User login
ALL mortality gains bypass older adults
From 1999 to 2020, age-adjusted mortality rates for patients with ALL aged 55 and up didn’t change, oncologist-hematologist Jamie L. Koprivnikar, MD, of New Jersey’s Hackensack University Medical Center, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. The rates were 10.8 per 1 million in 1999 and 10.6 per 1 million in 2020.
By contrast, the mortality rates for children aged 0-15 improved from 3.5 per 1 million in 1999 to 2.2 per 1 million in 2020.
“The findings were particularly surprising and disappointing to me,” Dr. Koprivnikar said in an interview. “My overall sense is that we’ve really improved our outcomes of treating patients with ALL and are making great strides forward, moving away from so much chemotherapy and toward more kinds of immunotherapies and targeted therapies. So we need to understand what’s driving this.”
According to Dr. Koprivnikar, ALL is more common in children than adults. However, “even though the majority of cases tend to occur in children, we know that the majority of deaths are actually in the adult patient population,” she said.
One challenge for treatment is that therapies that work well in the pediatric population aren’t as effective in adults, she said. ALL is biologically different in adults in some ways, she added, and older patients may have more comorbidities. “It ends up being a really complicated story with all of these different factors playing into the complexity.”
For the new study, Dr. Koprivnikar and colleagues analyzed death certificate data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research database. They found that 17,238 people died from ALL between 1999 and 2020. There were no significant differences in terms of gender, race, and region.
The study authors noted that mortality rates didn’t change despite medical advances in ALL such as blinatumomab, inotuzumab, and targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based therapy. It’s unclear if the treatments have made it to the older-adult setting yet, Dr. Koprivnikar said.
There may be problems with access due to socioeconomic factors as well, she said. “ALL is actually more common among those of Hispanic heritage, and we don’t completely understand that.”
Marlise R. Luskin, MD, a leukemia specialist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, said in an interview that the study “is a reminder that clinical trial outcomes are limited — specifically trial results that often emphasize early results and report on a select population of older patients who generally are socially resourced and physically and mentally more fit.”
Dr. Luskin added that the study reports on outcomes through 2020, including years when newer regimens were not broadly disseminated outside of clinical trials.
Moving forward, she said, “this report suggests we need to continue to develop novel approaches and understand long-term outcomes as well as ‘real world’ outcomes. A similar study should be repeated again in 3-5 years as novel regimens become standard. We hope to see improvements.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Koprivnikar disclosed consulting relationships with Alexion, GSK, Novartis, and Apellis. Other authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Luskin disclosed ties with Pfizer, Novartis, Jazz, Kite, and AbbVie.
From 1999 to 2020, age-adjusted mortality rates for patients with ALL aged 55 and up didn’t change, oncologist-hematologist Jamie L. Koprivnikar, MD, of New Jersey’s Hackensack University Medical Center, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. The rates were 10.8 per 1 million in 1999 and 10.6 per 1 million in 2020.
By contrast, the mortality rates for children aged 0-15 improved from 3.5 per 1 million in 1999 to 2.2 per 1 million in 2020.
“The findings were particularly surprising and disappointing to me,” Dr. Koprivnikar said in an interview. “My overall sense is that we’ve really improved our outcomes of treating patients with ALL and are making great strides forward, moving away from so much chemotherapy and toward more kinds of immunotherapies and targeted therapies. So we need to understand what’s driving this.”
According to Dr. Koprivnikar, ALL is more common in children than adults. However, “even though the majority of cases tend to occur in children, we know that the majority of deaths are actually in the adult patient population,” she said.
One challenge for treatment is that therapies that work well in the pediatric population aren’t as effective in adults, she said. ALL is biologically different in adults in some ways, she added, and older patients may have more comorbidities. “It ends up being a really complicated story with all of these different factors playing into the complexity.”
For the new study, Dr. Koprivnikar and colleagues analyzed death certificate data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research database. They found that 17,238 people died from ALL between 1999 and 2020. There were no significant differences in terms of gender, race, and region.
The study authors noted that mortality rates didn’t change despite medical advances in ALL such as blinatumomab, inotuzumab, and targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based therapy. It’s unclear if the treatments have made it to the older-adult setting yet, Dr. Koprivnikar said.
There may be problems with access due to socioeconomic factors as well, she said. “ALL is actually more common among those of Hispanic heritage, and we don’t completely understand that.”
Marlise R. Luskin, MD, a leukemia specialist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, said in an interview that the study “is a reminder that clinical trial outcomes are limited — specifically trial results that often emphasize early results and report on a select population of older patients who generally are socially resourced and physically and mentally more fit.”
Dr. Luskin added that the study reports on outcomes through 2020, including years when newer regimens were not broadly disseminated outside of clinical trials.
Moving forward, she said, “this report suggests we need to continue to develop novel approaches and understand long-term outcomes as well as ‘real world’ outcomes. A similar study should be repeated again in 3-5 years as novel regimens become standard. We hope to see improvements.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Koprivnikar disclosed consulting relationships with Alexion, GSK, Novartis, and Apellis. Other authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Luskin disclosed ties with Pfizer, Novartis, Jazz, Kite, and AbbVie.
From 1999 to 2020, age-adjusted mortality rates for patients with ALL aged 55 and up didn’t change, oncologist-hematologist Jamie L. Koprivnikar, MD, of New Jersey’s Hackensack University Medical Center, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. The rates were 10.8 per 1 million in 1999 and 10.6 per 1 million in 2020.
By contrast, the mortality rates for children aged 0-15 improved from 3.5 per 1 million in 1999 to 2.2 per 1 million in 2020.
“The findings were particularly surprising and disappointing to me,” Dr. Koprivnikar said in an interview. “My overall sense is that we’ve really improved our outcomes of treating patients with ALL and are making great strides forward, moving away from so much chemotherapy and toward more kinds of immunotherapies and targeted therapies. So we need to understand what’s driving this.”
According to Dr. Koprivnikar, ALL is more common in children than adults. However, “even though the majority of cases tend to occur in children, we know that the majority of deaths are actually in the adult patient population,” she said.
One challenge for treatment is that therapies that work well in the pediatric population aren’t as effective in adults, she said. ALL is biologically different in adults in some ways, she added, and older patients may have more comorbidities. “It ends up being a really complicated story with all of these different factors playing into the complexity.”
For the new study, Dr. Koprivnikar and colleagues analyzed death certificate data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research database. They found that 17,238 people died from ALL between 1999 and 2020. There were no significant differences in terms of gender, race, and region.
The study authors noted that mortality rates didn’t change despite medical advances in ALL such as blinatumomab, inotuzumab, and targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based therapy. It’s unclear if the treatments have made it to the older-adult setting yet, Dr. Koprivnikar said.
There may be problems with access due to socioeconomic factors as well, she said. “ALL is actually more common among those of Hispanic heritage, and we don’t completely understand that.”
Marlise R. Luskin, MD, a leukemia specialist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, said in an interview that the study “is a reminder that clinical trial outcomes are limited — specifically trial results that often emphasize early results and report on a select population of older patients who generally are socially resourced and physically and mentally more fit.”
Dr. Luskin added that the study reports on outcomes through 2020, including years when newer regimens were not broadly disseminated outside of clinical trials.
Moving forward, she said, “this report suggests we need to continue to develop novel approaches and understand long-term outcomes as well as ‘real world’ outcomes. A similar study should be repeated again in 3-5 years as novel regimens become standard. We hope to see improvements.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Koprivnikar disclosed consulting relationships with Alexion, GSK, Novartis, and Apellis. Other authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Luskin disclosed ties with Pfizer, Novartis, Jazz, Kite, and AbbVie.
FROM ASH 2023
How scientists are uncovering the mysteries of ARDS
, the devastating disorder that floods the lungs with fluid and has ushered countless millions to death after infection with pneumonia, sepsis, and COVID-19.
Two centuries after the lung damage caused by the disorder was first described in medicine, it’s now clear that ARDS is an autoimmune condition spurred by the body’s overactive defenses. There’s interest in disrupting “crosstalk” between cells, and rise of a new form of genetic analysis is allowing researchers to test their hypotheses more effectively than ever before. And, perhaps most importantly, recent findings reveal how stem cells in the epithelial lining of the lungs get stalled in an intermediate stage before regenerating into new cells. Reversing this process could trigger repair and recovery.
There’s still a ways to go before clinical trials can test therapies to turn things around at the epithelial level, acknowledged University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, professor of internal medicine Rachel L. Zemans, MD, in an interview. Still, “it’s a pretty exciting time,” said Dr Zemans, who manages a lab that explores how the lung epithelium responds to injury.
A lung disorder’s deep roots in human history
A British doctor first described the traits of ARDS in 1821, although this form of pulmonary edema had been described in “ancient writings,” according to a 2005 report by Gordon Bernard, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee. Sometimes called “double pneumonia,” ARDS was almost always fatal until the last few decades of the 20th century. “The advent of well-equipped ICUs, well-trained staff, and the availability of reliable positive pressure ventilators has allowed patients to be kept alive much longer and thus have the opportunity to heal the pulmonary injury and survive,” Dr Bernard wrote.
According to the Mayo Clinic, there are many causes of ARDS. Sepsis is the most common, and others include severe pneumonia, head/chest injuries, massive blood transfusions, pancreatitis, burns, and inhalation of harmful substances. Since 2020, ARDS has been a hallmark of COVID-19.
In an interview, University of Washington, Seattle, emeritus professor of medicine Thomas R. Martin MD, explained that ARDS occurs when the epithelium barrier in the lungs breaks down. Unlike the permeable endothelial barrier, the alveolar epithelium is “like a brick wall or a big dam, keeping red cells and plasma out of the airspace.”
In cases of pulmonary edema due to heart failure, fluid can back up into the lungs, said Dr Martin, who studies ARDS. However, pumps in the epithelium can clear that excess fluid pretty quickly because the epithelium remains in a normal state, he said. “Given enough time and enough medical support, people with heart failure and pulmonary edema can get better without lung injury.”
In ARDS, however, “the epithelium is damaged. Cells die in the alveolar wall, the scaffolding is exposed, and the fluid in the alveoli cannot be cleared out. You’ve got a disaster on your hands because all of the fluid and red blood cells and inflammatory products in the blood are going right into the airspace. The patient gets extremely short of breath because their oxygen level falls.”
COVID-19 virus finds a weak spot in the lungs
COVID-19 is “a classic example of an attack on the alveolar epithelium,” Dr Martin said.
By chance, the virus evolved to recognize receptors in the epithelium, allowing it to enter and propagate. “To make matters worse, defense mechanisms in the body attack those dying epithelial cells because the virus is visible on the surface cells. So lymphocytes from the immune system and macrophages attack the outer walls and cause further damage.”
Other scientists agree about this general picture of ARDS. “Studies of human lung tissue support the notion that failure of alveolar repair and regeneration mechanisms underlie the chronic lung dysfunction that can result from ARD,” wrote researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, in a 2022 report.
According to Dr Martin, researchers and clinicians have discovered a pair of strategies to help vanquish COVID-19: Control viral entry through antiviral medication and dampen the body’s inflammatory response via steroids.
Still, “although we’ve learned lessons from COVID-19, we’re not good at all at promoting repair,” Dr Martin said. While new drugs have dramatically improved treatment for lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, he said, “we don’t have good examples of new therapies that promote repair in ARDS.”
Looking for a way to turn the tide of fluid buildup
Dr Zemans and colleagues have uncovered a crucial obstacle to repair: the failure of stem cells to fully differentiate and become functional alveolar epithelial cells.
Researchers only began to understand a few years ago that the stem cells go through a transitional stage from type 2 to type 1, which make up 98% of cells in the epithelial surface, Dr Zemans said. In patients with ARDS who don’t get better quickly, “it looks like the cells get hung up in this intermediate state. They can’t finish that regeneration.”
As a 2022 study by Dr Zemans and colleagues put it, this process can lead to “ongoing barrier permeability, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, and ventilator dependence, and mortality.” In fact, she said, “when we look at the lungs of people who died of ARDS, their cells were all in that intermediate stage.”
The discovery of the intermediate state only came about because of new technology called single-cell RNA sequencing, she said. “Now, these transitional cells are being found in other organs.”
Why do the epithelial cells get only part way through the regeneration process? It’s not entirely clear, Dr Zemans said, but researcher are intrigued by the idea that “cross-talk” between cells is playing a role.
“When the cells are in that stage, they also activate neighboring cells, including inflammatory cells, like macrophages, and fibroblasts,” she said. “And once those cells become activated, they become pathologic. What we think is that those cells then can talk back to the epithelial cells and prevent the epithelial cells from finishing that differentiation. It’s really hard to snap out of that positive feedback loop.”
This interaction probably evolved “for a good reason,” she said, “but it also became pathologic.” If the cells stay in the intermediate stage too long, she said, fibrosis develops. “They have scar tissue that never goes away. It takes a lot of work to expand the lungs when they’re so stiff when they should be stretchy like a rubber band. Scar tissue also gets in the way of the oxygen absorption, so some people have low oxygen levels.”
Future directions: Teaching cells to get “unstuck”
What’s next for research? One direction is exploring the variety of types of cells in the epithelium. Recent finding are revealing “new cell subpopulations that maintain alveolar homeostasis, communicate injury signals, and participate in normal and maladaptive repair. Emerging data illuminate the complexity of alveolar physiology and pathology to provide a more complete picture of how alveoli maintain health and respond to injurious stimuli,” write the researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in their 2022 report.
Meanwhile, “we’re trying to look at the signaling pathways, the proteins or molecules, to understand the signals that tell a cell how to get unstuck,” Dr Zemans said. And researchers are exploring whether knocking out certain genes expressed by transitional cells in mice will lead to better outcomes, she said.
The 2022 study by Dr Zeman and colleagues described the potential ramifications of better understanding of the entire process: “Ultimately, investigation of the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying ineffectual alveolar regeneration in ARDS and fibrosis may lead to novel therapies to promote physiological regeneration, thus accelerating restoration of barrier integrity, resolution of edema, liberation from the ventilator and survival in ARDS, and preventing fibrosis in fibroproliferative ARDS and [idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis].”
To put it more simply, “if you can seal the barrier, you can get the fluid out of the lungs, and you can get the patients off the ventilator, get out of the ICU, and go home,” Dr Zemans said.
Dr Zemans and Dr Martin have no disclosures.
, the devastating disorder that floods the lungs with fluid and has ushered countless millions to death after infection with pneumonia, sepsis, and COVID-19.
Two centuries after the lung damage caused by the disorder was first described in medicine, it’s now clear that ARDS is an autoimmune condition spurred by the body’s overactive defenses. There’s interest in disrupting “crosstalk” between cells, and rise of a new form of genetic analysis is allowing researchers to test their hypotheses more effectively than ever before. And, perhaps most importantly, recent findings reveal how stem cells in the epithelial lining of the lungs get stalled in an intermediate stage before regenerating into new cells. Reversing this process could trigger repair and recovery.
There’s still a ways to go before clinical trials can test therapies to turn things around at the epithelial level, acknowledged University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, professor of internal medicine Rachel L. Zemans, MD, in an interview. Still, “it’s a pretty exciting time,” said Dr Zemans, who manages a lab that explores how the lung epithelium responds to injury.
A lung disorder’s deep roots in human history
A British doctor first described the traits of ARDS in 1821, although this form of pulmonary edema had been described in “ancient writings,” according to a 2005 report by Gordon Bernard, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee. Sometimes called “double pneumonia,” ARDS was almost always fatal until the last few decades of the 20th century. “The advent of well-equipped ICUs, well-trained staff, and the availability of reliable positive pressure ventilators has allowed patients to be kept alive much longer and thus have the opportunity to heal the pulmonary injury and survive,” Dr Bernard wrote.
According to the Mayo Clinic, there are many causes of ARDS. Sepsis is the most common, and others include severe pneumonia, head/chest injuries, massive blood transfusions, pancreatitis, burns, and inhalation of harmful substances. Since 2020, ARDS has been a hallmark of COVID-19.
In an interview, University of Washington, Seattle, emeritus professor of medicine Thomas R. Martin MD, explained that ARDS occurs when the epithelium barrier in the lungs breaks down. Unlike the permeable endothelial barrier, the alveolar epithelium is “like a brick wall or a big dam, keeping red cells and plasma out of the airspace.”
In cases of pulmonary edema due to heart failure, fluid can back up into the lungs, said Dr Martin, who studies ARDS. However, pumps in the epithelium can clear that excess fluid pretty quickly because the epithelium remains in a normal state, he said. “Given enough time and enough medical support, people with heart failure and pulmonary edema can get better without lung injury.”
In ARDS, however, “the epithelium is damaged. Cells die in the alveolar wall, the scaffolding is exposed, and the fluid in the alveoli cannot be cleared out. You’ve got a disaster on your hands because all of the fluid and red blood cells and inflammatory products in the blood are going right into the airspace. The patient gets extremely short of breath because their oxygen level falls.”
COVID-19 virus finds a weak spot in the lungs
COVID-19 is “a classic example of an attack on the alveolar epithelium,” Dr Martin said.
By chance, the virus evolved to recognize receptors in the epithelium, allowing it to enter and propagate. “To make matters worse, defense mechanisms in the body attack those dying epithelial cells because the virus is visible on the surface cells. So lymphocytes from the immune system and macrophages attack the outer walls and cause further damage.”
Other scientists agree about this general picture of ARDS. “Studies of human lung tissue support the notion that failure of alveolar repair and regeneration mechanisms underlie the chronic lung dysfunction that can result from ARD,” wrote researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, in a 2022 report.
According to Dr Martin, researchers and clinicians have discovered a pair of strategies to help vanquish COVID-19: Control viral entry through antiviral medication and dampen the body’s inflammatory response via steroids.
Still, “although we’ve learned lessons from COVID-19, we’re not good at all at promoting repair,” Dr Martin said. While new drugs have dramatically improved treatment for lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, he said, “we don’t have good examples of new therapies that promote repair in ARDS.”
Looking for a way to turn the tide of fluid buildup
Dr Zemans and colleagues have uncovered a crucial obstacle to repair: the failure of stem cells to fully differentiate and become functional alveolar epithelial cells.
Researchers only began to understand a few years ago that the stem cells go through a transitional stage from type 2 to type 1, which make up 98% of cells in the epithelial surface, Dr Zemans said. In patients with ARDS who don’t get better quickly, “it looks like the cells get hung up in this intermediate state. They can’t finish that regeneration.”
As a 2022 study by Dr Zemans and colleagues put it, this process can lead to “ongoing barrier permeability, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, and ventilator dependence, and mortality.” In fact, she said, “when we look at the lungs of people who died of ARDS, their cells were all in that intermediate stage.”
The discovery of the intermediate state only came about because of new technology called single-cell RNA sequencing, she said. “Now, these transitional cells are being found in other organs.”
Why do the epithelial cells get only part way through the regeneration process? It’s not entirely clear, Dr Zemans said, but researcher are intrigued by the idea that “cross-talk” between cells is playing a role.
“When the cells are in that stage, they also activate neighboring cells, including inflammatory cells, like macrophages, and fibroblasts,” she said. “And once those cells become activated, they become pathologic. What we think is that those cells then can talk back to the epithelial cells and prevent the epithelial cells from finishing that differentiation. It’s really hard to snap out of that positive feedback loop.”
This interaction probably evolved “for a good reason,” she said, “but it also became pathologic.” If the cells stay in the intermediate stage too long, she said, fibrosis develops. “They have scar tissue that never goes away. It takes a lot of work to expand the lungs when they’re so stiff when they should be stretchy like a rubber band. Scar tissue also gets in the way of the oxygen absorption, so some people have low oxygen levels.”
Future directions: Teaching cells to get “unstuck”
What’s next for research? One direction is exploring the variety of types of cells in the epithelium. Recent finding are revealing “new cell subpopulations that maintain alveolar homeostasis, communicate injury signals, and participate in normal and maladaptive repair. Emerging data illuminate the complexity of alveolar physiology and pathology to provide a more complete picture of how alveoli maintain health and respond to injurious stimuli,” write the researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in their 2022 report.
Meanwhile, “we’re trying to look at the signaling pathways, the proteins or molecules, to understand the signals that tell a cell how to get unstuck,” Dr Zemans said. And researchers are exploring whether knocking out certain genes expressed by transitional cells in mice will lead to better outcomes, she said.
The 2022 study by Dr Zeman and colleagues described the potential ramifications of better understanding of the entire process: “Ultimately, investigation of the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying ineffectual alveolar regeneration in ARDS and fibrosis may lead to novel therapies to promote physiological regeneration, thus accelerating restoration of barrier integrity, resolution of edema, liberation from the ventilator and survival in ARDS, and preventing fibrosis in fibroproliferative ARDS and [idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis].”
To put it more simply, “if you can seal the barrier, you can get the fluid out of the lungs, and you can get the patients off the ventilator, get out of the ICU, and go home,” Dr Zemans said.
Dr Zemans and Dr Martin have no disclosures.
, the devastating disorder that floods the lungs with fluid and has ushered countless millions to death after infection with pneumonia, sepsis, and COVID-19.
Two centuries after the lung damage caused by the disorder was first described in medicine, it’s now clear that ARDS is an autoimmune condition spurred by the body’s overactive defenses. There’s interest in disrupting “crosstalk” between cells, and rise of a new form of genetic analysis is allowing researchers to test their hypotheses more effectively than ever before. And, perhaps most importantly, recent findings reveal how stem cells in the epithelial lining of the lungs get stalled in an intermediate stage before regenerating into new cells. Reversing this process could trigger repair and recovery.
There’s still a ways to go before clinical trials can test therapies to turn things around at the epithelial level, acknowledged University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, professor of internal medicine Rachel L. Zemans, MD, in an interview. Still, “it’s a pretty exciting time,” said Dr Zemans, who manages a lab that explores how the lung epithelium responds to injury.
A lung disorder’s deep roots in human history
