User login
MDedge conference coverage features onsite reporting of the latest study results and expert perspectives from leading researchers.
Topical gene therapy for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa shows promise
INDIANAPOLIS – An investigational compared with placebo, according to results from a small phase 3 study.
DEB is a serious, ultra-rare genetic blistering disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, encoding for type VII collagen and leading to skin fragility and wounds. No approved therapies are currently available. In the study, treatment was generally well tolerated.
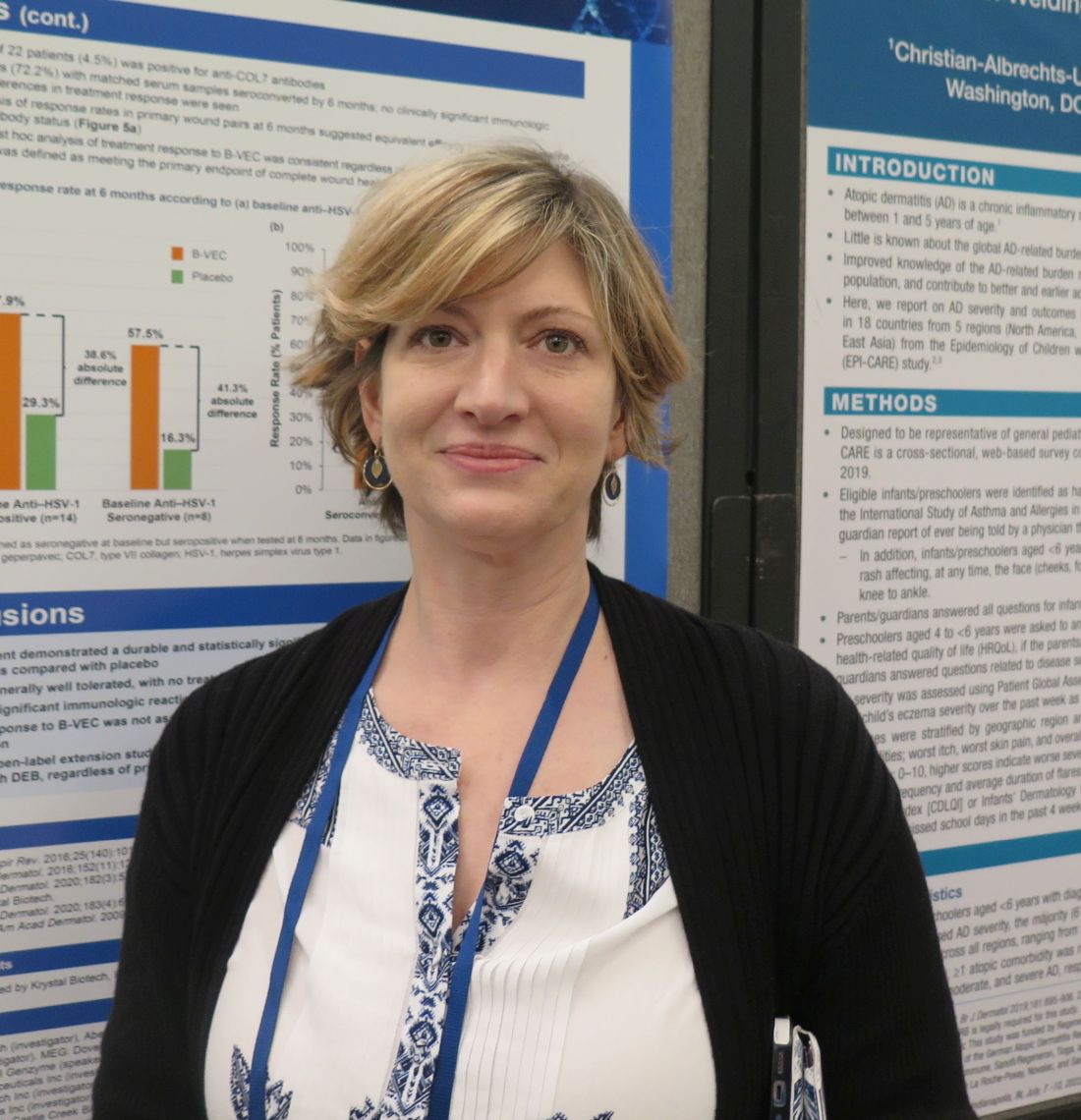
“B-VEC is the first treatment that has not only been shown to be effective, but the first to directly target the defect through topical application,” the study’s principal investigator, Shireen V. Guide, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “It delivers type VII collagen gene therapy to these patients, which allows healing in areas that they may have had open since birth. It’s been life-changing for them.”
B-VEC is a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)-based topical, redosable gene therapy being developed by Krystal Biotech that is designed to restore functional COL7 protein by delivering the COL7A1 gene. For the phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study known GEM-3, Dr. Guide, who practices dermatology in Rancho Santa Margarita, Calif., and her colleagues, including Peter Marinkovich, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, and Mercedes Gonzalez, MD, from the University of Miami, enrolled 31 patients aged 6 months and older with genetically confirmed DEB. Each patient had one wound treated randomized 1:1 to treatment with B-VEC once a week or placebo for 6 months. The mean age of the 31 study participants was 17 years, 65% were male, 65% were White, and 19% were Asian.
The primary endpoint was complete wound healing (defined as 100% wound closure from exact wound area at baseline, specified as skin re-epithelialization without drainage) at 6 months. Additional endpoints included complete wound healing at 3 months and change in pain associated with wound dressing changes.
At 3 months, 70% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing, compared with 20% of wounds treated with placebo (P < .005). At 6 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing compared with 22% of those treated with placebo (P < .005).
Of the total wounds that closed at 3 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC were also closed at 6 months, compared with 33% of those treated with placebo (P = .02). In other findings, a trend toward decreased pain was observed in wounds treated with B-VEC vs. those treated with placebo.
B-VEC was well tolerated with no treatment-related serious adverse events or discontinuations. Three patients experienced a total of five serious adverse events during the study: anemia (two events), and cellulitis, diarrhea, and positive blood culture (one event each). None were considered related to the study drug.
Dr. Guide, who is on staff at Children’s Health of Orange County, Orange, Calif., characterized B-VEC as “very novel because it’s very practical.”
To date, all treatments for DEB “have been extremely labor intensive, including skin grafting and hospitalizations. It’s a topical application that can be done in the office and potentially applied at home in the future. It’s also durable. Not only are the [treated] areas closing, but they are staying closed.”
Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was asked to comment on the study, said that topical application of B-VEC “allows the side effect profile to be very favorable. The results are remarkable in the amount of wound healing and reduction in pain.”
The tolerability of this medication “is crucial,” she added. “EB patients have a lot of pain from their wounds and so any treatment needs to be as painless as possible for it to be usable. I’m very excited about the next phase of studies for this medication and hopeful that it heralds new treatments for our EB patients.”
In June 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had submitted a biologics license application to the Food and Drug Administration for approval of B-VEC for the treatment of DEB, and that it anticipates submitting an application for marketing authorization with the European Medical Agency (EMA) in the second half of 2022.
Dr. Guide disclosed that she has served as an investigator for Krystal Biotech, Innovaderm Research, Arcutis, Premier Research, Paidion, and Castle Biosciences. Dr. Marathe disclosed that she has served as an adviser for Verrica, and that Cincinnati Children’s Hospital is a site for the next phase studies for B-VEC.
*This story was updated on July 25.
INDIANAPOLIS – An investigational compared with placebo, according to results from a small phase 3 study.
DEB is a serious, ultra-rare genetic blistering disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, encoding for type VII collagen and leading to skin fragility and wounds. No approved therapies are currently available. In the study, treatment was generally well tolerated.
“B-VEC is the first treatment that has not only been shown to be effective, but the first to directly target the defect through topical application,” the study’s principal investigator, Shireen V. Guide, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “It delivers type VII collagen gene therapy to these patients, which allows healing in areas that they may have had open since birth. It’s been life-changing for them.”
B-VEC is a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)-based topical, redosable gene therapy being developed by Krystal Biotech that is designed to restore functional COL7 protein by delivering the COL7A1 gene. For the phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study known GEM-3, Dr. Guide, who practices dermatology in Rancho Santa Margarita, Calif., and her colleagues, including Peter Marinkovich, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, and Mercedes Gonzalez, MD, from the University of Miami, enrolled 31 patients aged 6 months and older with genetically confirmed DEB. Each patient had one wound treated randomized 1:1 to treatment with B-VEC once a week or placebo for 6 months. The mean age of the 31 study participants was 17 years, 65% were male, 65% were White, and 19% were Asian.
The primary endpoint was complete wound healing (defined as 100% wound closure from exact wound area at baseline, specified as skin re-epithelialization without drainage) at 6 months. Additional endpoints included complete wound healing at 3 months and change in pain associated with wound dressing changes.
At 3 months, 70% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing, compared with 20% of wounds treated with placebo (P < .005). At 6 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing compared with 22% of those treated with placebo (P < .005).
Of the total wounds that closed at 3 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC were also closed at 6 months, compared with 33% of those treated with placebo (P = .02). In other findings, a trend toward decreased pain was observed in wounds treated with B-VEC vs. those treated with placebo.
B-VEC was well tolerated with no treatment-related serious adverse events or discontinuations. Three patients experienced a total of five serious adverse events during the study: anemia (two events), and cellulitis, diarrhea, and positive blood culture (one event each). None were considered related to the study drug.
Dr. Guide, who is on staff at Children’s Health of Orange County, Orange, Calif., characterized B-VEC as “very novel because it’s very practical.”
To date, all treatments for DEB “have been extremely labor intensive, including skin grafting and hospitalizations. It’s a topical application that can be done in the office and potentially applied at home in the future. It’s also durable. Not only are the [treated] areas closing, but they are staying closed.”
Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was asked to comment on the study, said that topical application of B-VEC “allows the side effect profile to be very favorable. The results are remarkable in the amount of wound healing and reduction in pain.”
The tolerability of this medication “is crucial,” she added. “EB patients have a lot of pain from their wounds and so any treatment needs to be as painless as possible for it to be usable. I’m very excited about the next phase of studies for this medication and hopeful that it heralds new treatments for our EB patients.”
In June 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had submitted a biologics license application to the Food and Drug Administration for approval of B-VEC for the treatment of DEB, and that it anticipates submitting an application for marketing authorization with the European Medical Agency (EMA) in the second half of 2022.
Dr. Guide disclosed that she has served as an investigator for Krystal Biotech, Innovaderm Research, Arcutis, Premier Research, Paidion, and Castle Biosciences. Dr. Marathe disclosed that she has served as an adviser for Verrica, and that Cincinnati Children’s Hospital is a site for the next phase studies for B-VEC.
*This story was updated on July 25.
INDIANAPOLIS – An investigational compared with placebo, according to results from a small phase 3 study.
DEB is a serious, ultra-rare genetic blistering disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, encoding for type VII collagen and leading to skin fragility and wounds. No approved therapies are currently available. In the study, treatment was generally well tolerated.
“B-VEC is the first treatment that has not only been shown to be effective, but the first to directly target the defect through topical application,” the study’s principal investigator, Shireen V. Guide, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “It delivers type VII collagen gene therapy to these patients, which allows healing in areas that they may have had open since birth. It’s been life-changing for them.”
B-VEC is a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)-based topical, redosable gene therapy being developed by Krystal Biotech that is designed to restore functional COL7 protein by delivering the COL7A1 gene. For the phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study known GEM-3, Dr. Guide, who practices dermatology in Rancho Santa Margarita, Calif., and her colleagues, including Peter Marinkovich, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, and Mercedes Gonzalez, MD, from the University of Miami, enrolled 31 patients aged 6 months and older with genetically confirmed DEB. Each patient had one wound treated randomized 1:1 to treatment with B-VEC once a week or placebo for 6 months. The mean age of the 31 study participants was 17 years, 65% were male, 65% were White, and 19% were Asian.
The primary endpoint was complete wound healing (defined as 100% wound closure from exact wound area at baseline, specified as skin re-epithelialization without drainage) at 6 months. Additional endpoints included complete wound healing at 3 months and change in pain associated with wound dressing changes.
At 3 months, 70% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing, compared with 20% of wounds treated with placebo (P < .005). At 6 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing compared with 22% of those treated with placebo (P < .005).
Of the total wounds that closed at 3 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC were also closed at 6 months, compared with 33% of those treated with placebo (P = .02). In other findings, a trend toward decreased pain was observed in wounds treated with B-VEC vs. those treated with placebo.
B-VEC was well tolerated with no treatment-related serious adverse events or discontinuations. Three patients experienced a total of five serious adverse events during the study: anemia (two events), and cellulitis, diarrhea, and positive blood culture (one event each). None were considered related to the study drug.
Dr. Guide, who is on staff at Children’s Health of Orange County, Orange, Calif., characterized B-VEC as “very novel because it’s very practical.”
To date, all treatments for DEB “have been extremely labor intensive, including skin grafting and hospitalizations. It’s a topical application that can be done in the office and potentially applied at home in the future. It’s also durable. Not only are the [treated] areas closing, but they are staying closed.”
Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was asked to comment on the study, said that topical application of B-VEC “allows the side effect profile to be very favorable. The results are remarkable in the amount of wound healing and reduction in pain.”
The tolerability of this medication “is crucial,” she added. “EB patients have a lot of pain from their wounds and so any treatment needs to be as painless as possible for it to be usable. I’m very excited about the next phase of studies for this medication and hopeful that it heralds new treatments for our EB patients.”
In June 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had submitted a biologics license application to the Food and Drug Administration for approval of B-VEC for the treatment of DEB, and that it anticipates submitting an application for marketing authorization with the European Medical Agency (EMA) in the second half of 2022.
Dr. Guide disclosed that she has served as an investigator for Krystal Biotech, Innovaderm Research, Arcutis, Premier Research, Paidion, and Castle Biosciences. Dr. Marathe disclosed that she has served as an adviser for Verrica, and that Cincinnati Children’s Hospital is a site for the next phase studies for B-VEC.
*This story was updated on July 25.
AT SPD 2022
Clinical characteristics of recurrent RIME elucidated in chart review
INDIANAPOLIS – , in a single-center retrospective study. In addition, 71% of patients with recurrent disease experienced 1-2 recurrences – episodes that were generally milder and occurred at variable intervals.
Those are among key findings from the study of 50 patients with RIME, presented by Catherina X. Pan at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) is a novel term encompassing an array of rare, parainfectious mucositis diseases, noted Ms. Pan, a fourth-year medical student at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM), common clinical characteristics of RIME include less than 10% body surface area involvement of polymorphic skin lesions (vesiculobullous or targetoid macules/papules); erosive oral, genital, and/or ocular mucositis involving more than two sites, and evidence of prior infection including but not limited to upper respiratory infection, fever, and cough.
In addition to M. pneumoniae, other pathogens have been implicated, she said. “While the underlying etiology of the disease is not entirely clear, it’s become increasingly known that RIME tends to recur in a subset of patients.”
A cohort study of 13 patients with RIME found that Black race, male sex, and older age were predominant among the five patients who developed recurrent disease.
The estimated recurrence rate is between 8% and 38%, but the clinical characteristics of patients who develop recurrent RIME tend to be poorly understood, Ms. Pan said.
Along with her mentor, Sadaf Hussain, MD, of the department of dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital, Ms. Pan conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the clinical history and course of disease in patients diagnosed with recurrent RIME. They extracted data between January of 2000 and March of 2022 using ICD-10 codes used by board-certified dermatologists at Boston Children’s Hospital, as well as a text search for RIME or MIRM in the dermatology notes. Patients were included if they had a RIME/MIRM diagnosis by a board-certified dermatologist and/or infection on PCR/serology and mucositis involvement with limited skin involvement.
The study population included 50 patients: 24 with recurrent RIME and 26 with isolated RIME. The majority (66%) were male, and the mean age of RIME onset was between 11 and 12 years old, which is up to two years younger than previously reported in the case series of 13 patients. Most of the study participants (79%) were White, but there were no significant differences in patients who had recurrent RIME and those who had isolated RIME in terms of age, sex, or race.
Isolated vs. recurrent RIME
However, compared with patients who had isolated RIME, a greater proportion of those with recurrent RIME had a history of atopic disease (46% vs. 23%, respectively; P = .136), as well as a history of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (25% vs. 4%; P = .045). “This has not been previously observed, but it may generate a hypothesis that patients with a history of frequent infection as well as amplified immune responses may be associated with disease recurrence,” Ms. Pan said.
The average number of episodes among patients with recurrent RIME was 3.5 and the interval between episodes was variable, at a mean of 10.2 months. Ms. Pan reported that 71% of recurrent RIME patients experienced 1-2 episodes, although one patient experienced 9 episodes.
Clinically, episodes among all patients with RIME were characterized by infectious prodromal symptoms (69%), oral lesions (95%), ocular lesions (60%), genital lesions (41%) and cutaneous lesions (40%). However, RIME recurrences were less severe and more atypical, with 49% involving only one mucosal surface and 29% involving two mucosal surfaces. Also, except for oral lesions, rates of infectious prodromal symptoms and other lesions significantly decreased among recurrences compared with initial RIME.
“Notably, we found that M. pneumoniae was the most common known cause of RIME, particularly among the initial episodes,” Ms. Pan said. “However, 61% of recurrent RIME episodes did not have a known cause in terms of infectious etiology. And, concordant with prior studies, we also found decreased severity [of RIME recurrences] as indicated by decreased rates of emergency department presentation, hospitalization, and duration of hospitalization.”
In other findings, psychiatric complications such as anxiety and depression followed the onset of RIME in 33% of those with recurrent disease and 22% of those with isolated disease. In addition, the three most common treatments among all 50 patients were systemic steroids, topical steroids, and M. pneumoniae-specific antibiotics.
