User login
The SHOW UP Act Threatens VA Telehealth
In February, the US House of Representatives hurriedly passed the Stopping Home Office Work’s Unproductive Problems (SHOW UP) Act, H.R. 139, a bill that calls into question the contributions of federal employees allowed to work from home and resets telework policies to those in place in 2019. Its author, House Oversight Committee Chairman James Comer (R, Kentucky) claimed that this change was necessary because the expansion of federal telework during the COVID-19 pandemic “has crippled the ability of agencies to get their jobs done and created backlogs.” His targets included the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), where, he charged, “veterans have been unable…to obtain care they have earned.” He added, “it’s hard to argue that teleworking has helped the VA.”
While oversight of government programs is an authority of Congress, the SHOW UP Act is based on unsubstantiated assumptions of dereliction. It also disregards the devastating impact the proposed changes will have on veterans’ ability to receive care and inaccurately implies improving it. As the Senate considers the bill, they should take heed of these and other facts involving this often misunderstood form of labor.
COVID-19 irrevocably transformed the use of virtual care within the VA and across the world. Even as the pandemic subsides, public and private health care systems have continued to use telework-centered telehealth far above prepandemic levels, especially for mental health and primary care. Employers, including the VA, capitalize on telework for its benefits to both consumers and the workforce. For consumers, research supports the clinical effectiveness of telemental health service, as well as its cost-effectiveness and consumer satisfaction. On the workforce side, research has documented heightened productivity, lower distractibility, and higher job satisfaction among counselors who shifted to remote work.
Remote work also serves as a key tool in attracting and retaining a qualified workforce. As one VA service chief explained, “I am having enough trouble competing with the private sector, where extensive telework is now the norm. If telework options were rolled back, the private sector will have a field day picking off my best staff.” These comments are consistent with the data. McKinsey’s American Opportunity Survey shows that Americans have embraced remote work and want more of it. Recent data from Gallup show that 6 of 10 currently exclusively remote employees would be extremely likely to change companies if they lost their remote flexibility. Further, Gallup data show that when an employee’s location preference does not match their current work location, burnout rises, and engagement drops.
Between 2019 and 2023, the VA’s telework expansion is what has enabled it to meet the growing demand for mental health services. VA is keeping pace by having 2 or more clinicians rotate between home and a shared VA office. Forcing these hybrid practitioners to work full time at VA facilities would drastically reduce the number of patients they can care for. There simply are not enough offices on crammed VA grounds to house staff who telework today. The net result would be that fewer appointments would be available, creating longer wait times. And that is just for existing patients. It does not factor in the expected influx due to new veteran eligibility made possible by the toxic exposures PACT Act.
Here is another good example of crucial VA telework: With the advent of the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline, VA is adding more than 1000 new Veterans Crisis Line responders. All these new positions are remote. The SHOW UP Act would inhibit this expansion of lifesaving programs.
Veterans want more, not fewer, telehealth options. At a House Committee on Veterans’ Affairs hearing this past September, the VA reported that most veterans would prefer to receive mental health services virtually than to have to commute to a VA medical center or clinic. Telehealth benefits veterans in meaningful ways, including that it reduces their travel time, travel expense, depletion of sick leave, and need for childcare. Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder, military sexual trauma, those with mobility issues, or those who struggle with the stigma of mental health treatment may prefer the familiarity of their own homes for care. Virtual options also relieve a patient’s need to enter a hospital and be unnecessarily exposed to contagious viruses. That’s safer not only for veterans but also for VA staff.
Finally, virtual care improves treatment. Research has revealed that the likelihood of missing telehealth appointments is lower than for in-person appointments. When patients miss appointments, continuity of care is disrupted, and health care outcomes are diminished.
The pandemic is receding, but the advantages of telework-centered virtual care are greater than ever. Political representatives who want to show up for veterans should do everything in their power to expand—not cut—VA’s ability to authorize working from home.
In February, the US House of Representatives hurriedly passed the Stopping Home Office Work’s Unproductive Problems (SHOW UP) Act, H.R. 139, a bill that calls into question the contributions of federal employees allowed to work from home and resets telework policies to those in place in 2019. Its author, House Oversight Committee Chairman James Comer (R, Kentucky) claimed that this change was necessary because the expansion of federal telework during the COVID-19 pandemic “has crippled the ability of agencies to get their jobs done and created backlogs.” His targets included the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), where, he charged, “veterans have been unable…to obtain care they have earned.” He added, “it’s hard to argue that teleworking has helped the VA.”
While oversight of government programs is an authority of Congress, the SHOW UP Act is based on unsubstantiated assumptions of dereliction. It also disregards the devastating impact the proposed changes will have on veterans’ ability to receive care and inaccurately implies improving it. As the Senate considers the bill, they should take heed of these and other facts involving this often misunderstood form of labor.
COVID-19 irrevocably transformed the use of virtual care within the VA and across the world. Even as the pandemic subsides, public and private health care systems have continued to use telework-centered telehealth far above prepandemic levels, especially for mental health and primary care. Employers, including the VA, capitalize on telework for its benefits to both consumers and the workforce. For consumers, research supports the clinical effectiveness of telemental health service, as well as its cost-effectiveness and consumer satisfaction. On the workforce side, research has documented heightened productivity, lower distractibility, and higher job satisfaction among counselors who shifted to remote work.
Remote work also serves as a key tool in attracting and retaining a qualified workforce. As one VA service chief explained, “I am having enough trouble competing with the private sector, where extensive telework is now the norm. If telework options were rolled back, the private sector will have a field day picking off my best staff.” These comments are consistent with the data. McKinsey’s American Opportunity Survey shows that Americans have embraced remote work and want more of it. Recent data from Gallup show that 6 of 10 currently exclusively remote employees would be extremely likely to change companies if they lost their remote flexibility. Further, Gallup data show that when an employee’s location preference does not match their current work location, burnout rises, and engagement drops.
Between 2019 and 2023, the VA’s telework expansion is what has enabled it to meet the growing demand for mental health services. VA is keeping pace by having 2 or more clinicians rotate between home and a shared VA office. Forcing these hybrid practitioners to work full time at VA facilities would drastically reduce the number of patients they can care for. There simply are not enough offices on crammed VA grounds to house staff who telework today. The net result would be that fewer appointments would be available, creating longer wait times. And that is just for existing patients. It does not factor in the expected influx due to new veteran eligibility made possible by the toxic exposures PACT Act.
Here is another good example of crucial VA telework: With the advent of the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline, VA is adding more than 1000 new Veterans Crisis Line responders. All these new positions are remote. The SHOW UP Act would inhibit this expansion of lifesaving programs.
Veterans want more, not fewer, telehealth options. At a House Committee on Veterans’ Affairs hearing this past September, the VA reported that most veterans would prefer to receive mental health services virtually than to have to commute to a VA medical center or clinic. Telehealth benefits veterans in meaningful ways, including that it reduces their travel time, travel expense, depletion of sick leave, and need for childcare. Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder, military sexual trauma, those with mobility issues, or those who struggle with the stigma of mental health treatment may prefer the familiarity of their own homes for care. Virtual options also relieve a patient’s need to enter a hospital and be unnecessarily exposed to contagious viruses. That’s safer not only for veterans but also for VA staff.
Finally, virtual care improves treatment. Research has revealed that the likelihood of missing telehealth appointments is lower than for in-person appointments. When patients miss appointments, continuity of care is disrupted, and health care outcomes are diminished.
The pandemic is receding, but the advantages of telework-centered virtual care are greater than ever. Political representatives who want to show up for veterans should do everything in their power to expand—not cut—VA’s ability to authorize working from home.
In February, the US House of Representatives hurriedly passed the Stopping Home Office Work’s Unproductive Problems (SHOW UP) Act, H.R. 139, a bill that calls into question the contributions of federal employees allowed to work from home and resets telework policies to those in place in 2019. Its author, House Oversight Committee Chairman James Comer (R, Kentucky) claimed that this change was necessary because the expansion of federal telework during the COVID-19 pandemic “has crippled the ability of agencies to get their jobs done and created backlogs.” His targets included the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), where, he charged, “veterans have been unable…to obtain care they have earned.” He added, “it’s hard to argue that teleworking has helped the VA.”
While oversight of government programs is an authority of Congress, the SHOW UP Act is based on unsubstantiated assumptions of dereliction. It also disregards the devastating impact the proposed changes will have on veterans’ ability to receive care and inaccurately implies improving it. As the Senate considers the bill, they should take heed of these and other facts involving this often misunderstood form of labor.
COVID-19 irrevocably transformed the use of virtual care within the VA and across the world. Even as the pandemic subsides, public and private health care systems have continued to use telework-centered telehealth far above prepandemic levels, especially for mental health and primary care. Employers, including the VA, capitalize on telework for its benefits to both consumers and the workforce. For consumers, research supports the clinical effectiveness of telemental health service, as well as its cost-effectiveness and consumer satisfaction. On the workforce side, research has documented heightened productivity, lower distractibility, and higher job satisfaction among counselors who shifted to remote work.
Remote work also serves as a key tool in attracting and retaining a qualified workforce. As one VA service chief explained, “I am having enough trouble competing with the private sector, where extensive telework is now the norm. If telework options were rolled back, the private sector will have a field day picking off my best staff.” These comments are consistent with the data. McKinsey’s American Opportunity Survey shows that Americans have embraced remote work and want more of it. Recent data from Gallup show that 6 of 10 currently exclusively remote employees would be extremely likely to change companies if they lost their remote flexibility. Further, Gallup data show that when an employee’s location preference does not match their current work location, burnout rises, and engagement drops.
Between 2019 and 2023, the VA’s telework expansion is what has enabled it to meet the growing demand for mental health services. VA is keeping pace by having 2 or more clinicians rotate between home and a shared VA office. Forcing these hybrid practitioners to work full time at VA facilities would drastically reduce the number of patients they can care for. There simply are not enough offices on crammed VA grounds to house staff who telework today. The net result would be that fewer appointments would be available, creating longer wait times. And that is just for existing patients. It does not factor in the expected influx due to new veteran eligibility made possible by the toxic exposures PACT Act.
Here is another good example of crucial VA telework: With the advent of the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline, VA is adding more than 1000 new Veterans Crisis Line responders. All these new positions are remote. The SHOW UP Act would inhibit this expansion of lifesaving programs.
Veterans want more, not fewer, telehealth options. At a House Committee on Veterans’ Affairs hearing this past September, the VA reported that most veterans would prefer to receive mental health services virtually than to have to commute to a VA medical center or clinic. Telehealth benefits veterans in meaningful ways, including that it reduces their travel time, travel expense, depletion of sick leave, and need for childcare. Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder, military sexual trauma, those with mobility issues, or those who struggle with the stigma of mental health treatment may prefer the familiarity of their own homes for care. Virtual options also relieve a patient’s need to enter a hospital and be unnecessarily exposed to contagious viruses. That’s safer not only for veterans but also for VA staff.
Finally, virtual care improves treatment. Research has revealed that the likelihood of missing telehealth appointments is lower than for in-person appointments. When patients miss appointments, continuity of care is disrupted, and health care outcomes are diminished.
The pandemic is receding, but the advantages of telework-centered virtual care are greater than ever. Political representatives who want to show up for veterans should do everything in their power to expand—not cut—VA’s ability to authorize working from home.
Psychoactive supplements: What to tell patients
Mr. D, age 41, presents to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and suspected intoxication. His medical history includes alcohol use disorder and spinal injury. Upon initial examination, he is confused, disorganized, and agitated. He receives IM lorazepam 4 mg to manage his agitation. His laboratory workup includes a negative screening for blood alcohol, slightly elevated creatine kinase, and urine toxicology positive for barbiturates and opioids. During re-evaluation by the consulting psychiatrist the following morning, Mr. D is alert, oriented, and calm with an organized thought process. He does not appear to be in withdrawal from any substances and tells the psychiatrist that he takes butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine as needed for migraines. Mr. D says that 3 days before he came to the ED, he also began taking a supplement called phenibut that he purchased online for “well-being and sleep.”
Natural substances have been used throughout history as medicinal agents, sacred substances in religious rituals, and for recreational purposes.1 Supplement use in the United States is prevalent, with 57.6% of adults age ≥20 reporting supplement use in the past 30 days.2 Between 2000 and 2017, US poison control centers recorded a 74.1% increase in calls involving exposure to natural psychoactive substances, mostly driven by cases involving marijuana in adults and adolescents.3 Like synthetic drugs, herbal supplements may have psychoactive properties, including sedative, stimulant, psychedelic, euphoric, or anticholinergic effects. The variety and unregulated nature of supplements makes managing patients who use supplements particularly challenging.
Why patients use supplements
People may use supplements to treat or prevent vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, iron, calcium). Other reasons may include for promoting wellness in various disease states, for weight loss, for recreational use or misuse, or for overall well-being. In the mental health realm, patients report using supplements to treat depression, anxiety, insomnia, memory, or for vague indications such as “mood support.”4,5
Patients may view supplements as appealing alternatives to prescription medications because they are widely accessible, may be purchased over-the-counter, are inexpensive, and represent a “natural” treatment option.6 For these reasons, they may also falsely perceive supplements as categorically safe.1 People with psychiatric diagnoses may choose such alternative treatments due to a history of adverse effects or treatment failure with traditional psychiatric medications, mistrust of the health care or pharmaceutical industry, or based on the recommendations of others.7
Regulation, safety, and efficacy of dietary supplements
In the US, dietary supplements are regulated more like food products than medications. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the FDA regulates the quality, safety, and labeling of supplements using Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.8 The Federal Trade Commission monitors advertisements and marketing. Despite some regulations, dietary supplements may be adulterated or contaminated, contain unknown or toxic ingredients, have inconsistent potencies, or be sold at toxic doses.9 Importantly, supplements are not required to be evaluated for clinical efficacy. As a result, it is not known if most supplements are effective in treating the conditions for which they are promoted, mainly due to a lack of financial incentive for manufacturers to conduct large, high-quality trials.5
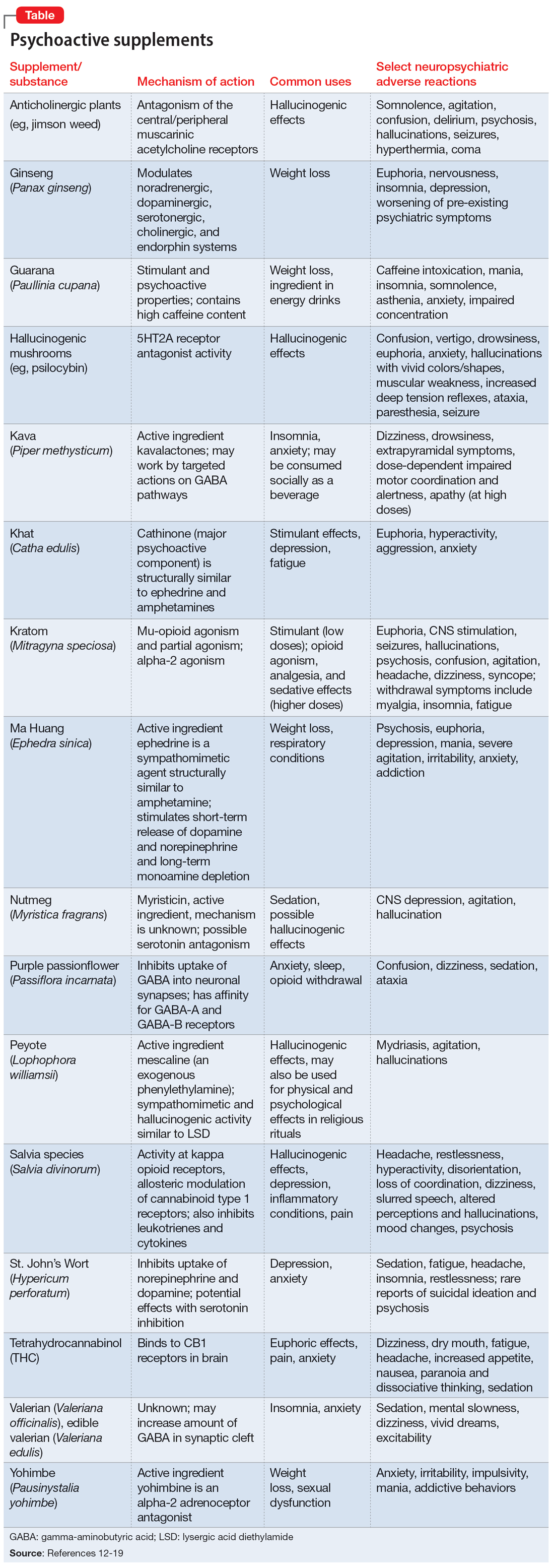
Further complicating matters is the inconsistent labeling of supplements or similar products that are easily obtainable via the internet. These products might be marketed as nutritional supplements or nootropics, which often are referred to as “cognitive enhancers” or “smart drugs.” New psychoactive substances (NPS) are drugs of misuse or abuse developed to imitate illicit drugs or controlled drug substances.10 They are sometimes referred to as “herbal highs” or “legal highs.”11 Supplements may also be labeled as performance- or image-enhancing agents and may include medications marketed to promote weight loss. This includes herbal substances (Table12-19) and medications associated with neuropsychiatric adverse effects that may be easily accessible online without a prescription.12,20
The growing popularity of the internet and social media plays an important role in the availability of supplements and nonregulated substances and may contribute to misleading claims of efficacy and safety. While many herbal supplements are available in pharmacies or supplement stores, NPS are usually sold through anonymous, low-risk means either via traditional online vendors or the deep web (parts of the internet that are not indexed via search engines). Strategies to circumvent regulation and legislative control include labeling NPS as research chemicals, fertilizers, incense, bath salts, or other identifiers and marketing them as “not for human consumption.”21 Manufacturers frequently change the chemical structures of NPS, which allows these products to exist within a legal gray area due to the lag time between when a new compound hits the market and when it is categorized as a regulated substance.10
Continue to: Another category of "supplements"...
