User login
Psoriasis associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 in real-world study
in patients, compared with those on topical therapy, a new study finds.
“Our study results suggest that psoriasis is an independent risk factor for COVID-19 illness,” study coauthor Jeffrey Liu, a medical student at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview after he presented the findings at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience. “And our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that certain systemic agents may confer a protective effect against COVID-19 illness.”
Mr. Liu and coinvestigators used a Symphony Health dataset to analyze the health records of 167,027 U.S. patients diagnosed with psoriasis and a control group of 1,002,162 patients. The participants, all at least 20 years old, had been treated for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from May 2019 through Jan. 1, 2020, and were tracked until Nov. 11, 2020.
The ages and races of peoples in the two groups were roughly similar. Overall, 55% were women and 75% were White, and their average age was 58 years. Type 2 diabetes was more common in the psoriasis group than the control group (23% vs. 16%), as was obesity (27% vs. 15%). Of the patients with psoriasis, 60% were on topical treatments, 19% were on oral therapies, and 22% were on biologic therapy, with only a few taking both oral and biologic therapies.
After adjustment for age and gender, patients with psoriasis were 33% more likely than the control group to develop COVID-19 (adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.38; P < .0001).
In a separate analysis, the gap persisted after adjustment for demographics and comorbidities: Patients with psoriasis had a higher rate of COVID-19 infection vs. controls (adjusted odds ratio, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.13-1.23; P < .0001). Among all patients, non-White race, older age, and comorbidities were all linked to higher risk of COVID-19 (all P < .0001).
Psoriasis might make patients more vulnerable to COVID-19 because the presence of up-regulated genes in psoriatic skin “may lead to systemic hyperinflammation and sensitization of patients with psoriasis to proinflammatory cytokine storm,” Mr. Liu said. This, in turn, may trigger more severe symptomatic disease that requires medical treatment, he said.
Reduced risk, compared with topical therapies
After adjustment for age and gender, those treated with TNF-alpha inhibitors, methotrexate, and apremilast (Otezla) all had statistically lower risks of COVID-19 vs. those on topical therapy (aIRR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.69-0.95; P < .0029 for TNF-alpha inhibitors; aIRR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.86; P < .0001 for methotrexate; and aIRR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.55-0.85; P < .0006 for apremilast).
Reduced risk held true for those in the separate analysis after adjustment for comorbidities and demographics (respectively, aOR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-1.00; P < .0469; aOR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.92; P < .0011; and aOR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.57-0.87; P < .0014).
Apremilast and methotrexate may boost protection against COVID-19 by inhibiting the body’s production of cytokines, Mr. Liu said.
One message of the study is that “dermatologists should not be scared of prescribing biologics or oral therapies for psoriasis,” the study’s lead author Jashin J. Wu, MD, of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation in Irvine, Calif., said in an interview.
However, the results on the effects of systemic therapies were not all positive. Interleukin (IL)–17 inhibitors were an outlier: After adjustment for age and gender, patients treated with this class of drugs were 36% more likely to develop COVID-19 than those on oral agents (aIRR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63; P < .0009).
Among patients on biologics, those taking IL-17 inhibitors had the highest risk of COVID-19, Mr. Liu said. “The risk was higher in this class regardless of reference group – general population, the topical cohort, and the oral cohort,” he said. “This may relate to the observation that this biologic class exerts more broad immunosuppressive effects on antiviral host immunity. Notably, large meta-estimates of pivotal trials have observed increased risk of respiratory tract infections for patients on IL-17 inhibitors.”
In an interview, Erica Dommasch, MD, MPH, of the department of dermatology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, cautioned that “the data from this study is very hard to interpret.”
It’s likely that some patients with psoriasis on systemic medications “may have been the most careful about limiting exposures,” she said. “Thus, it’s hard to account for behavioral changes in individuals that may have led to the decreased incidence in psoriasis in patients on systemic agents versus topical therapy alone.”
Patients with psoriasis may also be tested more often for COVID-19, and unmeasured comorbidities like chronic kidney disease may play a role too, she said. Still, she added, “it’s reassuring that the authors did not find an increased rate of COVID among psoriasis patients on systemic agents versus topicals alone.” And she agreed with Dr. Wu about the importance of treating psoriasis with therapy beyond topical treatments during the pandemic: “Providers should feel comfortable prescribing systemic medications to psoriasis patients when otherwise appropriate.”
As for the next steps, Dr. Wu said, “we will be exploring more about the prognosis of COVID-19 infection in psoriasis patients. In addition, we will be exploring the relationship of COVID-19 infection with other inflammatory skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis.”
No study funding is reported. Dr. Wu discloses investigator, consultant, or speaker relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Mindera, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Solius, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America, and Zerigo Health. Mr. Liu and Dr. Dommasch have no disclosures.
in patients, compared with those on topical therapy, a new study finds.
“Our study results suggest that psoriasis is an independent risk factor for COVID-19 illness,” study coauthor Jeffrey Liu, a medical student at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview after he presented the findings at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience. “And our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that certain systemic agents may confer a protective effect against COVID-19 illness.”
Mr. Liu and coinvestigators used a Symphony Health dataset to analyze the health records of 167,027 U.S. patients diagnosed with psoriasis and a control group of 1,002,162 patients. The participants, all at least 20 years old, had been treated for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from May 2019 through Jan. 1, 2020, and were tracked until Nov. 11, 2020.
The ages and races of peoples in the two groups were roughly similar. Overall, 55% were women and 75% were White, and their average age was 58 years. Type 2 diabetes was more common in the psoriasis group than the control group (23% vs. 16%), as was obesity (27% vs. 15%). Of the patients with psoriasis, 60% were on topical treatments, 19% were on oral therapies, and 22% were on biologic therapy, with only a few taking both oral and biologic therapies.
After adjustment for age and gender, patients with psoriasis were 33% more likely than the control group to develop COVID-19 (adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.38; P < .0001).
In a separate analysis, the gap persisted after adjustment for demographics and comorbidities: Patients with psoriasis had a higher rate of COVID-19 infection vs. controls (adjusted odds ratio, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.13-1.23; P < .0001). Among all patients, non-White race, older age, and comorbidities were all linked to higher risk of COVID-19 (all P < .0001).
Psoriasis might make patients more vulnerable to COVID-19 because the presence of up-regulated genes in psoriatic skin “may lead to systemic hyperinflammation and sensitization of patients with psoriasis to proinflammatory cytokine storm,” Mr. Liu said. This, in turn, may trigger more severe symptomatic disease that requires medical treatment, he said.
Reduced risk, compared with topical therapies
After adjustment for age and gender, those treated with TNF-alpha inhibitors, methotrexate, and apremilast (Otezla) all had statistically lower risks of COVID-19 vs. those on topical therapy (aIRR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.69-0.95; P < .0029 for TNF-alpha inhibitors; aIRR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.86; P < .0001 for methotrexate; and aIRR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.55-0.85; P < .0006 for apremilast).
Reduced risk held true for those in the separate analysis after adjustment for comorbidities and demographics (respectively, aOR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-1.00; P < .0469; aOR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.92; P < .0011; and aOR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.57-0.87; P < .0014).
Apremilast and methotrexate may boost protection against COVID-19 by inhibiting the body’s production of cytokines, Mr. Liu said.
One message of the study is that “dermatologists should not be scared of prescribing biologics or oral therapies for psoriasis,” the study’s lead author Jashin J. Wu, MD, of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation in Irvine, Calif., said in an interview.
However, the results on the effects of systemic therapies were not all positive. Interleukin (IL)–17 inhibitors were an outlier: After adjustment for age and gender, patients treated with this class of drugs were 36% more likely to develop COVID-19 than those on oral agents (aIRR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63; P < .0009).
Among patients on biologics, those taking IL-17 inhibitors had the highest risk of COVID-19, Mr. Liu said. “The risk was higher in this class regardless of reference group – general population, the topical cohort, and the oral cohort,” he said. “This may relate to the observation that this biologic class exerts more broad immunosuppressive effects on antiviral host immunity. Notably, large meta-estimates of pivotal trials have observed increased risk of respiratory tract infections for patients on IL-17 inhibitors.”
In an interview, Erica Dommasch, MD, MPH, of the department of dermatology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, cautioned that “the data from this study is very hard to interpret.”
It’s likely that some patients with psoriasis on systemic medications “may have been the most careful about limiting exposures,” she said. “Thus, it’s hard to account for behavioral changes in individuals that may have led to the decreased incidence in psoriasis in patients on systemic agents versus topical therapy alone.”
Patients with psoriasis may also be tested more often for COVID-19, and unmeasured comorbidities like chronic kidney disease may play a role too, she said. Still, she added, “it’s reassuring that the authors did not find an increased rate of COVID among psoriasis patients on systemic agents versus topicals alone.” And she agreed with Dr. Wu about the importance of treating psoriasis with therapy beyond topical treatments during the pandemic: “Providers should feel comfortable prescribing systemic medications to psoriasis patients when otherwise appropriate.”
As for the next steps, Dr. Wu said, “we will be exploring more about the prognosis of COVID-19 infection in psoriasis patients. In addition, we will be exploring the relationship of COVID-19 infection with other inflammatory skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis.”
No study funding is reported. Dr. Wu discloses investigator, consultant, or speaker relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Mindera, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Solius, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America, and Zerigo Health. Mr. Liu and Dr. Dommasch have no disclosures.
in patients, compared with those on topical therapy, a new study finds.
“Our study results suggest that psoriasis is an independent risk factor for COVID-19 illness,” study coauthor Jeffrey Liu, a medical student at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview after he presented the findings at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience. “And our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that certain systemic agents may confer a protective effect against COVID-19 illness.”
Mr. Liu and coinvestigators used a Symphony Health dataset to analyze the health records of 167,027 U.S. patients diagnosed with psoriasis and a control group of 1,002,162 patients. The participants, all at least 20 years old, had been treated for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from May 2019 through Jan. 1, 2020, and were tracked until Nov. 11, 2020.
The ages and races of peoples in the two groups were roughly similar. Overall, 55% were women and 75% were White, and their average age was 58 years. Type 2 diabetes was more common in the psoriasis group than the control group (23% vs. 16%), as was obesity (27% vs. 15%). Of the patients with psoriasis, 60% were on topical treatments, 19% were on oral therapies, and 22% were on biologic therapy, with only a few taking both oral and biologic therapies.
After adjustment for age and gender, patients with psoriasis were 33% more likely than the control group to develop COVID-19 (adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.38; P < .0001).
In a separate analysis, the gap persisted after adjustment for demographics and comorbidities: Patients with psoriasis had a higher rate of COVID-19 infection vs. controls (adjusted odds ratio, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.13-1.23; P < .0001). Among all patients, non-White race, older age, and comorbidities were all linked to higher risk of COVID-19 (all P < .0001).
Psoriasis might make patients more vulnerable to COVID-19 because the presence of up-regulated genes in psoriatic skin “may lead to systemic hyperinflammation and sensitization of patients with psoriasis to proinflammatory cytokine storm,” Mr. Liu said. This, in turn, may trigger more severe symptomatic disease that requires medical treatment, he said.
Reduced risk, compared with topical therapies
After adjustment for age and gender, those treated with TNF-alpha inhibitors, methotrexate, and apremilast (Otezla) all had statistically lower risks of COVID-19 vs. those on topical therapy (aIRR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.69-0.95; P < .0029 for TNF-alpha inhibitors; aIRR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.86; P < .0001 for methotrexate; and aIRR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.55-0.85; P < .0006 for apremilast).
Reduced risk held true for those in the separate analysis after adjustment for comorbidities and demographics (respectively, aOR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-1.00; P < .0469; aOR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.92; P < .0011; and aOR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.57-0.87; P < .0014).
Apremilast and methotrexate may boost protection against COVID-19 by inhibiting the body’s production of cytokines, Mr. Liu said.
One message of the study is that “dermatologists should not be scared of prescribing biologics or oral therapies for psoriasis,” the study’s lead author Jashin J. Wu, MD, of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation in Irvine, Calif., said in an interview.
However, the results on the effects of systemic therapies were not all positive. Interleukin (IL)–17 inhibitors were an outlier: After adjustment for age and gender, patients treated with this class of drugs were 36% more likely to develop COVID-19 than those on oral agents (aIRR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63; P < .0009).
Among patients on biologics, those taking IL-17 inhibitors had the highest risk of COVID-19, Mr. Liu said. “The risk was higher in this class regardless of reference group – general population, the topical cohort, and the oral cohort,” he said. “This may relate to the observation that this biologic class exerts more broad immunosuppressive effects on antiviral host immunity. Notably, large meta-estimates of pivotal trials have observed increased risk of respiratory tract infections for patients on IL-17 inhibitors.”
In an interview, Erica Dommasch, MD, MPH, of the department of dermatology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, cautioned that “the data from this study is very hard to interpret.”
It’s likely that some patients with psoriasis on systemic medications “may have been the most careful about limiting exposures,” she said. “Thus, it’s hard to account for behavioral changes in individuals that may have led to the decreased incidence in psoriasis in patients on systemic agents versus topical therapy alone.”
Patients with psoriasis may also be tested more often for COVID-19, and unmeasured comorbidities like chronic kidney disease may play a role too, she said. Still, she added, “it’s reassuring that the authors did not find an increased rate of COVID among psoriasis patients on systemic agents versus topicals alone.” And she agreed with Dr. Wu about the importance of treating psoriasis with therapy beyond topical treatments during the pandemic: “Providers should feel comfortable prescribing systemic medications to psoriasis patients when otherwise appropriate.”
As for the next steps, Dr. Wu said, “we will be exploring more about the prognosis of COVID-19 infection in psoriasis patients. In addition, we will be exploring the relationship of COVID-19 infection with other inflammatory skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis.”
No study funding is reported. Dr. Wu discloses investigator, consultant, or speaker relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Mindera, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Solius, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America, and Zerigo Health. Mr. Liu and Dr. Dommasch have no disclosures.
FROM AAD VMX 2021
Debate: Should biologics be used for milder cases of psoriasis?
The issue was tackled in a debate at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
Taking the con side, Kenneth Gordon, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, argued that, with the high cost of biologics, availability of many alternatives, and other issues, “we should just say no. ... There is no good reason that we need to expand the use of biologics in patients with limited disease.”
