User login
Increase in Troublesome Fungal Infections Requires All-Out Approach
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
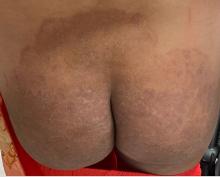
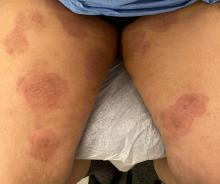
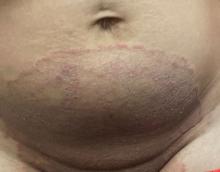
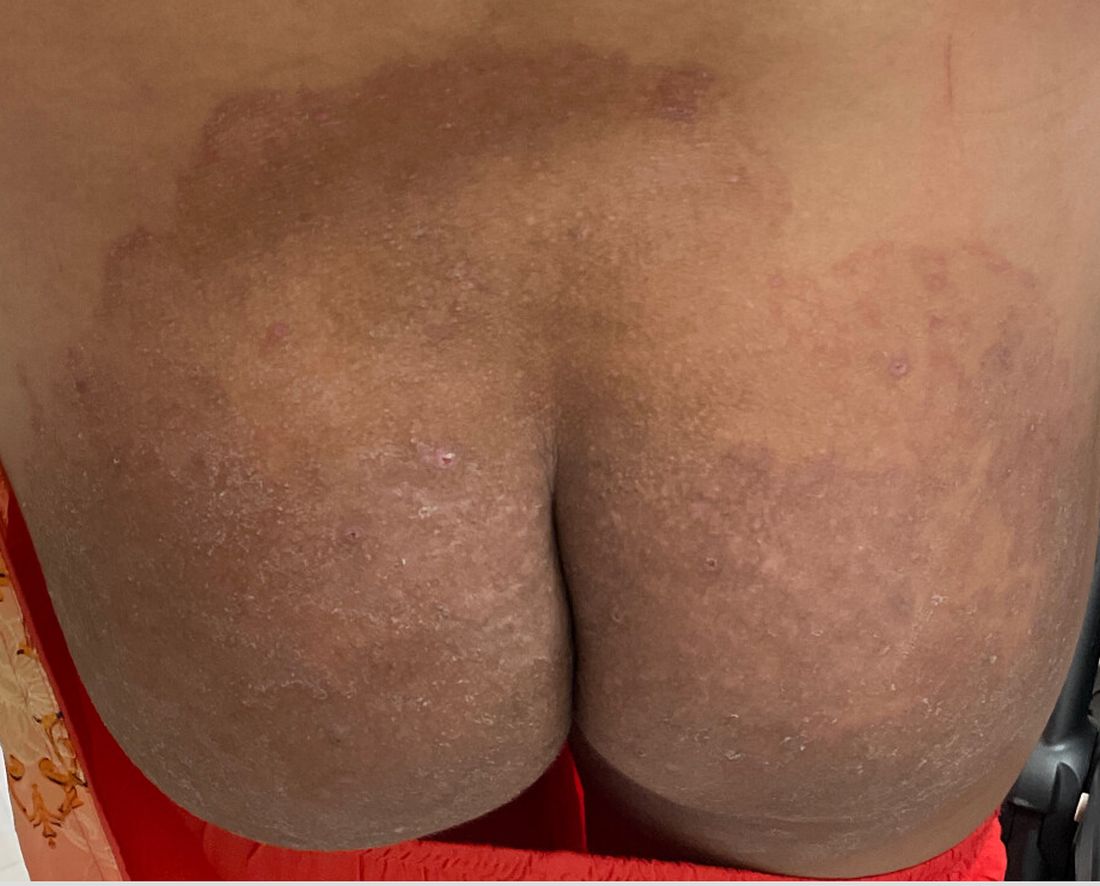
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A Dermatologist’s Tips for Supporting LGBTQ Youth
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIFORNIA —
“Sometimes in dermatology we might say, ‘This gender care stuff, that’s really for pediatricians and primary care doctors,’ ” Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. However, he added, “gender-affirming care happens not only with medications but with communication, curiosity, and respect.” For instance, an LGBTQ patient who is being treated with isotretinoin for acne is seen once a month by a dermatologist, which is probably more frequent than seeing their primary care physician, he said. “Every time you see that child, you can make them feel seen. You can respect them. You can let them know that you care about them. Hopefully then they understand what it feels like to get good care from a provider and then will not settle for poor care from someone else.”
According to Gallup polling, the proportion of people in the United States who identify as non-cisgender or nonheterosexual increased from 3.5% in 2012 to 7% in 2021. “The estimation is that 2.5%-3.5% of all teenagers identify as gay or bisexual, and another 1% identify as transgender, though some studies estimate the percentage of gender diverse youth to be as high as 9.2%,” said Boos.
He discussed several barriers to dermatologic care for LGBTQ youth, including availability. “There are only about 400 practicing pediatric dermatologists in the US, so there’s not a lot of pediatric dermatology care to go around for any child,” Boos said. “My plea to general dermatologists who see adolescents and teenagers: You can care for LGBTQ adolescents; they need your help.”
Accessibility is also an issue. For example, his clinic is in a wealthy and somewhat isolated area of Seattle, “which makes it hard for some patients to access our services because they may have to drive from far away or take multiple modes of public transportation to see us,” explained Boos, who came out as gay about 10 years ago after beginning his practice in Seattle. “Time matters, too. Children are in school. They don’t necessarily want to take time off to go to the doctor’s office. We want to make sure we have services at different times of day, including evenings or weekends if possible.”
Another potential barrier to care for this patient population is acceptability. “I can say that I welcome any patient to my practice, but if I’m not humble and informed about their concerns, especially queer or trans kids, if they feel that I’m not respecting them, that’s going to be a huge problem,” Boos said. “They won’t view that care as acceptable, and they’re not going to come back if they feel like I’m not looking out for their best interests.”
In a large cross-sectional study of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases published in 2023, sexual and gender minority (SGM) individuals were significantly more likely than non-SGM individuals to delay specialist care including dermatologic care (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.23), mental health care (AOR, 1.62), and filing a prescription (AOR, 1.30) because of cost. The barriers for SGM patients were transportation issues, not having a healthcare practitioner (HCP) from the same racial or ethnic background, “and they were more likely to report not always being treated with respect by HCPs,” said Boos, who was not involved with the study. “SGM patients of minoritized racial identities such as Black, Hispanic, and Latino were also more likely to experience barriers to care.”
Boos offered several tips for improving the dermatologic care of LGBTQ youth:
Use inclusive language and follow your patient’s lead. “There are many ways that people identify, both with respect to their sexual orientation and their gender identity,” he said. “We often think that a person is either gay or straight, or cisgender or transgender. There are many folks who reject these binaries and may view their gender identity or sexual orientation outside of these descriptors. You can be bisexual. You can be asexual.” He also emphasized that sexual orientation is different from sexual behavior.
Be deliberate about your phrasing. Boos said he strives to make new patients feel comfortable by asking them such questions as what pronouns they use, how he should address them, and whether they have a partner or are in a relationship. “Then, in general, just follow your patient’s lead,” Boos said. “If they’re referring to their partner in a certain way or to themselves with certain pronouns, go along with it. When in doubt, just ask. And if you make a mistake like using the wrong pronouns or name of a patient, the best thing to do is immediately apologize and try your best not to repeat that error.”
When asking about sexual practices, don’t make assumptions. Boos recommends a 2019 article on dermatologic care of LGBT persons, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which includes specific examples of how to elicit a sexual history from adults and teens. One of the recommendations is “to be very direct, say, ‘This may feel uncomfortable, but I have to ask you these direct questions about what you’re doing sexually because I need to understand if you’re at risk for things like sexually transmitted infections,’ ” Boos said. “It’s also important to use terminology that our patients know. If I ask someone if they’ve had sex before, they usually understand that as penile-vaginal intercourse, but it’s also important to understand if they have oral or anal sex. But if you ask, ‘Have you had insertive anal sex?’ they may not know what that means as opposed to receptive anal sex. Instead, you might ask, ‘Are you a top or a bottom?’ which are more commonly used and understood terms in the queer community. It may feel really uncomfortable to use that kind of language, but we want to make sure patients understand what we’re asking them so we can take the best possible care of them.”
Pay attention to the details. One way to demonstrate inclusivity in your practice includes collecting pronoun and sexual orientation information for the electronic medical record so your entire staff can use proper pronouns for the patient. “Also, acknowledge that for queer folks, family can mean more than just biological family,” Boos added. “I do not buy into the stereotype that all queer kids are ostracized from their families and not loved by their families, but it is true that they are at risk for those experiences. So, sometimes a member of the patient’s ‘chosen family’ accompanies them on their visit.”
Privacy is also key. “You never know who else is in the room when you’re on a telehealth call, so you need to address that before you ask about personal things,” Boos said. “One sticking point that can also come up is that parents often fill out their child’s patient demographic form, which may not tell the real story. I typically start to have confidential time without parents and may take a sexual history as early as 12 or 13 years of age if it’s a patient that I’m seeing for an extended period or if I’m worried about a skin finding that might suggest an STI.”
He highlighted the unique opportunity dermatologists have to transform the healthcare landscape for LGBTQ children and adolescents. “It’s about extending yourself to nurture the growth of another person,” Boos said. “This can feel challenging, but you want to see each person for who they are and help get them to where they want to go. That’s what we went into medicine for, right? We want to care about people.”
Boos had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIFORNIA —
“Sometimes in dermatology we might say, ‘This gender care stuff, that’s really for pediatricians and primary care doctors,’ ” Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. However, he added, “gender-affirming care happens not only with medications but with communication, curiosity, and respect.” For instance, an LGBTQ patient who is being treated with isotretinoin for acne is seen once a month by a dermatologist, which is probably more frequent than seeing their primary care physician, he said. “Every time you see that child, you can make them feel seen. You can respect them. You can let them know that you care about them. Hopefully then they understand what it feels like to get good care from a provider and then will not settle for poor care from someone else.”
According to Gallup polling, the proportion of people in the United States who identify as non-cisgender or nonheterosexual increased from 3.5% in 2012 to 7% in 2021. “The estimation is that 2.5%-3.5% of all teenagers identify as gay or bisexual, and another 1% identify as transgender, though some studies estimate the percentage of gender diverse youth to be as high as 9.2%,” said Boos.
He discussed several barriers to dermatologic care for LGBTQ youth, including availability. “There are only about 400 practicing pediatric dermatologists in the US, so there’s not a lot of pediatric dermatology care to go around for any child,” Boos said. “My plea to general dermatologists who see adolescents and teenagers: You can care for LGBTQ adolescents; they need your help.”
Accessibility is also an issue. For example, his clinic is in a wealthy and somewhat isolated area of Seattle, “which makes it hard for some patients to access our services because they may have to drive from far away or take multiple modes of public transportation to see us,” explained Boos, who came out as gay about 10 years ago after beginning his practice in Seattle. “Time matters, too. Children are in school. They don’t necessarily want to take time off to go to the doctor’s office. We want to make sure we have services at different times of day, including evenings or weekends if possible.”
Another potential barrier to care for this patient population is acceptability. “I can say that I welcome any patient to my practice, but if I’m not humble and informed about their concerns, especially queer or trans kids, if they feel that I’m not respecting them, that’s going to be a huge problem,” Boos said. “They won’t view that care as acceptable, and they’re not going to come back if they feel like I’m not looking out for their best interests.”
In a large cross-sectional study of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases published in 2023, sexual and gender minority (SGM) individuals were significantly more likely than non-SGM individuals to delay specialist care including dermatologic care (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.23), mental health care (AOR, 1.62), and filing a prescription (AOR, 1.30) because of cost. The barriers for SGM patients were transportation issues, not having a healthcare practitioner (HCP) from the same racial or ethnic background, “and they were more likely to report not always being treated with respect by HCPs,” said Boos, who was not involved with the study. “SGM patients of minoritized racial identities such as Black, Hispanic, and Latino were also more likely to experience barriers to care.”
Boos offered several tips for improving the dermatologic care of LGBTQ youth:
Use inclusive language and follow your patient’s lead. “There are many ways that people identify, both with respect to their sexual orientation and their gender identity,” he said. “We often think that a person is either gay or straight, or cisgender or transgender. There are many folks who reject these binaries and may view their gender identity or sexual orientation outside of these descriptors. You can be bisexual. You can be asexual.” He also emphasized that sexual orientation is different from sexual behavior.
Be deliberate about your phrasing. Boos said he strives to make new patients feel comfortable by asking them such questions as what pronouns they use, how he should address them, and whether they have a partner or are in a relationship. “Then, in general, just follow your patient’s lead,” Boos said. “If they’re referring to their partner in a certain way or to themselves with certain pronouns, go along with it. When in doubt, just ask. And if you make a mistake like using the wrong pronouns or name of a patient, the best thing to do is immediately apologize and try your best not to repeat that error.”
When asking about sexual practices, don’t make assumptions. Boos recommends a 2019 article on dermatologic care of LGBT persons, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which includes specific examples of how to elicit a sexual history from adults and teens. One of the recommendations is “to be very direct, say, ‘This may feel uncomfortable, but I have to ask you these direct questions about what you’re doing sexually because I need to understand if you’re at risk for things like sexually transmitted infections,’ ” Boos said. “It’s also important to use terminology that our patients know. If I ask someone if they’ve had sex before, they usually understand that as penile-vaginal intercourse, but it’s also important to understand if they have oral or anal sex. But if you ask, ‘Have you had insertive anal sex?’ they may not know what that means as opposed to receptive anal sex. Instead, you might ask, ‘Are you a top or a bottom?’ which are more commonly used and understood terms in the queer community. It may feel really uncomfortable to use that kind of language, but we want to make sure patients understand what we’re asking them so we can take the best possible care of them.”
Pay attention to the details. One way to demonstrate inclusivity in your practice includes collecting pronoun and sexual orientation information for the electronic medical record so your entire staff can use proper pronouns for the patient. “Also, acknowledge that for queer folks, family can mean more than just biological family,” Boos added. “I do not buy into the stereotype that all queer kids are ostracized from their families and not loved by their families, but it is true that they are at risk for those experiences. So, sometimes a member of the patient’s ‘chosen family’ accompanies them on their visit.”
Privacy is also key. “You never know who else is in the room when you’re on a telehealth call, so you need to address that before you ask about personal things,” Boos said. “One sticking point that can also come up is that parents often fill out their child’s patient demographic form, which may not tell the real story. I typically start to have confidential time without parents and may take a sexual history as early as 12 or 13 years of age if it’s a patient that I’m seeing for an extended period or if I’m worried about a skin finding that might suggest an STI.”
He highlighted the unique opportunity dermatologists have to transform the healthcare landscape for LGBTQ children and adolescents. “It’s about extending yourself to nurture the growth of another person,” Boos said. “This can feel challenging, but you want to see each person for who they are and help get them to where they want to go. That’s what we went into medicine for, right? We want to care about people.”
Boos had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIFORNIA —
“Sometimes in dermatology we might say, ‘This gender care stuff, that’s really for pediatricians and primary care doctors,’ ” Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. However, he added, “gender-affirming care happens not only with medications but with communication, curiosity, and respect.” For instance, an LGBTQ patient who is being treated with isotretinoin for acne is seen once a month by a dermatologist, which is probably more frequent than seeing their primary care physician, he said. “Every time you see that child, you can make them feel seen. You can respect them. You can let them know that you care about them. Hopefully then they understand what it feels like to get good care from a provider and then will not settle for poor care from someone else.”
According to Gallup polling, the proportion of people in the United States who identify as non-cisgender or nonheterosexual increased from 3.5% in 2012 to 7% in 2021. “The estimation is that 2.5%-3.5% of all teenagers identify as gay or bisexual, and another 1% identify as transgender, though some studies estimate the percentage of gender diverse youth to be as high as 9.2%,” said Boos.
He discussed several barriers to dermatologic care for LGBTQ youth, including availability. “There are only about 400 practicing pediatric dermatologists in the US, so there’s not a lot of pediatric dermatology care to go around for any child,” Boos said. “My plea to general dermatologists who see adolescents and teenagers: You can care for LGBTQ adolescents; they need your help.”
Accessibility is also an issue. For example, his clinic is in a wealthy and somewhat isolated area of Seattle, “which makes it hard for some patients to access our services because they may have to drive from far away or take multiple modes of public transportation to see us,” explained Boos, who came out as gay about 10 years ago after beginning his practice in Seattle. “Time matters, too. Children are in school. They don’t necessarily want to take time off to go to the doctor’s office. We want to make sure we have services at different times of day, including evenings or weekends if possible.”
Another potential barrier to care for this patient population is acceptability. “I can say that I welcome any patient to my practice, but if I’m not humble and informed about their concerns, especially queer or trans kids, if they feel that I’m not respecting them, that’s going to be a huge problem,” Boos said. “They won’t view that care as acceptable, and they’re not going to come back if they feel like I’m not looking out for their best interests.”
In a large cross-sectional study of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases published in 2023, sexual and gender minority (SGM) individuals were significantly more likely than non-SGM individuals to delay specialist care including dermatologic care (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.23), mental health care (AOR, 1.62), and filing a prescription (AOR, 1.30) because of cost. The barriers for SGM patients were transportation issues, not having a healthcare practitioner (HCP) from the same racial or ethnic background, “and they were more likely to report not always being treated with respect by HCPs,” said Boos, who was not involved with the study. “SGM patients of minoritized racial identities such as Black, Hispanic, and Latino were also more likely to experience barriers to care.”
Boos offered several tips for improving the dermatologic care of LGBTQ youth:
Use inclusive language and follow your patient’s lead. “There are many ways that people identify, both with respect to their sexual orientation and their gender identity,” he said. “We often think that a person is either gay or straight, or cisgender or transgender. There are many folks who reject these binaries and may view their gender identity or sexual orientation outside of these descriptors. You can be bisexual. You can be asexual.” He also emphasized that sexual orientation is different from sexual behavior.
Be deliberate about your phrasing. Boos said he strives to make new patients feel comfortable by asking them such questions as what pronouns they use, how he should address them, and whether they have a partner or are in a relationship. “Then, in general, just follow your patient’s lead,” Boos said. “If they’re referring to their partner in a certain way or to themselves with certain pronouns, go along with it. When in doubt, just ask. And if you make a mistake like using the wrong pronouns or name of a patient, the best thing to do is immediately apologize and try your best not to repeat that error.”
When asking about sexual practices, don’t make assumptions. Boos recommends a 2019 article on dermatologic care of LGBT persons, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which includes specific examples of how to elicit a sexual history from adults and teens. One of the recommendations is “to be very direct, say, ‘This may feel uncomfortable, but I have to ask you these direct questions about what you’re doing sexually because I need to understand if you’re at risk for things like sexually transmitted infections,’ ” Boos said. “It’s also important to use terminology that our patients know. If I ask someone if they’ve had sex before, they usually understand that as penile-vaginal intercourse, but it’s also important to understand if they have oral or anal sex. But if you ask, ‘Have you had insertive anal sex?’ they may not know what that means as opposed to receptive anal sex. Instead, you might ask, ‘Are you a top or a bottom?’ which are more commonly used and understood terms in the queer community. It may feel really uncomfortable to use that kind of language, but we want to make sure patients understand what we’re asking them so we can take the best possible care of them.”