“While RIME is considered as typically milder than Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis with low mortality rates, it can lead to severe complications including conjunctival shrinkage, corneal ulceration and scarring, blindness, and oral, ocular, urogenital synechiae,” Ms. Pan noted. “Increased use of corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents such as IVIG have also been observed. Multidisciplinary care with ophthalmology, urology, and mental health services is critical.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective, single-center design, and the possibility that milder cases may have been excluded due to a lack of accurate diagnosis or referral.
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study results, pointed out that nearly half (24) of patients in the cohort experienced recurrent RIME. “This is a high proportion, suggesting counseling about the possibility of recurrence is more important than previously thought,” said Dr. Coughlin, director of the section of pediatric dermatology Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
“Fortunately, recurrent cases tended to be less severe. However, many patients had more than one recurrence, making this challenging for affected patients.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
INDIANAPOLIS – , in a single-center retrospective study. In addition, 71% of patients with recurrent disease experienced 1-2 recurrences – episodes that were generally milder and occurred at variable intervals.
Those are among key findings from the study of 50 patients with RIME, presented by Catherina X. Pan at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) is a novel term encompassing an array of rare, parainfectious mucositis diseases, noted Ms. Pan, a fourth-year medical student at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM), common clinical characteristics of RIME include less than 10% body surface area involvement of polymorphic skin lesions (vesiculobullous or targetoid macules/papules); erosive oral, genital, and/or ocular mucositis involving more than two sites, and evidence of prior infection including but not limited to upper respiratory infection, fever, and cough.
In addition to M. pneumoniae, other pathogens have been implicated, she said. “While the underlying etiology of the disease is not entirely clear, it’s become increasingly known that RIME tends to recur in a subset of patients.”
A cohort study of 13 patients with RIME found that Black race, male sex, and older age were predominant among the five patients who developed recurrent disease.
The estimated recurrence rate is between 8% and 38%, but the clinical characteristics of patients who develop recurrent RIME tend to be poorly understood, Ms. Pan said.
Along with her mentor, Sadaf Hussain, MD, of the department of dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital, Ms. Pan conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the clinical history and course of disease in patients diagnosed with recurrent RIME. They extracted data between January of 2000 and March of 2022 using ICD-10 codes used by board-certified dermatologists at Boston Children’s Hospital, as well as a text search for RIME or MIRM in the dermatology notes. Patients were included if they had a RIME/MIRM diagnosis by a board-certified dermatologist and/or infection on PCR/serology and mucositis involvement with limited skin involvement.
The study population included 50 patients: 24 with recurrent RIME and 26 with isolated RIME. The majority (66%) were male, and the mean age of RIME onset was between 11 and 12 years old, which is up to two years younger than previously reported in the case series of 13 patients. Most of the study participants (79%) were White, but there were no significant differences in patients who had recurrent RIME and those who had isolated RIME in terms of age, sex, or race.
Isolated vs. recurrent RIME
However, compared with patients who had isolated RIME, a greater proportion of those with recurrent RIME had a history of atopic disease (46% vs. 23%, respectively; P = .136), as well as a history of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (25% vs. 4%; P = .045). “This has not been previously observed, but it may generate a hypothesis that patients with a history of frequent infection as well as amplified immune responses may be associated with disease recurrence,” Ms. Pan said.
The average number of episodes among patients with recurrent RIME was 3.5 and the interval between episodes was variable, at a mean of 10.2 months. Ms. Pan reported that 71% of recurrent RIME patients experienced 1-2 episodes, although one patient experienced 9 episodes.
Clinically, episodes among all patients with RIME were characterized by infectious prodromal symptoms (69%), oral lesions (95%), ocular lesions (60%), genital lesions (41%) and cutaneous lesions (40%). However, RIME recurrences were less severe and more atypical, with 49% involving only one mucosal surface and 29% involving two mucosal surfaces. Also, except for oral lesions, rates of infectious prodromal symptoms and other lesions significantly decreased among recurrences compared with initial RIME.
“Notably, we found that M. pneumoniae was the most common known cause of RIME, particularly among the initial episodes,” Ms. Pan said. “However, 61% of recurrent RIME episodes did not have a known cause in terms of infectious etiology. And, concordant with prior studies, we also found decreased severity [of RIME recurrences] as indicated by decreased rates of emergency department presentation, hospitalization, and duration of hospitalization.”
In other findings, psychiatric complications such as anxiety and depression followed the onset of RIME in 33% of those with recurrent disease and 22% of those with isolated disease. In addition, the three most common treatments among all 50 patients were systemic steroids, topical steroids, and M. pneumoniae-specific antibiotics.
“While RIME is considered as typically milder than Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis with low mortality rates, it can lead to severe complications including conjunctival shrinkage, corneal ulceration and scarring, blindness, and oral, ocular, urogenital synechiae,” Ms. Pan noted. “Increased use of corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents such as IVIG have also been observed. Multidisciplinary care with ophthalmology, urology, and mental health services is critical.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective, single-center design, and the possibility that milder cases may have been excluded due to a lack of accurate diagnosis or referral.
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study results, pointed out that nearly half (24) of patients in the cohort experienced recurrent RIME. “This is a high proportion, suggesting counseling about the possibility of recurrence is more important than previously thought,” said Dr. Coughlin, director of the section of pediatric dermatology Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
“Fortunately, recurrent cases tended to be less severe. However, many patients had more than one recurrence, making this challenging for affected patients.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
INDIANAPOLIS – , in a single-center retrospective study. In addition, 71% of patients with recurrent disease experienced 1-2 recurrences – episodes that were generally milder and occurred at variable intervals.
Those are among key findings from the study of 50 patients with RIME, presented by Catherina X. Pan at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) is a novel term encompassing an array of rare, parainfectious mucositis diseases, noted Ms. Pan, a fourth-year medical student at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM), common clinical characteristics of RIME include less than 10% body surface area involvement of polymorphic skin lesions (vesiculobullous or targetoid macules/papules); erosive oral, genital, and/or ocular mucositis involving more than two sites, and evidence of prior infection including but not limited to upper respiratory infection, fever, and cough.
In addition to M. pneumoniae, other pathogens have been implicated, she said. “While the underlying etiology of the disease is not entirely clear, it’s become increasingly known that RIME tends to recur in a subset of patients.”
A cohort study of 13 patients with RIME found that Black race, male sex, and older age were predominant among the five patients who developed recurrent disease.
The estimated recurrence rate is between 8% and 38%, but the clinical characteristics of patients who develop recurrent RIME tend to be poorly understood, Ms. Pan said.
Along with her mentor, Sadaf Hussain, MD, of the department of dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital, Ms. Pan conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the clinical history and course of disease in patients diagnosed with recurrent RIME. They extracted data between January of 2000 and March of 2022 using ICD-10 codes used by board-certified dermatologists at Boston Children’s Hospital, as well as a text search for RIME or MIRM in the dermatology notes. Patients were included if they had a RIME/MIRM diagnosis by a board-certified dermatologist and/or infection on PCR/serology and mucositis involvement with limited skin involvement.
The study population included 50 patients: 24 with recurrent RIME and 26 with isolated RIME. The majority (66%) were male, and the mean age of RIME onset was between 11 and 12 years old, which is up to two years younger than previously reported in the case series of 13 patients. Most of the study participants (79%) were White, but there were no significant differences in patients who had recurrent RIME and those who had isolated RIME in terms of age, sex, or race.
Isolated vs. recurrent RIME
However, compared with patients who had isolated RIME, a greater proportion of those with recurrent RIME had a history of atopic disease (46% vs. 23%, respectively; P = .136), as well as a history of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (25% vs. 4%; P = .045). “This has not been previously observed, but it may generate a hypothesis that patients with a history of frequent infection as well as amplified immune responses may be associated with disease recurrence,” Ms. Pan said.
The average number of episodes among patients with recurrent RIME was 3.5 and the interval between episodes was variable, at a mean of 10.2 months. Ms. Pan reported that 71% of recurrent RIME patients experienced 1-2 episodes, although one patient experienced 9 episodes.
Clinically, episodes among all patients with RIME were characterized by infectious prodromal symptoms (69%), oral lesions (95%), ocular lesions (60%), genital lesions (41%) and cutaneous lesions (40%). However, RIME recurrences were less severe and more atypical, with 49% involving only one mucosal surface and 29% involving two mucosal surfaces. Also, except for oral lesions, rates of infectious prodromal symptoms and other lesions significantly decreased among recurrences compared with initial RIME.
“Notably, we found that M. pneumoniae was the most common known cause of RIME, particularly among the initial episodes,” Ms. Pan said. “However, 61% of recurrent RIME episodes did not have a known cause in terms of infectious etiology. And, concordant with prior studies, we also found decreased severity [of RIME recurrences] as indicated by decreased rates of emergency department presentation, hospitalization, and duration of hospitalization.”
In other findings, psychiatric complications such as anxiety and depression followed the onset of RIME in 33% of those with recurrent disease and 22% of those with isolated disease. In addition, the three most common treatments among all 50 patients were systemic steroids, topical steroids, and M. pneumoniae-specific antibiotics.
“While RIME is considered as typically milder than Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis with low mortality rates, it can lead to severe complications including conjunctival shrinkage, corneal ulceration and scarring, blindness, and oral, ocular, urogenital synechiae,” Ms. Pan noted. “Increased use of corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents such as IVIG have also been observed. Multidisciplinary care with ophthalmology, urology, and mental health services is critical.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective, single-center design, and the possibility that milder cases may have been excluded due to a lack of accurate diagnosis or referral.
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study results, pointed out that nearly half (24) of patients in the cohort experienced recurrent RIME. “This is a high proportion, suggesting counseling about the possibility of recurrence is more important than previously thought,” said Dr. Coughlin, director of the section of pediatric dermatology Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
“Fortunately, recurrent cases tended to be less severe. However, many patients had more than one recurrence, making this challenging for affected patients.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
AT SPD 2022
NAFLD strongly correlated with psoriasis, PsA; risk linked to severity
NEW YORK – – and probably in those with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) as well, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Our findings imply that psoriatic patients should be screened with an ultrasonographic exam in cases where there are metabolic features that are associated with NAFLD,” reported Francesco Bellinato, MD, a researcher in the section of dermatology and venereology, University of Verona (Italy).
The data are strong. Of 76 nonduplicate publications found in the literature, the 11 observational studies included in the meta-analysis met stringent criteria, including a diagnosis of psoriasis and PsA based on objective criteria, NAFLD confirmed with liver biopsy or imaging, and odds rates calculated with 95% confidence intervals.
From these 11 studies, aggregate data were available for 249,333 psoriatic patients, of which 49% had NAFLD, and 1,491,402 were healthy controls. Among the controls, 36% had NAFLD. Four of the studies were from North America, four from Europe, and three from Asia.
In the pooled data, the risk of NAFLD among those with psoriasis relative to healthy controls fell just short of a twofold increase (odds ratio, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.70-2.26; P < .001). When stratified by studies that confirmed NAFLD by biopsy relative to ultrasonography, there was no significant heterogeneity.
Eight of the studies included an analysis of relative risk in the context of skin lesion severity defined by Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score. Relative to those without NAFLD, psoriatic patients with NAFLD had a significant greater mean PASI score on a pooled weighted mean difference analysis (OR, 3.93; 95% CI, 2.01-5.84; P < .0001).
For PsA relative to no PsA in the five studies that compared risk between these two groups, the risk of NAFLD was again nearly twofold higher. This fell short of conventional definition of statistical significance, but it was associated with a strong trend (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 0.98-3.43; P = .06).
The risk of NAFLD among patients with psoriasis was not found to vary significantly when assessed by univariable meta-regressions across numerous characteristics, such as sex and body mass index.
In one of the largest of the observational studies included in the meta-analysis by Alexis Ogdie, MD, associate professor of medicine and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues, data were analyzed in more than 1.5 million patients, which included 54,251 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. While the hazard ratio of NAFLD was increased for both psoriasis (HR, 2.23) and PsA (HR, 2.11), it was not elevated in those with RA (HR, 0.96).
Risk by severity, possible mechanisms
This study also included an analysis of NAFLD risk according to psoriasis severity. While risk was still significant among those with mild disease (HR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.07-1.30), it was almost twofold greater in those with moderate to severe psoriasis (HR, 2.23; 95% CI, 1.73-2.87).
Dr. Bellinato conceded that the mechanisms underlying the association between psoriasis and NAFLD are unknown, but he said “metaflammation” is suspected.
“The secretion of proinflammatory, prothrombotic, and oxidative stress mediators in both psoriatic skin and adipose tissue might act systemically and promote insulin resistance and other metabolic derangements that promote the development and progression of NAFLD,” Dr. Bellinato explained.
He thinks that noninvasive screening methods, such as currently used methods to calculate fibrosis score, might be useful for evaluating patients with psoriasis for NAFLD and referring them to a hepatologist when appropriate.
Given the strong association with NAFLD, Dr. Bellinato suggested that “the findings of this meta-analysis pave the way for novel, large, prospective, and histologically based studies.”
The association between psoriasis and NAFLD is clinically relevant, agreed Joel M. Gelfand, MD, vice-chair of clinical research and medical director of the clinical studies unit, department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“It is not clear if psoriasis causes fatty liver disease or vice versa, but clinicians should be aware of this association,” he said in an interview. Dr. Gelfand was a coauthor of the study by Dr. Ogdie and colleagues and led another more recent population-based study that implicated methotrexate as a factor in psoriasis-related hepatotoxicity.
If NAFLD is identified in a patient with psoriasis, treatments are limited, but Dr. Gelfand suggested that patients should be made aware of the risk. “Clinicians should encourage patients with psoriasis to take measures to protect their liver, such as avoiding drinking alcohol to excess and trying to maintain a healthy body weight,” he said.
Dr. Bellinato reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gelfand has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including those that make therapies for psoriasis.
NEW YORK – – and probably in those with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) as well, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Our findings imply that psoriatic patients should be screened with an ultrasonographic exam in cases where there are metabolic features that are associated with NAFLD,” reported Francesco Bellinato, MD, a researcher in the section of dermatology and venereology, University of Verona (Italy).
The data are strong. Of 76 nonduplicate publications found in the literature, the 11 observational studies included in the meta-analysis met stringent criteria, including a diagnosis of psoriasis and PsA based on objective criteria, NAFLD confirmed with liver biopsy or imaging, and odds rates calculated with 95% confidence intervals.
From these 11 studies, aggregate data were available for 249,333 psoriatic patients, of which 49% had NAFLD, and 1,491,402 were healthy controls. Among the controls, 36% had NAFLD. Four of the studies were from North America, four from Europe, and three from Asia.
In the pooled data, the risk of NAFLD among those with psoriasis relative to healthy controls fell just short of a twofold increase (odds ratio, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.70-2.26; P < .001). When stratified by studies that confirmed NAFLD by biopsy relative to ultrasonography, there was no significant heterogeneity.
Eight of the studies included an analysis of relative risk in the context of skin lesion severity defined by Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score. Relative to those without NAFLD, psoriatic patients with NAFLD had a significant greater mean PASI score on a pooled weighted mean difference analysis (OR, 3.93; 95% CI, 2.01-5.84; P < .0001).
For PsA relative to no PsA in the five studies that compared risk between these two groups, the risk of NAFLD was again nearly twofold higher. This fell short of conventional definition of statistical significance, but it was associated with a strong trend (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 0.98-3.43; P = .06).
The risk of NAFLD among patients with psoriasis was not found to vary significantly when assessed by univariable meta-regressions across numerous characteristics, such as sex and body mass index.
In one of the largest of the observational studies included in the meta-analysis by Alexis Ogdie, MD, associate professor of medicine and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues, data were analyzed in more than 1.5 million patients, which included 54,251 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. While the hazard ratio of NAFLD was increased for both psoriasis (HR, 2.23) and PsA (HR, 2.11), it was not elevated in those with RA (HR, 0.96).
Risk by severity, possible mechanisms
This study also included an analysis of NAFLD risk according to psoriasis severity. While risk was still significant among those with mild disease (HR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.07-1.30), it was almost twofold greater in those with moderate to severe psoriasis (HR, 2.23; 95% CI, 1.73-2.87).
Dr. Bellinato conceded that the mechanisms underlying the association between psoriasis and NAFLD are unknown, but he said “metaflammation” is suspected.
“The secretion of proinflammatory, prothrombotic, and oxidative stress mediators in both psoriatic skin and adipose tissue might act systemically and promote insulin resistance and other metabolic derangements that promote the development and progression of NAFLD,” Dr. Bellinato explained.
He thinks that noninvasive screening methods, such as currently used methods to calculate fibrosis score, might be useful for evaluating patients with psoriasis for NAFLD and referring them to a hepatologist when appropriate.
Given the strong association with NAFLD, Dr. Bellinato suggested that “the findings of this meta-analysis pave the way for novel, large, prospective, and histologically based studies.”
The association between psoriasis and NAFLD is clinically relevant, agreed Joel M. Gelfand, MD, vice-chair of clinical research and medical director of the clinical studies unit, department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“It is not clear if psoriasis causes fatty liver disease or vice versa, but clinicians should be aware of this association,” he said in an interview. Dr. Gelfand was a coauthor of the study by Dr. Ogdie and colleagues and led another more recent population-based study that implicated methotrexate as a factor in psoriasis-related hepatotoxicity.
If NAFLD is identified in a patient with psoriasis, treatments are limited, but Dr. Gelfand suggested that patients should be made aware of the risk. “Clinicians should encourage patients with psoriasis to take measures to protect their liver, such as avoiding drinking alcohol to excess and trying to maintain a healthy body weight,” he said.