On the pro side, Richard Langley, MD, professor of dermatology at Dalhousie University Halifax, N.S, argued for a nuanced approach. He noted that patients with smaller patches of disease can be just as miserable as patients who hit traditional benchmarks of increased severity, such as high body surface area involvement – especially if those small areas are in sensitive locations like the scalp, palms, or genitals.
The decision to use a biologic should hinge on how badly patients and their quality of life are affected, not on “some artificial and limiting definition” of severity, Dr. Langley said.
Dr. Gordon didn’t disagree, noting that current use criteria include objective measures as well as disease in sensitive areas and failure of alternative treatments.
Rather, he was concerned about “expanding the definition of who is eligible beyond these criteria ... to chase every last bit of” disease. “I don’t think we have” a good rationale for that approach, he said.
Cost is the most important issue, Dr. Gordon said.
With more biologics on the way and prices continuing to go up, “there is going to a be a huge challenge to our use of these expensive medicines over the next few years” from payers. “It is important that we use them smartly in order to make sure we are able to use them for people with severe disease” who really need them. If “we start using biologics for all our patients with psoriasis,” it will be a “cost disaster,” Dr. Gordon said.
In addition, topicals and home phototherapy can be effective as long as patients adhere to them, as can alternative systemic agents, such as methotrexate and apremilast.
Often with biologics, “the issue is mainly convenience” rather than a fundamental problem with the alternatives, and despite the good safety record in trials, “chasing the last bit” of psoriasis with a biologic “is not necessarily” without risk for the patient, Dr. Gordon said.
Still, there can be a “pretty significant disconnect” between how patients perceive their psoriasis and “what physicians are thinking and prescribing” for it based on objective measures, Dr. Langley noted. Sometimes patients who have limited disease but are in significant distress aren’t even receiving treatment or are only given another cream to add to their collection of ones that haven’t worked.
One problem with traditional severity classifications is that they don’t generally take patients’ subjective experience into account, he added. There’s also been a lack of standardization to the point that dermatologists, researchers, and payers can sometimes disagree over severity in a given patient.
There’s movement toward better incorporation of patient experience into severity considerations, but for now at least, a designation of mild psoriasis can underestimate the true severity of disease, Dr. Langley said.
Dr. Gordon and Dr. Langley reported receiving honoraria and/or research support from many pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Pfizer, and Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The issue was tackled in a debate at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
Taking the con side, Kenneth Gordon, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, argued that, with the high cost of biologics, availability of many alternatives, and other issues, “we should just say no. ... There is no good reason that we need to expand the use of biologics in patients with limited disease.”
On the pro side, Richard Langley, MD, professor of dermatology at Dalhousie University Halifax, N.S, argued for a nuanced approach. He noted that patients with smaller patches of disease can be just as miserable as patients who hit traditional benchmarks of increased severity, such as high body surface area involvement – especially if those small areas are in sensitive locations like the scalp, palms, or genitals.
The decision to use a biologic should hinge on how badly patients and their quality of life are affected, not on “some artificial and limiting definition” of severity, Dr. Langley said.
Dr. Gordon didn’t disagree, noting that current use criteria include objective measures as well as disease in sensitive areas and failure of alternative treatments.
Rather, he was concerned about “expanding the definition of who is eligible beyond these criteria ... to chase every last bit of” disease. “I don’t think we have” a good rationale for that approach, he said.
Cost is the most important issue, Dr. Gordon said.
With more biologics on the way and prices continuing to go up, “there is going to a be a huge challenge to our use of these expensive medicines over the next few years” from payers. “It is important that we use them smartly in order to make sure we are able to use them for people with severe disease” who really need them. If “we start using biologics for all our patients with psoriasis,” it will be a “cost disaster,” Dr. Gordon said.
In addition, topicals and home phototherapy can be effective as long as patients adhere to them, as can alternative systemic agents, such as methotrexate and apremilast.
Often with biologics, “the issue is mainly convenience” rather than a fundamental problem with the alternatives, and despite the good safety record in trials, “chasing the last bit” of psoriasis with a biologic “is not necessarily” without risk for the patient, Dr. Gordon said.
Still, there can be a “pretty significant disconnect” between how patients perceive their psoriasis and “what physicians are thinking and prescribing” for it based on objective measures, Dr. Langley noted. Sometimes patients who have limited disease but are in significant distress aren’t even receiving treatment or are only given another cream to add to their collection of ones that haven’t worked.
One problem with traditional severity classifications is that they don’t generally take patients’ subjective experience into account, he added. There’s also been a lack of standardization to the point that dermatologists, researchers, and payers can sometimes disagree over severity in a given patient.
There’s movement toward better incorporation of patient experience into severity considerations, but for now at least, a designation of mild psoriasis can underestimate the true severity of disease, Dr. Langley said.
Dr. Gordon and Dr. Langley reported receiving honoraria and/or research support from many pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Pfizer, and Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The issue was tackled in a debate at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
Taking the con side, Kenneth Gordon, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, argued that, with the high cost of biologics, availability of many alternatives, and other issues, “we should just say no. ... There is no good reason that we need to expand the use of biologics in patients with limited disease.”
On the pro side, Richard Langley, MD, professor of dermatology at Dalhousie University Halifax, N.S, argued for a nuanced approach. He noted that patients with smaller patches of disease can be just as miserable as patients who hit traditional benchmarks of increased severity, such as high body surface area involvement – especially if those small areas are in sensitive locations like the scalp, palms, or genitals.
The decision to use a biologic should hinge on how badly patients and their quality of life are affected, not on “some artificial and limiting definition” of severity, Dr. Langley said.
Dr. Gordon didn’t disagree, noting that current use criteria include objective measures as well as disease in sensitive areas and failure of alternative treatments.
Rather, he was concerned about “expanding the definition of who is eligible beyond these criteria ... to chase every last bit of” disease. “I don’t think we have” a good rationale for that approach, he said.
Cost is the most important issue, Dr. Gordon said.
With more biologics on the way and prices continuing to go up, “there is going to a be a huge challenge to our use of these expensive medicines over the next few years” from payers. “It is important that we use them smartly in order to make sure we are able to use them for people with severe disease” who really need them. If “we start using biologics for all our patients with psoriasis,” it will be a “cost disaster,” Dr. Gordon said.
In addition, topicals and home phototherapy can be effective as long as patients adhere to them, as can alternative systemic agents, such as methotrexate and apremilast.
Often with biologics, “the issue is mainly convenience” rather than a fundamental problem with the alternatives, and despite the good safety record in trials, “chasing the last bit” of psoriasis with a biologic “is not necessarily” without risk for the patient, Dr. Gordon said.
Still, there can be a “pretty significant disconnect” between how patients perceive their psoriasis and “what physicians are thinking and prescribing” for it based on objective measures, Dr. Langley noted. Sometimes patients who have limited disease but are in significant distress aren’t even receiving treatment or are only given another cream to add to their collection of ones that haven’t worked.
One problem with traditional severity classifications is that they don’t generally take patients’ subjective experience into account, he added. There’s also been a lack of standardization to the point that dermatologists, researchers, and payers can sometimes disagree over severity in a given patient.
There’s movement toward better incorporation of patient experience into severity considerations, but for now at least, a designation of mild psoriasis can underestimate the true severity of disease, Dr. Langley said.
Dr. Gordon and Dr. Langley reported receiving honoraria and/or research support from many pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Pfizer, and Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tofacitinib: Small study shows big cutaneous sarcoidosis response
Researchers are reporting impressive results in a small, , and all patients improved by an average of 83% via a scoring system.
“Not only did patients get better, but they were in many cases able to come off their baseline immunosuppressive regimen, including prednisone and methotrexate. They’d get off prednisone entirely or, in some cases, decrease it substantially,” study investigator William Damsky, MD, PhD, reported at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
Sarcoidosis is a common disease that affects an estimated 1 in 25 Black women and is believed to contribute to the deaths of about 4,000 people in the United States each year, noted Dr. Damsky of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. One famous patient is comedian Bernie Mac, who died from the condition in 2008.
“Approximately one third of patients have cutaneous involvement,” Dr. Damsky said, and skin may be the only manifestation of the disease. There is no Food and Drug Administration-approved therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis, he added. Prednisone, the first-line therapy in skin manifestations, is approved only for pulmonary sarcoidosis.
“Oftentimes, there’s an attempt to transition either partially or fully to other therapies, including methotrexate and TNF-alpha blockers. But there’s been mixed success in doing that,” he said. This is not always possible, “so a lot of patients end up on prednisone.”
Earlier, a team at Yale prescribed 5 mg tofacitinib (Xeljanz) for several patients with severe cutaneous sarcoidosis and saw impressive results, Dr. Damsky said, including a patient with pulmonary sarcoidosis that also improved. He noted that there are case reports in the medical literature with similar findings.
Those positive results inspired the new study. Researchers recruited 10 patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis (9 with internal organ involvement) with a Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Activity and Morphology Instrument ( CSAMI ) score of 10 or higher. Nine patients were in their 50s, one was aged 63 years, and five were men. Skin colors of the patients ranged from Fitzpatrick skin types I to VI, and all had been taking at least two medications, typically methotrexate and prednisone.
The patients received 5 mg of tofacitinib twice a day for 6 months. “Everyone got better during the study, and six patients had a complete response, which we defined as a CSAMI score of zero activity,” Dr. Damsky said. “It’s really quite remarkable to see that.” Overall, the patients saw an 83% improvement in CSAMI scores.
In regard to safety, “all patients completed the study,” he said. “Tofacitinib was well tolerated, and there were no serious adverse effects or events.”
Tofacitinib is approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
A month’s supply of twice-daily 5 mg tofacitinib pills would cost $4,900-$5,100 with free coupons, according to information accessed on April 24, 2021, on GoodRx.com. Generics are not available.
In an interview, Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, praised the study, and said “tofacitinib is a reasonable treatment for treatment-refractory or extensive cutaneous sarcoidosis,” although it will be helpful to get results from randomized-controlled trials.
She cautioned that the drug “is a powerful immunosuppressant, so the risk of infection must be discussed with patients before prescribing. Screening for chronic infections such as viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, and HIV should be completed prior to treatment initiation. Blood counts, liver function, and lipid panels should be regularly monitored. The vaccines necessary for those who are immunosuppressed should be administered as able, and age-appropriate cancer screening must be kept up to date.”
The study was funded by Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, and the Yale Department of Dermatology. Dr. Damsky disclosed research support (Pfizer), consulting fees (Eli Lilly, Pfizer, TWi Biotechnology), and licensing fees (EMD Millipore/MillporeSigma). Dr. Imadojemu has no disclosures.
This article was updated 5/5/21.
Researchers are reporting impressive results in a small, , and all patients improved by an average of 83% via a scoring system.
“Not only did patients get better, but they were in many cases able to come off their baseline immunosuppressive regimen, including prednisone and methotrexate. They’d get off prednisone entirely or, in some cases, decrease it substantially,” study investigator William Damsky, MD, PhD, reported at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
Sarcoidosis is a common disease that affects an estimated 1 in 25 Black women and is believed to contribute to the deaths of about 4,000 people in the United States each year, noted Dr. Damsky of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. One famous patient is comedian Bernie Mac, who died from the condition in 2008.
“Approximately one third of patients have cutaneous involvement,” Dr. Damsky said, and skin may be the only manifestation of the disease. There is no Food and Drug Administration-approved therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis, he added. Prednisone, the first-line therapy in skin manifestations, is approved only for pulmonary sarcoidosis.
“Oftentimes, there’s an attempt to transition either partially or fully to other therapies, including methotrexate and TNF-alpha blockers. But there’s been mixed success in doing that,” he said. This is not always possible, “so a lot of patients end up on prednisone.”
Earlier, a team at Yale prescribed 5 mg tofacitinib (Xeljanz) for several patients with severe cutaneous sarcoidosis and saw impressive results, Dr. Damsky said, including a patient with pulmonary sarcoidosis that also improved. He noted that there are case reports in the medical literature with similar findings.
Those positive results inspired the new study. Researchers recruited 10 patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis (9 with internal organ involvement) with a Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Activity and Morphology Instrument ( CSAMI ) score of 10 or higher. Nine patients were in their 50s, one was aged 63 years, and five were men. Skin colors of the patients ranged from Fitzpatrick skin types I to VI, and all had been taking at least two medications, typically methotrexate and prednisone.
The patients received 5 mg of tofacitinib twice a day for 6 months. “Everyone got better during the study, and six patients had a complete response, which we defined as a CSAMI score of zero activity,” Dr. Damsky said. “It’s really quite remarkable to see that.” Overall, the patients saw an 83% improvement in CSAMI scores.
In regard to safety, “all patients completed the study,” he said. “Tofacitinib was well tolerated, and there were no serious adverse effects or events.”
Tofacitinib is approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
A month’s supply of twice-daily 5 mg tofacitinib pills would cost $4,900-$5,100 with free coupons, according to information accessed on April 24, 2021, on GoodRx.com. Generics are not available.
In an interview, Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, praised the study, and said “tofacitinib is a reasonable treatment for treatment-refractory or extensive cutaneous sarcoidosis,” although it will be helpful to get results from randomized-controlled trials.
She cautioned that the drug “is a powerful immunosuppressant, so the risk of infection must be discussed with patients before prescribing. Screening for chronic infections such as viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, and HIV should be completed prior to treatment initiation. Blood counts, liver function, and lipid panels should be regularly monitored. The vaccines necessary for those who are immunosuppressed should be administered as able, and age-appropriate cancer screening must be kept up to date.”
The study was funded by Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, and the Yale Department of Dermatology. Dr. Damsky disclosed research support (Pfizer), consulting fees (Eli Lilly, Pfizer, TWi Biotechnology), and licensing fees (EMD Millipore/MillporeSigma). Dr. Imadojemu has no disclosures.
This article was updated 5/5/21.
Researchers are reporting impressive results in a small, , and all patients improved by an average of 83% via a scoring system.
“Not only did patients get better, but they were in many cases able to come off their baseline immunosuppressive regimen, including prednisone and methotrexate. They’d get off prednisone entirely or, in some cases, decrease it substantially,” study investigator William Damsky, MD, PhD, reported at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
Sarcoidosis is a common disease that affects an estimated 1 in 25 Black women and is believed to contribute to the deaths of about 4,000 people in the United States each year, noted Dr. Damsky of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. One famous patient is comedian Bernie Mac, who died from the condition in 2008.
“Approximately one third of patients have cutaneous involvement,” Dr. Damsky said, and skin may be the only manifestation of the disease. There is no Food and Drug Administration-approved therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis, he added. Prednisone, the first-line therapy in skin manifestations, is approved only for pulmonary sarcoidosis.
