User login
Not so fast food
As long as I can remember, children have been notoriously wasteful when dining in school cafeterias. Even those children who bring their own food often return home in the afternoon with their lunches half eaten. Not surprisingly, the food tossed out is often the healthier portion of the meal. Schools have tried a variety of strategies to curb this wastage, including using volunteer student monitors to police and encourage ecologically based recycling.
The authors of a recent study published on JAMA Network Open observed that when elementary and middle-school students were allowed a 20-minute seated lunch period they consumed more food and there was significantly less waste of fruits and vegetable compared with when the students’ lunch period was limited to 10 minutes. Interestingly, there was no difference in the beverage and entrée consumption when the lunch period was doubled.
The authors postulate that younger children may not have acquired the dexterity to feed themselves optimally in the shorter lunch period. I’m not sure I buy that argument. It may be simply that the children ate and drank their favorites first and needed a bit more time to allow their little guts to move things along. But, regardless of the explanation, the investigators’ observations deserve further study.
When I was in high school our lunch period was a full hour, which allowed me to make the half mile walk to home and back to eat a home-prepared meal. The noon hour was when school clubs and committees met and there was a full schedule of diversions to fill out the hour. I don’t recall the seated portion of the lunch period having any time restriction.
By the time my own children were in middle school, lunch periods lasted no longer than 20 minutes. I was not surprised to learn from this recent study that in some schools the seated lunch period has been shortened to 10 minutes. In some cases the truncated lunch periods are a response to space and time limitations. I fear that occasionally, educators and administrators have found it so difficult to keep young children who are accustomed to watching television while they eat engaged that the periods have been shortened to minimize the chaos.
Here in Maine, the governor has just announced plans to offer free breakfast and lunch to every student in response to a federal initiative. If we intend to make nutrition a cornerstone of the educational process this study from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign suggests that we must do more than simply provide the food at no cost. We must somehow carve out more time in the day for the children to eat a healthy diet.
But, where is this time going to come from? Many school systems have already cannibalized physical education to the point that most children are not getting a healthy amount of exercise. It is unfortunate that we have come to expect public school systems to solve all of our societal ills and compensate for less-than-healthy home environments. But that is the reality. If we think nutrition and physical activity are important components of our children’s educations then we must make the time necessary to provide them.
Will this mean longer school days? And will those longer days cost money? You bet they will, but that may be the price we have to pay for healthier, better educated children.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
As long as I can remember, children have been notoriously wasteful when dining in school cafeterias. Even those children who bring their own food often return home in the afternoon with their lunches half eaten. Not surprisingly, the food tossed out is often the healthier portion of the meal. Schools have tried a variety of strategies to curb this wastage, including using volunteer student monitors to police and encourage ecologically based recycling.
The authors of a recent study published on JAMA Network Open observed that when elementary and middle-school students were allowed a 20-minute seated lunch period they consumed more food and there was significantly less waste of fruits and vegetable compared with when the students’ lunch period was limited to 10 minutes. Interestingly, there was no difference in the beverage and entrée consumption when the lunch period was doubled.
The authors postulate that younger children may not have acquired the dexterity to feed themselves optimally in the shorter lunch period. I’m not sure I buy that argument. It may be simply that the children ate and drank their favorites first and needed a bit more time to allow their little guts to move things along. But, regardless of the explanation, the investigators’ observations deserve further study.
When I was in high school our lunch period was a full hour, which allowed me to make the half mile walk to home and back to eat a home-prepared meal. The noon hour was when school clubs and committees met and there was a full schedule of diversions to fill out the hour. I don’t recall the seated portion of the lunch period having any time restriction.
By the time my own children were in middle school, lunch periods lasted no longer than 20 minutes. I was not surprised to learn from this recent study that in some schools the seated lunch period has been shortened to 10 minutes. In some cases the truncated lunch periods are a response to space and time limitations. I fear that occasionally, educators and administrators have found it so difficult to keep young children who are accustomed to watching television while they eat engaged that the periods have been shortened to minimize the chaos.
Here in Maine, the governor has just announced plans to offer free breakfast and lunch to every student in response to a federal initiative. If we intend to make nutrition a cornerstone of the educational process this study from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign suggests that we must do more than simply provide the food at no cost. We must somehow carve out more time in the day for the children to eat a healthy diet.
But, where is this time going to come from? Many school systems have already cannibalized physical education to the point that most children are not getting a healthy amount of exercise. It is unfortunate that we have come to expect public school systems to solve all of our societal ills and compensate for less-than-healthy home environments. But that is the reality. If we think nutrition and physical activity are important components of our children’s educations then we must make the time necessary to provide them.
Will this mean longer school days? And will those longer days cost money? You bet they will, but that may be the price we have to pay for healthier, better educated children.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
As long as I can remember, children have been notoriously wasteful when dining in school cafeterias. Even those children who bring their own food often return home in the afternoon with their lunches half eaten. Not surprisingly, the food tossed out is often the healthier portion of the meal. Schools have tried a variety of strategies to curb this wastage, including using volunteer student monitors to police and encourage ecologically based recycling.
The authors of a recent study published on JAMA Network Open observed that when elementary and middle-school students were allowed a 20-minute seated lunch period they consumed more food and there was significantly less waste of fruits and vegetable compared with when the students’ lunch period was limited to 10 minutes. Interestingly, there was no difference in the beverage and entrée consumption when the lunch period was doubled.
The authors postulate that younger children may not have acquired the dexterity to feed themselves optimally in the shorter lunch period. I’m not sure I buy that argument. It may be simply that the children ate and drank their favorites first and needed a bit more time to allow their little guts to move things along. But, regardless of the explanation, the investigators’ observations deserve further study.
When I was in high school our lunch period was a full hour, which allowed me to make the half mile walk to home and back to eat a home-prepared meal. The noon hour was when school clubs and committees met and there was a full schedule of diversions to fill out the hour. I don’t recall the seated portion of the lunch period having any time restriction.
By the time my own children were in middle school, lunch periods lasted no longer than 20 minutes. I was not surprised to learn from this recent study that in some schools the seated lunch period has been shortened to 10 minutes. In some cases the truncated lunch periods are a response to space and time limitations. I fear that occasionally, educators and administrators have found it so difficult to keep young children who are accustomed to watching television while they eat engaged that the periods have been shortened to minimize the chaos.
Here in Maine, the governor has just announced plans to offer free breakfast and lunch to every student in response to a federal initiative. If we intend to make nutrition a cornerstone of the educational process this study from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign suggests that we must do more than simply provide the food at no cost. We must somehow carve out more time in the day for the children to eat a healthy diet.
But, where is this time going to come from? Many school systems have already cannibalized physical education to the point that most children are not getting a healthy amount of exercise. It is unfortunate that we have come to expect public school systems to solve all of our societal ills and compensate for less-than-healthy home environments. But that is the reality. If we think nutrition and physical activity are important components of our children’s educations then we must make the time necessary to provide them.
Will this mean longer school days? And will those longer days cost money? You bet they will, but that may be the price we have to pay for healthier, better educated children.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Children and COVID: New cases soar to near-record level
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children jumped by nearly 50% in the United States, posting the highest count since hitting a pandemic high back in mid-January, a new report shows.
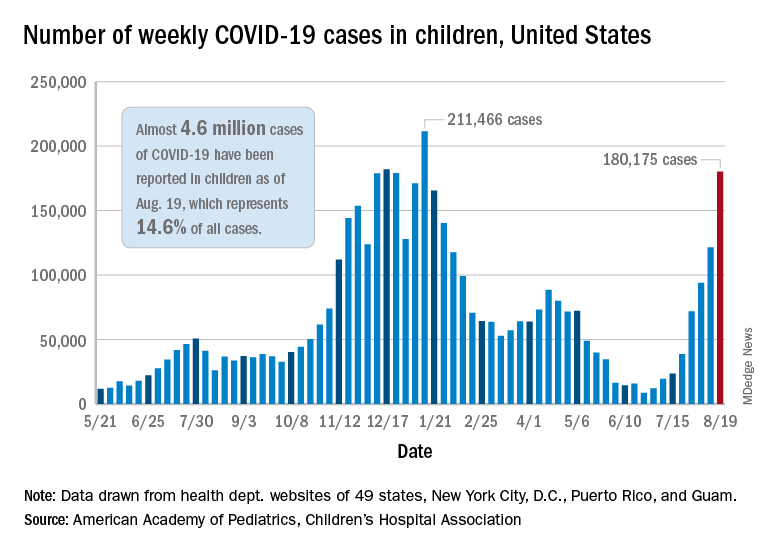
The latest weekly figure represents a 48% increase over the previous week and an increase of over 2,000% in the 8 weeks since the national count dropped to a low of 8,500 cases for the week of June 18-24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
Vaccinations, in the meantime, appear to be headed in the opposite direction. Vaccine initiations were down for the second consecutive week, falling by 18% among 12- to 15-year-olds and by 15% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, about 47% of children aged 12-15 and 56% of those aged 16-17 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Aug. 23, with 34% and 44%, respectively, reaching full vaccination. The total number of children with at least one dose is 11.6 million, including a relatively small number (about 200,000) of children under age 12 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
At the state level, vaccination is a source of considerable disparity. In Vermont, 73% of children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose by Aug. 18, and 63% were fully vaccinated. In Wyoming, however, just 25% of children had received at least one dose (17% are fully vaccinated), while Alabama has a lowest-in-the-nation full vaccination rate of 14%, based on a separate AAP analysis of CDC data.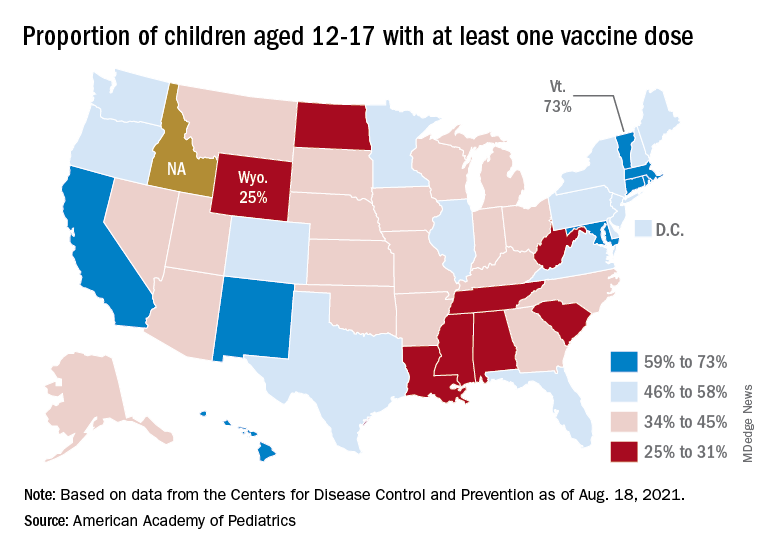
There are seven states in which over 60% of 12- to 17-year-olds have at least started the vaccine regimen and five states where less than 30% have received at least one dose, the AAP noted.