Another category of “supplements” includes medications that are not FDA-approved but are approved for therapeutic use in other countries and readily available in the US via online sources. Such medications include phenibut, a glutamic acid derivative that functions as a gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptor agonist in the brain, spinal cord, and autonomic nervous system. Phenibut was developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s, and outside of the US it is prescribed for anxiolysis and other psychiatric indications.22 In the US, phenibut may be used as a nootropic or as a dietary supplement to treat anxiety, sleep problems, and other psychiatric disorders.22 It may also be used recreationally to induce euphoria. Chronic phenibut use results in tolerance and abrupt discontinuation may mimic benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms.13,22
Educating patients about supplements
One of the most critical steps in assessing a patient’s supplement use is to directly ask them about their use of herbal or over-the-counter products. Research has consistently shown that patients are unlikely to disclose supplement use unless they are specifically asked.23,24
Additional strategies include25,26:
- Approach patients without judgment; ask open-ended questions to determine their motivations for using supplements.
- Explain the difference between supplements medically necessary to treat vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium) and those without robust clinical evidence.
- Counsel patients that many supplements with psychoactive properties, if indicated, are generally meant to be used short-term and not as substitutes for prescription medications.
- Educate patients that supplements have limited evidence regarding their safety and efficacy, but like prescription medications, supplements may cause organ damage, adverse effects, and drug-drug interactions.
- Remind patients that commonly used nutritional supplements/dietary aids, including protein or workout supplements, may contain potentially harmful ingredients.
- Utilize evidence-based resources such as the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database14 or the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (https://www.nccih.nih.gov) to review levels of evidence and educate patients.
- When toxicity or withdrawal is suspected, reach out to local poison control centers for guidance.
- For a patient with a potential supplement-related substance use disorder, urine drug screens may be of limited utility and evidence is often sparse; clinicians may need to rely on primary literature such as case reports to guide management.
- If patients wish to continue taking a supplement, recommend they purchase supplements from manufacturers that have achieved the US Pharmacopeia (USP) verification mark. Products with the USP mark undergo quality assurance measures to ensure the product contains the ingredients listed on the label in the declared potency and amounts, does not contain harmful levels of contaminants, will be metabolized in the body within a specified amount of time, and has been produced in keeping with FDA Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.
CASE CONTINUED
In the ED, the consulting psychiatry team discusses Mr. D’s use of phenibut with him, and asks if he uses any additional supplements or nonprescription medications. Mr. D discloses he has been anxious and having trouble sleeping, and a friend recommended phenibut as a safe, natural alternative to medication. The team explains to Mr. D that phenibut’s efficacy has not been studied in the US and that based on available evidence, it is likely unsafe. It may have serious adverse effects, drug-drug interactions, and is potentially addictive.
Mr. D says he was unaware of these risks and agrees to stop taking phenibut. The treatment team discharges him from the ED with a referral for outpatient psychiatric services to address his anxiety and insomnia.
Related Resources
- Tillman B. The hidden dangers of supplements: a case of substance-induced psychosis. Current Psychiatry. 2020; 19(7):e7-e8. doi:10.12788/cp.0018
- McQueen CE. Herb–drug interactions: caution patients when changing supplements. Current Psychiatry. 2017; 16(6):38-41.
Drug Brand Names
Butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine • Fioricet with Codeine
1. Graziano S, Orsolini L, Rotolo MC, et al. Herbal highs: review on psychoactive effects and neuropharmacology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):750-761.
2. Mishra S, Stierman B, Gahche JJ, et al. Dietary supplement use among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2021;(399):1-8.
3. O’Neill-Dee C, Spiller HA, Casavant MJ, et al. Natural psychoactive substance-related exposures reported to United States poison control centers, 2000-2017. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020;58(8):813-820.
4. Gray DC, Rutledge CM. Herbal supplements in primary care: patient perceptions, motivations, and effects on use. Holist Nurs Pract. 2013;27(1):6-12.
5. Wu K, Messamore E. Reimagining roles of dietary supplements in psychiatric care. AMA J Ethics. 2022;24(5):E437-E442.
6. Snyder FJ, Dundas ML, Kirkpatrick C, et al. Use and safety perceptions regarding herbal supplements: a study of older persons in southeast Idaho. J Nutr Elder. 2009;28(1):81-95.
7. Schulz P, Hede V. Alternative and complementary approaches in psychiatry: beliefs versus evidence. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20(3):207-214.
8. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, Pub L 103-417, 103rd Cong (1993-1994).
9. Starr RR. Too little, too late: ineffective regulation of dietary supplements in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(3):478-485.
10. New psychoactive substances. Alcohol and Drug Foundation. November 10, 2021. Updated November 28, 2022. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/new-psychoactive-substances/
11. Shafi A, Berry AJ, Sumnall H, et al. New psychoactive substances: a review and updates. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320967197.
12. Bersani FS, Coviello M, Imperatori C, et al. Adverse psychiatric effects associated with herbal weight-loss products. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:120679.
13. IBM Micromedex POISINDEX® System. IBM Watson Health. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://www.micromedexsolutions.com
14. Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. Therapeutic Research Center. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com
15. Savage KM, Stough CK, Byrne GJ, et al. Kava for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (K-GAD): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:493.
16. Swogger MT, Smith KE, Garcia-Romeu A, et al. Understanding kratom use: a guide for healthcare providers. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:801855.
17. Modabbernia A, Akhondzadeh S. Saffron, passionflower, valerian and sage for mental health. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2013;36(1):85-91.
18. Coffeen U, Pellicer F. Salvia divinorum: from recreational hallucinogenic use to analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. J Pain Res. 2019;12:1069-1076.
19. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. Valerian Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Updated March 15, 2013. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Valerian-HealthProfessional
20. An H, Sohn H, Chung S. Phentermine, sibutramine and affective disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(1):7-12.
21. Miliano C, Margiani G, Fattore L, et al. Sales and advertising channels of new psychoactive substances (NPS): internet, social networks, and smartphone apps. Brain Sci. 2018;8(7):123.
22. Hardman MI, Sprung J, Weingarten TN. Acute phenibut withdrawal: a comprehensive literature review and illustrative case report. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019;19(2):125-129.
23. Guzman JR, Paterniti DA, Liu Y, et al. Factors related to disclosure and nondisclosure of dietary supplements in primary care, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine. J Fam Med Dis Prev. 2019;5(4):10.23937/2469-5793/1510109.
24. Foley H, Steel A, Cramer H, et al. Disclosure of complementary medicine use to medical providers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1573.
25. Aldridge Young C. ‘No miracle cures’: counseling patients about dietary supplements. Pharmacy Today. 2014;February:35.
26. United States Pharmacopeia. USP Verified Mark. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://www.usp.org/verification-services/verified-mark
Mr. D, age 41, presents to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and suspected intoxication. His medical history includes alcohol use disorder and spinal injury. Upon initial examination, he is confused, disorganized, and agitated. He receives IM lorazepam 4 mg to manage his agitation. His laboratory workup includes a negative screening for blood alcohol, slightly elevated creatine kinase, and urine toxicology positive for barbiturates and opioids. During re-evaluation by the consulting psychiatrist the following morning, Mr. D is alert, oriented, and calm with an organized thought process. He does not appear to be in withdrawal from any substances and tells the psychiatrist that he takes butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine as needed for migraines. Mr. D says that 3 days before he came to the ED, he also began taking a supplement called phenibut that he purchased online for “well-being and sleep.”
Natural substances have been used throughout history as medicinal agents, sacred substances in religious rituals, and for recreational purposes.1 Supplement use in the United States is prevalent, with 57.6% of adults age ≥20 reporting supplement use in the past 30 days.2 Between 2000 and 2017, US poison control centers recorded a 74.1% increase in calls involving exposure to natural psychoactive substances, mostly driven by cases involving marijuana in adults and adolescents.3 Like synthetic drugs, herbal supplements may have psychoactive properties, including sedative, stimulant, psychedelic, euphoric, or anticholinergic effects. The variety and unregulated nature of supplements makes managing patients who use supplements particularly challenging.
Why patients use supplements
People may use supplements to treat or prevent vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, iron, calcium). Other reasons may include for promoting wellness in various disease states, for weight loss, for recreational use or misuse, or for overall well-being. In the mental health realm, patients report using supplements to treat depression, anxiety, insomnia, memory, or for vague indications such as “mood support.”4,5
Patients may view supplements as appealing alternatives to prescription medications because they are widely accessible, may be purchased over-the-counter, are inexpensive, and represent a “natural” treatment option.6 For these reasons, they may also falsely perceive supplements as categorically safe.1 People with psychiatric diagnoses may choose such alternative treatments due to a history of adverse effects or treatment failure with traditional psychiatric medications, mistrust of the health care or pharmaceutical industry, or based on the recommendations of others.7
Regulation, safety, and efficacy of dietary supplements
In the US, dietary supplements are regulated more like food products than medications. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the FDA regulates the quality, safety, and labeling of supplements using Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.8 The Federal Trade Commission monitors advertisements and marketing. Despite some regulations, dietary supplements may be adulterated or contaminated, contain unknown or toxic ingredients, have inconsistent potencies, or be sold at toxic doses.9 Importantly, supplements are not required to be evaluated for clinical efficacy. As a result, it is not known if most supplements are effective in treating the conditions for which they are promoted, mainly due to a lack of financial incentive for manufacturers to conduct large, high-quality trials.5
Further complicating matters is the inconsistent labeling of supplements or similar products that are easily obtainable via the internet. These products might be marketed as nutritional supplements or nootropics, which often are referred to as “cognitive enhancers” or “smart drugs.” New psychoactive substances (NPS) are drugs of misuse or abuse developed to imitate illicit drugs or controlled drug substances.10 They are sometimes referred to as “herbal highs” or “legal highs.”11 Supplements may also be labeled as performance- or image-enhancing agents and may include medications marketed to promote weight loss. This includes herbal substances (Table12-19) and medications associated with neuropsychiatric adverse effects that may be easily accessible online without a prescription.12,20

The growing popularity of the internet and social media plays an important role in the availability of supplements and nonregulated substances and may contribute to misleading claims of efficacy and safety. While many herbal supplements are available in pharmacies or supplement stores, NPS are usually sold through anonymous, low-risk means either via traditional online vendors or the deep web (parts of the internet that are not indexed via search engines). Strategies to circumvent regulation and legislative control include labeling NPS as research chemicals, fertilizers, incense, bath salts, or other identifiers and marketing them as “not for human consumption.”21 Manufacturers frequently change the chemical structures of NPS, which allows these products to exist within a legal gray area due to the lag time between when a new compound hits the market and when it is categorized as a regulated substance.10
Continue to: Another category of "supplements"...
Another category of “supplements” includes medications that are not FDA-approved but are approved for therapeutic use in other countries and readily available in the US via online sources. Such medications include phenibut, a glutamic acid derivative that functions as a gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptor agonist in the brain, spinal cord, and autonomic nervous system. Phenibut was developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s, and outside of the US it is prescribed for anxiolysis and other psychiatric indications.22 In the US, phenibut may be used as a nootropic or as a dietary supplement to treat anxiety, sleep problems, and other psychiatric disorders.22 It may also be used recreationally to induce euphoria. Chronic phenibut use results in tolerance and abrupt discontinuation may mimic benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms.13,22
Educating patients about supplements
One of the most critical steps in assessing a patient’s supplement use is to directly ask them about their use of herbal or over-the-counter products. Research has consistently shown that patients are unlikely to disclose supplement use unless they are specifically asked.23,24
Additional strategies include25,26:
- Approach patients without judgment; ask open-ended questions to determine their motivations for using supplements.
- Explain the difference between supplements medically necessary to treat vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium) and those without robust clinical evidence.
- Counsel patients that many supplements with psychoactive properties, if indicated, are generally meant to be used short-term and not as substitutes for prescription medications.
- Educate patients that supplements have limited evidence regarding their safety and efficacy, but like prescription medications, supplements may cause organ damage, adverse effects, and drug-drug interactions.
- Remind patients that commonly used nutritional supplements/dietary aids, including protein or workout supplements, may contain potentially harmful ingredients.
- Utilize evidence-based resources such as the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database14 or the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (https://www.nccih.nih.gov) to review levels of evidence and educate patients.
- When toxicity or withdrawal is suspected, reach out to local poison control centers for guidance.
- For a patient with a potential supplement-related substance use disorder, urine drug screens may be of limited utility and evidence is often sparse; clinicians may need to rely on primary literature such as case reports to guide management.
- If patients wish to continue taking a supplement, recommend they purchase supplements from manufacturers that have achieved the US Pharmacopeia (USP) verification mark. Products with the USP mark undergo quality assurance measures to ensure the product contains the ingredients listed on the label in the declared potency and amounts, does not contain harmful levels of contaminants, will be metabolized in the body within a specified amount of time, and has been produced in keeping with FDA Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.
CASE CONTINUED
In the ED, the consulting psychiatry team discusses Mr. D’s use of phenibut with him, and asks if he uses any additional supplements or nonprescription medications. Mr. D discloses he has been anxious and having trouble sleeping, and a friend recommended phenibut as a safe, natural alternative to medication. The team explains to Mr. D that phenibut’s efficacy has not been studied in the US and that based on available evidence, it is likely unsafe. It may have serious adverse effects, drug-drug interactions, and is potentially addictive.
Mr. D says he was unaware of these risks and agrees to stop taking phenibut. The treatment team discharges him from the ED with a referral for outpatient psychiatric services to address his anxiety and insomnia.
Related Resources
- Tillman B. The hidden dangers of supplements: a case of substance-induced psychosis. Current Psychiatry. 2020; 19(7):e7-e8. doi:10.12788/cp.0018
- McQueen CE. Herb–drug interactions: caution patients when changing supplements. Current Psychiatry. 2017; 16(6):38-41.
Drug Brand Names
Butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine • Fioricet with Codeine
Mr. D, age 41, presents to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and suspected intoxication. His medical history includes alcohol use disorder and spinal injury. Upon initial examination, he is confused, disorganized, and agitated. He receives IM lorazepam 4 mg to manage his agitation. His laboratory workup includes a negative screening for blood alcohol, slightly elevated creatine kinase, and urine toxicology positive for barbiturates and opioids. During re-evaluation by the consulting psychiatrist the following morning, Mr. D is alert, oriented, and calm with an organized thought process. He does not appear to be in withdrawal from any substances and tells the psychiatrist that he takes butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine as needed for migraines. Mr. D says that 3 days before he came to the ED, he also began taking a supplement called phenibut that he purchased online for “well-being and sleep.”
Natural substances have been used throughout history as medicinal agents, sacred substances in religious rituals, and for recreational purposes.1 Supplement use in the United States is prevalent, with 57.6% of adults age ≥20 reporting supplement use in the past 30 days.2 Between 2000 and 2017, US poison control centers recorded a 74.1% increase in calls involving exposure to natural psychoactive substances, mostly driven by cases involving marijuana in adults and adolescents.3 Like synthetic drugs, herbal supplements may have psychoactive properties, including sedative, stimulant, psychedelic, euphoric, or anticholinergic effects. The variety and unregulated nature of supplements makes managing patients who use supplements particularly challenging.
Why patients use supplements
People may use supplements to treat or prevent vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, iron, calcium). Other reasons may include for promoting wellness in various disease states, for weight loss, for recreational use or misuse, or for overall well-being. In the mental health realm, patients report using supplements to treat depression, anxiety, insomnia, memory, or for vague indications such as “mood support.”4,5
Patients may view supplements as appealing alternatives to prescription medications because they are widely accessible, may be purchased over-the-counter, are inexpensive, and represent a “natural” treatment option.6 For these reasons, they may also falsely perceive supplements as categorically safe.1 People with psychiatric diagnoses may choose such alternative treatments due to a history of adverse effects or treatment failure with traditional psychiatric medications, mistrust of the health care or pharmaceutical industry, or based on the recommendations of others.7
Regulation, safety, and efficacy of dietary supplements
In the US, dietary supplements are regulated more like food products than medications. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the FDA regulates the quality, safety, and labeling of supplements using Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.8 The Federal Trade Commission monitors advertisements and marketing. Despite some regulations, dietary supplements may be adulterated or contaminated, contain unknown or toxic ingredients, have inconsistent potencies, or be sold at toxic doses.9 Importantly, supplements are not required to be evaluated for clinical efficacy. As a result, it is not known if most supplements are effective in treating the conditions for which they are promoted, mainly due to a lack of financial incentive for manufacturers to conduct large, high-quality trials.5
Further complicating matters is the inconsistent labeling of supplements or similar products that are easily obtainable via the internet. These products might be marketed as nutritional supplements or nootropics, which often are referred to as “cognitive enhancers” or “smart drugs.” New psychoactive substances (NPS) are drugs of misuse or abuse developed to imitate illicit drugs or controlled drug substances.10 They are sometimes referred to as “herbal highs” or “legal highs.”11 Supplements may also be labeled as performance- or image-enhancing agents and may include medications marketed to promote weight loss. This includes herbal substances (Table12-19) and medications associated with neuropsychiatric adverse effects that may be easily accessible online without a prescription.12,20

The growing popularity of the internet and social media plays an important role in the availability of supplements and nonregulated substances and may contribute to misleading claims of efficacy and safety. While many herbal supplements are available in pharmacies or supplement stores, NPS are usually sold through anonymous, low-risk means either via traditional online vendors or the deep web (parts of the internet that are not indexed via search engines). Strategies to circumvent regulation and legislative control include labeling NPS as research chemicals, fertilizers, incense, bath salts, or other identifiers and marketing them as “not for human consumption.”21 Manufacturers frequently change the chemical structures of NPS, which allows these products to exist within a legal gray area due to the lag time between when a new compound hits the market and when it is categorized as a regulated substance.10
Continue to: Another category of "supplements"...
