User login
MDedge conference coverage features onsite reporting of the latest study results and expert perspectives from leading researchers.
Study identifies skin biomarkers that predict newborn eczema risk
It might be possible to develop a simple test to identify newborn children who are at risk of later developing atopic dermatitis (AD), according to findings from a Danish prospective birth cohort study.
but also for having more severe disease.
“We are able to identify predictive immune biomarkers of atopic dermatitis using a noninvasive method that was not associated with any pain,” one of the study’s investigators, Anne-Sofie Halling, MD, said at a press briefing at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“Importantly, we were able to predict atopic dermatitis occurring months after [sample] collection,” said Dr. Halling, who works at Bispebjerg Hospital and is a PhD student at the University of Copenhagen.
These findings could hopefully be used to help identify children “so that preventive strategies can target these children ... and decrease the incidence of this common disease,” she added.
AD is caused “by a complex interplay between skin barrier dysfunction and immune dysregulation,” Dr. Halling said, and it is “the first step in the so-called atopic march, where children also develop food allergy, asthma, and rhinitis.” Almost all cases of AD begin during the first years of life. Approximately 15%-20% of children can be affected, she noted, emphasizing the high burden of the disease and pointing out that strategies are shifting toward trying to prevent the disease in those at risk.
Copenhagen BABY cohort
This is where the BABY study comes in, Dr. Halling said. The study enrolled 450 children at birth and followed them until age 2 years. Gene mutation testing was performed at enrollment. All children underwent skin examination, and skin samples were taken using tape strips. Tape strips were applied to the back of the hand of children born at term and between the shoulder blades on the back of children who were premature.
Skin examinations were repeated, and skin samples were obtained again at age 2 months. They were taken again only if there were any signs of AD. For those diagnosed with AD, disease severity was assessed using the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) by the treating physician. Children were excluded if they had AD at the time the tape strip testing was due to be performed.
Comparing term and preterm children
Dr. Halling noted that analyses were performed separately for the 300 children born at term and for the 150 who were preterm.
The prevalence of AD was higher among children born at term than among the preterm children (34.6% vs. 21.2%), and the median time to onset was shorter (6 months vs. 8 months). There were also differences in the EASI scores among those who developed AD; median scores were higher in the children born at term than in the preterm children (4.1 vs. 1.6).
More children born at term than preterm children had moderate to severe AD (23.3% vs. 8%), Dr. Halling reported.
TARC, IL-8, and IL-18 predictive of AD
Multiple immune biomarkers were tested, including various cytokines and filaggrin degradation products. On examination of skin samples collected at birth, no particular biomarkers were found at higher levels among children who developed AD in comparison with those who did not develop AD.
With regard to biomarkers examined in skin samples at 2 months of age, however, the results were different, Dr. Halling said. One particular cytokine, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC), was seen to double the risk of AD in the first 2 years of a child’s life.
This doubled risk was seen not only among the children born at term but also among those born preterm, although the data were only significant with regard to the children born at term.
The unadjusted hazard ratios and adjusted HRs (adjusted for parental atopy and filaggrin gene mutations) in term children were 2.11 (95% confidence interval, 1.36-3.26; P = .0008) and 1.85 (95% CI, 1.18-2.89; P = .007), respectively.
For preterm children, the HRs were 2.23 (95% CI, 0.85-5.86; P = .1) and 2.60 (95% CI, 0.98-6.85; P =.05), respectively.
These findings were in line with findings of other studies, Dr. Halling said. “It is well recognized that TARC is currently the best biomarker in patients with established atopic dermatitis.” Moreover, she reported that TARC was associated with a cumulative increase in the risk for AD and that levels were found to be higher in children in whom onset occurred at a later age than among those diagnosed before 6 months of age.
“This is important, as these findings shows that TARC levels predict atopic dermatitis that occurred many months later,” Dr. Halling said.
And, in term-born children at least, TARC upped the chances that the severity of AD would be greater than had it not been present (adjusted HR, 4.65; 95% CI, 1.91-11.31; P = .0007).
Increased levels of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-18 at 2 months of age were also found to be predictive of having moderate to severe AD. The risk was more than double in comparison with those in whom levels were not increased, again only in term-born children.
‘Stimulating and interesting findings’
These data are “very stimulating and interesting,” Dedee Murrell, MD, professor and head of the department of dermatology at St. George Hospital, University of New South Wales, Sydney, observed at the press briefing.
“You found this significant association mainly in the newborn children born at term, and the association in the preterm babies wasn’t as high. Is that anything to do with how they were taken care of in the hospital?” Dr. Murrell asked.
“That’s a really good question,” Dr. Halling said. “Maybe they need to be exposed for a month or two before we are actually able to identify which children will develop atopic dermatitis.”
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation. Dr. Halling has acted as a consultant for Coloplast and as a speaker for Leo Pharma. Dr. Murrell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It might be possible to develop a simple test to identify newborn children who are at risk of later developing atopic dermatitis (AD), according to findings from a Danish prospective birth cohort study.
but also for having more severe disease.
“We are able to identify predictive immune biomarkers of atopic dermatitis using a noninvasive method that was not associated with any pain,” one of the study’s investigators, Anne-Sofie Halling, MD, said at a press briefing at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“Importantly, we were able to predict atopic dermatitis occurring months after [sample] collection,” said Dr. Halling, who works at Bispebjerg Hospital and is a PhD student at the University of Copenhagen.
These findings could hopefully be used to help identify children “so that preventive strategies can target these children ... and decrease the incidence of this common disease,” she added.
AD is caused “by a complex interplay between skin barrier dysfunction and immune dysregulation,” Dr. Halling said, and it is “the first step in the so-called atopic march, where children also develop food allergy, asthma, and rhinitis.” Almost all cases of AD begin during the first years of life. Approximately 15%-20% of children can be affected, she noted, emphasizing the high burden of the disease and pointing out that strategies are shifting toward trying to prevent the disease in those at risk.
Copenhagen BABY cohort
This is where the BABY study comes in, Dr. Halling said. The study enrolled 450 children at birth and followed them until age 2 years. Gene mutation testing was performed at enrollment. All children underwent skin examination, and skin samples were taken using tape strips. Tape strips were applied to the back of the hand of children born at term and between the shoulder blades on the back of children who were premature.
Skin examinations were repeated, and skin samples were obtained again at age 2 months. They were taken again only if there were any signs of AD. For those diagnosed with AD, disease severity was assessed using the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) by the treating physician. Children were excluded if they had AD at the time the tape strip testing was due to be performed.
Comparing term and preterm children
Dr. Halling noted that analyses were performed separately for the 300 children born at term and for the 150 who were preterm.
The prevalence of AD was higher among children born at term than among the preterm children (34.6% vs. 21.2%), and the median time to onset was shorter (6 months vs. 8 months). There were also differences in the EASI scores among those who developed AD; median scores were higher in the children born at term than in the preterm children (4.1 vs. 1.6).
More children born at term than preterm children had moderate to severe AD (23.3% vs. 8%), Dr. Halling reported.
TARC, IL-8, and IL-18 predictive of AD
Multiple immune biomarkers were tested, including various cytokines and filaggrin degradation products. On examination of skin samples collected at birth, no particular biomarkers were found at higher levels among children who developed AD in comparison with those who did not develop AD.
With regard to biomarkers examined in skin samples at 2 months of age, however, the results were different, Dr. Halling said. One particular cytokine, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC), was seen to double the risk of AD in the first 2 years of a child’s life.
This doubled risk was seen not only among the children born at term but also among those born preterm, although the data were only significant with regard to the children born at term.
The unadjusted hazard ratios and adjusted HRs (adjusted for parental atopy and filaggrin gene mutations) in term children were 2.11 (95% confidence interval, 1.36-3.26; P = .0008) and 1.85 (95% CI, 1.18-2.89; P = .007), respectively.
For preterm children, the HRs were 2.23 (95% CI, 0.85-5.86; P = .1) and 2.60 (95% CI, 0.98-6.85; P =.05), respectively.
These findings were in line with findings of other studies, Dr. Halling said. “It is well recognized that TARC is currently the best biomarker in patients with established atopic dermatitis.” Moreover, she reported that TARC was associated with a cumulative increase in the risk for AD and that levels were found to be higher in children in whom onset occurred at a later age than among those diagnosed before 6 months of age.
“This is important, as these findings shows that TARC levels predict atopic dermatitis that occurred many months later,” Dr. Halling said.
And, in term-born children at least, TARC upped the chances that the severity of AD would be greater than had it not been present (adjusted HR, 4.65; 95% CI, 1.91-11.31; P = .0007).
Increased levels of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-18 at 2 months of age were also found to be predictive of having moderate to severe AD. The risk was more than double in comparison with those in whom levels were not increased, again only in term-born children.
‘Stimulating and interesting findings’
These data are “very stimulating and interesting,” Dedee Murrell, MD, professor and head of the department of dermatology at St. George Hospital, University of New South Wales, Sydney, observed at the press briefing.
“You found this significant association mainly in the newborn children born at term, and the association in the preterm babies wasn’t as high. Is that anything to do with how they were taken care of in the hospital?” Dr. Murrell asked.
“That’s a really good question,” Dr. Halling said. “Maybe they need to be exposed for a month or two before we are actually able to identify which children will develop atopic dermatitis.”
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation. Dr. Halling has acted as a consultant for Coloplast and as a speaker for Leo Pharma. Dr. Murrell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It might be possible to develop a simple test to identify newborn children who are at risk of later developing atopic dermatitis (AD), according to findings from a Danish prospective birth cohort study.
but also for having more severe disease.
“We are able to identify predictive immune biomarkers of atopic dermatitis using a noninvasive method that was not associated with any pain,” one of the study’s investigators, Anne-Sofie Halling, MD, said at a press briefing at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“Importantly, we were able to predict atopic dermatitis occurring months after [sample] collection,” said Dr. Halling, who works at Bispebjerg Hospital and is a PhD student at the University of Copenhagen.
These findings could hopefully be used to help identify children “so that preventive strategies can target these children ... and decrease the incidence of this common disease,” she added.
AD is caused “by a complex interplay between skin barrier dysfunction and immune dysregulation,” Dr. Halling said, and it is “the first step in the so-called atopic march, where children also develop food allergy, asthma, and rhinitis.” Almost all cases of AD begin during the first years of life. Approximately 15%-20% of children can be affected, she noted, emphasizing the high burden of the disease and pointing out that strategies are shifting toward trying to prevent the disease in those at risk.
Copenhagen BABY cohort
This is where the BABY study comes in, Dr. Halling said. The study enrolled 450 children at birth and followed them until age 2 years. Gene mutation testing was performed at enrollment. All children underwent skin examination, and skin samples were taken using tape strips. Tape strips were applied to the back of the hand of children born at term and between the shoulder blades on the back of children who were premature.
Skin examinations were repeated, and skin samples were obtained again at age 2 months. They were taken again only if there were any signs of AD. For those diagnosed with AD, disease severity was assessed using the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) by the treating physician. Children were excluded if they had AD at the time the tape strip testing was due to be performed.
Comparing term and preterm children
Dr. Halling noted that analyses were performed separately for the 300 children born at term and for the 150 who were preterm.
The prevalence of AD was higher among children born at term than among the preterm children (34.6% vs. 21.2%), and the median time to onset was shorter (6 months vs. 8 months). There were also differences in the EASI scores among those who developed AD; median scores were higher in the children born at term than in the preterm children (4.1 vs. 1.6).
More children born at term than preterm children had moderate to severe AD (23.3% vs. 8%), Dr. Halling reported.
TARC, IL-8, and IL-18 predictive of AD
Multiple immune biomarkers were tested, including various cytokines and filaggrin degradation products. On examination of skin samples collected at birth, no particular biomarkers were found at higher levels among children who developed AD in comparison with those who did not develop AD.
With regard to biomarkers examined in skin samples at 2 months of age, however, the results were different, Dr. Halling said. One particular cytokine, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC), was seen to double the risk of AD in the first 2 years of a child’s life.
This doubled risk was seen not only among the children born at term but also among those born preterm, although the data were only significant with regard to the children born at term.
The unadjusted hazard ratios and adjusted HRs (adjusted for parental atopy and filaggrin gene mutations) in term children were 2.11 (95% confidence interval, 1.36-3.26; P = .0008) and 1.85 (95% CI, 1.18-2.89; P = .007), respectively.
For preterm children, the HRs were 2.23 (95% CI, 0.85-5.86; P = .1) and 2.60 (95% CI, 0.98-6.85; P =.05), respectively.
These findings were in line with findings of other studies, Dr. Halling said. “It is well recognized that TARC is currently the best biomarker in patients with established atopic dermatitis.” Moreover, she reported that TARC was associated with a cumulative increase in the risk for AD and that levels were found to be higher in children in whom onset occurred at a later age than among those diagnosed before 6 months of age.
“This is important, as these findings shows that TARC levels predict atopic dermatitis that occurred many months later,” Dr. Halling said.
And, in term-born children at least, TARC upped the chances that the severity of AD would be greater than had it not been present (adjusted HR, 4.65; 95% CI, 1.91-11.31; P = .0007).
Increased levels of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-18 at 2 months of age were also found to be predictive of having moderate to severe AD. The risk was more than double in comparison with those in whom levels were not increased, again only in term-born children.
‘Stimulating and interesting findings’
These data are “very stimulating and interesting,” Dedee Murrell, MD, professor and head of the department of dermatology at St. George Hospital, University of New South Wales, Sydney, observed at the press briefing.
“You found this significant association mainly in the newborn children born at term, and the association in the preterm babies wasn’t as high. Is that anything to do with how they were taken care of in the hospital?” Dr. Murrell asked.
“That’s a really good question,” Dr. Halling said. “Maybe they need to be exposed for a month or two before we are actually able to identify which children will develop atopic dermatitis.”
The study was funded by the Lundbeck Foundation. Dr. Halling has acted as a consultant for Coloplast and as a speaker for Leo Pharma. Dr. Murrell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
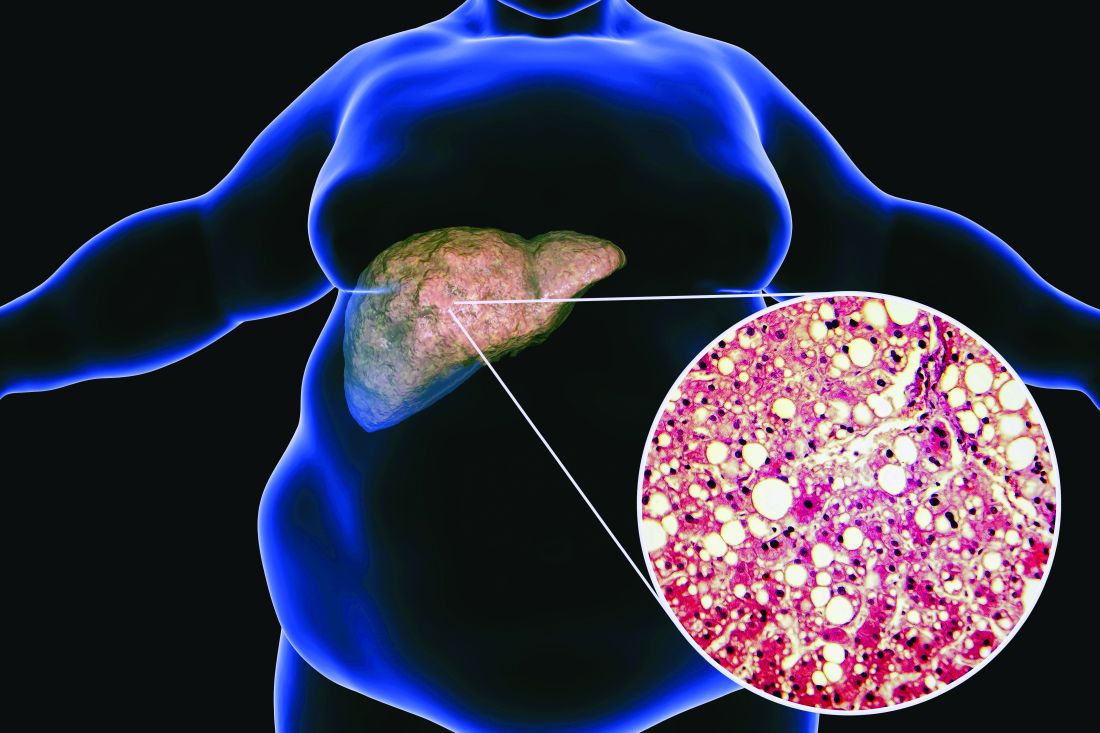
Ezetimibe-statin combo lowers liver fat in open-label trial
Ezetimibe given in combination with rosuvastatin has a beneficial effect on liver fat in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according results of a randomized, active-controlled trial.
The findings, which come from the investigator-initiated ESSENTIAL trial, are likely to add to the debate over whether or not the lipid-lowering combination could be of benefit beyond its effects in the blood.
“We used magnetic resonance imaging-derived proton density fat fraction [MRI-PDFF], which is highly reliable method of assessing hepatic steatosis,” Youngjoon Kim, PhD, one of the study investigators, said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in Barcelona.
“It enables accurate, repeatable and reproducible quantitative assessment of liver fat over the entire liver,” observed Dr. Kim, who works at Severance Hospital, part of Yonsei University in Seoul.
He reported that there was a significant 5.8% decrease in liver fat following 24 weeks’ treatment with ezetimibe and rosuvastatin comparing baseline with end of treatment MRI-PDFF values; a drop that was significant (18.2% vs. 12.3%, P < .001).
Rosuvastatin monotherapy also reduced liver fat from 15.0% at baseline to 12.4% after 24 weeks; this drop of 2.6% was also significant (P = .003).
This gave an absolute mean difference between the two study arms of 3.2% (P = .02).
Rationale for the ESSENTIAL study
Dr. Kim observed during his presentation that NAFLD is burgeoning problem around the world. Ezetimibe plus rosuvastatin was a combination treatment already used widely in clinical practice, and there had been some suggestion that ezetimibe might have an effect on liver fat.
“Although the effect of ezetimibe on hepatic steatosis is still controversial, ezetimibe has been reported to reduce visceral fat and improve insulin resistance in several studies” Dr. Kim said.
“Recently, our group reported that the use of ezetimibe affects autophagy of hepatocytes and the NLRP3 [NOD-like receptors containing pyrin domain 3] inflammasome,” he said.
Moreover, he added, “ezetimibe improved NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] in an animal model. However, the effects of ezetimibe have not been clearly shown in a human study.”