“Oftentimes, there’s an attempt to transition either partially or fully to other therapies, including methotrexate and TNF-alpha blockers. But there’s been mixed success in doing that,” he said. This is not always possible, “so a lot of patients end up on prednisone.”
Earlier, a team at Yale prescribed 5 mg tofacitinib (Xeljanz) for several patients with severe cutaneous sarcoidosis and saw impressive results, Dr. Damsky said, including a patient with pulmonary sarcoidosis that also improved. He noted that there are case reports in the medical literature with similar findings.
Those positive results inspired the new study. Researchers recruited 10 patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis (9 with internal organ involvement) with a Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Activity and Morphology Instrument ( CSAMI ) score of 10 or higher. Nine patients were in their 50s, one was aged 63 years, and five were men. Skin colors of the patients ranged from Fitzpatrick skin types I to VI, and all had been taking at least two medications, typically methotrexate and prednisone.
The patients received 5 mg of tofacitinib twice a day for 6 months. “Everyone got better during the study, and six patients had a complete response, which we defined as a CSAMI score of zero activity,” Dr. Damsky said. “It’s really quite remarkable to see that.” Overall, the patients saw an 83% improvement in CSAMI scores.
In regard to safety, “all patients completed the study,” he said. “Tofacitinib was well tolerated, and there were no serious adverse effects or events.”
Tofacitinib is approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
A month’s supply of twice-daily 5 mg tofacitinib pills would cost $4,900-$5,100 with free coupons, according to information accessed on April 24, 2021, on GoodRx.com. Generics are not available.
In an interview, Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, praised the study, and said “tofacitinib is a reasonable treatment for treatment-refractory or extensive cutaneous sarcoidosis,” although it will be helpful to get results from randomized-controlled trials.
She cautioned that the drug “is a powerful immunosuppressant, so the risk of infection must be discussed with patients before prescribing. Screening for chronic infections such as viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, and HIV should be completed prior to treatment initiation. Blood counts, liver function, and lipid panels should be regularly monitored. The vaccines necessary for those who are immunosuppressed should be administered as able, and age-appropriate cancer screening must be kept up to date.”
The study was funded by Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, and the Yale Department of Dermatology. Dr. Damsky disclosed research support (Pfizer), consulting fees (Eli Lilly, Pfizer, TWi Biotechnology), and licensing fees (EMD Millipore/MillporeSigma). Dr. Imadojemu has no disclosures.
This article was updated 5/5/21.
REPORTING FROM AAD VMX 2021
Topical anticholinergic for axillary hyperhidrosis shows fewer side effects
according to 48-week safety and outcome data.
A structural analogue of glycopyrrolate working through the same mechanism, sofpironium bromide was developed as a retrometabolic agent. This means it is rapidly transformed into an inactive metabolite after application, reducing risk of systemic effects, study investigator Stacy Smith, MD, explained in the late-breaking research session at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
The anticholinergic glycopyrrolate, which currently is the most commonly used therapy for hyperhidrosis, is absorbed through the skin and excreted through the urine. The systemic exposure to the active agent after topical application explains the substantial risk of adverse effects, said Dr. Smith, a clinician and researcher affiliated with the California Dermatology and Clinical Research Institute, Encinitas.
In contrast,“sofpironium bromide is the ideal topical medication, because it has strong activity at the application site but then reduced systemic activity due to the retrometabolism,” Dr. Smith said.
The 52-week data from the open-label, phase 3 trial supports the premise. In this study of 299 patients randomized to the 5% (102 patients) or 15% (197 patients) topical sofpironium bromide gel formulations, most anticholinergic adverse events were mild or moderate and transient, with complaints concentrated in the first 3 months of the trial.
“The retrometabolic pathway seems to work,” Dr. Smith said. He acknowledged that the treatment-naive patients who entered the study “had to get used to the drug over time,” but the data “show they did.”
The phase 3 trial of sofpironium bromide, which is already approved to treat axillary hyperhidrosis in Japan, did not have a placebo control. It was focused primarily on safety, but outcomes were assessed with the Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Measure–Axillary (HDSM-Ax).
At least a 1-point improvement in the 7-point HDSM-Ax scale, which is considered clinically meaningful, was achieved by 86.1% and 85.8% of those treated with the 5% and 15% gels, respectively. A 2-point or greater improvement at the end of the study was observed in 69.4% and 61.9%, respectively.
“The medication works well and there was improved efficacy over time. About two-thirds of the patients had at least a 2-point improvement in the HDSM-Ax score at the end of 48 weeks,” Dr. Smith reported.
While response rates climbed over the course of the study, rates of adverse events fell markedly.
After 2 weeks of treatment, the proportions of patients with a treatment-related adverse event were 6% and just under 15% for the 5% and 15% topical-gel groups, respectively. At each 2-week interval when reassessed, the rates fell. By week 12, the rates were less than 2% and about 4% in the two groups, respectively.
The discontinuation rates overall for anticholinergic side effects were 3% and 8.1% for the lower and higher doses. Blurred vision accounted for the vast majority of these discontinuations in both groups. The other discontinuations, which included those for dry mouth, urinary retention, and mydriasis, occurred in one patient each. Again, discontinuations were most common in the first few months of the study.
For the total study population, mild (10.8% vs. 24%) and moderate (10.8% vs. 20.3%) side effects accounted for almost all side effects with the lower and higher doses of the topical drug. Only one patient in the low-dose group had a severe adverse event. At 6.1%, the proportion of the high-dose group with a severe adverse event was higher, but none of the adverse events were considered serious. All were transient.
These rates of adverse events are lower than those reported historically with effective doses of glycopyrrolate, Dr. Smith said.
The data presented by Dr. Smith are part of a phase 3 pivotal trials program designed to gain FDA approval. Going forward, these trials, which are enrolling patients as young as 9 years old, are expected to focus on clinical development of the 15% gel, he added.
The gel is delivered with a metered-dose pump that has an applicator, according to Brickell Biotech, the company developing the treatment in the United States. The 5% formulation was approved in Japan in September 2020, for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
In an interview, David M. Pariser, MD, professor of dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said that he believes that this drug has could be helpful if the pivotal studies confirm efficacy with a lower risk of adverse events relative to glycopyrrolate. “If it is true that, in phase 3, placebo-controlled trials, there are fewer systemic anticholinergic effects, then this drug will be very useful,” said Dr. Pariser, cofounder of the International Hyperhidrosis Society and an investigator on a previously published dose-ranging, phase 2 study of sofpironium bromide.
The trial was sponsored by Brickell Biotech, which compensated Dr. Smith and other coauthors for their participation. Dr. Pariser has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies with dermatologic products, including Brickell Biotech.
This article was updated 4/26/21.
according to 48-week safety and outcome data.
A structural analogue of glycopyrrolate working through the same mechanism, sofpironium bromide was developed as a retrometabolic agent. This means it is rapidly transformed into an inactive metabolite after application, reducing risk of systemic effects, study investigator Stacy Smith, MD, explained in the late-breaking research session at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
The anticholinergic glycopyrrolate, which currently is the most commonly used therapy for hyperhidrosis, is absorbed through the skin and excreted through the urine. The systemic exposure to the active agent after topical application explains the substantial risk of adverse effects, said Dr. Smith, a clinician and researcher affiliated with the California Dermatology and Clinical Research Institute, Encinitas.
In contrast,“sofpironium bromide is the ideal topical medication, because it has strong activity at the application site but then reduced systemic activity due to the retrometabolism,” Dr. Smith said.
The 52-week data from the open-label, phase 3 trial supports the premise. In this study of 299 patients randomized to the 5% (102 patients) or 15% (197 patients) topical sofpironium bromide gel formulations, most anticholinergic adverse events were mild or moderate and transient, with complaints concentrated in the first 3 months of the trial.
“The retrometabolic pathway seems to work,” Dr. Smith said. He acknowledged that the treatment-naive patients who entered the study “had to get used to the drug over time,” but the data “show they did.”
The phase 3 trial of sofpironium bromide, which is already approved to treat axillary hyperhidrosis in Japan, did not have a placebo control. It was focused primarily on safety, but outcomes were assessed with the Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Measure–Axillary (HDSM-Ax).
At least a 1-point improvement in the 7-point HDSM-Ax scale, which is considered clinically meaningful, was achieved by 86.1% and 85.8% of those treated with the 5% and 15% gels, respectively. A 2-point or greater improvement at the end of the study was observed in 69.4% and 61.9%, respectively.
“The medication works well and there was improved efficacy over time. About two-thirds of the patients had at least a 2-point improvement in the HDSM-Ax score at the end of 48 weeks,” Dr. Smith reported.
While response rates climbed over the course of the study, rates of adverse events fell markedly.
After 2 weeks of treatment, the proportions of patients with a treatment-related adverse event were 6% and just under 15% for the 5% and 15% topical-gel groups, respectively. At each 2-week interval when reassessed, the rates fell. By week 12, the rates were less than 2% and about 4% in the two groups, respectively.
The discontinuation rates overall for anticholinergic side effects were 3% and 8.1% for the lower and higher doses. Blurred vision accounted for the vast majority of these discontinuations in both groups. The other discontinuations, which included those for dry mouth, urinary retention, and mydriasis, occurred in one patient each. Again, discontinuations were most common in the first few months of the study.
For the total study population, mild (10.8% vs. 24%) and moderate (10.8% vs. 20.3%) side effects accounted for almost all side effects with the lower and higher doses of the topical drug. Only one patient in the low-dose group had a severe adverse event. At 6.1%, the proportion of the high-dose group with a severe adverse event was higher, but none of the adverse events were considered serious. All were transient.
These rates of adverse events are lower than those reported historically with effective doses of glycopyrrolate, Dr. Smith said.
The data presented by Dr. Smith are part of a phase 3 pivotal trials program designed to gain FDA approval. Going forward, these trials, which are enrolling patients as young as 9 years old, are expected to focus on clinical development of the 15% gel, he added.
The gel is delivered with a metered-dose pump that has an applicator, according to Brickell Biotech, the company developing the treatment in the United States. The 5% formulation was approved in Japan in September 2020, for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
In an interview, David M. Pariser, MD, professor of dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said that he believes that this drug has could be helpful if the pivotal studies confirm efficacy with a lower risk of adverse events relative to glycopyrrolate. “If it is true that, in phase 3, placebo-controlled trials, there are fewer systemic anticholinergic effects, then this drug will be very useful,” said Dr. Pariser, cofounder of the International Hyperhidrosis Society and an investigator on a previously published dose-ranging, phase 2 study of sofpironium bromide.
The trial was sponsored by Brickell Biotech, which compensated Dr. Smith and other coauthors for their participation. Dr. Pariser has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies with dermatologic products, including Brickell Biotech.
This article was updated 4/26/21.
according to 48-week safety and outcome data.
A structural analogue of glycopyrrolate working through the same mechanism, sofpironium bromide was developed as a retrometabolic agent. This means it is rapidly transformed into an inactive metabolite after application, reducing risk of systemic effects, study investigator Stacy Smith, MD, explained in the late-breaking research session at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
The anticholinergic glycopyrrolate, which currently is the most commonly used therapy for hyperhidrosis, is absorbed through the skin and excreted through the urine. The systemic exposure to the active agent after topical application explains the substantial risk of adverse effects, said Dr. Smith, a clinician and researcher affiliated with the California Dermatology and Clinical Research Institute, Encinitas.
In contrast,“sofpironium bromide is the ideal topical medication, because it has strong activity at the application site but then reduced systemic activity due to the retrometabolism,” Dr. Smith said.
The 52-week data from the open-label, phase 3 trial supports the premise. In this study of 299 patients randomized to the 5% (102 patients) or 15% (197 patients) topical sofpironium bromide gel formulations, most anticholinergic adverse events were mild or moderate and transient, with complaints concentrated in the first 3 months of the trial.
“The retrometabolic pathway seems to work,” Dr. Smith said. He acknowledged that the treatment-naive patients who entered the study “had to get used to the drug over time,” but the data “show they did.”
The phase 3 trial of sofpironium bromide, which is already approved to treat axillary hyperhidrosis in Japan, did not have a placebo control. It was focused primarily on safety, but outcomes were assessed with the Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Measure–Axillary (HDSM-Ax).
At least a 1-point improvement in the 7-point HDSM-Ax scale, which is considered clinically meaningful, was achieved by 86.1% and 85.8% of those treated with the 5% and 15% gels, respectively. A 2-point or greater improvement at the end of the study was observed in 69.4% and 61.9%, respectively.
“The medication works well and there was improved efficacy over time. About two-thirds of the patients had at least a 2-point improvement in the HDSM-Ax score at the end of 48 weeks,” Dr. Smith reported.
While response rates climbed over the course of the study, rates of adverse events fell markedly.
After 2 weeks of treatment, the proportions of patients with a treatment-related adverse event were 6% and just under 15% for the 5% and 15% topical-gel groups, respectively. At each 2-week interval when reassessed, the rates fell. By week 12, the rates were less than 2% and about 4% in the two groups, respectively.
The discontinuation rates overall for anticholinergic side effects were 3% and 8.1% for the lower and higher doses. Blurred vision accounted for the vast majority of these discontinuations in both groups. The other discontinuations, which included those for dry mouth, urinary retention, and mydriasis, occurred in one patient each. Again, discontinuations were most common in the first few months of the study.
For the total study population, mild (10.8% vs. 24%) and moderate (10.8% vs. 20.3%) side effects accounted for almost all side effects with the lower and higher doses of the topical drug. Only one patient in the low-dose group had a severe adverse event. At 6.1%, the proportion of the high-dose group with a severe adverse event was higher, but none of the adverse events were considered serious. All were transient.
These rates of adverse events are lower than those reported historically with effective doses of glycopyrrolate, Dr. Smith said.
The data presented by Dr. Smith are part of a phase 3 pivotal trials program designed to gain FDA approval. Going forward, these trials, which are enrolling patients as young as 9 years old, are expected to focus on clinical development of the 15% gel, he added.
The gel is delivered with a metered-dose pump that has an applicator, according to Brickell Biotech, the company developing the treatment in the United States. The 5% formulation was approved in Japan in September 2020, for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
In an interview, David M. Pariser, MD, professor of dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said that he believes that this drug has could be helpful if the pivotal studies confirm efficacy with a lower risk of adverse events relative to glycopyrrolate. “If it is true that, in phase 3, placebo-controlled trials, there are fewer systemic anticholinergic effects, then this drug will be very useful,” said Dr. Pariser, cofounder of the International Hyperhidrosis Society and an investigator on a previously published dose-ranging, phase 2 study of sofpironium bromide.