Back on the incidence side of the pandemic, Mississippi and Hawaii had the largest increases in new cases over the past 2 weeks, followed by Florida and West Virginia. Cumulative figures show that California has had the most cases overall in children (550,337), Vermont has the highest proportion of all cases in children (22.9%), and Rhode Island has the highest rate of cases per 100,000 (10,636), the AAP and CHA said in the joint report based on data from 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Add up all those jurisdictions, and it works out to 4.6 million children infected with SARS-CoV-2 as of Aug. 19, with children representing 14.6% of all cases since the start of the pandemic. There have been over 18,000 hospitalizations so far, which is just 2.3% of the total for all ages in the 23 states (and New York City) that are reporting such data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of COVID-related deaths in children is now 402 after the largest 1-week increase (24) since late May of 2020, when the AAP/CHA coverage began. Mortality data by age are available from 44 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children jumped by nearly 50% in the United States, posting the highest count since hitting a pandemic high back in mid-January, a new report shows.

The latest weekly figure represents a 48% increase over the previous week and an increase of over 2,000% in the 8 weeks since the national count dropped to a low of 8,500 cases for the week of June 18-24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
Vaccinations, in the meantime, appear to be headed in the opposite direction. Vaccine initiations were down for the second consecutive week, falling by 18% among 12- to 15-year-olds and by 15% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, about 47% of children aged 12-15 and 56% of those aged 16-17 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Aug. 23, with 34% and 44%, respectively, reaching full vaccination. The total number of children with at least one dose is 11.6 million, including a relatively small number (about 200,000) of children under age 12 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
At the state level, vaccination is a source of considerable disparity. In Vermont, 73% of children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose by Aug. 18, and 63% were fully vaccinated. In Wyoming, however, just 25% of children had received at least one dose (17% are fully vaccinated), while Alabama has a lowest-in-the-nation full vaccination rate of 14%, based on a separate AAP analysis of CDC data.
There are seven states in which over 60% of 12- to 17-year-olds have at least started the vaccine regimen and five states where less than 30% have received at least one dose, the AAP noted.
Back on the incidence side of the pandemic, Mississippi and Hawaii had the largest increases in new cases over the past 2 weeks, followed by Florida and West Virginia. Cumulative figures show that California has had the most cases overall in children (550,337), Vermont has the highest proportion of all cases in children (22.9%), and Rhode Island has the highest rate of cases per 100,000 (10,636), the AAP and CHA said in the joint report based on data from 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Add up all those jurisdictions, and it works out to 4.6 million children infected with SARS-CoV-2 as of Aug. 19, with children representing 14.6% of all cases since the start of the pandemic. There have been over 18,000 hospitalizations so far, which is just 2.3% of the total for all ages in the 23 states (and New York City) that are reporting such data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of COVID-related deaths in children is now 402 after the largest 1-week increase (24) since late May of 2020, when the AAP/CHA coverage began. Mortality data by age are available from 44 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children jumped by nearly 50% in the United States, posting the highest count since hitting a pandemic high back in mid-January, a new report shows.

The latest weekly figure represents a 48% increase over the previous week and an increase of over 2,000% in the 8 weeks since the national count dropped to a low of 8,500 cases for the week of June 18-24, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
Vaccinations, in the meantime, appear to be headed in the opposite direction. Vaccine initiations were down for the second consecutive week, falling by 18% among 12- to 15-year-olds and by 15% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, about 47% of children aged 12-15 and 56% of those aged 16-17 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Aug. 23, with 34% and 44%, respectively, reaching full vaccination. The total number of children with at least one dose is 11.6 million, including a relatively small number (about 200,000) of children under age 12 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
At the state level, vaccination is a source of considerable disparity. In Vermont, 73% of children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose by Aug. 18, and 63% were fully vaccinated. In Wyoming, however, just 25% of children had received at least one dose (17% are fully vaccinated), while Alabama has a lowest-in-the-nation full vaccination rate of 14%, based on a separate AAP analysis of CDC data.
There are seven states in which over 60% of 12- to 17-year-olds have at least started the vaccine regimen and five states where less than 30% have received at least one dose, the AAP noted.
Back on the incidence side of the pandemic, Mississippi and Hawaii had the largest increases in new cases over the past 2 weeks, followed by Florida and West Virginia. Cumulative figures show that California has had the most cases overall in children (550,337), Vermont has the highest proportion of all cases in children (22.9%), and Rhode Island has the highest rate of cases per 100,000 (10,636), the AAP and CHA said in the joint report based on data from 49 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Add up all those jurisdictions, and it works out to 4.6 million children infected with SARS-CoV-2 as of Aug. 19, with children representing 14.6% of all cases since the start of the pandemic. There have been over 18,000 hospitalizations so far, which is just 2.3% of the total for all ages in the 23 states (and New York City) that are reporting such data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of COVID-related deaths in children is now 402 after the largest 1-week increase (24) since late May of 2020, when the AAP/CHA coverage began. Mortality data by age are available from 44 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
U.S. kidney transplants grow in number and success
During 2016-2019, U.S. centers performed kidney transplants in nearly 77,000 patients, a jump of almost 25% compared with 4-year averages of about 62,000 patients throughout 2004-2015. That works out to about 15,000 more patients receiving donor kidneys, Sundaram Hariharan, MD, and associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine in a review of all U.S. renal transplantations performed during 1996-2019.
Coupled with the volume uptick during this 24-year period were new lows in graft losses and patient deaths. By 2018, mortality during the first year following transplantation occurred at about a 1% rate among patients who had received a kidney from a living donor, and at about a 3% rate when the organ came from a deceased donor, nearly half the rate of 2 decades earlier, in 1996. Rates of first-year graft loss during 2017 were also about half of what they had been in 1996, occurring in about 2% of patients who received a living donor organ and in about 6% of those who got a kidney from a deceased donor during 2017.
“Twenty years ago, kidney transplantation was the preferred option compared with dialysis, and even more so now,” summed up Dr. Hariharan, a senior transplant nephrologist and professor of medicine and surgery at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and first author of the report. Kidney transplantation survival at U.S. centers “improved steadily over the past 24 years, despite patient variables becoming worse,” he said in an interview.
Kidney recipients are older, more obese, and have more prevalent diabetes
During the period studied, kidney transplant recipients became on average older and more obese, and had a higher prevalence of diabetes; the age of organ donors grew as well. The prevalence of diabetes among patients who received a kidney from a deceased donor increased from 24% during 1996-1999 to 36% during 2016-2019, while diabetes prevalence among recipients of an organ from a living donor rose from 25% in 1996-1999 to 29% during 2016-2019.
The improved graft and patient survival numbers “are very encouraging trends,” said Michelle A. Josephson, MD, professor and medical director of kidney transplantation at the University of Chicago, who was not involved with the report. “We have been hearing for a number of years that short-term graft survival had improved, but I’m thrilled to learn that long-term survival has also improved.”
The report documented 10-year survival of graft recipients during 2008-2011 of 67%, up from 61% during 1996-1999, and a 10-year overall graft survival rate of 54% in the 2008-2011 cohort, an improvement from the 42% rate in patients who received their organs in 1996-1999, changes Dr. Hariharan characterized as “modest.”
These improvements in long-term graft and patient survival are “meaningful, and particularly notable that outcomes improved despite increased complexity of the transplant population,” said Krista L. Lentine, MD, PhD, professor and medical director of living donation at Saint Louis University. But “despite these improvements, long-term graft survival remains limited,” she cautioned, especially because of risks for substantial complications from chronic immunosuppressive treatment including infection, cancer, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia.
The analysis reported by Dr. Hariharan and his associates used data collected by the Scientific Registry of Transplant Patients, run under contract with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which has tracked all patients who have had kidney transplants at U.S. centers since the late 1980s, said Dr. Hariharan. The database included just over 362,000 total transplants during the 24-year period studied, with 36% of all transplants involving organs from living donors with the remaining patients receiving kidneys from deceased donors.
Living donations still stagnant; deceased-donor kidneys rise
The data showed that the rate of transplants from living donors was stagnant for 2 decades, with 22,525 patients transplanted during 2000-2003, and 23,746 transplanted during 2016-2019, with very similar rates during the intervening years. The recent spurt in transplants during 2016-2019 compared with the preceding decade depended almost entirely on kidneys from deceased donors. This rate jumped from the steady, slow rise it showed during 1996-2015, when deceased-donor transplants rose from about 30,000 during 1996-1999 to about 41,000 during 2012-2015, to a more dramatic increase of about 12,000 additional transplants during the most recent period, adding up to a total of more than 53,000 transplants from deceased donors during 2016-2019.