Dr. Kim also acknowledged a prior randomized control trial that had looked at the role of ezetimibe in 50 patients with NASH, but had not shown a benefit for the drug over placebo in terms of liver fat reduction.
Addressing the Hawthorne effect
“The size of the effect by that might actually be more modest due to the Hawthorne effect,” said session chair Onno Holleboom, MD, PhD, of Amsterdam UMC in the Netherlands.
“What we observe in the large clinical trials is an enormous Hawthorne effect – participating in a NAFLD trial makes people live healthier because they have health checks,” he said.
“That’s a major problem for showing efficacy for the intervention arm,” he added, but of course the open design meant that the trial only had intervention arms; “there was no placebo arm.”
A randomized, active-controlled, clinician-initiated trial
The main objective of the ESSENTIAL trial was therefore to take another look at the potential effect of ezetimibe on hepatic steatosis and doing so in the setting of statin therapy.
In all, 70 patients with NAFLD that had been confirmed via ultrasound were recruited into the prospective, single center, phase 4 trial. Participants were randomized 1:1 to received either ezetimibe 10 mg plus rosuvastatin 5 mg daily or rosuvastatin 5 mg for up to 24 weeks.
Change in liver fat was measured via MRI-PDFF, taking the average values in each of nine liver segments. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) was also used to measure liver fibrosis, although results did not show any differences either from baseline to end of treatment values in either group or when the two treatment groups were compared.
Dr. Kim reported that both treatment with the ezetimibe-rosuvastatin combination and rosuvastatin monotherapy reduced parameters that might be associated with a negative outcome in NAFLD, such as body mass index and waist circumference, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol. There was also a reduction in C-reactive protein levels in the blood, and interleulin-18. There was no change in liver enzymes.
Several subgroup analyses were performed indicating that “individuals with higher BMI, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and severe liver fibrosis were likely to be good responders to ezetimibe treatment,” Dr. Kim said.
“These data indicate that ezetimibe plus rosuvastatin is a safe and effective therapeutic option to treat patients with NAFLD and dyslipidemia,” he concluded.
The results of the ESSENTIAL study have been published in BMC Medicine.
The study was funded by the Yuhan Corporation. Dr. Kim had no conflicts of interest to report. Dr. Holleboom was not involved in the study and had no conflicts of interest.
Ezetimibe given in combination with rosuvastatin has a beneficial effect on liver fat in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according results of a randomized, active-controlled trial.
The findings, which come from the investigator-initiated ESSENTIAL trial, are likely to add to the debate over whether or not the lipid-lowering combination could be of benefit beyond its effects in the blood.
“We used magnetic resonance imaging-derived proton density fat fraction [MRI-PDFF], which is highly reliable method of assessing hepatic steatosis,” Youngjoon Kim, PhD, one of the study investigators, said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in Barcelona.
“It enables accurate, repeatable and reproducible quantitative assessment of liver fat over the entire liver,” observed Dr. Kim, who works at Severance Hospital, part of Yonsei University in Seoul.
He reported that there was a significant 5.8% decrease in liver fat following 24 weeks’ treatment with ezetimibe and rosuvastatin comparing baseline with end of treatment MRI-PDFF values; a drop that was significant (18.2% vs. 12.3%, P < .001).
Rosuvastatin monotherapy also reduced liver fat from 15.0% at baseline to 12.4% after 24 weeks; this drop of 2.6% was also significant (P = .003).
This gave an absolute mean difference between the two study arms of 3.2% (P = .02).
Rationale for the ESSENTIAL study
Dr. Kim observed during his presentation that NAFLD is burgeoning problem around the world. Ezetimibe plus rosuvastatin was a combination treatment already used widely in clinical practice, and there had been some suggestion that ezetimibe might have an effect on liver fat.
“Although the effect of ezetimibe on hepatic steatosis is still controversial, ezetimibe has been reported to reduce visceral fat and improve insulin resistance in several studies” Dr. Kim said.
“Recently, our group reported that the use of ezetimibe affects autophagy of hepatocytes and the NLRP3 [NOD-like receptors containing pyrin domain 3] inflammasome,” he said.
Moreover, he added, “ezetimibe improved NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] in an animal model. However, the effects of ezetimibe have not been clearly shown in a human study.”
Dr. Kim also acknowledged a prior randomized control trial that had looked at the role of ezetimibe in 50 patients with NASH, but had not shown a benefit for the drug over placebo in terms of liver fat reduction.
Addressing the Hawthorne effect
“The size of the effect by that might actually be more modest due to the Hawthorne effect,” said session chair Onno Holleboom, MD, PhD, of Amsterdam UMC in the Netherlands.
“What we observe in the large clinical trials is an enormous Hawthorne effect – participating in a NAFLD trial makes people live healthier because they have health checks,” he said.
“That’s a major problem for showing efficacy for the intervention arm,” he added, but of course the open design meant that the trial only had intervention arms; “there was no placebo arm.”
A randomized, active-controlled, clinician-initiated trial
The main objective of the ESSENTIAL trial was therefore to take another look at the potential effect of ezetimibe on hepatic steatosis and doing so in the setting of statin therapy.
In all, 70 patients with NAFLD that had been confirmed via ultrasound were recruited into the prospective, single center, phase 4 trial. Participants were randomized 1:1 to received either ezetimibe 10 mg plus rosuvastatin 5 mg daily or rosuvastatin 5 mg for up to 24 weeks.
Change in liver fat was measured via MRI-PDFF, taking the average values in each of nine liver segments. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) was also used to measure liver fibrosis, although results did not show any differences either from baseline to end of treatment values in either group or when the two treatment groups were compared.
Dr. Kim reported that both treatment with the ezetimibe-rosuvastatin combination and rosuvastatin monotherapy reduced parameters that might be associated with a negative outcome in NAFLD, such as body mass index and waist circumference, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol. There was also a reduction in C-reactive protein levels in the blood, and interleulin-18. There was no change in liver enzymes.
Several subgroup analyses were performed indicating that “individuals with higher BMI, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and severe liver fibrosis were likely to be good responders to ezetimibe treatment,” Dr. Kim said.
“These data indicate that ezetimibe plus rosuvastatin is a safe and effective therapeutic option to treat patients with NAFLD and dyslipidemia,” he concluded.
The results of the ESSENTIAL study have been published in BMC Medicine.
The study was funded by the Yuhan Corporation. Dr. Kim had no conflicts of interest to report. Dr. Holleboom was not involved in the study and had no conflicts of interest.
Ezetimibe given in combination with rosuvastatin has a beneficial effect on liver fat in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according results of a randomized, active-controlled trial.
The findings, which come from the investigator-initiated ESSENTIAL trial, are likely to add to the debate over whether or not the lipid-lowering combination could be of benefit beyond its effects in the blood.
“We used magnetic resonance imaging-derived proton density fat fraction [MRI-PDFF], which is highly reliable method of assessing hepatic steatosis,” Youngjoon Kim, PhD, one of the study investigators, said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in Barcelona.
“It enables accurate, repeatable and reproducible quantitative assessment of liver fat over the entire liver,” observed Dr. Kim, who works at Severance Hospital, part of Yonsei University in Seoul.
He reported that there was a significant 5.8% decrease in liver fat following 24 weeks’ treatment with ezetimibe and rosuvastatin comparing baseline with end of treatment MRI-PDFF values; a drop that was significant (18.2% vs. 12.3%, P < .001).
Rosuvastatin monotherapy also reduced liver fat from 15.0% at baseline to 12.4% after 24 weeks; this drop of 2.6% was also significant (P = .003).
This gave an absolute mean difference between the two study arms of 3.2% (P = .02).
Rationale for the ESSENTIAL study
Dr. Kim observed during his presentation that NAFLD is burgeoning problem around the world. Ezetimibe plus rosuvastatin was a combination treatment already used widely in clinical practice, and there had been some suggestion that ezetimibe might have an effect on liver fat.
“Although the effect of ezetimibe on hepatic steatosis is still controversial, ezetimibe has been reported to reduce visceral fat and improve insulin resistance in several studies” Dr. Kim said.
“Recently, our group reported that the use of ezetimibe affects autophagy of hepatocytes and the NLRP3 [NOD-like receptors containing pyrin domain 3] inflammasome,” he said.
Moreover, he added, “ezetimibe improved NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] in an animal model. However, the effects of ezetimibe have not been clearly shown in a human study.”
Dr. Kim also acknowledged a prior randomized control trial that had looked at the role of ezetimibe in 50 patients with NASH, but had not shown a benefit for the drug over placebo in terms of liver fat reduction.
Addressing the Hawthorne effect
“The size of the effect by that might actually be more modest due to the Hawthorne effect,” said session chair Onno Holleboom, MD, PhD, of Amsterdam UMC in the Netherlands.
“What we observe in the large clinical trials is an enormous Hawthorne effect – participating in a NAFLD trial makes people live healthier because they have health checks,” he said.
“That’s a major problem for showing efficacy for the intervention arm,” he added, but of course the open design meant that the trial only had intervention arms; “there was no placebo arm.”
A randomized, active-controlled, clinician-initiated trial
The main objective of the ESSENTIAL trial was therefore to take another look at the potential effect of ezetimibe on hepatic steatosis and doing so in the setting of statin therapy.
In all, 70 patients with NAFLD that had been confirmed via ultrasound were recruited into the prospective, single center, phase 4 trial. Participants were randomized 1:1 to received either ezetimibe 10 mg plus rosuvastatin 5 mg daily or rosuvastatin 5 mg for up to 24 weeks.
Change in liver fat was measured via MRI-PDFF, taking the average values in each of nine liver segments. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) was also used to measure liver fibrosis, although results did not show any differences either from baseline to end of treatment values in either group or when the two treatment groups were compared.
Dr. Kim reported that both treatment with the ezetimibe-rosuvastatin combination and rosuvastatin monotherapy reduced parameters that might be associated with a negative outcome in NAFLD, such as body mass index and waist circumference, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol. There was also a reduction in C-reactive protein levels in the blood, and interleulin-18. There was no change in liver enzymes.
Several subgroup analyses were performed indicating that “individuals with higher BMI, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and severe liver fibrosis were likely to be good responders to ezetimibe treatment,” Dr. Kim said.
“These data indicate that ezetimibe plus rosuvastatin is a safe and effective therapeutic option to treat patients with NAFLD and dyslipidemia,” he concluded.
The results of the ESSENTIAL study have been published in BMC Medicine.
The study was funded by the Yuhan Corporation. Dr. Kim had no conflicts of interest to report. Dr. Holleboom was not involved in the study and had no conflicts of interest.
FROM EASD 2022
Does COVID-19 cause type 1 diabetes in children? Time will tell
STOCKHOLM – It remains inconclusive whether SARS-CoV-2 infection predisposes children and adolescents to a higher risk of type 1 diabetes. Data from two new studies and a recently published research letter add to the growing body of knowledge on the subject, but still can’t draw any definitive conclusions.
The latest results from a Norwegian and a Scottish study both examine incidence of type 1 diabetes in young people with a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection and were reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
A 60% increased risk for type 1 diabetes at least 31 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.63) was found in the Norwegian study, while in contrast, the Scottish study only found an increased risk in the first few months of the pandemic, in 2020, but importantly, no association over a much longer time period (March 2020–November 2021).
In a comment on Twitter on the two studies presented at EASD, session moderator Kamlesh Khunti, MD, professor of primary care diabetes and vascular medicine at the University of Leicester, (England), said: “In summary, two studies showing no or weak association of type 1 diabetes with COVID.”
But new data in the research letter published in JAMA Network Open, based on U.S. figures, also found an almost doubling of type 1 diabetes in children in the first few months after COVID-19 infection relative to infection with other respiratory viruses.
Lead author of the Scottish study, Helen Colhoun, PhD, honorary public health consultant at Public Health Scotland, commented: “Data in children are variable year on year, which emphasizes the need to be cautious over taking a tiny snapshot.”
Nevertheless, this is “a hugely important question and we must not drop the ball. [We must] keep looking at it and maintain scientific equipoise. ... [This] reinforces the need to carry on this analysis into the future to obtain an unequivocal picture,” she emphasized.
Norwegian study: If there is an association, the risk is small
German Tapia, PhD, from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health, Oslo, presented the results of a study of SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent risk of type 1 diabetes in 1.2 million children in Norway.
Of these, 424,354 children had been infected with SARS-CoV-2, and there were 990 incident cases of type 1 diabetes.
“What we do know about COVID-19 in children is that the symptoms are mild and only a small proportion are hospitalized with more serious symptoms. But we do not know the long-term effects of COVID-19 infection because this requires a longer follow-up period,” remarked Dr. Tapia, adding that other viral infections are thought to be linked to the development of type 1 diabetes, in particular, respiratory infections.
The data were sourced from the Norwegian Emergency Preparedness Register for COVID-19, which gathers daily data updates including infections (positive and negative results for free-of-charge testing), diagnoses (primary and secondary care), vaccinations (also free of charge), prescribed medications, and basic demographics.
“We link these data using the personal identification number that every Norwegian citizen has,” explained Dr. Tapia.
He presented results from two cohorts: firstly, results in children only, including those tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and secondly, a full national Norwegian population cohort.
Regarding the first cohort, those under 18 years who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, from March 2020 to March 2022, had a significantly increased risk of type 1 diabetes at least 31 days after infection, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.63 (95% confidence interval, 1.08-2.47; P = .02). Adjustments were made for age, sex, non-Nordic country of origin, geographic area, and socioeconomic factors.
For children who developed type 1 diabetes within 30 days of a SARS-CoV-2 infection, the HR was 1.26 (95% CI, 0.72-2.19; P = .42), which did not reach statistical significance.
“The fact that fewer people developed type 1 diabetes within 30 days is not surprising because we know that type 1 diabetes develops over a long period of time,” Dr. Tapia said.
“For this reason, we would not expect to find new cases of those people who develop type 1 diabetes within 30 days of COVID-19 infection,” he explained. In these cases, “it is most likely that they already had [type 1 diabetes], and the infection probably triggered clinical symptoms, so their type 1 diabetes was discovered.”
Turning to the full population cohort and diagnoses of type 1 diabetes over 30 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, the Norwegian researchers found an association, with an HR of 1.57 (95% CI, 1.06-2.33; P = .03), while diagnosis of type 1 diabetes at 30 days or less generated a hazard ratio of 1.22 (95% CI, 0.72-2.19; P = .42).
“So very similar results were found, and after adjustment for confounders, results were still similar,” reported Dr. Tapia.
He also conducted a similar analysis with vaccination as an exposure but found no association between vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 and diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
“From these results, we conclude that this suggests an increase in diagnosis of type 1 diabetes after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but it must be noted that the absolute risk of developing type 1 diabetes after infection in children is low, with most children not developing the disease,” he emphasized. “There are nearly half a million children who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Norway, but only a very small proportion develop type 1 diabetes.”
Scottish study: No association found over longer term
Dr. Colhoun and colleagues looked at the relationship between incident type 1 diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 infection in children in Scotland using e-health record linkage.
The study involved 1.8 million people under 35 years of age and found very weak, if any, evidence of an association between incident type 1 diabetes and SARS-CoV-2.
Examining data between March 2020 and November 2021, Dr. Colhoun and colleagues identified 365,080 individuals up to age 35 with at least one detected SARS-CoV-2 infection during follow-up and 1,074 who developed type 1 diabetes.
“In children under 16 years, suspected cases of type 1 diabetes are admitted to hospital, and 97% of diagnosis dates are recorded in the Scottish Care Information – Diabetes Collaboration register [SCI-Diabetes] prior to or within 2 days of the first hospital admission for type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Colhoun said, stressing the timeliness of the data.
“We found the incidence of type 1 diabetes diagnosis increased 1.2-fold in those aged 0-14 years, but we did not find any association at an individual level of COVID-19 infection over 30 days prior to a type 1 diabetes diagnosis, in this particular dataset,” she reported. In young people aged 15-34, there was a linear increase in incident type 1 diabetes from 2015 to 2021 with no pandemic increase.
Referring to the 1.2-fold increase soon after the pandemic started, she explained that, in 0- to 14-year-olds, the increase followed a drop in the preceding months prepandemic in 2019. They also found that the seasonal pattern of type 1 diabetes diagnoses remained roughly the same across the pandemic months, with typical peaks in February and September.
In the cohort of under 35s, researchers also found a rate ratio of 2.62 (95% CI, 1.81-3.78) within a 30-day window of SARS-CoV-2 infection, but beyond 30 days, no evidence was seen of an association, with a RR of 0.86 (95% CI, 0.62-1.21; P = .40), she reported.
She explained her reasons for not considering diagnoses within 30 days of COVID-19 as causative. Echoing Dr. Tapia, Dr. Colhoun said the median time from symptom onset to diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is 25 days. “This suggests that 50% have had symptoms for over 25 days at diagnosis.”
She also stressed that when they compared the timing of SARS-CoV-2 testing with diagnosis, they found a much higher rate of COVID-19 testing around diagnosis. “This was not least because everyone admitted to hospital had to have a COVID-19 test.”
Latest U.S. data point to a link
Meanwhile, for the new data reported in JAMA Network Open, medical student Ellen K. Kendall of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, matched 571,256 pediatric patients: 285,628 with COVID-19 and 285,628 with non–COVID-19 respiratory infections.
By 6 months after COVID-19, 123 patients (0.043%) had received a new diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, but only 72 (0.025%) were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes within 6 months after non–COVID-19 respiratory infection.
At 1, 3, and 6 months after infection, risk of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes was greater among those infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with those with non–COVID-19 respiratory infection (1 month: HR, 1.96; 3 months: HR, 2.10; and 6 months: HR, 1.83), and in subgroups of patients aged 0-9 years, a group unlikely to develop type 2 diabetes.
“In this study, new type 1 diabetes diagnoses were more likely to occur among pediatric patients with prior COVID-19 than among those with other respiratory infections (or with other encounters with health systems),” noted Ms. Kendall and coauthors. “Respiratory infections have previously been associated with onset of type 1 diabetes, but this risk was even higher among those with COVID-19 in our study, raising concern for long-term, post–COVID-19 autoimmune complications among youths.”
“The increased risk of new-onset type 1 diabetes after COVID-19 adds an important consideration for risk–benefit discussions for prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection in pediatric populations,” they concluded.
A study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention published in January 2022, also concluded there was a link between COVID-19 and diabetes in children, but not with other acute respiratory infections. Children were 2.5 times more likely to be diagnosed with diabetes following a SARS-CoV-2 infection, it found.