The trial was sponsored by Brickell Biotech, which compensated Dr. Smith and other coauthors for their participation. Dr. Pariser has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies with dermatologic products, including Brickell Biotech.
This article was updated 4/26/21.
FROM AAD VMX 2021
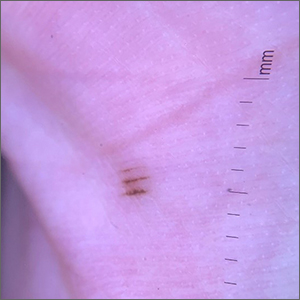
Pigmented palmar lesions
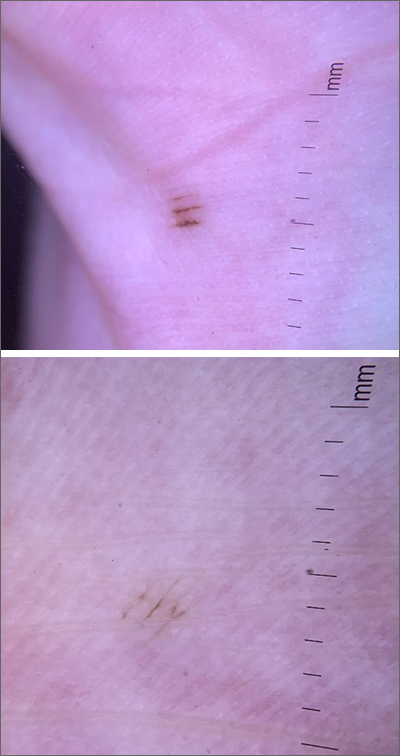
Fortunately, the dermoscopy images of these 2 small palmar lesions showed a pattern of pigmentation that aligned in the furrows and was consistent with benign palmar nevi.
It is not uncommon to have nevi on the palms or soles of the feet, so it is important to distinguish between acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) and benign nevi. ALM is the least common form of melanoma. In contrast to other types of melanoma, it is not considered secondary to excessive sun exposure. Clinically, ALM presents with irregular, enlarging pigmentation that follows, or crosses, the raised ridges of the palms or soles.1 The pigmented areas can progress to ulcerated or bleeding lesions. As with other melanomas, early diagnosis and removal is important to optimize prognosis.
Removal of lesions suspicious for ALM can be achieved in several ways: deep shave biopsy, punch excision if the lesion is small, excision with narrow margins, or, if the lesion is large, by a selective punch biopsy of the most suspicious portion of the lesion (typically the thickest and most irregular area). Larger diameter lesions that are raised and irregular are more worrisome than this patient’s 2-mm macular lesions.
In this case, the patient was reassured that the lesions did not require excision. She was advised to continue to monitor her lesions for growth or changes over time and to return for evaluation, as needed. She was also counseled regarding the American Cancer Society’s ABCDE rules (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color, Diameter, Elevation or Evolving) regarding melanomas.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque
1. Hall KH, Rapini RP. Acral lentiginous melanoma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Accessed April 5, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559113/

Fortunately, the dermoscopy images of these 2 small palmar lesions showed a pattern of pigmentation that aligned in the furrows and was consistent with benign palmar nevi.
It is not uncommon to have nevi on the palms or soles of the feet, so it is important to distinguish between acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) and benign nevi. ALM is the least common form of melanoma. In contrast to other types of melanoma, it is not considered secondary to excessive sun exposure. Clinically, ALM presents with irregular, enlarging pigmentation that follows, or crosses, the raised ridges of the palms or soles.1 The pigmented areas can progress to ulcerated or bleeding lesions. As with other melanomas, early diagnosis and removal is important to optimize prognosis.
Removal of lesions suspicious for ALM can be achieved in several ways: deep shave biopsy, punch excision if the lesion is small, excision with narrow margins, or, if the lesion is large, by a selective punch biopsy of the most suspicious portion of the lesion (typically the thickest and most irregular area). Larger diameter lesions that are raised and irregular are more worrisome than this patient’s 2-mm macular lesions.
In this case, the patient was reassured that the lesions did not require excision. She was advised to continue to monitor her lesions for growth or changes over time and to return for evaluation, as needed. She was also counseled regarding the American Cancer Society’s ABCDE rules (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color, Diameter, Elevation or Evolving) regarding melanomas.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque

Fortunately, the dermoscopy images of these 2 small palmar lesions showed a pattern of pigmentation that aligned in the furrows and was consistent with benign palmar nevi.
It is not uncommon to have nevi on the palms or soles of the feet, so it is important to distinguish between acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) and benign nevi. ALM is the least common form of melanoma. In contrast to other types of melanoma, it is not considered secondary to excessive sun exposure. Clinically, ALM presents with irregular, enlarging pigmentation that follows, or crosses, the raised ridges of the palms or soles.1 The pigmented areas can progress to ulcerated or bleeding lesions. As with other melanomas, early diagnosis and removal is important to optimize prognosis.
Removal of lesions suspicious for ALM can be achieved in several ways: deep shave biopsy, punch excision if the lesion is small, excision with narrow margins, or, if the lesion is large, by a selective punch biopsy of the most suspicious portion of the lesion (typically the thickest and most irregular area). Larger diameter lesions that are raised and irregular are more worrisome than this patient’s 2-mm macular lesions.
In this case, the patient was reassured that the lesions did not require excision. She was advised to continue to monitor her lesions for growth or changes over time and to return for evaluation, as needed. She was also counseled regarding the American Cancer Society’s ABCDE rules (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color, Diameter, Elevation or Evolving) regarding melanomas.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque
1. Hall KH, Rapini RP. Acral lentiginous melanoma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Accessed April 5, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559113/
1. Hall KH, Rapini RP. Acral lentiginous melanoma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Accessed April 5, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559113/
Boosting the presence of darker skin in rheumatology education
Studies are flagging racial and ethnic disparities in rheumatology training materials, pointing to a need to boost representation of darker skin tones and better educate physicians in evaluating this cohort.
Not enough is known about these disparities in rheumatology education, despite the fact that minorities make up 40% of the population in the United States.
The problem starts with books and references used in medical schools, Lynn McKinley-Grant, MD, immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and associate professor of dermatology at Howard University, Washington, said in an interview. “In the medical literature there has been a dearth of images in skin of color in all specialties,” she said. With an increased diversity in the U.S. population, there is a need for health care providers to be able to recognize disease patterns in all skin types.” If a physician is training at an institution where there are not many patients of color in the community, the rheumatologists are even more limited in terms of their clinical experience.
This lack of training in diagnosis of disease has serious clinical repercussions, as seen in COVID cases, Dr. McKinley-Grant noted. “You end up not being able to recognize early erythema, jaundice, anemia, or hypoxemia because those conditions are a different color or pattern in the darker skin types. This can lead to errors in treatment, diagnosis, and medical care, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality.”
Studies point to education gaps
A team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis called attention to this issue at the American College of Rhematology’s Convergence 2020 conference.
“Patients of color with lupus are especially vulnerable as they often carry a greater disease burden, yet studies show that individuals with darker skin tones are underrepresented in medical educational materials,” Vijay Kannuthurai, MD, and colleagues wrote in their study abstract. The team surveyed 132 providers in St. Louis, Mo., on their confidence in evaluating any rash, and rashes in patients with lupus and varied skin tones.
Participating clinicians, mostly rheumatologists, dermatologists, or internists, had a higher confidence level in diagnosing any rash versus lupus rashes, but were considerably less confident in diagnosing lupus rash on darker skin, compared with those on fair skin. This represents “a disparity between provider confidence and the patient population lupus traditionally affects,” the investigators concluded.
Another recent study found evidence of disparities in clinical education resources. “The lack of dark skin representation among rheumatology educational materials contributes to the implicit bias and structural racism present in medical education by promoting White-only models of disease,” lead author Adrienne Strait, a medical student at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “Given that rheumatic diseases disproportionately impact racial and ethnic minorities, we felt it was important to examine the representation of these groups within rheumatology training resources.”
She and her colleagues gathered images of rheumatic diseases from four major databases: the American College of Rheumatology’s Image Library, UpToDate, the New England Journal of Medicine Images in Clinical Medicine and Clinical Cases filtered by “Rheumatology,” and the 9th edition of Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. They used Fitzpatrick’s skin phototypes to independently code images depicting skin as “light” (skin types I-IV), “dark” (skin types V-VI), or “indeterminate,” focusing on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, two conditions with a known connection to racial and ethnic health disparities.
Taking into account the high incidence of sarcoidosis and SLE in Black patients when compared with White patients, the investigators did a secondary analysis that excluded these cases.
Among 1,043 patient images studied, just 13.4% represented dark skin, compared with 84% that represented light skin. More than 2% represented an indeterminate skin color. Comparing dark-skin representation in the clinical images and SLE images with the representation of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals in the United States and within lupus cases nationally, the investigators found significant underrepresentation of dark skin.
Only 4.2% of RA images had dark-skin representation, making RA one of the diseases with the lowest representation in the study, along with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the spondyloarthropathies, and Kawasaki disease. “Representation of dark skin in SLE was also lower than the proportion of Black individuals in SLE studies,” the investigators noted. Overall, representation of dark skin in SLE images was just 22.6%. Sarcoidosis comparatively had the largest representation of dark-skin images (69.6%, n = 32).
“Excluding sarcoidosis and SLE images, the overall representation of dark skin was 9.4% (n = 84), which was significantly lower than the proportion of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals within the U.S. Census population,” according to Ms. Strait and her associates. UpToDate contained the largest proportion of images of dark skin respective to other databases, whereas Kelley’s Textbook had the smallest.
Actionable steps
Many physicians are willing to improve upon their skills in identifying conditions on darker skin, as the study by Dr. Kannuthurai and associates suggests. Overall, 93% of the survey’s participants wanted to learn more about rashes in patients of color. “Future educational interventions may help practitioners improve their confidence when diagnosing rashes in lupus patients” with darker skin, they suggested.
Ms. Strait and her colleagues recommended a series of actionable steps to improve diversity and equity of dark skin tone representation in rheumatology curricula.
Editors of educational resources, for example, should make image diversity a priority for those diseases that are most commonly associated with cutaneous manifestations, such as SLE, vasculitis, inflammatory myopathies, systemic sclerosis, sarcoidosis, and psoriasis. They also called for educators in academic rheumatology programs to collaborate to improve diversity in resources used at the undergraduate and graduate medical education level.
Efforts should take place at the local, regional, and national level to publicly discuss and educate clinicians about rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. Speakers at rheumatology conferences should strive to educate learners about presentations of rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. The ACR in the meantime could establish a task force to enhance racial and ethnic diversity in their image library and other published resources.
“These steps may improve provider recognition and diagnosis of rheumatic disease manifestations in skin of color, which may in turn reduce health disparities among racial and ethnic minority groups,” Ms. Strait said.
Beth L. Jonas, MD, chair of the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues, called the findings of this study “timely and important.” The researchers highlighted a deficiency in rheumatology training materials that needs addressing, she said in an interview. “I definitely agree that ACR needs to be mindful of this. There’s no doubt that we need to take these recommendations and move along these lines.”
The ACR took a first step in 2020 with the creation of a diversity, equity, and inclusion committee. “We are undergoing a college-wide look at what we do, with an eye toward inclusion. There is a strong interest in addressing health disparities and being an equitable and inclusive community of rheumatology health care professionals,” said Dr. Jonas, chief of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology.
The American Academy of Dermatology is also working to improve the image library with images of disease in skin of color. “Everyone’s jumping on this now,” Dr. McKinley-Grant observed. The medical profession can’t afford not to. It’s a life-threatening issue when rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases in people of color aren’t diagnosed early and correctly, she added.
Technologies seek to reduce bias
While many organizations are taking steps to improve representation of darker skin images, VisualDx has taken the lead on this, she said. “They’ve been doing this for years now. There are over 14,000 images of disease in skin of color, including all the rheumatologic diseases. There’s a mobile app and desktop decision support system, and it is very popular. A majority of medical schools have this as a library resource, and hospital systems license it for EHR integration.” Doctors can also get it individually. This enables them to share images and handouts of a diagnosis and select images of patients of color, said Dr. McKinley-Grant, who uses the VisualDx smartphone app DermExpert, which is an app for nondermatologists that features an image library of skin lesions, including darker-skin images.
ProjectIMPACT, powered by VisualDx, is another effort to support reducing health care bias in darker skin. The project is a collaboration between the New England Journal of Medicine Group and the Skin Of Color Society. According to Dr. McKinley-Grant, the organizers are building awareness of the importance of reducing the educational and clinical gaps in diagnosing patients of color and trying to get students and educators to pledge to take meaningful steps and to have real-world impact.
This isn’t just exclusive to dermatology and rheumatology – it involves all medical specialties, she stressed.
ProjectIMPACT isn’t just a resource for physicians, she continued. Librarians can also use it to develop more resources on skin of color.
The Skin Of Color Society and VisualDx have also partnered with the NEJM Group to develop a comprehensive virtual series on the impact of skin color and ethnicity on clinical research. The four-part series addresses structural racism and racial bias in medicine, hair disorders in people of color, pigmentary disorders, keloids, COVID-19 comorbidities, and cutaneous manifestations of systemic diseases in children and adults.
Nuances of recognizing disease
As a medical student, Dr. McKinley-Grant said she was fortunate to attend the Albert Schweitzer Hospital in Lambarene, Gabon, on a fellowship. For 3 months, she gained a wealth of experience examining only African patients with brown skin.
In her other training in medicine, “I’ve been at institutions with diverse populations, in Boston, New York, and Washington,” learning more about all different skin pigments.
This type of training should be more widely available, especially now, with COVID-19 producing new manifestations of skin lesions, she emphasized. Such efforts involve a diversification of images physicians are being trained on so that they can recognize the same disease in a person of color.
“Doctors have to be able to recognize different colors, different shades of brown and shades of white. Not all white skin is the same color,” she noted. In looking at a rash or lesion, “you have to learn how to discern differences in the background color of the skin, which is determined by melanin in the skin (Fitzpatrick skin types I-VI) and by what’s going on in the blood, such as how much oxygen and hemoglobin the patient has in their blood.” Inflammation and infection (erythema) will appear more violaceous in IV-VI skin types, for example.
