User login
JAK inhibitors efficacious for atopic dermatitis in Asian patients, study finds
SINGAPORE – conducted in Singapore has found.
“Abrocitinib and upadacitinib surprisingly appeared to have better treatment efficacy compared to baricitinib,” said study lead Yik Weng Yew, MD, PhD, MPH, deputy head of research at Singapore’s National Skin Centre (NSC), who presented the results at the 25th World Congress of Dermatology. “But overall, as a group, I think they show a very good treatment response, as well as a good effect on itch response.”
JAK inhibitors are used to treat a variety of inflammatory diseases including alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Although treatment for severe eczema was previously limited to topical steroids and oral immunosuppressants, there are now two oral JAK inhibitors – abrocitinib and upadacitinib – approved in 2022 by the Food and Drug Administration for treating AD, which affects up to 2.4% of the global population. (A topical formulation of ruxolitinib, a JAK inhibitor, was approved for AD in 2021.)
The Singapore study is one of the few that have examined the safety and efficacy of JAK inhibitors for treatment of AD in a non-White population.
Chinese population
For the 12-week trial, conducted in 2022, Dr. Yew and associates recruited 35 patients from the NSC. More than half of participants (64%) were men and most (96%) were of Chinese ethnicity. Four of every five patients had previously received systemic agents: 17% had been treated with one systemic agent, 18.9% with two, 15.1% with three, 22.6% with four, and 3.8% with five. The most commonly used agents were cyclosporine (62.3%), methotrexate (47.2%), azathioprine (39.6%), and dupilumab (35.8%).
“The switch in therapy could have been a result of inadequate efficacy or cost reasons because in Singapore patients pay out of pocket for AD treatments,” said Dr. Yew.
Additionally, he offered a caveat on the profile of participants: “Perhaps they were more difficult atopic eczema patients, and therefore, the efficacy [of JAK inhibitors] might be a bit different.”
Clearer skin, less itch
Patients received one of the three study drugs: baricitinib (66%), abrocitinib (21%), and upadacitinib (13%). The distribution was “affected by reimbursement patterns and availability of the drug,” explained Dr. Yew.
They were assessed at weeks 4 and 12. By study end, the proportion of patients who self-reported an improvement in their condition was 100% for upadacitinib, 90% for abrocitinib, and 69% for baricitinib.
Scores on the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) also improved with treatment. Patients in the baricitinib group saw their mean score fall from 4.0 to 3.0 by week 4, then to 2.0 by week 12. With upadacitinib and abrocitinib, “you can see that there is a nice decrease in IGA responses,” said Dr. Yew, referring to the larger improvement in scores experienced by patients on those two treatments. For patients on upadacitinib, IGA decreased from 3.5 to 2 at 4 weeks, then to 0.5 at 12 weeks, while those taking abrocitinib had their scores drop from 4.0 to 2.0 at 4 weeks, then to 1.0 at 12 weeks.
When it came to itch reduction, the abrocitinib group experienced the biggest reduction, with a median reduction of 5.5 points in itch score. Median reduction in itch score was 4 points for the other two groups. “Oral JAK inhibitors appear to have a good effect on itch response,” said Dr. Yew.
However, the researchers observed no significant reduction in percentage of body surface area affected, the last outcome assessed.
The most commonly reported adverse events were increased creatine kinase levels (11.3% of patients), increased LDL cholesterol levels (9.4%), and herpes zoster (9.4%). Those in the abrocitinib reported a higher number of these adverse events, compared with the other two treatment groups. (There were no herpes zoster cases among those taking baricitinib.)
For herpes zoster, Dr. Yew said “the common recommendation” is to give the inactivated shingles vaccine. “But the problem is that, number one, these patients would have probably failed multiple agents so they probably can’t wait for you to vaccinate before you initiate treatment.”
In addition, people in Singapore have to pay out-of-pocket for the two vaccine doses, “which is probably a month’s worth of medication,” he noted. “So we have a lot of resistance from patients.”
Additionally, Dr. Yew noted that contrary to what has previously been reported in the literature, there were few complaints of acne as a side effect in the Singaporean study population.
Toward greater representation
Dr. Yew pointed out that the study was limited by a few factors: neither the Eczema Area and Severity Index or Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis index data was used, and the study population was small and not representative of the real world.
Still, the new findings contribute to the overall safety and efficacy profile of JAK inhibitors in AD, which has so far been scarce in non-White populations.
“In Western studies, unfortunately, the representation of the population of skin of color or different ethnicities is underrepresented,” said Yousef Binamer, MD, chair of the dermatology department at King Faisal Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, when approached for an independent comment on the results.
“This is now why researchers are looking into specific groups to study them,” which he pointed out, is crucial because “the immunophenotyping of AD is different for each background.”
The incidence and severity of AD tend to be higher in Asian and Middle Eastern populations, for instance, he noted. “It’s very common in Asia, and not so common in very white skin. I did my training in Canada so I see the difference,” said Dr. Binamer. “Asian people tend to be more itchy and have a tendency to scar on pigmentation.” Whereas White people “usually do not have this issue.”
“So I think real-world evidence of JAK inhibitors in the other populations is important,” he said. Studies such as the one conducted in Singapore, as well as the recently reported QUARTZ3 study, which examined the use of the JAK inhibitor ivarmacitinib in 256 Chinese patients with AD, are helping to pave the way.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Yew and Dr. Binamer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SINGAPORE – conducted in Singapore has found.
“Abrocitinib and upadacitinib surprisingly appeared to have better treatment efficacy compared to baricitinib,” said study lead Yik Weng Yew, MD, PhD, MPH, deputy head of research at Singapore’s National Skin Centre (NSC), who presented the results at the 25th World Congress of Dermatology. “But overall, as a group, I think they show a very good treatment response, as well as a good effect on itch response.”
JAK inhibitors are used to treat a variety of inflammatory diseases including alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Although treatment for severe eczema was previously limited to topical steroids and oral immunosuppressants, there are now two oral JAK inhibitors – abrocitinib and upadacitinib – approved in 2022 by the Food and Drug Administration for treating AD, which affects up to 2.4% of the global population. (A topical formulation of ruxolitinib, a JAK inhibitor, was approved for AD in 2021.)
The Singapore study is one of the few that have examined the safety and efficacy of JAK inhibitors for treatment of AD in a non-White population.
Chinese population
For the 12-week trial, conducted in 2022, Dr. Yew and associates recruited 35 patients from the NSC. More than half of participants (64%) were men and most (96%) were of Chinese ethnicity. Four of every five patients had previously received systemic agents: 17% had been treated with one systemic agent, 18.9% with two, 15.1% with three, 22.6% with four, and 3.8% with five. The most commonly used agents were cyclosporine (62.3%), methotrexate (47.2%), azathioprine (39.6%), and dupilumab (35.8%).
“The switch in therapy could have been a result of inadequate efficacy or cost reasons because in Singapore patients pay out of pocket for AD treatments,” said Dr. Yew.
Additionally, he offered a caveat on the profile of participants: “Perhaps they were more difficult atopic eczema patients, and therefore, the efficacy [of JAK inhibitors] might be a bit different.”
Clearer skin, less itch
Patients received one of the three study drugs: baricitinib (66%), abrocitinib (21%), and upadacitinib (13%). The distribution was “affected by reimbursement patterns and availability of the drug,” explained Dr. Yew.
They were assessed at weeks 4 and 12. By study end, the proportion of patients who self-reported an improvement in their condition was 100% for upadacitinib, 90% for abrocitinib, and 69% for baricitinib.
Scores on the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) also improved with treatment. Patients in the baricitinib group saw their mean score fall from 4.0 to 3.0 by week 4, then to 2.0 by week 12. With upadacitinib and abrocitinib, “you can see that there is a nice decrease in IGA responses,” said Dr. Yew, referring to the larger improvement in scores experienced by patients on those two treatments. For patients on upadacitinib, IGA decreased from 3.5 to 2 at 4 weeks, then to 0.5 at 12 weeks, while those taking abrocitinib had their scores drop from 4.0 to 2.0 at 4 weeks, then to 1.0 at 12 weeks.
When it came to itch reduction, the abrocitinib group experienced the biggest reduction, with a median reduction of 5.5 points in itch score. Median reduction in itch score was 4 points for the other two groups. “Oral JAK inhibitors appear to have a good effect on itch response,” said Dr. Yew.
However, the researchers observed no significant reduction in percentage of body surface area affected, the last outcome assessed.
The most commonly reported adverse events were increased creatine kinase levels (11.3% of patients), increased LDL cholesterol levels (9.4%), and herpes zoster (9.4%). Those in the abrocitinib reported a higher number of these adverse events, compared with the other two treatment groups. (There were no herpes zoster cases among those taking baricitinib.)
For herpes zoster, Dr. Yew said “the common recommendation” is to give the inactivated shingles vaccine. “But the problem is that, number one, these patients would have probably failed multiple agents so they probably can’t wait for you to vaccinate before you initiate treatment.”
In addition, people in Singapore have to pay out-of-pocket for the two vaccine doses, “which is probably a month’s worth of medication,” he noted. “So we have a lot of resistance from patients.”
Additionally, Dr. Yew noted that contrary to what has previously been reported in the literature, there were few complaints of acne as a side effect in the Singaporean study population.
Toward greater representation
Dr. Yew pointed out that the study was limited by a few factors: neither the Eczema Area and Severity Index or Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis index data was used, and the study population was small and not representative of the real world.
Still, the new findings contribute to the overall safety and efficacy profile of JAK inhibitors in AD, which has so far been scarce in non-White populations.
“In Western studies, unfortunately, the representation of the population of skin of color or different ethnicities is underrepresented,” said Yousef Binamer, MD, chair of the dermatology department at King Faisal Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, when approached for an independent comment on the results.
“This is now why researchers are looking into specific groups to study them,” which he pointed out, is crucial because “the immunophenotyping of AD is different for each background.”
The incidence and severity of AD tend to be higher in Asian and Middle Eastern populations, for instance, he noted. “It’s very common in Asia, and not so common in very white skin. I did my training in Canada so I see the difference,” said Dr. Binamer. “Asian people tend to be more itchy and have a tendency to scar on pigmentation.” Whereas White people “usually do not have this issue.”
“So I think real-world evidence of JAK inhibitors in the other populations is important,” he said. Studies such as the one conducted in Singapore, as well as the recently reported QUARTZ3 study, which examined the use of the JAK inhibitor ivarmacitinib in 256 Chinese patients with AD, are helping to pave the way.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Yew and Dr. Binamer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SINGAPORE – conducted in Singapore has found.
“Abrocitinib and upadacitinib surprisingly appeared to have better treatment efficacy compared to baricitinib,” said study lead Yik Weng Yew, MD, PhD, MPH, deputy head of research at Singapore’s National Skin Centre (NSC), who presented the results at the 25th World Congress of Dermatology. “But overall, as a group, I think they show a very good treatment response, as well as a good effect on itch response.”
JAK inhibitors are used to treat a variety of inflammatory diseases including alopecia areata, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Although treatment for severe eczema was previously limited to topical steroids and oral immunosuppressants, there are now two oral JAK inhibitors – abrocitinib and upadacitinib – approved in 2022 by the Food and Drug Administration for treating AD, which affects up to 2.4% of the global population. (A topical formulation of ruxolitinib, a JAK inhibitor, was approved for AD in 2021.)
The Singapore study is one of the few that have examined the safety and efficacy of JAK inhibitors for treatment of AD in a non-White population.
Chinese population
For the 12-week trial, conducted in 2022, Dr. Yew and associates recruited 35 patients from the NSC. More than half of participants (64%) were men and most (96%) were of Chinese ethnicity. Four of every five patients had previously received systemic agents: 17% had been treated with one systemic agent, 18.9% with two, 15.1% with three, 22.6% with four, and 3.8% with five. The most commonly used agents were cyclosporine (62.3%), methotrexate (47.2%), azathioprine (39.6%), and dupilumab (35.8%).
“The switch in therapy could have been a result of inadequate efficacy or cost reasons because in Singapore patients pay out of pocket for AD treatments,” said Dr. Yew.
Additionally, he offered a caveat on the profile of participants: “Perhaps they were more difficult atopic eczema patients, and therefore, the efficacy [of JAK inhibitors] might be a bit different.”
Clearer skin, less itch
Patients received one of the three study drugs: baricitinib (66%), abrocitinib (21%), and upadacitinib (13%). The distribution was “affected by reimbursement patterns and availability of the drug,” explained Dr. Yew.
They were assessed at weeks 4 and 12. By study end, the proportion of patients who self-reported an improvement in their condition was 100% for upadacitinib, 90% for abrocitinib, and 69% for baricitinib.
Scores on the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) also improved with treatment. Patients in the baricitinib group saw their mean score fall from 4.0 to 3.0 by week 4, then to 2.0 by week 12. With upadacitinib and abrocitinib, “you can see that there is a nice decrease in IGA responses,” said Dr. Yew, referring to the larger improvement in scores experienced by patients on those two treatments. For patients on upadacitinib, IGA decreased from 3.5 to 2 at 4 weeks, then to 0.5 at 12 weeks, while those taking abrocitinib had their scores drop from 4.0 to 2.0 at 4 weeks, then to 1.0 at 12 weeks.
When it came to itch reduction, the abrocitinib group experienced the biggest reduction, with a median reduction of 5.5 points in itch score. Median reduction in itch score was 4 points for the other two groups. “Oral JAK inhibitors appear to have a good effect on itch response,” said Dr. Yew.
However, the researchers observed no significant reduction in percentage of body surface area affected, the last outcome assessed.
The most commonly reported adverse events were increased creatine kinase levels (11.3% of patients), increased LDL cholesterol levels (9.4%), and herpes zoster (9.4%). Those in the abrocitinib reported a higher number of these adverse events, compared with the other two treatment groups. (There were no herpes zoster cases among those taking baricitinib.)
For herpes zoster, Dr. Yew said “the common recommendation” is to give the inactivated shingles vaccine. “But the problem is that, number one, these patients would have probably failed multiple agents so they probably can’t wait for you to vaccinate before you initiate treatment.”
In addition, people in Singapore have to pay out-of-pocket for the two vaccine doses, “which is probably a month’s worth of medication,” he noted. “So we have a lot of resistance from patients.”
Additionally, Dr. Yew noted that contrary to what has previously been reported in the literature, there were few complaints of acne as a side effect in the Singaporean study population.
Toward greater representation
Dr. Yew pointed out that the study was limited by a few factors: neither the Eczema Area and Severity Index or Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis index data was used, and the study population was small and not representative of the real world.
Still, the new findings contribute to the overall safety and efficacy profile of JAK inhibitors in AD, which has so far been scarce in non-White populations.
“In Western studies, unfortunately, the representation of the population of skin of color or different ethnicities is underrepresented,” said Yousef Binamer, MD, chair of the dermatology department at King Faisal Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, when approached for an independent comment on the results.
“This is now why researchers are looking into specific groups to study them,” which he pointed out, is crucial because “the immunophenotyping of AD is different for each background.”
The incidence and severity of AD tend to be higher in Asian and Middle Eastern populations, for instance, he noted. “It’s very common in Asia, and not so common in very white skin. I did my training in Canada so I see the difference,” said Dr. Binamer. “Asian people tend to be more itchy and have a tendency to scar on pigmentation.” Whereas White people “usually do not have this issue.”
“So I think real-world evidence of JAK inhibitors in the other populations is important,” he said. Studies such as the one conducted in Singapore, as well as the recently reported QUARTZ3 study, which examined the use of the JAK inhibitor ivarmacitinib in 256 Chinese patients with AD, are helping to pave the way.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Yew and Dr. Binamer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT WCD 2023
Affirmative action 2.0
The recent decisions by the United States Supreme Court (SCOTUS) declaring the current admission policies at Harvard and the University of North Carolina illegal have sent shock waves through the university and graduate school communities. In the minds of many observers, these decisions have effectively eliminated affirmative action as a tool for leveling the playing field for ethnic minorities.
However, there are some commentators who feel that affirmative action has never been as effective as others have believed. They point out that the number of students admitted to the most selective schools is very small compared with the entire nation’s collection of colleges and universities. Regardless of where you come down on the effectiveness of past affirmative action policies, the SCOTUS decision is a done deal. It’s time to move on and begin anew our search for inclusion-promoting strategies that will pass the Court’s litmus test of legality.
I count myself among those who are optimistic that there are enough of us committed individuals that a new and better version of affirmative action is just over the horizon. Some of my supporting evidence can be found in a New York Times article by Stephanie Saul describing the admissions policy at the University of California Davis Medical School. The keystone of the university’s policy is a “socioeconomic disadvantage scale” that takes into account the applicant’s life circumstances, such as parental education and family income. This ranking – on a scale of 0 to 99 – is tossed into the standard mix of grades, test scores, essays, interviews, and recommendations. It shouldn’t surprise that UC Davis is now one of the most diverse medical schools in the United States despite the fact that California voted to ban affirmative action in 1996.
The socioeconomic disadvantage scale may, in the long run, be more effective than the current affirmative action strategies that have been race based. It certainly makes more sense to me. For example, in 2020 the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) made a significant philosophical change by broadening and deepening its focus on the social sciences. To some extent, this refocusing may have reflected the American Association of Medical Colleges’ search for more well-rounded students and, by extension, more physicians sensitive to the plight of their disadvantaged patients. By weighting the questions more toward subjects such as how bias can influence patient care, it was hoped that the newly minted physicians would view and treat patients not just as victims of illness but as multifaceted individuals who reside in an environment that may be influencing their health.
While I agree with the goal of creating physicians with a broader and more holistic view, the notion that adding questions from social science disciplines is going to achieve this goal never made much sense to me. Answering questions posed by social scientists teaching in a selective academic setting doesn’t necessarily guarantee that the applicant has a full understanding of the real-world consequences of poverty and bias.
On the other hand, an applicant’s responses to a questionnaire about the socioeconomic conditions in which she or he grew up is far more likely to unearth candidates with a deep, broad, and very personal understanding of the challenges that disadvantaged patients face. It’s another one of those been-there-know-how-it-feels kind of things. Reading a book about how to ride a bicycle cannot quite capture the challenge of balancing yourself on two thin wheels.
The pathway to becoming a practicing physician takes a minimum of 6 or 7 years. Much of that education comes in the form of watching and listening to physicians who, in turn, modeled their behavior after the cohort that preceded them in a very old system, and so on. There is no guarantee that even the most sensitively selected students will remain immune to incorporating into their practice style some of the systemic bias that will inevitably surround them. But a socioeconomic disadvantage scale is certainly worth a try.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
The recent decisions by the United States Supreme Court (SCOTUS) declaring the current admission policies at Harvard and the University of North Carolina illegal have sent shock waves through the university and graduate school communities. In the minds of many observers, these decisions have effectively eliminated affirmative action as a tool for leveling the playing field for ethnic minorities.
However, there are some commentators who feel that affirmative action has never been as effective as others have believed. They point out that the number of students admitted to the most selective schools is very small compared with the entire nation’s collection of colleges and universities. Regardless of where you come down on the effectiveness of past affirmative action policies, the SCOTUS decision is a done deal. It’s time to move on and begin anew our search for inclusion-promoting strategies that will pass the Court’s litmus test of legality.
I count myself among those who are optimistic that there are enough of us committed individuals that a new and better version of affirmative action is just over the horizon. Some of my supporting evidence can be found in a New York Times article by Stephanie Saul describing the admissions policy at the University of California Davis Medical School. The keystone of the university’s policy is a “socioeconomic disadvantage scale” that takes into account the applicant’s life circumstances, such as parental education and family income. This ranking – on a scale of 0 to 99 – is tossed into the standard mix of grades, test scores, essays, interviews, and recommendations. It shouldn’t surprise that UC Davis is now one of the most diverse medical schools in the United States despite the fact that California voted to ban affirmative action in 1996.
The socioeconomic disadvantage scale may, in the long run, be more effective than the current affirmative action strategies that have been race based. It certainly makes more sense to me. For example, in 2020 the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) made a significant philosophical change by broadening and deepening its focus on the social sciences. To some extent, this refocusing may have reflected the American Association of Medical Colleges’ search for more well-rounded students and, by extension, more physicians sensitive to the plight of their disadvantaged patients. By weighting the questions more toward subjects such as how bias can influence patient care, it was hoped that the newly minted physicians would view and treat patients not just as victims of illness but as multifaceted individuals who reside in an environment that may be influencing their health.
While I agree with the goal of creating physicians with a broader and more holistic view, the notion that adding questions from social science disciplines is going to achieve this goal never made much sense to me. Answering questions posed by social scientists teaching in a selective academic setting doesn’t necessarily guarantee that the applicant has a full understanding of the real-world consequences of poverty and bias.
On the other hand, an applicant’s responses to a questionnaire about the socioeconomic conditions in which she or he grew up is far more likely to unearth candidates with a deep, broad, and very personal understanding of the challenges that disadvantaged patients face. It’s another one of those been-there-know-how-it-feels kind of things. Reading a book about how to ride a bicycle cannot quite capture the challenge of balancing yourself on two thin wheels.
The pathway to becoming a practicing physician takes a minimum of 6 or 7 years. Much of that education comes in the form of watching and listening to physicians who, in turn, modeled their behavior after the cohort that preceded them in a very old system, and so on. There is no guarantee that even the most sensitively selected students will remain immune to incorporating into their practice style some of the systemic bias that will inevitably surround them. But a socioeconomic disadvantage scale is certainly worth a try.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
The recent decisions by the United States Supreme Court (SCOTUS) declaring the current admission policies at Harvard and the University of North Carolina illegal have sent shock waves through the university and graduate school communities. In the minds of many observers, these decisions have effectively eliminated affirmative action as a tool for leveling the playing field for ethnic minorities.
However, there are some commentators who feel that affirmative action has never been as effective as others have believed. They point out that the number of students admitted to the most selective schools is very small compared with the entire nation’s collection of colleges and universities. Regardless of where you come down on the effectiveness of past affirmative action policies, the SCOTUS decision is a done deal. It’s time to move on and begin anew our search for inclusion-promoting strategies that will pass the Court’s litmus test of legality.
I count myself among those who are optimistic that there are enough of us committed individuals that a new and better version of affirmative action is just over the horizon. Some of my supporting evidence can be found in a New York Times article by Stephanie Saul describing the admissions policy at the University of California Davis Medical School. The keystone of the university’s policy is a “socioeconomic disadvantage scale” that takes into account the applicant’s life circumstances, such as parental education and family income. This ranking – on a scale of 0 to 99 – is tossed into the standard mix of grades, test scores, essays, interviews, and recommendations. It shouldn’t surprise that UC Davis is now one of the most diverse medical schools in the United States despite the fact that California voted to ban affirmative action in 1996.
The socioeconomic disadvantage scale may, in the long run, be more effective than the current affirmative action strategies that have been race based. It certainly makes more sense to me. For example, in 2020 the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) made a significant philosophical change by broadening and deepening its focus on the social sciences. To some extent, this refocusing may have reflected the American Association of Medical Colleges’ search for more well-rounded students and, by extension, more physicians sensitive to the plight of their disadvantaged patients. By weighting the questions more toward subjects such as how bias can influence patient care, it was hoped that the newly minted physicians would view and treat patients not just as victims of illness but as multifaceted individuals who reside in an environment that may be influencing their health.
While I agree with the goal of creating physicians with a broader and more holistic view, the notion that adding questions from social science disciplines is going to achieve this goal never made much sense to me. Answering questions posed by social scientists teaching in a selective academic setting doesn’t necessarily guarantee that the applicant has a full understanding of the real-world consequences of poverty and bias.
On the other hand, an applicant’s responses to a questionnaire about the socioeconomic conditions in which she or he grew up is far more likely to unearth candidates with a deep, broad, and very personal understanding of the challenges that disadvantaged patients face. It’s another one of those been-there-know-how-it-feels kind of things. Reading a book about how to ride a bicycle cannot quite capture the challenge of balancing yourself on two thin wheels.
The pathway to becoming a practicing physician takes a minimum of 6 or 7 years. Much of that education comes in the form of watching and listening to physicians who, in turn, modeled their behavior after the cohort that preceded them in a very old system, and so on. There is no guarantee that even the most sensitively selected students will remain immune to incorporating into their practice style some of the systemic bias that will inevitably surround them. But a socioeconomic disadvantage scale is certainly worth a try.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Does racial bias taint the Apgar score?
Experts say overhaul needed
In 1952, when Dr. Virginia Apgar developed her 10-point scale for assessing neonates’ health, the U.S. obstetrical anesthesiologst may not have foreseen it would one day become one of the commonest medical tests in the world.
Assigned even before the mother first holds her newborn, the score rapidly evaluates neonates with a score of 0-10, which leads to an algorithm of potential medical interventions. The scale evaluates heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin coloring (typically described as blue body, pink body/blue limbs, or pink body).
“The Apgar is a very important tool used in millions of babies around the world in the very first minute after birth,” said Amos Grunebaum, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and director of perinatal research at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital in Manhattan.
But recently the venerable system has increasingly come under fire for colorism and racial bias, with some calling for an overhaul. That pressure is due to the 2 out of 10 points allotted to an overall “pink” skin tone, a measure that lowers the scores of non-White newborns and may expose them to unnecessary measures such as resuscitation, neonatal intensive care, and intubation.
“This is their first encounter with systemic racism,” said Dr. Grunebaum in an interview. “The score is prejudiced against Black babies because they can’t get perfect scores.”
Propagating ‘race-based medicine’
Concern about racial bias embedded in the Apgar score is not new, Dr. Grunebaum noted.
“Decades ago, when I was doing my training in Brooklyn, the nurses said that using skin color was ridiculous since Black and brown babies couldn’t be pink. And skin color looks different in different lighting. Dr. Apgar herself recognized the problem.”
Furthermore, men see color differently than women do, and some people are actually color-blind.“But nobody wanted to speak out,” Dr. Grunebaum said. “It was like the emperor’s new clothes scenario.”
In his view, embedding skin color scoring into basic data and health care decisions propagates race-based medicine. “It should not be used for White, Black, or brown babies,” he said.
Removing the skin color portion of the Apgar score – and its racial, colorist, and ethnic bias – will provide more accurate and equitable evaluation of newborn babies worldwide, Dr. Grunebaum said.
“I think there’s a pretty good argument to be made that the skin color measure should be eliminated,” agreed Sara E. Edwards, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the University of Illinois Hospital in Chicago, who has also studied Apgar and racial bias in the clinical care of Black babies.
And such clinical bias may soon be illegal in the United States thanks to a proposed new antidiscrimination provision to the Affordable Care Act regarding the use of clinical algorithms in decision-making. The proposed section, § 92.210, states that a covered entity must not discriminate against any individual on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, or disability through clinical algorithms used in decision-making. Hospitals may soon have to alter clinical algorithms in response.
Dr. Grunebaum’s research in the area of clinical racism includes a large 2022 cohort study of almost 10 million mothers and more than 8 million fathers using 2016-2019 natality data from the National Center for Health Statistics, and Division of Vital Statistics. This study found that Black newborns had a less than 50% chance of having a 5-minute Apgar score of 10, compared with White newborns. White babies, both non-Hispanic and Hispanic, had the highest proportion of perfect 10s.
But can the 2-point skin tone indicator be easily replaced? According to Dr. Grunebaum, substituting indicators such as oral mucosa color or oximetry readings are not satisfactory either. “For one thing, oximetry gives different readings in Black [people],” he said.
In her group’s Apgar research, Dr. Edwards found that care providers applied variable and inaccurate scores based on neonatal race – independently of clinical factors and umbilical-cord gas values.
“In Black neonates umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores,” she said. In her view, these inaccuracies point to the existence of colorism and racial bias among health care providers.
Bias ‘creeping in’ to neonatal care
Dr. Edwards’s research was prompted by anecdotal observations that Black babies generally had lower Apgar scores and were more frequently sent to the NICU. “Admission to the NICU can have a negative effect on maternal-child bonding and contribute to PTSD in mothers,” she said.
Her group looked at Apgar scores by race for the year 2019 in an academic hospital cohort of 977 neonates, of whom 56.5% were Black, while controlling for confounding clinical factors.
“Our anecdotal observations of how we score Black neonates were confirmed,” she said. Providers assigned Black babies significantly lower Apgar scores at 1 minute and 5 minutes (odds ratios, .63 and .64) when controlling for umbilical artery gases, gestational age, and maternal-fetal complications.
This difference was specifically associated with lower assigned color Apgar scores at 1 minute (odds ratio, .52). Moreover, full-term Black neonates were sent to neonatal intensive care at higher rates (odds ratio, 1.29) than non-Black neonates when controlling for all the above factors.
Providers applied inaccurate Apgar scores to Black neonates given that the umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores, suggesting that colorism and racial biases do exist among health care providers. “We saw bias creeping in because of subjective decisions about color,” Dr. Edwards said. But by the more objective measure of umbilical-cord gas, Black neonates did not have the abnormal values to support NICU admission. The mean umbilical artery pH was 7.259 for Black vs. 7.256 for non-Black neonates.
The solution may lie in switching to an 8 out of 8 score or looking at other indicators such as the eyes and the nail beds, she said. “Or there may be a way to score skin tone accurately when providers are appropriately trained to do so on neonates of all races, to recognize what a well-perfused skin color looks like in all babies.”
New scoring system needed
Interest in this issue continues. In 2022, a population study was conducted by Emma Gillette, MPH, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues in a cohort of almost 7 million singletons born in 2016-2017.
“We found that overall, Apgar scores were highly associated with mortality across the first year of life,” Ms. Gillette said in an interview. “But non-Hispanic Black infants were more likely to be assigned low Apgar scores compared to White infants, and the odds of death in the first year of life are not as strongly correlated with Apgar scores as in White infants.”
That finding was surprising. “Apgar scores are meant to be an indicator of newborn health and well-being and predictors of infant mortality, and therefore should not vary significantly by race or skin color,” she said. “So I think further study into the component scores of the Apgar score is warranted to try to tease out the reasons behind the differences we’re seeing.”
Ms. Gillette agreed that the skin coloring component of the variable could be inaccurate since variables related to skin color more generally are subjective and difficult to measure. What’s needed is a scoring system that performs equally well across racial groups.
In the meantime, some clinicians may be making practical accommodations. “I hate to tell you, but some people fake the skin score,” said Dr. Grunebaum. “I recently asked a doctor from Ethiopia how they handled it there, and he laughed and said they just automatically give skin color a 2. But faking it is not what you should have to do in medicine.”
Dr. Grunebaum, Dr. Edwards, and Ms. Gillette disclosed no relevant competing interests with respect to their comments.
Experts say overhaul needed
Experts say overhaul needed
In 1952, when Dr. Virginia Apgar developed her 10-point scale for assessing neonates’ health, the U.S. obstetrical anesthesiologst may not have foreseen it would one day become one of the commonest medical tests in the world.
Assigned even before the mother first holds her newborn, the score rapidly evaluates neonates with a score of 0-10, which leads to an algorithm of potential medical interventions. The scale evaluates heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin coloring (typically described as blue body, pink body/blue limbs, or pink body).
“The Apgar is a very important tool used in millions of babies around the world in the very first minute after birth,” said Amos Grunebaum, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and director of perinatal research at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital in Manhattan.
But recently the venerable system has increasingly come under fire for colorism and racial bias, with some calling for an overhaul. That pressure is due to the 2 out of 10 points allotted to an overall “pink” skin tone, a measure that lowers the scores of non-White newborns and may expose them to unnecessary measures such as resuscitation, neonatal intensive care, and intubation.
“This is their first encounter with systemic racism,” said Dr. Grunebaum in an interview. “The score is prejudiced against Black babies because they can’t get perfect scores.”
Propagating ‘race-based medicine’
Concern about racial bias embedded in the Apgar score is not new, Dr. Grunebaum noted.
“Decades ago, when I was doing my training in Brooklyn, the nurses said that using skin color was ridiculous since Black and brown babies couldn’t be pink. And skin color looks different in different lighting. Dr. Apgar herself recognized the problem.”
Furthermore, men see color differently than women do, and some people are actually color-blind.“But nobody wanted to speak out,” Dr. Grunebaum said. “It was like the emperor’s new clothes scenario.”
In his view, embedding skin color scoring into basic data and health care decisions propagates race-based medicine. “It should not be used for White, Black, or brown babies,” he said.
Removing the skin color portion of the Apgar score – and its racial, colorist, and ethnic bias – will provide more accurate and equitable evaluation of newborn babies worldwide, Dr. Grunebaum said.
“I think there’s a pretty good argument to be made that the skin color measure should be eliminated,” agreed Sara E. Edwards, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the University of Illinois Hospital in Chicago, who has also studied Apgar and racial bias in the clinical care of Black babies.
And such clinical bias may soon be illegal in the United States thanks to a proposed new antidiscrimination provision to the Affordable Care Act regarding the use of clinical algorithms in decision-making. The proposed section, § 92.210, states that a covered entity must not discriminate against any individual on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, or disability through clinical algorithms used in decision-making. Hospitals may soon have to alter clinical algorithms in response.
Dr. Grunebaum’s research in the area of clinical racism includes a large 2022 cohort study of almost 10 million mothers and more than 8 million fathers using 2016-2019 natality data from the National Center for Health Statistics, and Division of Vital Statistics. This study found that Black newborns had a less than 50% chance of having a 5-minute Apgar score of 10, compared with White newborns. White babies, both non-Hispanic and Hispanic, had the highest proportion of perfect 10s.
But can the 2-point skin tone indicator be easily replaced? According to Dr. Grunebaum, substituting indicators such as oral mucosa color or oximetry readings are not satisfactory either. “For one thing, oximetry gives different readings in Black [people],” he said.
In her group’s Apgar research, Dr. Edwards found that care providers applied variable and inaccurate scores based on neonatal race – independently of clinical factors and umbilical-cord gas values.
“In Black neonates umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores,” she said. In her view, these inaccuracies point to the existence of colorism and racial bias among health care providers.
Bias ‘creeping in’ to neonatal care
Dr. Edwards’s research was prompted by anecdotal observations that Black babies generally had lower Apgar scores and were more frequently sent to the NICU. “Admission to the NICU can have a negative effect on maternal-child bonding and contribute to PTSD in mothers,” she said.
Her group looked at Apgar scores by race for the year 2019 in an academic hospital cohort of 977 neonates, of whom 56.5% were Black, while controlling for confounding clinical factors.
“Our anecdotal observations of how we score Black neonates were confirmed,” she said. Providers assigned Black babies significantly lower Apgar scores at 1 minute and 5 minutes (odds ratios, .63 and .64) when controlling for umbilical artery gases, gestational age, and maternal-fetal complications.
This difference was specifically associated with lower assigned color Apgar scores at 1 minute (odds ratio, .52). Moreover, full-term Black neonates were sent to neonatal intensive care at higher rates (odds ratio, 1.29) than non-Black neonates when controlling for all the above factors.
Providers applied inaccurate Apgar scores to Black neonates given that the umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores, suggesting that colorism and racial biases do exist among health care providers. “We saw bias creeping in because of subjective decisions about color,” Dr. Edwards said. But by the more objective measure of umbilical-cord gas, Black neonates did not have the abnormal values to support NICU admission. The mean umbilical artery pH was 7.259 for Black vs. 7.256 for non-Black neonates.
The solution may lie in switching to an 8 out of 8 score or looking at other indicators such as the eyes and the nail beds, she said. “Or there may be a way to score skin tone accurately when providers are appropriately trained to do so on neonates of all races, to recognize what a well-perfused skin color looks like in all babies.”
New scoring system needed
Interest in this issue continues. In 2022, a population study was conducted by Emma Gillette, MPH, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues in a cohort of almost 7 million singletons born in 2016-2017.
“We found that overall, Apgar scores were highly associated with mortality across the first year of life,” Ms. Gillette said in an interview. “But non-Hispanic Black infants were more likely to be assigned low Apgar scores compared to White infants, and the odds of death in the first year of life are not as strongly correlated with Apgar scores as in White infants.”
That finding was surprising. “Apgar scores are meant to be an indicator of newborn health and well-being and predictors of infant mortality, and therefore should not vary significantly by race or skin color,” she said. “So I think further study into the component scores of the Apgar score is warranted to try to tease out the reasons behind the differences we’re seeing.”
Ms. Gillette agreed that the skin coloring component of the variable could be inaccurate since variables related to skin color more generally are subjective and difficult to measure. What’s needed is a scoring system that performs equally well across racial groups.
In the meantime, some clinicians may be making practical accommodations. “I hate to tell you, but some people fake the skin score,” said Dr. Grunebaum. “I recently asked a doctor from Ethiopia how they handled it there, and he laughed and said they just automatically give skin color a 2. But faking it is not what you should have to do in medicine.”
Dr. Grunebaum, Dr. Edwards, and Ms. Gillette disclosed no relevant competing interests with respect to their comments.
In 1952, when Dr. Virginia Apgar developed her 10-point scale for assessing neonates’ health, the U.S. obstetrical anesthesiologst may not have foreseen it would one day become one of the commonest medical tests in the world.
Assigned even before the mother first holds her newborn, the score rapidly evaluates neonates with a score of 0-10, which leads to an algorithm of potential medical interventions. The scale evaluates heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin coloring (typically described as blue body, pink body/blue limbs, or pink body).
“The Apgar is a very important tool used in millions of babies around the world in the very first minute after birth,” said Amos Grunebaum, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and director of perinatal research at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital in Manhattan.
But recently the venerable system has increasingly come under fire for colorism and racial bias, with some calling for an overhaul. That pressure is due to the 2 out of 10 points allotted to an overall “pink” skin tone, a measure that lowers the scores of non-White newborns and may expose them to unnecessary measures such as resuscitation, neonatal intensive care, and intubation.
“This is their first encounter with systemic racism,” said Dr. Grunebaum in an interview. “The score is prejudiced against Black babies because they can’t get perfect scores.”
Propagating ‘race-based medicine’
Concern about racial bias embedded in the Apgar score is not new, Dr. Grunebaum noted.
“Decades ago, when I was doing my training in Brooklyn, the nurses said that using skin color was ridiculous since Black and brown babies couldn’t be pink. And skin color looks different in different lighting. Dr. Apgar herself recognized the problem.”
Furthermore, men see color differently than women do, and some people are actually color-blind.“But nobody wanted to speak out,” Dr. Grunebaum said. “It was like the emperor’s new clothes scenario.”
In his view, embedding skin color scoring into basic data and health care decisions propagates race-based medicine. “It should not be used for White, Black, or brown babies,” he said.
Removing the skin color portion of the Apgar score – and its racial, colorist, and ethnic bias – will provide more accurate and equitable evaluation of newborn babies worldwide, Dr. Grunebaum said.
“I think there’s a pretty good argument to be made that the skin color measure should be eliminated,” agreed Sara E. Edwards, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the University of Illinois Hospital in Chicago, who has also studied Apgar and racial bias in the clinical care of Black babies.
And such clinical bias may soon be illegal in the United States thanks to a proposed new antidiscrimination provision to the Affordable Care Act regarding the use of clinical algorithms in decision-making. The proposed section, § 92.210, states that a covered entity must not discriminate against any individual on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, or disability through clinical algorithms used in decision-making. Hospitals may soon have to alter clinical algorithms in response.
Dr. Grunebaum’s research in the area of clinical racism includes a large 2022 cohort study of almost 10 million mothers and more than 8 million fathers using 2016-2019 natality data from the National Center for Health Statistics, and Division of Vital Statistics. This study found that Black newborns had a less than 50% chance of having a 5-minute Apgar score of 10, compared with White newborns. White babies, both non-Hispanic and Hispanic, had the highest proportion of perfect 10s.
But can the 2-point skin tone indicator be easily replaced? According to Dr. Grunebaum, substituting indicators such as oral mucosa color or oximetry readings are not satisfactory either. “For one thing, oximetry gives different readings in Black [people],” he said.
In her group’s Apgar research, Dr. Edwards found that care providers applied variable and inaccurate scores based on neonatal race – independently of clinical factors and umbilical-cord gas values.
“In Black neonates umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores,” she said. In her view, these inaccuracies point to the existence of colorism and racial bias among health care providers.
Bias ‘creeping in’ to neonatal care
Dr. Edwards’s research was prompted by anecdotal observations that Black babies generally had lower Apgar scores and were more frequently sent to the NICU. “Admission to the NICU can have a negative effect on maternal-child bonding and contribute to PTSD in mothers,” she said.
Her group looked at Apgar scores by race for the year 2019 in an academic hospital cohort of 977 neonates, of whom 56.5% were Black, while controlling for confounding clinical factors.
“Our anecdotal observations of how we score Black neonates were confirmed,” she said. Providers assigned Black babies significantly lower Apgar scores at 1 minute and 5 minutes (odds ratios, .63 and .64) when controlling for umbilical artery gases, gestational age, and maternal-fetal complications.
This difference was specifically associated with lower assigned color Apgar scores at 1 minute (odds ratio, .52). Moreover, full-term Black neonates were sent to neonatal intensive care at higher rates (odds ratio, 1.29) than non-Black neonates when controlling for all the above factors.
Providers applied inaccurate Apgar scores to Black neonates given that the umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores, suggesting that colorism and racial biases do exist among health care providers. “We saw bias creeping in because of subjective decisions about color,” Dr. Edwards said. But by the more objective measure of umbilical-cord gas, Black neonates did not have the abnormal values to support NICU admission. The mean umbilical artery pH was 7.259 for Black vs. 7.256 for non-Black neonates.
The solution may lie in switching to an 8 out of 8 score or looking at other indicators such as the eyes and the nail beds, she said. “Or there may be a way to score skin tone accurately when providers are appropriately trained to do so on neonates of all races, to recognize what a well-perfused skin color looks like in all babies.”
New scoring system needed
Interest in this issue continues. In 2022, a population study was conducted by Emma Gillette, MPH, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues in a cohort of almost 7 million singletons born in 2016-2017.
“We found that overall, Apgar scores were highly associated with mortality across the first year of life,” Ms. Gillette said in an interview. “But non-Hispanic Black infants were more likely to be assigned low Apgar scores compared to White infants, and the odds of death in the first year of life are not as strongly correlated with Apgar scores as in White infants.”
That finding was surprising. “Apgar scores are meant to be an indicator of newborn health and well-being and predictors of infant mortality, and therefore should not vary significantly by race or skin color,” she said. “So I think further study into the component scores of the Apgar score is warranted to try to tease out the reasons behind the differences we’re seeing.”
Ms. Gillette agreed that the skin coloring component of the variable could be inaccurate since variables related to skin color more generally are subjective and difficult to measure. What’s needed is a scoring system that performs equally well across racial groups.
In the meantime, some clinicians may be making practical accommodations. “I hate to tell you, but some people fake the skin score,” said Dr. Grunebaum. “I recently asked a doctor from Ethiopia how they handled it there, and he laughed and said they just automatically give skin color a 2. But faking it is not what you should have to do in medicine.”
Dr. Grunebaum, Dr. Edwards, and Ms. Gillette disclosed no relevant competing interests with respect to their comments.
Racial Disparities in Hidradenitis Suppurativa–Related Pain: A Cross-sectional Analysis
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic inflammatory disease that is characterized by tender inflamed nodules of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, disproportionately affects postpubertal females as well as Black/African American individuals. The nodules can rupture, form sinus tracts, and scar. 1 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, depression, suicide, and substance use disorders. Because of the symptom burden and associated conditions, HS can be a painful and distressing disease that substantially impairs the quality of life for individuals with this condition. 2
Pain is a commonly reported symptom in HS that often goes untreated. Furthermore, HS-related pain is complex due to the involvement of different pain types that require various treatment modalities.3 According to Savage et al,4 recognizing whether HS-related pain is acute, chronic, neuropathic, or nociceptive is vital in establishing a framework for an effective pain management scheme. Currently, such established multimodal pain management strategies in dermatology do not exist. In 2021, dermatology-specific pain management strategies proposed the use of a multimodal regimen to address the multifaceted nature of HS-related pain.4 However, these strategies failed to recognize the systemic racial and ethnic biases in the US health care system that undermine pain management care for minority groups.5,6 One approach to combatting racial disparities in pain management is determining average pain levels across racial groups.7 This study sought to compare HS-related pain scores by racial groups. Furthermore, we assessed differences in perception of patients’ respective pain management regimens by race. We hypothesized that the average HS-related pain intensities and pain management would differ between self-reported racial groups.
Methods
This cross-sectional study took place over 5 months (August through December 2021). A survey was emailed to 2198 adult patients with HS in the University of Alabama Health System. The survey consisted of demographic and general questions about a patient’s HS. Pain scores were captured using the numeric rating scale (NRS), a measurement tool for pain intensity on a scale from 0 to 10. 8 Age at diagnosis, gender, education level, household income, total body areas affected by HS, disease severity (categorized as mild, moderate, and severe), comorbidities including mood disorders, tobacco use, and HS and HS-related pain medication regimens also were collected. Additionally, participants were asked about their level of agreement with the following statements: “I am satisfied with how my pain related to HS is being managed by my doctors” and “My pain related to HS is under control.” The level of agreement was measured using a 5-point Likert scale, with responses ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree. All data included in the analysis were self-reported. The study received institutional review board approval for the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were used to assess statistical differences in patient characteristics of Black/African American participants compared to other participants, including White, Asian, and Hispanic/Latino participants. Thirteen participants were excluded from the final analysis: 2 participants were missing data, and 11 biracial participants were excluded due to overlapping White and Black/African American races that may have confounded the analysis. Categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages, and χ2 and Fisher exact tests, when necessary, were used to test for statistically significant differences. Continuous variables were summarized with means and standard deviations, and a t test was used for statistically significant differences.
Logistic regression was performed to assess the relationship between race and pain after adjusting for confounding variables such as obesity, current tobacco use, self-reported HS severity, and the presence of comorbidities. A total of 204 patient records were included in the analysis, of which 70 (34.3%) had a pain score of 8 or higher, which indicates very severe pain intensity levels on the NRS,8 and were selected as a cut point based on the distribution of responses. For this cross-sectional cohort, our approach was to compare characteristics of those classified with a top score of 8 or higher (n=70) vs a top score of 0 to 7 (n=134)(cases vs noncases). Statistical analyses were performed using JMP Pro 16 (JMP Statistical Discovery LLC) at an α=.05 significance level; logistic regression was performed using SPSS Statistics (IBM). For the logistic regression, we grouped patient race into 2 categories: Black/African American and Other, which included White, Asian, and Hispanic/Latino participants.
Crude and adjusted multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to calculate prevalence odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals. Covariate inclusion in the multivariable logistic regression was based on a priori hypothesis/knowledge and was meant to estimate the independent effect of race after adjustment for income, HS severity, and history of prescription pain medication use. Other variables, including tobacco use, obesity, mood disorders, and current HS treatments, were all individually tested in the multivariate analysis and did not significantly impact the odds ratio for high pain. Statistical adjustment slightly decreased (19%) the magnitude between crude and adjusted prevalence odds ratios for the association between Black/African American race and high pain score.
Results
Survey Demographics —The final analysis included 204 survey respondents. Most respondents were Black/African American (58.82%), and nearly all were female (89.71%)(Table 1). The mean age (SD) of respondents was 37.37 (11.29) years (range, 19-70 years). Many respondents reported having completed some college (36.27%) or receiving a bachelor’s degree (19.12%). Of patients who were not Black/African American, 10.71% had higher than a master’s degree, whereas no Black/African American patients held a degree higher than a master’s ( P = .0052). Additionally, more Black/African American respondents (35.83%) reported an annual household income level of less than $25,000 compared with respondents who were not Black/African American (19.05%, P = .0001). Most respondents rated the severity of their HS as moderate or severe (46.57% and 41.67%, respectively), and there was no significant difference in reported severity of HS between racial groups ( P = .5395).


