User login
Patient-reported outcomes show impairment decades after acute knee injury
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND – Decades after they were sustained, acute knee injuries caused clinically significant impairments in patient-reported outcomes, as well as upped the risk for knee osteoarthritis (OA) in an observational study.
Results of the study, which followed up individuals 32-37 years after they were treated for a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury between 1980 and 1985, showed that, compared with the general population, they experienced greater levels of knee pain, participated less in physical activities, and had a reduced quality of life.
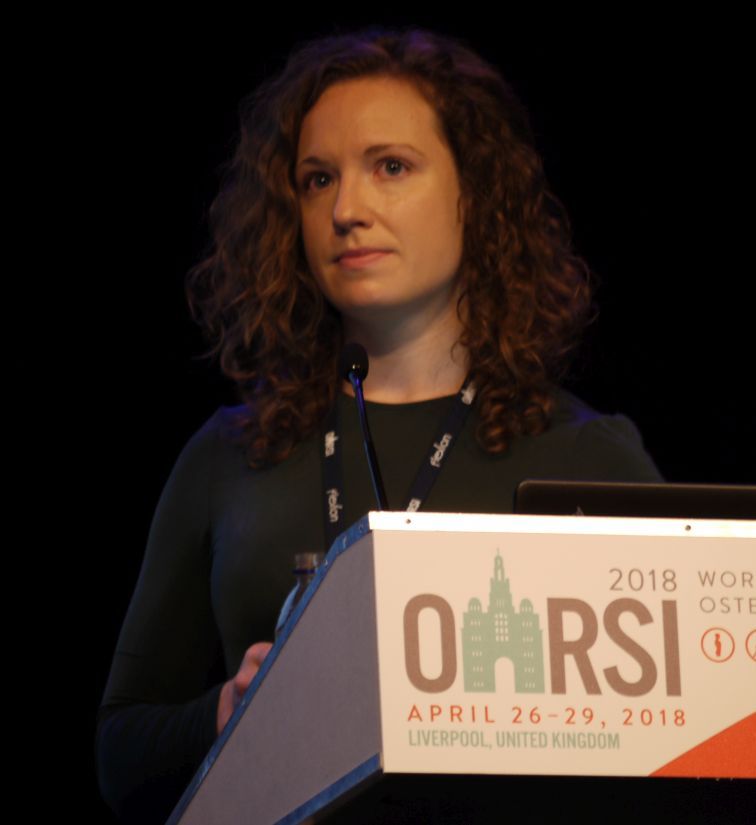
The link between OA and ACL injury is not new, with prior estimates suggesting that up to half of all patients with ACL injury develop OA within 10 years of the injury, said Stephanie Filbay, PhD, who presented the results of the study at the World Congress on Osteoarthritis. There have also been reports of knee pain and other symptoms, and poor quality of life more than 5 years later. What’s not been known until now, however, is what happens with even longer term follow-up, said Dr. Filbay, a postdoctoral research fellow in sport, exercise, and osteoarthritis at the University of Oxford, England.
The aims of the study were to compare patient-reported outcomes at 32-37-years’ follow-up against the general population, then to see if the baseline injury or treatment approach, or knee function 3-7 years after the initial injury had any influence on outcomes.
The study included 223 patients who were between aged 15 and 40 years at the time of the acute ACL injury between 1980 and 1985 and who had been seen within 2 weeks of ACL rupture at Linköping University Hospital in Linköping, Sweden. Patients had been allocated to early surgical or non-surgical treatment based on having an odd or even birth year. They had then been assessed 3-7 years later using a variety of tests to determine the strength of their quadriceps and hamstrings and the ability to hop on one leg.
All patients were then invited 32-37 years later after the initial injury to complete questionnaires and undergo clinical examination and X-rays. Only four people declined and 38 did not answer, leaving 181 (81%) people who agreed to participate and complete the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) and the ACL quality of life questionnaire (ACL-QOL).
The average age of participants at follow-up was 59 years (range, 47-74 years); 30% were female. 58% of all patients had been treated non-surgically initially, and 38% remained non-surgically treated at the longterm follow-up. At baseline, 58% had a meniscus injury.
Compared with an age- and sex-matched Swedish population, patients with ACL injuries had a lower KOOS for pain, sport/recreational activities, and quality of life. For example, KOOS for knee pain was around 65-70 for those with prior ACL injuries, compared with 80-90 for those without ACL injuries, where 100 indicates the best outcome or least pain and zero the worst.
KOOS was not affected by whether or not patients had initial ACL surgery or surgery at any point in their follow up. It also did not appear to matter if patients had a meniscal injury at baseline or not.
Quadriceps and hamstring strength at the 3-7 year postinjury assessment did not affect the longterm KOOS, but the ability to hop on one leg did: Those who were not able to hop on one leg for more than 90% of the time on the unaffected limb at the 3-7 years follow-up had worse pain, symptoms, function, and quality of life at the longterm follow-up point.
With regards to OA, “overall, more than one in two individuals had Kellgren-Lawrence grade 4 that could be considered severe radiographic changes in at least one compartment,” Dr. Filbay said at the meeting, which is sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Severe radiographic changes were most common in the tibiofemoral joint, with around 47% having Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grade 4. About 35% of tibiofemoral joints and about 60% of patellofemoral joints were KL grade 1.
Interestingly, different factors were found to be associated with OA in the tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joints, according to Dr. Filbay. Patients who had been treated non-surgically, whether initially or at any time during the 32-37 year follow-up, were more likely to have tibiofemoral OA, whereas those who had been treated surgically tended to have patellofemoral OA.
“Perhaps not surprisingly, meniscal injury at baseline was related to a higher percentage of tibiofemoral OA at long-term follow-up,” Dr. Filbay said.
Another finding was that patients with weaker hamstrings 3-7 years after the injury were more likely to develop patellofemoral joint OA.
Dr. Filbay had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Filbay S, et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018:26(1):S52-3. Abstract 80.
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND – Decades after they were sustained, acute knee injuries caused clinically significant impairments in patient-reported outcomes, as well as upped the risk for knee osteoarthritis (OA) in an observational study.
Results of the study, which followed up individuals 32-37 years after they were treated for a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury between 1980 and 1985, showed that, compared with the general population, they experienced greater levels of knee pain, participated less in physical activities, and had a reduced quality of life.
The link between OA and ACL injury is not new, with prior estimates suggesting that up to half of all patients with ACL injury develop OA within 10 years of the injury, said Stephanie Filbay, PhD, who presented the results of the study at the World Congress on Osteoarthritis. There have also been reports of knee pain and other symptoms, and poor quality of life more than 5 years later. What’s not been known until now, however, is what happens with even longer term follow-up, said Dr. Filbay, a postdoctoral research fellow in sport, exercise, and osteoarthritis at the University of Oxford, England.
The aims of the study were to compare patient-reported outcomes at 32-37-years’ follow-up against the general population, then to see if the baseline injury or treatment approach, or knee function 3-7 years after the initial injury had any influence on outcomes.
The study included 223 patients who were between aged 15 and 40 years at the time of the acute ACL injury between 1980 and 1985 and who had been seen within 2 weeks of ACL rupture at Linköping University Hospital in Linköping, Sweden. Patients had been allocated to early surgical or non-surgical treatment based on having an odd or even birth year. They had then been assessed 3-7 years later using a variety of tests to determine the strength of their quadriceps and hamstrings and the ability to hop on one leg.
All patients were then invited 32-37 years later after the initial injury to complete questionnaires and undergo clinical examination and X-rays. Only four people declined and 38 did not answer, leaving 181 (81%) people who agreed to participate and complete the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) and the ACL quality of life questionnaire (ACL-QOL).
The average age of participants at follow-up was 59 years (range, 47-74 years); 30% were female. 58% of all patients had been treated non-surgically initially, and 38% remained non-surgically treated at the longterm follow-up. At baseline, 58% had a meniscus injury.
Compared with an age- and sex-matched Swedish population, patients with ACL injuries had a lower KOOS for pain, sport/recreational activities, and quality of life. For example, KOOS for knee pain was around 65-70 for those with prior ACL injuries, compared with 80-90 for those without ACL injuries, where 100 indicates the best outcome or least pain and zero the worst.
KOOS was not affected by whether or not patients had initial ACL surgery or surgery at any point in their follow up. It also did not appear to matter if patients had a meniscal injury at baseline or not.
Quadriceps and hamstring strength at the 3-7 year postinjury assessment did not affect the longterm KOOS, but the ability to hop on one leg did: Those who were not able to hop on one leg for more than 90% of the time on the unaffected limb at the 3-7 years follow-up had worse pain, symptoms, function, and quality of life at the longterm follow-up point.
With regards to OA, “overall, more than one in two individuals had Kellgren-Lawrence grade 4 that could be considered severe radiographic changes in at least one compartment,” Dr. Filbay said at the meeting, which is sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Severe radiographic changes were most common in the tibiofemoral joint, with around 47% having Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grade 4. About 35% of tibiofemoral joints and about 60% of patellofemoral joints were KL grade 1.
Interestingly, different factors were found to be associated with OA in the tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joints, according to Dr. Filbay. Patients who had been treated non-surgically, whether initially or at any time during the 32-37 year follow-up, were more likely to have tibiofemoral OA, whereas those who had been treated surgically tended to have patellofemoral OA.
“Perhaps not surprisingly, meniscal injury at baseline was related to a higher percentage of tibiofemoral OA at long-term follow-up,” Dr. Filbay said.
Another finding was that patients with weaker hamstrings 3-7 years after the injury were more likely to develop patellofemoral joint OA.
Dr. Filbay had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Filbay S, et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018:26(1):S52-3. Abstract 80.
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND – Decades after they were sustained, acute knee injuries caused clinically significant impairments in patient-reported outcomes, as well as upped the risk for knee osteoarthritis (OA) in an observational study.
Results of the study, which followed up individuals 32-37 years after they were treated for a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury between 1980 and 1985, showed that, compared with the general population, they experienced greater levels of knee pain, participated less in physical activities, and had a reduced quality of life.
The link between OA and ACL injury is not new, with prior estimates suggesting that up to half of all patients with ACL injury develop OA within 10 years of the injury, said Stephanie Filbay, PhD, who presented the results of the study at the World Congress on Osteoarthritis. There have also been reports of knee pain and other symptoms, and poor quality of life more than 5 years later. What’s not been known until now, however, is what happens with even longer term follow-up, said Dr. Filbay, a postdoctoral research fellow in sport, exercise, and osteoarthritis at the University of Oxford, England.
The aims of the study were to compare patient-reported outcomes at 32-37-years’ follow-up against the general population, then to see if the baseline injury or treatment approach, or knee function 3-7 years after the initial injury had any influence on outcomes.
The study included 223 patients who were between aged 15 and 40 years at the time of the acute ACL injury between 1980 and 1985 and who had been seen within 2 weeks of ACL rupture at Linköping University Hospital in Linköping, Sweden. Patients had been allocated to early surgical or non-surgical treatment based on having an odd or even birth year. They had then been assessed 3-7 years later using a variety of tests to determine the strength of their quadriceps and hamstrings and the ability to hop on one leg.
All patients were then invited 32-37 years later after the initial injury to complete questionnaires and undergo clinical examination and X-rays. Only four people declined and 38 did not answer, leaving 181 (81%) people who agreed to participate and complete the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) and the ACL quality of life questionnaire (ACL-QOL).
The average age of participants at follow-up was 59 years (range, 47-74 years); 30% were female. 58% of all patients had been treated non-surgically initially, and 38% remained non-surgically treated at the longterm follow-up. At baseline, 58% had a meniscus injury.
Compared with an age- and sex-matched Swedish population, patients with ACL injuries had a lower KOOS for pain, sport/recreational activities, and quality of life. For example, KOOS for knee pain was around 65-70 for those with prior ACL injuries, compared with 80-90 for those without ACL injuries, where 100 indicates the best outcome or least pain and zero the worst.
KOOS was not affected by whether or not patients had initial ACL surgery or surgery at any point in their follow up. It also did not appear to matter if patients had a meniscal injury at baseline or not.
Quadriceps and hamstring strength at the 3-7 year postinjury assessment did not affect the longterm KOOS, but the ability to hop on one leg did: Those who were not able to hop on one leg for more than 90% of the time on the unaffected limb at the 3-7 years follow-up had worse pain, symptoms, function, and quality of life at the longterm follow-up point.