A British doctor first described the traits of ARDS in 1821, although this form of pulmonary edema had been described in “ancient writings,” according to a 2005 report by Gordon Bernard, MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee. Sometimes called “double pneumonia,” ARDS was almost always fatal until the last few decades of the 20th century. “The advent of well-equipped ICUs, well-trained staff, and the availability of reliable positive pressure ventilators has allowed patients to be kept alive much longer and thus have the opportunity to heal the pulmonary injury and survive,” Dr Bernard wrote.
According to the Mayo Clinic, there are many causes of ARDS. Sepsis is the most common, and others include severe pneumonia, head/chest injuries, massive blood transfusions, pancreatitis, burns, and inhalation of harmful substances. Since 2020, ARDS has been a hallmark of COVID-19.
In an interview, University of Washington, Seattle, emeritus professor of medicine Thomas R. Martin MD, explained that ARDS occurs when the epithelium barrier in the lungs breaks down. Unlike the permeable endothelial barrier, the alveolar epithelium is “like a brick wall or a big dam, keeping red cells and plasma out of the airspace.”
In cases of pulmonary edema due to heart failure, fluid can back up into the lungs, said Dr Martin, who studies ARDS. However, pumps in the epithelium can clear that excess fluid pretty quickly because the epithelium remains in a normal state, he said. “Given enough time and enough medical support, people with heart failure and pulmonary edema can get better without lung injury.”
In ARDS, however, “the epithelium is damaged. Cells die in the alveolar wall, the scaffolding is exposed, and the fluid in the alveoli cannot be cleared out. You’ve got a disaster on your hands because all of the fluid and red blood cells and inflammatory products in the blood are going right into the airspace. The patient gets extremely short of breath because their oxygen level falls.”
COVID-19 virus finds a weak spot in the lungs
COVID-19 is “a classic example of an attack on the alveolar epithelium,” Dr Martin said.
By chance, the virus evolved to recognize receptors in the epithelium, allowing it to enter and propagate. “To make matters worse, defense mechanisms in the body attack those dying epithelial cells because the virus is visible on the surface cells. So lymphocytes from the immune system and macrophages attack the outer walls and cause further damage.”
Other scientists agree about this general picture of ARDS. “Studies of human lung tissue support the notion that failure of alveolar repair and regeneration mechanisms underlie the chronic lung dysfunction that can result from ARD,” wrote researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, in a 2022 report.
According to Dr Martin, researchers and clinicians have discovered a pair of strategies to help vanquish COVID-19: Control viral entry through antiviral medication and dampen the body’s inflammatory response via steroids.
Still, “although we’ve learned lessons from COVID-19, we’re not good at all at promoting repair,” Dr Martin said. While new drugs have dramatically improved treatment for lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, he said, “we don’t have good examples of new therapies that promote repair in ARDS.”
Looking for a way to turn the tide of fluid buildup
Dr Zemans and colleagues have uncovered a crucial obstacle to repair: the failure of stem cells to fully differentiate and become functional alveolar epithelial cells.
Researchers only began to understand a few years ago that the stem cells go through a transitional stage from type 2 to type 1, which make up 98% of cells in the epithelial surface, Dr Zemans said. In patients with ARDS who don’t get better quickly, “it looks like the cells get hung up in this intermediate state. They can’t finish that regeneration.”
As a 2022 study by Dr Zemans and colleagues put it, this process can lead to “ongoing barrier permeability, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, and ventilator dependence, and mortality.” In fact, she said, “when we look at the lungs of people who died of ARDS, their cells were all in that intermediate stage.”
The discovery of the intermediate state only came about because of new technology called single-cell RNA sequencing, she said. “Now, these transitional cells are being found in other organs.”
Why do the epithelial cells get only part way through the regeneration process? It’s not entirely clear, Dr Zemans said, but researcher are intrigued by the idea that “cross-talk” between cells is playing a role.
“When the cells are in that stage, they also activate neighboring cells, including inflammatory cells, like macrophages, and fibroblasts,” she said. “And once those cells become activated, they become pathologic. What we think is that those cells then can talk back to the epithelial cells and prevent the epithelial cells from finishing that differentiation. It’s really hard to snap out of that positive feedback loop.”
This interaction probably evolved “for a good reason,” she said, “but it also became pathologic.” If the cells stay in the intermediate stage too long, she said, fibrosis develops. “They have scar tissue that never goes away. It takes a lot of work to expand the lungs when they’re so stiff when they should be stretchy like a rubber band. Scar tissue also gets in the way of the oxygen absorption, so some people have low oxygen levels.”
Future directions: Teaching cells to get “unstuck”
What’s next for research? One direction is exploring the variety of types of cells in the epithelium. Recent finding are revealing “new cell subpopulations that maintain alveolar homeostasis, communicate injury signals, and participate in normal and maladaptive repair. Emerging data illuminate the complexity of alveolar physiology and pathology to provide a more complete picture of how alveoli maintain health and respond to injurious stimuli,” write the researchers from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in their 2022 report.
Meanwhile, “we’re trying to look at the signaling pathways, the proteins or molecules, to understand the signals that tell a cell how to get unstuck,” Dr Zemans said. And researchers are exploring whether knocking out certain genes expressed by transitional cells in mice will lead to better outcomes, she said.
The 2022 study by Dr Zeman and colleagues described the potential ramifications of better understanding of the entire process: “Ultimately, investigation of the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying ineffectual alveolar regeneration in ARDS and fibrosis may lead to novel therapies to promote physiological regeneration, thus accelerating restoration of barrier integrity, resolution of edema, liberation from the ventilator and survival in ARDS, and preventing fibrosis in fibroproliferative ARDS and [idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis].”
To put it more simply, “if you can seal the barrier, you can get the fluid out of the lungs, and you can get the patients off the ventilator, get out of the ICU, and go home,” Dr Zemans said.
Dr Zemans and Dr Martin have no disclosures.
Expert Highlights Biologics in the Pipeline for Atopic Dermatitis
In the opinion of David Rosmarin, MD, the approval of dupilumab in 2017 for the treatment of moderate to severe, resistant atopic dermatitis (AD) marked an inflection point in dermatology.
“Dupilumab has revolutionized AD, and the [interleukin] IL-4 receptor target isn’t going away,” Dr. Rosmarin, who chairs the department of dermatology at Indiana University, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference. “It’s truly an exciting time because we have a lot of different treatments in the pipeline that target IL-4 and other receptors.”
which is being developed by Keymed Biosciences, inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. In a phase 3 randomized study of patients with moderate to severe AD, presented as an abstract at the 2023 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting, it showed results similar to those of dupilumab. Specifically, at week 16, Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI)-75 scores were achieved in 66.9% of patients in the CM310 group and 25.8% of patients in the placebo group, while the proportion of patients achieving an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) with a reduction of greater than or equal to 2 points from baseline was 44.2% in the CM310 group, compared with 16.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both associations). According to Dr. Rosmarin, other novel anti-IL-4 receptor antibodies for AD include AK120, which is being developed by Akeso Biopharma, and CBP-201 (rademikibart), which is being developed by Connect Biopharma.
Eblasakimab. Under development by ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, this biologic is a potential first-in-class, monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-13Ralpha1 with high affinity and blocks the signaling of IL-4 and IL-13 through the type-2 receptor. In the TREK-AD monotherapy phase 2b trial in patients with moderate to severe AD, presented as an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, the primary endpoint of EASI percent change from baseline to week 16, was met for eblasakimab doses 600 mg Q4W, 300mg Q2W, and 400mg Q2W vs. placebo (73.0% [P = .001], 69.8% [P = .005], and 65.8% [P = .029] vs. 51.1%), respectively.
Nemolizumab. Under development by Galderma, nemolizumab is a first-in-class IL-31 receptor alpha antagonist. “Many people refer to IL-31 as the itch cytokine,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “That’s probably a little oversimplified, but it’s certainly a powerful medication in development for prurigo nodularis as well as AD.”
Results from the ARCADIA 1 and 2 trials, which included the concurrent use of topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors and were presented as an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, showed that nemolizumab significantly improved skin lesions and itch in adolescent and adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, compared with placebo. Specifically, 35.6% and 37.7% of nemolizumab-treated patients in ARCADIA 1 and 2, respectively, reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions when assessed using the IGA score, compared with 24.6% and 26.0% in the placebo group (P < .0006, P = .001). In addition, 43.5% and 42.1% of nemolizumab-treated patients in ARCADIA 1 and 2, respectively, achieved a 75% reduction in the EASI, compared with 29.0% and 30.2% in the placebo group (P < .0001, P = .0011). “There are similar results regardless of the degree of itch patients are starting out with at baseline,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It’s a very rapid response, by week 4, and that continues to improve through week 16.”
Amlitelimab. Under development by Sanofi, this monoclonal antibody binds to OX40-Ligand, and is designed for patients with moderate to severe AD. According to results of a phase 2b trial that were presented in an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, patients treated with amlitelimab 250 mg Q4W with a 500 mg loading dose showed a 61.5% improvement in the average EASI score from baseline at week 16, compared with 29.4% of those who received placebo (P <.0001), with continued improvement seen through 24 weeks. “There are really strong results with EASI scores; clearly this medicine works compared to the placebo,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It’s also improving other biomarkers as well, including eosinophils, IL-13, TARC [serum thymus and activation-regulated chemokine], and IL-22.”
138559 (Temtokibart). Under development by LEO, 138559 is the first biologic to show the efficacy and safety of an IL-22RA1 targeting antibody for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD. In a phase 2a study abstract presented at the 2023 EADV meeting, the mean change in EASI from baseline to Week 16 was significantly greater for patients in the 138559-treated group compared with those in the placebo group (–15.3 vs. –3.5; P = .003). In addition, at week 16, significantly greater proportions of patients in the 138559 group relative to those in the placebo group achieved an EASI75 score (41.6% vs. 13.7%; P = .011) and an EASI-90 score (30.8% vs. 3.5%; P = .003). “With this particular receptor you’re not only blocking IL-22, but you’re blocking IL-20 and IL-24 as well,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It really may be that it’s IL-20 and IL-24 that are more responsible for the pathogenic effect.”
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he is speaker for and/or a consultant and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies, including Galderma and Sanofi.
In the opinion of David Rosmarin, MD, the approval of dupilumab in 2017 for the treatment of moderate to severe, resistant atopic dermatitis (AD) marked an inflection point in dermatology.
“Dupilumab has revolutionized AD, and the [interleukin] IL-4 receptor target isn’t going away,” Dr. Rosmarin, who chairs the department of dermatology at Indiana University, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference. “It’s truly an exciting time because we have a lot of different treatments in the pipeline that target IL-4 and other receptors.”
which is being developed by Keymed Biosciences, inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. In a phase 3 randomized study of patients with moderate to severe AD, presented as an abstract at the 2023 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting, it showed results similar to those of dupilumab. Specifically, at week 16, Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI)-75 scores were achieved in 66.9% of patients in the CM310 group and 25.8% of patients in the placebo group, while the proportion of patients achieving an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) with a reduction of greater than or equal to 2 points from baseline was 44.2% in the CM310 group, compared with 16.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both associations). According to Dr. Rosmarin, other novel anti-IL-4 receptor antibodies for AD include AK120, which is being developed by Akeso Biopharma, and CBP-201 (rademikibart), which is being developed by Connect Biopharma.
Eblasakimab. Under development by ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, this biologic is a potential first-in-class, monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-13Ralpha1 with high affinity and blocks the signaling of IL-4 and IL-13 through the type-2 receptor. In the TREK-AD monotherapy phase 2b trial in patients with moderate to severe AD, presented as an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, the primary endpoint of EASI percent change from baseline to week 16, was met for eblasakimab doses 600 mg Q4W, 300mg Q2W, and 400mg Q2W vs. placebo (73.0% [P = .001], 69.8% [P = .005], and 65.8% [P = .029] vs. 51.1%), respectively.
Nemolizumab. Under development by Galderma, nemolizumab is a first-in-class IL-31 receptor alpha antagonist. “Many people refer to IL-31 as the itch cytokine,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “That’s probably a little oversimplified, but it’s certainly a powerful medication in development for prurigo nodularis as well as AD.”
Results from the ARCADIA 1 and 2 trials, which included the concurrent use of topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors and were presented as an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, showed that nemolizumab significantly improved skin lesions and itch in adolescent and adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, compared with placebo. Specifically, 35.6% and 37.7% of nemolizumab-treated patients in ARCADIA 1 and 2, respectively, reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions when assessed using the IGA score, compared with 24.6% and 26.0% in the placebo group (P < .0006, P = .001). In addition, 43.5% and 42.1% of nemolizumab-treated patients in ARCADIA 1 and 2, respectively, achieved a 75% reduction in the EASI, compared with 29.0% and 30.2% in the placebo group (P < .0001, P = .0011). “There are similar results regardless of the degree of itch patients are starting out with at baseline,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It’s a very rapid response, by week 4, and that continues to improve through week 16.”
Amlitelimab. Under development by Sanofi, this monoclonal antibody binds to OX40-Ligand, and is designed for patients with moderate to severe AD. According to results of a phase 2b trial that were presented in an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, patients treated with amlitelimab 250 mg Q4W with a 500 mg loading dose showed a 61.5% improvement in the average EASI score from baseline at week 16, compared with 29.4% of those who received placebo (P <.0001), with continued improvement seen through 24 weeks. “There are really strong results with EASI scores; clearly this medicine works compared to the placebo,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It’s also improving other biomarkers as well, including eosinophils, IL-13, TARC [serum thymus and activation-regulated chemokine], and IL-22.”
138559 (Temtokibart). Under development by LEO, 138559 is the first biologic to show the efficacy and safety of an IL-22RA1 targeting antibody for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD. In a phase 2a study abstract presented at the 2023 EADV meeting, the mean change in EASI from baseline to Week 16 was significantly greater for patients in the 138559-treated group compared with those in the placebo group (–15.3 vs. –3.5; P = .003). In addition, at week 16, significantly greater proportions of patients in the 138559 group relative to those in the placebo group achieved an EASI75 score (41.6% vs. 13.7%; P = .011) and an EASI-90 score (30.8% vs. 3.5%; P = .003). “With this particular receptor you’re not only blocking IL-22, but you’re blocking IL-20 and IL-24 as well,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It really may be that it’s IL-20 and IL-24 that are more responsible for the pathogenic effect.”
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he is speaker for and/or a consultant and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies, including Galderma and Sanofi.
In the opinion of David Rosmarin, MD, the approval of dupilumab in 2017 for the treatment of moderate to severe, resistant atopic dermatitis (AD) marked an inflection point in dermatology.
“Dupilumab has revolutionized AD, and the [interleukin] IL-4 receptor target isn’t going away,” Dr. Rosmarin, who chairs the department of dermatology at Indiana University, said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis (RAD) Virtual Conference. “It’s truly an exciting time because we have a lot of different treatments in the pipeline that target IL-4 and other receptors.”
which is being developed by Keymed Biosciences, inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. In a phase 3 randomized study of patients with moderate to severe AD, presented as an abstract at the 2023 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting, it showed results similar to those of dupilumab. Specifically, at week 16, Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI)-75 scores were achieved in 66.9% of patients in the CM310 group and 25.8% of patients in the placebo group, while the proportion of patients achieving an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear) with a reduction of greater than or equal to 2 points from baseline was 44.2% in the CM310 group, compared with 16.1% in the placebo group (P < .0001 for both associations). According to Dr. Rosmarin, other novel anti-IL-4 receptor antibodies for AD include AK120, which is being developed by Akeso Biopharma, and CBP-201 (rademikibart), which is being developed by Connect Biopharma.
Eblasakimab. Under development by ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, this biologic is a potential first-in-class, monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-13Ralpha1 with high affinity and blocks the signaling of IL-4 and IL-13 through the type-2 receptor. In the TREK-AD monotherapy phase 2b trial in patients with moderate to severe AD, presented as an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, the primary endpoint of EASI percent change from baseline to week 16, was met for eblasakimab doses 600 mg Q4W, 300mg Q2W, and 400mg Q2W vs. placebo (73.0% [P = .001], 69.8% [P = .005], and 65.8% [P = .029] vs. 51.1%), respectively.
Nemolizumab. Under development by Galderma, nemolizumab is a first-in-class IL-31 receptor alpha antagonist. “Many people refer to IL-31 as the itch cytokine,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “That’s probably a little oversimplified, but it’s certainly a powerful medication in development for prurigo nodularis as well as AD.”
Results from the ARCADIA 1 and 2 trials, which included the concurrent use of topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors and were presented as an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, showed that nemolizumab significantly improved skin lesions and itch in adolescent and adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, compared with placebo. Specifically, 35.6% and 37.7% of nemolizumab-treated patients in ARCADIA 1 and 2, respectively, reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions when assessed using the IGA score, compared with 24.6% and 26.0% in the placebo group (P < .0006, P = .001). In addition, 43.5% and 42.1% of nemolizumab-treated patients in ARCADIA 1 and 2, respectively, achieved a 75% reduction in the EASI, compared with 29.0% and 30.2% in the placebo group (P < .0001, P = .0011). “There are similar results regardless of the degree of itch patients are starting out with at baseline,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It’s a very rapid response, by week 4, and that continues to improve through week 16.”
Amlitelimab. Under development by Sanofi, this monoclonal antibody binds to OX40-Ligand, and is designed for patients with moderate to severe AD. According to results of a phase 2b trial that were presented in an abstract at the 2023 EADV meeting, patients treated with amlitelimab 250 mg Q4W with a 500 mg loading dose showed a 61.5% improvement in the average EASI score from baseline at week 16, compared with 29.4% of those who received placebo (P <.0001), with continued improvement seen through 24 weeks. “There are really strong results with EASI scores; clearly this medicine works compared to the placebo,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It’s also improving other biomarkers as well, including eosinophils, IL-13, TARC [serum thymus and activation-regulated chemokine], and IL-22.”
138559 (Temtokibart). Under development by LEO, 138559 is the first biologic to show the efficacy and safety of an IL-22RA1 targeting antibody for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD. In a phase 2a study abstract presented at the 2023 EADV meeting, the mean change in EASI from baseline to Week 16 was significantly greater for patients in the 138559-treated group compared with those in the placebo group (–15.3 vs. –3.5; P = .003). In addition, at week 16, significantly greater proportions of patients in the 138559 group relative to those in the placebo group achieved an EASI75 score (41.6% vs. 13.7%; P = .011) and an EASI-90 score (30.8% vs. 3.5%; P = .003). “With this particular receptor you’re not only blocking IL-22, but you’re blocking IL-20 and IL-24 as well,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “It really may be that it’s IL-20 and IL-24 that are more responsible for the pathogenic effect.”
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he is speaker for and/or a consultant and advisory board member to many pharmaceutical companies, including Galderma and Sanofi.
FROM RAD 2023
Botanical Briefs: Contact Dermatitis Induced by Western Poison Ivy (Toxicodendron rydbergii)
Clinical Importance
Western poison ivy (Toxicodendron rydbergii) is responsible for many of the cases of Toxicodendron contact dermatitis (TCD) reported in the western and northern United States. Toxicodendron plants cause more cases of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) in North America than any other allergen1; 9 million Americans present to physician offices and 1.6 million present to emergency departments annually for ACD, emphasizing the notable medical burden of this condition.2,3 Exposure to urushiol, a plant resin containing potent allergens, precipitates this form of ACD.
An estimated 50% to 75% of adults in the United States demonstrate clinical sensitivity and exhibit ACD following contact with T rydbergii.4 Campers, hikers, firefighters, and forest workers often risk increased exposure through physical contact or aerosolized allergens in smoke. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the incidence of visits to US emergency departments for TCD nearly doubled from 2002 to 2012,5 which may be explained by atmospheric CO2 levels that both promote increased growth of Toxicodendron species and augment their toxicity.6
Cutaneous Manifestations
The clinical presentation of T rydbergii contact dermatitis is similar to other allergenic members of the Toxicodendron genus. Patients sensitive to urushiol typically develop a pruritic erythematous rash within 1 to 2 days of exposure (range, 5 hours to 15 days).7 Erythematous and edematous streaks initially manifest on the extremities and often progress to bullae and oozing papulovesicles. In early disease, patients also may display black lesions on or near the rash8 (so-called black-dot dermatitis) caused by oxidized urushiol deposited on the skin—an uncommon yet classic presentation of TCD. Generally, symptoms resolve without complications and with few sequalae, though hyperpigmentation or a secondary infection can develop on or near affected areas.9,10
Taxonomy
The Toxicodendron genus belongs to the Anacardiaceae family, which includes pistachios, mangos, and cashews, and causes more cases of ACD than every other plant combined.4 (Shelled pistachios and cashews do not possess cross-reacting allergens and should not worry consumers; mango skin does contain urushiol.)
Toxicodendron (formerly part of the Rhus genus) includes several species of poison oak, poison ivy, and poison sumac and can be found in shrubs (T rydbergii and Toxicodendron diversilobum), vines (Toxicodendron radicans and Toxicodendron pubescens), and trees (Toxicodendron vernix). In addition, Toxicodendron taxa can hybridize with other taxa in close geographic proximity to form morphologic intermediates. Some individual plants have features of multiple species.11
Etymology
The common name of T rydbergii—western poison ivy—misleads the public; the plant contains no poison that can cause death and does not grow as ivy by wrapping around trees, as T radicans and English ivy (Hedera helix) do. Its formal genus, Toxicodendron, means “poison tree” in Greek and was given its generic name by the English botanist Phillip Miller in 1768,12 which caused the renaming of Rhus rydbergii as T rydbergii. The species name honors Per Axel Rydberg, a 19th and 20th century Swedish-American botanist.
Distribution
Toxicodendron rydbergii grows in California and other states in the western half of the United States as well as the states bordering Canada and Mexico. In Canada, it reigns as the most dominant form of poison ivy.13 Hikers and campers find T rydbergii in a variety of areas, including roadsides, river bottoms, sandy shores, talus slopes, precipices, and floodplains.11 This taxon grows under a variety of conditions and in distinct regions, and it thrives in both full sun or shade.
Identifying Features
Toxicodendron rydbergii turns red earlier than most plants; early red summer leaves should serve as a warning sign to hikers from a distance (Figure 1). It displays trifoliate ovate leaves (ie, each leaf contains 3 leaflets) on a dwarf nonclimbing shrub (Figure 2). Although the plant shares common features with its cousin T radicans (eastern poison ivy), T rydbergii is easily distinguished by its thicker stems, absence of aerial rootlets (abundant in T radicans), and short (approximately 1 meter) height.4
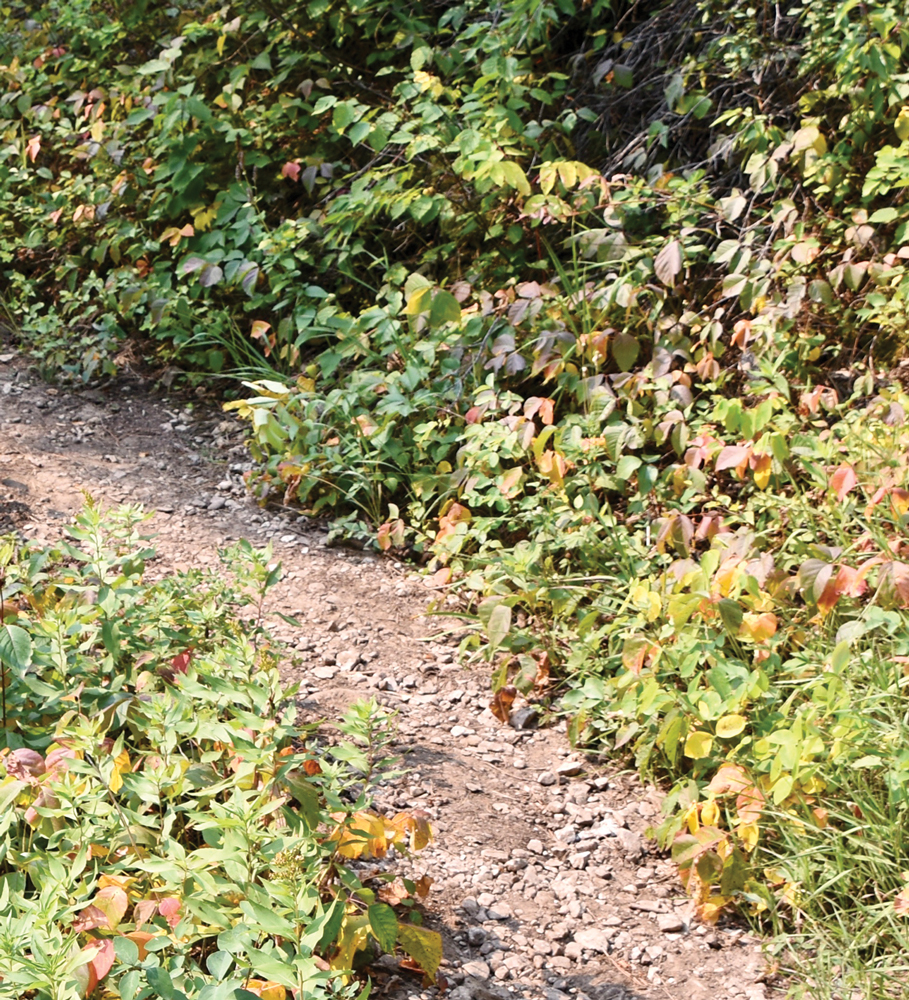