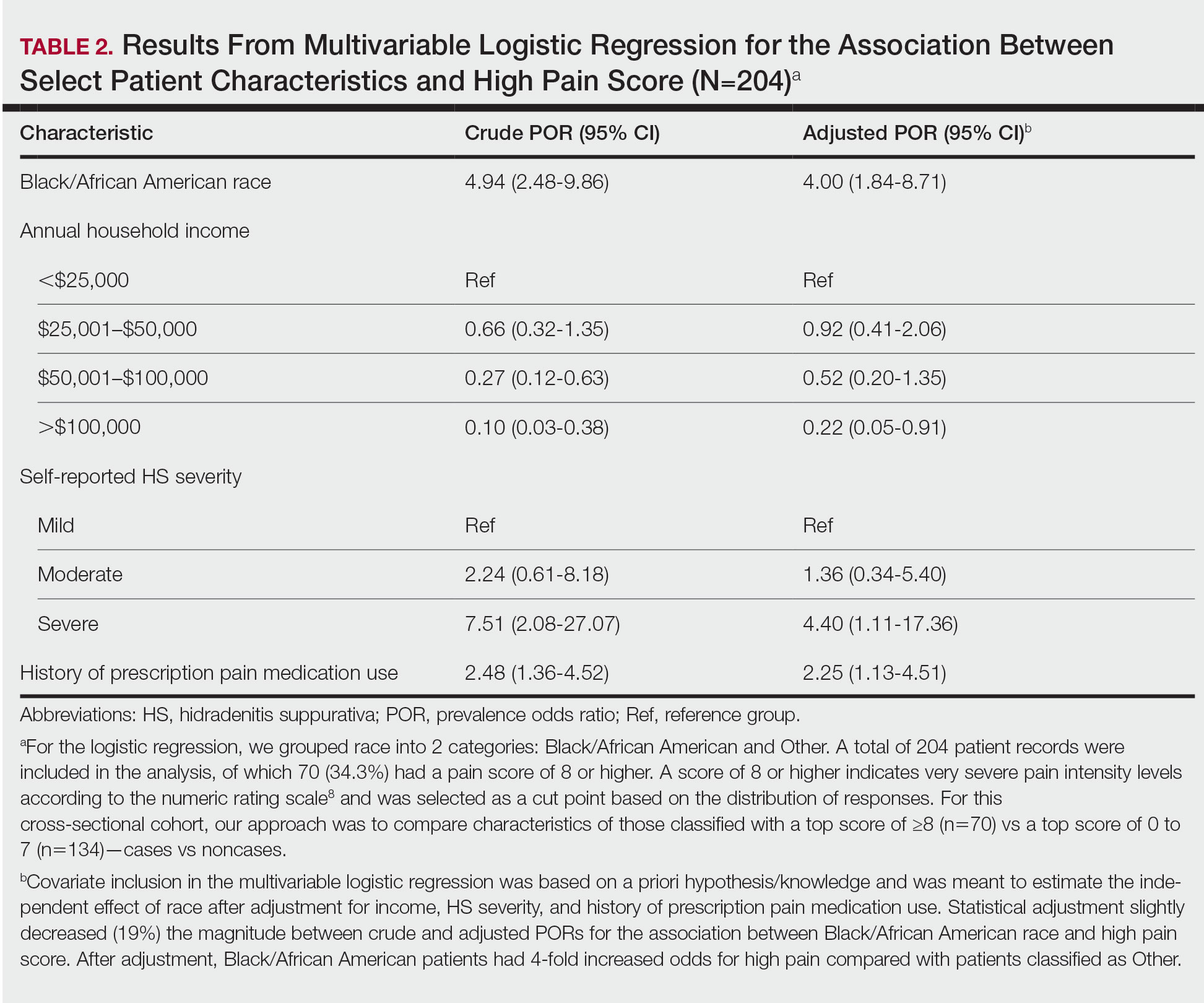
Pain Scores—As documented in the Methods, respondents were asked to rate their HS-related pain intensity from 0 to 10 using the NRS. The average pain score (SD)—the level of pain intensity over the prior month—was 6.39 (2.56)(range, 0–10). The mean pain score (SD) at the time of the survey was 3.61 (2.98)(range, 0–10)(Table 1). These data revealed that Black/African American patients had a significantly higher average pain score (SD) than patients with HS who were not Black/African American (7.08 [2.49] and 5.40 [2.35], respectively; P<.0001). After adjustment with multivariable logistical regression, Black/African American patients had 4-fold increased odds for very severe levels of pain (score of ≥8) compared with patients who were not Black/African American.
Pain Management—Although pain scores were higher for Black/African American patients with HS, there was no significant difference in the perception of pain control between racial groups (P=.0761). Additionally, we found low income (adjusted prevalence odds ratio [POR], 0.22; 95% CI, 0.05-0.91), a history of prescription pain medication use (adjusted POR, 2.25; 95% CI, 1.13-4.51), and HS severity (adjusted POR, 4.40; 95% CI, 1.11-17.36) all to be independent risk factors contributing to higher pain scores in patients with HS (Table 2). Lastly, we noted current or reported history of pain medication use was significantly correlated with higher pain scores (P=.0280 and P=.0213, respectively).
Satisfaction With Pain Management—The level of satisfaction with physician management of HS-related pain was significantly different between Black/African American patients and those who were not Black/African American (P=.0129). Of those who identified as Black/African American, 26.7% (n=32) strongly disagreed with the statement, “I am satisfied with how my pain related to HS is being managed by my doctors,” whereas only 15.5% (n=13) of patients who were not Black/African American strongly disagreed.
Comment
There is no cure for HS, and a large focus of treatment is pain management. Because racial disparities in the treatment of chronic pain will affect those with HS, we conducted a cross-sectional analysis of pain and pain management among HS patients. We found that Black/African American patients with HS have higher average pain scores than those who are not Black/African American and were 4 times more likely to experience very severe pain. Prior studies have established that patients with HS often report higher pain levels than patients with other chronic inflammatory skin conditions, 7,8 and our study identified racial disparities in HS-related pain management.
Measuring pain is challenging because of its multidimensional and subjective nature, making it essential to consider underlying causes and patients’ emotional responses to pain.9 By adjusting for confounding factors that may influence pain, such as mood disorders, disease severity, comorbidities, and medication use, we were able to gain better insight into fundamental differences in average pain intensity levels among racial groups and assess what factors may be contributing to a patient’s pain perception. Our study determined that lower income levels, higher HS disease severity, and a history of prescription pain medication use were all independent risk factors for high pain. Of note, obesity, tobacco use, and mood disorders such as anxiety and depression did not significantly differ between racial groups or increase the odds of high pain between racial groups identified.
With low income being an independent risk factor for high pain, we must consider the social determinants of health and how they may influence the pain experience in HS. We speculate that low income may be associated with other social determinants of health for the patients assessed in this study, such as lack of social and community support or limited health care access that contribute to worse health outcomes.10,11 In addition, low income contributes to limited access to medical care or treatments12; without access to effective HS management, lower-income patients may be at risk for higher disease severity and thus higher pain levels. However, economic stability is only a part of the whole picture; therefore, assessing the other social determinants of health in patients with HS may lead to better health outcomes and quality of life.
Another identified risk factor for high pain was a reported history of prescription pain medication use. This finding suggests that patients with moderate to severe pain likely have required stronger analgesic medications in the past. We further speculate that high pain levels in patients who have received prescription pain medications indicate either undertreatment, mistreatment, or recalcitrant pain. More research is needed to assess the relationship between HS-related pain intensity, analgesic medications, and providers who manage HS-related pain.
We also found that Black/African American patients with HS had a significantly higher dissatisfaction with their physician’s management of their pain, which could be attributable to several factors, including biological differences in medication metabolism (in which the patient has medication-resistant HS), undertreatment of pain, and/or poor doctor-patient relations. These reasons coincide with other diseases where health disparities are found.13-15 Recognizing these factors will be key to dismantling the disparities in HS that are noted within this study. The limitations of this work include the cross-sectional study design and its inability to evaluate causal factors of high pain levels across racial groups, the NRS lack of insight on pain chronicity or pain experience,7 the lack of provider or institution perspectives, and self-reported data. Additionally, only patients with email access were included, which may have excluded vulnerable populations with more pain associated with their HS.
Our findings highlight an area for further investigation to assess why these racial differences exist in HS-related pain. The results also emphasize the need for research evaluating whether systemic or health care provider biases contribute to racial differences in HS-related pain management.
Acknowledgment — Dr. Weir was supported by the Predoctoral Clinical/Translational Research Program (TL1), a National Institutes of Health Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA), through the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCTS).
- Garg A, Kirby JS, Lavian J, et al. Sex- and age-adjusted population analysis of prevalence estimates for hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760-764. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.0201
- Nguyen TV, Damiani G, Orenstein LAV, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on epidemiology, phenotypes, diagnosis, pathogenesis, comorbidities and quality of life. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:50-61. doi:10.1111/jdv.16677
- Krajewski PK, Matusiak Ł, von Stebut E, et al. Pain in hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross-sectional study of 1,795 patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00364. doi:10.2340/00015555-3724
- Savage KT, Singh V, Patel ZS, et al. Pain management in hidradenitis suppurativa and a proposed treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:187-199. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.039
- Morales ME, Yong RJ. Racial and ethnic disparities in the treatment of chronic pain. Pain Med. 2021;22:75-90. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa427
- US Department of Health and Human Services. 2019 National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report. December 2020. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/research/findings/nhqrdr/2019qdr.pdf
- Hoffman KM, Trawalter S, Axt JR, et al. Racial bias in pain assessment and treatment recommendations, and false beliefs about biological differences between blacks and whites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:4296-4301. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516047113
- Patel ZS, Hoffman LK, Buse DC, et al. Pain, psychological comorbidities, disability, and impaired quality of life in hidradenitis suppurativa. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017;21:49. doi:10.1007/s11916-017-0647-3. Published correction appears in Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017;21:52.
- McDowell I. Pain measurements. In: Measuring Health: A Guide to Rating Scales and Questionnaires. Oxford University Press; 2006:477-478.
- Singh GK, Daus GP, Allender M, et al. Social determinants of health in the United States: addressing major health inequality trends for the nation, 1935-2016. Int J MCH AIDS. 2017;6:139-164. doi:10.21106/ijma.236
- Sulley S, Bayssie M. Social determinants of health: an evaluation of risk factors associated with inpatient presentations in the United States. Cureus. 2021;13:E13287. doi:10.7759/cureus.13287
- Lazar M, Davenport L. Barriers to health care access for low income families: a review of literature. J Community Health Nurs. 2018;35:28-37. doi:10.1080/07370016.2018.1404832
- Ghoshal M, Shapiro H, Todd K, et al. Chronic noncancer pain management and systemic racism: time to move toward equal care standards.J Pain Res. 2020;13:2825-2836. doi:10.214/JPR.S287314
- Cintron A, Morrison RS. Pain and ethnicity in the United States: a systematic review. J Palliat Med. 2006;9:1454-1473. doi:10.1089/jpm.2006.9.1454
- Green CR, Anderson KO, Baker TA, et al. The unequal burden of pain: confronting racial and ethnic disparities in pain. Pain Med. 2003;4:277-294. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4637.2003.03034.x. Published correction appears in Pain Med. 2005;6:99.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic inflammatory disease that is characterized by tender inflamed nodules of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, disproportionately affects postpubertal females as well as Black/African American individuals. The nodules can rupture, form sinus tracts, and scar. 1 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, depression, suicide, and substance use disorders. Because of the symptom burden and associated conditions, HS can be a painful and distressing disease that substantially impairs the quality of life for individuals with this condition. 2
Pain is a commonly reported symptom in HS that often goes untreated. Furthermore, HS-related pain is complex due to the involvement of different pain types that require various treatment modalities.3 According to Savage et al,4 recognizing whether HS-related pain is acute, chronic, neuropathic, or nociceptive is vital in establishing a framework for an effective pain management scheme. Currently, such established multimodal pain management strategies in dermatology do not exist. In 2021, dermatology-specific pain management strategies proposed the use of a multimodal regimen to address the multifaceted nature of HS-related pain.4 However, these strategies failed to recognize the systemic racial and ethnic biases in the US health care system that undermine pain management care for minority groups.5,6 One approach to combatting racial disparities in pain management is determining average pain levels across racial groups.7 This study sought to compare HS-related pain scores by racial groups. Furthermore, we assessed differences in perception of patients’ respective pain management regimens by race. We hypothesized that the average HS-related pain intensities and pain management would differ between self-reported racial groups.
Methods
This cross-sectional study took place over 5 months (August through December 2021). A survey was emailed to 2198 adult patients with HS in the University of Alabama Health System. The survey consisted of demographic and general questions about a patient’s HS. Pain scores were captured using the numeric rating scale (NRS), a measurement tool for pain intensity on a scale from 0 to 10. 8 Age at diagnosis, gender, education level, household income, total body areas affected by HS, disease severity (categorized as mild, moderate, and severe), comorbidities including mood disorders, tobacco use, and HS and HS-related pain medication regimens also were collected. Additionally, participants were asked about their level of agreement with the following statements: “I am satisfied with how my pain related to HS is being managed by my doctors” and “My pain related to HS is under control.” The level of agreement was measured using a 5-point Likert scale, with responses ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree. All data included in the analysis were self-reported. The study received institutional review board approval for the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were used to assess statistical differences in patient characteristics of Black/African American participants compared to other participants, including White, Asian, and Hispanic/Latino participants. Thirteen participants were excluded from the final analysis: 2 participants were missing data, and 11 biracial participants were excluded due to overlapping White and Black/African American races that may have confounded the analysis. Categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages, and χ2 and Fisher exact tests, when necessary, were used to test for statistically significant differences. Continuous variables were summarized with means and standard deviations, and a t test was used for statistically significant differences.
Logistic regression was performed to assess the relationship between race and pain after adjusting for confounding variables such as obesity, current tobacco use, self-reported HS severity, and the presence of comorbidities. A total of 204 patient records were included in the analysis, of which 70 (34.3%) had a pain score of 8 or higher, which indicates very severe pain intensity levels on the NRS,8 and were selected as a cut point based on the distribution of responses. For this cross-sectional cohort, our approach was to compare characteristics of those classified with a top score of 8 or higher (n=70) vs a top score of 0 to 7 (n=134)(cases vs noncases). Statistical analyses were performed using JMP Pro 16 (JMP Statistical Discovery LLC) at an α=.05 significance level; logistic regression was performed using SPSS Statistics (IBM). For the logistic regression, we grouped patient race into 2 categories: Black/African American and Other, which included White, Asian, and Hispanic/Latino participants.
Crude and adjusted multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to calculate prevalence odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals. Covariate inclusion in the multivariable logistic regression was based on a priori hypothesis/knowledge and was meant to estimate the independent effect of race after adjustment for income, HS severity, and history of prescription pain medication use. Other variables, including tobacco use, obesity, mood disorders, and current HS treatments, were all individually tested in the multivariate analysis and did not significantly impact the odds ratio for high pain. Statistical adjustment slightly decreased (19%) the magnitude between crude and adjusted prevalence odds ratios for the association between Black/African American race and high pain score.
Results
Survey Demographics —The final analysis included 204 survey respondents. Most respondents were Black/African American (58.82%), and nearly all were female (89.71%)(Table 1). The mean age (SD) of respondents was 37.37 (11.29) years (range, 19-70 years). Many respondents reported having completed some college (36.27%) or receiving a bachelor’s degree (19.12%). Of patients who were not Black/African American, 10.71% had higher than a master’s degree, whereas no Black/African American patients held a degree higher than a master’s ( P = .0052). Additionally, more Black/African American respondents (35.83%) reported an annual household income level of less than $25,000 compared with respondents who were not Black/African American (19.05%, P = .0001). Most respondents rated the severity of their HS as moderate or severe (46.57% and 41.67%, respectively), and there was no significant difference in reported severity of HS between racial groups ( P = .5395).