Dr. Bellinato reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gelfand has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including those that make therapies for psoriasis.
NEW YORK – – and probably in those with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) as well, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Our findings imply that psoriatic patients should be screened with an ultrasonographic exam in cases where there are metabolic features that are associated with NAFLD,” reported Francesco Bellinato, MD, a researcher in the section of dermatology and venereology, University of Verona (Italy).
The data are strong. Of 76 nonduplicate publications found in the literature, the 11 observational studies included in the meta-analysis met stringent criteria, including a diagnosis of psoriasis and PsA based on objective criteria, NAFLD confirmed with liver biopsy or imaging, and odds rates calculated with 95% confidence intervals.
From these 11 studies, aggregate data were available for 249,333 psoriatic patients, of which 49% had NAFLD, and 1,491,402 were healthy controls. Among the controls, 36% had NAFLD. Four of the studies were from North America, four from Europe, and three from Asia.
In the pooled data, the risk of NAFLD among those with psoriasis relative to healthy controls fell just short of a twofold increase (odds ratio, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.70-2.26; P < .001). When stratified by studies that confirmed NAFLD by biopsy relative to ultrasonography, there was no significant heterogeneity.
Eight of the studies included an analysis of relative risk in the context of skin lesion severity defined by Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score. Relative to those without NAFLD, psoriatic patients with NAFLD had a significant greater mean PASI score on a pooled weighted mean difference analysis (OR, 3.93; 95% CI, 2.01-5.84; P < .0001).
For PsA relative to no PsA in the five studies that compared risk between these two groups, the risk of NAFLD was again nearly twofold higher. This fell short of conventional definition of statistical significance, but it was associated with a strong trend (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 0.98-3.43; P = .06).
The risk of NAFLD among patients with psoriasis was not found to vary significantly when assessed by univariable meta-regressions across numerous characteristics, such as sex and body mass index.
In one of the largest of the observational studies included in the meta-analysis by Alexis Ogdie, MD, associate professor of medicine and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues, data were analyzed in more than 1.5 million patients, which included 54,251 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. While the hazard ratio of NAFLD was increased for both psoriasis (HR, 2.23) and PsA (HR, 2.11), it was not elevated in those with RA (HR, 0.96).
Risk by severity, possible mechanisms
This study also included an analysis of NAFLD risk according to psoriasis severity. While risk was still significant among those with mild disease (HR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.07-1.30), it was almost twofold greater in those with moderate to severe psoriasis (HR, 2.23; 95% CI, 1.73-2.87).
Dr. Bellinato conceded that the mechanisms underlying the association between psoriasis and NAFLD are unknown, but he said “metaflammation” is suspected.
“The secretion of proinflammatory, prothrombotic, and oxidative stress mediators in both psoriatic skin and adipose tissue might act systemically and promote insulin resistance and other metabolic derangements that promote the development and progression of NAFLD,” Dr. Bellinato explained.
He thinks that noninvasive screening methods, such as currently used methods to calculate fibrosis score, might be useful for evaluating patients with psoriasis for NAFLD and referring them to a hepatologist when appropriate.
Given the strong association with NAFLD, Dr. Bellinato suggested that “the findings of this meta-analysis pave the way for novel, large, prospective, and histologically based studies.”
The association between psoriasis and NAFLD is clinically relevant, agreed Joel M. Gelfand, MD, vice-chair of clinical research and medical director of the clinical studies unit, department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“It is not clear if psoriasis causes fatty liver disease or vice versa, but clinicians should be aware of this association,” he said in an interview. Dr. Gelfand was a coauthor of the study by Dr. Ogdie and colleagues and led another more recent population-based study that implicated methotrexate as a factor in psoriasis-related hepatotoxicity.
If NAFLD is identified in a patient with psoriasis, treatments are limited, but Dr. Gelfand suggested that patients should be made aware of the risk. “Clinicians should encourage patients with psoriasis to take measures to protect their liver, such as avoiding drinking alcohol to excess and trying to maintain a healthy body weight,” he said.
Dr. Bellinato reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gelfand has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including those that make therapies for psoriasis.
AT GRAPPA 2022
Methotrexate’s impact on COVID-19 vaccination: New insights made
Patients who take methotrexate for a variety of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and pause taking the drug following receipt of a COVID-19 vaccine dose did not have a higher risk of disease flare and had higher antireceptor binding domain (anti-RBD) antibody titers and increased immunogenicity when compared with continuing the drug, three recent studies suggest.
In one study, British researchers examined the effects of a 2-week break in methotrexate therapy on anti-RBD titers following receipt of a third COVID-19 vaccine dose. In their paper published in The Lancet: Respiratory Medicine, they reported results from a randomized, open-label, superiority trial that suggested pausing the drug improved immunogenicity, compared with no break.
In two trials presented at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) 2022 Congress, a team from India set out to determine whether holding methotrexate after receiving both doses of a COVID-19 vaccine, or holding it only after the second dose, was safe and effective. They found that pausing methotrexate only following the second dose contributed to a lower flare risk, and that patients had higher anti-RBD titers when holding methotrexate for 2 weeks following each dose.
Pausing methotrexate after booster
The 2-week methotrexate break and booster vaccine dose data in the Vaccine Response On Off Methotrexate (VROOM) trial showed that after a month, the geometric mean antispike 1 (S1)-RBD antibody titer was 10,798 U/mL (95% confidence interval [CI], 8,970-12,997) in the group that continued methotrexate and 22,750 U/mL (95% CI, 19,314-26,796) in the group that suspended methotrexate; the geometric mean ratio was 2.19 (P < .0001; mixed-effects model), reported Abhishek Abhishek, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Nottingham in Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
Prior research showed that stopping methotrexate therapy for 2 weeks following the seasonal influenza vaccine contributed to better vaccine immunity among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but there was no impact of stopping the drug for up to 4 weeks before vaccination on vaccine-related immunity, the researchers noted.
It is crucial in maximizing long-lasting vaccine protection in people who are possibly susceptible through immune suppression at this point in the COVID-19 vaccination regimen, the study team noted.
“Evidence from this study will be useful for policymakers, national immunization advisory committees, and specialist societies formulating recommendations on the use of methotrexate around the time of COVID-19 vaccination. This evidence will help patients and clinicians make informed choices about the risks and benefits of interrupting methotrexate treatment around the time of COVID-19 vaccination, with implications for the potential to extend such approaches to other therapeutics,” they wrote.
In American College of Rheumatology (ACR) guidance for COVID-19 vaccination, the organization advised against using standard synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines such as methotrexate “for 1-2 weeks (as disease activity allows) after each COVID-19 vaccine dose,” given the at-risk population and public health concerns, Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, assistant professor of medicine and associate physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, noted in an accompanying editorial in The Lancet: Respiratory Medicine.
However, when the ACR developed this statement, there was only one trial involving patients with rheumatoid arthritis who paused methotrexate following seasonal influenza vaccination, the editorialists said.
“Although this finding adds to the evidence base to support interruption of methotrexate after vaccination, a shared decision process is needed to weigh the possible benefit of optimizing protection from COVID-19 and the possible risk of underlying disease flare,” they added.
Dr. Abhishek and colleagues assessed 254 patients with immune-mediated inflammatory disease from dermatology and rheumatology clinics across 26 hospitals in the United Kingdom. Participants had been diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, atopic dermatitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, axial spondyloarthritis, and psoriasis without or with arthritis. They had also been taking up to 25 mg of methotrexate per week for 3 months or longer and had received two doses of either the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine or AstraZeneca/Oxford viral vector vaccine. The booster dose was most often the Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine (82%). The patients’ mean age was 59 years, with females comprising 61% of the cohort. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to either group.
Investigators performing laboratory analysis were masked to cohort assignment, and clinical research staff, data analysts, participants, and researchers were unmasked.
The elevated antibody response of patients who suspended methotrexate was the same across different kinds of immune-mediated inflammatory disease, primary vaccination platform, SARS-CoV-2 infection history, and age.
Notably, no intervention-associated adverse events were reported, the study team noted.
The conclusions that could be drawn from the booster-dose study were limited by the trial’s modest cohort size, the small number of patients in exploratory subgroup analyses, a lack of information about differences in prescription drug behavior, and early termination’s effect on the researchers’ ability to identify differences between subgroups and in secondary outcomes, the authors noted.
Other limitations included a lack of generalizability to patients with active disease who couldn’t stop therapy and were not included in the investigation, and participants were not blinded to what group they were in, the researchers said.
Expert commentary
This current study is consistent with other studies over the last several months showing that methotrexate harms both humoral and cell-mediated COVID-19 responses, noted Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious disease and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who was not involved in the study. “And so now the new wave of studies are like this one, where they are holding methotrexate experimentally and seeing if it makes a difference,” he said.
“The one shortcoming of this study – and so far, the studies to date – is that no one has looked at whether the experimental hold has resulted in a change in T-cell responses, which ... we are [now] recognizing [the importance of] more and more in long-term protection, particularly in severe disease. Theoretically, holding [methotrexate] might help enhance T-cell responses, but that hasn’t been shown experimentally.”
Dr. Winthrop pointed out that one might get the same benefit from holding methotrexate for 1 week instead of 2 and that there likely is a reduced risk of flare-up from underlying autoimmune disease.
It is still not certain that this benefit extends to other vaccines, Dr. Winthrop noted. “It is probably true for most vaccines that if you hold methotrexate for 1 or 2 weeks, you might see some short-term benefit in responsiveness, but you don’t know that there is any clinical meaningfulness of this. That’s going to take other long-term studies. You don’t know how long this benefit lasts.”
Pausing methotrexate during initial COVID vaccine doses
Patients with either rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis had higher anti-RBD antibody titers when methotrexate was stopped after both doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine, or simply after the second dose, than when methotrexate was continued, according to results from two single-center, randomized controlled trials called MIVAC I and II, Anu Sreekanth, MD, of Sree Sudheendra Medical Mission in Kochi, Kerala, India, and colleagues reported at EULAR 2022.
Results from MIVAC I indicated that there was a higher flare rate when methotrexate was stopped after both vaccine doses, but there was no difference in flare rate in MIVAC II when methotrexate was stopped only after the second dose as opposed to stopping it after both doses.
In the MIVAC I trial, 158 unvaccinated patients were randomized 1:1 to a cohort in which methotrexate was held for 2 weeks after both doses and a cohort in which methotrexate was continued despite the vaccine. In MIVAC II, 157 patients continued methotrexate while receiving the first vaccine dose. These patients were subsequently randomized either to continue or to stop methotrexate for 2 weeks following the second dose.
The findings from MIVAC I demonstrated the flare rate was lower in the methotrexate-continue group than in the methotrexate-pause group (8% vs. 25%; P = .005) and that the median anti-RBD titer was significantly higher for the methotrexate-pause group than the methotrexate-continue group (2,484 vs. 1,147; P = .001).
The results from MIVAC II trial indicated that there was no difference in flare rates between the two study groups (7.9% vs. 11.8%; P = .15). Yet, the median anti-RBD titer was significantly higher in the methotrexate-pause cohort than in the methotrexate-continue cohort (2,553 vs. 990; P = .001).
The report suggests there is a flare risk when methotrexate is stopped, Dr. Sreekanth noted. “It appears more logical to hold only after the second dose, as comparable anti-RBD titers are generated” with either approach, Dr. Sreekanth said.
Expert commentary: MIVAC I and II
Inés Colmegna, MD, associate professor at McGill University in Montreal, noted that it was intriguing that the risk of flares in MIVAC II is half of that reported after each of the doses of MIVAC I. “It is also worth emphasizing that despite the reported frequency of flares, the actual disease activity [as measured by the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints] in patients who did or did not withhold methotrexate was similar.
“MIVAC I and II have practical implications as they help to adequately inform patients about the risk and benefit trade of withholding methotrexate post–COVID-19 vaccination,” Dr. Colmegna told this news organization.
“Additional information would help to [further] interpret the findings of these studies, including whether any of the participants were taking any other DMARDs; data on the severity of the flares and functional impact; analysis of factors that predict the risk of flares, such as higher doses of methotrexate; [and change in] disease activity scores pre- and postvaccination,” Dr. Colmegna concluded.
Dr. Abhishek disclosed relationships with Springer, UpTodate, Oxford, Immunotec, AstraZeneca, Inflazome, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Menarini Pharmaceuticals, and Cadila Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Abhishek is cochair of the ACR/EULAR CPPD Classification Criteria Working Group and the OMERACT CPPD Working Group. Dr. Sparks disclosed relationships with Gilead, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AbbVie, unrelated to this study. Dr. Tedeschi disclosed relationships with ModernaTx and NGM Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Winthrop disclosed a research grant and serving as a scientific consultant for Pfizer. Dr. Sreekanth and Dr. Colmegna have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who take methotrexate for a variety of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and pause taking the drug following receipt of a COVID-19 vaccine dose did not have a higher risk of disease flare and had higher antireceptor binding domain (anti-RBD) antibody titers and increased immunogenicity when compared with continuing the drug, three recent studies suggest.
In one study, British researchers examined the effects of a 2-week break in methotrexate therapy on anti-RBD titers following receipt of a third COVID-19 vaccine dose. In their paper published in The Lancet: Respiratory Medicine, they reported results from a randomized, open-label, superiority trial that suggested pausing the drug improved immunogenicity, compared with no break.
In two trials presented at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) 2022 Congress, a team from India set out to determine whether holding methotrexate after receiving both doses of a COVID-19 vaccine, or holding it only after the second dose, was safe and effective. They found that pausing methotrexate only following the second dose contributed to a lower flare risk, and that patients had higher anti-RBD titers when holding methotrexate for 2 weeks following each dose.
Pausing methotrexate after booster
The 2-week methotrexate break and booster vaccine dose data in the Vaccine Response On Off Methotrexate (VROOM) trial showed that after a month, the geometric mean antispike 1 (S1)-RBD antibody titer was 10,798 U/mL (95% confidence interval [CI], 8,970-12,997) in the group that continued methotrexate and 22,750 U/mL (95% CI, 19,314-26,796) in the group that suspended methotrexate; the geometric mean ratio was 2.19 (P < .0001; mixed-effects model), reported Abhishek Abhishek, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Nottingham in Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
Prior research showed that stopping methotrexate therapy for 2 weeks following the seasonal influenza vaccine contributed to better vaccine immunity among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but there was no impact of stopping the drug for up to 4 weeks before vaccination on vaccine-related immunity, the researchers noted.
It is crucial in maximizing long-lasting vaccine protection in people who are possibly susceptible through immune suppression at this point in the COVID-19 vaccination regimen, the study team noted.
“Evidence from this study will be useful for policymakers, national immunization advisory committees, and specialist societies formulating recommendations on the use of methotrexate around the time of COVID-19 vaccination. This evidence will help patients and clinicians make informed choices about the risks and benefits of interrupting methotrexate treatment around the time of COVID-19 vaccination, with implications for the potential to extend such approaches to other therapeutics,” they wrote.
In American College of Rheumatology (ACR) guidance for COVID-19 vaccination, the organization advised against using standard synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines such as methotrexate “for 1-2 weeks (as disease activity allows) after each COVID-19 vaccine dose,” given the at-risk population and public health concerns, Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, assistant professor of medicine and associate physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, noted in an accompanying editorial in The Lancet: Respiratory Medicine.
However, when the ACR developed this statement, there was only one trial involving patients with rheumatoid arthritis who paused methotrexate following seasonal influenza vaccination, the editorialists said.
“Although this finding adds to the evidence base to support interruption of methotrexate after vaccination, a shared decision process is needed to weigh the possible benefit of optimizing protection from COVID-19 and the possible risk of underlying disease flare,” they added.
Dr. Abhishek and colleagues assessed 254 patients with immune-mediated inflammatory disease from dermatology and rheumatology clinics across 26 hospitals in the United Kingdom. Participants had been diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, atopic dermatitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, axial spondyloarthritis, and psoriasis without or with arthritis. They had also been taking up to 25 mg of methotrexate per week for 3 months or longer and had received two doses of either the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine or AstraZeneca/Oxford viral vector vaccine. The booster dose was most often the Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine (82%). The patients’ mean age was 59 years, with females comprising 61% of the cohort. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to either group.
Investigators performing laboratory analysis were masked to cohort assignment, and clinical research staff, data analysts, participants, and researchers were unmasked.
The elevated antibody response of patients who suspended methotrexate was the same across different kinds of immune-mediated inflammatory disease, primary vaccination platform, SARS-CoV-2 infection history, and age.
Notably, no intervention-associated adverse events were reported, the study team noted.
The conclusions that could be drawn from the booster-dose study were limited by the trial’s modest cohort size, the small number of patients in exploratory subgroup analyses, a lack of information about differences in prescription drug behavior, and early termination’s effect on the researchers’ ability to identify differences between subgroups and in secondary outcomes, the authors noted.
Other limitations included a lack of generalizability to patients with active disease who couldn’t stop therapy and were not included in the investigation, and participants were not blinded to what group they were in, the researchers said.
Expert commentary
This current study is consistent with other studies over the last several months showing that methotrexate harms both humoral and cell-mediated COVID-19 responses, noted Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious disease and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who was not involved in the study. “And so now the new wave of studies are like this one, where they are holding methotrexate experimentally and seeing if it makes a difference,” he said.
“The one shortcoming of this study – and so far, the studies to date – is that no one has looked at whether the experimental hold has resulted in a change in T-cell responses, which ... we are [now] recognizing [the importance of] more and more in long-term protection, particularly in severe disease. Theoretically, holding [methotrexate] might help enhance T-cell responses, but that hasn’t been shown experimentally.”