Another category of “supplements” includes medications that are not FDA-approved but are approved for therapeutic use in other countries and readily available in the US via online sources. Such medications include phenibut, a glutamic acid derivative that functions as a gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptor agonist in the brain, spinal cord, and autonomic nervous system. Phenibut was developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s, and outside of the US it is prescribed for anxiolysis and other psychiatric indications.22 In the US, phenibut may be used as a nootropic or as a dietary supplement to treat anxiety, sleep problems, and other psychiatric disorders.22 It may also be used recreationally to induce euphoria. Chronic phenibut use results in tolerance and abrupt discontinuation may mimic benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms.13,22
Educating patients about supplements
One of the most critical steps in assessing a patient’s supplement use is to directly ask them about their use of herbal or over-the-counter products. Research has consistently shown that patients are unlikely to disclose supplement use unless they are specifically asked.23,24
Additional strategies include25,26:
- Approach patients without judgment; ask open-ended questions to determine their motivations for using supplements.
- Explain the difference between supplements medically necessary to treat vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium) and those without robust clinical evidence.
- Counsel patients that many supplements with psychoactive properties, if indicated, are generally meant to be used short-term and not as substitutes for prescription medications.
- Educate patients that supplements have limited evidence regarding their safety and efficacy, but like prescription medications, supplements may cause organ damage, adverse effects, and drug-drug interactions.
- Remind patients that commonly used nutritional supplements/dietary aids, including protein or workout supplements, may contain potentially harmful ingredients.
- Utilize evidence-based resources such as the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database14 or the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (https://www.nccih.nih.gov) to review levels of evidence and educate patients.
- When toxicity or withdrawal is suspected, reach out to local poison control centers for guidance.
- For a patient with a potential supplement-related substance use disorder, urine drug screens may be of limited utility and evidence is often sparse; clinicians may need to rely on primary literature such as case reports to guide management.
- If patients wish to continue taking a supplement, recommend they purchase supplements from manufacturers that have achieved the US Pharmacopeia (USP) verification mark. Products with the USP mark undergo quality assurance measures to ensure the product contains the ingredients listed on the label in the declared potency and amounts, does not contain harmful levels of contaminants, will be metabolized in the body within a specified amount of time, and has been produced in keeping with FDA Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.
CASE CONTINUED
In the ED, the consulting psychiatry team discusses Mr. D’s use of phenibut with him, and asks if he uses any additional supplements or nonprescription medications. Mr. D discloses he has been anxious and having trouble sleeping, and a friend recommended phenibut as a safe, natural alternative to medication. The team explains to Mr. D that phenibut’s efficacy has not been studied in the US and that based on available evidence, it is likely unsafe. It may have serious adverse effects, drug-drug interactions, and is potentially addictive.
Mr. D says he was unaware of these risks and agrees to stop taking phenibut. The treatment team discharges him from the ED with a referral for outpatient psychiatric services to address his anxiety and insomnia.
Related Resources
- Tillman B. The hidden dangers of supplements: a case of substance-induced psychosis. Current Psychiatry. 2020; 19(7):e7-e8. doi:10.12788/cp.0018
- McQueen CE. Herb–drug interactions: caution patients when changing supplements. Current Psychiatry. 2017; 16(6):38-41.
Drug Brand Names
Butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine • Fioricet with Codeine
1. Graziano S, Orsolini L, Rotolo MC, et al. Herbal highs: review on psychoactive effects and neuropharmacology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):750-761.
2. Mishra S, Stierman B, Gahche JJ, et al. Dietary supplement use among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2021;(399):1-8.
3. O’Neill-Dee C, Spiller HA, Casavant MJ, et al. Natural psychoactive substance-related exposures reported to United States poison control centers, 2000-2017. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020;58(8):813-820.
4. Gray DC, Rutledge CM. Herbal supplements in primary care: patient perceptions, motivations, and effects on use. Holist Nurs Pract. 2013;27(1):6-12.
5. Wu K, Messamore E. Reimagining roles of dietary supplements in psychiatric care. AMA J Ethics. 2022;24(5):E437-E442.
6. Snyder FJ, Dundas ML, Kirkpatrick C, et al. Use and safety perceptions regarding herbal supplements: a study of older persons in southeast Idaho. J Nutr Elder. 2009;28(1):81-95.
7. Schulz P, Hede V. Alternative and complementary approaches in psychiatry: beliefs versus evidence. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20(3):207-214.
8. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, Pub L 103-417, 103rd Cong (1993-1994).
9. Starr RR. Too little, too late: ineffective regulation of dietary supplements in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(3):478-485.
10. New psychoactive substances. Alcohol and Drug Foundation. November 10, 2021. Updated November 28, 2022. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/new-psychoactive-substances/
11. Shafi A, Berry AJ, Sumnall H, et al. New psychoactive substances: a review and updates. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320967197.
12. Bersani FS, Coviello M, Imperatori C, et al. Adverse psychiatric effects associated with herbal weight-loss products. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:120679.
13. IBM Micromedex POISINDEX® System. IBM Watson Health. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://www.micromedexsolutions.com
14. Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. Therapeutic Research Center. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com
15. Savage KM, Stough CK, Byrne GJ, et al. Kava for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (K-GAD): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:493.
16. Swogger MT, Smith KE, Garcia-Romeu A, et al. Understanding kratom use: a guide for healthcare providers. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:801855.
17. Modabbernia A, Akhondzadeh S. Saffron, passionflower, valerian and sage for mental health. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2013;36(1):85-91.
18. Coffeen U, Pellicer F. Salvia divinorum: from recreational hallucinogenic use to analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. J Pain Res. 2019;12:1069-1076.
19. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. Valerian Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Updated March 15, 2013. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Valerian-HealthProfessional
20. An H, Sohn H, Chung S. Phentermine, sibutramine and affective disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(1):7-12.
21. Miliano C, Margiani G, Fattore L, et al. Sales and advertising channels of new psychoactive substances (NPS): internet, social networks, and smartphone apps. Brain Sci. 2018;8(7):123.
22. Hardman MI, Sprung J, Weingarten TN. Acute phenibut withdrawal: a comprehensive literature review and illustrative case report. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019;19(2):125-129.
23. Guzman JR, Paterniti DA, Liu Y, et al. Factors related to disclosure and nondisclosure of dietary supplements in primary care, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine. J Fam Med Dis Prev. 2019;5(4):10.23937/2469-5793/1510109.
24. Foley H, Steel A, Cramer H, et al. Disclosure of complementary medicine use to medical providers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1573.
25. Aldridge Young C. ‘No miracle cures’: counseling patients about dietary supplements. Pharmacy Today. 2014;February:35.
26. United States Pharmacopeia. USP Verified Mark. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://www.usp.org/verification-services/verified-mark
1. Graziano S, Orsolini L, Rotolo MC, et al. Herbal highs: review on psychoactive effects and neuropharmacology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):750-761.
2. Mishra S, Stierman B, Gahche JJ, et al. Dietary supplement use among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2021;(399):1-8.
3. O’Neill-Dee C, Spiller HA, Casavant MJ, et al. Natural psychoactive substance-related exposures reported to United States poison control centers, 2000-2017. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020;58(8):813-820.
4. Gray DC, Rutledge CM. Herbal supplements in primary care: patient perceptions, motivations, and effects on use. Holist Nurs Pract. 2013;27(1):6-12.
5. Wu K, Messamore E. Reimagining roles of dietary supplements in psychiatric care. AMA J Ethics. 2022;24(5):E437-E442.
6. Snyder FJ, Dundas ML, Kirkpatrick C, et al. Use and safety perceptions regarding herbal supplements: a study of older persons in southeast Idaho. J Nutr Elder. 2009;28(1):81-95.
7. Schulz P, Hede V. Alternative and complementary approaches in psychiatry: beliefs versus evidence. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20(3):207-214.
8. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, Pub L 103-417, 103rd Cong (1993-1994).
9. Starr RR. Too little, too late: ineffective regulation of dietary supplements in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(3):478-485.
10. New psychoactive substances. Alcohol and Drug Foundation. November 10, 2021. Updated November 28, 2022. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/new-psychoactive-substances/
11. Shafi A, Berry AJ, Sumnall H, et al. New psychoactive substances: a review and updates. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320967197.
12. Bersani FS, Coviello M, Imperatori C, et al. Adverse psychiatric effects associated with herbal weight-loss products. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:120679.
13. IBM Micromedex POISINDEX® System. IBM Watson Health. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://www.micromedexsolutions.com
14. Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. Therapeutic Research Center. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com
15. Savage KM, Stough CK, Byrne GJ, et al. Kava for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (K-GAD): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:493.
16. Swogger MT, Smith KE, Garcia-Romeu A, et al. Understanding kratom use: a guide for healthcare providers. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:801855.
17. Modabbernia A, Akhondzadeh S. Saffron, passionflower, valerian and sage for mental health. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2013;36(1):85-91.
18. Coffeen U, Pellicer F. Salvia divinorum: from recreational hallucinogenic use to analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. J Pain Res. 2019;12:1069-1076.
19. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. Valerian Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Updated March 15, 2013. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Valerian-HealthProfessional
20. An H, Sohn H, Chung S. Phentermine, sibutramine and affective disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(1):7-12.
21. Miliano C, Margiani G, Fattore L, et al. Sales and advertising channels of new psychoactive substances (NPS): internet, social networks, and smartphone apps. Brain Sci. 2018;8(7):123.
22. Hardman MI, Sprung J, Weingarten TN. Acute phenibut withdrawal: a comprehensive literature review and illustrative case report. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019;19(2):125-129.
23. Guzman JR, Paterniti DA, Liu Y, et al. Factors related to disclosure and nondisclosure of dietary supplements in primary care, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine. J Fam Med Dis Prev. 2019;5(4):10.23937/2469-5793/1510109.
24. Foley H, Steel A, Cramer H, et al. Disclosure of complementary medicine use to medical providers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1573.
25. Aldridge Young C. ‘No miracle cures’: counseling patients about dietary supplements. Pharmacy Today. 2014;February:35.
26. United States Pharmacopeia. USP Verified Mark. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://www.usp.org/verification-services/verified-mark
Lack of motivation to change can be deadly
For 15 years I rounded at Jefferson Medical College in Philadelphia as a psychiatric consultant with the chair of the department of otolaryngology, his residents, and medical students to see severely ill head and neck cancer patients.
Most of these patients were very depressed, dealing with the severe losses of disfigurement, with decreased self-esteem, and the functional losses of mastication, smell, hearing, and taste. Further exacerbating their depression were the functional limitations of social skills they experienced, with attendant alienation, decreased concentration, persistence, and pace – as well as decreased adaptive skills.
Many of these patients were interjecting a great deal of anger and were very anxious dealing with their disabling surgeries and nonideal recoveries. I witnessed patients dealing with horrific losses – of their tongues, their mandibles, and facial bones – that were chilling, even more horrific than the textbook pictures that I saw in medical school.
Many of these patients I followed with medication management and psychotherapy as outpatients after seeing them during their hospitalization. Throughout the medical literature a direct relationship has been shown between head and neck cancers and alcohol abuse, chewing tobacco, and smoking, and it became apparent that many of these patients were dealing with alcohol and tobacco issues before their cancers. I would have thought that having gone through these horrendous experiences would have been an incentive to stop abusing. To the contrary, after following these patients, I found the majority (about two-thirds) continued with their old habits, even with my interventions.
Susan A. Cohen, DMD, a dentist who has practiced for over 20 years, has also witnessed comparable outcomes, having seen and referred similar cancer patients to the appropriate medical specialists, and upon following these patients noticed that about the same percentage (two-thirds) continued their alcohol and tobacco habits. A common theme and defense mechanism of these patients was denial, and they would often say something like “I have a great doctor who can fix anything, and I don’t have to worry about my habits.” In using the primitive oral defense mechanism of denial, they had problems taking responsibility for their own actions and changing their habits.
Furthermore, Dr. Susan Cohen reveals that abusing tobacco causes severe periodontal problems, including the loss of teeth. She also notes that the same patients have exhibited decreased personal oral hygiene, which further aggravates periodontal disease, loss of dentition, and increases the likelihood of cancers of the mouth and esophagus. She discovered that the losses that occur cause patients to become more depressed and continue the vicious cycle of self-medication with alcohol and tobacco.
In conclusion, we both found that despite disfigurement and loss of function, these postsurgical patients – for the most part – continued their abusive habits.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for more than 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
For 15 years I rounded at Jefferson Medical College in Philadelphia as a psychiatric consultant with the chair of the department of otolaryngology, his residents, and medical students to see severely ill head and neck cancer patients.
Most of these patients were very depressed, dealing with the severe losses of disfigurement, with decreased self-esteem, and the functional losses of mastication, smell, hearing, and taste. Further exacerbating their depression were the functional limitations of social skills they experienced, with attendant alienation, decreased concentration, persistence, and pace – as well as decreased adaptive skills.
Many of these patients were interjecting a great deal of anger and were very anxious dealing with their disabling surgeries and nonideal recoveries. I witnessed patients dealing with horrific losses – of their tongues, their mandibles, and facial bones – that were chilling, even more horrific than the textbook pictures that I saw in medical school.
Many of these patients I followed with medication management and psychotherapy as outpatients after seeing them during their hospitalization. Throughout the medical literature a direct relationship has been shown between head and neck cancers and alcohol abuse, chewing tobacco, and smoking, and it became apparent that many of these patients were dealing with alcohol and tobacco issues before their cancers. I would have thought that having gone through these horrendous experiences would have been an incentive to stop abusing. To the contrary, after following these patients, I found the majority (about two-thirds) continued with their old habits, even with my interventions.
Susan A. Cohen, DMD, a dentist who has practiced for over 20 years, has also witnessed comparable outcomes, having seen and referred similar cancer patients to the appropriate medical specialists, and upon following these patients noticed that about the same percentage (two-thirds) continued their alcohol and tobacco habits. A common theme and defense mechanism of these patients was denial, and they would often say something like “I have a great doctor who can fix anything, and I don’t have to worry about my habits.” In using the primitive oral defense mechanism of denial, they had problems taking responsibility for their own actions and changing their habits.
Furthermore, Dr. Susan Cohen reveals that abusing tobacco causes severe periodontal problems, including the loss of teeth. She also notes that the same patients have exhibited decreased personal oral hygiene, which further aggravates periodontal disease, loss of dentition, and increases the likelihood of cancers of the mouth and esophagus. She discovered that the losses that occur cause patients to become more depressed and continue the vicious cycle of self-medication with alcohol and tobacco.
In conclusion, we both found that despite disfigurement and loss of function, these postsurgical patients – for the most part – continued their abusive habits.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for more than 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
For 15 years I rounded at Jefferson Medical College in Philadelphia as a psychiatric consultant with the chair of the department of otolaryngology, his residents, and medical students to see severely ill head and neck cancer patients.
Most of these patients were very depressed, dealing with the severe losses of disfigurement, with decreased self-esteem, and the functional losses of mastication, smell, hearing, and taste. Further exacerbating their depression were the functional limitations of social skills they experienced, with attendant alienation, decreased concentration, persistence, and pace – as well as decreased adaptive skills.
Many of these patients were interjecting a great deal of anger and were very anxious dealing with their disabling surgeries and nonideal recoveries. I witnessed patients dealing with horrific losses – of their tongues, their mandibles, and facial bones – that were chilling, even more horrific than the textbook pictures that I saw in medical school.
Many of these patients I followed with medication management and psychotherapy as outpatients after seeing them during their hospitalization. Throughout the medical literature a direct relationship has been shown between head and neck cancers and alcohol abuse, chewing tobacco, and smoking, and it became apparent that many of these patients were dealing with alcohol and tobacco issues before their cancers. I would have thought that having gone through these horrendous experiences would have been an incentive to stop abusing. To the contrary, after following these patients, I found the majority (about two-thirds) continued with their old habits, even with my interventions.
Susan A. Cohen, DMD, a dentist who has practiced for over 20 years, has also witnessed comparable outcomes, having seen and referred similar cancer patients to the appropriate medical specialists, and upon following these patients noticed that about the same percentage (two-thirds) continued their alcohol and tobacco habits. A common theme and defense mechanism of these patients was denial, and they would often say something like “I have a great doctor who can fix anything, and I don’t have to worry about my habits.” In using the primitive oral defense mechanism of denial, they had problems taking responsibility for their own actions and changing their habits.
Furthermore, Dr. Susan Cohen reveals that abusing tobacco causes severe periodontal problems, including the loss of teeth. She also notes that the same patients have exhibited decreased personal oral hygiene, which further aggravates periodontal disease, loss of dentition, and increases the likelihood of cancers of the mouth and esophagus. She discovered that the losses that occur cause patients to become more depressed and continue the vicious cycle of self-medication with alcohol and tobacco.