Pain Scores—As documented in the Methods, respondents were asked to rate their HS-related pain intensity from 0 to 10 using the NRS. The average pain score (SD)—the level of pain intensity over the prior month—was 6.39 (2.56)(range, 0–10). The mean pain score (SD) at the time of the survey was 3.61 (2.98)(range, 0–10)(Table 1). These data revealed that Black/African American patients had a significantly higher average pain score (SD) than patients with HS who were not Black/African American (7.08 [2.49] and 5.40 [2.35], respectively; P<.0001). After adjustment with multivariable logistical regression, Black/African American patients had 4-fold increased odds for very severe levels of pain (score of ≥8) compared with patients who were not Black/African American.
Pain Management—Although pain scores were higher for Black/African American patients with HS, there was no significant difference in the perception of pain control between racial groups (P=.0761). Additionally, we found low income (adjusted prevalence odds ratio [POR], 0.22; 95% CI, 0.05-0.91), a history of prescription pain medication use (adjusted POR, 2.25; 95% CI, 1.13-4.51), and HS severity (adjusted POR, 4.40; 95% CI, 1.11-17.36) all to be independent risk factors contributing to higher pain scores in patients with HS (Table 2). Lastly, we noted current or reported history of pain medication use was significantly correlated with higher pain scores (P=.0280 and P=.0213, respectively).