With regards to OA, “overall, more than one in two individuals had Kellgren-Lawrence grade 4 that could be considered severe radiographic changes in at least one compartment,” Dr. Filbay said at the meeting, which is sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
Severe radiographic changes were most common in the tibiofemoral joint, with around 47% having Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grade 4. About 35% of tibiofemoral joints and about 60% of patellofemoral joints were KL grade 1.
Interestingly, different factors were found to be associated with OA in the tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joints, according to Dr. Filbay. Patients who had been treated non-surgically, whether initially or at any time during the 32-37 year follow-up, were more likely to have tibiofemoral OA, whereas those who had been treated surgically tended to have patellofemoral OA.
“Perhaps not surprisingly, meniscal injury at baseline was related to a higher percentage of tibiofemoral OA at long-term follow-up,” Dr. Filbay said.
Another finding was that patients with weaker hamstrings 3-7 years after the injury were more likely to develop patellofemoral joint OA.
Dr. Filbay had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Filbay S, et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018:26(1):S52-3. Abstract 80.
REPORTING FROM OARSI 2018
Key clinical point: Decades after rupturing the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), patients can experience significant impairments.
Major finding: 70% of 136 of the patients in the study developed knee osteoarthritis 32-37 years after an ACL injury.Study details: A population-based, observational follow-up study of 181 individuals who had an acute ACL injury in 1980-1985. Disclosures: Stephanie Filbay, PhD., had no disclosures. Source: Filbay S, et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018:26(1):S52-53. Abstract 80.
Rare paraneoplastic dermatomyositis secondary to high-grade bladder cancer
The clinical presentation of bladder cancer typically presents with hematuria; changes in voiding habits such as urgency, frequency, and pain; or less commonly, obstructive symptoms. Rarely does bladder cancer first present as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome with an inflammatory myopathy. Inflammatory myopathies such as dermatomyositis have been known to be associated with malignancy, however, in a meta-analysis by Yang and colleagues of 449 patients with dermatomyositis and malignancy there were only 8 cases reported of bladder cancer.1 Herein, we report a paraneoplastic dermatomyositis in the setting of a bladder cancer.
Case presentation and summary
A 65-year-old man with a medical history of hypertension and alcohol use presented to the emergency department with worsening pain, stiffness in the neck, shoulders, and inability to lift his arms above his shoulders. During the physical exam, an erythematous purple rash was noted over his chest, neck, and arms. Upon further evaluation, his creatine phosphokinase was 3,500 U/L (reference range 52-336 U/L) suggesting muscle breakdown and possible inflammatory myopathy. A biopsy of the left deltoid and quadriceps muscles was performed and yielded a diagnosis of dermatomyositis. He was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily for his inflammatory myopathy. The patient also reported an unintentional weight loss of 20 lbs. and increasing weakness and inability to swallow, which caused aspiration events without developing pneumonia.
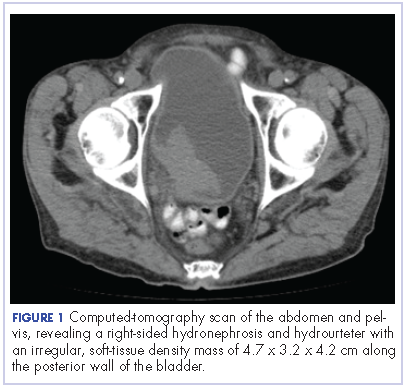
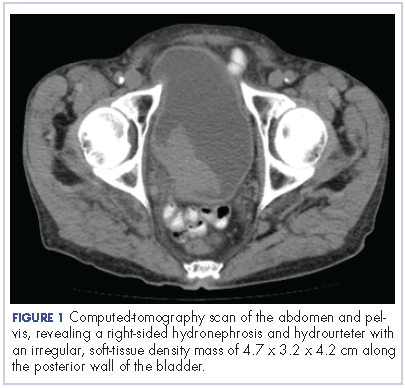
The patient’s symptoms worsened while he was on steroids, and we became concerned about the possibility of a primary malignancy, which led to further work-up. The results of a computed-tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis showed right-sided hydronephrosis and hydrourteter with an irregular, soft-tissue density mass of 4.7 x 3.2 x 4.2 cm along the posterior wall of the bladder (Figure 1).
A cystoscopy was performed with transurethral resection of a bladder tumor that was more than 8 cm in diameter. Because the mass was not fully resectable, only 25% of the tumor burden was removed. The pathology report revealed an invasive, high-grade urothelial cell carcinoma (Figure 2, see PDF). Further imaging ruled out metastatic spread. The patient was continued on steroids. He was not a candidate for neoadjuvant chemotherapy because of his comorbidities and cisplatin ineligibility owing to his significant bilateral hearing deficiencies. Members of a multidisciplinary tumor board decided to move forward with definitive surgery. The patient underwent a robotic-assisted laparoscoptic cystoprostatectomy with bilateral pelvic lymph node dissection and open ileal conduit urinary diversion. Staging of tumor was determined as pT3b N1 (1/30) M0, LVI+. After the surgery, the patient had resolution of his rash and significant improvement in his muscle weakness with the ability to raise his arms over his head and climb stairs. Adjuvant chemotherapy was not given since he was cisplatin ineligible as a result of his hearing loss. Active surveillance was preferred.
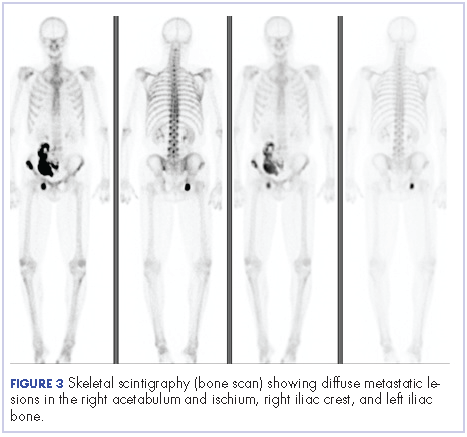
Four months after his cystoprostatectomy, he experienced new-onset hip pain and further imaging, including a bone scan, was performed. It showed metastatic disease in the ischium and iliac crest (Figure 3).
The patient decided to forgo any palliative chemotherapy and to have palliative radiation for pain and enroll in hospice. He died nine months after the initial diagnosis of urothelial cell carcinoma.
Discussion
Dermatomyositis is one of the inflammatory myopathies with a clinical presentation of proximal muscle weakness and characteristic skin findings of Gottron papules and heliotrope eruption. The most common subgroups of inflammatory myopathies are dermatomyositis, polymyositis, necrotizing autoimmune myopathy, and inclusion body myopathy. The pathogenesis of inflammatory myopathies is not well understood; however, some theories have been described, including: type 1 interferon signaling causing myofiber injury and antibody-complement mediated processes causing ischemia resulting in myofiber injury. 2,3 The diagnoses of inflammatory myopathies may be suggested based on history, physical examination findings, laboratory values showing muscle injury (creatine kinase, aldolase, ALT, AST, LDH), myositis-specific antibodies (antisynthetase autoantibodies), electromyogram, and magnetic-resonance imaging. However, muscle biopsy remains the gold standard.4
The initial treatment of inflammatory myopathies begins with glucocorticoid therapy at 0.5-1.0 mg/kg. This regimen may be titrated down over 6 weeks to a level adequate to control symptoms. Even while on glucocorticoid therapy, this patient’s symptoms continued, along with the development of dysphagia. Dysphagia is another notable symptom of dermatomyositis that may result in aspiration pneumonia with fatal outcomes.5,6,7 Not only did this patient initially respond poorly to corticosteroids, but the unintentional weight loss was another alarming feature prompting further evaluation. That led to the diagnosis of urothelial cell carcinoma, which was causing the paraneoplastic syndrome.
A paraneoplastic syndrome is a collection of symptoms that are observed in organ systems separate from the primary disease. This process is mostly caused by an autoimmune response to the tumor and nervous system.8 Inflammatory myopathies, such as dermatomyositis, have been shown to be associated with a variety of malignancies as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome. The most common cancers associated with dermatomyositis are ovarian, lung, pancreatic, stomach, colorectal, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.9 Although an association between dermatomyositis and bladder cancer has been established, very few cases have been reported in the literature. In the Yang meta-analysis, the relative risk of malignancy for patients with dermatomyositis was 5.5%, and of the 449 patients with dermatomyositis who had malignancy, only 8 cases of bladder cancer were reported.1
After a patient has been diagnosed with an inflammatory myopathy, there should be further evaluation for an underling malignancy causing a paraneoplastic process. The risk of these patients having a malignancy overall is 4.5 times higher than patients without dermatomyositis.1 Definite screening recommendations have not been established, but screening should be based on patient’s age, gender, and clinical scenario. The European Federation of Neurological Societies formed a task force to focus on malignancy screening of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes and included dermatomyositis as one of the signs.10 Patients should have a CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. Women should have a mammogram and a pelvis ultrasound. Men younger than 50 years should consider testes ultrasound, and patients older than 50 years should undergo usual colonoscopy screening.
The risk of malignancy is highest in the first year after diagnosis, but may extend to 5 years after the diagnosis, so repeat screening should be performed 3-6 months after diagnosis, followed with biannual testing for 4 years. If a malignancy is present, then treatment should be tailored to the neoplasm to improve symptoms of myositis; however, response is generally worse than it would be with dermatomyositis in the absence of malignancy. In the present case with bladder cancer, therapies may include platinum-based-chemotherapy, resection, and radiation. Dermatomyositis as a result of a bladder cancer paraneoplastic syndrome is associated with a poor prognosis as demonstrated in the case of this patient and others reported in the literature.11
Even though dermatomyositis is usually a chronic disease process, 87% of patients respond initially to corticosteroid treatment.12 Therefore, treatment should be escalated with an agent such as azathioprine or methotrexate, or, like in this case, an underlying malignancy should be suspected. This case emphasizes the importance of screening patients appropriately for malignancy in patients with an inflammatory myopathy and reveals the poor prognosis associated with this disease.
1. Yang Z, Lin F, Qin B, Liang Y, Zhong R. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis and malignancy risk: a metaanalysis study. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(2):282-291.
2. Greenberg, SA. Dermatomyositis and type 1 interferons. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2010;12(3):198-203.
3. Dalakas, MC, Hohlfeld, R. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet. 2003;362(9388):971-982.
4. Malik A, Hayat G, Kalia JS, Guzman MA. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: clinical approach and management. Front Neurol. 2016;7:64.
5. Sabio JM, Vargas-Hitos JA, Jiménez-Alonso J. Paraneoplastic dermatomyositis associated with bladder cancer. Lupus. 2006;15(9):619-620.
6. Mallon E, Osborne G, Dinneen M, Lane RJ, Glaser M, Bunker CB. Dermatomyositis in association with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999;24(2):94-96.
7. Hafejee A, Coulson IH. Dysphagia in dermatomyositis secondary to bladder cancer: rapid response to combined immunoglobulin and methylprednisolone. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30(1):93-94.
8. Dalmau J, Gultekin HS, Posner JB. Paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes: pathogenesis and physiopathology. Brain Pathol. 1999;9(2):275-284.
9. Hill CL, Zhang Y, Sigureirsson B, et al. Frequency of specific cancer types in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: a population-based study. Lancet. 2001;357(9250):96-100.
10. Titulaer, MJ, Soffietti R, Dalmau J, et al. Screening for tumours in paraneoplastic syndromes: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18(1):19-e3.
11. Xu R, Zhong Z, Jiang H, Zhang L, Zhao X. A rare paraneoplastic dermatomyositis in bladder cancer with fatal outcome. Urol J. 2013;10(1):815-817.
12. Troyanov Y, Targoff IN, Tremblay JL, Goulet JR, Raymond Y, Senecal JL. Novel classification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies based on overlap syndrome features and autoantibodies: analysis of 100 French Canadian patients. Medicine (Baltimore), 2005;84(4):231-249.
The clinical presentation of bladder cancer typically presents with hematuria; changes in voiding habits such as urgency, frequency, and pain; or less commonly, obstructive symptoms. Rarely does bladder cancer first present as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome with an inflammatory myopathy. Inflammatory myopathies such as dermatomyositis have been known to be associated with malignancy, however, in a meta-analysis by Yang and colleagues of 449 patients with dermatomyositis and malignancy there were only 8 cases reported of bladder cancer.1 Herein, we report a paraneoplastic dermatomyositis in the setting of a bladder cancer.
Case presentation and summary
A 65-year-old man with a medical history of hypertension and alcohol use presented to the emergency department with worsening pain, stiffness in the neck, shoulders, and inability to lift his arms above his shoulders. During the physical exam, an erythematous purple rash was noted over his chest, neck, and arms. Upon further evaluation, his creatine phosphokinase was 3,500 U/L (reference range 52-336 U/L) suggesting muscle breakdown and possible inflammatory myopathy. A biopsy of the left deltoid and quadriceps muscles was performed and yielded a diagnosis of dermatomyositis. He was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily for his inflammatory myopathy. The patient also reported an unintentional weight loss of 20 lbs. and increasing weakness and inability to swallow, which caused aspiration events without developing pneumonia.
The patient’s symptoms worsened while he was on steroids, and we became concerned about the possibility of a primary malignancy, which led to further work-up. The results of a computed-tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis showed right-sided hydronephrosis and hydrourteter with an irregular, soft-tissue density mass of 4.7 x 3.2 x 4.2 cm along the posterior wall of the bladder (Figure 1).
A cystoscopy was performed with transurethral resection of a bladder tumor that was more than 8 cm in diameter. Because the mass was not fully resectable, only 25% of the tumor burden was removed. The pathology report revealed an invasive, high-grade urothelial cell carcinoma (Figure 2, see PDF). Further imaging ruled out metastatic spread. The patient was continued on steroids. He was not a candidate for neoadjuvant chemotherapy because of his comorbidities and cisplatin ineligibility owing to his significant bilateral hearing deficiencies. Members of a multidisciplinary tumor board decided to move forward with definitive surgery. The patient underwent a robotic-assisted laparoscoptic cystoprostatectomy with bilateral pelvic lymph node dissection and open ileal conduit urinary diversion. Staging of tumor was determined as pT3b N1 (1/30) M0, LVI+. After the surgery, the patient had resolution of his rash and significant improvement in his muscle weakness with the ability to raise his arms over his head and climb stairs. Adjuvant chemotherapy was not given since he was cisplatin ineligible as a result of his hearing loss. Active surveillance was preferred.
Four months after his cystoprostatectomy, he experienced new-onset hip pain and further imaging, including a bone scan, was performed. It showed metastatic disease in the ischium and iliac crest (Figure 3).
The patient decided to forgo any palliative chemotherapy and to have palliative radiation for pain and enroll in hospice. He died nine months after the initial diagnosis of urothelial cell carcinoma.
Discussion
Dermatomyositis is one of the inflammatory myopathies with a clinical presentation of proximal muscle weakness and characteristic skin findings of Gottron papules and heliotrope eruption. The most common subgroups of inflammatory myopathies are dermatomyositis, polymyositis, necrotizing autoimmune myopathy, and inclusion body myopathy. The pathogenesis of inflammatory myopathies is not well understood; however, some theories have been described, including: type 1 interferon signaling causing myofiber injury and antibody-complement mediated processes causing ischemia resulting in myofiber injury. 2,3 The diagnoses of inflammatory myopathies may be suggested based on history, physical examination findings, laboratory values showing muscle injury (creatine kinase, aldolase, ALT, AST, LDH), myositis-specific antibodies (antisynthetase autoantibodies), electromyogram, and magnetic-resonance imaging. However, muscle biopsy remains the gold standard.4
The initial treatment of inflammatory myopathies begins with glucocorticoid therapy at 0.5-1.0 mg/kg. This regimen may be titrated down over 6 weeks to a level adequate to control symptoms. Even while on glucocorticoid therapy, this patient’s symptoms continued, along with the development of dysphagia. Dysphagia is another notable symptom of dermatomyositis that may result in aspiration pneumonia with fatal outcomes.5,6,7 Not only did this patient initially respond poorly to corticosteroids, but the unintentional weight loss was another alarming feature prompting further evaluation. That led to the diagnosis of urothelial cell carcinoma, which was causing the paraneoplastic syndrome.
A paraneoplastic syndrome is a collection of symptoms that are observed in organ systems separate from the primary disease. This process is mostly caused by an autoimmune response to the tumor and nervous system.8 Inflammatory myopathies, such as dermatomyositis, have been shown to be associated with a variety of malignancies as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome. The most common cancers associated with dermatomyositis are ovarian, lung, pancreatic, stomach, colorectal, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.9 Although an association between dermatomyositis and bladder cancer has been established, very few cases have been reported in the literature. In the Yang meta-analysis, the relative risk of malignancy for patients with dermatomyositis was 5.5%, and of the 449 patients with dermatomyositis who had malignancy, only 8 cases of bladder cancer were reported.1
After a patient has been diagnosed with an inflammatory myopathy, there should be further evaluation for an underling malignancy causing a paraneoplastic process. The risk of these patients having a malignancy overall is 4.5 times higher than patients without dermatomyositis.1 Definite screening recommendations have not been established, but screening should be based on patient’s age, gender, and clinical scenario. The European Federation of Neurological Societies formed a task force to focus on malignancy screening of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes and included dermatomyositis as one of the signs.10 Patients should have a CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. Women should have a mammogram and a pelvis ultrasound. Men younger than 50 years should consider testes ultrasound, and patients older than 50 years should undergo usual colonoscopy screening.
The risk of malignancy is highest in the first year after diagnosis, but may extend to 5 years after the diagnosis, so repeat screening should be performed 3-6 months after diagnosis, followed with biannual testing for 4 years. If a malignancy is present, then treatment should be tailored to the neoplasm to improve symptoms of myositis; however, response is generally worse than it would be with dermatomyositis in the absence of malignancy. In the present case with bladder cancer, therapies may include platinum-based-chemotherapy, resection, and radiation. Dermatomyositis as a result of a bladder cancer paraneoplastic syndrome is associated with a poor prognosis as demonstrated in the case of this patient and others reported in the literature.11
Even though dermatomyositis is usually a chronic disease process, 87% of patients respond initially to corticosteroid treatment.12 Therefore, treatment should be escalated with an agent such as azathioprine or methotrexate, or, like in this case, an underlying malignancy should be suspected. This case emphasizes the importance of screening patients appropriately for malignancy in patients with an inflammatory myopathy and reveals the poor prognosis associated with this disease.
The clinical presentation of bladder cancer typically presents with hematuria; changes in voiding habits such as urgency, frequency, and pain; or less commonly, obstructive symptoms. Rarely does bladder cancer first present as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome with an inflammatory myopathy. Inflammatory myopathies such as dermatomyositis have been known to be associated with malignancy, however, in a meta-analysis by Yang and colleagues of 449 patients with dermatomyositis and malignancy there were only 8 cases reported of bladder cancer.1 Herein, we report a paraneoplastic dermatomyositis in the setting of a bladder cancer.
Case presentation and summary
A 65-year-old man with a medical history of hypertension and alcohol use presented to the emergency department with worsening pain, stiffness in the neck, shoulders, and inability to lift his arms above his shoulders. During the physical exam, an erythematous purple rash was noted over his chest, neck, and arms. Upon further evaluation, his creatine phosphokinase was 3,500 U/L (reference range 52-336 U/L) suggesting muscle breakdown and possible inflammatory myopathy. A biopsy of the left deltoid and quadriceps muscles was performed and yielded a diagnosis of dermatomyositis. He was treated with prednisone 60 mg daily for his inflammatory myopathy. The patient also reported an unintentional weight loss of 20 lbs. and increasing weakness and inability to swallow, which caused aspiration events without developing pneumonia.
The patient’s symptoms worsened while he was on steroids, and we became concerned about the possibility of a primary malignancy, which led to further work-up. The results of a computed-tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis showed right-sided hydronephrosis and hydrourteter with an irregular, soft-tissue density mass of 4.7 x 3.2 x 4.2 cm along the posterior wall of the bladder (Figure 1).
A cystoscopy was performed with transurethral resection of a bladder tumor that was more than 8 cm in diameter. Because the mass was not fully resectable, only 25% of the tumor burden was removed. The pathology report revealed an invasive, high-grade urothelial cell carcinoma (Figure 2, see PDF). Further imaging ruled out metastatic spread. The patient was continued on steroids. He was not a candidate for neoadjuvant chemotherapy because of his comorbidities and cisplatin ineligibility owing to his significant bilateral hearing deficiencies. Members of a multidisciplinary tumor board decided to move forward with definitive surgery. The patient underwent a robotic-assisted laparoscoptic cystoprostatectomy with bilateral pelvic lymph node dissection and open ileal conduit urinary diversion. Staging of tumor was determined as pT3b N1 (1/30) M0, LVI+. After the surgery, the patient had resolution of his rash and significant improvement in his muscle weakness with the ability to raise his arms over his head and climb stairs. Adjuvant chemotherapy was not given since he was cisplatin ineligible as a result of his hearing loss. Active surveillance was preferred.
Four months after his cystoprostatectomy, he experienced new-onset hip pain and further imaging, including a bone scan, was performed. It showed metastatic disease in the ischium and iliac crest (Figure 3).
The patient decided to forgo any palliative chemotherapy and to have palliative radiation for pain and enroll in hospice. He died nine months after the initial diagnosis of urothelial cell carcinoma.
Discussion
Dermatomyositis is one of the inflammatory myopathies with a clinical presentation of proximal muscle weakness and characteristic skin findings of Gottron papules and heliotrope eruption. The most common subgroups of inflammatory myopathies are dermatomyositis, polymyositis, necrotizing autoimmune myopathy, and inclusion body myopathy. The pathogenesis of inflammatory myopathies is not well understood; however, some theories have been described, including: type 1 interferon signaling causing myofiber injury and antibody-complement mediated processes causing ischemia resulting in myofiber injury. 2,3 The diagnoses of inflammatory myopathies may be suggested based on history, physical examination findings, laboratory values showing muscle injury (creatine kinase, aldolase, ALT, AST, LDH), myositis-specific antibodies (antisynthetase autoantibodies), electromyogram, and magnetic-resonance imaging. However, muscle biopsy remains the gold standard.4
The initial treatment of inflammatory myopathies begins with glucocorticoid therapy at 0.5-1.0 mg/kg. This regimen may be titrated down over 6 weeks to a level adequate to control symptoms. Even while on glucocorticoid therapy, this patient’s symptoms continued, along with the development of dysphagia. Dysphagia is another notable symptom of dermatomyositis that may result in aspiration pneumonia with fatal outcomes.5,6,7 Not only did this patient initially respond poorly to corticosteroids, but the unintentional weight loss was another alarming feature prompting further evaluation. That led to the diagnosis of urothelial cell carcinoma, which was causing the paraneoplastic syndrome.
A paraneoplastic syndrome is a collection of symptoms that are observed in organ systems separate from the primary disease. This process is mostly caused by an autoimmune response to the tumor and nervous system.8 Inflammatory myopathies, such as dermatomyositis, have been shown to be associated with a variety of malignancies as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome. The most common cancers associated with dermatomyositis are ovarian, lung, pancreatic, stomach, colorectal, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.9 Although an association between dermatomyositis and bladder cancer has been established, very few cases have been reported in the literature. In the Yang meta-analysis, the relative risk of malignancy for patients with dermatomyositis was 5.5%, and of the 449 patients with dermatomyositis who had malignancy, only 8 cases of bladder cancer were reported.1
After a patient has been diagnosed with an inflammatory myopathy, there should be further evaluation for an underling malignancy causing a paraneoplastic process. The risk of these patients having a malignancy overall is 4.5 times higher than patients without dermatomyositis.1 Definite screening recommendations have not been established, but screening should be based on patient’s age, gender, and clinical scenario. The European Federation of Neurological Societies formed a task force to focus on malignancy screening of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes and included dermatomyositis as one of the signs.10 Patients should have a CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. Women should have a mammogram and a pelvis ultrasound. Men younger than 50 years should consider testes ultrasound, and patients older than 50 years should undergo usual colonoscopy screening.
The risk of malignancy is highest in the first year after diagnosis, but may extend to 5 years after the diagnosis, so repeat screening should be performed 3-6 months after diagnosis, followed with biannual testing for 4 years. If a malignancy is present, then treatment should be tailored to the neoplasm to improve symptoms of myositis; however, response is generally worse than it would be with dermatomyositis in the absence of malignancy. In the present case with bladder cancer, therapies may include platinum-based-chemotherapy, resection, and radiation. Dermatomyositis as a result of a bladder cancer paraneoplastic syndrome is associated with a poor prognosis as demonstrated in the case of this patient and others reported in the literature.11
Even though dermatomyositis is usually a chronic disease process, 87% of patients respond initially to corticosteroid treatment.12 Therefore, treatment should be escalated with an agent such as azathioprine or methotrexate, or, like in this case, an underlying malignancy should be suspected. This case emphasizes the importance of screening patients appropriately for malignancy in patients with an inflammatory myopathy and reveals the poor prognosis associated with this disease.