In conclusion, we both found that despite disfigurement and loss of function, these postsurgical patients – for the most part – continued their abusive habits.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for more than 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
Joint effort: CBD not just innocent bystander in weed
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
I visited a legal cannabis dispensary in Massachusetts a few years ago, mostly to see what the hype was about. There I was, knowing basically nothing about pot, as the gentle stoner behind the counter explained to me the differences between the various strains. Acapulco Gold is buoyant and energizing; Purple Kush is sleepy, relaxed, dissociative. Here’s a strain that makes you feel nostalgic; here’s one that helps you focus. It was as complicated and as oddly specific as a fancy wine tasting – and, I had a feeling, about as reliable.
It’s a plant, after all, and though delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the chemical responsible for its euphoric effects, it is far from the only substance in there.
The second most important compound in cannabis is cannabidiol, and most people will tell you that CBD is the gentle yin to THC’s paranoiac yang. Hence your local ganja barista reminding you that, if you don›t want all those anxiety-inducing side effects of THC, grab a strain with a nice CBD balance.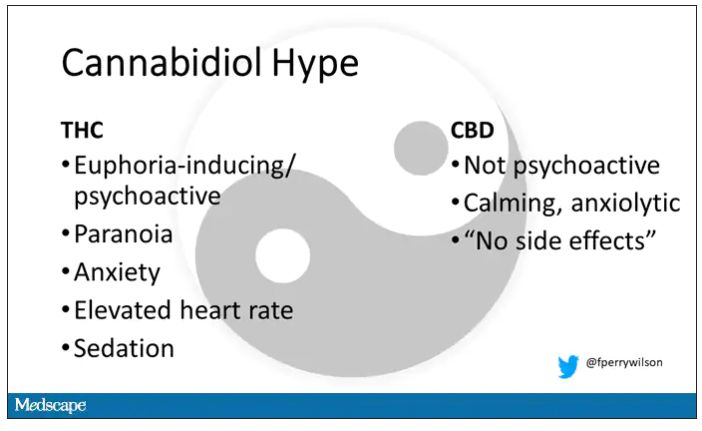
But is it true? A new study appearing in JAMA Network Open suggests, in fact, that it’s quite the opposite. This study is from Austin Zamarripa and colleagues, who clearly sit at the researcher cool kids table.
Eighteen adults who had abstained from marijuana use for at least a month participated in this trial (which is way more fun than anything we do in my lab at Yale). In random order, separated by at least a week, they ate some special brownies.
Condition one was a control brownie, condition two was a brownie containing 20 mg of THC, and condition three was a brownie containing 20 mg of THC and 640 mg of CBD. Participants were assigned each condition in random order, separated by at least a week.
A side note on doses for those of you who, like me, are not totally weed literate. A dose of 20 mg of THC is about a third of what you might find in a typical joint these days (though it’s about double the THC content of a joint in the ‘70s – I believe the technical term is “doobie”). And 640 mg of CBD is a decent dose, as 5 mg per kilogram is what some folks start with to achieve therapeutic effects.
Both THC and CBD interact with the cytochrome p450 system in the liver. This matters when you’re ingesting them instead of smoking them because you have first-pass metabolism to contend with. And, because of that p450 inhibition, it’s possible that CBD might actually increase the amount of THC that gets into your bloodstream from the brownie, or gummy, or pizza sauce, or whatever.
Let’s get to the results, starting with blood THC concentration. It’s not subtle. With CBD on board the THC concentration rises higher faster, with roughly double the area under the curve.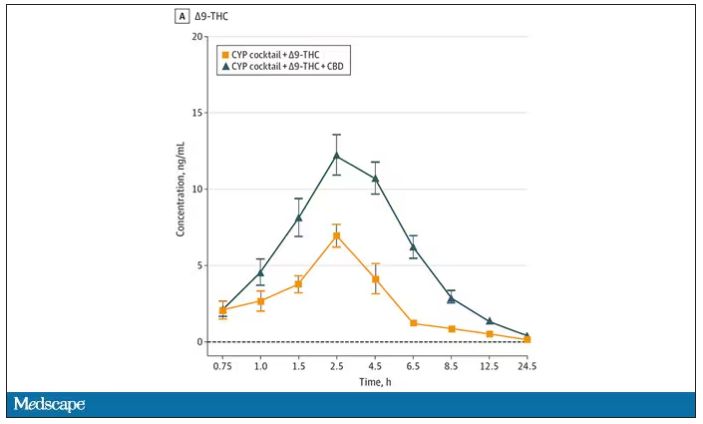
And, unsurprisingly, the subjective experience correlated with those higher levels. Individuals rated the “drug effect” higher with the combo. But, interestingly, the “pleasant” drug effect didn’t change much, while the unpleasant effects were substantially higher. No mitigation of THC anxiety here – quite the opposite. CBD made the anxiety worse.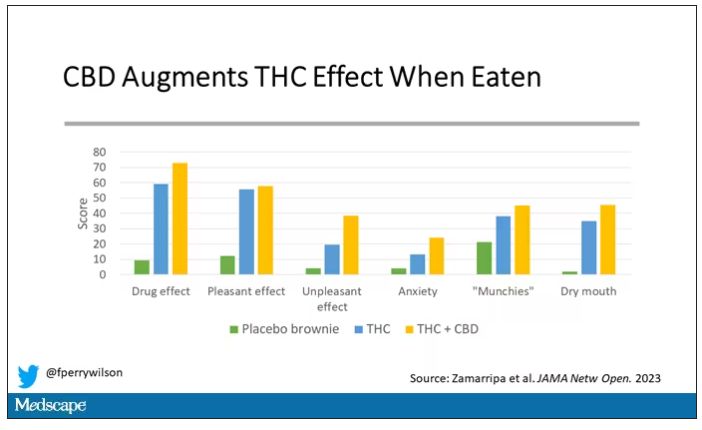
Cognitive effects were equally profound. Scores on a digit symbol substitution test and a paced serial addition task were all substantially worse when CBD was mixed with THC.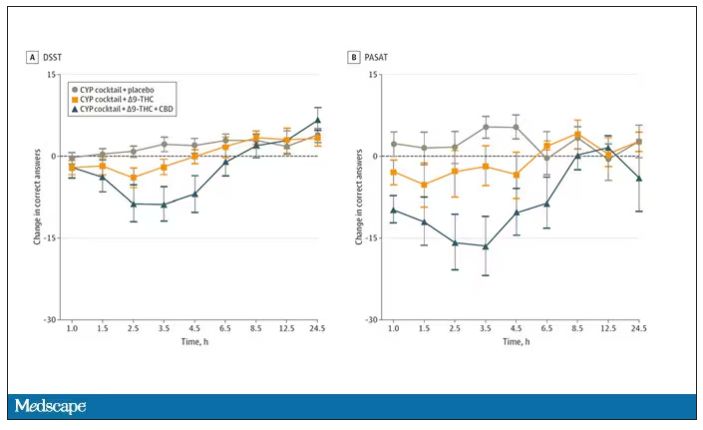
And for those of you who want some more objective measures, check out the heart rate. Despite the purported “calming” nature of CBD, heart rates were way higher when individuals were exposed to both chemicals.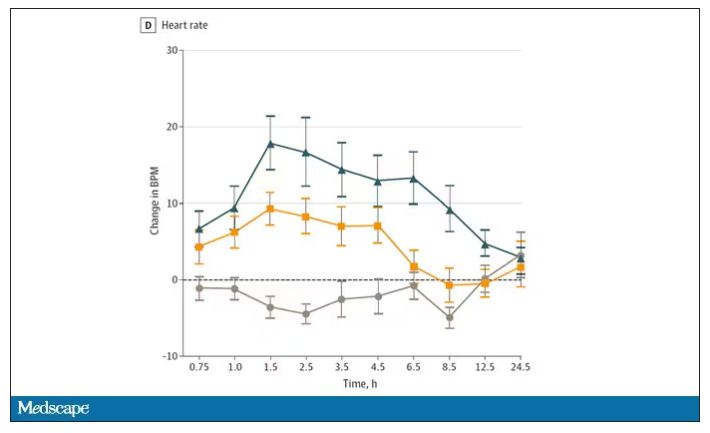
The picture here is quite clear, though the mechanism is not. At least when talking edibles, CBD enhances the effects of THC, and not necessarily for the better. It may be that CBD is competing with some of the proteins that metabolize THC, thus prolonging its effects. CBD may also directly inhibit those enzymes. But whatever the case, I think we can safely say the myth that CBD makes the effects of THC more mild or more tolerable is busted.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
I visited a legal cannabis dispensary in Massachusetts a few years ago, mostly to see what the hype was about. There I was, knowing basically nothing about pot, as the gentle stoner behind the counter explained to me the differences between the various strains. Acapulco Gold is buoyant and energizing; Purple Kush is sleepy, relaxed, dissociative. Here’s a strain that makes you feel nostalgic; here’s one that helps you focus. It was as complicated and as oddly specific as a fancy wine tasting – and, I had a feeling, about as reliable.
It’s a plant, after all, and though delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the chemical responsible for its euphoric effects, it is far from the only substance in there.
The second most important compound in cannabis is cannabidiol, and most people will tell you that CBD is the gentle yin to THC’s paranoiac yang. Hence your local ganja barista reminding you that, if you don›t want all those anxiety-inducing side effects of THC, grab a strain with a nice CBD balance.
But is it true? A new study appearing in JAMA Network Open suggests, in fact, that it’s quite the opposite. This study is from Austin Zamarripa and colleagues, who clearly sit at the researcher cool kids table.
Eighteen adults who had abstained from marijuana use for at least a month participated in this trial (which is way more fun than anything we do in my lab at Yale). In random order, separated by at least a week, they ate some special brownies.
Condition one was a control brownie, condition two was a brownie containing 20 mg of THC, and condition three was a brownie containing 20 mg of THC and 640 mg of CBD. Participants were assigned each condition in random order, separated by at least a week.
A side note on doses for those of you who, like me, are not totally weed literate. A dose of 20 mg of THC is about a third of what you might find in a typical joint these days (though it’s about double the THC content of a joint in the ‘70s – I believe the technical term is “doobie”). And 640 mg of CBD is a decent dose, as 5 mg per kilogram is what some folks start with to achieve therapeutic effects.
Both THC and CBD interact with the cytochrome p450 system in the liver. This matters when you’re ingesting them instead of smoking them because you have first-pass metabolism to contend with. And, because of that p450 inhibition, it’s possible that CBD might actually increase the amount of THC that gets into your bloodstream from the brownie, or gummy, or pizza sauce, or whatever.
Let’s get to the results, starting with blood THC concentration. It’s not subtle. With CBD on board the THC concentration rises higher faster, with roughly double the area under the curve.
And, unsurprisingly, the subjective experience correlated with those higher levels. Individuals rated the “drug effect” higher with the combo. But, interestingly, the “pleasant” drug effect didn’t change much, while the unpleasant effects were substantially higher. No mitigation of THC anxiety here – quite the opposite. CBD made the anxiety worse.
Cognitive effects were equally profound. Scores on a digit symbol substitution test and a paced serial addition task were all substantially worse when CBD was mixed with THC.
And for those of you who want some more objective measures, check out the heart rate. Despite the purported “calming” nature of CBD, heart rates were way higher when individuals were exposed to both chemicals.
The picture here is quite clear, though the mechanism is not. At least when talking edibles, CBD enhances the effects of THC, and not necessarily for the better. It may be that CBD is competing with some of the proteins that metabolize THC, thus prolonging its effects. CBD may also directly inhibit those enzymes. But whatever the case, I think we can safely say the myth that CBD makes the effects of THC more mild or more tolerable is busted.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
I visited a legal cannabis dispensary in Massachusetts a few years ago, mostly to see what the hype was about. There I was, knowing basically nothing about pot, as the gentle stoner behind the counter explained to me the differences between the various strains. Acapulco Gold is buoyant and energizing; Purple Kush is sleepy, relaxed, dissociative. Here’s a strain that makes you feel nostalgic; here’s one that helps you focus. It was as complicated and as oddly specific as a fancy wine tasting – and, I had a feeling, about as reliable.
It’s a plant, after all, and though delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the chemical responsible for its euphoric effects, it is far from the only substance in there.
The second most important compound in cannabis is cannabidiol, and most people will tell you that CBD is the gentle yin to THC’s paranoiac yang. Hence your local ganja barista reminding you that, if you don›t want all those anxiety-inducing side effects of THC, grab a strain with a nice CBD balance.
But is it true? A new study appearing in JAMA Network Open suggests, in fact, that it’s quite the opposite. This study is from Austin Zamarripa and colleagues, who clearly sit at the researcher cool kids table.
Eighteen adults who had abstained from marijuana use for at least a month participated in this trial (which is way more fun than anything we do in my lab at Yale). In random order, separated by at least a week, they ate some special brownies.
Condition one was a control brownie, condition two was a brownie containing 20 mg of THC, and condition three was a brownie containing 20 mg of THC and 640 mg of CBD. Participants were assigned each condition in random order, separated by at least a week.
A side note on doses for those of you who, like me, are not totally weed literate. A dose of 20 mg of THC is about a third of what you might find in a typical joint these days (though it’s about double the THC content of a joint in the ‘70s – I believe the technical term is “doobie”). And 640 mg of CBD is a decent dose, as 5 mg per kilogram is what some folks start with to achieve therapeutic effects.
Both THC and CBD interact with the cytochrome p450 system in the liver. This matters when you’re ingesting them instead of smoking them because you have first-pass metabolism to contend with. And, because of that p450 inhibition, it’s possible that CBD might actually increase the amount of THC that gets into your bloodstream from the brownie, or gummy, or pizza sauce, or whatever.
Let’s get to the results, starting with blood THC concentration. It’s not subtle. With CBD on board the THC concentration rises higher faster, with roughly double the area under the curve.
And, unsurprisingly, the subjective experience correlated with those higher levels. Individuals rated the “drug effect” higher with the combo. But, interestingly, the “pleasant” drug effect didn’t change much, while the unpleasant effects were substantially higher. No mitigation of THC anxiety here – quite the opposite. CBD made the anxiety worse.
Cognitive effects were equally profound. Scores on a digit symbol substitution test and a paced serial addition task were all substantially worse when CBD was mixed with THC.
And for those of you who want some more objective measures, check out the heart rate. Despite the purported “calming” nature of CBD, heart rates were way higher when individuals were exposed to both chemicals.
The picture here is quite clear, though the mechanism is not. At least when talking edibles, CBD enhances the effects of THC, and not necessarily for the better. It may be that CBD is competing with some of the proteins that metabolize THC, thus prolonging its effects. CBD may also directly inhibit those enzymes. But whatever the case, I think we can safely say the myth that CBD makes the effects of THC more mild or more tolerable is busted.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Repetitive TMS effective for comorbid depression, substance use
In a retrospective observational study, participants receiving 20-30 rTMS sessions delivered over a course of 4-6 weeks showed significant reductions in both craving and depression symptom scores.
In addition, the researchers found that the number of rTMS sessions significantly predicted the number of days of drug abstinence, even after controlling for confounders.
“For each additional TMS session, there was an additional 10 days of abstinence in the community,” principal investigator Wael Foad, MD, medical director, Erada Center for Treatment and Rehabilitation, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, told this news organization.
However, Dr. Foad noted that he would need to construct a randomized controlled trial to further explore that “interesting” finding.
The results were published in the Annals of Clinical Psychiatry.
Inpatient program
The researchers retrospectively analyzed medical records of men admitted to the inpatient unit at the Erada Center between June 2019 and September 2020. The vast majority were native to the UAE.
The inpatient program focuses on treating patients with SUDs and is the only dedicated addiction rehabilitation service in Dubai, the investigators noted.
They analyzed outcomes for 55 men with mild to moderate MDD who received rTMS as standard treatment.
Participants were excluded from the data analysis if they had another comorbid diagnosis from the DSM-5 other than SUD or MDD. They were also excluded if they used an illicit substance 2 weeks before the study or used certain medications, including antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, or mood stabilizers.
When patients first arrived on the unit, they were detoxed for a period of time before they began receiving rTMS sessions.
The 55 men received 20-30 high-frequency rTMS sessions over the course of 4-6 weeks in the area of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Each session consisted of 3,000 pulses delivered over a period of 37.5 minutes. Severity of depression was measured with the Clinical Global Impression–Severity Scale (CGI-S), which uses a 7-point Likert scale.
In addition, participants’ scores were tracked on the Brief Substance Craving Scale (BSCS), a self-report scale that measures craving for primary and secondary substances of abuse over a 24-hr period.
Of all participants, 47% said opiates and 35% said methamphetamine were their primary substances of abuse.
Significant improvement
Results showed a statistically significant improvement (P < .05) between baseline and post-rTMS treatment scores in severity of depression and drug craving, as measured by the BSCS and the CGI-S.
The researchers noted that eight participants dropped out of the study after their first rTMS session for various reasons.
Dr. Foad explained that investigators contracted with study participants to receive 20 rTMS sessions; if the sessions were not fully completed during the inpatient stay, the rTMS sessions were continued on an outpatient basis. A study clinician closely monitored patients until they finished their sessions.
For each additional rTMS session the patients completed beyond 20 sessions, there was an associated excess of 10 more days of abstinence from the primary drug in the community.
The investigators speculated that rTMS may reduce drug craving by increasing dopaminergic binding in the striatum, or by releasing dopamine in the caudate nucleus.
Study limitations cited include the lack of a control group and the fact that the study sample was limited to male inpatients, which limits generalizability of the findings to other populations.