Satisfaction With Pain Management—The level of satisfaction with physician management of HS-related pain was significantly different between Black/African American patients and those who were not Black/African American (P=.0129). Of those who identified as Black/African American, 26.7% (n=32) strongly disagreed with the statement, “I am satisfied with how my pain related to HS is being managed by my doctors,” whereas only 15.5% (n=13) of patients who were not Black/African American strongly disagreed.
Comment
There is no cure for HS, and a large focus of treatment is pain management. Because racial disparities in the treatment of chronic pain will affect those with HS, we conducted a cross-sectional analysis of pain and pain management among HS patients. We found that Black/African American patients with HS have higher average pain scores than those who are not Black/African American and were 4 times more likely to experience very severe pain. Prior studies have established that patients with HS often report higher pain levels than patients with other chronic inflammatory skin conditions, 7,8 and our study identified racial disparities in HS-related pain management.
Measuring pain is challenging because of its multidimensional and subjective nature, making it essential to consider underlying causes and patients’ emotional responses to pain.9 By adjusting for confounding factors that may influence pain, such as mood disorders, disease severity, comorbidities, and medication use, we were able to gain better insight into fundamental differences in average pain intensity levels among racial groups and assess what factors may be contributing to a patient’s pain perception. Our study determined that lower income levels, higher HS disease severity, and a history of prescription pain medication use were all independent risk factors for high pain. Of note, obesity, tobacco use, and mood disorders such as anxiety and depression did not significantly differ between racial groups or increase the odds of high pain between racial groups identified.
With low income being an independent risk factor for high pain, we must consider the social determinants of health and how they may influence the pain experience in HS. We speculate that low income may be associated with other social determinants of health for the patients assessed in this study, such as lack of social and community support or limited health care access that contribute to worse health outcomes.10,11 In addition, low income contributes to limited access to medical care or treatments12; without access to effective HS management, lower-income patients may be at risk for higher disease severity and thus higher pain levels. However, economic stability is only a part of the whole picture; therefore, assessing the other social determinants of health in patients with HS may lead to better health outcomes and quality of life.
Another identified risk factor for high pain was a reported history of prescription pain medication use. This finding suggests that patients with moderate to severe pain likely have required stronger analgesic medications in the past. We further speculate that high pain levels in patients who have received prescription pain medications indicate either undertreatment, mistreatment, or recalcitrant pain. More research is needed to assess the relationship between HS-related pain intensity, analgesic medications, and providers who manage HS-related pain.
We also found that Black/African American patients with HS had a significantly higher dissatisfaction with their physician’s management of their pain, which could be attributable to several factors, including biological differences in medication metabolism (in which the patient has medication-resistant HS), undertreatment of pain, and/or poor doctor-patient relations. These reasons coincide with other diseases where health disparities are found.13-15 Recognizing these factors will be key to dismantling the disparities in HS that are noted within this study. The limitations of this work include the cross-sectional study design and its inability to evaluate causal factors of high pain levels across racial groups, the NRS lack of insight on pain chronicity or pain experience,7 the lack of provider or institution perspectives, and self-reported data. Additionally, only patients with email access were included, which may have excluded vulnerable populations with more pain associated with their HS.
Our findings highlight an area for further investigation to assess why these racial differences exist in HS-related pain. The results also emphasize the need for research evaluating whether systemic or health care provider biases contribute to racial differences in HS-related pain management.
Acknowledgment — Dr. Weir was supported by the Predoctoral Clinical/Translational Research Program (TL1), a National Institutes of Health Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA), through the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCTS).
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic inflammatory disease that is characterized by tender inflamed nodules of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, disproportionately affects postpubertal females as well as Black/African American individuals. The nodules can rupture, form sinus tracts, and scar. 1 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, depression, suicide, and substance use disorders. Because of the symptom burden and associated conditions, HS can be a painful and distressing disease that substantially impairs the quality of life for individuals with this condition. 2
Pain is a commonly reported symptom in HS that often goes untreated. Furthermore, HS-related pain is complex due to the involvement of different pain types that require various treatment modalities.3 According to Savage et al,4 recognizing whether HS-related pain is acute, chronic, neuropathic, or nociceptive is vital in establishing a framework for an effective pain management scheme. Currently, such established multimodal pain management strategies in dermatology do not exist. In 2021, dermatology-specific pain management strategies proposed the use of a multimodal regimen to address the multifaceted nature of HS-related pain.4 However, these strategies failed to recognize the systemic racial and ethnic biases in the US health care system that undermine pain management care for minority groups.5,6 One approach to combatting racial disparities in pain management is determining average pain levels across racial groups.7 This study sought to compare HS-related pain scores by racial groups. Furthermore, we assessed differences in perception of patients’ respective pain management regimens by race. We hypothesized that the average HS-related pain intensities and pain management would differ between self-reported racial groups.
Methods
This cross-sectional study took place over 5 months (August through December 2021). A survey was emailed to 2198 adult patients with HS in the University of Alabama Health System. The survey consisted of demographic and general questions about a patient’s HS. Pain scores were captured using the numeric rating scale (NRS), a measurement tool for pain intensity on a scale from 0 to 10. 8 Age at diagnosis, gender, education level, household income, total body areas affected by HS, disease severity (categorized as mild, moderate, and severe), comorbidities including mood disorders, tobacco use, and HS and HS-related pain medication regimens also were collected. Additionally, participants were asked about their level of agreement with the following statements: “I am satisfied with how my pain related to HS is being managed by my doctors” and “My pain related to HS is under control.” The level of agreement was measured using a 5-point Likert scale, with responses ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree. All data included in the analysis were self-reported. The study received institutional review board approval for the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were used to assess statistical differences in patient characteristics of Black/African American participants compared to other participants, including White, Asian, and Hispanic/Latino participants. Thirteen participants were excluded from the final analysis: 2 participants were missing data, and 11 biracial participants were excluded due to overlapping White and Black/African American races that may have confounded the analysis. Categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages, and χ2 and Fisher exact tests, when necessary, were used to test for statistically significant differences. Continuous variables were summarized with means and standard deviations, and a t test was used for statistically significant differences.
Logistic regression was performed to assess the relationship between race and pain after adjusting for confounding variables such as obesity, current tobacco use, self-reported HS severity, and the presence of comorbidities. A total of 204 patient records were included in the analysis, of which 70 (34.3%) had a pain score of 8 or higher, which indicates very severe pain intensity levels on the NRS,8 and were selected as a cut point based on the distribution of responses. For this cross-sectional cohort, our approach was to compare characteristics of those classified with a top score of 8 or higher (n=70) vs a top score of 0 to 7 (n=134)(cases vs noncases). Statistical analyses were performed using JMP Pro 16 (JMP Statistical Discovery LLC) at an α=.05 significance level; logistic regression was performed using SPSS Statistics (IBM). For the logistic regression, we grouped patient race into 2 categories: Black/African American and Other, which included White, Asian, and Hispanic/Latino participants.
Crude and adjusted multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to calculate prevalence odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals. Covariate inclusion in the multivariable logistic regression was based on a priori hypothesis/knowledge and was meant to estimate the independent effect of race after adjustment for income, HS severity, and history of prescription pain medication use. Other variables, including tobacco use, obesity, mood disorders, and current HS treatments, were all individually tested in the multivariate analysis and did not significantly impact the odds ratio for high pain. Statistical adjustment slightly decreased (19%) the magnitude between crude and adjusted prevalence odds ratios for the association between Black/African American race and high pain score.
Results
Survey Demographics —The final analysis included 204 survey respondents. Most respondents were Black/African American (58.82%), and nearly all were female (89.71%)(Table 1). The mean age (SD) of respondents was 37.37 (11.29) years (range, 19-70 years). Many respondents reported having completed some college (36.27%) or receiving a bachelor’s degree (19.12%). Of patients who were not Black/African American, 10.71% had higher than a master’s degree, whereas no Black/African American patients held a degree higher than a master’s ( P = .0052). Additionally, more Black/African American respondents (35.83%) reported an annual household income level of less than $25,000 compared with respondents who were not Black/African American (19.05%, P = .0001). Most respondents rated the severity of their HS as moderate or severe (46.57% and 41.67%, respectively), and there was no significant difference in reported severity of HS between racial groups ( P = .5395).


Pain Scores—As documented in the Methods, respondents were asked to rate their HS-related pain intensity from 0 to 10 using the NRS. The average pain score (SD)—the level of pain intensity over the prior month—was 6.39 (2.56)(range, 0–10). The mean pain score (SD) at the time of the survey was 3.61 (2.98)(range, 0–10)(Table 1). These data revealed that Black/African American patients had a significantly higher average pain score (SD) than patients with HS who were not Black/African American (7.08 [2.49] and 5.40 [2.35], respectively; P<.0001). After adjustment with multivariable logistical regression, Black/African American patients had 4-fold increased odds for very severe levels of pain (score of ≥8) compared with patients who were not Black/African American.
Pain Management—Although pain scores were higher for Black/African American patients with HS, there was no significant difference in the perception of pain control between racial groups (P=.0761). Additionally, we found low income (adjusted prevalence odds ratio [POR], 0.22; 95% CI, 0.05-0.91), a history of prescription pain medication use (adjusted POR, 2.25; 95% CI, 1.13-4.51), and HS severity (adjusted POR, 4.40; 95% CI, 1.11-17.36) all to be independent risk factors contributing to higher pain scores in patients with HS (Table 2). Lastly, we noted current or reported history of pain medication use was significantly correlated with higher pain scores (P=.0280 and P=.0213, respectively).