“I strongly recommend organs from living donors” when feasible, said Dr. Hariharan. “At some centers, a high proportion of transplants use living donors, but not at other centers,” he said.
It’s unknown why transplants using organs from deceased donors has shown this growth, but Dr. Hariharan suggested a multifactorial explanation. Those factors include growth in the number of patients with end-stage renal disease who require dialysis, increased numbers of patients listed for kidney transplant, new approaches that allow organs from older donors and those infected with pathogens such as hepatitis C virus or HIV, greater numbers of people and families agreeing to donate organs, and possibly the opioid crisis that may have led to increased organ donation. The number of U.S. centers performing kidney transplants rose from fewer than 200 about a quarter of a century ago to about 250 today, he added.
‘Immuno Bill’ guarantees Medicare coverage for immunosuppression
Dr. Hariharan voiced optimism that graft and patient survival rates will continue to improve going forward. One factor will likely be the passage in late 2020 of the “Immuno Bill” by the U.S. Congress, which among other things mandated ongoing coverage starting in 2023 for immunosuppressive drugs for all Medicare beneficiaries with a kidney transplant. Until then, Medicare provides coverage for only 36 months, a time limit that has resulted in nearly 400 kidney recipients annually losing coverage of their immunosuppression medications.
Dr. Hariharan and coauthors called the existing potential for discontinuation of immunosuppressive drug an “unnecessary impediment to long-term survival for which patients and society paid a heavy price.”
“Kidney transplantation, especially from living donors, offers patients with kidney failure the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life, with lower cost to the health care system,” Dr. Lentine said in an interview. Despite the many positive trends detailed in the report from Dr. Hariharan and coauthors, “the vast majority of the more than 700,000 people in the United States with kidney failure will not have an opportunity to receive a transplant due to limitations in organ supply.” And many patients who receive a kidney transplant eventually must resume dialysis because of “limited long-term graft survival resulting from allograft nephropathy, recurrent native disease, medication nonadherence, or other causes.” Plus many potentially transplantable organs go unused.
Dr. Lentine cited a position statement issued in July 2021 by the National Kidney Foundation that made several recommendations on how to improve access to kidney transplants and improve outcomes. “Expanding opportunities for safe living donation, eliminating racial disparities in living-donor access, improving wait-list access and transport readiness, maximizing use of deceased-donor organs, and extending graft longevity are critical priorities,” said Dr. Lentine, lead author on the statement.
“For many or even most patients with kidney failure transplantation is the optimal form of renal replacement. The better recent outcomes and evolving management strategies make transplantation an even more attractive option,” said Dr. Josephson. Improved outcomes among U.S. transplant patients also highlights the “importance of increasing access to kidney transplantation” for all people with kidney failure who could benefit from this treatment, she added.
Dr. Hariharan and Dr. Lentine had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Josephson has been a consultant to UCB and has an ownership interest in Seagen.
During 2016-2019, U.S. centers performed kidney transplants in nearly 77,000 patients, a jump of almost 25% compared with 4-year averages of about 62,000 patients throughout 2004-2015. That works out to about 15,000 more patients receiving donor kidneys, Sundaram Hariharan, MD, and associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine in a review of all U.S. renal transplantations performed during 1996-2019.
Coupled with the volume uptick during this 24-year period were new lows in graft losses and patient deaths. By 2018, mortality during the first year following transplantation occurred at about a 1% rate among patients who had received a kidney from a living donor, and at about a 3% rate when the organ came from a deceased donor, nearly half the rate of 2 decades earlier, in 1996. Rates of first-year graft loss during 2017 were also about half of what they had been in 1996, occurring in about 2% of patients who received a living donor organ and in about 6% of those who got a kidney from a deceased donor during 2017.
“Twenty years ago, kidney transplantation was the preferred option compared with dialysis, and even more so now,” summed up Dr. Hariharan, a senior transplant nephrologist and professor of medicine and surgery at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and first author of the report. Kidney transplantation survival at U.S. centers “improved steadily over the past 24 years, despite patient variables becoming worse,” he said in an interview.
Kidney recipients are older, more obese, and have more prevalent diabetes
During the period studied, kidney transplant recipients became on average older and more obese, and had a higher prevalence of diabetes; the age of organ donors grew as well. The prevalence of diabetes among patients who received a kidney from a deceased donor increased from 24% during 1996-1999 to 36% during 2016-2019, while diabetes prevalence among recipients of an organ from a living donor rose from 25% in 1996-1999 to 29% during 2016-2019.
The improved graft and patient survival numbers “are very encouraging trends,” said Michelle A. Josephson, MD, professor and medical director of kidney transplantation at the University of Chicago, who was not involved with the report. “We have been hearing for a number of years that short-term graft survival had improved, but I’m thrilled to learn that long-term survival has also improved.”
The report documented 10-year survival of graft recipients during 2008-2011 of 67%, up from 61% during 1996-1999, and a 10-year overall graft survival rate of 54% in the 2008-2011 cohort, an improvement from the 42% rate in patients who received their organs in 1996-1999, changes Dr. Hariharan characterized as “modest.”
These improvements in long-term graft and patient survival are “meaningful, and particularly notable that outcomes improved despite increased complexity of the transplant population,” said Krista L. Lentine, MD, PhD, professor and medical director of living donation at Saint Louis University. But “despite these improvements, long-term graft survival remains limited,” she cautioned, especially because of risks for substantial complications from chronic immunosuppressive treatment including infection, cancer, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia.
The analysis reported by Dr. Hariharan and his associates used data collected by the Scientific Registry of Transplant Patients, run under contract with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which has tracked all patients who have had kidney transplants at U.S. centers since the late 1980s, said Dr. Hariharan. The database included just over 362,000 total transplants during the 24-year period studied, with 36% of all transplants involving organs from living donors with the remaining patients receiving kidneys from deceased donors.
Living donations still stagnant; deceased-donor kidneys rise
The data showed that the rate of transplants from living donors was stagnant for 2 decades, with 22,525 patients transplanted during 2000-2003, and 23,746 transplanted during 2016-2019, with very similar rates during the intervening years. The recent spurt in transplants during 2016-2019 compared with the preceding decade depended almost entirely on kidneys from deceased donors. This rate jumped from the steady, slow rise it showed during 1996-2015, when deceased-donor transplants rose from about 30,000 during 1996-1999 to about 41,000 during 2012-2015, to a more dramatic increase of about 12,000 additional transplants during the most recent period, adding up to a total of more than 53,000 transplants from deceased donors during 2016-2019.
“I strongly recommend organs from living donors” when feasible, said Dr. Hariharan. “At some centers, a high proportion of transplants use living donors, but not at other centers,” he said.
It’s unknown why transplants using organs from deceased donors has shown this growth, but Dr. Hariharan suggested a multifactorial explanation. Those factors include growth in the number of patients with end-stage renal disease who require dialysis, increased numbers of patients listed for kidney transplant, new approaches that allow organs from older donors and those infected with pathogens such as hepatitis C virus or HIV, greater numbers of people and families agreeing to donate organs, and possibly the opioid crisis that may have led to increased organ donation. The number of U.S. centers performing kidney transplants rose from fewer than 200 about a quarter of a century ago to about 250 today, he added.
‘Immuno Bill’ guarantees Medicare coverage for immunosuppression
Dr. Hariharan voiced optimism that graft and patient survival rates will continue to improve going forward. One factor will likely be the passage in late 2020 of the “Immuno Bill” by the U.S. Congress, which among other things mandated ongoing coverage starting in 2023 for immunosuppressive drugs for all Medicare beneficiaries with a kidney transplant. Until then, Medicare provides coverage for only 36 months, a time limit that has resulted in nearly 400 kidney recipients annually losing coverage of their immunosuppression medications.
Dr. Hariharan and coauthors called the existing potential for discontinuation of immunosuppressive drug an “unnecessary impediment to long-term survival for which patients and society paid a heavy price.”
“Kidney transplantation, especially from living donors, offers patients with kidney failure the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life, with lower cost to the health care system,” Dr. Lentine said in an interview. Despite the many positive trends detailed in the report from Dr. Hariharan and coauthors, “the vast majority of the more than 700,000 people in the United States with kidney failure will not have an opportunity to receive a transplant due to limitations in organ supply.” And many patients who receive a kidney transplant eventually must resume dialysis because of “limited long-term graft survival resulting from allograft nephropathy, recurrent native disease, medication nonadherence, or other causes.” Plus many potentially transplantable organs go unused.
Dr. Lentine cited a position statement issued in July 2021 by the National Kidney Foundation that made several recommendations on how to improve access to kidney transplants and improve outcomes. “Expanding opportunities for safe living donation, eliminating racial disparities in living-donor access, improving wait-list access and transport readiness, maximizing use of deceased-donor organs, and extending graft longevity are critical priorities,” said Dr. Lentine, lead author on the statement.
“For many or even most patients with kidney failure transplantation is the optimal form of renal replacement. The better recent outcomes and evolving management strategies make transplantation an even more attractive option,” said Dr. Josephson. Improved outcomes among U.S. transplant patients also highlights the “importance of increasing access to kidney transplantation” for all people with kidney failure who could benefit from this treatment, she added.
Dr. Hariharan and Dr. Lentine had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Josephson has been a consultant to UCB and has an ownership interest in Seagen.
During 2016-2019, U.S. centers performed kidney transplants in nearly 77,000 patients, a jump of almost 25% compared with 4-year averages of about 62,000 patients throughout 2004-2015. That works out to about 15,000 more patients receiving donor kidneys, Sundaram Hariharan, MD, and associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine in a review of all U.S. renal transplantations performed during 1996-2019.