At the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, a group of students and faculty have created a dermatology image library to address the deficiency in the availability of images for teaching purposes. “Our medical students recognized the gap and started this,” Dr. Jonas said. Julie Mervak, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, is spearheading this effort, with students Linnea Westerkam and Anuj Pranav Sanghvi.
“I understand that others around the country are working on similar initiatives,” Dr. Jonas said.
None of the sources for this story had any relevant disclosures.
Studies are flagging racial and ethnic disparities in rheumatology training materials, pointing to a need to boost representation of darker skin tones and better educate physicians in evaluating this cohort.
Not enough is known about these disparities in rheumatology education, despite the fact that minorities make up 40% of the population in the United States.
The problem starts with books and references used in medical schools, Lynn McKinley-Grant, MD, immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and associate professor of dermatology at Howard University, Washington, said in an interview. “In the medical literature there has been a dearth of images in skin of color in all specialties,” she said. With an increased diversity in the U.S. population, there is a need for health care providers to be able to recognize disease patterns in all skin types.” If a physician is training at an institution where there are not many patients of color in the community, the rheumatologists are even more limited in terms of their clinical experience.
This lack of training in diagnosis of disease has serious clinical repercussions, as seen in COVID cases, Dr. McKinley-Grant noted. “You end up not being able to recognize early erythema, jaundice, anemia, or hypoxemia because those conditions are a different color or pattern in the darker skin types. This can lead to errors in treatment, diagnosis, and medical care, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality.”
Studies point to education gaps
A team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis called attention to this issue at the American College of Rhematology’s Convergence 2020 conference.
“Patients of color with lupus are especially vulnerable as they often carry a greater disease burden, yet studies show that individuals with darker skin tones are underrepresented in medical educational materials,” Vijay Kannuthurai, MD, and colleagues wrote in their study abstract. The team surveyed 132 providers in St. Louis, Mo., on their confidence in evaluating any rash, and rashes in patients with lupus and varied skin tones.
Participating clinicians, mostly rheumatologists, dermatologists, or internists, had a higher confidence level in diagnosing any rash versus lupus rashes, but were considerably less confident in diagnosing lupus rash on darker skin, compared with those on fair skin. This represents “a disparity between provider confidence and the patient population lupus traditionally affects,” the investigators concluded.
Another recent study found evidence of disparities in clinical education resources. “The lack of dark skin representation among rheumatology educational materials contributes to the implicit bias and structural racism present in medical education by promoting White-only models of disease,” lead author Adrienne Strait, a medical student at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “Given that rheumatic diseases disproportionately impact racial and ethnic minorities, we felt it was important to examine the representation of these groups within rheumatology training resources.”
She and her colleagues gathered images of rheumatic diseases from four major databases: the American College of Rheumatology’s Image Library, UpToDate, the New England Journal of Medicine Images in Clinical Medicine and Clinical Cases filtered by “Rheumatology,” and the 9th edition of Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. They used Fitzpatrick’s skin phototypes to independently code images depicting skin as “light” (skin types I-IV), “dark” (skin types V-VI), or “indeterminate,” focusing on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, two conditions with a known connection to racial and ethnic health disparities.
Taking into account the high incidence of sarcoidosis and SLE in Black patients when compared with White patients, the investigators did a secondary analysis that excluded these cases.
Among 1,043 patient images studied, just 13.4% represented dark skin, compared with 84% that represented light skin. More than 2% represented an indeterminate skin color. Comparing dark-skin representation in the clinical images and SLE images with the representation of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals in the United States and within lupus cases nationally, the investigators found significant underrepresentation of dark skin.
Only 4.2% of RA images had dark-skin representation, making RA one of the diseases with the lowest representation in the study, along with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the spondyloarthropathies, and Kawasaki disease. “Representation of dark skin in SLE was also lower than the proportion of Black individuals in SLE studies,” the investigators noted. Overall, representation of dark skin in SLE images was just 22.6%. Sarcoidosis comparatively had the largest representation of dark-skin images (69.6%, n = 32).
“Excluding sarcoidosis and SLE images, the overall representation of dark skin was 9.4% (n = 84), which was significantly lower than the proportion of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals within the U.S. Census population,” according to Ms. Strait and her associates. UpToDate contained the largest proportion of images of dark skin respective to other databases, whereas Kelley’s Textbook had the smallest.
Actionable steps
Many physicians are willing to improve upon their skills in identifying conditions on darker skin, as the study by Dr. Kannuthurai and associates suggests. Overall, 93% of the survey’s participants wanted to learn more about rashes in patients of color. “Future educational interventions may help practitioners improve their confidence when diagnosing rashes in lupus patients” with darker skin, they suggested.
Ms. Strait and her colleagues recommended a series of actionable steps to improve diversity and equity of dark skin tone representation in rheumatology curricula.
Editors of educational resources, for example, should make image diversity a priority for those diseases that are most commonly associated with cutaneous manifestations, such as SLE, vasculitis, inflammatory myopathies, systemic sclerosis, sarcoidosis, and psoriasis. They also called for educators in academic rheumatology programs to collaborate to improve diversity in resources used at the undergraduate and graduate medical education level.
Efforts should take place at the local, regional, and national level to publicly discuss and educate clinicians about rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. Speakers at rheumatology conferences should strive to educate learners about presentations of rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. The ACR in the meantime could establish a task force to enhance racial and ethnic diversity in their image library and other published resources.
“These steps may improve provider recognition and diagnosis of rheumatic disease manifestations in skin of color, which may in turn reduce health disparities among racial and ethnic minority groups,” Ms. Strait said.
Beth L. Jonas, MD, chair of the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues, called the findings of this study “timely and important.” The researchers highlighted a deficiency in rheumatology training materials that needs addressing, she said in an interview. “I definitely agree that ACR needs to be mindful of this. There’s no doubt that we need to take these recommendations and move along these lines.”
The ACR took a first step in 2020 with the creation of a diversity, equity, and inclusion committee. “We are undergoing a college-wide look at what we do, with an eye toward inclusion. There is a strong interest in addressing health disparities and being an equitable and inclusive community of rheumatology health care professionals,” said Dr. Jonas, chief of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology.
The American Academy of Dermatology is also working to improve the image library with images of disease in skin of color. “Everyone’s jumping on this now,” Dr. McKinley-Grant observed. The medical profession can’t afford not to. It’s a life-threatening issue when rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases in people of color aren’t diagnosed early and correctly, she added.
Technologies seek to reduce bias
While many organizations are taking steps to improve representation of darker skin images, VisualDx has taken the lead on this, she said. “They’ve been doing this for years now. There are over 14,000 images of disease in skin of color, including all the rheumatologic diseases. There’s a mobile app and desktop decision support system, and it is very popular. A majority of medical schools have this as a library resource, and hospital systems license it for EHR integration.” Doctors can also get it individually. This enables them to share images and handouts of a diagnosis and select images of patients of color, said Dr. McKinley-Grant, who uses the VisualDx smartphone app DermExpert, which is an app for nondermatologists that features an image library of skin lesions, including darker-skin images.
ProjectIMPACT, powered by VisualDx, is another effort to support reducing health care bias in darker skin. The project is a collaboration between the New England Journal of Medicine Group and the Skin Of Color Society. According to Dr. McKinley-Grant, the organizers are building awareness of the importance of reducing the educational and clinical gaps in diagnosing patients of color and trying to get students and educators to pledge to take meaningful steps and to have real-world impact.
This isn’t just exclusive to dermatology and rheumatology – it involves all medical specialties, she stressed.
ProjectIMPACT isn’t just a resource for physicians, she continued. Librarians can also use it to develop more resources on skin of color.
The Skin Of Color Society and VisualDx have also partnered with the NEJM Group to develop a comprehensive virtual series on the impact of skin color and ethnicity on clinical research. The four-part series addresses structural racism and racial bias in medicine, hair disorders in people of color, pigmentary disorders, keloids, COVID-19 comorbidities, and cutaneous manifestations of systemic diseases in children and adults.
Nuances of recognizing disease
As a medical student, Dr. McKinley-Grant said she was fortunate to attend the Albert Schweitzer Hospital in Lambarene, Gabon, on a fellowship. For 3 months, she gained a wealth of experience examining only African patients with brown skin.
In her other training in medicine, “I’ve been at institutions with diverse populations, in Boston, New York, and Washington,” learning more about all different skin pigments.
This type of training should be more widely available, especially now, with COVID-19 producing new manifestations of skin lesions, she emphasized. Such efforts involve a diversification of images physicians are being trained on so that they can recognize the same disease in a person of color.
“Doctors have to be able to recognize different colors, different shades of brown and shades of white. Not all white skin is the same color,” she noted. In looking at a rash or lesion, “you have to learn how to discern differences in the background color of the skin, which is determined by melanin in the skin (Fitzpatrick skin types I-VI) and by what’s going on in the blood, such as how much oxygen and hemoglobin the patient has in their blood.” Inflammation and infection (erythema) will appear more violaceous in IV-VI skin types, for example.
At the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, a group of students and faculty have created a dermatology image library to address the deficiency in the availability of images for teaching purposes. “Our medical students recognized the gap and started this,” Dr. Jonas said. Julie Mervak, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, is spearheading this effort, with students Linnea Westerkam and Anuj Pranav Sanghvi.
“I understand that others around the country are working on similar initiatives,” Dr. Jonas said.
None of the sources for this story had any relevant disclosures.
Studies are flagging racial and ethnic disparities in rheumatology training materials, pointing to a need to boost representation of darker skin tones and better educate physicians in evaluating this cohort.
Not enough is known about these disparities in rheumatology education, despite the fact that minorities make up 40% of the population in the United States.
The problem starts with books and references used in medical schools, Lynn McKinley-Grant, MD, immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and associate professor of dermatology at Howard University, Washington, said in an interview. “In the medical literature there has been a dearth of images in skin of color in all specialties,” she said. With an increased diversity in the U.S. population, there is a need for health care providers to be able to recognize disease patterns in all skin types.” If a physician is training at an institution where there are not many patients of color in the community, the rheumatologists are even more limited in terms of their clinical experience.
This lack of training in diagnosis of disease has serious clinical repercussions, as seen in COVID cases, Dr. McKinley-Grant noted. “You end up not being able to recognize early erythema, jaundice, anemia, or hypoxemia because those conditions are a different color or pattern in the darker skin types. This can lead to errors in treatment, diagnosis, and medical care, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality.”
Studies point to education gaps
A team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis called attention to this issue at the American College of Rhematology’s Convergence 2020 conference.
“Patients of color with lupus are especially vulnerable as they often carry a greater disease burden, yet studies show that individuals with darker skin tones are underrepresented in medical educational materials,” Vijay Kannuthurai, MD, and colleagues wrote in their study abstract. The team surveyed 132 providers in St. Louis, Mo., on their confidence in evaluating any rash, and rashes in patients with lupus and varied skin tones.
Participating clinicians, mostly rheumatologists, dermatologists, or internists, had a higher confidence level in diagnosing any rash versus lupus rashes, but were considerably less confident in diagnosing lupus rash on darker skin, compared with those on fair skin. This represents “a disparity between provider confidence and the patient population lupus traditionally affects,” the investigators concluded.
Another recent study found evidence of disparities in clinical education resources. “The lack of dark skin representation among rheumatology educational materials contributes to the implicit bias and structural racism present in medical education by promoting White-only models of disease,” lead author Adrienne Strait, a medical student at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “Given that rheumatic diseases disproportionately impact racial and ethnic minorities, we felt it was important to examine the representation of these groups within rheumatology training resources.”
She and her colleagues gathered images of rheumatic diseases from four major databases: the American College of Rheumatology’s Image Library, UpToDate, the New England Journal of Medicine Images in Clinical Medicine and Clinical Cases filtered by “Rheumatology,” and the 9th edition of Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. They used Fitzpatrick’s skin phototypes to independently code images depicting skin as “light” (skin types I-IV), “dark” (skin types V-VI), or “indeterminate,” focusing on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, two conditions with a known connection to racial and ethnic health disparities.
Taking into account the high incidence of sarcoidosis and SLE in Black patients when compared with White patients, the investigators did a secondary analysis that excluded these cases.
Among 1,043 patient images studied, just 13.4% represented dark skin, compared with 84% that represented light skin. More than 2% represented an indeterminate skin color. Comparing dark-skin representation in the clinical images and SLE images with the representation of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals in the United States and within lupus cases nationally, the investigators found significant underrepresentation of dark skin.
Only 4.2% of RA images had dark-skin representation, making RA one of the diseases with the lowest representation in the study, along with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the spondyloarthropathies, and Kawasaki disease. “Representation of dark skin in SLE was also lower than the proportion of Black individuals in SLE studies,” the investigators noted. Overall, representation of dark skin in SLE images was just 22.6%. Sarcoidosis comparatively had the largest representation of dark-skin images (69.6%, n = 32).
“Excluding sarcoidosis and SLE images, the overall representation of dark skin was 9.4% (n = 84), which was significantly lower than the proportion of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals within the U.S. Census population,” according to Ms. Strait and her associates. UpToDate contained the largest proportion of images of dark skin respective to other databases, whereas Kelley’s Textbook had the smallest.
Actionable steps
Many physicians are willing to improve upon their skills in identifying conditions on darker skin, as the study by Dr. Kannuthurai and associates suggests. Overall, 93% of the survey’s participants wanted to learn more about rashes in patients of color. “Future educational interventions may help practitioners improve their confidence when diagnosing rashes in lupus patients” with darker skin, they suggested.
Ms. Strait and her colleagues recommended a series of actionable steps to improve diversity and equity of dark skin tone representation in rheumatology curricula.
Editors of educational resources, for example, should make image diversity a priority for those diseases that are most commonly associated with cutaneous manifestations, such as SLE, vasculitis, inflammatory myopathies, systemic sclerosis, sarcoidosis, and psoriasis. They also called for educators in academic rheumatology programs to collaborate to improve diversity in resources used at the undergraduate and graduate medical education level.
Efforts should take place at the local, regional, and national level to publicly discuss and educate clinicians about rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. Speakers at rheumatology conferences should strive to educate learners about presentations of rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. The ACR in the meantime could establish a task force to enhance racial and ethnic diversity in their image library and other published resources.
“These steps may improve provider recognition and diagnosis of rheumatic disease manifestations in skin of color, which may in turn reduce health disparities among racial and ethnic minority groups,” Ms. Strait said.