Promising intervention
Commenting on the study, Colleen Ann Hanlon, PhD, noted that, from years of work using TMS for depression, “we know that more sessions of TMS during the acute treatment phase tends to lead to stronger and possibly more durable results long-term.”
Dr. Hanlon, who was not involved with the current research, formerly headed a clinical neuromodulation lab at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. She is now vice president of medical affairs at BrainsWay, an international health technology company specializing in Deep TMS.
She noted that Deep TMS was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for smoking cessation in 2020, “which was a tremendous win for our field at large, and requires only 15 acute sessions followed by 3 weekly sessions” of deep TMS.
“I suspect this is just the beginning of a new era in neuromodulation-based therapeutics for people struggling with drug and alcohol use disorders,” Dr. Hanlon said.
The study behind the FDA approval for smoking approval was a large double-blind, sham-controlled multisite clinical trial where investigators used an H4 coil – a TMS coil that modulates multiple brain areas involved in addictive behaviors simultaneously.
Results from that study showed that 15 sessions of deep TMS significantly improved smoking cessation rates relative to sham (10 Hz, 120% motor threshold, H4 coil, 1,800 pulses/session).
“The difference in cigarette consumption and craving was significant as early as 2 weeks after treatment initiation,” said Dr. Hanlon. “I am looking forward to the future of this field for all people suffering from drug and alcohol use disorders.”
The study and services provided through the Erada Center were funded by the government of Dubai. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a retrospective observational study, participants receiving 20-30 rTMS sessions delivered over a course of 4-6 weeks showed significant reductions in both craving and depression symptom scores.
In addition, the researchers found that the number of rTMS sessions significantly predicted the number of days of drug abstinence, even after controlling for confounders.
“For each additional TMS session, there was an additional 10 days of abstinence in the community,” principal investigator Wael Foad, MD, medical director, Erada Center for Treatment and Rehabilitation, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, told this news organization.
However, Dr. Foad noted that he would need to construct a randomized controlled trial to further explore that “interesting” finding.
The results were published in the Annals of Clinical Psychiatry.
Inpatient program
The researchers retrospectively analyzed medical records of men admitted to the inpatient unit at the Erada Center between June 2019 and September 2020. The vast majority were native to the UAE.
The inpatient program focuses on treating patients with SUDs and is the only dedicated addiction rehabilitation service in Dubai, the investigators noted.
They analyzed outcomes for 55 men with mild to moderate MDD who received rTMS as standard treatment.
Participants were excluded from the data analysis if they had another comorbid diagnosis from the DSM-5 other than SUD or MDD. They were also excluded if they used an illicit substance 2 weeks before the study or used certain medications, including antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, or mood stabilizers.
When patients first arrived on the unit, they were detoxed for a period of time before they began receiving rTMS sessions.
The 55 men received 20-30 high-frequency rTMS sessions over the course of 4-6 weeks in the area of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Each session consisted of 3,000 pulses delivered over a period of 37.5 minutes. Severity of depression was measured with the Clinical Global Impression–Severity Scale (CGI-S), which uses a 7-point Likert scale.
In addition, participants’ scores were tracked on the Brief Substance Craving Scale (BSCS), a self-report scale that measures craving for primary and secondary substances of abuse over a 24-hr period.
Of all participants, 47% said opiates and 35% said methamphetamine were their primary substances of abuse.
Significant improvement
Results showed a statistically significant improvement (P < .05) between baseline and post-rTMS treatment scores in severity of depression and drug craving, as measured by the BSCS and the CGI-S.
The researchers noted that eight participants dropped out of the study after their first rTMS session for various reasons.
Dr. Foad explained that investigators contracted with study participants to receive 20 rTMS sessions; if the sessions were not fully completed during the inpatient stay, the rTMS sessions were continued on an outpatient basis. A study clinician closely monitored patients until they finished their sessions.
For each additional rTMS session the patients completed beyond 20 sessions, there was an associated excess of 10 more days of abstinence from the primary drug in the community.
The investigators speculated that rTMS may reduce drug craving by increasing dopaminergic binding in the striatum, or by releasing dopamine in the caudate nucleus.
Study limitations cited include the lack of a control group and the fact that the study sample was limited to male inpatients, which limits generalizability of the findings to other populations.
Promising intervention
Commenting on the study, Colleen Ann Hanlon, PhD, noted that, from years of work using TMS for depression, “we know that more sessions of TMS during the acute treatment phase tends to lead to stronger and possibly more durable results long-term.”
Dr. Hanlon, who was not involved with the current research, formerly headed a clinical neuromodulation lab at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. She is now vice president of medical affairs at BrainsWay, an international health technology company specializing in Deep TMS.
She noted that Deep TMS was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for smoking cessation in 2020, “which was a tremendous win for our field at large, and requires only 15 acute sessions followed by 3 weekly sessions” of deep TMS.
“I suspect this is just the beginning of a new era in neuromodulation-based therapeutics for people struggling with drug and alcohol use disorders,” Dr. Hanlon said.
The study behind the FDA approval for smoking approval was a large double-blind, sham-controlled multisite clinical trial where investigators used an H4 coil – a TMS coil that modulates multiple brain areas involved in addictive behaviors simultaneously.
Results from that study showed that 15 sessions of deep TMS significantly improved smoking cessation rates relative to sham (10 Hz, 120% motor threshold, H4 coil, 1,800 pulses/session).
“The difference in cigarette consumption and craving was significant as early as 2 weeks after treatment initiation,” said Dr. Hanlon. “I am looking forward to the future of this field for all people suffering from drug and alcohol use disorders.”
The study and services provided through the Erada Center were funded by the government of Dubai. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a retrospective observational study, participants receiving 20-30 rTMS sessions delivered over a course of 4-6 weeks showed significant reductions in both craving and depression symptom scores.
In addition, the researchers found that the number of rTMS sessions significantly predicted the number of days of drug abstinence, even after controlling for confounders.
“For each additional TMS session, there was an additional 10 days of abstinence in the community,” principal investigator Wael Foad, MD, medical director, Erada Center for Treatment and Rehabilitation, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, told this news organization.
However, Dr. Foad noted that he would need to construct a randomized controlled trial to further explore that “interesting” finding.
The results were published in the Annals of Clinical Psychiatry.
Inpatient program
The researchers retrospectively analyzed medical records of men admitted to the inpatient unit at the Erada Center between June 2019 and September 2020. The vast majority were native to the UAE.
The inpatient program focuses on treating patients with SUDs and is the only dedicated addiction rehabilitation service in Dubai, the investigators noted.
They analyzed outcomes for 55 men with mild to moderate MDD who received rTMS as standard treatment.
Participants were excluded from the data analysis if they had another comorbid diagnosis from the DSM-5 other than SUD or MDD. They were also excluded if they used an illicit substance 2 weeks before the study or used certain medications, including antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, or mood stabilizers.
When patients first arrived on the unit, they were detoxed for a period of time before they began receiving rTMS sessions.
The 55 men received 20-30 high-frequency rTMS sessions over the course of 4-6 weeks in the area of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Each session consisted of 3,000 pulses delivered over a period of 37.5 minutes. Severity of depression was measured with the Clinical Global Impression–Severity Scale (CGI-S), which uses a 7-point Likert scale.
In addition, participants’ scores were tracked on the Brief Substance Craving Scale (BSCS), a self-report scale that measures craving for primary and secondary substances of abuse over a 24-hr period.
Of all participants, 47% said opiates and 35% said methamphetamine were their primary substances of abuse.
Significant improvement
Results showed a statistically significant improvement (P < .05) between baseline and post-rTMS treatment scores in severity of depression and drug craving, as measured by the BSCS and the CGI-S.
The researchers noted that eight participants dropped out of the study after their first rTMS session for various reasons.
Dr. Foad explained that investigators contracted with study participants to receive 20 rTMS sessions; if the sessions were not fully completed during the inpatient stay, the rTMS sessions were continued on an outpatient basis. A study clinician closely monitored patients until they finished their sessions.
For each additional rTMS session the patients completed beyond 20 sessions, there was an associated excess of 10 more days of abstinence from the primary drug in the community.
The investigators speculated that rTMS may reduce drug craving by increasing dopaminergic binding in the striatum, or by releasing dopamine in the caudate nucleus.
Study limitations cited include the lack of a control group and the fact that the study sample was limited to male inpatients, which limits generalizability of the findings to other populations.
Promising intervention
Commenting on the study, Colleen Ann Hanlon, PhD, noted that, from years of work using TMS for depression, “we know that more sessions of TMS during the acute treatment phase tends to lead to stronger and possibly more durable results long-term.”
Dr. Hanlon, who was not involved with the current research, formerly headed a clinical neuromodulation lab at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C. She is now vice president of medical affairs at BrainsWay, an international health technology company specializing in Deep TMS.
She noted that Deep TMS was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for smoking cessation in 2020, “which was a tremendous win for our field at large, and requires only 15 acute sessions followed by 3 weekly sessions” of deep TMS.
“I suspect this is just the beginning of a new era in neuromodulation-based therapeutics for people struggling with drug and alcohol use disorders,” Dr. Hanlon said.
The study behind the FDA approval for smoking approval was a large double-blind, sham-controlled multisite clinical trial where investigators used an H4 coil – a TMS coil that modulates multiple brain areas involved in addictive behaviors simultaneously.
Results from that study showed that 15 sessions of deep TMS significantly improved smoking cessation rates relative to sham (10 Hz, 120% motor threshold, H4 coil, 1,800 pulses/session).
“The difference in cigarette consumption and craving was significant as early as 2 weeks after treatment initiation,” said Dr. Hanlon. “I am looking forward to the future of this field for all people suffering from drug and alcohol use disorders.”
The study and services provided through the Erada Center were funded by the government of Dubai. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE ANNALS OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
NICU use up, birth weights down in babies of mothers with HCV
Infants born to women infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) faced twice the risk of stays in the neonatal ICU (NICU) and 2.7 times the risk of low birth weight, a new analysis finds, even when researchers adjusted their data to control for injectable drug use and maternal medical comorbidity.
Clinicians should be “aware that the infants of pregnant people with HCV may have a high rate of need for higher-level pediatric care,” said Brenna L. Hughes, MD, MSc, chief of maternal fetal medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. She spoke in an interview about the findings, which were presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
As Dr. Hughes noted, “HCV remains a serious problem in pregnancy because it often goes undiagnosed and/or untreated prior to pregnancy. It can be passed to infants, and this can cause significant health-related outcomes for children as they age.”
For the multicenter U.S. study, researchers identified 249 pregnant mothers with HCV from a 2012-2018 cohort and matched them by gestational age to controls (n = 486). The average age was 28; 71.1% of the cases were non-Hispanic White versus 41.6% of the controls; 8.4% of cases were non-Hispanic Black versus 32.1% of controls (P < .001 for race/ethnicity analysis); and 73% of cases were smokers versus 18% of controls (P < .001). More than 19% of cases reported injectable drug use during pregnancy versus 0.2% of controls (P < .001).
The researchers adjusted their findings for maternal age, body mass index, injectable drug use, and maternal comorbidity.
An earlier analysis of the study data found that 6% of pregnant women with HCV passed it on to their infants, especially those with high levels of virus in their systems. For the new study, researchers focused on various outcomes to test the assumption that “adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with HCV are related to prematurity or to ongoing use of injection drugs,” Dr. Hughes said.
There was no increase in rates of preterm birth or adverse maternal outcomes in the HCV cases. However, infants born to women with HCV were more likely than the controls to require a stay in the NICU (45% vs. 19%; adjusted relative risk, 1.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.58). They were also more likely to have lower birth weights (small for gestational age < 5th percentile) (10.6% vs. 3.1%; ARR, 2.72; 95% CI, 1.38-5.34).
No difference in outcomes was seen when HCV cases with viremia (33%) were excluded.
“The most surprising finding was that the need for higher-level pediatric care was so high even though there wasn’t an increased risk of prematurity,” Dr. Hughes said.
She added it’s not clear why NICU stays and low birth weights were more common in infants of women with HCV. “It is possible that the higher risk of need for higher-level pediatric care was related to a need for observation or treatment due to use of opioid replacement therapies with opioid agonists.” As for lower birth weight, “there may be other unmeasured risk factors.”
Tatyana Kushner, MD, MSCE, of the division of liver diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview that the study adds to limited data about HCV in pregnancy. “These findings have been demonstrated in prior studies, and it would be important to tease apart whether [low birth weight] is related to the virus itself or more related to other confounding associated factors such as maternal substance use as well as other associated social determinants of health among women with HCV.”
As for the study’s message, Dr. Kushner said it makes it clear that “hepatitis C adversely impacts outcomes of pregnancy and it is important to identify women of childbearing age for treatment early, ideally prior to pregnancy, in order to improve their pregnancy outcomes. In addition, treatment of hepatitis C during pregnancy should be explored further to determine if treatment during pregnancy can improve outcomes.”
At the moment, she said, “there are ongoing studies to delineate the safety and efficacy of hepatitis C treatment during pregnancy. Given that we are screening for hepatitis C during pregnancy, we need clear recommendations on the use of direct-acting antivirals in people who screen positive.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The authors have no disclosures. Dr. Kushner disclosed research support (Gilead) and advisory board service (Gilead, AbbVie, Bausch, GlaxoSmithKline, and Eiger).
Infants born to women infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) faced twice the risk of stays in the neonatal ICU (NICU) and 2.7 times the risk of low birth weight, a new analysis finds, even when researchers adjusted their data to control for injectable drug use and maternal medical comorbidity.
Clinicians should be “aware that the infants of pregnant people with HCV may have a high rate of need for higher-level pediatric care,” said Brenna L. Hughes, MD, MSc, chief of maternal fetal medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. She spoke in an interview about the findings, which were presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
As Dr. Hughes noted, “HCV remains a serious problem in pregnancy because it often goes undiagnosed and/or untreated prior to pregnancy. It can be passed to infants, and this can cause significant health-related outcomes for children as they age.”
For the multicenter U.S. study, researchers identified 249 pregnant mothers with HCV from a 2012-2018 cohort and matched them by gestational age to controls (n = 486). The average age was 28; 71.1% of the cases were non-Hispanic White versus 41.6% of the controls; 8.4% of cases were non-Hispanic Black versus 32.1% of controls (P < .001 for race/ethnicity analysis); and 73% of cases were smokers versus 18% of controls (P < .001). More than 19% of cases reported injectable drug use during pregnancy versus 0.2% of controls (P < .001).
The researchers adjusted their findings for maternal age, body mass index, injectable drug use, and maternal comorbidity.
An earlier analysis of the study data found that 6% of pregnant women with HCV passed it on to their infants, especially those with high levels of virus in their systems. For the new study, researchers focused on various outcomes to test the assumption that “adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with HCV are related to prematurity or to ongoing use of injection drugs,” Dr. Hughes said.
There was no increase in rates of preterm birth or adverse maternal outcomes in the HCV cases. However, infants born to women with HCV were more likely than the controls to require a stay in the NICU (45% vs. 19%; adjusted relative risk, 1.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.58). They were also more likely to have lower birth weights (small for gestational age < 5th percentile) (10.6% vs. 3.1%; ARR, 2.72; 95% CI, 1.38-5.34).
No difference in outcomes was seen when HCV cases with viremia (33%) were excluded.
“The most surprising finding was that the need for higher-level pediatric care was so high even though there wasn’t an increased risk of prematurity,” Dr. Hughes said.
She added it’s not clear why NICU stays and low birth weights were more common in infants of women with HCV. “It is possible that the higher risk of need for higher-level pediatric care was related to a need for observation or treatment due to use of opioid replacement therapies with opioid agonists.” As for lower birth weight, “there may be other unmeasured risk factors.”
Tatyana Kushner, MD, MSCE, of the division of liver diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview that the study adds to limited data about HCV in pregnancy. “These findings have been demonstrated in prior studies, and it would be important to tease apart whether [low birth weight] is related to the virus itself or more related to other confounding associated factors such as maternal substance use as well as other associated social determinants of health among women with HCV.”
As for the study’s message, Dr. Kushner said it makes it clear that “hepatitis C adversely impacts outcomes of pregnancy and it is important to identify women of childbearing age for treatment early, ideally prior to pregnancy, in order to improve their pregnancy outcomes. In addition, treatment of hepatitis C during pregnancy should be explored further to determine if treatment during pregnancy can improve outcomes.”
At the moment, she said, “there are ongoing studies to delineate the safety and efficacy of hepatitis C treatment during pregnancy. Given that we are screening for hepatitis C during pregnancy, we need clear recommendations on the use of direct-acting antivirals in people who screen positive.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The authors have no disclosures. Dr. Kushner disclosed research support (Gilead) and advisory board service (Gilead, AbbVie, Bausch, GlaxoSmithKline, and Eiger).
Infants born to women infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) faced twice the risk of stays in the neonatal ICU (NICU) and 2.7 times the risk of low birth weight, a new analysis finds, even when researchers adjusted their data to control for injectable drug use and maternal medical comorbidity.
Clinicians should be “aware that the infants of pregnant people with HCV may have a high rate of need for higher-level pediatric care,” said Brenna L. Hughes, MD, MSc, chief of maternal fetal medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. She spoke in an interview about the findings, which were presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
As Dr. Hughes noted, “HCV remains a serious problem in pregnancy because it often goes undiagnosed and/or untreated prior to pregnancy. It can be passed to infants, and this can cause significant health-related outcomes for children as they age.”
