User login
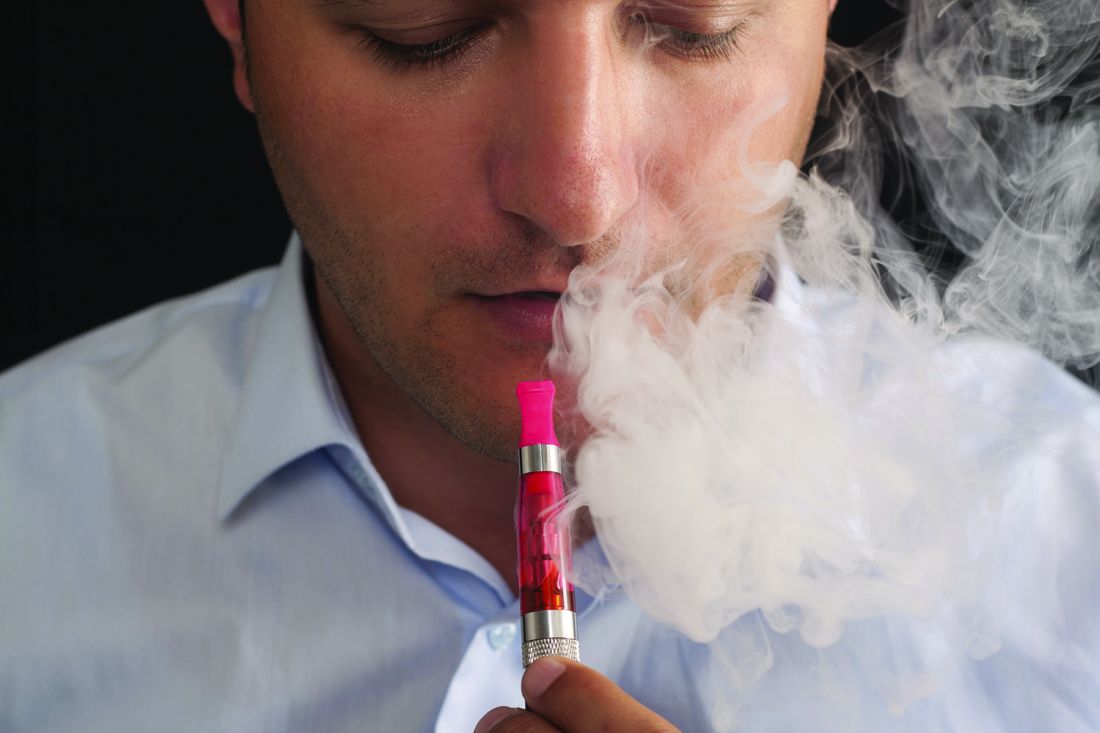
CDC identifies probable culprit in vaping lung injuries
found in lung fluid of victims.
In a telebriefing on Friday, Anne Schuchat, MD, the CDC’s principal deputy director, provided an update on recent lab findings and on case and death numbers reported so far to the CDC. The findings and more case information were published in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
At the telebriefing, Dr. Schuchat stated that CDC has received 29 samples of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from EVALI patients from 10 states and that vitamin E acetate was identified in all samples. Vitamin E acetate has already been found in some vaping devices and the discovery of the chemical in the lungs of patients increases the likelihood that this toxin is at least one source of EVALI. These findings are the first to link substances found in vaping products with biological samples from patients hospitalized with EVALI.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was found in 23 of 28 samples tested and nicotine was found in 16 of 26 samples tested. Other diluents and additives of concern (such as plant oils, medium chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes) were not detected in BAL fluid specimens from EVALI patients.
BAL fluid specimens were collected from hospitalized EVALI patients in the course of their treatment, although not for the specific purpose of the CDC investigation, and sent to the CDC by public health laboratories and health departments in California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Texas, Utah, and Wisconsin for analysis.
Dr. Schuchat stated that, as of Nov. 5, there have been 2,051 cases of EVALI reported to the CDC and 39 EVALI patients have died, with other deaths still under investigation as possibly related to EVALI. She said that the trend in new EVALI cases reported appears to be decreasing, but some states continue to see new cases. She cautioned that the lab findings of vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid do not rule out other possible compounds or ingredients that may contribute to EVALI and said the investigation will continue.
E-cigarette user survey
During the telebriefing, Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist with the Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH), gave an update on her department’s efforts to investigate vaping behaviors that might have led to EVALI in e-cigarette users and also to obtain more information on sources of vaping devices that could be linked to EVALI. The data were also reported in a MMWR.
The IDPH conducted an online public survey during September 2019 to October 2019 targeting e-cigarette, or vaping, product users in Illinois. The survey was promoted via social media on the IDPH website, local health departments, and other outlets. The survey yielded 4,631 respondents who answered questions about the frequency of vaping, sources of supply, and types of substances used. The investigators were then able to compare vaping-use habits and behaviors with similar information gleaned from EVALI patients.
Among survey respondents, 94% reported using any nicotine-containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products in the past 3 months; 21% used any THC-containing products; and 11% used both THC-containing products and nicotine-containing products. THC-containing product use was highest among survey respondents aged 18-24 years (36%) and decreased with increasing age. Compared with these survey respondents, EVALI patients were more likely to report exclusive use of THC-containing products (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-3.6), frequent use (more than five times per day) of these products (aOR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.6-6.0), and obtaining these products from informal sources, such as from a dealer, off the street, or from a friend (aOR, 9.2; 95% CI, 2.2-39.4). In addition, “the odds of using Dank Vapes, a class of largely counterfeit THC-containing products, was also higher among EVALI patients” (aOR, 8.5; 95% CI, 3.8-19.0), according to the MMWR.
Recommendations
CDC recommends that people should not buy any type of e-cigarette, or vaping, products, particularly those containing THC, off the street. They should also refrain from modifying or adding any substances to e-cigarette, or vaping, products that are not intended by the manufacturer, including products purchased through retail establishments.
Dr. Layden concluded, “we are in a better place today than we were a few weeks ago in terms of having one very strong culprit of concern based on the lung fluid testing,” but since the specific substances causing lung injury are not yet known, the only way to assure that individuals are not at risk while the investigation continues is to consider refraining from use of all vaping products.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
found in lung fluid of victims.
In a telebriefing on Friday, Anne Schuchat, MD, the CDC’s principal deputy director, provided an update on recent lab findings and on case and death numbers reported so far to the CDC. The findings and more case information were published in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
At the telebriefing, Dr. Schuchat stated that CDC has received 29 samples of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from EVALI patients from 10 states and that vitamin E acetate was identified in all samples. Vitamin E acetate has already been found in some vaping devices and the discovery of the chemical in the lungs of patients increases the likelihood that this toxin is at least one source of EVALI. These findings are the first to link substances found in vaping products with biological samples from patients hospitalized with EVALI.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was found in 23 of 28 samples tested and nicotine was found in 16 of 26 samples tested. Other diluents and additives of concern (such as plant oils, medium chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes) were not detected in BAL fluid specimens from EVALI patients.
BAL fluid specimens were collected from hospitalized EVALI patients in the course of their treatment, although not for the specific purpose of the CDC investigation, and sent to the CDC by public health laboratories and health departments in California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Texas, Utah, and Wisconsin for analysis.
Dr. Schuchat stated that, as of Nov. 5, there have been 2,051 cases of EVALI reported to the CDC and 39 EVALI patients have died, with other deaths still under investigation as possibly related to EVALI. She said that the trend in new EVALI cases reported appears to be decreasing, but some states continue to see new cases. She cautioned that the lab findings of vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid do not rule out other possible compounds or ingredients that may contribute to EVALI and said the investigation will continue.
E-cigarette user survey
During the telebriefing, Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist with the Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH), gave an update on her department’s efforts to investigate vaping behaviors that might have led to EVALI in e-cigarette users and also to obtain more information on sources of vaping devices that could be linked to EVALI. The data were also reported in a MMWR.
The IDPH conducted an online public survey during September 2019 to October 2019 targeting e-cigarette, or vaping, product users in Illinois. The survey was promoted via social media on the IDPH website, local health departments, and other outlets. The survey yielded 4,631 respondents who answered questions about the frequency of vaping, sources of supply, and types of substances used. The investigators were then able to compare vaping-use habits and behaviors with similar information gleaned from EVALI patients.
Among survey respondents, 94% reported using any nicotine-containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products in the past 3 months; 21% used any THC-containing products; and 11% used both THC-containing products and nicotine-containing products. THC-containing product use was highest among survey respondents aged 18-24 years (36%) and decreased with increasing age. Compared with these survey respondents, EVALI patients were more likely to report exclusive use of THC-containing products (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-3.6), frequent use (more than five times per day) of these products (aOR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.6-6.0), and obtaining these products from informal sources, such as from a dealer, off the street, or from a friend (aOR, 9.2; 95% CI, 2.2-39.4). In addition, “the odds of using Dank Vapes, a class of largely counterfeit THC-containing products, was also higher among EVALI patients” (aOR, 8.5; 95% CI, 3.8-19.0), according to the MMWR.
Recommendations
CDC recommends that people should not buy any type of e-cigarette, or vaping, products, particularly those containing THC, off the street. They should also refrain from modifying or adding any substances to e-cigarette, or vaping, products that are not intended by the manufacturer, including products purchased through retail establishments.
Dr. Layden concluded, “we are in a better place today than we were a few weeks ago in terms of having one very strong culprit of concern based on the lung fluid testing,” but since the specific substances causing lung injury are not yet known, the only way to assure that individuals are not at risk while the investigation continues is to consider refraining from use of all vaping products.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
found in lung fluid of victims.