Beth L. Jonas, MD, chair of the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues, called the findings of this study “timely and important.” The researchers highlighted a deficiency in rheumatology training materials that needs addressing, she said in an interview. “I definitely agree that ACR needs to be mindful of this. There’s no doubt that we need to take these recommendations and move along these lines.”
The ACR took a first step in 2020 with the creation of a diversity, equity, and inclusion committee. “We are undergoing a college-wide look at what we do, with an eye toward inclusion. There is a strong interest in addressing health disparities and being an equitable and inclusive community of rheumatology health care professionals,” said Dr. Jonas, chief of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology.
The American Academy of Dermatology is also working to improve the image library with images of disease in skin of color. “Everyone’s jumping on this now,” Dr. McKinley-Grant observed. The medical profession can’t afford not to. It’s a life-threatening issue when rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases in people of color aren’t diagnosed early and correctly, she added.
Technologies seek to reduce bias
While many organizations are taking steps to improve representation of darker skin images, VisualDx has taken the lead on this, she said. “They’ve been doing this for years now. There are over 14,000 images of disease in skin of color, including all the rheumatologic diseases. There’s a mobile app and desktop decision support system, and it is very popular. A majority of medical schools have this as a library resource, and hospital systems license it for EHR integration.” Doctors can also get it individually. This enables them to share images and handouts of a diagnosis and select images of patients of color, said Dr. McKinley-Grant, who uses the VisualDx smartphone app DermExpert, which is an app for nondermatologists that features an image library of skin lesions, including darker-skin images.
ProjectIMPACT, powered by VisualDx, is another effort to support reducing health care bias in darker skin. The project is a collaboration between the New England Journal of Medicine Group and the Skin Of Color Society. According to Dr. McKinley-Grant, the organizers are building awareness of the importance of reducing the educational and clinical gaps in diagnosing patients of color and trying to get students and educators to pledge to take meaningful steps and to have real-world impact.
This isn’t just exclusive to dermatology and rheumatology – it involves all medical specialties, she stressed.
ProjectIMPACT isn’t just a resource for physicians, she continued. Librarians can also use it to develop more resources on skin of color.
The Skin Of Color Society and VisualDx have also partnered with the NEJM Group to develop a comprehensive virtual series on the impact of skin color and ethnicity on clinical research. The four-part series addresses structural racism and racial bias in medicine, hair disorders in people of color, pigmentary disorders, keloids, COVID-19 comorbidities, and cutaneous manifestations of systemic diseases in children and adults.
Nuances of recognizing disease
As a medical student, Dr. McKinley-Grant said she was fortunate to attend the Albert Schweitzer Hospital in Lambarene, Gabon, on a fellowship. For 3 months, she gained a wealth of experience examining only African patients with brown skin.
In her other training in medicine, “I’ve been at institutions with diverse populations, in Boston, New York, and Washington,” learning more about all different skin pigments.
This type of training should be more widely available, especially now, with COVID-19 producing new manifestations of skin lesions, she emphasized. Such efforts involve a diversification of images physicians are being trained on so that they can recognize the same disease in a person of color.
“Doctors have to be able to recognize different colors, different shades of brown and shades of white. Not all white skin is the same color,” she noted. In looking at a rash or lesion, “you have to learn how to discern differences in the background color of the skin, which is determined by melanin in the skin (Fitzpatrick skin types I-VI) and by what’s going on in the blood, such as how much oxygen and hemoglobin the patient has in their blood.” Inflammation and infection (erythema) will appear more violaceous in IV-VI skin types, for example.
At the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, a group of students and faculty have created a dermatology image library to address the deficiency in the availability of images for teaching purposes. “Our medical students recognized the gap and started this,” Dr. Jonas said. Julie Mervak, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, is spearheading this effort, with students Linnea Westerkam and Anuj Pranav Sanghvi.
“I understand that others around the country are working on similar initiatives,” Dr. Jonas said.
None of the sources for this story had any relevant disclosures.
Most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases have sufficient response to COVID-19 vaccination
Glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies are trouble spots
Although most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases mounted immune responses after two doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies markedly reduced the response, according to a recently published preprint of a new study.
The study, published on MedRxiv and not yet peer reviewed, involved a prospective look at 133 patients with chronic inflammatory disease (CID) and 53 patients with healthy immune systems at Washington University, St. Louis, and the University of California, San Francisco. It is regarded as the largest and most detailed study yet in how vaccines perform in people with immune-mediated inflammatory disease. The patients were enrolled between December 2020 and March 2021, and the most common diseases were inflammatory bowel disease (32%), rheumatoid arthritis (29%), spondyloarthritis (15%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (11%).
A ‘modest’ reduction in antibody response
Senior author Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of medicine at Washington University, said the overall results so far are encouraging.
“Most patients with an autoimmune disease that are on immunosuppression can mount antibody responses,” he said. “We’re seeing the majority of our subjects respond.”
The immune-healthy controls and most of the patients with CID had a robust immune response against the spike protein, although the CID group had a mean reduction in antibody titers that was three times lower than the controls (P = .0092). The CID group similarly had a 2.7-fold reduction in preventing neutralization, or halting the virus’ ability to infect (P < .0001), researchers reported.
This reduction in response is “modest,” he said.
“Is the level of reduction going to be detrimental for protection? Time will tell,” he said, adding that researchers anticipate that it won’t have a critical effect on protection because responses tended to be within the range of the immunocompetent controls, who themselves had wildly varied antibody titers across a 20-fold range. “ ‘Optimal’ isn’t necessarily the same as ‘sufficient.’ ”
Type of medication has big impact on antibody titers
But there was a wide variety of effects on the immune response depending on the medication. Glucorticoids resulted in a response that was 10 times lower than the immune-healthy controls, as well as fewer circulating plasmablasts after vaccination. Researchers found that 98% of controls were seropositive for antibody, compared with 92% of those with CID who were not taking prednisone, and 65% of CID patients on prednisone (P = .0006 and .0115, respectively). Prevention of neutralization of the virus was similarly reduced in those groups, compared with the controls. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 15 patients. These effects were seen regardless of the dose.
“We would’ve anticipated this would have been dose dependent, so this was a little bit surprising,” Dr. Kim said.
B-cell–depleting therapies, such as rituximab (Rituxan) and ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), reduced antibody titers by 36 times, compared with controls (P < .0001), with a similar reduction in preventing infection (P = .0066), the researchers found. The reduction in antibody titers was the most pronounced among those who had received B-cell–depleting therapies within the previous 6 months. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 10 patients.
CID study subjects taking an antimetabolite, including methotrexate, had an average of a two- to threefold reduction in antibody titers and in neutralization (P = .0006). This reduction was greatest with methotrexate, researchers found (P = .0027).
JAK inhibitors also significantly reduced antibody titers (P = .0066), but the reduction in neutralization of the virus was not significant. In addition, researchers found a reduction in antibody titers, the prevention of viral infection, and circulating plasmablasts among those on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, compared with controls, but these were insignificant statistically except for virus neutralization.
Dr. Kim said he hopes the glucocorticoid data spur physicians to try harder to wean patients off the drugs, when possible, in keeping with recommendations already in place.
“The general culture in rheumatology has been very lax about the need to reduce glucocorticoids,” he said. “This reinvigorates that call.” Questions about possible drug holidays from glucocorticoids remain, regarding how long a holiday would be needed, he said. He noted that many patients on glucocorticoids nonetheless mounted responses.
Those on B-cell–depleting therapies present a “much more difficult” question, he said. Some patients possibly could wait a bit longer than their normal, every-6-month schedule, but it’s an individual decision, he said. Since a booster of influenza vaccine has been found to enhance the response even within the 6-month window among ocrelizumab patients, a booster of COVID-19 vaccine might also help, although this remains to be studied.
The study group has already increased its sample size and is looking at adverse reactions and long-term immune responses, Dr. Kim said.
Encouraging, rather than discouraging, results
Leonard Calabrese, DO, professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said the findings shouldn’t discourage clinicians from encouraging vaccination.
“There’s still a preponderance of people who will develop a robust antibody vaccine response,” he said.
He cautioned that the findings look only at antibodies to the spike protein and at plasmablasts. The reduction in these titers is “of concern,” he said, but “we don’t really know with certainty what are the effects of these drugs, and these data are on the overall biologic protective effect of the vaccine. There’s much more to a vaccine response than anti–spike protein and plasmablasts,” including cell-mediated immune response.
For an individual patient, the findings “mean a lot,” he said.
“I think that people who are on significant prednisone and B-cell–depleting agents, I think you have to share with them that there’s a reasonable chance that you’re not going to be making a response similar to healthy people,” he said. “Thus, even with your vaccine, we’re not going to cut you loose to do things that are violating social distancing and group settings. … Should you be hugging your grandchildren if you’re a rituximab vaccine recipient? I think I would wait until we have a little bit more data.”
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of ophthalmology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, where he studies vaccinations in the immunocompromised, said that glucocorticoids tend to have little effect on vaccinations generally at low doses.
When effects are seen they can be difficult to interpret, he said.
“It’s hard to extricate that from the effect of the underlying disease,” he said. The drug can be a proxy for worse disease control.
Although it’s a small study, it’s reassuring that overall the responses were similar to healthy controls.
For B-cell–depleting therapies, his usual guidance is to not give vaccine until a patient is at least 3 months out from their last dose, and not to restart until at least 2 weeks after vaccination.
“It’s not surprising that some of these DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] do negatively affect vaccine response, particularly B-cell–depletion therapy. We need to do some studies to find a way to overcome that, or optimize delivery of the vaccine.”
Dr. Kim reported participating in consulting, advisory board, or speaker’s bureau for Alexion, Aurinia, Annexon Biosciences, Exagen Diagnostics, and GlaxoSmithKline, and receiving funding under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Winthrop reported receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. Dr. Calabrese reported no relevant disclosures.
Glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies are trouble spots
Glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies are trouble spots
Although most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases mounted immune responses after two doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies markedly reduced the response, according to a recently published preprint of a new study.
The study, published on MedRxiv and not yet peer reviewed, involved a prospective look at 133 patients with chronic inflammatory disease (CID) and 53 patients with healthy immune systems at Washington University, St. Louis, and the University of California, San Francisco. It is regarded as the largest and most detailed study yet in how vaccines perform in people with immune-mediated inflammatory disease. The patients were enrolled between December 2020 and March 2021, and the most common diseases were inflammatory bowel disease (32%), rheumatoid arthritis (29%), spondyloarthritis (15%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (11%).
A ‘modest’ reduction in antibody response
Senior author Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of medicine at Washington University, said the overall results so far are encouraging.
“Most patients with an autoimmune disease that are on immunosuppression can mount antibody responses,” he said. “We’re seeing the majority of our subjects respond.”
The immune-healthy controls and most of the patients with CID had a robust immune response against the spike protein, although the CID group had a mean reduction in antibody titers that was three times lower than the controls (P = .0092). The CID group similarly had a 2.7-fold reduction in preventing neutralization, or halting the virus’ ability to infect (P < .0001), researchers reported.
This reduction in response is “modest,” he said.
“Is the level of reduction going to be detrimental for protection? Time will tell,” he said, adding that researchers anticipate that it won’t have a critical effect on protection because responses tended to be within the range of the immunocompetent controls, who themselves had wildly varied antibody titers across a 20-fold range. “ ‘Optimal’ isn’t necessarily the same as ‘sufficient.’ ”
Type of medication has big impact on antibody titers
But there was a wide variety of effects on the immune response depending on the medication. Glucorticoids resulted in a response that was 10 times lower than the immune-healthy controls, as well as fewer circulating plasmablasts after vaccination. Researchers found that 98% of controls were seropositive for antibody, compared with 92% of those with CID who were not taking prednisone, and 65% of CID patients on prednisone (P = .0006 and .0115, respectively). Prevention of neutralization of the virus was similarly reduced in those groups, compared with the controls. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 15 patients. These effects were seen regardless of the dose.
“We would’ve anticipated this would have been dose dependent, so this was a little bit surprising,” Dr. Kim said.
B-cell–depleting therapies, such as rituximab (Rituxan) and ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), reduced antibody titers by 36 times, compared with controls (P < .0001), with a similar reduction in preventing infection (P = .0066), the researchers found. The reduction in antibody titers was the most pronounced among those who had received B-cell–depleting therapies within the previous 6 months. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 10 patients.
CID study subjects taking an antimetabolite, including methotrexate, had an average of a two- to threefold reduction in antibody titers and in neutralization (P = .0006). This reduction was greatest with methotrexate, researchers found (P = .0027).
JAK inhibitors also significantly reduced antibody titers (P = .0066), but the reduction in neutralization of the virus was not significant. In addition, researchers found a reduction in antibody titers, the prevention of viral infection, and circulating plasmablasts among those on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, compared with controls, but these were insignificant statistically except for virus neutralization.
Dr. Kim said he hopes the glucocorticoid data spur physicians to try harder to wean patients off the drugs, when possible, in keeping with recommendations already in place.
“The general culture in rheumatology has been very lax about the need to reduce glucocorticoids,” he said. “This reinvigorates that call.” Questions about possible drug holidays from glucocorticoids remain, regarding how long a holiday would be needed, he said. He noted that many patients on glucocorticoids nonetheless mounted responses.
Those on B-cell–depleting therapies present a “much more difficult” question, he said. Some patients possibly could wait a bit longer than their normal, every-6-month schedule, but it’s an individual decision, he said. Since a booster of influenza vaccine has been found to enhance the response even within the 6-month window among ocrelizumab patients, a booster of COVID-19 vaccine might also help, although this remains to be studied.
The study group has already increased its sample size and is looking at adverse reactions and long-term immune responses, Dr. Kim said.
Encouraging, rather than discouraging, results
Leonard Calabrese, DO, professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said the findings shouldn’t discourage clinicians from encouraging vaccination.
“There’s still a preponderance of people who will develop a robust antibody vaccine response,” he said.
He cautioned that the findings look only at antibodies to the spike protein and at plasmablasts. The reduction in these titers is “of concern,” he said, but “we don’t really know with certainty what are the effects of these drugs, and these data are on the overall biologic protective effect of the vaccine. There’s much more to a vaccine response than anti–spike protein and plasmablasts,” including cell-mediated immune response.
For an individual patient, the findings “mean a lot,” he said.