Curly hairs occupy the underside of T rydbergii leaflets and along the midrib; leaflet margins appear lobed or rounded. Lenticels appear as small holes in the bark that turn gray in the cold and become brighter come spring.13
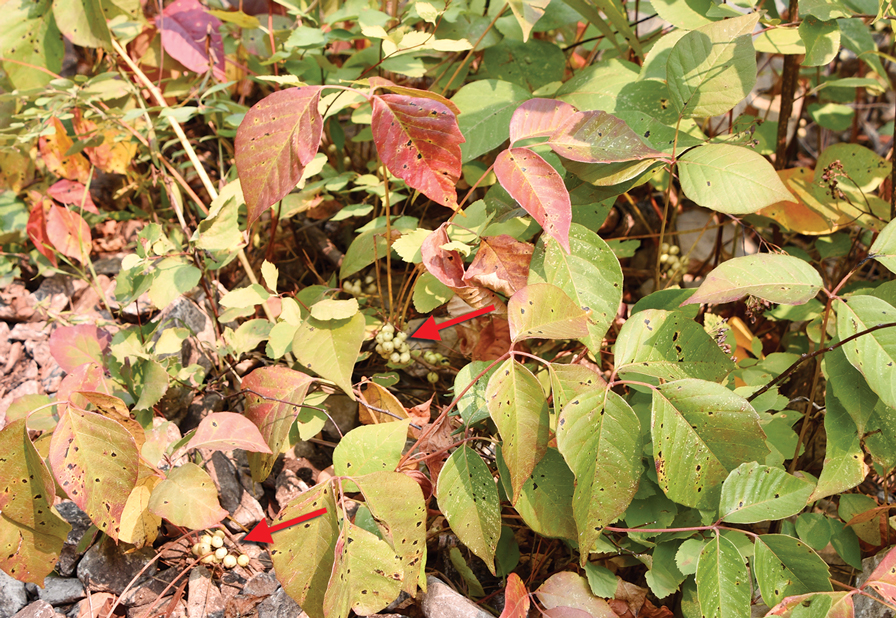