In a telebriefing on Friday, Anne Schuchat, MD, the CDC’s principal deputy director, provided an update on recent lab findings and on case and death numbers reported so far to the CDC. The findings and more case information were published in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
At the telebriefing, Dr. Schuchat stated that CDC has received 29 samples of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from EVALI patients from 10 states and that vitamin E acetate was identified in all samples. Vitamin E acetate has already been found in some vaping devices and the discovery of the chemical in the lungs of patients increases the likelihood that this toxin is at least one source of EVALI. These findings are the first to link substances found in vaping products with biological samples from patients hospitalized with EVALI.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was found in 23 of 28 samples tested and nicotine was found in 16 of 26 samples tested. Other diluents and additives of concern (such as plant oils, medium chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes) were not detected in BAL fluid specimens from EVALI patients.
BAL fluid specimens were collected from hospitalized EVALI patients in the course of their treatment, although not for the specific purpose of the CDC investigation, and sent to the CDC by public health laboratories and health departments in California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Texas, Utah, and Wisconsin for analysis.
Dr. Schuchat stated that, as of Nov. 5, there have been 2,051 cases of EVALI reported to the CDC and 39 EVALI patients have died, with other deaths still under investigation as possibly related to EVALI. She said that the trend in new EVALI cases reported appears to be decreasing, but some states continue to see new cases. She cautioned that the lab findings of vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid do not rule out other possible compounds or ingredients that may contribute to EVALI and said the investigation will continue.
E-cigarette user survey
During the telebriefing, Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist with the Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH), gave an update on her department’s efforts to investigate vaping behaviors that might have led to EVALI in e-cigarette users and also to obtain more information on sources of vaping devices that could be linked to EVALI. The data were also reported in a MMWR.
The IDPH conducted an online public survey during September 2019 to October 2019 targeting e-cigarette, or vaping, product users in Illinois. The survey was promoted via social media on the IDPH website, local health departments, and other outlets. The survey yielded 4,631 respondents who answered questions about the frequency of vaping, sources of supply, and types of substances used. The investigators were then able to compare vaping-use habits and behaviors with similar information gleaned from EVALI patients.
Among survey respondents, 94% reported using any nicotine-containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products in the past 3 months; 21% used any THC-containing products; and 11% used both THC-containing products and nicotine-containing products. THC-containing product use was highest among survey respondents aged 18-24 years (36%) and decreased with increasing age. Compared with these survey respondents, EVALI patients were more likely to report exclusive use of THC-containing products (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-3.6), frequent use (more than five times per day) of these products (aOR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.6-6.0), and obtaining these products from informal sources, such as from a dealer, off the street, or from a friend (aOR, 9.2; 95% CI, 2.2-39.4). In addition, “the odds of using Dank Vapes, a class of largely counterfeit THC-containing products, was also higher among EVALI patients” (aOR, 8.5; 95% CI, 3.8-19.0), according to the MMWR.
Recommendations
CDC recommends that people should not buy any type of e-cigarette, or vaping, products, particularly those containing THC, off the street. They should also refrain from modifying or adding any substances to e-cigarette, or vaping, products that are not intended by the manufacturer, including products purchased through retail establishments.
Dr. Layden concluded, “we are in a better place today than we were a few weeks ago in terms of having one very strong culprit of concern based on the lung fluid testing,” but since the specific substances causing lung injury are not yet known, the only way to assure that individuals are not at risk while the investigation continues is to consider refraining from use of all vaping products.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
New model for CKD risk draws on clinical, demographic factors
Data from more than 5 million individuals has been used to develop an equation for predicting the risk of incident chronic kidney disease (CKD) in people with or without diabetes, according to a presentation at Kidney Week 2019, sponsored by the American Society of Nephrology.
In a paper published simultaneously online in JAMA, researchers reported the outcome of an individual-level data analysis of 34 multinational cohorts involving 5,222,711 individuals – including 781,627 with diabetes – from 28 countries as part of the Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium.
“An equation for kidney failure risk may help improve care for patients with established CKD, but relatively little work has been performed to develop predictive tools to identify those at increased risk of developing CKD – defined by reduced eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate], despite the high lifetime risk of CKD – which is estimated to be 59.1% in the United States,” wrote Robert G. Nelson, MD, PhD, from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases in Phoenix and colleagues.
Over a mean follow-up of 4 years, 15% of individuals without diabetes and 40% of individuals with diabetes developed incident chronic kidney disease, defined as an eGFR below 60 mL/min per 1.73m2.
The key risk factors were older age, female sex, black race, hypertension, history of cardiovascular disease, lower eGFR values, and higher urine albumin to creatinine ratio. Smoking was also significantly associated with reduced eGFR but only in cohorts without diabetes. In cohorts with diabetes, elevated hemoglobin A1c and the presence and type of diabetes medication were also significantly associated with reduced eGFR.
Using this information, the researchers developed a prediction model built from weighted-average hazard ratios and validated it in nine external validation cohorts of 18 study populations involving a total of 2,253,540 individuals. They found that in 16 of the 18 study populations, the slope of observed to predicted risk ranged from 0.80 to 1.25.
Moreover, in the cohorts without diabetes, the risk equations had a median C-statistic for the 5-year predicted probability of 0.845 (interquartile range, 0.789-0.890) and of 0.801 (IQR, 0.750-0.819) in the cohorts with diabetes, the investigators reported.
“Several models have been developed for estimating the risk of prevalent and incident CKD and end-stage kidney disease, but even those with good discriminative performance have not always performed well for cohorts of people outside the original derivation cohort,” the authors wrote. They argued that their model “demonstrated high discrimination and variable calibration in diverse populations.”
However, they stressed that further study was needed to determine if use of the equations would actually lead to improvements in clinical care and patient outcomes. In an accompanying editorial, Sri Lekha Tummalapalli, MD, and Michelle M. Estrella, MD, of the Kidney Health Research Collaborative at the University of California, San Francisco, said the study and its focus on primary, rather than secondary, prevention of kidney disease is a critical step toward reducing the burden of that disease, especially given that an estimated 37 million people in the United States have chronic kidney disease.
It is also important, they added, that primary prevention of kidney disease is tailored to the individual patient’s risk because risk prediction and screening strategies are unlikely to improve outcomes if they are not paired with effective individualized interventions, such as lifestyle modification or management of blood pressure.
These risk equations could be more holistic by integrating the prediction of both elevated albuminuria and reduced eGFR because more than 40% of individuals with chronic kidney disease have increased albuminuria without reduced eGFR, they noted (JAMA. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17378).
The study and CKD Prognosis Consortium were supported by the U.S. National Kidney Foundation and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One author was supported by a grant from the German Research Foundation. Nine authors declared grants, consultancies, and other support from the private sector and research organizations. No other conflicts of interest were declared. Dr. Tummalapalli and Dr. Estrella reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nelson R et al. JAMA. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17379.
Data from more than 5 million individuals has been used to develop an equation for predicting the risk of incident chronic kidney disease (CKD) in people with or without diabetes, according to a presentation at Kidney Week 2019, sponsored by the American Society of Nephrology.
In a paper published simultaneously online in JAMA, researchers reported the outcome of an individual-level data analysis of 34 multinational cohorts involving 5,222,711 individuals – including 781,627 with diabetes – from 28 countries as part of the Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium.
“An equation for kidney failure risk may help improve care for patients with established CKD, but relatively little work has been performed to develop predictive tools to identify those at increased risk of developing CKD – defined by reduced eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate], despite the high lifetime risk of CKD – which is estimated to be 59.1% in the United States,” wrote Robert G. Nelson, MD, PhD, from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases in Phoenix and colleagues.
Over a mean follow-up of 4 years, 15% of individuals without diabetes and 40% of individuals with diabetes developed incident chronic kidney disease, defined as an eGFR below 60 mL/min per 1.73m2.
The key risk factors were older age, female sex, black race, hypertension, history of cardiovascular disease, lower eGFR values, and higher urine albumin to creatinine ratio. Smoking was also significantly associated with reduced eGFR but only in cohorts without diabetes. In cohorts with diabetes, elevated hemoglobin A1c and the presence and type of diabetes medication were also significantly associated with reduced eGFR.
Using this information, the researchers developed a prediction model built from weighted-average hazard ratios and validated it in nine external validation cohorts of 18 study populations involving a total of 2,253,540 individuals. They found that in 16 of the 18 study populations, the slope of observed to predicted risk ranged from 0.80 to 1.25.
Moreover, in the cohorts without diabetes, the risk equations had a median C-statistic for the 5-year predicted probability of 0.845 (interquartile range, 0.789-0.890) and of 0.801 (IQR, 0.750-0.819) in the cohorts with diabetes, the investigators reported.
“Several models have been developed for estimating the risk of prevalent and incident CKD and end-stage kidney disease, but even those with good discriminative performance have not always performed well for cohorts of people outside the original derivation cohort,” the authors wrote. They argued that their model “demonstrated high discrimination and variable calibration in diverse populations.”
However, they stressed that further study was needed to determine if use of the equations would actually lead to improvements in clinical care and patient outcomes. In an accompanying editorial, Sri Lekha Tummalapalli, MD, and Michelle M. Estrella, MD, of the Kidney Health Research Collaborative at the University of California, San Francisco, said the study and its focus on primary, rather than secondary, prevention of kidney disease is a critical step toward reducing the burden of that disease, especially given that an estimated 37 million people in the United States have chronic kidney disease.
It is also important, they added, that primary prevention of kidney disease is tailored to the individual patient’s risk because risk prediction and screening strategies are unlikely to improve outcomes if they are not paired with effective individualized interventions, such as lifestyle modification or management of blood pressure.
These risk equations could be more holistic by integrating the prediction of both elevated albuminuria and reduced eGFR because more than 40% of individuals with chronic kidney disease have increased albuminuria without reduced eGFR, they noted (JAMA. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17378).
The study and CKD Prognosis Consortium were supported by the U.S. National Kidney Foundation and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One author was supported by a grant from the German Research Foundation. Nine authors declared grants, consultancies, and other support from the private sector and research organizations. No other conflicts of interest were declared. Dr. Tummalapalli and Dr. Estrella reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nelson R et al. JAMA. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17379.