“I think that people who are on significant prednisone and B-cell–depleting agents, I think you have to share with them that there’s a reasonable chance that you’re not going to be making a response similar to healthy people,” he said. “Thus, even with your vaccine, we’re not going to cut you loose to do things that are violating social distancing and group settings. … Should you be hugging your grandchildren if you’re a rituximab vaccine recipient? I think I would wait until we have a little bit more data.”
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of ophthalmology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, where he studies vaccinations in the immunocompromised, said that glucocorticoids tend to have little effect on vaccinations generally at low doses.
When effects are seen they can be difficult to interpret, he said.
“It’s hard to extricate that from the effect of the underlying disease,” he said. The drug can be a proxy for worse disease control.
Although it’s a small study, it’s reassuring that overall the responses were similar to healthy controls.
For B-cell–depleting therapies, his usual guidance is to not give vaccine until a patient is at least 3 months out from their last dose, and not to restart until at least 2 weeks after vaccination.
“It’s not surprising that some of these DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] do negatively affect vaccine response, particularly B-cell–depletion therapy. We need to do some studies to find a way to overcome that, or optimize delivery of the vaccine.”
Dr. Kim reported participating in consulting, advisory board, or speaker’s bureau for Alexion, Aurinia, Annexon Biosciences, Exagen Diagnostics, and GlaxoSmithKline, and receiving funding under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Winthrop reported receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. Dr. Calabrese reported no relevant disclosures.
Although most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases mounted immune responses after two doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies markedly reduced the response, according to a recently published preprint of a new study.
The study, published on MedRxiv and not yet peer reviewed, involved a prospective look at 133 patients with chronic inflammatory disease (CID) and 53 patients with healthy immune systems at Washington University, St. Louis, and the University of California, San Francisco. It is regarded as the largest and most detailed study yet in how vaccines perform in people with immune-mediated inflammatory disease. The patients were enrolled between December 2020 and March 2021, and the most common diseases were inflammatory bowel disease (32%), rheumatoid arthritis (29%), spondyloarthritis (15%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (11%).
A ‘modest’ reduction in antibody response
Senior author Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of medicine at Washington University, said the overall results so far are encouraging.
“Most patients with an autoimmune disease that are on immunosuppression can mount antibody responses,” he said. “We’re seeing the majority of our subjects respond.”
The immune-healthy controls and most of the patients with CID had a robust immune response against the spike protein, although the CID group had a mean reduction in antibody titers that was three times lower than the controls (P = .0092). The CID group similarly had a 2.7-fold reduction in preventing neutralization, or halting the virus’ ability to infect (P < .0001), researchers reported.
This reduction in response is “modest,” he said.
“Is the level of reduction going to be detrimental for protection? Time will tell,” he said, adding that researchers anticipate that it won’t have a critical effect on protection because responses tended to be within the range of the immunocompetent controls, who themselves had wildly varied antibody titers across a 20-fold range. “ ‘Optimal’ isn’t necessarily the same as ‘sufficient.’ ”
Type of medication has big impact on antibody titers
But there was a wide variety of effects on the immune response depending on the medication. Glucorticoids resulted in a response that was 10 times lower than the immune-healthy controls, as well as fewer circulating plasmablasts after vaccination. Researchers found that 98% of controls were seropositive for antibody, compared with 92% of those with CID who were not taking prednisone, and 65% of CID patients on prednisone (P = .0006 and .0115, respectively). Prevention of neutralization of the virus was similarly reduced in those groups, compared with the controls. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 15 patients. These effects were seen regardless of the dose.
“We would’ve anticipated this would have been dose dependent, so this was a little bit surprising,” Dr. Kim said.
B-cell–depleting therapies, such as rituximab (Rituxan) and ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), reduced antibody titers by 36 times, compared with controls (P < .0001), with a similar reduction in preventing infection (P = .0066), the researchers found. The reduction in antibody titers was the most pronounced among those who had received B-cell–depleting therapies within the previous 6 months. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 10 patients.
CID study subjects taking an antimetabolite, including methotrexate, had an average of a two- to threefold reduction in antibody titers and in neutralization (P = .0006). This reduction was greatest with methotrexate, researchers found (P = .0027).
JAK inhibitors also significantly reduced antibody titers (P = .0066), but the reduction in neutralization of the virus was not significant. In addition, researchers found a reduction in antibody titers, the prevention of viral infection, and circulating plasmablasts among those on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, compared with controls, but these were insignificant statistically except for virus neutralization.
Dr. Kim said he hopes the glucocorticoid data spur physicians to try harder to wean patients off the drugs, when possible, in keeping with recommendations already in place.
“The general culture in rheumatology has been very lax about the need to reduce glucocorticoids,” he said. “This reinvigorates that call.” Questions about possible drug holidays from glucocorticoids remain, regarding how long a holiday would be needed, he said. He noted that many patients on glucocorticoids nonetheless mounted responses.
Those on B-cell–depleting therapies present a “much more difficult” question, he said. Some patients possibly could wait a bit longer than their normal, every-6-month schedule, but it’s an individual decision, he said. Since a booster of influenza vaccine has been found to enhance the response even within the 6-month window among ocrelizumab patients, a booster of COVID-19 vaccine might also help, although this remains to be studied.
The study group has already increased its sample size and is looking at adverse reactions and long-term immune responses, Dr. Kim said.
Encouraging, rather than discouraging, results
Leonard Calabrese, DO, professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said the findings shouldn’t discourage clinicians from encouraging vaccination.
“There’s still a preponderance of people who will develop a robust antibody vaccine response,” he said.
He cautioned that the findings look only at antibodies to the spike protein and at plasmablasts. The reduction in these titers is “of concern,” he said, but “we don’t really know with certainty what are the effects of these drugs, and these data are on the overall biologic protective effect of the vaccine. There’s much more to a vaccine response than anti–spike protein and plasmablasts,” including cell-mediated immune response.
For an individual patient, the findings “mean a lot,” he said.
“I think that people who are on significant prednisone and B-cell–depleting agents, I think you have to share with them that there’s a reasonable chance that you’re not going to be making a response similar to healthy people,” he said. “Thus, even with your vaccine, we’re not going to cut you loose to do things that are violating social distancing and group settings. … Should you be hugging your grandchildren if you’re a rituximab vaccine recipient? I think I would wait until we have a little bit more data.”
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of ophthalmology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, where he studies vaccinations in the immunocompromised, said that glucocorticoids tend to have little effect on vaccinations generally at low doses.
When effects are seen they can be difficult to interpret, he said.
“It’s hard to extricate that from the effect of the underlying disease,” he said. The drug can be a proxy for worse disease control.
Although it’s a small study, it’s reassuring that overall the responses were similar to healthy controls.
For B-cell–depleting therapies, his usual guidance is to not give vaccine until a patient is at least 3 months out from their last dose, and not to restart until at least 2 weeks after vaccination.
“It’s not surprising that some of these DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] do negatively affect vaccine response, particularly B-cell–depletion therapy. We need to do some studies to find a way to overcome that, or optimize delivery of the vaccine.”
Dr. Kim reported participating in consulting, advisory board, or speaker’s bureau for Alexion, Aurinia, Annexon Biosciences, Exagen Diagnostics, and GlaxoSmithKline, and receiving funding under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Winthrop reported receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. Dr. Calabrese reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM MEDRXIV
Teen tanning bed ban would prevent more than 15,000 melanoma cases
and cost less than other, well-established public health interventions, according to a microsimulation of that age group’s virtual life course.
“Even with extensive sensitivity analyses on the costs of inspections, noncompliance with a ban, and the risk of developing melanoma in those who have used tanning beds, a ban can be considered highly cost effective,” Antoine Eskander, MD, ScM, of the University of Toronto, and associates said in Cancer.
Compared with no ban, such an intervention could save over $205 million in lifetime health care costs among the 17.1 million young people (based on the 2010 Census population) who would be affected, they said.
The more than 15,000 melanoma cases and 3,300 recurrences prevented would save $12 per average minor after adjusting for societal costs, such as lost productivity, formal and informal health care, economic losses to the tanning bed industry, and the need for monitoring, the investigators reported.
Switching to quality-adjusted life-years shows an improvement of 0.0002 QALYs per child for a ban, based on an overall cost of almost $24.9 per QALY, compared with no ban, they said, which makes it “more cost effective than many well-established public health interventions”:
- Processed meats taxation ($270/QALY).
- Smoking education campaign ($1,337/QALY).
- Cervical cancer screening ($2,166/QALY).
- Breast cancer screening ($29,284/QALY).
- Lung cancer screening ($49,200-$96,700/QALY).
Among the many parameters included in the microsimulation were the odds ratio of developing melanoma from exposure to tanning beds before age 25 (1.35), melanoma stage at presentation, risk of recurrence, and the cost of four annual inspections for each of the nation’s more than 13,000 tanning salons, Dr. Eskander and associates explained.
and cost less than other, well-established public health interventions, according to a microsimulation of that age group’s virtual life course.

“Even with extensive sensitivity analyses on the costs of inspections, noncompliance with a ban, and the risk of developing melanoma in those who have used tanning beds, a ban can be considered highly cost effective,” Antoine Eskander, MD, ScM, of the University of Toronto, and associates said in Cancer.
Compared with no ban, such an intervention could save over $205 million in lifetime health care costs among the 17.1 million young people (based on the 2010 Census population) who would be affected, they said.
The more than 15,000 melanoma cases and 3,300 recurrences prevented would save $12 per average minor after adjusting for societal costs, such as lost productivity, formal and informal health care, economic losses to the tanning bed industry, and the need for monitoring, the investigators reported.
Switching to quality-adjusted life-years shows an improvement of 0.0002 QALYs per child for a ban, based on an overall cost of almost $24.9 per QALY, compared with no ban, they said, which makes it “more cost effective than many well-established public health interventions”:
- Processed meats taxation ($270/QALY).
- Smoking education campaign ($1,337/QALY).
- Cervical cancer screening ($2,166/QALY).
- Breast cancer screening ($29,284/QALY).
- Lung cancer screening ($49,200-$96,700/QALY).
Among the many parameters included in the microsimulation were the odds ratio of developing melanoma from exposure to tanning beds before age 25 (1.35), melanoma stage at presentation, risk of recurrence, and the cost of four annual inspections for each of the nation’s more than 13,000 tanning salons, Dr. Eskander and associates explained.
and cost less than other, well-established public health interventions, according to a microsimulation of that age group’s virtual life course.

“Even with extensive sensitivity analyses on the costs of inspections, noncompliance with a ban, and the risk of developing melanoma in those who have used tanning beds, a ban can be considered highly cost effective,” Antoine Eskander, MD, ScM, of the University of Toronto, and associates said in Cancer.
Compared with no ban, such an intervention could save over $205 million in lifetime health care costs among the 17.1 million young people (based on the 2010 Census population) who would be affected, they said.
The more than 15,000 melanoma cases and 3,300 recurrences prevented would save $12 per average minor after adjusting for societal costs, such as lost productivity, formal and informal health care, economic losses to the tanning bed industry, and the need for monitoring, the investigators reported.
Switching to quality-adjusted life-years shows an improvement of 0.0002 QALYs per child for a ban, based on an overall cost of almost $24.9 per QALY, compared with no ban, they said, which makes it “more cost effective than many well-established public health interventions”:
- Processed meats taxation ($270/QALY).
- Smoking education campaign ($1,337/QALY).
- Cervical cancer screening ($2,166/QALY).
- Breast cancer screening ($29,284/QALY).
- Lung cancer screening ($49,200-$96,700/QALY).
Among the many parameters included in the microsimulation were the odds ratio of developing melanoma from exposure to tanning beds before age 25 (1.35), melanoma stage at presentation, risk of recurrence, and the cost of four annual inspections for each of the nation’s more than 13,000 tanning salons, Dr. Eskander and associates explained.
FROM CANCER
Survey finds Mohs surgeons favor nicotinamide for chemoprevention
, in a survey of members of the American College of Mohs Surgeons.
Although nicotinamide, a vitamin B3 derivative, has been shown to reduce keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) in high-risk patients, it is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for chemoprevention, and no safe upper limit has been established in clinical trials to date, wrote Sheena Desai of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
The investigators emailed an anonymous 12-question survey to 1,500 members of the American College of Mohs Surgeons. Of the 170 who responded, 10 were excluded for discordant responses, leaving 160 participants whose replies were included in a multiple logistic regression analysis. The respondents were mainly U.S. board-certified dermatologists and Mohs surgeons (99.4% for both); 86.9% were in clinical practice, including 78.8% in private practice, according to the report of the results, published in Dermatologic Surgery.
Overall, 76.9% of the respondents said they recommended nicotinamide for preventing KC, and 20% said they had recommended nicotinamide to more than 100 patients in the past year. In addition, 45% of respondents reported patients who had been taking nicotinamide for 2 years or more. Overall, 63.8% of the respondents expressed no concerns about long-term safety of nicotinamide, compared with 28.1% who said they were uncertain about long-term safety. Those who expressed concern or uncertainty about long-term safety were significantly less likely to recommend nicotinamide for KC prevention in the past year (odds ratio, 0.30; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.13-0.71). Clinicians with more than 10 years in practice were significantly less likely to recommend nicotinamide for chemoprevention (OR, 0.20; 95% CI 0.05-0.82).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the low number of responses and the potential lack of generalizability to clinicians other than Mohs surgeons, the researchers noted. “Additional studies on nicotinamide safety and use patterns, including cost-effectiveness analyses, are needed given the widespread use identified in this study,” they concluded.
Limited safety data highlight research gaps
The study is particularly important at this time because nicotinamide has been increasingly used for KC chemoprevention since a randomized, controlled trial published in 2015 in the New England Journal of Medicine showed benefits, corresponding author Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston, said in an interview. That study of high-risk patients found that nicotinamide, 500 mg twice a day, was safe and effective in lowering the rates of new nonmelanoma skin cancers and AKs after 12 months .
“However, because this is not a prescription medication, but rather an OTC vitamin supplement, data on its use are not available,” she said.
Dr. Hartman said she was not surprised that nicotinamide is being used frequently by a majority of the survey respondents. “Most are using this if someone has two KCs over 2 years, which is a quite common occurrence,” she noted. However, “I was a bit surprised that nearly two-thirds had no safety concerns with long-term use, even though this has not been well-studied,” she added.