Dr. Winthrop pointed out that one might get the same benefit from holding methotrexate for 1 week instead of 2 and that there likely is a reduced risk of flare-up from underlying autoimmune disease.
It is still not certain that this benefit extends to other vaccines, Dr. Winthrop noted. “It is probably true for most vaccines that if you hold methotrexate for 1 or 2 weeks, you might see some short-term benefit in responsiveness, but you don’t know that there is any clinical meaningfulness of this. That’s going to take other long-term studies. You don’t know how long this benefit lasts.”
Pausing methotrexate during initial COVID vaccine doses
Patients with either rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis had higher anti-RBD antibody titers when methotrexate was stopped after both doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine, or simply after the second dose, than when methotrexate was continued, according to results from two single-center, randomized controlled trials called MIVAC I and II, Anu Sreekanth, MD, of Sree Sudheendra Medical Mission in Kochi, Kerala, India, and colleagues reported at EULAR 2022.
Results from MIVAC I indicated that there was a higher flare rate when methotrexate was stopped after both vaccine doses, but there was no difference in flare rate in MIVAC II when methotrexate was stopped only after the second dose as opposed to stopping it after both doses.
In the MIVAC I trial, 158 unvaccinated patients were randomized 1:1 to a cohort in which methotrexate was held for 2 weeks after both doses and a cohort in which methotrexate was continued despite the vaccine. In MIVAC II, 157 patients continued methotrexate while receiving the first vaccine dose. These patients were subsequently randomized either to continue or to stop methotrexate for 2 weeks following the second dose.
The findings from MIVAC I demonstrated the flare rate was lower in the methotrexate-continue group than in the methotrexate-pause group (8% vs. 25%; P = .005) and that the median anti-RBD titer was significantly higher for the methotrexate-pause group than the methotrexate-continue group (2,484 vs. 1,147; P = .001).
The results from MIVAC II trial indicated that there was no difference in flare rates between the two study groups (7.9% vs. 11.8%; P = .15). Yet, the median anti-RBD titer was significantly higher in the methotrexate-pause cohort than in the methotrexate-continue cohort (2,553 vs. 990; P = .001).
The report suggests there is a flare risk when methotrexate is stopped, Dr. Sreekanth noted. “It appears more logical to hold only after the second dose, as comparable anti-RBD titers are generated” with either approach, Dr. Sreekanth said.
Expert commentary: MIVAC I and II
Inés Colmegna, MD, associate professor at McGill University in Montreal, noted that it was intriguing that the risk of flares in MIVAC II is half of that reported after each of the doses of MIVAC I. “It is also worth emphasizing that despite the reported frequency of flares, the actual disease activity [as measured by the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints] in patients who did or did not withhold methotrexate was similar.
“MIVAC I and II have practical implications as they help to adequately inform patients about the risk and benefit trade of withholding methotrexate post–COVID-19 vaccination,” Dr. Colmegna told this news organization.
“Additional information would help to [further] interpret the findings of these studies, including whether any of the participants were taking any other DMARDs; data on the severity of the flares and functional impact; analysis of factors that predict the risk of flares, such as higher doses of methotrexate; [and change in] disease activity scores pre- and postvaccination,” Dr. Colmegna concluded.
Dr. Abhishek disclosed relationships with Springer, UpTodate, Oxford, Immunotec, AstraZeneca, Inflazome, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Menarini Pharmaceuticals, and Cadila Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Abhishek is cochair of the ACR/EULAR CPPD Classification Criteria Working Group and the OMERACT CPPD Working Group. Dr. Sparks disclosed relationships with Gilead, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AbbVie, unrelated to this study. Dr. Tedeschi disclosed relationships with ModernaTx and NGM Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Winthrop disclosed a research grant and serving as a scientific consultant for Pfizer. Dr. Sreekanth and Dr. Colmegna have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who take methotrexate for a variety of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and pause taking the drug following receipt of a COVID-19 vaccine dose did not have a higher risk of disease flare and had higher antireceptor binding domain (anti-RBD) antibody titers and increased immunogenicity when compared with continuing the drug, three recent studies suggest.
In one study, British researchers examined the effects of a 2-week break in methotrexate therapy on anti-RBD titers following receipt of a third COVID-19 vaccine dose. In their paper published in The Lancet: Respiratory Medicine, they reported results from a randomized, open-label, superiority trial that suggested pausing the drug improved immunogenicity, compared with no break.
In two trials presented at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) 2022 Congress, a team from India set out to determine whether holding methotrexate after receiving both doses of a COVID-19 vaccine, or holding it only after the second dose, was safe and effective. They found that pausing methotrexate only following the second dose contributed to a lower flare risk, and that patients had higher anti-RBD titers when holding methotrexate for 2 weeks following each dose.
Pausing methotrexate after booster
The 2-week methotrexate break and booster vaccine dose data in the Vaccine Response On Off Methotrexate (VROOM) trial showed that after a month, the geometric mean antispike 1 (S1)-RBD antibody titer was 10,798 U/mL (95% confidence interval [CI], 8,970-12,997) in the group that continued methotrexate and 22,750 U/mL (95% CI, 19,314-26,796) in the group that suspended methotrexate; the geometric mean ratio was 2.19 (P < .0001; mixed-effects model), reported Abhishek Abhishek, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Nottingham in Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
Prior research showed that stopping methotrexate therapy for 2 weeks following the seasonal influenza vaccine contributed to better vaccine immunity among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but there was no impact of stopping the drug for up to 4 weeks before vaccination on vaccine-related immunity, the researchers noted.
It is crucial in maximizing long-lasting vaccine protection in people who are possibly susceptible through immune suppression at this point in the COVID-19 vaccination regimen, the study team noted.
“Evidence from this study will be useful for policymakers, national immunization advisory committees, and specialist societies formulating recommendations on the use of methotrexate around the time of COVID-19 vaccination. This evidence will help patients and clinicians make informed choices about the risks and benefits of interrupting methotrexate treatment around the time of COVID-19 vaccination, with implications for the potential to extend such approaches to other therapeutics,” they wrote.
In American College of Rheumatology (ACR) guidance for COVID-19 vaccination, the organization advised against using standard synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines such as methotrexate “for 1-2 weeks (as disease activity allows) after each COVID-19 vaccine dose,” given the at-risk population and public health concerns, Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, assistant professor of medicine and associate physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, noted in an accompanying editorial in The Lancet: Respiratory Medicine.
However, when the ACR developed this statement, there was only one trial involving patients with rheumatoid arthritis who paused methotrexate following seasonal influenza vaccination, the editorialists said.
“Although this finding adds to the evidence base to support interruption of methotrexate after vaccination, a shared decision process is needed to weigh the possible benefit of optimizing protection from COVID-19 and the possible risk of underlying disease flare,” they added.
Dr. Abhishek and colleagues assessed 254 patients with immune-mediated inflammatory disease from dermatology and rheumatology clinics across 26 hospitals in the United Kingdom. Participants had been diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, atopic dermatitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, axial spondyloarthritis, and psoriasis without or with arthritis. They had also been taking up to 25 mg of methotrexate per week for 3 months or longer and had received two doses of either the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine or AstraZeneca/Oxford viral vector vaccine. The booster dose was most often the Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine (82%). The patients’ mean age was 59 years, with females comprising 61% of the cohort. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to either group.
Investigators performing laboratory analysis were masked to cohort assignment, and clinical research staff, data analysts, participants, and researchers were unmasked.
The elevated antibody response of patients who suspended methotrexate was the same across different kinds of immune-mediated inflammatory disease, primary vaccination platform, SARS-CoV-2 infection history, and age.
Notably, no intervention-associated adverse events were reported, the study team noted.
The conclusions that could be drawn from the booster-dose study were limited by the trial’s modest cohort size, the small number of patients in exploratory subgroup analyses, a lack of information about differences in prescription drug behavior, and early termination’s effect on the researchers’ ability to identify differences between subgroups and in secondary outcomes, the authors noted.
Other limitations included a lack of generalizability to patients with active disease who couldn’t stop therapy and were not included in the investigation, and participants were not blinded to what group they were in, the researchers said.
Expert commentary
This current study is consistent with other studies over the last several months showing that methotrexate harms both humoral and cell-mediated COVID-19 responses, noted Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious disease and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who was not involved in the study. “And so now the new wave of studies are like this one, where they are holding methotrexate experimentally and seeing if it makes a difference,” he said.
“The one shortcoming of this study – and so far, the studies to date – is that no one has looked at whether the experimental hold has resulted in a change in T-cell responses, which ... we are [now] recognizing [the importance of] more and more in long-term protection, particularly in severe disease. Theoretically, holding [methotrexate] might help enhance T-cell responses, but that hasn’t been shown experimentally.”
Dr. Winthrop pointed out that one might get the same benefit from holding methotrexate for 1 week instead of 2 and that there likely is a reduced risk of flare-up from underlying autoimmune disease.
It is still not certain that this benefit extends to other vaccines, Dr. Winthrop noted. “It is probably true for most vaccines that if you hold methotrexate for 1 or 2 weeks, you might see some short-term benefit in responsiveness, but you don’t know that there is any clinical meaningfulness of this. That’s going to take other long-term studies. You don’t know how long this benefit lasts.”
Pausing methotrexate during initial COVID vaccine doses
Patients with either rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis had higher anti-RBD antibody titers when methotrexate was stopped after both doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine, or simply after the second dose, than when methotrexate was continued, according to results from two single-center, randomized controlled trials called MIVAC I and II, Anu Sreekanth, MD, of Sree Sudheendra Medical Mission in Kochi, Kerala, India, and colleagues reported at EULAR 2022.
Results from MIVAC I indicated that there was a higher flare rate when methotrexate was stopped after both vaccine doses, but there was no difference in flare rate in MIVAC II when methotrexate was stopped only after the second dose as opposed to stopping it after both doses.
In the MIVAC I trial, 158 unvaccinated patients were randomized 1:1 to a cohort in which methotrexate was held for 2 weeks after both doses and a cohort in which methotrexate was continued despite the vaccine. In MIVAC II, 157 patients continued methotrexate while receiving the first vaccine dose. These patients were subsequently randomized either to continue or to stop methotrexate for 2 weeks following the second dose.
The findings from MIVAC I demonstrated the flare rate was lower in the methotrexate-continue group than in the methotrexate-pause group (8% vs. 25%; P = .005) and that the median anti-RBD titer was significantly higher for the methotrexate-pause group than the methotrexate-continue group (2,484 vs. 1,147; P = .001).
The results from MIVAC II trial indicated that there was no difference in flare rates between the two study groups (7.9% vs. 11.8%; P = .15). Yet, the median anti-RBD titer was significantly higher in the methotrexate-pause cohort than in the methotrexate-continue cohort (2,553 vs. 990; P = .001).
The report suggests there is a flare risk when methotrexate is stopped, Dr. Sreekanth noted. “It appears more logical to hold only after the second dose, as comparable anti-RBD titers are generated” with either approach, Dr. Sreekanth said.
Expert commentary: MIVAC I and II
Inés Colmegna, MD, associate professor at McGill University in Montreal, noted that it was intriguing that the risk of flares in MIVAC II is half of that reported after each of the doses of MIVAC I. “It is also worth emphasizing that despite the reported frequency of flares, the actual disease activity [as measured by the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints] in patients who did or did not withhold methotrexate was similar.
“MIVAC I and II have practical implications as they help to adequately inform patients about the risk and benefit trade of withholding methotrexate post–COVID-19 vaccination,” Dr. Colmegna told this news organization.
“Additional information would help to [further] interpret the findings of these studies, including whether any of the participants were taking any other DMARDs; data on the severity of the flares and functional impact; analysis of factors that predict the risk of flares, such as higher doses of methotrexate; [and change in] disease activity scores pre- and postvaccination,” Dr. Colmegna concluded.
Dr. Abhishek disclosed relationships with Springer, UpTodate, Oxford, Immunotec, AstraZeneca, Inflazome, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Menarini Pharmaceuticals, and Cadila Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Abhishek is cochair of the ACR/EULAR CPPD Classification Criteria Working Group and the OMERACT CPPD Working Group. Dr. Sparks disclosed relationships with Gilead, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AbbVie, unrelated to this study. Dr. Tedeschi disclosed relationships with ModernaTx and NGM Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Winthrop disclosed a research grant and serving as a scientific consultant for Pfizer. Dr. Sreekanth and Dr. Colmegna have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Think of pediatric morphea as a systemic, chronic disease, expert advises
INDIANAPOLIS – In the opinion of Elena Pope, MD, MSc,
“There is no correlation between the extent and activity of skin lesions and the presence, severity, and activity of extracutaneous manifestations,” Dr. Pope, professor of pediatrics at the University of Toronto and division head of pediatric dermatology at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, said during the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “Treatment needs to be tailored to the extent of cutaneous manifestations, and I think we need to be aware of and address the impact on patients’ quality of life,” she added. There is also a need for more research “on targeted and better-tolerated therapies to put a stop to the progression of disease.”
Congenital morphea is a form of localized scleroderma that presents at birth but can be confused with port wine stain. Results from a multicenter retrospective review of 25 cases conducted by Dr. Pope and colleagues found that the median age at diagnosis was 2.9 years and 76% had linear-type lesions. In addition, 48% had extracutaneous involvement (all of these patients had linear morphea), most commonly of the central nervous system.
“It’s important to realize these lesions may become active over time,” Dr. Pope said. “In my experience, there are two different courses. Either you have innocuous lesions when the patients are born and they may become active around 3-4 years of age, or you have early intrauterine involvement, with lesions inactive at birth but with potential for significant damage in utero.”
She cautioned against treating a suspected port wine stain lesion with laser until congenital morphea is ruled out. “I’m aware of at least one lawsuit of a child where someone used a laser in a child who had progression with significant sclerosis,” she said. “The parents assumed it was the use of the laser that led to the progression, not the actual disease.”
Extracutaneous manifestations are common in morphea patients. A multicenter study of 750 patients with juvenile scleroderma found that 22% had extracutaneous manifestations. Almost half of patients (47%) had arthritis, but 17% had neurologic findings such as seizures and headaches, 9% had vascular manifestations, and 8% had uveitis. Subsequent studies found that neurological disease affects between 11% and 19% of cases, especially in those involving the head and neck.
“There is a wide range of manifestations from headache and neuropsychiatric changes to brain atrophy, seizures, and CNS cavernoma,” Dr. Pope said. “There also can be orthodental involvement such as malocclusion. It’s important to do a brain MRI, eye exam for uveitis, and don’t forget the orthodental assessment.”
She recalled a 10-year-old boy who presented to the Hospital for Sick Children with tissue loss on the forehead and eyebrow and eyelashes. He had no other congenital morphea symptoms and the MRI was normal, but the eye exam revealed uveitis. “It’s important to remember that uveitis is asymptomatic, so unless you look for it, you’re not going to find it,” she said.
According to unpublished data in 42 congenital morphea patients with lesions limited to the head and neck, who underwent MRI imaging at the Hospital for Sick Children, 57% had CNS changes that were ipsilateral in 68% of cases. “White matter changes were the most common, and to our surprise, there were patients who had progressive CNS disease, including CNS vasculitis, new lesions, and enhancement of prior stable lesions,” Dr. Pope said.
She recalled the case of an 8-year-old boy who presented to the hospital with intractable seizures. Upon completion of the MRI, one of the radiologists noted that the imaging showed subtle thinning of the forehead, and he was referred to Dr. Pope and colleagues for assessment. In the span of 4 years, despite aggressive treatment, the boy’s CNS disease progressed. “There was more enhancement, more tissue loss, his seizures are very hard to control, and he has many neurodevelopmental changes,” she recalled. “What I learned from this case is that skin activity does not correlate with imaging. Don’t assume that just because the skin is burnt out that the CNS will be the same. Also, the extent of skin disease does not predict involvement or progression of the CNS.”
Linear lesions on the lower extremities are a harbinger of orthopedic complications, which can occur in about half of patients. Joint contractures in this subset of patients are seen in about 81% of cases, while other sequelae can include arthritis, limb atrophy, leg-leg discrepancy, and angular deformity. “About 14% of patients require intervention,” Dr. Pope said. “In terms of working those patients up, you need to do an MRI and assess the extent of muscle and fascial involvement. Early physiotherapy and an orthopedic evaluation are also recommended.”
As for possible markers of morphea, antinuclear antibody is positive in 22%-68% of cases and correlates with disease severity, extracutaneous manifestations, and disease flare-up. Antihistone antibodies (AHA) are positive in about 47% of cases, “and that tends to correlate with the extent of skin and muscle involvement,” Dr. Pope said. “Anti–double-stranded DNA correlates with extent of disease, but the only known biomarker to date that correlates with disease activity is CXCL9/10. This has been documented in the skin as well as in the blood. So, this marker may help us determine if the patient needs to be treated or not.”
Treatments
For treatment of active localized disease, topical medications are helpful in some cases. Options include topical steroids, calcipotriol with or without betamethasone, imiquimod, and tacrolimus. “In my experience the combination of calcipotriol with betamethasone is best,” she said. “It really shuts down the activity fairly soon, and you can scale down to calcipotriol alone. I don’t find imiquimod very helpful for active lesions, although it has a role for inactive lesions.”
For patients with linear or generalized/mixed disease, “the combination of methotrexate and corticosteroids or methotrexate alone is probably the way to go,” Dr. Pope said. “The addition of steroids really depends on where the lesion is and how worried you are about other problems.”
According to the best available literature, 88% of patients should respond to treatment with methotrexate (MTX) and/or steroids within 3-6 months, and 74% within 3 months. “If they don’t, you have to wonder if the patient’s taking the medication, or you need to think about other alternative treatments,” she said. “Complete remission is possible in most of the patients, and the longer you treat the more you will see that. On average, most of us treat patients for about 3 years, but there are treatment failures as well. This can occur in up to 16% of patients.”
As for second-line treatment agents for congenital morphea, clinicians often turn to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Results from a retrospective longitudinal study of juvenile localized scleroderma patients found that after a mean of 9 years 91% of patients on MMF and 100% of patients on MTX had inactive disease. “There were no differences in relapse rates, although MMF seems to have a more sustained long-term effect and overall is better tolerated,” said Dr. Pope, who was not involved with the study. “However, it’s more immunosuppressive than MTX, which is important, especially in the era of COVID-19. You also need to think about the potential for more hematological suppression with MMF use.” If standard therapy fails, there is anecdotal data supporting the use of abatacept (which suppresses the T-cell activity in affected patients), tofacitinib (which inhibits transforming growth factor–beta), or dupilumab (which inhibits interleukin-4).
Dr. Pope emphasized the effect congenital morphea has on quality of life. Remarks from patients with facial morphea and their parents who participated in a focus group on the topic organized by the Hospital for Sick Children included, “You just want to stay inside because you are afraid of what people will say,” “They laugh at her. They make fun of her, and it’s terrible,” and “MTX makes me feel weird. I would throw up, feel dizzy.”
“You have to take that into consideration, because we cannot make the treatment worse than the disease,” Dr. Pope said. “There are many domains where patients could be affected, including skin symptoms, physical functioning, body image and social support, side effects of medication, and presence of extracutaneous manifestations. Predictors of poor quality of life include female sex and involvement of hands and feet.”
Dr. Pope disclosed that she has received grants/research support from AbbVie, Centocor, and Amgen. She has also received consulting fees from AbbVie, Sanofi, Novartis, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Phoenix, Amryt Pharma, and Timber Pharmaceuticals.
INDIANAPOLIS – In the opinion of Elena Pope, MD, MSc,
“There is no correlation between the extent and activity of skin lesions and the presence, severity, and activity of extracutaneous manifestations,” Dr. Pope, professor of pediatrics at the University of Toronto and division head of pediatric dermatology at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, said during the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “Treatment needs to be tailored to the extent of cutaneous manifestations, and I think we need to be aware of and address the impact on patients’ quality of life,” she added. There is also a need for more research “on targeted and better-tolerated therapies to put a stop to the progression of disease.”
Congenital morphea is a form of localized scleroderma that presents at birth but can be confused with port wine stain. Results from a multicenter retrospective review of 25 cases conducted by Dr. Pope and colleagues found that the median age at diagnosis was 2.9 years and 76% had linear-type lesions. In addition, 48% had extracutaneous involvement (all of these patients had linear morphea), most commonly of the central nervous system.
“It’s important to realize these lesions may become active over time,” Dr. Pope said. “In my experience, there are two different courses. Either you have innocuous lesions when the patients are born and they may become active around 3-4 years of age, or you have early intrauterine involvement, with lesions inactive at birth but with potential for significant damage in utero.”
She cautioned against treating a suspected port wine stain lesion with laser until congenital morphea is ruled out. “I’m aware of at least one lawsuit of a child where someone used a laser in a child who had progression with significant sclerosis,” she said. “The parents assumed it was the use of the laser that led to the progression, not the actual disease.”
Extracutaneous manifestations are common in morphea patients. A multicenter study of 750 patients with juvenile scleroderma found that 22% had extracutaneous manifestations. Almost half of patients (47%) had arthritis, but 17% had neurologic findings such as seizures and headaches, 9% had vascular manifestations, and 8% had uveitis. Subsequent studies found that neurological disease affects between 11% and 19% of cases, especially in those involving the head and neck.
“There is a wide range of manifestations from headache and neuropsychiatric changes to brain atrophy, seizures, and CNS cavernoma,” Dr. Pope said. “There also can be orthodental involvement such as malocclusion. It’s important to do a brain MRI, eye exam for uveitis, and don’t forget the orthodental assessment.”
She recalled a 10-year-old boy who presented to the Hospital for Sick Children with tissue loss on the forehead and eyebrow and eyelashes. He had no other congenital morphea symptoms and the MRI was normal, but the eye exam revealed uveitis. “It’s important to remember that uveitis is asymptomatic, so unless you look for it, you’re not going to find it,” she said.
According to unpublished data in 42 congenital morphea patients with lesions limited to the head and neck, who underwent MRI imaging at the Hospital for Sick Children, 57% had CNS changes that were ipsilateral in 68% of cases. “White matter changes were the most common, and to our surprise, there were patients who had progressive CNS disease, including CNS vasculitis, new lesions, and enhancement of prior stable lesions,” Dr. Pope said.
She recalled the case of an 8-year-old boy who presented to the hospital with intractable seizures. Upon completion of the MRI, one of the radiologists noted that the imaging showed subtle thinning of the forehead, and he was referred to Dr. Pope and colleagues for assessment. In the span of 4 years, despite aggressive treatment, the boy’s CNS disease progressed. “There was more enhancement, more tissue loss, his seizures are very hard to control, and he has many neurodevelopmental changes,” she recalled. “What I learned from this case is that skin activity does not correlate with imaging. Don’t assume that just because the skin is burnt out that the CNS will be the same. Also, the extent of skin disease does not predict involvement or progression of the CNS.”
Linear lesions on the lower extremities are a harbinger of orthopedic complications, which can occur in about half of patients. Joint contractures in this subset of patients are seen in about 81% of cases, while other sequelae can include arthritis, limb atrophy, leg-leg discrepancy, and angular deformity. “About 14% of patients require intervention,” Dr. Pope said. “In terms of working those patients up, you need to do an MRI and assess the extent of muscle and fascial involvement. Early physiotherapy and an orthopedic evaluation are also recommended.”
As for possible markers of morphea, antinuclear antibody is positive in 22%-68% of cases and correlates with disease severity, extracutaneous manifestations, and disease flare-up. Antihistone antibodies (AHA) are positive in about 47% of cases, “and that tends to correlate with the extent of skin and muscle involvement,” Dr. Pope said. “Anti–double-stranded DNA correlates with extent of disease, but the only known biomarker to date that correlates with disease activity is CXCL9/10. This has been documented in the skin as well as in the blood. So, this marker may help us determine if the patient needs to be treated or not.”
Treatments
For treatment of active localized disease, topical medications are helpful in some cases. Options include topical steroids, calcipotriol with or without betamethasone, imiquimod, and tacrolimus. “In my experience the combination of calcipotriol with betamethasone is best,” she said. “It really shuts down the activity fairly soon, and you can scale down to calcipotriol alone. I don’t find imiquimod very helpful for active lesions, although it has a role for inactive lesions.”
For patients with linear or generalized/mixed disease, “the combination of methotrexate and corticosteroids or methotrexate alone is probably the way to go,” Dr. Pope said. “The addition of steroids really depends on where the lesion is and how worried you are about other problems.”
According to the best available literature, 88% of patients should respond to treatment with methotrexate (MTX) and/or steroids within 3-6 months, and 74% within 3 months. “If they don’t, you have to wonder if the patient’s taking the medication, or you need to think about other alternative treatments,” she said. “Complete remission is possible in most of the patients, and the longer you treat the more you will see that. On average, most of us treat patients for about 3 years, but there are treatment failures as well. This can occur in up to 16% of patients.”
As for second-line treatment agents for congenital morphea, clinicians often turn to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Results from a retrospective longitudinal study of juvenile localized scleroderma patients found that after a mean of 9 years 91% of patients on MMF and 100% of patients on MTX had inactive disease. “There were no differences in relapse rates, although MMF seems to have a more sustained long-term effect and overall is better tolerated,” said Dr. Pope, who was not involved with the study. “However, it’s more immunosuppressive than MTX, which is important, especially in the era of COVID-19. You also need to think about the potential for more hematological suppression with MMF use.” If standard therapy fails, there is anecdotal data supporting the use of abatacept (which suppresses the T-cell activity in affected patients), tofacitinib (which inhibits transforming growth factor–beta), or dupilumab (which inhibits interleukin-4).
Dr. Pope emphasized the effect congenital morphea has on quality of life. Remarks from patients with facial morphea and their parents who participated in a focus group on the topic organized by the Hospital for Sick Children included, “You just want to stay inside because you are afraid of what people will say,” “They laugh at her. They make fun of her, and it’s terrible,” and “MTX makes me feel weird. I would throw up, feel dizzy.”
“You have to take that into consideration, because we cannot make the treatment worse than the disease,” Dr. Pope said. “There are many domains where patients could be affected, including skin symptoms, physical functioning, body image and social support, side effects of medication, and presence of extracutaneous manifestations. Predictors of poor quality of life include female sex and involvement of hands and feet.”
Dr. Pope disclosed that she has received grants/research support from AbbVie, Centocor, and Amgen. She has also received consulting fees from AbbVie, Sanofi, Novartis, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Phoenix, Amryt Pharma, and Timber Pharmaceuticals.
INDIANAPOLIS – In the opinion of Elena Pope, MD, MSc,
“There is no correlation between the extent and activity of skin lesions and the presence, severity, and activity of extracutaneous manifestations,” Dr. Pope, professor of pediatrics at the University of Toronto and division head of pediatric dermatology at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, said during the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “Treatment needs to be tailored to the extent of cutaneous manifestations, and I think we need to be aware of and address the impact on patients’ quality of life,” she added. There is also a need for more research “on targeted and better-tolerated therapies to put a stop to the progression of disease.”
Congenital morphea is a form of localized scleroderma that presents at birth but can be confused with port wine stain. Results from a multicenter retrospective review of 25 cases conducted by Dr. Pope and colleagues found that the median age at diagnosis was 2.9 years and 76% had linear-type lesions. In addition, 48% had extracutaneous involvement (all of these patients had linear morphea), most commonly of the central nervous system.
“It’s important to realize these lesions may become active over time,” Dr. Pope said. “In my experience, there are two different courses. Either you have innocuous lesions when the patients are born and they may become active around 3-4 years of age, or you have early intrauterine involvement, with lesions inactive at birth but with potential for significant damage in utero.”
She cautioned against treating a suspected port wine stain lesion with laser until congenital morphea is ruled out. “I’m aware of at least one lawsuit of a child where someone used a laser in a child who had progression with significant sclerosis,” she said. “The parents assumed it was the use of the laser that led to the progression, not the actual disease.”
Extracutaneous manifestations are common in morphea patients. A multicenter study of 750 patients with juvenile scleroderma found that 22% had extracutaneous manifestations. Almost half of patients (47%) had arthritis, but 17% had neurologic findings such as seizures and headaches, 9% had vascular manifestations, and 8% had uveitis. Subsequent studies found that neurological disease affects between 11% and 19% of cases, especially in those involving the head and neck.
“There is a wide range of manifestations from headache and neuropsychiatric changes to brain atrophy, seizures, and CNS cavernoma,” Dr. Pope said. “There also can be orthodental involvement such as malocclusion. It’s important to do a brain MRI, eye exam for uveitis, and don’t forget the orthodental assessment.”
She recalled a 10-year-old boy who presented to the Hospital for Sick Children with tissue loss on the forehead and eyebrow and eyelashes. He had no other congenital morphea symptoms and the MRI was normal, but the eye exam revealed uveitis. “It’s important to remember that uveitis is asymptomatic, so unless you look for it, you’re not going to find it,” she said.
According to unpublished data in 42 congenital morphea patients with lesions limited to the head and neck, who underwent MRI imaging at the Hospital for Sick Children, 57% had CNS changes that were ipsilateral in 68% of cases. “White matter changes were the most common, and to our surprise, there were patients who had progressive CNS disease, including CNS vasculitis, new lesions, and enhancement of prior stable lesions,” Dr. Pope said.
She recalled the case of an 8-year-old boy who presented to the hospital with intractable seizures. Upon completion of the MRI, one of the radiologists noted that the imaging showed subtle thinning of the forehead, and he was referred to Dr. Pope and colleagues for assessment. In the span of 4 years, despite aggressive treatment, the boy’s CNS disease progressed. “There was more enhancement, more tissue loss, his seizures are very hard to control, and he has many neurodevelopmental changes,” she recalled. “What I learned from this case is that skin activity does not correlate with imaging. Don’t assume that just because the skin is burnt out that the CNS will be the same. Also, the extent of skin disease does not predict involvement or progression of the CNS.”
Linear lesions on the lower extremities are a harbinger of orthopedic complications, which can occur in about half of patients. Joint contractures in this subset of patients are seen in about 81% of cases, while other sequelae can include arthritis, limb atrophy, leg-leg discrepancy, and angular deformity. “About 14% of patients require intervention,” Dr. Pope said. “In terms of working those patients up, you need to do an MRI and assess the extent of muscle and fascial involvement. Early physiotherapy and an orthopedic evaluation are also recommended.”
As for possible markers of morphea, antinuclear antibody is positive in 22%-68% of cases and correlates with disease severity, extracutaneous manifestations, and disease flare-up. Antihistone antibodies (AHA) are positive in about 47% of cases, “and that tends to correlate with the extent of skin and muscle involvement,” Dr. Pope said. “Anti–double-stranded DNA correlates with extent of disease, but the only known biomarker to date that correlates with disease activity is CXCL9/10. This has been documented in the skin as well as in the blood. So, this marker may help us determine if the patient needs to be treated or not.”
Treatments
For treatment of active localized disease, topical medications are helpful in some cases. Options include topical steroids, calcipotriol with or without betamethasone, imiquimod, and tacrolimus. “In my experience the combination of calcipotriol with betamethasone is best,” she said. “It really shuts down the activity fairly soon, and you can scale down to calcipotriol alone. I don’t find imiquimod very helpful for active lesions, although it has a role for inactive lesions.”
For patients with linear or generalized/mixed disease, “the combination of methotrexate and corticosteroids or methotrexate alone is probably the way to go,” Dr. Pope said. “The addition of steroids really depends on where the lesion is and how worried you are about other problems.”
According to the best available literature, 88% of patients should respond to treatment with methotrexate (MTX) and/or steroids within 3-6 months, and 74% within 3 months. “If they don’t, you have to wonder if the patient’s taking the medication, or you need to think about other alternative treatments,” she said. “Complete remission is possible in most of the patients, and the longer you treat the more you will see that. On average, most of us treat patients for about 3 years, but there are treatment failures as well. This can occur in up to 16% of patients.”
As for second-line treatment agents for congenital morphea, clinicians often turn to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Results from a retrospective longitudinal study of juvenile localized scleroderma patients found that after a mean of 9 years 91% of patients on MMF and 100% of patients on MTX had inactive disease. “There were no differences in relapse rates, although MMF seems to have a more sustained long-term effect and overall is better tolerated,” said Dr. Pope, who was not involved with the study. “However, it’s more immunosuppressive than MTX, which is important, especially in the era of COVID-19. You also need to think about the potential for more hematological suppression with MMF use.” If standard therapy fails, there is anecdotal data supporting the use of abatacept (which suppresses the T-cell activity in affected patients), tofacitinib (which inhibits transforming growth factor–beta), or dupilumab (which inhibits interleukin-4).
Dr. Pope emphasized the effect congenital morphea has on quality of life. Remarks from patients with facial morphea and their parents who participated in a focus group on the topic organized by the Hospital for Sick Children included, “You just want to stay inside because you are afraid of what people will say,” “They laugh at her. They make fun of her, and it’s terrible,” and “MTX makes me feel weird. I would throw up, feel dizzy.”
“You have to take that into consideration, because we cannot make the treatment worse than the disease,” Dr. Pope said. “There are many domains where patients could be affected, including skin symptoms, physical functioning, body image and social support, side effects of medication, and presence of extracutaneous manifestations. Predictors of poor quality of life include female sex and involvement of hands and feet.”
Dr. Pope disclosed that she has received grants/research support from AbbVie, Centocor, and Amgen. She has also received consulting fees from AbbVie, Sanofi, Novartis, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Phoenix, Amryt Pharma, and Timber Pharmaceuticals.
AT SPD 2022
Neural networks can distinguish PsA from rheumatoid arthritis on MRI
Hand images are sufficient
NEW YORK – On the basis of MRI images of the hand, a neural network has been trained to distinguish seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from psoriatic arthritis (PsA) as well as from each other, according to a study that was presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
In the work so far, the neural network was correct about 70% of the time in the absence of any further clinical analyses, according to David Simon, MD, a rheumatologist in the department of internal medicine at Friedrich-Alexander University, Erlangen, Germany.
Previous to this work, “there has been no study that has exclusively used hand MRI data and deep learning without requiring further expert input for the classification of arthritides,” Dr. Simon said.
In fact, when demographic and clinical data were added, there was no improvement in the performance of patient classification relative to the deep learning classification alone, according to the data presented by Dr. Simon.
The images were evaluated with residual neural networks (ResNet), which represents a sophisticated form of deep learning to facilitate the flow of information across the network layers as they form to improve accuracy in their ability to distinguish one form of disease from the other. The training was performed on images from the T1 coronal, T2 corona1, T1 coronal fat suppressed with contrast, T1 axial fat suppressed with contrast, and T2 fat suppressed axial sequences.
The study included hand MRI scans from 135 patients with seronegative RA, 190 with seropositive RA, 177 with PsA, and 147 with psoriasis. The performance was judged on the basis of area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC) with and without input of clinical characteristics. Patients who had psoriasis without clinical arthritis were included as a control population.
The AUROC for accuracy was 75% for seropositive RA relative to PsA, 74% for seronegative RA relative to PsA, and 67% for seropositive relative to seronegative RA. Of the patients who had psoriasis without arthritis, 98% were classified as PsA and 2% as RA.
Subsequent to the classification of the patients with psoriasis, 14 of the 147 (9.5%) have developed PsA so far over a relatively short follow-up. All of these were among those identified as PsA by neural network evaluation of the hand MRIs.
This suggests that “a PsA-like pattern may be present early in the course of psoriatic disease,” Dr. Simon said.
In the groups with joint disease, who had mean ages ranging from 56 to 65, the mean disease durations were 2.6 years for those with seropositive RA, 1.3 years for those with seronegative RA, and 0.8 years for those with PsA. The patients with psoriasis were younger (mean age, 40.5 years) but had a longer disease duration (mean 4.2 years).
All of the MRI sequences were relevant for classification, but contrast did not appear to help with accuracy.
“If the images with contrast enhancement were deleted, the loss of performance was only marginal,” Dr. Simon reported.
The accuracy of neural networks increases with data, making it likely that further refinements in methodology will lead to a greater degree of accuracy, according to Dr. Simon. While the methodology is not yet ready for routine use in the clinic, the study demonstrates that neural network analysis of hand MRI to distinguish forms of arthritis “is possible.” Further studies are planned toward the goal of creating a viable clinical tool.
“Of course, if we could create an accurate tool with ultrasound, this would be even more practical,” said Dr. Simon, recognizing the value of an office tool, but he cautioned that this would be far more challenging.
“The precision of MRI is an important factor for effective neural network training,” he said.
Utility: ‘In challenging cases if the accuracy improves’?
A viable method for objectively and rapidly distinguishing inflammatory joint diseases, particularly in patients with an ambiguous clinical presentation, is an unmet need, according to Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle.
Although the data presented are promising, Dr. Mease said in an interview that he believes there is a fair amount of work to be done before imaging analysis based on deep learning makes its way into routine clinical care. He is also hoping for methods to distinguish RA from PsA that are easier and less expensive, such as serum biomarkers. However, he agreed that a MRI-based tool could be useful when differentiating disease that is challenging.
“MRI is an expensive way for routine classification of disease, but this approach could be useful in challenging cases if the accuracy improves,” he said.
Meanwhile, other clinical researchers might want to test the principle. “You can try it,” said Dr. Simon, who reported that his team has made the methodology publicly available.
Dr. Simon reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mease reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, most of which make products used for the treatment of inflammatory joint diseases.
Hand images are sufficient
Hand images are sufficient
NEW YORK – On the basis of MRI images of the hand, a neural network has been trained to distinguish seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from psoriatic arthritis (PsA) as well as from each other, according to a study that was presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
In the work so far, the neural network was correct about 70% of the time in the absence of any further clinical analyses, according to David Simon, MD, a rheumatologist in the department of internal medicine at Friedrich-Alexander University, Erlangen, Germany.
Previous to this work, “there has been no study that has exclusively used hand MRI data and deep learning without requiring further expert input for the classification of arthritides,” Dr. Simon said.
In fact, when demographic and clinical data were added, there was no improvement in the performance of patient classification relative to the deep learning classification alone, according to the data presented by Dr. Simon.
The images were evaluated with residual neural networks (ResNet), which represents a sophisticated form of deep learning to facilitate the flow of information across the network layers as they form to improve accuracy in their ability to distinguish one form of disease from the other. The training was performed on images from the T1 coronal, T2 corona1, T1 coronal fat suppressed with contrast, T1 axial fat suppressed with contrast, and T2 fat suppressed axial sequences.
The study included hand MRI scans from 135 patients with seronegative RA, 190 with seropositive RA, 177 with PsA, and 147 with psoriasis. The performance was judged on the basis of area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC) with and without input of clinical characteristics. Patients who had psoriasis without clinical arthritis were included as a control population.
The AUROC for accuracy was 75% for seropositive RA relative to PsA, 74% for seronegative RA relative to PsA, and 67% for seropositive relative to seronegative RA. Of the patients who had psoriasis without arthritis, 98% were classified as PsA and 2% as RA.
Subsequent to the classification of the patients with psoriasis, 14 of the 147 (9.5%) have developed PsA so far over a relatively short follow-up. All of these were among those identified as PsA by neural network evaluation of the hand MRIs.
This suggests that “a PsA-like pattern may be present early in the course of psoriatic disease,” Dr. Simon said.
In the groups with joint disease, who had mean ages ranging from 56 to 65, the mean disease durations were 2.6 years for those with seropositive RA, 1.3 years for those with seronegative RA, and 0.8 years for those with PsA. The patients with psoriasis were younger (mean age, 40.5 years) but had a longer disease duration (mean 4.2 years).
All of the MRI sequences were relevant for classification, but contrast did not appear to help with accuracy.
“If the images with contrast enhancement were deleted, the loss of performance was only marginal,” Dr. Simon reported.
The accuracy of neural networks increases with data, making it likely that further refinements in methodology will lead to a greater degree of accuracy, according to Dr. Simon. While the methodology is not yet ready for routine use in the clinic, the study demonstrates that neural network analysis of hand MRI to distinguish forms of arthritis “is possible.” Further studies are planned toward the goal of creating a viable clinical tool.
“Of course, if we could create an accurate tool with ultrasound, this would be even more practical,” said Dr. Simon, recognizing the value of an office tool, but he cautioned that this would be far more challenging.
“The precision of MRI is an important factor for effective neural network training,” he said.
Utility: ‘In challenging cases if the accuracy improves’?
A viable method for objectively and rapidly distinguishing inflammatory joint diseases, particularly in patients with an ambiguous clinical presentation, is an unmet need, according to Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle.
Although the data presented are promising, Dr. Mease said in an interview that he believes there is a fair amount of work to be done before imaging analysis based on deep learning makes its way into routine clinical care. He is also hoping for methods to distinguish RA from PsA that are easier and less expensive, such as serum biomarkers. However, he agreed that a MRI-based tool could be useful when differentiating disease that is challenging.
“MRI is an expensive way for routine classification of disease, but this approach could be useful in challenging cases if the accuracy improves,” he said.
Meanwhile, other clinical researchers might want to test the principle. “You can try it,” said Dr. Simon, who reported that his team has made the methodology publicly available.
Dr. Simon reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mease reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, most of which make products used for the treatment of inflammatory joint diseases.
NEW YORK – On the basis of MRI images of the hand, a neural network has been trained to distinguish seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from psoriatic arthritis (PsA) as well as from each other, according to a study that was presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
In the work so far, the neural network was correct about 70% of the time in the absence of any further clinical analyses, according to David Simon, MD, a rheumatologist in the department of internal medicine at Friedrich-Alexander University, Erlangen, Germany.
Previous to this work, “there has been no study that has exclusively used hand MRI data and deep learning without requiring further expert input for the classification of arthritides,” Dr. Simon said.
In fact, when demographic and clinical data were added, there was no improvement in the performance of patient classification relative to the deep learning classification alone, according to the data presented by Dr. Simon.
The images were evaluated with residual neural networks (ResNet), which represents a sophisticated form of deep learning to facilitate the flow of information across the network layers as they form to improve accuracy in their ability to distinguish one form of disease from the other. The training was performed on images from the T1 coronal, T2 corona1, T1 coronal fat suppressed with contrast, T1 axial fat suppressed with contrast, and T2 fat suppressed axial sequences.
The study included hand MRI scans from 135 patients with seronegative RA, 190 with seropositive RA, 177 with PsA, and 147 with psoriasis. The performance was judged on the basis of area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC) with and without input of clinical characteristics. Patients who had psoriasis without clinical arthritis were included as a control population.
The AUROC for accuracy was 75% for seropositive RA relative to PsA, 74% for seronegative RA relative to PsA, and 67% for seropositive relative to seronegative RA. Of the patients who had psoriasis without arthritis, 98% were classified as PsA and 2% as RA.
Subsequent to the classification of the patients with psoriasis, 14 of the 147 (9.5%) have developed PsA so far over a relatively short follow-up. All of these were among those identified as PsA by neural network evaluation of the hand MRIs.
This suggests that “a PsA-like pattern may be present early in the course of psoriatic disease,” Dr. Simon said.
In the groups with joint disease, who had mean ages ranging from 56 to 65, the mean disease durations were 2.6 years for those with seropositive RA, 1.3 years for those with seronegative RA, and 0.8 years for those with PsA. The patients with psoriasis were younger (mean age, 40.5 years) but had a longer disease duration (mean 4.2 years).
All of the MRI sequences were relevant for classification, but contrast did not appear to help with accuracy.
“If the images with contrast enhancement were deleted, the loss of performance was only marginal,” Dr. Simon reported.
The accuracy of neural networks increases with data, making it likely that further refinements in methodology will lead to a greater degree of accuracy, according to Dr. Simon. While the methodology is not yet ready for routine use in the clinic, the study demonstrates that neural network analysis of hand MRI to distinguish forms of arthritis “is possible.” Further studies are planned toward the goal of creating a viable clinical tool.
“Of course, if we could create an accurate tool with ultrasound, this would be even more practical,” said Dr. Simon, recognizing the value of an office tool, but he cautioned that this would be far more challenging.
“The precision of MRI is an important factor for effective neural network training,” he said.
Utility: ‘In challenging cases if the accuracy improves’?
A viable method for objectively and rapidly distinguishing inflammatory joint diseases, particularly in patients with an ambiguous clinical presentation, is an unmet need, according to Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle.
Although the data presented are promising, Dr. Mease said in an interview that he believes there is a fair amount of work to be done before imaging analysis based on deep learning makes its way into routine clinical care. He is also hoping for methods to distinguish RA from PsA that are easier and less expensive, such as serum biomarkers. However, he agreed that a MRI-based tool could be useful when differentiating disease that is challenging.
“MRI is an expensive way for routine classification of disease, but this approach could be useful in challenging cases if the accuracy improves,” he said.
Meanwhile, other clinical researchers might want to test the principle. “You can try it,” said Dr. Simon, who reported that his team has made the methodology publicly available.
Dr. Simon reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mease reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, most of which make products used for the treatment of inflammatory joint diseases.
AT GRAPPA 2022
New algorithm for initial PsA treatment choice is driven by T-cell behavior
T-cell behavior
Biologic selection is cytokine based
NEW YORK – An algorithm in development for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is showing promise for directing patients to the biologic with the greatest likelihood of producing disease control, according to a proof-of-concept study presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Our technique involves a more precise functional assay showing exact T-cell behavior, compared to the previous assessments that only analyzed cellular phenotypes,” reported Gizem Ayan, MD, a fellow in rheumatology at Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey.
The concept of precision medicine in PsA as well as other autoimmune diseases is not new. Phenotypes and biomarkers have already shown potential for guiding treatment, according to Dr. Ayan, but she said none are yet guideline recommended or proven to improve patient outcomes.
The principle of the new algorithm that she and her coinvestigators are pursing is based on immunophenotype analysis conducted with a flow-cytometric cytokine secretion assay (FCCSA). In the protocol, monocytes obtained from peripheral blood undergo activation before an FCCSA to distinguish patients by their T-cell behavior.
The treatment decision tree is based on median ratios of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)–22, IL-17, and interferon-gamma expression among CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Based on a yes-or-no response to specific immune patterns, the patient is funneled to a biologic that inhibits a dominant cytokine.
The proof-of-concept study, which enrolled 8 patients with PsA who were naive to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and 11 patients with PsA who were naive to biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs), was designed to demonstrate feasibility. It did not test clinical benefit, but it did show that immunophenotyping with this methodology can be performed efficiently.
“From the time a blood sample is obtained, the method provided results within 24 hours,” according to Dr. Ayan, who is now planning a randomized trial to test the ability of the algorithm to improve clinical outcomes.
In the decision tree, there are five yes-no pathways to a treatment choice. The first step of the algorithm is to test the ratio of TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD4+ T cells. A “yes’ response is produced if the ratio is greater than or equal to 2. These patients are then evaluated for the ratio of TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD8+ T cells. A yes response is produced if the ratio is greater than or equal to 0.5. If yes, they are candidates for a TNF-alpha inhibitor. If no, they are directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
If the answer at the first decision point in the algorithm is a “no,” meaning they do not have a TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD4+ ratio of 2 or higher, they are evaluated for percentage of CD4+ T cells expressing IL-22 or IL-17. Is it greater than or equal to 2%? If the answer is “no,” they are candidates for an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
If “yes,” they are evaluated for percentage of IL-22 to IL-17 CD4+. If the IL-22 CD4+ percentage is lower than the IL-17 CD4+ percentage, meaning a “yes” to this decision point, they are directed to an IL-17 inhibitor. If the answer at this decision point is “no,” they are directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
Prior to enrollment in this proof-of-concept study, 10 of the bDMARD patients were scheduled to receive an anti-TNF drug and 1 was scheduled to receive an IL-12/23 inhibitor. On the basis of this algorithm, only 5 patients were directed to an anti-TNF drug. Of the remaining, 5 were directed to an IL-17 inhibitor, and 1 was directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
All 19 participants in the proof-of-concept study had peripheral arthritis; their median age was 45 years. Approximately 90% had skin lesions. Axial involvement was present in only one patient. Based on these and other characteristics and the median ratios of the cytokines measured, Dr. Ayan called this a representative population.
Based on the feasibility of this method for subtyping patients by T-cell behavior to guide drug selection, Dr. Ayan anticipates pursuing the additional steps that would show the algorithm makes a difference to patient care, including such adjunctive benefits as more cost-effective treatment selection.
“We aim to develop a treatment decision algorithm that can be implemented in daily practice,” Dr. Ayan said.
Is peripheral blood sampling adequate?
In addition to saying that the algorithm will need to prove that it alters outcomes, Samuel Tzen-yue Hwang, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of California, Davis, Sacramento, pointed out some potential practical issues.
“Flow cytometry is not typically available as a rapid throughput, and the cost is high,” he said. Moreover, he remains skeptical about performing this algorithm on the basis of peripheral blood samples.
“It is debatable that looking at peripheral cells would provide adequate information about what is taking place at sites of inflammation,” he said. Although it would “be fantastic” to develop an algorithm that required only a peripheral blood sample, he pointed out that “only a fraction of these cells is relevant” to disease activity.
Aspirating fluid from an involved joint “might be more useful,” but it is more work, he added. Yet, Dr. Hwang acknowledged that this approach is intriguing. He agreed that there is considerable heterogeneity among patients with PsA in their response to specific biologics, and a method to better direct patients to the treatment most likely to elicit a response is needed.
Dr. Ayan and Dr. Hwang reported no potential conflicts of interest.
Biologic selection is cytokine based
Biologic selection is cytokine based
NEW YORK – An algorithm in development for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is showing promise for directing patients to the biologic with the greatest likelihood of producing disease control, according to a proof-of-concept study presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Our technique involves a more precise functional assay showing exact T-cell behavior, compared to the previous assessments that only analyzed cellular phenotypes,” reported Gizem Ayan, MD, a fellow in rheumatology at Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey.
The concept of precision medicine in PsA as well as other autoimmune diseases is not new. Phenotypes and biomarkers have already shown potential for guiding treatment, according to Dr. Ayan, but she said none are yet guideline recommended or proven to improve patient outcomes.
The principle of the new algorithm that she and her coinvestigators are pursing is based on immunophenotype analysis conducted with a flow-cytometric cytokine secretion assay (FCCSA). In the protocol, monocytes obtained from peripheral blood undergo activation before an FCCSA to distinguish patients by their T-cell behavior.
The treatment decision tree is based on median ratios of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)–22, IL-17, and interferon-gamma expression among CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Based on a yes-or-no response to specific immune patterns, the patient is funneled to a biologic that inhibits a dominant cytokine.
The proof-of-concept study, which enrolled 8 patients with PsA who were naive to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and 11 patients with PsA who were naive to biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs), was designed to demonstrate feasibility. It did not test clinical benefit, but it did show that immunophenotyping with this methodology can be performed efficiently.
“From the time a blood sample is obtained, the method provided results within 24 hours,” according to Dr. Ayan, who is now planning a randomized trial to test the ability of the algorithm to improve clinical outcomes.
In the decision tree, there are five yes-no pathways to a treatment choice. The first step of the algorithm is to test the ratio of TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD4+ T cells. A “yes’ response is produced if the ratio is greater than or equal to 2. These patients are then evaluated for the ratio of TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD8+ T cells. A yes response is produced if the ratio is greater than or equal to 0.5. If yes, they are candidates for a TNF-alpha inhibitor. If no, they are directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
If the answer at the first decision point in the algorithm is a “no,” meaning they do not have a TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD4+ ratio of 2 or higher, they are evaluated for percentage of CD4+ T cells expressing IL-22 or IL-17. Is it greater than or equal to 2%? If the answer is “no,” they are candidates for an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
If “yes,” they are evaluated for percentage of IL-22 to IL-17 CD4+. If the IL-22 CD4+ percentage is lower than the IL-17 CD4+ percentage, meaning a “yes” to this decision point, they are directed to an IL-17 inhibitor. If the answer at this decision point is “no,” they are directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
Prior to enrollment in this proof-of-concept study, 10 of the bDMARD patients were scheduled to receive an anti-TNF drug and 1 was scheduled to receive an IL-12/23 inhibitor. On the basis of this algorithm, only 5 patients were directed to an anti-TNF drug. Of the remaining, 5 were directed to an IL-17 inhibitor, and 1 was directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
All 19 participants in the proof-of-concept study had peripheral arthritis; their median age was 45 years. Approximately 90% had skin lesions. Axial involvement was present in only one patient. Based on these and other characteristics and the median ratios of the cytokines measured, Dr. Ayan called this a representative population.
Based on the feasibility of this method for subtyping patients by T-cell behavior to guide drug selection, Dr. Ayan anticipates pursuing the additional steps that would show the algorithm makes a difference to patient care, including such adjunctive benefits as more cost-effective treatment selection.
“We aim to develop a treatment decision algorithm that can be implemented in daily practice,” Dr. Ayan said.
Is peripheral blood sampling adequate?
In addition to saying that the algorithm will need to prove that it alters outcomes, Samuel Tzen-yue Hwang, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of California, Davis, Sacramento, pointed out some potential practical issues.
“Flow cytometry is not typically available as a rapid throughput, and the cost is high,” he said. Moreover, he remains skeptical about performing this algorithm on the basis of peripheral blood samples.
“It is debatable that looking at peripheral cells would provide adequate information about what is taking place at sites of inflammation,” he said. Although it would “be fantastic” to develop an algorithm that required only a peripheral blood sample, he pointed out that “only a fraction of these cells is relevant” to disease activity.
Aspirating fluid from an involved joint “might be more useful,” but it is more work, he added. Yet, Dr. Hwang acknowledged that this approach is intriguing. He agreed that there is considerable heterogeneity among patients with PsA in their response to specific biologics, and a method to better direct patients to the treatment most likely to elicit a response is needed.
Dr. Ayan and Dr. Hwang reported no potential conflicts of interest.
NEW YORK – An algorithm in development for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is showing promise for directing patients to the biologic with the greatest likelihood of producing disease control, according to a proof-of-concept study presented at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Our technique involves a more precise functional assay showing exact T-cell behavior, compared to the previous assessments that only analyzed cellular phenotypes,” reported Gizem Ayan, MD, a fellow in rheumatology at Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey.
The concept of precision medicine in PsA as well as other autoimmune diseases is not new. Phenotypes and biomarkers have already shown potential for guiding treatment, according to Dr. Ayan, but she said none are yet guideline recommended or proven to improve patient outcomes.
The principle of the new algorithm that she and her coinvestigators are pursing is based on immunophenotype analysis conducted with a flow-cytometric cytokine secretion assay (FCCSA). In the protocol, monocytes obtained from peripheral blood undergo activation before an FCCSA to distinguish patients by their T-cell behavior.
The treatment decision tree is based on median ratios of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)–22, IL-17, and interferon-gamma expression among CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Based on a yes-or-no response to specific immune patterns, the patient is funneled to a biologic that inhibits a dominant cytokine.
The proof-of-concept study, which enrolled 8 patients with PsA who were naive to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and 11 patients with PsA who were naive to biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs), was designed to demonstrate feasibility. It did not test clinical benefit, but it did show that immunophenotyping with this methodology can be performed efficiently.
“From the time a blood sample is obtained, the method provided results within 24 hours,” according to Dr. Ayan, who is now planning a randomized trial to test the ability of the algorithm to improve clinical outcomes.
In the decision tree, there are five yes-no pathways to a treatment choice. The first step of the algorithm is to test the ratio of TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD4+ T cells. A “yes’ response is produced if the ratio is greater than or equal to 2. These patients are then evaluated for the ratio of TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD8+ T cells. A yes response is produced if the ratio is greater than or equal to 0.5. If yes, they are candidates for a TNF-alpha inhibitor. If no, they are directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
If the answer at the first decision point in the algorithm is a “no,” meaning they do not have a TNF-alpha to interferon-gamma CD4+ ratio of 2 or higher, they are evaluated for percentage of CD4+ T cells expressing IL-22 or IL-17. Is it greater than or equal to 2%? If the answer is “no,” they are candidates for an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
If “yes,” they are evaluated for percentage of IL-22 to IL-17 CD4+. If the IL-22 CD4+ percentage is lower than the IL-17 CD4+ percentage, meaning a “yes” to this decision point, they are directed to an IL-17 inhibitor. If the answer at this decision point is “no,” they are directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
Prior to enrollment in this proof-of-concept study, 10 of the bDMARD patients were scheduled to receive an anti-TNF drug and 1 was scheduled to receive an IL-12/23 inhibitor. On the basis of this algorithm, only 5 patients were directed to an anti-TNF drug. Of the remaining, 5 were directed to an IL-17 inhibitor, and 1 was directed to an IL-12/23 inhibitor.
All 19 participants in the proof-of-concept study had peripheral arthritis; their median age was 45 years. Approximately 90% had skin lesions. Axial involvement was present in only one patient. Based on these and other characteristics and the median ratios of the cytokines measured, Dr. Ayan called this a representative population.
Based on the feasibility of this method for subtyping patients by T-cell behavior to guide drug selection, Dr. Ayan anticipates pursuing the additional steps that would show the algorithm makes a difference to patient care, including such adjunctive benefits as more cost-effective treatment selection.
“We aim to develop a treatment decision algorithm that can be implemented in daily practice,” Dr. Ayan said.
Is peripheral blood sampling adequate?
In addition to saying that the algorithm will need to prove that it alters outcomes, Samuel Tzen-yue Hwang, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of California, Davis, Sacramento, pointed out some potential practical issues.
“Flow cytometry is not typically available as a rapid throughput, and the cost is high,” he said. Moreover, he remains skeptical about performing this algorithm on the basis of peripheral blood samples.
“It is debatable that looking at peripheral cells would provide adequate information about what is taking place at sites of inflammation,” he said. Although it would “be fantastic” to develop an algorithm that required only a peripheral blood sample, he pointed out that “only a fraction of these cells is relevant” to disease activity.
Aspirating fluid from an involved joint “might be more useful,” but it is more work, he added. Yet, Dr. Hwang acknowledged that this approach is intriguing. He agreed that there is considerable heterogeneity among patients with PsA in their response to specific biologics, and a method to better direct patients to the treatment most likely to elicit a response is needed.
Dr. Ayan and Dr. Hwang reported no potential conflicts of interest.
T-cell behavior
T-cell behavior
AT GRAPPA 2022
The shifting sands of lung cancer screening
An analysis of trends in lung cancer screening since March 2021 when the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) expanded the eligibility criteria for lung cancer screening, shows that significantly more Black men have been screened for lung cancer, but not women or undereducated people.
The eligibility for lung cancer screening was expanded in 2021 to include men and women under 50 years old and people who smoke at least one pack of cigarettes a day for the last 20 years. “
“Expansion of screening criteria is a critical first step to achieving equity in lung cancer screening for all high-risk populations, but myriad challenges remain before individuals enter the door for screening,” wrote the authors, led by Julie A. Barta, MD, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. “Health policy changes must occur simultaneously with efforts to expand community outreach, overcome logistical barriers, and facilitate screening adherence. Only after comprehensive strategies to dismantle screening barriers are identified, validated, and implemented can there be a truly equitable landscape for lung cancer screening.”
For the study, published in JAMA Open Network, researchers examined rates of centralized lung cancer screening in the Baltimore area. In addition to expanding lung cancer screening generally, there was hope that the expanded criteria might increase uptake of screening in populations that are traditionally underserved, such as African American, Hispanic, and female patients. Of 815 people screened during the study period (March-December 2021), 161 were newly eligible for screening under the 2021 criteria.
“There’s been quite a bit of work in the field demonstrating that Black men and women develop lung cancer at more advanced stages of disease, and they often are diagnosed at younger ages and have fewer pack-years of smoking. So the hypothesis was that this would reduce some of the disparities seen in lung cancer screening by making more people eligible,” Dr. Barta said in an interview.
The researchers categorized participants as those who would have been eligible for screening under the USPSTF 2013 guideline (age 55 or older, 30 or more pack-years, quit within the past 15 years), and those who would be eligible under the 2021 guideline (age 50 or older, 20 or more pack-years, quit within the past 15 years). Of the 2021 cohort, 54.5% were African American, versus 39.5% of the 2013 cohort (P = .002). There were no differences between the cohorts with respect to education level or gender.
“Although we’ve seen some encouraging improvement in terms of getting more eligible patients into our screening program, there’s still a lot of work to be done in the field,” Dr. Barta said. “Diagnosing lung cancer at earlier stages of disease is more cost effective in general for the health care system than fighting lung cancer at advanced stages, which requires more complex and multimodal and prolonged therapies.”
New evidence: Chest CTs for lung cancer screening reduces incidence of advanced lung cancer
In an analysis of the SEER database presented in June at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the adoption of low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) led to fewer diagnoses of advanced lung cancer, although these declines varied significantly by race and ethnicity. Non-Hispanic Blacks seemed to benefit the most with a 55% decline (P < .01), while Hispanics had the lowest rate of decline at 41% (P < .01). The change was recommended by USPSTF in 2013 after the National Lung Screening Trial revealed a 20% relative reduction in mortality when CT scans were used instead of chest radiography. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approved coverage of the screen in 2015.
The SEER study looked at data from 400,343 individuals from 2004-2014 (preintervention) and 2015-2018 (postintervention). The age-adjusted incidence of advanced lung cancer declined during both periods, but the decline was sharper between 2015 and 2018, with three fewer cases per 100,000 people than 2004-2014 (P < .01). Similar patterns were seen in subanalyses of males and females, non-Hispanic Whites, non-Hispanic Blacks, and Hispanics. The relative declines were largest in women, non-Hispanic Blacks, and people who lived outside of Metropolitan areas.
During a Q&A session that followed the presentation, Robert Smith, PhD, pointed out that the bar for eligibility of lung cancer risk has been set quite high, following the eligibility criteria for clinical trials. He noted that . “We are missing opportunities to prevent avertable lung cancer deaths,” said Dr. Smith, senior vice president of cancer screening at the American Cancer Society.
On the other hand, screening-prompted biopsies have the potential to cause harm, particularly in patients who already have lung disease, said Douglas Allen Arenberg, MD, professor at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think that’s what scares most people is the potential downside, which is very hard to measure outside of a clinical trial,” said Dr. Arenberg, who served as a discussant for the presentation.
One way to reduce that risk is to identify biomarkers, either for screens or for incidentally-detected nodules, that have good negative predictive value. “If I had a blood test that is as good as a negative PET scan, I’m going to be much more likely to say, ‘Yeah, you’re 40 and your grandfather had lung cancer. Maybe you should get a CT. If we had that, we could screen a lot more people. Right now, I would discourage anybody who is at low risk from getting screened because when they come to me, the biggest opportunity I have to do harm is when I do a biopsy, and you always remember the ones that go wrong,” he said.
Dr. Arenberg also called for improvements in electronic medical records to better flag at-risk patients. “I think we as physicians have to demand more of the software developers that create these EMRs for us,” he said.
Another study in the same session used data from 1,391,088 patients drawn from the National Cancer Database between 2010 and 2017 to examine trends in diagnosis of stage I cancer. In 2010, 23.5% of patients were diagnosed as stage I, versus 29.1% in 2017. Stage I incidence increased from 25.8% to 31.7% in non–small cell lung cancer, but there was no statistically significant change in small cell lung cancer. As with the SEER database study, the researchers noted that the shift toward stage I diagnoses predated the recommendation of LDCT.
Dr. Arenberg suggested that the trend may come down to increased frequency of CT scans, which often collect incidental images of the lungs. He added that better access to care may also be helping to drive the change. “How much of that might have had something to do with the introduction 5 or 10 years earlier of the Affordable Care Act and people just simply having access to care and taking advantage of that?” Dr. Arenberg said.
But Dr. Arenberg said that not even screening can explain all the data. He referenced a stage shift in patients of all age groups in the National Cancer Database study, even those too young to be eligible for screening. “There’s something else going on here. It would be nice for us to understand what caused these trends, so perhaps we could accentuate that trend even more, but stage shifts are clearly occurring in lung cancer,” Dr. Arenberg said.
Dr. Barta has received grants from Genentech Health Equity Innovations Fund. Dr. Arenberg has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Smith’s potential disclosures could not be ascertained.
An analysis of trends in lung cancer screening since March 2021 when the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) expanded the eligibility criteria for lung cancer screening, shows that significantly more Black men have been screened for lung cancer, but not women or undereducated people.
The eligibility for lung cancer screening was expanded in 2021 to include men and women under 50 years old and people who smoke at least one pack of cigarettes a day for the last 20 years. “
“Expansion of screening criteria is a critical first step to achieving equity in lung cancer screening for all high-risk populations, but myriad challenges remain before individuals enter the door for screening,” wrote the authors, led by Julie A. Barta, MD, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. “Health policy changes must occur simultaneously with efforts to expand community outreach, overcome logistical barriers, and facilitate screening adherence. Only after comprehensive strategies to dismantle screening barriers are identified, validated, and implemented can there be a truly equitable landscape for lung cancer screening.”
For the study, published in JAMA Open Network, researchers examined rates of centralized lung cancer screening in the Baltimore area. In addition to expanding lung cancer screening generally, there was hope that the expanded criteria might increase uptake of screening in populations that are traditionally underserved, such as African American, Hispanic, and female patients. Of 815 people screened during the study period (March-December 2021), 161 were newly eligible for screening under the 2021 criteria.
“There’s been quite a bit of work in the field demonstrating that Black men and women develop lung cancer at more advanced stages of disease, and they often are diagnosed at younger ages and have fewer pack-years of smoking. So the hypothesis was that this would reduce some of the disparities seen in lung cancer screening by making more people eligible,” Dr. Barta said in an interview.
The researchers categorized participants as those who would have been eligible for screening under the USPSTF 2013 guideline (age 55 or older, 30 or more pack-years, quit within the past 15 years), and those who would be eligible under the 2021 guideline (age 50 or older, 20 or more pack-years, quit within the past 15 years). Of the 2021 cohort, 54.5% were African American, versus 39.5% of the 2013 cohort (P = .002). There were no differences between the cohorts with respect to education level or gender.
“Although we’ve seen some encouraging improvement in terms of getting more eligible patients into our screening program, there’s still a lot of work to be done in the field,” Dr. Barta said. “Diagnosing lung cancer at earlier stages of disease is more cost effective in general for the health care system than fighting lung cancer at advanced stages, which requires more complex and multimodal and prolonged therapies.”
New evidence: Chest CTs for lung cancer screening reduces incidence of advanced lung cancer
In an analysis of the SEER database presented in June at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the adoption of low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) led to fewer diagnoses of advanced lung cancer, although these declines varied significantly by race and ethnicity. Non-Hispanic Blacks seemed to benefit the most with a 55% decline (P < .01), while Hispanics had the lowest rate of decline at 41% (P < .01). The change was recommended by USPSTF in 2013 after the National Lung Screening Trial revealed a 20% relative reduction in mortality when CT scans were used instead of chest radiography. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approved coverage of the screen in 2015.
The SEER study looked at data from 400,343 individuals from 2004-2014 (preintervention) and 2015-2018 (postintervention). The age-adjusted incidence of advanced lung cancer declined during both periods, but the decline was sharper between 2015 and 2018, with three fewer cases per 100,000 people than 2004-2014 (P < .01). Similar patterns were seen in subanalyses of males and females, non-Hispanic Whites, non-Hispanic Blacks, and Hispanics. The relative declines were largest in women, non-Hispanic Blacks, and people who lived outside of Metropolitan areas.
During a Q&A session that followed the presentation, Robert Smith, PhD, pointed out that the bar for eligibility of lung cancer risk has been set quite high, following the eligibility criteria for clinical trials. He noted that . “We are missing opportunities to prevent avertable lung cancer deaths,” said Dr. Smith, senior vice president of cancer screening at the American Cancer Society.
On the other hand, screening-prompted biopsies have the potential to cause harm, particularly in patients who already have lung disease, said Douglas Allen Arenberg, MD, professor at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think that’s what scares most people is the potential downside, which is very hard to measure outside of a clinical trial,” said Dr. Arenberg, who served as a discussant for the presentation.
One way to reduce that risk is to identify biomarkers, either for screens or for incidentally-detected nodules, that have good negative predictive value. “If I had a blood test that is as good as a negative PET scan, I’m going to be much more likely to say, ‘Yeah, you’re 40 and your grandfather had lung cancer. Maybe you should get a CT. If we had that, we could screen a lot more people. Right now, I would discourage anybody who is at low risk from getting screened because when they come to me, the biggest opportunity I have to do harm is when I do a biopsy, and you always remember the ones that go wrong,” he said.
Dr. Arenberg also called for improvements in electronic medical records to better flag at-risk patients. “I think we as physicians have to demand more of the software developers that create these EMRs for us,” he said.
Another study in the same session used data from 1,391,088 patients drawn from the National Cancer Database between 2010 and 2017 to examine trends in diagnosis of stage I cancer. In 2010, 23.5% of patients were diagnosed as stage I, versus 29.1% in 2017. Stage I incidence increased from 25.8% to 31.7% in non–small cell lung cancer, but there was no statistically significant change in small cell lung cancer. As with the SEER database study, the researchers noted that the shift toward stage I diagnoses predated the recommendation of LDCT.
Dr. Arenberg suggested that the trend may come down to increased frequency of CT scans, which often collect incidental images of the lungs. He added that better access to care may also be helping to drive the change. “How much of that might have had something to do with the introduction 5 or 10 years earlier of the Affordable Care Act and people just simply having access to care and taking advantage of that?” Dr. Arenberg said.
But Dr. Arenberg said that not even screening can explain all the data. He referenced a stage shift in patients of all age groups in the National Cancer Database study, even those too young to be eligible for screening. “There’s something else going on here. It would be nice for us to understand what caused these trends, so perhaps we could accentuate that trend even more, but stage shifts are clearly occurring in lung cancer,” Dr. Arenberg said.
Dr. Barta has received grants from Genentech Health Equity Innovations Fund. Dr. Arenberg has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Smith’s potential disclosures could not be ascertained.
An analysis of trends in lung cancer screening since March 2021 when the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) expanded the eligibility criteria for lung cancer screening, shows that significantly more Black men have been screened for lung cancer, but not women or undereducated people.
The eligibility for lung cancer screening was expanded in 2021 to include men and women under 50 years old and people who smoke at least one pack of cigarettes a day for the last 20 years. “
“Expansion of screening criteria is a critical first step to achieving equity in lung cancer screening for all high-risk populations, but myriad challenges remain before individuals enter the door for screening,” wrote the authors, led by Julie A. Barta, MD, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. “Health policy changes must occur simultaneously with efforts to expand community outreach, overcome logistical barriers, and facilitate screening adherence. Only after comprehensive strategies to dismantle screening barriers are identified, validated, and implemented can there be a truly equitable landscape for lung cancer screening.”
For the study, published in JAMA Open Network, researchers examined rates of centralized lung cancer screening in the Baltimore area. In addition to expanding lung cancer screening generally, there was hope that the expanded criteria might increase uptake of screening in populations that are traditionally underserved, such as African American, Hispanic, and female patients. Of 815 people screened during the study period (March-December 2021), 161 were newly eligible for screening under the 2021 criteria.
“There’s been quite a bit of work in the field demonstrating that Black men and women develop lung cancer at more advanced stages of disease, and they often are diagnosed at younger ages and have fewer pack-years of smoking. So the hypothesis was that this would reduce some of the disparities seen in lung cancer screening by making more people eligible,” Dr. Barta said in an interview.
The researchers categorized participants as those who would have been eligible for screening under the USPSTF 2013 guideline (age 55 or older, 30 or more pack-years, quit within the past 15 years), and those who would be eligible under the 2021 guideline (age 50 or older, 20 or more pack-years, quit within the past 15 years). Of the 2021 cohort, 54.5% were African American, versus 39.5% of the 2013 cohort (P = .002). There were no differences between the cohorts with respect to education level or gender.
“Although we’ve seen some encouraging improvement in terms of getting more eligible patients into our screening program, there’s still a lot of work to be done in the field,” Dr. Barta said. “Diagnosing lung cancer at earlier stages of disease is more cost effective in general for the health care system than fighting lung cancer at advanced stages, which requires more complex and multimodal and prolonged therapies.”
New evidence: Chest CTs for lung cancer screening reduces incidence of advanced lung cancer
In an analysis of the SEER database presented in June at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the adoption of low-dose chest computed tomography (LDCT) led to fewer diagnoses of advanced lung cancer, although these declines varied significantly by race and ethnicity. Non-Hispanic Blacks seemed to benefit the most with a 55% decline (P < .01), while Hispanics had the lowest rate of decline at 41% (P < .01). The change was recommended by USPSTF in 2013 after the National Lung Screening Trial revealed a 20% relative reduction in mortality when CT scans were used instead of chest radiography. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approved coverage of the screen in 2015.
The SEER study looked at data from 400,343 individuals from 2004-2014 (preintervention) and 2015-2018 (postintervention). The age-adjusted incidence of advanced lung cancer declined during both periods, but the decline was sharper between 2015 and 2018, with three fewer cases per 100,000 people than 2004-2014 (P < .01). Similar patterns were seen in subanalyses of males and females, non-Hispanic Whites, non-Hispanic Blacks, and Hispanics. The relative declines were largest in women, non-Hispanic Blacks, and people who lived outside of Metropolitan areas.
During a Q&A session that followed the presentation, Robert Smith, PhD, pointed out that the bar for eligibility of lung cancer risk has been set quite high, following the eligibility criteria for clinical trials. He noted that . “We are missing opportunities to prevent avertable lung cancer deaths,” said Dr. Smith, senior vice president of cancer screening at the American Cancer Society.
On the other hand, screening-prompted biopsies have the potential to cause harm, particularly in patients who already have lung disease, said Douglas Allen Arenberg, MD, professor at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think that’s what scares most people is the potential downside, which is very hard to measure outside of a clinical trial,” said Dr. Arenberg, who served as a discussant for the presentation.
One way to reduce that risk is to identify biomarkers, either for screens or for incidentally-detected nodules, that have good negative predictive value. “If I had a blood test that is as good as a negative PET scan, I’m going to be much more likely to say, ‘Yeah, you’re 40 and your grandfather had lung cancer. Maybe you should get a CT. If we had that, we could screen a lot more people. Right now, I would discourage anybody who is at low risk from getting screened because when they come to me, the biggest opportunity I have to do harm is when I do a biopsy, and you always remember the ones that go wrong,” he said.
Dr. Arenberg also called for improvements in electronic medical records to better flag at-risk patients. “I think we as physicians have to demand more of the software developers that create these EMRs for us,” he said.
Another study in the same session used data from 1,391,088 patients drawn from the National Cancer Database between 2010 and 2017 to examine trends in diagnosis of stage I cancer. In 2010, 23.5% of patients were diagnosed as stage I, versus 29.1% in 2017. Stage I incidence increased from 25.8% to 31.7% in non–small cell lung cancer, but there was no statistically significant change in small cell lung cancer. As with the SEER database study, the researchers noted that the shift toward stage I diagnoses predated the recommendation of LDCT.
Dr. Arenberg suggested that the trend may come down to increased frequency of CT scans, which often collect incidental images of the lungs. He added that better access to care may also be helping to drive the change. “How much of that might have had something to do with the introduction 5 or 10 years earlier of the Affordable Care Act and people just simply having access to care and taking advantage of that?” Dr. Arenberg said.
But Dr. Arenberg said that not even screening can explain all the data. He referenced a stage shift in patients of all age groups in the National Cancer Database study, even those too young to be eligible for screening. “There’s something else going on here. It would be nice for us to understand what caused these trends, so perhaps we could accentuate that trend even more, but stage shifts are clearly occurring in lung cancer,” Dr. Arenberg said.
Dr. Barta has received grants from Genentech Health Equity Innovations Fund. Dr. Arenberg has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Smith’s potential disclosures could not be ascertained.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Study eyes characteristics of pediatric patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.
“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.
“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.
“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
AT SPD 2022
Pembrolizumab for melanoma bittersweet, doctor says
CHICAGO – Pembrolizumab has shown promise as adjuvant therapy for stage IIB and IIC melanoma, shows the first interim analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-716 study recently published in The Lancet.
The findings meet an unmet need as the recurrence risk in stage IIB and IIC melanoma is “underrecognized,” said author Georgina Long, MD, comedical director of the Melanoma Institute Australia, University of Sydney.
In fact, their risk of recurrence is similar to patients with stage IIIB disease, wrote David Killock, PhD, in a related commentary published in Nature Reviews.
The adjuvant treatment resulted in an 89% recurrence-free survival in patients who received pembrolizumab, compared with 83% of patients in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.65; P = .0066). These findings were used as the basis for Food and Drug Administration approval of pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) for this patient population in December 2021.
Despite the positive findings, Dr. Killock called for more research on distant metastasis-free survival, overall survival, and quality of life data to “establish the true clinical benefit of adjuvant pembrolizumab.”
At the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Long presented the third interim analysis which showed pembrolizumab reduced recurrence and distant metastases at 24 months, although the clinical benefit was relatively small at an approximately 8% improvement in recurrence-free survival and about a 6% improvement in distant metastasis-free survival. About 83% in the pembrolizumab group had treatment-related toxicities versus 64% in the placebo group. There were no deaths caused by treatment. About 90% of pembrolizumab-related endocrinopathies led to long-term hormone replacement.
In a discussion that followed the presentation at ASCO, Charlotte Eielson Ariyan, MD, PhD, said the results are bittersweet. Higher-risk stage IIC patients have a risk of recurrence of about 40%. “It’s high, but the absolute risk reduction is about 8%. This is a very personalized discussion with the patient and the physician in understanding their risk of toxicity is about 17% and higher than their absolute risk reduction with the treatment. For me, this is a bitter pill to swallow because you’re treating people longer and you’re not sure if you’re really helping them. Until we can further define who the highest-risk patients are, I think it’s hard to give it to everyone,” said Dr. Ariyan, who is a surgeon with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
In addition to weighing short-term benefits and toxicity, there are longer-term concerns. Toxicity experienced from PD-1 inhibitors in the adjuvant setting could impact future treatment decisions. “We’re very lucky here in melanoma to know that systemic therapies are effective and we can cure people who recur. I would argue this is why we probably will never really see a difference in the survival benefit in this group because people who cross over will probably do well,” Dr. Ariyan said.
During the Q&A session, Vernon Sondek, MD, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, encouraged physician colleagues to have an open mind about treatments. “Beware of dogma. We thought that adjuvant immunotherapy works much better in patients with ulcerated primary tumors. That’s a dogma in some parts of the world. Yet the T4a patients in KEYNOTE-716 dramatically outperformed the ulcerated T3b and T4b [patients]. We still don’t know what we don’t know.”
The study details
KEYNOTE-716 included 976 patients 12 years or older with newly diagnosed completely resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma with a negative sentinel lymph node. Patients were randomized to placebo or 200 mg pembrolizumab every 3 weeks, or 2 mg/kg in pediatric patients, over 17 cycles. Almost 40% of patients were age 65 or older. T3b and T4b were the most common melanoma subcategories at 41% and 35%, respectively.
The planned third interim analysis occurred after the occurrence of 146 distant metastases. After a median follow-up of 27.4 months, distant metastasis-free survival favored the pembrolizumab group (HR, 0.64; P = .0029). At 24 months, the pembrolizumab group had a higher distant metastasis-free survival at 88.1% versus 82.2% and a lower recurrence rate at 81.2% versus 72.8% (HR, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-0.84).
At 24 months, only the T4a patients had a statistically significant reduction in distant metastases at 58% (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.19-0.96), although there were numerical reductions in T3a (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.41-1.22) and T4b (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.44-1.33) patients. Of patients experiencing a distant metastasis, 73% of the placebo group had a first distant metastasis to the lung compared with 49% of the pembrolizumab group.
Dr. Long has held consulting or advisory roles for Merck Sharpe & Dohme, which funded this study.
CHICAGO – Pembrolizumab has shown promise as adjuvant therapy for stage IIB and IIC melanoma, shows the first interim analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-716 study recently published in The Lancet.
The findings meet an unmet need as the recurrence risk in stage IIB and IIC melanoma is “underrecognized,” said author Georgina Long, MD, comedical director of the Melanoma Institute Australia, University of Sydney.
In fact, their risk of recurrence is similar to patients with stage IIIB disease, wrote David Killock, PhD, in a related commentary published in Nature Reviews.
The adjuvant treatment resulted in an 89% recurrence-free survival in patients who received pembrolizumab, compared with 83% of patients in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.65; P = .0066). These findings were used as the basis for Food and Drug Administration approval of pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) for this patient population in December 2021.
Despite the positive findings, Dr. Killock called for more research on distant metastasis-free survival, overall survival, and quality of life data to “establish the true clinical benefit of adjuvant pembrolizumab.”
At the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Long presented the third interim analysis which showed pembrolizumab reduced recurrence and distant metastases at 24 months, although the clinical benefit was relatively small at an approximately 8% improvement in recurrence-free survival and about a 6% improvement in distant metastasis-free survival. About 83% in the pembrolizumab group had treatment-related toxicities versus 64% in the placebo group. There were no deaths caused by treatment. About 90% of pembrolizumab-related endocrinopathies led to long-term hormone replacement.
In a discussion that followed the presentation at ASCO, Charlotte Eielson Ariyan, MD, PhD, said the results are bittersweet. Higher-risk stage IIC patients have a risk of recurrence of about 40%. “It’s high, but the absolute risk reduction is about 8%. This is a very personalized discussion with the patient and the physician in understanding their risk of toxicity is about 17% and higher than their absolute risk reduction with the treatment. For me, this is a bitter pill to swallow because you’re treating people longer and you’re not sure if you’re really helping them. Until we can further define who the highest-risk patients are, I think it’s hard to give it to everyone,” said Dr. Ariyan, who is a surgeon with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
In addition to weighing short-term benefits and toxicity, there are longer-term concerns. Toxicity experienced from PD-1 inhibitors in the adjuvant setting could impact future treatment decisions. “We’re very lucky here in melanoma to know that systemic therapies are effective and we can cure people who recur. I would argue this is why we probably will never really see a difference in the survival benefit in this group because people who cross over will probably do well,” Dr. Ariyan said.
During the Q&A session, Vernon Sondek, MD, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, encouraged physician colleagues to have an open mind about treatments. “Beware of dogma. We thought that adjuvant immunotherapy works much better in patients with ulcerated primary tumors. That’s a dogma in some parts of the world. Yet the T4a patients in KEYNOTE-716 dramatically outperformed the ulcerated T3b and T4b [patients]. We still don’t know what we don’t know.”
The study details
KEYNOTE-716 included 976 patients 12 years or older with newly diagnosed completely resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma with a negative sentinel lymph node. Patients were randomized to placebo or 200 mg pembrolizumab every 3 weeks, or 2 mg/kg in pediatric patients, over 17 cycles. Almost 40% of patients were age 65 or older. T3b and T4b were the most common melanoma subcategories at 41% and 35%, respectively.
The planned third interim analysis occurred after the occurrence of 146 distant metastases. After a median follow-up of 27.4 months, distant metastasis-free survival favored the pembrolizumab group (HR, 0.64; P = .0029). At 24 months, the pembrolizumab group had a higher distant metastasis-free survival at 88.1% versus 82.2% and a lower recurrence rate at 81.2% versus 72.8% (HR, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-0.84).
At 24 months, only the T4a patients had a statistically significant reduction in distant metastases at 58% (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.19-0.96), although there were numerical reductions in T3a (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.41-1.22) and T4b (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.44-1.33) patients. Of patients experiencing a distant metastasis, 73% of the placebo group had a first distant metastasis to the lung compared with 49% of the pembrolizumab group.
Dr. Long has held consulting or advisory roles for Merck Sharpe & Dohme, which funded this study.
CHICAGO – Pembrolizumab has shown promise as adjuvant therapy for stage IIB and IIC melanoma, shows the first interim analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-716 study recently published in The Lancet.
The findings meet an unmet need as the recurrence risk in stage IIB and IIC melanoma is “underrecognized,” said author Georgina Long, MD, comedical director of the Melanoma Institute Australia, University of Sydney.
In fact, their risk of recurrence is similar to patients with stage IIIB disease, wrote David Killock, PhD, in a related commentary published in Nature Reviews.
The adjuvant treatment resulted in an 89% recurrence-free survival in patients who received pembrolizumab, compared with 83% of patients in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.65; P = .0066). These findings were used as the basis for Food and Drug Administration approval of pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) for this patient population in December 2021.
Despite the positive findings, Dr. Killock called for more research on distant metastasis-free survival, overall survival, and quality of life data to “establish the true clinical benefit of adjuvant pembrolizumab.”
At the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Long presented the third interim analysis which showed pembrolizumab reduced recurrence and distant metastases at 24 months, although the clinical benefit was relatively small at an approximately 8% improvement in recurrence-free survival and about a 6% improvement in distant metastasis-free survival. About 83% in the pembrolizumab group had treatment-related toxicities versus 64% in the placebo group. There were no deaths caused by treatment. About 90% of pembrolizumab-related endocrinopathies led to long-term hormone replacement.
In a discussion that followed the presentation at ASCO, Charlotte Eielson Ariyan, MD, PhD, said the results are bittersweet. Higher-risk stage IIC patients have a risk of recurrence of about 40%. “It’s high, but the absolute risk reduction is about 8%. This is a very personalized discussion with the patient and the physician in understanding their risk of toxicity is about 17% and higher than their absolute risk reduction with the treatment. For me, this is a bitter pill to swallow because you’re treating people longer and you’re not sure if you’re really helping them. Until we can further define who the highest-risk patients are, I think it’s hard to give it to everyone,” said Dr. Ariyan, who is a surgeon with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
In addition to weighing short-term benefits and toxicity, there are longer-term concerns. Toxicity experienced from PD-1 inhibitors in the adjuvant setting could impact future treatment decisions. “We’re very lucky here in melanoma to know that systemic therapies are effective and we can cure people who recur. I would argue this is why we probably will never really see a difference in the survival benefit in this group because people who cross over will probably do well,” Dr. Ariyan said.
During the Q&A session, Vernon Sondek, MD, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, encouraged physician colleagues to have an open mind about treatments. “Beware of dogma. We thought that adjuvant immunotherapy works much better in patients with ulcerated primary tumors. That’s a dogma in some parts of the world. Yet the T4a patients in KEYNOTE-716 dramatically outperformed the ulcerated T3b and T4b [patients]. We still don’t know what we don’t know.”
The study details
KEYNOTE-716 included 976 patients 12 years or older with newly diagnosed completely resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma with a negative sentinel lymph node. Patients were randomized to placebo or 200 mg pembrolizumab every 3 weeks, or 2 mg/kg in pediatric patients, over 17 cycles. Almost 40% of patients were age 65 or older. T3b and T4b were the most common melanoma subcategories at 41% and 35%, respectively.
The planned third interim analysis occurred after the occurrence of 146 distant metastases. After a median follow-up of 27.4 months, distant metastasis-free survival favored the pembrolizumab group (HR, 0.64; P = .0029). At 24 months, the pembrolizumab group had a higher distant metastasis-free survival at 88.1% versus 82.2% and a lower recurrence rate at 81.2% versus 72.8% (HR, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-0.84).
At 24 months, only the T4a patients had a statistically significant reduction in distant metastases at 58% (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.19-0.96), although there were numerical reductions in T3a (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.41-1.22) and T4b (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.44-1.33) patients. Of patients experiencing a distant metastasis, 73% of the placebo group had a first distant metastasis to the lung compared with 49% of the pembrolizumab group.
Dr. Long has held consulting or advisory roles for Merck Sharpe & Dohme, which funded this study.
AT ASCO 2022