Data from more than 5 million individuals has been used to develop an equation for predicting the risk of incident chronic kidney disease (CKD) in people with or without diabetes, according to a presentation at Kidney Week 2019, sponsored by the American Society of Nephrology.
In a paper published simultaneously online in JAMA, researchers reported the outcome of an individual-level data analysis of 34 multinational cohorts involving 5,222,711 individuals – including 781,627 with diabetes – from 28 countries as part of the Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium.
“An equation for kidney failure risk may help improve care for patients with established CKD, but relatively little work has been performed to develop predictive tools to identify those at increased risk of developing CKD – defined by reduced eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate], despite the high lifetime risk of CKD – which is estimated to be 59.1% in the United States,” wrote Robert G. Nelson, MD, PhD, from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases in Phoenix and colleagues.
Over a mean follow-up of 4 years, 15% of individuals without diabetes and 40% of individuals with diabetes developed incident chronic kidney disease, defined as an eGFR below 60 mL/min per 1.73m2.
The key risk factors were older age, female sex, black race, hypertension, history of cardiovascular disease, lower eGFR values, and higher urine albumin to creatinine ratio. Smoking was also significantly associated with reduced eGFR but only in cohorts without diabetes. In cohorts with diabetes, elevated hemoglobin A1c and the presence and type of diabetes medication were also significantly associated with reduced eGFR.
Using this information, the researchers developed a prediction model built from weighted-average hazard ratios and validated it in nine external validation cohorts of 18 study populations involving a total of 2,253,540 individuals. They found that in 16 of the 18 study populations, the slope of observed to predicted risk ranged from 0.80 to 1.25.
Moreover, in the cohorts without diabetes, the risk equations had a median C-statistic for the 5-year predicted probability of 0.845 (interquartile range, 0.789-0.890) and of 0.801 (IQR, 0.750-0.819) in the cohorts with diabetes, the investigators reported.
“Several models have been developed for estimating the risk of prevalent and incident CKD and end-stage kidney disease, but even those with good discriminative performance have not always performed well for cohorts of people outside the original derivation cohort,” the authors wrote. They argued that their model “demonstrated high discrimination and variable calibration in diverse populations.”
However, they stressed that further study was needed to determine if use of the equations would actually lead to improvements in clinical care and patient outcomes. In an accompanying editorial, Sri Lekha Tummalapalli, MD, and Michelle M. Estrella, MD, of the Kidney Health Research Collaborative at the University of California, San Francisco, said the study and its focus on primary, rather than secondary, prevention of kidney disease is a critical step toward reducing the burden of that disease, especially given that an estimated 37 million people in the United States have chronic kidney disease.
It is also important, they added, that primary prevention of kidney disease is tailored to the individual patient’s risk because risk prediction and screening strategies are unlikely to improve outcomes if they are not paired with effective individualized interventions, such as lifestyle modification or management of blood pressure.
These risk equations could be more holistic by integrating the prediction of both elevated albuminuria and reduced eGFR because more than 40% of individuals with chronic kidney disease have increased albuminuria without reduced eGFR, they noted (JAMA. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17378).
The study and CKD Prognosis Consortium were supported by the U.S. National Kidney Foundation and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One author was supported by a grant from the German Research Foundation. Nine authors declared grants, consultancies, and other support from the private sector and research organizations. No other conflicts of interest were declared. Dr. Tummalapalli and Dr. Estrella reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nelson R et al. JAMA. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17379.
REPORTING FROM KIDNEY WEEK 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: In the cohorts without diabetes, the risk equations had a median C-statistic for the 5-year predicted probability of 0.845 (interquartile range, 0.789-0.890), and of 0.801 (IQR, 0.750-0.819) in the cohorts with diabetes,
Study details: Analysis of cohort data from 5,222,711 individuals, including 781,627 with diabetes.
Disclosures: The study and CKD Prognosis Consortium were supported by the U.S. National Kidney Foundation and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. One author was supported by a grant from the German Research Foundation. Nine authors declared grants, consultancies, and other support from the private sector and research organizations. No other conflicts of interest were declared. Dr. Tummalapalli and Dr. Estrella reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: Nelson R et al. JAMA. 2019 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17379.
Aspirin for primary prevention reduces risk of CV events, increases bleeding
Background: Aspirin is beneficial in secondary prevention of stroke and MI. There is no consensus on its role in primary prevention of the same.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: PubMed and Embase search on Cochrane from the earliest publication available through Nov. 1, 2018.
Synopsis: This meta-analysis included randomized, controlled trials that compared aspirin use versus no aspirin use in more than 1,000 participants without known cardiovascular (CV) disease. The primary CV outcome was a composite of CV mortality, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke. The primary bleeding outcome was major bleeding (defined by individual studies). Thirteen studies enrolling 164,225 participants and including 1,050,511 participant-years were included. Compared with no aspirin use, aspirin use showed a reduction in composite CV outcomes (hazard ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-0.95; number needed to treat, 265) and an increased risk of major bleeding (HR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30-1.56; number needed to harm, 210). Limitations of the study include variations in data quality, outcome definitions, and aspirin doses among trials. The study authors advocate for including the lower risk of CV events and increased risk of major bleeding as part of discussions with patients about the use of aspirin for primary prevention.
Bottom line: Aspirin for primary prevention lowers risk of CV events and increases risk of major bleeding. Health care providers should include this as part of informed decision-making discussions with patients about the use of aspirin for primary prevention.
Citation: Zheng S et al. Association of aspirin use for primary prevention with cardiovascular events and bleeding events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2019 Jan 22;321(3):277-87.
Dr. Radhakrishnan is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Background: Aspirin is beneficial in secondary prevention of stroke and MI. There is no consensus on its role in primary prevention of the same.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: PubMed and Embase search on Cochrane from the earliest publication available through Nov. 1, 2018.
Synopsis: This meta-analysis included randomized, controlled trials that compared aspirin use versus no aspirin use in more than 1,000 participants without known cardiovascular (CV) disease. The primary CV outcome was a composite of CV mortality, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke. The primary bleeding outcome was major bleeding (defined by individual studies). Thirteen studies enrolling 164,225 participants and including 1,050,511 participant-years were included. Compared with no aspirin use, aspirin use showed a reduction in composite CV outcomes (hazard ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-0.95; number needed to treat, 265) and an increased risk of major bleeding (HR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30-1.56; number needed to harm, 210). Limitations of the study include variations in data quality, outcome definitions, and aspirin doses among trials. The study authors advocate for including the lower risk of CV events and increased risk of major bleeding as part of discussions with patients about the use of aspirin for primary prevention.
Bottom line: Aspirin for primary prevention lowers risk of CV events and increases risk of major bleeding. Health care providers should include this as part of informed decision-making discussions with patients about the use of aspirin for primary prevention.
Citation: Zheng S et al. Association of aspirin use for primary prevention with cardiovascular events and bleeding events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2019 Jan 22;321(3):277-87.
Dr. Radhakrishnan is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Background: Aspirin is beneficial in secondary prevention of stroke and MI. There is no consensus on its role in primary prevention of the same.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: PubMed and Embase search on Cochrane from the earliest publication available through Nov. 1, 2018.
Synopsis: This meta-analysis included randomized, controlled trials that compared aspirin use versus no aspirin use in more than 1,000 participants without known cardiovascular (CV) disease. The primary CV outcome was a composite of CV mortality, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke. The primary bleeding outcome was major bleeding (defined by individual studies). Thirteen studies enrolling 164,225 participants and including 1,050,511 participant-years were included. Compared with no aspirin use, aspirin use showed a reduction in composite CV outcomes (hazard ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-0.95; number needed to treat, 265) and an increased risk of major bleeding (HR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.30-1.56; number needed to harm, 210). Limitations of the study include variations in data quality, outcome definitions, and aspirin doses among trials. The study authors advocate for including the lower risk of CV events and increased risk of major bleeding as part of discussions with patients about the use of aspirin for primary prevention.
Bottom line: Aspirin for primary prevention lowers risk of CV events and increases risk of major bleeding. Health care providers should include this as part of informed decision-making discussions with patients about the use of aspirin for primary prevention.
Citation: Zheng S et al. Association of aspirin use for primary prevention with cardiovascular events and bleeding events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2019 Jan 22;321(3):277-87.
Dr. Radhakrishnan is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Spanish risk score predicts 30-day mortality in acute HF in ED patients
Background: The MEESSI-AHF (Multiple Estimation of Risk based on the Emergency Department Spanish Score In patients with Acute Heart Failure) score is a risk-stratification tool that includes systolic blood pressure, age, NT-proBNP, potassium, cardiac troponin T, New York Heart Association class 4 disease, respiratory rate, low-output symptoms, oxygen saturation, episode associated with acute coronary syndrome, signs of left ventricular hypertrophy on EKG, creatinine, and Barthel Index Score. Prior research has shown that it accurately risk-stratified ED patients with AHF in Spain. It has not been studied in other populations.
Study design: Prospective multicenter cohort study.
Setting: Adult ED patients with acute dyspnea in four hospitals in Switzerland.
Synopsis: The study included 1,247 nonhemodialysis patients who presented to the ED with acute dyspnea, were found to have all the necessary variables to calculate the MEESSI-AHF score, and were adjudicated to have acute heart failure. The authors calculated a modified MEESSI-AHF score, excluding the Barthel Index for all patients. The authors found that a six-group modified MEESSI-AHF risk-stratification model could predict 30-day mortality with excellent discrimination (C-Statistic, 0.80). Limitations of the study include the exclusion of all hemodynamically unstable patients and those on hemodialysis.
Bottom line: The MEESSI-AHF score effectively predicts 30-day mortality in AHF in Swiss and Spanish ED patients.
Citation: Wussler D et al. External validation of the MEESSI acute heart failure risk score: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170:248-56.