For the multicenter U.S. study, researchers identified 249 pregnant mothers with HCV from a 2012-2018 cohort and matched them by gestational age to controls (n = 486). The average age was 28; 71.1% of the cases were non-Hispanic White versus 41.6% of the controls; 8.4% of cases were non-Hispanic Black versus 32.1% of controls (P < .001 for race/ethnicity analysis); and 73% of cases were smokers versus 18% of controls (P < .001). More than 19% of cases reported injectable drug use during pregnancy versus 0.2% of controls (P < .001).
The researchers adjusted their findings for maternal age, body mass index, injectable drug use, and maternal comorbidity.
An earlier analysis of the study data found that 6% of pregnant women with HCV passed it on to their infants, especially those with high levels of virus in their systems. For the new study, researchers focused on various outcomes to test the assumption that “adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with HCV are related to prematurity or to ongoing use of injection drugs,” Dr. Hughes said.
There was no increase in rates of preterm birth or adverse maternal outcomes in the HCV cases. However, infants born to women with HCV were more likely than the controls to require a stay in the NICU (45% vs. 19%; adjusted relative risk, 1.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.58). They were also more likely to have lower birth weights (small for gestational age < 5th percentile) (10.6% vs. 3.1%; ARR, 2.72; 95% CI, 1.38-5.34).
No difference in outcomes was seen when HCV cases with viremia (33%) were excluded.
“The most surprising finding was that the need for higher-level pediatric care was so high even though there wasn’t an increased risk of prematurity,” Dr. Hughes said.
She added it’s not clear why NICU stays and low birth weights were more common in infants of women with HCV. “It is possible that the higher risk of need for higher-level pediatric care was related to a need for observation or treatment due to use of opioid replacement therapies with opioid agonists.” As for lower birth weight, “there may be other unmeasured risk factors.”
Tatyana Kushner, MD, MSCE, of the division of liver diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview that the study adds to limited data about HCV in pregnancy. “These findings have been demonstrated in prior studies, and it would be important to tease apart whether [low birth weight] is related to the virus itself or more related to other confounding associated factors such as maternal substance use as well as other associated social determinants of health among women with HCV.”
As for the study’s message, Dr. Kushner said it makes it clear that “hepatitis C adversely impacts outcomes of pregnancy and it is important to identify women of childbearing age for treatment early, ideally prior to pregnancy, in order to improve their pregnancy outcomes. In addition, treatment of hepatitis C during pregnancy should be explored further to determine if treatment during pregnancy can improve outcomes.”
At the moment, she said, “there are ongoing studies to delineate the safety and efficacy of hepatitis C treatment during pregnancy. Given that we are screening for hepatitis C during pregnancy, we need clear recommendations on the use of direct-acting antivirals in people who screen positive.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The authors have no disclosures. Dr. Kushner disclosed research support (Gilead) and advisory board service (Gilead, AbbVie, Bausch, GlaxoSmithKline, and Eiger).
FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
Mental health system failing kids leaving ED
Only 56% of children enrolled in Medicaid received any outpatient follow-up within 30 days after a mental health emergency department discharge, according to results of a large study released in Pediatrics.
Fewer than one-third (31.2%) had an outpatient visit within a week after a mental health ED discharge.
Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 28,551 children ages 6-17 years old who had mental health discharges from EDs from January 2018 to June 2019.
The researchers, led by Jennifer A. Hoffmann, MD, MS, with the division of emergency medicine, Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Northwestern University, Chicago, also analyzed the effect that having a timely follow-up had on whether the child was likely to return to the ED.
Follow-up within 30 days cuts risk of quick return to ED
They found that follow-up within 30 days was linked with a 26% decreased risk of return within 5 days of the initial ED discharge (hazard ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.91).
The researchers also found racial disparities in the data. The odds for getting follow-up outpatient care were lower for non-Hispanic Black children, for children with fee-for-service insurance, and for children with no previous mental health outpatient visits.
The numbers were particularly striking for Black children, who were 10% less likely to get outpatient follow-up than their White counterparts.
In addition, 27% of all children in this sample returned to the ED for mental health-related symptoms within 6 months, 20% spent more than 48 hours in the ED for their initial mental health visit, and children with 14 or more mental health outpatient visits had five times higher adjusted odds of follow-up within 7 days and 9.5 times higher adjusted odds of follow-up within 30 days, compared with children with no outpatient mental health visits in the previous year.
A ‘mental health system of care in crisis’
In an accompanying editorial, Hannah E. Karpman, MSW, PhD, with the department of pediatrics, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, and colleagues said those statistics help expose other signs of “a pediatric mental health system of care in crisis.”
If one in five children are spending more than 2 days in the ED for their initial mental health visit, they wrote, that signals the follow-up care they need is not readily available.
The 27% returning to the ED shows that, even if the children are getting outpatient services, that environment is failing them, they noted.
Additionally, 28% of children presented with more than four mental health diagnoses, “suggesting poor diagnostic specificity or perhaps inadequate diagnostic categories to characterize their needs.”
The authors called for interventions that link patients to outpatient care within 5 days of a mental health ED discharge.
The editorialists wrote: “We believe it is time for a “child mental health moonshot,” and call on the field and its funders to come together to launch the next wave of bold mental health research for the benefit of these children and their families who so desperately need our support.”
Things may even be worse in light of COVID
David Rettew, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview the numbers won’t surprise clinicians who support these children or the patients’ families.
He added that he wouldn’t be surprised if things are even worse now after this study’s data collection, “as COVID and other factors have driven more mental health professionals away from many of the people who need them the most.”
The study does present new evidence that quick access to care is particularly tough for young people who aren’t already established in care, he noted.
“As wait lists grow at outpatient clinics, we are seeing ever stronger need for centers willing and able to provide actual mental health assessment and treatment for people right ‘off the street,’” he said.
Dr. Rettew emphasized that, because mental health conditions rarely improve quickly, having a timely follow-up appointment is important, but won’t likely bring quick improvement.
He agreed with the editorialists’ argument and emphasized, “not only do we need to focus on more rapid care, but also more comprehensive and effective care.
“For an adolescent in crisis, achieving stability often involves more than a medication tweak and a supportive conversation,” Dr. Rettew said. “Rather, it can require an intensive multimodal approach that addresses things like family financial stressors, parental mental health and substance use concerns, school supports, and health promotion or lifestyle changes. What we desperately need are more teams that can quickly intervene on all these levels.”
Addressing problems before crisis is essential
Ideally, teams would address these issues before a crisis. That helps support the “moonshot” charge the editorialists suggest, which “would significantly disrupt the current way we value different components of our health care system,” Dr. Rettew said.
He highlighted a statistic that may get lost in the data: Nearly 40% of youth in enough danger to need an ED visit had no more than one health-related appointment of any kind in the previous year.
“To me, this speaks volumes about the need for earlier involvement before things escalate to the level of an emergency,” Dr. Rettew said.
The authors and editorialists declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rettew is author of the book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows about the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.”
Only 56% of children enrolled in Medicaid received any outpatient follow-up within 30 days after a mental health emergency department discharge, according to results of a large study released in Pediatrics.
Fewer than one-third (31.2%) had an outpatient visit within a week after a mental health ED discharge.
Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 28,551 children ages 6-17 years old who had mental health discharges from EDs from January 2018 to June 2019.
The researchers, led by Jennifer A. Hoffmann, MD, MS, with the division of emergency medicine, Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Northwestern University, Chicago, also analyzed the effect that having a timely follow-up had on whether the child was likely to return to the ED.
Follow-up within 30 days cuts risk of quick return to ED
They found that follow-up within 30 days was linked with a 26% decreased risk of return within 5 days of the initial ED discharge (hazard ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.91).
The researchers also found racial disparities in the data. The odds for getting follow-up outpatient care were lower for non-Hispanic Black children, for children with fee-for-service insurance, and for children with no previous mental health outpatient visits.
The numbers were particularly striking for Black children, who were 10% less likely to get outpatient follow-up than their White counterparts.
In addition, 27% of all children in this sample returned to the ED for mental health-related symptoms within 6 months, 20% spent more than 48 hours in the ED for their initial mental health visit, and children with 14 or more mental health outpatient visits had five times higher adjusted odds of follow-up within 7 days and 9.5 times higher adjusted odds of follow-up within 30 days, compared with children with no outpatient mental health visits in the previous year.
A ‘mental health system of care in crisis’
In an accompanying editorial, Hannah E. Karpman, MSW, PhD, with the department of pediatrics, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, and colleagues said those statistics help expose other signs of “a pediatric mental health system of care in crisis.”
If one in five children are spending more than 2 days in the ED for their initial mental health visit, they wrote, that signals the follow-up care they need is not readily available.
The 27% returning to the ED shows that, even if the children are getting outpatient services, that environment is failing them, they noted.
Additionally, 28% of children presented with more than four mental health diagnoses, “suggesting poor diagnostic specificity or perhaps inadequate diagnostic categories to characterize their needs.”
The authors called for interventions that link patients to outpatient care within 5 days of a mental health ED discharge.
The editorialists wrote: “We believe it is time for a “child mental health moonshot,” and call on the field and its funders to come together to launch the next wave of bold mental health research for the benefit of these children and their families who so desperately need our support.”
Things may even be worse in light of COVID
David Rettew, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview the numbers won’t surprise clinicians who support these children or the patients’ families.
He added that he wouldn’t be surprised if things are even worse now after this study’s data collection, “as COVID and other factors have driven more mental health professionals away from many of the people who need them the most.”
The study does present new evidence that quick access to care is particularly tough for young people who aren’t already established in care, he noted.
“As wait lists grow at outpatient clinics, we are seeing ever stronger need for centers willing and able to provide actual mental health assessment and treatment for people right ‘off the street,’” he said.
Dr. Rettew emphasized that, because mental health conditions rarely improve quickly, having a timely follow-up appointment is important, but won’t likely bring quick improvement.
He agreed with the editorialists’ argument and emphasized, “not only do we need to focus on more rapid care, but also more comprehensive and effective care.
“For an adolescent in crisis, achieving stability often involves more than a medication tweak and a supportive conversation,” Dr. Rettew said. “Rather, it can require an intensive multimodal approach that addresses things like family financial stressors, parental mental health and substance use concerns, school supports, and health promotion or lifestyle changes. What we desperately need are more teams that can quickly intervene on all these levels.”
Addressing problems before crisis is essential
Ideally, teams would address these issues before a crisis. That helps support the “moonshot” charge the editorialists suggest, which “would significantly disrupt the current way we value different components of our health care system,” Dr. Rettew said.
He highlighted a statistic that may get lost in the data: Nearly 40% of youth in enough danger to need an ED visit had no more than one health-related appointment of any kind in the previous year.
“To me, this speaks volumes about the need for earlier involvement before things escalate to the level of an emergency,” Dr. Rettew said.
The authors and editorialists declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rettew is author of the book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows about the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.”
Only 56% of children enrolled in Medicaid received any outpatient follow-up within 30 days after a mental health emergency department discharge, according to results of a large study released in Pediatrics.
Fewer than one-third (31.2%) had an outpatient visit within a week after a mental health ED discharge.
Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 28,551 children ages 6-17 years old who had mental health discharges from EDs from January 2018 to June 2019.
The researchers, led by Jennifer A. Hoffmann, MD, MS, with the division of emergency medicine, Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Northwestern University, Chicago, also analyzed the effect that having a timely follow-up had on whether the child was likely to return to the ED.
Follow-up within 30 days cuts risk of quick return to ED
They found that follow-up within 30 days was linked with a 26% decreased risk of return within 5 days of the initial ED discharge (hazard ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.91).
The researchers also found racial disparities in the data. The odds for getting follow-up outpatient care were lower for non-Hispanic Black children, for children with fee-for-service insurance, and for children with no previous mental health outpatient visits.
The numbers were particularly striking for Black children, who were 10% less likely to get outpatient follow-up than their White counterparts.
In addition, 27% of all children in this sample returned to the ED for mental health-related symptoms within 6 months, 20% spent more than 48 hours in the ED for their initial mental health visit, and children with 14 or more mental health outpatient visits had five times higher adjusted odds of follow-up within 7 days and 9.5 times higher adjusted odds of follow-up within 30 days, compared with children with no outpatient mental health visits in the previous year.
A ‘mental health system of care in crisis’
In an accompanying editorial, Hannah E. Karpman, MSW, PhD, with the department of pediatrics, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, and colleagues said those statistics help expose other signs of “a pediatric mental health system of care in crisis.”
If one in five children are spending more than 2 days in the ED for their initial mental health visit, they wrote, that signals the follow-up care they need is not readily available.
The 27% returning to the ED shows that, even if the children are getting outpatient services, that environment is failing them, they noted.
Additionally, 28% of children presented with more than four mental health diagnoses, “suggesting poor diagnostic specificity or perhaps inadequate diagnostic categories to characterize their needs.”
The authors called for interventions that link patients to outpatient care within 5 days of a mental health ED discharge.
The editorialists wrote: “We believe it is time for a “child mental health moonshot,” and call on the field and its funders to come together to launch the next wave of bold mental health research for the benefit of these children and their families who so desperately need our support.”
Things may even be worse in light of COVID
David Rettew, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview the numbers won’t surprise clinicians who support these children or the patients’ families.
He added that he wouldn’t be surprised if things are even worse now after this study’s data collection, “as COVID and other factors have driven more mental health professionals away from many of the people who need them the most.”
The study does present new evidence that quick access to care is particularly tough for young people who aren’t already established in care, he noted.
“As wait lists grow at outpatient clinics, we are seeing ever stronger need for centers willing and able to provide actual mental health assessment and treatment for people right ‘off the street,’” he said.
Dr. Rettew emphasized that, because mental health conditions rarely improve quickly, having a timely follow-up appointment is important, but won’t likely bring quick improvement.
He agreed with the editorialists’ argument and emphasized, “not only do we need to focus on more rapid care, but also more comprehensive and effective care.
“For an adolescent in crisis, achieving stability often involves more than a medication tweak and a supportive conversation,” Dr. Rettew said. “Rather, it can require an intensive multimodal approach that addresses things like family financial stressors, parental mental health and substance use concerns, school supports, and health promotion or lifestyle changes. What we desperately need are more teams that can quickly intervene on all these levels.”
Addressing problems before crisis is essential
Ideally, teams would address these issues before a crisis. That helps support the “moonshot” charge the editorialists suggest, which “would significantly disrupt the current way we value different components of our health care system,” Dr. Rettew said.
He highlighted a statistic that may get lost in the data: Nearly 40% of youth in enough danger to need an ED visit had no more than one health-related appointment of any kind in the previous year.
“To me, this speaks volumes about the need for earlier involvement before things escalate to the level of an emergency,” Dr. Rettew said.
The authors and editorialists declared no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rettew is author of the book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows about the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.”
FROM PEDIATRICS
The X-waiver is dead
In 2016, when Erin Schanning lost her brother Ethan to an overdose, she wanted to know what could have been done to have helped him. Ethan, who had struggled with opioids since getting a prescription for the drugs after a dental procedure in middle school, had tried dozens of treatments. But at the age of 30, he was gone.
“After my brother died, I started researching and was surprised to learn that there were many evidence-based ways to treat substance use disorder that he hadn’t had access to, even though he had doggedly pursued treatment,” Ms. Schanning told me in an interview. One of those treatments, buprenorphine, is one of the most effective tools that health care providers have to treat opioid use disorder. A partial opioid agonist, it reduces cravings and prevents overdose, decreasing mortality more effectively than almost any medication for any disease. Yet most providers have never prescribed it.
That may be about to change. The special license to prescribe the medication, commonly known as the “X-waiver,” was officially eliminated as part of the passage of the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment (MAT) Act. Immediately, following the passage of the Act, any provider with a DEA license became eligible to prescribe buprenorphine to treat opioid use disorder, and limits on the number of patients they could treat were eliminated.
Previously, buprenorphine, which has a better safety profile than almost any other prescription opioid because of its ceiling effect on respiratory depression,nonetheless required providers to obtain a special license to prescribe it, and – prior to an executive order from the Biden administration – 8 to 24 hours of training to do so. This led to a misconception that buprenorphine was dangerous, and created barriers for treatment during the worst overdose crisis in our country’s history. More than 110,00 overdose deaths occurred in 2021, representing a 468% increase in the last 2 decades.
Along with the MAT Act, the Medication Access and Training Expansion Act was passed in the same spending bill, requiring all prescribers who obtain a DEA license to do 8 hours of training on the treatment of substance use disorders. According to the Act, addiction specialty societies will have a role in creating trainings. Medical schools and residencies will also be able to fulfill this requirement with a “comprehensive” curriculum that covers all approved medications for the treatment of substance use disorders.
The DEA has not yet confirmed what training will be accepted, according to the Chief Medical Officer of the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Neeraj Gandotra, MD, who spoke to me in an interview. However, it is required to do so by April 5, 2023. Dr. Gandotra also emphasized that state and local laws, as well as insurance requirements, remain in place, and may place other constraints on prescribing. According to the Act, this new rule will be in effect by June 2023.
As an addiction medicine specialist and longtime buprenorphine prescriber, I am excited about these changes but wary of lingering resistance among health care providers. Will providers who have chosen not to get an X-waiver now look for another reason to not treat patients with substance use disorders?
Ms. Schanning remains hopeful. “I’m incredibly optimistic that health care providers are going to learn about buprenorphine and prescribe it to patients, and that patients are going to start asking about this medication,” she told me. “Seven in 10 providers say that they do feel an obligation to treat their patients with [opioid use disorder], but the federal government has made it very difficult to do so.”