Satisfaction With Pain Management—The level of satisfaction with physician management of HS-related pain was significantly different between Black/African American patients and those who were not Black/African American (P=.0129). Of those who identified as Black/African American, 26.7% (n=32) strongly disagreed with the statement, “I am satisfied with how my pain related to HS is being managed by my doctors,” whereas only 15.5% (n=13) of patients who were not Black/African American strongly disagreed.
Comment
There is no cure for HS, and a large focus of treatment is pain management. Because racial disparities in the treatment of chronic pain will affect those with HS, we conducted a cross-sectional analysis of pain and pain management among HS patients. We found that Black/African American patients with HS have higher average pain scores than those who are not Black/African American and were 4 times more likely to experience very severe pain. Prior studies have established that patients with HS often report higher pain levels than patients with other chronic inflammatory skin conditions, 7,8 and our study identified racial disparities in HS-related pain management.
Measuring pain is challenging because of its multidimensional and subjective nature, making it essential to consider underlying causes and patients’ emotional responses to pain.9 By adjusting for confounding factors that may influence pain, such as mood disorders, disease severity, comorbidities, and medication use, we were able to gain better insight into fundamental differences in average pain intensity levels among racial groups and assess what factors may be contributing to a patient’s pain perception. Our study determined that lower income levels, higher HS disease severity, and a history of prescription pain medication use were all independent risk factors for high pain. Of note, obesity, tobacco use, and mood disorders such as anxiety and depression did not significantly differ between racial groups or increase the odds of high pain between racial groups identified.
With low income being an independent risk factor for high pain, we must consider the social determinants of health and how they may influence the pain experience in HS. We speculate that low income may be associated with other social determinants of health for the patients assessed in this study, such as lack of social and community support or limited health care access that contribute to worse health outcomes.10,11 In addition, low income contributes to limited access to medical care or treatments12; without access to effective HS management, lower-income patients may be at risk for higher disease severity and thus higher pain levels. However, economic stability is only a part of the whole picture; therefore, assessing the other social determinants of health in patients with HS may lead to better health outcomes and quality of life.
Another identified risk factor for high pain was a reported history of prescription pain medication use. This finding suggests that patients with moderate to severe pain likely have required stronger analgesic medications in the past. We further speculate that high pain levels in patients who have received prescription pain medications indicate either undertreatment, mistreatment, or recalcitrant pain. More research is needed to assess the relationship between HS-related pain intensity, analgesic medications, and providers who manage HS-related pain.
We also found that Black/African American patients with HS had a significantly higher dissatisfaction with their physician’s management of their pain, which could be attributable to several factors, including biological differences in medication metabolism (in which the patient has medication-resistant HS), undertreatment of pain, and/or poor doctor-patient relations. These reasons coincide with other diseases where health disparities are found.13-15 Recognizing these factors will be key to dismantling the disparities in HS that are noted within this study. The limitations of this work include the cross-sectional study design and its inability to evaluate causal factors of high pain levels across racial groups, the NRS lack of insight on pain chronicity or pain experience,7 the lack of provider or institution perspectives, and self-reported data. Additionally, only patients with email access were included, which may have excluded vulnerable populations with more pain associated with their HS.
Our findings highlight an area for further investigation to assess why these racial differences exist in HS-related pain. The results also emphasize the need for research evaluating whether systemic or health care provider biases contribute to racial differences in HS-related pain management.
Acknowledgment — Dr. Weir was supported by the Predoctoral Clinical/Translational Research Program (TL1), a National Institutes of Health Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA), through the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCTS).
- Garg A, Kirby JS, Lavian J, et al. Sex- and age-adjusted population analysis of prevalence estimates for hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760-764. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.0201
- Nguyen TV, Damiani G, Orenstein LAV, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on epidemiology, phenotypes, diagnosis, pathogenesis, comorbidities and quality of life. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:50-61. doi:10.1111/jdv.16677
- Krajewski PK, Matusiak Ł, von Stebut E, et al. Pain in hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross-sectional study of 1,795 patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00364. doi:10.2340/00015555-3724
- Savage KT, Singh V, Patel ZS, et al. Pain management in hidradenitis suppurativa and a proposed treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:187-199. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.039
- Morales ME, Yong RJ. Racial and ethnic disparities in the treatment of chronic pain. Pain Med. 2021;22:75-90. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa427
- US Department of Health and Human Services. 2019 National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report. December 2020. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/research/findings/nhqrdr/2019qdr.pdf
- Hoffman KM, Trawalter S, Axt JR, et al. Racial bias in pain assessment and treatment recommendations, and false beliefs about biological differences between blacks and whites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:4296-4301. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516047113
- Patel ZS, Hoffman LK, Buse DC, et al. Pain, psychological comorbidities, disability, and impaired quality of life in hidradenitis suppurativa. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017;21:49. doi:10.1007/s11916-017-0647-3. Published correction appears in Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017;21:52.
- McDowell I. Pain measurements. In: Measuring Health: A Guide to Rating Scales and Questionnaires. Oxford University Press; 2006:477-478.
- Singh GK, Daus GP, Allender M, et al. Social determinants of health in the United States: addressing major health inequality trends for the nation, 1935-2016. Int J MCH AIDS. 2017;6:139-164. doi:10.21106/ijma.236
- Sulley S, Bayssie M. Social determinants of health: an evaluation of risk factors associated with inpatient presentations in the United States. Cureus. 2021;13:E13287. doi:10.7759/cureus.13287
- Lazar M, Davenport L. Barriers to health care access for low income families: a review of literature. J Community Health Nurs. 2018;35:28-37. doi:10.1080/07370016.2018.1404832
- Ghoshal M, Shapiro H, Todd K, et al. Chronic noncancer pain management and systemic racism: time to move toward equal care standards.J Pain Res. 2020;13:2825-2836. doi:10.214/JPR.S287314
- Cintron A, Morrison RS. Pain and ethnicity in the United States: a systematic review. J Palliat Med. 2006;9:1454-1473. doi:10.1089/jpm.2006.9.1454
- Green CR, Anderson KO, Baker TA, et al. The unequal burden of pain: confronting racial and ethnic disparities in pain. Pain Med. 2003;4:277-294. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4637.2003.03034.x. Published correction appears in Pain Med. 2005;6:99.
- Garg A, Kirby JS, Lavian J, et al. Sex- and age-adjusted population analysis of prevalence estimates for hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760-764. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.0201
- Nguyen TV, Damiani G, Orenstein LAV, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on epidemiology, phenotypes, diagnosis, pathogenesis, comorbidities and quality of life. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:50-61. doi:10.1111/jdv.16677
- Krajewski PK, Matusiak Ł, von Stebut E, et al. Pain in hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross-sectional study of 1,795 patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021;101:adv00364. doi:10.2340/00015555-3724
- Savage KT, Singh V, Patel ZS, et al. Pain management in hidradenitis suppurativa and a proposed treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:187-199. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.039
- Morales ME, Yong RJ. Racial and ethnic disparities in the treatment of chronic pain. Pain Med. 2021;22:75-90. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa427
- US Department of Health and Human Services. 2019 National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report. December 2020. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/research/findings/nhqrdr/2019qdr.pdf
- Hoffman KM, Trawalter S, Axt JR, et al. Racial bias in pain assessment and treatment recommendations, and false beliefs about biological differences between blacks and whites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:4296-4301. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516047113
- Patel ZS, Hoffman LK, Buse DC, et al. Pain, psychological comorbidities, disability, and impaired quality of life in hidradenitis suppurativa. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017;21:49. doi:10.1007/s11916-017-0647-3. Published correction appears in Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017;21:52.
- McDowell I. Pain measurements. In: Measuring Health: A Guide to Rating Scales and Questionnaires. Oxford University Press; 2006:477-478.
- Singh GK, Daus GP, Allender M, et al. Social determinants of health in the United States: addressing major health inequality trends for the nation, 1935-2016. Int J MCH AIDS. 2017;6:139-164. doi:10.21106/ijma.236
- Sulley S, Bayssie M. Social determinants of health: an evaluation of risk factors associated with inpatient presentations in the United States. Cureus. 2021;13:E13287. doi:10.7759/cureus.13287
- Lazar M, Davenport L. Barriers to health care access for low income families: a review of literature. J Community Health Nurs. 2018;35:28-37. doi:10.1080/07370016.2018.1404832
- Ghoshal M, Shapiro H, Todd K, et al. Chronic noncancer pain management and systemic racism: time to move toward equal care standards.J Pain Res. 2020;13:2825-2836. doi:10.214/JPR.S287314
- Cintron A, Morrison RS. Pain and ethnicity in the United States: a systematic review. J Palliat Med. 2006;9:1454-1473. doi:10.1089/jpm.2006.9.1454
- Green CR, Anderson KO, Baker TA, et al. The unequal burden of pain: confronting racial and ethnic disparities in pain. Pain Med. 2003;4:277-294. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4637.2003.03034.x. Published correction appears in Pain Med. 2005;6:99.
Practice Points
- Racial disparities exist in the management of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)–related pain.
- Black/African American patients with HS are 4 times more likely to experience very severe pain than patients of other races or ethnicities.
- Lower income levels, higher HS disease severity, and a history of prescription pain medication use are all independent risk factors for very severe pain in patients with HS.
Geriatric care principles should apply to ICUs as well
Baseball legend Leroy “Satchel” Paige famously said that “age is a question of mind over matter: If you don’t mind, it doesn’t matter.”
But even the strongest and most supple minds can’t avoid the effects of advanced age and accompanying physical frailty, and for community-dwelling elderly with pulmonary diseases frailty is a predictor of both hospitalization and death, investigators have found.
For example, among 1,188 community-dwelling older adults enrolled in the Toledo (Spain) Study for Healthy Aging, declining pulmonary function measured by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) was associated with increased risk for frailty and hospitalization, and a more than twofold greater risk for death in participants both with and without respiratory diseases. These findings were reported by Walter Sepulveda-Loyola, PT, MSC, PhD, from the Faculty of Health and Social Sciences at Universidad de Las Americas in Santiago, Chile, and colleagues in the journal Heart & Lung.
Similarly, results of a meta-analysis performed by investigators at Jiangsu (China) University showed that among 13,203 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), frailty was associated with a more than 2.6-fold relative increase in risk for death from any cause, and “prefrailty,” an intermediate state between frailty and “robustness,” was associated with a 48% relative increase in all-cause mortality. Frailty was also associated with a 2.2-fold risk for COPD exacerbations of any severity, the authors reported in JAMDA: The Journal of Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine.
The good (old) USA
In June 2023 the U.S. Census Bureau announced that the median age of the U.S. population is now 38.9 years, and according to a 2016 Census Bureau report funded by the National Institutes of Health, “America’s 65-and-over population is projected to nearly double over the next three decades, from 48 million to 88 million by 2050.”
With the graying of the U.S. population the burden on pulmonary and critical care experts will almost inevitably increase, as evidenced by research from Julien Cobert, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
The investigators looked at trends over time in older adults admitted to ICUs from 1988 through 2015 using data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), a nationally representative, longitudinal study of older adults. They found that rates of preexisting frailty, disability, and multimorbidity increased over the study period.
“Our findings suggest a growing prevalence of geriatric conditions among older adults admitted to the ICU, suggesting a pressing need to integrate geriatric principles into critical care medicine. Further research could examine if early interventions emphasizing physical, cognitive, mental health, delirium prevention, advance care planning, and rehabilitation individualized to critically ill elderly patients with preexisting geriatric conditions could improve ICU outcomes and post-ICU recovery,” they wrote in a study published in the journal CHEST.
In an editorial accompanying the study by Dr. Cobert and colleagues, Nathan E. Brummel, MD, from The Ohio State University College of Medicine and Davis Heart and Lung Research Institute in Columbus, said “the finding that nearly 30% of overall HRS participants were admitted to the ICU provides novel data about the extent to which older Americans are affected by critical illness. Because the number of older Americans is projected to continue to increase for the next 30 years or more, these data make clear the ongoing importance of aging-focused research and clinical care.”
Dr. Brummel also noted that older adults who are admitted to the ICU today are at greater risk for poor outcomes than those admitted in prior years, as evidenced by the increased prevalence of disability, frailty, and multimorbidity.
“Moreover, because the average age of those admitted to the ICU only changed by 1 year during the study, these data show that increases in vulnerability are not simply due to chronological age, and they suggest that to identify those with greater baseline vulnerability, screening for geriatric syndromes at ICU admission may be warranted,” he wrote.
Geriatric principles in the ICU
“I think what’s most important is that we think about patients from a geriatric principles standpoint, not just when they’re admitted to the hospital but especially when they’re admitted to the ICU,” Dr. Cobert said in an interview.
“The first step is ensuring that we’re asking questions about their underlying comorbidities, especially around frailty, hearing, vision loss, falls, multimorbidities, polypharmacy – things that are primarily done on the outpatient side in geriatric clinics, but things that we should probably be a little bit more cognizant of, given that we’re starting to see higher rates of patients coming in with these issues,” he said.
Critical care specialists need to take a more holistic approach and try to understand as best they can each patients’ goals and then determine whether the ICU staff are acting in concordance with those goals, he emphasized.
For example, ICU clinicians should try to understand whether patients were losing function or having mobility difficulties before hospital and ICU admission, and what they hope to retain when or if they are discharged. ICU staff can then try as much as reasonably possible to minimize interventions that could contribute to impairment after discharge.
Frailty and COPD in the ICU
There are special considerations for frail elderly with obstructive airway disease, Dr. Cobert noted.
Patients with advanced COPD, for example, are likely to be on home oxygen.
“Home oxygen is a big deal,” he said. “It can definitely help with functioning and there’s potentially a mortality benefit in certain populations. But that said, it’s a flammable object that they have to carry around and lug with them all the time. It contributes to falls, it’s tethering, it’s life-limiting in many ways.”
In addition, many patients with COPD have multiple re-hospitalizations, and for clinicians the challenge is “understanding what their goals are, what their motivations are, especially when they live with dyspnea, with advanced lung disease. Is intubation within their goals of care? Has their functional status been declining over time? Are there things that we can optimize holistically and globally as their COPD advances over time?”
Another important component of critical care for the frail elderly is consideration of patients’ palliative care needs and what their symptoms and symptom burdens were like prior to hospitalizations.
“The ICU experience and the critical illness experience may serve as an inflexion point – more likely a downward inflection point – whereby their needs increase, their symptoms can worsen, and their health, especially their global health, worsens. Their preexisting geriatric conditions might be a moving target after another hit and another traumatic stressor like the ICU setting,” Dr. Cobert said.
The study by Dr. Cobert and colleagues was supported by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Cobert had no reported conflicts of interest.
Baseball legend Leroy “Satchel” Paige famously said that “age is a question of mind over matter: If you don’t mind, it doesn’t matter.”
But even the strongest and most supple minds can’t avoid the effects of advanced age and accompanying physical frailty, and for community-dwelling elderly with pulmonary diseases frailty is a predictor of both hospitalization and death, investigators have found.
For example, among 1,188 community-dwelling older adults enrolled in the Toledo (Spain) Study for Healthy Aging, declining pulmonary function measured by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) was associated with increased risk for frailty and hospitalization, and a more than twofold greater risk for death in participants both with and without respiratory diseases. These findings were reported by Walter Sepulveda-Loyola, PT, MSC, PhD, from the Faculty of Health and Social Sciences at Universidad de Las Americas in Santiago, Chile, and colleagues in the journal Heart & Lung.
Similarly, results of a meta-analysis performed by investigators at Jiangsu (China) University showed that among 13,203 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), frailty was associated with a more than 2.6-fold relative increase in risk for death from any cause, and “prefrailty,” an intermediate state between frailty and “robustness,” was associated with a 48% relative increase in all-cause mortality. Frailty was also associated with a 2.2-fold risk for COPD exacerbations of any severity, the authors reported in JAMDA: The Journal of Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine.
The good (old) USA
In June 2023 the U.S. Census Bureau announced that the median age of the U.S. population is now 38.9 years, and according to a 2016 Census Bureau report funded by the National Institutes of Health, “America’s 65-and-over population is projected to nearly double over the next three decades, from 48 million to 88 million by 2050.”
With the graying of the U.S. population the burden on pulmonary and critical care experts will almost inevitably increase, as evidenced by research from Julien Cobert, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
The investigators looked at trends over time in older adults admitted to ICUs from 1988 through 2015 using data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), a nationally representative, longitudinal study of older adults. They found that rates of preexisting frailty, disability, and multimorbidity increased over the study period.
“Our findings suggest a growing prevalence of geriatric conditions among older adults admitted to the ICU, suggesting a pressing need to integrate geriatric principles into critical care medicine. Further research could examine if early interventions emphasizing physical, cognitive, mental health, delirium prevention, advance care planning, and rehabilitation individualized to critically ill elderly patients with preexisting geriatric conditions could improve ICU outcomes and post-ICU recovery,” they wrote in a study published in the journal CHEST.
In an editorial accompanying the study by Dr. Cobert and colleagues, Nathan E. Brummel, MD, from The Ohio State University College of Medicine and Davis Heart and Lung Research Institute in Columbus, said “the finding that nearly 30% of overall HRS participants were admitted to the ICU provides novel data about the extent to which older Americans are affected by critical illness. Because the number of older Americans is projected to continue to increase for the next 30 years or more, these data make clear the ongoing importance of aging-focused research and clinical care.”
Dr. Brummel also noted that older adults who are admitted to the ICU today are at greater risk for poor outcomes than those admitted in prior years, as evidenced by the increased prevalence of disability, frailty, and multimorbidity.
“Moreover, because the average age of those admitted to the ICU only changed by 1 year during the study, these data show that increases in vulnerability are not simply due to chronological age, and they suggest that to identify those with greater baseline vulnerability, screening for geriatric syndromes at ICU admission may be warranted,” he wrote.
Geriatric principles in the ICU
“I think what’s most important is that we think about patients from a geriatric principles standpoint, not just when they’re admitted to the hospital but especially when they’re admitted to the ICU,” Dr. Cobert said in an interview.
“The first step is ensuring that we’re asking questions about their underlying comorbidities, especially around frailty, hearing, vision loss, falls, multimorbidities, polypharmacy – things that are primarily done on the outpatient side in geriatric clinics, but things that we should probably be a little bit more cognizant of, given that we’re starting to see higher rates of patients coming in with these issues,” he said.
Critical care specialists need to take a more holistic approach and try to understand as best they can each patients’ goals and then determine whether the ICU staff are acting in concordance with those goals, he emphasized.
For example, ICU clinicians should try to understand whether patients were losing function or having mobility difficulties before hospital and ICU admission, and what they hope to retain when or if they are discharged. ICU staff can then try as much as reasonably possible to minimize interventions that could contribute to impairment after discharge.
Frailty and COPD in the ICU
There are special considerations for frail elderly with obstructive airway disease, Dr. Cobert noted.
Patients with advanced COPD, for example, are likely to be on home oxygen.
“Home oxygen is a big deal,” he said. “It can definitely help with functioning and there’s potentially a mortality benefit in certain populations. But that said, it’s a flammable object that they have to carry around and lug with them all the time. It contributes to falls, it’s tethering, it’s life-limiting in many ways.”
In addition, many patients with COPD have multiple re-hospitalizations, and for clinicians the challenge is “understanding what their goals are, what their motivations are, especially when they live with dyspnea, with advanced lung disease. Is intubation within their goals of care? Has their functional status been declining over time? Are there things that we can optimize holistically and globally as their COPD advances over time?”
Another important component of critical care for the frail elderly is consideration of patients’ palliative care needs and what their symptoms and symptom burdens were like prior to hospitalizations.
“The ICU experience and the critical illness experience may serve as an inflexion point – more likely a downward inflection point – whereby their needs increase, their symptoms can worsen, and their health, especially their global health, worsens. Their preexisting geriatric conditions might be a moving target after another hit and another traumatic stressor like the ICU setting,” Dr. Cobert said.
The study by Dr. Cobert and colleagues was supported by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Cobert had no reported conflicts of interest.
Baseball legend Leroy “Satchel” Paige famously said that “age is a question of mind over matter: If you don’t mind, it doesn’t matter.”
But even the strongest and most supple minds can’t avoid the effects of advanced age and accompanying physical frailty, and for community-dwelling elderly with pulmonary diseases frailty is a predictor of both hospitalization and death, investigators have found.
For example, among 1,188 community-dwelling older adults enrolled in the Toledo (Spain) Study for Healthy Aging, declining pulmonary function measured by forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) was associated with increased risk for frailty and hospitalization, and a more than twofold greater risk for death in participants both with and without respiratory diseases. These findings were reported by Walter Sepulveda-Loyola, PT, MSC, PhD, from the Faculty of Health and Social Sciences at Universidad de Las Americas in Santiago, Chile, and colleagues in the journal Heart & Lung.
Similarly, results of a meta-analysis performed by investigators at Jiangsu (China) University showed that among 13,203 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), frailty was associated with a more than 2.6-fold relative increase in risk for death from any cause, and “prefrailty,” an intermediate state between frailty and “robustness,” was associated with a 48% relative increase in all-cause mortality. Frailty was also associated with a 2.2-fold risk for COPD exacerbations of any severity, the authors reported in JAMDA: The Journal of Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Medicine.
The good (old) USA
In June 2023 the U.S. Census Bureau announced that the median age of the U.S. population is now 38.9 years, and according to a 2016 Census Bureau report funded by the National Institutes of Health, “America’s 65-and-over population is projected to nearly double over the next three decades, from 48 million to 88 million by 2050.”
With the graying of the U.S. population the burden on pulmonary and critical care experts will almost inevitably increase, as evidenced by research from Julien Cobert, MD, from the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues.
The investigators looked at trends over time in older adults admitted to ICUs from 1988 through 2015 using data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), a nationally representative, longitudinal study of older adults. They found that rates of preexisting frailty, disability, and multimorbidity increased over the study period.
“Our findings suggest a growing prevalence of geriatric conditions among older adults admitted to the ICU, suggesting a pressing need to integrate geriatric principles into critical care medicine. Further research could examine if early interventions emphasizing physical, cognitive, mental health, delirium prevention, advance care planning, and rehabilitation individualized to critically ill elderly patients with preexisting geriatric conditions could improve ICU outcomes and post-ICU recovery,” they wrote in a study published in the journal CHEST.
In an editorial accompanying the study by Dr. Cobert and colleagues, Nathan E. Brummel, MD, from The Ohio State University College of Medicine and Davis Heart and Lung Research Institute in Columbus, said “the finding that nearly 30% of overall HRS participants were admitted to the ICU provides novel data about the extent to which older Americans are affected by critical illness. Because the number of older Americans is projected to continue to increase for the next 30 years or more, these data make clear the ongoing importance of aging-focused research and clinical care.”
Dr. Brummel also noted that older adults who are admitted to the ICU today are at greater risk for poor outcomes than those admitted in prior years, as evidenced by the increased prevalence of disability, frailty, and multimorbidity.
“Moreover, because the average age of those admitted to the ICU only changed by 1 year during the study, these data show that increases in vulnerability are not simply due to chronological age, and they suggest that to identify those with greater baseline vulnerability, screening for geriatric syndromes at ICU admission may be warranted,” he wrote.
Geriatric principles in the ICU
“I think what’s most important is that we think about patients from a geriatric principles standpoint, not just when they’re admitted to the hospital but especially when they’re admitted to the ICU,” Dr. Cobert said in an interview.
“The first step is ensuring that we’re asking questions about their underlying comorbidities, especially around frailty, hearing, vision loss, falls, multimorbidities, polypharmacy – things that are primarily done on the outpatient side in geriatric clinics, but things that we should probably be a little bit more cognizant of, given that we’re starting to see higher rates of patients coming in with these issues,” he said.
Critical care specialists need to take a more holistic approach and try to understand as best they can each patients’ goals and then determine whether the ICU staff are acting in concordance with those goals, he emphasized.
For example, ICU clinicians should try to understand whether patients were losing function or having mobility difficulties before hospital and ICU admission, and what they hope to retain when or if they are discharged. ICU staff can then try as much as reasonably possible to minimize interventions that could contribute to impairment after discharge.
Frailty and COPD in the ICU
There are special considerations for frail elderly with obstructive airway disease, Dr. Cobert noted.
Patients with advanced COPD, for example, are likely to be on home oxygen.
“Home oxygen is a big deal,” he said. “It can definitely help with functioning and there’s potentially a mortality benefit in certain populations. But that said, it’s a flammable object that they have to carry around and lug with them all the time. It contributes to falls, it’s tethering, it’s life-limiting in many ways.”
In addition, many patients with COPD have multiple re-hospitalizations, and for clinicians the challenge is “understanding what their goals are, what their motivations are, especially when they live with dyspnea, with advanced lung disease. Is intubation within their goals of care? Has their functional status been declining over time? Are there things that we can optimize holistically and globally as their COPD advances over time?”
Another important component of critical care for the frail elderly is consideration of patients’ palliative care needs and what their symptoms and symptom burdens were like prior to hospitalizations.
“The ICU experience and the critical illness experience may serve as an inflexion point – more likely a downward inflection point – whereby their needs increase, their symptoms can worsen, and their health, especially their global health, worsens. Their preexisting geriatric conditions might be a moving target after another hit and another traumatic stressor like the ICU setting,” Dr. Cobert said.
The study by Dr. Cobert and colleagues was supported by the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Cobert had no reported conflicts of interest.
The invisible effect medical notes could have on care
In the mid-1990s, when Somnath Saha was a medical resident at the University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine, he came across a cluster of studies showing that Black people with cardiovascular disease were treated less aggressively, compared with White people. The findings were “appalling” to the young physician who describes himself as a “Brown kid from suburban St. Louis, Missouri.”
Dr. Saha had experienced racism growing up, but was surprised to see such clear signs of inequity within the field of medicine. “There was an injustice happening in my own backyard,” he said.
Indeed, bias towards Black patients can be challenging because many doctors either don’t realize their biases or won’t admit to them. Dr. Saha, now a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, likens implicit bias – unconscious judgments that can affect behavior – to “an invisible force.”
While numerous studies have found evidence of racial discrimination in medicine through patient reports, less is known about how implicit bias shows up in medical records, and how stigmatizing language in patient notes can affect the care that Black patients receive.
That’s part of the reason why, about 7 years ago, Dr. Saha began poring through medical records. For him, they offered a window into doctors’ feelings about their patients.
As part of his latest research, Dr. Saha’s team examined the records of nearly 19,000 patients, paying particular attention to negative descriptions that may influence a clinician’s decision-making. The data, which were recently presented at the 2023 American Association for the Advancement of Science annual meeting, aren’t yet published, but it suggests what researchers have long speculated: The notes provide, at times, a surprisingly candid view of how patients are perceived by doctors, and how their race may affect treatment.
The study adds to a concerning body of literature that explores how racial bias manifests in health care. Researchers like Dr. Saha are interested in how such prejudice leaves a paper trail, which can then reinforce negative stereotypes. Because medical notes get passed between physicians, Dr. Saha’s research suggests they can affect the health of Black patients down the line.
“The medical record is like a rap sheet, it stays with you,” Dr. Saha said, adding that “these things that we say about patients get eternalized.”
Research has long shown that Black patients experience worse health outcomes, compared with White patients, in part because of biased medical care. Black women, for example, are three times more likely to die from pregnancy-related complications, compared with White women. And Black patients often report feeling like physicians don’t listen to their needs or don’t believe their concerns.
Studies appear to back that up. Last year, researchers at the University of Washington found that non-Hispanic White children who went to the emergency room for migraines were more likely to receive pain medications, compared with children of color – even though the two groups reported similar pain scores. Other studies echo similar results for adults as well.
While Michael Sun, a resident physician at the University of Chicago, knew about such health disparities, by his own admission, he was naive about the biases in medical records. At that time, Dr. Sun had “no experience in the medical record, in documentation, or in physician language and culture,” he said.
But in Dr. Sun’s first year of medical school, his professor shared the story of a longtime patient, whom she had referred to an outside specialist. In his recollection, the professor regarded her patient in kind terms, having worked with her for some time to treat a chronic illness. But when she got the specialist’s notes back, she was confused by the description of her patient: Terms like “really difficult,” “noncompliant,” and “uninterested in their health.” This was not the patient she remembered.
“This, as a first-year medical student, really shocked me because I had taken at face value that any words used in notes were true, were valid, or rightfully used,” said Dr. Sun. “I realized all the ways that bias, untold stories, and unknown context may change the way that we view our patients.”
Like Dr. Saha, Dr. Sun became interested in how bias influenced the relationship between doctor and patient, and how these interactions were memorialized in the medical record. In a study published last year, he and his colleagues looked at more than 40,000 medical notes from 18,459 patients. Researchers first manually combed through the notes, then used this information to teach a machine learning algorithm to interpret the connotations of words. Compared with White patients, Black patients were about 2.5 times more likely to be described negatively, with terms like “challenging,” “angry,” and “noncompliant.”
Dr. Saha has used similar methodology – and found similar results – in his own research. For the study presented at the AAAS meeting, his team first read through more than 100,000 medical notes to identify language their team considered to be disparaging – which they chose based on a list of words and phrases from prior research. They then used machine learning to find those terms in medical notes, taking care to ensure context was considered. For example, if the word “aggressive” was used to describe a treatment plan, it was excluded from their analysis. But if “aggressive” was used to describe the patient, it was included.
Dr. Saha pointed to three categories of stigmatizing language that were the most pronounced: expressing doubt or disbelief in what the patient said, such as reporting they “claimed” to experience pain; insinuating that the patient was confrontational, using words like “belligerent” or combative;” and suggesting a patient was not cooperating with a doctor’s orders by saying they “refused” medical advice.
“We’ve known for some time that in health care we sometimes use language that can be confusing or even insulting,” Matthew Wynia, director of the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, wrote in an email to Undark. But he noted that research such as Dr. Saha’s has drawn attention to a previously overlooked issue. Describing a patient as “noncompliant” with medications, he said, “makes it sound like the patient is intentionally refusing to follow advice when, in fact, there are many reasons why people might not be able to follow our advice and intentional refusal isn’t even a very common one.”
Dr. Saha noted that, if a patient isn’t taking their medication, it’s important that doctors note that, so that the next physician doesn’t overprescribe them. But the concern, he said, is whether doctors are using these terms appropriately and for the right reasons because of the implications they have for patients.
If a doctor portrays their patient negatively, Dr. Saha said, it can “trigger the next clinician to read them and formulate a potentially negative opinion about that patient” before they’ve even had a chance to interact.
Still, stigmatizing language is only one small piece of the puzzle. What also matters, Dr. Saha said, is how those words can have an impact on care. In prior work, Dr. Saha has shown how implicit and, in some cases, explicit bias, affects a patient’s treatment recommendations.
In a 2018 study, Dr. Saha, along with his wife, Mary Catherine Beach – also a professor at Johns Hopkins University – combed through reports of patients with sickle cell anemia. Their team focused on that particular population since sickle cell patients are some of the most stigmatized in the health care system: Most patients are Black and many require regular doses of opioids for pain management.
In the notes, they found numerous examples of details that were irrelevant to patients’ health concerns: phrases like “girlfriend requests bus token,” “cursing at nurse,” “girlfriend on bed with shoes on,” and “narcotic dependent.”
Dr. Saha and Dr. Beach wanted to see how these remarks might influence a physician’s treatment recommendations, so they used vignettes they had found in the medical records of sickle cell patients. They showed either a vignette which had described patients negatively, or one that was edited with neutral language. Then they asked medical students and residents about the dose of pain medication they would hypothetically recommend. Dr. Beach said that the purpose was to see how what she called “dog whistles about social class or race or something that would make the person seem less educated” would impact treatment recommendations.
The study found that medical notes with stigmatizing language were associated with “less aggressive management of the patient’s pain.” Doctors who read the stigmatizing language chart notes prescribed less pain medication to patients even in cases when they commented that their pain was a 10 out of 10.
“The fact that we were able to show that this bias transmits to the next doctor has been the thing that I think motivates doctors to take it seriously,” said Dr. Beach.
Pain management has become a focal point for researchers because many of the most glaring racial tropes about patient care have revolved around pain. In 2016, a study conducted at the University of Virginia found that half of the 418 medical students and residents surveyed endorsed false beliefs about Black patients. For example, that “Blacks’ nerve endings are less sensitive than whites” and “Blacks’ skin is thicker than whites.” What’s more, those who endorsed these false beliefs also rated Black patients’ pain as lower than White patients’.
Antoinette M. Schoenthaler, a professor of population health and medicine at New York University and associate director of research at the school’s Institute for Excellence in Health Equity, said that disparities in pain management are pervasive and widespread across the medical profession. They seep into treatments for sickle cell anemia, but also prenatal care. As a result, she said, Black patients across the board are often fearful of attending appointments.
“Patients of color go into an appointment with feelings of heightened anxiety because they’re expecting mistreatment,” said Dr. Schoenthaler. “We’ve seen minoritized patients have higher blood pressure in the context of a clinical visit because of these expectations of anxiety and fear, and disappointment.”
Disparities in health care between Black and White patients is a complex issue – one which can’t be solved by addressing medical records alone. But, for researchers like Dr. Saha, Dr. Beach, and Dr. Sun, they can offer a road map that outlines where differences in care begin. The words a clinician uses sets the path for how a patient may be treated in the future.
One way to combat implicit bias, Dr. Saha suggested, is to use an algorithm that identifies stigmatizing language to “give hospital departments or clinicians report cards on how much of this language that they’re using.” By benchmarking averages against one another, clinicians could know if they’re using stigmatizing language at an above average rate. This is something he is considering for future research.
When clinicians are made aware of their biases – when the unconscious becomes conscious – Dr. Saha told Undark that he’s optimistic they’ll work to change them: “We’re using language that we’ve used forever without realizing the potential impact that it has on patient care.”
This article originated on Undark. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In the mid-1990s, when Somnath Saha was a medical resident at the University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine, he came across a cluster of studies showing that Black people with cardiovascular disease were treated less aggressively, compared with White people. The findings were “appalling” to the young physician who describes himself as a “Brown kid from suburban St. Louis, Missouri.”
Dr. Saha had experienced racism growing up, but was surprised to see such clear signs of inequity within the field of medicine. “There was an injustice happening in my own backyard,” he said.
Indeed, bias towards Black patients can be challenging because many doctors either don’t realize their biases or won’t admit to them. Dr. Saha, now a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, likens implicit bias – unconscious judgments that can affect behavior – to “an invisible force.”
While numerous studies have found evidence of racial discrimination in medicine through patient reports, less is known about how implicit bias shows up in medical records, and how stigmatizing language in patient notes can affect the care that Black patients receive.
That’s part of the reason why, about 7 years ago, Dr. Saha began poring through medical records. For him, they offered a window into doctors’ feelings about their patients.