Dr. Radhakrishnan is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Background: The MEESSI-AHF (Multiple Estimation of Risk based on the Emergency Department Spanish Score In patients with Acute Heart Failure) score is a risk-stratification tool that includes systolic blood pressure, age, NT-proBNP, potassium, cardiac troponin T, New York Heart Association class 4 disease, respiratory rate, low-output symptoms, oxygen saturation, episode associated with acute coronary syndrome, signs of left ventricular hypertrophy on EKG, creatinine, and Barthel Index Score. Prior research has shown that it accurately risk-stratified ED patients with AHF in Spain. It has not been studied in other populations.
Study design: Prospective multicenter cohort study.
Setting: Adult ED patients with acute dyspnea in four hospitals in Switzerland.
Synopsis: The study included 1,247 nonhemodialysis patients who presented to the ED with acute dyspnea, were found to have all the necessary variables to calculate the MEESSI-AHF score, and were adjudicated to have acute heart failure. The authors calculated a modified MEESSI-AHF score, excluding the Barthel Index for all patients. The authors found that a six-group modified MEESSI-AHF risk-stratification model could predict 30-day mortality with excellent discrimination (C-Statistic, 0.80). Limitations of the study include the exclusion of all hemodynamically unstable patients and those on hemodialysis.
Bottom line: The MEESSI-AHF score effectively predicts 30-day mortality in AHF in Swiss and Spanish ED patients.
Citation: Wussler D et al. External validation of the MEESSI acute heart failure risk score: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170:248-56.
Dr. Radhakrishnan is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Background: The MEESSI-AHF (Multiple Estimation of Risk based on the Emergency Department Spanish Score In patients with Acute Heart Failure) score is a risk-stratification tool that includes systolic blood pressure, age, NT-proBNP, potassium, cardiac troponin T, New York Heart Association class 4 disease, respiratory rate, low-output symptoms, oxygen saturation, episode associated with acute coronary syndrome, signs of left ventricular hypertrophy on EKG, creatinine, and Barthel Index Score. Prior research has shown that it accurately risk-stratified ED patients with AHF in Spain. It has not been studied in other populations.
Study design: Prospective multicenter cohort study.
Setting: Adult ED patients with acute dyspnea in four hospitals in Switzerland.
Synopsis: The study included 1,247 nonhemodialysis patients who presented to the ED with acute dyspnea, were found to have all the necessary variables to calculate the MEESSI-AHF score, and were adjudicated to have acute heart failure. The authors calculated a modified MEESSI-AHF score, excluding the Barthel Index for all patients. The authors found that a six-group modified MEESSI-AHF risk-stratification model could predict 30-day mortality with excellent discrimination (C-Statistic, 0.80). Limitations of the study include the exclusion of all hemodynamically unstable patients and those on hemodialysis.
Bottom line: The MEESSI-AHF score effectively predicts 30-day mortality in AHF in Swiss and Spanish ED patients.
Citation: Wussler D et al. External validation of the MEESSI acute heart failure risk score: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170:248-56.
Dr. Radhakrishnan is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
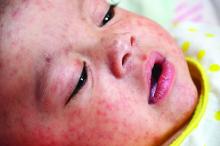
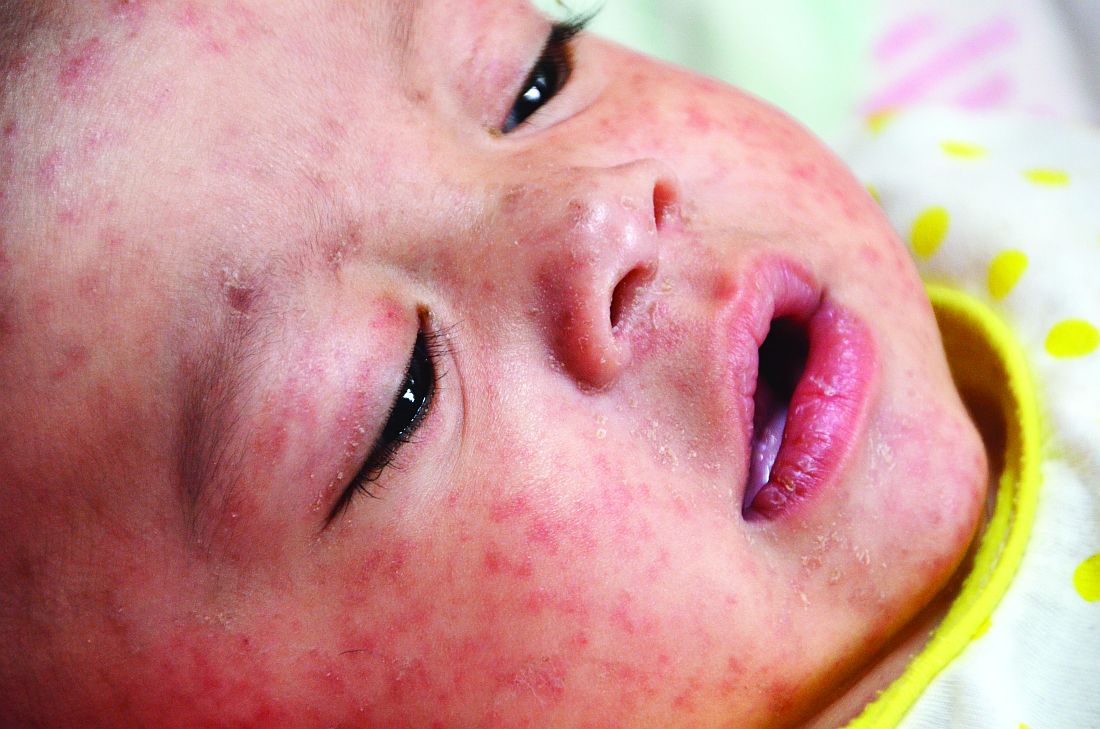
Measles infection linked to impaired ‘immune memory’
Infection with the measles virus appears to reduce immunity to other pathogens, according to a paper published in Science.
The hypothesis that the measles virus could cause “immunological amnesia” by impairing immune memory is supported by early research showing children with measles had negative cutaneous tuberculin reactions after having previously tested positive.
“Subsequent studies have shown decreased interferon signaling, skewed cytokine responses, lymphopenia, and suppression of lymphocyte proliferation shortly after infection,” wrote Michael Mina, MD, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and coauthors.
“Given the variation in the degree of immune repertoire modulation we observed, we anticipate that future risk of morbidity and mortality after measles would not be homogeneous but would be skewed toward individuals with the most severe elimination of immunological memory,” they wrote. “These findings underscore the crucial need for continued widespread vaccination.”
In this study, researchers compared the levels of around 400 pathogen-specific antibodies in blood samples from 77 unvaccinated children, taken before and 2 months after natural measles infection, with 5 unvaccinated children who did not contract measles. A total of 34 the children experienced mild measles, and 43 had severe measles.
They found that the samples taken after measles infection showed “substantial” reductions in the number of pathogen epitopes, compared with the samples from children who did not get infected with measles.
This amounted to approximately a 20% mean reduction in overall diversity or size of the antibody repertoire. However, in children who experienced severe measles, there was a median loss of 40% (range, 11%-62%) of antibody repertoire, compared with a median of 33% (range, 12%-73%) range in children who experienced mild infection. Meanwhile, the control subjects retained approximately 90% of their antibody repertoire over a similar or longer time period. Some children lost up to 70% of antibodies for specific pathogens.
The study did find increases in measles virus–specific antigens in children both after measles infection and MMR vaccination. However the authors did not detect any changes in total IgG, IgA, or IgM levels.
Dr. Mina and associates wrote.
They also noted that controls who received the MMR vaccine showed a marked increase in overall antibody repertoire.
In a separate investigation reported in Science Immunology, Velislava N. Petrova, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Cambridge, England, and coauthors investigated genetic changes in 26 unvaccinated children from the Netherlands who previously had measles to determine if B-cell impairment can lead to measles-associated immunosuppression. Their antibody genes were sequenced before any symptoms of measles developed and roughly 40 days after rash. Two control groups also were sequenced accordingly: vaccinated adults and three unvaccinated children from the same community who were not infected with measles.
Naive B cells from individuals in the vaccinated and uninfected control groups showed high correlation of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgVH-J) gene frequencies across time periods (R2 = 0.96 and 0.92, respectively) but no significant differences in gene expression (P greater than .05). At the same time, although B-cell frequencies in measles patients recovered to levels before infection, they had significant changes in IgVH-J gene frequencies (P = .01) and decreased correlation in gene expression (R2 = 0.78).
In addition, individuals in the control groups had “a stable genetic composition of B memory cells” but no significant changes in the third complementarity-determining region (CDR3) lengths or mutational frequency of IgVH-J genes (P greater than .05). B memory cells in measles patients, however, showed increases in mutational frequency (P = .0008) and a reduction in CDR3 length (P = .017) of IgVH genes, Dr. Petrova and associates reported.
The study by Mina et al. was supported by grants from various U.S., European, and Finnish foundations and national organizations. Some of the coauthors had relationships with biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, and three reported a patent holding related to technology used in the study. The study by Petrova et al. was funded by grants to the investigators from various Indonesian and German organizations and the Wellcome Trust. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Mina M et al. Science. 2019 Nov 1;366:599-606; Petrova VN et al. Sci Immunol. 2019 Nov 1. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aay6125.
As a result of reduced vaccination, after decades of decline, the number of worldwide cases of measles has increased by nearly 300% since 2018. Epidemiologic evidence has associated measles infections with increases in morbidity and mortality for as long as 5 years after the infection and suggests that, in the prevaccine era, measles virus may have been associated with up to 50% of all childhood deaths, mostly because of nonmeasles infections. Measles replication in immune cells has been hypothesized to impair immune memory, potentially causing what some scientists call “immunological amnesia.”A measles virus receptor, called CD150/ SLAMF1, is highly expressed on memory T, B, and plasma cells. Measles virus gains entry to these immune memory cells using that receptor and kills the cells.
The scientists stated that it could take months or years to return the immune repertoire back to baseline. During the rebuilding process, children would be at increased risk for infectious diseases they had previously experienced.
In a second outstanding paper, Petrova et al. in Science Immunology studied B cells before and after measles infection, and identified two immunologic consequences: The naive B-cell pool was depleted, leading to a return to immunologic immaturity, and the memory B-cell pool was depleted, resulting in compromised immune memory to previously encountered pathogens.
Thus, the link between measles infections and increased susceptibility to other infections and increased deaths from nonmeasles infectious diseases in the aftermath of measles has been revealed. This information adds new data to share with parents who consider refusing measles vaccination. The risks are far greater than getting measles.
Michael E. Pichichero, MD, is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He was asked to comment on the articles. Dr. Pichichero has no conflicts to declare.
As a result of reduced vaccination, after decades of decline, the number of worldwide cases of measles has increased by nearly 300% since 2018. Epidemiologic evidence has associated measles infections with increases in morbidity and mortality for as long as 5 years after the infection and suggests that, in the prevaccine era, measles virus may have been associated with up to 50% of all childhood deaths, mostly because of nonmeasles infections. Measles replication in immune cells has been hypothesized to impair immune memory, potentially causing what some scientists call “immunological amnesia.”A measles virus receptor, called CD150/ SLAMF1, is highly expressed on memory T, B, and plasma cells. Measles virus gains entry to these immune memory cells using that receptor and kills the cells.
The scientists stated that it could take months or years to return the immune repertoire back to baseline. During the rebuilding process, children would be at increased risk for infectious diseases they had previously experienced.
In a second outstanding paper, Petrova et al. in Science Immunology studied B cells before and after measles infection, and identified two immunologic consequences: The naive B-cell pool was depleted, leading to a return to immunologic immaturity, and the memory B-cell pool was depleted, resulting in compromised immune memory to previously encountered pathogens.
Thus, the link between measles infections and increased susceptibility to other infections and increased deaths from nonmeasles infectious diseases in the aftermath of measles has been revealed. This information adds new data to share with parents who consider refusing measles vaccination. The risks are far greater than getting measles.
Michael E. Pichichero, MD, is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He was asked to comment on the articles. Dr. Pichichero has no conflicts to declare.
As a result of reduced vaccination, after decades of decline, the number of worldwide cases of measles has increased by nearly 300% since 2018. Epidemiologic evidence has associated measles infections with increases in morbidity and mortality for as long as 5 years after the infection and suggests that, in the prevaccine era, measles virus may have been associated with up to 50% of all childhood deaths, mostly because of nonmeasles infections. Measles replication in immune cells has been hypothesized to impair immune memory, potentially causing what some scientists call “immunological amnesia.”A measles virus receptor, called CD150/ SLAMF1, is highly expressed on memory T, B, and plasma cells. Measles virus gains entry to these immune memory cells using that receptor and kills the cells.
The scientists stated that it could take months or years to return the immune repertoire back to baseline. During the rebuilding process, children would be at increased risk for infectious diseases they had previously experienced.
In a second outstanding paper, Petrova et al. in Science Immunology studied B cells before and after measles infection, and identified two immunologic consequences: The naive B-cell pool was depleted, leading to a return to immunologic immaturity, and the memory B-cell pool was depleted, resulting in compromised immune memory to previously encountered pathogens.
Thus, the link between measles infections and increased susceptibility to other infections and increased deaths from nonmeasles infectious diseases in the aftermath of measles has been revealed. This information adds new data to share with parents who consider refusing measles vaccination. The risks are far greater than getting measles.
Michael E. Pichichero, MD, is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He was asked to comment on the articles. Dr. Pichichero has no conflicts to declare.
Infection with the measles virus appears to reduce immunity to other pathogens, according to a paper published in Science.
The hypothesis that the measles virus could cause “immunological amnesia” by impairing immune memory is supported by early research showing children with measles had negative cutaneous tuberculin reactions after having previously tested positive.
“Subsequent studies have shown decreased interferon signaling, skewed cytokine responses, lymphopenia, and suppression of lymphocyte proliferation shortly after infection,” wrote Michael Mina, MD, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and coauthors.
“Given the variation in the degree of immune repertoire modulation we observed, we anticipate that future risk of morbidity and mortality after measles would not be homogeneous but would be skewed toward individuals with the most severe elimination of immunological memory,” they wrote. “These findings underscore the crucial need for continued widespread vaccination.”
In this study, researchers compared the levels of around 400 pathogen-specific antibodies in blood samples from 77 unvaccinated children, taken before and 2 months after natural measles infection, with 5 unvaccinated children who did not contract measles. A total of 34 the children experienced mild measles, and 43 had severe measles.
They found that the samples taken after measles infection showed “substantial” reductions in the number of pathogen epitopes, compared with the samples from children who did not get infected with measles.
This amounted to approximately a 20% mean reduction in overall diversity or size of the antibody repertoire. However, in children who experienced severe measles, there was a median loss of 40% (range, 11%-62%) of antibody repertoire, compared with a median of 33% (range, 12%-73%) range in children who experienced mild infection. Meanwhile, the control subjects retained approximately 90% of their antibody repertoire over a similar or longer time period. Some children lost up to 70% of antibodies for specific pathogens.
The study did find increases in measles virus–specific antigens in children both after measles infection and MMR vaccination. However the authors did not detect any changes in total IgG, IgA, or IgM levels.
Dr. Mina and associates wrote.
They also noted that controls who received the MMR vaccine showed a marked increase in overall antibody repertoire.
In a separate investigation reported in Science Immunology, Velislava N. Petrova, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Cambridge, England, and coauthors investigated genetic changes in 26 unvaccinated children from the Netherlands who previously had measles to determine if B-cell impairment can lead to measles-associated immunosuppression. Their antibody genes were sequenced before any symptoms of measles developed and roughly 40 days after rash. Two control groups also were sequenced accordingly: vaccinated adults and three unvaccinated children from the same community who were not infected with measles.
Naive B cells from individuals in the vaccinated and uninfected control groups showed high correlation of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgVH-J) gene frequencies across time periods (R2 = 0.96 and 0.92, respectively) but no significant differences in gene expression (P greater than .05). At the same time, although B-cell frequencies in measles patients recovered to levels before infection, they had significant changes in IgVH-J gene frequencies (P = .01) and decreased correlation in gene expression (R2 = 0.78).
In addition, individuals in the control groups had “a stable genetic composition of B memory cells” but no significant changes in the third complementarity-determining region (CDR3) lengths or mutational frequency of IgVH-J genes (P greater than .05). B memory cells in measles patients, however, showed increases in mutational frequency (P = .0008) and a reduction in CDR3 length (P = .017) of IgVH genes, Dr. Petrova and associates reported.
The study by Mina et al. was supported by grants from various U.S., European, and Finnish foundations and national organizations. Some of the coauthors had relationships with biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, and three reported a patent holding related to technology used in the study. The study by Petrova et al. was funded by grants to the investigators from various Indonesian and German organizations and the Wellcome Trust. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Mina M et al. Science. 2019 Nov 1;366:599-606; Petrova VN et al. Sci Immunol. 2019 Nov 1. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aay6125.
Infection with the measles virus appears to reduce immunity to other pathogens, according to a paper published in Science.
The hypothesis that the measles virus could cause “immunological amnesia” by impairing immune memory is supported by early research showing children with measles had negative cutaneous tuberculin reactions after having previously tested positive.
“Subsequent studies have shown decreased interferon signaling, skewed cytokine responses, lymphopenia, and suppression of lymphocyte proliferation shortly after infection,” wrote Michael Mina, MD, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and coauthors.
“Given the variation in the degree of immune repertoire modulation we observed, we anticipate that future risk of morbidity and mortality after measles would not be homogeneous but would be skewed toward individuals with the most severe elimination of immunological memory,” they wrote. “These findings underscore the crucial need for continued widespread vaccination.”
In this study, researchers compared the levels of around 400 pathogen-specific antibodies in blood samples from 77 unvaccinated children, taken before and 2 months after natural measles infection, with 5 unvaccinated children who did not contract measles. A total of 34 the children experienced mild measles, and 43 had severe measles.
They found that the samples taken after measles infection showed “substantial” reductions in the number of pathogen epitopes, compared with the samples from children who did not get infected with measles.
This amounted to approximately a 20% mean reduction in overall diversity or size of the antibody repertoire. However, in children who experienced severe measles, there was a median loss of 40% (range, 11%-62%) of antibody repertoire, compared with a median of 33% (range, 12%-73%) range in children who experienced mild infection. Meanwhile, the control subjects retained approximately 90% of their antibody repertoire over a similar or longer time period. Some children lost up to 70% of antibodies for specific pathogens.
The study did find increases in measles virus–specific antigens in children both after measles infection and MMR vaccination. However the authors did not detect any changes in total IgG, IgA, or IgM levels.
Dr. Mina and associates wrote.
They also noted that controls who received the MMR vaccine showed a marked increase in overall antibody repertoire.
In a separate investigation reported in Science Immunology, Velislava N. Petrova, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Cambridge, England, and coauthors investigated genetic changes in 26 unvaccinated children from the Netherlands who previously had measles to determine if B-cell impairment can lead to measles-associated immunosuppression. Their antibody genes were sequenced before any symptoms of measles developed and roughly 40 days after rash. Two control groups also were sequenced accordingly: vaccinated adults and three unvaccinated children from the same community who were not infected with measles.
Naive B cells from individuals in the vaccinated and uninfected control groups showed high correlation of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgVH-J) gene frequencies across time periods (R2 = 0.96 and 0.92, respectively) but no significant differences in gene expression (P greater than .05). At the same time, although B-cell frequencies in measles patients recovered to levels before infection, they had significant changes in IgVH-J gene frequencies (P = .01) and decreased correlation in gene expression (R2 = 0.78).
In addition, individuals in the control groups had “a stable genetic composition of B memory cells” but no significant changes in the third complementarity-determining region (CDR3) lengths or mutational frequency of IgVH-J genes (P greater than .05). B memory cells in measles patients, however, showed increases in mutational frequency (P = .0008) and a reduction in CDR3 length (P = .017) of IgVH genes, Dr. Petrova and associates reported.
The study by Mina et al. was supported by grants from various U.S., European, and Finnish foundations and national organizations. Some of the coauthors had relationships with biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, and three reported a patent holding related to technology used in the study. The study by Petrova et al. was funded by grants to the investigators from various Indonesian and German organizations and the Wellcome Trust. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Mina M et al. Science. 2019 Nov 1;366:599-606; Petrova VN et al. Sci Immunol. 2019 Nov 1. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aay6125.
FROM SCIENCE
Oral antibiotics as effective as IV for stable endocarditis patients
Background: Patients with left-sided infective endocarditis often are treated with prolonged courses of intravenous (IV) antibiotics. The safety of switching from IV to oral antibiotics is unknown.
Study design: Randomized, multicenter, noninferiority study.
Setting: Cardiac centers in Denmark during July 2011–August 2017.
Synopsis: The study enrolled 400 patients with left-sided infective endocarditis and positive blood cultures from Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, or coagulase-negative staph (non–methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), without evidence of valvular abscess. Following at least 7 days (for those who required surgical intervention) or 10 days (for those who did not require surgical intervention) of IV antibiotics, patients with ongoing fever, leukocytosis, elevated C-reactive protein, or concurrent infections were excluded from the study. Patients were randomized to receive continued IV antibiotic treatment or switch to oral antibiotic treatment. The IV treatment group received a median of 19 additional days of therapy, compared with 17 days in the oral group. The primary composite outcome of death, unplanned cardiac surgery, embolic event, and relapse of bacteremia occurred in 12.1% in the IV therapy group and 9% in the oral therapy group (difference of 3.1%; 95% confidence interval, –3.4 to 9.6; P = .40), meeting the studies prespecified noninferiority criteria. Poor representation of women, obese patients, and patients who use IV drugs may limit the study’s generalizability. An accompanying editorial advocated for additional research before widespread change to current treatment recommendations are made.
Bottom line: For patients with left-sided infective endocarditis who have been stabilized on IV antibiotic treatment, transitioning to an oral antibiotic regimen may be a noninferior approach.
Citation: Iverson K et al. Partial oral versus intravenous antibiotic treatment of endocarditis. N Eng J Med. 2019 Jan 31;380(5):415-24.
Dr. Phillips is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Background: Patients with left-sided infective endocarditis often are treated with prolonged courses of intravenous (IV) antibiotics. The safety of switching from IV to oral antibiotics is unknown.
Study design: Randomized, multicenter, noninferiority study.
Setting: Cardiac centers in Denmark during July 2011–August 2017.
Synopsis: The study enrolled 400 patients with left-sided infective endocarditis and positive blood cultures from Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, or coagulase-negative staph (non–methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), without evidence of valvular abscess. Following at least 7 days (for those who required surgical intervention) or 10 days (for those who did not require surgical intervention) of IV antibiotics, patients with ongoing fever, leukocytosis, elevated C-reactive protein, or concurrent infections were excluded from the study. Patients were randomized to receive continued IV antibiotic treatment or switch to oral antibiotic treatment. The IV treatment group received a median of 19 additional days of therapy, compared with 17 days in the oral group. The primary composite outcome of death, unplanned cardiac surgery, embolic event, and relapse of bacteremia occurred in 12.1% in the IV therapy group and 9% in the oral therapy group (difference of 3.1%; 95% confidence interval, –3.4 to 9.6; P = .40), meeting the studies prespecified noninferiority criteria. Poor representation of women, obese patients, and patients who use IV drugs may limit the study’s generalizability. An accompanying editorial advocated for additional research before widespread change to current treatment recommendations are made.
Bottom line: For patients with left-sided infective endocarditis who have been stabilized on IV antibiotic treatment, transitioning to an oral antibiotic regimen may be a noninferior approach.
Citation: Iverson K et al. Partial oral versus intravenous antibiotic treatment of endocarditis. N Eng J Med. 2019 Jan 31;380(5):415-24.
Dr. Phillips is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Background: Patients with left-sided infective endocarditis often are treated with prolonged courses of intravenous (IV) antibiotics. The safety of switching from IV to oral antibiotics is unknown.
Study design: Randomized, multicenter, noninferiority study.
Setting: Cardiac centers in Denmark during July 2011–August 2017.
Synopsis: The study enrolled 400 patients with left-sided infective endocarditis and positive blood cultures from Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, or coagulase-negative staph (non–methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), without evidence of valvular abscess. Following at least 7 days (for those who required surgical intervention) or 10 days (for those who did not require surgical intervention) of IV antibiotics, patients with ongoing fever, leukocytosis, elevated C-reactive protein, or concurrent infections were excluded from the study. Patients were randomized to receive continued IV antibiotic treatment or switch to oral antibiotic treatment. The IV treatment group received a median of 19 additional days of therapy, compared with 17 days in the oral group. The primary composite outcome of death, unplanned cardiac surgery, embolic event, and relapse of bacteremia occurred in 12.1% in the IV therapy group and 9% in the oral therapy group (difference of 3.1%; 95% confidence interval, –3.4 to 9.6; P = .40), meeting the studies prespecified noninferiority criteria. Poor representation of women, obese patients, and patients who use IV drugs may limit the study’s generalizability. An accompanying editorial advocated for additional research before widespread change to current treatment recommendations are made.
Bottom line: For patients with left-sided infective endocarditis who have been stabilized on IV antibiotic treatment, transitioning to an oral antibiotic regimen may be a noninferior approach.
Citation: Iverson K et al. Partial oral versus intravenous antibiotic treatment of endocarditis. N Eng J Med. 2019 Jan 31;380(5):415-24.
Dr. Phillips is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Previously healthy patients hospitalized for sepsis show increased mortality
WASHINGTON – Although severe, community-acquired sepsis in previously healthy U.S. adults is relatively uncommon, it occurs often enough to strike about 40,000 people annually, and when previously healthy people are hospitalized for severe sepsis, their rate of in-hospital mortality was double the rate in people with one or more comorbidities who have severe, community-acquired sepsis, based on a review of almost 7 million Americans hospitalized for sepsis.
The findings “underscore the importance of improving public awareness of sepsis and emphasizing early sepsis recognition and treatment in all patients,” including those without comorbidities, Chanu Rhee, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. He hypothesized that the increased sepsis mortality among previously healthy patients may have stemmed from factors such as delayed sepsis recognition resulting in hospitalization at a more advanced stage and less aggressive management.
In addition, “the findings provide context for high-profile reports about sepsis death in previously healthy people,” said Dr. Rhee, an infectious diseases and critical care physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Dr. Rhee and associates found that, among patients hospitalized with what the researchers defined as “community-acquired” sepsis, 3% were judged previously healthy by having no identified major or minor comorbidity or pregnancy at the time of hospitalization, a percentage that – while small – still translates into roughly 40,000 such cases annually in the United States. That helps explain why every so often a headline appears about a famous person who died suddenly and unexpectedly from sepsis, he noted.
The study used data collected on hospitalized U.S. patients in the Cerner Health Facts, HCA Healthcare, and Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation databases, which included about 6.7 million people total including 337,983 identified as having community-acquired sepsis, defined as patients who met the criteria for adult sepsis advanced by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention within 2 days of their hospital admission. The researchers looked further into the hospital records of these patients and divided them into patients with one or more major comorbidities (96% of the cohort), patients who were pregnant or had a “minor” comorbidity such as a lipid disorder, benign neoplasm, or obesity (1% of the study group), or those with no chronic comorbidity (3%; the subgroup the researchers deemed previously healthy).
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for patients’ age, sex, race, infection site, and illness severity at the time of hospital admission the researchers found that the rate of in-hospital death among the previously healthy patients was exactly twice the rate of those who had at least one major chronic comorbidity, Dr. Rhee reported. Differences in the treatment received by the previously-healthy patients or in their medical status compared with patients with a major comorbidity suggested that the previously health patients were sicker. They had a higher rate of mechanical ventilation, 30%, compared with about 18% for those with a comorbidity; a higher rate of acute kidney injury, about 43% in those previously healthy and 28% in those with a comorbidity; and a higher percentage had an elevated lactate level, about 41% among the previously healthy patients and about 22% among those with a comorbidity.
SOURCE: Alrawashdeh M et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 23;6. Abstract 891.
WASHINGTON – Although severe, community-acquired sepsis in previously healthy U.S. adults is relatively uncommon, it occurs often enough to strike about 40,000 people annually, and when previously healthy people are hospitalized for severe sepsis, their rate of in-hospital mortality was double the rate in people with one or more comorbidities who have severe, community-acquired sepsis, based on a review of almost 7 million Americans hospitalized for sepsis.
The findings “underscore the importance of improving public awareness of sepsis and emphasizing early sepsis recognition and treatment in all patients,” including those without comorbidities, Chanu Rhee, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. He hypothesized that the increased sepsis mortality among previously healthy patients may have stemmed from factors such as delayed sepsis recognition resulting in hospitalization at a more advanced stage and less aggressive management.
In addition, “the findings provide context for high-profile reports about sepsis death in previously healthy people,” said Dr. Rhee, an infectious diseases and critical care physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Dr. Rhee and associates found that, among patients hospitalized with what the researchers defined as “community-acquired” sepsis, 3% were judged previously healthy by having no identified major or minor comorbidity or pregnancy at the time of hospitalization, a percentage that – while small – still translates into roughly 40,000 such cases annually in the United States. That helps explain why every so often a headline appears about a famous person who died suddenly and unexpectedly from sepsis, he noted.
The study used data collected on hospitalized U.S. patients in the Cerner Health Facts, HCA Healthcare, and Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation databases, which included about 6.7 million people total including 337,983 identified as having community-acquired sepsis, defined as patients who met the criteria for adult sepsis advanced by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention within 2 days of their hospital admission. The researchers looked further into the hospital records of these patients and divided them into patients with one or more major comorbidities (96% of the cohort), patients who were pregnant or had a “minor” comorbidity such as a lipid disorder, benign neoplasm, or obesity (1% of the study group), or those with no chronic comorbidity (3%; the subgroup the researchers deemed previously healthy).
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for patients’ age, sex, race, infection site, and illness severity at the time of hospital admission the researchers found that the rate of in-hospital death among the previously healthy patients was exactly twice the rate of those who had at least one major chronic comorbidity, Dr. Rhee reported. Differences in the treatment received by the previously-healthy patients or in their medical status compared with patients with a major comorbidity suggested that the previously health patients were sicker. They had a higher rate of mechanical ventilation, 30%, compared with about 18% for those with a comorbidity; a higher rate of acute kidney injury, about 43% in those previously healthy and 28% in those with a comorbidity; and a higher percentage had an elevated lactate level, about 41% among the previously healthy patients and about 22% among those with a comorbidity.
SOURCE: Alrawashdeh M et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 23;6. Abstract 891.
WASHINGTON – Although severe, community-acquired sepsis in previously healthy U.S. adults is relatively uncommon, it occurs often enough to strike about 40,000 people annually, and when previously healthy people are hospitalized for severe sepsis, their rate of in-hospital mortality was double the rate in people with one or more comorbidities who have severe, community-acquired sepsis, based on a review of almost 7 million Americans hospitalized for sepsis.
The findings “underscore the importance of improving public awareness of sepsis and emphasizing early sepsis recognition and treatment in all patients,” including those without comorbidities, Chanu Rhee, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. He hypothesized that the increased sepsis mortality among previously healthy patients may have stemmed from factors such as delayed sepsis recognition resulting in hospitalization at a more advanced stage and less aggressive management.
In addition, “the findings provide context for high-profile reports about sepsis death in previously healthy people,” said Dr. Rhee, an infectious diseases and critical care physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Dr. Rhee and associates found that, among patients hospitalized with what the researchers defined as “community-acquired” sepsis, 3% were judged previously healthy by having no identified major or minor comorbidity or pregnancy at the time of hospitalization, a percentage that – while small – still translates into roughly 40,000 such cases annually in the United States. That helps explain why every so often a headline appears about a famous person who died suddenly and unexpectedly from sepsis, he noted.
The study used data collected on hospitalized U.S. patients in the Cerner Health Facts, HCA Healthcare, and Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation databases, which included about 6.7 million people total including 337,983 identified as having community-acquired sepsis, defined as patients who met the criteria for adult sepsis advanced by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention within 2 days of their hospital admission. The researchers looked further into the hospital records of these patients and divided them into patients with one or more major comorbidities (96% of the cohort), patients who were pregnant or had a “minor” comorbidity such as a lipid disorder, benign neoplasm, or obesity (1% of the study group), or those with no chronic comorbidity (3%; the subgroup the researchers deemed previously healthy).
In a multivariate analysis that adjusted for patients’ age, sex, race, infection site, and illness severity at the time of hospital admission the researchers found that the rate of in-hospital death among the previously healthy patients was exactly twice the rate of those who had at least one major chronic comorbidity, Dr. Rhee reported. Differences in the treatment received by the previously-healthy patients or in their medical status compared with patients with a major comorbidity suggested that the previously health patients were sicker. They had a higher rate of mechanical ventilation, 30%, compared with about 18% for those with a comorbidity; a higher rate of acute kidney injury, about 43% in those previously healthy and 28% in those with a comorbidity; and a higher percentage had an elevated lactate level, about 41% among the previously healthy patients and about 22% among those with a comorbidity.
SOURCE: Alrawashdeh M et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 23;6. Abstract 891.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2019
New score predicts benefits of prolonged cardiac monitoring for TIA, stroke patients
Background: Identifying paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFib) as the etiology of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke has implications for treatment as well as secondary prevention. Currently, there is not a universal, practical way to help determine which patients would benefit from prolonged cardiac monitoring to establish the diagnosis of AFib.
Study design: Logistic regression analysis of three prospective multicenter trials examining TIA and stroke patients who received Holter-ECG monitoring.
Setting: Patients who presented with TIA or stroke in Central Europe.
Synopsis: Using data from 1,556 patients, the authors identified age and NIH stroke scale score as being predictive of which patients were at highest risk for AFib detection within 72 hours of Holter-ECG monitor initiation. The authors developed a formula, titled AS5F; this formula scores each year of age as 0.76 points and then an NIH stroke scale score of 5 or less as 9 points or greater than 5 as 21 points. The authors found that the high-risk group (defined as those with AS5F scores of 67.5 or higher) had a predicted risk of 5.2%-40.8%, with a number needed to screen of 3. Given that a majority of the European patients included in the study were white, generalizability to other populations is unclear.
Bottom line: AS5F score may be able to predict those TIA and stroke patients who are most likely to be diagnosed with AFib with 72-hour cardiac monitoring.
Citation: Uphaus T et al. Development and validation of a score to detect paroxysmal atrial fibrillation after stroke. Neurology. 2019 Jan 8. doi. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006727.
Dr. Phillips is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Background: Identifying paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFib) as the etiology of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke has implications for treatment as well as secondary prevention. Currently, there is not a universal, practical way to help determine which patients would benefit from prolonged cardiac monitoring to establish the diagnosis of AFib.
Study design: Logistic regression analysis of three prospective multicenter trials examining TIA and stroke patients who received Holter-ECG monitoring.
Setting: Patients who presented with TIA or stroke in Central Europe.
Synopsis: Using data from 1,556 patients, the authors identified age and NIH stroke scale score as being predictive of which patients were at highest risk for AFib detection within 72 hours of Holter-ECG monitor initiation. The authors developed a formula, titled AS5F; this formula scores each year of age as 0.76 points and then an NIH stroke scale score of 5 or less as 9 points or greater than 5 as 21 points. The authors found that the high-risk group (defined as those with AS5F scores of 67.5 or higher) had a predicted risk of 5.2%-40.8%, with a number needed to screen of 3. Given that a majority of the European patients included in the study were white, generalizability to other populations is unclear.
Bottom line: AS5F score may be able to predict those TIA and stroke patients who are most likely to be diagnosed with AFib with 72-hour cardiac monitoring.
Citation: Uphaus T et al. Development and validation of a score to detect paroxysmal atrial fibrillation after stroke. Neurology. 2019 Jan 8. doi. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006727.
Dr. Phillips is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Background: Identifying paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFib) as the etiology of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke has implications for treatment as well as secondary prevention. Currently, there is not a universal, practical way to help determine which patients would benefit from prolonged cardiac monitoring to establish the diagnosis of AFib.
Study design: Logistic regression analysis of three prospective multicenter trials examining TIA and stroke patients who received Holter-ECG monitoring.
Setting: Patients who presented with TIA or stroke in Central Europe.
Synopsis: Using data from 1,556 patients, the authors identified age and NIH stroke scale score as being predictive of which patients were at highest risk for AFib detection within 72 hours of Holter-ECG monitor initiation. The authors developed a formula, titled AS5F; this formula scores each year of age as 0.76 points and then an NIH stroke scale score of 5 or less as 9 points or greater than 5 as 21 points. The authors found that the high-risk group (defined as those with AS5F scores of 67.5 or higher) had a predicted risk of 5.2%-40.8%, with a number needed to screen of 3. Given that a majority of the European patients included in the study were white, generalizability to other populations is unclear.
Bottom line: AS5F score may be able to predict those TIA and stroke patients who are most likely to be diagnosed with AFib with 72-hour cardiac monitoring.
Citation: Uphaus T et al. Development and validation of a score to detect paroxysmal atrial fibrillation after stroke. Neurology. 2019 Jan 8. doi. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006727.
Dr. Phillips is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and instructor in medicine at Harvard Medical School.
Fewer bloodstream infections with FMT for C. difficile
Treating Clostridioides difficile infection with fecal microbiota transplantation is associated with a lower risk of bloodstream infection and recurrence than treatment with antibiotics, new research has found.
A paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine presents outcomes of a prospective cohort study in 290 inpatients with recurrent C. difficile infection, 109 of whom were treated with fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT); the remainder were treated with antibiotics including metronidazole, vancomycin, and fidaxomicin.
While the FMT group had a higher mean number of previous C. difficile infections than the antibiotics group (2.82 vs. 1.23, respectively), a sustained cure was achieved in 97% of the FMT group, compared with 38% in the antibiotics group.
Blood cultures were done if patients developed a temperature above 30° C or showed symptoms that might be attributable to sepsis. Bloodstream infections were diagnosed in 5% (5 patients) of those treated with FMT, and 22% (40 patients) in the antibiotics group.
The patients in the FMT group with bloodstream infections all had bacterial infections – one of which was polymicrobial – and there were no cases of fungal bloodstream infections. In the antibiotics group, 28 patients (15%) had bacterial bloodstream infections – 11 of which were polymicrobial – and 12 (7%) had fungal bloodstream infections.
Bloodstream infections were particularly evident among the 11 patients whose C. difficile infection was treated with fidaxomicin, 4 of whom developed a bloodstream infection.
Overall, 27% of patients died during the 90-day follow-up, with 7% dying because of bloodstream infections, all of whom were in the antibiotic-treated cohort. Three patients in the FMT group died because of overwhelming C. difficile infection, compared with 12 in the antibiotic cohort.
Nearly three-quarters of deaths occurred within 30 days of the end of treatment; 5 of these deaths were in the FMT group, and 53 were in the antibiotics group.
“These findings suggest that the longer 90-day [overall survival] of patients in the FMT group is attributable to cure of [C. difficile infection] leading to an improvement in clinical condition,” wrote Gianluca Ianiro, MD, from the Catholic University of the Sacred Heart in Rome, and coauthors.