Now with the X-waiver gone, providers and patients may be able to push for a long overdue shift in how we treat and conceptualize substance use disorders, she noted.
“Health care providers need to recognize substance use disorder as a medical condition that deserves treatment, and to speak about it like a medical condition,” Ms. Schanning said, by, for instance, moving away from using words such as “abuse” and “clean” and, instead, talking about treatable substance use disorders that can improve with evidence-based care, such as buprenorphine and methadone. “We also need to share stories of success and hope with people,” she added. “Once you’ve seen how someone can be transformed by treatment, it’s really difficult to say that substance use disorder is a character flaw, or their fault.”
A patient-centered approach
Over the past decade of practicing medicine, I have experienced this transformation personally. In residency, I believed that people had to be ready for help, to stop using, to change. I failed to recognize that many of those same people were asking me for help, and I wasn’t offering what they needed. The person who had to change was me.
As I moved toward a patient-centered approach, lowering barriers to starting and remaining in treatment, and collaborating with teams that could meet people wherever they might be, addictions became the most rewarding part of my practice.
I have never had more people thank me spontaneously and deeply for the care I provide. Plus, I have never seen a more profound change in the students I work with than when they witness someone with a substance use disorder offered treatment that works.
The X-waiver was not the only barrier to care, and the overdose crisis is not slowing down. But maybe with a new tool widely accessible, more of us will be ready to help.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures, and she serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
In 2016, when Erin Schanning lost her brother Ethan to an overdose, she wanted to know what could have been done to have helped him. Ethan, who had struggled with opioids since getting a prescription for the drugs after a dental procedure in middle school, had tried dozens of treatments. But at the age of 30, he was gone.
“After my brother died, I started researching and was surprised to learn that there were many evidence-based ways to treat substance use disorder that he hadn’t had access to, even though he had doggedly pursued treatment,” Ms. Schanning told me in an interview. One of those treatments, buprenorphine, is one of the most effective tools that health care providers have to treat opioid use disorder. A partial opioid agonist, it reduces cravings and prevents overdose, decreasing mortality more effectively than almost any medication for any disease. Yet most providers have never prescribed it.
That may be about to change. The special license to prescribe the medication, commonly known as the “X-waiver,” was officially eliminated as part of the passage of the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment (MAT) Act. Immediately, following the passage of the Act, any provider with a DEA license became eligible to prescribe buprenorphine to treat opioid use disorder, and limits on the number of patients they could treat were eliminated.
Previously, buprenorphine, which has a better safety profile than almost any other prescription opioid because of its ceiling effect on respiratory depression,nonetheless required providers to obtain a special license to prescribe it, and – prior to an executive order from the Biden administration – 8 to 24 hours of training to do so. This led to a misconception that buprenorphine was dangerous, and created barriers for treatment during the worst overdose crisis in our country’s history. More than 110,00 overdose deaths occurred in 2021, representing a 468% increase in the last 2 decades.
Along with the MAT Act, the Medication Access and Training Expansion Act was passed in the same spending bill, requiring all prescribers who obtain a DEA license to do 8 hours of training on the treatment of substance use disorders. According to the Act, addiction specialty societies will have a role in creating trainings. Medical schools and residencies will also be able to fulfill this requirement with a “comprehensive” curriculum that covers all approved medications for the treatment of substance use disorders.
The DEA has not yet confirmed what training will be accepted, according to the Chief Medical Officer of the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Neeraj Gandotra, MD, who spoke to me in an interview. However, it is required to do so by April 5, 2023. Dr. Gandotra also emphasized that state and local laws, as well as insurance requirements, remain in place, and may place other constraints on prescribing. According to the Act, this new rule will be in effect by June 2023.
As an addiction medicine specialist and longtime buprenorphine prescriber, I am excited about these changes but wary of lingering resistance among health care providers. Will providers who have chosen not to get an X-waiver now look for another reason to not treat patients with substance use disorders?
Ms. Schanning remains hopeful. “I’m incredibly optimistic that health care providers are going to learn about buprenorphine and prescribe it to patients, and that patients are going to start asking about this medication,” she told me. “Seven in 10 providers say that they do feel an obligation to treat their patients with [opioid use disorder], but the federal government has made it very difficult to do so.”
Now with the X-waiver gone, providers and patients may be able to push for a long overdue shift in how we treat and conceptualize substance use disorders, she noted.
“Health care providers need to recognize substance use disorder as a medical condition that deserves treatment, and to speak about it like a medical condition,” Ms. Schanning said, by, for instance, moving away from using words such as “abuse” and “clean” and, instead, talking about treatable substance use disorders that can improve with evidence-based care, such as buprenorphine and methadone. “We also need to share stories of success and hope with people,” she added. “Once you’ve seen how someone can be transformed by treatment, it’s really difficult to say that substance use disorder is a character flaw, or their fault.”
A patient-centered approach
Over the past decade of practicing medicine, I have experienced this transformation personally. In residency, I believed that people had to be ready for help, to stop using, to change. I failed to recognize that many of those same people were asking me for help, and I wasn’t offering what they needed. The person who had to change was me.
As I moved toward a patient-centered approach, lowering barriers to starting and remaining in treatment, and collaborating with teams that could meet people wherever they might be, addictions became the most rewarding part of my practice.
I have never had more people thank me spontaneously and deeply for the care I provide. Plus, I have never seen a more profound change in the students I work with than when they witness someone with a substance use disorder offered treatment that works.
The X-waiver was not the only barrier to care, and the overdose crisis is not slowing down. But maybe with a new tool widely accessible, more of us will be ready to help.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures, and she serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
In 2016, when Erin Schanning lost her brother Ethan to an overdose, she wanted to know what could have been done to have helped him. Ethan, who had struggled with opioids since getting a prescription for the drugs after a dental procedure in middle school, had tried dozens of treatments. But at the age of 30, he was gone.
“After my brother died, I started researching and was surprised to learn that there were many evidence-based ways to treat substance use disorder that he hadn’t had access to, even though he had doggedly pursued treatment,” Ms. Schanning told me in an interview. One of those treatments, buprenorphine, is one of the most effective tools that health care providers have to treat opioid use disorder. A partial opioid agonist, it reduces cravings and prevents overdose, decreasing mortality more effectively than almost any medication for any disease. Yet most providers have never prescribed it.
That may be about to change. The special license to prescribe the medication, commonly known as the “X-waiver,” was officially eliminated as part of the passage of the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment (MAT) Act. Immediately, following the passage of the Act, any provider with a DEA license became eligible to prescribe buprenorphine to treat opioid use disorder, and limits on the number of patients they could treat were eliminated.
Previously, buprenorphine, which has a better safety profile than almost any other prescription opioid because of its ceiling effect on respiratory depression,nonetheless required providers to obtain a special license to prescribe it, and – prior to an executive order from the Biden administration – 8 to 24 hours of training to do so. This led to a misconception that buprenorphine was dangerous, and created barriers for treatment during the worst overdose crisis in our country’s history. More than 110,00 overdose deaths occurred in 2021, representing a 468% increase in the last 2 decades.
Along with the MAT Act, the Medication Access and Training Expansion Act was passed in the same spending bill, requiring all prescribers who obtain a DEA license to do 8 hours of training on the treatment of substance use disorders. According to the Act, addiction specialty societies will have a role in creating trainings. Medical schools and residencies will also be able to fulfill this requirement with a “comprehensive” curriculum that covers all approved medications for the treatment of substance use disorders.
The DEA has not yet confirmed what training will be accepted, according to the Chief Medical Officer of the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Neeraj Gandotra, MD, who spoke to me in an interview. However, it is required to do so by April 5, 2023. Dr. Gandotra also emphasized that state and local laws, as well as insurance requirements, remain in place, and may place other constraints on prescribing. According to the Act, this new rule will be in effect by June 2023.
As an addiction medicine specialist and longtime buprenorphine prescriber, I am excited about these changes but wary of lingering resistance among health care providers. Will providers who have chosen not to get an X-waiver now look for another reason to not treat patients with substance use disorders?
Ms. Schanning remains hopeful. “I’m incredibly optimistic that health care providers are going to learn about buprenorphine and prescribe it to patients, and that patients are going to start asking about this medication,” she told me. “Seven in 10 providers say that they do feel an obligation to treat their patients with [opioid use disorder], but the federal government has made it very difficult to do so.”
Now with the X-waiver gone, providers and patients may be able to push for a long overdue shift in how we treat and conceptualize substance use disorders, she noted.
“Health care providers need to recognize substance use disorder as a medical condition that deserves treatment, and to speak about it like a medical condition,” Ms. Schanning said, by, for instance, moving away from using words such as “abuse” and “clean” and, instead, talking about treatable substance use disorders that can improve with evidence-based care, such as buprenorphine and methadone. “We also need to share stories of success and hope with people,” she added. “Once you’ve seen how someone can be transformed by treatment, it’s really difficult to say that substance use disorder is a character flaw, or their fault.”
A patient-centered approach
Over the past decade of practicing medicine, I have experienced this transformation personally. In residency, I believed that people had to be ready for help, to stop using, to change. I failed to recognize that many of those same people were asking me for help, and I wasn’t offering what they needed. The person who had to change was me.
As I moved toward a patient-centered approach, lowering barriers to starting and remaining in treatment, and collaborating with teams that could meet people wherever they might be, addictions became the most rewarding part of my practice.
I have never had more people thank me spontaneously and deeply for the care I provide. Plus, I have never seen a more profound change in the students I work with than when they witness someone with a substance use disorder offered treatment that works.
The X-waiver was not the only barrier to care, and the overdose crisis is not slowing down. But maybe with a new tool widely accessible, more of us will be ready to help.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures, and she serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Unexpected link between light drinking and dementia risk
new research suggests.
Investigators assessed dementia risk using changes in alcohol consumption over a 2-year period in nearly 4 million people in South Korea. After about 7 years, dementia was 21% less likely in mild drinkers and 17% less likely in moderate drinkers. Heavy drinking was linked to an 8% increased risk.
Other studies of the relationship between alcohol and dementia have yielded mixed results, and this study does little to clear those murky waters. Nor do the results mean that drinking is recommended, the investigators note.
But the study does offer new information on how risk changes over time as people change their drinking habits, lead investigator Keun Hye Jeon, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at Cha Gumi Medical Center at Cha University, Gumi, South Korea, told this news organization.
“Although numerous studies have shown a relationship between alcohol consumption and dementia, there is a paucity of understanding as to how the incidence of dementia changes with changes in drinking habits,” Dr. Jeon said.
“By measuring alcohol consumption at two time points, we were able to study the relationship between reducing, ceasing, maintaining, and increasing alcohol consumption and incident dementia,” he added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Tracking drinking habits
Researchers analyzed data from nearly 4 million individuals aged 40 years and older in the Korean National Health Insurance Service who completed questionnaires and underwent physical exams in 2009 and 2011.
Study participants completed questionnaires on their drinking habits and were assigned to one of five groups according to change in alcohol consumption during the study period. These groups consisted of sustained nondrinkers; those who stopped drinking (quitters); those who reduced their consumption of alcohol but did not stop drinking (reducers); those who maintained the same level of consumption (sustainers); and those who increased their level of consumption (increasers).
A standard drink in the United States contains 14 g of alcohol. For this study, mild drinking was defined as less than 15 g/day, or one drink; moderate consumption as 15-29.9 g/day, or one to two drinks; and heavy drinking as 30 g/day or more, or three or more drinks.
At baseline, 54.8% of participants were nondrinkers, 26.7% were mild drinkers, 11.0% were moderate drinkers, and 7.5% were heavy drinkers.
From 2009 to 2011, 24.2% of mild drinkers, 8.4% of moderate drinkers, and 7.6% of heavy drinkers became quitters. In the same period, 13.9% of nondrinkers, 16.1% of mild drinkers, and 17.4% of moderate drinkers increased their drinking level.
After a mean follow-up of 6.3 years, 2.5% of participants were diagnosed with dementia, 2.0% with Alzheimer’s disease, and 0.3% with vascular dementia.
Unexpected finding
Compared with consistently not drinking, mild and moderate alcohol consumption was associated with a 21% (adjust hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.81) and 17% (aHR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.88) decreased risk for dementia, respectively.
Heavy drinking was linked to an 8% increased risk (aHR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
Similar associations were found between alcohol consumption and risk for Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
Reducing drinking habits from heavy to moderate led to a reduction in risk for dementia and Alzheimer’s, and increasing drinking levels led to an increase in risk for both conditions.
But when the researchers analyzed dementia risk for nondrinkers who began drinking at mild levels during the study period, they found something unexpected – the risk in this group decreased by 7% for dementia (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.90-0.96) and by 8% for Alzheimer’s (aHR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.89-0.95), compared with sustained mild drinkers.
“Our study showed that initiation of mild alcohol consumption leads to a reduced risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, which has never been reported in previous studies,” Dr. Jeon said.
However, Dr. Jeon was quick to point out that this doesn’t mean that people who don’t drink should start.
Previous studies have shown that heavy alcohol use can triple an individual’s dementia risk, while other studies have shown that no amount of alcohol consumption is good for the brain.
“None of the existing health guidelines recommend starting alcohol drinking,” Dr. Jeon said. “Our findings regarding an initiation of mild alcohol consumption cannot be directly translated into clinical recommendations,” but the findings do warrant additional study, he added.
Risks persist
Commenting on the findings, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association in Chicago, agrees.
“While this study is interesting, and this topic deserves further study, no one should drink alcohol as a method of reducing risk of Alzheimer’s disease or other dementia based on this study,” said Dr. Griffin, who was not part of the study.
The exact tipping point in alcohol consumption that can lead to problems with cognition or increased dementia risk is unknown, Dr. Griffin said. Nor do researchers understand why mild drinking may have a protective effect.
“We do know, however, that excessive alcohol consumption has negative effects on heart health and general health, which can lead to problems with brain function,” he said. “Clinicians should have discussions with their patients around their alcohol consumption patterns and the risks associated with drinking in excess, including potential damage to their cognition.”
Funding for the study was not disclosed. Dr. Jeon and Dr. Griffin report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators assessed dementia risk using changes in alcohol consumption over a 2-year period in nearly 4 million people in South Korea. After about 7 years, dementia was 21% less likely in mild drinkers and 17% less likely in moderate drinkers. Heavy drinking was linked to an 8% increased risk.
Other studies of the relationship between alcohol and dementia have yielded mixed results, and this study does little to clear those murky waters. Nor do the results mean that drinking is recommended, the investigators note.
But the study does offer new information on how risk changes over time as people change their drinking habits, lead investigator Keun Hye Jeon, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at Cha Gumi Medical Center at Cha University, Gumi, South Korea, told this news organization.
“Although numerous studies have shown a relationship between alcohol consumption and dementia, there is a paucity of understanding as to how the incidence of dementia changes with changes in drinking habits,” Dr. Jeon said.
“By measuring alcohol consumption at two time points, we were able to study the relationship between reducing, ceasing, maintaining, and increasing alcohol consumption and incident dementia,” he added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Tracking drinking habits
Researchers analyzed data from nearly 4 million individuals aged 40 years and older in the Korean National Health Insurance Service who completed questionnaires and underwent physical exams in 2009 and 2011.
Study participants completed questionnaires on their drinking habits and were assigned to one of five groups according to change in alcohol consumption during the study period. These groups consisted of sustained nondrinkers; those who stopped drinking (quitters); those who reduced their consumption of alcohol but did not stop drinking (reducers); those who maintained the same level of consumption (sustainers); and those who increased their level of consumption (increasers).
A standard drink in the United States contains 14 g of alcohol. For this study, mild drinking was defined as less than 15 g/day, or one drink; moderate consumption as 15-29.9 g/day, or one to two drinks; and heavy drinking as 30 g/day or more, or three or more drinks.
At baseline, 54.8% of participants were nondrinkers, 26.7% were mild drinkers, 11.0% were moderate drinkers, and 7.5% were heavy drinkers.
From 2009 to 2011, 24.2% of mild drinkers, 8.4% of moderate drinkers, and 7.6% of heavy drinkers became quitters. In the same period, 13.9% of nondrinkers, 16.1% of mild drinkers, and 17.4% of moderate drinkers increased their drinking level.
After a mean follow-up of 6.3 years, 2.5% of participants were diagnosed with dementia, 2.0% with Alzheimer’s disease, and 0.3% with vascular dementia.
Unexpected finding
Compared with consistently not drinking, mild and moderate alcohol consumption was associated with a 21% (adjust hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.81) and 17% (aHR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.88) decreased risk for dementia, respectively.
Heavy drinking was linked to an 8% increased risk (aHR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
Similar associations were found between alcohol consumption and risk for Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
Reducing drinking habits from heavy to moderate led to a reduction in risk for dementia and Alzheimer’s, and increasing drinking levels led to an increase in risk for both conditions.
But when the researchers analyzed dementia risk for nondrinkers who began drinking at mild levels during the study period, they found something unexpected – the risk in this group decreased by 7% for dementia (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.90-0.96) and by 8% for Alzheimer’s (aHR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.89-0.95), compared with sustained mild drinkers.
“Our study showed that initiation of mild alcohol consumption leads to a reduced risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, which has never been reported in previous studies,” Dr. Jeon said.
However, Dr. Jeon was quick to point out that this doesn’t mean that people who don’t drink should start.
Previous studies have shown that heavy alcohol use can triple an individual’s dementia risk, while other studies have shown that no amount of alcohol consumption is good for the brain.
“None of the existing health guidelines recommend starting alcohol drinking,” Dr. Jeon said. “Our findings regarding an initiation of mild alcohol consumption cannot be directly translated into clinical recommendations,” but the findings do warrant additional study, he added.