As part of his latest research, Dr. Saha’s team examined the records of nearly 19,000 patients, paying particular attention to negative descriptions that may influence a clinician’s decision-making. The data, which were recently presented at the 2023 American Association for the Advancement of Science annual meeting, aren’t yet published, but it suggests what researchers have long speculated: The notes provide, at times, a surprisingly candid view of how patients are perceived by doctors, and how their race may affect treatment.
The study adds to a concerning body of literature that explores how racial bias manifests in health care. Researchers like Dr. Saha are interested in how such prejudice leaves a paper trail, which can then reinforce negative stereotypes. Because medical notes get passed between physicians, Dr. Saha’s research suggests they can affect the health of Black patients down the line.
“The medical record is like a rap sheet, it stays with you,” Dr. Saha said, adding that “these things that we say about patients get eternalized.”
Research has long shown that Black patients experience worse health outcomes, compared with White patients, in part because of biased medical care. Black women, for example, are three times more likely to die from pregnancy-related complications, compared with White women. And Black patients often report feeling like physicians don’t listen to their needs or don’t believe their concerns.
Studies appear to back that up. Last year, researchers at the University of Washington found that non-Hispanic White children who went to the emergency room for migraines were more likely to receive pain medications, compared with children of color – even though the two groups reported similar pain scores. Other studies echo similar results for adults as well.
While Michael Sun, a resident physician at the University of Chicago, knew about such health disparities, by his own admission, he was naive about the biases in medical records. At that time, Dr. Sun had “no experience in the medical record, in documentation, or in physician language and culture,” he said.
But in Dr. Sun’s first year of medical school, his professor shared the story of a longtime patient, whom she had referred to an outside specialist. In his recollection, the professor regarded her patient in kind terms, having worked with her for some time to treat a chronic illness. But when she got the specialist’s notes back, she was confused by the description of her patient: Terms like “really difficult,” “noncompliant,” and “uninterested in their health.” This was not the patient she remembered.
“This, as a first-year medical student, really shocked me because I had taken at face value that any words used in notes were true, were valid, or rightfully used,” said Dr. Sun. “I realized all the ways that bias, untold stories, and unknown context may change the way that we view our patients.”
Like Dr. Saha, Dr. Sun became interested in how bias influenced the relationship between doctor and patient, and how these interactions were memorialized in the medical record. In a study published last year, he and his colleagues looked at more than 40,000 medical notes from 18,459 patients. Researchers first manually combed through the notes, then used this information to teach a machine learning algorithm to interpret the connotations of words. Compared with White patients, Black patients were about 2.5 times more likely to be described negatively, with terms like “challenging,” “angry,” and “noncompliant.”
Dr. Saha has used similar methodology – and found similar results – in his own research. For the study presented at the AAAS meeting, his team first read through more than 100,000 medical notes to identify language their team considered to be disparaging – which they chose based on a list of words and phrases from prior research. They then used machine learning to find those terms in medical notes, taking care to ensure context was considered. For example, if the word “aggressive” was used to describe a treatment plan, it was excluded from their analysis. But if “aggressive” was used to describe the patient, it was included.
Dr. Saha pointed to three categories of stigmatizing language that were the most pronounced: expressing doubt or disbelief in what the patient said, such as reporting they “claimed” to experience pain; insinuating that the patient was confrontational, using words like “belligerent” or combative;” and suggesting a patient was not cooperating with a doctor’s orders by saying they “refused” medical advice.
“We’ve known for some time that in health care we sometimes use language that can be confusing or even insulting,” Matthew Wynia, director of the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, wrote in an email to Undark. But he noted that research such as Dr. Saha’s has drawn attention to a previously overlooked issue. Describing a patient as “noncompliant” with medications, he said, “makes it sound like the patient is intentionally refusing to follow advice when, in fact, there are many reasons why people might not be able to follow our advice and intentional refusal isn’t even a very common one.”
Dr. Saha noted that, if a patient isn’t taking their medication, it’s important that doctors note that, so that the next physician doesn’t overprescribe them. But the concern, he said, is whether doctors are using these terms appropriately and for the right reasons because of the implications they have for patients.
If a doctor portrays their patient negatively, Dr. Saha said, it can “trigger the next clinician to read them and formulate a potentially negative opinion about that patient” before they’ve even had a chance to interact.
Still, stigmatizing language is only one small piece of the puzzle. What also matters, Dr. Saha said, is how those words can have an impact on care. In prior work, Dr. Saha has shown how implicit and, in some cases, explicit bias, affects a patient’s treatment recommendations.
In a 2018 study, Dr. Saha, along with his wife, Mary Catherine Beach – also a professor at Johns Hopkins University – combed through reports of patients with sickle cell anemia. Their team focused on that particular population since sickle cell patients are some of the most stigmatized in the health care system: Most patients are Black and many require regular doses of opioids for pain management.
In the notes, they found numerous examples of details that were irrelevant to patients’ health concerns: phrases like “girlfriend requests bus token,” “cursing at nurse,” “girlfriend on bed with shoes on,” and “narcotic dependent.”
Dr. Saha and Dr. Beach wanted to see how these remarks might influence a physician’s treatment recommendations, so they used vignettes they had found in the medical records of sickle cell patients. They showed either a vignette which had described patients negatively, or one that was edited with neutral language. Then they asked medical students and residents about the dose of pain medication they would hypothetically recommend. Dr. Beach said that the purpose was to see how what she called “dog whistles about social class or race or something that would make the person seem less educated” would impact treatment recommendations.
The study found that medical notes with stigmatizing language were associated with “less aggressive management of the patient’s pain.” Doctors who read the stigmatizing language chart notes prescribed less pain medication to patients even in cases when they commented that their pain was a 10 out of 10.
“The fact that we were able to show that this bias transmits to the next doctor has been the thing that I think motivates doctors to take it seriously,” said Dr. Beach.
Pain management has become a focal point for researchers because many of the most glaring racial tropes about patient care have revolved around pain. In 2016, a study conducted at the University of Virginia found that half of the 418 medical students and residents surveyed endorsed false beliefs about Black patients. For example, that “Blacks’ nerve endings are less sensitive than whites” and “Blacks’ skin is thicker than whites.” What’s more, those who endorsed these false beliefs also rated Black patients’ pain as lower than White patients’.
Antoinette M. Schoenthaler, a professor of population health and medicine at New York University and associate director of research at the school’s Institute for Excellence in Health Equity, said that disparities in pain management are pervasive and widespread across the medical profession. They seep into treatments for sickle cell anemia, but also prenatal care. As a result, she said, Black patients across the board are often fearful of attending appointments.
“Patients of color go into an appointment with feelings of heightened anxiety because they’re expecting mistreatment,” said Dr. Schoenthaler. “We’ve seen minoritized patients have higher blood pressure in the context of a clinical visit because of these expectations of anxiety and fear, and disappointment.”
Disparities in health care between Black and White patients is a complex issue – one which can’t be solved by addressing medical records alone. But, for researchers like Dr. Saha, Dr. Beach, and Dr. Sun, they can offer a road map that outlines where differences in care begin. The words a clinician uses sets the path for how a patient may be treated in the future.
One way to combat implicit bias, Dr. Saha suggested, is to use an algorithm that identifies stigmatizing language to “give hospital departments or clinicians report cards on how much of this language that they’re using.” By benchmarking averages against one another, clinicians could know if they’re using stigmatizing language at an above average rate. This is something he is considering for future research.
When clinicians are made aware of their biases – when the unconscious becomes conscious – Dr. Saha told Undark that he’s optimistic they’ll work to change them: “We’re using language that we’ve used forever without realizing the potential impact that it has on patient care.”
This article originated on Undark. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In the mid-1990s, when Somnath Saha was a medical resident at the University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine, he came across a cluster of studies showing that Black people with cardiovascular disease were treated less aggressively, compared with White people. The findings were “appalling” to the young physician who describes himself as a “Brown kid from suburban St. Louis, Missouri.”
Dr. Saha had experienced racism growing up, but was surprised to see such clear signs of inequity within the field of medicine. “There was an injustice happening in my own backyard,” he said.
Indeed, bias towards Black patients can be challenging because many doctors either don’t realize their biases or won’t admit to them. Dr. Saha, now a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, likens implicit bias – unconscious judgments that can affect behavior – to “an invisible force.”
While numerous studies have found evidence of racial discrimination in medicine through patient reports, less is known about how implicit bias shows up in medical records, and how stigmatizing language in patient notes can affect the care that Black patients receive.
That’s part of the reason why, about 7 years ago, Dr. Saha began poring through medical records. For him, they offered a window into doctors’ feelings about their patients.
As part of his latest research, Dr. Saha’s team examined the records of nearly 19,000 patients, paying particular attention to negative descriptions that may influence a clinician’s decision-making. The data, which were recently presented at the 2023 American Association for the Advancement of Science annual meeting, aren’t yet published, but it suggests what researchers have long speculated: The notes provide, at times, a surprisingly candid view of how patients are perceived by doctors, and how their race may affect treatment.
The study adds to a concerning body of literature that explores how racial bias manifests in health care. Researchers like Dr. Saha are interested in how such prejudice leaves a paper trail, which can then reinforce negative stereotypes. Because medical notes get passed between physicians, Dr. Saha’s research suggests they can affect the health of Black patients down the line.
“The medical record is like a rap sheet, it stays with you,” Dr. Saha said, adding that “these things that we say about patients get eternalized.”
Research has long shown that Black patients experience worse health outcomes, compared with White patients, in part because of biased medical care. Black women, for example, are three times more likely to die from pregnancy-related complications, compared with White women. And Black patients often report feeling like physicians don’t listen to their needs or don’t believe their concerns.
Studies appear to back that up. Last year, researchers at the University of Washington found that non-Hispanic White children who went to the emergency room for migraines were more likely to receive pain medications, compared with children of color – even though the two groups reported similar pain scores. Other studies echo similar results for adults as well.
While Michael Sun, a resident physician at the University of Chicago, knew about such health disparities, by his own admission, he was naive about the biases in medical records. At that time, Dr. Sun had “no experience in the medical record, in documentation, or in physician language and culture,” he said.
But in Dr. Sun’s first year of medical school, his professor shared the story of a longtime patient, whom she had referred to an outside specialist. In his recollection, the professor regarded her patient in kind terms, having worked with her for some time to treat a chronic illness. But when she got the specialist’s notes back, she was confused by the description of her patient: Terms like “really difficult,” “noncompliant,” and “uninterested in their health.” This was not the patient she remembered.
“This, as a first-year medical student, really shocked me because I had taken at face value that any words used in notes were true, were valid, or rightfully used,” said Dr. Sun. “I realized all the ways that bias, untold stories, and unknown context may change the way that we view our patients.”
Like Dr. Saha, Dr. Sun became interested in how bias influenced the relationship between doctor and patient, and how these interactions were memorialized in the medical record. In a study published last year, he and his colleagues looked at more than 40,000 medical notes from 18,459 patients. Researchers first manually combed through the notes, then used this information to teach a machine learning algorithm to interpret the connotations of words. Compared with White patients, Black patients were about 2.5 times more likely to be described negatively, with terms like “challenging,” “angry,” and “noncompliant.”
Dr. Saha has used similar methodology – and found similar results – in his own research. For the study presented at the AAAS meeting, his team first read through more than 100,000 medical notes to identify language their team considered to be disparaging – which they chose based on a list of words and phrases from prior research. They then used machine learning to find those terms in medical notes, taking care to ensure context was considered. For example, if the word “aggressive” was used to describe a treatment plan, it was excluded from their analysis. But if “aggressive” was used to describe the patient, it was included.
Dr. Saha pointed to three categories of stigmatizing language that were the most pronounced: expressing doubt or disbelief in what the patient said, such as reporting they “claimed” to experience pain; insinuating that the patient was confrontational, using words like “belligerent” or combative;” and suggesting a patient was not cooperating with a doctor’s orders by saying they “refused” medical advice.
“We’ve known for some time that in health care we sometimes use language that can be confusing or even insulting,” Matthew Wynia, director of the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, wrote in an email to Undark. But he noted that research such as Dr. Saha’s has drawn attention to a previously overlooked issue. Describing a patient as “noncompliant” with medications, he said, “makes it sound like the patient is intentionally refusing to follow advice when, in fact, there are many reasons why people might not be able to follow our advice and intentional refusal isn’t even a very common one.”
Dr. Saha noted that, if a patient isn’t taking their medication, it’s important that doctors note that, so that the next physician doesn’t overprescribe them. But the concern, he said, is whether doctors are using these terms appropriately and for the right reasons because of the implications they have for patients.
If a doctor portrays their patient negatively, Dr. Saha said, it can “trigger the next clinician to read them and formulate a potentially negative opinion about that patient” before they’ve even had a chance to interact.
Still, stigmatizing language is only one small piece of the puzzle. What also matters, Dr. Saha said, is how those words can have an impact on care. In prior work, Dr. Saha has shown how implicit and, in some cases, explicit bias, affects a patient’s treatment recommendations.
In a 2018 study, Dr. Saha, along with his wife, Mary Catherine Beach – also a professor at Johns Hopkins University – combed through reports of patients with sickle cell anemia. Their team focused on that particular population since sickle cell patients are some of the most stigmatized in the health care system: Most patients are Black and many require regular doses of opioids for pain management.
In the notes, they found numerous examples of details that were irrelevant to patients’ health concerns: phrases like “girlfriend requests bus token,” “cursing at nurse,” “girlfriend on bed with shoes on,” and “narcotic dependent.”
Dr. Saha and Dr. Beach wanted to see how these remarks might influence a physician’s treatment recommendations, so they used vignettes they had found in the medical records of sickle cell patients. They showed either a vignette which had described patients negatively, or one that was edited with neutral language. Then they asked medical students and residents about the dose of pain medication they would hypothetically recommend. Dr. Beach said that the purpose was to see how what she called “dog whistles about social class or race or something that would make the person seem less educated” would impact treatment recommendations.
The study found that medical notes with stigmatizing language were associated with “less aggressive management of the patient’s pain.” Doctors who read the stigmatizing language chart notes prescribed less pain medication to patients even in cases when they commented that their pain was a 10 out of 10.
“The fact that we were able to show that this bias transmits to the next doctor has been the thing that I think motivates doctors to take it seriously,” said Dr. Beach.
Pain management has become a focal point for researchers because many of the most glaring racial tropes about patient care have revolved around pain. In 2016, a study conducted at the University of Virginia found that half of the 418 medical students and residents surveyed endorsed false beliefs about Black patients. For example, that “Blacks’ nerve endings are less sensitive than whites” and “Blacks’ skin is thicker than whites.” What’s more, those who endorsed these false beliefs also rated Black patients’ pain as lower than White patients’.
Antoinette M. Schoenthaler, a professor of population health and medicine at New York University and associate director of research at the school’s Institute for Excellence in Health Equity, said that disparities in pain management are pervasive and widespread across the medical profession. They seep into treatments for sickle cell anemia, but also prenatal care. As a result, she said, Black patients across the board are often fearful of attending appointments.
“Patients of color go into an appointment with feelings of heightened anxiety because they’re expecting mistreatment,” said Dr. Schoenthaler. “We’ve seen minoritized patients have higher blood pressure in the context of a clinical visit because of these expectations of anxiety and fear, and disappointment.”
Disparities in health care between Black and White patients is a complex issue – one which can’t be solved by addressing medical records alone. But, for researchers like Dr. Saha, Dr. Beach, and Dr. Sun, they can offer a road map that outlines where differences in care begin. The words a clinician uses sets the path for how a patient may be treated in the future.
One way to combat implicit bias, Dr. Saha suggested, is to use an algorithm that identifies stigmatizing language to “give hospital departments or clinicians report cards on how much of this language that they’re using.” By benchmarking averages against one another, clinicians could know if they’re using stigmatizing language at an above average rate. This is something he is considering for future research.
When clinicians are made aware of their biases – when the unconscious becomes conscious – Dr. Saha told Undark that he’s optimistic they’ll work to change them: “We’re using language that we’ve used forever without realizing the potential impact that it has on patient care.”
This article originated on Undark. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Med students, doctor groups react to SCOTUS affirmative action ban
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled on June 29 that using race as a factor in college admissions is unconstitutional, rolling back more than 40 years of affirmative action standards and changing how medical schools evaluate applicants to attract students from diverse backgrounds.
Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, said in a prepared statement that the Supreme Court ruling will result in a less diverse physician workforce, which is “bad for health care, bad for medicine, and undermines the health of our nation.” He cited the AMA’s recent adoption of a policy advising medical schools to increase enrollment of people from racial and ethnic groups traditionally underrepresented in medicine – even if that means considering race as a factor in admissions criteria.
“Supporting racial and ethnic diversity in the health professions – spanning classrooms, labs, and clinical settings – enriches the educational experiences of all medical and health professions students and the teaching experiences of faculty, and it is essential to improving the overall health of our nation,” the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) said in a prepared statement.
The American Medical Student Association also denounced the Supreme Court decision. “As future physicians committed to justice and equality, we are profoundly outraged ... We strongly support increased representation of minority students in all levels of education, including colleges and medical schools. By fostering diversity and inclusion, institutions have the power to create more empathetic and inclusive learning environments,” the organization said in a press release.
“Diversity in the health care workforce not only benefits underserved patients but improves care for all patients” by increasing understanding and empathy for people of various cultures, Omar T. Atiq, MD, president of the American College of Physicians, said in a press release.
The Supreme Court ruling stems from a lawsuit by the Students for Fair Admissions against Harvard University and the University of North Carolina. The lawsuit alleges that considering race in the college admission process constitutes discrimination and violates the Equal Protection Clause.
Chief Justice John Roberts, who delivered the court’s decision, stated that an applicant’s personal experiences should carry the most weight in admission decisions and that historically, universities have “wrongly concluded that the touchstone of an individual’s identity is not challenges bested, skills built, or lessons learned, but the color of their skin. Our constitutional history does not tolerate that choice.”
Still, Justice Roberts said the opinion does not prohibit universities from considering how race has affected an applicant’s life, “be it through discrimination, inspiration, or otherwise.”
Diversity in medical schools increased last year, with more Black, Hispanic, and female students applying and enrolling. But continued diversity efforts were expected to prove challenging with affirmative action off the table, according to an amicus brief filed last year by the AMA, the AAMC, and dozens of other professional health care organizations.
The brief supported continued use of race in college admissions, stating that eliminating that factor could slow efforts to achieve greater health equity because fewer doctors would be training and working with colleagues from diverse backgrounds.
Several universities with medical programs, such as Yale and Johns Hopkins universities, filed a separate brief citing similar concerns. After the June 29 decision, Harvard and the University of North Carolina released statements stating they would comply with the ruling.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled on June 29 that using race as a factor in college admissions is unconstitutional, rolling back more than 40 years of affirmative action standards and changing how medical schools evaluate applicants to attract students from diverse backgrounds.
Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, said in a prepared statement that the Supreme Court ruling will result in a less diverse physician workforce, which is “bad for health care, bad for medicine, and undermines the health of our nation.” He cited the AMA’s recent adoption of a policy advising medical schools to increase enrollment of people from racial and ethnic groups traditionally underrepresented in medicine – even if that means considering race as a factor in admissions criteria.
“Supporting racial and ethnic diversity in the health professions – spanning classrooms, labs, and clinical settings – enriches the educational experiences of all medical and health professions students and the teaching experiences of faculty, and it is essential to improving the overall health of our nation,” the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) said in a prepared statement.
The American Medical Student Association also denounced the Supreme Court decision. “As future physicians committed to justice and equality, we are profoundly outraged ... We strongly support increased representation of minority students in all levels of education, including colleges and medical schools. By fostering diversity and inclusion, institutions have the power to create more empathetic and inclusive learning environments,” the organization said in a press release.
“Diversity in the health care workforce not only benefits underserved patients but improves care for all patients” by increasing understanding and empathy for people of various cultures, Omar T. Atiq, MD, president of the American College of Physicians, said in a press release.
The Supreme Court ruling stems from a lawsuit by the Students for Fair Admissions against Harvard University and the University of North Carolina. The lawsuit alleges that considering race in the college admission process constitutes discrimination and violates the Equal Protection Clause.
Chief Justice John Roberts, who delivered the court’s decision, stated that an applicant’s personal experiences should carry the most weight in admission decisions and that historically, universities have “wrongly concluded that the touchstone of an individual’s identity is not challenges bested, skills built, or lessons learned, but the color of their skin. Our constitutional history does not tolerate that choice.”
Still, Justice Roberts said the opinion does not prohibit universities from considering how race has affected an applicant’s life, “be it through discrimination, inspiration, or otherwise.”
Diversity in medical schools increased last year, with more Black, Hispanic, and female students applying and enrolling. But continued diversity efforts were expected to prove challenging with affirmative action off the table, according to an amicus brief filed last year by the AMA, the AAMC, and dozens of other professional health care organizations.
The brief supported continued use of race in college admissions, stating that eliminating that factor could slow efforts to achieve greater health equity because fewer doctors would be training and working with colleagues from diverse backgrounds.
Several universities with medical programs, such as Yale and Johns Hopkins universities, filed a separate brief citing similar concerns. After the June 29 decision, Harvard and the University of North Carolina released statements stating they would comply with the ruling.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled on June 29 that using race as a factor in college admissions is unconstitutional, rolling back more than 40 years of affirmative action standards and changing how medical schools evaluate applicants to attract students from diverse backgrounds.
Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, said in a prepared statement that the Supreme Court ruling will result in a less diverse physician workforce, which is “bad for health care, bad for medicine, and undermines the health of our nation.” He cited the AMA’s recent adoption of a policy advising medical schools to increase enrollment of people from racial and ethnic groups traditionally underrepresented in medicine – even if that means considering race as a factor in admissions criteria.
“Supporting racial and ethnic diversity in the health professions – spanning classrooms, labs, and clinical settings – enriches the educational experiences of all medical and health professions students and the teaching experiences of faculty, and it is essential to improving the overall health of our nation,” the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) said in a prepared statement.
The American Medical Student Association also denounced the Supreme Court decision. “As future physicians committed to justice and equality, we are profoundly outraged ... We strongly support increased representation of minority students in all levels of education, including colleges and medical schools. By fostering diversity and inclusion, institutions have the power to create more empathetic and inclusive learning environments,” the organization said in a press release.
“Diversity in the health care workforce not only benefits underserved patients but improves care for all patients” by increasing understanding and empathy for people of various cultures, Omar T. Atiq, MD, president of the American College of Physicians, said in a press release.
The Supreme Court ruling stems from a lawsuit by the Students for Fair Admissions against Harvard University and the University of North Carolina. The lawsuit alleges that considering race in the college admission process constitutes discrimination and violates the Equal Protection Clause.
Chief Justice John Roberts, who delivered the court’s decision, stated that an applicant’s personal experiences should carry the most weight in admission decisions and that historically, universities have “wrongly concluded that the touchstone of an individual’s identity is not challenges bested, skills built, or lessons learned, but the color of their skin. Our constitutional history does not tolerate that choice.”
Still, Justice Roberts said the opinion does not prohibit universities from considering how race has affected an applicant’s life, “be it through discrimination, inspiration, or otherwise.”
Diversity in medical schools increased last year, with more Black, Hispanic, and female students applying and enrolling. But continued diversity efforts were expected to prove challenging with affirmative action off the table, according to an amicus brief filed last year by the AMA, the AAMC, and dozens of other professional health care organizations.
The brief supported continued use of race in college admissions, stating that eliminating that factor could slow efforts to achieve greater health equity because fewer doctors would be training and working with colleagues from diverse backgrounds.
Several universities with medical programs, such as Yale and Johns Hopkins universities, filed a separate brief citing similar concerns. After the June 29 decision, Harvard and the University of North Carolina released statements stating they would comply with the ruling.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy in Skin of Color Using an Educational Module
Dermatologic disparities disproportionately affect patients with skin of color (SOC). Two studies assessing the diagnostic accuracy of medical students have shown disparities in diagnosing common skin conditions presenting in darker skin compared to lighter skin at early stages of training.1,2 This knowledge gap could be attributed to the underrepresentation of SOC in dermatologic textbooks, journals, and educational curricula.3-6 It is important for dermatologists as well as physicians in other specialties and ancillary health care workers involved in treating or triaging dermatologic diseases to recognize common skin conditions presenting in SOC. We sought to evaluate the effectiveness of a focused educational module for improving diagnostic accuracy and confidence in treating SOC among interprofessional health care providers.
Methods
Interprofessional health care providers—medical students, residents/fellows, attending physicians, advanced practice providers (APPs), and nurses practicing across various medical specialties—at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School and Ascension Medical Group (both in Austin, Texas) were invited to participate in an institutional review board–exempt study involving a virtual SOC educational module from February through May 2021. The 1-hour module involved a pretest, a 15-minute lecture, an immediate posttest, and a 3-month posttest. All tests included the same 40 multiple-choice questions of 20 dermatologic conditions portrayed in lighter and darker skin types from VisualDx.com, and participants were asked to identify the condition in each photograph. Questions appeared one at a time in a randomized order, and answers could not be changed once submitted.
For analysis, the dermatologic conditions were categorized into 4 groups: cancerous, infectious, inflammatory, and SOC-associated conditions. Cancerous conditions included basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Infectious conditions included herpes zoster, tinea corporis, tinea versicolor, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, and verruca vulgaris. Inflammatory conditions included acne, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis rosea, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, lichen planus, and urticaria. Skin of color–associated conditions included hidradenitis suppurativa, acanthosis nigricans, keloid, and melasma. Two questions utilizing a 5-point Likert scale assessing confidence in diagnosing light and dark skin also were included.
The pre-recorded 15-minute video lecture was given by 2 dermatology residents (P.L.K. and C.P.), and the learning objectives covered morphologic differences in lighter skin and darker skin, comparisons of common dermatologic diseases in lighter skin and darker skin, diseases more commonly affecting patients with SOC, and treatment considerations for conditions affecting skin and hair in patients with SOC. Photographs from the diagnostic accuracy assessment were not reused in the lecture. Detailed explanations on morphology, diagnostic pearls, and treatment options for all conditions tested were provided to participants upon completion of the 3-month posttest.
Statistical Analysis—Test scores were compared between conditions shown in lighter and darker skin types and from the pretest to the immediate posttest and 3-month posttest. Multiple linear regression was used to assess for intervention effects on lighter and darker skin scores controlling for provider type and specialty. All tests were 2-sided with significance at P<.05. Analyses were conducted using Stata 17.
Results
One hundred participants completed the pretest and immediate posttest, 36 of whom also completed the 3-month posttest (Table). There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics between the pretest and 3-month posttest groups.
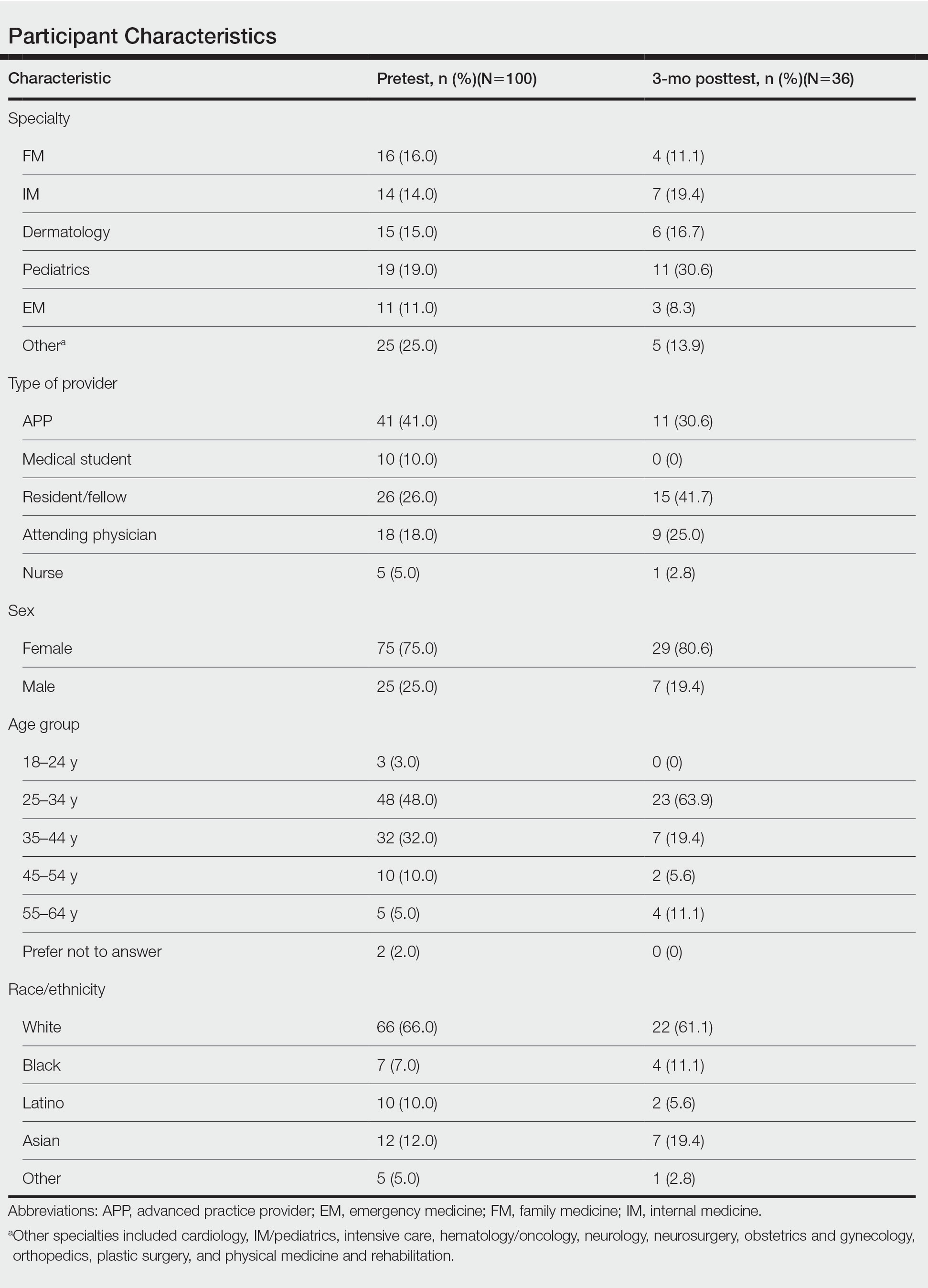
Test scores were correlated with provider type and specialty but not age, sex, or race/ethnicity. Specializing in dermatology and being a resident or attending physician were independently associated with higher test scores. Mean pretest diagnostic accuracy and confidence scores were higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with those shown in darker skin (13.6 vs 11.3 and 2.7 vs 1.9, respectively; both P<.001). Pretest diagnostic accuracy was significantly higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin for cancerous, inflammatory, and infectious conditions (72% vs 50%, 68% vs 55%, and 57% vs 47%, respectively; P<.001 for all)(Figure 1). Skin of color–associated conditions were not associated with significantly different scores for lighter skin compared with darker skin (79% vs 75%; P=.059).
Controlling for provider type and specialty, significantly improved diagnostic accuracy was seen in immediate posttest scores compared with pretest scores for conditions shown in both lighter and darker skin types (lighter: 15.2 vs 13.6; darker: 13.3 vs 11.3; both P<.001)(Figure 2). The immediate posttest demonstrated higher mean diagnostic accuracy and confidence scores for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin (diagnostic accuracy: 15.2 vs 13.3; confidence: 3.0 vs 2.6; both P<.001), but the disparity between scores was less than in the pretest.
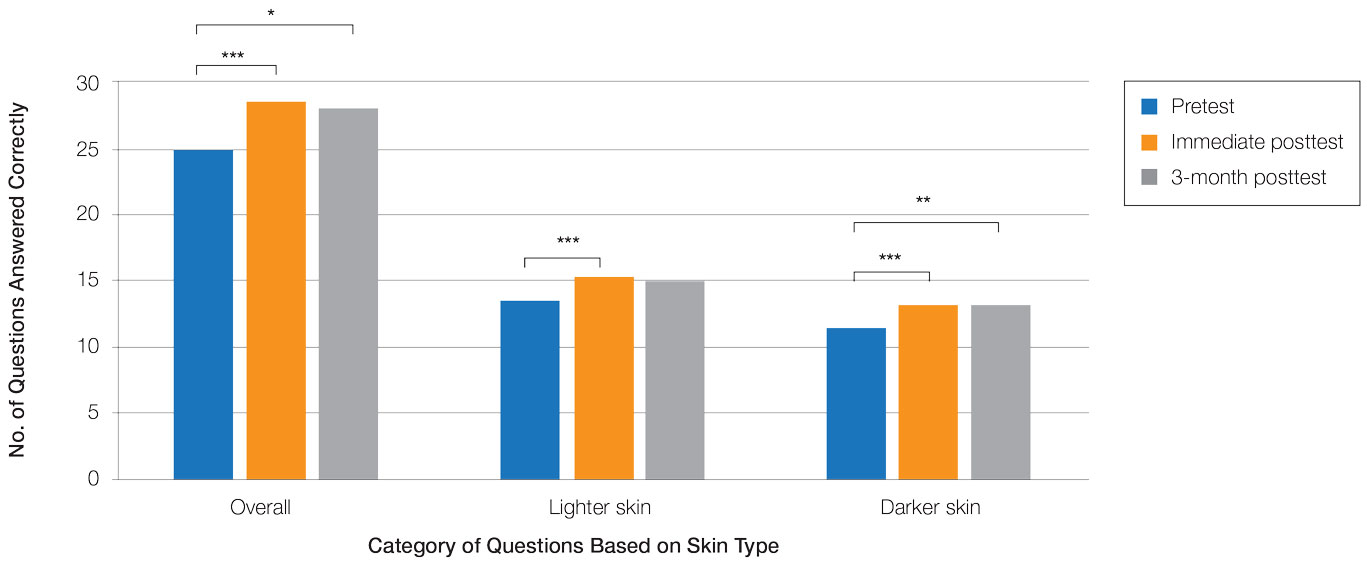
Following the 3-month posttest, improvement in diagnostic accuracy was noted among both lighter and darker skin types compared with the pretest, but the difference remained significant only for conditions shown in darker skin (mean scores, 11.3 vs 13.3; P<.01). Similarly, confidence in diagnosing conditions in both lighter and darker skin improved following the immediate posttest (mean scores, 2.7 vs 3.0 and 1.9 vs 2.6; both P<.001), and this improvement remained significant for only darker skin following the 3-month posttest (mean scores, 1.9 vs 2.3; P<.001). Despite these improvements, diagnostic accuracy and confidence remained higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin (diagnostic accuracy: 14.7 vs 13.3; P<.01; confidence: 2.8 vs 2.3; P<.001), though the disparity between scores was again less than in the pretest.
Comment
Our study showed that there are diagnostic disparities between lighter and darker skin types among interprofessional health care providers. Education on SOC should extend to interprofessional health care providers and other medical specialties involved in treating or triaging dermatologic diseases. A focused educational module may provide long-term improvements in diagnostic accuracy and confidence for conditions presenting in SOC. Differences in diagnostic accuracy between conditions shown in lighter and darker skin types were noted for the disease categories of infectious, cancerous, and inflammatory conditions, with the exception of conditions more frequently seen in patients with SOC. Learning resources for SOC-associated conditions are more likely to have greater representation of images depicting darker skin types.7 Future educational interventions may need to focus on dermatologic conditions that are not preferentially seen in patients with SOC. In our study, the pretest scores for conditions shown in darker skin were lowest among infectious and cancerous conditions. For infections, certain morphologic clues such as erythema are important for diagnosis but may be more subtle or difficult to discern in darker skin. It also is possible that providers may be less likely to suspect skin cancer in patients with SOC given that the morphologic presentation and/or anatomic site of involvement for skin cancers in SOC differs from those in lighter skin. Future educational interventions targeting disparities in diagnostic accuracy should focus on conditions that are not specifically associated with SOC.
Limitations of our study included the small number of participants, the study population came from a single institution, and a possible selection bias for providers interested in dermatology.
Conclusion
Disparities exist among interprofessional health care providers when treating conditions in patients with lighter skin compared to darker skin. An educational module for health care providers may provide long-term improvements in diagnostic accuracy and confidence for conditions presenting in patients with SOC.
- Fenton A, Elliott E, Shahbandi A, et al. Medical students’ ability to diagnose common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:957-958. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.078
- Mamo A, Szeto MD, Rietcheck H, et al. Evaluating medical student assessment of common dermatologic conditions across Fitzpatrick phototypes and skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:167-169. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.868
- Guda VA, Paek SY. Skin of color representation in commonly utilized medical student dermatology resources. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:799. doi:10.36849/JDD.5726
- Wilson BN, Sun M, Ashbaugh AG, et al. Assessment of skin of color and diversity and inclusion content of dermatologic published literature: an analysis and call to action. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:391-397. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.04.001
- Ibraheim MK, Gupta R, Dao H, et al. Evaluating skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: data from a national survey. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:228-233. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.11.015
- Gupta R, Ibraheim MK, Dao H Jr, et al. Assessing dermatology resident confidence in caring for patients with skin of color. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:873-878. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.08.019
- Chang MJ, Lipner SR. Analysis of skin color on the American Academy of Dermatology public education website. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:1236-1237. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5545
Dermatologic disparities disproportionately affect patients with skin of color (SOC). Two studies assessing the diagnostic accuracy of medical students have shown disparities in diagnosing common skin conditions presenting in darker skin compared to lighter skin at early stages of training.1,2 This knowledge gap could be attributed to the underrepresentation of SOC in dermatologic textbooks, journals, and educational curricula.3-6 It is important for dermatologists as well as physicians in other specialties and ancillary health care workers involved in treating or triaging dermatologic diseases to recognize common skin conditions presenting in SOC. We sought to evaluate the effectiveness of a focused educational module for improving diagnostic accuracy and confidence in treating SOC among interprofessional health care providers.
Methods
Interprofessional health care providers—medical students, residents/fellows, attending physicians, advanced practice providers (APPs), and nurses practicing across various medical specialties—at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School and Ascension Medical Group (both in Austin, Texas) were invited to participate in an institutional review board–exempt study involving a virtual SOC educational module from February through May 2021. The 1-hour module involved a pretest, a 15-minute lecture, an immediate posttest, and a 3-month posttest. All tests included the same 40 multiple-choice questions of 20 dermatologic conditions portrayed in lighter and darker skin types from VisualDx.com, and participants were asked to identify the condition in each photograph. Questions appeared one at a time in a randomized order, and answers could not be changed once submitted.
For analysis, the dermatologic conditions were categorized into 4 groups: cancerous, infectious, inflammatory, and SOC-associated conditions. Cancerous conditions included basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Infectious conditions included herpes zoster, tinea corporis, tinea versicolor, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, and verruca vulgaris. Inflammatory conditions included acne, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis rosea, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, lichen planus, and urticaria. Skin of color–associated conditions included hidradenitis suppurativa, acanthosis nigricans, keloid, and melasma. Two questions utilizing a 5-point Likert scale assessing confidence in diagnosing light and dark skin also were included.
The pre-recorded 15-minute video lecture was given by 2 dermatology residents (P.L.K. and C.P.), and the learning objectives covered morphologic differences in lighter skin and darker skin, comparisons of common dermatologic diseases in lighter skin and darker skin, diseases more commonly affecting patients with SOC, and treatment considerations for conditions affecting skin and hair in patients with SOC. Photographs from the diagnostic accuracy assessment were not reused in the lecture. Detailed explanations on morphology, diagnostic pearls, and treatment options for all conditions tested were provided to participants upon completion of the 3-month posttest.
Statistical Analysis—Test scores were compared between conditions shown in lighter and darker skin types and from the pretest to the immediate posttest and 3-month posttest. Multiple linear regression was used to assess for intervention effects on lighter and darker skin scores controlling for provider type and specialty. All tests were 2-sided with significance at P<.05. Analyses were conducted using Stata 17.
Results
One hundred participants completed the pretest and immediate posttest, 36 of whom also completed the 3-month posttest (Table). There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics between the pretest and 3-month posttest groups.

Test scores were correlated with provider type and specialty but not age, sex, or race/ethnicity. Specializing in dermatology and being a resident or attending physician were independently associated with higher test scores. Mean pretest diagnostic accuracy and confidence scores were higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with those shown in darker skin (13.6 vs 11.3 and 2.7 vs 1.9, respectively; both P<.001). Pretest diagnostic accuracy was significantly higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin for cancerous, inflammatory, and infectious conditions (72% vs 50%, 68% vs 55%, and 57% vs 47%, respectively; P<.001 for all)(Figure 1). Skin of color–associated conditions were not associated with significantly different scores for lighter skin compared with darker skin (79% vs 75%; P=.059).

Controlling for provider type and specialty, significantly improved diagnostic accuracy was seen in immediate posttest scores compared with pretest scores for conditions shown in both lighter and darker skin types (lighter: 15.2 vs 13.6; darker: 13.3 vs 11.3; both P<.001)(Figure 2). The immediate posttest demonstrated higher mean diagnostic accuracy and confidence scores for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin (diagnostic accuracy: 15.2 vs 13.3; confidence: 3.0 vs 2.6; both P<.001), but the disparity between scores was less than in the pretest.

Following the 3-month posttest, improvement in diagnostic accuracy was noted among both lighter and darker skin types compared with the pretest, but the difference remained significant only for conditions shown in darker skin (mean scores, 11.3 vs 13.3; P<.01). Similarly, confidence in diagnosing conditions in both lighter and darker skin improved following the immediate posttest (mean scores, 2.7 vs 3.0 and 1.9 vs 2.6; both P<.001), and this improvement remained significant for only darker skin following the 3-month posttest (mean scores, 1.9 vs 2.3; P<.001). Despite these improvements, diagnostic accuracy and confidence remained higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin (diagnostic accuracy: 14.7 vs 13.3; P<.01; confidence: 2.8 vs 2.3; P<.001), though the disparity between scores was again less than in the pretest.
Comment
Our study showed that there are diagnostic disparities between lighter and darker skin types among interprofessional health care providers. Education on SOC should extend to interprofessional health care providers and other medical specialties involved in treating or triaging dermatologic diseases. A focused educational module may provide long-term improvements in diagnostic accuracy and confidence for conditions presenting in SOC. Differences in diagnostic accuracy between conditions shown in lighter and darker skin types were noted for the disease categories of infectious, cancerous, and inflammatory conditions, with the exception of conditions more frequently seen in patients with SOC. Learning resources for SOC-associated conditions are more likely to have greater representation of images depicting darker skin types.7 Future educational interventions may need to focus on dermatologic conditions that are not preferentially seen in patients with SOC. In our study, the pretest scores for conditions shown in darker skin were lowest among infectious and cancerous conditions. For infections, certain morphologic clues such as erythema are important for diagnosis but may be more subtle or difficult to discern in darker skin. It also is possible that providers may be less likely to suspect skin cancer in patients with SOC given that the morphologic presentation and/or anatomic site of involvement for skin cancers in SOC differs from those in lighter skin. Future educational interventions targeting disparities in diagnostic accuracy should focus on conditions that are not specifically associated with SOC.
Limitations of our study included the small number of participants, the study population came from a single institution, and a possible selection bias for providers interested in dermatology.
Conclusion
Disparities exist among interprofessional health care providers when treating conditions in patients with lighter skin compared to darker skin. An educational module for health care providers may provide long-term improvements in diagnostic accuracy and confidence for conditions presenting in patients with SOC.
Dermatologic disparities disproportionately affect patients with skin of color (SOC). Two studies assessing the diagnostic accuracy of medical students have shown disparities in diagnosing common skin conditions presenting in darker skin compared to lighter skin at early stages of training.1,2 This knowledge gap could be attributed to the underrepresentation of SOC in dermatologic textbooks, journals, and educational curricula.3-6 It is important for dermatologists as well as physicians in other specialties and ancillary health care workers involved in treating or triaging dermatologic diseases to recognize common skin conditions presenting in SOC. We sought to evaluate the effectiveness of a focused educational module for improving diagnostic accuracy and confidence in treating SOC among interprofessional health care providers.
Methods
Interprofessional health care providers—medical students, residents/fellows, attending physicians, advanced practice providers (APPs), and nurses practicing across various medical specialties—at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School and Ascension Medical Group (both in Austin, Texas) were invited to participate in an institutional review board–exempt study involving a virtual SOC educational module from February through May 2021. The 1-hour module involved a pretest, a 15-minute lecture, an immediate posttest, and a 3-month posttest. All tests included the same 40 multiple-choice questions of 20 dermatologic conditions portrayed in lighter and darker skin types from VisualDx.com, and participants were asked to identify the condition in each photograph. Questions appeared one at a time in a randomized order, and answers could not be changed once submitted.
For analysis, the dermatologic conditions were categorized into 4 groups: cancerous, infectious, inflammatory, and SOC-associated conditions. Cancerous conditions included basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Infectious conditions included herpes zoster, tinea corporis, tinea versicolor, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, and verruca vulgaris. Inflammatory conditions included acne, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis rosea, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, lichen planus, and urticaria. Skin of color–associated conditions included hidradenitis suppurativa, acanthosis nigricans, keloid, and melasma. Two questions utilizing a 5-point Likert scale assessing confidence in diagnosing light and dark skin also were included.
The pre-recorded 15-minute video lecture was given by 2 dermatology residents (P.L.K. and C.P.), and the learning objectives covered morphologic differences in lighter skin and darker skin, comparisons of common dermatologic diseases in lighter skin and darker skin, diseases more commonly affecting patients with SOC, and treatment considerations for conditions affecting skin and hair in patients with SOC. Photographs from the diagnostic accuracy assessment were not reused in the lecture. Detailed explanations on morphology, diagnostic pearls, and treatment options for all conditions tested were provided to participants upon completion of the 3-month posttest.
Statistical Analysis—Test scores were compared between conditions shown in lighter and darker skin types and from the pretest to the immediate posttest and 3-month posttest. Multiple linear regression was used to assess for intervention effects on lighter and darker skin scores controlling for provider type and specialty. All tests were 2-sided with significance at P<.05. Analyses were conducted using Stata 17.
Results
One hundred participants completed the pretest and immediate posttest, 36 of whom also completed the 3-month posttest (Table). There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics between the pretest and 3-month posttest groups.

Test scores were correlated with provider type and specialty but not age, sex, or race/ethnicity. Specializing in dermatology and being a resident or attending physician were independently associated with higher test scores. Mean pretest diagnostic accuracy and confidence scores were higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with those shown in darker skin (13.6 vs 11.3 and 2.7 vs 1.9, respectively; both P<.001). Pretest diagnostic accuracy was significantly higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin for cancerous, inflammatory, and infectious conditions (72% vs 50%, 68% vs 55%, and 57% vs 47%, respectively; P<.001 for all)(Figure 1). Skin of color–associated conditions were not associated with significantly different scores for lighter skin compared with darker skin (79% vs 75%; P=.059).

Controlling for provider type and specialty, significantly improved diagnostic accuracy was seen in immediate posttest scores compared with pretest scores for conditions shown in both lighter and darker skin types (lighter: 15.2 vs 13.6; darker: 13.3 vs 11.3; both P<.001)(Figure 2). The immediate posttest demonstrated higher mean diagnostic accuracy and confidence scores for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin (diagnostic accuracy: 15.2 vs 13.3; confidence: 3.0 vs 2.6; both P<.001), but the disparity between scores was less than in the pretest.

Following the 3-month posttest, improvement in diagnostic accuracy was noted among both lighter and darker skin types compared with the pretest, but the difference remained significant only for conditions shown in darker skin (mean scores, 11.3 vs 13.3; P<.01). Similarly, confidence in diagnosing conditions in both lighter and darker skin improved following the immediate posttest (mean scores, 2.7 vs 3.0 and 1.9 vs 2.6; both P<.001), and this improvement remained significant for only darker skin following the 3-month posttest (mean scores, 1.9 vs 2.3; P<.001). Despite these improvements, diagnostic accuracy and confidence remained higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin (diagnostic accuracy: 14.7 vs 13.3; P<.01; confidence: 2.8 vs 2.3; P<.001), though the disparity between scores was again less than in the pretest.
Comment
Our study showed that there are diagnostic disparities between lighter and darker skin types among interprofessional health care providers. Education on SOC should extend to interprofessional health care providers and other medical specialties involved in treating or triaging dermatologic diseases. A focused educational module may provide long-term improvements in diagnostic accuracy and confidence for conditions presenting in SOC. Differences in diagnostic accuracy between conditions shown in lighter and darker skin types were noted for the disease categories of infectious, cancerous, and inflammatory conditions, with the exception of conditions more frequently seen in patients with SOC. Learning resources for SOC-associated conditions are more likely to have greater representation of images depicting darker skin types.7 Future educational interventions may need to focus on dermatologic conditions that are not preferentially seen in patients with SOC. In our study, the pretest scores for conditions shown in darker skin were lowest among infectious and cancerous conditions. For infections, certain morphologic clues such as erythema are important for diagnosis but may be more subtle or difficult to discern in darker skin. It also is possible that providers may be less likely to suspect skin cancer in patients with SOC given that the morphologic presentation and/or anatomic site of involvement for skin cancers in SOC differs from those in lighter skin. Future educational interventions targeting disparities in diagnostic accuracy should focus on conditions that are not specifically associated with SOC.
Limitations of our study included the small number of participants, the study population came from a single institution, and a possible selection bias for providers interested in dermatology.
Conclusion
Disparities exist among interprofessional health care providers when treating conditions in patients with lighter skin compared to darker skin. An educational module for health care providers may provide long-term improvements in diagnostic accuracy and confidence for conditions presenting in patients with SOC.
- Fenton A, Elliott E, Shahbandi A, et al. Medical students’ ability to diagnose common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:957-958. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.078
- Mamo A, Szeto MD, Rietcheck H, et al. Evaluating medical student assessment of common dermatologic conditions across Fitzpatrick phototypes and skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:167-169. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.868
- Guda VA, Paek SY. Skin of color representation in commonly utilized medical student dermatology resources. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:799. doi:10.36849/JDD.5726
- Wilson BN, Sun M, Ashbaugh AG, et al. Assessment of skin of color and diversity and inclusion content of dermatologic published literature: an analysis and call to action. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:391-397. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.04.001
- Ibraheim MK, Gupta R, Dao H, et al. Evaluating skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: data from a national survey. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:228-233. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.11.015
- Gupta R, Ibraheim MK, Dao H Jr, et al. Assessing dermatology resident confidence in caring for patients with skin of color. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:873-878. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.08.019
- Chang MJ, Lipner SR. Analysis of skin color on the American Academy of Dermatology public education website. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:1236-1237. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5545
- Fenton A, Elliott E, Shahbandi A, et al. Medical students’ ability to diagnose common dermatologic conditions in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:957-958. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.078
- Mamo A, Szeto MD, Rietcheck H, et al. Evaluating medical student assessment of common dermatologic conditions across Fitzpatrick phototypes and skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:167-169. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.868
- Guda VA, Paek SY. Skin of color representation in commonly utilized medical student dermatology resources. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:799. doi:10.36849/JDD.5726
- Wilson BN, Sun M, Ashbaugh AG, et al. Assessment of skin of color and diversity and inclusion content of dermatologic published literature: an analysis and call to action. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:391-397. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.04.001
- Ibraheim MK, Gupta R, Dao H, et al. Evaluating skin of color education in dermatology residency programs: data from a national survey. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:228-233. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.11.015
- Gupta R, Ibraheim MK, Dao H Jr, et al. Assessing dermatology resident confidence in caring for patients with skin of color. Clin Dermatol. 2021;39:873-878. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.08.019
- Chang MJ, Lipner SR. Analysis of skin color on the American Academy of Dermatology public education website. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:1236-1237. doi:10.36849/JDD.2020.5545
Practice Points
- Disparities exist among interprofessional health care providers when diagnosing conditions in patients with lighter and darker skin, specifically for infectious, cancerous, or inflammatory conditions vs conditions that are preferentially seen in patients with skin of color (SOC).
- A focused educational module for health care providers may provide long-term improvements in diagnostic accuracy and confidence for conditions presenting in patients with SOC.
White Spots on the Extremities
The Diagnosis: Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides
Histopathology showed an atypical lymphoid infiltrate with expanded cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei of irregular contours in the dermoepidermal junction (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical stains of atypical lymphocytes demonstrated the presence of CD3, CD8, and CD5, as well as the absence of CD7 and CD4 lymphocytes (Figure 2). The T-cell γ rearrangement showed polyclonal lymphocytes with 5% tumor cells. The histologic and clinical findings along with our patient’s medical history led to a diagnosis of stage IA (<10% body surface area involvement) hypopigmented mycosis fungoides (hMF).1 Our patient was treated with triamcinolone cream 0.1%; she noted an improvement in her symptoms at 2-month follow-up.
Hypopigmented MF is an uncommon manifestation of MF with unknown prevalence and incidence rates. Mycosis fungoides is considered the most common subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that classically presents as a chronic, indolent, hypopigmented or depigmented macule or patch, commonly with scaling, in sunprotected areas such as the trunk and proximal arms and legs. It predominantly affects younger adults with darker skin tones and may be present in the pediatric population within the first decade of life.1 Classically, MF affects White patients aged 55 to 60 years. Disease progression is slow, with an incidence rate of 10% of tumor or extracutaneous involvement in the early stages of disease. A lack of specificity on the clinical and histopathologic findings in the initial stage often contributes to the diagnostic delay of hMF. As seen in our patient, this disease can be misdiagnosed as tinea versicolor, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, vitiligo, pityriasis alba, subcutaneous lupus erythematosus, or Hansen disease due to prolonged hypopigmented lesions.2 The clinical findings and histopathologic results including immunohistochemistry confirmed the diagnosis of hMF and ruled out pityriasis alba, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, subcutaneous lupus erythematosus, and vitiligo.
The etiology and pathophysiology of hMF are not fully understood; however, it is hypothesized that melanocyte degeneration, abnormal melanogenesis, and disturbance of melanosome transfer result from the clonal expansion of T helper memory cells. T-cell dyscrasia has been reported to evolve into hMF during etanercept therapy.3 Clinically, hMF presents as hypopigmented papulosquamous, eczematous, or erythrodermic patches, plaques, and tumors with poorly defined atrophied borders. Multiple biopsies of steroid-naive lesions are needed for the diagnosis, as the initial hMF histologic finding cannot be specific for diagnostic confirmation. Common histopathologic findings include a bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate with epidermotropism, intraepidermal nests of atypical cells, or cerebriform nuclei lymphocytes on hematoxylin and eosin staining. In comparison to classical MF epidermotropism, CD4− and CD8+ atypical cells aid in the diagnosis of hMF. Although hMF carries a good prognosis and a benign clinical course,4 full-body computed tomography or positron emission tomography/computed tomography as well as laboratory analysis for lactate dehydrogenase should be pursued if lymphadenopathy, systemic symptoms, or advancedstage hMF are present.
Treatment of hMF depends on the disease stage. Psoralen plus UVA and narrowband UVB can be utilized for the initial stages with a relatively fast response and remission of lesions as early as the first 2 months of treatment. In addition to phototherapy, stage IA to IIA mycosis fungoides with localized skin lesions can benefit from topical steroids, topical retinoids, imiquimod, nitrogen mustard, and carmustine. For advanced stages of mycosis fungoides, combination therapy consisting of psoralen plus UVA with an oral retinoid, interferon alfa, and systemic chemotherapy commonly are prescribed. Maintenance therapy is used for prolonging remission; however, long-term phototherapy is not recommended due to the risk for skin cancer. Unfortunately, hMF requires long-term treatment due to its waxing and waning course, and recurrence may occur after complete resolution.5
- Furlan FC, Sanches JA. Hypopigmented mycosis fungoides: a review of its clinical features and pathophysiology. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:954-960.
- Lambroza E, Cohen SR, Lebwohl M, et al. Hypopigmented variant of mycosis fungoides: demography, histopathology, and treatment of seven cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:987-993.
- Chuang GS, Wasserman DI, Byers HR, et al. Hypopigmented T-cell dyscrasia evolving to hypopigmented mycosis fungoides during etanercept therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59(5 suppl):S121-S122.
- Agar NS, Wedgeworth E, Crichton S, et al. Survival outcomes and prognostic factors in mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome: validation of the revised International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas/ European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer staging proposal. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4730-4739.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part II. prognosis, management, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014; 70:223.e1-17; quiz 240-242.
The Diagnosis: Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides
Histopathology showed an atypical lymphoid infiltrate with expanded cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei of irregular contours in the dermoepidermal junction (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical stains of atypical lymphocytes demonstrated the presence of CD3, CD8, and CD5, as well as the absence of CD7 and CD4 lymphocytes (Figure 2). The T-cell γ rearrangement showed polyclonal lymphocytes with 5% tumor cells. The histologic and clinical findings along with our patient’s medical history led to a diagnosis of stage IA (<10% body surface area involvement) hypopigmented mycosis fungoides (hMF).1 Our patient was treated with triamcinolone cream 0.1%; she noted an improvement in her symptoms at 2-month follow-up.

Hypopigmented MF is an uncommon manifestation of MF with unknown prevalence and incidence rates. Mycosis fungoides is considered the most common subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that classically presents as a chronic, indolent, hypopigmented or depigmented macule or patch, commonly with scaling, in sunprotected areas such as the trunk and proximal arms and legs. It predominantly affects younger adults with darker skin tones and may be present in the pediatric population within the first decade of life.1 Classically, MF affects White patients aged 55 to 60 years. Disease progression is slow, with an incidence rate of 10% of tumor or extracutaneous involvement in the early stages of disease. A lack of specificity on the clinical and histopathologic findings in the initial stage often contributes to the diagnostic delay of hMF. As seen in our patient, this disease can be misdiagnosed as tinea versicolor, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, vitiligo, pityriasis alba, subcutaneous lupus erythematosus, or Hansen disease due to prolonged hypopigmented lesions.2 The clinical findings and histopathologic results including immunohistochemistry confirmed the diagnosis of hMF and ruled out pityriasis alba, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, subcutaneous lupus erythematosus, and vitiligo.

The etiology and pathophysiology of hMF are not fully understood; however, it is hypothesized that melanocyte degeneration, abnormal melanogenesis, and disturbance of melanosome transfer result from the clonal expansion of T helper memory cells. T-cell dyscrasia has been reported to evolve into hMF during etanercept therapy.3 Clinically, hMF presents as hypopigmented papulosquamous, eczematous, or erythrodermic patches, plaques, and tumors with poorly defined atrophied borders. Multiple biopsies of steroid-naive lesions are needed for the diagnosis, as the initial hMF histologic finding cannot be specific for diagnostic confirmation. Common histopathologic findings include a bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate with epidermotropism, intraepidermal nests of atypical cells, or cerebriform nuclei lymphocytes on hematoxylin and eosin staining. In comparison to classical MF epidermotropism, CD4− and CD8+ atypical cells aid in the diagnosis of hMF. Although hMF carries a good prognosis and a benign clinical course,4 full-body computed tomography or positron emission tomography/computed tomography as well as laboratory analysis for lactate dehydrogenase should be pursued if lymphadenopathy, systemic symptoms, or advancedstage hMF are present.
Treatment of hMF depends on the disease stage. Psoralen plus UVA and narrowband UVB can be utilized for the initial stages with a relatively fast response and remission of lesions as early as the first 2 months of treatment. In addition to phototherapy, stage IA to IIA mycosis fungoides with localized skin lesions can benefit from topical steroids, topical retinoids, imiquimod, nitrogen mustard, and carmustine. For advanced stages of mycosis fungoides, combination therapy consisting of psoralen plus UVA with an oral retinoid, interferon alfa, and systemic chemotherapy commonly are prescribed. Maintenance therapy is used for prolonging remission; however, long-term phototherapy is not recommended due to the risk for skin cancer. Unfortunately, hMF requires long-term treatment due to its waxing and waning course, and recurrence may occur after complete resolution.5
The Diagnosis: Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides
Histopathology showed an atypical lymphoid infiltrate with expanded cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei of irregular contours in the dermoepidermal junction (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical stains of atypical lymphocytes demonstrated the presence of CD3, CD8, and CD5, as well as the absence of CD7 and CD4 lymphocytes (Figure 2). The T-cell γ rearrangement showed polyclonal lymphocytes with 5% tumor cells. The histologic and clinical findings along with our patient’s medical history led to a diagnosis of stage IA (<10% body surface area involvement) hypopigmented mycosis fungoides (hMF).1 Our patient was treated with triamcinolone cream 0.1%; she noted an improvement in her symptoms at 2-month follow-up.

Hypopigmented MF is an uncommon manifestation of MF with unknown prevalence and incidence rates. Mycosis fungoides is considered the most common subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that classically presents as a chronic, indolent, hypopigmented or depigmented macule or patch, commonly with scaling, in sunprotected areas such as the trunk and proximal arms and legs. It predominantly affects younger adults with darker skin tones and may be present in the pediatric population within the first decade of life.1 Classically, MF affects White patients aged 55 to 60 years. Disease progression is slow, with an incidence rate of 10% of tumor or extracutaneous involvement in the early stages of disease. A lack of specificity on the clinical and histopathologic findings in the initial stage often contributes to the diagnostic delay of hMF. As seen in our patient, this disease can be misdiagnosed as tinea versicolor, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, vitiligo, pityriasis alba, subcutaneous lupus erythematosus, or Hansen disease due to prolonged hypopigmented lesions.2 The clinical findings and histopathologic results including immunohistochemistry confirmed the diagnosis of hMF and ruled out pityriasis alba, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, subcutaneous lupus erythematosus, and vitiligo.

The etiology and pathophysiology of hMF are not fully understood; however, it is hypothesized that melanocyte degeneration, abnormal melanogenesis, and disturbance of melanosome transfer result from the clonal expansion of T helper memory cells. T-cell dyscrasia has been reported to evolve into hMF during etanercept therapy.3 Clinically, hMF presents as hypopigmented papulosquamous, eczematous, or erythrodermic patches, plaques, and tumors with poorly defined atrophied borders. Multiple biopsies of steroid-naive lesions are needed for the diagnosis, as the initial hMF histologic finding cannot be specific for diagnostic confirmation. Common histopathologic findings include a bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate with epidermotropism, intraepidermal nests of atypical cells, or cerebriform nuclei lymphocytes on hematoxylin and eosin staining. In comparison to classical MF epidermotropism, CD4− and CD8+ atypical cells aid in the diagnosis of hMF. Although hMF carries a good prognosis and a benign clinical course,4 full-body computed tomography or positron emission tomography/computed tomography as well as laboratory analysis for lactate dehydrogenase should be pursued if lymphadenopathy, systemic symptoms, or advancedstage hMF are present.
Treatment of hMF depends on the disease stage. Psoralen plus UVA and narrowband UVB can be utilized for the initial stages with a relatively fast response and remission of lesions as early as the first 2 months of treatment. In addition to phototherapy, stage IA to IIA mycosis fungoides with localized skin lesions can benefit from topical steroids, topical retinoids, imiquimod, nitrogen mustard, and carmustine. For advanced stages of mycosis fungoides, combination therapy consisting of psoralen plus UVA with an oral retinoid, interferon alfa, and systemic chemotherapy commonly are prescribed. Maintenance therapy is used for prolonging remission; however, long-term phototherapy is not recommended due to the risk for skin cancer. Unfortunately, hMF requires long-term treatment due to its waxing and waning course, and recurrence may occur after complete resolution.5
- Furlan FC, Sanches JA. Hypopigmented mycosis fungoides: a review of its clinical features and pathophysiology. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:954-960.
- Lambroza E, Cohen SR, Lebwohl M, et al. Hypopigmented variant of mycosis fungoides: demography, histopathology, and treatment of seven cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:987-993.
- Chuang GS, Wasserman DI, Byers HR, et al. Hypopigmented T-cell dyscrasia evolving to hypopigmented mycosis fungoides during etanercept therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59(5 suppl):S121-S122.
- Agar NS, Wedgeworth E, Crichton S, et al. Survival outcomes and prognostic factors in mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome: validation of the revised International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas/ European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer staging proposal. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4730-4739.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part II. prognosis, management, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014; 70:223.e1-17; quiz 240-242.
- Furlan FC, Sanches JA. Hypopigmented mycosis fungoides: a review of its clinical features and pathophysiology. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:954-960.
- Lambroza E, Cohen SR, Lebwohl M, et al. Hypopigmented variant of mycosis fungoides: demography, histopathology, and treatment of seven cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:987-993.
- Chuang GS, Wasserman DI, Byers HR, et al. Hypopigmented T-cell dyscrasia evolving to hypopigmented mycosis fungoides during etanercept therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59(5 suppl):S121-S122.
- Agar NS, Wedgeworth E, Crichton S, et al. Survival outcomes and prognostic factors in mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome: validation of the revised International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas/ European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer staging proposal. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4730-4739.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part II. prognosis, management, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014; 70:223.e1-17; quiz 240-242.
A 52-year-old Black woman presented with self-described whitened spots on the arms and legs of 2 years’ duration. She experienced no improvement with ketoconazole cream and topical calcineurin inhibitors prescribed during a prior dermatology visit at an outside institution. She denied pain or pruritus. A review of systems as well as the patient’s medical history were noncontributory. A prior biopsy at an outside institution revealed an interface dermatitis suggestive of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The patient noted social drinking and denied tobacco use. She had no known allergies to medications and currently was on tamoxifen for breast cancer following a right mastectomy. Physical examination showed hypopigmented macules and patches on the left upper arm and right proximal leg. The center of the lesions was not erythematous or scaly. Palpation did not reveal enlarged lymph nodes, and laboratory analyses ruled out low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. Punch biopsies from the left arm and right thigh were performed.
Multiprong strategy makes clinical trials less White
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023