The plant bears glabrous long petioles (leaf stems) and densely grouped clusters of yellow flowers. In autumn, the globose fruit—formed in clusters between each twig and leaf petiole (known as an axillary position)—change from yellow-green to tan (Figure 3). When urushiol exudes from damaged leaflets or other plant parts, it oxidizes on exposure to air and creates hardened black deposits on the plant. Even when grown in garden pots, T rydbergii maintains its distinguishing features.11
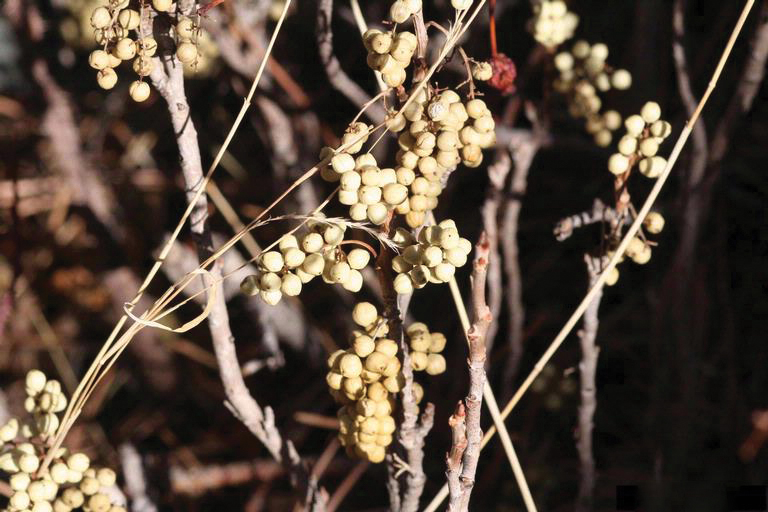

Dermatitis-Inducing Plant Parts
All parts of T rydbergii including leaves, stems, roots, and fruit contain the allergenic sap throughout the year.14 A person must damage or bruise the plant for urushiol to be released and produce its allergenic effects; softly brushing against undamaged plants typically does not induce dermatitis.4
Pathophysiology of Urushiol
Urushiol, a pale yellow, oily mixture of organic compounds conserved throughout all Toxicodendron species, contains highly allergenic alkyl catechols. These catechols possess hydroxyl groups at positions 1 and 2 on a benzene ring; the hydrocarbon side chain of poison ivies (typically 15–carbon atoms long) attaches at position 3.15 The catechols and the aliphatic side chain contribute to the plant’s antigenic and dermatitis-inducing properties.16
The high lipophilicity of urushiol allows for rapid and unforgiving absorption into the skin, notwithstanding attempts to wash it off. Upon direct contact, catechols of urushiol penetrate the epidermis and become oxidized to quinone intermediates that bind to antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and dermis. Epidermal Langerhans cells and dermal macrophages internalize and present the antigen to CD4+ T cells in nearby lymph nodes. This sequence results in production of inflammatory mediators, clonal expansion of T-effector and T-memory cells specific to the allergenic catechols, and an ensuing cytotoxic response against epidermal cells and the dermal vasculature. Keratinocytes and monocytes mediate the inflammatory response by releasing other cytokines.4,17
Sensitization to urushiol generally occurs at 8 to 14 years of age; therefore, infants have lower susceptibility to dermatitis upon contact with T rydbergii.18 Most animals do not experience sensitization upon contact; in fact, birds and forest animals consume the urushiol-rich fruit of T rydbergii without harm.3
Prevention and Treatment
Toxicodendron dermatitis typically lasts 1 to 3 weeks but can remain for as long as 6 weeks without treatment.19 Recognition and physical avoidance of the plant provides the most promising preventive strategy. Immediate rinsing with soap and water can prevent TCD by breaking down urushiol and its allergenic components; however, this is an option for only a short time, as the skin absorbs 50% of urushiol within 10 minutes after contact.20 Nevertheless, patients must seize the earliest opportunity to wash off the affected area and remove any residual urushiol. Patients must be cautious when removing and washing clothing to prevent further contact.
Most health care providers treat TCD with a corticosteroid to reduce inflammation and intense pruritus. A high-potency topical corticosteroid (eg, clobetasol) may prove effective in providing early therapeutic relief in mild disease.21 A short course of a systemic steroid quickly and effectively quenches intense itching and should not be limited to what the clinician considers severe disease. Do not underestimate the patient’s symptoms with this eruption.
Prednisone dosing begins at 1 mg/kg daily and is then tapered slowly over 2 weeks (no shorter a time) for an optimal treatment course of 15 days.22 Prescribing an inadequate dosage and course of a corticosteroid leaves the patient susceptible to rebound dermatitis—and loss of trust in their provider.
Intramuscular injection of the long-acting corticosteroid triamcinolone acetonide with rapid-onset betamethasone provides rapid relief and fewer adverse effects than an oral corticosteroid.22 Despite the long-standing use of sedating oral antihistamines by clinicians, these drugs provide no benefit for pruritus or sleep because the histamine does not cause the itching of TCD, and antihistamines disrupt normal sleep architecture.23-25
Patients can consider several over-the-counter products that have varying degrees of efficacy.4,26 The few products for which prospective studies support their use include Tecnu (Tec Laboraties Inc), Zanfel (RhusTox), and the well-known soaps Dial (Henkel Corporation) and Goop (Critzas Industries, Inc).27,28
Aside from treating the direct effects of TCD, clinicians also must take note of any look for signs of secondary infection and occasionally should consider supplementing treatment with an antibiotic.
- Lofgran T, Mahabal GD. Toxicodendron toxicity. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated May 16, 2023. Accessed December 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557866/
- The Lewin Group. The Burden of Skin Diseases 2005. Society for Investigative Dermatology and American Academy of Dermatology Association; 2005:37-40. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.lewin.com/content/dam/Lewin/Resources/Site_Sections/Publications/april2005skindisease.pdf
- Monroe J. Toxicodendron contact dermatitis: a case report and brief review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13(9 Suppl 1):S29-S34.
- Gladman AC. Toxicodendron dermatitis: poison ivy, oak, and sumac. Wilderness Environ Med. 2006;17:120-128. doi:10.1580/pr31-05.1
- Fretwell S. Poison ivy cases on the rise. The State. Updated May 15,2017. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.thestate.com/news/local/article150403932.html
- Mohan JE, Ziska LH, Schlesinger WH, et al. Biomass and toxicity responses of poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans) to elevated atmospheric CO2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:9086-9089. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602392103
- Williams JV, Light J, Marks JG Jr. Individual variations in allergic contact dermatitis from urushiol. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:1002-1003. doi:10.1001/archderm.135.8.1002
- Kurlan JG, Lucky AW. Black spot poison ivy: a report of 5 cases and a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:246-249. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114295
- Fisher AA. Poison ivy/oak/sumac. part II: specific features. Cutis. 1996;58:22-24.
- Brook I, Frazier EH, Yeager JK. Microbiology of infected poison ivy dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:943-946. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03475.x
- Gillis WT. The systematics and ecology of poison-ivy and the poison-oaks (Toxicodendron, Anacardiaceae). Rhodora. 1971;73:370-443.
- Reveal JL. Typification of six Philip Miller names of temperate North American Toxicodendron (Anacardiaceae) with proposals (999-1000) to reject T. crenatum and T. volubile. TAXON. 1991;40:333-335. doi:10.2307/1222994
- Guin JD, Gillis WT, Beaman JH. Recognizing the Toxicodendrons (poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;4:99-114. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(81)70014-8
- Lee NP, Arriola ER. Poison ivy, oak, and sumac dermatitis. West J Med. 1999;171:354-355.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA, eds. Contact and Occupational Dermatology. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd; 2016.
- Dawson CR. The chemistry of poison ivy. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1956;18:427-443. doi:10.1111/j.2164-0947.1956.tb00465.x
- Kalish RS. Recent developments in the pathogenesis of allergic contact dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1558-1563.
- Fisher AA, Mitchell J. Toxicodendron plants and spices. In: Rietschel RL, Fowler JF Jr. Fisher’s Contact Dermatitis. 4th ed. Williams & Wilkins; 1995:461-523.
- Labib A, Yosipovitch G. Itchy Toxicodendron plant dermatitis. Allergies. 2022;2:16-22. doi:10.3390/allergies2010002
- Fisher AA. Poison ivy/oak dermatitis part I: prevention—soap and water, topical barriers, hyposensitization. Cutis. 1996;57:384-386.
- Kim Y, Flamm A, ElSohly MA, et al. Poison ivy, oak, and sumac dermatitis: what is known and what is new? 2019;30:183-190. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000472
- Prok L, McGovern T. Poison ivy (Toxicodendron) dermatitis. UpToDate. Updated October 16, 2023. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/poison-ivy-toxicodendron-dermatitis
- Klein PA, Clark RA. An evidence-based review of the efficacy of antihistamines in relieving pruritus in atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:1522-1525. doi:10.1001/archderm.135.12.1522
- He A, Feldman SR, Fleischer AB Jr. An assessment of the use of antihistamines in the management of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:92-96. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.077
- van Zuuren EJ, Apfelbacher CJ, Fedorowicz Z, et al. No high level evidence to support the use of oral H1 antihistamines as monotherapy for eczema: a summary of a Cochrane systematic review. Syst Rev. 2014;3:25. doi:10.1186/2046-4053-3-25
- Neill BC, Neill JA, Brauker J, et al. Postexposure prevention of Toxicodendron dermatitis by early forceful unidirectional washing with liquid dishwashing soap. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:E25. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.081
- Stibich AS, Yagan M, Sharma V, et al. Cost-effective post-exposure prevention of poison ivy dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:515-518. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00003.x
- Davila A, Laurora M, Fulton J, et al. A new topical agent, Zanfel, ameliorates urushiol-induced Toxicodendron allergic contact dermatitis [abstract]. Ann Emerg Med. 2003;42:S98.
Clinical Importance
Western poison ivy (Toxicodendron rydbergii) is responsible for many of the cases of Toxicodendron contact dermatitis (TCD) reported in the western and northern United States. Toxicodendron plants cause more cases of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) in North America than any other allergen1; 9 million Americans present to physician offices and 1.6 million present to emergency departments annually for ACD, emphasizing the notable medical burden of this condition.2,3 Exposure to urushiol, a plant resin containing potent allergens, precipitates this form of ACD.
An estimated 50% to 75% of adults in the United States demonstrate clinical sensitivity and exhibit ACD following contact with T rydbergii.4 Campers, hikers, firefighters, and forest workers often risk increased exposure through physical contact or aerosolized allergens in smoke. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the incidence of visits to US emergency departments for TCD nearly doubled from 2002 to 2012,5 which may be explained by atmospheric CO2 levels that both promote increased growth of Toxicodendron species and augment their toxicity.6
Cutaneous Manifestations
The clinical presentation of T rydbergii contact dermatitis is similar to other allergenic members of the Toxicodendron genus. Patients sensitive to urushiol typically develop a pruritic erythematous rash within 1 to 2 days of exposure (range, 5 hours to 15 days).7 Erythematous and edematous streaks initially manifest on the extremities and often progress to bullae and oozing papulovesicles. In early disease, patients also may display black lesions on or near the rash8 (so-called black-dot dermatitis) caused by oxidized urushiol deposited on the skin—an uncommon yet classic presentation of TCD. Generally, symptoms resolve without complications and with few sequalae, though hyperpigmentation or a secondary infection can develop on or near affected areas.9,10
Taxonomy
The Toxicodendron genus belongs to the Anacardiaceae family, which includes pistachios, mangos, and cashews, and causes more cases of ACD than every other plant combined.4 (Shelled pistachios and cashews do not possess cross-reacting allergens and should not worry consumers; mango skin does contain urushiol.)
Toxicodendron (formerly part of the Rhus genus) includes several species of poison oak, poison ivy, and poison sumac and can be found in shrubs (T rydbergii and Toxicodendron diversilobum), vines (Toxicodendron radicans and Toxicodendron pubescens), and trees (Toxicodendron vernix). In addition, Toxicodendron taxa can hybridize with other taxa in close geographic proximity to form morphologic intermediates. Some individual plants have features of multiple species.11
Etymology
The common name of T rydbergii—western poison ivy—misleads the public; the plant contains no poison that can cause death and does not grow as ivy by wrapping around trees, as T radicans and English ivy (Hedera helix) do. Its formal genus, Toxicodendron, means “poison tree” in Greek and was given its generic name by the English botanist Phillip Miller in 1768,12 which caused the renaming of Rhus rydbergii as T rydbergii. The species name honors Per Axel Rydberg, a 19th and 20th century Swedish-American botanist.
Distribution
Toxicodendron rydbergii grows in California and other states in the western half of the United States as well as the states bordering Canada and Mexico. In Canada, it reigns as the most dominant form of poison ivy.13 Hikers and campers find T rydbergii in a variety of areas, including roadsides, river bottoms, sandy shores, talus slopes, precipices, and floodplains.11 This taxon grows under a variety of conditions and in distinct regions, and it thrives in both full sun or shade.
Identifying Features
Toxicodendron rydbergii turns red earlier than most plants; early red summer leaves should serve as a warning sign to hikers from a distance (Figure 1). It displays trifoliate ovate leaves (ie, each leaf contains 3 leaflets) on a dwarf nonclimbing shrub (Figure 2). Although the plant shares common features with its cousin T radicans (eastern poison ivy), T rydbergii is easily distinguished by its thicker stems, absence of aerial rootlets (abundant in T radicans), and short (approximately 1 meter) height.4

