medical pearl: Gentian violet to highlight the cornoid lamella in disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(3 pt 1):513-514.
- Kelly SC, Purcell SM. Prevention of nosocomial infection during dermoscopy? Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:552-555.
- Blattner CM, Perry B, Snider K, et al. Clinical pearl: increasing utility of isopropyl alcohol for cutaneous dyschromia. Cutis. 2016;97:287;301.
- Vogt KN, Chadi S, Parry N, et al. Daily incision cleansing with alcohol reduces the rate of surgical site infections: a pilot study. Am Surg. 2015;81:1182-1186.