Pay attention to the details. One way to demonstrate inclusivity in your practice includes collecting pronoun and sexual orientation information for the electronic medical record so your entire staff can use proper pronouns for the patient. “Also, acknowledge that for queer folks, family can mean more than just biological family,” Boos added. “I do not buy into the stereotype that all queer kids are ostracized from their families and not loved by their families, but it is true that they are at risk for those experiences. So, sometimes a member of the patient’s ‘chosen family’ accompanies them on their visit.”
Privacy is also key. “You never know who else is in the room when you’re on a telehealth call, so you need to address that before you ask about personal things,” Boos said. “One sticking point that can also come up is that parents often fill out their child’s patient demographic form, which may not tell the real story. I typically start to have confidential time without parents and may take a sexual history as early as 12 or 13 years of age if it’s a patient that I’m seeing for an extended period or if I’m worried about a skin finding that might suggest an STI.”
He highlighted the unique opportunity dermatologists have to transform the healthcare landscape for LGBTQ children and adolescents. “It’s about extending yourself to nurture the growth of another person,” Boos said. “This can feel challenging, but you want to see each person for who they are and help get them to where they want to go. That’s what we went into medicine for, right? We want to care about people.”
Boos had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PDA 2024
Should First-Line Dual Checkpoint Blockade Be Used for NSCLC With Specific Mutations?
according to the authors of a new paper.
These findings, drawn from a post hoc analysis of phase 3 data, are backed up by cell line and mouse data revealing clear mechanisms of efficacy, making the collective evidence compelling enough to reshape clinical practice, reported lead author Ferdinandos Skoulidis, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“Although STK11 and KEAP1 mutations are associated with limited benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 [PD-(L)1] inhibition, the association between these mutations and benefit from combinations of PD-(L)1 inhibitors with chemotherapy is not yet as well established,” the investigators wrote in Nature.
Skoulidis and colleagues conducted the subgroup analysis of POSEIDON trial data and characterized underlying biologic mechanisms using mouse models to address this knowledge gap.
What Were the Original Findings of POSEIDON?
The POSEIDON trial involved 1013 patients with metastatic NSCLC. Treatment arms included standard chemotherapy alone, chemotherapy plus programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor durvalumab, and chemotherapy plus durvalumab and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor tremelimumab.
Adding durvalumab to chemotherapy significantly improved median progression-free survival (PFS) but not median overall survival (OS), while dual checkpoint blockade boosted both PFS and OS.
These findings provided support for the dual approach in the first-line setting, but not preferentially so. Experts called for more long-term data, questioned the survival benefit in terms of the increased toxicity, and noted the lack of biomarkers for patient selection.
What Did Post Hoc Analysis Highlight About POSEIDON?
The present analysis aimed to validate two actionable biomarkers.
“We and others have previously observed that alterations in STK11 and KEAP1 can promote an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and together might be responsible for half or more of the primary resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition among patients with nsNSCLC when given as monotherapy,” Skoulidis and colleagues wrote.
From the original 1013 patients, 612 had non-squamous NSCLC and were evaluable for mutations. Among them, 87 had STK11 mutations and 37 had KEAP1 mutations.
As anticipated, patients in the STK11/KEAP1 subgroup saw little to no benefit from adding durvalumab to chemotherapy, but adding tremelimumab on top yielded notable improvement.
This was first observed in the objective response rate, which was 42.9% with dual checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy vs 30.2% with single checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy and 28% for chemotherapy alone. Durations of response improved in kind.
Survival outcomes also trended toward improvement in the dual checkpoint arm, which had a median OS of 15.8 months vs 7.3 months for durvalumab plus chemotherapy (hazard ratio [HR], 0.64; 95% CI, 0.40-1.04) and 10.5 months for chemotherapy alone (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.29-0.87). PFS showed similar trends.
How Do Findings Relate to Previous NSCLC Subgroup Research?
Skoulidis and colleagues noted that their findings align with those of the CheckMate 9LA trial, which showed that patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations had better outcomes with dual checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy than with chemotherapy alone.
“These data support the hypothesis that CTLA-4 inhibition can mitigate the resistance to chemotherapy plus PD-(L)1 inhibition observed in patients who have STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations and suggest that this group of patients derives greater benefit from CTLA-4 inhibition than do patients who lack either alteration,” Skoulidis and colleagues wrote.
Grace Dy, MD, professor of oncology in the Department of Medicine at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, noted that in the present analysis, PD-L1 expression status did not predict outcomes; however, patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations typically have low or negative PD-L1 expression, which has been linked with better responses to CTLA-4 inhibition in multiple trials.
“In the CheckMate 227 and CheckMate 9LA studies, we have seen that patients with PD-L1–negative tumors appear to derive greater and more durable long-term overall survival benefit from dual immune checkpoint blockade compared to patients receiving anti-PD1-based therapy alone,” Dy said in a written comment. “While we take the necessary caveats on cross-trial comparisons, the same survival trend favoring CTLA-4-based immune checkpoint blockade is seen compared to the tail of the survival curves observed in PD-L1–negative patients enrolled in the KEYNOTE studies (KEYNOTE-189, KEYNOTE-407).”
Detecting improvements in survival within PD-L1 patients “may not be readily apparent until later when looking at the tail of the survival curves,” she added.
What Mechanisms of Action Explain Relative Benefits of Dual Checkpoint Blockade?
To elucidate underlying mechanisms of action, Skoulidis and colleagues conducted a series of experiments involving cell lines and mouse models of Stk11- and Keap1-deficient NSCLC.
“For us, it was critical to provide mechanistic support for the observed clinical benefit in POSEIDON, especially since this is based on a retrospective subgroup analysis,” Skoulidis said in an interview.
Their efforts revealed a strong link between the mutations and resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition.
Inactivation of Stk11 and Keap1 promoted an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, marked by increased infiltration of suppressive myeloid cells and a reduction in CD8+ effector T cells. This immune imbalance contributed to evasion of immune destruction and limited the efficacy of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade.
Dual checkpoint blockade reprogrammed the immune microenvironment, leading to increased activation of CD4+ T helper (Th) cells, specifically the Th1 subtype, while inducing tumoricidal changes in myeloid cells. Consequently, antitumor responses improved, resulting in tumor regression and prolonged survival, compared with PD-1 monotherapy.
“Addition of CTLA-4 [inhibition] turns the two cardinal components of the suppressive microenvironment of these tumors on its head, and that’s why we believe we are observing this clinical benefit,” Skoulidis said. “This is not a mere association…but also based on very solid mechanistic data across a multitude of different models.”
Are Data Sufficient to Shift to First-Line Dual Checkpoint Blockade?
“Our work strengthens the available evidence that this regimen — and chemoimmunotherapy more broadly, with dual immune checkpoint blockade — constitutes a preferred approach for these patients,” Skoulidis said. “I personally, and I think physicians within MD Anderson, as well as a lot of physicians that I talk to, are already using — based on these data — the POSEIDON regimen, as well as, more broadly, chemoimmunotherapy with dual immune checkpoint for patients with these alterations.”
This view, however, remains contested by some oncologists.
Lei Deng, MD, assistant professor in the Division of Hematology and Oncology at the University of Washington, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, called the new data “intriguing” and “hypothesis-generating,” but stopped short of supporting preferential first-line use.
“This study is a post hoc analysis, so you don’t have a lot of patients,” Deng said. “It is still not strong enough or definitive enough to make it standard of care to use dual checkpoint blockade for [patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations].”
The cell line and mouse data help explain biologic mechanisms of efficacy, he said, but these findings do not obviate toxicity concerns.
“You are adding one more agent, and this agent is more toxic than single checkpoint blockade,” Deng said. “So, if you weigh the risk, it is known, [but] the benefit is suggestive. I am not sure if the risk-benefit ratio would argue for routine implementation of this regimen yet.”
On the other hand, he noted, the combination is the US Food and Drug Administration–approved in this setting, so “it is not wrong to use it.”
Jyoti Malhotra, MD, director of thoracic medical oncology at City of Hope Orange County in Irvine, California, had a similar take.
“The clinical data presented so far is exploratory and limited by the small sample size,” Malhotra said in a written comment. “Data from an ongoing phase 3 trial (TRITON) is awaited before dual checkpoint blockade becomes the standard of care in this setting.”
Hossein Borghaei, DO, chief of the Division of Thoracic Medical Oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, was also unequivocal when asked if dual checkpoint blockade with chemotherapy should be considered the preferred first-line treatment option in patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations.
“No,” he said in a written comment. “The data and the hypothesis are very strong, but it is all based on retrospective clinical data, cell line data, and mouse models. We need a randomized study to test the hypothesis.”
Incidentally, Borghaei is on the steering committee for the TRITON trial. He shared this potential conflict of interest before praising Skoulidis and colleagues for their efforts, noting that the present findings underscore the broader importance of widespread tumor profiling and access to resultant data.
“This is a beautiful story that has developed over the last few years based on the research by the group from MD Anderson who has reported the current Nature article,” he said. “This highlights the possible utility of collecting sequencing data on [all] patients’ tumors. These sorts of understandings and new ideas could arise only if there is access to this information.”
The study was supported by AstraZeneca, the National Cancer Institute, the Gunnigar Fund, and others. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Novartis, Merck, Amgen, and others. Deng disclosed relationships with Merck, BridgeBio, MJH Life Sciences, and others. Dy disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Meru, and others. Malhotra has previously served as a consultant for AstraZeneca. Borghaei has served as a consultant for AstraZeneca and is on the steering committee for the TRITON trial.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the authors of a new paper.
These findings, drawn from a post hoc analysis of phase 3 data, are backed up by cell line and mouse data revealing clear mechanisms of efficacy, making the collective evidence compelling enough to reshape clinical practice, reported lead author Ferdinandos Skoulidis, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“Although STK11 and KEAP1 mutations are associated with limited benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 [PD-(L)1] inhibition, the association between these mutations and benefit from combinations of PD-(L)1 inhibitors with chemotherapy is not yet as well established,” the investigators wrote in Nature.
Skoulidis and colleagues conducted the subgroup analysis of POSEIDON trial data and characterized underlying biologic mechanisms using mouse models to address this knowledge gap.
What Were the Original Findings of POSEIDON?
The POSEIDON trial involved 1013 patients with metastatic NSCLC. Treatment arms included standard chemotherapy alone, chemotherapy plus programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor durvalumab, and chemotherapy plus durvalumab and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor tremelimumab.
Adding durvalumab to chemotherapy significantly improved median progression-free survival (PFS) but not median overall survival (OS), while dual checkpoint blockade boosted both PFS and OS.
These findings provided support for the dual approach in the first-line setting, but not preferentially so. Experts called for more long-term data, questioned the survival benefit in terms of the increased toxicity, and noted the lack of biomarkers for patient selection.
What Did Post Hoc Analysis Highlight About POSEIDON?
The present analysis aimed to validate two actionable biomarkers.
“We and others have previously observed that alterations in STK11 and KEAP1 can promote an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and together might be responsible for half or more of the primary resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition among patients with nsNSCLC when given as monotherapy,” Skoulidis and colleagues wrote.
From the original 1013 patients, 612 had non-squamous NSCLC and were evaluable for mutations. Among them, 87 had STK11 mutations and 37 had KEAP1 mutations.
As anticipated, patients in the STK11/KEAP1 subgroup saw little to no benefit from adding durvalumab to chemotherapy, but adding tremelimumab on top yielded notable improvement.
This was first observed in the objective response rate, which was 42.9% with dual checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy vs 30.2% with single checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy and 28% for chemotherapy alone. Durations of response improved in kind.
Survival outcomes also trended toward improvement in the dual checkpoint arm, which had a median OS of 15.8 months vs 7.3 months for durvalumab plus chemotherapy (hazard ratio [HR], 0.64; 95% CI, 0.40-1.04) and 10.5 months for chemotherapy alone (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.29-0.87). PFS showed similar trends.
How Do Findings Relate to Previous NSCLC Subgroup Research?
Skoulidis and colleagues noted that their findings align with those of the CheckMate 9LA trial, which showed that patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations had better outcomes with dual checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy than with chemotherapy alone.
“These data support the hypothesis that CTLA-4 inhibition can mitigate the resistance to chemotherapy plus PD-(L)1 inhibition observed in patients who have STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations and suggest that this group of patients derives greater benefit from CTLA-4 inhibition than do patients who lack either alteration,” Skoulidis and colleagues wrote.
Grace Dy, MD, professor of oncology in the Department of Medicine at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, noted that in the present analysis, PD-L1 expression status did not predict outcomes; however, patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations typically have low or negative PD-L1 expression, which has been linked with better responses to CTLA-4 inhibition in multiple trials.
“In the CheckMate 227 and CheckMate 9LA studies, we have seen that patients with PD-L1–negative tumors appear to derive greater and more durable long-term overall survival benefit from dual immune checkpoint blockade compared to patients receiving anti-PD1-based therapy alone,” Dy said in a written comment. “While we take the necessary caveats on cross-trial comparisons, the same survival trend favoring CTLA-4-based immune checkpoint blockade is seen compared to the tail of the survival curves observed in PD-L1–negative patients enrolled in the KEYNOTE studies (KEYNOTE-189, KEYNOTE-407).”
Detecting improvements in survival within PD-L1 patients “may not be readily apparent until later when looking at the tail of the survival curves,” she added.
What Mechanisms of Action Explain Relative Benefits of Dual Checkpoint Blockade?
To elucidate underlying mechanisms of action, Skoulidis and colleagues conducted a series of experiments involving cell lines and mouse models of Stk11- and Keap1-deficient NSCLC.
“For us, it was critical to provide mechanistic support for the observed clinical benefit in POSEIDON, especially since this is based on a retrospective subgroup analysis,” Skoulidis said in an interview.
Their efforts revealed a strong link between the mutations and resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition.
Inactivation of Stk11 and Keap1 promoted an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, marked by increased infiltration of suppressive myeloid cells and a reduction in CD8+ effector T cells. This immune imbalance contributed to evasion of immune destruction and limited the efficacy of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade.
Dual checkpoint blockade reprogrammed the immune microenvironment, leading to increased activation of CD4+ T helper (Th) cells, specifically the Th1 subtype, while inducing tumoricidal changes in myeloid cells. Consequently, antitumor responses improved, resulting in tumor regression and prolonged survival, compared with PD-1 monotherapy.
“Addition of CTLA-4 [inhibition] turns the two cardinal components of the suppressive microenvironment of these tumors on its head, and that’s why we believe we are observing this clinical benefit,” Skoulidis said. “This is not a mere association…but also based on very solid mechanistic data across a multitude of different models.”
Are Data Sufficient to Shift to First-Line Dual Checkpoint Blockade?
“Our work strengthens the available evidence that this regimen — and chemoimmunotherapy more broadly, with dual immune checkpoint blockade — constitutes a preferred approach for these patients,” Skoulidis said. “I personally, and I think physicians within MD Anderson, as well as a lot of physicians that I talk to, are already using — based on these data — the POSEIDON regimen, as well as, more broadly, chemoimmunotherapy with dual immune checkpoint for patients with these alterations.”
This view, however, remains contested by some oncologists.
Lei Deng, MD, assistant professor in the Division of Hematology and Oncology at the University of Washington, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, called the new data “intriguing” and “hypothesis-generating,” but stopped short of supporting preferential first-line use.
“This study is a post hoc analysis, so you don’t have a lot of patients,” Deng said. “It is still not strong enough or definitive enough to make it standard of care to use dual checkpoint blockade for [patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations].”
The cell line and mouse data help explain biologic mechanisms of efficacy, he said, but these findings do not obviate toxicity concerns.
“You are adding one more agent, and this agent is more toxic than single checkpoint blockade,” Deng said. “So, if you weigh the risk, it is known, [but] the benefit is suggestive. I am not sure if the risk-benefit ratio would argue for routine implementation of this regimen yet.”
On the other hand, he noted, the combination is the US Food and Drug Administration–approved in this setting, so “it is not wrong to use it.”
Jyoti Malhotra, MD, director of thoracic medical oncology at City of Hope Orange County in Irvine, California, had a similar take.
“The clinical data presented so far is exploratory and limited by the small sample size,” Malhotra said in a written comment. “Data from an ongoing phase 3 trial (TRITON) is awaited before dual checkpoint blockade becomes the standard of care in this setting.”
Hossein Borghaei, DO, chief of the Division of Thoracic Medical Oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, was also unequivocal when asked if dual checkpoint blockade with chemotherapy should be considered the preferred first-line treatment option in patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations.
“No,” he said in a written comment. “The data and the hypothesis are very strong, but it is all based on retrospective clinical data, cell line data, and mouse models. We need a randomized study to test the hypothesis.”
Incidentally, Borghaei is on the steering committee for the TRITON trial. He shared this potential conflict of interest before praising Skoulidis and colleagues for their efforts, noting that the present findings underscore the broader importance of widespread tumor profiling and access to resultant data.
“This is a beautiful story that has developed over the last few years based on the research by the group from MD Anderson who has reported the current Nature article,” he said. “This highlights the possible utility of collecting sequencing data on [all] patients’ tumors. These sorts of understandings and new ideas could arise only if there is access to this information.”
The study was supported by AstraZeneca, the National Cancer Institute, the Gunnigar Fund, and others. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Novartis, Merck, Amgen, and others. Deng disclosed relationships with Merck, BridgeBio, MJH Life Sciences, and others. Dy disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Meru, and others. Malhotra has previously served as a consultant for AstraZeneca. Borghaei has served as a consultant for AstraZeneca and is on the steering committee for the TRITON trial.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the authors of a new paper.
These findings, drawn from a post hoc analysis of phase 3 data, are backed up by cell line and mouse data revealing clear mechanisms of efficacy, making the collective evidence compelling enough to reshape clinical practice, reported lead author Ferdinandos Skoulidis, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“Although STK11 and KEAP1 mutations are associated with limited benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 [PD-(L)1] inhibition, the association between these mutations and benefit from combinations of PD-(L)1 inhibitors with chemotherapy is not yet as well established,” the investigators wrote in Nature.
Skoulidis and colleagues conducted the subgroup analysis of POSEIDON trial data and characterized underlying biologic mechanisms using mouse models to address this knowledge gap.
What Were the Original Findings of POSEIDON?
The POSEIDON trial involved 1013 patients with metastatic NSCLC. Treatment arms included standard chemotherapy alone, chemotherapy plus programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor durvalumab, and chemotherapy plus durvalumab and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor tremelimumab.
Adding durvalumab to chemotherapy significantly improved median progression-free survival (PFS) but not median overall survival (OS), while dual checkpoint blockade boosted both PFS and OS.
These findings provided support for the dual approach in the first-line setting, but not preferentially so. Experts called for more long-term data, questioned the survival benefit in terms of the increased toxicity, and noted the lack of biomarkers for patient selection.
What Did Post Hoc Analysis Highlight About POSEIDON?
The present analysis aimed to validate two actionable biomarkers.
“We and others have previously observed that alterations in STK11 and KEAP1 can promote an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and together might be responsible for half or more of the primary resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition among patients with nsNSCLC when given as monotherapy,” Skoulidis and colleagues wrote.
From the original 1013 patients, 612 had non-squamous NSCLC and were evaluable for mutations. Among them, 87 had STK11 mutations and 37 had KEAP1 mutations.
As anticipated, patients in the STK11/KEAP1 subgroup saw little to no benefit from adding durvalumab to chemotherapy, but adding tremelimumab on top yielded notable improvement.
This was first observed in the objective response rate, which was 42.9% with dual checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy vs 30.2% with single checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy and 28% for chemotherapy alone. Durations of response improved in kind.
Survival outcomes also trended toward improvement in the dual checkpoint arm, which had a median OS of 15.8 months vs 7.3 months for durvalumab plus chemotherapy (hazard ratio [HR], 0.64; 95% CI, 0.40-1.04) and 10.5 months for chemotherapy alone (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.29-0.87). PFS showed similar trends.
How Do Findings Relate to Previous NSCLC Subgroup Research?
Skoulidis and colleagues noted that their findings align with those of the CheckMate 9LA trial, which showed that patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations had better outcomes with dual checkpoint blockade plus chemotherapy than with chemotherapy alone.
“These data support the hypothesis that CTLA-4 inhibition can mitigate the resistance to chemotherapy plus PD-(L)1 inhibition observed in patients who have STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations and suggest that this group of patients derives greater benefit from CTLA-4 inhibition than do patients who lack either alteration,” Skoulidis and colleagues wrote.
Grace Dy, MD, professor of oncology in the Department of Medicine at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, noted that in the present analysis, PD-L1 expression status did not predict outcomes; however, patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations typically have low or negative PD-L1 expression, which has been linked with better responses to CTLA-4 inhibition in multiple trials.
“In the CheckMate 227 and CheckMate 9LA studies, we have seen that patients with PD-L1–negative tumors appear to derive greater and more durable long-term overall survival benefit from dual immune checkpoint blockade compared to patients receiving anti-PD1-based therapy alone,” Dy said in a written comment. “While we take the necessary caveats on cross-trial comparisons, the same survival trend favoring CTLA-4-based immune checkpoint blockade is seen compared to the tail of the survival curves observed in PD-L1–negative patients enrolled in the KEYNOTE studies (KEYNOTE-189, KEYNOTE-407).”
Detecting improvements in survival within PD-L1 patients “may not be readily apparent until later when looking at the tail of the survival curves,” she added.
What Mechanisms of Action Explain Relative Benefits of Dual Checkpoint Blockade?
To elucidate underlying mechanisms of action, Skoulidis and colleagues conducted a series of experiments involving cell lines and mouse models of Stk11- and Keap1-deficient NSCLC.
“For us, it was critical to provide mechanistic support for the observed clinical benefit in POSEIDON, especially since this is based on a retrospective subgroup analysis,” Skoulidis said in an interview.
Their efforts revealed a strong link between the mutations and resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition.
Inactivation of Stk11 and Keap1 promoted an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, marked by increased infiltration of suppressive myeloid cells and a reduction in CD8+ effector T cells. This immune imbalance contributed to evasion of immune destruction and limited the efficacy of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade.
Dual checkpoint blockade reprogrammed the immune microenvironment, leading to increased activation of CD4+ T helper (Th) cells, specifically the Th1 subtype, while inducing tumoricidal changes in myeloid cells. Consequently, antitumor responses improved, resulting in tumor regression and prolonged survival, compared with PD-1 monotherapy.
“Addition of CTLA-4 [inhibition] turns the two cardinal components of the suppressive microenvironment of these tumors on its head, and that’s why we believe we are observing this clinical benefit,” Skoulidis said. “This is not a mere association…but also based on very solid mechanistic data across a multitude of different models.”
Are Data Sufficient to Shift to First-Line Dual Checkpoint Blockade?
“Our work strengthens the available evidence that this regimen — and chemoimmunotherapy more broadly, with dual immune checkpoint blockade — constitutes a preferred approach for these patients,” Skoulidis said. “I personally, and I think physicians within MD Anderson, as well as a lot of physicians that I talk to, are already using — based on these data — the POSEIDON regimen, as well as, more broadly, chemoimmunotherapy with dual immune checkpoint for patients with these alterations.”
This view, however, remains contested by some oncologists.
Lei Deng, MD, assistant professor in the Division of Hematology and Oncology at the University of Washington, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, called the new data “intriguing” and “hypothesis-generating,” but stopped short of supporting preferential first-line use.
“This study is a post hoc analysis, so you don’t have a lot of patients,” Deng said. “It is still not strong enough or definitive enough to make it standard of care to use dual checkpoint blockade for [patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations].”
The cell line and mouse data help explain biologic mechanisms of efficacy, he said, but these findings do not obviate toxicity concerns.
“You are adding one more agent, and this agent is more toxic than single checkpoint blockade,” Deng said. “So, if you weigh the risk, it is known, [but] the benefit is suggestive. I am not sure if the risk-benefit ratio would argue for routine implementation of this regimen yet.”
On the other hand, he noted, the combination is the US Food and Drug Administration–approved in this setting, so “it is not wrong to use it.”
Jyoti Malhotra, MD, director of thoracic medical oncology at City of Hope Orange County in Irvine, California, had a similar take.
“The clinical data presented so far is exploratory and limited by the small sample size,” Malhotra said in a written comment. “Data from an ongoing phase 3 trial (TRITON) is awaited before dual checkpoint blockade becomes the standard of care in this setting.”
Hossein Borghaei, DO, chief of the Division of Thoracic Medical Oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, was also unequivocal when asked if dual checkpoint blockade with chemotherapy should be considered the preferred first-line treatment option in patients with STK11 and/or KEAP1 mutations.
“No,” he said in a written comment. “The data and the hypothesis are very strong, but it is all based on retrospective clinical data, cell line data, and mouse models. We need a randomized study to test the hypothesis.”
Incidentally, Borghaei is on the steering committee for the TRITON trial. He shared this potential conflict of interest before praising Skoulidis and colleagues for their efforts, noting that the present findings underscore the broader importance of widespread tumor profiling and access to resultant data.
“This is a beautiful story that has developed over the last few years based on the research by the group from MD Anderson who has reported the current Nature article,” he said. “This highlights the possible utility of collecting sequencing data on [all] patients’ tumors. These sorts of understandings and new ideas could arise only if there is access to this information.”
The study was supported by AstraZeneca, the National Cancer Institute, the Gunnigar Fund, and others. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Novartis, Merck, Amgen, and others. Deng disclosed relationships with Merck, BridgeBio, MJH Life Sciences, and others. Dy disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Meru, and others. Malhotra has previously served as a consultant for AstraZeneca. Borghaei has served as a consultant for AstraZeneca and is on the steering committee for the TRITON trial.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Scientists Are Linking More Diseases to Light at Night
This October, millions of Americans missed out on two of the most spectacular shows in the universe: the northern lights and a rare comet. Even if you were aware of them, light pollution made them difficult to see, unless you went to a dark area and let your eyes adjust.
It’s not getting any easier — the night sky over North America has been growing brighter by about 10% per year since 2011. More and more research is linking all that light pollution to a surprising range of health consequences: cancer, heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and even low sperm quality, though the reasons for these troubling associations are not always clear.
“We’ve lost the contrast between light and dark, and we are confusing our physiology on a regular basis,” said John Hanifin, PhD, associate director of Thomas Jefferson University’s Light Research Program.
Our own galaxy is invisible to nearly 80% of people in North America. In 1994, an earthquake-triggered blackout in Los Angeles led to calls to the Griffith Observatory from people wondering about that hazy blob of light in the night sky. It was the Milky Way.
Glaring headlights, illuminated buildings, blazing billboards, and streetlights fill our urban skies with a glow that even affects rural residents. Inside, since the invention of the lightbulb, we’ve kept our homes bright at night. Now, we’ve also added blue light-emitting devices — smartphones, television screens, tablets — which have been linked to sleep problems.
But outdoor light may matter for our health, too. “Every photon counts,” Hanifin said.
Bright Lights, Big Problems
For one 2024 study researchers used satellite data to measure light pollution at residential addresses of over 13,000 people. They found that those who lived in places with the brightest skies at night had a 31% higher risk of high blood pressure. Another study out of Hong Kong showed a 29% higher risk of death from coronary heart disease. And yet another found a 17%higher risk of cerebrovascular disease, such as strokes or brain aneurysms.
Of course, urban areas also have air pollution, noise, and a lack of greenery. So, for some studies, scientists controlled for these factors, and the correlation remained strong (although air pollution with fine particulate matter appeared to be worse for heart health than outdoor light).
Research has found links between the nighttime glow outside and other diseases:
Breast cancer. “It’s a very strong correlation,” said Randy Nelson, PhD, a neuroscientist at West Virginia University. A study of over 100,000 teachers in California revealed that women living in areas with the most light pollution had a 12%higher risk. That effect is comparable to increasing your intake of ultra-processed foods by 10%.
Alzheimer’s disease. In a study published this fall, outdoor light at night was more strongly linked to the disease than even alcohol misuse or obesity.
Diabetes. In one recent study, people living in the most illuminated areas had a 28% higher risk of diabetes than those residing in much darker places. In a country like China, scientists concluded that 9 million cases of diabetes could be linked to light pollution.
What Happens in Your Body When You’re Exposed to Light at Night
, the “hormone of darkness.” “Darkness is very important,” Hanifin said. When he and his colleagues decades ago started studying the effects of light on human physiology, “people thought we were borderline crazy,” he said.
Nighttime illumination affects the health and behavior of species as diverse as Siberian hamsters, zebra finches, mice, crickets, and mosquitoes. Like most creatures on Earth, humans have internal clocks that are synced to the 24-hour cycle of day and night. The master clock is in your hypothalamus, a diamond-shaped part of the brain, but every cell in your body has its own clock, too. Many physiological processes run on circadian rhythms (a term derived from a Latin phrase meaning “about a day”), from sleep-wake cycle to hormone secretion, as well as processes involved in cancer progression, such as cell division.
“There are special photoreceptors in the eye that don’t deal with visual information. They just send light information,” Nelson said. “If you get light at the wrong time, you’re resetting the clocks.”
This internal clock “prepares the body for various recurrent challenges, such as eating,” said Christian Benedict, PhD, a sleep researcher at Uppsala University, Sweden. “Light exposure [at night] can mess up this very important system.” This could mean, for instance, that your insulin is released at the wrong time, Benedict said, causing “a jet lag-ish condition that will then impair the ability to handle blood sugar.” Animal studies confirm that exposure to light at night can reduce glucose tolerance and alter insulin secretion – potential pathways to diabetes.
The hormone melatonin, produced when it’s dark by the pineal gland in the brain, is a key player in this modern struggle. Melatonin helps you sleep, synchronizes the body’s circadian rhythms, protects neurons from damage, regulates the immune system, and fights inflammation. But even a sliver of light at night can suppress its secretion. Less than 30 lux of light, about the level of a pedestrian street at night, can slash melatonin by half.
When lab animals are exposed to nighttime light, they “show enormous neuroinflammation” — that is, inflammation of nervous tissue, Nelson said. In one experiment on humans, those who slept immersed in weak light had higher levels of C-reactive protein in their blood, a marker of inflammation.
Low melatonin has also been linked to cancer. It “allows the metabolic machinery of the cancer cells to be active,” Hanifin said. One of melatonin’s effects is stimulation of natural killer cells, which can recognize and destroy cancer cells. What’s more, when melatonin plunges, estrogen may go up, which could explain the link between light at night and breast cancer (estrogen fuels tumor growth in breast cancers).
Researchers concede that satellite data might be too coarse to estimate how much light people are actually exposed to while they sleep. Plus, many of us are staring at bright screens. “But the studies keep coming,” Nelson said, suggesting that outdoor light pollution does have an impact.
When researchers put wrist-worn light sensors on over 80,000 British people, they found that the more light the device registered between half-past midnight and 6 a.m., the more its wearer was at risk of having diabetes several years down the road — no matter how long they’ve actually slept. This, according to the study’s authors, supports the findings of satellite data.
A similar study that used actigraphy with built-in light sensors, measuring whether people had been sleeping in complete darkness for at least five hours, found that light pollution upped the risk of heart disease by 74%.
What Can You Do About This?
Not everyone’s melatonin is affected by nighttime light to the same degree. “Some people are very much sensitive to very dim light, whereas others are not as sensitive and need far, far more light stimulation [to impact melatonin],” Benedict said. In one study, some volunteers needed 350 lux to lower their melatonin by half. For such people, flipping on the light in the bathroom at night wouldn’t matter; for others, though, a mere 6 lux was already as harmful – which is darker than twilight.
You can protect yourself by keeping your bedroom lights off and your screens stashed away, but avoiding outdoor light pollution may be harder. You can invest in high-quality blackout curtains, of course, although some light may still seep inside. You can plant trees in front of your windows, reorient any motion-detector lights, and even petition your local government to reduce over-illumination of buildings and to choose better streetlights. You can support organizations, such as the International Dark-Sky Association, that work to preserve darkness.
Last but not least, you might want to change your habits. If you live in a particularly light-polluted area, such as the District of Columbia, America’s top place for urban blaze, you might reconsider late-night walks or drives around the neighborhood. Instead, Hanifin said, read a book in bed, while keeping the light “as dim as you can.” It’s “a much better idea versus being outside in midtown Manhattan,” he said. According to recent recommendations published by Hanifin and his colleagues, when you sleep, there should be no more than 1 lux of illumination at the level of your eyes — about as much as you’d get from having a lit candle 1 meter away.
And if we manage to preserve outdoor darkness, and the stars reappear (including the breathtaking Milky Way), we could reap more benefits — some research suggests that stargazing can elicit positive emotions, a sense of personal growth, and “a variety of transcendent thoughts and experiences.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
This October, millions of Americans missed out on two of the most spectacular shows in the universe: the northern lights and a rare comet. Even if you were aware of them, light pollution made them difficult to see, unless you went to a dark area and let your eyes adjust.
It’s not getting any easier — the night sky over North America has been growing brighter by about 10% per year since 2011. More and more research is linking all that light pollution to a surprising range of health consequences: cancer, heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and even low sperm quality, though the reasons for these troubling associations are not always clear.
“We’ve lost the contrast between light and dark, and we are confusing our physiology on a regular basis,” said John Hanifin, PhD, associate director of Thomas Jefferson University’s Light Research Program.
Our own galaxy is invisible to nearly 80% of people in North America. In 1994, an earthquake-triggered blackout in Los Angeles led to calls to the Griffith Observatory from people wondering about that hazy blob of light in the night sky. It was the Milky Way.
Glaring headlights, illuminated buildings, blazing billboards, and streetlights fill our urban skies with a glow that even affects rural residents. Inside, since the invention of the lightbulb, we’ve kept our homes bright at night. Now, we’ve also added blue light-emitting devices — smartphones, television screens, tablets — which have been linked to sleep problems.
But outdoor light may matter for our health, too. “Every photon counts,” Hanifin said.
Bright Lights, Big Problems
For one 2024 study researchers used satellite data to measure light pollution at residential addresses of over 13,000 people. They found that those who lived in places with the brightest skies at night had a 31% higher risk of high blood pressure. Another study out of Hong Kong showed a 29% higher risk of death from coronary heart disease. And yet another found a 17%higher risk of cerebrovascular disease, such as strokes or brain aneurysms.
Of course, urban areas also have air pollution, noise, and a lack of greenery. So, for some studies, scientists controlled for these factors, and the correlation remained strong (although air pollution with fine particulate matter appeared to be worse for heart health than outdoor light).
Research has found links between the nighttime glow outside and other diseases:
Breast cancer. “It’s a very strong correlation,” said Randy Nelson, PhD, a neuroscientist at West Virginia University. A study of over 100,000 teachers in California revealed that women living in areas with the most light pollution had a 12%higher risk. That effect is comparable to increasing your intake of ultra-processed foods by 10%.
Alzheimer’s disease. In a study published this fall, outdoor light at night was more strongly linked to the disease than even alcohol misuse or obesity.
Diabetes. In one recent study, people living in the most illuminated areas had a 28% higher risk of diabetes than those residing in much darker places. In a country like China, scientists concluded that 9 million cases of diabetes could be linked to light pollution.
What Happens in Your Body When You’re Exposed to Light at Night
, the “hormone of darkness.” “Darkness is very important,” Hanifin said. When he and his colleagues decades ago started studying the effects of light on human physiology, “people thought we were borderline crazy,” he said.
Nighttime illumination affects the health and behavior of species as diverse as Siberian hamsters, zebra finches, mice, crickets, and mosquitoes. Like most creatures on Earth, humans have internal clocks that are synced to the 24-hour cycle of day and night. The master clock is in your hypothalamus, a diamond-shaped part of the brain, but every cell in your body has its own clock, too. Many physiological processes run on circadian rhythms (a term derived from a Latin phrase meaning “about a day”), from sleep-wake cycle to hormone secretion, as well as processes involved in cancer progression, such as cell division.
“There are special photoreceptors in the eye that don’t deal with visual information. They just send light information,” Nelson said. “If you get light at the wrong time, you’re resetting the clocks.”
This internal clock “prepares the body for various recurrent challenges, such as eating,” said Christian Benedict, PhD, a sleep researcher at Uppsala University, Sweden. “Light exposure [at night] can mess up this very important system.” This could mean, for instance, that your insulin is released at the wrong time, Benedict said, causing “a jet lag-ish condition that will then impair the ability to handle blood sugar.” Animal studies confirm that exposure to light at night can reduce glucose tolerance and alter insulin secretion – potential pathways to diabetes.
The hormone melatonin, produced when it’s dark by the pineal gland in the brain, is a key player in this modern struggle. Melatonin helps you sleep, synchronizes the body’s circadian rhythms, protects neurons from damage, regulates the immune system, and fights inflammation. But even a sliver of light at night can suppress its secretion. Less than 30 lux of light, about the level of a pedestrian street at night, can slash melatonin by half.
When lab animals are exposed to nighttime light, they “show enormous neuroinflammation” — that is, inflammation of nervous tissue, Nelson said. In one experiment on humans, those who slept immersed in weak light had higher levels of C-reactive protein in their blood, a marker of inflammation.
Low melatonin has also been linked to cancer. It “allows the metabolic machinery of the cancer cells to be active,” Hanifin said. One of melatonin’s effects is stimulation of natural killer cells, which can recognize and destroy cancer cells. What’s more, when melatonin plunges, estrogen may go up, which could explain the link between light at night and breast cancer (estrogen fuels tumor growth in breast cancers).
Researchers concede that satellite data might be too coarse to estimate how much light people are actually exposed to while they sleep. Plus, many of us are staring at bright screens. “But the studies keep coming,” Nelson said, suggesting that outdoor light pollution does have an impact.
When researchers put wrist-worn light sensors on over 80,000 British people, they found that the more light the device registered between half-past midnight and 6 a.m., the more its wearer was at risk of having diabetes several years down the road — no matter how long they’ve actually slept. This, according to the study’s authors, supports the findings of satellite data.
A similar study that used actigraphy with built-in light sensors, measuring whether people had been sleeping in complete darkness for at least five hours, found that light pollution upped the risk of heart disease by 74%.
What Can You Do About This?
Not everyone’s melatonin is affected by nighttime light to the same degree. “Some people are very much sensitive to very dim light, whereas others are not as sensitive and need far, far more light stimulation [to impact melatonin],” Benedict said. In one study, some volunteers needed 350 lux to lower their melatonin by half. For such people, flipping on the light in the bathroom at night wouldn’t matter; for others, though, a mere 6 lux was already as harmful – which is darker than twilight.
You can protect yourself by keeping your bedroom lights off and your screens stashed away, but avoiding outdoor light pollution may be harder. You can invest in high-quality blackout curtains, of course, although some light may still seep inside. You can plant trees in front of your windows, reorient any motion-detector lights, and even petition your local government to reduce over-illumination of buildings and to choose better streetlights. You can support organizations, such as the International Dark-Sky Association, that work to preserve darkness.
Last but not least, you might want to change your habits. If you live in a particularly light-polluted area, such as the District of Columbia, America’s top place for urban blaze, you might reconsider late-night walks or drives around the neighborhood. Instead, Hanifin said, read a book in bed, while keeping the light “as dim as you can.” It’s “a much better idea versus being outside in midtown Manhattan,” he said. According to recent recommendations published by Hanifin and his colleagues, when you sleep, there should be no more than 1 lux of illumination at the level of your eyes — about as much as you’d get from having a lit candle 1 meter away.
And if we manage to preserve outdoor darkness, and the stars reappear (including the breathtaking Milky Way), we could reap more benefits — some research suggests that stargazing can elicit positive emotions, a sense of personal growth, and “a variety of transcendent thoughts and experiences.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
This October, millions of Americans missed out on two of the most spectacular shows in the universe: the northern lights and a rare comet. Even if you were aware of them, light pollution made them difficult to see, unless you went to a dark area and let your eyes adjust.
It’s not getting any easier — the night sky over North America has been growing brighter by about 10% per year since 2011. More and more research is linking all that light pollution to a surprising range of health consequences: cancer, heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and even low sperm quality, though the reasons for these troubling associations are not always clear.
“We’ve lost the contrast between light and dark, and we are confusing our physiology on a regular basis,” said John Hanifin, PhD, associate director of Thomas Jefferson University’s Light Research Program.
Our own galaxy is invisible to nearly 80% of people in North America. In 1994, an earthquake-triggered blackout in Los Angeles led to calls to the Griffith Observatory from people wondering about that hazy blob of light in the night sky. It was the Milky Way.
Glaring headlights, illuminated buildings, blazing billboards, and streetlights fill our urban skies with a glow that even affects rural residents. Inside, since the invention of the lightbulb, we’ve kept our homes bright at night. Now, we’ve also added blue light-emitting devices — smartphones, television screens, tablets — which have been linked to sleep problems.
But outdoor light may matter for our health, too. “Every photon counts,” Hanifin said.
Bright Lights, Big Problems
For one 2024 study researchers used satellite data to measure light pollution at residential addresses of over 13,000 people. They found that those who lived in places with the brightest skies at night had a 31% higher risk of high blood pressure. Another study out of Hong Kong showed a 29% higher risk of death from coronary heart disease. And yet another found a 17%higher risk of cerebrovascular disease, such as strokes or brain aneurysms.
Of course, urban areas also have air pollution, noise, and a lack of greenery. So, for some studies, scientists controlled for these factors, and the correlation remained strong (although air pollution with fine particulate matter appeared to be worse for heart health than outdoor light).
Research has found links between the nighttime glow outside and other diseases:
Breast cancer. “It’s a very strong correlation,” said Randy Nelson, PhD, a neuroscientist at West Virginia University. A study of over 100,000 teachers in California revealed that women living in areas with the most light pollution had a 12%higher risk. That effect is comparable to increasing your intake of ultra-processed foods by 10%.
Alzheimer’s disease. In a study published this fall, outdoor light at night was more strongly linked to the disease than even alcohol misuse or obesity.
Diabetes. In one recent study, people living in the most illuminated areas had a 28% higher risk of diabetes than those residing in much darker places. In a country like China, scientists concluded that 9 million cases of diabetes could be linked to light pollution.
What Happens in Your Body When You’re Exposed to Light at Night
, the “hormone of darkness.” “Darkness is very important,” Hanifin said. When he and his colleagues decades ago started studying the effects of light on human physiology, “people thought we were borderline crazy,” he said.
Nighttime illumination affects the health and behavior of species as diverse as Siberian hamsters, zebra finches, mice, crickets, and mosquitoes. Like most creatures on Earth, humans have internal clocks that are synced to the 24-hour cycle of day and night. The master clock is in your hypothalamus, a diamond-shaped part of the brain, but every cell in your body has its own clock, too. Many physiological processes run on circadian rhythms (a term derived from a Latin phrase meaning “about a day”), from sleep-wake cycle to hormone secretion, as well as processes involved in cancer progression, such as cell division.
“There are special photoreceptors in the eye that don’t deal with visual information. They just send light information,” Nelson said. “If you get light at the wrong time, you’re resetting the clocks.”
This internal clock “prepares the body for various recurrent challenges, such as eating,” said Christian Benedict, PhD, a sleep researcher at Uppsala University, Sweden. “Light exposure [at night] can mess up this very important system.” This could mean, for instance, that your insulin is released at the wrong time, Benedict said, causing “a jet lag-ish condition that will then impair the ability to handle blood sugar.” Animal studies confirm that exposure to light at night can reduce glucose tolerance and alter insulin secretion – potential pathways to diabetes.
The hormone melatonin, produced when it’s dark by the pineal gland in the brain, is a key player in this modern struggle. Melatonin helps you sleep, synchronizes the body’s circadian rhythms, protects neurons from damage, regulates the immune system, and fights inflammation. But even a sliver of light at night can suppress its secretion. Less than 30 lux of light, about the level of a pedestrian street at night, can slash melatonin by half.
When lab animals are exposed to nighttime light, they “show enormous neuroinflammation” — that is, inflammation of nervous tissue, Nelson said. In one experiment on humans, those who slept immersed in weak light had higher levels of C-reactive protein in their blood, a marker of inflammation.
Low melatonin has also been linked to cancer. It “allows the metabolic machinery of the cancer cells to be active,” Hanifin said. One of melatonin’s effects is stimulation of natural killer cells, which can recognize and destroy cancer cells. What’s more, when melatonin plunges, estrogen may go up, which could explain the link between light at night and breast cancer (estrogen fuels tumor growth in breast cancers).
Researchers concede that satellite data might be too coarse to estimate how much light people are actually exposed to while they sleep. Plus, many of us are staring at bright screens. “But the studies keep coming,” Nelson said, suggesting that outdoor light pollution does have an impact.
When researchers put wrist-worn light sensors on over 80,000 British people, they found that the more light the device registered between half-past midnight and 6 a.m., the more its wearer was at risk of having diabetes several years down the road — no matter how long they’ve actually slept. This, according to the study’s authors, supports the findings of satellite data.
A similar study that used actigraphy with built-in light sensors, measuring whether people had been sleeping in complete darkness for at least five hours, found that light pollution upped the risk of heart disease by 74%.
What Can You Do About This?
Not everyone’s melatonin is affected by nighttime light to the same degree. “Some people are very much sensitive to very dim light, whereas others are not as sensitive and need far, far more light stimulation [to impact melatonin],” Benedict said. In one study, some volunteers needed 350 lux to lower their melatonin by half. For such people, flipping on the light in the bathroom at night wouldn’t matter; for others, though, a mere 6 lux was already as harmful – which is darker than twilight.
You can protect yourself by keeping your bedroom lights off and your screens stashed away, but avoiding outdoor light pollution may be harder. You can invest in high-quality blackout curtains, of course, although some light may still seep inside. You can plant trees in front of your windows, reorient any motion-detector lights, and even petition your local government to reduce over-illumination of buildings and to choose better streetlights. You can support organizations, such as the International Dark-Sky Association, that work to preserve darkness.
Last but not least, you might want to change your habits. If you live in a particularly light-polluted area, such as the District of Columbia, America’s top place for urban blaze, you might reconsider late-night walks or drives around the neighborhood. Instead, Hanifin said, read a book in bed, while keeping the light “as dim as you can.” It’s “a much better idea versus being outside in midtown Manhattan,” he said. According to recent recommendations published by Hanifin and his colleagues, when you sleep, there should be no more than 1 lux of illumination at the level of your eyes — about as much as you’d get from having a lit candle 1 meter away.
And if we manage to preserve outdoor darkness, and the stars reappear (including the breathtaking Milky Way), we could reap more benefits — some research suggests that stargazing can elicit positive emotions, a sense of personal growth, and “a variety of transcendent thoughts and experiences.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Blood Tests for Alzheimer’s Are Here... Are Clinicians Ready?
With the approval of anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies to treat early-stage Alzheimer’s disease, the need for accurate and early diagnosis is crucial.
Recently, an expert workgroup convened by the Global CEO Initiative on Alzheimer’s Disease published recommendations for the clinical implementation of Alzheimer’s disease blood-based biomarkers.
“Our hope was to provide some recommendations that clinicians could use to develop the best pathways for their clinical practice,” said workgroup co-chair Michelle M. Mielke, PhD, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Triage and Confirmatory Pathways
The group recommends two implementation pathways for Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers — one for current use for triaging and another for future use to confirm amyloid pathology once blood biomarker tests have reached sufficient performance for this purpose.
In the triage pathway, a negative blood biomarker test would flag individuals unlikely to have detectable brain amyloid pathology. This outcome would prompt clinicians to focus on evaluating non–Alzheimer’s disease-related causes of cognitive impairment, which may streamline the diagnosis of other causes of cognitive impairment, the authors said.
A positive triage blood test would suggest a higher likelihood of amyloid pathology and prompt referral to secondary care for further assessment and consideration for a second, more accurate test, such as amyloid PET or CSF for amyloid confirmation.
In the confirmatory pathway, a positive blood biomarker test result would identify amyloid pathology without the need for a second test, providing a faster route to diagnosis, the authors noted.
Mielke emphasized that these recommendations represent a “first step” and will need to be updated as experiences with the Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers in clinical care increase and additional barriers and facilitators are identified.
“These updates will likely include community-informed approaches that incorporate feedback from patients as well as healthcare providers, alongside results from validation in diverse real-world settings,” said workgroup co-chair Chi Udeh-Momoh, PhD, MSc, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the Brain and Mind Institute, Aga Khan University, Nairobi, Kenya.
The Alzheimer’s Association published “appropriate use” recommendations for blood biomarkers in 2022.
“Currently, the Alzheimer’s Association is building an updated library of clinical guidance that distills the scientific evidence using de novo systematic reviews and translates them into clear and actionable recommendations for clinical practice,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, vice president of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association.
“The first major effort with our new process will be the upcoming Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guideline on the Use of Blood-based Biomarkers (BBMs) in Specialty Care Settings. This guideline’s recommendations will be published in early 2025,” Edelmayer said.
Availability and Accuracy
Research has shown that amyloid beta and tau protein blood biomarkers — especially a high plasma phosphorylated (p)–tau217 levels — are highly accurate in identifying Alzheimer’s disease in patients with cognitive symptoms attending primary and secondary care clinics.
Several tests targeting plasma p-tau217 are now available for use. They include the PrecivityAD2 blood test from C2N Diagnostics and the Simoa p-Tau 217 Planar Kit and LucentAD p-Tau 217 — both from Quanterix.
In a recent head-to-head comparison of seven leading blood tests for AD pathology, measures of plasma p-tau217, either individually or in combination with other plasma biomarkers, had the strongest relationships with Alzheimer’s disease outcomes.
A recent Swedish study showed that the PrecivityAD2 test had an accuracy of 91% for correctly classifying clinical, biomarker-verified Alzheimer’s disease.
“We’ve been using these blood biomarkers in research for a long time and we’re now taking the jump to start using them in clinic to risk stratify patients,” said Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD, director of fluid biomarker research for the Barbara and Maurice Deane Center for Wellness and Cognitive Health at Icahn Mount Sinai in New York City.
New York’s Mount Sinai Health System is among the first in the northeast to offer blood tests across primary and specialty care settings for early diagnosis of AD and related dementias.
Edelmayer cautioned, “There is no single, stand-alone test to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease today. Blood testing is one piece of the diagnostic process.”
“Currently, physicians use well-established diagnostic tools combined with medical history and other information, including neurological exams, cognitive and functional assessments as well as brain imaging and spinal fluid analysis and blood to make an accurate diagnosis and to understand which patients are eligible for approved treatments,” she said.
There are also emerging biomarkers in the research pipeline, Edelmayer said.
“For example, some researchers think retinal imaging has the potential to detect biological signs of Alzheimer’s disease within certain areas of the eye,” she explained.
“Other emerging biomarkers include examining components in saliva and the skin for signals that may indicate early biological changes in the brain. These biomarkers are still very exploratory, and more research is needed before these tests or biomarkers can be used more routinely to study risk or aid in diagnosis,” Edelmayer said.
Ideal Candidates for Alzheimer’s Disease Blood Testing?
Experts agree that blood tests represent a convenient and scalable option to address the anticipated surge in demand for biomarker testing with the availability of disease-modifying treatments. For now, however, they are not for all older adults worried about their memory.
“Current practice should focus on using these blood biomarkers in individuals with cognitive impairment rather than in those with normal cognition or subjective cognitive decline until further research demonstrates effective interventions for individuals considered cognitively normal with elevated levels of amyloid,” the authors of a recent JAMA editorial noted.
At Mount Sinai, “we’re not starting with stone-cold asymptomatic individuals. But ultimately, this is what the blood tests are intended for — screening,” Elahi noted.
She also noted that Mount Sinai has a “very diverse population” — some with young onset cognitive symptoms, so the entry criteria for testing are “very wide.”
“Anyone above age 40 with symptoms can qualify to get a blood test. We do ask at this stage that either the individual report symptoms or someone in their life or their clinician be worried about their cognition or their brain function,” Elahi said.
Ethical Considerations, Counseling
Elahi emphasized the importance of counseling patients who come to the clinic seeking an Alzheimer’s disease blood test. This should include how the diagnostic process will unfold and what the next steps are with a given result.
Elahi said patients need to be informed that Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers are still “relatively new,” and a test can help a patient “know the likelihood of having the disease, but it won’t be 100% definitive.”
To ensure the ethical principle of “do no harm,” counseling should ensure that patients are fully prepared for the implications of the test results and ensure that the decision to test aligns with the patient’s readiness and well-being, Elahi said.
Edelmayer said the forthcoming clinical practice guidelines will provide “evidence-based recommendations for physicians to help guide them through the decision-making process around who should be tested and when. In the meantime, the Alzheimer’s Association urges providers to refer to the 2022 appropriate use recommendations for blood tests in clinical practice and trial settings.”
Mielke has served on scientific advisory boards and/or having consulted for Acadia, Biogen, Eisai, LabCorp, Lilly, Merck, PeerView Institute, Roche, Siemens Healthineers, and Sunbird Bio. Edelmayer and Elahi had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With the approval of anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies to treat early-stage Alzheimer’s disease, the need for accurate and early diagnosis is crucial.
Recently, an expert workgroup convened by the Global CEO Initiative on Alzheimer’s Disease published recommendations for the clinical implementation of Alzheimer’s disease blood-based biomarkers.
“Our hope was to provide some recommendations that clinicians could use to develop the best pathways for their clinical practice,” said workgroup co-chair Michelle M. Mielke, PhD, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Triage and Confirmatory Pathways
The group recommends two implementation pathways for Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers — one for current use for triaging and another for future use to confirm amyloid pathology once blood biomarker tests have reached sufficient performance for this purpose.
In the triage pathway, a negative blood biomarker test would flag individuals unlikely to have detectable brain amyloid pathology. This outcome would prompt clinicians to focus on evaluating non–Alzheimer’s disease-related causes of cognitive impairment, which may streamline the diagnosis of other causes of cognitive impairment, the authors said.
A positive triage blood test would suggest a higher likelihood of amyloid pathology and prompt referral to secondary care for further assessment and consideration for a second, more accurate test, such as amyloid PET or CSF for amyloid confirmation.
In the confirmatory pathway, a positive blood biomarker test result would identify amyloid pathology without the need for a second test, providing a faster route to diagnosis, the authors noted.
Mielke emphasized that these recommendations represent a “first step” and will need to be updated as experiences with the Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers in clinical care increase and additional barriers and facilitators are identified.
“These updates will likely include community-informed approaches that incorporate feedback from patients as well as healthcare providers, alongside results from validation in diverse real-world settings,” said workgroup co-chair Chi Udeh-Momoh, PhD, MSc, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the Brain and Mind Institute, Aga Khan University, Nairobi, Kenya.
The Alzheimer’s Association published “appropriate use” recommendations for blood biomarkers in 2022.
“Currently, the Alzheimer’s Association is building an updated library of clinical guidance that distills the scientific evidence using de novo systematic reviews and translates them into clear and actionable recommendations for clinical practice,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, vice president of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association.
“The first major effort with our new process will be the upcoming Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guideline on the Use of Blood-based Biomarkers (BBMs) in Specialty Care Settings. This guideline’s recommendations will be published in early 2025,” Edelmayer said.
Availability and Accuracy
Research has shown that amyloid beta and tau protein blood biomarkers — especially a high plasma phosphorylated (p)–tau217 levels — are highly accurate in identifying Alzheimer’s disease in patients with cognitive symptoms attending primary and secondary care clinics.
Several tests targeting plasma p-tau217 are now available for use. They include the PrecivityAD2 blood test from C2N Diagnostics and the Simoa p-Tau 217 Planar Kit and LucentAD p-Tau 217 — both from Quanterix.
In a recent head-to-head comparison of seven leading blood tests for AD pathology, measures of plasma p-tau217, either individually or in combination with other plasma biomarkers, had the strongest relationships with Alzheimer’s disease outcomes.
A recent Swedish study showed that the PrecivityAD2 test had an accuracy of 91% for correctly classifying clinical, biomarker-verified Alzheimer’s disease.
“We’ve been using these blood biomarkers in research for a long time and we’re now taking the jump to start using them in clinic to risk stratify patients,” said Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD, director of fluid biomarker research for the Barbara and Maurice Deane Center for Wellness and Cognitive Health at Icahn Mount Sinai in New York City.
New York’s Mount Sinai Health System is among the first in the northeast to offer blood tests across primary and specialty care settings for early diagnosis of AD and related dementias.
Edelmayer cautioned, “There is no single, stand-alone test to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease today. Blood testing is one piece of the diagnostic process.”
“Currently, physicians use well-established diagnostic tools combined with medical history and other information, including neurological exams, cognitive and functional assessments as well as brain imaging and spinal fluid analysis and blood to make an accurate diagnosis and to understand which patients are eligible for approved treatments,” she said.
There are also emerging biomarkers in the research pipeline, Edelmayer said.
“For example, some researchers think retinal imaging has the potential to detect biological signs of Alzheimer’s disease within certain areas of the eye,” she explained.
“Other emerging biomarkers include examining components in saliva and the skin for signals that may indicate early biological changes in the brain. These biomarkers are still very exploratory, and more research is needed before these tests or biomarkers can be used more routinely to study risk or aid in diagnosis,” Edelmayer said.
Ideal Candidates for Alzheimer’s Disease Blood Testing?
Experts agree that blood tests represent a convenient and scalable option to address the anticipated surge in demand for biomarker testing with the availability of disease-modifying treatments. For now, however, they are not for all older adults worried about their memory.
“Current practice should focus on using these blood biomarkers in individuals with cognitive impairment rather than in those with normal cognition or subjective cognitive decline until further research demonstrates effective interventions for individuals considered cognitively normal with elevated levels of amyloid,” the authors of a recent JAMA editorial noted.
At Mount Sinai, “we’re not starting with stone-cold asymptomatic individuals. But ultimately, this is what the blood tests are intended for — screening,” Elahi noted.
She also noted that Mount Sinai has a “very diverse population” — some with young onset cognitive symptoms, so the entry criteria for testing are “very wide.”
“Anyone above age 40 with symptoms can qualify to get a blood test. We do ask at this stage that either the individual report symptoms or someone in their life or their clinician be worried about their cognition or their brain function,” Elahi said.
Ethical Considerations, Counseling
Elahi emphasized the importance of counseling patients who come to the clinic seeking an Alzheimer’s disease blood test. This should include how the diagnostic process will unfold and what the next steps are with a given result.
Elahi said patients need to be informed that Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers are still “relatively new,” and a test can help a patient “know the likelihood of having the disease, but it won’t be 100% definitive.”
To ensure the ethical principle of “do no harm,” counseling should ensure that patients are fully prepared for the implications of the test results and ensure that the decision to test aligns with the patient’s readiness and well-being, Elahi said.
Edelmayer said the forthcoming clinical practice guidelines will provide “evidence-based recommendations for physicians to help guide them through the decision-making process around who should be tested and when. In the meantime, the Alzheimer’s Association urges providers to refer to the 2022 appropriate use recommendations for blood tests in clinical practice and trial settings.”
Mielke has served on scientific advisory boards and/or having consulted for Acadia, Biogen, Eisai, LabCorp, Lilly, Merck, PeerView Institute, Roche, Siemens Healthineers, and Sunbird Bio. Edelmayer and Elahi had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With the approval of anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies to treat early-stage Alzheimer’s disease, the need for accurate and early diagnosis is crucial.
Recently, an expert workgroup convened by the Global CEO Initiative on Alzheimer’s Disease published recommendations for the clinical implementation of Alzheimer’s disease blood-based biomarkers.
“Our hope was to provide some recommendations that clinicians could use to develop the best pathways for their clinical practice,” said workgroup co-chair Michelle M. Mielke, PhD, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Triage and Confirmatory Pathways
The group recommends two implementation pathways for Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers — one for current use for triaging and another for future use to confirm amyloid pathology once blood biomarker tests have reached sufficient performance for this purpose.
In the triage pathway, a negative blood biomarker test would flag individuals unlikely to have detectable brain amyloid pathology. This outcome would prompt clinicians to focus on evaluating non–Alzheimer’s disease-related causes of cognitive impairment, which may streamline the diagnosis of other causes of cognitive impairment, the authors said.
A positive triage blood test would suggest a higher likelihood of amyloid pathology and prompt referral to secondary care for further assessment and consideration for a second, more accurate test, such as amyloid PET or CSF for amyloid confirmation.
In the confirmatory pathway, a positive blood biomarker test result would identify amyloid pathology without the need for a second test, providing a faster route to diagnosis, the authors noted.
Mielke emphasized that these recommendations represent a “first step” and will need to be updated as experiences with the Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers in clinical care increase and additional barriers and facilitators are identified.
“These updates will likely include community-informed approaches that incorporate feedback from patients as well as healthcare providers, alongside results from validation in diverse real-world settings,” said workgroup co-chair Chi Udeh-Momoh, PhD, MSc, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the Brain and Mind Institute, Aga Khan University, Nairobi, Kenya.
The Alzheimer’s Association published “appropriate use” recommendations for blood biomarkers in 2022.
“Currently, the Alzheimer’s Association is building an updated library of clinical guidance that distills the scientific evidence using de novo systematic reviews and translates them into clear and actionable recommendations for clinical practice,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, vice president of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association.
“The first major effort with our new process will be the upcoming Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guideline on the Use of Blood-based Biomarkers (BBMs) in Specialty Care Settings. This guideline’s recommendations will be published in early 2025,” Edelmayer said.
Availability and Accuracy
Research has shown that amyloid beta and tau protein blood biomarkers — especially a high plasma phosphorylated (p)–tau217 levels — are highly accurate in identifying Alzheimer’s disease in patients with cognitive symptoms attending primary and secondary care clinics.
Several tests targeting plasma p-tau217 are now available for use. They include the PrecivityAD2 blood test from C2N Diagnostics and the Simoa p-Tau 217 Planar Kit and LucentAD p-Tau 217 — both from Quanterix.
In a recent head-to-head comparison of seven leading blood tests for AD pathology, measures of plasma p-tau217, either individually or in combination with other plasma biomarkers, had the strongest relationships with Alzheimer’s disease outcomes.
A recent Swedish study showed that the PrecivityAD2 test had an accuracy of 91% for correctly classifying clinical, biomarker-verified Alzheimer’s disease.
“We’ve been using these blood biomarkers in research for a long time and we’re now taking the jump to start using them in clinic to risk stratify patients,” said Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD, director of fluid biomarker research for the Barbara and Maurice Deane Center for Wellness and Cognitive Health at Icahn Mount Sinai in New York City.
New York’s Mount Sinai Health System is among the first in the northeast to offer blood tests across primary and specialty care settings for early diagnosis of AD and related dementias.
Edelmayer cautioned, “There is no single, stand-alone test to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease today. Blood testing is one piece of the diagnostic process.”
“Currently, physicians use well-established diagnostic tools combined with medical history and other information, including neurological exams, cognitive and functional assessments as well as brain imaging and spinal fluid analysis and blood to make an accurate diagnosis and to understand which patients are eligible for approved treatments,” she said.
There are also emerging biomarkers in the research pipeline, Edelmayer said.
“For example, some researchers think retinal imaging has the potential to detect biological signs of Alzheimer’s disease within certain areas of the eye,” she explained.
“Other emerging biomarkers include examining components in saliva and the skin for signals that may indicate early biological changes in the brain. These biomarkers are still very exploratory, and more research is needed before these tests or biomarkers can be used more routinely to study risk or aid in diagnosis,” Edelmayer said.
Ideal Candidates for Alzheimer’s Disease Blood Testing?
Experts agree that blood tests represent a convenient and scalable option to address the anticipated surge in demand for biomarker testing with the availability of disease-modifying treatments. For now, however, they are not for all older adults worried about their memory.
“Current practice should focus on using these blood biomarkers in individuals with cognitive impairment rather than in those with normal cognition or subjective cognitive decline until further research demonstrates effective interventions for individuals considered cognitively normal with elevated levels of amyloid,” the authors of a recent JAMA editorial noted.
At Mount Sinai, “we’re not starting with stone-cold asymptomatic individuals. But ultimately, this is what the blood tests are intended for — screening,” Elahi noted.
She also noted that Mount Sinai has a “very diverse population” — some with young onset cognitive symptoms, so the entry criteria for testing are “very wide.”
“Anyone above age 40 with symptoms can qualify to get a blood test. We do ask at this stage that either the individual report symptoms or someone in their life or their clinician be worried about their cognition or their brain function,” Elahi said.
Ethical Considerations, Counseling
Elahi emphasized the importance of counseling patients who come to the clinic seeking an Alzheimer’s disease blood test. This should include how the diagnostic process will unfold and what the next steps are with a given result.
Elahi said patients need to be informed that Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers are still “relatively new,” and a test can help a patient “know the likelihood of having the disease, but it won’t be 100% definitive.”
To ensure the ethical principle of “do no harm,” counseling should ensure that patients are fully prepared for the implications of the test results and ensure that the decision to test aligns with the patient’s readiness and well-being, Elahi said.
Edelmayer said the forthcoming clinical practice guidelines will provide “evidence-based recommendations for physicians to help guide them through the decision-making process around who should be tested and when. In the meantime, the Alzheimer’s Association urges providers to refer to the 2022 appropriate use recommendations for blood tests in clinical practice and trial settings.”
Mielke has served on scientific advisory boards and/or having consulted for Acadia, Biogen, Eisai, LabCorp, Lilly, Merck, PeerView Institute, Roche, Siemens Healthineers, and Sunbird Bio. Edelmayer and Elahi had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ACIP Recommends Pneumococcal Vaccine for Adults 50 Years or Older
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) for all PCV-naive adults aged 50 years or older. The new recommendation, which passed with an ACIP member vote of 14 for and one against, expands the current age-based recommendations, which include children younger than 5 years and adults older than 65 years, as well as adults aged 19-64 years with underlying conditions or risk factors who have not received a PCV and certain adults who have received PCV13 but not PCV20.
The decision was based in part on economic analyses of the use of PCV in adults aged 50-64 years in the United States. Miwako Kobayashi, MD, presented the summary of the Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group’s interpretation of the evidence and the proposed recommendation in a meeting of the ACIP on October 23, 2024, when the ACIP voting occurred.
Data from the CDC show an increase in the relative burden of pneumococcal disease in adults aged 50-64 years based in part on the success of the pediatric PCV program, she said.
Health equity was another main factor in the Work Group’s decision to recommend vaccination for adults aged 50 years or older. “Disparities in pneumococcal vaccine coverage by race and ethnicity exist for both age-based and risk-based indications,” Kobayashi noted in her presentation. The Work Group acknowledged that the overall effect of a vaccine recommendation on health equity is complex, but the majority agreed that the update would improve health equity by increasing vaccine coverage for those with known or unknown risk factors and providing protection at an earlier age when some populations already experience elevated disease rates, she said.
As for safety, the Work Group concluded that the undesirable anticipated effects of PCVs are minimal, despite the potential signal for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, and the CDC and US Food and Drug Administration will continue to monitor post-licensure safety of PCVs.
Support Not Universal
A majority of the ACIP Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group supported the approved option, but agreed that a future booster dose may be needed, Work Group Chair James Loehr, MD, said in his introductory presentation.
Overall, key uncertainties remain, including indirect effects of new pediatric pneumococcal vaccines on adults, data on the duration of protection with adult vaccinations, and the impact new higher-valency vaccines have on adults, several of which are in development, Loehr said.
A new 21-valent PCV, known as PCV 21, was approved by the FDA for adults aged 18 years or older in June 2024, said Loehr. “PCV21 is not PCV20 with one additional serotype” and provides additional protection, he emphasized. The Work Group examined models involving PCV21 and the existing PCV20. However, a majority of the Work Group agreed that having age-based recommendations based on vaccine product would be more challenging to implement and that insurance coverage may be a factor given the recent approval of PCV21. Therefore, the proposal submitted to the full ACIP was not for a specific PCV.
Notably, Loehr said that, although as Work Group Chair he was tasked with making the motion in favor of the recommendation, he voted against it as a voting member because of his strong opinion that only the PCV21 vaccine is needed for vaccine-naive adults aged 50 or older. “I think that PCV21 is a better vaccine that targets more serotypes,” he said during the discussion. Data presented at the February 2024 ACIP meeting showed more than 80% coverage vs less than 60% coverage for invasive pneumococcal disease with PCV21 vs PCV20 among adults aged 65 years or older and those aged 19-64 years with a risk-based indication, Loehr said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) for all PCV-naive adults aged 50 years or older. The new recommendation, which passed with an ACIP member vote of 14 for and one against, expands the current age-based recommendations, which include children younger than 5 years and adults older than 65 years, as well as adults aged 19-64 years with underlying conditions or risk factors who have not received a PCV and certain adults who have received PCV13 but not PCV20.
The decision was based in part on economic analyses of the use of PCV in adults aged 50-64 years in the United States. Miwako Kobayashi, MD, presented the summary of the Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group’s interpretation of the evidence and the proposed recommendation in a meeting of the ACIP on October 23, 2024, when the ACIP voting occurred.
Data from the CDC show an increase in the relative burden of pneumococcal disease in adults aged 50-64 years based in part on the success of the pediatric PCV program, she said.
Health equity was another main factor in the Work Group’s decision to recommend vaccination for adults aged 50 years or older. “Disparities in pneumococcal vaccine coverage by race and ethnicity exist for both age-based and risk-based indications,” Kobayashi noted in her presentation. The Work Group acknowledged that the overall effect of a vaccine recommendation on health equity is complex, but the majority agreed that the update would improve health equity by increasing vaccine coverage for those with known or unknown risk factors and providing protection at an earlier age when some populations already experience elevated disease rates, she said.
As for safety, the Work Group concluded that the undesirable anticipated effects of PCVs are minimal, despite the potential signal for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, and the CDC and US Food and Drug Administration will continue to monitor post-licensure safety of PCVs.
Support Not Universal
A majority of the ACIP Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group supported the approved option, but agreed that a future booster dose may be needed, Work Group Chair James Loehr, MD, said in his introductory presentation.
Overall, key uncertainties remain, including indirect effects of new pediatric pneumococcal vaccines on adults, data on the duration of protection with adult vaccinations, and the impact new higher-valency vaccines have on adults, several of which are in development, Loehr said.
A new 21-valent PCV, known as PCV 21, was approved by the FDA for adults aged 18 years or older in June 2024, said Loehr. “PCV21 is not PCV20 with one additional serotype” and provides additional protection, he emphasized. The Work Group examined models involving PCV21 and the existing PCV20. However, a majority of the Work Group agreed that having age-based recommendations based on vaccine product would be more challenging to implement and that insurance coverage may be a factor given the recent approval of PCV21. Therefore, the proposal submitted to the full ACIP was not for a specific PCV.
Notably, Loehr said that, although as Work Group Chair he was tasked with making the motion in favor of the recommendation, he voted against it as a voting member because of his strong opinion that only the PCV21 vaccine is needed for vaccine-naive adults aged 50 or older. “I think that PCV21 is a better vaccine that targets more serotypes,” he said during the discussion. Data presented at the February 2024 ACIP meeting showed more than 80% coverage vs less than 60% coverage for invasive pneumococcal disease with PCV21 vs PCV20 among adults aged 65 years or older and those aged 19-64 years with a risk-based indication, Loehr said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) for all PCV-naive adults aged 50 years or older. The new recommendation, which passed with an ACIP member vote of 14 for and one against, expands the current age-based recommendations, which include children younger than 5 years and adults older than 65 years, as well as adults aged 19-64 years with underlying conditions or risk factors who have not received a PCV and certain adults who have received PCV13 but not PCV20.
The decision was based in part on economic analyses of the use of PCV in adults aged 50-64 years in the United States. Miwako Kobayashi, MD, presented the summary of the Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group’s interpretation of the evidence and the proposed recommendation in a meeting of the ACIP on October 23, 2024, when the ACIP voting occurred.
Data from the CDC show an increase in the relative burden of pneumococcal disease in adults aged 50-64 years based in part on the success of the pediatric PCV program, she said.
Health equity was another main factor in the Work Group’s decision to recommend vaccination for adults aged 50 years or older. “Disparities in pneumococcal vaccine coverage by race and ethnicity exist for both age-based and risk-based indications,” Kobayashi noted in her presentation. The Work Group acknowledged that the overall effect of a vaccine recommendation on health equity is complex, but the majority agreed that the update would improve health equity by increasing vaccine coverage for those with known or unknown risk factors and providing protection at an earlier age when some populations already experience elevated disease rates, she said.
As for safety, the Work Group concluded that the undesirable anticipated effects of PCVs are minimal, despite the potential signal for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, and the CDC and US Food and Drug Administration will continue to monitor post-licensure safety of PCVs.
Support Not Universal
A majority of the ACIP Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group supported the approved option, but agreed that a future booster dose may be needed, Work Group Chair James Loehr, MD, said in his introductory presentation.
Overall, key uncertainties remain, including indirect effects of new pediatric pneumococcal vaccines on adults, data on the duration of protection with adult vaccinations, and the impact new higher-valency vaccines have on adults, several of which are in development, Loehr said.
A new 21-valent PCV, known as PCV 21, was approved by the FDA for adults aged 18 years or older in June 2024, said Loehr. “PCV21 is not PCV20 with one additional serotype” and provides additional protection, he emphasized. The Work Group examined models involving PCV21 and the existing PCV20. However, a majority of the Work Group agreed that having age-based recommendations based on vaccine product would be more challenging to implement and that insurance coverage may be a factor given the recent approval of PCV21. Therefore, the proposal submitted to the full ACIP was not for a specific PCV.
Notably, Loehr said that, although as Work Group Chair he was tasked with making the motion in favor of the recommendation, he voted against it as a voting member because of his strong opinion that only the PCV21 vaccine is needed for vaccine-naive adults aged 50 or older. “I think that PCV21 is a better vaccine that targets more serotypes,” he said during the discussion. Data presented at the February 2024 ACIP meeting showed more than 80% coverage vs less than 60% coverage for invasive pneumococcal disease with PCV21 vs PCV20 among adults aged 65 years or older and those aged 19-64 years with a risk-based indication, Loehr said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Remote Assessments: A Win-Win for ALS Patients and Clinics?
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , results of a retrospective study showed.
The findings, along with those of another study by the same group, suggest that remote monitoring of patients with ALS is a feasible option for both maximizing quality of life and minimizing cost and disruption.
Both studies were presented at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024.
“What we’re trying to do is look for screening tools that we can use when these patients are in the community to see if a specific score transition is associated with a high probability of needing an intervention that would require bringing them in to do gold standard tests,” said study investigator Tefani Perera, MD, a neurology resident at the University of Calgary, in Alberta, Canada.
Optimizing Quality of Life
Tailoring in-person care is particularly important for patients with ALS who often face significant challenges with mobility, Perera said. However, most multidisciplinary ALS clinics schedule in-person follow-ups at regular intervals rather than “as needed.
“These are very long clinic days where they are assessed for one thing after another, even if they don’t need it. So maybe we can actually select for what they need to be assessed for at each specific visit? Life expectancy is not that long for these patients, so we want to make sure their quality of life is optimized.”
For the BiPAP study, the investigators used the Pooled Resource Open-Access ALS Clinical Trials database to identify patients with ALS with two or more respiratory assessments on the Revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R).
The ALSFRS-R is a 12-item questionnaire, which includes three respiratory sub-scores for respiratory insufficiency (RiS), dyspnea (DyS) and orthopnea (OS).
Patients with a baseline RiS sub-score of 4 — meaning no need for BiPAP — were included in the study (n = 3838), with the primary outcome being a drop in RiS sub-score indicating the need for BiPAP.
The median time from baseline to transition to BiPAP was 563 days, with 3.4% of patients reaching this outcome by 3 months.
Results showed the probability of needing BiPAP was significantly associated with baseline DyS and OS scores (P < .0001). Among patients with baseline DyS scores of 3, 2, and 1, the percentages of patients needing BiPAP within 3 months were 5.5%, 8.7%, and 20.1%, respectively. In addition, in patients with baseline OS scores of 3, 2, and 1, the percentages of patients needing BiPAP within 3 months were 9.1%, 12.7%, and 24.2%, respectively.
Regardless of the baseline score, any drop in either of these sub-scores over the study period was also associated with an increased likelihood of requiring BiPAP within 3 months, with a DyS transition from 3 to 2 and an OS transition from 4 to 3 being most notable.
These scores could be used to trigger gold standard assessments for BiPAP, such as nocturnal oximetry, overnight polysomnography, daytime hypercapnia, and forced and slow vital capacities, Perera said. On the other hand, the scores could also help patients and clinicians avoid unnecessary visits.
“When the dyspnea and orthopnea scores are high, they might not need this intervention until 2 years later, so do we even need to bring them in to do these tests or see a respirologist when they don’t actually need it?”
The group’s second study was a systematic review of 26 papers on ALS remote assessment devices and methods, including accelerometers (15.4%), telenursing protocols (3.8%), speech collection apps (26.9%), questionnaires (15.4%), multifactorial sensors (15.4%), and respiratory function monitors (19.2%). Domains of symptoms monitored included speech (12 studies), motor (11 studies), respiratory (11 studies), cardiac (three studies), and bulbar, psychiatric, and autonomic (one study each).
The researchers characterized various remote tools as having potential and concluded that a multidomain approach to symptom monitoring is achievable. They also noted that the majority of studies assessing adherence and patient feedback indicated a favorable response to patient monitoring.
“I work in a resource-rich center, where we have these huge multidisciplinary clinics, and we have the capacity to bring patients back every 3 months, but outside these big centers, in resource-limited settings, to have an ability to track remotely and bring patients in when they really need it is very important,” said Perera.
Best of Both Worlds
Ileana Howard, MD, physiatrist and professor of rehabilitation medicine at the University of Washington and medical co-director of the ALS Center of Excellence at VA Puget Sound in Seattle, agreed.
“One of the biggest challenges in ALS care today is ensuring equitable access to high quality care and supports, and telehealth was adopted by the VA early on as a means of doing that,” she said. “Remote monitoring technology is a really key development to help improve that type of care.”
However, she added that it should not be a question of one type of care versus the other. “The ideal care is when we have access to providing both face-to-face and virtual care for our patients so that we can meet their needs and preferences for care,” she said.
“Sometimes, in my experience, patients don’t understand why it’s important to go to an ALS specialty center. In those cases, I’ve been able to make initial contact with those individuals through telehealth and be able to provide education, which, in turn, often results in them making the decision to come to the specialty center once they understand what resources we have to offer.”
Also commenting on the research, Ghazala Hayat, MD, also endorsed a mixed approach.
“Telehealth is a very good tool that we should use interspersed with in-person visits,” said Hayat, director of the multidisciplinary ALS clinic at St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, and professor of neurology and director of neuromuscular and clinical neurophysiology.
“I think the first few visits should always be in person — you need to connect with the patient,” she said. “But then, once they feel comfortable, remote monitoring is a very good idea, especially later in the disease process, when it becomes really difficult for the family to bring the patient in.”
The authors reported no relevant disclosures. Howard reported no disclosures. Hayat reported serving as a speaker and in advisory roles for argenx, Alexion, and MTPA. The study was funded by Amylyx Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , results of a retrospective study showed.
The findings, along with those of another study by the same group, suggest that remote monitoring of patients with ALS is a feasible option for both maximizing quality of life and minimizing cost and disruption.
Both studies were presented at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024.
“What we’re trying to do is look for screening tools that we can use when these patients are in the community to see if a specific score transition is associated with a high probability of needing an intervention that would require bringing them in to do gold standard tests,” said study investigator Tefani Perera, MD, a neurology resident at the University of Calgary, in Alberta, Canada.
Optimizing Quality of Life
Tailoring in-person care is particularly important for patients with ALS who often face significant challenges with mobility, Perera said. However, most multidisciplinary ALS clinics schedule in-person follow-ups at regular intervals rather than “as needed.
“These are very long clinic days where they are assessed for one thing after another, even if they don’t need it. So maybe we can actually select for what they need to be assessed for at each specific visit? Life expectancy is not that long for these patients, so we want to make sure their quality of life is optimized.”
For the BiPAP study, the investigators used the Pooled Resource Open-Access ALS Clinical Trials database to identify patients with ALS with two or more respiratory assessments on the Revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R).
The ALSFRS-R is a 12-item questionnaire, which includes three respiratory sub-scores for respiratory insufficiency (RiS), dyspnea (DyS) and orthopnea (OS).
Patients with a baseline RiS sub-score of 4 — meaning no need for BiPAP — were included in the study (n = 3838), with the primary outcome being a drop in RiS sub-score indicating the need for BiPAP.
The median time from baseline to transition to BiPAP was 563 days, with 3.4% of patients reaching this outcome by 3 months.
Results showed the probability of needing BiPAP was significantly associated with baseline DyS and OS scores (P < .0001). Among patients with baseline DyS scores of 3, 2, and 1, the percentages of patients needing BiPAP within 3 months were 5.5%, 8.7%, and 20.1%, respectively. In addition, in patients with baseline OS scores of 3, 2, and 1, the percentages of patients needing BiPAP within 3 months were 9.1%, 12.7%, and 24.2%, respectively.
Regardless of the baseline score, any drop in either of these sub-scores over the study period was also associated with an increased likelihood of requiring BiPAP within 3 months, with a DyS transition from 3 to 2 and an OS transition from 4 to 3 being most notable.
These scores could be used to trigger gold standard assessments for BiPAP, such as nocturnal oximetry, overnight polysomnography, daytime hypercapnia, and forced and slow vital capacities, Perera said. On the other hand, the scores could also help patients and clinicians avoid unnecessary visits.
“When the dyspnea and orthopnea scores are high, they might not need this intervention until 2 years later, so do we even need to bring them in to do these tests or see a respirologist when they don’t actually need it?”
The group’s second study was a systematic review of 26 papers on ALS remote assessment devices and methods, including accelerometers (15.4%), telenursing protocols (3.8%), speech collection apps (26.9%), questionnaires (15.4%), multifactorial sensors (15.4%), and respiratory function monitors (19.2%). Domains of symptoms monitored included speech (12 studies), motor (11 studies), respiratory (11 studies), cardiac (three studies), and bulbar, psychiatric, and autonomic (one study each).
The researchers characterized various remote tools as having potential and concluded that a multidomain approach to symptom monitoring is achievable. They also noted that the majority of studies assessing adherence and patient feedback indicated a favorable response to patient monitoring.
“I work in a resource-rich center, where we have these huge multidisciplinary clinics, and we have the capacity to bring patients back every 3 months, but outside these big centers, in resource-limited settings, to have an ability to track remotely and bring patients in when they really need it is very important,” said Perera.
Best of Both Worlds
Ileana Howard, MD, physiatrist and professor of rehabilitation medicine at the University of Washington and medical co-director of the ALS Center of Excellence at VA Puget Sound in Seattle, agreed.
“One of the biggest challenges in ALS care today is ensuring equitable access to high quality care and supports, and telehealth was adopted by the VA early on as a means of doing that,” she said. “Remote monitoring technology is a really key development to help improve that type of care.”
However, she added that it should not be a question of one type of care versus the other. “The ideal care is when we have access to providing both face-to-face and virtual care for our patients so that we can meet their needs and preferences for care,” she said.
“Sometimes, in my experience, patients don’t understand why it’s important to go to an ALS specialty center. In those cases, I’ve been able to make initial contact with those individuals through telehealth and be able to provide education, which, in turn, often results in them making the decision to come to the specialty center once they understand what resources we have to offer.”
Also commenting on the research, Ghazala Hayat, MD, also endorsed a mixed approach.
“Telehealth is a very good tool that we should use interspersed with in-person visits,” said Hayat, director of the multidisciplinary ALS clinic at St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, and professor of neurology and director of neuromuscular and clinical neurophysiology.
“I think the first few visits should always be in person — you need to connect with the patient,” she said. “But then, once they feel comfortable, remote monitoring is a very good idea, especially later in the disease process, when it becomes really difficult for the family to bring the patient in.”
The authors reported no relevant disclosures. Howard reported no disclosures. Hayat reported serving as a speaker and in advisory roles for argenx, Alexion, and MTPA. The study was funded by Amylyx Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , results of a retrospective study showed.
The findings, along with those of another study by the same group, suggest that remote monitoring of patients with ALS is a feasible option for both maximizing quality of life and minimizing cost and disruption.
Both studies were presented at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024.
“What we’re trying to do is look for screening tools that we can use when these patients are in the community to see if a specific score transition is associated with a high probability of needing an intervention that would require bringing them in to do gold standard tests,” said study investigator Tefani Perera, MD, a neurology resident at the University of Calgary, in Alberta, Canada.
Optimizing Quality of Life
Tailoring in-person care is particularly important for patients with ALS who often face significant challenges with mobility, Perera said. However, most multidisciplinary ALS clinics schedule in-person follow-ups at regular intervals rather than “as needed.
“These are very long clinic days where they are assessed for one thing after another, even if they don’t need it. So maybe we can actually select for what they need to be assessed for at each specific visit? Life expectancy is not that long for these patients, so we want to make sure their quality of life is optimized.”
For the BiPAP study, the investigators used the Pooled Resource Open-Access ALS Clinical Trials database to identify patients with ALS with two or more respiratory assessments on the Revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R).
The ALSFRS-R is a 12-item questionnaire, which includes three respiratory sub-scores for respiratory insufficiency (RiS), dyspnea (DyS) and orthopnea (OS).
Patients with a baseline RiS sub-score of 4 — meaning no need for BiPAP — were included in the study (n = 3838), with the primary outcome being a drop in RiS sub-score indicating the need for BiPAP.
The median time from baseline to transition to BiPAP was 563 days, with 3.4% of patients reaching this outcome by 3 months.
Results showed the probability of needing BiPAP was significantly associated with baseline DyS and OS scores (P < .0001). Among patients with baseline DyS scores of 3, 2, and 1, the percentages of patients needing BiPAP within 3 months were 5.5%, 8.7%, and 20.1%, respectively. In addition, in patients with baseline OS scores of 3, 2, and 1, the percentages of patients needing BiPAP within 3 months were 9.1%, 12.7%, and 24.2%, respectively.
Regardless of the baseline score, any drop in either of these sub-scores over the study period was also associated with an increased likelihood of requiring BiPAP within 3 months, with a DyS transition from 3 to 2 and an OS transition from 4 to 3 being most notable.
These scores could be used to trigger gold standard assessments for BiPAP, such as nocturnal oximetry, overnight polysomnography, daytime hypercapnia, and forced and slow vital capacities, Perera said. On the other hand, the scores could also help patients and clinicians avoid unnecessary visits.
“When the dyspnea and orthopnea scores are high, they might not need this intervention until 2 years later, so do we even need to bring them in to do these tests or see a respirologist when they don’t actually need it?”
The group’s second study was a systematic review of 26 papers on ALS remote assessment devices and methods, including accelerometers (15.4%), telenursing protocols (3.8%), speech collection apps (26.9%), questionnaires (15.4%), multifactorial sensors (15.4%), and respiratory function monitors (19.2%). Domains of symptoms monitored included speech (12 studies), motor (11 studies), respiratory (11 studies), cardiac (three studies), and bulbar, psychiatric, and autonomic (one study each).
The researchers characterized various remote tools as having potential and concluded that a multidomain approach to symptom monitoring is achievable. They also noted that the majority of studies assessing adherence and patient feedback indicated a favorable response to patient monitoring.
“I work in a resource-rich center, where we have these huge multidisciplinary clinics, and we have the capacity to bring patients back every 3 months, but outside these big centers, in resource-limited settings, to have an ability to track remotely and bring patients in when they really need it is very important,” said Perera.
Best of Both Worlds
Ileana Howard, MD, physiatrist and professor of rehabilitation medicine at the University of Washington and medical co-director of the ALS Center of Excellence at VA Puget Sound in Seattle, agreed.
“One of the biggest challenges in ALS care today is ensuring equitable access to high quality care and supports, and telehealth was adopted by the VA early on as a means of doing that,” she said. “Remote monitoring technology is a really key development to help improve that type of care.”
However, she added that it should not be a question of one type of care versus the other. “The ideal care is when we have access to providing both face-to-face and virtual care for our patients so that we can meet their needs and preferences for care,” she said.
“Sometimes, in my experience, patients don’t understand why it’s important to go to an ALS specialty center. In those cases, I’ve been able to make initial contact with those individuals through telehealth and be able to provide education, which, in turn, often results in them making the decision to come to the specialty center once they understand what resources we have to offer.”
Also commenting on the research, Ghazala Hayat, MD, also endorsed a mixed approach.
“Telehealth is a very good tool that we should use interspersed with in-person visits,” said Hayat, director of the multidisciplinary ALS clinic at St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri, and professor of neurology and director of neuromuscular and clinical neurophysiology.
“I think the first few visits should always be in person — you need to connect with the patient,” she said. “But then, once they feel comfortable, remote monitoring is a very good idea, especially later in the disease process, when it becomes really difficult for the family to bring the patient in.”
The authors reported no relevant disclosures. Howard reported no disclosures. Hayat reported serving as a speaker and in advisory roles for argenx, Alexion, and MTPA. The study was funded by Amylyx Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AANEM 2024
Industry Payments to Peer Reviewers Scrutinized at Four Major Medical Journals
TOPLINE:
More than half of the US peer reviewers for four major medical journals received industry payments between 2020-2022, new research shows. Altogether they received more than $64 million in general, non-research payments, with a median payment per physician of $7614. Research payments — including money paid directly to physicians as well as funds related to research for which a physician was registered as a principal investigator — exceeded $1 billion.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers identified peer reviewers in 2022 for The BMJ, JAMA, The Lancet, and The New England Journal of Medicine using each journal’s list of reviewers for that year. They included 1962 US-based physicians in their analysis.
- General and research payments made to the peer reviewers between 2020-2022 were extracted from the Open Payments database.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly 59% of the peer reviewers received industry payments between 2020-2022.
- Payments included $34.31 million in consulting fees and $11.8 million for speaking compensation unrelated to continuing medical education programs.
- Male reviewers received a significantly higher median total payment than did female reviewers ($38,959 vs $19,586). General payments were higher for men as well ($8663 vs $4183).
- For comparison, the median general payment to all physicians in 2018 was $216, the researchers noted.
IN PRACTICE:
“Additional research and transparency regarding industry payments in the peer review process are needed,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Christopher J. D. Wallis, MD, PhD, with the division of urology at the University of Toronto, Canada, was the corresponding author for the study. The article was published online October 10 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
Whether the financial ties were relevant to any of the papers that the peer reviewers critiqued is not known. Some reviewers might have received additional payments from insurance and technology companies that were not captured in this study. The findings might not apply to other journals, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
Wallis disclosed personal fees from Janssen Oncology, Nanostics, Precision Point Specialty, Sesen Bio, AbbVie, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, EMD Serono, Knight Therapeutics, Merck, Science and Medicine Canada, TerSera, and Tolmar. He and some coauthors also disclosed support and grants from foundations and government institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
More than half of the US peer reviewers for four major medical journals received industry payments between 2020-2022, new research shows. Altogether they received more than $64 million in general, non-research payments, with a median payment per physician of $7614. Research payments — including money paid directly to physicians as well as funds related to research for which a physician was registered as a principal investigator — exceeded $1 billion.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers identified peer reviewers in 2022 for The BMJ, JAMA, The Lancet, and The New England Journal of Medicine using each journal’s list of reviewers for that year. They included 1962 US-based physicians in their analysis.
- General and research payments made to the peer reviewers between 2020-2022 were extracted from the Open Payments database.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly 59% of the peer reviewers received industry payments between 2020-2022.
- Payments included $34.31 million in consulting fees and $11.8 million for speaking compensation unrelated to continuing medical education programs.
- Male reviewers received a significantly higher median total payment than did female reviewers ($38,959 vs $19,586). General payments were higher for men as well ($8663 vs $4183).
- For comparison, the median general payment to all physicians in 2018 was $216, the researchers noted.
IN PRACTICE:
“Additional research and transparency regarding industry payments in the peer review process are needed,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Christopher J. D. Wallis, MD, PhD, with the division of urology at the University of Toronto, Canada, was the corresponding author for the study. The article was published online October 10 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
Whether the financial ties were relevant to any of the papers that the peer reviewers critiqued is not known. Some reviewers might have received additional payments from insurance and technology companies that were not captured in this study. The findings might not apply to other journals, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
Wallis disclosed personal fees from Janssen Oncology, Nanostics, Precision Point Specialty, Sesen Bio, AbbVie, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, EMD Serono, Knight Therapeutics, Merck, Science and Medicine Canada, TerSera, and Tolmar. He and some coauthors also disclosed support and grants from foundations and government institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
More than half of the US peer reviewers for four major medical journals received industry payments between 2020-2022, new research shows. Altogether they received more than $64 million in general, non-research payments, with a median payment per physician of $7614. Research payments — including money paid directly to physicians as well as funds related to research for which a physician was registered as a principal investigator — exceeded $1 billion.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers identified peer reviewers in 2022 for The BMJ, JAMA, The Lancet, and The New England Journal of Medicine using each journal’s list of reviewers for that year. They included 1962 US-based physicians in their analysis.
- General and research payments made to the peer reviewers between 2020-2022 were extracted from the Open Payments database.
TAKEAWAY:
- Nearly 59% of the peer reviewers received industry payments between 2020-2022.
- Payments included $34.31 million in consulting fees and $11.8 million for speaking compensation unrelated to continuing medical education programs.
- Male reviewers received a significantly higher median total payment than did female reviewers ($38,959 vs $19,586). General payments were higher for men as well ($8663 vs $4183).
- For comparison, the median general payment to all physicians in 2018 was $216, the researchers noted.
IN PRACTICE:
“Additional research and transparency regarding industry payments in the peer review process are needed,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Christopher J. D. Wallis, MD, PhD, with the division of urology at the University of Toronto, Canada, was the corresponding author for the study. The article was published online October 10 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
Whether the financial ties were relevant to any of the papers that the peer reviewers critiqued is not known. Some reviewers might have received additional payments from insurance and technology companies that were not captured in this study. The findings might not apply to other journals, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
Wallis disclosed personal fees from Janssen Oncology, Nanostics, Precision Point Specialty, Sesen Bio, AbbVie, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, EMD Serono, Knight Therapeutics, Merck, Science and Medicine Canada, TerSera, and Tolmar. He and some coauthors also disclosed support and grants from foundations and government institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Rising Tide of Atrial Fibrillation: Is Primary Care Ready?
The incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) is on the rise, and recent joint guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) stress the role of primary care clinicians in prevention and management.
One in three White and one in five Black Americans will develop AF in their lifetime, and the projected number of individuals diagnosed with AF in the United States is expected to double by 2050.
Cardiologists who spoke to Medscape Medical News said primary care clinicians can help control AF by focusing on diabetes and hypertension, along with lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and alcohol intake.
“It’s not just a rhythm abnormality, but a complex disease that needs to be addressed in a multidisciplinary, holistic way,” said Jose Joglar, MD, a professor in the Department of Internal Medicine at the UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas and lead author of the guidelines.
Joglar said primary care clinicians can play an important role in counseling on lifestyle changes for patients with the most common etiologies such as poorly controlled hypertension, diabetes, and obesity.
The Primary Care Physicians ABCs: Risk Factors and Comorbidities
“As a primary care physician or as a cardiologist, I often think that if I do these things, I’m going to help with a lot of conditions, not just atrial fibrillation,” said Manesh Patel, MD, chief of the Divisions of Cardiology and Clinical Pharmacology at the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
Lifestyle choices such as sleeping habits can play a big part in AF outcomes. Although the guidelines specifically address obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor, he said more data are needed on the effect of sleep hygiene — getting 8 hours of sleep a night — a goal few people attain.
“What we do know is people that can routinely try to go to sleep and sleep with some regularity seem to have less cardiovascular risk,” Patel said.
Although existing data are limited, literature reviews have found evidence that sleep disruptions, sleep duration, circadian rhythm, and insomnia are associated with heart disease, independent of obstructive sleep apnea.
Use of alcohol should also be discussed with patients, as many are unaware of the effects of the drug on cardiovascular disease, said Joglar, who is also the program director of the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship program at the UT Southwestern Medical Center.
“Doctors can inform the patient that this is not a judgment call but simple medical fact,” he said.
Joglar also said many physicians need to become educated on a common misconception.
“Every time a patient develops palpitations or atrial fibrillation, the first thing every patient tells me is, I quit drinking coffee,” Joglar said.
However, as the guidelines point out, the link between caffeine and AF is uncertain at best.
Preventing AF
A newer class of drugs may help clinicians manage comorbidities that contribute to AF, such as hypertension, sleep apnea, and obesity, said John Mandrola, MD, an electrophysiologist in Louisville, Kentucky, who hosts This Week in Cardiology on Medscape.
Although originally approved for treatment of diabetes, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors are also approved for management of heart failure. Mandrola started prescribing these drugs 2 years ago for patients, given the links of both conditions with AF.
“I think the next frontier for us in cardiology and AF management will be the GLP-1 agonists,” Mandrola said. He hasn’t started prescribing these drugs for his patients yet but said they will likely play a role in the management of patients with AF with the common constellation of comorbidities such as obesity, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
“The GLP-1 agonists have a really good chance of competing with AF ablation for rhythm control over the long term,” he said.
Decisions, Decisions: Stroke Risk Scoring Systems
The risk for stroke varies widely among patients with AF, so primary care clinicians can pick among several scoring systems to estimate the risk for stroke and guide the decision on whether to initiate anticoagulation therapy.
The ACC/AHA guidelines do not state a preference for a particular instrument. The Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age, Diabetes mellitus, Stroke, Vascular disease, Sex (CHA2DS2-VASc) score is the most widely used and validated instrument, Joglar said. He usually recommends anticoagulation if the CHA2DS2-VASc score is > 2, dependent on individual patient factors.
“If you have a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 1, and you only had one episode of AF for a few hours a year ago, then your risk of stroke is not as high as somebody who has a score of 1 but has more frequent or persistent AF,” Joglar said.
None of the systems is perfect at predicting risk for stroke, so clinicians should discuss options with patients.
“The real message is, are you talking about the risk of stroke and systemic embolism to your patient, so that the patient understands that risk?” he said.
Patel also said measuring creatine clearance can be analogous to using an instrument like CHA2DS2-VASc.
“I often think about renal disease as a very good risk marker and something that does elevate your risk,” he said.
Which Anticoagulant?
Although the ACC/AHA guidelines still recommend warfarin for patients with AF with mechanical heart valves or moderate to severe rheumatic fever, direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are the first-line therapy for all other patients with AF.
In terms of which DOACs to use, the differences are subtle, according to Patel.
“I don’t know that they’re that different from each other,” he said. “All of the new drugs are better than warfarin by far.”
Patel pointed out that dabigatran at 150 mg is the only DOAC shown to reduce the incidence of ischemic stroke. For patients with renal dysfunction, he has a slight preference for a 15-mg dose of rivaroxaban.
Mandrola said he mainly prescribes apixaban and rivaroxaban, the latter of which requires only once a day dosing.
“We stopped using dabigatran because 10% of people get gastrointestinal upset,” he said.
Although studies suggest aspirin is less effective than either warfarin or DOACs for the prevention of stroke, Joglar said he still sees patients who come to him after being prescribed low-dose aspirin from primary care clinicians.
“We made it very clear that it should not be recommended just for mitigating stroke risk in atrial fibrillation,” Joglar said. “You could use it if the patient has another indication, such as a prior heart attack.”
Does My Patient Have to Be in Normal Sinus Rhythm?
The new guidelines present evidence maintaining sinus rhythm should be favored over controlling heart rate for managing AF.
“We’ve focused on rhythm control as a better strategy, especially catheter ablation, which seems to be particularly effective in parallel to lifestyle interventions and management of comorbidities,” Joglar said. Rhythm control is of particular benefit for patients with AF triggered by heart failure. Control of rhythm in these patients has been shown to improve multiple outcomes such as ejection fraction, symptoms, and survival.
Patel said as a patient’s symptoms increase, the more likely a clinician will be able to control sinus rhythm. Some patients do not notice their arrhythmia, but others feel dizzy or have chest pain.
“The less symptomatic the patient is, the more likely they’re going to tolerate it, especially if they’re older, and it’s hard to get them into sinus rhythm,” Patel said.
When to Refer for Catheter Ablation?
The new guidelines upgraded the recommendation for catheter ablation to class I (strong recommendation) for patients with symptomatic AF in whom anti-arrhythmic therapy is unsuccessful, not tolerated, or contraindicated; patients with symptomatic paroxysmal AF (typically younger patients with few comorbidities); and patients with symptomatic or clinically significant atrial flutter. The previous iteration recommended trying drug therapy first.
Multiple randomized clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of catheter ablation.
“In somebody who is younger, with a healthy heart, the 1-year success rate of the procedure might be about 70%,” Joglar said. While 70% of patients receiving a catheter have no AF episodes in the following year, Joglar said 20%-25% of those who do have recurrences will experience fewer or shorter episodes.
Conversations about rate vs rhythm control and whether to pursue catheter ablation often come down to preference, Patel said. He would tend to intervene earlier using ablation in patients with heart failure or those experiencing symptoms of AF who cannot be controlled with a heart rate < 100 beats/min.
But he said he prefers using medication for rate control in many of his patients who are older, have chronic AF, and do not have heart failure.
Mandrola takes a more conservative approach, reserving catheter ablation for patients in whom risk factor management and anti-arrhythmic drugs have not been successful.
“In my hospital, it’s done for patients who have symptomatic AF that’s really impacting their quality of life,” he said. But for those with fewer symptoms, his advice is to provide education, reassurance, and time because AF can resolve on its own.
What About Data From Implantables and Wearables?
The guidelines provide an algorithm for when to treat non-symptomatic atrial high-rate episodes detected by a cardiovascular implantable electronic device such as a pacemaker or defibrillator. Episodes less than 5 minutes can be ignored, while treatment could be considered for those with episodes lasting 5 minutes up to 24 hours with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 3, or lasting longer than 24 hours with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 2.
But whether anticoagulation improves outcomes is unclear.
“That is a $64,000 question,” Mandrola said. “I would bet every day I get a notification in the electronic health record that says Mr. Smith had 2 hours of AFib 2 weeks ago.”
He also hears from patients who report their Apple Watch has detected an episode of AF.
Mandrola cited evidence from two recent studies of patients who had an atrial high-rate episode longer than 6 minutes detected by implantable devices. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial randomized patients over 65 years with one or more risk factors for stroke to receive a DOAC or placebo, while the ARTESIA trial used similar inclusion criteria to assign patients to receive either DOAC or aspirin. Both studies reported modest reductions in stroke that were outweighed by a higher incidence of major bleeding in the group receiving anticoagulation.
Shared decision-making should play a role in deciding how aggressively to treat episodes of AF detected by implantable or wearable devices.
He said some patients fear having a stroke, while others are adamantly opposed to taking an anticoagulant.
For patients who present with a documented episode of AF but who otherwise have no symptoms, Patel said clinicians should consider risk for stroke and frequency and duration of episodes.
“One way clinicians should be thinking about it is, the more risk factors they have, the lower burden of AF I need to treat,” Patel said. Even for patients who are having only short episodes of AF, he has a low threshold for recommending an anticoagulation drug if the patient’s CHA2DS2-VASc score is high.
Patel reported research grants from Bayer, Novartis, Idorsia, NHLBI, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals and served as a consultant on the advisory boards of Bayer, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Esperion Therapeutics.
Joglar and Mandrola had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) is on the rise, and recent joint guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) stress the role of primary care clinicians in prevention and management.
One in three White and one in five Black Americans will develop AF in their lifetime, and the projected number of individuals diagnosed with AF in the United States is expected to double by 2050.
Cardiologists who spoke to Medscape Medical News said primary care clinicians can help control AF by focusing on diabetes and hypertension, along with lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and alcohol intake.
“It’s not just a rhythm abnormality, but a complex disease that needs to be addressed in a multidisciplinary, holistic way,” said Jose Joglar, MD, a professor in the Department of Internal Medicine at the UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas and lead author of the guidelines.
Joglar said primary care clinicians can play an important role in counseling on lifestyle changes for patients with the most common etiologies such as poorly controlled hypertension, diabetes, and obesity.
The Primary Care Physicians ABCs: Risk Factors and Comorbidities
“As a primary care physician or as a cardiologist, I often think that if I do these things, I’m going to help with a lot of conditions, not just atrial fibrillation,” said Manesh Patel, MD, chief of the Divisions of Cardiology and Clinical Pharmacology at the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
Lifestyle choices such as sleeping habits can play a big part in AF outcomes. Although the guidelines specifically address obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor, he said more data are needed on the effect of sleep hygiene — getting 8 hours of sleep a night — a goal few people attain.
“What we do know is people that can routinely try to go to sleep and sleep with some regularity seem to have less cardiovascular risk,” Patel said.
Although existing data are limited, literature reviews have found evidence that sleep disruptions, sleep duration, circadian rhythm, and insomnia are associated with heart disease, independent of obstructive sleep apnea.
Use of alcohol should also be discussed with patients, as many are unaware of the effects of the drug on cardiovascular disease, said Joglar, who is also the program director of the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship program at the UT Southwestern Medical Center.
“Doctors can inform the patient that this is not a judgment call but simple medical fact,” he said.
Joglar also said many physicians need to become educated on a common misconception.
“Every time a patient develops palpitations or atrial fibrillation, the first thing every patient tells me is, I quit drinking coffee,” Joglar said.
However, as the guidelines point out, the link between caffeine and AF is uncertain at best.
Preventing AF
A newer class of drugs may help clinicians manage comorbidities that contribute to AF, such as hypertension, sleep apnea, and obesity, said John Mandrola, MD, an electrophysiologist in Louisville, Kentucky, who hosts This Week in Cardiology on Medscape.
Although originally approved for treatment of diabetes, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors are also approved for management of heart failure. Mandrola started prescribing these drugs 2 years ago for patients, given the links of both conditions with AF.
“I think the next frontier for us in cardiology and AF management will be the GLP-1 agonists,” Mandrola said. He hasn’t started prescribing these drugs for his patients yet but said they will likely play a role in the management of patients with AF with the common constellation of comorbidities such as obesity, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
“The GLP-1 agonists have a really good chance of competing with AF ablation for rhythm control over the long term,” he said.
Decisions, Decisions: Stroke Risk Scoring Systems
The risk for stroke varies widely among patients with AF, so primary care clinicians can pick among several scoring systems to estimate the risk for stroke and guide the decision on whether to initiate anticoagulation therapy.
The ACC/AHA guidelines do not state a preference for a particular instrument. The Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age, Diabetes mellitus, Stroke, Vascular disease, Sex (CHA2DS2-VASc) score is the most widely used and validated instrument, Joglar said. He usually recommends anticoagulation if the CHA2DS2-VASc score is > 2, dependent on individual patient factors.
“If you have a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 1, and you only had one episode of AF for a few hours a year ago, then your risk of stroke is not as high as somebody who has a score of 1 but has more frequent or persistent AF,” Joglar said.
None of the systems is perfect at predicting risk for stroke, so clinicians should discuss options with patients.
“The real message is, are you talking about the risk of stroke and systemic embolism to your patient, so that the patient understands that risk?” he said.
Patel also said measuring creatine clearance can be analogous to using an instrument like CHA2DS2-VASc.
“I often think about renal disease as a very good risk marker and something that does elevate your risk,” he said.
Which Anticoagulant?
Although the ACC/AHA guidelines still recommend warfarin for patients with AF with mechanical heart valves or moderate to severe rheumatic fever, direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are the first-line therapy for all other patients with AF.
In terms of which DOACs to use, the differences are subtle, according to Patel.
“I don’t know that they’re that different from each other,” he said. “All of the new drugs are better than warfarin by far.”
Patel pointed out that dabigatran at 150 mg is the only DOAC shown to reduce the incidence of ischemic stroke. For patients with renal dysfunction, he has a slight preference for a 15-mg dose of rivaroxaban.
Mandrola said he mainly prescribes apixaban and rivaroxaban, the latter of which requires only once a day dosing.
“We stopped using dabigatran because 10% of people get gastrointestinal upset,” he said.
Although studies suggest aspirin is less effective than either warfarin or DOACs for the prevention of stroke, Joglar said he still sees patients who come to him after being prescribed low-dose aspirin from primary care clinicians.
“We made it very clear that it should not be recommended just for mitigating stroke risk in atrial fibrillation,” Joglar said. “You could use it if the patient has another indication, such as a prior heart attack.”
Does My Patient Have to Be in Normal Sinus Rhythm?
The new guidelines present evidence maintaining sinus rhythm should be favored over controlling heart rate for managing AF.
“We’ve focused on rhythm control as a better strategy, especially catheter ablation, which seems to be particularly effective in parallel to lifestyle interventions and management of comorbidities,” Joglar said. Rhythm control is of particular benefit for patients with AF triggered by heart failure. Control of rhythm in these patients has been shown to improve multiple outcomes such as ejection fraction, symptoms, and survival.
Patel said as a patient’s symptoms increase, the more likely a clinician will be able to control sinus rhythm. Some patients do not notice their arrhythmia, but others feel dizzy or have chest pain.
“The less symptomatic the patient is, the more likely they’re going to tolerate it, especially if they’re older, and it’s hard to get them into sinus rhythm,” Patel said.
When to Refer for Catheter Ablation?
The new guidelines upgraded the recommendation for catheter ablation to class I (strong recommendation) for patients with symptomatic AF in whom anti-arrhythmic therapy is unsuccessful, not tolerated, or contraindicated; patients with symptomatic paroxysmal AF (typically younger patients with few comorbidities); and patients with symptomatic or clinically significant atrial flutter. The previous iteration recommended trying drug therapy first.
Multiple randomized clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of catheter ablation.
“In somebody who is younger, with a healthy heart, the 1-year success rate of the procedure might be about 70%,” Joglar said. While 70% of patients receiving a catheter have no AF episodes in the following year, Joglar said 20%-25% of those who do have recurrences will experience fewer or shorter episodes.
Conversations about rate vs rhythm control and whether to pursue catheter ablation often come down to preference, Patel said. He would tend to intervene earlier using ablation in patients with heart failure or those experiencing symptoms of AF who cannot be controlled with a heart rate < 100 beats/min.
But he said he prefers using medication for rate control in many of his patients who are older, have chronic AF, and do not have heart failure.
Mandrola takes a more conservative approach, reserving catheter ablation for patients in whom risk factor management and anti-arrhythmic drugs have not been successful.
“In my hospital, it’s done for patients who have symptomatic AF that’s really impacting their quality of life,” he said. But for those with fewer symptoms, his advice is to provide education, reassurance, and time because AF can resolve on its own.
What About Data From Implantables and Wearables?
The guidelines provide an algorithm for when to treat non-symptomatic atrial high-rate episodes detected by a cardiovascular implantable electronic device such as a pacemaker or defibrillator. Episodes less than 5 minutes can be ignored, while treatment could be considered for those with episodes lasting 5 minutes up to 24 hours with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 3, or lasting longer than 24 hours with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 2.
But whether anticoagulation improves outcomes is unclear.
“That is a $64,000 question,” Mandrola said. “I would bet every day I get a notification in the electronic health record that says Mr. Smith had 2 hours of AFib 2 weeks ago.”
He also hears from patients who report their Apple Watch has detected an episode of AF.
Mandrola cited evidence from two recent studies of patients who had an atrial high-rate episode longer than 6 minutes detected by implantable devices. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial randomized patients over 65 years with one or more risk factors for stroke to receive a DOAC or placebo, while the ARTESIA trial used similar inclusion criteria to assign patients to receive either DOAC or aspirin. Both studies reported modest reductions in stroke that were outweighed by a higher incidence of major bleeding in the group receiving anticoagulation.
Shared decision-making should play a role in deciding how aggressively to treat episodes of AF detected by implantable or wearable devices.
He said some patients fear having a stroke, while others are adamantly opposed to taking an anticoagulant.
For patients who present with a documented episode of AF but who otherwise have no symptoms, Patel said clinicians should consider risk for stroke and frequency and duration of episodes.
“One way clinicians should be thinking about it is, the more risk factors they have, the lower burden of AF I need to treat,” Patel said. Even for patients who are having only short episodes of AF, he has a low threshold for recommending an anticoagulation drug if the patient’s CHA2DS2-VASc score is high.
Patel reported research grants from Bayer, Novartis, Idorsia, NHLBI, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals and served as a consultant on the advisory boards of Bayer, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Esperion Therapeutics.
Joglar and Mandrola had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) is on the rise, and recent joint guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) stress the role of primary care clinicians in prevention and management.
One in three White and one in five Black Americans will develop AF in their lifetime, and the projected number of individuals diagnosed with AF in the United States is expected to double by 2050.
Cardiologists who spoke to Medscape Medical News said primary care clinicians can help control AF by focusing on diabetes and hypertension, along with lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and alcohol intake.
“It’s not just a rhythm abnormality, but a complex disease that needs to be addressed in a multidisciplinary, holistic way,” said Jose Joglar, MD, a professor in the Department of Internal Medicine at the UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas and lead author of the guidelines.
Joglar said primary care clinicians can play an important role in counseling on lifestyle changes for patients with the most common etiologies such as poorly controlled hypertension, diabetes, and obesity.
The Primary Care Physicians ABCs: Risk Factors and Comorbidities
“As a primary care physician or as a cardiologist, I often think that if I do these things, I’m going to help with a lot of conditions, not just atrial fibrillation,” said Manesh Patel, MD, chief of the Divisions of Cardiology and Clinical Pharmacology at the Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
Lifestyle choices such as sleeping habits can play a big part in AF outcomes. Although the guidelines specifically address obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor, he said more data are needed on the effect of sleep hygiene — getting 8 hours of sleep a night — a goal few people attain.
“What we do know is people that can routinely try to go to sleep and sleep with some regularity seem to have less cardiovascular risk,” Patel said.
Although existing data are limited, literature reviews have found evidence that sleep disruptions, sleep duration, circadian rhythm, and insomnia are associated with heart disease, independent of obstructive sleep apnea.
Use of alcohol should also be discussed with patients, as many are unaware of the effects of the drug on cardiovascular disease, said Joglar, who is also the program director of the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship program at the UT Southwestern Medical Center.
“Doctors can inform the patient that this is not a judgment call but simple medical fact,” he said.
Joglar also said many physicians need to become educated on a common misconception.
“Every time a patient develops palpitations or atrial fibrillation, the first thing every patient tells me is, I quit drinking coffee,” Joglar said.
However, as the guidelines point out, the link between caffeine and AF is uncertain at best.
Preventing AF
A newer class of drugs may help clinicians manage comorbidities that contribute to AF, such as hypertension, sleep apnea, and obesity, said John Mandrola, MD, an electrophysiologist in Louisville, Kentucky, who hosts This Week in Cardiology on Medscape.
Although originally approved for treatment of diabetes, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors are also approved for management of heart failure. Mandrola started prescribing these drugs 2 years ago for patients, given the links of both conditions with AF.
“I think the next frontier for us in cardiology and AF management will be the GLP-1 agonists,” Mandrola said. He hasn’t started prescribing these drugs for his patients yet but said they will likely play a role in the management of patients with AF with the common constellation of comorbidities such as obesity, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
“The GLP-1 agonists have a really good chance of competing with AF ablation for rhythm control over the long term,” he said.
Decisions, Decisions: Stroke Risk Scoring Systems
The risk for stroke varies widely among patients with AF, so primary care clinicians can pick among several scoring systems to estimate the risk for stroke and guide the decision on whether to initiate anticoagulation therapy.
The ACC/AHA guidelines do not state a preference for a particular instrument. The Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age, Diabetes mellitus, Stroke, Vascular disease, Sex (CHA2DS2-VASc) score is the most widely used and validated instrument, Joglar said. He usually recommends anticoagulation if the CHA2DS2-VASc score is > 2, dependent on individual patient factors.
“If you have a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 1, and you only had one episode of AF for a few hours a year ago, then your risk of stroke is not as high as somebody who has a score of 1 but has more frequent or persistent AF,” Joglar said.
None of the systems is perfect at predicting risk for stroke, so clinicians should discuss options with patients.
“The real message is, are you talking about the risk of stroke and systemic embolism to your patient, so that the patient understands that risk?” he said.
Patel also said measuring creatine clearance can be analogous to using an instrument like CHA2DS2-VASc.
“I often think about renal disease as a very good risk marker and something that does elevate your risk,” he said.
Which Anticoagulant?
Although the ACC/AHA guidelines still recommend warfarin for patients with AF with mechanical heart valves or moderate to severe rheumatic fever, direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are the first-line therapy for all other patients with AF.
In terms of which DOACs to use, the differences are subtle, according to Patel.
“I don’t know that they’re that different from each other,” he said. “All of the new drugs are better than warfarin by far.”
Patel pointed out that dabigatran at 150 mg is the only DOAC shown to reduce the incidence of ischemic stroke. For patients with renal dysfunction, he has a slight preference for a 15-mg dose of rivaroxaban.
Mandrola said he mainly prescribes apixaban and rivaroxaban, the latter of which requires only once a day dosing.
“We stopped using dabigatran because 10% of people get gastrointestinal upset,” he said.
Although studies suggest aspirin is less effective than either warfarin or DOACs for the prevention of stroke, Joglar said he still sees patients who come to him after being prescribed low-dose aspirin from primary care clinicians.
“We made it very clear that it should not be recommended just for mitigating stroke risk in atrial fibrillation,” Joglar said. “You could use it if the patient has another indication, such as a prior heart attack.”
Does My Patient Have to Be in Normal Sinus Rhythm?
The new guidelines present evidence maintaining sinus rhythm should be favored over controlling heart rate for managing AF.
“We’ve focused on rhythm control as a better strategy, especially catheter ablation, which seems to be particularly effective in parallel to lifestyle interventions and management of comorbidities,” Joglar said. Rhythm control is of particular benefit for patients with AF triggered by heart failure. Control of rhythm in these patients has been shown to improve multiple outcomes such as ejection fraction, symptoms, and survival.
Patel said as a patient’s symptoms increase, the more likely a clinician will be able to control sinus rhythm. Some patients do not notice their arrhythmia, but others feel dizzy or have chest pain.
“The less symptomatic the patient is, the more likely they’re going to tolerate it, especially if they’re older, and it’s hard to get them into sinus rhythm,” Patel said.
When to Refer for Catheter Ablation?
The new guidelines upgraded the recommendation for catheter ablation to class I (strong recommendation) for patients with symptomatic AF in whom anti-arrhythmic therapy is unsuccessful, not tolerated, or contraindicated; patients with symptomatic paroxysmal AF (typically younger patients with few comorbidities); and patients with symptomatic or clinically significant atrial flutter. The previous iteration recommended trying drug therapy first.
Multiple randomized clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of catheter ablation.
“In somebody who is younger, with a healthy heart, the 1-year success rate of the procedure might be about 70%,” Joglar said. While 70% of patients receiving a catheter have no AF episodes in the following year, Joglar said 20%-25% of those who do have recurrences will experience fewer or shorter episodes.
Conversations about rate vs rhythm control and whether to pursue catheter ablation often come down to preference, Patel said. He would tend to intervene earlier using ablation in patients with heart failure or those experiencing symptoms of AF who cannot be controlled with a heart rate < 100 beats/min.
But he said he prefers using medication for rate control in many of his patients who are older, have chronic AF, and do not have heart failure.
Mandrola takes a more conservative approach, reserving catheter ablation for patients in whom risk factor management and anti-arrhythmic drugs have not been successful.
“In my hospital, it’s done for patients who have symptomatic AF that’s really impacting their quality of life,” he said. But for those with fewer symptoms, his advice is to provide education, reassurance, and time because AF can resolve on its own.
What About Data From Implantables and Wearables?
The guidelines provide an algorithm for when to treat non-symptomatic atrial high-rate episodes detected by a cardiovascular implantable electronic device such as a pacemaker or defibrillator. Episodes less than 5 minutes can be ignored, while treatment could be considered for those with episodes lasting 5 minutes up to 24 hours with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 3, or lasting longer than 24 hours with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 2.
But whether anticoagulation improves outcomes is unclear.
“That is a $64,000 question,” Mandrola said. “I would bet every day I get a notification in the electronic health record that says Mr. Smith had 2 hours of AFib 2 weeks ago.”
He also hears from patients who report their Apple Watch has detected an episode of AF.
Mandrola cited evidence from two recent studies of patients who had an atrial high-rate episode longer than 6 minutes detected by implantable devices. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial randomized patients over 65 years with one or more risk factors for stroke to receive a DOAC or placebo, while the ARTESIA trial used similar inclusion criteria to assign patients to receive either DOAC or aspirin. Both studies reported modest reductions in stroke that were outweighed by a higher incidence of major bleeding in the group receiving anticoagulation.
Shared decision-making should play a role in deciding how aggressively to treat episodes of AF detected by implantable or wearable devices.
He said some patients fear having a stroke, while others are adamantly opposed to taking an anticoagulant.
For patients who present with a documented episode of AF but who otherwise have no symptoms, Patel said clinicians should consider risk for stroke and frequency and duration of episodes.
“One way clinicians should be thinking about it is, the more risk factors they have, the lower burden of AF I need to treat,” Patel said. Even for patients who are having only short episodes of AF, he has a low threshold for recommending an anticoagulation drug if the patient’s CHA2DS2-VASc score is high.
Patel reported research grants from Bayer, Novartis, Idorsia, NHLBI, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals and served as a consultant on the advisory boards of Bayer, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Esperion Therapeutics.
Joglar and Mandrola had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Game We Play Every Day
Words do have power. Names have power. Words are events, they do things, change things. They transform both speaker and hearer ... They feed understanding or emotion back and forth and amplify it. — Ursula K. Le Guin
Every medical student should have a class in linguistics. I’m just unsure what it might replace. Maybe physiology? (When was the last time you used Fick’s or Fourier’s Laws anyway?). Even if we don’t supplant any core curriculum, it’s worth noting that we spend more time in our daily work calculating how to communicate things than calculating cardiac outputs. That we can convey so much so consistently and without specific training is a marvel. Making the diagnosis or a plan is often the easy part.
Linguistics is a broad field. At its essence, it studies how we communicate. It’s fascinating how we use tone, word choice, gestures, syntax, and grammar to explain, reassure, instruct or implore patients. Medical appointments are sometimes high stakes and occur within a huge variety of circumstances. In a single day of clinic, I had a patient with dementia, and one pursuing a PhD in P-Chem. I had English speakers, second language English speakers, and a Vietnamese patient who knew no English. In just one day, I explained things to toddlers and adults, a Black woman from Oklahoma and a Jewish woman from New York. For a brief few minutes, each of them was my partner in a game of medical charades. For each one, I had to figure out how to get them to know what I’m thinking.
I learned of this game of charades concept from a podcast featuring Morten Christiansen, professor of psychology at Cornell University, and professor in Cognitive Science of Language, at Aarhus University, Denmark. The idea is that language can be thought of as a game where speakers constantly improvise based on the topic, each one’s expertise, and the shared understanding. I found this intriguing. In his explanation, grammar and definitions are less important than the mutual understanding of what is being communicated. It helps explain the wide variations of speech even among those speaking the same language. It also flips the idea that brains are designed for language, a concept proposed by linguistic greats such as Noam Chomsky and Steven Pinker. Rather, what we call language is just the best solution our brains could create to convey information.
I thought about how each of us instinctively varies the complexity of sentences and tone of voice based on the ability of each patient to understand. Gestures, storytelling and analogies are linguistic tools we use without thinking about them. We’ve a unique communications conundrum in that we often need patients to understand a complex idea, but only have minutes to get them there. We don’t want them to panic. We also don’t want them to be so dispassionate as to not act. To speed things up, we often use a technique known as chunking, short phrases that capture an idea in one bite. For example, “soak and smear” to get atopic patients to moisturize or “scrape and burn” to describe a curettage and electrodesiccation of a basal cell carcinoma or “a stick and a burn” before injecting them (I never liked that one). These are pithy, efficient. But they don’t always work.
One afternoon I had a 93-year-old woman with glossodynia. She had dementia and her 96-year-old husband was helping. When I explained how she’d “swish and spit” her magic mouthwash, he looked perplexed. Is she swishing a wand or something? I shook my head, “No” and gestured with my hands palms down, waving back and forth. It is just a mouthwash. She should rinse, then spit it out. I lost that round.
Then a 64-year-old woman whom I had to advise that the pink bump on her arm was a cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor. Do I call it a Merkel cell carcinoma? Do I say, “You know, like the one Jimmy Buffett had?” (Nope, not a good use of storytelling). She wanted to know how she got it. Sun exposure, we think. Or, perhaps a virus. Just how does one explain a virus called MCPyV that is ubiquitous but somehow caused cancer just for you? How do you convey, “This is serious, but you might not die like Jimmy Buffett?” I had to use all my language skills to get this right.
Then there is the Henderson-Hasselbalch problem of linguistics: communicating through a translator. When doing so, I’m cognizant of choosing short, simple sentences. Subject, verb, object. First this, then that. This mitigates what’s lost in translation and reduces waiting for translations (especially when your patient is storytelling in paragraphs). But try doing this with an emotionally wrought condition like alopecia. Finding the fewest words to convey that your FSH and estrogen levels are irrelevant to your telogen effluvium to a Vietnamese speaker is tricky. “Yes, I see your primary care physician ordered these tests. No, the numbers do not matter.” Did that translate as they are normal? Or that they don’t matter because she is 54? Or that they don’t matter to me because I didn’t order them?
When you find yourself exhausted at the day’s end, perhaps you’ll better appreciate how it was not only the graduate level medicine you did today; you’ve practically got a PhD in linguistics as well. You just didn’t realize it.
Dr. Benabio is chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Words do have power. Names have power. Words are events, they do things, change things. They transform both speaker and hearer ... They feed understanding or emotion back and forth and amplify it. — Ursula K. Le Guin
Every medical student should have a class in linguistics. I’m just unsure what it might replace. Maybe physiology? (When was the last time you used Fick’s or Fourier’s Laws anyway?). Even if we don’t supplant any core curriculum, it’s worth noting that we spend more time in our daily work calculating how to communicate things than calculating cardiac outputs. That we can convey so much so consistently and without specific training is a marvel. Making the diagnosis or a plan is often the easy part.
Linguistics is a broad field. At its essence, it studies how we communicate. It’s fascinating how we use tone, word choice, gestures, syntax, and grammar to explain, reassure, instruct or implore patients. Medical appointments are sometimes high stakes and occur within a huge variety of circumstances. In a single day of clinic, I had a patient with dementia, and one pursuing a PhD in P-Chem. I had English speakers, second language English speakers, and a Vietnamese patient who knew no English. In just one day, I explained things to toddlers and adults, a Black woman from Oklahoma and a Jewish woman from New York. For a brief few minutes, each of them was my partner in a game of medical charades. For each one, I had to figure out how to get them to know what I’m thinking.
I learned of this game of charades concept from a podcast featuring Morten Christiansen, professor of psychology at Cornell University, and professor in Cognitive Science of Language, at Aarhus University, Denmark. The idea is that language can be thought of as a game where speakers constantly improvise based on the topic, each one’s expertise, and the shared understanding. I found this intriguing. In his explanation, grammar and definitions are less important than the mutual understanding of what is being communicated. It helps explain the wide variations of speech even among those speaking the same language. It also flips the idea that brains are designed for language, a concept proposed by linguistic greats such as Noam Chomsky and Steven Pinker. Rather, what we call language is just the best solution our brains could create to convey information.
I thought about how each of us instinctively varies the complexity of sentences and tone of voice based on the ability of each patient to understand. Gestures, storytelling and analogies are linguistic tools we use without thinking about them. We’ve a unique communications conundrum in that we often need patients to understand a complex idea, but only have minutes to get them there. We don’t want them to panic. We also don’t want them to be so dispassionate as to not act. To speed things up, we often use a technique known as chunking, short phrases that capture an idea in one bite. For example, “soak and smear” to get atopic patients to moisturize or “scrape and burn” to describe a curettage and electrodesiccation of a basal cell carcinoma or “a stick and a burn” before injecting them (I never liked that one). These are pithy, efficient. But they don’t always work.
One afternoon I had a 93-year-old woman with glossodynia. She had dementia and her 96-year-old husband was helping. When I explained how she’d “swish and spit” her magic mouthwash, he looked perplexed. Is she swishing a wand or something? I shook my head, “No” and gestured with my hands palms down, waving back and forth. It is just a mouthwash. She should rinse, then spit it out. I lost that round.
Then a 64-year-old woman whom I had to advise that the pink bump on her arm was a cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor. Do I call it a Merkel cell carcinoma? Do I say, “You know, like the one Jimmy Buffett had?” (Nope, not a good use of storytelling). She wanted to know how she got it. Sun exposure, we think. Or, perhaps a virus. Just how does one explain a virus called MCPyV that is ubiquitous but somehow caused cancer just for you? How do you convey, “This is serious, but you might not die like Jimmy Buffett?” I had to use all my language skills to get this right.
Then there is the Henderson-Hasselbalch problem of linguistics: communicating through a translator. When doing so, I’m cognizant of choosing short, simple sentences. Subject, verb, object. First this, then that. This mitigates what’s lost in translation and reduces waiting for translations (especially when your patient is storytelling in paragraphs). But try doing this with an emotionally wrought condition like alopecia. Finding the fewest words to convey that your FSH and estrogen levels are irrelevant to your telogen effluvium to a Vietnamese speaker is tricky. “Yes, I see your primary care physician ordered these tests. No, the numbers do not matter.” Did that translate as they are normal? Or that they don’t matter because she is 54? Or that they don’t matter to me because I didn’t order them?
When you find yourself exhausted at the day’s end, perhaps you’ll better appreciate how it was not only the graduate level medicine you did today; you’ve practically got a PhD in linguistics as well. You just didn’t realize it.
Dr. Benabio is chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Words do have power. Names have power. Words are events, they do things, change things. They transform both speaker and hearer ... They feed understanding or emotion back and forth and amplify it. — Ursula K. Le Guin
Every medical student should have a class in linguistics. I’m just unsure what it might replace. Maybe physiology? (When was the last time you used Fick’s or Fourier’s Laws anyway?). Even if we don’t supplant any core curriculum, it’s worth noting that we spend more time in our daily work calculating how to communicate things than calculating cardiac outputs. That we can convey so much so consistently and without specific training is a marvel. Making the diagnosis or a plan is often the easy part.
Linguistics is a broad field. At its essence, it studies how we communicate. It’s fascinating how we use tone, word choice, gestures, syntax, and grammar to explain, reassure, instruct or implore patients. Medical appointments are sometimes high stakes and occur within a huge variety of circumstances. In a single day of clinic, I had a patient with dementia, and one pursuing a PhD in P-Chem. I had English speakers, second language English speakers, and a Vietnamese patient who knew no English. In just one day, I explained things to toddlers and adults, a Black woman from Oklahoma and a Jewish woman from New York. For a brief few minutes, each of them was my partner in a game of medical charades. For each one, I had to figure out how to get them to know what I’m thinking.
I learned of this game of charades concept from a podcast featuring Morten Christiansen, professor of psychology at Cornell University, and professor in Cognitive Science of Language, at Aarhus University, Denmark. The idea is that language can be thought of as a game where speakers constantly improvise based on the topic, each one’s expertise, and the shared understanding. I found this intriguing. In his explanation, grammar and definitions are less important than the mutual understanding of what is being communicated. It helps explain the wide variations of speech even among those speaking the same language. It also flips the idea that brains are designed for language, a concept proposed by linguistic greats such as Noam Chomsky and Steven Pinker. Rather, what we call language is just the best solution our brains could create to convey information.
I thought about how each of us instinctively varies the complexity of sentences and tone of voice based on the ability of each patient to understand. Gestures, storytelling and analogies are linguistic tools we use without thinking about them. We’ve a unique communications conundrum in that we often need patients to understand a complex idea, but only have minutes to get them there. We don’t want them to panic. We also don’t want them to be so dispassionate as to not act. To speed things up, we often use a technique known as chunking, short phrases that capture an idea in one bite. For example, “soak and smear” to get atopic patients to moisturize or “scrape and burn” to describe a curettage and electrodesiccation of a basal cell carcinoma or “a stick and a burn” before injecting them (I never liked that one). These are pithy, efficient. But they don’t always work.
One afternoon I had a 93-year-old woman with glossodynia. She had dementia and her 96-year-old husband was helping. When I explained how she’d “swish and spit” her magic mouthwash, he looked perplexed. Is she swishing a wand or something? I shook my head, “No” and gestured with my hands palms down, waving back and forth. It is just a mouthwash. She should rinse, then spit it out. I lost that round.
Then a 64-year-old woman whom I had to advise that the pink bump on her arm was a cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor. Do I call it a Merkel cell carcinoma? Do I say, “You know, like the one Jimmy Buffett had?” (Nope, not a good use of storytelling). She wanted to know how she got it. Sun exposure, we think. Or, perhaps a virus. Just how does one explain a virus called MCPyV that is ubiquitous but somehow caused cancer just for you? How do you convey, “This is serious, but you might not die like Jimmy Buffett?” I had to use all my language skills to get this right.
Then there is the Henderson-Hasselbalch problem of linguistics: communicating through a translator. When doing so, I’m cognizant of choosing short, simple sentences. Subject, verb, object. First this, then that. This mitigates what’s lost in translation and reduces waiting for translations (especially when your patient is storytelling in paragraphs). But try doing this with an emotionally wrought condition like alopecia. Finding the fewest words to convey that your FSH and estrogen levels are irrelevant to your telogen effluvium to a Vietnamese speaker is tricky. “Yes, I see your primary care physician ordered these tests. No, the numbers do not matter.” Did that translate as they are normal? Or that they don’t matter because she is 54? Or that they don’t matter to me because I didn’t order them?
When you find yourself exhausted at the day’s end, perhaps you’ll better appreciate how it was not only the graduate level medicine you did today; you’ve practically got a PhD in linguistics as well. You just didn’t realize it.
Dr. Benabio is chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.