Curly hairs occupy the underside of T rydbergii leaflets and along the midrib; leaflet margins appear lobed or rounded. Lenticels appear as small holes in the bark that turn gray in the cold and become brighter come spring.13

The plant bears glabrous long petioles (leaf stems) and densely grouped clusters of yellow flowers. In autumn, the globose fruit—formed in clusters between each twig and leaf petiole (known as an axillary position)—change from yellow-green to tan (Figure 3). When urushiol exudes from damaged leaflets or other plant parts, it oxidizes on exposure to air and creates hardened black deposits on the plant. Even when grown in garden pots, T rydbergii maintains its distinguishing features.11

Dermatitis-Inducing Plant Parts
All parts of T rydbergii including leaves, stems, roots, and fruit contain the allergenic sap throughout the year.14 A person must damage or bruise the plant for urushiol to be released and produce its allergenic effects; softly brushing against undamaged plants typically does not induce dermatitis.4
Pathophysiology of Urushiol
Urushiol, a pale yellow, oily mixture of organic compounds conserved throughout all Toxicodendron species, contains highly allergenic alkyl catechols. These catechols possess hydroxyl groups at positions 1 and 2 on a benzene ring; the hydrocarbon side chain of poison ivies (typically 15–carbon atoms long) attaches at position 3.15 The catechols and the aliphatic side chain contribute to the plant’s antigenic and dermatitis-inducing properties.16
The high lipophilicity of urushiol allows for rapid and unforgiving absorption into the skin, notwithstanding attempts to wash it off. Upon direct contact, catechols of urushiol penetrate the epidermis and become oxidized to quinone intermediates that bind to antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and dermis. Epidermal Langerhans cells and dermal macrophages internalize and present the antigen to CD4+ T cells in nearby lymph nodes. This sequence results in production of inflammatory mediators, clonal expansion of T-effector and T-memory cells specific to the allergenic catechols, and an ensuing cytotoxic response against epidermal cells and the dermal vasculature. Keratinocytes and monocytes mediate the inflammatory response by releasing other cytokines.4,17
Sensitization to urushiol generally occurs at 8 to 14 years of age; therefore, infants have lower susceptibility to dermatitis upon contact with T rydbergii.18 Most animals do not experience sensitization upon contact; in fact, birds and forest animals consume the urushiol-rich fruit of T rydbergii without harm.3
Prevention and Treatment
Toxicodendron dermatitis typically lasts 1 to 3 weeks but can remain for as long as 6 weeks without treatment.19 Recognition and physical avoidance of the plant provides the most promising preventive strategy. Immediate rinsing with soap and water can prevent TCD by breaking down urushiol and its allergenic components; however, this is an option for only a short time, as the skin absorbs 50% of urushiol within 10 minutes after contact.20 Nevertheless, patients must seize the earliest opportunity to wash off the affected area and remove any residual urushiol. Patients must be cautious when removing and washing clothing to prevent further contact.
Most health care providers treat TCD with a corticosteroid to reduce inflammation and intense pruritus. A high-potency topical corticosteroid (eg, clobetasol) may prove effective in providing early therapeutic relief in mild disease.21 A short course of a systemic steroid quickly and effectively quenches intense itching and should not be limited to what the clinician considers severe disease. Do not underestimate the patient’s symptoms with this eruption.
Prednisone dosing begins at 1 mg/kg daily and is then tapered slowly over 2 weeks (no shorter a time) for an optimal treatment course of 15 days.22 Prescribing an inadequate dosage and course of a corticosteroid leaves the patient susceptible to rebound dermatitis—and loss of trust in their provider.
Intramuscular injection of the long-acting corticosteroid triamcinolone acetonide with rapid-onset betamethasone provides rapid relief and fewer adverse effects than an oral corticosteroid.22 Despite the long-standing use of sedating oral antihistamines by clinicians, these drugs provide no benefit for pruritus or sleep because the histamine does not cause the itching of TCD, and antihistamines disrupt normal sleep architecture.23-25
Patients can consider several over-the-counter products that have varying degrees of efficacy.4,26 The few products for which prospective studies support their use include Tecnu (Tec Laboraties Inc), Zanfel (RhusTox), and the well-known soaps Dial (Henkel Corporation) and Goop (Critzas Industries, Inc).27,28
Aside from treating the direct effects of TCD, clinicians also must take note of any look for signs of secondary infection and occasionally should consider supplementing treatment with an antibiotic.
Clinical Importance
Western poison ivy (Toxicodendron rydbergii) is responsible for many of the cases of Toxicodendron contact dermatitis (TCD) reported in the western and northern United States. Toxicodendron plants cause more cases of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) in North America than any other allergen1; 9 million Americans present to physician offices and 1.6 million present to emergency departments annually for ACD, emphasizing the notable medical burden of this condition.2,3 Exposure to urushiol, a plant resin containing potent allergens, precipitates this form of ACD.
An estimated 50% to 75% of adults in the United States demonstrate clinical sensitivity and exhibit ACD following contact with T rydbergii.4 Campers, hikers, firefighters, and forest workers often risk increased exposure through physical contact or aerosolized allergens in smoke. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the incidence of visits to US emergency departments for TCD nearly doubled from 2002 to 2012,5 which may be explained by atmospheric CO2 levels that both promote increased growth of Toxicodendron species and augment their toxicity.6
Cutaneous Manifestations
The clinical presentation of T rydbergii contact dermatitis is similar to other allergenic members of the Toxicodendron genus. Patients sensitive to urushiol typically develop a pruritic erythematous rash within 1 to 2 days of exposure (range, 5 hours to 15 days).7 Erythematous and edematous streaks initially manifest on the extremities and often progress to bullae and oozing papulovesicles. In early disease, patients also may display black lesions on or near the rash8 (so-called black-dot dermatitis) caused by oxidized urushiol deposited on the skin—an uncommon yet classic presentation of TCD. Generally, symptoms resolve without complications and with few sequalae, though hyperpigmentation or a secondary infection can develop on or near affected areas.9,10
Taxonomy
The Toxicodendron genus belongs to the Anacardiaceae family, which includes pistachios, mangos, and cashews, and causes more cases of ACD than every other plant combined.4 (Shelled pistachios and cashews do not possess cross-reacting allergens and should not worry consumers; mango skin does contain urushiol.)
Toxicodendron (formerly part of the Rhus genus) includes several species of poison oak, poison ivy, and poison sumac and can be found in shrubs (T rydbergii and Toxicodendron diversilobum), vines (Toxicodendron radicans and Toxicodendron pubescens), and trees (Toxicodendron vernix). In addition, Toxicodendron taxa can hybridize with other taxa in close geographic proximity to form morphologic intermediates. Some individual plants have features of multiple species.11
Etymology
The common name of T rydbergii—western poison ivy—misleads the public; the plant contains no poison that can cause death and does not grow as ivy by wrapping around trees, as T radicans and English ivy (Hedera helix) do. Its formal genus, Toxicodendron, means “poison tree” in Greek and was given its generic name by the English botanist Phillip Miller in 1768,12 which caused the renaming of Rhus rydbergii as T rydbergii. The species name honors Per Axel Rydberg, a 19th and 20th century Swedish-American botanist.
Distribution
Toxicodendron rydbergii grows in California and other states in the western half of the United States as well as the states bordering Canada and Mexico. In Canada, it reigns as the most dominant form of poison ivy.13 Hikers and campers find T rydbergii in a variety of areas, including roadsides, river bottoms, sandy shores, talus slopes, precipices, and floodplains.11 This taxon grows under a variety of conditions and in distinct regions, and it thrives in both full sun or shade.
Identifying Features
Toxicodendron rydbergii turns red earlier than most plants; early red summer leaves should serve as a warning sign to hikers from a distance (Figure 1). It displays trifoliate ovate leaves (ie, each leaf contains 3 leaflets) on a dwarf nonclimbing shrub (Figure 2). Although the plant shares common features with its cousin T radicans (eastern poison ivy), T rydbergii is easily distinguished by its thicker stems, absence of aerial rootlets (abundant in T radicans), and short (approximately 1 meter) height.4

Curly hairs occupy the underside of T rydbergii leaflets and along the midrib; leaflet margins appear lobed or rounded. Lenticels appear as small holes in the bark that turn gray in the cold and become brighter come spring.13

The plant bears glabrous long petioles (leaf stems) and densely grouped clusters of yellow flowers. In autumn, the globose fruit—formed in clusters between each twig and leaf petiole (known as an axillary position)—change from yellow-green to tan (Figure 3). When urushiol exudes from damaged leaflets or other plant parts, it oxidizes on exposure to air and creates hardened black deposits on the plant. Even when grown in garden pots, T rydbergii maintains its distinguishing features.11