Risks persist
Commenting on the findings, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association in Chicago, agrees.
“While this study is interesting, and this topic deserves further study, no one should drink alcohol as a method of reducing risk of Alzheimer’s disease or other dementia based on this study,” said Dr. Griffin, who was not part of the study.
The exact tipping point in alcohol consumption that can lead to problems with cognition or increased dementia risk is unknown, Dr. Griffin said. Nor do researchers understand why mild drinking may have a protective effect.
“We do know, however, that excessive alcohol consumption has negative effects on heart health and general health, which can lead to problems with brain function,” he said. “Clinicians should have discussions with their patients around their alcohol consumption patterns and the risks associated with drinking in excess, including potential damage to their cognition.”
Funding for the study was not disclosed. Dr. Jeon and Dr. Griffin report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators assessed dementia risk using changes in alcohol consumption over a 2-year period in nearly 4 million people in South Korea. After about 7 years, dementia was 21% less likely in mild drinkers and 17% less likely in moderate drinkers. Heavy drinking was linked to an 8% increased risk.
Other studies of the relationship between alcohol and dementia have yielded mixed results, and this study does little to clear those murky waters. Nor do the results mean that drinking is recommended, the investigators note.
But the study does offer new information on how risk changes over time as people change their drinking habits, lead investigator Keun Hye Jeon, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at Cha Gumi Medical Center at Cha University, Gumi, South Korea, told this news organization.
“Although numerous studies have shown a relationship between alcohol consumption and dementia, there is a paucity of understanding as to how the incidence of dementia changes with changes in drinking habits,” Dr. Jeon said.
“By measuring alcohol consumption at two time points, we were able to study the relationship between reducing, ceasing, maintaining, and increasing alcohol consumption and incident dementia,” he added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Tracking drinking habits
Researchers analyzed data from nearly 4 million individuals aged 40 years and older in the Korean National Health Insurance Service who completed questionnaires and underwent physical exams in 2009 and 2011.
Study participants completed questionnaires on their drinking habits and were assigned to one of five groups according to change in alcohol consumption during the study period. These groups consisted of sustained nondrinkers; those who stopped drinking (quitters); those who reduced their consumption of alcohol but did not stop drinking (reducers); those who maintained the same level of consumption (sustainers); and those who increased their level of consumption (increasers).
A standard drink in the United States contains 14 g of alcohol. For this study, mild drinking was defined as less than 15 g/day, or one drink; moderate consumption as 15-29.9 g/day, or one to two drinks; and heavy drinking as 30 g/day or more, or three or more drinks.
At baseline, 54.8% of participants were nondrinkers, 26.7% were mild drinkers, 11.0% were moderate drinkers, and 7.5% were heavy drinkers.
From 2009 to 2011, 24.2% of mild drinkers, 8.4% of moderate drinkers, and 7.6% of heavy drinkers became quitters. In the same period, 13.9% of nondrinkers, 16.1% of mild drinkers, and 17.4% of moderate drinkers increased their drinking level.
After a mean follow-up of 6.3 years, 2.5% of participants were diagnosed with dementia, 2.0% with Alzheimer’s disease, and 0.3% with vascular dementia.
Unexpected finding
Compared with consistently not drinking, mild and moderate alcohol consumption was associated with a 21% (adjust hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.81) and 17% (aHR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.88) decreased risk for dementia, respectively.
Heavy drinking was linked to an 8% increased risk (aHR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12).
Similar associations were found between alcohol consumption and risk for Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
Reducing drinking habits from heavy to moderate led to a reduction in risk for dementia and Alzheimer’s, and increasing drinking levels led to an increase in risk for both conditions.
But when the researchers analyzed dementia risk for nondrinkers who began drinking at mild levels during the study period, they found something unexpected – the risk in this group decreased by 7% for dementia (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.90-0.96) and by 8% for Alzheimer’s (aHR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.89-0.95), compared with sustained mild drinkers.
“Our study showed that initiation of mild alcohol consumption leads to a reduced risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, which has never been reported in previous studies,” Dr. Jeon said.
However, Dr. Jeon was quick to point out that this doesn’t mean that people who don’t drink should start.
Previous studies have shown that heavy alcohol use can triple an individual’s dementia risk, while other studies have shown that no amount of alcohol consumption is good for the brain.
“None of the existing health guidelines recommend starting alcohol drinking,” Dr. Jeon said. “Our findings regarding an initiation of mild alcohol consumption cannot be directly translated into clinical recommendations,” but the findings do warrant additional study, he added.
Risks persist
Commenting on the findings, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association in Chicago, agrees.
“While this study is interesting, and this topic deserves further study, no one should drink alcohol as a method of reducing risk of Alzheimer’s disease or other dementia based on this study,” said Dr. Griffin, who was not part of the study.
The exact tipping point in alcohol consumption that can lead to problems with cognition or increased dementia risk is unknown, Dr. Griffin said. Nor do researchers understand why mild drinking may have a protective effect.
“We do know, however, that excessive alcohol consumption has negative effects on heart health and general health, which can lead to problems with brain function,” he said. “Clinicians should have discussions with their patients around their alcohol consumption patterns and the risks associated with drinking in excess, including potential damage to their cognition.”
Funding for the study was not disclosed. Dr. Jeon and Dr. Griffin report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
No spike in overdose deaths from relaxed buprenorphine regulations
Researchers say the data add weight to the argument for permanently adopting the pandemic-era prescribing regulations for buprenorphine, a treatment for opioid use disorder.
“We saw no evidence that increased availability of buprenorphine through the loosening of rules around prescribing and dispensing of buprenorphine during the pandemic increased overdose deaths,” investigator Wilson Compton, MD, deputy director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, told this news organization.
“This is reassuring that, even when we opened up the doors to easier access to buprenorphine, we didn’t see that most serious consequence,” Dr. Compton said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open .
Cause and effect
Federal agencies relaxed prescribing regulations for buprenorphine in March 2020 to make it easier for clinicians to prescribe the drug via telemedicine and for patients to take the medication at home.
The number of buprenorphine prescriptions has increased since that change, with more than 1 million people receiving the medication in 2021 from retail pharmacies in the United States.
However, questions remained about whether increased access would lead to an increase in buprenorphine-involved overdose.
Researchers with NIDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed data from the State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, a CDC database that combines medical examiner and coroner reports and postmortem toxicology testing.
The study included information about overdose deaths from July 2019 to June 2021 in 46 states and the District of Columbia.
Between July 2019 and June 2021, there were 1,955 buprenorphine-involved overdose deaths, which accounted for 2.2% of all drug overdose deaths and 2.6% of opioid-involved overdose deaths.
However, researchers went beyond overall numbers and evaluated details from coroner’s and medical examiner reports, something they had not done before.
“For the first time we looked at the characteristics of decedents from buprenorphine because this has not been studied in this type of detail with a near-national sample,” Dr. Compton said.
“That allowed us to look at patterns of use of other substances as well as the circumstances that are recorded at the death scene that are in the data set,” he added.
Important insights
Reports from nearly all buprenorphine-involved deaths included the presence of at least one other drug, compared with opioid overdose deaths that typically involved only one drug.
“This is consistent with the pharmacology of buprenorphine being a partial agonist, so it may not be as fatal all by itself as some of the other opioids,” Dr. Compton said.
Deaths involving buprenorphine were less likely to include illicitly manufactured fentanyls, and other prescription medications were more often found on the scene, such as antidepressants.
Compared with opioid decedents, buprenorphine decedents were more likely to be women, age 35-44, White, and receiving treatment for mental health conditions, including for substance use disorder (SUD).
These kinds of characteristics provide important insights about potential ways to improve safety and clinical outcomes, Dr. Compton noted.
“When we see things like a little higher rate of SUD treatment and this evidence of other prescription drugs on the scene, and some higher rates of antidepressants in these decedents than I might have expected, I’m very curious about their use of other medical services outside of substance use treatment, because that might be a place where some interventions could be implemented,” he said.
A similar study showed pandemic-era policy changes that allowed methadone to be taken at home was followed by a decrease in methadone-related overdose deaths.
The new findings are consistent with those results, Dr. Compton said.
‘Chipping away’ at stigma
Commenting on the study, O. Trent Hall, DO, assistant professor of addiction medicine, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said that, although he welcomed the findings, they aren’t unexpected.
“Buprenorphine is well established as a safe and effective medication for opioid use disorder and as a physician who routinely cares for patients in the hospital after opioid overdose, I am not at all surprised by these results,” said Dr. Hall, who was not involved with the research.
“When my patients leave the hospital with a buprenorphine prescription, they are much less likely to return with another overdose or serious opioid-related medical problem,” he added.
U.S. drug overdose deaths topped 100,000 for the first time in 2021, and most were opioid-related. Although the latest data from the CDC shows drug overdose deaths have been declining slowly since early 2022, the numbers remain high.
Buprenorphine is one of only two drugs known to reduce the risk of opioid overdose. While prescriptions have increased since 2020, the medication remains underutilized, despite its known effectiveness in treating opioid use disorder.
Dr. Hall noted that research such as the new study could help increase buprenorphine’s use.
“Studies like this one chip away at the stigma that has been misapplied to buprenorphine,” he said. “I hope this article will encourage more providers to offer buprenorphine to patients with opioid use disorder.”
The study was funded internally by NIDA and the CDC. Dr. Compton reported owning stock in General Electric, 3M, and Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Hall has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers say the data add weight to the argument for permanently adopting the pandemic-era prescribing regulations for buprenorphine, a treatment for opioid use disorder.
“We saw no evidence that increased availability of buprenorphine through the loosening of rules around prescribing and dispensing of buprenorphine during the pandemic increased overdose deaths,” investigator Wilson Compton, MD, deputy director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, told this news organization.
“This is reassuring that, even when we opened up the doors to easier access to buprenorphine, we didn’t see that most serious consequence,” Dr. Compton said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open .
Cause and effect
Federal agencies relaxed prescribing regulations for buprenorphine in March 2020 to make it easier for clinicians to prescribe the drug via telemedicine and for patients to take the medication at home.
The number of buprenorphine prescriptions has increased since that change, with more than 1 million people receiving the medication in 2021 from retail pharmacies in the United States.
However, questions remained about whether increased access would lead to an increase in buprenorphine-involved overdose.
Researchers with NIDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed data from the State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, a CDC database that combines medical examiner and coroner reports and postmortem toxicology testing.
The study included information about overdose deaths from July 2019 to June 2021 in 46 states and the District of Columbia.
Between July 2019 and June 2021, there were 1,955 buprenorphine-involved overdose deaths, which accounted for 2.2% of all drug overdose deaths and 2.6% of opioid-involved overdose deaths.
However, researchers went beyond overall numbers and evaluated details from coroner’s and medical examiner reports, something they had not done before.
“For the first time we looked at the characteristics of decedents from buprenorphine because this has not been studied in this type of detail with a near-national sample,” Dr. Compton said.
“That allowed us to look at patterns of use of other substances as well as the circumstances that are recorded at the death scene that are in the data set,” he added.
Important insights
Reports from nearly all buprenorphine-involved deaths included the presence of at least one other drug, compared with opioid overdose deaths that typically involved only one drug.
“This is consistent with the pharmacology of buprenorphine being a partial agonist, so it may not be as fatal all by itself as some of the other opioids,” Dr. Compton said.
Deaths involving buprenorphine were less likely to include illicitly manufactured fentanyls, and other prescription medications were more often found on the scene, such as antidepressants.
Compared with opioid decedents, buprenorphine decedents were more likely to be women, age 35-44, White, and receiving treatment for mental health conditions, including for substance use disorder (SUD).
These kinds of characteristics provide important insights about potential ways to improve safety and clinical outcomes, Dr. Compton noted.
“When we see things like a little higher rate of SUD treatment and this evidence of other prescription drugs on the scene, and some higher rates of antidepressants in these decedents than I might have expected, I’m very curious about their use of other medical services outside of substance use treatment, because that might be a place where some interventions could be implemented,” he said.
A similar study showed pandemic-era policy changes that allowed methadone to be taken at home was followed by a decrease in methadone-related overdose deaths.
The new findings are consistent with those results, Dr. Compton said.
‘Chipping away’ at stigma
Commenting on the study, O. Trent Hall, DO, assistant professor of addiction medicine, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said that, although he welcomed the findings, they aren’t unexpected.
“Buprenorphine is well established as a safe and effective medication for opioid use disorder and as a physician who routinely cares for patients in the hospital after opioid overdose, I am not at all surprised by these results,” said Dr. Hall, who was not involved with the research.
“When my patients leave the hospital with a buprenorphine prescription, they are much less likely to return with another overdose or serious opioid-related medical problem,” he added.
U.S. drug overdose deaths topped 100,000 for the first time in 2021, and most were opioid-related. Although the latest data from the CDC shows drug overdose deaths have been declining slowly since early 2022, the numbers remain high.
Buprenorphine is one of only two drugs known to reduce the risk of opioid overdose. While prescriptions have increased since 2020, the medication remains underutilized, despite its known effectiveness in treating opioid use disorder.
Dr. Hall noted that research such as the new study could help increase buprenorphine’s use.
“Studies like this one chip away at the stigma that has been misapplied to buprenorphine,” he said. “I hope this article will encourage more providers to offer buprenorphine to patients with opioid use disorder.”
The study was funded internally by NIDA and the CDC. Dr. Compton reported owning stock in General Electric, 3M, and Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Hall has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers say the data add weight to the argument for permanently adopting the pandemic-era prescribing regulations for buprenorphine, a treatment for opioid use disorder.
“We saw no evidence that increased availability of buprenorphine through the loosening of rules around prescribing and dispensing of buprenorphine during the pandemic increased overdose deaths,” investigator Wilson Compton, MD, deputy director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, told this news organization.
“This is reassuring that, even when we opened up the doors to easier access to buprenorphine, we didn’t see that most serious consequence,” Dr. Compton said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open .
Cause and effect
Federal agencies relaxed prescribing regulations for buprenorphine in March 2020 to make it easier for clinicians to prescribe the drug via telemedicine and for patients to take the medication at home.
The number of buprenorphine prescriptions has increased since that change, with more than 1 million people receiving the medication in 2021 from retail pharmacies in the United States.
However, questions remained about whether increased access would lead to an increase in buprenorphine-involved overdose.
Researchers with NIDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed data from the State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, a CDC database that combines medical examiner and coroner reports and postmortem toxicology testing.
The study included information about overdose deaths from July 2019 to June 2021 in 46 states and the District of Columbia.
Between July 2019 and June 2021, there were 1,955 buprenorphine-involved overdose deaths, which accounted for 2.2% of all drug overdose deaths and 2.6% of opioid-involved overdose deaths.
However, researchers went beyond overall numbers and evaluated details from coroner’s and medical examiner reports, something they had not done before.
“For the first time we looked at the characteristics of decedents from buprenorphine because this has not been studied in this type of detail with a near-national sample,” Dr. Compton said.
“That allowed us to look at patterns of use of other substances as well as the circumstances that are recorded at the death scene that are in the data set,” he added.
Important insights
Reports from nearly all buprenorphine-involved deaths included the presence of at least one other drug, compared with opioid overdose deaths that typically involved only one drug.
“This is consistent with the pharmacology of buprenorphine being a partial agonist, so it may not be as fatal all by itself as some of the other opioids,” Dr. Compton said.
Deaths involving buprenorphine were less likely to include illicitly manufactured fentanyls, and other prescription medications were more often found on the scene, such as antidepressants.
Compared with opioid decedents, buprenorphine decedents were more likely to be women, age 35-44, White, and receiving treatment for mental health conditions, including for substance use disorder (SUD).
These kinds of characteristics provide important insights about potential ways to improve safety and clinical outcomes, Dr. Compton noted.
“When we see things like a little higher rate of SUD treatment and this evidence of other prescription drugs on the scene, and some higher rates of antidepressants in these decedents than I might have expected, I’m very curious about their use of other medical services outside of substance use treatment, because that might be a place where some interventions could be implemented,” he said.
A similar study showed pandemic-era policy changes that allowed methadone to be taken at home was followed by a decrease in methadone-related overdose deaths.
The new findings are consistent with those results, Dr. Compton said.
‘Chipping away’ at stigma
Commenting on the study, O. Trent Hall, DO, assistant professor of addiction medicine, Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said that, although he welcomed the findings, they aren’t unexpected.
“Buprenorphine is well established as a safe and effective medication for opioid use disorder and as a physician who routinely cares for patients in the hospital after opioid overdose, I am not at all surprised by these results,” said Dr. Hall, who was not involved with the research.
“When my patients leave the hospital with a buprenorphine prescription, they are much less likely to return with another overdose or serious opioid-related medical problem,” he added.
U.S. drug overdose deaths topped 100,000 for the first time in 2021, and most were opioid-related. Although the latest data from the CDC shows drug overdose deaths have been declining slowly since early 2022, the numbers remain high.
Buprenorphine is one of only two drugs known to reduce the risk of opioid overdose. While prescriptions have increased since 2020, the medication remains underutilized, despite its known effectiveness in treating opioid use disorder.
Dr. Hall noted that research such as the new study could help increase buprenorphine’s use.
“Studies like this one chip away at the stigma that has been misapplied to buprenorphine,” he said. “I hope this article will encourage more providers to offer buprenorphine to patients with opioid use disorder.”
The study was funded internally by NIDA and the CDC. Dr. Compton reported owning stock in General Electric, 3M, and Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr. Hall has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN








