User login
Tuberculosis Management: Returning to Pre-Pandemic Priorities
- Global tuberculosis report 2022. World Health Organization. Published October 27, 2022. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729
- WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment – drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, 2022 update. World Health Organization. Published December 15, 2022. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240063129
- Migliori GB, Tiberi S. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022 ;26(7):590-591. doi:10.5588/ijtld.22.0263.
- Lange C et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(10):1142-1144. doi:10.1164/rccm.202202-0393ED
- Esmail A et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(10):1214-1227. doi:10.1164/rccm.202107-1779OC
- WHO BPaLM Accelerator Platform: to support the call to action for implementation of the shorter and more effective treatment for all people suffering from drug-resistant TB. World Health Organization. Published May 9, 2023. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2023/05/09/default-calendar/who-bpalm-accelerator-platform–to-support-the-call-to-action-for-implementation-of-the-shorter-and-moreeffective-
- Trevisi L et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207(11):1525-1532. doi:10.1164/rccm.202211-2125OC
- Domínguez J et al; TBnet and RESIST-TB networks. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023;23(4):e122-e137. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00875-1
- WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis: module 3: diagnosis: rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detection, 2021 update. World Health Organization. Published July 7, 2021. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240030589treatment-for-all-people-suffering-from-drug-resistant-tb
- Global tuberculosis report 2022. World Health Organization. Published October 27, 2022. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729
- WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment – drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, 2022 update. World Health Organization. Published December 15, 2022. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240063129
- Migliori GB, Tiberi S. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022 ;26(7):590-591. doi:10.5588/ijtld.22.0263.
- Lange C et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(10):1142-1144. doi:10.1164/rccm.202202-0393ED
- Esmail A et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(10):1214-1227. doi:10.1164/rccm.202107-1779OC
- WHO BPaLM Accelerator Platform: to support the call to action for implementation of the shorter and more effective treatment for all people suffering from drug-resistant TB. World Health Organization. Published May 9, 2023. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2023/05/09/default-calendar/who-bpalm-accelerator-platform–to-support-the-call-to-action-for-implementation-of-the-shorter-and-moreeffective-
- Trevisi L et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207(11):1525-1532. doi:10.1164/rccm.202211-2125OC
- Domínguez J et al; TBnet and RESIST-TB networks. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023;23(4):e122-e137. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00875-1
- WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis: module 3: diagnosis: rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detection, 2021 update. World Health Organization. Published July 7, 2021. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240030589treatment-for-all-people-suffering-from-drug-resistant-tb
- Global tuberculosis report 2022. World Health Organization. Published October 27, 2022. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729
- WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment – drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, 2022 update. World Health Organization. Published December 15, 2022. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240063129
- Migliori GB, Tiberi S. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2022 ;26(7):590-591. doi:10.5588/ijtld.22.0263.
- Lange C et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(10):1142-1144. doi:10.1164/rccm.202202-0393ED
- Esmail A et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(10):1214-1227. doi:10.1164/rccm.202107-1779OC
- WHO BPaLM Accelerator Platform: to support the call to action for implementation of the shorter and more effective treatment for all people suffering from drug-resistant TB. World Health Organization. Published May 9, 2023. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2023/05/09/default-calendar/who-bpalm-accelerator-platform–to-support-the-call-to-action-for-implementation-of-the-shorter-and-moreeffective-
- Trevisi L et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207(11):1525-1532. doi:10.1164/rccm.202211-2125OC
- Domínguez J et al; TBnet and RESIST-TB networks. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023;23(4):e122-e137. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00875-1
- WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis: module 3: diagnosis: rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detection, 2021 update. World Health Organization. Published July 7, 2021. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240030589treatment-for-all-people-suffering-from-drug-resistant-tb
Severity score predicts mortality in pulmonary tuberculosis
, based on data from approximately 400 individuals.
Although a mortality risk-prediction score could improve treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis patients, such a score has not been previously reported, wrote Takeshi Osawa, MD, of Fukujuji Hospital, Tokyo, and colleagues.
In a study published in the journal CHEST, the researchers used 252 patients from a previous perspective study of newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis as the development cohort, and recruited 165 additional patients between March 2021 and September 2022.
The primary endpoint was all-cause in-hospital mortality. Based on data from the development group, the researchers found that age 65 years and older and age 80 years and older, hypoxemia, activities of daily living, bilateral pulmonary lesions, lymphocyte count of less than 720 microliters, serum albumin less than 2.86 mg/dL, C-reactive protein (CRP) 3.97 mg/dL or higher, and procalcitonin (PCT) 0.130 ng/mL or higher were predictors of all-cause in hospital mortality.
The researchers used this information to create the disease severity score, known as the AHL score. The AHL included three clinical parameters: activity in daily living (semi-dependent, 1 point; totally dependent, 2 points); hypoxemia (1 point) and lymphocytes (< 720 /mcL, 1 point).
The scoring systems for the three parameters were, respectively, 1 point for semi-dependent and 2 points totally dependent (for activity in daily living), 1 point for presence of hypoxemia, and 1 point for lymphocytes less than 720 per microliter. The researchers stratified the scores into levels of low, intermediate, and high risk, with scores of 0, 1-2, and 3-4, respectively.
All-cause in hospital mortality occurred in 39 (15.5%) and 17 (10.3%) of patients in the developmental and validation cohorts, respectively.
The AHL score effectively predicted mortality, dividing patients into three groups of 1.3% low-risk, 8.9% intermediate risk, and 39.3% high-risk in the validation cohort, with a Harrell’s c-statistic of 0.842.
The corresponding numbers for the development cohort were 0, 13.5%, and 55.8%, with a c-statistic of 0.902.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data from “smear-negative” patients who were treated as outpatients, and more research is needed to determine the applicability of the AHL score in an outpatient population, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on long-term mortality in surviving patients who were discharged, and the reliance on assessments that can be performed only in clinical settings in developed countries, they said.
However, the results support the feasibility of the AHL score in clinical settings to accurately predict mortality in patients with pulmonary TB, and may help optimize treatments for this population, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. All authors disclosed nonfinancial support in the form of measuring reagents from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation during the study but had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on data from approximately 400 individuals.
Although a mortality risk-prediction score could improve treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis patients, such a score has not been previously reported, wrote Takeshi Osawa, MD, of Fukujuji Hospital, Tokyo, and colleagues.
In a study published in the journal CHEST, the researchers used 252 patients from a previous perspective study of newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis as the development cohort, and recruited 165 additional patients between March 2021 and September 2022.
The primary endpoint was all-cause in-hospital mortality. Based on data from the development group, the researchers found that age 65 years and older and age 80 years and older, hypoxemia, activities of daily living, bilateral pulmonary lesions, lymphocyte count of less than 720 microliters, serum albumin less than 2.86 mg/dL, C-reactive protein (CRP) 3.97 mg/dL or higher, and procalcitonin (PCT) 0.130 ng/mL or higher were predictors of all-cause in hospital mortality.
The researchers used this information to create the disease severity score, known as the AHL score. The AHL included three clinical parameters: activity in daily living (semi-dependent, 1 point; totally dependent, 2 points); hypoxemia (1 point) and lymphocytes (< 720 /mcL, 1 point).
The scoring systems for the three parameters were, respectively, 1 point for semi-dependent and 2 points totally dependent (for activity in daily living), 1 point for presence of hypoxemia, and 1 point for lymphocytes less than 720 per microliter. The researchers stratified the scores into levels of low, intermediate, and high risk, with scores of 0, 1-2, and 3-4, respectively.
All-cause in hospital mortality occurred in 39 (15.5%) and 17 (10.3%) of patients in the developmental and validation cohorts, respectively.
The AHL score effectively predicted mortality, dividing patients into three groups of 1.3% low-risk, 8.9% intermediate risk, and 39.3% high-risk in the validation cohort, with a Harrell’s c-statistic of 0.842.
The corresponding numbers for the development cohort were 0, 13.5%, and 55.8%, with a c-statistic of 0.902.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data from “smear-negative” patients who were treated as outpatients, and more research is needed to determine the applicability of the AHL score in an outpatient population, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on long-term mortality in surviving patients who were discharged, and the reliance on assessments that can be performed only in clinical settings in developed countries, they said.
However, the results support the feasibility of the AHL score in clinical settings to accurately predict mortality in patients with pulmonary TB, and may help optimize treatments for this population, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. All authors disclosed nonfinancial support in the form of measuring reagents from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation during the study but had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on data from approximately 400 individuals.
Although a mortality risk-prediction score could improve treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis patients, such a score has not been previously reported, wrote Takeshi Osawa, MD, of Fukujuji Hospital, Tokyo, and colleagues.
In a study published in the journal CHEST, the researchers used 252 patients from a previous perspective study of newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis as the development cohort, and recruited 165 additional patients between March 2021 and September 2022.
The primary endpoint was all-cause in-hospital mortality. Based on data from the development group, the researchers found that age 65 years and older and age 80 years and older, hypoxemia, activities of daily living, bilateral pulmonary lesions, lymphocyte count of less than 720 microliters, serum albumin less than 2.86 mg/dL, C-reactive protein (CRP) 3.97 mg/dL or higher, and procalcitonin (PCT) 0.130 ng/mL or higher were predictors of all-cause in hospital mortality.
The researchers used this information to create the disease severity score, known as the AHL score. The AHL included three clinical parameters: activity in daily living (semi-dependent, 1 point; totally dependent, 2 points); hypoxemia (1 point) and lymphocytes (< 720 /mcL, 1 point).
The scoring systems for the three parameters were, respectively, 1 point for semi-dependent and 2 points totally dependent (for activity in daily living), 1 point for presence of hypoxemia, and 1 point for lymphocytes less than 720 per microliter. The researchers stratified the scores into levels of low, intermediate, and high risk, with scores of 0, 1-2, and 3-4, respectively.
All-cause in hospital mortality occurred in 39 (15.5%) and 17 (10.3%) of patients in the developmental and validation cohorts, respectively.
The AHL score effectively predicted mortality, dividing patients into three groups of 1.3% low-risk, 8.9% intermediate risk, and 39.3% high-risk in the validation cohort, with a Harrell’s c-statistic of 0.842.
The corresponding numbers for the development cohort were 0, 13.5%, and 55.8%, with a c-statistic of 0.902.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data from “smear-negative” patients who were treated as outpatients, and more research is needed to determine the applicability of the AHL score in an outpatient population, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on long-term mortality in surviving patients who were discharged, and the reliance on assessments that can be performed only in clinical settings in developed countries, they said.
However, the results support the feasibility of the AHL score in clinical settings to accurately predict mortality in patients with pulmonary TB, and may help optimize treatments for this population, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. All authors disclosed nonfinancial support in the form of measuring reagents from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation during the study but had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST
Pulmonary aspergillosis predicts poor outcomes in critically ill flu patients
Critically ill influenza patients with associated pulmonary aspergillosis were more than twice as likely to die in intensive care than those without the added infection, based on data from a meta-analysis of more than 1,700 individuals.
Reports of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA) are rising in critically ill patients, but data on risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes are limited, Lawrence Y. Lu, MD, of The Prince Charles Hospital, Brisbane, Australia, and colleagues wrote. In addition, diagnosis of IAPA can be challenging, and many clinicians report low awareness of the condition.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 10 observational studies including 1,720 critically ill influenza patients aged 16 years and older; of these, 331 had IAPA, for a prevalence of 19.2%. The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality in the hospital and in the ICU. Secondary outcomes included ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, and the need for supportive care (invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, pressor support, and extracorporeal membranous oxygenation).
Overall, mortality among flu patients in the ICU was significantly higher for those with IAPA than those without IAPA (45.0% vs. 23.8%, respectively), as was all-cause mortality (46.4% vs. 26.2%, respectively; odds ratio, 2.6 and P < .001 for both ICU and all-cause mortality).
Factors significantly associated with an increased risk for IAPA included organ transplant (OR, 4.8), hematogenous malignancy (OR, 2.5), being immunocompromised in some way (OR, 2.2), and prolonged corticosteroid use prior to hospital admission (OR, 2.4).
IAPA also was associated with more severe disease, a higher rate of complications, longer ICU stays, and a greater need for organ supports, the researchers noted. Clinical features not significantly more common in patients with IAPA included fever, hemoptysis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design of the included studies and inability to control for all potential confounders, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the variations in study design, variability of practice patterns across locations, and inclusion of data mainly from countries of high socioeconomic status.
“Given the apparent waning of the COVID-19 pandemic and re-emergence of influenza, our analysis also revealed other gaps in the current literature, including the need to validate newer diagnostic methods and to develop a system to measure severity of IAPA,” the researchers added.
However, the current study results reflect IAPA prevalence from previous studies, and support the need to have a lower threshold for IAPA testing and initiation of antifungal treatment, even with limited data for clinical guidance, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Critically ill influenza patients with associated pulmonary aspergillosis were more than twice as likely to die in intensive care than those without the added infection, based on data from a meta-analysis of more than 1,700 individuals.
Reports of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA) are rising in critically ill patients, but data on risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes are limited, Lawrence Y. Lu, MD, of The Prince Charles Hospital, Brisbane, Australia, and colleagues wrote. In addition, diagnosis of IAPA can be challenging, and many clinicians report low awareness of the condition.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 10 observational studies including 1,720 critically ill influenza patients aged 16 years and older; of these, 331 had IAPA, for a prevalence of 19.2%. The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality in the hospital and in the ICU. Secondary outcomes included ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, and the need for supportive care (invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, pressor support, and extracorporeal membranous oxygenation).
Overall, mortality among flu patients in the ICU was significantly higher for those with IAPA than those without IAPA (45.0% vs. 23.8%, respectively), as was all-cause mortality (46.4% vs. 26.2%, respectively; odds ratio, 2.6 and P < .001 for both ICU and all-cause mortality).
Factors significantly associated with an increased risk for IAPA included organ transplant (OR, 4.8), hematogenous malignancy (OR, 2.5), being immunocompromised in some way (OR, 2.2), and prolonged corticosteroid use prior to hospital admission (OR, 2.4).
IAPA also was associated with more severe disease, a higher rate of complications, longer ICU stays, and a greater need for organ supports, the researchers noted. Clinical features not significantly more common in patients with IAPA included fever, hemoptysis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design of the included studies and inability to control for all potential confounders, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the variations in study design, variability of practice patterns across locations, and inclusion of data mainly from countries of high socioeconomic status.
“Given the apparent waning of the COVID-19 pandemic and re-emergence of influenza, our analysis also revealed other gaps in the current literature, including the need to validate newer diagnostic methods and to develop a system to measure severity of IAPA,” the researchers added.
However, the current study results reflect IAPA prevalence from previous studies, and support the need to have a lower threshold for IAPA testing and initiation of antifungal treatment, even with limited data for clinical guidance, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Critically ill influenza patients with associated pulmonary aspergillosis were more than twice as likely to die in intensive care than those without the added infection, based on data from a meta-analysis of more than 1,700 individuals.
Reports of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA) are rising in critically ill patients, but data on risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes are limited, Lawrence Y. Lu, MD, of The Prince Charles Hospital, Brisbane, Australia, and colleagues wrote. In addition, diagnosis of IAPA can be challenging, and many clinicians report low awareness of the condition.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 10 observational studies including 1,720 critically ill influenza patients aged 16 years and older; of these, 331 had IAPA, for a prevalence of 19.2%. The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality in the hospital and in the ICU. Secondary outcomes included ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, and the need for supportive care (invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, pressor support, and extracorporeal membranous oxygenation).
Overall, mortality among flu patients in the ICU was significantly higher for those with IAPA than those without IAPA (45.0% vs. 23.8%, respectively), as was all-cause mortality (46.4% vs. 26.2%, respectively; odds ratio, 2.6 and P < .001 for both ICU and all-cause mortality).
Factors significantly associated with an increased risk for IAPA included organ transplant (OR, 4.8), hematogenous malignancy (OR, 2.5), being immunocompromised in some way (OR, 2.2), and prolonged corticosteroid use prior to hospital admission (OR, 2.4).
IAPA also was associated with more severe disease, a higher rate of complications, longer ICU stays, and a greater need for organ supports, the researchers noted. Clinical features not significantly more common in patients with IAPA included fever, hemoptysis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design of the included studies and inability to control for all potential confounders, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the variations in study design, variability of practice patterns across locations, and inclusion of data mainly from countries of high socioeconomic status.
“Given the apparent waning of the COVID-19 pandemic and re-emergence of influenza, our analysis also revealed other gaps in the current literature, including the need to validate newer diagnostic methods and to develop a system to measure severity of IAPA,” the researchers added.
However, the current study results reflect IAPA prevalence from previous studies, and support the need to have a lower threshold for IAPA testing and initiation of antifungal treatment, even with limited data for clinical guidance, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST
Data Trends 2023: Respiratory Illnesses
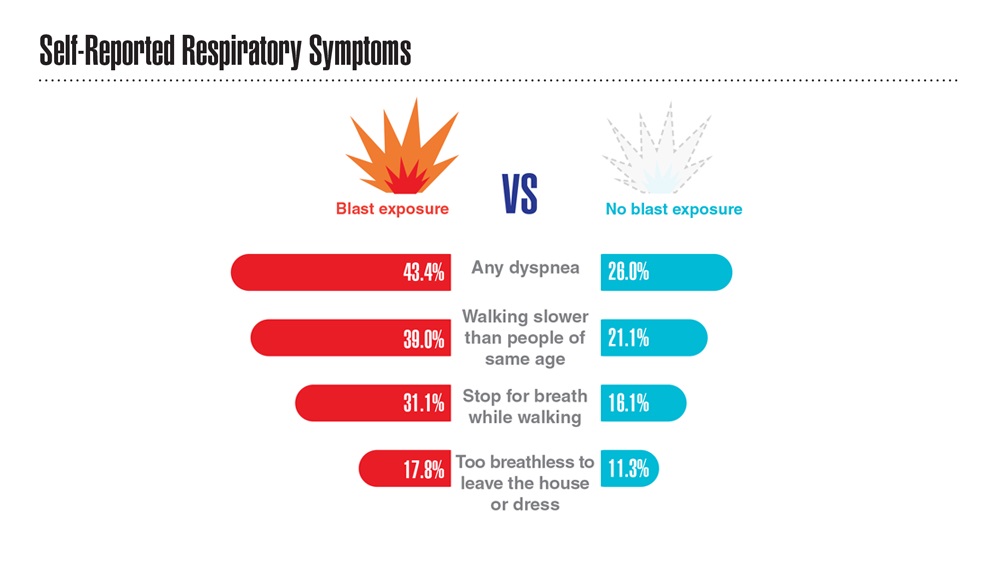
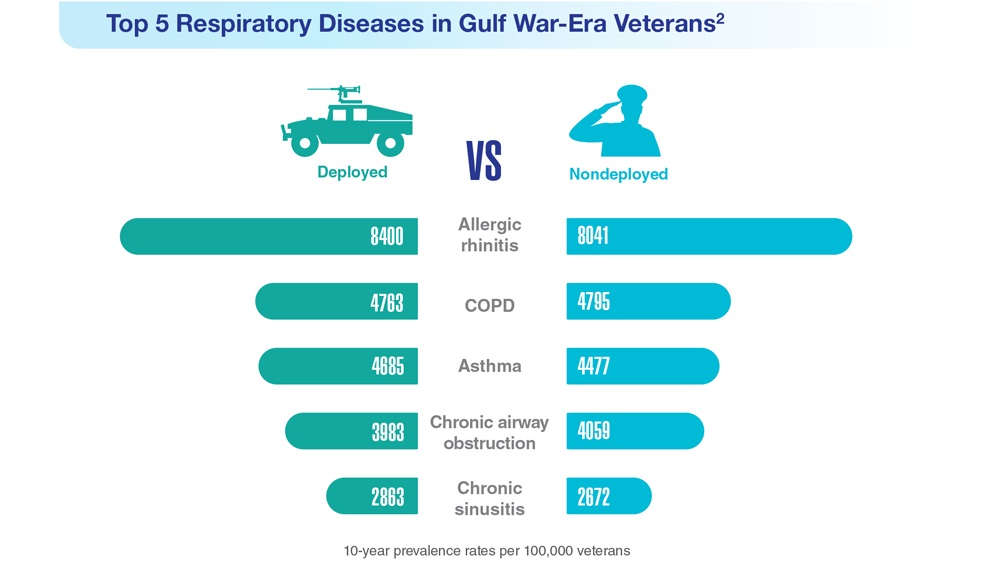
- Hines SE et al. Respir Med. 2022;202:106963. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106963
- Dursa EK et al. Am J Ind Med. 2020;63(11):980-987. doi:10.1002/ajim.23172
- Bamonti PM et al. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Hines SE et al. Respir Med. 2022;202:106963. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106963
- Dursa EK et al. Am J Ind Med. 2020;63(11):980-987. doi:10.1002/ajim.23172
- Bamonti PM et al. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Hines SE et al. Respir Med. 2022;202:106963. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106963
- Dursa EK et al. Am J Ind Med. 2020;63(11):980-987. doi:10.1002/ajim.23172
- Bamonti PM et al. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
Federal Health Care Data Trends 2023
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
Three antibiotic regimens show similar effectiveness for CAP
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CHEST
Progressive pulmonary fibrosis: treatment and support
MILAN – Numerous unresolved questions surround progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) treatment, according to Elisabeth Bendstrup, MD, PhD, a researcher and clinical professor in the department of clinical medicine – department of respiratory diseases and allergy, Aarhus (Denmark) University, Denmark. These questions regard the optimal timing for treatment initiation, the role of available medications, either as monotherapy or in combination, and nonpharmacologic support options.
What’s in the toolbox?
Pulmonologists who manage PPF have a range of treatment options at their disposal. This includes careful patient observation, with treatment initiation based on clinical necessity. The therapeutic arsenal comprises immunomodulatory treatments, antifibrotic agents, palliative and supportive care, and, for a minority of patients, lung transplantation.
“Once a patient is diagnosed with PPF, it is important to remember that the diagnostic criteria from the guidelines are not exactly the same of those accepted for the reimbursement of antifibrotic treatments in different countries,” Dr. Bendstrup said, suggesting that nonclinical considerations could also potentially influence the treatment choice. She spoke at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society.
Michael Kreuter, MD, director of the Lung Center at the University Hospital in Mainz, Germany, provided insight into the introduction of antifibrotic drugs for the treatment of PPF. Drawing from nearly a decade ago when the first antifibrotic medication was approved for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), Dr. Kreuter noted its effectiveness in slowing disease progression, although it does not reverse it. Subsequently, the discovery that non-IPF diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, exhibited IPF-like behavior led to the exploration of the use of the same drugs for similar conditions, even if not IPF.
“That’s how antifibrotic treatments came into place. Now we have more trials and data to be discussed in the future,” Dr. Kreuter added. He highlighted that antifibrotic drugs are effective for several diseases. Most of those diseases are treated with different anti-inflammatory drugs, which makes it difficult to decide when to start antifibrotic therapy and how to eventually combine it with different pharmacologic approaches.
A pivotal starting point
a question only partially addressed by existing guidelines. Dr. Bendstrup advocated for a comprehensive baseline evaluation. Factors to be considered include symptom burden, the severity of lung decline, radiologic characteristics, signs of alveolar inflammation, progression risk factors, quality of life, patient preferences, and medical history. “All these should be best discussed in a multidisciplinary team, including pulmonologists, nurses, experts in palliative care, occupational physicians, and more,” she said.
Current guidelines recommend nintedanib for PPF treatment for patients who have failed standard management for fibrotic interstitial lung disease (ILD) other than IPF. However, the definition of “standard management” remains a topic of debate, and it is acknowledged that evidence-based guidance for a standard of care varies among patients. Dr. Bendstrup pointed out the limited guidance clinicians receive from these guidelines. “As clinicians, we are not left with very much help from here.”
Choosing the right approach
Dr. Bendstrup delved into the factors influencing the choice between antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory therapies. This decision hinges on whether the patient presents with a predominantly inflammatory or a fibrotic progressive phenotype. Certain clinical characteristics contribute to the decision. Factors such as younger age, female gender, and the presence of connective tissue disease lean toward an inflammatory phenotype. Radiologic patterns, such as organized pneumonia, hypersensitivity pneumonia, or usual interstitial pneumonia–like patterns also provide valuable clues. Additionally, genetics plays a role, with shorter telomeres indicating a more fibrotic phenotype and an increased risk of immunomodulatory treatment side effects in non-IPF ILDs.
Bendstrup referred to a recent position paper on treatment recommendations and many other studies that support the use of different treatments for patients with PPF. The authors highlighted limited evidence for immunomodulation in fibrotic ILD, though such treatment is generally used except for ILD associated with systemic sclerosis. Moreover, the guidelines conditionally recommend nintedanib and call for further research on pirfenidone in PPF.
“We need intelligent, well-designed trials looking at subgroups of patients at higher risk, maybe based on molecular identification. We also need to have good biomarkers to better classify our patients based on disease behavior and treatment response. There’s a lot of discussion of biomarkers for progression, much less – if any – on biomarkers for the response to treatment. And we need them as well,” Dr. Bendstrup said in an interview.
The role of supportive care
Effective PPF treatment extends beyond pharmacologic interventions. It encompasses symptom management, patient education on vaccination and smoking cessation, and fostering social support networks. Psychological support, supplemental oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation are integral components of care.
Elisabeth Robertson, a PPF patient representative from the United Kingdom, emphasized the importance of palliative care, not just in end-of-life scenarios but throughout the patient’s journey. Palliative care encompasses symptom alleviation, enabling patients to stay at home when possible, addressing mental health, and preparing for the end of life. Such holistic care can significantly enhance the patient’s quality of life.
The cochair of the session, Marlies S. Wijsenbeek, MD, PhD, pulmonary physician and head of the ILD Centre at the Erasmus University Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, underscored that palliative care begins at diagnosis and involves managing symptom burdens. “Supportive care also includes nurses, as they are precious for the patients while answering their questions and can help save time for the doctors,” she said in an interview.
In the discussion on treatment decisions, experts agreed on the pivotal role of patients in decision-making. However, Dr. Kreuter highlighted two critical factors that influence successful patient-doctor interactions: the cultural backgrounds of patients and their relatives, and the attitudes of health care providers.
Dr. Bendstrup has received honoraria or consultation fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Astra Zeneca, Chiesi, and Daiichi Sankyo. Ms. Robertson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN – Numerous unresolved questions surround progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) treatment, according to Elisabeth Bendstrup, MD, PhD, a researcher and clinical professor in the department of clinical medicine – department of respiratory diseases and allergy, Aarhus (Denmark) University, Denmark. These questions regard the optimal timing for treatment initiation, the role of available medications, either as monotherapy or in combination, and nonpharmacologic support options.
What’s in the toolbox?
Pulmonologists who manage PPF have a range of treatment options at their disposal. This includes careful patient observation, with treatment initiation based on clinical necessity. The therapeutic arsenal comprises immunomodulatory treatments, antifibrotic agents, palliative and supportive care, and, for a minority of patients, lung transplantation.
“Once a patient is diagnosed with PPF, it is important to remember that the diagnostic criteria from the guidelines are not exactly the same of those accepted for the reimbursement of antifibrotic treatments in different countries,” Dr. Bendstrup said, suggesting that nonclinical considerations could also potentially influence the treatment choice. She spoke at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society.
Michael Kreuter, MD, director of the Lung Center at the University Hospital in Mainz, Germany, provided insight into the introduction of antifibrotic drugs for the treatment of PPF. Drawing from nearly a decade ago when the first antifibrotic medication was approved for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), Dr. Kreuter noted its effectiveness in slowing disease progression, although it does not reverse it. Subsequently, the discovery that non-IPF diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, exhibited IPF-like behavior led to the exploration of the use of the same drugs for similar conditions, even if not IPF.
“That’s how antifibrotic treatments came into place. Now we have more trials and data to be discussed in the future,” Dr. Kreuter added. He highlighted that antifibrotic drugs are effective for several diseases. Most of those diseases are treated with different anti-inflammatory drugs, which makes it difficult to decide when to start antifibrotic therapy and how to eventually combine it with different pharmacologic approaches.
A pivotal starting point
a question only partially addressed by existing guidelines. Dr. Bendstrup advocated for a comprehensive baseline evaluation. Factors to be considered include symptom burden, the severity of lung decline, radiologic characteristics, signs of alveolar inflammation, progression risk factors, quality of life, patient preferences, and medical history. “All these should be best discussed in a multidisciplinary team, including pulmonologists, nurses, experts in palliative care, occupational physicians, and more,” she said.
Current guidelines recommend nintedanib for PPF treatment for patients who have failed standard management for fibrotic interstitial lung disease (ILD) other than IPF. However, the definition of “standard management” remains a topic of debate, and it is acknowledged that evidence-based guidance for a standard of care varies among patients. Dr. Bendstrup pointed out the limited guidance clinicians receive from these guidelines. “As clinicians, we are not left with very much help from here.”
Choosing the right approach
Dr. Bendstrup delved into the factors influencing the choice between antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory therapies. This decision hinges on whether the patient presents with a predominantly inflammatory or a fibrotic progressive phenotype. Certain clinical characteristics contribute to the decision. Factors such as younger age, female gender, and the presence of connective tissue disease lean toward an inflammatory phenotype. Radiologic patterns, such as organized pneumonia, hypersensitivity pneumonia, or usual interstitial pneumonia–like patterns also provide valuable clues. Additionally, genetics plays a role, with shorter telomeres indicating a more fibrotic phenotype and an increased risk of immunomodulatory treatment side effects in non-IPF ILDs.
Bendstrup referred to a recent position paper on treatment recommendations and many other studies that support the use of different treatments for patients with PPF. The authors highlighted limited evidence for immunomodulation in fibrotic ILD, though such treatment is generally used except for ILD associated with systemic sclerosis. Moreover, the guidelines conditionally recommend nintedanib and call for further research on pirfenidone in PPF.
“We need intelligent, well-designed trials looking at subgroups of patients at higher risk, maybe based on molecular identification. We also need to have good biomarkers to better classify our patients based on disease behavior and treatment response. There’s a lot of discussion of biomarkers for progression, much less – if any – on biomarkers for the response to treatment. And we need them as well,” Dr. Bendstrup said in an interview.
The role of supportive care
Effective PPF treatment extends beyond pharmacologic interventions. It encompasses symptom management, patient education on vaccination and smoking cessation, and fostering social support networks. Psychological support, supplemental oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation are integral components of care.
Elisabeth Robertson, a PPF patient representative from the United Kingdom, emphasized the importance of palliative care, not just in end-of-life scenarios but throughout the patient’s journey. Palliative care encompasses symptom alleviation, enabling patients to stay at home when possible, addressing mental health, and preparing for the end of life. Such holistic care can significantly enhance the patient’s quality of life.
The cochair of the session, Marlies S. Wijsenbeek, MD, PhD, pulmonary physician and head of the ILD Centre at the Erasmus University Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, underscored that palliative care begins at diagnosis and involves managing symptom burdens. “Supportive care also includes nurses, as they are precious for the patients while answering their questions and can help save time for the doctors,” she said in an interview.
In the discussion on treatment decisions, experts agreed on the pivotal role of patients in decision-making. However, Dr. Kreuter highlighted two critical factors that influence successful patient-doctor interactions: the cultural backgrounds of patients and their relatives, and the attitudes of health care providers.
Dr. Bendstrup has received honoraria or consultation fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Astra Zeneca, Chiesi, and Daiichi Sankyo. Ms. Robertson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN – Numerous unresolved questions surround progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) treatment, according to Elisabeth Bendstrup, MD, PhD, a researcher and clinical professor in the department of clinical medicine – department of respiratory diseases and allergy, Aarhus (Denmark) University, Denmark. These questions regard the optimal timing for treatment initiation, the role of available medications, either as monotherapy or in combination, and nonpharmacologic support options.
What’s in the toolbox?
Pulmonologists who manage PPF have a range of treatment options at their disposal. This includes careful patient observation, with treatment initiation based on clinical necessity. The therapeutic arsenal comprises immunomodulatory treatments, antifibrotic agents, palliative and supportive care, and, for a minority of patients, lung transplantation.
“Once a patient is diagnosed with PPF, it is important to remember that the diagnostic criteria from the guidelines are not exactly the same of those accepted for the reimbursement of antifibrotic treatments in different countries,” Dr. Bendstrup said, suggesting that nonclinical considerations could also potentially influence the treatment choice. She spoke at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society.
Michael Kreuter, MD, director of the Lung Center at the University Hospital in Mainz, Germany, provided insight into the introduction of antifibrotic drugs for the treatment of PPF. Drawing from nearly a decade ago when the first antifibrotic medication was approved for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), Dr. Kreuter noted its effectiveness in slowing disease progression, although it does not reverse it. Subsequently, the discovery that non-IPF diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, exhibited IPF-like behavior led to the exploration of the use of the same drugs for similar conditions, even if not IPF.
“That’s how antifibrotic treatments came into place. Now we have more trials and data to be discussed in the future,” Dr. Kreuter added. He highlighted that antifibrotic drugs are effective for several diseases. Most of those diseases are treated with different anti-inflammatory drugs, which makes it difficult to decide when to start antifibrotic therapy and how to eventually combine it with different pharmacologic approaches.
A pivotal starting point
a question only partially addressed by existing guidelines. Dr. Bendstrup advocated for a comprehensive baseline evaluation. Factors to be considered include symptom burden, the severity of lung decline, radiologic characteristics, signs of alveolar inflammation, progression risk factors, quality of life, patient preferences, and medical history. “All these should be best discussed in a multidisciplinary team, including pulmonologists, nurses, experts in palliative care, occupational physicians, and more,” she said.
Current guidelines recommend nintedanib for PPF treatment for patients who have failed standard management for fibrotic interstitial lung disease (ILD) other than IPF. However, the definition of “standard management” remains a topic of debate, and it is acknowledged that evidence-based guidance for a standard of care varies among patients. Dr. Bendstrup pointed out the limited guidance clinicians receive from these guidelines. “As clinicians, we are not left with very much help from here.”
Choosing the right approach
Dr. Bendstrup delved into the factors influencing the choice between antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory therapies. This decision hinges on whether the patient presents with a predominantly inflammatory or a fibrotic progressive phenotype. Certain clinical characteristics contribute to the decision. Factors such as younger age, female gender, and the presence of connective tissue disease lean toward an inflammatory phenotype. Radiologic patterns, such as organized pneumonia, hypersensitivity pneumonia, or usual interstitial pneumonia–like patterns also provide valuable clues. Additionally, genetics plays a role, with shorter telomeres indicating a more fibrotic phenotype and an increased risk of immunomodulatory treatment side effects in non-IPF ILDs.
Bendstrup referred to a recent position paper on treatment recommendations and many other studies that support the use of different treatments for patients with PPF. The authors highlighted limited evidence for immunomodulation in fibrotic ILD, though such treatment is generally used except for ILD associated with systemic sclerosis. Moreover, the guidelines conditionally recommend nintedanib and call for further research on pirfenidone in PPF.
“We need intelligent, well-designed trials looking at subgroups of patients at higher risk, maybe based on molecular identification. We also need to have good biomarkers to better classify our patients based on disease behavior and treatment response. There’s a lot of discussion of biomarkers for progression, much less – if any – on biomarkers for the response to treatment. And we need them as well,” Dr. Bendstrup said in an interview.
The role of supportive care
Effective PPF treatment extends beyond pharmacologic interventions. It encompasses symptom management, patient education on vaccination and smoking cessation, and fostering social support networks. Psychological support, supplemental oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation are integral components of care.
Elisabeth Robertson, a PPF patient representative from the United Kingdom, emphasized the importance of palliative care, not just in end-of-life scenarios but throughout the patient’s journey. Palliative care encompasses symptom alleviation, enabling patients to stay at home when possible, addressing mental health, and preparing for the end of life. Such holistic care can significantly enhance the patient’s quality of life.
The cochair of the session, Marlies S. Wijsenbeek, MD, PhD, pulmonary physician and head of the ILD Centre at the Erasmus University Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, underscored that palliative care begins at diagnosis and involves managing symptom burdens. “Supportive care also includes nurses, as they are precious for the patients while answering their questions and can help save time for the doctors,” she said in an interview.
In the discussion on treatment decisions, experts agreed on the pivotal role of patients in decision-making. However, Dr. Kreuter highlighted two critical factors that influence successful patient-doctor interactions: the cultural backgrounds of patients and their relatives, and the attitudes of health care providers.
Dr. Bendstrup has received honoraria or consultation fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Astra Zeneca, Chiesi, and Daiichi Sankyo. Ms. Robertson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ERS 2023
Paxlovid and Lagevrio benefit COVID outpatients in Omicron era
The American College of Physicians has issued an updated version of its living, rapid practice point guideline on the best treatment options for outpatients with confirmed COVID-19 in the era of the dominant Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The recommendations in version 2 apply to persons presenting with mild to moderate infection and symptom onset in the past 5 days who are at high risk for progression to severe disease and potential hospitalization or death.
Version 1 appeared in late 2022.
While outpatient management is appropriate for most patients, treatment should be personalized and based on careful risk stratification and informed decision-making, said the guideline authors, led by Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, MHA, vice president of clinical policy and the Center for Evidence Reviews at the ACP in Philadelphia.
Practice points
- Consider the oral antivirals nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) or molnupiravir (Lagevrio) for symptomatic outpatients with confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 who are within 5 days of the onset of symptoms and at high risk for progressing to severe disease.
New evidence for the Omicron variant suggests a possible net benefit of the antiviral molnupiravir versus standard or no treatment in terms of reducing recovery time if treatment is initiated within 5 days of symptom onset. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with reductions in COVID-19 hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
“The practice points only address [whether] treatments work compared to placebo, no treatment, or usual care,” cautioned Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH, MACP, chair of the ACP’s Population Health and Medical Science Committee and a professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University VA Portland Health Care System. The ACP continues to monitor the evidence. “Once enough evidence has emerged, it will be possible to compare treatments to each other. Until that time we are unable to determine if there is an advantage to using one treatment over another.”
- Do not use the antiparasitic ivermectin (Stromectol) or the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab (Xevudy) to treat this patient population. “It is not expected to be effective against the Omicron variant,” Dr. Humphrey said.
There was no evidence to support the use of medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, antihistamines, SSRIs, and multiple other agents.
“The guideline is not a departure from previous knowledge and reflects what appears in other guidelines and is already being done generally in practice,” said Mirella Salvatore, MD, an associate professor of medicine and population health sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was not involved in the ACP statement. It is therefore unlikely the recommendations will trigger controversy or negative feedback, added Dr. Salvatore, who is also a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. “We believe that our evidence-based approach, which considers the balance of benefits and harms of various treatments, will be embraced by the physician community,” Dr. Humphrey said.
The updated recommendations are based on new data from the evidence review of multiple treatments, which concluded that both nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir likely improve outcomes for outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. The review was conducted after the emergence of the Omicron variant by the ACP Center for Evidence Reviews at Cochrane Austria/University for Continuing Education Krems (Austria).
Review details
Inclusion criteria were modified to focus on the Omicron variant by limiting eligible studies to only those enrolling patients on or after Nov. 26, 2021. The investigators included two randomized controlled trials and six retrospective cohort studies and ranked quality of evidence for the effectiveness of the following treatments, compared with usual care or no treatment: azithromycin, camostat mesylate, chloroquine-hydroxychloroquine, chlorpheniramine, colchicine, convalescent plasma, corticosteroids, ensitrelvir, favipiravir, fluvoxamine, ivermectin, lopinavir-ritonavir, molnupiravir, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, metformin, niclosamide, nitazoxanide, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and remdesivir.
It compared results for all-cause and COVID-specific mortality, recovery, time to recovery, COVID hospitalization, and adverse and serious adverse events.
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a reduction in hospitalization caused by COVID-19 of 0.7% versus 1.2% (moderate certainty of evidence [COE]) and a reduction in all-cause mortality of less than 0.1% versus 0.2% (moderate COE).
Molnupiravir led to a higher recovery rate of 31.8% versus 22.6% (moderate COE) and a reduced time to recovery of 9 versus 15 median days (moderate COE). It had no effect, however, on all-cause mortality: 0.02% versus 0.04% (moderate COE). Nor did it affect the incidence of serious adverse events: 0.4% versus 0.3% (moderate COE).
“There have been no head-to-head comparative studies of these two treatments, but nirmatrelvir-ritonavir appears to be the preferred treatment,” Dr. Salvatore said. She noted that molnupiravir cannot be used in pregnant women or young persons under age 18, while nirmatrelvir-ritonavir carries the risk of drug interactions. Viral rebound and recurrence of symptoms have been reported in some patients receiving nirmatrelvir-ritonavir.
In other review findings, ivermectin had no effect on time to recovery (moderate COE) and adverse events versus placebo (low COE). Sotrovimab resulted in no difference in all-cause mortality, compared with no treatment (low COE). There were no eligible studies for all of the other treatments of interest nor were there any that specifically evaluated the benefits and harms of treatments for the Omicron variant.
The panel pointed to the need for more evaluation of the efficacy, effectiveness, and comparative effectiveness, as well as harms of pharmacologic and biologic treatments of COVID-19 in the outpatient setting, particularly in the context of changing dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants and subvariants.
Another area requiring further research is the effectiveness of retreatment in patients with previous COVID-19 infection. Subgroup analyses are also needed to assess whether the efficacy and effectiveness of outpatient treatments vary by age, sex, socioeconomic status, and comorbid conditions – or by SARS-CoV-2 variant, immunity status (prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination status, or time since infection or vaccination), symptom duration, or disease severity.
Dr. Salvatore agreed that more research is needed in special convalescent groups. “For instance, those with cancer who are immunocompromised may need longer treatment and adjunctive treatment with convalescent plasma. But is difficult to find a large enough study with 5,000 immunocompromised patients.”
Financial support for the development of the practice points came exclusively from the ACP operating budget. The evidence review was funded by the ACP. The authors disclosed no relevant high-level competing interests with regard to this guidance, although several authors reported intellectual interests in various areas of research. Dr. Salvatore disclosed no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments but is engaged in influenza research for Genentech.
The American College of Physicians has issued an updated version of its living, rapid practice point guideline on the best treatment options for outpatients with confirmed COVID-19 in the era of the dominant Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The recommendations in version 2 apply to persons presenting with mild to moderate infection and symptom onset in the past 5 days who are at high risk for progression to severe disease and potential hospitalization or death.
Version 1 appeared in late 2022.
While outpatient management is appropriate for most patients, treatment should be personalized and based on careful risk stratification and informed decision-making, said the guideline authors, led by Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, MHA, vice president of clinical policy and the Center for Evidence Reviews at the ACP in Philadelphia.
Practice points
- Consider the oral antivirals nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) or molnupiravir (Lagevrio) for symptomatic outpatients with confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 who are within 5 days of the onset of symptoms and at high risk for progressing to severe disease.
New evidence for the Omicron variant suggests a possible net benefit of the antiviral molnupiravir versus standard or no treatment in terms of reducing recovery time if treatment is initiated within 5 days of symptom onset. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with reductions in COVID-19 hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
“The practice points only address [whether] treatments work compared to placebo, no treatment, or usual care,” cautioned Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH, MACP, chair of the ACP’s Population Health and Medical Science Committee and a professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University VA Portland Health Care System. The ACP continues to monitor the evidence. “Once enough evidence has emerged, it will be possible to compare treatments to each other. Until that time we are unable to determine if there is an advantage to using one treatment over another.”
- Do not use the antiparasitic ivermectin (Stromectol) or the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab (Xevudy) to treat this patient population. “It is not expected to be effective against the Omicron variant,” Dr. Humphrey said.
There was no evidence to support the use of medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, antihistamines, SSRIs, and multiple other agents.
“The guideline is not a departure from previous knowledge and reflects what appears in other guidelines and is already being done generally in practice,” said Mirella Salvatore, MD, an associate professor of medicine and population health sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was not involved in the ACP statement. It is therefore unlikely the recommendations will trigger controversy or negative feedback, added Dr. Salvatore, who is also a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. “We believe that our evidence-based approach, which considers the balance of benefits and harms of various treatments, will be embraced by the physician community,” Dr. Humphrey said.
The updated recommendations are based on new data from the evidence review of multiple treatments, which concluded that both nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir likely improve outcomes for outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. The review was conducted after the emergence of the Omicron variant by the ACP Center for Evidence Reviews at Cochrane Austria/University for Continuing Education Krems (Austria).
Review details
Inclusion criteria were modified to focus on the Omicron variant by limiting eligible studies to only those enrolling patients on or after Nov. 26, 2021. The investigators included two randomized controlled trials and six retrospective cohort studies and ranked quality of evidence for the effectiveness of the following treatments, compared with usual care or no treatment: azithromycin, camostat mesylate, chloroquine-hydroxychloroquine, chlorpheniramine, colchicine, convalescent plasma, corticosteroids, ensitrelvir, favipiravir, fluvoxamine, ivermectin, lopinavir-ritonavir, molnupiravir, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, metformin, niclosamide, nitazoxanide, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and remdesivir.
It compared results for all-cause and COVID-specific mortality, recovery, time to recovery, COVID hospitalization, and adverse and serious adverse events.
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a reduction in hospitalization caused by COVID-19 of 0.7% versus 1.2% (moderate certainty of evidence [COE]) and a reduction in all-cause mortality of less than 0.1% versus 0.2% (moderate COE).
Molnupiravir led to a higher recovery rate of 31.8% versus 22.6% (moderate COE) and a reduced time to recovery of 9 versus 15 median days (moderate COE). It had no effect, however, on all-cause mortality: 0.02% versus 0.04% (moderate COE). Nor did it affect the incidence of serious adverse events: 0.4% versus 0.3% (moderate COE).
“There have been no head-to-head comparative studies of these two treatments, but nirmatrelvir-ritonavir appears to be the preferred treatment,” Dr. Salvatore said. She noted that molnupiravir cannot be used in pregnant women or young persons under age 18, while nirmatrelvir-ritonavir carries the risk of drug interactions. Viral rebound and recurrence of symptoms have been reported in some patients receiving nirmatrelvir-ritonavir.
In other review findings, ivermectin had no effect on time to recovery (moderate COE) and adverse events versus placebo (low COE). Sotrovimab resulted in no difference in all-cause mortality, compared with no treatment (low COE). There were no eligible studies for all of the other treatments of interest nor were there any that specifically evaluated the benefits and harms of treatments for the Omicron variant.
The panel pointed to the need for more evaluation of the efficacy, effectiveness, and comparative effectiveness, as well as harms of pharmacologic and biologic treatments of COVID-19 in the outpatient setting, particularly in the context of changing dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants and subvariants.
Another area requiring further research is the effectiveness of retreatment in patients with previous COVID-19 infection. Subgroup analyses are also needed to assess whether the efficacy and effectiveness of outpatient treatments vary by age, sex, socioeconomic status, and comorbid conditions – or by SARS-CoV-2 variant, immunity status (prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination status, or time since infection or vaccination), symptom duration, or disease severity.
Dr. Salvatore agreed that more research is needed in special convalescent groups. “For instance, those with cancer who are immunocompromised may need longer treatment and adjunctive treatment with convalescent plasma. But is difficult to find a large enough study with 5,000 immunocompromised patients.”
Financial support for the development of the practice points came exclusively from the ACP operating budget. The evidence review was funded by the ACP. The authors disclosed no relevant high-level competing interests with regard to this guidance, although several authors reported intellectual interests in various areas of research. Dr. Salvatore disclosed no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments but is engaged in influenza research for Genentech.
The American College of Physicians has issued an updated version of its living, rapid practice point guideline on the best treatment options for outpatients with confirmed COVID-19 in the era of the dominant Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The recommendations in version 2 apply to persons presenting with mild to moderate infection and symptom onset in the past 5 days who are at high risk for progression to severe disease and potential hospitalization or death.
Version 1 appeared in late 2022.
While outpatient management is appropriate for most patients, treatment should be personalized and based on careful risk stratification and informed decision-making, said the guideline authors, led by Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, MHA, vice president of clinical policy and the Center for Evidence Reviews at the ACP in Philadelphia.
Practice points
- Consider the oral antivirals nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) or molnupiravir (Lagevrio) for symptomatic outpatients with confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 who are within 5 days of the onset of symptoms and at high risk for progressing to severe disease.
New evidence for the Omicron variant suggests a possible net benefit of the antiviral molnupiravir versus standard or no treatment in terms of reducing recovery time if treatment is initiated within 5 days of symptom onset. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with reductions in COVID-19 hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
“The practice points only address [whether] treatments work compared to placebo, no treatment, or usual care,” cautioned Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH, MACP, chair of the ACP’s Population Health and Medical Science Committee and a professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University VA Portland Health Care System. The ACP continues to monitor the evidence. “Once enough evidence has emerged, it will be possible to compare treatments to each other. Until that time we are unable to determine if there is an advantage to using one treatment over another.”
- Do not use the antiparasitic ivermectin (Stromectol) or the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab (Xevudy) to treat this patient population. “It is not expected to be effective against the Omicron variant,” Dr. Humphrey said.
There was no evidence to support the use of medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, antihistamines, SSRIs, and multiple other agents.
“The guideline is not a departure from previous knowledge and reflects what appears in other guidelines and is already being done generally in practice,” said Mirella Salvatore, MD, an associate professor of medicine and population health sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was not involved in the ACP statement. It is therefore unlikely the recommendations will trigger controversy or negative feedback, added Dr. Salvatore, who is also a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. “We believe that our evidence-based approach, which considers the balance of benefits and harms of various treatments, will be embraced by the physician community,” Dr. Humphrey said.
The updated recommendations are based on new data from the evidence review of multiple treatments, which concluded that both nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir likely improve outcomes for outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. The review was conducted after the emergence of the Omicron variant by the ACP Center for Evidence Reviews at Cochrane Austria/University for Continuing Education Krems (Austria).
Review details
Inclusion criteria were modified to focus on the Omicron variant by limiting eligible studies to only those enrolling patients on or after Nov. 26, 2021. The investigators included two randomized controlled trials and six retrospective cohort studies and ranked quality of evidence for the effectiveness of the following treatments, compared with usual care or no treatment: azithromycin, camostat mesylate, chloroquine-hydroxychloroquine, chlorpheniramine, colchicine, convalescent plasma, corticosteroids, ensitrelvir, favipiravir, fluvoxamine, ivermectin, lopinavir-ritonavir, molnupiravir, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, metformin, niclosamide, nitazoxanide, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and remdesivir.
It compared results for all-cause and COVID-specific mortality, recovery, time to recovery, COVID hospitalization, and adverse and serious adverse events.
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a reduction in hospitalization caused by COVID-19 of 0.7% versus 1.2% (moderate certainty of evidence [COE]) and a reduction in all-cause mortality of less than 0.1% versus 0.2% (moderate COE).
Molnupiravir led to a higher recovery rate of 31.8% versus 22.6% (moderate COE) and a reduced time to recovery of 9 versus 15 median days (moderate COE). It had no effect, however, on all-cause mortality: 0.02% versus 0.04% (moderate COE). Nor did it affect the incidence of serious adverse events: 0.4% versus 0.3% (moderate COE).
“There have been no head-to-head comparative studies of these two treatments, but nirmatrelvir-ritonavir appears to be the preferred treatment,” Dr. Salvatore said. She noted that molnupiravir cannot be used in pregnant women or young persons under age 18, while nirmatrelvir-ritonavir carries the risk of drug interactions. Viral rebound and recurrence of symptoms have been reported in some patients receiving nirmatrelvir-ritonavir.
In other review findings, ivermectin had no effect on time to recovery (moderate COE) and adverse events versus placebo (low COE). Sotrovimab resulted in no difference in all-cause mortality, compared with no treatment (low COE). There were no eligible studies for all of the other treatments of interest nor were there any that specifically evaluated the benefits and harms of treatments for the Omicron variant.
The panel pointed to the need for more evaluation of the efficacy, effectiveness, and comparative effectiveness, as well as harms of pharmacologic and biologic treatments of COVID-19 in the outpatient setting, particularly in the context of changing dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants and subvariants.
Another area requiring further research is the effectiveness of retreatment in patients with previous COVID-19 infection. Subgroup analyses are also needed to assess whether the efficacy and effectiveness of outpatient treatments vary by age, sex, socioeconomic status, and comorbid conditions – or by SARS-CoV-2 variant, immunity status (prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination status, or time since infection or vaccination), symptom duration, or disease severity.
Dr. Salvatore agreed that more research is needed in special convalescent groups. “For instance, those with cancer who are immunocompromised may need longer treatment and adjunctive treatment with convalescent plasma. But is difficult to find a large enough study with 5,000 immunocompromised patients.”
Financial support for the development of the practice points came exclusively from the ACP operating budget. The evidence review was funded by the ACP. The authors disclosed no relevant high-level competing interests with regard to this guidance, although several authors reported intellectual interests in various areas of research. Dr. Salvatore disclosed no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments but is engaged in influenza research for Genentech.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Sotatercept tied to disease modification in pulmonary arterial hypertension
MILAN – Sotatercept, a first-in-class activin signaling inhibitor, is currently under scrutiny as a potential game-changer in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Data unveiled at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society, held in Milan, suggest that sotatercept treatment has the capacity to deliver significant clinical benefits and could reshape the trajectory of this challenging disease. Experts are cautiously optimistic that this drug may soon find a place within the PAH treatment algorithm.
The STELLAR trial: A milestone in PAH research
PAH is intricately linked to the dysregulation of members within the TGF-beta superfamily, including activin receptor type IIA (ActRIIA) and its ligands activin A and activin B. This signaling pathway is believed to be a driving force behind the pulmonary vascular remodeling observed in PAH patients. Sotatercept, a fusion protein acting as a ligand trap for selected TGF-beta superfamily members, has been proposed to recalibrate pulmonary vascular homeostasis by promoting growth-inhibiting and pro-apoptotic signaling.
Sotatercept was tested first in a phase 2 trial (PULSAR) and later in a phase 3 trial (STELLAR). The STELLAR clinical trial, funded by Acceleron Pharma (now a subsidiary of Merck), was the subject of two presentations given by Marius M. Hoeper, MD, director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany.
Dr. Hoeper commented on results published in the New England Journal of Medicine during a session titled, “Disease modification in pulmonary arterial hypertension.” Later, during the “From the Editor’s Desk” session, he presented new results recently published in the European Respiratory Journal about the effects of sotatercept on hemodynamics and right heart function.
Disease modification in PAH
In his initial address, Dr. Hoeper expounded on the concept of reverse remodeling as a therapeutic avenue for PAH. “PAH is not a disease of pulmonary vasoconstriction,” he clarified, “but a disease of proliferation. Endothelial cells and pulmonary vascular muscle cells proliferate and obliterate the lumen. It has been hypothesized that when we target this system successfully, we may not only stop disease progression, but we may have a chance to have at least some reverse remodeling, because, if these cells go into apoptosis, there may be a partial reopening of the vessels.”
“Sotatercept is probably going to be a game changer in our field,” Dr. Hoeper continued. “Is sotatercept a disease-modifying agent? It certainly induces disease improvement; in a few patients, although not in the majority, we see a normalization of hemodynamics. We target the underlying pathophysiology; this is clearly distinct from symptomatic treatment.” Dr. Hoeper went through the list of characteristics that a disease-modifying agent should have.
“To be able to say that a drug endures sustained clinical benefit, according to the FDA, you need to withdraw the drug, and this is something we do not know. We know that we can interrupt the treatment once or twice, but long-term I do not believe that,” he said, while acknowledging the need for more extended-term safety and efficacy data.
Unmasking hemodynamic impact
Dr. Hoeper’s second presentation focused on a post hoc analysis of the STELLAR trial never presented before. He analyzed right heart catheterization (RHC) and echocardiography (ECHO) data. With sotatercept treatment at week 24, the researchers observed:
- A small increase in systemic blood pressure and systemic vascular resistance.
- No changes in systolic and diastolic volumes of the left ventricle (lv).
- A small but significant reduction in lv ejection fraction.
- A great reduction in the mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP).
- No change in cardiac output.
- An improvement in pulmonary artery compliance.
- A reduction in the right ventricle work and in right atrial pressure.
- An improvement of echocardiographic parameters, including a significant decrease in tricuspid regurgitation.
“A drop of roughly 14 mm Hg in mPAP is something that we have never seen in PAH with any other add-on medication. This was entirely driven by improvement in the sotatercept group, not by deterioration in the placebo group,” Dr. Hoeper pointed out. Of note, change in mPAP correlated with changes in NT-proNBP and with changes in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), the primary endpoint of the STELLAR trial. “We effectively unload the right ventricle by lowing the artery pressure. What we observe is exactly what we want to achieve in patients with PAH, because the heart is what really matters,” he concluded.
A new course in PAH treatment?
Olivier Sitbon, MD, PhD, professor of respiratory medicine at Université Paris-Saclay and consultant at the French Referral Center for Pulmonary Hypertension, echoed Dr. Hoeper’s enthusiasm. ,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Sitbon highlighted ongoing studies with sotatercept, including the ZENITH trial, focused on high-risk PAH patients, and the HYPERION trial, aimed at patients diagnosed within the first year of their PAH journey. He acknowledged that experts currently lack consensus on the ideal position for sotatercept within the PAH treatment algorithm. However, he anticipates a lively debate and expects sotatercept to find its place as a second-line treatment for intermediate low-risk or intermediate high-risk patients, with potential consideration for high-risk patients.
“There are two more studies ongoing with sotatercept: the ZENITH trial, dedicated to PAH patients at high risk, whose primary endpoint is mortality/need for lung transplant, and the HYPERION trial, dedicated to patients diagnosed less than 1 year (not really newly diagnosed but quite incident, while patients included in previous trial were very prevalent), whose primary endpoint is time to clinical worsening,” Dr. Sitbon noted, pointing out that there is currently no consensus among the experts about where to place sotatercept in the PAH treatment algorithm.
Further insights into sotatercept
The ERS Congress also unveiled two additional studies that provided fresh perspectives on sotatercept’s potential. Ioana R. Preston, MD, from Tufts Medical Center in Boston, presented the first interim analysis of SOTERIA, a long-term follow-up study involving 409 patients with a median exposure duration of 462 days to sotatercept. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported by 80% of patients, with 20% reporting a serious TEAE. Overall, four serious TEAEs (1% of patients) led to death, but only five patients (1.2%) discontinued sotatercept because of TEAE.
Notably, improvements in clinical efficacy measures persisted after 1 year. During SOTERIA, roughly 3% of patients on any prostacyclin discontinued it. “Results of SOTERIA support the long-term durable clinical benefit and safety of sotatercept for the treatment of PAH. Of note, patients were offered home self-administration therapy, so they do not need to come back to the office,” Dr. Preston said.
A second late-breaking abstract presented by Vallerie McLaughlin, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, described the possible long-term impact of sotatercept on morbidity and mortality. STELLAR trial data were analyzed to see how the risk profile of patients changed in the 24 weeks of study. Real-world registry data from the COMPERA registry were then used to extrapolate mortality and transplant need over 30 years based on risk transition. According to the simulation model, adding sotatercept to background therapy is expected to increase life expectancy by threefold, while avoiding nearly 700 hospitalizations and four lung/heart-lung transplantations per 1,000 patients. “Real-world data are needed to confirm these findings,” cautioned Dr. McLaughlin.
Dr. Hoeper disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Acceleron, Actelion, Altavant, AOP Health, Bayer, Ferrer, Janssen, Keros, and MSD. Dr. Sitbon disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Acceleron Pharmaceuticals, Altavant Sciences, AOP Orphan, Bayer, Ferrer, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, MSD, and United Therapeutics, and grant/research support from Acceleron Pharmaceuticals, AOP Orphan, Bayer, Janssen, and MSD. Dr. Preston disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Janssen and United Therapeutics, and grant/research support from Janssen and Respira Therapeutics. She has participated in scientific advisory boards for Aereovate, Altavant, and Gossamer Bio, and was in the Steering Committee of Acceleron, Liquidia, and United Therapeutics. Dr. McLaughlin has received speaking and consulting fees from Aerami, Aereovate, Caremark, Corvista, Enzyvant, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, Merck, United Therapeutics, and Vertex, and grant/research support from Aerovate, Enzyvant, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, Merck, and Sonovia. She is a member of the Board of Directors of Clene.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN – Sotatercept, a first-in-class activin signaling inhibitor, is currently under scrutiny as a potential game-changer in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Data unveiled at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society, held in Milan, suggest that sotatercept treatment has the capacity to deliver significant clinical benefits and could reshape the trajectory of this challenging disease. Experts are cautiously optimistic that this drug may soon find a place within the PAH treatment algorithm.
The STELLAR trial: A milestone in PAH research
PAH is intricately linked to the dysregulation of members within the TGF-beta superfamily, including activin receptor type IIA (ActRIIA) and its ligands activin A and activin B. This signaling pathway is believed to be a driving force behind the pulmonary vascular remodeling observed in PAH patients. Sotatercept, a fusion protein acting as a ligand trap for selected TGF-beta superfamily members, has been proposed to recalibrate pulmonary vascular homeostasis by promoting growth-inhibiting and pro-apoptotic signaling.
Sotatercept was tested first in a phase 2 trial (PULSAR) and later in a phase 3 trial (STELLAR). The STELLAR clinical trial, funded by Acceleron Pharma (now a subsidiary of Merck), was the subject of two presentations given by Marius M. Hoeper, MD, director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany.
Dr. Hoeper commented on results published in the New England Journal of Medicine during a session titled, “Disease modification in pulmonary arterial hypertension.” Later, during the “From the Editor’s Desk” session, he presented new results recently published in the European Respiratory Journal about the effects of sotatercept on hemodynamics and right heart function.
Disease modification in PAH
In his initial address, Dr. Hoeper expounded on the concept of reverse remodeling as a therapeutic avenue for PAH. “PAH is not a disease of pulmonary vasoconstriction,” he clarified, “but a disease of proliferation. Endothelial cells and pulmonary vascular muscle cells proliferate and obliterate the lumen. It has been hypothesized that when we target this system successfully, we may not only stop disease progression, but we may have a chance to have at least some reverse remodeling, because, if these cells go into apoptosis, there may be a partial reopening of the vessels.”
“Sotatercept is probably going to be a game changer in our field,” Dr. Hoeper continued. “Is sotatercept a disease-modifying agent? It certainly induces disease improvement; in a few patients, although not in the majority, we see a normalization of hemodynamics. We target the underlying pathophysiology; this is clearly distinct from symptomatic treatment.” Dr. Hoeper went through the list of characteristics that a disease-modifying agent should have.
“To be able to say that a drug endures sustained clinical benefit, according to the FDA, you need to withdraw the drug, and this is something we do not know. We know that we can interrupt the treatment once or twice, but long-term I do not believe that,” he said, while acknowledging the need for more extended-term safety and efficacy data.
Unmasking hemodynamic impact
Dr. Hoeper’s second presentation focused on a post hoc analysis of the STELLAR trial never presented before. He analyzed right heart catheterization (RHC) and echocardiography (ECHO) data. With sotatercept treatment at week 24, the researchers observed:
- A small increase in systemic blood pressure and systemic vascular resistance.
- No changes in systolic and diastolic volumes of the left ventricle (lv).
- A small but significant reduction in lv ejection fraction.
- A great reduction in the mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP).
- No change in cardiac output.
- An improvement in pulmonary artery compliance.
- A reduction in the right ventricle work and in right atrial pressure.
- An improvement of echocardiographic parameters, including a significant decrease in tricuspid regurgitation.
“A drop of roughly 14 mm Hg in mPAP is something that we have never seen in PAH with any other add-on medication. This was entirely driven by improvement in the sotatercept group, not by deterioration in the placebo group,” Dr. Hoeper pointed out. Of note, change in mPAP correlated with changes in NT-proNBP and with changes in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), the primary endpoint of the STELLAR trial. “We effectively unload the right ventricle by lowing the artery pressure. What we observe is exactly what we want to achieve in patients with PAH, because the heart is what really matters,” he concluded.
A new course in PAH treatment?
Olivier Sitbon, MD, PhD, professor of respiratory medicine at Université Paris-Saclay and consultant at the French Referral Center for Pulmonary Hypertension, echoed Dr. Hoeper’s enthusiasm. ,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Sitbon highlighted ongoing studies with sotatercept, including the ZENITH trial, focused on high-risk PAH patients, and the HYPERION trial, aimed at patients diagnosed within the first year of their PAH journey. He acknowledged that experts currently lack consensus on the ideal position for sotatercept within the PAH treatment algorithm. However, he anticipates a lively debate and expects sotatercept to find its place as a second-line treatment for intermediate low-risk or intermediate high-risk patients, with potential consideration for high-risk patients.
“There are two more studies ongoing with sotatercept: the ZENITH trial, dedicated to PAH patients at high risk, whose primary endpoint is mortality/need for lung transplant, and the HYPERION trial, dedicated to patients diagnosed less than 1 year (not really newly diagnosed but quite incident, while patients included in previous trial were very prevalent), whose primary endpoint is time to clinical worsening,” Dr. Sitbon noted, pointing out that there is currently no consensus among the experts about where to place sotatercept in the PAH treatment algorithm.
Further insights into sotatercept
The ERS Congress also unveiled two additional studies that provided fresh perspectives on sotatercept’s potential. Ioana R. Preston, MD, from Tufts Medical Center in Boston, presented the first interim analysis of SOTERIA, a long-term follow-up study involving 409 patients with a median exposure duration of 462 days to sotatercept. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported by 80% of patients, with 20% reporting a serious TEAE. Overall, four serious TEAEs (1% of patients) led to death, but only five patients (1.2%) discontinued sotatercept because of TEAE.
Notably, improvements in clinical efficacy measures persisted after 1 year. During SOTERIA, roughly 3% of patients on any prostacyclin discontinued it. “Results of SOTERIA support the long-term durable clinical benefit and safety of sotatercept for the treatment of PAH. Of note, patients were offered home self-administration therapy, so they do not need to come back to the office,” Dr. Preston said.
A second late-breaking abstract presented by Vallerie McLaughlin, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, described the possible long-term impact of sotatercept on morbidity and mortality. STELLAR trial data were analyzed to see how the risk profile of patients changed in the 24 weeks of study. Real-world registry data from the COMPERA registry were then used to extrapolate mortality and transplant need over 30 years based on risk transition. According to the simulation model, adding sotatercept to background therapy is expected to increase life expectancy by threefold, while avoiding nearly 700 hospitalizations and four lung/heart-lung transplantations per 1,000 patients. “Real-world data are needed to confirm these findings,” cautioned Dr. McLaughlin.
Dr. Hoeper disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Acceleron, Actelion, Altavant, AOP Health, Bayer, Ferrer, Janssen, Keros, and MSD. Dr. Sitbon disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Acceleron Pharmaceuticals, Altavant Sciences, AOP Orphan, Bayer, Ferrer, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, MSD, and United Therapeutics, and grant/research support from Acceleron Pharmaceuticals, AOP Orphan, Bayer, Janssen, and MSD. Dr. Preston disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Janssen and United Therapeutics, and grant/research support from Janssen and Respira Therapeutics. She has participated in scientific advisory boards for Aereovate, Altavant, and Gossamer Bio, and was in the Steering Committee of Acceleron, Liquidia, and United Therapeutics. Dr. McLaughlin has received speaking and consulting fees from Aerami, Aereovate, Caremark, Corvista, Enzyvant, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, Merck, United Therapeutics, and Vertex, and grant/research support from Aerovate, Enzyvant, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, Merck, and Sonovia. She is a member of the Board of Directors of Clene.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN – Sotatercept, a first-in-class activin signaling inhibitor, is currently under scrutiny as a potential game-changer in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Data unveiled at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society, held in Milan, suggest that sotatercept treatment has the capacity to deliver significant clinical benefits and could reshape the trajectory of this challenging disease. Experts are cautiously optimistic that this drug may soon find a place within the PAH treatment algorithm.
The STELLAR trial: A milestone in PAH research
PAH is intricately linked to the dysregulation of members within the TGF-beta superfamily, including activin receptor type IIA (ActRIIA) and its ligands activin A and activin B. This signaling pathway is believed to be a driving force behind the pulmonary vascular remodeling observed in PAH patients. Sotatercept, a fusion protein acting as a ligand trap for selected TGF-beta superfamily members, has been proposed to recalibrate pulmonary vascular homeostasis by promoting growth-inhibiting and pro-apoptotic signaling.
Sotatercept was tested first in a phase 2 trial (PULSAR) and later in a phase 3 trial (STELLAR). The STELLAR clinical trial, funded by Acceleron Pharma (now a subsidiary of Merck), was the subject of two presentations given by Marius M. Hoeper, MD, director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany.
Dr. Hoeper commented on results published in the New England Journal of Medicine during a session titled, “Disease modification in pulmonary arterial hypertension.” Later, during the “From the Editor’s Desk” session, he presented new results recently published in the European Respiratory Journal about the effects of sotatercept on hemodynamics and right heart function.
Disease modification in PAH
In his initial address, Dr. Hoeper expounded on the concept of reverse remodeling as a therapeutic avenue for PAH. “PAH is not a disease of pulmonary vasoconstriction,” he clarified, “but a disease of proliferation. Endothelial cells and pulmonary vascular muscle cells proliferate and obliterate the lumen. It has been hypothesized that when we target this system successfully, we may not only stop disease progression, but we may have a chance to have at least some reverse remodeling, because, if these cells go into apoptosis, there may be a partial reopening of the vessels.”
“Sotatercept is probably going to be a game changer in our field,” Dr. Hoeper continued. “Is sotatercept a disease-modifying agent? It certainly induces disease improvement; in a few patients, although not in the majority, we see a normalization of hemodynamics. We target the underlying pathophysiology; this is clearly distinct from symptomatic treatment.” Dr. Hoeper went through the list of characteristics that a disease-modifying agent should have.
“To be able to say that a drug endures sustained clinical benefit, according to the FDA, you need to withdraw the drug, and this is something we do not know. We know that we can interrupt the treatment once or twice, but long-term I do not believe that,” he said, while acknowledging the need for more extended-term safety and efficacy data.
Unmasking hemodynamic impact
Dr. Hoeper’s second presentation focused on a post hoc analysis of the STELLAR trial never presented before. He analyzed right heart catheterization (RHC) and echocardiography (ECHO) data. With sotatercept treatment at week 24, the researchers observed:
- A small increase in systemic blood pressure and systemic vascular resistance.
- No changes in systolic and diastolic volumes of the left ventricle (lv).
- A small but significant reduction in lv ejection fraction.
- A great reduction in the mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP).
- No change in cardiac output.
- An improvement in pulmonary artery compliance.
- A reduction in the right ventricle work and in right atrial pressure.
- An improvement of echocardiographic parameters, including a significant decrease in tricuspid regurgitation.
“A drop of roughly 14 mm Hg in mPAP is something that we have never seen in PAH with any other add-on medication. This was entirely driven by improvement in the sotatercept group, not by deterioration in the placebo group,” Dr. Hoeper pointed out. Of note, change in mPAP correlated with changes in NT-proNBP and with changes in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), the primary endpoint of the STELLAR trial. “We effectively unload the right ventricle by lowing the artery pressure. What we observe is exactly what we want to achieve in patients with PAH, because the heart is what really matters,” he concluded.
A new course in PAH treatment?
Olivier Sitbon, MD, PhD, professor of respiratory medicine at Université Paris-Saclay and consultant at the French Referral Center for Pulmonary Hypertension, echoed Dr. Hoeper’s enthusiasm. ,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Sitbon highlighted ongoing studies with sotatercept, including the ZENITH trial, focused on high-risk PAH patients, and the HYPERION trial, aimed at patients diagnosed within the first year of their PAH journey. He acknowledged that experts currently lack consensus on the ideal position for sotatercept within the PAH treatment algorithm. However, he anticipates a lively debate and expects sotatercept to find its place as a second-line treatment for intermediate low-risk or intermediate high-risk patients, with potential consideration for high-risk patients.
“There are two more studies ongoing with sotatercept: the ZENITH trial, dedicated to PAH patients at high risk, whose primary endpoint is mortality/need for lung transplant, and the HYPERION trial, dedicated to patients diagnosed less than 1 year (not really newly diagnosed but quite incident, while patients included in previous trial were very prevalent), whose primary endpoint is time to clinical worsening,” Dr. Sitbon noted, pointing out that there is currently no consensus among the experts about where to place sotatercept in the PAH treatment algorithm.
Further insights into sotatercept
The ERS Congress also unveiled two additional studies that provided fresh perspectives on sotatercept’s potential. Ioana R. Preston, MD, from Tufts Medical Center in Boston, presented the first interim analysis of SOTERIA, a long-term follow-up study involving 409 patients with a median exposure duration of 462 days to sotatercept. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported by 80% of patients, with 20% reporting a serious TEAE. Overall, four serious TEAEs (1% of patients) led to death, but only five patients (1.2%) discontinued sotatercept because of TEAE.
Notably, improvements in clinical efficacy measures persisted after 1 year. During SOTERIA, roughly 3% of patients on any prostacyclin discontinued it. “Results of SOTERIA support the long-term durable clinical benefit and safety of sotatercept for the treatment of PAH. Of note, patients were offered home self-administration therapy, so they do not need to come back to the office,” Dr. Preston said.
A second late-breaking abstract presented by Vallerie McLaughlin, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, described the possible long-term impact of sotatercept on morbidity and mortality. STELLAR trial data were analyzed to see how the risk profile of patients changed in the 24 weeks of study. Real-world registry data from the COMPERA registry were then used to extrapolate mortality and transplant need over 30 years based on risk transition. According to the simulation model, adding sotatercept to background therapy is expected to increase life expectancy by threefold, while avoiding nearly 700 hospitalizations and four lung/heart-lung transplantations per 1,000 patients. “Real-world data are needed to confirm these findings,” cautioned Dr. McLaughlin.
Dr. Hoeper disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Acceleron, Actelion, Altavant, AOP Health, Bayer, Ferrer, Janssen, Keros, and MSD. Dr. Sitbon disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Acceleron Pharmaceuticals, Altavant Sciences, AOP Orphan, Bayer, Ferrer, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, MSD, and United Therapeutics, and grant/research support from Acceleron Pharmaceuticals, AOP Orphan, Bayer, Janssen, and MSD. Dr. Preston disclosed speaking and consulting fees from Janssen and United Therapeutics, and grant/research support from Janssen and Respira Therapeutics. She has participated in scientific advisory boards for Aereovate, Altavant, and Gossamer Bio, and was in the Steering Committee of Acceleron, Liquidia, and United Therapeutics. Dr. McLaughlin has received speaking and consulting fees from Aerami, Aereovate, Caremark, Corvista, Enzyvant, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, Merck, United Therapeutics, and Vertex, and grant/research support from Aerovate, Enzyvant, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, Merck, and Sonovia. She is a member of the Board of Directors of Clene.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ERS 2023
Beyond cystic fibrosis: Genetics of PF and other lung diseases
The remarkable story of cystic fibrosis (CF) – from gene discovery in 1989 to highly effective precision-medicine therapies today – inspires Christine Kim Garcia, MD, PhD, as she searches for rare mutations in genes linked to inherited forms of lung fibrosis, termed familial pulmonary fibrosis (FPF).
“Cystic fibrosis has provided a framework for approaching the genetics of lung fibrosis,” said Dr. Garcia, Frode Jensen Professor of Medicine and chief of the pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine division at Columbia University, and director of the Columbia Precision Medicine Initiative, both in New York.
Pulmonary fibrosis is more complicated than CF. “Mutations in more than 10 different genes can lead to the increased heritable risk of pulmonary fibrosis that we find in families. Different mutations exist for each gene. Sometimes the mutations are so rare that they are only found in a single family,” she said. “In addition, different subtypes of fibrotic interstitial lung disease can be linked to the same mutation and found in the same family.”
Despite these complexities, genetic discoveries in PF have illuminated pathophysiologic pathways and are driving the research that Dr. Garcia and other experts hope will lead to helpful prognostic tools and to precision therapies. And already, at institutions like Columbia, genetic discoveries are changing clinical care, driving treatment decisions and spurring family screening.
Thomas Ferkol, MD, whose research focuses on genetic factors that contribute to suppurative airway diseases such as CF and primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), similarly regards CF as a road map for genetics research and genetic testing in practice.
“The treatments we’re doing now for CF are increasingly based on the genetics of the individual,” said Dr. Ferkol, professor and division chief for pediatric pulmonology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, where the UNC Children’s Hospital hosts a rare and genetic lung disease program. For PCD, genetic testing has become a front-line diagnostic tool. But in the future, he hopes, it will also become a determinant for personalized treatment for children with PCD.
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene was the first lung disease gene to be discovered using gene-mapping techniques. Since then, and especially in the last 15-20 years, “there’s been a lot of progress in the identification of genes for which mutations and variations cause specific forms of pulmonary disease, many of which can now establish a firm diagnosis, and some of which lead to very directed changes in management. There has also been great progress in the availability of genetic testing,” said Benjamin A. Raby, MD, MPH, director of the Pulmonary Genetics Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, which sees patients with a host of cystic lung diseases, bronchiectasic lung diseases, fibrotic lung diseases, and other conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis and PCD.
Pulmonary fibrosis in adults and PCD in children are two examples of lung diseases for which genetic discoveries have exploded in recent years, with important implications for care now and in the future.
Leveraging genetic testing in PF
FPF describes families with two or more members with PF within three degrees of relationship; it is a designation believed to affect 20%-25% of people with PF and occurs predominantly later in the adult years (after 50 years of age), most commonly in autosomal dominant fashion, and amidst a stew of genetic risks, environmental exposures, and other insults.
Dr. Garcia and other researchers have uncovered two main types of genes in which rare variants can give rise to a heritable risk of FP: Genes that contribute to the maintenance of telomere length, and genes involved in surfactant metabolism. [Last year, Dr. Garcia and colleagues reported their discovery of both rare and common variants in a “spindle gene,” KIF15, in patients with IPF, suggesting an additional pathogenic pathway. The gene controls dynamics of cell division. (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;206[1]:p 56-69.)]
Detection of telomere pathway involvement – most commonly involving the TERT gene – is consequential because patients with telomere-associated gene mutations “tend to progress faster and have a more aggressive disease course than patients without these mutations … regardless of how their scans or biopsies look,” as do patients who have short age-adjusted telomere length, said Dr. Chad Newton, MD, who directs the Interstitial Lung Disease program at the University of Texas Southwestern and researches the genetics of ILD.
Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia advise patients with PF and a positive family history to undergo panel-based genetic sequencing, along with telomere length measurement. They also advise that undiagnosed first-degree relatives consider what’s called “cascade testing” – genetic sequencing for any pathogenic or likely pathogenic rare variants found in the patient’s investigation. (Dr. Garcia, who cochairs a National Institutes of Health–funded interstitial lung disease curation panel, said she finds evidence of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in about 25% of patients with a family history of PF.)
“We can use this genetic information to consider starting early [antifibrotic] treatment to try to delay progression … just as we would with other forms of pulmonary fibrosis,” Dr. Newton said, “and to expand our reach to others not sitting in our clinics who have the same rare condition or are at risk.”
After cascade testing, Dr. Garcia said, she invites family members with positive results to have baseline CT scans and pulmonary function testing. “And if there’s anything abnormal, we’re inviting them to have regular follow-up testing,” she said, “because we advise starting antifibrotic treatment at the very first sign of disease worsening.”
Such an approach to genetic testing for patients and relatives is described in a statement commissioned by the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation and published last year in the journal Chest (2022:162[2]:394-405). The statement, for which Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia were among the authors, also lists clinical features within patients and families suggestive of a possible genetic pathway, and describes the potential yield for identifying a variant in different clinical scenarios.
Pathogenic variants in telomere genes as well as findings of short telomere length are associated with various extrapulmonary manifestations such as liver dysfunction, bone marrow dysfunction, and head and neck cancers, Dr. Newton said, making surveillance and referrals important. (Rare variants and short telomere length are associated with disease progression across several non-IPF diagnoses as well.)
Moreover, short telomeres may signal the need to avoid long-term immunosuppression. Research published in 2019 from multiple cohorts, and led by Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia, showed that short telomere length is associated with worse outcomes (faster time to composite death, transplant, FVC decline, and hospitalization) in patients with IPF who received immunosuppression. These adverse outcomes were not found in IPF patients with normal telomere lengths who received similar immunosuppression (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(3):336-347).
Gene sequencing and telomere length measurement are described in the 2020 Chest statement on the role of genetic testing in PF as yielding “different yet complementary information.” Short age-adjusted telomere length (less than the 10th percentile) is common in those with pathogenic variants in telomere genes, but it can also occur in the absence of identifiable rare telomere-related variants, the statement says. Telomere length testing can be helpful, it notes, in determining the significance of a “variant of unknown significance (VUS)” if gene sequencing identifies one.
The future of genetic screening for PF
Future genetic screening approaches for PF may cast an even wider net while better stratifying risk for family members. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, where family screening was a major impetus for the 2008 founding of the Pulmonary Genetics Center, research published several years ago by Dr. Raby and his colleagues found that 31% of 107 asymptomatic first-degree relatives of patients with PF had interstitial lung abnormalities on chest CTs – whether or not a family history was reported – and 18% had clear radiographic or physiological manifestations of fibrosis (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201[10]:1240-8).
“That’s more than 10-fold higher than what we thought we’d see, based on prior literature. … And the numbers were pretty much the same whether or not there was a family history of fibrosis reported by the patient,” said Dr. Raby, also the Leila and Irving Perlmutter professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief of the division of pulmonary medicine at Boston Children’s Hospital. “We used to think we only needed to worry about genetic risk when there was a family history. But now we see that sporadic cases are also driven by genetics.”
Their study also included a 2-year follow-up chest CT, in which the majority of the screened relatives participated. Of those, 65% who had interstitial changes at baseline showed progression. Four percent of those without interstitial abnormalities at baseline developed abnormalities (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207[2]:211-4). “The fact that 65% progressed suggests that in the majority of patients what we’re finding is something that’s real and is going to be clinically meaningful for patients,” he said.
Genetic signatures
A next phase of research at Brigham & Women’s and Boston Children’s, he said, will address PF’s “complex genetic signature” and test polygenic risk scores for idiopathic PF that take into account not only rare genetic variants that can be solidly linked to disease but many common genetic variants being detected in genome-wide association studies. [By definition, common variants, otherwise known as single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur with greater frequency in the general population (> 5%), generally reside within noncoding regions, and may contribute to disease risk but alone do not cause disease.]
“As technologies and genetic studies improve, we’re seeing we can estimate much better the likelihood of disease than we could 10 years ago,” he said. A “potent” common variant called the MUC5B promoter polymorphism has been shown to confer a 3-fold to 20-fold increased risk for PF, he noted. (Polygenic risk scores are also being developed, he said, for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.)
“Every time one sees a patient with PF that is thought to be idiopathic one should start thinking about their at-risk family members, particularly their siblings,” Dr. Raby said. But in doing so, “wouldn’t it be wonderful if we could use polygenic risk scores to assure some [family members] that they’re in the lowest tier of risk and might need pulmonary function studies every 5 years, for example, versus someone we’d want to see more frequently, versus someone [for whom] we’d want to start preventive therapy at the earlier signs of declining lung function?”