1. Yang Z, Lin F, Qin B, Liang Y, Zhong R. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis and malignancy risk: a metaanalysis study. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(2):282-291.
2. Greenberg, SA. Dermatomyositis and type 1 interferons. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2010;12(3):198-203.
3. Dalakas, MC, Hohlfeld, R. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet. 2003;362(9388):971-982.
4. Malik A, Hayat G, Kalia JS, Guzman MA. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: clinical approach and management. Front Neurol. 2016;7:64.
5. Sabio JM, Vargas-Hitos JA, Jiménez-Alonso J. Paraneoplastic dermatomyositis associated with bladder cancer. Lupus. 2006;15(9):619-620.
6. Mallon E, Osborne G, Dinneen M, Lane RJ, Glaser M, Bunker CB. Dermatomyositis in association with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999;24(2):94-96.
7. Hafejee A, Coulson IH. Dysphagia in dermatomyositis secondary to bladder cancer: rapid response to combined immunoglobulin and methylprednisolone. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30(1):93-94.
8. Dalmau J, Gultekin HS, Posner JB. Paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes: pathogenesis and physiopathology. Brain Pathol. 1999;9(2):275-284.
9. Hill CL, Zhang Y, Sigureirsson B, et al. Frequency of specific cancer types in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: a population-based study. Lancet. 2001;357(9250):96-100.
10. Titulaer, MJ, Soffietti R, Dalmau J, et al. Screening for tumours in paraneoplastic syndromes: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18(1):19-e3.
11. Xu R, Zhong Z, Jiang H, Zhang L, Zhao X. A rare paraneoplastic dermatomyositis in bladder cancer with fatal outcome. Urol J. 2013;10(1):815-817.
12. Troyanov Y, Targoff IN, Tremblay JL, Goulet JR, Raymond Y, Senecal JL. Novel classification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies based on overlap syndrome features and autoantibodies: analysis of 100 French Canadian patients. Medicine (Baltimore), 2005;84(4):231-249.
1. Yang Z, Lin F, Qin B, Liang Y, Zhong R. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis and malignancy risk: a metaanalysis study. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(2):282-291.
2. Greenberg, SA. Dermatomyositis and type 1 interferons. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2010;12(3):198-203.
3. Dalakas, MC, Hohlfeld, R. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet. 2003;362(9388):971-982.
4. Malik A, Hayat G, Kalia JS, Guzman MA. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: clinical approach and management. Front Neurol. 2016;7:64.
5. Sabio JM, Vargas-Hitos JA, Jiménez-Alonso J. Paraneoplastic dermatomyositis associated with bladder cancer. Lupus. 2006;15(9):619-620.
6. Mallon E, Osborne G, Dinneen M, Lane RJ, Glaser M, Bunker CB. Dermatomyositis in association with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999;24(2):94-96.
7. Hafejee A, Coulson IH. Dysphagia in dermatomyositis secondary to bladder cancer: rapid response to combined immunoglobulin and methylprednisolone. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30(1):93-94.
8. Dalmau J, Gultekin HS, Posner JB. Paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes: pathogenesis and physiopathology. Brain Pathol. 1999;9(2):275-284.
9. Hill CL, Zhang Y, Sigureirsson B, et al. Frequency of specific cancer types in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: a population-based study. Lancet. 2001;357(9250):96-100.
10. Titulaer, MJ, Soffietti R, Dalmau J, et al. Screening for tumours in paraneoplastic syndromes: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18(1):19-e3.
11. Xu R, Zhong Z, Jiang H, Zhang L, Zhao X. A rare paraneoplastic dermatomyositis in bladder cancer with fatal outcome. Urol J. 2013;10(1):815-817.
12. Troyanov Y, Targoff IN, Tremblay JL, Goulet JR, Raymond Y, Senecal JL. Novel classification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies based on overlap syndrome features and autoantibodies: analysis of 100 French Canadian patients. Medicine (Baltimore), 2005;84(4):231-249.
Avoiding in-hospital acute kidney injury is a new imperative
NEW ORLEANS– Preventing acute kidney injury and its progression in hospitalized patients deserves to be a high priority – and now there is finally proof that it’s doable, Harold M. Szerlip, MD, declared at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
The PrevAKI study, a recent randomized controlled clinical trial conducted by German investigators, has demonstrated that the use of renal biomarkers to identify patients at high risk for acute kidney injury (AKI) after major cardiac surgery and providing them with a range of internationally recommended supportive measures known as the KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) care bundle reduced the occurrence of moderate-to-severe AKI by 34% (Intensive Care Med. 2017 Nov;43[11]:1551-61).
The enthusiasm that greeted the PrevAKI trial findings is reflected in an editorial entitled, “AKI: the Myth of Inevitability is Finally Shattered,” by John A. Kellum, MD, professor of critical care medicine and director of the Center for Critical Care Nephrology at the University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Kellum noted that the renal biomarker-based approach to implementation of the KDIGO care bundle resulted in an attractively low number needed to treat (NNT) of only 6, whereas without biomarker-based enrichment of the target population, the NNT would have been more than 33.
“,” Dr. Kellum declared in the editorial (Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Mar;13[3]:140-1).
Indeed, another way to do it was recently demonstrated in the SALT-ED trial, in which 13,347 noncritically ill hospitalized patients requiring intravenous fluid administration were randomized to conventional saline or balanced crystalloids. The incidence of AKI and other major adverse kidney events was 4.7% in the balanced crystalloids group, for a significant 18% risk reduction relative to the 5.6% rate with saline (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 1;378[9]:819-28).
While that absolute 0.9% risk reduction might initially not sound like much, with 35 million people per year getting IV saline while in the hospital, it translates into 315,000 fewer major adverse kidney events as a result of a simple switch to balanced crystalloids, Dr. Szerlip observed.
The PrevAKI findings validate the concept of AKI ‘golden hours’ during which time potentially reversible early kidney injury detectable via renal biomarkers is occurring prior to the abrupt decline in kidney function measured by change in serum creatinine. “The problem with using change in creatinine to define AKI is the delay in diagnosis, which makes AKI more difficult to treat,” he explained.
The renal biomarkers utilized in PrevAKI were insulin-like growth factor binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2), as incorporated in the commercially available urinary NephroCheck test, which was administered to study participants 4 hours after cardiopulmonary bypass. A test result of 0.3 or more identified a group at high risk for AKI for randomization to the KDIGO bundle or usual care. The KDIGO bundle consists of discontinuation of nephrotoxic agents when feasible, early optimization of fluid status, and maintenance of perfusion pressure.
Patients known to be at increased risk for in-hospital AKI include the elderly, those with diabetes, patients with heart failure or other conditions prone to volume contraction or overload, those undergoing major surgery, individuals with chronic kidney disease, and patients with sepsis.
Dr. Szerlip singled out as particularly nephrotoxic several drugs widely used in hospitalized patients, including the combination of vancomycin plus piperacillin-tazobactam, which in a recent metaanalysis was found to have a number needed to harm of 11 in terms of AKI in comparison to vancomycin monotherapy or vancomycin in combination with cefepime or carbapenem (Crit Care Med. 2018 Jan;46[1]:12-20). He was also critical of the American Society of Anesthesiologists practice parameter recommending that in-hospital pain management plans for surgical patients include continuous regimens of NSAIDs or COX-2 inhibitors as a means of combating the ongoing opioid epidemic.
“These are highly toxic drugs to the kidney and we shouldn’t be using them,” Dr. Szerlip said.
He reported receiving research grants from LaJolla, Bayer, Akebia, and BioPorto, serving on a speakers’ bureau for Astute Medical, and acting as a consultant to Zs Pharma, Amarin, and LaJolla.
NEW ORLEANS– Preventing acute kidney injury and its progression in hospitalized patients deserves to be a high priority – and now there is finally proof that it’s doable, Harold M. Szerlip, MD, declared at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
The PrevAKI study, a recent randomized controlled clinical trial conducted by German investigators, has demonstrated that the use of renal biomarkers to identify patients at high risk for acute kidney injury (AKI) after major cardiac surgery and providing them with a range of internationally recommended supportive measures known as the KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) care bundle reduced the occurrence of moderate-to-severe AKI by 34% (Intensive Care Med. 2017 Nov;43[11]:1551-61).
The enthusiasm that greeted the PrevAKI trial findings is reflected in an editorial entitled, “AKI: the Myth of Inevitability is Finally Shattered,” by John A. Kellum, MD, professor of critical care medicine and director of the Center for Critical Care Nephrology at the University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Kellum noted that the renal biomarker-based approach to implementation of the KDIGO care bundle resulted in an attractively low number needed to treat (NNT) of only 6, whereas without biomarker-based enrichment of the target population, the NNT would have been more than 33.
“,” Dr. Kellum declared in the editorial (Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Mar;13[3]:140-1).
Indeed, another way to do it was recently demonstrated in the SALT-ED trial, in which 13,347 noncritically ill hospitalized patients requiring intravenous fluid administration were randomized to conventional saline or balanced crystalloids. The incidence of AKI and other major adverse kidney events was 4.7% in the balanced crystalloids group, for a significant 18% risk reduction relative to the 5.6% rate with saline (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 1;378[9]:819-28).
While that absolute 0.9% risk reduction might initially not sound like much, with 35 million people per year getting IV saline while in the hospital, it translates into 315,000 fewer major adverse kidney events as a result of a simple switch to balanced crystalloids, Dr. Szerlip observed.
The PrevAKI findings validate the concept of AKI ‘golden hours’ during which time potentially reversible early kidney injury detectable via renal biomarkers is occurring prior to the abrupt decline in kidney function measured by change in serum creatinine. “The problem with using change in creatinine to define AKI is the delay in diagnosis, which makes AKI more difficult to treat,” he explained.
The renal biomarkers utilized in PrevAKI were insulin-like growth factor binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2), as incorporated in the commercially available urinary NephroCheck test, which was administered to study participants 4 hours after cardiopulmonary bypass. A test result of 0.3 or more identified a group at high risk for AKI for randomization to the KDIGO bundle or usual care. The KDIGO bundle consists of discontinuation of nephrotoxic agents when feasible, early optimization of fluid status, and maintenance of perfusion pressure.
Patients known to be at increased risk for in-hospital AKI include the elderly, those with diabetes, patients with heart failure or other conditions prone to volume contraction or overload, those undergoing major surgery, individuals with chronic kidney disease, and patients with sepsis.
Dr. Szerlip singled out as particularly nephrotoxic several drugs widely used in hospitalized patients, including the combination of vancomycin plus piperacillin-tazobactam, which in a recent metaanalysis was found to have a number needed to harm of 11 in terms of AKI in comparison to vancomycin monotherapy or vancomycin in combination with cefepime or carbapenem (Crit Care Med. 2018 Jan;46[1]:12-20). He was also critical of the American Society of Anesthesiologists practice parameter recommending that in-hospital pain management plans for surgical patients include continuous regimens of NSAIDs or COX-2 inhibitors as a means of combating the ongoing opioid epidemic.
“These are highly toxic drugs to the kidney and we shouldn’t be using them,” Dr. Szerlip said.
He reported receiving research grants from LaJolla, Bayer, Akebia, and BioPorto, serving on a speakers’ bureau for Astute Medical, and acting as a consultant to Zs Pharma, Amarin, and LaJolla.
NEW ORLEANS– Preventing acute kidney injury and its progression in hospitalized patients deserves to be a high priority – and now there is finally proof that it’s doable, Harold M. Szerlip, MD, declared at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
The PrevAKI study, a recent randomized controlled clinical trial conducted by German investigators, has demonstrated that the use of renal biomarkers to identify patients at high risk for acute kidney injury (AKI) after major cardiac surgery and providing them with a range of internationally recommended supportive measures known as the KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) care bundle reduced the occurrence of moderate-to-severe AKI by 34% (Intensive Care Med. 2017 Nov;43[11]:1551-61).
The enthusiasm that greeted the PrevAKI trial findings is reflected in an editorial entitled, “AKI: the Myth of Inevitability is Finally Shattered,” by John A. Kellum, MD, professor of critical care medicine and director of the Center for Critical Care Nephrology at the University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Kellum noted that the renal biomarker-based approach to implementation of the KDIGO care bundle resulted in an attractively low number needed to treat (NNT) of only 6, whereas without biomarker-based enrichment of the target population, the NNT would have been more than 33.
“,” Dr. Kellum declared in the editorial (Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Mar;13[3]:140-1).
Indeed, another way to do it was recently demonstrated in the SALT-ED trial, in which 13,347 noncritically ill hospitalized patients requiring intravenous fluid administration were randomized to conventional saline or balanced crystalloids. The incidence of AKI and other major adverse kidney events was 4.7% in the balanced crystalloids group, for a significant 18% risk reduction relative to the 5.6% rate with saline (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 1;378[9]:819-28).
While that absolute 0.9% risk reduction might initially not sound like much, with 35 million people per year getting IV saline while in the hospital, it translates into 315,000 fewer major adverse kidney events as a result of a simple switch to balanced crystalloids, Dr. Szerlip observed.
The PrevAKI findings validate the concept of AKI ‘golden hours’ during which time potentially reversible early kidney injury detectable via renal biomarkers is occurring prior to the abrupt decline in kidney function measured by change in serum creatinine. “The problem with using change in creatinine to define AKI is the delay in diagnosis, which makes AKI more difficult to treat,” he explained.
The renal biomarkers utilized in PrevAKI were insulin-like growth factor binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2), as incorporated in the commercially available urinary NephroCheck test, which was administered to study participants 4 hours after cardiopulmonary bypass. A test result of 0.3 or more identified a group at high risk for AKI for randomization to the KDIGO bundle or usual care. The KDIGO bundle consists of discontinuation of nephrotoxic agents when feasible, early optimization of fluid status, and maintenance of perfusion pressure.
Patients known to be at increased risk for in-hospital AKI include the elderly, those with diabetes, patients with heart failure or other conditions prone to volume contraction or overload, those undergoing major surgery, individuals with chronic kidney disease, and patients with sepsis.
Dr. Szerlip singled out as particularly nephrotoxic several drugs widely used in hospitalized patients, including the combination of vancomycin plus piperacillin-tazobactam, which in a recent metaanalysis was found to have a number needed to harm of 11 in terms of AKI in comparison to vancomycin monotherapy or vancomycin in combination with cefepime or carbapenem (Crit Care Med. 2018 Jan;46[1]:12-20). He was also critical of the American Society of Anesthesiologists practice parameter recommending that in-hospital pain management plans for surgical patients include continuous regimens of NSAIDs or COX-2 inhibitors as a means of combating the ongoing opioid epidemic.
“These are highly toxic drugs to the kidney and we shouldn’t be using them,” Dr. Szerlip said.
He reported receiving research grants from LaJolla, Bayer, Akebia, and BioPorto, serving on a speakers’ bureau for Astute Medical, and acting as a consultant to Zs Pharma, Amarin, and LaJolla.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACP INTERNAL MECICINE
VIDEO: Novel postpartum depression drug effective in phase 3 trial
AUSTIN, TEXAS – A novel therapeutic agent shows promise for postpartum depression in a phase 3 trial presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
, according to presenter Christine Clemson, PhD, senior medical director at Sage Therapeutics, the company developing brexanolone.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study enrolled 138 women who were 6 months postpartum or less, and had been diagnosed with a major depressive episode during the third trimester or at 4 or fewer weeks postpartum, and had a 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D) score of 26 or greater.
They were randomized to either brexanolone 60 mcg/kg/hour or 90 mcg/kg/hour administered intravenously over 60 hours as inpatients, or placebo. All three groups were an average aged 27 years old, the majority were white, and they had a HAM-D score between 28.4 and 29.1 at baseline.
After the first 60 hours of treatment, patients in the brexanolone group had mean reductions in the HAM-D score of about 20 in the 60 mcg group (P less than .01) and 18 in the 90 mcg group (P less than .05), compared with almost 14 in the placebo group. This was the primary endpoint,
Patients retained improvement through day 30, while those in the placebo group experienced a slight swing in the opposite direction.
Adverse effects in the brexanolone-treated groups were minimal; the majority of events reported were headaches or dizziness. However, Dr. Clemson said that some patients had to stop breastfeeding for a week.
An application for brexanolone for treating postpartum depression was submitted to the Food and Drug Administration on April 23; if approved, it would be the first drug of its kind to become available to treat postpartum depression.
The study was funded by Sage Therapeutics; two of the six authors are company employees. Two authors, including the lead author, are from the department of psychiatry, at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
SOURCE: S. Meltzer-Brody S et al. ACOG 2018, Poster 29B.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – A novel therapeutic agent shows promise for postpartum depression in a phase 3 trial presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
, according to presenter Christine Clemson, PhD, senior medical director at Sage Therapeutics, the company developing brexanolone.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study enrolled 138 women who were 6 months postpartum or less, and had been diagnosed with a major depressive episode during the third trimester or at 4 or fewer weeks postpartum, and had a 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D) score of 26 or greater.
They were randomized to either brexanolone 60 mcg/kg/hour or 90 mcg/kg/hour administered intravenously over 60 hours as inpatients, or placebo. All three groups were an average aged 27 years old, the majority were white, and they had a HAM-D score between 28.4 and 29.1 at baseline.
After the first 60 hours of treatment, patients in the brexanolone group had mean reductions in the HAM-D score of about 20 in the 60 mcg group (P less than .01) and 18 in the 90 mcg group (P less than .05), compared with almost 14 in the placebo group. This was the primary endpoint,
Patients retained improvement through day 30, while those in the placebo group experienced a slight swing in the opposite direction.
Adverse effects in the brexanolone-treated groups were minimal; the majority of events reported were headaches or dizziness. However, Dr. Clemson said that some patients had to stop breastfeeding for a week.
An application for brexanolone for treating postpartum depression was submitted to the Food and Drug Administration on April 23; if approved, it would be the first drug of its kind to become available to treat postpartum depression.
The study was funded by Sage Therapeutics; two of the six authors are company employees. Two authors, including the lead author, are from the department of psychiatry, at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
SOURCE: S. Meltzer-Brody S et al. ACOG 2018, Poster 29B.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – A novel therapeutic agent shows promise for postpartum depression in a phase 3 trial presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
, according to presenter Christine Clemson, PhD, senior medical director at Sage Therapeutics, the company developing brexanolone.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study enrolled 138 women who were 6 months postpartum or less, and had been diagnosed with a major depressive episode during the third trimester or at 4 or fewer weeks postpartum, and had a 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D) score of 26 or greater.
They were randomized to either brexanolone 60 mcg/kg/hour or 90 mcg/kg/hour administered intravenously over 60 hours as inpatients, or placebo. All three groups were an average aged 27 years old, the majority were white, and they had a HAM-D score between 28.4 and 29.1 at baseline.
After the first 60 hours of treatment, patients in the brexanolone group had mean reductions in the HAM-D score of about 20 in the 60 mcg group (P less than .01) and 18 in the 90 mcg group (P less than .05), compared with almost 14 in the placebo group. This was the primary endpoint,
Patients retained improvement through day 30, while those in the placebo group experienced a slight swing in the opposite direction.
Adverse effects in the brexanolone-treated groups were minimal; the majority of events reported were headaches or dizziness. However, Dr. Clemson said that some patients had to stop breastfeeding for a week.
An application for brexanolone for treating postpartum depression was submitted to the Food and Drug Administration on April 23; if approved, it would be the first drug of its kind to become available to treat postpartum depression.
The study was funded by Sage Therapeutics; two of the six authors are company employees. Two authors, including the lead author, are from the department of psychiatry, at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
SOURCE: S. Meltzer-Brody S et al. ACOG 2018, Poster 29B.
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2018
Drug receives breakthrough designation for HSCT-TMA
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted a second breakthrough therapy designation to OMS721.
OMS721 is a monoclonal antibody targeting MASP-2, the effector enzyme of the lectin pathway of the complement system.
The new breakthrough designation is for OMS721 as a treatment for patients with high-risk hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HSCT-TMA) who have persistent TMA despite modification of immunosuppressive therapy.
OMS721 also has breakthrough designation from the FDA for the treatment of immunoglobulin A nephropathy.
Phase 2 trial
The breakthrough designation for HSCT-TMA was granted based on data from an ongoing phase 2 trial (NCT02222545). Omeros Corporation, the company developing OMS721, released some results from this study in February.
The trial is enrolling adults with HSCT-TMA persisting for at least 2 weeks following immunosuppressive regimen modification or more than 30 days post-transplant. Patients receive weekly OMS721 treatments for 4 to 8 weeks at the discretion of the investigator.
At the time of Omeros’s announcement, 18 patients had been treated on this study.
These patients had a significantly longer median overall survival than historical controls—347 days and 21 days, respectively (P<0.0001).
Omeros also reported that markers of TMA activity significantly improved following OMS721 treatment.
The mean platelet count increased from 18,100 x 106/mL at baseline to 52,300 x 106/mL (P=0.017). The mean LDH decreased from 591 U/L to 250 U/L (P<0.001). And the mean haptoglobin increased from 8 mg/dL to 141 mg/dL (P=0.003).
Mean creatinine remained stable—at approximately 120 μmol/L—but a majority of patients had co-existing conditions for which they were receiving nephrotoxic medications. These conditions included graft-versus-host disease, cytomegalovirus and human herpes virus 6 infections, prior sepsis, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, and residual underlying malignancies.
The most commonly reported adverse events in this trial are diarrhea and neutropenia.
Four deaths occurred. One of these—due to acute renal and respiratory failure—was considered possibly related to OMS721.
The other deaths were due to progression of acute myeloid leukemia (n=1) and neutropenic sepsis (n=2).
About breakthrough designation
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new treatments for serious or life-threatening conditions.
The designation entitles the company developing a therapy to more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient and accelerated development program, as well as eligibility for other actions to expedite FDA review, such as rolling submission and priority review.
To earn breakthrough designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted a second breakthrough therapy designation to OMS721.
OMS721 is a monoclonal antibody targeting MASP-2, the effector enzyme of the lectin pathway of the complement system.
The new breakthrough designation is for OMS721 as a treatment for patients with high-risk hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HSCT-TMA) who have persistent TMA despite modification of immunosuppressive therapy.
OMS721 also has breakthrough designation from the FDA for the treatment of immunoglobulin A nephropathy.
Phase 2 trial
The breakthrough designation for HSCT-TMA was granted based on data from an ongoing phase 2 trial (NCT02222545). Omeros Corporation, the company developing OMS721, released some results from this study in February.
The trial is enrolling adults with HSCT-TMA persisting for at least 2 weeks following immunosuppressive regimen modification or more than 30 days post-transplant. Patients receive weekly OMS721 treatments for 4 to 8 weeks at the discretion of the investigator.
At the time of Omeros’s announcement, 18 patients had been treated on this study.
These patients had a significantly longer median overall survival than historical controls—347 days and 21 days, respectively (P<0.0001).
Omeros also reported that markers of TMA activity significantly improved following OMS721 treatment.
The mean platelet count increased from 18,100 x 106/mL at baseline to 52,300 x 106/mL (P=0.017). The mean LDH decreased from 591 U/L to 250 U/L (P<0.001). And the mean haptoglobin increased from 8 mg/dL to 141 mg/dL (P=0.003).
Mean creatinine remained stable—at approximately 120 μmol/L—but a majority of patients had co-existing conditions for which they were receiving nephrotoxic medications. These conditions included graft-versus-host disease, cytomegalovirus and human herpes virus 6 infections, prior sepsis, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, and residual underlying malignancies.
The most commonly reported adverse events in this trial are diarrhea and neutropenia.
Four deaths occurred. One of these—due to acute renal and respiratory failure—was considered possibly related to OMS721.
The other deaths were due to progression of acute myeloid leukemia (n=1) and neutropenic sepsis (n=2).
About breakthrough designation
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new treatments for serious or life-threatening conditions.
The designation entitles the company developing a therapy to more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient and accelerated development program, as well as eligibility for other actions to expedite FDA review, such as rolling submission and priority review.
To earn breakthrough designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted a second breakthrough therapy designation to OMS721.
OMS721 is a monoclonal antibody targeting MASP-2, the effector enzyme of the lectin pathway of the complement system.
The new breakthrough designation is for OMS721 as a treatment for patients with high-risk hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HSCT-TMA) who have persistent TMA despite modification of immunosuppressive therapy.
OMS721 also has breakthrough designation from the FDA for the treatment of immunoglobulin A nephropathy.
Phase 2 trial
The breakthrough designation for HSCT-TMA was granted based on data from an ongoing phase 2 trial (NCT02222545). Omeros Corporation, the company developing OMS721, released some results from this study in February.
The trial is enrolling adults with HSCT-TMA persisting for at least 2 weeks following immunosuppressive regimen modification or more than 30 days post-transplant. Patients receive weekly OMS721 treatments for 4 to 8 weeks at the discretion of the investigator.
At the time of Omeros’s announcement, 18 patients had been treated on this study.
These patients had a significantly longer median overall survival than historical controls—347 days and 21 days, respectively (P<0.0001).
Omeros also reported that markers of TMA activity significantly improved following OMS721 treatment.
The mean platelet count increased from 18,100 x 106/mL at baseline to 52,300 x 106/mL (P=0.017). The mean LDH decreased from 591 U/L to 250 U/L (P<0.001). And the mean haptoglobin increased from 8 mg/dL to 141 mg/dL (P=0.003).
Mean creatinine remained stable—at approximately 120 μmol/L—but a majority of patients had co-existing conditions for which they were receiving nephrotoxic medications. These conditions included graft-versus-host disease, cytomegalovirus and human herpes virus 6 infections, prior sepsis, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, and residual underlying malignancies.
The most commonly reported adverse events in this trial are diarrhea and neutropenia.
Four deaths occurred. One of these—due to acute renal and respiratory failure—was considered possibly related to OMS721.
The other deaths were due to progression of acute myeloid leukemia (n=1) and neutropenic sepsis (n=2).
About breakthrough designation
The FDA’s breakthrough designation is intended to expedite the development and review of new treatments for serious or life-threatening conditions.
The designation entitles the company developing a therapy to more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient and accelerated development program, as well as eligibility for other actions to expedite FDA review, such as rolling submission and priority review.
To earn breakthrough designation, a treatment must show encouraging early clinical results demonstrating substantial improvement over available therapies with regard to a clinically significant endpoint, or it must fulfill an unmet need.
Universal BRCA testing worthwhile for relatives of high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients
AUSTIN, TEX. – Universal BRCA mutation testing for first-degree relatives of women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer could prevent significantly more cases, according to a study presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer have a 20% chance of having a BRCA mutation; however, the risk is 50% for first degree relatives of someone with that mutation.
“Until we find an effective screening test for ovarian cancer, which can identify women at an early stage for which there is curative treatment, we need to maximize opportunities for prevention,” said Janice S. Kwon, MD, the gynecologic oncology fellowship program director at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver. “An obvious target group,” she added, are women “at highest risk of developing ovarian cancers, specifically those who inherit mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2.”
First-degree relatives of ovarian cancer patients have three conceivable options if their BRCA status is unknown, and have no other risk factor for BRCA testing: To not undergo testing; to get tested and, if found to have the mutation, undergo risk-reducing surgery (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy); or to undergo surgery without testing.
To estimate the efficiency and cost effectiveness of universal BRCA testing of female first-degree relatives of women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer, Dr. Kwon and her colleagues used the “Markov Monte Carlo” simulation model, with a time horizon of 50 years, evaluating the costs and benefits of those three strategies.
They acknowledged that testing excluded women with a personal history of breast cancer and did not include nonhormonal interventions in their analysis.
They found that the average quality-adjusted life year (QUALY) gain of universal BRCA testing was 19.20 years, compared with 18.99 years for no BRCA testing, and 18.48 years for universal surgery with no BRCA testing.
The reason universal surgery was the lowest is because most of these women will be premenopausal at the time of surgery, according to Dr. Kwon. A procedure like a premenopausal oophorectomy has been associated with a 40% increase in all-cause mortality, putting the patient at unnecessary risk, she noted.
Financially, no BRCA testing cost the least, an average of $8,524 Canadian dollars (about US$6,648) followed by universal BRCA at CA$10,103 (about US$7,880) . Universal surgery, with no BRCA testing, cost CA$13,959 (about US$10,888).
Despite the increased cost, the chance to give patients who may be at risk for ovarian cancer a better chance is a good investment, according to Dr. Kwon.
“Any opportunity to prevent ovarian cancer is worthwhile,” Dr. Kwon commented. “If an ovarian cancer patient cannot be tested because she declines testing or, more commonly, because she is deceased, her first-degree relative should have BRCA mutation testing, regardless of other personal or family history or ethnicity.”
She and her coinvestigators reported no relevant financial disclosures.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Universal BRCA mutation testing for first-degree relatives of women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer could prevent significantly more cases, according to a study presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer have a 20% chance of having a BRCA mutation; however, the risk is 50% for first degree relatives of someone with that mutation.
“Until we find an effective screening test for ovarian cancer, which can identify women at an early stage for which there is curative treatment, we need to maximize opportunities for prevention,” said Janice S. Kwon, MD, the gynecologic oncology fellowship program director at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver. “An obvious target group,” she added, are women “at highest risk of developing ovarian cancers, specifically those who inherit mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2.”
First-degree relatives of ovarian cancer patients have three conceivable options if their BRCA status is unknown, and have no other risk factor for BRCA testing: To not undergo testing; to get tested and, if found to have the mutation, undergo risk-reducing surgery (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy); or to undergo surgery without testing.
To estimate the efficiency and cost effectiveness of universal BRCA testing of female first-degree relatives of women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer, Dr. Kwon and her colleagues used the “Markov Monte Carlo” simulation model, with a time horizon of 50 years, evaluating the costs and benefits of those three strategies.
They acknowledged that testing excluded women with a personal history of breast cancer and did not include nonhormonal interventions in their analysis.
They found that the average quality-adjusted life year (QUALY) gain of universal BRCA testing was 19.20 years, compared with 18.99 years for no BRCA testing, and 18.48 years for universal surgery with no BRCA testing.
The reason universal surgery was the lowest is because most of these women will be premenopausal at the time of surgery, according to Dr. Kwon. A procedure like a premenopausal oophorectomy has been associated with a 40% increase in all-cause mortality, putting the patient at unnecessary risk, she noted.
Financially, no BRCA testing cost the least, an average of $8,524 Canadian dollars (about US$6,648) followed by universal BRCA at CA$10,103 (about US$7,880) . Universal surgery, with no BRCA testing, cost CA$13,959 (about US$10,888).
Despite the increased cost, the chance to give patients who may be at risk for ovarian cancer a better chance is a good investment, according to Dr. Kwon.
“Any opportunity to prevent ovarian cancer is worthwhile,” Dr. Kwon commented. “If an ovarian cancer patient cannot be tested because she declines testing or, more commonly, because she is deceased, her first-degree relative should have BRCA mutation testing, regardless of other personal or family history or ethnicity.”
She and her coinvestigators reported no relevant financial disclosures.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Universal BRCA mutation testing for first-degree relatives of women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer could prevent significantly more cases, according to a study presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer have a 20% chance of having a BRCA mutation; however, the risk is 50% for first degree relatives of someone with that mutation.
“Until we find an effective screening test for ovarian cancer, which can identify women at an early stage for which there is curative treatment, we need to maximize opportunities for prevention,” said Janice S. Kwon, MD, the gynecologic oncology fellowship program director at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver. “An obvious target group,” she added, are women “at highest risk of developing ovarian cancers, specifically those who inherit mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2.”
First-degree relatives of ovarian cancer patients have three conceivable options if their BRCA status is unknown, and have no other risk factor for BRCA testing: To not undergo testing; to get tested and, if found to have the mutation, undergo risk-reducing surgery (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy); or to undergo surgery without testing.
To estimate the efficiency and cost effectiveness of universal BRCA testing of female first-degree relatives of women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer, Dr. Kwon and her colleagues used the “Markov Monte Carlo” simulation model, with a time horizon of 50 years, evaluating the costs and benefits of those three strategies.
They acknowledged that testing excluded women with a personal history of breast cancer and did not include nonhormonal interventions in their analysis.
They found that the average quality-adjusted life year (QUALY) gain of universal BRCA testing was 19.20 years, compared with 18.99 years for no BRCA testing, and 18.48 years for universal surgery with no BRCA testing.
The reason universal surgery was the lowest is because most of these women will be premenopausal at the time of surgery, according to Dr. Kwon. A procedure like a premenopausal oophorectomy has been associated with a 40% increase in all-cause mortality, putting the patient at unnecessary risk, she noted.
Financially, no BRCA testing cost the least, an average of $8,524 Canadian dollars (about US$6,648) followed by universal BRCA at CA$10,103 (about US$7,880) . Universal surgery, with no BRCA testing, cost CA$13,959 (about US$10,888).
Despite the increased cost, the chance to give patients who may be at risk for ovarian cancer a better chance is a good investment, according to Dr. Kwon.
“Any opportunity to prevent ovarian cancer is worthwhile,” Dr. Kwon commented. “If an ovarian cancer patient cannot be tested because she declines testing or, more commonly, because she is deceased, her first-degree relative should have BRCA mutation testing, regardless of other personal or family history or ethnicity.”
She and her coinvestigators reported no relevant financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2018
Key clinical point: BCRA testing should be extended to all first degree family members of ovarian cancer patients.
Major finding: Quality-adjusted life year gain was higher in patients given universal BRCA testing (an average of 19.20 years) compared with universal surgery (18.48 years) and no BRCA testing (18.99 years).
Study details: A simulation model, was used to evaluate the costs and benefits of three possible approaches for female first-degree relatives of women with high-grade serous ovarian cancer.
Disclosures: The authors had no disclosures.
New law allows Maryland students to use sunscreen at school
In early April, Maryland Governor Larry Hogan signed HB 427 into law, making Maryland the second state in 2018 to ensure that state policy allows students to possess and use sunscreen at school.
“The passing of this bill helps encourage children to develop sun-safe behaviors early on, like sunscreen application,” American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association president Lisa Donofrio, MD, said in a statement issued by the ASDSA. “Maryland’s efforts reinforce the importance of teaching children the risks of sun exposure during outdoor activities and how to best avoid skin cancer,” she added.
ASDSA worked with the Maryland Dermatologic Society in advocating for passage of the law. In the statement, ASDSA Board Member Lawrence Green, MD, of Rockville, Maryland, who testified in favor of SB 217, said, “allowing children to put on sunscreen before recess … would really help protect them from the dangers of the sun.”
More information about SUNucate is available here.
In early April, Maryland Governor Larry Hogan signed HB 427 into law, making Maryland the second state in 2018 to ensure that state policy allows students to possess and use sunscreen at school.
“The passing of this bill helps encourage children to develop sun-safe behaviors early on, like sunscreen application,” American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association president Lisa Donofrio, MD, said in a statement issued by the ASDSA. “Maryland’s efforts reinforce the importance of teaching children the risks of sun exposure during outdoor activities and how to best avoid skin cancer,” she added.
ASDSA worked with the Maryland Dermatologic Society in advocating for passage of the law. In the statement, ASDSA Board Member Lawrence Green, MD, of Rockville, Maryland, who testified in favor of SB 217, said, “allowing children to put on sunscreen before recess … would really help protect them from the dangers of the sun.”
More information about SUNucate is available here.
In early April, Maryland Governor Larry Hogan signed HB 427 into law, making Maryland the second state in 2018 to ensure that state policy allows students to possess and use sunscreen at school.
“The passing of this bill helps encourage children to develop sun-safe behaviors early on, like sunscreen application,” American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association president Lisa Donofrio, MD, said in a statement issued by the ASDSA. “Maryland’s efforts reinforce the importance of teaching children the risks of sun exposure during outdoor activities and how to best avoid skin cancer,” she added.
ASDSA worked with the Maryland Dermatologic Society in advocating for passage of the law. In the statement, ASDSA Board Member Lawrence Green, MD, of Rockville, Maryland, who testified in favor of SB 217, said, “allowing children to put on sunscreen before recess … would really help protect them from the dangers of the sun.”
More information about SUNucate is available here.
REM sleep behavior disorder predicts impending synucleinopathy
LOS ANGELES – , according to a years-long, multicenter investigation of 1,280 patients – the largest study of the issue to date.
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) has been known for years to increase the risk for synucleinopathies, namely Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. However, previous studies have mostly been conducted at single institutions, so the exact extent to which RBD increases the risk wasn’t clear.
These findings have important implications for the field. Now that it’s known who’s at risk, “we have a chance to do neuroprotective therapy. It’s time to move forward and start preventing disease,” Dr. Postuma said at the American Academy of Neurology annual meeting. He estimated that it would take only a few hundred patients to do a 2-year trial of neuroprotective therapy.
The 1,280 study subjects were culled from 24 sleep centers on four continents, all participants in the international RBD study group. The patients needed for a trial “are sitting right now” in the study group, “so maybe we can get on with this,” he said.
REM sleep – the dream state – normally paralyzes people, but something breaks down in RBD, and people act out their dreams, sometimes to disturbing effects. It occurs in about 1% of the population, usually in older people and in slightly more men than women.
The risk of neurodegenerative disease in RBD increases even more if patients test positive at baseline for movement declines, cognitive issues, olfactory problems, constipation, color vision loss, erectile dysfunction, or abnormal dopamine transporter scans. Dr. Postuma and his team found no predictive value for somnolence, insomnia, urinary problems, depression, or anxiety. These negative findings were surprising, he said, because mood disorders and sleep troubles are known to increase the risk in the general population.
The subjects all had polysomnographic-proven RBD at baseline, without neurodegenerative disease. Most of them were men and were about 70 years old, on average. Subjects were tested for synucleinopathies and risk variables annually. The mean disease-free follow-up was about 4 years, but ranged out to 19 years. Risks were adjusted for age, sex, and study center.
Cognition deficits were the only thing that distinguished future dementia patients from those destined for movement disorders. “Everything [else] is really the same between who gets dementia and who gets Parkinsonism,” Dr. Postuma said.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research and the Fonds de la Recherche Sante Quebec. Dr. Postuma disclosed consulting, speaking, and other fees from Biotie, Roche/Prothena, Teva Neurosciences, Novartis Canada, Theranexus, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and GE HealthCare.
SOURCE: Postuma R et al. AAN 2018, plenary session.
LOS ANGELES – , according to a years-long, multicenter investigation of 1,280 patients – the largest study of the issue to date.
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) has been known for years to increase the risk for synucleinopathies, namely Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. However, previous studies have mostly been conducted at single institutions, so the exact extent to which RBD increases the risk wasn’t clear.
These findings have important implications for the field. Now that it’s known who’s at risk, “we have a chance to do neuroprotective therapy. It’s time to move forward and start preventing disease,” Dr. Postuma said at the American Academy of Neurology annual meeting. He estimated that it would take only a few hundred patients to do a 2-year trial of neuroprotective therapy.
The 1,280 study subjects were culled from 24 sleep centers on four continents, all participants in the international RBD study group. The patients needed for a trial “are sitting right now” in the study group, “so maybe we can get on with this,” he said.
REM sleep – the dream state – normally paralyzes people, but something breaks down in RBD, and people act out their dreams, sometimes to disturbing effects. It occurs in about 1% of the population, usually in older people and in slightly more men than women.
The risk of neurodegenerative disease in RBD increases even more if patients test positive at baseline for movement declines, cognitive issues, olfactory problems, constipation, color vision loss, erectile dysfunction, or abnormal dopamine transporter scans. Dr. Postuma and his team found no predictive value for somnolence, insomnia, urinary problems, depression, or anxiety. These negative findings were surprising, he said, because mood disorders and sleep troubles are known to increase the risk in the general population.
The subjects all had polysomnographic-proven RBD at baseline, without neurodegenerative disease. Most of them were men and were about 70 years old, on average. Subjects were tested for synucleinopathies and risk variables annually. The mean disease-free follow-up was about 4 years, but ranged out to 19 years. Risks were adjusted for age, sex, and study center.
Cognition deficits were the only thing that distinguished future dementia patients from those destined for movement disorders. “Everything [else] is really the same between who gets dementia and who gets Parkinsonism,” Dr. Postuma said.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research and the Fonds de la Recherche Sante Quebec. Dr. Postuma disclosed consulting, speaking, and other fees from Biotie, Roche/Prothena, Teva Neurosciences, Novartis Canada, Theranexus, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and GE HealthCare.
SOURCE: Postuma R et al. AAN 2018, plenary session.
LOS ANGELES – , according to a years-long, multicenter investigation of 1,280 patients – the largest study of the issue to date.
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) has been known for years to increase the risk for synucleinopathies, namely Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. However, previous studies have mostly been conducted at single institutions, so the exact extent to which RBD increases the risk wasn’t clear.
These findings have important implications for the field. Now that it’s known who’s at risk, “we have a chance to do neuroprotective therapy. It’s time to move forward and start preventing disease,” Dr. Postuma said at the American Academy of Neurology annual meeting. He estimated that it would take only a few hundred patients to do a 2-year trial of neuroprotective therapy.
The 1,280 study subjects were culled from 24 sleep centers on four continents, all participants in the international RBD study group. The patients needed for a trial “are sitting right now” in the study group, “so maybe we can get on with this,” he said.
REM sleep – the dream state – normally paralyzes people, but something breaks down in RBD, and people act out their dreams, sometimes to disturbing effects. It occurs in about 1% of the population, usually in older people and in slightly more men than women.
The risk of neurodegenerative disease in RBD increases even more if patients test positive at baseline for movement declines, cognitive issues, olfactory problems, constipation, color vision loss, erectile dysfunction, or abnormal dopamine transporter scans. Dr. Postuma and his team found no predictive value for somnolence, insomnia, urinary problems, depression, or anxiety. These negative findings were surprising, he said, because mood disorders and sleep troubles are known to increase the risk in the general population.
The subjects all had polysomnographic-proven RBD at baseline, without neurodegenerative disease. Most of them were men and were about 70 years old, on average. Subjects were tested for synucleinopathies and risk variables annually. The mean disease-free follow-up was about 4 years, but ranged out to 19 years. Risks were adjusted for age, sex, and study center.
Cognition deficits were the only thing that distinguished future dementia patients from those destined for movement disorders. “Everything [else] is really the same between who gets dementia and who gets Parkinsonism,” Dr. Postuma said.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research and the Fonds de la Recherche Sante Quebec. Dr. Postuma disclosed consulting, speaking, and other fees from Biotie, Roche/Prothena, Teva Neurosciences, Novartis Canada, Theranexus, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and GE HealthCare.
SOURCE: Postuma R et al. AAN 2018, plenary session.
REPORTING FROM AAN 2018
Key clinical point: Idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder patients need neuroprotection.
Major finding: At least 70% of patients with idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) will develop a neurodegenerative disease within about a decade.
Study details: An observational study of 1,280 RBD patients from 24 asleep centers on four continents.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research and the Fonds de la Recherche Sante Quebec. Dr. Postuma disclosed consulting, speaking, and other fees from Biotie, Roche/Prothena, Teva Neurosciences, Novartis Canada, Theranexus, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and GE HealthCare.
Source: Postuma R et al. AAN 2018, plenary session.
VIDEO: Office-based hereditary cancer risk testing is doable
AUSTIN, TEXAS – , according to Mark S. DeFrancesco, MD, and his associates.
Few community-based ob.gyns. routinely screen their patients for hereditary cancer risks, Dr. DeFrancesco said at the annual meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, despite ACOG’s position that they are fully trained and qualified to do so. He and his colleagues studied an intervention aimed at streamlining and standardizing genetic assessment in their practice.
A team of physicians, staff, genetic counselors, and process engineers analyzed how hereditary cancer risk assessment was being done at five clinical sites of two community ob.gyn. practices – Dr. DeFrancesco’s practice in Waterbury, Conn., and that of Richard Waldman, MD, in Syracuse, N.Y. – then refined workflows and added tools to create a turnkey process for assessment and screening, Dr. DeFrancesco said.
Under the new process, patients completed a family cancer history in the exam room prior to seeing their physician. Genetic testing was offered to patients who met National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines for hereditary/familial high-risk assessment for breast and ovarian cancer (J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017 Jan;15[1]:9-20). Those who chose to be tested were able to provide a saliva sample in the office. Counseling was provided to appropriate patients.
The number of patients tested for hereditary risk of breast and ovarian cancer increased dramatically with the new process. During the 8-week period after the intervention, 4% (165) were tested out of 4,107 total patients seen; during the 8 weeks preceding, 1% (43) of 3,882 patients were tested.
Overall, 92.8% (3,811) of patients seen after the intervention provided a family cancer history. Almost a quarter – 23.5% (906) – met NCCN criteria for genetic testing.
A total of 318 patients agreed to undergo genetic testing and 165 (51.9%) completed the process. Nine patients (5.5%) were found to carry a pathogenic gene variant associated with hereditary breast and/or ovarian cancer or Lynch syndrome, Dr. DeFrancesco and colleagues reported.
Patients and providers also were surveyed regarding their experience with the new process. Patients overwhelming noted that they understood the information provided (98.8%), and that they were satisfied with the overall process (97.6%). All 15 providers said that they would continue to use the new process in their practice and most – 13 of 15 – said they found the process thorough and felt comfortable recommending genetic counseling without referral to a genetic counselor (2 were undecided).
“I think that this study really proves the concept that in a community-based practice, we can test our patients,” Dr. DeFrancesco said in an interview.
Myriad Genetics sponsored the study. Dr. DeFrancesco reported no financial conflicts of interest. His coauthors include employees of Myriad Genetics, some with ownership interests.
SOURCE: DeFrancesco, MS et al. ACOG 2018 3K.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – , according to Mark S. DeFrancesco, MD, and his associates.
Few community-based ob.gyns. routinely screen their patients for hereditary cancer risks, Dr. DeFrancesco said at the annual meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, despite ACOG’s position that they are fully trained and qualified to do so. He and his colleagues studied an intervention aimed at streamlining and standardizing genetic assessment in their practice.
A team of physicians, staff, genetic counselors, and process engineers analyzed how hereditary cancer risk assessment was being done at five clinical sites of two community ob.gyn. practices – Dr. DeFrancesco’s practice in Waterbury, Conn., and that of Richard Waldman, MD, in Syracuse, N.Y. – then refined workflows and added tools to create a turnkey process for assessment and screening, Dr. DeFrancesco said.
Under the new process, patients completed a family cancer history in the exam room prior to seeing their physician. Genetic testing was offered to patients who met National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines for hereditary/familial high-risk assessment for breast and ovarian cancer (J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017 Jan;15[1]:9-20). Those who chose to be tested were able to provide a saliva sample in the office. Counseling was provided to appropriate patients.
The number of patients tested for hereditary risk of breast and ovarian cancer increased dramatically with the new process. During the 8-week period after the intervention, 4% (165) were tested out of 4,107 total patients seen; during the 8 weeks preceding, 1% (43) of 3,882 patients were tested.
Overall, 92.8% (3,811) of patients seen after the intervention provided a family cancer history. Almost a quarter – 23.5% (906) – met NCCN criteria for genetic testing.
A total of 318 patients agreed to undergo genetic testing and 165 (51.9%) completed the process. Nine patients (5.5%) were found to carry a pathogenic gene variant associated with hereditary breast and/or ovarian cancer or Lynch syndrome, Dr. DeFrancesco and colleagues reported.
Patients and providers also were surveyed regarding their experience with the new process. Patients overwhelming noted that they understood the information provided (98.8%), and that they were satisfied with the overall process (97.6%). All 15 providers said that they would continue to use the new process in their practice and most – 13 of 15 – said they found the process thorough and felt comfortable recommending genetic counseling without referral to a genetic counselor (2 were undecided).
“I think that this study really proves the concept that in a community-based practice, we can test our patients,” Dr. DeFrancesco said in an interview.
Myriad Genetics sponsored the study. Dr. DeFrancesco reported no financial conflicts of interest. His coauthors include employees of Myriad Genetics, some with ownership interests.
SOURCE: DeFrancesco, MS et al. ACOG 2018 3K.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – , according to Mark S. DeFrancesco, MD, and his associates.
Few community-based ob.gyns. routinely screen their patients for hereditary cancer risks, Dr. DeFrancesco said at the annual meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, despite ACOG’s position that they are fully trained and qualified to do so. He and his colleagues studied an intervention aimed at streamlining and standardizing genetic assessment in their practice.
A team of physicians, staff, genetic counselors, and process engineers analyzed how hereditary cancer risk assessment was being done at five clinical sites of two community ob.gyn. practices – Dr. DeFrancesco’s practice in Waterbury, Conn., and that of Richard Waldman, MD, in Syracuse, N.Y. – then refined workflows and added tools to create a turnkey process for assessment and screening, Dr. DeFrancesco said.
Under the new process, patients completed a family cancer history in the exam room prior to seeing their physician. Genetic testing was offered to patients who met National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines for hereditary/familial high-risk assessment for breast and ovarian cancer (J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017 Jan;15[1]:9-20). Those who chose to be tested were able to provide a saliva sample in the office. Counseling was provided to appropriate patients.
The number of patients tested for hereditary risk of breast and ovarian cancer increased dramatically with the new process. During the 8-week period after the intervention, 4% (165) were tested out of 4,107 total patients seen; during the 8 weeks preceding, 1% (43) of 3,882 patients were tested.
Overall, 92.8% (3,811) of patients seen after the intervention provided a family cancer history. Almost a quarter – 23.5% (906) – met NCCN criteria for genetic testing.
A total of 318 patients agreed to undergo genetic testing and 165 (51.9%) completed the process. Nine patients (5.5%) were found to carry a pathogenic gene variant associated with hereditary breast and/or ovarian cancer or Lynch syndrome, Dr. DeFrancesco and colleagues reported.
Patients and providers also were surveyed regarding their experience with the new process. Patients overwhelming noted that they understood the information provided (98.8%), and that they were satisfied with the overall process (97.6%). All 15 providers said that they would continue to use the new process in their practice and most – 13 of 15 – said they found the process thorough and felt comfortable recommending genetic counseling without referral to a genetic counselor (2 were undecided).
“I think that this study really proves the concept that in a community-based practice, we can test our patients,” Dr. DeFrancesco said in an interview.
Myriad Genetics sponsored the study. Dr. DeFrancesco reported no financial conflicts of interest. His coauthors include employees of Myriad Genetics, some with ownership interests.
SOURCE: DeFrancesco, MS et al. ACOG 2018 3K.
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2018
Key clinical point: Ob.gyns. can successfully integrate hereditary cancer risk testing into their practices.
Major finding: Office-based genetic testing increased from 1% to 4% of patients seen.
Study details: Prospective, single-arm process intervention study screening more than 4,000 women at 5 ob.gyn. practice sites.
Disclosures: Myriad Genetics sponsored the study. Dr. DeFrancesco reported no financial conflicts of interest. His coauthors included employees of Myriad Genetics, some with ownership interests.
Source: DeFrancesco, MS et al. ACOG 2018 poster 3K.
VIDEO: Prepaid prenatal care bundle delivers quality care to uninsured
AUSTIN, TEXAS – The experiences of one safety net hospital showed the feasibility of delivering prenatal care to low-risk, uninsured women in a prepaid, bundled package.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
. The adjusted odds ratio for predefined adequacy of care was 3.75 for the low-risk bundled care recipients compared with those on Medicaid (P = .015), according to the experience at Grady Memorial Hospital, Atlanta, presented at the annual clinical and scientific sessions of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For hospitals with large numbers of undocumented patients and others who are uninsured but ineligible for Medicaid, considerable cost savings could be realized, said Erin Duncan, MD, who completed the work while in training at Emory University.
“Using data from previous studies, Grady Memorial Hospital could see a savings of over $1 million per year by providing care to its undocumented population,” she and her collaborators wrote in the poster accompanying the presentation.
Dr. Duncan said that since implementation in 2010, about 40% of deliveries at the facility have occurred under the “Grady Healthy Baby” (GHB) bundle.
The one-payment package of bundled prenatal care was developed assuming that most participants would have low-risk pregnancies, said Dr. Duncan, who is currently an ob.gyn. in private practice in the Atlanta area.
To look further into maternal and pregnancy characteristics of GHB participants and compare them with those on Medicaid, Dr. Duncan and her collaborators performed a retrospective cohort study. Examining viable singleton pregnancies delivered at Grady between 2011 and 2014, the investigators compared 100 randomly selected GHB participants with 100 randomly selected Medicaid participants.
Comparing patients receiving care under GHB and Medicaid, Dr. Duncan and her colleagues found that “GHB participants were older, more likely to be Hispanic, and less likely to be black compared to Medicaid recipients (P less than .001 for all,)” they wrote in the poster accompanying the presentation.
Hispanic patients made up 59% of the GHB group, compared with 8% of the Medicaid group, said Dr. Duncan, adding in an interview that over half of Hispanics in the state of Georgia during the study period were undocumented.
Parity was similar between the two groups, as were gestational age at delivery and mode of delivery.
In their analysis, Dr. Duncan and her collaborators looked at both complexity and adequacy of care for the 200 patients studied. They found that there was no significant difference in the number of patients in each care group who remained low risk throughout their pregnancies, transitioned from low risk to high risk, or entered prenatal care with a high risk pregnancy, a circumstance that occurred in about 1 in 10 pregnancies.
For the approximately 50% of patients who remained low risk through their pregnancies, care under the GHB model was significantly more likely to be assessed as adequate throughout pregnancy than for those patients on Medicaid (61.7% vs 35.5%, P = .001).
Patients who became high risk during prenatal care were no more likely to receive adequate care under one model than the other.
For high risk patients, delivery of adequate care happened only under the Medicaid care model. Numbers in this group were small; 7 of 100 GHB and 15 of 100 Medicaid patients entered prenatal care with high risk pregnancies. However, no high risk GHB patients received adequate care, while that standard was met for 80% of the Medicaid patients (P less than .001).
Adequacy of care was assessed using the Kotelchuck index for low-risk pregnancies; this model assumes care is “adequate” when 80% of the number of expected visits were attended by the woman receiving prenatal care. Additionally, care was deemed adequate for high-risk pregnancies if at least 80% of the number of expected ultrasound appointments were attended.
“In the current political climate, this study has implications for all pregnancies that begin as uninsured, regardless of maternal documentation status,” wrote Dr. Duncan and her colleagues.
Dr. Duncan reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Duncan, E et al. ACOG 2018, Abstract 28C.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – The experiences of one safety net hospital showed the feasibility of delivering prenatal care to low-risk, uninsured women in a prepaid, bundled package.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
. The adjusted odds ratio for predefined adequacy of care was 3.75 for the low-risk bundled care recipients compared with those on Medicaid (P = .015), according to the experience at Grady Memorial Hospital, Atlanta, presented at the annual clinical and scientific sessions of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For hospitals with large numbers of undocumented patients and others who are uninsured but ineligible for Medicaid, considerable cost savings could be realized, said Erin Duncan, MD, who completed the work while in training at Emory University.
“Using data from previous studies, Grady Memorial Hospital could see a savings of over $1 million per year by providing care to its undocumented population,” she and her collaborators wrote in the poster accompanying the presentation.
Dr. Duncan said that since implementation in 2010, about 40% of deliveries at the facility have occurred under the “Grady Healthy Baby” (GHB) bundle.
The one-payment package of bundled prenatal care was developed assuming that most participants would have low-risk pregnancies, said Dr. Duncan, who is currently an ob.gyn. in private practice in the Atlanta area.
To look further into maternal and pregnancy characteristics of GHB participants and compare them with those on Medicaid, Dr. Duncan and her collaborators performed a retrospective cohort study. Examining viable singleton pregnancies delivered at Grady between 2011 and 2014, the investigators compared 100 randomly selected GHB participants with 100 randomly selected Medicaid participants.
Comparing patients receiving care under GHB and Medicaid, Dr. Duncan and her colleagues found that “GHB participants were older, more likely to be Hispanic, and less likely to be black compared to Medicaid recipients (P less than .001 for all,)” they wrote in the poster accompanying the presentation.
Hispanic patients made up 59% of the GHB group, compared with 8% of the Medicaid group, said Dr. Duncan, adding in an interview that over half of Hispanics in the state of Georgia during the study period were undocumented.
Parity was similar between the two groups, as were gestational age at delivery and mode of delivery.
In their analysis, Dr. Duncan and her collaborators looked at both complexity and adequacy of care for the 200 patients studied. They found that there was no significant difference in the number of patients in each care group who remained low risk throughout their pregnancies, transitioned from low risk to high risk, or entered prenatal care with a high risk pregnancy, a circumstance that occurred in about 1 in 10 pregnancies.
For the approximately 50% of patients who remained low risk through their pregnancies, care under the GHB model was significantly more likely to be assessed as adequate throughout pregnancy than for those patients on Medicaid (61.7% vs 35.5%, P = .001).
Patients who became high risk during prenatal care were no more likely to receive adequate care under one model than the other.
For high risk patients, delivery of adequate care happened only under the Medicaid care model. Numbers in this group were small; 7 of 100 GHB and 15 of 100 Medicaid patients entered prenatal care with high risk pregnancies. However, no high risk GHB patients received adequate care, while that standard was met for 80% of the Medicaid patients (P less than .001).
Adequacy of care was assessed using the Kotelchuck index for low-risk pregnancies; this model assumes care is “adequate” when 80% of the number of expected visits were attended by the woman receiving prenatal care. Additionally, care was deemed adequate for high-risk pregnancies if at least 80% of the number of expected ultrasound appointments were attended.
“In the current political climate, this study has implications for all pregnancies that begin as uninsured, regardless of maternal documentation status,” wrote Dr. Duncan and her colleagues.
Dr. Duncan reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Duncan, E et al. ACOG 2018, Abstract 28C.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – The experiences of one safety net hospital showed the feasibility of delivering prenatal care to low-risk, uninsured women in a prepaid, bundled package.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
. The adjusted odds ratio for predefined adequacy of care was 3.75 for the low-risk bundled care recipients compared with those on Medicaid (P = .015), according to the experience at Grady Memorial Hospital, Atlanta, presented at the annual clinical and scientific sessions of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For hospitals with large numbers of undocumented patients and others who are uninsured but ineligible for Medicaid, considerable cost savings could be realized, said Erin Duncan, MD, who completed the work while in training at Emory University.
“Using data from previous studies, Grady Memorial Hospital could see a savings of over $1 million per year by providing care to its undocumented population,” she and her collaborators wrote in the poster accompanying the presentation.
Dr. Duncan said that since implementation in 2010, about 40% of deliveries at the facility have occurred under the “Grady Healthy Baby” (GHB) bundle.
The one-payment package of bundled prenatal care was developed assuming that most participants would have low-risk pregnancies, said Dr. Duncan, who is currently an ob.gyn. in private practice in the Atlanta area.
To look further into maternal and pregnancy characteristics of GHB participants and compare them with those on Medicaid, Dr. Duncan and her collaborators performed a retrospective cohort study. Examining viable singleton pregnancies delivered at Grady between 2011 and 2014, the investigators compared 100 randomly selected GHB participants with 100 randomly selected Medicaid participants.
Comparing patients receiving care under GHB and Medicaid, Dr. Duncan and her colleagues found that “GHB participants were older, more likely to be Hispanic, and less likely to be black compared to Medicaid recipients (P less than .001 for all,)” they wrote in the poster accompanying the presentation.
Hispanic patients made up 59% of the GHB group, compared with 8% of the Medicaid group, said Dr. Duncan, adding in an interview that over half of Hispanics in the state of Georgia during the study period were undocumented.
Parity was similar between the two groups, as were gestational age at delivery and mode of delivery.
In their analysis, Dr. Duncan and her collaborators looked at both complexity and adequacy of care for the 200 patients studied. They found that there was no significant difference in the number of patients in each care group who remained low risk throughout their pregnancies, transitioned from low risk to high risk, or entered prenatal care with a high risk pregnancy, a circumstance that occurred in about 1 in 10 pregnancies.
For the approximately 50% of patients who remained low risk through their pregnancies, care under the GHB model was significantly more likely to be assessed as adequate throughout pregnancy than for those patients on Medicaid (61.7% vs 35.5%, P = .001).
Patients who became high risk during prenatal care were no more likely to receive adequate care under one model than the other.
For high risk patients, delivery of adequate care happened only under the Medicaid care model. Numbers in this group were small; 7 of 100 GHB and 15 of 100 Medicaid patients entered prenatal care with high risk pregnancies. However, no high risk GHB patients received adequate care, while that standard was met for 80% of the Medicaid patients (P less than .001).
Adequacy of care was assessed using the Kotelchuck index for low-risk pregnancies; this model assumes care is “adequate” when 80% of the number of expected visits were attended by the woman receiving prenatal care. Additionally, care was deemed adequate for high-risk pregnancies if at least 80% of the number of expected ultrasound appointments were attended.
“In the current political climate, this study has implications for all pregnancies that begin as uninsured, regardless of maternal documentation status,” wrote Dr. Duncan and her colleagues.
Dr. Duncan reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Duncan, E et al. ACOG 2018, Abstract 28C.
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2018