However, the study has been criticized because it pooled all types of diabetes together and did not account for other health conditions, medications that can increase blood glucose levels, race, obesity, and other social determinants of health that might influence a child’s risk of acquiring COVID-19 or diabetes.
“I’ve no doubt that the CDC data were incorrect because the incidence rate for ... diabetes, even in those never exposed to COVID-19 infection, was 10 times the rate ever reported in the U.S.,” Dr. Colhoun said. “There’s no way these data are correct. I believe there was a confusion between incidence and prevalence of diabetes.”
“This paper caused a great deal of panic, especially among those who have a child with type 1diabetes, so we need to be very careful not to cause undue alarm until we have more definitive evidence in this arena,” she stressed.
However, she also acknowledged that the new Norwegian study was well conducted, and she has no methodological concerns about it, so “I think we just have to wait and see.”
Given the inconclusiveness on the issue, there is an ongoing CoviDiab registry collecting data on this very subject.
Dr. Tapia presented on behalf of lead author Dr. Gulseth, who has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Colhoun also reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – It remains inconclusive whether SARS-CoV-2 infection predisposes children and adolescents to a higher risk of type 1 diabetes. Data from two new studies and a recently published research letter add to the growing body of knowledge on the subject, but still can’t draw any definitive conclusions.
The latest results from a Norwegian and a Scottish study both examine incidence of type 1 diabetes in young people with a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection and were reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
A 60% increased risk for type 1 diabetes at least 31 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.63) was found in the Norwegian study, while in contrast, the Scottish study only found an increased risk in the first few months of the pandemic, in 2020, but importantly, no association over a much longer time period (March 2020–November 2021).
In a comment on Twitter on the two studies presented at EASD, session moderator Kamlesh Khunti, MD, professor of primary care diabetes and vascular medicine at the University of Leicester, (England), said: “In summary, two studies showing no or weak association of type 1 diabetes with COVID.”
But new data in the research letter published in JAMA Network Open, based on U.S. figures, also found an almost doubling of type 1 diabetes in children in the first few months after COVID-19 infection relative to infection with other respiratory viruses.
Lead author of the Scottish study, Helen Colhoun, PhD, honorary public health consultant at Public Health Scotland, commented: “Data in children are variable year on year, which emphasizes the need to be cautious over taking a tiny snapshot.”
Nevertheless, this is “a hugely important question and we must not drop the ball. [We must] keep looking at it and maintain scientific equipoise. ... [This] reinforces the need to carry on this analysis into the future to obtain an unequivocal picture,” she emphasized.
Norwegian study: If there is an association, the risk is small
German Tapia, PhD, from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health, Oslo, presented the results of a study of SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent risk of type 1 diabetes in 1.2 million children in Norway.
Of these, 424,354 children had been infected with SARS-CoV-2, and there were 990 incident cases of type 1 diabetes.
“What we do know about COVID-19 in children is that the symptoms are mild and only a small proportion are hospitalized with more serious symptoms. But we do not know the long-term effects of COVID-19 infection because this requires a longer follow-up period,” remarked Dr. Tapia, adding that other viral infections are thought to be linked to the development of type 1 diabetes, in particular, respiratory infections.
The data were sourced from the Norwegian Emergency Preparedness Register for COVID-19, which gathers daily data updates including infections (positive and negative results for free-of-charge testing), diagnoses (primary and secondary care), vaccinations (also free of charge), prescribed medications, and basic demographics.
“We link these data using the personal identification number that every Norwegian citizen has,” explained Dr. Tapia.
He presented results from two cohorts: firstly, results in children only, including those tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and secondly, a full national Norwegian population cohort.
Regarding the first cohort, those under 18 years who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, from March 2020 to March 2022, had a significantly increased risk of type 1 diabetes at least 31 days after infection, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.63 (95% confidence interval, 1.08-2.47; P = .02). Adjustments were made for age, sex, non-Nordic country of origin, geographic area, and socioeconomic factors.
For children who developed type 1 diabetes within 30 days of a SARS-CoV-2 infection, the HR was 1.26 (95% CI, 0.72-2.19; P = .42), which did not reach statistical significance.
“The fact that fewer people developed type 1 diabetes within 30 days is not surprising because we know that type 1 diabetes develops over a long period of time,” Dr. Tapia said.
“For this reason, we would not expect to find new cases of those people who develop type 1 diabetes within 30 days of COVID-19 infection,” he explained. In these cases, “it is most likely that they already had [type 1 diabetes], and the infection probably triggered clinical symptoms, so their type 1 diabetes was discovered.”
Turning to the full population cohort and diagnoses of type 1 diabetes over 30 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, the Norwegian researchers found an association, with an HR of 1.57 (95% CI, 1.06-2.33; P = .03), while diagnosis of type 1 diabetes at 30 days or less generated a hazard ratio of 1.22 (95% CI, 0.72-2.19; P = .42).
“So very similar results were found, and after adjustment for confounders, results were still similar,” reported Dr. Tapia.
He also conducted a similar analysis with vaccination as an exposure but found no association between vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 and diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
“From these results, we conclude that this suggests an increase in diagnosis of type 1 diabetes after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but it must be noted that the absolute risk of developing type 1 diabetes after infection in children is low, with most children not developing the disease,” he emphasized. “There are nearly half a million children who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Norway, but only a very small proportion develop type 1 diabetes.”
Scottish study: No association found over longer term
Dr. Colhoun and colleagues looked at the relationship between incident type 1 diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 infection in children in Scotland using e-health record linkage.
The study involved 1.8 million people under 35 years of age and found very weak, if any, evidence of an association between incident type 1 diabetes and SARS-CoV-2.
Examining data between March 2020 and November 2021, Dr. Colhoun and colleagues identified 365,080 individuals up to age 35 with at least one detected SARS-CoV-2 infection during follow-up and 1,074 who developed type 1 diabetes.
“In children under 16 years, suspected cases of type 1 diabetes are admitted to hospital, and 97% of diagnosis dates are recorded in the Scottish Care Information – Diabetes Collaboration register [SCI-Diabetes] prior to or within 2 days of the first hospital admission for type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Colhoun said, stressing the timeliness of the data.
“We found the incidence of type 1 diabetes diagnosis increased 1.2-fold in those aged 0-14 years, but we did not find any association at an individual level of COVID-19 infection over 30 days prior to a type 1 diabetes diagnosis, in this particular dataset,” she reported. In young people aged 15-34, there was a linear increase in incident type 1 diabetes from 2015 to 2021 with no pandemic increase.
Referring to the 1.2-fold increase soon after the pandemic started, she explained that, in 0- to 14-year-olds, the increase followed a drop in the preceding months prepandemic in 2019. They also found that the seasonal pattern of type 1 diabetes diagnoses remained roughly the same across the pandemic months, with typical peaks in February and September.
In the cohort of under 35s, researchers also found a rate ratio of 2.62 (95% CI, 1.81-3.78) within a 30-day window of SARS-CoV-2 infection, but beyond 30 days, no evidence was seen of an association, with a RR of 0.86 (95% CI, 0.62-1.21; P = .40), she reported.
She explained her reasons for not considering diagnoses within 30 days of COVID-19 as causative. Echoing Dr. Tapia, Dr. Colhoun said the median time from symptom onset to diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is 25 days. “This suggests that 50% have had symptoms for over 25 days at diagnosis.”
She also stressed that when they compared the timing of SARS-CoV-2 testing with diagnosis, they found a much higher rate of COVID-19 testing around diagnosis. “This was not least because everyone admitted to hospital had to have a COVID-19 test.”
Latest U.S. data point to a link
Meanwhile, for the new data reported in JAMA Network Open, medical student Ellen K. Kendall of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, matched 571,256 pediatric patients: 285,628 with COVID-19 and 285,628 with non–COVID-19 respiratory infections.
By 6 months after COVID-19, 123 patients (0.043%) had received a new diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, but only 72 (0.025%) were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes within 6 months after non–COVID-19 respiratory infection.
At 1, 3, and 6 months after infection, risk of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes was greater among those infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with those with non–COVID-19 respiratory infection (1 month: HR, 1.96; 3 months: HR, 2.10; and 6 months: HR, 1.83), and in subgroups of patients aged 0-9 years, a group unlikely to develop type 2 diabetes.
“In this study, new type 1 diabetes diagnoses were more likely to occur among pediatric patients with prior COVID-19 than among those with other respiratory infections (or with other encounters with health systems),” noted Ms. Kendall and coauthors. “Respiratory infections have previously been associated with onset of type 1 diabetes, but this risk was even higher among those with COVID-19 in our study, raising concern for long-term, post–COVID-19 autoimmune complications among youths.”
“The increased risk of new-onset type 1 diabetes after COVID-19 adds an important consideration for risk–benefit discussions for prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection in pediatric populations,” they concluded.
A study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention published in January 2022, also concluded there was a link between COVID-19 and diabetes in children, but not with other acute respiratory infections. Children were 2.5 times more likely to be diagnosed with diabetes following a SARS-CoV-2 infection, it found.
However, the study has been criticized because it pooled all types of diabetes together and did not account for other health conditions, medications that can increase blood glucose levels, race, obesity, and other social determinants of health that might influence a child’s risk of acquiring COVID-19 or diabetes.
“I’ve no doubt that the CDC data were incorrect because the incidence rate for ... diabetes, even in those never exposed to COVID-19 infection, was 10 times the rate ever reported in the U.S.,” Dr. Colhoun said. “There’s no way these data are correct. I believe there was a confusion between incidence and prevalence of diabetes.”
“This paper caused a great deal of panic, especially among those who have a child with type 1diabetes, so we need to be very careful not to cause undue alarm until we have more definitive evidence in this arena,” she stressed.
However, she also acknowledged that the new Norwegian study was well conducted, and she has no methodological concerns about it, so “I think we just have to wait and see.”
Given the inconclusiveness on the issue, there is an ongoing CoviDiab registry collecting data on this very subject.
Dr. Tapia presented on behalf of lead author Dr. Gulseth, who has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Colhoun also reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – It remains inconclusive whether SARS-CoV-2 infection predisposes children and adolescents to a higher risk of type 1 diabetes. Data from two new studies and a recently published research letter add to the growing body of knowledge on the subject, but still can’t draw any definitive conclusions.
The latest results from a Norwegian and a Scottish study both examine incidence of type 1 diabetes in young people with a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection and were reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
A 60% increased risk for type 1 diabetes at least 31 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.63) was found in the Norwegian study, while in contrast, the Scottish study only found an increased risk in the first few months of the pandemic, in 2020, but importantly, no association over a much longer time period (March 2020–November 2021).
In a comment on Twitter on the two studies presented at EASD, session moderator Kamlesh Khunti, MD, professor of primary care diabetes and vascular medicine at the University of Leicester, (England), said: “In summary, two studies showing no or weak association of type 1 diabetes with COVID.”
But new data in the research letter published in JAMA Network Open, based on U.S. figures, also found an almost doubling of type 1 diabetes in children in the first few months after COVID-19 infection relative to infection with other respiratory viruses.
Lead author of the Scottish study, Helen Colhoun, PhD, honorary public health consultant at Public Health Scotland, commented: “Data in children are variable year on year, which emphasizes the need to be cautious over taking a tiny snapshot.”
Nevertheless, this is “a hugely important question and we must not drop the ball. [We must] keep looking at it and maintain scientific equipoise. ... [This] reinforces the need to carry on this analysis into the future to obtain an unequivocal picture,” she emphasized.
Norwegian study: If there is an association, the risk is small
German Tapia, PhD, from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health, Oslo, presented the results of a study of SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent risk of type 1 diabetes in 1.2 million children in Norway.
Of these, 424,354 children had been infected with SARS-CoV-2, and there were 990 incident cases of type 1 diabetes.
“What we do know about COVID-19 in children is that the symptoms are mild and only a small proportion are hospitalized with more serious symptoms. But we do not know the long-term effects of COVID-19 infection because this requires a longer follow-up period,” remarked Dr. Tapia, adding that other viral infections are thought to be linked to the development of type 1 diabetes, in particular, respiratory infections.
The data were sourced from the Norwegian Emergency Preparedness Register for COVID-19, which gathers daily data updates including infections (positive and negative results for free-of-charge testing), diagnoses (primary and secondary care), vaccinations (also free of charge), prescribed medications, and basic demographics.
“We link these data using the personal identification number that every Norwegian citizen has,” explained Dr. Tapia.
He presented results from two cohorts: firstly, results in children only, including those tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and secondly, a full national Norwegian population cohort.
Regarding the first cohort, those under 18 years who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, from March 2020 to March 2022, had a significantly increased risk of type 1 diabetes at least 31 days after infection, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.63 (95% confidence interval, 1.08-2.47; P = .02). Adjustments were made for age, sex, non-Nordic country of origin, geographic area, and socioeconomic factors.
For children who developed type 1 diabetes within 30 days of a SARS-CoV-2 infection, the HR was 1.26 (95% CI, 0.72-2.19; P = .42), which did not reach statistical significance.
“The fact that fewer people developed type 1 diabetes within 30 days is not surprising because we know that type 1 diabetes develops over a long period of time,” Dr. Tapia said.
“For this reason, we would not expect to find new cases of those people who develop type 1 diabetes within 30 days of COVID-19 infection,” he explained. In these cases, “it is most likely that they already had [type 1 diabetes], and the infection probably triggered clinical symptoms, so their type 1 diabetes was discovered.”
Turning to the full population cohort and diagnoses of type 1 diabetes over 30 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, the Norwegian researchers found an association, with an HR of 1.57 (95% CI, 1.06-2.33; P = .03), while diagnosis of type 1 diabetes at 30 days or less generated a hazard ratio of 1.22 (95% CI, 0.72-2.19; P = .42).
“So very similar results were found, and after adjustment for confounders, results were still similar,” reported Dr. Tapia.
He also conducted a similar analysis with vaccination as an exposure but found no association between vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 and diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
“From these results, we conclude that this suggests an increase in diagnosis of type 1 diabetes after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but it must be noted that the absolute risk of developing type 1 diabetes after infection in children is low, with most children not developing the disease,” he emphasized. “There are nearly half a million children who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Norway, but only a very small proportion develop type 1 diabetes.”
Scottish study: No association found over longer term
Dr. Colhoun and colleagues looked at the relationship between incident type 1 diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 infection in children in Scotland using e-health record linkage.
The study involved 1.8 million people under 35 years of age and found very weak, if any, evidence of an association between incident type 1 diabetes and SARS-CoV-2.
Examining data between March 2020 and November 2021, Dr. Colhoun and colleagues identified 365,080 individuals up to age 35 with at least one detected SARS-CoV-2 infection during follow-up and 1,074 who developed type 1 diabetes.
“In children under 16 years, suspected cases of type 1 diabetes are admitted to hospital, and 97% of diagnosis dates are recorded in the Scottish Care Information – Diabetes Collaboration register [SCI-Diabetes] prior to or within 2 days of the first hospital admission for type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Colhoun said, stressing the timeliness of the data.
“We found the incidence of type 1 diabetes diagnosis increased 1.2-fold in those aged 0-14 years, but we did not find any association at an individual level of COVID-19 infection over 30 days prior to a type 1 diabetes diagnosis, in this particular dataset,” she reported. In young people aged 15-34, there was a linear increase in incident type 1 diabetes from 2015 to 2021 with no pandemic increase.
Referring to the 1.2-fold increase soon after the pandemic started, she explained that, in 0- to 14-year-olds, the increase followed a drop in the preceding months prepandemic in 2019. They also found that the seasonal pattern of type 1 diabetes diagnoses remained roughly the same across the pandemic months, with typical peaks in February and September.
In the cohort of under 35s, researchers also found a rate ratio of 2.62 (95% CI, 1.81-3.78) within a 30-day window of SARS-CoV-2 infection, but beyond 30 days, no evidence was seen of an association, with a RR of 0.86 (95% CI, 0.62-1.21; P = .40), she reported.
She explained her reasons for not considering diagnoses within 30 days of COVID-19 as causative. Echoing Dr. Tapia, Dr. Colhoun said the median time from symptom onset to diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is 25 days. “This suggests that 50% have had symptoms for over 25 days at diagnosis.”
She also stressed that when they compared the timing of SARS-CoV-2 testing with diagnosis, they found a much higher rate of COVID-19 testing around diagnosis. “This was not least because everyone admitted to hospital had to have a COVID-19 test.”
Latest U.S. data point to a link
Meanwhile, for the new data reported in JAMA Network Open, medical student Ellen K. Kendall of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, matched 571,256 pediatric patients: 285,628 with COVID-19 and 285,628 with non–COVID-19 respiratory infections.
By 6 months after COVID-19, 123 patients (0.043%) had received a new diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, but only 72 (0.025%) were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes within 6 months after non–COVID-19 respiratory infection.
At 1, 3, and 6 months after infection, risk of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes was greater among those infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with those with non–COVID-19 respiratory infection (1 month: HR, 1.96; 3 months: HR, 2.10; and 6 months: HR, 1.83), and in subgroups of patients aged 0-9 years, a group unlikely to develop type 2 diabetes.
“In this study, new type 1 diabetes diagnoses were more likely to occur among pediatric patients with prior COVID-19 than among those with other respiratory infections (or with other encounters with health systems),” noted Ms. Kendall and coauthors. “Respiratory infections have previously been associated with onset of type 1 diabetes, but this risk was even higher among those with COVID-19 in our study, raising concern for long-term, post–COVID-19 autoimmune complications among youths.”
“The increased risk of new-onset type 1 diabetes after COVID-19 adds an important consideration for risk–benefit discussions for prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection in pediatric populations,” they concluded.
A study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention published in January 2022, also concluded there was a link between COVID-19 and diabetes in children, but not with other acute respiratory infections. Children were 2.5 times more likely to be diagnosed with diabetes following a SARS-CoV-2 infection, it found.
However, the study has been criticized because it pooled all types of diabetes together and did not account for other health conditions, medications that can increase blood glucose levels, race, obesity, and other social determinants of health that might influence a child’s risk of acquiring COVID-19 or diabetes.
“I’ve no doubt that the CDC data were incorrect because the incidence rate for ... diabetes, even in those never exposed to COVID-19 infection, was 10 times the rate ever reported in the U.S.,” Dr. Colhoun said. “There’s no way these data are correct. I believe there was a confusion between incidence and prevalence of diabetes.”
“This paper caused a great deal of panic, especially among those who have a child with type 1diabetes, so we need to be very careful not to cause undue alarm until we have more definitive evidence in this arena,” she stressed.