Moving forward, he and the others said, the field needs more research to determine how genetic risk factors predict disease progression and prospective clinical trials to test whether long-term outcomes are indeed improved by early institution of antifibrotic therapy and other genetics-driven management decisions. “The data we’re using to inform prognosis and treatment decisions are compelling, but a lot of it is based on cohort studies and retrospective research,” Dr. Newton said.
Multi-institutional transomics studies and other research projects are underway, meanwhile, to build upon gene identifications and learn more about the pathobiology of PF. “We know about two big genetic pathways … but we need to sort it all out,” he said. For instance, “are there intermediate pathways? And where does it actually start? What kind of cell?”
Genetics’ impact on PCD
About 20 years ago, only two genes were linked to PCD, a largely autosomal recessive disorder that results from abnormalities in the cilia and subsequently improper airway clearance. Today, said Dr. Ferkol, there are over 50 known genes that, if defective, can lead to PCD.
“Based on our latest estimates, I’d say we can diagnose people using genetics about 70%, maybe 80%, of the time,” Dr. Ferkol said. Genetic testing has become a first-line diagnostic tool for PCD in North America – a significant development given that a definitive diagnosis has long been challenging, he said.
A genetics-based diagnosis of PCD is sometimes challenged by the finding of variants of unknown significance (VUSs) on genetic testing (often missense mutations) “because some of the genes involved are huge,” noted Dr. Ferkol, who coleads the NIH-funded Genetic Disorders of Mucociliary Clearance Consortium. “But many times, it’s straightforward.”
Children with PCD have repeated or persistent upper respiratory tract infections beginning early in life – like chronic rhinosinusitis or suppurative otitis media – and chronic bronchitis, leading to bronchiectasis. About half of patients have a spectrum of laterality defects, where organs are malpositioned in a mirror image of normal. Some individuals also have cardiac defects, and subfertility in both males and females can frequently occur.
Just as it has become increasingly clear that CF exists as a continuum, with milder and variant forms having been recognized since the advent of genetic testing, “we’re finding genotype-phenotype relationships in PCD,” Dr. Ferkol said. “Certain individuals have more rapid pulmonary decline, which is related in part to their genetics.”
With PCD, “I’m convinced this is a continuum. Some patients have unmistakable, clear-cut PCD, but I’m sure we’re going to find individuals who have milder variants in these PCD-associated genes that lead to milder disease,” he said.
There are no specific treatments that will correct cilia dysfunction, and current therapy options are borrowed from other diseases such as asthma and CF. However, newer treatments targeting specific genetic defects are in early clinical studies. Will the gene discoveries and more research open up new avenues for treating PCD, as happened in CF? Dr. Ferkol hopes so.
Approximately 2,000 genetic variants have been identified in the CFTR gene, though not all are pathogenic. “The newer, highly effective modulators used in CF target a particular CFTR mutation class, so some drugs will work for some people with the disease, but not all,” Dr. Ferkol said. “It’s personalized medicine.”
Modulator therapies designed to correct the malfunctioning proteins made by the CFTR gene have profoundly changed the lives of many with CF, improving lung function and everyday symptoms for patients, allowing them to lead near-normal lives. “It’s astonishing,” he said.
Dr. Garcia reported consulting for Rejuvenation Technologies and Rejuveron Telomere Therapeutics; in addition, her laboratory has received support from Boehringer Ingelheim and Astrazeneca for investigator-initiated research. Dr. Newton reported he has performed consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Ferkol reported involvement in a longitudinal study defining endpoints for future clinical PCD trials funded by ReCode Therapeutics and leadership of an international clinical trial for PCD supported by Parion Sciences. He has received honoraria from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation and serves as a member of the ReCode Therapeutics PCD Clinical Steering Committee. Dr. Raby reported no relevant disclosures.
The remarkable story of cystic fibrosis (CF) – from gene discovery in 1989 to highly effective precision-medicine therapies today – inspires Christine Kim Garcia, MD, PhD, as she searches for rare mutations in genes linked to inherited forms of lung fibrosis, termed familial pulmonary fibrosis (FPF).
“Cystic fibrosis has provided a framework for approaching the genetics of lung fibrosis,” said Dr. Garcia, Frode Jensen Professor of Medicine and chief of the pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine division at Columbia University, and director of the Columbia Precision Medicine Initiative, both in New York.
Pulmonary fibrosis is more complicated than CF. “Mutations in more than 10 different genes can lead to the increased heritable risk of pulmonary fibrosis that we find in families. Different mutations exist for each gene. Sometimes the mutations are so rare that they are only found in a single family,” she said. “In addition, different subtypes of fibrotic interstitial lung disease can be linked to the same mutation and found in the same family.”
Despite these complexities, genetic discoveries in PF have illuminated pathophysiologic pathways and are driving the research that Dr. Garcia and other experts hope will lead to helpful prognostic tools and to precision therapies. And already, at institutions like Columbia, genetic discoveries are changing clinical care, driving treatment decisions and spurring family screening.
Thomas Ferkol, MD, whose research focuses on genetic factors that contribute to suppurative airway diseases such as CF and primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), similarly regards CF as a road map for genetics research and genetic testing in practice.
“The treatments we’re doing now for CF are increasingly based on the genetics of the individual,” said Dr. Ferkol, professor and division chief for pediatric pulmonology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, where the UNC Children’s Hospital hosts a rare and genetic lung disease program. For PCD, genetic testing has become a front-line diagnostic tool. But in the future, he hopes, it will also become a determinant for personalized treatment for children with PCD.
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene was the first lung disease gene to be discovered using gene-mapping techniques. Since then, and especially in the last 15-20 years, “there’s been a lot of progress in the identification of genes for which mutations and variations cause specific forms of pulmonary disease, many of which can now establish a firm diagnosis, and some of which lead to very directed changes in management. There has also been great progress in the availability of genetic testing,” said Benjamin A. Raby, MD, MPH, director of the Pulmonary Genetics Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, which sees patients with a host of cystic lung diseases, bronchiectasic lung diseases, fibrotic lung diseases, and other conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis and PCD.
Pulmonary fibrosis in adults and PCD in children are two examples of lung diseases for which genetic discoveries have exploded in recent years, with important implications for care now and in the future.
Leveraging genetic testing in PF
FPF describes families with two or more members with PF within three degrees of relationship; it is a designation believed to affect 20%-25% of people with PF and occurs predominantly later in the adult years (after 50 years of age), most commonly in autosomal dominant fashion, and amidst a stew of genetic risks, environmental exposures, and other insults.
Dr. Garcia and other researchers have uncovered two main types of genes in which rare variants can give rise to a heritable risk of FP: Genes that contribute to the maintenance of telomere length, and genes involved in surfactant metabolism. [Last year, Dr. Garcia and colleagues reported their discovery of both rare and common variants in a “spindle gene,” KIF15, in patients with IPF, suggesting an additional pathogenic pathway. The gene controls dynamics of cell division. (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;206[1]:p 56-69.)]
Detection of telomere pathway involvement – most commonly involving the TERT gene – is consequential because patients with telomere-associated gene mutations “tend to progress faster and have a more aggressive disease course than patients without these mutations … regardless of how their scans or biopsies look,” as do patients who have short age-adjusted telomere length, said Dr. Chad Newton, MD, who directs the Interstitial Lung Disease program at the University of Texas Southwestern and researches the genetics of ILD.
Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia advise patients with PF and a positive family history to undergo panel-based genetic sequencing, along with telomere length measurement. They also advise that undiagnosed first-degree relatives consider what’s called “cascade testing” – genetic sequencing for any pathogenic or likely pathogenic rare variants found in the patient’s investigation. (Dr. Garcia, who cochairs a National Institutes of Health–funded interstitial lung disease curation panel, said she finds evidence of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in about 25% of patients with a family history of PF.)
“We can use this genetic information to consider starting early [antifibrotic] treatment to try to delay progression … just as we would with other forms of pulmonary fibrosis,” Dr. Newton said, “and to expand our reach to others not sitting in our clinics who have the same rare condition or are at risk.”
After cascade testing, Dr. Garcia said, she invites family members with positive results to have baseline CT scans and pulmonary function testing. “And if there’s anything abnormal, we’re inviting them to have regular follow-up testing,” she said, “because we advise starting antifibrotic treatment at the very first sign of disease worsening.”
Such an approach to genetic testing for patients and relatives is described in a statement commissioned by the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation and published last year in the journal Chest (2022:162[2]:394-405). The statement, for which Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia were among the authors, also lists clinical features within patients and families suggestive of a possible genetic pathway, and describes the potential yield for identifying a variant in different clinical scenarios.
Pathogenic variants in telomere genes as well as findings of short telomere length are associated with various extrapulmonary manifestations such as liver dysfunction, bone marrow dysfunction, and head and neck cancers, Dr. Newton said, making surveillance and referrals important. (Rare variants and short telomere length are associated with disease progression across several non-IPF diagnoses as well.)
Moreover, short telomeres may signal the need to avoid long-term immunosuppression. Research published in 2019 from multiple cohorts, and led by Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia, showed that short telomere length is associated with worse outcomes (faster time to composite death, transplant, FVC decline, and hospitalization) in patients with IPF who received immunosuppression. These adverse outcomes were not found in IPF patients with normal telomere lengths who received similar immunosuppression (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(3):336-347).
Gene sequencing and telomere length measurement are described in the 2020 Chest statement on the role of genetic testing in PF as yielding “different yet complementary information.” Short age-adjusted telomere length (less than the 10th percentile) is common in those with pathogenic variants in telomere genes, but it can also occur in the absence of identifiable rare telomere-related variants, the statement says. Telomere length testing can be helpful, it notes, in determining the significance of a “variant of unknown significance (VUS)” if gene sequencing identifies one.
The future of genetic screening for PF
Future genetic screening approaches for PF may cast an even wider net while better stratifying risk for family members. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, where family screening was a major impetus for the 2008 founding of the Pulmonary Genetics Center, research published several years ago by Dr. Raby and his colleagues found that 31% of 107 asymptomatic first-degree relatives of patients with PF had interstitial lung abnormalities on chest CTs – whether or not a family history was reported – and 18% had clear radiographic or physiological manifestations of fibrosis (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201[10]:1240-8).
“That’s more than 10-fold higher than what we thought we’d see, based on prior literature. … And the numbers were pretty much the same whether or not there was a family history of fibrosis reported by the patient,” said Dr. Raby, also the Leila and Irving Perlmutter professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief of the division of pulmonary medicine at Boston Children’s Hospital. “We used to think we only needed to worry about genetic risk when there was a family history. But now we see that sporadic cases are also driven by genetics.”
Their study also included a 2-year follow-up chest CT, in which the majority of the screened relatives participated. Of those, 65% who had interstitial changes at baseline showed progression. Four percent of those without interstitial abnormalities at baseline developed abnormalities (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207[2]:211-4). “The fact that 65% progressed suggests that in the majority of patients what we’re finding is something that’s real and is going to be clinically meaningful for patients,” he said.
Genetic signatures
A next phase of research at Brigham & Women’s and Boston Children’s, he said, will address PF’s “complex genetic signature” and test polygenic risk scores for idiopathic PF that take into account not only rare genetic variants that can be solidly linked to disease but many common genetic variants being detected in genome-wide association studies. [By definition, common variants, otherwise known as single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur with greater frequency in the general population (> 5%), generally reside within noncoding regions, and may contribute to disease risk but alone do not cause disease.]
“As technologies and genetic studies improve, we’re seeing we can estimate much better the likelihood of disease than we could 10 years ago,” he said. A “potent” common variant called the MUC5B promoter polymorphism has been shown to confer a 3-fold to 20-fold increased risk for PF, he noted. (Polygenic risk scores are also being developed, he said, for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.)
“Every time one sees a patient with PF that is thought to be idiopathic one should start thinking about their at-risk family members, particularly their siblings,” Dr. Raby said. But in doing so, “wouldn’t it be wonderful if we could use polygenic risk scores to assure some [family members] that they’re in the lowest tier of risk and might need pulmonary function studies every 5 years, for example, versus someone we’d want to see more frequently, versus someone [for whom] we’d want to start preventive therapy at the earlier signs of declining lung function?”
Moving forward, he and the others said, the field needs more research to determine how genetic risk factors predict disease progression and prospective clinical trials to test whether long-term outcomes are indeed improved by early institution of antifibrotic therapy and other genetics-driven management decisions. “The data we’re using to inform prognosis and treatment decisions are compelling, but a lot of it is based on cohort studies and retrospective research,” Dr. Newton said.
Multi-institutional transomics studies and other research projects are underway, meanwhile, to build upon gene identifications and learn more about the pathobiology of PF. “We know about two big genetic pathways … but we need to sort it all out,” he said. For instance, “are there intermediate pathways? And where does it actually start? What kind of cell?”
Genetics’ impact on PCD
About 20 years ago, only two genes were linked to PCD, a largely autosomal recessive disorder that results from abnormalities in the cilia and subsequently improper airway clearance. Today, said Dr. Ferkol, there are over 50 known genes that, if defective, can lead to PCD.
“Based on our latest estimates, I’d say we can diagnose people using genetics about 70%, maybe 80%, of the time,” Dr. Ferkol said. Genetic testing has become a first-line diagnostic tool for PCD in North America – a significant development given that a definitive diagnosis has long been challenging, he said.
A genetics-based diagnosis of PCD is sometimes challenged by the finding of variants of unknown significance (VUSs) on genetic testing (often missense mutations) “because some of the genes involved are huge,” noted Dr. Ferkol, who coleads the NIH-funded Genetic Disorders of Mucociliary Clearance Consortium. “But many times, it’s straightforward.”
Children with PCD have repeated or persistent upper respiratory tract infections beginning early in life – like chronic rhinosinusitis or suppurative otitis media – and chronic bronchitis, leading to bronchiectasis. About half of patients have a spectrum of laterality defects, where organs are malpositioned in a mirror image of normal. Some individuals also have cardiac defects, and subfertility in both males and females can frequently occur.
Just as it has become increasingly clear that CF exists as a continuum, with milder and variant forms having been recognized since the advent of genetic testing, “we’re finding genotype-phenotype relationships in PCD,” Dr. Ferkol said. “Certain individuals have more rapid pulmonary decline, which is related in part to their genetics.”
With PCD, “I’m convinced this is a continuum. Some patients have unmistakable, clear-cut PCD, but I’m sure we’re going to find individuals who have milder variants in these PCD-associated genes that lead to milder disease,” he said.
There are no specific treatments that will correct cilia dysfunction, and current therapy options are borrowed from other diseases such as asthma and CF. However, newer treatments targeting specific genetic defects are in early clinical studies. Will the gene discoveries and more research open up new avenues for treating PCD, as happened in CF? Dr. Ferkol hopes so.
Approximately 2,000 genetic variants have been identified in the CFTR gene, though not all are pathogenic. “The newer, highly effective modulators used in CF target a particular CFTR mutation class, so some drugs will work for some people with the disease, but not all,” Dr. Ferkol said. “It’s personalized medicine.”
Modulator therapies designed to correct the malfunctioning proteins made by the CFTR gene have profoundly changed the lives of many with CF, improving lung function and everyday symptoms for patients, allowing them to lead near-normal lives. “It’s astonishing,” he said.
Dr. Garcia reported consulting for Rejuvenation Technologies and Rejuveron Telomere Therapeutics; in addition, her laboratory has received support from Boehringer Ingelheim and Astrazeneca for investigator-initiated research. Dr. Newton reported he has performed consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Ferkol reported involvement in a longitudinal study defining endpoints for future clinical PCD trials funded by ReCode Therapeutics and leadership of an international clinical trial for PCD supported by Parion Sciences. He has received honoraria from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation and serves as a member of the ReCode Therapeutics PCD Clinical Steering Committee. Dr. Raby reported no relevant disclosures.
The remarkable story of cystic fibrosis (CF) – from gene discovery in 1989 to highly effective precision-medicine therapies today – inspires Christine Kim Garcia, MD, PhD, as she searches for rare mutations in genes linked to inherited forms of lung fibrosis, termed familial pulmonary fibrosis (FPF).
“Cystic fibrosis has provided a framework for approaching the genetics of lung fibrosis,” said Dr. Garcia, Frode Jensen Professor of Medicine and chief of the pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine division at Columbia University, and director of the Columbia Precision Medicine Initiative, both in New York.
Pulmonary fibrosis is more complicated than CF. “Mutations in more than 10 different genes can lead to the increased heritable risk of pulmonary fibrosis that we find in families. Different mutations exist for each gene. Sometimes the mutations are so rare that they are only found in a single family,” she said. “In addition, different subtypes of fibrotic interstitial lung disease can be linked to the same mutation and found in the same family.”
Despite these complexities, genetic discoveries in PF have illuminated pathophysiologic pathways and are driving the research that Dr. Garcia and other experts hope will lead to helpful prognostic tools and to precision therapies. And already, at institutions like Columbia, genetic discoveries are changing clinical care, driving treatment decisions and spurring family screening.
Thomas Ferkol, MD, whose research focuses on genetic factors that contribute to suppurative airway diseases such as CF and primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), similarly regards CF as a road map for genetics research and genetic testing in practice.
“The treatments we’re doing now for CF are increasingly based on the genetics of the individual,” said Dr. Ferkol, professor and division chief for pediatric pulmonology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, where the UNC Children’s Hospital hosts a rare and genetic lung disease program. For PCD, genetic testing has become a front-line diagnostic tool. But in the future, he hopes, it will also become a determinant for personalized treatment for children with PCD.
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene was the first lung disease gene to be discovered using gene-mapping techniques. Since then, and especially in the last 15-20 years, “there’s been a lot of progress in the identification of genes for which mutations and variations cause specific forms of pulmonary disease, many of which can now establish a firm diagnosis, and some of which lead to very directed changes in management. There has also been great progress in the availability of genetic testing,” said Benjamin A. Raby, MD, MPH, director of the Pulmonary Genetics Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, which sees patients with a host of cystic lung diseases, bronchiectasic lung diseases, fibrotic lung diseases, and other conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis and PCD.
Pulmonary fibrosis in adults and PCD in children are two examples of lung diseases for which genetic discoveries have exploded in recent years, with important implications for care now and in the future.
Leveraging genetic testing in PF
FPF describes families with two or more members with PF within three degrees of relationship; it is a designation believed to affect 20%-25% of people with PF and occurs predominantly later in the adult years (after 50 years of age), most commonly in autosomal dominant fashion, and amidst a stew of genetic risks, environmental exposures, and other insults.
Dr. Garcia and other researchers have uncovered two main types of genes in which rare variants can give rise to a heritable risk of FP: Genes that contribute to the maintenance of telomere length, and genes involved in surfactant metabolism. [Last year, Dr. Garcia and colleagues reported their discovery of both rare and common variants in a “spindle gene,” KIF15, in patients with IPF, suggesting an additional pathogenic pathway. The gene controls dynamics of cell division. (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;206[1]:p 56-69.)]
Detection of telomere pathway involvement – most commonly involving the TERT gene – is consequential because patients with telomere-associated gene mutations “tend to progress faster and have a more aggressive disease course than patients without these mutations … regardless of how their scans or biopsies look,” as do patients who have short age-adjusted telomere length, said Dr. Chad Newton, MD, who directs the Interstitial Lung Disease program at the University of Texas Southwestern and researches the genetics of ILD.
Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia advise patients with PF and a positive family history to undergo panel-based genetic sequencing, along with telomere length measurement. They also advise that undiagnosed first-degree relatives consider what’s called “cascade testing” – genetic sequencing for any pathogenic or likely pathogenic rare variants found in the patient’s investigation. (Dr. Garcia, who cochairs a National Institutes of Health–funded interstitial lung disease curation panel, said she finds evidence of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in about 25% of patients with a family history of PF.)
“We can use this genetic information to consider starting early [antifibrotic] treatment to try to delay progression … just as we would with other forms of pulmonary fibrosis,” Dr. Newton said, “and to expand our reach to others not sitting in our clinics who have the same rare condition or are at risk.”
After cascade testing, Dr. Garcia said, she invites family members with positive results to have baseline CT scans and pulmonary function testing. “And if there’s anything abnormal, we’re inviting them to have regular follow-up testing,” she said, “because we advise starting antifibrotic treatment at the very first sign of disease worsening.”
Such an approach to genetic testing for patients and relatives is described in a statement commissioned by the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation and published last year in the journal Chest (2022:162[2]:394-405). The statement, for which Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia were among the authors, also lists clinical features within patients and families suggestive of a possible genetic pathway, and describes the potential yield for identifying a variant in different clinical scenarios.
Pathogenic variants in telomere genes as well as findings of short telomere length are associated with various extrapulmonary manifestations such as liver dysfunction, bone marrow dysfunction, and head and neck cancers, Dr. Newton said, making surveillance and referrals important. (Rare variants and short telomere length are associated with disease progression across several non-IPF diagnoses as well.)
Moreover, short telomeres may signal the need to avoid long-term immunosuppression. Research published in 2019 from multiple cohorts, and led by Dr. Newton and Dr. Garcia, showed that short telomere length is associated with worse outcomes (faster time to composite death, transplant, FVC decline, and hospitalization) in patients with IPF who received immunosuppression. These adverse outcomes were not found in IPF patients with normal telomere lengths who received similar immunosuppression (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(3):336-347).
Gene sequencing and telomere length measurement are described in the 2020 Chest statement on the role of genetic testing in PF as yielding “different yet complementary information.” Short age-adjusted telomere length (less than the 10th percentile) is common in those with pathogenic variants in telomere genes, but it can also occur in the absence of identifiable rare telomere-related variants, the statement says. Telomere length testing can be helpful, it notes, in determining the significance of a “variant of unknown significance (VUS)” if gene sequencing identifies one.
The future of genetic screening for PF
Future genetic screening approaches for PF may cast an even wider net while better stratifying risk for family members. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, where family screening was a major impetus for the 2008 founding of the Pulmonary Genetics Center, research published several years ago by Dr. Raby and his colleagues found that 31% of 107 asymptomatic first-degree relatives of patients with PF had interstitial lung abnormalities on chest CTs – whether or not a family history was reported – and 18% had clear radiographic or physiological manifestations of fibrosis (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201[10]:1240-8).
“That’s more than 10-fold higher than what we thought we’d see, based on prior literature. … And the numbers were pretty much the same whether or not there was a family history of fibrosis reported by the patient,” said Dr. Raby, also the Leila and Irving Perlmutter professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief of the division of pulmonary medicine at Boston Children’s Hospital. “We used to think we only needed to worry about genetic risk when there was a family history. But now we see that sporadic cases are also driven by genetics.”
Their study also included a 2-year follow-up chest CT, in which the majority of the screened relatives participated. Of those, 65% who had interstitial changes at baseline showed progression. Four percent of those without interstitial abnormalities at baseline developed abnormalities (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207[2]:211-4). “The fact that 65% progressed suggests that in the majority of patients what we’re finding is something that’s real and is going to be clinically meaningful for patients,” he said.
Genetic signatures
A next phase of research at Brigham & Women’s and Boston Children’s, he said, will address PF’s “complex genetic signature” and test polygenic risk scores for idiopathic PF that take into account not only rare genetic variants that can be solidly linked to disease but many common genetic variants being detected in genome-wide association studies. [By definition, common variants, otherwise known as single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur with greater frequency in the general population (> 5%), generally reside within noncoding regions, and may contribute to disease risk but alone do not cause disease.]
“As technologies and genetic studies improve, we’re seeing we can estimate much better the likelihood of disease than we could 10 years ago,” he said. A “potent” common variant called the MUC5B promoter polymorphism has been shown to confer a 3-fold to 20-fold increased risk for PF, he noted. (Polygenic risk scores are also being developed, he said, for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.)
“Every time one sees a patient with PF that is thought to be idiopathic one should start thinking about their at-risk family members, particularly their siblings,” Dr. Raby said. But in doing so, “wouldn’t it be wonderful if we could use polygenic risk scores to assure some [family members] that they’re in the lowest tier of risk and might need pulmonary function studies every 5 years, for example, versus someone we’d want to see more frequently, versus someone [for whom] we’d want to start preventive therapy at the earlier signs of declining lung function?”
Moving forward, he and the others said, the field needs more research to determine how genetic risk factors predict disease progression and prospective clinical trials to test whether long-term outcomes are indeed improved by early institution of antifibrotic therapy and other genetics-driven management decisions. “The data we’re using to inform prognosis and treatment decisions are compelling, but a lot of it is based on cohort studies and retrospective research,” Dr. Newton said.
Multi-institutional transomics studies and other research projects are underway, meanwhile, to build upon gene identifications and learn more about the pathobiology of PF. “We know about two big genetic pathways … but we need to sort it all out,” he said. For instance, “are there intermediate pathways? And where does it actually start? What kind of cell?”
Genetics’ impact on PCD
About 20 years ago, only two genes were linked to PCD, a largely autosomal recessive disorder that results from abnormalities in the cilia and subsequently improper airway clearance. Today, said Dr. Ferkol, there are over 50 known genes that, if defective, can lead to PCD.
“Based on our latest estimates, I’d say we can diagnose people using genetics about 70%, maybe 80%, of the time,” Dr. Ferkol said. Genetic testing has become a first-line diagnostic tool for PCD in North America – a significant development given that a definitive diagnosis has long been challenging, he said.
A genetics-based diagnosis of PCD is sometimes challenged by the finding of variants of unknown significance (VUSs) on genetic testing (often missense mutations) “because some of the genes involved are huge,” noted Dr. Ferkol, who coleads the NIH-funded Genetic Disorders of Mucociliary Clearance Consortium. “But many times, it’s straightforward.”
Children with PCD have repeated or persistent upper respiratory tract infections beginning early in life – like chronic rhinosinusitis or suppurative otitis media – and chronic bronchitis, leading to bronchiectasis. About half of patients have a spectrum of laterality defects, where organs are malpositioned in a mirror image of normal. Some individuals also have cardiac defects, and subfertility in both males and females can frequently occur.
Just as it has become increasingly clear that CF exists as a continuum, with milder and variant forms having been recognized since the advent of genetic testing, “we’re finding genotype-phenotype relationships in PCD,” Dr. Ferkol said. “Certain individuals have more rapid pulmonary decline, which is related in part to their genetics.”
With PCD, “I’m convinced this is a continuum. Some patients have unmistakable, clear-cut PCD, but I’m sure we’re going to find individuals who have milder variants in these PCD-associated genes that lead to milder disease,” he said.
There are no specific treatments that will correct cilia dysfunction, and current therapy options are borrowed from other diseases such as asthma and CF. However, newer treatments targeting specific genetic defects are in early clinical studies. Will the gene discoveries and more research open up new avenues for treating PCD, as happened in CF? Dr. Ferkol hopes so.
Approximately 2,000 genetic variants have been identified in the CFTR gene, though not all are pathogenic. “The newer, highly effective modulators used in CF target a particular CFTR mutation class, so some drugs will work for some people with the disease, but not all,” Dr. Ferkol said. “It’s personalized medicine.”
Modulator therapies designed to correct the malfunctioning proteins made by the CFTR gene have profoundly changed the lives of many with CF, improving lung function and everyday symptoms for patients, allowing them to lead near-normal lives. “It’s astonishing,” he said.
Dr. Garcia reported consulting for Rejuvenation Technologies and Rejuveron Telomere Therapeutics; in addition, her laboratory has received support from Boehringer Ingelheim and Astrazeneca for investigator-initiated research. Dr. Newton reported he has performed consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Ferkol reported involvement in a longitudinal study defining endpoints for future clinical PCD trials funded by ReCode Therapeutics and leadership of an international clinical trial for PCD supported by Parion Sciences. He has received honoraria from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation and serves as a member of the ReCode Therapeutics PCD Clinical Steering Committee. Dr. Raby reported no relevant disclosures.