Dermatitis-Inducing Plant Parts
All parts of T rydbergii including leaves, stems, roots, and fruit contain the allergenic sap throughout the year.14 A person must damage or bruise the plant for urushiol to be released and produce its allergenic effects; softly brushing against undamaged plants typically does not induce dermatitis.4
Pathophysiology of Urushiol
Urushiol, a pale yellow, oily mixture of organic compounds conserved throughout all Toxicodendron species, contains highly allergenic alkyl catechols. These catechols possess hydroxyl groups at positions 1 and 2 on a benzene ring; the hydrocarbon side chain of poison ivies (typically 15–carbon atoms long) attaches at position 3.15 The catechols and the aliphatic side chain contribute to the plant’s antigenic and dermatitis-inducing properties.16
The high lipophilicity of urushiol allows for rapid and unforgiving absorption into the skin, notwithstanding attempts to wash it off. Upon direct contact, catechols of urushiol penetrate the epidermis and become oxidized to quinone intermediates that bind to antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis and dermis. Epidermal Langerhans cells and dermal macrophages internalize and present the antigen to CD4+ T cells in nearby lymph nodes. This sequence results in production of inflammatory mediators, clonal expansion of T-effector and T-memory cells specific to the allergenic catechols, and an ensuing cytotoxic response against epidermal cells and the dermal vasculature. Keratinocytes and monocytes mediate the inflammatory response by releasing other cytokines.4,17
Sensitization to urushiol generally occurs at 8 to 14 years of age; therefore, infants have lower susceptibility to dermatitis upon contact with T rydbergii.18 Most animals do not experience sensitization upon contact; in fact, birds and forest animals consume the urushiol-rich fruit of T rydbergii without harm.3
Prevention and Treatment
Toxicodendron dermatitis typically lasts 1 to 3 weeks but can remain for as long as 6 weeks without treatment.19 Recognition and physical avoidance of the plant provides the most promising preventive strategy. Immediate rinsing with soap and water can prevent TCD by breaking down urushiol and its allergenic components; however, this is an option for only a short time, as the skin absorbs 50% of urushiol within 10 minutes after contact.20 Nevertheless, patients must seize the earliest opportunity to wash off the affected area and remove any residual urushiol. Patients must be cautious when removing and washing clothing to prevent further contact.
Most health care providers treat TCD with a corticosteroid to reduce inflammation and intense pruritus. A high-potency topical corticosteroid (eg, clobetasol) may prove effective in providing early therapeutic relief in mild disease.21 A short course of a systemic steroid quickly and effectively quenches intense itching and should not be limited to what the clinician considers severe disease. Do not underestimate the patient’s symptoms with this eruption.
Prednisone dosing begins at 1 mg/kg daily and is then tapered slowly over 2 weeks (no shorter a time) for an optimal treatment course of 15 days.22 Prescribing an inadequate dosage and course of a corticosteroid leaves the patient susceptible to rebound dermatitis—and loss of trust in their provider.
Intramuscular injection of the long-acting corticosteroid triamcinolone acetonide with rapid-onset betamethasone provides rapid relief and fewer adverse effects than an oral corticosteroid.22 Despite the long-standing use of sedating oral antihistamines by clinicians, these drugs provide no benefit for pruritus or sleep because the histamine does not cause the itching of TCD, and antihistamines disrupt normal sleep architecture.23-25
Patients can consider several over-the-counter products that have varying degrees of efficacy.4,26 The few products for which prospective studies support their use include Tecnu (Tec Laboraties Inc), Zanfel (RhusTox), and the well-known soaps Dial (Henkel Corporation) and Goop (Critzas Industries, Inc).27,28
Aside from treating the direct effects of TCD, clinicians also must take note of any look for signs of secondary infection and occasionally should consider supplementing treatment with an antibiotic.
- Lofgran T, Mahabal GD. Toxicodendron toxicity. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated May 16, 2023. Accessed December 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557866/
- The Lewin Group. The Burden of Skin Diseases 2005. Society for Investigative Dermatology and American Academy of Dermatology Association; 2005:37-40. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.lewin.com/content/dam/Lewin/Resources/Site_Sections/Publications/april2005skindisease.pdf
- Monroe J. Toxicodendron contact dermatitis: a case report and brief review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13(9 Suppl 1):S29-S34.
- Gladman AC. Toxicodendron dermatitis: poison ivy, oak, and sumac. Wilderness Environ Med. 2006;17:120-128. doi:10.1580/pr31-05.1
- Fretwell S. Poison ivy cases on the rise. The State. Updated May 15,2017. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.thestate.com/news/local/article150403932.html
- Mohan JE, Ziska LH, Schlesinger WH, et al. Biomass and toxicity responses of poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans) to elevated atmospheric CO2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:9086-9089. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602392103
- Williams JV, Light J, Marks JG Jr. Individual variations in allergic contact dermatitis from urushiol. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:1002-1003. doi:10.1001/archderm.135.8.1002
- Kurlan JG, Lucky AW. Black spot poison ivy: a report of 5 cases and a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:246-249. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114295
- Fisher AA. Poison ivy/oak/sumac. part II: specific features. Cutis. 1996;58:22-24.
- Brook I, Frazier EH, Yeager JK. Microbiology of infected poison ivy dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:943-946. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03475.x
- Gillis WT. The systematics and ecology of poison-ivy and the poison-oaks (Toxicodendron, Anacardiaceae). Rhodora. 1971;73:370-443.
- Reveal JL. Typification of six Philip Miller names of temperate North American Toxicodendron (Anacardiaceae) with proposals (999-1000) to reject T. crenatum and T. volubile. TAXON. 1991;40:333-335. doi:10.2307/1222994
- Guin JD, Gillis WT, Beaman JH. Recognizing the Toxicodendrons (poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;4:99-114. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(81)70014-8
- Lee NP, Arriola ER. Poison ivy, oak, and sumac dermatitis. West J Med. 1999;171:354-355.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA, eds. Contact and Occupational Dermatology. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd; 2016.
- Dawson CR. The chemistry of poison ivy. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1956;18:427-443. doi:10.1111/j.2164-0947.1956.tb00465.x
- Kalish RS. Recent developments in the pathogenesis of allergic contact dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1558-1563.
- Fisher AA, Mitchell J. Toxicodendron plants and spices. In: Rietschel RL, Fowler JF Jr. Fisher’s Contact Dermatitis. 4th ed. Williams & Wilkins; 1995:461-523.
- Labib A, Yosipovitch G. Itchy Toxicodendron plant dermatitis. Allergies. 2022;2:16-22. doi:10.3390/allergies2010002
- Fisher AA. Poison ivy/oak dermatitis part I: prevention—soap and water, topical barriers, hyposensitization. Cutis. 1996;57:384-386.
- Kim Y, Flamm A, ElSohly MA, et al. Poison ivy, oak, and sumac dermatitis: what is known and what is new? 2019;30:183-190. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000472
- Prok L, McGovern T. Poison ivy (Toxicodendron) dermatitis. UpToDate. Updated October 16, 2023. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/poison-ivy-toxicodendron-dermatitis
- Klein PA, Clark RA. An evidence-based review of the efficacy of antihistamines in relieving pruritus in atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:1522-1525. doi:10.1001/archderm.135.12.1522
- He A, Feldman SR, Fleischer AB Jr. An assessment of the use of antihistamines in the management of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:92-96. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.077
- van Zuuren EJ, Apfelbacher CJ, Fedorowicz Z, et al. No high level evidence to support the use of oral H1 antihistamines as monotherapy for eczema: a summary of a Cochrane systematic review. Syst Rev. 2014;3:25. doi:10.1186/2046-4053-3-25
- Neill BC, Neill JA, Brauker J, et al. Postexposure prevention of Toxicodendron dermatitis by early forceful unidirectional washing with liquid dishwashing soap. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:E25. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.081
- Stibich AS, Yagan M, Sharma V, et al. Cost-effective post-exposure prevention of poison ivy dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:515-518. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00003.x
- Davila A, Laurora M, Fulton J, et al. A new topical agent, Zanfel, ameliorates urushiol-induced Toxicodendron allergic contact dermatitis [abstract]. Ann Emerg Med. 2003;42:S98.
- Lofgran T, Mahabal GD. Toxicodendron toxicity. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated May 16, 2023. Accessed December 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557866/
- The Lewin Group. The Burden of Skin Diseases 2005. Society for Investigative Dermatology and American Academy of Dermatology Association; 2005:37-40. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.lewin.com/content/dam/Lewin/Resources/Site_Sections/Publications/april2005skindisease.pdf
- Monroe J. Toxicodendron contact dermatitis: a case report and brief review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13(9 Suppl 1):S29-S34.
- Gladman AC. Toxicodendron dermatitis: poison ivy, oak, and sumac. Wilderness Environ Med. 2006;17:120-128. doi:10.1580/pr31-05.1
- Fretwell S. Poison ivy cases on the rise. The State. Updated May 15,2017. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.thestate.com/news/local/article150403932.html
- Mohan JE, Ziska LH, Schlesinger WH, et al. Biomass and toxicity responses of poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans) to elevated atmospheric CO2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:9086-9089. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602392103
- Williams JV, Light J, Marks JG Jr. Individual variations in allergic contact dermatitis from urushiol. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:1002-1003. doi:10.1001/archderm.135.8.1002
- Kurlan JG, Lucky AW. Black spot poison ivy: a report of 5 cases and a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:246-249. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114295
- Fisher AA. Poison ivy/oak/sumac. part II: specific features. Cutis. 1996;58:22-24.
- Brook I, Frazier EH, Yeager JK. Microbiology of infected poison ivy dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:943-946. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03475.x
- Gillis WT. The systematics and ecology of poison-ivy and the poison-oaks (Toxicodendron, Anacardiaceae). Rhodora. 1971;73:370-443.
- Reveal JL. Typification of six Philip Miller names of temperate North American Toxicodendron (Anacardiaceae) with proposals (999-1000) to reject T. crenatum and T. volubile. TAXON. 1991;40:333-335. doi:10.2307/1222994
- Guin JD, Gillis WT, Beaman JH. Recognizing the Toxicodendrons (poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;4:99-114. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(81)70014-8
- Lee NP, Arriola ER. Poison ivy, oak, and sumac dermatitis. West J Med. 1999;171:354-355.
- Marks JG Jr, Anderson BE, DeLeo VA, eds. Contact and Occupational Dermatology. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd; 2016.
- Dawson CR. The chemistry of poison ivy. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1956;18:427-443. doi:10.1111/j.2164-0947.1956.tb00465.x
- Kalish RS. Recent developments in the pathogenesis of allergic contact dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1558-1563.
- Fisher AA, Mitchell J. Toxicodendron plants and spices. In: Rietschel RL, Fowler JF Jr. Fisher’s Contact Dermatitis. 4th ed. Williams & Wilkins; 1995:461-523.
- Labib A, Yosipovitch G. Itchy Toxicodendron plant dermatitis. Allergies. 2022;2:16-22. doi:10.3390/allergies2010002
- Fisher AA. Poison ivy/oak dermatitis part I: prevention—soap and water, topical barriers, hyposensitization. Cutis. 1996;57:384-386.
- Kim Y, Flamm A, ElSohly MA, et al. Poison ivy, oak, and sumac dermatitis: what is known and what is new? 2019;30:183-190. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000472
- Prok L, McGovern T. Poison ivy (Toxicodendron) dermatitis. UpToDate. Updated October 16, 2023. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/poison-ivy-toxicodendron-dermatitis
- Klein PA, Clark RA. An evidence-based review of the efficacy of antihistamines in relieving pruritus in atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:1522-1525. doi:10.1001/archderm.135.12.1522
- He A, Feldman SR, Fleischer AB Jr. An assessment of the use of antihistamines in the management of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:92-96. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.077
- van Zuuren EJ, Apfelbacher CJ, Fedorowicz Z, et al. No high level evidence to support the use of oral H1 antihistamines as monotherapy for eczema: a summary of a Cochrane systematic review. Syst Rev. 2014;3:25. doi:10.1186/2046-4053-3-25
- Neill BC, Neill JA, Brauker J, et al. Postexposure prevention of Toxicodendron dermatitis by early forceful unidirectional washing with liquid dishwashing soap. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:E25. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.081
- Stibich AS, Yagan M, Sharma V, et al. Cost-effective post-exposure prevention of poison ivy dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:515-518. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00003.x
- Davila A, Laurora M, Fulton J, et al. A new topical agent, Zanfel, ameliorates urushiol-induced Toxicodendron allergic contact dermatitis [abstract]. Ann Emerg Med. 2003;42:S98.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Western poison ivy (Toxicodendron rydbergii) accounts for many of the cases of Toxicodendron contact dermatitis (TCD) in the western and northern United States. Individuals in these regions should be educated on how to identify T rydbergii to avoid TCD.
- Dermatologists should include TCD in the differential diagnosis when a patient presents with an erythematous pruritic rash in a linear pattern with sharp borders.
- Most patients who experience intense itching and pain from TCD benefit greatly from prompt treatment with an oral or intramuscular corticosteroid. Topical steroids rarely provide relief; oral antihistamines provide no benefit.
US Dermatologic Drug Approvals Rose Between 2012 and 2022
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Multiple New-Onset Pyogenic Granulomas During Treatment With Paclitaxel and Ramucirumab
To the Editor:
Pyogenic granuloma (PG) is a benign vascular tumor that clinically is characterized as a small eruptive friable papule.1 Lesions typically are solitary and most commonly occur in children but also are associated with pregnancy; trauma to the skin or mucosa; and use of certain medications such as isotretinoin, capecitabine, vemurafenib, or indinavir.1 Numerous antineoplastic medications have been associated with the development of solitary PGs, including the taxane mitotic inhibitor paclitaxel (PTX) and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) monoclonal antibody ramucirumab.2 We report a case of multiple PGs in a patient undergoing treatment with PTX and ramucirumab.

A 59-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with red, itchy, bleeding skin lesions on the breast, superior chest, left cheek, and forearm of 1 month’s duration. She denied any preceding trauma to the areas. Her medical history was notable for gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma diagnosed more than 2 years prior to presentation. Her original treatment regimen included nivolumab, which was discontinued for unknown reasons 5 months prior to presentation, and she was started on combination therapy with PTX and ramucirumab at that time. She noted the formation of small red papules 2 months after the initiation of PTX-ramucirumab combination therapy, which grew larger over the course of the next month. Physical examination revealed 5 friable hemorrhagic papules and nodules ranging in size from 3 to 10 mm on the chest, cheek, and forearm consistent with PGs (Figure 1). Several scattered cherry angiomas were noted on the scalp and torso, but the patient reported these were not new. Biopsies of the PGs demonstrated lobular aggregates of small-caliber vessels set in an edematous inflamed stroma and partially enclosed by small collarettes of adnexal epithelium, confirming the clinical diagnosis of multiple PGs (Figure 2).
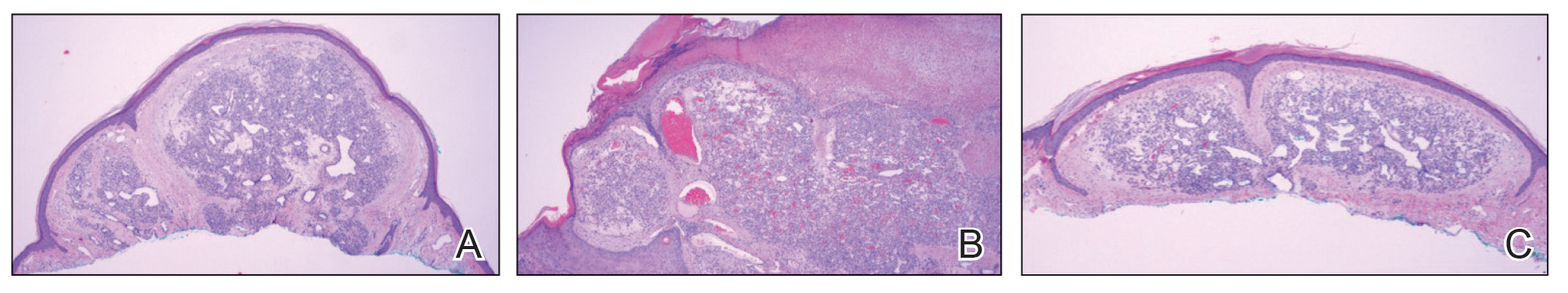
The first case of PTX-associated PG was reported in 2012.3 Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms pyogenic granuloma, lobular capillary hemangioma, paclitaxel, taxane, and ramucirumab, there have been 9 cases of solitary PG development in the setting of PTX alone or in combination with ramucirumab since 2019 (Table).3-8 Pyogenic granulomas reported in patients who were treated exclusively with PTX were subungual, while the cases resulting from combined therapy were present on the scalp, face, oral mucosa, and surfaces of the hands sparing the nails. Ibe et al6 reported PG in a patient who received ramucirumab therapy without PTX but in combination with another taxane, docetaxel, which itself has been reported to cause subungual PG when used alone.9 Our case of the simultaneous development of multiple PGs in the setting of combined PTX and ramucirumab therapy added to the cutaneous distributions for which therapy-induced PGs have been observed (Table).

The development of PG, a vascular tumor, during treatment with the VEGFR2 inhibitor ramucirumab—whose mechanism of action is to inhibit angioneogenesis—is inherently paradoxical. In 2015, a rapidly expanding angioma with a mutation in the kinase domain receptor gene, KDR, that encodes VEGFR2 was identified in a patient undergoing ramucirumab therapy. The authors suggested that KDR mutation resulted in paradoxical activation of VEGFR2 in the setting of ramucirumab therapy.10 Since then, ramucirumab and PTX were suggested to have a synergistic effect in vascular proliferation,5 though an exact mechanism has not been proposed. Other authors have identified increased expression of VEGFR2 in biopsy specimens of PG during combined ramucirumab and taxane therapy.6 Although genetic studies have not been used to evaluate for the presence of KDR mutations specifically in our patient population, it is possible that patients who develop PG and other vascular tumors during combined taxane and ramucirumab therapy have a mutation that makes them more susceptible to VEGFR2 upregulation. UV exposure may have a role in the formation of PG in patients on combined ramucirumab and taxane therapy7; however, our patient’s lesions were distributed on both sun-exposed and unexposed areas. Although potential clinical implications have not yet been thoroughly investigated, following long-term outcomes for these patients may provide important information on the efficacy of the antineoplastic regimen in the subset of patients who develop cutaneous vascular tumors during antiangiogenic treatment.
Combination therapy with PTX and ramucirumab has been associated with the paradoxical development of cutaneous vascular tumors. We report a case of multiple new-onset PGs in a patient undergoing this treatment regimen.
- Elston D, Neuhaus I, James WD, et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Pierson JC. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma) clinical presentation. Medscape. Updated February 21, 2020. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1084701-clinical#showall
- Paul LJ, Cohen PR. Paclitaxel-associated subungual pyogenic granuloma: report in a patient with breast cancer receiving paclitaxel and review of drug-induced pyogenic granulomas adjacent to and beneath the nail. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:262-268.
- Alessandrini A, Starace M, Cerè G, et al. Management and outcome of taxane-induced nail side effects: experience of 79 patients from a single centre. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:276-282.
- Watanabe R, Nakano E, Kawazoe A, et al. Four cases of paradoxical cephalocervical pyogenic granuloma during treatment with paclitaxel and ramucirumab. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E178-E180.
- Ibe T, Hamamoto Y, Takabatake M, et al. Development of pyogenic granuloma with strong vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression during ramucirumab treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12:E231464.
- Choi YH, Byun HJ, Lee JH, et al. Multiple cherry angiomas and pyogenic granuloma in a patient treated with ramucirumab and paclitaxel. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:199-202.
- Aragaki T, Tomomatsu N, Michi Y, et al. Ramucirumab-related oral pyogenic granuloma: a report of two cases [published online March 8, 2021]. Intern Med. 2021;60:2601-2605. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.6650-20
- Devillers C, Vanhooteghem O, Henrijean A, et al. Subungual pyogenic granuloma secondary to docetaxel therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:251-252.
- Lim YH, Odell ID, Ko CJ, et al. Somatic p.T771R KDR (VEGFR2) mutation arising in a sporadic angioma during ramucirumab therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1240-1243.
To the Editor:
Pyogenic granuloma (PG) is a benign vascular tumor that clinically is characterized as a small eruptive friable papule.1 Lesions typically are solitary and most commonly occur in children but also are associated with pregnancy; trauma to the skin or mucosa; and use of certain medications such as isotretinoin, capecitabine, vemurafenib, or indinavir.1 Numerous antineoplastic medications have been associated with the development of solitary PGs, including the taxane mitotic inhibitor paclitaxel (PTX) and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) monoclonal antibody ramucirumab.2 We report a case of multiple PGs in a patient undergoing treatment with PTX and ramucirumab.

A 59-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with red, itchy, bleeding skin lesions on the breast, superior chest, left cheek, and forearm of 1 month’s duration. She denied any preceding trauma to the areas. Her medical history was notable for gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma diagnosed more than 2 years prior to presentation. Her original treatment regimen included nivolumab, which was discontinued for unknown reasons 5 months prior to presentation, and she was started on combination therapy with PTX and ramucirumab at that time. She noted the formation of small red papules 2 months after the initiation of PTX-ramucirumab combination therapy, which grew larger over the course of the next month. Physical examination revealed 5 friable hemorrhagic papules and nodules ranging in size from 3 to 10 mm on the chest, cheek, and forearm consistent with PGs (Figure 1). Several scattered cherry angiomas were noted on the scalp and torso, but the patient reported these were not new. Biopsies of the PGs demonstrated lobular aggregates of small-caliber vessels set in an edematous inflamed stroma and partially enclosed by small collarettes of adnexal epithelium, confirming the clinical diagnosis of multiple PGs (Figure 2).

The first case of PTX-associated PG was reported in 2012.3 Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms pyogenic granuloma, lobular capillary hemangioma, paclitaxel, taxane, and ramucirumab, there have been 9 cases of solitary PG development in the setting of PTX alone or in combination with ramucirumab since 2019 (Table).3-8 Pyogenic granulomas reported in patients who were treated exclusively with PTX were subungual, while the cases resulting from combined therapy were present on the scalp, face, oral mucosa, and surfaces of the hands sparing the nails. Ibe et al6 reported PG in a patient who received ramucirumab therapy without PTX but in combination with another taxane, docetaxel, which itself has been reported to cause subungual PG when used alone.9 Our case of the simultaneous development of multiple PGs in the setting of combined PTX and ramucirumab therapy added to the cutaneous distributions for which therapy-induced PGs have been observed (Table).

The development of PG, a vascular tumor, during treatment with the VEGFR2 inhibitor ramucirumab—whose mechanism of action is to inhibit angioneogenesis—is inherently paradoxical. In 2015, a rapidly expanding angioma with a mutation in the kinase domain receptor gene, KDR, that encodes VEGFR2 was identified in a patient undergoing ramucirumab therapy. The authors suggested that KDR mutation resulted in paradoxical activation of VEGFR2 in the setting of ramucirumab therapy.10 Since then, ramucirumab and PTX were suggested to have a synergistic effect in vascular proliferation,5 though an exact mechanism has not been proposed. Other authors have identified increased expression of VEGFR2 in biopsy specimens of PG during combined ramucirumab and taxane therapy.6 Although genetic studies have not been used to evaluate for the presence of KDR mutations specifically in our patient population, it is possible that patients who develop PG and other vascular tumors during combined taxane and ramucirumab therapy have a mutation that makes them more susceptible to VEGFR2 upregulation. UV exposure may have a role in the formation of PG in patients on combined ramucirumab and taxane therapy7; however, our patient’s lesions were distributed on both sun-exposed and unexposed areas. Although potential clinical implications have not yet been thoroughly investigated, following long-term outcomes for these patients may provide important information on the efficacy of the antineoplastic regimen in the subset of patients who develop cutaneous vascular tumors during antiangiogenic treatment.
Combination therapy with PTX and ramucirumab has been associated with the paradoxical development of cutaneous vascular tumors. We report a case of multiple new-onset PGs in a patient undergoing this treatment regimen.
To the Editor:
Pyogenic granuloma (PG) is a benign vascular tumor that clinically is characterized as a small eruptive friable papule.1 Lesions typically are solitary and most commonly occur in children but also are associated with pregnancy; trauma to the skin or mucosa; and use of certain medications such as isotretinoin, capecitabine, vemurafenib, or indinavir.1 Numerous antineoplastic medications have been associated with the development of solitary PGs, including the taxane mitotic inhibitor paclitaxel (PTX) and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) monoclonal antibody ramucirumab.2 We report a case of multiple PGs in a patient undergoing treatment with PTX and ramucirumab.

A 59-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with red, itchy, bleeding skin lesions on the breast, superior chest, left cheek, and forearm of 1 month’s duration. She denied any preceding trauma to the areas. Her medical history was notable for gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma diagnosed more than 2 years prior to presentation. Her original treatment regimen included nivolumab, which was discontinued for unknown reasons 5 months prior to presentation, and she was started on combination therapy with PTX and ramucirumab at that time. She noted the formation of small red papules 2 months after the initiation of PTX-ramucirumab combination therapy, which grew larger over the course of the next month. Physical examination revealed 5 friable hemorrhagic papules and nodules ranging in size from 3 to 10 mm on the chest, cheek, and forearm consistent with PGs (Figure 1). Several scattered cherry angiomas were noted on the scalp and torso, but the patient reported these were not new. Biopsies of the PGs demonstrated lobular aggregates of small-caliber vessels set in an edematous inflamed stroma and partially enclosed by small collarettes of adnexal epithelium, confirming the clinical diagnosis of multiple PGs (Figure 2).