However, she also acknowledged that the new Norwegian study was well conducted, and she has no methodological concerns about it, so “I think we just have to wait and see.”
Given the inconclusiveness on the issue, there is an ongoing CoviDiab registry collecting data on this very subject.
Dr. Tapia presented on behalf of lead author Dr. Gulseth, who has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Colhoun also reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2022
Severe COVID-19–related outcomes found worse in men with RA
A retrospective study that analyzed sex disparities in patients with COVID-19 and rheumatoid arthritis found that men had more baseline comorbidities and increased risk of COVID-19–related outcomes, compared with women.
“Differences in genetics between sex and sex steroid hormones may play a role in predisposition to COVID-19 infection as well as modulating the disease progression,” according to Xiaofeng Zhou, PhD, senior director at Pfizer, New York, and the study’s lead author.
Dr. Zhou presented her findings at The Lancet Summit on Sex and Gender in Rheumatology.
Patients with chronic rheumatic diseases treated with immunomodulatory therapies may be at higher risk for more severe COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization, complications, and death. Research on sex-based disparities in RA patients with COVID-19 in the United States is limited, said Dr. Zhou, who embarked on a retrospective cohort study to examine the demographic and clinical characteristics of RA patients with COVID-19 and estimate the risk of possible COVID-19 outcomes by sex.
Dr. Zhou and colleagues used U.S. COVID-19 data collected through electronic health records by Optum during 2020 to June 2021. The study included adult patients with RA and a COVID-19 diagnosis (≥ 1 diagnosis code or positive SARS-CoV-2 laboratory test) and greater than or equal to 183 days of database enrollment who received treatment with immunomodulatory therapies prior to the diagnosis date. They were stratified by sex.
Investigators used logistic regression to estimate the risk of 11 possible COVID-19–related outcomes within 30 days of the COVID-19 diagnosis (hospitalization, ICU admission, pneumonia, kidney failure, thrombotic event, heart failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], sepsis/septic shock, mechanical ventilation/extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO], in-hospital death, and all-cause mortality), adjusting for demographics and baseline clinical covariates.
A total of 4,476 COVID-19 patients with RA (78% female) took part in the study. Male patients trended older (64 vs. 60 years) and had lower African American representation and Medicaid enrollment than female patients, but they had more baseline comorbidities such as hypertension (55% vs. 45%), hyperlipidemia (45% vs. 33%), diabetes (25% vs. 20%), coronary artery disease (28% vs. 12%), and chronic kidney disease (20% vs. 15%).
Eight of the eleven COVID-19 outcomes were significantly more likely to occur in men than women (hospitalization: odds ratio, 1.32 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.11-1.56]; ICU admission: OR, 1.80 [95% CI, 1.36-2.40]; mechanical ventilation/ECMO: OR, 1.48 [95% CI, 1.04-2.11]; in-hospital death: OR, 1.53 [95% CI, 1.13-2.07]; all-cause mortality: OR, 1.42 [95% CI, 1.09-1.86]; sepsis: OR, 1.55 [95% CI, 1.20-2.02]; kidney failure: OR, 1.46 [95% CI, 1.15-1.85]; ARDS: OR, 1.39 [95% CI, 1.15-1.69]).
Sex hormones factor into risk
The data illustrated that men with RA had more baseline comorbidities and increased risk of COVID-19 outcomes than women.
Sex hormones regulate virus entry into host cells, respiratory function, immune response, the cardiovascular system, and coagulation, explained Dr. Zhou.
Estrogen and progesterone in women could help develop stronger and efficient immune responses to viruses and reduce virus entry into the host cells. Also, “[the] larger number of copies of ACE2 genes in women, [which] is linked with protection in the lungs against edema, permeability, and pulmonary damage, could be associated with lower incidence of severe COVID-19 outcomes, such as respiratory-related mortality and mortality,” Dr. Zhou said.
By comparison, androgens in men may increase virus entry into the host cells and promote unfavorable immune response through the induction of cytokine production and reducing the antibody response to the virus. This could lead to severe infection, Dr. Zhou said.
Sex-based differences in steroid hormones may also explain the higher incidence of morbidity and fatality that’s been observed in other studies of male patients with other infectious diseases, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome.
Study bolsters evidence on sex disparities
The results add real-world evidence to the limited literature on sex disparities in COVID-19 outcomes among patients with RA in the United States, Dr. Zhou said. “The differential role in sex steroid hormones among women and men may shed light on clinical management of COVID-19 patients and the need to consider sex-specific approaches in clinical trials in preventing and treating COVID-19 patients,” she said.
Considering that all patients are recommended to get COVID-19 vaccinations, “it is difficult to say how this impacts clinical practice,” said Janet Pope, MD, MPH, professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Western Ontario, London, who was not involved with the study.
Sharing results with some patients may help to encourage vaccination, thus reducing risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes, Dr. Pope said.
In future studies, Dr. Zhou suggests using multiple databases and considering other geographies beyond the United States to further understand the etiology of sexual dimorphism in COVID-19 and expand generalizability. “In addition, future research will seek to provide insights into health equity gaps in the management of COVID-19. This may inform development of precision medicines and vaccines, especially among patients on immunosuppressive treatments,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Zhou and other study authors are Pfizer employees and hold Pfizer stock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A retrospective study that analyzed sex disparities in patients with COVID-19 and rheumatoid arthritis found that men had more baseline comorbidities and increased risk of COVID-19–related outcomes, compared with women.
“Differences in genetics between sex and sex steroid hormones may play a role in predisposition to COVID-19 infection as well as modulating the disease progression,” according to Xiaofeng Zhou, PhD, senior director at Pfizer, New York, and the study’s lead author.
Dr. Zhou presented her findings at The Lancet Summit on Sex and Gender in Rheumatology.
Patients with chronic rheumatic diseases treated with immunomodulatory therapies may be at higher risk for more severe COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization, complications, and death. Research on sex-based disparities in RA patients with COVID-19 in the United States is limited, said Dr. Zhou, who embarked on a retrospective cohort study to examine the demographic and clinical characteristics of RA patients with COVID-19 and estimate the risk of possible COVID-19 outcomes by sex.
Dr. Zhou and colleagues used U.S. COVID-19 data collected through electronic health records by Optum during 2020 to June 2021. The study included adult patients with RA and a COVID-19 diagnosis (≥ 1 diagnosis code or positive SARS-CoV-2 laboratory test) and greater than or equal to 183 days of database enrollment who received treatment with immunomodulatory therapies prior to the diagnosis date. They were stratified by sex.
Investigators used logistic regression to estimate the risk of 11 possible COVID-19–related outcomes within 30 days of the COVID-19 diagnosis (hospitalization, ICU admission, pneumonia, kidney failure, thrombotic event, heart failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], sepsis/septic shock, mechanical ventilation/extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO], in-hospital death, and all-cause mortality), adjusting for demographics and baseline clinical covariates.
A total of 4,476 COVID-19 patients with RA (78% female) took part in the study. Male patients trended older (64 vs. 60 years) and had lower African American representation and Medicaid enrollment than female patients, but they had more baseline comorbidities such as hypertension (55% vs. 45%), hyperlipidemia (45% vs. 33%), diabetes (25% vs. 20%), coronary artery disease (28% vs. 12%), and chronic kidney disease (20% vs. 15%).
Eight of the eleven COVID-19 outcomes were significantly more likely to occur in men than women (hospitalization: odds ratio, 1.32 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.11-1.56]; ICU admission: OR, 1.80 [95% CI, 1.36-2.40]; mechanical ventilation/ECMO: OR, 1.48 [95% CI, 1.04-2.11]; in-hospital death: OR, 1.53 [95% CI, 1.13-2.07]; all-cause mortality: OR, 1.42 [95% CI, 1.09-1.86]; sepsis: OR, 1.55 [95% CI, 1.20-2.02]; kidney failure: OR, 1.46 [95% CI, 1.15-1.85]; ARDS: OR, 1.39 [95% CI, 1.15-1.69]).
Sex hormones factor into risk
The data illustrated that men with RA had more baseline comorbidities and increased risk of COVID-19 outcomes than women.
Sex hormones regulate virus entry into host cells, respiratory function, immune response, the cardiovascular system, and coagulation, explained Dr. Zhou.
Estrogen and progesterone in women could help develop stronger and efficient immune responses to viruses and reduce virus entry into the host cells. Also, “[the] larger number of copies of ACE2 genes in women, [which] is linked with protection in the lungs against edema, permeability, and pulmonary damage, could be associated with lower incidence of severe COVID-19 outcomes, such as respiratory-related mortality and mortality,” Dr. Zhou said.
By comparison, androgens in men may increase virus entry into the host cells and promote unfavorable immune response through the induction of cytokine production and reducing the antibody response to the virus. This could lead to severe infection, Dr. Zhou said.
Sex-based differences in steroid hormones may also explain the higher incidence of morbidity and fatality that’s been observed in other studies of male patients with other infectious diseases, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome.
Study bolsters evidence on sex disparities
The results add real-world evidence to the limited literature on sex disparities in COVID-19 outcomes among patients with RA in the United States, Dr. Zhou said. “The differential role in sex steroid hormones among women and men may shed light on clinical management of COVID-19 patients and the need to consider sex-specific approaches in clinical trials in preventing and treating COVID-19 patients,” she said.
Considering that all patients are recommended to get COVID-19 vaccinations, “it is difficult to say how this impacts clinical practice,” said Janet Pope, MD, MPH, professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Western Ontario, London, who was not involved with the study.
Sharing results with some patients may help to encourage vaccination, thus reducing risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes, Dr. Pope said.
In future studies, Dr. Zhou suggests using multiple databases and considering other geographies beyond the United States to further understand the etiology of sexual dimorphism in COVID-19 and expand generalizability. “In addition, future research will seek to provide insights into health equity gaps in the management of COVID-19. This may inform development of precision medicines and vaccines, especially among patients on immunosuppressive treatments,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Zhou and other study authors are Pfizer employees and hold Pfizer stock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A retrospective study that analyzed sex disparities in patients with COVID-19 and rheumatoid arthritis found that men had more baseline comorbidities and increased risk of COVID-19–related outcomes, compared with women.
“Differences in genetics between sex and sex steroid hormones may play a role in predisposition to COVID-19 infection as well as modulating the disease progression,” according to Xiaofeng Zhou, PhD, senior director at Pfizer, New York, and the study’s lead author.
Dr. Zhou presented her findings at The Lancet Summit on Sex and Gender in Rheumatology.
Patients with chronic rheumatic diseases treated with immunomodulatory therapies may be at higher risk for more severe COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization, complications, and death. Research on sex-based disparities in RA patients with COVID-19 in the United States is limited, said Dr. Zhou, who embarked on a retrospective cohort study to examine the demographic and clinical characteristics of RA patients with COVID-19 and estimate the risk of possible COVID-19 outcomes by sex.
Dr. Zhou and colleagues used U.S. COVID-19 data collected through electronic health records by Optum during 2020 to June 2021. The study included adult patients with RA and a COVID-19 diagnosis (≥ 1 diagnosis code or positive SARS-CoV-2 laboratory test) and greater than or equal to 183 days of database enrollment who received treatment with immunomodulatory therapies prior to the diagnosis date. They were stratified by sex.
Investigators used logistic regression to estimate the risk of 11 possible COVID-19–related outcomes within 30 days of the COVID-19 diagnosis (hospitalization, ICU admission, pneumonia, kidney failure, thrombotic event, heart failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], sepsis/septic shock, mechanical ventilation/extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO], in-hospital death, and all-cause mortality), adjusting for demographics and baseline clinical covariates.
A total of 4,476 COVID-19 patients with RA (78% female) took part in the study. Male patients trended older (64 vs. 60 years) and had lower African American representation and Medicaid enrollment than female patients, but they had more baseline comorbidities such as hypertension (55% vs. 45%), hyperlipidemia (45% vs. 33%), diabetes (25% vs. 20%), coronary artery disease (28% vs. 12%), and chronic kidney disease (20% vs. 15%).
Eight of the eleven COVID-19 outcomes were significantly more likely to occur in men than women (hospitalization: odds ratio, 1.32 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.11-1.56]; ICU admission: OR, 1.80 [95% CI, 1.36-2.40]; mechanical ventilation/ECMO: OR, 1.48 [95% CI, 1.04-2.11]; in-hospital death: OR, 1.53 [95% CI, 1.13-2.07]; all-cause mortality: OR, 1.42 [95% CI, 1.09-1.86]; sepsis: OR, 1.55 [95% CI, 1.20-2.02]; kidney failure: OR, 1.46 [95% CI, 1.15-1.85]; ARDS: OR, 1.39 [95% CI, 1.15-1.69]).
Sex hormones factor into risk
The data illustrated that men with RA had more baseline comorbidities and increased risk of COVID-19 outcomes than women.
Sex hormones regulate virus entry into host cells, respiratory function, immune response, the cardiovascular system, and coagulation, explained Dr. Zhou.
Estrogen and progesterone in women could help develop stronger and efficient immune responses to viruses and reduce virus entry into the host cells. Also, “[the] larger number of copies of ACE2 genes in women, [which] is linked with protection in the lungs against edema, permeability, and pulmonary damage, could be associated with lower incidence of severe COVID-19 outcomes, such as respiratory-related mortality and mortality,” Dr. Zhou said.
By comparison, androgens in men may increase virus entry into the host cells and promote unfavorable immune response through the induction of cytokine production and reducing the antibody response to the virus. This could lead to severe infection, Dr. Zhou said.
Sex-based differences in steroid hormones may also explain the higher incidence of morbidity and fatality that’s been observed in other studies of male patients with other infectious diseases, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome.
Study bolsters evidence on sex disparities
The results add real-world evidence to the limited literature on sex disparities in COVID-19 outcomes among patients with RA in the United States, Dr. Zhou said. “The differential role in sex steroid hormones among women and men may shed light on clinical management of COVID-19 patients and the need to consider sex-specific approaches in clinical trials in preventing and treating COVID-19 patients,” she said.
Considering that all patients are recommended to get COVID-19 vaccinations, “it is difficult to say how this impacts clinical practice,” said Janet Pope, MD, MPH, professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Western Ontario, London, who was not involved with the study.
Sharing results with some patients may help to encourage vaccination, thus reducing risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes, Dr. Pope said.
In future studies, Dr. Zhou suggests using multiple databases and considering other geographies beyond the United States to further understand the etiology of sexual dimorphism in COVID-19 and expand generalizability. “In addition, future research will seek to provide insights into health equity gaps in the management of COVID-19. This may inform development of precision medicines and vaccines, especially among patients on immunosuppressive treatments,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Zhou and other study authors are Pfizer employees and hold Pfizer stock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET SUMMIT ON SEX AND GENDER IN RHEUMATOLOGY
Consider the mnemonic ‘CLEAR’ when counseling acne patients
to use when treating this group of patients.
During a presentation at Medscape Live’s annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, Dr. Harper, who practices at Dermatology and Skin Care of Birmingham, Ala., elaborated on the mnemonic, as follows:
C: Communicate expectations. “I look right at the acne patient and say, ‘I know you don’t just want to be better; I know you want to be clear,’ ” she said at the meeting. “ ‘That’s my goal for you, too. That may take us more than one visit and more than one treatment, but I am on your team, and that’s what we’re shooting for.’ If you don’t communicate that, they’re going to think that their acne is not that important to you.”
L: Listen for clues to customize the patient’s treatment. “We’re quick to say, ‘my patients don’t do what I recommend,’ or ‘they didn’t do what the last doctor recommended,’ ” Dr. Harper said. “Sometimes that is true, but there may be a reason why. Maybe the medication was too expensive. Maybe it was bleaching their fabrics. Maybe the regimen was too complex. Listen for opportunities to make adjustments to get their acne closer to clear.”
E: Treat early to improve quality of life and to decrease the risk of scarring. “I have a laser in my practice that is good at treating acne scarring,” she said. “Do I ever look at my patient and say, ‘don’t worry about those scars; I can make them go away?’ No. I look at them and say, ‘we can maybe make this 40% better,’ something like that. We have to prevent acne scars, because we’re not good at treating them.”
A: Treat aggressively with more combination therapies, more hormonal therapies, more isotretinoin, and perhaps more prior authorizations. She characterized the effort to obtain a prior authorization as “our megaphone back to insurance companies that says, ‘we think it is worth taking the time to do this prior authorization because the acne patient will benefit.’ ”
R: Don’t resist isotretinoin. Dr. Harper, who began practicing dermatology more than 20 years ago, said that over time, she has gradually prescribed more isotretinoin for her patients with acne. “It’s not a first-line [treatment], but I’m not afraid of it. If I can’t get somebody clear on other oral or topical treatments, we are going to try isotretinoin.”
The goal of acne treatment, she added, is to affect four key aspects of pathogenesis: follicular epithelial hyperproliferation, inflammation, Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes), and sebum. “That’s what we’re always shooting for,” she said.
Dr. Harper is a past president of the American Acne & Rosacea Society. She disclosed that she serves as an advisor or consultant for Almirall, BioPharmX, Cassiopeia, Cutanea, Cutera, Dermira, EPI, Galderma, LaRoche-Posay, Ortho, Vyne, Sol Gel, and Sun. She also serves as a speaker or member of a speaker’s bureau for Almirall, EPI, Galderma, Ortho, and Vyne.
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
to use when treating this group of patients.
During a presentation at Medscape Live’s annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, Dr. Harper, who practices at Dermatology and Skin Care of Birmingham, Ala., elaborated on the mnemonic, as follows:
C: Communicate expectations. “I look right at the acne patient and say, ‘I know you don’t just want to be better; I know you want to be clear,’ ” she said at the meeting. “ ‘That’s my goal for you, too. That may take us more than one visit and more than one treatment, but I am on your team, and that’s what we’re shooting for.’ If you don’t communicate that, they’re going to think that their acne is not that important to you.”
L: Listen for clues to customize the patient’s treatment. “We’re quick to say, ‘my patients don’t do what I recommend,’ or ‘they didn’t do what the last doctor recommended,’ ” Dr. Harper said. “Sometimes that is true, but there may be a reason why. Maybe the medication was too expensive. Maybe it was bleaching their fabrics. Maybe the regimen was too complex. Listen for opportunities to make adjustments to get their acne closer to clear.”
E: Treat early to improve quality of life and to decrease the risk of scarring. “I have a laser in my practice that is good at treating acne scarring,” she said. “Do I ever look at my patient and say, ‘don’t worry about those scars; I can make them go away?’ No. I look at them and say, ‘we can maybe make this 40% better,’ something like that. We have to prevent acne scars, because we’re not good at treating them.”
A: Treat aggressively with more combination therapies, more hormonal therapies, more isotretinoin, and perhaps more prior authorizations. She characterized the effort to obtain a prior authorization as “our megaphone back to insurance companies that says, ‘we think it is worth taking the time to do this prior authorization because the acne patient will benefit.’ ”
R: Don’t resist isotretinoin. Dr. Harper, who began practicing dermatology more than 20 years ago, said that over time, she has gradually prescribed more isotretinoin for her patients with acne. “It’s not a first-line [treatment], but I’m not afraid of it. If I can’t get somebody clear on other oral or topical treatments, we are going to try isotretinoin.”
The goal of acne treatment, she added, is to affect four key aspects of pathogenesis: follicular epithelial hyperproliferation, inflammation, Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes), and sebum. “That’s what we’re always shooting for,” she said.
Dr. Harper is a past president of the American Acne & Rosacea Society. She disclosed that she serves as an advisor or consultant for Almirall, BioPharmX, Cassiopeia, Cutanea, Cutera, Dermira, EPI, Galderma, LaRoche-Posay, Ortho, Vyne, Sol Gel, and Sun. She also serves as a speaker or member of a speaker’s bureau for Almirall, EPI, Galderma, Ortho, and Vyne.
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
to use when treating this group of patients.
During a presentation at Medscape Live’s annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, Dr. Harper, who practices at Dermatology and Skin Care of Birmingham, Ala., elaborated on the mnemonic, as follows:
C: Communicate expectations. “I look right at the acne patient and say, ‘I know you don’t just want to be better; I know you want to be clear,’ ” she said at the meeting. “ ‘That’s my goal for you, too. That may take us more than one visit and more than one treatment, but I am on your team, and that’s what we’re shooting for.’ If you don’t communicate that, they’re going to think that their acne is not that important to you.”
L: Listen for clues to customize the patient’s treatment. “We’re quick to say, ‘my patients don’t do what I recommend,’ or ‘they didn’t do what the last doctor recommended,’ ” Dr. Harper said. “Sometimes that is true, but there may be a reason why. Maybe the medication was too expensive. Maybe it was bleaching their fabrics. Maybe the regimen was too complex. Listen for opportunities to make adjustments to get their acne closer to clear.”
E: Treat early to improve quality of life and to decrease the risk of scarring. “I have a laser in my practice that is good at treating acne scarring,” she said. “Do I ever look at my patient and say, ‘don’t worry about those scars; I can make them go away?’ No. I look at them and say, ‘we can maybe make this 40% better,’ something like that. We have to prevent acne scars, because we’re not good at treating them.”
A: Treat aggressively with more combination therapies, more hormonal therapies, more isotretinoin, and perhaps more prior authorizations. She characterized the effort to obtain a prior authorization as “our megaphone back to insurance companies that says, ‘we think it is worth taking the time to do this prior authorization because the acne patient will benefit.’ ”
R: Don’t resist isotretinoin. Dr. Harper, who began practicing dermatology more than 20 years ago, said that over time, she has gradually prescribed more isotretinoin for her patients with acne. “It’s not a first-line [treatment], but I’m not afraid of it. If I can’t get somebody clear on other oral or topical treatments, we are going to try isotretinoin.”
The goal of acne treatment, she added, is to affect four key aspects of pathogenesis: follicular epithelial hyperproliferation, inflammation, Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes), and sebum. “That’s what we’re always shooting for,” she said.
Dr. Harper is a past president of the American Acne & Rosacea Society. She disclosed that she serves as an advisor or consultant for Almirall, BioPharmX, Cassiopeia, Cutanea, Cutera, Dermira, EPI, Galderma, LaRoche-Posay, Ortho, Vyne, Sol Gel, and Sun. She also serves as a speaker or member of a speaker’s bureau for Almirall, EPI, Galderma, Ortho, and Vyne.
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM MEDSCAPE LIVE COASTAL DERM
Type 1 diabetes cases poised to double worldwide by 2040
STOCKHOLM – The number of people living with type 1 diabetes worldwide is expected to double by 2040, with most new cases among adults living in low- and middle-income countries, new modeling data suggest.
The forecast, developed from available data collected in the newly established open-source Type 1 Diabetes Index, provides estimates for type 1 diabetes prevalence, incidence, associated mortality, and life expectancy for 201 countries for 2021.
The model also projects estimates for prevalent cases in 2040. It is the first type 1 diabetes dataset to account for the lack of prevalence because of premature mortality, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
“The worldwide prevalence of type 1 diabetes is substantial and growing. Improved surveillance – particularly in adults who make up most of the population living with type 1 diabetes – is essential to enable improvements to care and outcomes. There is an opportunity to save millions of lives in the coming decades by raising the standard of care (including ensuring universal access to insulin and other essential supplies) and increasing awareness of the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes to enable a 100% rate of diagnosis in all countries,” the authors write.
“This work spells out the need for early diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and timely access to quality care,” said Chantal Mathieu, MD, at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes annual meeting.
One in five deaths from type 1 diabetes in under 25s
The new findings were published in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology by Gabriel A. Gregory, MD, of Life for a Child Program, New South Wales, Australia, and colleagues. The T1D Index Project database was published Sept. 21, 2022.
According to the model, about 8.4 million people were living with type 1 diabetes in 2021, with one-fifth from low- and middle-income countries. An additional 3.7 million died prematurely and would have been added to that count had they lived. One in five of all deaths caused by type 1 diabetes in 2021 is estimated to have occurred in people younger than age 25 years because of nondiagnosis.
“It is unacceptable that, in 2022, some 35,000 people worldwide are dying undiagnosed within a year of onset of symptoms. There also continues to be a huge disparity in life expectancy for people with type 1 diabetes, hitting those in the poorest countries hardest,” noted Dr. Mathieu, who is senior vice-president of EASD and an endocrinologist based at KU Leuven, Belgium.
By 2040, the model predicts that between 13.5 million and 17.4 million people will be living with the condition, with the largest relative increase from 2021 in low-income and lower-middle-income countries. The majority of incident and prevalent cases of type 1 diabetes are in adults, with an estimated 62% of 510,000 new diagnoses worldwide in 2021 occurring in people aged 20 years and older.
Type 1 diabetes is not predominantly a disease of childhood
Dr. Mathieu also noted that the data dispute the long-held view of type 1 diabetes as a predominantly pediatric condition. Indeed, worldwide, the median age for a person living with type 1 diabetes is 37 years.
“While type 1 diabetes is often referred to as ‘child-onset’ diabetes, this important study shows that only around one in five living with the condition are aged 20 years or younger, two-thirds are aged 20-64 years, and a further one in five are aged 65 years or older.”
“This condition does not stop at age 18 years – the children become adults, and the adults become elderly. All countries must examine and strengthen their diagnosis and care pathways for people of all ages living with type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Mathieu emphasized.
And in an accompanying editorial, Serena Jingchuan Guo, MD, PhD, and Hui Shao, MD, PhD, point out that most studies that estimate diabetes burden have focused on type 2 diabetes, noting, “type 1 diabetes faces the challenges of misdiagnosis, underdiagnosis, high risk of complications, and premature mortality.”
The insulin affordability issue is central, point out Dr. Guo and Dr. Shao of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Safety, department of pharmaceutical evaluation and policy, University of Florida College of Pharmacy, Gainesville.
“Countries need to strengthen the price regulation and reimbursement policy for insulin while building subsidy programs to ensure insulin access and to cope with the growing demand for insulin. Meanwhile, optimizing the insulin supply chain between manufacturers and patients while seeking alternative treatment options (for example, biosimilar products) will also improve the current situation,” they conclude.
The study was funded by JDRF, of which four coauthors are employees. The editorialists have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – The number of people living with type 1 diabetes worldwide is expected to double by 2040, with most new cases among adults living in low- and middle-income countries, new modeling data suggest.
The forecast, developed from available data collected in the newly established open-source Type 1 Diabetes Index, provides estimates for type 1 diabetes prevalence, incidence, associated mortality, and life expectancy for 201 countries for 2021.
The model also projects estimates for prevalent cases in 2040. It is the first type 1 diabetes dataset to account for the lack of prevalence because of premature mortality, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
“The worldwide prevalence of type 1 diabetes is substantial and growing. Improved surveillance – particularly in adults who make up most of the population living with type 1 diabetes – is essential to enable improvements to care and outcomes. There is an opportunity to save millions of lives in the coming decades by raising the standard of care (including ensuring universal access to insulin and other essential supplies) and increasing awareness of the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes to enable a 100% rate of diagnosis in all countries,” the authors write.
“This work spells out the need for early diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and timely access to quality care,” said Chantal Mathieu, MD, at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes annual meeting.
One in five deaths from type 1 diabetes in under 25s
The new findings were published in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology by Gabriel A. Gregory, MD, of Life for a Child Program, New South Wales, Australia, and colleagues. The T1D Index Project database was published Sept. 21, 2022.
According to the model, about 8.4 million people were living with type 1 diabetes in 2021, with one-fifth from low- and middle-income countries. An additional 3.7 million died prematurely and would have been added to that count had they lived. One in five of all deaths caused by type 1 diabetes in 2021 is estimated to have occurred in people younger than age 25 years because of nondiagnosis.
“It is unacceptable that, in 2022, some 35,000 people worldwide are dying undiagnosed within a year of onset of symptoms. There also continues to be a huge disparity in life expectancy for people with type 1 diabetes, hitting those in the poorest countries hardest,” noted Dr. Mathieu, who is senior vice-president of EASD and an endocrinologist based at KU Leuven, Belgium.
By 2040, the model predicts that between 13.5 million and 17.4 million people will be living with the condition, with the largest relative increase from 2021 in low-income and lower-middle-income countries. The majority of incident and prevalent cases of type 1 diabetes are in adults, with an estimated 62% of 510,000 new diagnoses worldwide in 2021 occurring in people aged 20 years and older.
Type 1 diabetes is not predominantly a disease of childhood
Dr. Mathieu also noted that the data dispute the long-held view of type 1 diabetes as a predominantly pediatric condition. Indeed, worldwide, the median age for a person living with type 1 diabetes is 37 years.
“While type 1 diabetes is often referred to as ‘child-onset’ diabetes, this important study shows that only around one in five living with the condition are aged 20 years or younger, two-thirds are aged 20-64 years, and a further one in five are aged 65 years or older.”
“This condition does not stop at age 18 years – the children become adults, and the adults become elderly. All countries must examine and strengthen their diagnosis and care pathways for people of all ages living with type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Mathieu emphasized.
And in an accompanying editorial, Serena Jingchuan Guo, MD, PhD, and Hui Shao, MD, PhD, point out that most studies that estimate diabetes burden have focused on type 2 diabetes, noting, “type 1 diabetes faces the challenges of misdiagnosis, underdiagnosis, high risk of complications, and premature mortality.”
The insulin affordability issue is central, point out Dr. Guo and Dr. Shao of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Safety, department of pharmaceutical evaluation and policy, University of Florida College of Pharmacy, Gainesville.
“Countries need to strengthen the price regulation and reimbursement policy for insulin while building subsidy programs to ensure insulin access and to cope with the growing demand for insulin. Meanwhile, optimizing the insulin supply chain between manufacturers and patients while seeking alternative treatment options (for example, biosimilar products) will also improve the current situation,” they conclude.
The study was funded by JDRF, of which four coauthors are employees. The editorialists have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – The number of people living with type 1 diabetes worldwide is expected to double by 2040, with most new cases among adults living in low- and middle-income countries, new modeling data suggest.
The forecast, developed from available data collected in the newly established open-source Type 1 Diabetes Index, provides estimates for type 1 diabetes prevalence, incidence, associated mortality, and life expectancy for 201 countries for 2021.
The model also projects estimates for prevalent cases in 2040. It is the first type 1 diabetes dataset to account for the lack of prevalence because of premature mortality, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
“The worldwide prevalence of type 1 diabetes is substantial and growing. Improved surveillance – particularly in adults who make up most of the population living with type 1 diabetes – is essential to enable improvements to care and outcomes. There is an opportunity to save millions of lives in the coming decades by raising the standard of care (including ensuring universal access to insulin and other essential supplies) and increasing awareness of the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes to enable a 100% rate of diagnosis in all countries,” the authors write.
“This work spells out the need for early diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and timely access to quality care,” said Chantal Mathieu, MD, at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes annual meeting.
One in five deaths from type 1 diabetes in under 25s
The new findings were published in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology by Gabriel A. Gregory, MD, of Life for a Child Program, New South Wales, Australia, and colleagues. The T1D Index Project database was published Sept. 21, 2022.
According to the model, about 8.4 million people were living with type 1 diabetes in 2021, with one-fifth from low- and middle-income countries. An additional 3.7 million died prematurely and would have been added to that count had they lived. One in five of all deaths caused by type 1 diabetes in 2021 is estimated to have occurred in people younger than age 25 years because of nondiagnosis.
“It is unacceptable that, in 2022, some 35,000 people worldwide are dying undiagnosed within a year of onset of symptoms. There also continues to be a huge disparity in life expectancy for people with type 1 diabetes, hitting those in the poorest countries hardest,” noted Dr. Mathieu, who is senior vice-president of EASD and an endocrinologist based at KU Leuven, Belgium.
By 2040, the model predicts that between 13.5 million and 17.4 million people will be living with the condition, with the largest relative increase from 2021 in low-income and lower-middle-income countries. The majority of incident and prevalent cases of type 1 diabetes are in adults, with an estimated 62% of 510,000 new diagnoses worldwide in 2021 occurring in people aged 20 years and older.
Type 1 diabetes is not predominantly a disease of childhood
Dr. Mathieu also noted that the data dispute the long-held view of type 1 diabetes as a predominantly pediatric condition. Indeed, worldwide, the median age for a person living with type 1 diabetes is 37 years.
“While type 1 diabetes is often referred to as ‘child-onset’ diabetes, this important study shows that only around one in five living with the condition are aged 20 years or younger, two-thirds are aged 20-64 years, and a further one in five are aged 65 years or older.”
“This condition does not stop at age 18 years – the children become adults, and the adults become elderly. All countries must examine and strengthen their diagnosis and care pathways for people of all ages living with type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Mathieu emphasized.
And in an accompanying editorial, Serena Jingchuan Guo, MD, PhD, and Hui Shao, MD, PhD, point out that most studies that estimate diabetes burden have focused on type 2 diabetes, noting, “type 1 diabetes faces the challenges of misdiagnosis, underdiagnosis, high risk of complications, and premature mortality.”
The insulin affordability issue is central, point out Dr. Guo and Dr. Shao of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Safety, department of pharmaceutical evaluation and policy, University of Florida College of Pharmacy, Gainesville.
“Countries need to strengthen the price regulation and reimbursement policy for insulin while building subsidy programs to ensure insulin access and to cope with the growing demand for insulin. Meanwhile, optimizing the insulin supply chain between manufacturers and patients while seeking alternative treatment options (for example, biosimilar products) will also improve the current situation,” they conclude.
The study was funded by JDRF, of which four coauthors are employees. The editorialists have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2022
Cre8 EVO stent loses sweet spot in diabetes at 2 years: SUGAR
BOSTON – Despite a promising start, extended follow-up from the SUGAR trial found that the Cre8 EVO drug-eluting stent could not maintain superiority over the Resolute Onyx DES at 2 years in patients with diabetes undergoing revascularization for coronary artery disease.
The Cre8 EVO stent (Alvimedica) is not available in the United States but, as previously reported, caused a stir last year after demonstrating a 35% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint of target lesion failure (TLF) at 1 year in a prespecified superiority analysis.
At 2 years, however, the TLF rate was 10.4% with the polymer-free Cre8 EVO amphilimus-eluting stent and 12.1% with the durable polymer Resolute Onyx (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting stent, which did not achieve superiority (hazard ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-1.19).
Rates were numerically lower with the Cre8 EVO stent for the endpoint’s individual components of cardiac death (3.1% vs. 3.4%), target vessel MI (6.6% vs. 7.6%), and target lesion revascularization (4.3% vs. 4.6%).
Results were also similar between the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stents for all-cause mortality (7.1% vs. 6.8%), any MI (9.0% vs. 9.2%), target vessel revascularization (5.5% vs. 5.1%), all new revascularizations (7.6% vs. 9.4%), definite stent thrombosis (1.0% vs. 1.2%), and major adverse cardiac events (18.3% vs. 20.8%), Pablo Salinas, MD, PhD, of Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, reported at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
He noted that all-cause mortality was 7% in just 2 years in the diabetic cohort, or twice the number of cardiac deaths. “In other words, these patients had the same chance of dying from cardiac causes and noncardiac causes, so we need a more comprehensive approach to the disease. Also, if you look at all new revascularizations, roughly 50% were off target, so there is disease progression at 2 years in this population.”
Among the 586 Cre8 EVO and 589 Resolute Onyx patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), roughly half had multivessel coronary artery disease, 83% had hypertension, 81% had dyslipidemia, and 21% were current smokers. Nearly all patients had diabetes type 2 for an average of 10.6 years for Cre8 EVO and 11.4 years for Resolute Onyx, with hemoglobin A1c levels of 7.4% and 7.5%, respectively.
Although there is “insufficient evidence” the Cre8 EVO stent is superior to the Resolute Onyx stent with regard to TLF, Dr. Salinas concluded extended follow-up until 5 years is warranted.
During a discussion of the results, Dr. Salinas said he expects the 5-year results will “probably go parallel” but that it’s worth following this very valuable cohort. “There are not so many trials with 1,000 diabetic patients. We always speak about how complex they are, the results are bad, but we don’t use the diabetic population in trials,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Asked during a TCT press conference what could have caused the catch-up in TLF at 2 years, Dr. Salinas said there were only 25 primary events from years 1 to 2, driven primarily by periprocedural MI, but that the timing of restenosis was different. Events accrued “drop by drop” with the Cre8 EVO, whereas with the Resolute Onyx there was a “bump in restenosis” after 6 months “but then it is very nice to see it is flat, which means that durable polymers are also safe because we have not seen late events.”
Press conference discussant Carlo Di Mario, MD, from Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy, who was not involved in the study, said the reversal of superiority for the Cre8 EVO might be a “bitter note” for the investigators but “maybe it is not bitter for us because overall, the percentage of figures are so low that it’s very difficult to find a difference” between the two stents.
Roxana Mehran, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who previously described the 1-year results as “almost too good to be true,” commented to this news organization, “We just saw in this trial, no benefit whatsoever at 2 years in terms of target lesion failure. So it’s very important for us to evaluate this going forward.”
She continued, “We’ve always been talking about these biodegradable polymers and then going back to the bare metal stent – oh that’s great because polymers aren’t so good – but now we’re seeing durable polymers may be okay, especially with the current technology.”
Asked whether Cre8 EVO, which is CE mark certified in Europe, remains an option in light of the new results, Dr. Mehran said, “I don’t think it kills it. It’s not worse; it’s another stent that’s available.”
Nevertheless, “what we’re looking for is some efficacious benefit for diabetic patients. We don’t have one yet,” observed Dr. Mehran, who is leading the ABILITY Diabetes Global trial, which just finished enrolling 3,000 patients with diabetes and is testing PCI with the Abluminus DES+ sirolimus-eluting stent system vs. the Xience everolimus-eluting stent. The study is estimated to be complete in August 2024.
The study was funded by the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Dr. Salinas reported consulting fees/honoraria from Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Biomenco, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – Despite a promising start, extended follow-up from the SUGAR trial found that the Cre8 EVO drug-eluting stent could not maintain superiority over the Resolute Onyx DES at 2 years in patients with diabetes undergoing revascularization for coronary artery disease.
The Cre8 EVO stent (Alvimedica) is not available in the United States but, as previously reported, caused a stir last year after demonstrating a 35% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint of target lesion failure (TLF) at 1 year in a prespecified superiority analysis.
At 2 years, however, the TLF rate was 10.4% with the polymer-free Cre8 EVO amphilimus-eluting stent and 12.1% with the durable polymer Resolute Onyx (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting stent, which did not achieve superiority (hazard ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-1.19).
Rates were numerically lower with the Cre8 EVO stent for the endpoint’s individual components of cardiac death (3.1% vs. 3.4%), target vessel MI (6.6% vs. 7.6%), and target lesion revascularization (4.3% vs. 4.6%).
Results were also similar between the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stents for all-cause mortality (7.1% vs. 6.8%), any MI (9.0% vs. 9.2%), target vessel revascularization (5.5% vs. 5.1%), all new revascularizations (7.6% vs. 9.4%), definite stent thrombosis (1.0% vs. 1.2%), and major adverse cardiac events (18.3% vs. 20.8%), Pablo Salinas, MD, PhD, of Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, reported at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
He noted that all-cause mortality was 7% in just 2 years in the diabetic cohort, or twice the number of cardiac deaths. “In other words, these patients had the same chance of dying from cardiac causes and noncardiac causes, so we need a more comprehensive approach to the disease. Also, if you look at all new revascularizations, roughly 50% were off target, so there is disease progression at 2 years in this population.”
Among the 586 Cre8 EVO and 589 Resolute Onyx patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), roughly half had multivessel coronary artery disease, 83% had hypertension, 81% had dyslipidemia, and 21% were current smokers. Nearly all patients had diabetes type 2 for an average of 10.6 years for Cre8 EVO and 11.4 years for Resolute Onyx, with hemoglobin A1c levels of 7.4% and 7.5%, respectively.
Although there is “insufficient evidence” the Cre8 EVO stent is superior to the Resolute Onyx stent with regard to TLF, Dr. Salinas concluded extended follow-up until 5 years is warranted.
During a discussion of the results, Dr. Salinas said he expects the 5-year results will “probably go parallel” but that it’s worth following this very valuable cohort. “There are not so many trials with 1,000 diabetic patients. We always speak about how complex they are, the results are bad, but we don’t use the diabetic population in trials,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Asked during a TCT press conference what could have caused the catch-up in TLF at 2 years, Dr. Salinas said there were only 25 primary events from years 1 to 2, driven primarily by periprocedural MI, but that the timing of restenosis was different. Events accrued “drop by drop” with the Cre8 EVO, whereas with the Resolute Onyx there was a “bump in restenosis” after 6 months “but then it is very nice to see it is flat, which means that durable polymers are also safe because we have not seen late events.”
Press conference discussant Carlo Di Mario, MD, from Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy, who was not involved in the study, said the reversal of superiority for the Cre8 EVO might be a “bitter note” for the investigators but “maybe it is not bitter for us because overall, the percentage of figures are so low that it’s very difficult to find a difference” between the two stents.
Roxana Mehran, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who previously described the 1-year results as “almost too good to be true,” commented to this news organization, “We just saw in this trial, no benefit whatsoever at 2 years in terms of target lesion failure. So it’s very important for us to evaluate this going forward.”
She continued, “We’ve always been talking about these biodegradable polymers and then going back to the bare metal stent – oh that’s great because polymers aren’t so good – but now we’re seeing durable polymers may be okay, especially with the current technology.”
Asked whether Cre8 EVO, which is CE mark certified in Europe, remains an option in light of the new results, Dr. Mehran said, “I don’t think it kills it. It’s not worse; it’s another stent that’s available.”
Nevertheless, “what we’re looking for is some efficacious benefit for diabetic patients. We don’t have one yet,” observed Dr. Mehran, who is leading the ABILITY Diabetes Global trial, which just finished enrolling 3,000 patients with diabetes and is testing PCI with the Abluminus DES+ sirolimus-eluting stent system vs. the Xience everolimus-eluting stent. The study is estimated to be complete in August 2024.
The study was funded by the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Dr. Salinas reported consulting fees/honoraria from Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Biomenco, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – Despite a promising start, extended follow-up from the SUGAR trial found that the Cre8 EVO drug-eluting stent could not maintain superiority over the Resolute Onyx DES at 2 years in patients with diabetes undergoing revascularization for coronary artery disease.
The Cre8 EVO stent (Alvimedica) is not available in the United States but, as previously reported, caused a stir last year after demonstrating a 35% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint of target lesion failure (TLF) at 1 year in a prespecified superiority analysis.
At 2 years, however, the TLF rate was 10.4% with the polymer-free Cre8 EVO amphilimus-eluting stent and 12.1% with the durable polymer Resolute Onyx (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting stent, which did not achieve superiority (hazard ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-1.19).
Rates were numerically lower with the Cre8 EVO stent for the endpoint’s individual components of cardiac death (3.1% vs. 3.4%), target vessel MI (6.6% vs. 7.6%), and target lesion revascularization (4.3% vs. 4.6%).
Results were also similar between the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stents for all-cause mortality (7.1% vs. 6.8%), any MI (9.0% vs. 9.2%), target vessel revascularization (5.5% vs. 5.1%), all new revascularizations (7.6% vs. 9.4%), definite stent thrombosis (1.0% vs. 1.2%), and major adverse cardiac events (18.3% vs. 20.8%), Pablo Salinas, MD, PhD, of Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, reported at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting.
He noted that all-cause mortality was 7% in just 2 years in the diabetic cohort, or twice the number of cardiac deaths. “In other words, these patients had the same chance of dying from cardiac causes and noncardiac causes, so we need a more comprehensive approach to the disease. Also, if you look at all new revascularizations, roughly 50% were off target, so there is disease progression at 2 years in this population.”
Among the 586 Cre8 EVO and 589 Resolute Onyx patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), roughly half had multivessel coronary artery disease, 83% had hypertension, 81% had dyslipidemia, and 21% were current smokers. Nearly all patients had diabetes type 2 for an average of 10.6 years for Cre8 EVO and 11.4 years for Resolute Onyx, with hemoglobin A1c levels of 7.4% and 7.5%, respectively.
Although there is “insufficient evidence” the Cre8 EVO stent is superior to the Resolute Onyx stent with regard to TLF, Dr. Salinas concluded extended follow-up until 5 years is warranted.
During a discussion of the results, Dr. Salinas said he expects the 5-year results will “probably go parallel” but that it’s worth following this very valuable cohort. “There are not so many trials with 1,000 diabetic patients. We always speak about how complex they are, the results are bad, but we don’t use the diabetic population in trials,” he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Asked during a TCT press conference what could have caused the catch-up in TLF at 2 years, Dr. Salinas said there were only 25 primary events from years 1 to 2, driven primarily by periprocedural MI, but that the timing of restenosis was different. Events accrued “drop by drop” with the Cre8 EVO, whereas with the Resolute Onyx there was a “bump in restenosis” after 6 months “but then it is very nice to see it is flat, which means that durable polymers are also safe because we have not seen late events.”
Press conference discussant Carlo Di Mario, MD, from Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy, who was not involved in the study, said the reversal of superiority for the Cre8 EVO might be a “bitter note” for the investigators but “maybe it is not bitter for us because overall, the percentage of figures are so low that it’s very difficult to find a difference” between the two stents.
Roxana Mehran, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who previously described the 1-year results as “almost too good to be true,” commented to this news organization, “We just saw in this trial, no benefit whatsoever at 2 years in terms of target lesion failure. So it’s very important for us to evaluate this going forward.”
She continued, “We’ve always been talking about these biodegradable polymers and then going back to the bare metal stent – oh that’s great because polymers aren’t so good – but now we’re seeing durable polymers may be okay, especially with the current technology.”
Asked whether Cre8 EVO, which is CE mark certified in Europe, remains an option in light of the new results, Dr. Mehran said, “I don’t think it kills it. It’s not worse; it’s another stent that’s available.”
Nevertheless, “what we’re looking for is some efficacious benefit for diabetic patients. We don’t have one yet,” observed Dr. Mehran, who is leading the ABILITY Diabetes Global trial, which just finished enrolling 3,000 patients with diabetes and is testing PCI with the Abluminus DES+ sirolimus-eluting stent system vs. the Xience everolimus-eluting stent. The study is estimated to be complete in August 2024.
The study was funded by the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Dr. Salinas reported consulting fees/honoraria from Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Biomenco, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT TCT 2022
Emphasis on weight loss in new type 2 diabetes guidance
STOCKHOLM – Weight loss should be a co–primary management goal for type 2 diabetes in adults, according to a new comprehensive joint consensus report from the European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association.
And while metformin is still recommended as first-line therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes with no other comorbidities, the statement expands the indications for use of other agents or combinations of agents as initial therapy for subgroups of patients, as part of individualized and patient-centered decision-making.
Last updated in 2019, the new “Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes” statement also places increased emphasis on social determinants of health, incorporates recent clinical trial data for cardiovascular and kidney outcomes for sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonists to broaden recommendations for cardiorenal protection, and discusses health behaviors such as sleep and sitting. It also targets a wider audience than in the past by addressing health system organization to optimize delivery of diabetes care.
The new statement was presented during a 90-minute session at the annual meeting of the EASD, with 12 of its 14 European and American authors as presenters. The document was simultaneously published in Diabetologia and Diabetes Care.
During the discussion, panel member Jennifer Brigitte Green, MD, commented: “Many of these recommendations are not new. They’re modest revisions of recommendations that have been in place for years, but we know that actual implementation rates of use of these drugs in patients with established comorbidities are very low.”
“I think it’s time for communities, health care systems, etc, to actually introduce these as expectations of care... to assess quality because unless it’s considered formally to be a requirement of care I just don’t think we’re going to move that needle very much,” added Dr. Green, who is professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Vanita R. Aroda, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, commented: “In the past, sometimes these recommendations created fodder for debate, but I don’t think this one will. It’s just really solidly evidence based, with the rationales presented throughout, including the figures. I think just having very clear evidence-based directions should support their dissemination and use.”
Weight management plays a prominent role in treatment
In an interview, writing panel cochair John B. Buse, MD, PhD, said: “We are saying that the four major components of type 2 diabetes care are glycemic management, cardiovascular risk management, weight management, and prevention of end-organ damage, particularly with regard to cardiorenal risk.”
“The weight management piece is much more explicit now,” said Dr. Buse, director of the Diabetes Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
He noted that recent evidence from the intensive lifestyle trial DiRECT, conducted in the United Kingdom, the bariatric surgery literature, and the emergence of potent weight-loss drugs have meant that “achieving 10%-15% body weight loss is now possible.
“So, aiming for remission is something that might be attractive to patients and providers. This could be based on weight management, with the [chosen] method based on shared decision-making.”
According to the new report: “Weight loss of 5%-10% confers metabolic improvement; weight loss of 10%-15% or more can have a disease-modifying effect and lead to remission of diabetes, defined as normal blood glucose levels for 3 months or more in the absence of pharmacological therapy in a 2021 consensus report.”
“Weight loss may exert benefits that extend beyond glycemic management to improve risk factors for cardiometabolic disease and quality of life,” it adds.
Individualization featured throughout
The report’s sections cover principles of care, including the importance of diabetes self-management education and support and avoidance of therapeutic inertia. Detailed guidance addresses therapeutic options including lifestyle, weight management, and pharmacotherapy for treating type 2 diabetes.
Another entire section is devoted to personalizing treatment approaches based on individual characteristics, including new evidence from cardiorenal outcomes studies for SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists that have come out since the last consensus report.
The document advises: “Consider initial combination therapy with glucose-lowering agents, especially in those with high [hemoglobin] A1c at diagnosis (that is, > 70 mmol/mol [> 8.5%]), in younger people with type 2 diabetes (regardless of A1c), and in those in whom a stepwise approach would delay access to agents that provide cardiorenal protection beyond their glucose-lowering effects.”
Designed to be used and user-friendly
Under the “Putting it all together: strategies for implementation” section, several lists of “practical tips for clinicians” are provided for many of the topics covered.
A series of colorful infographics are included as well, addressing the “decision cycle for person-centered glycemic management in type 2 diabetes,” including a chart summarizing characteristics of available glucose-lowering medications, including cardiorenal protection.
Also mentioned is the importance of 24-hour physical behaviors (including sleep, sitting, and sweating) and the impact on cardiometabolic health, use of a “holistic person-centered approach” to type 2 diabetes management, and an algorithm on insulin use.
Dr. Buse has financial ties to numerous drug and device companies. Dr. Green is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim/Lilly, Bayer, Sanofi, Anji, Vertex/ICON, and Valo. Dr. Aroda has served as a consultant for Applied Therapeutics, Duke, Fractyl, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Weight loss should be a co–primary management goal for type 2 diabetes in adults, according to a new comprehensive joint consensus report from the European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association.
And while metformin is still recommended as first-line therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes with no other comorbidities, the statement expands the indications for use of other agents or combinations of agents as initial therapy for subgroups of patients, as part of individualized and patient-centered decision-making.
Last updated in 2019, the new “Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes” statement also places increased emphasis on social determinants of health, incorporates recent clinical trial data for cardiovascular and kidney outcomes for sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonists to broaden recommendations for cardiorenal protection, and discusses health behaviors such as sleep and sitting. It also targets a wider audience than in the past by addressing health system organization to optimize delivery of diabetes care.
The new statement was presented during a 90-minute session at the annual meeting of the EASD, with 12 of its 14 European and American authors as presenters. The document was simultaneously published in Diabetologia and Diabetes Care.
During the discussion, panel member Jennifer Brigitte Green, MD, commented: “Many of these recommendations are not new. They’re modest revisions of recommendations that have been in place for years, but we know that actual implementation rates of use of these drugs in patients with established comorbidities are very low.”
“I think it’s time for communities, health care systems, etc, to actually introduce these as expectations of care... to assess quality because unless it’s considered formally to be a requirement of care I just don’t think we’re going to move that needle very much,” added Dr. Green, who is professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Vanita R. Aroda, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, commented: “In the past, sometimes these recommendations created fodder for debate, but I don’t think this one will. It’s just really solidly evidence based, with the rationales presented throughout, including the figures. I think just having very clear evidence-based directions should support their dissemination and use.”
Weight management plays a prominent role in treatment
In an interview, writing panel cochair John B. Buse, MD, PhD, said: “We are saying that the four major components of type 2 diabetes care are glycemic management, cardiovascular risk management, weight management, and prevention of end-organ damage, particularly with regard to cardiorenal risk.”
“The weight management piece is much more explicit now,” said Dr. Buse, director of the Diabetes Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
He noted that recent evidence from the intensive lifestyle trial DiRECT, conducted in the United Kingdom, the bariatric surgery literature, and the emergence of potent weight-loss drugs have meant that “achieving 10%-15% body weight loss is now possible.
“So, aiming for remission is something that might be attractive to patients and providers. This could be based on weight management, with the [chosen] method based on shared decision-making.”
According to the new report: “Weight loss of 5%-10% confers metabolic improvement; weight loss of 10%-15% or more can have a disease-modifying effect and lead to remission of diabetes, defined as normal blood glucose levels for 3 months or more in the absence of pharmacological therapy in a 2021 consensus report.”
“Weight loss may exert benefits that extend beyond glycemic management to improve risk factors for cardiometabolic disease and quality of life,” it adds.
Individualization featured throughout
The report’s sections cover principles of care, including the importance of diabetes self-management education and support and avoidance of therapeutic inertia. Detailed guidance addresses therapeutic options including lifestyle, weight management, and pharmacotherapy for treating type 2 diabetes.
Another entire section is devoted to personalizing treatment approaches based on individual characteristics, including new evidence from cardiorenal outcomes studies for SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists that have come out since the last consensus report.
The document advises: “Consider initial combination therapy with glucose-lowering agents, especially in those with high [hemoglobin] A1c at diagnosis (that is, > 70 mmol/mol [> 8.5%]), in younger people with type 2 diabetes (regardless of A1c), and in those in whom a stepwise approach would delay access to agents that provide cardiorenal protection beyond their glucose-lowering effects.”
Designed to be used and user-friendly
Under the “Putting it all together: strategies for implementation” section, several lists of “practical tips for clinicians” are provided for many of the topics covered.
A series of colorful infographics are included as well, addressing the “decision cycle for person-centered glycemic management in type 2 diabetes,” including a chart summarizing characteristics of available glucose-lowering medications, including cardiorenal protection.
Also mentioned is the importance of 24-hour physical behaviors (including sleep, sitting, and sweating) and the impact on cardiometabolic health, use of a “holistic person-centered approach” to type 2 diabetes management, and an algorithm on insulin use.
Dr. Buse has financial ties to numerous drug and device companies. Dr. Green is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim/Lilly, Bayer, Sanofi, Anji, Vertex/ICON, and Valo. Dr. Aroda has served as a consultant for Applied Therapeutics, Duke, Fractyl, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Weight loss should be a co–primary management goal for type 2 diabetes in adults, according to a new comprehensive joint consensus report from the European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association.
And while metformin is still recommended as first-line therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes with no other comorbidities, the statement expands the indications for use of other agents or combinations of agents as initial therapy for subgroups of patients, as part of individualized and patient-centered decision-making.
Last updated in 2019, the new “Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes” statement also places increased emphasis on social determinants of health, incorporates recent clinical trial data for cardiovascular and kidney outcomes for sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) agonists to broaden recommendations for cardiorenal protection, and discusses health behaviors such as sleep and sitting. It also targets a wider audience than in the past by addressing health system organization to optimize delivery of diabetes care.
The new statement was presented during a 90-minute session at the annual meeting of the EASD, with 12 of its 14 European and American authors as presenters. The document was simultaneously published in Diabetologia and Diabetes Care.
During the discussion, panel member Jennifer Brigitte Green, MD, commented: “Many of these recommendations are not new. They’re modest revisions of recommendations that have been in place for years, but we know that actual implementation rates of use of these drugs in patients with established comorbidities are very low.”
“I think it’s time for communities, health care systems, etc, to actually introduce these as expectations of care... to assess quality because unless it’s considered formally to be a requirement of care I just don’t think we’re going to move that needle very much,” added Dr. Green, who is professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Vanita R. Aroda, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, commented: “In the past, sometimes these recommendations created fodder for debate, but I don’t think this one will. It’s just really solidly evidence based, with the rationales presented throughout, including the figures. I think just having very clear evidence-based directions should support their dissemination and use.”
Weight management plays a prominent role in treatment
In an interview, writing panel cochair John B. Buse, MD, PhD, said: “We are saying that the four major components of type 2 diabetes care are glycemic management, cardiovascular risk management, weight management, and prevention of end-organ damage, particularly with regard to cardiorenal risk.”
“The weight management piece is much more explicit now,” said Dr. Buse, director of the Diabetes Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
He noted that recent evidence from the intensive lifestyle trial DiRECT, conducted in the United Kingdom, the bariatric surgery literature, and the emergence of potent weight-loss drugs have meant that “achieving 10%-15% body weight loss is now possible.
“So, aiming for remission is something that might be attractive to patients and providers. This could be based on weight management, with the [chosen] method based on shared decision-making.”
According to the new report: “Weight loss of 5%-10% confers metabolic improvement; weight loss of 10%-15% or more can have a disease-modifying effect and lead to remission of diabetes, defined as normal blood glucose levels for 3 months or more in the absence of pharmacological therapy in a 2021 consensus report.”
“Weight loss may exert benefits that extend beyond glycemic management to improve risk factors for cardiometabolic disease and quality of life,” it adds.
Individualization featured throughout
The report’s sections cover principles of care, including the importance of diabetes self-management education and support and avoidance of therapeutic inertia. Detailed guidance addresses therapeutic options including lifestyle, weight management, and pharmacotherapy for treating type 2 diabetes.
Another entire section is devoted to personalizing treatment approaches based on individual characteristics, including new evidence from cardiorenal outcomes studies for SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists that have come out since the last consensus report.
The document advises: “Consider initial combination therapy with glucose-lowering agents, especially in those with high [hemoglobin] A1c at diagnosis (that is, > 70 mmol/mol [> 8.5%]), in younger people with type 2 diabetes (regardless of A1c), and in those in whom a stepwise approach would delay access to agents that provide cardiorenal protection beyond their glucose-lowering effects.”
Designed to be used and user-friendly
Under the “Putting it all together: strategies for implementation” section, several lists of “practical tips for clinicians” are provided for many of the topics covered.
A series of colorful infographics are included as well, addressing the “decision cycle for person-centered glycemic management in type 2 diabetes,” including a chart summarizing characteristics of available glucose-lowering medications, including cardiorenal protection.
Also mentioned is the importance of 24-hour physical behaviors (including sleep, sitting, and sweating) and the impact on cardiometabolic health, use of a “holistic person-centered approach” to type 2 diabetes management, and an algorithm on insulin use.
Dr. Buse has financial ties to numerous drug and device companies. Dr. Green is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim/Lilly, Bayer, Sanofi, Anji, Vertex/ICON, and Valo. Dr. Aroda has served as a consultant for Applied Therapeutics, Duke, Fractyl, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2022
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy shows promise for resectable CSCC
according to results from a stage 2 clinical trial.
CSCC hasn’t received much attention from pharmaceutical companies, in part because it so often responds well to surgery or local therapy. Still, some patients develop more advanced cancer that requires surgery, often on exposed surfaces like the scalp, face, or neck. That can lead to cosmetic and functional impairment.
“Having witnessed the toxicity of treatments over time has really kind of kind of pushed me for a long time to seek better ways to treat this,” lead author Neil Gross, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Gross is director of clinical research in the department of head and neck surgery at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was presented at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Gross and colleagues conducted a pilot study that examined neoadjuvant immunotherapy with cemiplimab (Libtayo, Regeneron). It received Food and Drug Administration approval in 2018 for metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. The aim of the study was to determine how cells responded to the therapy and learn more about the biology, but the results turned heads. “We were surprised to learn just how well the patients responded, Over half of the patients had a complete pathologic response to treatment, and another 4 patients out of 20 had a near-complete pathological response. It prompted a multicenter trial to confirm whether or not what we’re seeing was real,” Dr. Gross said.
The new phase 2 study, conducted in 79 patients at centers in Australia, Germany, and the United States, was encouraging. “The results were very, very similar. About 63% overall had this really impressive pathologic response to treatment. And, it may even be an underestimation of the responses because there were several patients in the trial who responded so well that they refused surgery. Those patients were counted as nonresponders just to be most conservative,” Dr. Gross said.
“I think it will change practice. The results are just so dramatic that it’s hard to imagine it’s not going to influence how patients are treated,” he said.
Dramatic results and an attractive option
Among 79 patients in the new trial, the median age was 73 years, 85% were male, and 87% were White. About 91% of primary tumors were head and neck; 6% were stage II, 48% stage III, and 46% stage IV. All patients received four doses of 350 mg cemiplimab at 3-week intervals.
After a median follow-up of 9.7 months (range, 1.3-19.6 months), 51% achieved a pathological complete response (95% confidence interval, 39%-62%). The null hypothesis was that 25% would achieve a pathologic response. An additional 13% had a pathological major response (95% CI, 6%-22%). 25% did not achieve a pathological complete or pathological major response, which was defined as viable tumor cells representing at least 10% of the surgical specimen.
72% of patients experienced an adverse event considered by the investigator to be related to treatment, most commonly fatigue (28%), maculopapular rash (14%), and diarrhea (11%). 15% of patients experienced immune-related adverse events. 4% experienced a grade 3 immune-related adverse event.
Despite the encouraging results, more research needs to be done. One key question is the optimal number of treatments prior to surgery. The pilot study used two doses while the phase 2 study used four doses. Another is whether the surgical excision can be safely reduced after treatment to reduce morbidity, and still another is whether some patients can avoid radiation. “There are lots of unanswered questions that are really important to how this gets rolled out into clinical practice, but I do think that there’s no turning back. The results are so dramatic that it’s a very attractive option to patients and providers. We will have to figure out how to learn the best way to use this in practice while it’s being used,” Dr. Gross said.
Additional studies are in the planning phase, though the results are so encouraging that they might hinder future research. “Will patients be willing in the future to be randomized to the current standard of care, which would be upfront surgery and radiation for advanced disease? I don’t know. There’s a lot of thought being put into the best way to design these studies moving forward that are really advantageous to patients, but still answer these some of these fundamental questions,” Dr. Gross said.
He also noted that these studies looked at pathological responses, not overall survival or clinical outcomes. “We believe that these responses will be durable, but this has to be borne out as the data matures.”
The study was funded by Regeneron. Dr. Gross has consulted for DragonFly Therapeutics, Intuitive Surgical, Regeneron, and Sanofi/Genzyme. He has been on scientific advisory boards for PDS Biotechnology and Shattuck Labs.
according to results from a stage 2 clinical trial.
CSCC hasn’t received much attention from pharmaceutical companies, in part because it so often responds well to surgery or local therapy. Still, some patients develop more advanced cancer that requires surgery, often on exposed surfaces like the scalp, face, or neck. That can lead to cosmetic and functional impairment.
“Having witnessed the toxicity of treatments over time has really kind of kind of pushed me for a long time to seek better ways to treat this,” lead author Neil Gross, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Gross is director of clinical research in the department of head and neck surgery at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was presented at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Gross and colleagues conducted a pilot study that examined neoadjuvant immunotherapy with cemiplimab (Libtayo, Regeneron). It received Food and Drug Administration approval in 2018 for metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. The aim of the study was to determine how cells responded to the therapy and learn more about the biology, but the results turned heads. “We were surprised to learn just how well the patients responded, Over half of the patients had a complete pathologic response to treatment, and another 4 patients out of 20 had a near-complete pathological response. It prompted a multicenter trial to confirm whether or not what we’re seeing was real,” Dr. Gross said.
The new phase 2 study, conducted in 79 patients at centers in Australia, Germany, and the United States, was encouraging. “The results were very, very similar. About 63% overall had this really impressive pathologic response to treatment. And, it may even be an underestimation of the responses because there were several patients in the trial who responded so well that they refused surgery. Those patients were counted as nonresponders just to be most conservative,” Dr. Gross said.
“I think it will change practice. The results are just so dramatic that it’s hard to imagine it’s not going to influence how patients are treated,” he said.
Dramatic results and an attractive option
Among 79 patients in the new trial, the median age was 73 years, 85% were male, and 87% were White. About 91% of primary tumors were head and neck; 6% were stage II, 48% stage III, and 46% stage IV. All patients received four doses of 350 mg cemiplimab at 3-week intervals.
After a median follow-up of 9.7 months (range, 1.3-19.6 months), 51% achieved a pathological complete response (95% confidence interval, 39%-62%). The null hypothesis was that 25% would achieve a pathologic response. An additional 13% had a pathological major response (95% CI, 6%-22%). 25% did not achieve a pathological complete or pathological major response, which was defined as viable tumor cells representing at least 10% of the surgical specimen.
72% of patients experienced an adverse event considered by the investigator to be related to treatment, most commonly fatigue (28%), maculopapular rash (14%), and diarrhea (11%). 15% of patients experienced immune-related adverse events. 4% experienced a grade 3 immune-related adverse event.
Despite the encouraging results, more research needs to be done. One key question is the optimal number of treatments prior to surgery. The pilot study used two doses while the phase 2 study used four doses. Another is whether the surgical excision can be safely reduced after treatment to reduce morbidity, and still another is whether some patients can avoid radiation. “There are lots of unanswered questions that are really important to how this gets rolled out into clinical practice, but I do think that there’s no turning back. The results are so dramatic that it’s a very attractive option to patients and providers. We will have to figure out how to learn the best way to use this in practice while it’s being used,” Dr. Gross said.
Additional studies are in the planning phase, though the results are so encouraging that they might hinder future research. “Will patients be willing in the future to be randomized to the current standard of care, which would be upfront surgery and radiation for advanced disease? I don’t know. There’s a lot of thought being put into the best way to design these studies moving forward that are really advantageous to patients, but still answer these some of these fundamental questions,” Dr. Gross said.
He also noted that these studies looked at pathological responses, not overall survival or clinical outcomes. “We believe that these responses will be durable, but this has to be borne out as the data matures.”
The study was funded by Regeneron. Dr. Gross has consulted for DragonFly Therapeutics, Intuitive Surgical, Regeneron, and Sanofi/Genzyme. He has been on scientific advisory boards for PDS Biotechnology and Shattuck Labs.
according to results from a stage 2 clinical trial.
CSCC hasn’t received much attention from pharmaceutical companies, in part because it so often responds well to surgery or local therapy. Still, some patients develop more advanced cancer that requires surgery, often on exposed surfaces like the scalp, face, or neck. That can lead to cosmetic and functional impairment.
“Having witnessed the toxicity of treatments over time has really kind of kind of pushed me for a long time to seek better ways to treat this,” lead author Neil Gross, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Gross is director of clinical research in the department of head and neck surgery at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was presented at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Gross and colleagues conducted a pilot study that examined neoadjuvant immunotherapy with cemiplimab (Libtayo, Regeneron). It received Food and Drug Administration approval in 2018 for metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. The aim of the study was to determine how cells responded to the therapy and learn more about the biology, but the results turned heads. “We were surprised to learn just how well the patients responded, Over half of the patients had a complete pathologic response to treatment, and another 4 patients out of 20 had a near-complete pathological response. It prompted a multicenter trial to confirm whether or not what we’re seeing was real,” Dr. Gross said.
The new phase 2 study, conducted in 79 patients at centers in Australia, Germany, and the United States, was encouraging. “The results were very, very similar. About 63% overall had this really impressive pathologic response to treatment. And, it may even be an underestimation of the responses because there were several patients in the trial who responded so well that they refused surgery. Those patients were counted as nonresponders just to be most conservative,” Dr. Gross said.
“I think it will change practice. The results are just so dramatic that it’s hard to imagine it’s not going to influence how patients are treated,” he said.
Dramatic results and an attractive option
Among 79 patients in the new trial, the median age was 73 years, 85% were male, and 87% were White. About 91% of primary tumors were head and neck; 6% were stage II, 48% stage III, and 46% stage IV. All patients received four doses of 350 mg cemiplimab at 3-week intervals.
After a median follow-up of 9.7 months (range, 1.3-19.6 months), 51% achieved a pathological complete response (95% confidence interval, 39%-62%). The null hypothesis was that 25% would achieve a pathologic response. An additional 13% had a pathological major response (95% CI, 6%-22%). 25% did not achieve a pathological complete or pathological major response, which was defined as viable tumor cells representing at least 10% of the surgical specimen.
72% of patients experienced an adverse event considered by the investigator to be related to treatment, most commonly fatigue (28%), maculopapular rash (14%), and diarrhea (11%). 15% of patients experienced immune-related adverse events. 4% experienced a grade 3 immune-related adverse event.
Despite the encouraging results, more research needs to be done. One key question is the optimal number of treatments prior to surgery. The pilot study used two doses while the phase 2 study used four doses. Another is whether the surgical excision can be safely reduced after treatment to reduce morbidity, and still another is whether some patients can avoid radiation. “There are lots of unanswered questions that are really important to how this gets rolled out into clinical practice, but I do think that there’s no turning back. The results are so dramatic that it’s a very attractive option to patients and providers. We will have to figure out how to learn the best way to use this in practice while it’s being used,” Dr. Gross said.
Additional studies are in the planning phase, though the results are so encouraging that they might hinder future research. “Will patients be willing in the future to be randomized to the current standard of care, which would be upfront surgery and radiation for advanced disease? I don’t know. There’s a lot of thought being put into the best way to design these studies moving forward that are really advantageous to patients, but still answer these some of these fundamental questions,” Dr. Gross said.
He also noted that these studies looked at pathological responses, not overall survival or clinical outcomes. “We believe that these responses will be durable, but this has to be borne out as the data matures.”
The study was funded by Regeneron. Dr. Gross has consulted for DragonFly Therapeutics, Intuitive Surgical, Regeneron, and Sanofi/Genzyme. He has been on scientific advisory boards for PDS Biotechnology and Shattuck Labs.
FROM ESMO CONGRESS 2022
Add PCSK9 inhibitor to high-intensity statin at primary PCI, proposes sham-controlled EPIC-STEMI
It’s best to have patients on aggressive lipid-lowering therapy before discharge after an acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), so why not start it right away – even in the cath lab – using some of the most potent LDL cholesterol–lowering agents available?
That was a main idea behind the randomized, sham-controlled EPIC-STEMI trial, in which STEMI patients were started on a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibitor immediately before direct percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and on top of high-intensity statins.
Those in the trial getting the active agent showed a 22% drop in LDL cholesterol levels by 6 weeks, compared with the control group given a sham injection along with high-intensity statins. They were also more likely to meet LDL cholesterol goals specified in some guidelines, including reduction by at least 50%. And those outcomes were achieved regardless of baseline LDL cholesterol levels or prior statin use.
Adoption of the trial’s early, aggressive LDL cholesterolreduction strategy in practice “has the potential to substantially reduce morbidity and mortality” in such cases “by further reducing LDL beyond statins in a much greater number of high-risk patients than are currently being treated with these agents,” suggested principal investigator Shamir R. Mehta, MD, MSc, when presenting the findings at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Adherence to secondary prevention measures in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is much better if they are started before hospital discharge, explained Dr. Mehta, senior scientist with Population Health Research Institute and professor of medicine at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. But “as soon as the patient has left the hospital, it is much more difficult to get these therapies on board.”
Routine adoption of such aggressive in-hospital, lipid-lowering therapy for the vast population with ACS would likely mean far fewer deaths and cardiovascular events “across a broader patient population.”
EPIC-STEMI is among the first studies to explore the strategy. “I think that’s the point of the trial that we wanted to make, that we don’t yet have data on this. We’re treading very carefully with PCSK9 inhibitors, and it’s just inching forward in populations. And I think we need a bold trial to see whether or not this changes things.”
The PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab (Praluent) was used in EPIC-STEMI, which was published in EuroIntervention, with Dr. Mehta as lead author, the same day as his presentation. The drug and its sham injection were given on top of either atorvastatin 40-80 mg or rosuvastatin 40 mg.
Early initiation of statins in patients with acute STEMI has become standard, but there’s good evidence from intracoronary imaging studies suggesting that the addition of PCSK9 inhibitors might promote further stabilization of plaques that could potentially cause recurrent ischemic events.
Treatment with the injectable drugs plus statins led to significant coronary lesion regression in the GLAGOV trial of patients with stable coronary disease. And initiation of PCSK9 inhibitors with high-intensity statins soon after PCI for ACS improved atheroma shrinkage in non–infarct-related arteries over 1 year in the recent, placebo-controlled PACMAN-AMI trial.
Dr. Mehta pointed out that LDL reductions on PCSK9 inhibition, compared with the sham control, weren’t necessarily as impressive as might be expected from the major trials of long-term therapy with the drugs.
“You need longer [therapy] in order to see a difference in LDL levels when you use a PCSK9 inhibitor acutely. This is shown also on measures of infarct size.” There was no difference between treatment groups in infarct size as measured by levels of the MB fraction of creatine kinase, he reported.
“What this is telling us is that the acute use of a PCSK9 inhibitor did not modify the size or the severity of the baseline STEMI event.”
And EPIC-STEMI was too small and never intended to assess clinical outcomes; it was more about feasibility and what degree of LDL cholesterol lowering might be expected.
The trial was needed, Dr. Mehta said, because the PCSK9 inhibitors haven’t been extensively adopted into clinical practice and are not getting to the patients who could most benefit. One of the reasons for that is quite clear to him. “We are missing the high-risk patients because we are not treating them acutely,” Dr. Mehta said in an interview.
The strategy “has not yet been evaluated, and there have been barriers,” he observed. “Cost has been a barrier. Access to the drug has been a barrier. But in terms of the science, in terms of reducing cardiovascular events, this is a strategy that has to be tested.”
The aggressive, early LDL cholesterol reduction strategy should be evaluated for its effect on long-term outcomes, “especially knowing that in the first 30 days to 6 months post STEMI there’s a tremendous uptick in ischemic events, including recurrent myocardial infarction,” Roxana Mehran, MD, said at a media briefing on EPIC-STEMI held before Dr. Mehta’s formal presentation.
The “fantastic reduction acutely” with a PCSK9 inhibitor on top of statins, “hopefully reducing inflammation” similarly to what’s been observed in past trials, “absolutely warrants” a STEMI clinical outcomes trial, said Dr. Mehran, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who isn’t connected with EPIC-STEMI.
If better post-discharge medication adherence is one of the acute strategy’s goals, it will be important to consider the potential influence of prescribing a periodically injected drug, proposed Eric A. Cohen, MD, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center, Toronto, at the press conference.
“Keep in mind that STEMI patients typically come to the hospital on zero medications and leave 2 days later on five medications,” Dr. Cohen observed. “I’m curious whether having one of those as a sub-Q injection every 2 weeks, and reducing the pill burden, will help or deter adherence to therapy. I think it’s worth studying.”
The trial originally included 97 patients undergoing PCI for STEMI who were randomly assigned to receive the PCSK9 inhibitor or a sham injection on top of high-intensity statins, without regard to LDL cholesterol levels. Randomization took place after diagnostic angiography but before PCI.
The analysis, however, subsequently excluded 29 patients who could not continue with the study, “mainly because of hospital research clinic closure due to the COVID-19 pandemic,” the published report states.
That left 68 patients who had received at least one dose of PCSK9 inhibitor, alirocumab 150 mg subcutaneously, or the sham injection, and had at least one blood draw for LDL cholesterol response which, Dr. Mehta said, still left adequate statistical power for the LDL cholesterol–based primary endpoint.
By 6 weeks, LDL cholesterol levels had fallen 72.9% in the active-therapy group and by 48.1% in the control group (P < .001). Also, 92.1% and 56.7% of patients, respectively (P = .002), had achieved levels below the 1.4 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) goal in the European guidelines, Dr. Mehta reported.
Levels fell more than 50% compared with baseline in 89.5% of alirocumab patients and 60% (P = .007) of controls, respectively.
There was no significant difference in rates of attaining LDL cholesterol levels below the 70 mg/dL (1.8 mmol/L) threshold specified in U.S. guidelines for very high-risk patients: 94.7% of alirocumab patients and 83.4% of controls (P = .26).
Nor did the groups differ significantly in natriuretic peptide levels, which reflect ventricular remodeling; or in 6-week change in the inflammatory biomarker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
An open-label, randomized trial scheduled to launch before the end of 2022 will explore similarly early initiation of a PCSK9 inhibitor, compared with standard lipid management, in an estimated 4,000 patients hospitalized with STEMI or non-STEMI.
The EVOLVE MI trial is looking at the monoclonal antibody evolocumab (Repatha) for its effect on the primary endpoint of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, arterial revascularization, or death from any cause over an expected 3-4 years.
EPIC-STEMI was supported in part by Sanofi. Dr. Mehta reported an unrestricted grant from Sanofi to Hamilton Health Sciences for the present study and consulting fees from Amgen, Sanofi, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen disclosed receiving grant support from and holding research contracts with Abbott Vascular; and receiving fees for consulting, honoraria, or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, and Baylis. Dr. Mehran disclosed receiving grants or research support from numerous pharmaceutical companies; receiving consultant fee or honoraria or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Novartis, Abbott Vascular, Janssen, Medtronic, Medscape/WebMD, and Cine-Med Research; and holding equity, stock, or stock options with Control Rad, Applied Therapeutics, and Elixir Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s best to have patients on aggressive lipid-lowering therapy before discharge after an acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), so why not start it right away – even in the cath lab – using some of the most potent LDL cholesterol–lowering agents available?
That was a main idea behind the randomized, sham-controlled EPIC-STEMI trial, in which STEMI patients were started on a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibitor immediately before direct percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and on top of high-intensity statins.
Those in the trial getting the active agent showed a 22% drop in LDL cholesterol levels by 6 weeks, compared with the control group given a sham injection along with high-intensity statins. They were also more likely to meet LDL cholesterol goals specified in some guidelines, including reduction by at least 50%. And those outcomes were achieved regardless of baseline LDL cholesterol levels or prior statin use.
Adoption of the trial’s early, aggressive LDL cholesterolreduction strategy in practice “has the potential to substantially reduce morbidity and mortality” in such cases “by further reducing LDL beyond statins in a much greater number of high-risk patients than are currently being treated with these agents,” suggested principal investigator Shamir R. Mehta, MD, MSc, when presenting the findings at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Adherence to secondary prevention measures in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is much better if they are started before hospital discharge, explained Dr. Mehta, senior scientist with Population Health Research Institute and professor of medicine at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. But “as soon as the patient has left the hospital, it is much more difficult to get these therapies on board.”
Routine adoption of such aggressive in-hospital, lipid-lowering therapy for the vast population with ACS would likely mean far fewer deaths and cardiovascular events “across a broader patient population.”
EPIC-STEMI is among the first studies to explore the strategy. “I think that’s the point of the trial that we wanted to make, that we don’t yet have data on this. We’re treading very carefully with PCSK9 inhibitors, and it’s just inching forward in populations. And I think we need a bold trial to see whether or not this changes things.”
The PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab (Praluent) was used in EPIC-STEMI, which was published in EuroIntervention, with Dr. Mehta as lead author, the same day as his presentation. The drug and its sham injection were given on top of either atorvastatin 40-80 mg or rosuvastatin 40 mg.
Early initiation of statins in patients with acute STEMI has become standard, but there’s good evidence from intracoronary imaging studies suggesting that the addition of PCSK9 inhibitors might promote further stabilization of plaques that could potentially cause recurrent ischemic events.
Treatment with the injectable drugs plus statins led to significant coronary lesion regression in the GLAGOV trial of patients with stable coronary disease. And initiation of PCSK9 inhibitors with high-intensity statins soon after PCI for ACS improved atheroma shrinkage in non–infarct-related arteries over 1 year in the recent, placebo-controlled PACMAN-AMI trial.
Dr. Mehta pointed out that LDL reductions on PCSK9 inhibition, compared with the sham control, weren’t necessarily as impressive as might be expected from the major trials of long-term therapy with the drugs.
“You need longer [therapy] in order to see a difference in LDL levels when you use a PCSK9 inhibitor acutely. This is shown also on measures of infarct size.” There was no difference between treatment groups in infarct size as measured by levels of the MB fraction of creatine kinase, he reported.
“What this is telling us is that the acute use of a PCSK9 inhibitor did not modify the size or the severity of the baseline STEMI event.”
And EPIC-STEMI was too small and never intended to assess clinical outcomes; it was more about feasibility and what degree of LDL cholesterol lowering might be expected.
The trial was needed, Dr. Mehta said, because the PCSK9 inhibitors haven’t been extensively adopted into clinical practice and are not getting to the patients who could most benefit. One of the reasons for that is quite clear to him. “We are missing the high-risk patients because we are not treating them acutely,” Dr. Mehta said in an interview.
The strategy “has not yet been evaluated, and there have been barriers,” he observed. “Cost has been a barrier. Access to the drug has been a barrier. But in terms of the science, in terms of reducing cardiovascular events, this is a strategy that has to be tested.”
The aggressive, early LDL cholesterol reduction strategy should be evaluated for its effect on long-term outcomes, “especially knowing that in the first 30 days to 6 months post STEMI there’s a tremendous uptick in ischemic events, including recurrent myocardial infarction,” Roxana Mehran, MD, said at a media briefing on EPIC-STEMI held before Dr. Mehta’s formal presentation.
The “fantastic reduction acutely” with a PCSK9 inhibitor on top of statins, “hopefully reducing inflammation” similarly to what’s been observed in past trials, “absolutely warrants” a STEMI clinical outcomes trial, said Dr. Mehran, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who isn’t connected with EPIC-STEMI.
If better post-discharge medication adherence is one of the acute strategy’s goals, it will be important to consider the potential influence of prescribing a periodically injected drug, proposed Eric A. Cohen, MD, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center, Toronto, at the press conference.
“Keep in mind that STEMI patients typically come to the hospital on zero medications and leave 2 days later on five medications,” Dr. Cohen observed. “I’m curious whether having one of those as a sub-Q injection every 2 weeks, and reducing the pill burden, will help or deter adherence to therapy. I think it’s worth studying.”
The trial originally included 97 patients undergoing PCI for STEMI who were randomly assigned to receive the PCSK9 inhibitor or a sham injection on top of high-intensity statins, without regard to LDL cholesterol levels. Randomization took place after diagnostic angiography but before PCI.
The analysis, however, subsequently excluded 29 patients who could not continue with the study, “mainly because of hospital research clinic closure due to the COVID-19 pandemic,” the published report states.
That left 68 patients who had received at least one dose of PCSK9 inhibitor, alirocumab 150 mg subcutaneously, or the sham injection, and had at least one blood draw for LDL cholesterol response which, Dr. Mehta said, still left adequate statistical power for the LDL cholesterol–based primary endpoint.
By 6 weeks, LDL cholesterol levels had fallen 72.9% in the active-therapy group and by 48.1% in the control group (P < .001). Also, 92.1% and 56.7% of patients, respectively (P = .002), had achieved levels below the 1.4 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) goal in the European guidelines, Dr. Mehta reported.
Levels fell more than 50% compared with baseline in 89.5% of alirocumab patients and 60% (P = .007) of controls, respectively.
There was no significant difference in rates of attaining LDL cholesterol levels below the 70 mg/dL (1.8 mmol/L) threshold specified in U.S. guidelines for very high-risk patients: 94.7% of alirocumab patients and 83.4% of controls (P = .26).
Nor did the groups differ significantly in natriuretic peptide levels, which reflect ventricular remodeling; or in 6-week change in the inflammatory biomarker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
An open-label, randomized trial scheduled to launch before the end of 2022 will explore similarly early initiation of a PCSK9 inhibitor, compared with standard lipid management, in an estimated 4,000 patients hospitalized with STEMI or non-STEMI.
The EVOLVE MI trial is looking at the monoclonal antibody evolocumab (Repatha) for its effect on the primary endpoint of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, arterial revascularization, or death from any cause over an expected 3-4 years.
EPIC-STEMI was supported in part by Sanofi. Dr. Mehta reported an unrestricted grant from Sanofi to Hamilton Health Sciences for the present study and consulting fees from Amgen, Sanofi, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen disclosed receiving grant support from and holding research contracts with Abbott Vascular; and receiving fees for consulting, honoraria, or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, and Baylis. Dr. Mehran disclosed receiving grants or research support from numerous pharmaceutical companies; receiving consultant fee or honoraria or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Novartis, Abbott Vascular, Janssen, Medtronic, Medscape/WebMD, and Cine-Med Research; and holding equity, stock, or stock options with Control Rad, Applied Therapeutics, and Elixir Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s best to have patients on aggressive lipid-lowering therapy before discharge after an acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), so why not start it right away – even in the cath lab – using some of the most potent LDL cholesterol–lowering agents available?
That was a main idea behind the randomized, sham-controlled EPIC-STEMI trial, in which STEMI patients were started on a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) inhibitor immediately before direct percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and on top of high-intensity statins.
Those in the trial getting the active agent showed a 22% drop in LDL cholesterol levels by 6 weeks, compared with the control group given a sham injection along with high-intensity statins. They were also more likely to meet LDL cholesterol goals specified in some guidelines, including reduction by at least 50%. And those outcomes were achieved regardless of baseline LDL cholesterol levels or prior statin use.
Adoption of the trial’s early, aggressive LDL cholesterolreduction strategy in practice “has the potential to substantially reduce morbidity and mortality” in such cases “by further reducing LDL beyond statins in a much greater number of high-risk patients than are currently being treated with these agents,” suggested principal investigator Shamir R. Mehta, MD, MSc, when presenting the findings at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Adherence to secondary prevention measures in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is much better if they are started before hospital discharge, explained Dr. Mehta, senior scientist with Population Health Research Institute and professor of medicine at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. But “as soon as the patient has left the hospital, it is much more difficult to get these therapies on board.”
Routine adoption of such aggressive in-hospital, lipid-lowering therapy for the vast population with ACS would likely mean far fewer deaths and cardiovascular events “across a broader patient population.”
EPIC-STEMI is among the first studies to explore the strategy. “I think that’s the point of the trial that we wanted to make, that we don’t yet have data on this. We’re treading very carefully with PCSK9 inhibitors, and it’s just inching forward in populations. And I think we need a bold trial to see whether or not this changes things.”
The PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab (Praluent) was used in EPIC-STEMI, which was published in EuroIntervention, with Dr. Mehta as lead author, the same day as his presentation. The drug and its sham injection were given on top of either atorvastatin 40-80 mg or rosuvastatin 40 mg.
Early initiation of statins in patients with acute STEMI has become standard, but there’s good evidence from intracoronary imaging studies suggesting that the addition of PCSK9 inhibitors might promote further stabilization of plaques that could potentially cause recurrent ischemic events.
Treatment with the injectable drugs plus statins led to significant coronary lesion regression in the GLAGOV trial of patients with stable coronary disease. And initiation of PCSK9 inhibitors with high-intensity statins soon after PCI for ACS improved atheroma shrinkage in non–infarct-related arteries over 1 year in the recent, placebo-controlled PACMAN-AMI trial.
Dr. Mehta pointed out that LDL reductions on PCSK9 inhibition, compared with the sham control, weren’t necessarily as impressive as might be expected from the major trials of long-term therapy with the drugs.
“You need longer [therapy] in order to see a difference in LDL levels when you use a PCSK9 inhibitor acutely. This is shown also on measures of infarct size.” There was no difference between treatment groups in infarct size as measured by levels of the MB fraction of creatine kinase, he reported.
“What this is telling us is that the acute use of a PCSK9 inhibitor did not modify the size or the severity of the baseline STEMI event.”
And EPIC-STEMI was too small and never intended to assess clinical outcomes; it was more about feasibility and what degree of LDL cholesterol lowering might be expected.
The trial was needed, Dr. Mehta said, because the PCSK9 inhibitors haven’t been extensively adopted into clinical practice and are not getting to the patients who could most benefit. One of the reasons for that is quite clear to him. “We are missing the high-risk patients because we are not treating them acutely,” Dr. Mehta said in an interview.
The strategy “has not yet been evaluated, and there have been barriers,” he observed. “Cost has been a barrier. Access to the drug has been a barrier. But in terms of the science, in terms of reducing cardiovascular events, this is a strategy that has to be tested.”
The aggressive, early LDL cholesterol reduction strategy should be evaluated for its effect on long-term outcomes, “especially knowing that in the first 30 days to 6 months post STEMI there’s a tremendous uptick in ischemic events, including recurrent myocardial infarction,” Roxana Mehran, MD, said at a media briefing on EPIC-STEMI held before Dr. Mehta’s formal presentation.
The “fantastic reduction acutely” with a PCSK9 inhibitor on top of statins, “hopefully reducing inflammation” similarly to what’s been observed in past trials, “absolutely warrants” a STEMI clinical outcomes trial, said Dr. Mehran, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who isn’t connected with EPIC-STEMI.
If better post-discharge medication adherence is one of the acute strategy’s goals, it will be important to consider the potential influence of prescribing a periodically injected drug, proposed Eric A. Cohen, MD, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center, Toronto, at the press conference.
“Keep in mind that STEMI patients typically come to the hospital on zero medications and leave 2 days later on five medications,” Dr. Cohen observed. “I’m curious whether having one of those as a sub-Q injection every 2 weeks, and reducing the pill burden, will help or deter adherence to therapy. I think it’s worth studying.”
The trial originally included 97 patients undergoing PCI for STEMI who were randomly assigned to receive the PCSK9 inhibitor or a sham injection on top of high-intensity statins, without regard to LDL cholesterol levels. Randomization took place after diagnostic angiography but before PCI.
The analysis, however, subsequently excluded 29 patients who could not continue with the study, “mainly because of hospital research clinic closure due to the COVID-19 pandemic,” the published report states.
That left 68 patients who had received at least one dose of PCSK9 inhibitor, alirocumab 150 mg subcutaneously, or the sham injection, and had at least one blood draw for LDL cholesterol response which, Dr. Mehta said, still left adequate statistical power for the LDL cholesterol–based primary endpoint.
By 6 weeks, LDL cholesterol levels had fallen 72.9% in the active-therapy group and by 48.1% in the control group (P < .001). Also, 92.1% and 56.7% of patients, respectively (P = .002), had achieved levels below the 1.4 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) goal in the European guidelines, Dr. Mehta reported.
Levels fell more than 50% compared with baseline in 89.5% of alirocumab patients and 60% (P = .007) of controls, respectively.
There was no significant difference in rates of attaining LDL cholesterol levels below the 70 mg/dL (1.8 mmol/L) threshold specified in U.S. guidelines for very high-risk patients: 94.7% of alirocumab patients and 83.4% of controls (P = .26).
Nor did the groups differ significantly in natriuretic peptide levels, which reflect ventricular remodeling; or in 6-week change in the inflammatory biomarker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
An open-label, randomized trial scheduled to launch before the end of 2022 will explore similarly early initiation of a PCSK9 inhibitor, compared with standard lipid management, in an estimated 4,000 patients hospitalized with STEMI or non-STEMI.
The EVOLVE MI trial is looking at the monoclonal antibody evolocumab (Repatha) for its effect on the primary endpoint of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, arterial revascularization, or death from any cause over an expected 3-4 years.
EPIC-STEMI was supported in part by Sanofi. Dr. Mehta reported an unrestricted grant from Sanofi to Hamilton Health Sciences for the present study and consulting fees from Amgen, Sanofi, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen disclosed receiving grant support from and holding research contracts with Abbott Vascular; and receiving fees for consulting, honoraria, or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, and Baylis. Dr. Mehran disclosed receiving grants or research support from numerous pharmaceutical companies; receiving consultant fee or honoraria or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Novartis, Abbott Vascular, Janssen, Medtronic, Medscape/WebMD, and Cine-Med Research; and holding equity, stock, or stock options with Control Rad, Applied Therapeutics, and Elixir Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM TCT 2022