“Like anything we recommend, we must consider the risks and benefits,” Dr. Hartman said of nicotinamide. “Unfortunately, we don’t know the risks well, since this hasn’t been well-characterized with regular long-term use in these doses,” and more research is needed, she said. “The risks are likely low, as this is a vitamin that has been used for years in various OTC supplements,” she added. “However, there are some data showing slightly increased all-cause mortality with similar doses of a related medicine, niacin, in cardiovascular patients. For this reason, I recommend the medication when a patient’s KCs are really becoming burdensome – several KCs in a year or two – or when they are high-risk due to immunosuppression,” she explained.
“We also must consider the individual patient. For a healthy younger patient who has a public-facing job and as a result is very averse to developing any KCs on his or her face and very motivated to try prevention, it may make sense to try nicotinamide,” Dr. Hartman said. But for an older patient with cardiovascular comorbidities who is not bothered by a KC on his or her back or extremities, “this medication may not have a favorable risk-benefit profile.”
To address safety concerns, “researchers need to examine whether there are any harms in long-term regular nicotinamide use for KC prevention,” Dr. Hartman said. “This is something we hope to do in our patients; however, it is challenging to study in a retrospective way since the harm is likely small and there are so many other features that influence mortality as an outcome,” she noted.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
, in a survey of members of the American College of Mohs Surgeons.
Although nicotinamide, a vitamin B3 derivative, has been shown to reduce keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) in high-risk patients, it is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for chemoprevention, and no safe upper limit has been established in clinical trials to date, wrote Sheena Desai of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
The investigators emailed an anonymous 12-question survey to 1,500 members of the American College of Mohs Surgeons. Of the 170 who responded, 10 were excluded for discordant responses, leaving 160 participants whose replies were included in a multiple logistic regression analysis. The respondents were mainly U.S. board-certified dermatologists and Mohs surgeons (99.4% for both); 86.9% were in clinical practice, including 78.8% in private practice, according to the report of the results, published in Dermatologic Surgery.
Overall, 76.9% of the respondents said they recommended nicotinamide for preventing KC, and 20% said they had recommended nicotinamide to more than 100 patients in the past year. In addition, 45% of respondents reported patients who had been taking nicotinamide for 2 years or more. Overall, 63.8% of the respondents expressed no concerns about long-term safety of nicotinamide, compared with 28.1% who said they were uncertain about long-term safety. Those who expressed concern or uncertainty about long-term safety were significantly less likely to recommend nicotinamide for KC prevention in the past year (odds ratio, 0.30; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.13-0.71). Clinicians with more than 10 years in practice were significantly less likely to recommend nicotinamide for chemoprevention (OR, 0.20; 95% CI 0.05-0.82).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the low number of responses and the potential lack of generalizability to clinicians other than Mohs surgeons, the researchers noted. “Additional studies on nicotinamide safety and use patterns, including cost-effectiveness analyses, are needed given the widespread use identified in this study,” they concluded.
Limited safety data highlight research gaps
The study is particularly important at this time because nicotinamide has been increasingly used for KC chemoprevention since a randomized, controlled trial published in 2015 in the New England Journal of Medicine showed benefits, corresponding author Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston, said in an interview. That study of high-risk patients found that nicotinamide, 500 mg twice a day, was safe and effective in lowering the rates of new nonmelanoma skin cancers and AKs after 12 months .
“However, because this is not a prescription medication, but rather an OTC vitamin supplement, data on its use are not available,” she said.
Dr. Hartman said she was not surprised that nicotinamide is being used frequently by a majority of the survey respondents. “Most are using this if someone has two KCs over 2 years, which is a quite common occurrence,” she noted. However, “I was a bit surprised that nearly two-thirds had no safety concerns with long-term use, even though this has not been well-studied,” she added.
“Like anything we recommend, we must consider the risks and benefits,” Dr. Hartman said of nicotinamide. “Unfortunately, we don’t know the risks well, since this hasn’t been well-characterized with regular long-term use in these doses,” and more research is needed, she said. “The risks are likely low, as this is a vitamin that has been used for years in various OTC supplements,” she added. “However, there are some data showing slightly increased all-cause mortality with similar doses of a related medicine, niacin, in cardiovascular patients. For this reason, I recommend the medication when a patient’s KCs are really becoming burdensome – several KCs in a year or two – or when they are high-risk due to immunosuppression,” she explained.
“We also must consider the individual patient. For a healthy younger patient who has a public-facing job and as a result is very averse to developing any KCs on his or her face and very motivated to try prevention, it may make sense to try nicotinamide,” Dr. Hartman said. But for an older patient with cardiovascular comorbidities who is not bothered by a KC on his or her back or extremities, “this medication may not have a favorable risk-benefit profile.”
To address safety concerns, “researchers need to examine whether there are any harms in long-term regular nicotinamide use for KC prevention,” Dr. Hartman said. “This is something we hope to do in our patients; however, it is challenging to study in a retrospective way since the harm is likely small and there are so many other features that influence mortality as an outcome,” she noted.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
, in a survey of members of the American College of Mohs Surgeons.
Although nicotinamide, a vitamin B3 derivative, has been shown to reduce keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) in high-risk patients, it is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for chemoprevention, and no safe upper limit has been established in clinical trials to date, wrote Sheena Desai of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
The investigators emailed an anonymous 12-question survey to 1,500 members of the American College of Mohs Surgeons. Of the 170 who responded, 10 were excluded for discordant responses, leaving 160 participants whose replies were included in a multiple logistic regression analysis. The respondents were mainly U.S. board-certified dermatologists and Mohs surgeons (99.4% for both); 86.9% were in clinical practice, including 78.8% in private practice, according to the report of the results, published in Dermatologic Surgery.
Overall, 76.9% of the respondents said they recommended nicotinamide for preventing KC, and 20% said they had recommended nicotinamide to more than 100 patients in the past year. In addition, 45% of respondents reported patients who had been taking nicotinamide for 2 years or more. Overall, 63.8% of the respondents expressed no concerns about long-term safety of nicotinamide, compared with 28.1% who said they were uncertain about long-term safety. Those who expressed concern or uncertainty about long-term safety were significantly less likely to recommend nicotinamide for KC prevention in the past year (odds ratio, 0.30; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.13-0.71). Clinicians with more than 10 years in practice were significantly less likely to recommend nicotinamide for chemoprevention (OR, 0.20; 95% CI 0.05-0.82).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the low number of responses and the potential lack of generalizability to clinicians other than Mohs surgeons, the researchers noted. “Additional studies on nicotinamide safety and use patterns, including cost-effectiveness analyses, are needed given the widespread use identified in this study,” they concluded.
Limited safety data highlight research gaps
The study is particularly important at this time because nicotinamide has been increasingly used for KC chemoprevention since a randomized, controlled trial published in 2015 in the New England Journal of Medicine showed benefits, corresponding author Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston, said in an interview. That study of high-risk patients found that nicotinamide, 500 mg twice a day, was safe and effective in lowering the rates of new nonmelanoma skin cancers and AKs after 12 months .
“However, because this is not a prescription medication, but rather an OTC vitamin supplement, data on its use are not available,” she said.
Dr. Hartman said she was not surprised that nicotinamide is being used frequently by a majority of the survey respondents. “Most are using this if someone has two KCs over 2 years, which is a quite common occurrence,” she noted. However, “I was a bit surprised that nearly two-thirds had no safety concerns with long-term use, even though this has not been well-studied,” she added.
“Like anything we recommend, we must consider the risks and benefits,” Dr. Hartman said of nicotinamide. “Unfortunately, we don’t know the risks well, since this hasn’t been well-characterized with regular long-term use in these doses,” and more research is needed, she said. “The risks are likely low, as this is a vitamin that has been used for years in various OTC supplements,” she added. “However, there are some data showing slightly increased all-cause mortality with similar doses of a related medicine, niacin, in cardiovascular patients. For this reason, I recommend the medication when a patient’s KCs are really becoming burdensome – several KCs in a year or two – or when they are high-risk due to immunosuppression,” she explained.
“We also must consider the individual patient. For a healthy younger patient who has a public-facing job and as a result is very averse to developing any KCs on his or her face and very motivated to try prevention, it may make sense to try nicotinamide,” Dr. Hartman said. But for an older patient with cardiovascular comorbidities who is not bothered by a KC on his or her back or extremities, “this medication may not have a favorable risk-benefit profile.”
To address safety concerns, “researchers need to examine whether there are any harms in long-term regular nicotinamide use for KC prevention,” Dr. Hartman said. “This is something we hope to do in our patients; however, it is challenging to study in a retrospective way since the harm is likely small and there are so many other features that influence mortality as an outcome,” she noted.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM DERMATOLOGIC SURGERY
A Rash Against the Grain
ANSWER
The correct answer is dermatitis herpetiformis (DH; choice “b”).
DISCUSSION
DH is unusual, although not rare, and it is often overlooked in the investigation of itchy rashes—even by dermatologists. As is so often the case, the biopsy was the missing piece of the puzzle, since it clearly showed changes consistent with this condition.
The history of DH has some interesting overlap with that of biopsy. It was Rudolph Virchow, an 18th century Austrian pathologist, who first connected clinical disease to specific arrangements of disordered tissue seen microscopically—at that time, a giant leap for medicine. An American dermatologist, Louis Adolphus Duhring, had the good fortune to study under Virchow and his successors in Vienna and brought this cutting-edge knowledge back to this country, where he began the process of categorizing diseases by their histologic patterns as well as by their presentation and clinical course. This was when he discovered the basis for the condition that became known as Duhring disease, also known as dermatitis herpetiformis.
It was much later (1967) that a connection was made between DH and the ingestion of gluten. Our patient experienced a rapid decline in his itching and rash as soon as he started a gluten-free diet. However, since many patients find such a diet difficult to maintain, there are pharmacologic options as well: dapsone, colchicine, sulfa drugs, drugs from the tetracycline family, and nicotinamide. All have potential adverse effects with which the prescriber needs to become familiar.
With a combination of medication and reduced gluten intake, it’s entirely possible that the patient’s DH will permanently resolve, although he will remain at increased risk for other autoimmune conditions.
ANSWER
The correct answer is dermatitis herpetiformis (DH; choice “b”).
DISCUSSION
DH is unusual, although not rare, and it is often overlooked in the investigation of itchy rashes—even by dermatologists. As is so often the case, the biopsy was the missing piece of the puzzle, since it clearly showed changes consistent with this condition.
The history of DH has some interesting overlap with that of biopsy. It was Rudolph Virchow, an 18th century Austrian pathologist, who first connected clinical disease to specific arrangements of disordered tissue seen microscopically—at that time, a giant leap for medicine. An American dermatologist, Louis Adolphus Duhring, had the good fortune to study under Virchow and his successors in Vienna and brought this cutting-edge knowledge back to this country, where he began the process of categorizing diseases by their histologic patterns as well as by their presentation and clinical course. This was when he discovered the basis for the condition that became known as Duhring disease, also known as dermatitis herpetiformis.
It was much later (1967) that a connection was made between DH and the ingestion of gluten. Our patient experienced a rapid decline in his itching and rash as soon as he started a gluten-free diet. However, since many patients find such a diet difficult to maintain, there are pharmacologic options as well: dapsone, colchicine, sulfa drugs, drugs from the tetracycline family, and nicotinamide. All have potential adverse effects with which the prescriber needs to become familiar.
With a combination of medication and reduced gluten intake, it’s entirely possible that the patient’s DH will permanently resolve, although he will remain at increased risk for other autoimmune conditions.
ANSWER
The correct answer is dermatitis herpetiformis (DH; choice “b”).
DISCUSSION
DH is unusual, although not rare, and it is often overlooked in the investigation of itchy rashes—even by dermatologists. As is so often the case, the biopsy was the missing piece of the puzzle, since it clearly showed changes consistent with this condition.
The history of DH has some interesting overlap with that of biopsy. It was Rudolph Virchow, an 18th century Austrian pathologist, who first connected clinical disease to specific arrangements of disordered tissue seen microscopically—at that time, a giant leap for medicine. An American dermatologist, Louis Adolphus Duhring, had the good fortune to study under Virchow and his successors in Vienna and brought this cutting-edge knowledge back to this country, where he began the process of categorizing diseases by their histologic patterns as well as by their presentation and clinical course. This was when he discovered the basis for the condition that became known as Duhring disease, also known as dermatitis herpetiformis.
It was much later (1967) that a connection was made between DH and the ingestion of gluten. Our patient experienced a rapid decline in his itching and rash as soon as he started a gluten-free diet. However, since many patients find such a diet difficult to maintain, there are pharmacologic options as well: dapsone, colchicine, sulfa drugs, drugs from the tetracycline family, and nicotinamide. All have potential adverse effects with which the prescriber needs to become familiar.
With a combination of medication and reduced gluten intake, it’s entirely possible that the patient’s DH will permanently resolve, although he will remain at increased risk for other autoimmune conditions.
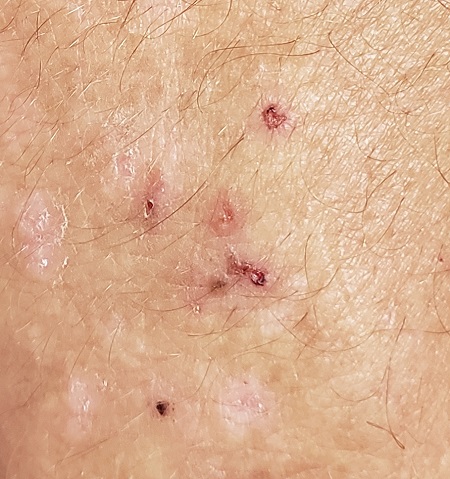
A 56-year-old man began to itch almost 10 years ago, when lesions appeared on his extensor forearms; they later branched out to his knees, scalp, and waistline. He has continued to suffer despite seeing numerous providers, including dermatologists.
An allergist pronounced him free of any significant allergies. Another provider was certain the patient had scabies, although his household was unaffected and the prescribed treatment—permethrin lotion and oral ivermectin—had no impact on the rash or the symptoms. Most of the other consulted providers diagnosed eczema, despite a complete lack of atopy in the patient or his family of origin. Furthermore, treatment with topical, oral, and intramuscular steroids had offered minimal and very short-lived relief. No one took a scraping or performed a biopsy of the rash.
The patient claims to be otherwise healthy, with no gastrointestinal symptoms and no new medications. Examination reveals a slightly overweight man in no distress.
The lesions in question are patches of excoriated papulovesicular lesions. Microscopic examination of a KOH prep shows no scabetic elements. His volar wrists, the sides of his fingers, and his genitals are free of lesions.
A shave biopsy is performed under local anesthetic. The pathology report indicates subepidermal collections of eosinophils.