The first case of PTX-associated PG was reported in 2012.3 Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms pyogenic granuloma, lobular capillary hemangioma, paclitaxel, taxane, and ramucirumab, there have been 9 cases of solitary PG development in the setting of PTX alone or in combination with ramucirumab since 2019 (Table).3-8 Pyogenic granulomas reported in patients who were treated exclusively with PTX were subungual, while the cases resulting from combined therapy were present on the scalp, face, oral mucosa, and surfaces of the hands sparing the nails. Ibe et al6 reported PG in a patient who received ramucirumab therapy without PTX but in combination with another taxane, docetaxel, which itself has been reported to cause subungual PG when used alone.9 Our case of the simultaneous development of multiple PGs in the setting of combined PTX and ramucirumab therapy added to the cutaneous distributions for which therapy-induced PGs have been observed (Table).

The development of PG, a vascular tumor, during treatment with the VEGFR2 inhibitor ramucirumab—whose mechanism of action is to inhibit angioneogenesis—is inherently paradoxical. In 2015, a rapidly expanding angioma with a mutation in the kinase domain receptor gene, KDR, that encodes VEGFR2 was identified in a patient undergoing ramucirumab therapy. The authors suggested that KDR mutation resulted in paradoxical activation of VEGFR2 in the setting of ramucirumab therapy.10 Since then, ramucirumab and PTX were suggested to have a synergistic effect in vascular proliferation,5 though an exact mechanism has not been proposed. Other authors have identified increased expression of VEGFR2 in biopsy specimens of PG during combined ramucirumab and taxane therapy.6 Although genetic studies have not been used to evaluate for the presence of KDR mutations specifically in our patient population, it is possible that patients who develop PG and other vascular tumors during combined taxane and ramucirumab therapy have a mutation that makes them more susceptible to VEGFR2 upregulation. UV exposure may have a role in the formation of PG in patients on combined ramucirumab and taxane therapy7; however, our patient’s lesions were distributed on both sun-exposed and unexposed areas. Although potential clinical implications have not yet been thoroughly investigated, following long-term outcomes for these patients may provide important information on the efficacy of the antineoplastic regimen in the subset of patients who develop cutaneous vascular tumors during antiangiogenic treatment.
Combination therapy with PTX and ramucirumab has been associated with the paradoxical development of cutaneous vascular tumors. We report a case of multiple new-onset PGs in a patient undergoing this treatment regimen.
- Elston D, Neuhaus I, James WD, et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Pierson JC. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma) clinical presentation. Medscape. Updated February 21, 2020. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1084701-clinical#showall
- Paul LJ, Cohen PR. Paclitaxel-associated subungual pyogenic granuloma: report in a patient with breast cancer receiving paclitaxel and review of drug-induced pyogenic granulomas adjacent to and beneath the nail. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:262-268.
- Alessandrini A, Starace M, Cerè G, et al. Management and outcome of taxane-induced nail side effects: experience of 79 patients from a single centre. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:276-282.
- Watanabe R, Nakano E, Kawazoe A, et al. Four cases of paradoxical cephalocervical pyogenic granuloma during treatment with paclitaxel and ramucirumab. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E178-E180.
- Ibe T, Hamamoto Y, Takabatake M, et al. Development of pyogenic granuloma with strong vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression during ramucirumab treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12:E231464.
- Choi YH, Byun HJ, Lee JH, et al. Multiple cherry angiomas and pyogenic granuloma in a patient treated with ramucirumab and paclitaxel. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:199-202.
- Aragaki T, Tomomatsu N, Michi Y, et al. Ramucirumab-related oral pyogenic granuloma: a report of two cases [published online March 8, 2021]. Intern Med. 2021;60:2601-2605. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.6650-20
- Devillers C, Vanhooteghem O, Henrijean A, et al. Subungual pyogenic granuloma secondary to docetaxel therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:251-252.
- Lim YH, Odell ID, Ko CJ, et al. Somatic p.T771R KDR (VEGFR2) mutation arising in a sporadic angioma during ramucirumab therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1240-1243.
- Elston D, Neuhaus I, James WD, et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Pierson JC. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma) clinical presentation. Medscape. Updated February 21, 2020. Accessed December 26, 2023. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1084701-clinical#showall
- Paul LJ, Cohen PR. Paclitaxel-associated subungual pyogenic granuloma: report in a patient with breast cancer receiving paclitaxel and review of drug-induced pyogenic granulomas adjacent to and beneath the nail. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:262-268.
- Alessandrini A, Starace M, Cerè G, et al. Management and outcome of taxane-induced nail side effects: experience of 79 patients from a single centre. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:276-282.
- Watanabe R, Nakano E, Kawazoe A, et al. Four cases of paradoxical cephalocervical pyogenic granuloma during treatment with paclitaxel and ramucirumab. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E178-E180.
- Ibe T, Hamamoto Y, Takabatake M, et al. Development of pyogenic granuloma with strong vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression during ramucirumab treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12:E231464.
- Choi YH, Byun HJ, Lee JH, et al. Multiple cherry angiomas and pyogenic granuloma in a patient treated with ramucirumab and paclitaxel. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020;86:199-202.
- Aragaki T, Tomomatsu N, Michi Y, et al. Ramucirumab-related oral pyogenic granuloma: a report of two cases [published online March 8, 2021]. Intern Med. 2021;60:2601-2605. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.6650-20
- Devillers C, Vanhooteghem O, Henrijean A, et al. Subungual pyogenic granuloma secondary to docetaxel therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:251-252.
- Lim YH, Odell ID, Ko CJ, et al. Somatic p.T771R KDR (VEGFR2) mutation arising in a sporadic angioma during ramucirumab therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1240-1243.
Practice Points
- Pyogenic granulomas (PGs) are benign vascular tumors that clinically are characterized as small, eruptive, friable papules.
- Ramucirumab is a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.
- Some patients experience paradoxical formation of vascular tumors such as PGs when treated with combination therapy with ramucirumab and a taxane such as paclitaxel.
AI Shows Potential for Detecting Mucosal Healing in Ulcerative Colitis
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems show high potential for detecting mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis with optimal diagnostic performance, according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis.
AI algorithms replicated expert opinion with high sensitivity and specificity when evaluating images and videos. At the same time, moderate-high heterogeneity of the data was found, the authors noted.
“Artificial intelligence software is expected to potentially solve the longstanding issue of low-to-moderate interobserver agreement when human endoscopists are required to indicate mucosal healing or different grades of inflammation in ulcerative colitis,” Alessandro Rimondi, lead author and clinical fellow at the Royal Free Hospital and University College London Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, London, England, told this news organization.
“However, high levels of heterogeneity have been found, potentially linked to how differently the AI software was trained and how many cases it has been tested on,” he said. “This partially limits the quality of the body of evidence.”
The study was published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Evaluating AI Detection
In clinical practice, assessing mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is critical for evaluating a patient’s response to therapy and guiding strategies for treatment, surgery, and endoscopic surveillance. In an era of precision medicine, assessment of mucosal healing should be precise, readily available in an endoscopic report, and highly reproducible, which requires high accuracy and agreement in endoscopic diagnosis, the authors noted.
AI systems — particularly deep learning algorithms based on convolutional neural network architecture — may allow endoscopists to establish an objective and real-time diagnosis of mucosal healing and improve the average quality standards at primary and tertiary care centers, the authors wrote. Research on AI in IBD has looked at potential implications for endoscopy and clinical management, which opens new areas to explore.
Dr. Rimondi and colleagues conducted a systematic review of studies up to December 2022 that involved an AI-based system used to estimate any degree of endoscopic inflammation in IBD, whether ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. After that, they conducted a diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis restricted to the field in which more than five studies providing diagnostic performance — mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis based on luminal imaging — were available.
The researchers identified 12 studies with luminal imaging in patients with ulcerative colitis. Four evaluated the performance of AI systems on videos, six focused on fixed images, and two looked at both.
Overall, the AI systems achieved a satisfactory performance in evaluating mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. When evaluating fixed images, the algorithms achieved a sensitivity of 0.91 and specificity of 0.89, with a diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 92.42, summary receiver operating characteristic curve (SROC) of 0.957, and area under the curve (AUC) of 0.957. When evaluating videos, the algorithms achieved 0.86 sensitivity, 0.91 specificity, 70.86 DOR, 0.941 SROC, and 0.941 AUC.
“It is exciting to see artificial intelligence expand and be effective for conditions beyond colon polyps,” Seth Gross, MD, professor of medicine and clinical chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at NYU Langone Health, New York, told this news organization.
Dr. Gross, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched AI applications in endoscopy and colonoscopy. He and colleagues have found that machine learning software can improve lesion and polyp detection, serving as a “second set of eyes” for practitioners.
“Mucosal healing interpretation can be variable amongst providers,” he said. “AI has the potential to help standardize the assessment of mucosal healing in patients with ulcerative colitis.”
Improving AI Training
The authors found moderate-high levels of heterogeneity among the studies, which limited the quality of the evidence. Only 2 of the 12 studies used an external dataset to validate the AI systems, and 1 evaluated the AI system on a mixed database. However, seven used an internal validation dataset separate from the training dataset.
It is crucial to find a shared consensus on training for AI models, with a shared definition of mucosal healing and cutoff thresholds based on recent guidelines, Dr. Rimondi and colleagues noted. Training data ideally should be on the basis of a broad and shared database containing images and videos with high interobserver agreement on the degree of inflammation, they added.
“We probably need a consensus or guidelines that identify the standards for training and testing newly developed software, stating the bare minimum number of images or videos for the training and testing sections,” Dr. Rimondi said.
In addition, due to interobserver misalignment, an expert-validated database could help serve the purpose of a gold standard, he added.
“In my opinion, artificial intelligence tends to better perform when it is required to evaluate a dichotomic outcome (such as polyp detection, which is a yes or no task) than when it is required to replicate more difficult tasks (such as polyp characterization or judging a degree of inflammation), which have a continuous range of expression,” Dr. Rimondi said.
The authors declared no financial support for this study. Dr. Rimondi and Dr. Gross reported no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems show high potential for detecting mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis with optimal diagnostic performance, according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis.
AI algorithms replicated expert opinion with high sensitivity and specificity when evaluating images and videos. At the same time, moderate-high heterogeneity of the data was found, the authors noted.
“Artificial intelligence software is expected to potentially solve the longstanding issue of low-to-moderate interobserver agreement when human endoscopists are required to indicate mucosal healing or different grades of inflammation in ulcerative colitis,” Alessandro Rimondi, lead author and clinical fellow at the Royal Free Hospital and University College London Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, London, England, told this news organization.
“However, high levels of heterogeneity have been found, potentially linked to how differently the AI software was trained and how many cases it has been tested on,” he said. “This partially limits the quality of the body of evidence.”
The study was published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Evaluating AI Detection
In clinical practice, assessing mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is critical for evaluating a patient’s response to therapy and guiding strategies for treatment, surgery, and endoscopic surveillance. In an era of precision medicine, assessment of mucosal healing should be precise, readily available in an endoscopic report, and highly reproducible, which requires high accuracy and agreement in endoscopic diagnosis, the authors noted.
AI systems — particularly deep learning algorithms based on convolutional neural network architecture — may allow endoscopists to establish an objective and real-time diagnosis of mucosal healing and improve the average quality standards at primary and tertiary care centers, the authors wrote. Research on AI in IBD has looked at potential implications for endoscopy and clinical management, which opens new areas to explore.
Dr. Rimondi and colleagues conducted a systematic review of studies up to December 2022 that involved an AI-based system used to estimate any degree of endoscopic inflammation in IBD, whether ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. After that, they conducted a diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis restricted to the field in which more than five studies providing diagnostic performance — mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis based on luminal imaging — were available.
The researchers identified 12 studies with luminal imaging in patients with ulcerative colitis. Four evaluated the performance of AI systems on videos, six focused on fixed images, and two looked at both.
Overall, the AI systems achieved a satisfactory performance in evaluating mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. When evaluating fixed images, the algorithms achieved a sensitivity of 0.91 and specificity of 0.89, with a diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 92.42, summary receiver operating characteristic curve (SROC) of 0.957, and area under the curve (AUC) of 0.957. When evaluating videos, the algorithms achieved 0.86 sensitivity, 0.91 specificity, 70.86 DOR, 0.941 SROC, and 0.941 AUC.
“It is exciting to see artificial intelligence expand and be effective for conditions beyond colon polyps,” Seth Gross, MD, professor of medicine and clinical chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at NYU Langone Health, New York, told this news organization.
Dr. Gross, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched AI applications in endoscopy and colonoscopy. He and colleagues have found that machine learning software can improve lesion and polyp detection, serving as a “second set of eyes” for practitioners.
“Mucosal healing interpretation can be variable amongst providers,” he said. “AI has the potential to help standardize the assessment of mucosal healing in patients with ulcerative colitis.”
Improving AI Training
The authors found moderate-high levels of heterogeneity among the studies, which limited the quality of the evidence. Only 2 of the 12 studies used an external dataset to validate the AI systems, and 1 evaluated the AI system on a mixed database. However, seven used an internal validation dataset separate from the training dataset.
It is crucial to find a shared consensus on training for AI models, with a shared definition of mucosal healing and cutoff thresholds based on recent guidelines, Dr. Rimondi and colleagues noted. Training data ideally should be on the basis of a broad and shared database containing images and videos with high interobserver agreement on the degree of inflammation, they added.
“We probably need a consensus or guidelines that identify the standards for training and testing newly developed software, stating the bare minimum number of images or videos for the training and testing sections,” Dr. Rimondi said.
In addition, due to interobserver misalignment, an expert-validated database could help serve the purpose of a gold standard, he added.
“In my opinion, artificial intelligence tends to better perform when it is required to evaluate a dichotomic outcome (such as polyp detection, which is a yes or no task) than when it is required to replicate more difficult tasks (such as polyp characterization or judging a degree of inflammation), which have a continuous range of expression,” Dr. Rimondi said.
The authors declared no financial support for this study. Dr. Rimondi and Dr. Gross reported no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems show high potential for detecting mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis with optimal diagnostic performance, according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis.
AI algorithms replicated expert opinion with high sensitivity and specificity when evaluating images and videos. At the same time, moderate-high heterogeneity of the data was found, the authors noted.
“Artificial intelligence software is expected to potentially solve the longstanding issue of low-to-moderate interobserver agreement when human endoscopists are required to indicate mucosal healing or different grades of inflammation in ulcerative colitis,” Alessandro Rimondi, lead author and clinical fellow at the Royal Free Hospital and University College London Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, London, England, told this news organization.
“However, high levels of heterogeneity have been found, potentially linked to how differently the AI software was trained and how many cases it has been tested on,” he said. “This partially limits the quality of the body of evidence.”
The study was published online in Digestive and Liver Disease.
Evaluating AI Detection
In clinical practice, assessing mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is critical for evaluating a patient’s response to therapy and guiding strategies for treatment, surgery, and endoscopic surveillance. In an era of precision medicine, assessment of mucosal healing should be precise, readily available in an endoscopic report, and highly reproducible, which requires high accuracy and agreement in endoscopic diagnosis, the authors noted.
AI systems — particularly deep learning algorithms based on convolutional neural network architecture — may allow endoscopists to establish an objective and real-time diagnosis of mucosal healing and improve the average quality standards at primary and tertiary care centers, the authors wrote. Research on AI in IBD has looked at potential implications for endoscopy and clinical management, which opens new areas to explore.
Dr. Rimondi and colleagues conducted a systematic review of studies up to December 2022 that involved an AI-based system used to estimate any degree of endoscopic inflammation in IBD, whether ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. After that, they conducted a diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis restricted to the field in which more than five studies providing diagnostic performance — mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis based on luminal imaging — were available.
The researchers identified 12 studies with luminal imaging in patients with ulcerative colitis. Four evaluated the performance of AI systems on videos, six focused on fixed images, and two looked at both.
Overall, the AI systems achieved a satisfactory performance in evaluating mucosal healing in ulcerative colitis. When evaluating fixed images, the algorithms achieved a sensitivity of 0.91 and specificity of 0.89, with a diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 92.42, summary receiver operating characteristic curve (SROC) of 0.957, and area under the curve (AUC) of 0.957. When evaluating videos, the algorithms achieved 0.86 sensitivity, 0.91 specificity, 70.86 DOR, 0.941 SROC, and 0.941 AUC.
“It is exciting to see artificial intelligence expand and be effective for conditions beyond colon polyps,” Seth Gross, MD, professor of medicine and clinical chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at NYU Langone Health, New York, told this news organization.
Dr. Gross, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched AI applications in endoscopy and colonoscopy. He and colleagues have found that machine learning software can improve lesion and polyp detection, serving as a “second set of eyes” for practitioners.
“Mucosal healing interpretation can be variable amongst providers,” he said. “AI has the potential to help standardize the assessment of mucosal healing in patients with ulcerative colitis.”
Improving AI Training
The authors found moderate-high levels of heterogeneity among the studies, which limited the quality of the evidence. Only 2 of the 12 studies used an external dataset to validate the AI systems, and 1 evaluated the AI system on a mixed database. However, seven used an internal validation dataset separate from the training dataset.
It is crucial to find a shared consensus on training for AI models, with a shared definition of mucosal healing and cutoff thresholds based on recent guidelines, Dr. Rimondi and colleagues noted. Training data ideally should be on the basis of a broad and shared database containing images and videos with high interobserver agreement on the degree of inflammation, they added.
“We probably need a consensus or guidelines that identify the standards for training and testing newly developed software, stating the bare minimum number of images or videos for the training and testing sections,” Dr. Rimondi said.
In addition, due to interobserver misalignment, an expert-validated database could help serve the purpose of a gold standard, he added.
“In my opinion, artificial intelligence tends to better perform when it is required to evaluate a dichotomic outcome (such as polyp detection, which is a yes or no task) than when it is required to replicate more difficult tasks (such as polyp characterization or judging a degree of inflammation), which have a continuous range of expression,” Dr. Rimondi said.
The authors declared no financial support for this study. Dr. Rimondi and Dr. Gross reported no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIGESTIVE AND LIVER DISEASE
No Added Benefit From Chemo in This Breast Cancer Subtype
TOPLINE:
Women with estrogen receptor (ER)–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative invasive lobular carcinoma who are treated with endocrine therapy do not derive any additional survival benefit from neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies evaluating the long-term effects of chemotherapy in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma are limited and often “show inconclusive results,” the authors explained.
- Female patients diagnosed with ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma who received endocrine therapy were identified from the breast cancer database at Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- Linked information on patient and tumor characteristics, vital status, and treatment were then obtained from the Netherlands Cancer Registry.
- Patients also had to have an indication for chemotherapy based on lymph node status, tumor size, histologic tumor grade, and hormone receptor status, in line with national guidelines.
- Among 716 patients with ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma, 520 who had an indication for chemotherapy were included. Of those, 379 received chemotherapy and 141 did not.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients who received chemotherapy were younger at diagnosis than those who did not (51 vs 61 years), had an earlier average year of diagnosis (2010 vs 2015), and had longer follow-up (7.8 years vs 5.2 years).
- Chemotherapy recipients were more likely to have T3+ disease (33% vs 14%) and positive lymph node involvement (80% vs 49%), and less likely to undergo breast-conserving surgery (31% vs 43%).
- Researchers, however, found no difference between the chemotherapy and no-chemotherapy groups in terms of recurrence-free survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.20; 95% CI, 0.63-2.31), breast cancer–specific survival (HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.60-2.58), and overall survival (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.56-1.66) after adjustment for confounders.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors “observed no evidence for added value of chemotherapy” for ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma who received endocrine therapy. “In view of the adverse effects of chemotherapy, our study takes an important step in answering a valuable question from the patient’s perspective,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, conducted by Bernadette A.M. Heemskerk-Gerritsen, PhD, from Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, was published in Cancer on November 20, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design means that there is a risk for residual confounding from factors not recorded in the database. The researchers believe that some patients did not receive chemotherapy owing to having comorbidities or patient preference, which could have influenced the results. Moreover, the duration of endocrine therapy was not recorded.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was declared. One author declares relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Menarini Silicon Biosystems, and Novartis. No other relevant financial relationships were declared.
TOPLINE:
Women with estrogen receptor (ER)–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative invasive lobular carcinoma who are treated with endocrine therapy do not derive any additional survival benefit from neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies evaluating the long-term effects of chemotherapy in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma are limited and often “show inconclusive results,” the authors explained.
- Female patients diagnosed with ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma who received endocrine therapy were identified from the breast cancer database at Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- Linked information on patient and tumor characteristics, vital status, and treatment were then obtained from the Netherlands Cancer Registry.
- Patients also had to have an indication for chemotherapy based on lymph node status, tumor size, histologic tumor grade, and hormone receptor status, in line with national guidelines.
- Among 716 patients with ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma, 520 who had an indication for chemotherapy were included. Of those, 379 received chemotherapy and 141 did not.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients who received chemotherapy were younger at diagnosis than those who did not (51 vs 61 years), had an earlier average year of diagnosis (2010 vs 2015), and had longer follow-up (7.8 years vs 5.2 years).
- Chemotherapy recipients were more likely to have T3+ disease (33% vs 14%) and positive lymph node involvement (80% vs 49%), and less likely to undergo breast-conserving surgery (31% vs 43%).
- Researchers, however, found no difference between the chemotherapy and no-chemotherapy groups in terms of recurrence-free survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.20; 95% CI, 0.63-2.31), breast cancer–specific survival (HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.60-2.58), and overall survival (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.56-1.66) after adjustment for confounders.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors “observed no evidence for added value of chemotherapy” for ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma who received endocrine therapy. “In view of the adverse effects of chemotherapy, our study takes an important step in answering a valuable question from the patient’s perspective,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, conducted by Bernadette A.M. Heemskerk-Gerritsen, PhD, from Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, was published in Cancer on November 20, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design means that there is a risk for residual confounding from factors not recorded in the database. The researchers believe that some patients did not receive chemotherapy owing to having comorbidities or patient preference, which could have influenced the results. Moreover, the duration of endocrine therapy was not recorded.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was declared. One author declares relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Menarini Silicon Biosystems, and Novartis. No other relevant financial relationships were declared.
TOPLINE:
Women with estrogen receptor (ER)–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative invasive lobular carcinoma who are treated with endocrine therapy do not derive any additional survival benefit from neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies evaluating the long-term effects of chemotherapy in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma are limited and often “show inconclusive results,” the authors explained.
- Female patients diagnosed with ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma who received endocrine therapy were identified from the breast cancer database at Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- Linked information on patient and tumor characteristics, vital status, and treatment were then obtained from the Netherlands Cancer Registry.
- Patients also had to have an indication for chemotherapy based on lymph node status, tumor size, histologic tumor grade, and hormone receptor status, in line with national guidelines.
- Among 716 patients with ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma, 520 who had an indication for chemotherapy were included. Of those, 379 received chemotherapy and 141 did not.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients who received chemotherapy were younger at diagnosis than those who did not (51 vs 61 years), had an earlier average year of diagnosis (2010 vs 2015), and had longer follow-up (7.8 years vs 5.2 years).
- Chemotherapy recipients were more likely to have T3+ disease (33% vs 14%) and positive lymph node involvement (80% vs 49%), and less likely to undergo breast-conserving surgery (31% vs 43%).
- Researchers, however, found no difference between the chemotherapy and no-chemotherapy groups in terms of recurrence-free survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.20; 95% CI, 0.63-2.31), breast cancer–specific survival (HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.60-2.58), and overall survival (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.56-1.66) after adjustment for confounders.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors “observed no evidence for added value of chemotherapy” for ER-positive, HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma who received endocrine therapy. “In view of the adverse effects of chemotherapy, our study takes an important step in answering a valuable question from the patient’s perspective,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, conducted by Bernadette A.M. Heemskerk-Gerritsen, PhD, from Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, was published in Cancer on November 20, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design means that there is a risk for residual confounding from factors not recorded in the database. The researchers believe that some patients did not receive chemotherapy owing to having comorbidities or patient preference, which could have influenced the results. Moreover, the duration of endocrine therapy was not recorded.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was declared. One author declares relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Menarini Silicon Biosystems, and Novartis. No other relevant financial relationships were declared.
ADHD Plus Comorbidities Linked to Increased Schizophrenia Risk
TOPLINE:
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and comorbid psychiatric disorders are associated with a twofold increased risk for schizophrenia, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators analyzed the data of 211,705 people aged 5-19 years (74% male; 54% aged 5-9 years) diagnosed with ADHD during 2010-2018 from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database of South Korea.
- Participants with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or psychosis anytime in the 3 years prior to ADHD diagnosis were excluded.
- Investigators split participants into two groups — a group of those diagnosed with at least one psychiatric comorbidity within a year of ADHD diagnosis and another group comprising those with ADHD and no psychiatric comorbidities.
TAKEAWAY:
- 37% (77,890) of those with ADHD had at least one comorbid psychiatric disorder.
- Participants with one psychiatric comorbidity had a 2.1-fold increased risk for a schizophrenia diagnosis than participants with no comorbidity (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.14; 95% CI, 2.05-2.23).
- Schizophrenia risk increased with each additional comorbidity. There was a fourfold increased risk for schizophrenia in study participants with three or more psychiatric comorbidities (aHR, 4.26; 95% CI, 3.90-4.65) than those with no comorbidity.
- Psychiatric comorbidities included autism spectrum disorder, which had the strongest link to increased schizophrenia risk (aHR, 2.43; 95% CI, 2.26-2.62). Other comorbidities that showed strong associations were intellectual disability (aHR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.72-1.95), tic disorder (aHR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.66-1.88), depression (aHR,1.68; 95% CI, 1.60-1.77), and bipolar disorder (aHR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.53-1.83).
IN PRACTICE:
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate schizophrenia risk among children and adolescents with ADHD, with a particular focus on psychiatric comorbidities,” the researchers wrote. They also noted that although patients had no psychiatric comorbidities at the time of ADHD diagnosis, the occurrence of psychiatric comorbidities was frequently observed prior to schizophrenia diagnosis.
“These findings highlighted the significance of carefully monitoring psychiatric comorbidities in patients with ADHD to effectively mitigate the burden of schizophrenia,” they noted.
SOURCE:
Soo Min Jeon, PharmD, PhD, of Jeju National University in Jeju, South Korea, led the study, which was published online on November 30, 2023 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Since the diagnosis of ADHD, schizophrenia, and other psychiatric comorbidities were based on diagnostic codes, the possibility of underdiagnosis or overdiagnosis cannot be ruled out. Also, some patients with ADHD chose the general health consultation (International Classification of Diseases - Z code) due to the social stigma surrounding mental health problems.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the Ministry of Education and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Author disclosures can be found in the original paper.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and comorbid psychiatric disorders are associated with a twofold increased risk for schizophrenia, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators analyzed the data of 211,705 people aged 5-19 years (74% male; 54% aged 5-9 years) diagnosed with ADHD during 2010-2018 from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database of South Korea.
- Participants with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or psychosis anytime in the 3 years prior to ADHD diagnosis were excluded.
- Investigators split participants into two groups — a group of those diagnosed with at least one psychiatric comorbidity within a year of ADHD diagnosis and another group comprising those with ADHD and no psychiatric comorbidities.
TAKEAWAY:
- 37% (77,890) of those with ADHD had at least one comorbid psychiatric disorder.
- Participants with one psychiatric comorbidity had a 2.1-fold increased risk for a schizophrenia diagnosis than participants with no comorbidity (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.14; 95% CI, 2.05-2.23).
- Schizophrenia risk increased with each additional comorbidity. There was a fourfold increased risk for schizophrenia in study participants with three or more psychiatric comorbidities (aHR, 4.26; 95% CI, 3.90-4.65) than those with no comorbidity.
- Psychiatric comorbidities included autism spectrum disorder, which had the strongest link to increased schizophrenia risk (aHR, 2.43; 95% CI, 2.26-2.62). Other comorbidities that showed strong associations were intellectual disability (aHR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.72-1.95), tic disorder (aHR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.66-1.88), depression (aHR,1.68; 95% CI, 1.60-1.77), and bipolar disorder (aHR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.53-1.83).
IN PRACTICE:
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate schizophrenia risk among children and adolescents with ADHD, with a particular focus on psychiatric comorbidities,” the researchers wrote. They also noted that although patients had no psychiatric comorbidities at the time of ADHD diagnosis, the occurrence of psychiatric comorbidities was frequently observed prior to schizophrenia diagnosis.
“These findings highlighted the significance of carefully monitoring psychiatric comorbidities in patients with ADHD to effectively mitigate the burden of schizophrenia,” they noted.
SOURCE:
Soo Min Jeon, PharmD, PhD, of Jeju National University in Jeju, South Korea, led the study, which was published online on November 30, 2023 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Since the diagnosis of ADHD, schizophrenia, and other psychiatric comorbidities were based on diagnostic codes, the possibility of underdiagnosis or overdiagnosis cannot be ruled out. Also, some patients with ADHD chose the general health consultation (International Classification of Diseases - Z code) due to the social stigma surrounding mental health problems.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the Ministry of Education and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Author disclosures can be found in the original paper.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and comorbid psychiatric disorders are associated with a twofold increased risk for schizophrenia, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators analyzed the data of 211,705 people aged 5-19 years (74% male; 54% aged 5-9 years) diagnosed with ADHD during 2010-2018 from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database of South Korea.
- Participants with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or psychosis anytime in the 3 years prior to ADHD diagnosis were excluded.
- Investigators split participants into two groups — a group of those diagnosed with at least one psychiatric comorbidity within a year of ADHD diagnosis and another group comprising those with ADHD and no psychiatric comorbidities.
TAKEAWAY:
- 37% (77,890) of those with ADHD had at least one comorbid psychiatric disorder.
- Participants with one psychiatric comorbidity had a 2.1-fold increased risk for a schizophrenia diagnosis than participants with no comorbidity (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.14; 95% CI, 2.05-2.23).
- Schizophrenia risk increased with each additional comorbidity. There was a fourfold increased risk for schizophrenia in study participants with three or more psychiatric comorbidities (aHR, 4.26; 95% CI, 3.90-4.65) than those with no comorbidity.
- Psychiatric comorbidities included autism spectrum disorder, which had the strongest link to increased schizophrenia risk (aHR, 2.43; 95% CI, 2.26-2.62). Other comorbidities that showed strong associations were intellectual disability (aHR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.72-1.95), tic disorder (aHR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.66-1.88), depression (aHR,1.68; 95% CI, 1.60-1.77), and bipolar disorder (aHR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.53-1.83).
IN PRACTICE:
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate schizophrenia risk among children and adolescents with ADHD, with a particular focus on psychiatric comorbidities,” the researchers wrote. They also noted that although patients had no psychiatric comorbidities at the time of ADHD diagnosis, the occurrence of psychiatric comorbidities was frequently observed prior to schizophrenia diagnosis.
“These findings highlighted the significance of carefully monitoring psychiatric comorbidities in patients with ADHD to effectively mitigate the burden of schizophrenia,” they noted.
SOURCE:
Soo Min Jeon, PharmD, PhD, of Jeju National University in Jeju, South Korea, led the study, which was published online on November 30, 2023 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Since the diagnosis of ADHD, schizophrenia, and other psychiatric comorbidities were based on diagnostic codes, the possibility of underdiagnosis or overdiagnosis cannot be ruled out. Also, some patients with ADHD chose the general health consultation (International Classification of Diseases - Z code) due to the social stigma surrounding mental health problems.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the Ministry of Education and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Author disclosures can be found in the original paper.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Who Is Helped by AI Use During Colonoscopy?
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds the promise of identifying premalignant and advanced malignant lesions during colonoscopy that might otherwise be missed.
Is it living up to that promise?
It seems that depends on where, how, and by whom it’s being implemented.
Clinical Trials vs the Real World
The majority of randomized clinical trials of AI use conducted worldwide “clearly show an increase in the adenoma detection rate (ADR) during colonoscopy,” Prateek Sharma, MD, a gastroenterologist at The University of Kansas Cancer Center, Kansas City, told this news. “But the real-world results have been quite varied; some show improvement, and others don’t.”
Dr. Sharma is coauthor of a recent pooled analysis of nine randomized controlled trials on the impact of AI on colonoscopy surveillance after polyp removal. It found that AI use increased the proportion of patients requiring intensive surveillance by approximately 35% in the United States and 20% in Europe (absolute increases of 2.9% and 1.3%, respectively).
“While this may contribute to improved cancer prevention, it significantly adds patient burden and healthcare costs,” the authors concluded.
A recent retrospective analysis of staggered implementation of a computer-aided detection (CADe) system at a single academic center in Chicago found that for screening and surveillance colonoscopy combined, endoscopists using CADe identified more adenomas and serrated polyps — but only endoscopists who used CADe regularly (“majority” users).
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 21 randomized controlled trials comparing CADe with standard colonoscopy found increased detection of adenomas, but not of advanced adenomas, as well as higher rates of unnecessary removal of non-neoplastic polyps.
Adding to the mix, a multicenter randomized controlled trial of patients with a positive fecal immunochemical test found that AI use was not associated with better detection of advanced neoplasias. Lead author Carolina Mangas Sanjuán, MD, PhD, Hospital General Universitario Dr. Balmis, Alicante, Spain, told this news organization the results were “surprising,” given previous studies showing benefit.
Similarly, a pragmatic implementation trial conducted by Stanford, California, researchers showed no significant effect of CADe on ADR, adenomas per colonoscopy, or any other detection metric. Furthermore, CADe had no effect on procedure times or non-neoplastic detection rates.
The authors cautioned against viewing their study as an “outlier,” however, and pointed to an Israeli study comparing adenoma and polyp detection rates 6 months before and after the introduction of AI-aided colonoscopy. Those authors reported no performance improvement with the AI device and concluded that it was not useful in routine practice.
A ‘Mishmash’ of Methods
“It’s not clear why some studies are positive, and some are negative,” Dr. Sharma acknowledged.
Study design is a factor, particularly in real-world studies, he said. Some researchers use the before/after approach, as in the Israeli study; others compare use in different rooms — that is, one with a CADe device and one without. Like the Chicago analysis, findings from such studies probably depend on whether the colonoscopists with the CADe device in the room actually use it.
Other real-world studies look at detection by time, Dr. Sharma said.
For example, a study of 1780 colonoscopies in China found that AI systems showed higher assistance ability among colonoscopies performed later in the day, when adenoma detection rates typically declined, perhaps owing to fatigue.
These authors suggest that AI may have the potential to maintain high quality and homogeneity of colonoscopies and improve endoscopist performance in large screening programs and centers with high workloads.
“There’s a mishmash of different kinds of real-world studies coming in, and it’s very difficult to figure it all out,” Dr. Sharma said. “We just have to look at these devices as innovations and embrace them and work with them to see how it fits it in our practice.”
Perceptions and Expectations
Emerging evidence suggests that endoscopists’ perceptions and expectations may affect assessments of AI’s potential benefits in practice, Dr. Sharma noted.
“Someone might say, ‘I’m a trained physician. Why do I need a machine to help me?’ That can create a situation in which the endoscopist is constantly challenging the device, trying to overrule it or not give it credit.”
Others might perceive that the AI device will definitely help and therefore not look as carefully themselves for adenomas.
A study at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston in which activation of the AI system was at the discretion of the endoscopist found that real-time CADe did not improve adenoma detection among endoscopists with high baseline detection rates.
However, despite its availability, AI-assisted colonoscopy was activated in only half of the cases, and multiple concerns were raised by staff and endoscopists in a postprocedural survey. In particular, endoscopists were concerned that the system would result in too many false-positive signals (82.4%), was too distracting (58.8%), and prolonged procedure time (47.1%).
The authors of the Stanford study that found no benefit with CADe in routine practice noted, “Most concerning would be if, inadvertently, CADe use was accompanied by a simultaneous unconscious degradation in the quality of mucosal exposure, possibly due to a false sense of comfort that CADe would ensure a high-quality examination.”
“We’re trying to evaluate some of these interactions between endoscopists and AI devices both pragmatically in practice as well as in clinical trials,” Dr. Sharma said. “Much depends on the context of how you approach and present the devices. We tell physicians that this is an assist device, not something you’re competing against and not something that’s here to replace you. This is something which may make your lives easier, so try it out.”
Are Less Experienced Endoscopists Helped More?
It seems intuitive that less experienced endoscopists would be helped by AI, and indeed, some recent studies confirm this.
A small randomized controlled trial in Japan, presented during the Presidential Plenary at the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) annual meeting in May 2023, showed that a CADe system was “particularly useful” for beginning endoscopists, who had lower adenoma miss rates with the device vs a white light control device.
Another randomized controlled trial in Japan found that CADe use was associated with an increased overall ADR among endoscopists in training.
But experienced endoscopists probably can benefit as well, noted Jennifer Christie, MD, Division Director, Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora.
“We know that these AI devices can be useful in training our fellows to detect certain lesions in the colon,” she said. “However, they’re also helpful for many very seasoned practitioners, as an adjunctive tool to help in terms of diagnosis.”
Some studies reflect that dual benefit.
The AID-2 study, designed specifically to look at whether experience had an effect on AI findings during colonoscopy, was conducted among nonexpert endoscopists (lifetime volume of less than 2000 colonoscopies). The researchers, including Dr. Sharma, found that CADe increased the ADR by 22% compared with the control group.
An earlier study, AID-1 , used a similar design but was conducted among experienced endoscopists. In AID-1, the ADR was also significantly higher in the CADe group (54.8%) compared with the control group (40.4%), and adenomas detected per colonoscopy were significantly higher in the CADe group (mean, 1.07) than in the control group (mean, 0.71).
A multivariate post hoc analysis that pooled results from both AID-1 and AID-2 showed that use of CADe and colonoscopy indication, but not the level of examiner experience, were associated with ADR differences. This led the researchers to conclude, “Experience appears to play a minor role as a determining factor for ADR.”
Similarly, a 2023 study from China looked at the mean number of adenomas detected per colonoscopy according to the endoscopist’s experience. All rates were significantly higher in AI-assisted colonoscopies compared with conventional non-AI colonoscopy: overall ADR, 39.9% vs 32.4%; advanced ADR, 6.6% vs 4.9%; ADR of expert endoscopists, 42.3% vs 32.8%; ADR of nonexpert endoscopists, 37.5% vs 32.1%; and adenomas per colonoscopy, 0.59 vs 0.45, respectively.
The authors concluded that “AI-assisted colonoscopy improved overall ADR, advanced ADR, and ADR of both expert and nonexpert attending endoscopists.”
Improving the Algorithms
Experts agree that current and future research will improve the accuracy and quality of AI colonoscopy for all users, leading to new standards and more consistent outcomes in both clinical trials and real-world applications.
Work underway now to improve the algorithms will be an important step in that direction, according to Dr. Christie.
“We need to have enough information to create AI algorithms that allow us to detect early lesions, at least from an imaging standpoint, and we need to improve and increase the sensitivity and the specificity, as well as the predictive value,” she said.
AI can also play a role in health equity, she noted.
“But it’s a double-edged sword, because it depends again on algorithms and machine learning. Perhaps AI can eliminate some of the bias in our clinical decision-making. However, if we don’t train the machine properly with a good, diverse sample of patients and figure out how to integrate some of the social determinants of health that a computer may not otherwise consider, it can create larger disparities and larger biases. AI devices can only be as good and as inclusive as we make them,” Dr. Christie said.
Looking Ahead
Dr. Sharma predicts that “the next slew of studies are going to be on characterization — not just saying there’s an abnormality but distinguishing it further and saying whether the lesion is noncancerous, precancerous, or cancer.”
Other studies will focus on quality improvement of factors, such as withdrawal time and bowel preparation.
In its clinical practice update on AI, the American Gastroenterological Association states, “Eventually, we predict an AI suite of tools for colonoscopy will seem indispensable, as a powerful adjunct to support safe and efficient clinical practice. AI tools that improve colonoscopy quality may become more accepted, and perhaps demanded, by payors, administrators, and possibly even by well-informed patients who want to ensure the highest-quality examination of their colon.”
Dr. Sharma and Dr. Christie disclose no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds the promise of identifying premalignant and advanced malignant lesions during colonoscopy that might otherwise be missed.
Is it living up to that promise?
It seems that depends on where, how, and by whom it’s being implemented.
Clinical Trials vs the Real World
The majority of randomized clinical trials of AI use conducted worldwide “clearly show an increase in the adenoma detection rate (ADR) during colonoscopy,” Prateek Sharma, MD, a gastroenterologist at The University of Kansas Cancer Center, Kansas City, told this news. “But the real-world results have been quite varied; some show improvement, and others don’t.”
Dr. Sharma is coauthor of a recent pooled analysis of nine randomized controlled trials on the impact of AI on colonoscopy surveillance after polyp removal. It found that AI use increased the proportion of patients requiring intensive surveillance by approximately 35% in the United States and 20% in Europe (absolute increases of 2.9% and 1.3%, respectively).
“While this may contribute to improved cancer prevention, it significantly adds patient burden and healthcare costs,” the authors concluded.
A recent retrospective analysis of staggered implementation of a computer-aided detection (CADe) system at a single academic center in Chicago found that for screening and surveillance colonoscopy combined, endoscopists using CADe identified more adenomas and serrated polyps — but only endoscopists who used CADe regularly (“majority” users).
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 21 randomized controlled trials comparing CADe with standard colonoscopy found increased detection of adenomas, but not of advanced adenomas, as well as higher rates of unnecessary removal of non-neoplastic polyps.
Adding to the mix, a multicenter randomized controlled trial of patients with a positive fecal immunochemical test found that AI use was not associated with better detection of advanced neoplasias. Lead author Carolina Mangas Sanjuán, MD, PhD, Hospital General Universitario Dr. Balmis, Alicante, Spain, told this news organization the results were “surprising,” given previous studies showing benefit.
Similarly, a pragmatic implementation trial conducted by Stanford, California, researchers showed no significant effect of CADe on ADR, adenomas per colonoscopy, or any other detection metric. Furthermore, CADe had no effect on procedure times or non-neoplastic detection rates.
The authors cautioned against viewing their study as an “outlier,” however, and pointed to an Israeli study comparing adenoma and polyp detection rates 6 months before and after the introduction of AI-aided colonoscopy. Those authors reported no performance improvement with the AI device and concluded that it was not useful in routine practice.
A ‘Mishmash’ of Methods
“It’s not clear why some studies are positive, and some are negative,” Dr. Sharma acknowledged.
Study design is a factor, particularly in real-world studies, he said. Some researchers use the before/after approach, as in the Israeli study; others compare use in different rooms — that is, one with a CADe device and one without. Like the Chicago analysis, findings from such studies probably depend on whether the colonoscopists with the CADe device in the room actually use it.
Other real-world studies look at detection by time, Dr. Sharma said.
For example, a study of 1780 colonoscopies in China found that AI systems showed higher assistance ability among colonoscopies performed later in the day, when adenoma detection rates typically declined, perhaps owing to fatigue.
These authors suggest that AI may have the potential to maintain high quality and homogeneity of colonoscopies and improve endoscopist performance in large screening programs and centers with high workloads.
“There’s a mishmash of different kinds of real-world studies coming in, and it’s very difficult to figure it all out,” Dr. Sharma said. “We just have to look at these devices as innovations and embrace them and work with them to see how it fits it in our practice.”
Perceptions and Expectations
Emerging evidence suggests that endoscopists’ perceptions and expectations may affect assessments of AI’s potential benefits in practice, Dr. Sharma noted.
“Someone might say, ‘I’m a trained physician. Why do I need a machine to help me?’ That can create a situation in which the endoscopist is constantly challenging the device, trying to overrule it or not give it credit.”
Others might perceive that the AI device will definitely help and therefore not look as carefully themselves for adenomas.
A study at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston in which activation of the AI system was at the discretion of the endoscopist found that real-time CADe did not improve adenoma detection among endoscopists with high baseline detection rates.
However, despite its availability, AI-assisted colonoscopy was activated in only half of the cases, and multiple concerns were raised by staff and endoscopists in a postprocedural survey. In particular, endoscopists were concerned that the system would result in too many false-positive signals (82.4%), was too distracting (58.8%), and prolonged procedure time (47.1%).
The authors of the Stanford study that found no benefit with CADe in routine practice noted, “Most concerning would be if, inadvertently, CADe use was accompanied by a simultaneous unconscious degradation in the quality of mucosal exposure, possibly due to a false sense of comfort that CADe would ensure a high-quality examination.”
“We’re trying to evaluate some of these interactions between endoscopists and AI devices both pragmatically in practice as well as in clinical trials,” Dr. Sharma said. “Much depends on the context of how you approach and present the devices. We tell physicians that this is an assist device, not something you’re competing against and not something that’s here to replace you. This is something which may make your lives easier, so try it out.”
Are Less Experienced Endoscopists Helped More?
It seems intuitive that less experienced endoscopists would be helped by AI, and indeed, some recent studies confirm this.
A small randomized controlled trial in Japan, presented during the Presidential Plenary at the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) annual meeting in May 2023, showed that a CADe system was “particularly useful” for beginning endoscopists, who had lower adenoma miss rates with the device vs a white light control device.
Another randomized controlled trial in Japan found that CADe use was associated with an increased overall ADR among endoscopists in training.
But experienced endoscopists probably can benefit as well, noted Jennifer Christie, MD, Division Director, Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora.
“We know that these AI devices can be useful in training our fellows to detect certain lesions in the colon,” she said. “However, they’re also helpful for many very seasoned practitioners, as an adjunctive tool to help in terms of diagnosis.”
Some studies reflect that dual benefit.
The AID-2 study, designed specifically to look at whether experience had an effect on AI findings during colonoscopy, was conducted among nonexpert endoscopists (lifetime volume of less than 2000 colonoscopies). The researchers, including Dr. Sharma, found that CADe increased the ADR by 22% compared with the control group.
An earlier study, AID-1 , used a similar design but was conducted among experienced endoscopists. In AID-1, the ADR was also significantly higher in the CADe group (54.8%) compared with the control group (40.4%), and adenomas detected per colonoscopy were significantly higher in the CADe group (mean, 1.07) than in the control group (mean, 0.71).
A multivariate post hoc analysis that pooled results from both AID-1 and AID-2 showed that use of CADe and colonoscopy indication, but not the level of examiner experience, were associated with ADR differences. This led the researchers to conclude, “Experience appears to play a minor role as a determining factor for ADR.”
Similarly, a 2023 study from China looked at the mean number of adenomas detected per colonoscopy according to the endoscopist’s experience. All rates were significantly higher in AI-assisted colonoscopies compared with conventional non-AI colonoscopy: overall ADR, 39.9% vs 32.4%; advanced ADR, 6.6% vs 4.9%; ADR of expert endoscopists, 42.3% vs 32.8%; ADR of nonexpert endoscopists, 37.5% vs 32.1%; and adenomas per colonoscopy, 0.59 vs 0.45, respectively.
The authors concluded that “AI-assisted colonoscopy improved overall ADR, advanced ADR, and ADR of both expert and nonexpert attending endoscopists.”
Improving the Algorithms
Experts agree that current and future research will improve the accuracy and quality of AI colonoscopy for all users, leading to new standards and more consistent outcomes in both clinical trials and real-world applications.
Work underway now to improve the algorithms will be an important step in that direction, according to Dr. Christie.
“We need to have enough information to create AI algorithms that allow us to detect early lesions, at least from an imaging standpoint, and we need to improve and increase the sensitivity and the specificity, as well as the predictive value,” she said.
AI can also play a role in health equity, she noted.
“But it’s a double-edged sword, because it depends again on algorithms and machine learning. Perhaps AI can eliminate some of the bias in our clinical decision-making. However, if we don’t train the machine properly with a good, diverse sample of patients and figure out how to integrate some of the social determinants of health that a computer may not otherwise consider, it can create larger disparities and larger biases. AI devices can only be as good and as inclusive as we make them,” Dr. Christie said.
Looking Ahead
Dr. Sharma predicts that “the next slew of studies are going to be on characterization — not just saying there’s an abnormality but distinguishing it further and saying whether the lesion is noncancerous, precancerous, or cancer.”
Other studies will focus on quality improvement of factors, such as withdrawal time and bowel preparation.
In its clinical practice update on AI, the American Gastroenterological Association states, “Eventually, we predict an AI suite of tools for colonoscopy will seem indispensable, as a powerful adjunct to support safe and efficient clinical practice. AI tools that improve colonoscopy quality may become more accepted, and perhaps demanded, by payors, administrators, and possibly even by well-informed patients who want to ensure the highest-quality examination of their colon.”
Dr. Sharma and Dr. Christie disclose no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds the promise of identifying premalignant and advanced malignant lesions during colonoscopy that might otherwise be missed.
Is it living up to that promise?
It seems that depends on where, how, and by whom it’s being implemented.
Clinical Trials vs the Real World
The majority of randomized clinical trials of AI use conducted worldwide “clearly show an increase in the adenoma detection rate (ADR) during colonoscopy,” Prateek Sharma, MD, a gastroenterologist at The University of Kansas Cancer Center, Kansas City, told this news. “But the real-world results have been quite varied; some show improvement, and others don’t.”
Dr. Sharma is coauthor of a recent pooled analysis of nine randomized controlled trials on the impact of AI on colonoscopy surveillance after polyp removal. It found that AI use increased the proportion of patients requiring intensive surveillance by approximately 35% in the United States and 20% in Europe (absolute increases of 2.9% and 1.3%, respectively).
“While this may contribute to improved cancer prevention, it significantly adds patient burden and healthcare costs,” the authors concluded.
A recent retrospective analysis of staggered implementation of a computer-aided detection (CADe) system at a single academic center in Chicago found that for screening and surveillance colonoscopy combined, endoscopists using CADe identified more adenomas and serrated polyps — but only endoscopists who used CADe regularly (“majority” users).
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 21 randomized controlled trials comparing CADe with standard colonoscopy found increased detection of adenomas, but not of advanced adenomas, as well as higher rates of unnecessary removal of non-neoplastic polyps.
Adding to the mix, a multicenter randomized controlled trial of patients with a positive fecal immunochemical test found that AI use was not associated with better detection of advanced neoplasias. Lead author Carolina Mangas Sanjuán, MD, PhD, Hospital General Universitario Dr. Balmis, Alicante, Spain, told this news organization the results were “surprising,” given previous studies showing benefit.
Similarly, a pragmatic implementation trial conducted by Stanford, California, researchers showed no significant effect of CADe on ADR, adenomas per colonoscopy, or any other detection metric. Furthermore, CADe had no effect on procedure times or non-neoplastic detection rates.
The authors cautioned against viewing their study as an “outlier,” however, and pointed to an Israeli study comparing adenoma and polyp detection rates 6 months before and after the introduction of AI-aided colonoscopy. Those authors reported no performance improvement with the AI device and concluded that it was not useful in routine practice.
A ‘Mishmash’ of Methods
“It’s not clear why some studies are positive, and some are negative,” Dr. Sharma acknowledged.
Study design is a factor, particularly in real-world studies, he said. Some researchers use the before/after approach, as in the Israeli study; others compare use in different rooms — that is, one with a CADe device and one without. Like the Chicago analysis, findings from such studies probably depend on whether the colonoscopists with the CADe device in the room actually use it.
Other real-world studies look at detection by time, Dr. Sharma said.
For example, a study of 1780 colonoscopies in China found that AI systems showed higher assistance ability among colonoscopies performed later in the day, when adenoma detection rates typically declined, perhaps owing to fatigue.
These authors suggest that AI may have the potential to maintain high quality and homogeneity of colonoscopies and improve endoscopist performance in large screening programs and centers with high workloads.
“There’s a mishmash of different kinds of real-world studies coming in, and it’s very difficult to figure it all out,” Dr. Sharma said. “We just have to look at these devices as innovations and embrace them and work with them to see how it fits it in our practice.”
Perceptions and Expectations
Emerging evidence suggests that endoscopists’ perceptions and expectations may affect assessments of AI’s potential benefits in practice, Dr. Sharma noted.
“Someone might say, ‘I’m a trained physician. Why do I need a machine to help me?’ That can create a situation in which the endoscopist is constantly challenging the device, trying to overrule it or not give it credit.”
Others might perceive that the AI device will definitely help and therefore not look as carefully themselves for adenomas.
A study at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston in which activation of the AI system was at the discretion of the endoscopist found that real-time CADe did not improve adenoma detection among endoscopists with high baseline detection rates.
However, despite its availability, AI-assisted colonoscopy was activated in only half of the cases, and multiple concerns were raised by staff and endoscopists in a postprocedural survey. In particular, endoscopists were concerned that the system would result in too many false-positive signals (82.4%), was too distracting (58.8%), and prolonged procedure time (47.1%).
The authors of the Stanford study that found no benefit with CADe in routine practice noted, “Most concerning would be if, inadvertently, CADe use was accompanied by a simultaneous unconscious degradation in the quality of mucosal exposure, possibly due to a false sense of comfort that CADe would ensure a high-quality examination.”
“We’re trying to evaluate some of these interactions between endoscopists and AI devices both pragmatically in practice as well as in clinical trials,” Dr. Sharma said. “Much depends on the context of how you approach and present the devices. We tell physicians that this is an assist device, not something you’re competing against and not something that’s here to replace you. This is something which may make your lives easier, so try it out.”
Are Less Experienced Endoscopists Helped More?
It seems intuitive that less experienced endoscopists would be helped by AI, and indeed, some recent studies confirm this.
A small randomized controlled trial in Japan, presented during the Presidential Plenary at the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) annual meeting in May 2023, showed that a CADe system was “particularly useful” for beginning endoscopists, who had lower adenoma miss rates with the device vs a white light control device.
Another randomized controlled trial in Japan found that CADe use was associated with an increased overall ADR among endoscopists in training.
But experienced endoscopists probably can benefit as well, noted Jennifer Christie, MD, Division Director, Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora.
“We know that these AI devices can be useful in training our fellows to detect certain lesions in the colon,” she said. “However, they’re also helpful for many very seasoned practitioners, as an adjunctive tool to help in terms of diagnosis.”
Some studies reflect that dual benefit.
The AID-2 study, designed specifically to look at whether experience had an effect on AI findings during colonoscopy, was conducted among nonexpert endoscopists (lifetime volume of less than 2000 colonoscopies). The researchers, including Dr. Sharma, found that CADe increased the ADR by 22% compared with the control group.
An earlier study, AID-1 , used a similar design but was conducted among experienced endoscopists. In AID-1, the ADR was also significantly higher in the CADe group (54.8%) compared with the control group (40.4%), and adenomas detected per colonoscopy were significantly higher in the CADe group (mean, 1.07) than in the control group (mean, 0.71).
A multivariate post hoc analysis that pooled results from both AID-1 and AID-2 showed that use of CADe and colonoscopy indication, but not the level of examiner experience, were associated with ADR differences. This led the researchers to conclude, “Experience appears to play a minor role as a determining factor for ADR.”
Similarly, a 2023 study from China looked at the mean number of adenomas detected per colonoscopy according to the endoscopist’s experience. All rates were significantly higher in AI-assisted colonoscopies compared with conventional non-AI colonoscopy: overall ADR, 39.9% vs 32.4%; advanced ADR, 6.6% vs 4.9%; ADR of expert endoscopists, 42.3% vs 32.8%; ADR of nonexpert endoscopists, 37.5% vs 32.1%; and adenomas per colonoscopy, 0.59 vs 0.45, respectively.
The authors concluded that “AI-assisted colonoscopy improved overall ADR, advanced ADR, and ADR of both expert and nonexpert attending endoscopists.”
Improving the Algorithms
Experts agree that current and future research will improve the accuracy and quality of AI colonoscopy for all users, leading to new standards and more consistent outcomes in both clinical trials and real-world applications.
Work underway now to improve the algorithms will be an important step in that direction, according to Dr. Christie.
“We need to have enough information to create AI algorithms that allow us to detect early lesions, at least from an imaging standpoint, and we need to improve and increase the sensitivity and the specificity, as well as the predictive value,” she said.
AI can also play a role in health equity, she noted.
“But it’s a double-edged sword, because it depends again on algorithms and machine learning. Perhaps AI can eliminate some of the bias in our clinical decision-making. However, if we don’t train the machine properly with a good, diverse sample of patients and figure out how to integrate some of the social determinants of health that a computer may not otherwise consider, it can create larger disparities and larger biases. AI devices can only be as good and as inclusive as we make them,” Dr. Christie said.
Looking Ahead
Dr. Sharma predicts that “the next slew of studies are going to be on characterization — not just saying there’s an abnormality but distinguishing it further and saying whether the lesion is noncancerous, precancerous, or cancer.”
Other studies will focus on quality improvement of factors, such as withdrawal time and bowel preparation.
In its clinical practice update on AI, the American Gastroenterological Association states, “Eventually, we predict an AI suite of tools for colonoscopy will seem indispensable, as a powerful adjunct to support safe and efficient clinical practice. AI tools that improve colonoscopy quality may become more accepted, and perhaps demanded, by payors, administrators, and possibly even by well-informed patients who want to ensure the highest-quality examination of their colon.”
Dr. Sharma and Dr. Christie disclose no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.