The 90-day overall survival rate was 92% in the FMT group and 61% in the antibiotic group. Patients treated with FMT also showed significantly shorter mean duration of hospital stay at 13.3 days, compared with 29.7 days in patients treated with antibiotics.
The authors noted the results should be interpreted with caution because of baseline differences between the two groups that were not entirely accounted for by using propensity matching. However, even in the propensity-matched cohort of 57 patients from each group, there was still a significantly higher overall survival at 90 days among patients treated with FMT.
One author declared grants from the pharmaceutical sector outside the submitted work. No funding or other conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Ianiro G et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Nov 4. doi: 10.7326/M18-3635.
Treating Clostridioides difficile infection with fecal microbiota transplantation is associated with a lower risk of bloodstream infection and recurrence than treatment with antibiotics, new research has found.
A paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine presents outcomes of a prospective cohort study in 290 inpatients with recurrent C. difficile infection, 109 of whom were treated with fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT); the remainder were treated with antibiotics including metronidazole, vancomycin, and fidaxomicin.
While the FMT group had a higher mean number of previous C. difficile infections than the antibiotics group (2.82 vs. 1.23, respectively), a sustained cure was achieved in 97% of the FMT group, compared with 38% in the antibiotics group.
Blood cultures were done if patients developed a temperature above 30° C or showed symptoms that might be attributable to sepsis. Bloodstream infections were diagnosed in 5% (5 patients) of those treated with FMT, and 22% (40 patients) in the antibiotics group.
The patients in the FMT group with bloodstream infections all had bacterial infections – one of which was polymicrobial – and there were no cases of fungal bloodstream infections. In the antibiotics group, 28 patients (15%) had bacterial bloodstream infections – 11 of which were polymicrobial – and 12 (7%) had fungal bloodstream infections.
Bloodstream infections were particularly evident among the 11 patients whose C. difficile infection was treated with fidaxomicin, 4 of whom developed a bloodstream infection.
Overall, 27% of patients died during the 90-day follow-up, with 7% dying because of bloodstream infections, all of whom were in the antibiotic-treated cohort. Three patients in the FMT group died because of overwhelming C. difficile infection, compared with 12 in the antibiotic cohort.
Nearly three-quarters of deaths occurred within 30 days of the end of treatment; 5 of these deaths were in the FMT group, and 53 were in the antibiotics group.
“These findings suggest that the longer 90-day [overall survival] of patients in the FMT group is attributable to cure of [C. difficile infection] leading to an improvement in clinical condition,” wrote Gianluca Ianiro, MD, from the Catholic University of the Sacred Heart in Rome, and coauthors.
The 90-day overall survival rate was 92% in the FMT group and 61% in the antibiotic group. Patients treated with FMT also showed significantly shorter mean duration of hospital stay at 13.3 days, compared with 29.7 days in patients treated with antibiotics.
The authors noted the results should be interpreted with caution because of baseline differences between the two groups that were not entirely accounted for by using propensity matching. However, even in the propensity-matched cohort of 57 patients from each group, there was still a significantly higher overall survival at 90 days among patients treated with FMT.
One author declared grants from the pharmaceutical sector outside the submitted work. No funding or other conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Ianiro G et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Nov 4. doi: 10.7326/M18-3635.
Treating Clostridioides difficile infection with fecal microbiota transplantation is associated with a lower risk of bloodstream infection and recurrence than treatment with antibiotics, new research has found.
A paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine presents outcomes of a prospective cohort study in 290 inpatients with recurrent C. difficile infection, 109 of whom were treated with fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT); the remainder were treated with antibiotics including metronidazole, vancomycin, and fidaxomicin.
While the FMT group had a higher mean number of previous C. difficile infections than the antibiotics group (2.82 vs. 1.23, respectively), a sustained cure was achieved in 97% of the FMT group, compared with 38% in the antibiotics group.
Blood cultures were done if patients developed a temperature above 30° C or showed symptoms that might be attributable to sepsis. Bloodstream infections were diagnosed in 5% (5 patients) of those treated with FMT, and 22% (40 patients) in the antibiotics group.
The patients in the FMT group with bloodstream infections all had bacterial infections – one of which was polymicrobial – and there were no cases of fungal bloodstream infections. In the antibiotics group, 28 patients (15%) had bacterial bloodstream infections – 11 of which were polymicrobial – and 12 (7%) had fungal bloodstream infections.
Bloodstream infections were particularly evident among the 11 patients whose C. difficile infection was treated with fidaxomicin, 4 of whom developed a bloodstream infection.
Overall, 27% of patients died during the 90-day follow-up, with 7% dying because of bloodstream infections, all of whom were in the antibiotic-treated cohort. Three patients in the FMT group died because of overwhelming C. difficile infection, compared with 12 in the antibiotic cohort.
Nearly three-quarters of deaths occurred within 30 days of the end of treatment; 5 of these deaths were in the FMT group, and 53 were in the antibiotics group.
“These findings suggest that the longer 90-day [overall survival] of patients in the FMT group is attributable to cure of [C. difficile infection] leading to an improvement in clinical condition,” wrote Gianluca Ianiro, MD, from the Catholic University of the Sacred Heart in Rome, and coauthors.
The 90-day overall survival rate was 92% in the FMT group and 61% in the antibiotic group. Patients treated with FMT also showed significantly shorter mean duration of hospital stay at 13.3 days, compared with 29.7 days in patients treated with antibiotics.
The authors noted the results should be interpreted with caution because of baseline differences between the two groups that were not entirely accounted for by using propensity matching. However, even in the propensity-matched cohort of 57 patients from each group, there was still a significantly higher overall survival at 90 days among patients treated with FMT.
One author declared grants from the pharmaceutical sector outside the submitted work. No funding or other conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Ianiro G et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Nov 4. doi: 10.7326/M18-3635.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Patient-reported complications regarding PICC lines after inpatient discharge
Background: Despite the rise in utilization of PICC lines, few studies have addressed complications experienced by patients following PICC placement, especially subsequent to discharge from the inpatient setting.
Study design: Prospective longitudinal study.
Setting: Medical inpatient wards at four U.S. hospitals in Michigan and Texas.
Synopsis: Standardized questionnaires were completed by 438 patients who underwent PICC line placement during inpatient hospitalization within 3 days of placement and at 14, 30, and 70 days. The authors found that 61.4% of patients reported at least one possible PICC-related complication or complaint. A total of 17.6% reported signs and symptoms associated with a possible bloodstream infection; however, a central line–associated bloodstream infection was documented in only 1.6% of patients in the medical record. Furthermore, 30.6% of patients reported possible symptoms associated with deep venous thrombosis (DVT), which was documented in the medical record in 7.1% of patients. These data highlight that the frequency of PICC-related complications may be underestimated when relying solely on the medical record, especially when patients receive follow-up care at different facilities. Functionally, 26% of patients reported restrictions in activities of daily living and 19.2% reported difficulty with flushing and operating the PICC.
Bottom line: More than 60% of patients with PICC lines report signs or symptoms of a PICC-related complication or an adverse impact on physical or social function.
Citation: Krein SL et al. Patient-reported complications related to peripherally inserted central catheters: A multicenter prospective cohort study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2019 Jan 25. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2018-008726.
Dr. Cooke is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Background: Despite the rise in utilization of PICC lines, few studies have addressed complications experienced by patients following PICC placement, especially subsequent to discharge from the inpatient setting.
Study design: Prospective longitudinal study.
Setting: Medical inpatient wards at four U.S. hospitals in Michigan and Texas.
Synopsis: Standardized questionnaires were completed by 438 patients who underwent PICC line placement during inpatient hospitalization within 3 days of placement and at 14, 30, and 70 days. The authors found that 61.4% of patients reported at least one possible PICC-related complication or complaint. A total of 17.6% reported signs and symptoms associated with a possible bloodstream infection; however, a central line–associated bloodstream infection was documented in only 1.6% of patients in the medical record. Furthermore, 30.6% of patients reported possible symptoms associated with deep venous thrombosis (DVT), which was documented in the medical record in 7.1% of patients. These data highlight that the frequency of PICC-related complications may be underestimated when relying solely on the medical record, especially when patients receive follow-up care at different facilities. Functionally, 26% of patients reported restrictions in activities of daily living and 19.2% reported difficulty with flushing and operating the PICC.
Bottom line: More than 60% of patients with PICC lines report signs or symptoms of a PICC-related complication or an adverse impact on physical or social function.
Citation: Krein SL et al. Patient-reported complications related to peripherally inserted central catheters: A multicenter prospective cohort study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2019 Jan 25. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2018-008726.
Dr. Cooke is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Background: Despite the rise in utilization of PICC lines, few studies have addressed complications experienced by patients following PICC placement, especially subsequent to discharge from the inpatient setting.
Study design: Prospective longitudinal study.
Setting: Medical inpatient wards at four U.S. hospitals in Michigan and Texas.
Synopsis: Standardized questionnaires were completed by 438 patients who underwent PICC line placement during inpatient hospitalization within 3 days of placement and at 14, 30, and 70 days. The authors found that 61.4% of patients reported at least one possible PICC-related complication or complaint. A total of 17.6% reported signs and symptoms associated with a possible bloodstream infection; however, a central line–associated bloodstream infection was documented in only 1.6% of patients in the medical record. Furthermore, 30.6% of patients reported possible symptoms associated with deep venous thrombosis (DVT), which was documented in the medical record in 7.1% of patients. These data highlight that the frequency of PICC-related complications may be underestimated when relying solely on the medical record, especially when patients receive follow-up care at different facilities. Functionally, 26% of patients reported restrictions in activities of daily living and 19.2% reported difficulty with flushing and operating the PICC.
Bottom line: More than 60% of patients with PICC lines report signs or symptoms of a PICC-related complication or an adverse impact on physical or social function.
Citation: Krein SL et al. Patient-reported complications related to peripherally inserted central catheters: A multicenter prospective cohort study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2019 Jan 25. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2018-008726.
Dr. Cooke is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.