Coupled with the volume uptick during this 24-year period were new lows in graft losses and patient deaths. By 2018, mortality during the first year following transplantation occurred at about a 1% rate among patients who had received a kidney from a living donor, and at about a 3% rate when the organ came from a deceased donor, nearly half the rate of 2 decades earlier, in 1996. Rates of first-year graft loss during 2017 were also about half of what they had been in 1996, occurring in about 2% of patients who received a living donor organ and in about 6% of those who got a kidney from a deceased donor during 2017.
“Twenty years ago, kidney transplantation was the preferred option compared with dialysis, and even more so now,” summed up Dr. Hariharan, a senior transplant nephrologist and professor of medicine and surgery at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and first author of the report. Kidney transplantation survival at U.S. centers “improved steadily over the past 24 years, despite patient variables becoming worse,” he said in an interview.
Kidney recipients are older, more obese, and have more prevalent diabetes
During the period studied, kidney transplant recipients became on average older and more obese, and had a higher prevalence of diabetes; the age of organ donors grew as well. The prevalence of diabetes among patients who received a kidney from a deceased donor increased from 24% during 1996-1999 to 36% during 2016-2019, while diabetes prevalence among recipients of an organ from a living donor rose from 25% in 1996-1999 to 29% during 2016-2019.
The improved graft and patient survival numbers “are very encouraging trends,” said Michelle A. Josephson, MD, professor and medical director of kidney transplantation at the University of Chicago, who was not involved with the report. “We have been hearing for a number of years that short-term graft survival had improved, but I’m thrilled to learn that long-term survival has also improved.”
The report documented 10-year survival of graft recipients during 2008-2011 of 67%, up from 61% during 1996-1999, and a 10-year overall graft survival rate of 54% in the 2008-2011 cohort, an improvement from the 42% rate in patients who received their organs in 1996-1999, changes Dr. Hariharan characterized as “modest.”
These improvements in long-term graft and patient survival are “meaningful, and particularly notable that outcomes improved despite increased complexity of the transplant population,” said Krista L. Lentine, MD, PhD, professor and medical director of living donation at Saint Louis University. But “despite these improvements, long-term graft survival remains limited,” she cautioned, especially because of risks for substantial complications from chronic immunosuppressive treatment including infection, cancer, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia.
The analysis reported by Dr. Hariharan and his associates used data collected by the Scientific Registry of Transplant Patients, run under contract with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which has tracked all patients who have had kidney transplants at U.S. centers since the late 1980s, said Dr. Hariharan. The database included just over 362,000 total transplants during the 24-year period studied, with 36% of all transplants involving organs from living donors with the remaining patients receiving kidneys from deceased donors.
Living donations still stagnant; deceased-donor kidneys rise
The data showed that the rate of transplants from living donors was stagnant for 2 decades, with 22,525 patients transplanted during 2000-2003, and 23,746 transplanted during 2016-2019, with very similar rates during the intervening years. The recent spurt in transplants during 2016-2019 compared with the preceding decade depended almost entirely on kidneys from deceased donors. This rate jumped from the steady, slow rise it showed during 1996-2015, when deceased-donor transplants rose from about 30,000 during 1996-1999 to about 41,000 during 2012-2015, to a more dramatic increase of about 12,000 additional transplants during the most recent period, adding up to a total of more than 53,000 transplants from deceased donors during 2016-2019.
“I strongly recommend organs from living donors” when feasible, said Dr. Hariharan. “At some centers, a high proportion of transplants use living donors, but not at other centers,” he said.
It’s unknown why transplants using organs from deceased donors has shown this growth, but Dr. Hariharan suggested a multifactorial explanation. Those factors include growth in the number of patients with end-stage renal disease who require dialysis, increased numbers of patients listed for kidney transplant, new approaches that allow organs from older donors and those infected with pathogens such as hepatitis C virus or HIV, greater numbers of people and families agreeing to donate organs, and possibly the opioid crisis that may have led to increased organ donation. The number of U.S. centers performing kidney transplants rose from fewer than 200 about a quarter of a century ago to about 250 today, he added.
‘Immuno Bill’ guarantees Medicare coverage for immunosuppression
Dr. Hariharan voiced optimism that graft and patient survival rates will continue to improve going forward. One factor will likely be the passage in late 2020 of the “Immuno Bill” by the U.S. Congress, which among other things mandated ongoing coverage starting in 2023 for immunosuppressive drugs for all Medicare beneficiaries with a kidney transplant. Until then, Medicare provides coverage for only 36 months, a time limit that has resulted in nearly 400 kidney recipients annually losing coverage of their immunosuppression medications.
Dr. Hariharan and coauthors called the existing potential for discontinuation of immunosuppressive drug an “unnecessary impediment to long-term survival for which patients and society paid a heavy price.”
“Kidney transplantation, especially from living donors, offers patients with kidney failure the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life, with lower cost to the health care system,” Dr. Lentine said in an interview. Despite the many positive trends detailed in the report from Dr. Hariharan and coauthors, “the vast majority of the more than 700,000 people in the United States with kidney failure will not have an opportunity to receive a transplant due to limitations in organ supply.” And many patients who receive a kidney transplant eventually must resume dialysis because of “limited long-term graft survival resulting from allograft nephropathy, recurrent native disease, medication nonadherence, or other causes.” Plus many potentially transplantable organs go unused.
Dr. Lentine cited a position statement issued in July 2021 by the National Kidney Foundation that made several recommendations on how to improve access to kidney transplants and improve outcomes. “Expanding opportunities for safe living donation, eliminating racial disparities in living-donor access, improving wait-list access and transport readiness, maximizing use of deceased-donor organs, and extending graft longevity are critical priorities,” said Dr. Lentine, lead author on the statement.
“For many or even most patients with kidney failure transplantation is the optimal form of renal replacement. The better recent outcomes and evolving management strategies make transplantation an even more attractive option,” said Dr. Josephson. Improved outcomes among U.S. transplant patients also highlights the “importance of increasing access to kidney transplantation” for all people with kidney failure who could benefit from this treatment, she added.
Dr. Hariharan and Dr. Lentine had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Josephson has been a consultant to UCB and has an ownership interest in Seagen.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Prevalence of youth-onset diabetes climbing, type 2 disease more so in racial/ethnic minorities
The prevalence of youth-onset diabetes in the United States rose significantly from 2001 to 2017, with rates of type 2 diabetes climbing disproportionately among racial/ethnic minorities, according to investigators.
In individuals aged 19 years or younger, prevalence rates of type 1 and type 2 diabetes increased 45.1% and 95.3%, respectively, reported lead author Jean M. Lawrence, ScD, MPH, MSSA, program director of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., and colleagues.
“Elucidating differences in diabetes prevalence trends by diabetes type and demographic characteristics is essential to describe the burden of disease and to estimate current and future resource needs,” Dr. Lawrence and colleagues wrote in JAMA.
The retrospective analysis was a part of the ongoing SEARCH study, which includes data from individuals in six areas across the United States: Colorado, California, Ohio, South Carolina, Washington state, and Arizona/New Mexico (Indian Health Services). In the present report, three prevalence years were evaluated: 2001, 2009, and 2017. For each year, approximately 3.5 million youths were included. Findings were reported in terms of diabetes type, race/ethnicity, age at diagnosis, and sex.
Absolute prevalence of type 1 diabetes per 1,000 youths increased from 1.48 in 2001, to 1.93 in 2009, and finally 2.15 in 2017. Across the 16-year period, this represents an absolute increase of 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.70), and a relative increase of 45.1% (95% CI, 40.0%-50.4%). In absolute terms, prevalence increased most among non-Hispanic White (0.93 per 1,000) and non-Hispanic Black (0.89 per 1,000) youths.
While type 2 diabetes was comparatively less common than type 1 diabetes, absolute prevalence per 1,000 youths increased to a greater degree, rising from 0.34 in 2001 to 0.46 in 2009 and to 0.67 in 2017. This amounts to relative increase across the period of 95.3% (95% CI, 77.0%-115.4%). Absolute increases were disproportionate among racial/ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Hispanic youths, who had absolute increases per 1,000 youths of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.74-0.97) and 0.57 (95% CI, 0.51-0.64), respectively, compared with 0.05 (95% CI, 0.03-0.07) for White youths.
“Increases [among Black and Hispanic youths] were not linear,” the investigators noted. “Hispanic youths had a significantly greater increase in the first interval compared with the second interval, while Black youths had no significant increase in the first interval and a significant increase in the second interval.”
Dr. Lawrence and colleagues offered several possible factors driving these trends in type 2 diabetes.
“Changes in anthropometric risk factors appear to play a significant role,” they wrote, noting that “Black and Mexican American teenagers experienced the greatest increase in prevalence of obesity/severe obesity from 1999 to 2018, which may contribute to race and ethnicity differences. Other contributing factors may include increases in exposure to maternal obesity and diabetes (gestational and type 2 diabetes) and exposure to environmental chemicals.”
According to Megan Kelsey, MD, associate professor of pediatric endocrinology, director of lifestyle medicine endocrinology, and medical director of the bariatric surgery center at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, the increased rates of type 2 diabetes reported by the study are alarming, yet they pale in comparison with what’s been happening since the pandemic began.
“Individual institutions have reported anywhere between a 50% – which is basically what we’re seeing at our hospital – to a 300% increase in new diagnoses [of type 2 diabetes] in a single-year time period,” Dr. Kelsey said in an interview. “So what is reported [in the present study] doesn’t even get at what’s been going on over the past year and a half.”
Dr. Kelsey offered some speculative drivers of this recent surge in cases, including stress, weight gain caused by sedentary behavior and more access to food, and the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 may infect pancreatic islet beta cells, thereby interfering with insulin production.
Type 2 diabetes is particularly concerning among young people, Dr. Kelsey noted, as it is more challenging to manage than adult-onset disease.
Young patients “also develop complications much sooner than you’d expect,” she added. “So we really need to understand why these rates are increasing, how we can identify kids at risk, and how we can better prevent it, so we aren’t stuck with a disease that’s really difficult to treat.”
To this end, the NIH recently opened applications for investigators to participate in a prospective longitudinal study of youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Young people at risk of diabetes will be followed through puberty, a period of increased risk, according to Dr. Kelsey.
“The goal will be to take kids who don’t yet have [type 2] diabetes, but are at risk, and try to better understand, as some of them progress to developing diabetes, what is going on,” Dr. Kelsey said. “What are other factors that we can use to better predict who’s going to develop diabetes? And can we use the information from this [upcoming] study to understand how to better prevent it? Because nothing that has been tried so far has worked.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NIDDK, and others. The investigators and Dr. Kelsey reported no conflicts of interest.
The prevalence of youth-onset diabetes in the United States rose significantly from 2001 to 2017, with rates of type 2 diabetes climbing disproportionately among racial/ethnic minorities, according to investigators.
In individuals aged 19 years or younger, prevalence rates of type 1 and type 2 diabetes increased 45.1% and 95.3%, respectively, reported lead author Jean M. Lawrence, ScD, MPH, MSSA, program director of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., and colleagues.
“Elucidating differences in diabetes prevalence trends by diabetes type and demographic characteristics is essential to describe the burden of disease and to estimate current and future resource needs,” Dr. Lawrence and colleagues wrote in JAMA.
The retrospective analysis was a part of the ongoing SEARCH study, which includes data from individuals in six areas across the United States: Colorado, California, Ohio, South Carolina, Washington state, and Arizona/New Mexico (Indian Health Services). In the present report, three prevalence years were evaluated: 2001, 2009, and 2017. For each year, approximately 3.5 million youths were included. Findings were reported in terms of diabetes type, race/ethnicity, age at diagnosis, and sex.
Absolute prevalence of type 1 diabetes per 1,000 youths increased from 1.48 in 2001, to 1.93 in 2009, and finally 2.15 in 2017. Across the 16-year period, this represents an absolute increase of 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.70), and a relative increase of 45.1% (95% CI, 40.0%-50.4%). In absolute terms, prevalence increased most among non-Hispanic White (0.93 per 1,000) and non-Hispanic Black (0.89 per 1,000) youths.
While type 2 diabetes was comparatively less common than type 1 diabetes, absolute prevalence per 1,000 youths increased to a greater degree, rising from 0.34 in 2001 to 0.46 in 2009 and to 0.67 in 2017. This amounts to relative increase across the period of 95.3% (95% CI, 77.0%-115.4%). Absolute increases were disproportionate among racial/ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Hispanic youths, who had absolute increases per 1,000 youths of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.74-0.97) and 0.57 (95% CI, 0.51-0.64), respectively, compared with 0.05 (95% CI, 0.03-0.07) for White youths.
“Increases [among Black and Hispanic youths] were not linear,” the investigators noted. “Hispanic youths had a significantly greater increase in the first interval compared with the second interval, while Black youths had no significant increase in the first interval and a significant increase in the second interval.”
Dr. Lawrence and colleagues offered several possible factors driving these trends in type 2 diabetes.
“Changes in anthropometric risk factors appear to play a significant role,” they wrote, noting that “Black and Mexican American teenagers experienced the greatest increase in prevalence of obesity/severe obesity from 1999 to 2018, which may contribute to race and ethnicity differences. Other contributing factors may include increases in exposure to maternal obesity and diabetes (gestational and type 2 diabetes) and exposure to environmental chemicals.”
According to Megan Kelsey, MD, associate professor of pediatric endocrinology, director of lifestyle medicine endocrinology, and medical director of the bariatric surgery center at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, the increased rates of type 2 diabetes reported by the study are alarming, yet they pale in comparison with what’s been happening since the pandemic began.
“Individual institutions have reported anywhere between a 50% – which is basically what we’re seeing at our hospital – to a 300% increase in new diagnoses [of type 2 diabetes] in a single-year time period,” Dr. Kelsey said in an interview. “So what is reported [in the present study] doesn’t even get at what’s been going on over the past year and a half.”
Dr. Kelsey offered some speculative drivers of this recent surge in cases, including stress, weight gain caused by sedentary behavior and more access to food, and the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 may infect pancreatic islet beta cells, thereby interfering with insulin production.
Type 2 diabetes is particularly concerning among young people, Dr. Kelsey noted, as it is more challenging to manage than adult-onset disease.
Young patients “also develop complications much sooner than you’d expect,” she added. “So we really need to understand why these rates are increasing, how we can identify kids at risk, and how we can better prevent it, so we aren’t stuck with a disease that’s really difficult to treat.”
To this end, the NIH recently opened applications for investigators to participate in a prospective longitudinal study of youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Young people at risk of diabetes will be followed through puberty, a period of increased risk, according to Dr. Kelsey.
“The goal will be to take kids who don’t yet have [type 2] diabetes, but are at risk, and try to better understand, as some of them progress to developing diabetes, what is going on,” Dr. Kelsey said. “What are other factors that we can use to better predict who’s going to develop diabetes? And can we use the information from this [upcoming] study to understand how to better prevent it? Because nothing that has been tried so far has worked.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NIDDK, and others. The investigators and Dr. Kelsey reported no conflicts of interest.
The prevalence of youth-onset diabetes in the United States rose significantly from 2001 to 2017, with rates of type 2 diabetes climbing disproportionately among racial/ethnic minorities, according to investigators.
In individuals aged 19 years or younger, prevalence rates of type 1 and type 2 diabetes increased 45.1% and 95.3%, respectively, reported lead author Jean M. Lawrence, ScD, MPH, MSSA, program director of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., and colleagues.
“Elucidating differences in diabetes prevalence trends by diabetes type and demographic characteristics is essential to describe the burden of disease and to estimate current and future resource needs,” Dr. Lawrence and colleagues wrote in JAMA.
The retrospective analysis was a part of the ongoing SEARCH study, which includes data from individuals in six areas across the United States: Colorado, California, Ohio, South Carolina, Washington state, and Arizona/New Mexico (Indian Health Services). In the present report, three prevalence years were evaluated: 2001, 2009, and 2017. For each year, approximately 3.5 million youths were included. Findings were reported in terms of diabetes type, race/ethnicity, age at diagnosis, and sex.
Absolute prevalence of type 1 diabetes per 1,000 youths increased from 1.48 in 2001, to 1.93 in 2009, and finally 2.15 in 2017. Across the 16-year period, this represents an absolute increase of 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.70), and a relative increase of 45.1% (95% CI, 40.0%-50.4%). In absolute terms, prevalence increased most among non-Hispanic White (0.93 per 1,000) and non-Hispanic Black (0.89 per 1,000) youths.
While type 2 diabetes was comparatively less common than type 1 diabetes, absolute prevalence per 1,000 youths increased to a greater degree, rising from 0.34 in 2001 to 0.46 in 2009 and to 0.67 in 2017. This amounts to relative increase across the period of 95.3% (95% CI, 77.0%-115.4%). Absolute increases were disproportionate among racial/ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Hispanic youths, who had absolute increases per 1,000 youths of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.74-0.97) and 0.57 (95% CI, 0.51-0.64), respectively, compared with 0.05 (95% CI, 0.03-0.07) for White youths.
“Increases [among Black and Hispanic youths] were not linear,” the investigators noted. “Hispanic youths had a significantly greater increase in the first interval compared with the second interval, while Black youths had no significant increase in the first interval and a significant increase in the second interval.”
Dr. Lawrence and colleagues offered several possible factors driving these trends in type 2 diabetes.
“Changes in anthropometric risk factors appear to play a significant role,” they wrote, noting that “Black and Mexican American teenagers experienced the greatest increase in prevalence of obesity/severe obesity from 1999 to 2018, which may contribute to race and ethnicity differences. Other contributing factors may include increases in exposure to maternal obesity and diabetes (gestational and type 2 diabetes) and exposure to environmental chemicals.”
According to Megan Kelsey, MD, associate professor of pediatric endocrinology, director of lifestyle medicine endocrinology, and medical director of the bariatric surgery center at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, the increased rates of type 2 diabetes reported by the study are alarming, yet they pale in comparison with what’s been happening since the pandemic began.
“Individual institutions have reported anywhere between a 50% – which is basically what we’re seeing at our hospital – to a 300% increase in new diagnoses [of type 2 diabetes] in a single-year time period,” Dr. Kelsey said in an interview. “So what is reported [in the present study] doesn’t even get at what’s been going on over the past year and a half.”
Dr. Kelsey offered some speculative drivers of this recent surge in cases, including stress, weight gain caused by sedentary behavior and more access to food, and the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 may infect pancreatic islet beta cells, thereby interfering with insulin production.
Type 2 diabetes is particularly concerning among young people, Dr. Kelsey noted, as it is more challenging to manage than adult-onset disease.
Young patients “also develop complications much sooner than you’d expect,” she added. “So we really need to understand why these rates are increasing, how we can identify kids at risk, and how we can better prevent it, so we aren’t stuck with a disease that’s really difficult to treat.”
To this end, the NIH recently opened applications for investigators to participate in a prospective longitudinal study of youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Young people at risk of diabetes will be followed through puberty, a period of increased risk, according to Dr. Kelsey.
“The goal will be to take kids who don’t yet have [type 2] diabetes, but are at risk, and try to better understand, as some of them progress to developing diabetes, what is going on,” Dr. Kelsey said. “What are other factors that we can use to better predict who’s going to develop diabetes? And can we use the information from this [upcoming] study to understand how to better prevent it? Because nothing that has been tried so far has worked.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NIDDK, and others. The investigators and Dr. Kelsey reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA
Prevalence of high-risk HPV types dwindled since vaccine approval
Young women who received the quadrivalent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine had fewer and fewer infections with high-risk HPV strains covered by the vaccine year after year, but the incidence of high-risk strains that were not covered by the vaccine increased over the same 12-year period, researchers report in a study published August 23 in JAMA Open Network.
“One of the unique contributions that this study provides is the evaluation of a real-world example of the HPV infection rates following immunization in a population of adolescent girls and young adult women at a single health center in a large U.S. city, reflecting strong evidence of vaccine effectiveness,” write Nicolas F. Schlecht, PhD, a professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, and his colleagues. “Previous surveillance studies from the U.S. have involved older women and populations with relatively low vaccine coverage.”
In addition to supporting the value of continuing to vaccinate teens against HPV, the findings underscore the importance of continuing to screen women for cervical cancer, Dr. Schlecht said in an interview.
“HPV has not and is not going away,” he said. “We need to keep on our toes with screening and other measures to continue to prevent the development of cervix cancer,” including monitoring different high-risk HPV types and keeping a close eye on cervical precancer rates, particularly CIN3 and cervix cancer, he said. “The vaccines are definitely a good thing. Just getting rid of HPV16 is an amazing accomplishment.”
Kevin Ault, MD, a professor of ob/gyn and academic specialist director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, told this news organization that other studies have had similar findings, but this one is larger with longer follow-up.
“The take-home message is that vaccines work, and this is especially true for the HPV vaccine,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the research. “The vaccine prevents HPV infections and the consequences of these infections, such as cervical cancer. The results are consistent with other studies in different settings, so they are likely generalizable.”
The researchers collected data from October 2007, shortly after the vaccine was approved, through September 2019 on sexually active adolescent and young women aged 13 to 21 years who had received the HPV vaccine and had agreed to follow-up assessments every 6 months until they turned 26. Each follow-up included the collecting of samples of cervical and anal cells for polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of HPV types.
More than half of the 1,453 participants were Hispanic (58.8%), and half were Black (50.4%), including 15% Hispanic and Black patients. The average age of the participants was 18 years. They were tracked for a median 2.4 years. Nearly half the participants (48%) received the HPV vaccine prior to sexual debut.
For the longitudinal study, the researchers adjusted for participants’ age, the year they received the vaccine, and the years since they were vaccinated. They also tracked breakthrough infections for the four types of HPV covered by the vaccine in participants who received the vaccine before sexual debut.
“We evaluated whether infection rates for HPV have changed since the administration of the vaccine by assessing longitudinally the probability of HPV detection over time among vaccinated participants while adjusting for changes in cohort characteristics over time,” the researchers write. In their statistical analysis, they made adjustments for the number of vaccine doses participants received before their first study visit, age at sexual debut, age at first vaccine dose, number of sexual partners in the preceding 6 months, consistency of condom use during sex, history of a positive chlamydia test, and, for anal HPV analyses, whether the participants had had anal sex in the previous 6 months.
The average age at first intercourse remained steady at 15 years throughout the study, but the average age of vaccination dropped from 18 years in 2008 to 12 years in 2019 (P < .001). More than half the participants (64%) had had at least three lifetime sexual partners at baseline.
After adjustment for age, the researchers found that the incidence of the four HPV types covered by the vaccine – HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18 – dropped more each year, shifting from 9.1% from 2008-2010 to 4.7% from 2017-2019. The effect was even greater among those vaccinated prior to sexual debut; for those patients, the incidence of the four vaccine types dropped from 8.8% to 1.7% over the course of the study. Declines over time also occurred for anal types HPV-31 (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.76) and HPV-45 (aOR = 0.77). Those vaccinated prior to any sexual intercourse had 19% lower odds of infection per year with a vaccine-covered HPV type.
“We were really excited to see that the types targeted by the vaccines were considerably lower over time in our population,” Dr. Schlecht told this news organization. “This is an important observation, since most of these types are the most worrisome for cervical cancer.”
They were surprised, however, to see overall HPV prevalence increase over time, particularly with the high-risk HPV types that were not covered by the quadrivalent vaccine.
Prevalence of cervical high-risk types not in the vaccine increased from 25.1% from 2008-2010 to 30.5% from 2017-2019. Odds of detection of high-risk HPV types not covered by the vaccine increased 8% each year, particularly for HPV-56 and HPV-68; anal HPV types increased 11% each year. Neither age nor recent number of sexual partners affected the findings.
“The underlying mechanisms for the observed increased detection of specific non-vaccine HPV types over time are not yet clear.”
“We hope this doesn’t translate into some increase in cervical neoplasia that is unanticipated,” Dr. Schlecht said. He noted that the attributable risks for cancer associated with nonvaccine high-risk HPV types remain low. “Theoretical concerns are one thing; actual data is what drives the show,” he said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Schlecht has served on advisory boards for Merck, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and PDS Biotechnology. One author previously served on a GSK advisory board, and another worked with Merck on an early vaccine trial. Dr. Ault has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Young women who received the quadrivalent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine had fewer and fewer infections with high-risk HPV strains covered by the vaccine year after year, but the incidence of high-risk strains that were not covered by the vaccine increased over the same 12-year period, researchers report in a study published August 23 in JAMA Open Network.
“One of the unique contributions that this study provides is the evaluation of a real-world example of the HPV infection rates following immunization in a population of adolescent girls and young adult women at a single health center in a large U.S. city, reflecting strong evidence of vaccine effectiveness,” write Nicolas F. Schlecht, PhD, a professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, and his colleagues. “Previous surveillance studies from the U.S. have involved older women and populations with relatively low vaccine coverage.”
In addition to supporting the value of continuing to vaccinate teens against HPV, the findings underscore the importance of continuing to screen women for cervical cancer, Dr. Schlecht said in an interview.
“HPV has not and is not going away,” he said. “We need to keep on our toes with screening and other measures to continue to prevent the development of cervix cancer,” including monitoring different high-risk HPV types and keeping a close eye on cervical precancer rates, particularly CIN3 and cervix cancer, he said. “The vaccines are definitely a good thing. Just getting rid of HPV16 is an amazing accomplishment.”
Kevin Ault, MD, a professor of ob/gyn and academic specialist director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, told this news organization that other studies have had similar findings, but this one is larger with longer follow-up.
“The take-home message is that vaccines work, and this is especially true for the HPV vaccine,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the research. “The vaccine prevents HPV infections and the consequences of these infections, such as cervical cancer. The results are consistent with other studies in different settings, so they are likely generalizable.”
The researchers collected data from October 2007, shortly after the vaccine was approved, through September 2019 on sexually active adolescent and young women aged 13 to 21 years who had received the HPV vaccine and had agreed to follow-up assessments every 6 months until they turned 26. Each follow-up included the collecting of samples of cervical and anal cells for polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of HPV types.
More than half of the 1,453 participants were Hispanic (58.8%), and half were Black (50.4%), including 15% Hispanic and Black patients. The average age of the participants was 18 years. They were tracked for a median 2.4 years. Nearly half the participants (48%) received the HPV vaccine prior to sexual debut.
For the longitudinal study, the researchers adjusted for participants’ age, the year they received the vaccine, and the years since they were vaccinated. They also tracked breakthrough infections for the four types of HPV covered by the vaccine in participants who received the vaccine before sexual debut.
“We evaluated whether infection rates for HPV have changed since the administration of the vaccine by assessing longitudinally the probability of HPV detection over time among vaccinated participants while adjusting for changes in cohort characteristics over time,” the researchers write. In their statistical analysis, they made adjustments for the number of vaccine doses participants received before their first study visit, age at sexual debut, age at first vaccine dose, number of sexual partners in the preceding 6 months, consistency of condom use during sex, history of a positive chlamydia test, and, for anal HPV analyses, whether the participants had had anal sex in the previous 6 months.
The average age at first intercourse remained steady at 15 years throughout the study, but the average age of vaccination dropped from 18 years in 2008 to 12 years in 2019 (P < .001). More than half the participants (64%) had had at least three lifetime sexual partners at baseline.
After adjustment for age, the researchers found that the incidence of the four HPV types covered by the vaccine – HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18 – dropped more each year, shifting from 9.1% from 2008-2010 to 4.7% from 2017-2019. The effect was even greater among those vaccinated prior to sexual debut; for those patients, the incidence of the four vaccine types dropped from 8.8% to 1.7% over the course of the study. Declines over time also occurred for anal types HPV-31 (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.76) and HPV-45 (aOR = 0.77). Those vaccinated prior to any sexual intercourse had 19% lower odds of infection per year with a vaccine-covered HPV type.
“We were really excited to see that the types targeted by the vaccines were considerably lower over time in our population,” Dr. Schlecht told this news organization. “This is an important observation, since most of these types are the most worrisome for cervical cancer.”
They were surprised, however, to see overall HPV prevalence increase over time, particularly with the high-risk HPV types that were not covered by the quadrivalent vaccine.
Prevalence of cervical high-risk types not in the vaccine increased from 25.1% from 2008-2010 to 30.5% from 2017-2019. Odds of detection of high-risk HPV types not covered by the vaccine increased 8% each year, particularly for HPV-56 and HPV-68; anal HPV types increased 11% each year. Neither age nor recent number of sexual partners affected the findings.
“The underlying mechanisms for the observed increased detection of specific non-vaccine HPV types over time are not yet clear.”
“We hope this doesn’t translate into some increase in cervical neoplasia that is unanticipated,” Dr. Schlecht said. He noted that the attributable risks for cancer associated with nonvaccine high-risk HPV types remain low. “Theoretical concerns are one thing; actual data is what drives the show,” he said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Schlecht has served on advisory boards for Merck, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and PDS Biotechnology. One author previously served on a GSK advisory board, and another worked with Merck on an early vaccine trial. Dr. Ault has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Young women who received the quadrivalent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine had fewer and fewer infections with high-risk HPV strains covered by the vaccine year after year, but the incidence of high-risk strains that were not covered by the vaccine increased over the same 12-year period, researchers report in a study published August 23 in JAMA Open Network.
“One of the unique contributions that this study provides is the evaluation of a real-world example of the HPV infection rates following immunization in a population of adolescent girls and young adult women at a single health center in a large U.S. city, reflecting strong evidence of vaccine effectiveness,” write Nicolas F. Schlecht, PhD, a professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, and his colleagues. “Previous surveillance studies from the U.S. have involved older women and populations with relatively low vaccine coverage.”
In addition to supporting the value of continuing to vaccinate teens against HPV, the findings underscore the importance of continuing to screen women for cervical cancer, Dr. Schlecht said in an interview.
“HPV has not and is not going away,” he said. “We need to keep on our toes with screening and other measures to continue to prevent the development of cervix cancer,” including monitoring different high-risk HPV types and keeping a close eye on cervical precancer rates, particularly CIN3 and cervix cancer, he said. “The vaccines are definitely a good thing. Just getting rid of HPV16 is an amazing accomplishment.”
Kevin Ault, MD, a professor of ob/gyn and academic specialist director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas, Kansas City, told this news organization that other studies have had similar findings, but this one is larger with longer follow-up.
“The take-home message is that vaccines work, and this is especially true for the HPV vaccine,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the research. “The vaccine prevents HPV infections and the consequences of these infections, such as cervical cancer. The results are consistent with other studies in different settings, so they are likely generalizable.”
The researchers collected data from October 2007, shortly after the vaccine was approved, through September 2019 on sexually active adolescent and young women aged 13 to 21 years who had received the HPV vaccine and had agreed to follow-up assessments every 6 months until they turned 26. Each follow-up included the collecting of samples of cervical and anal cells for polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of HPV types.
More than half of the 1,453 participants were Hispanic (58.8%), and half were Black (50.4%), including 15% Hispanic and Black patients. The average age of the participants was 18 years. They were tracked for a median 2.4 years. Nearly half the participants (48%) received the HPV vaccine prior to sexual debut.
For the longitudinal study, the researchers adjusted for participants’ age, the year they received the vaccine, and the years since they were vaccinated. They also tracked breakthrough infections for the four types of HPV covered by the vaccine in participants who received the vaccine before sexual debut.
“We evaluated whether infection rates for HPV have changed since the administration of the vaccine by assessing longitudinally the probability of HPV detection over time among vaccinated participants while adjusting for changes in cohort characteristics over time,” the researchers write. In their statistical analysis, they made adjustments for the number of vaccine doses participants received before their first study visit, age at sexual debut, age at first vaccine dose, number of sexual partners in the preceding 6 months, consistency of condom use during sex, history of a positive chlamydia test, and, for anal HPV analyses, whether the participants had had anal sex in the previous 6 months.
The average age at first intercourse remained steady at 15 years throughout the study, but the average age of vaccination dropped from 18 years in 2008 to 12 years in 2019 (P < .001). More than half the participants (64%) had had at least three lifetime sexual partners at baseline.
After adjustment for age, the researchers found that the incidence of the four HPV types covered by the vaccine – HPV-6, HPV-11, HPV-16, and HPV-18 – dropped more each year, shifting from 9.1% from 2008-2010 to 4.7% from 2017-2019. The effect was even greater among those vaccinated prior to sexual debut; for those patients, the incidence of the four vaccine types dropped from 8.8% to 1.7% over the course of the study. Declines over time also occurred for anal types HPV-31 (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.76) and HPV-45 (aOR = 0.77). Those vaccinated prior to any sexual intercourse had 19% lower odds of infection per year with a vaccine-covered HPV type.
“We were really excited to see that the types targeted by the vaccines were considerably lower over time in our population,” Dr. Schlecht told this news organization. “This is an important observation, since most of these types are the most worrisome for cervical cancer.”
They were surprised, however, to see overall HPV prevalence increase over time, particularly with the high-risk HPV types that were not covered by the quadrivalent vaccine.
Prevalence of cervical high-risk types not in the vaccine increased from 25.1% from 2008-2010 to 30.5% from 2017-2019. Odds of detection of high-risk HPV types not covered by the vaccine increased 8% each year, particularly for HPV-56 and HPV-68; anal HPV types increased 11% each year. Neither age nor recent number of sexual partners affected the findings.
“The underlying mechanisms for the observed increased detection of specific non-vaccine HPV types over time are not yet clear.”
“We hope this doesn’t translate into some increase in cervical neoplasia that is unanticipated,” Dr. Schlecht said. He noted that the attributable risks for cancer associated with nonvaccine high-risk HPV types remain low. “Theoretical concerns are one thing; actual data is what drives the show,” he said.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. Schlecht has served on advisory boards for Merck, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and PDS Biotechnology. One author previously served on a GSK advisory board, and another worked with Merck on an early vaccine trial. Dr. Ault has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flavonoid-rich foods, aided by gut bacteria, tied to lower BP
, an association that is partially explained by bacteria in an individual’s gut microbiome, new research suggests.
In a population-based study of more than 900 individuals, those with the highest intake of flavonoid-containing foods had significantly lower systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, as well as greater gut microbial diversity, compared with those with the lowest intakes.
Up to 15% of this observed association was explained by the gut microbiome, suggesting that these microbes play a key role in metabolizing flavonoids to enhance their cardioprotective effects, according to the researchers.
The study was published online in the journal Hypertension.
“We know what we eat plays a critical role in shaping our gut microbiome, but little is known about the relative importance of plant foods and specific constituents called flavonoids,” lead researcher Aedin Cassidy, PhD, chair and professor of nutrition and medicine at the Institute for Global Food Security, Queen’s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland, said in an interview.
“Unlike many other food constituents, flavonoids are predominantly metabolized in the gut, suggesting that the gut microbiome may be more important in enhancing their biological activity than for other things we eat,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“There is mounting evidence from population-based studies and clinical trials that a higher intake of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich foods can improve heart health, but for the first time, we provide data highlighting the key role of the gut microbiome in explaining the association between such foods and blood pressure,” she noted. “This is one of the first studies to address this.”
For this analysis, Dr. Cassidy and her group sought to assess to what extent the composition of the gut microbiome might explain the association of habitual flavonoid and flavonoid-rich food intake with systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a community-based sample of 904 individuals aged 25-82 years from Germany’s PopGen biobank.
The researchers evaluated participants’ food intake, gut microbiome, and blood pressure levels together with other clinical and molecular phenotyping at regular follow-up examinations.
Participants’ intake of flavonoid-rich foods during the previous year was calculated from a self-reported food questionnaire detailing the frequency and quantity eaten of 112 foods, and flavonoid values were assigned to foods according to United States Department of Agriculture data on flavonoid content in food.
Participants’ gut microbiome was assessed by fecal bacterial DNA extracted from stool samples.
After an overnight fast, participants’ blood pressure levels were measured three times in 3-minute intervals after an initial 5-minute rest period. Researchers also collected participants’ diet and lifestyle information.
Analysis of the data showed the following:
- Eating 1.5 servings of berries per day (about 1 cup) was associated with a 4.1–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 12% of this association was explained by gut microbiome factors.
- Drinking three glasses of red wine per week was associated with a 3.7–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 15% of this association was explained by the gut microbiome.
“These blood pressure–lowering effects are achievable with simple changes to the daily diet,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“Incorporating flavonoid-rich foods into the diet can have clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, and a healthy gut microbiome is important to break down flavonoids to a more cardioprotective form,” she said.
“Our findings indicate future trials should look at participants according to metabolic profile in order to more accurately study the roles of metabolism and the gut microbiome in regulating the effects of flavonoids on blood pressure,” said Dr. Cassidy.
“A better understanding of the highly individual variability of flavonoid metabolism could very well explain why some people have greater cardiovascular protection benefits from flavonoid-rich foods than others.”
‘Interesting’ data
“The data are interesting,” David Jenkins, MD, PhD, DSc, professor of medicine and nutrition at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“Berries and red wine appear to be associated with lower systolic blood pressures. Lower blood pressures have been found in general in people who consume more plant-based diets, especially those high in fruits and vegetables,” noted Dr. Jenkins, who was not involved with this study.
“Berries and grapes high in polyphenols may have many health benefits as antioxidants, and in a recent study have been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality. The change in chronic microflora is also of interest as this will change with increased fruit and vegetable consumption,” he said.
Perhaps one word of caveat, Dr. Jenkins added: “Alcohol has been found to increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke. Presumably the beneficial effects as seen here were when wine is consumed in moderation.”
Supports recommendations
The study by Cassidy and colleagues supports the dietary recommendations from the American Heart Association (AHA) for heart health, Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, RDN, professor of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, Pa., and chair, AHA Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, said in an interview.
“The AHA recommends a healthy dietary pattern that emphasizes a variety of plant foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds and is low in sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars. Lean protein foods, including plant protein foods, are recommended, and red meat should be limited. If alcohol is consumed it should be done in moderation,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Based on these AHA dietary recommendations, a wide variety of plant foods will promote consumption of many flavonoids that have demonstrated CVD benefits, such as lowering systolic blood pressure as reported by the authors, as well as promoting healthy endothelial function and having antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects,” she said in email.
“This recommended dietary pattern will have other cardiovascular health benefits, such as decreasing LDL cholesterol, due to its very healthy nutrient profile. The exciting new finding reported by Cassidy et al. is that the effects of dietary flavonoids on lowering systolic blood pressure are modulated by the gut microbiome,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Further research needs to be done to confirm these findings and to identify how different foods affect specific gut bacteria that benefit cardiovascular health.”
The research was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. Cassidy and Dr. Jenkins have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kris-Etherton is a spokesperson for the AHA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, an association that is partially explained by bacteria in an individual’s gut microbiome, new research suggests.
In a population-based study of more than 900 individuals, those with the highest intake of flavonoid-containing foods had significantly lower systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, as well as greater gut microbial diversity, compared with those with the lowest intakes.
Up to 15% of this observed association was explained by the gut microbiome, suggesting that these microbes play a key role in metabolizing flavonoids to enhance their cardioprotective effects, according to the researchers.
The study was published online in the journal Hypertension.
“We know what we eat plays a critical role in shaping our gut microbiome, but little is known about the relative importance of plant foods and specific constituents called flavonoids,” lead researcher Aedin Cassidy, PhD, chair and professor of nutrition and medicine at the Institute for Global Food Security, Queen’s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland, said in an interview.
“Unlike many other food constituents, flavonoids are predominantly metabolized in the gut, suggesting that the gut microbiome may be more important in enhancing their biological activity than for other things we eat,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“There is mounting evidence from population-based studies and clinical trials that a higher intake of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich foods can improve heart health, but for the first time, we provide data highlighting the key role of the gut microbiome in explaining the association between such foods and blood pressure,” she noted. “This is one of the first studies to address this.”
For this analysis, Dr. Cassidy and her group sought to assess to what extent the composition of the gut microbiome might explain the association of habitual flavonoid and flavonoid-rich food intake with systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a community-based sample of 904 individuals aged 25-82 years from Germany’s PopGen biobank.
The researchers evaluated participants’ food intake, gut microbiome, and blood pressure levels together with other clinical and molecular phenotyping at regular follow-up examinations.
Participants’ intake of flavonoid-rich foods during the previous year was calculated from a self-reported food questionnaire detailing the frequency and quantity eaten of 112 foods, and flavonoid values were assigned to foods according to United States Department of Agriculture data on flavonoid content in food.
Participants’ gut microbiome was assessed by fecal bacterial DNA extracted from stool samples.
After an overnight fast, participants’ blood pressure levels were measured three times in 3-minute intervals after an initial 5-minute rest period. Researchers also collected participants’ diet and lifestyle information.
Analysis of the data showed the following:
- Eating 1.5 servings of berries per day (about 1 cup) was associated with a 4.1–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 12% of this association was explained by gut microbiome factors.
- Drinking three glasses of red wine per week was associated with a 3.7–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 15% of this association was explained by the gut microbiome.
“These blood pressure–lowering effects are achievable with simple changes to the daily diet,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“Incorporating flavonoid-rich foods into the diet can have clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, and a healthy gut microbiome is important to break down flavonoids to a more cardioprotective form,” she said.
“Our findings indicate future trials should look at participants according to metabolic profile in order to more accurately study the roles of metabolism and the gut microbiome in regulating the effects of flavonoids on blood pressure,” said Dr. Cassidy.
“A better understanding of the highly individual variability of flavonoid metabolism could very well explain why some people have greater cardiovascular protection benefits from flavonoid-rich foods than others.”
‘Interesting’ data
“The data are interesting,” David Jenkins, MD, PhD, DSc, professor of medicine and nutrition at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“Berries and red wine appear to be associated with lower systolic blood pressures. Lower blood pressures have been found in general in people who consume more plant-based diets, especially those high in fruits and vegetables,” noted Dr. Jenkins, who was not involved with this study.
“Berries and grapes high in polyphenols may have many health benefits as antioxidants, and in a recent study have been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality. The change in chronic microflora is also of interest as this will change with increased fruit and vegetable consumption,” he said.
Perhaps one word of caveat, Dr. Jenkins added: “Alcohol has been found to increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke. Presumably the beneficial effects as seen here were when wine is consumed in moderation.”
Supports recommendations
The study by Cassidy and colleagues supports the dietary recommendations from the American Heart Association (AHA) for heart health, Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, RDN, professor of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, Pa., and chair, AHA Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, said in an interview.
“The AHA recommends a healthy dietary pattern that emphasizes a variety of plant foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds and is low in sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars. Lean protein foods, including plant protein foods, are recommended, and red meat should be limited. If alcohol is consumed it should be done in moderation,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Based on these AHA dietary recommendations, a wide variety of plant foods will promote consumption of many flavonoids that have demonstrated CVD benefits, such as lowering systolic blood pressure as reported by the authors, as well as promoting healthy endothelial function and having antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects,” she said in email.
“This recommended dietary pattern will have other cardiovascular health benefits, such as decreasing LDL cholesterol, due to its very healthy nutrient profile. The exciting new finding reported by Cassidy et al. is that the effects of dietary flavonoids on lowering systolic blood pressure are modulated by the gut microbiome,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Further research needs to be done to confirm these findings and to identify how different foods affect specific gut bacteria that benefit cardiovascular health.”
The research was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. Cassidy and Dr. Jenkins have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kris-Etherton is a spokesperson for the AHA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, an association that is partially explained by bacteria in an individual’s gut microbiome, new research suggests.
In a population-based study of more than 900 individuals, those with the highest intake of flavonoid-containing foods had significantly lower systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, as well as greater gut microbial diversity, compared with those with the lowest intakes.
Up to 15% of this observed association was explained by the gut microbiome, suggesting that these microbes play a key role in metabolizing flavonoids to enhance their cardioprotective effects, according to the researchers.
The study was published online in the journal Hypertension.
“We know what we eat plays a critical role in shaping our gut microbiome, but little is known about the relative importance of plant foods and specific constituents called flavonoids,” lead researcher Aedin Cassidy, PhD, chair and professor of nutrition and medicine at the Institute for Global Food Security, Queen’s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland, said in an interview.
“Unlike many other food constituents, flavonoids are predominantly metabolized in the gut, suggesting that the gut microbiome may be more important in enhancing their biological activity than for other things we eat,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“There is mounting evidence from population-based studies and clinical trials that a higher intake of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich foods can improve heart health, but for the first time, we provide data highlighting the key role of the gut microbiome in explaining the association between such foods and blood pressure,” she noted. “This is one of the first studies to address this.”
For this analysis, Dr. Cassidy and her group sought to assess to what extent the composition of the gut microbiome might explain the association of habitual flavonoid and flavonoid-rich food intake with systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a community-based sample of 904 individuals aged 25-82 years from Germany’s PopGen biobank.
The researchers evaluated participants’ food intake, gut microbiome, and blood pressure levels together with other clinical and molecular phenotyping at regular follow-up examinations.
Participants’ intake of flavonoid-rich foods during the previous year was calculated from a self-reported food questionnaire detailing the frequency and quantity eaten of 112 foods, and flavonoid values were assigned to foods according to United States Department of Agriculture data on flavonoid content in food.
Participants’ gut microbiome was assessed by fecal bacterial DNA extracted from stool samples.
After an overnight fast, participants’ blood pressure levels were measured three times in 3-minute intervals after an initial 5-minute rest period. Researchers also collected participants’ diet and lifestyle information.
Analysis of the data showed the following:
- Eating 1.5 servings of berries per day (about 1 cup) was associated with a 4.1–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 12% of this association was explained by gut microbiome factors.
- Drinking three glasses of red wine per week was associated with a 3.7–mm Hg reduction in systolic BP; 15% of this association was explained by the gut microbiome.
“These blood pressure–lowering effects are achievable with simple changes to the daily diet,” Dr. Cassidy said.
“Incorporating flavonoid-rich foods into the diet can have clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure, and a healthy gut microbiome is important to break down flavonoids to a more cardioprotective form,” she said.
“Our findings indicate future trials should look at participants according to metabolic profile in order to more accurately study the roles of metabolism and the gut microbiome in regulating the effects of flavonoids on blood pressure,” said Dr. Cassidy.
“A better understanding of the highly individual variability of flavonoid metabolism could very well explain why some people have greater cardiovascular protection benefits from flavonoid-rich foods than others.”
‘Interesting’ data
“The data are interesting,” David Jenkins, MD, PhD, DSc, professor of medicine and nutrition at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“Berries and red wine appear to be associated with lower systolic blood pressures. Lower blood pressures have been found in general in people who consume more plant-based diets, especially those high in fruits and vegetables,” noted Dr. Jenkins, who was not involved with this study.
“Berries and grapes high in polyphenols may have many health benefits as antioxidants, and in a recent study have been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality. The change in chronic microflora is also of interest as this will change with increased fruit and vegetable consumption,” he said.
Perhaps one word of caveat, Dr. Jenkins added: “Alcohol has been found to increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke. Presumably the beneficial effects as seen here were when wine is consumed in moderation.”
Supports recommendations
The study by Cassidy and colleagues supports the dietary recommendations from the American Heart Association (AHA) for heart health, Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, RDN, professor of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, Pa., and chair, AHA Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, said in an interview.
“The AHA recommends a healthy dietary pattern that emphasizes a variety of plant foods including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds and is low in sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars. Lean protein foods, including plant protein foods, are recommended, and red meat should be limited. If alcohol is consumed it should be done in moderation,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Based on these AHA dietary recommendations, a wide variety of plant foods will promote consumption of many flavonoids that have demonstrated CVD benefits, such as lowering systolic blood pressure as reported by the authors, as well as promoting healthy endothelial function and having antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects,” she said in email.
“This recommended dietary pattern will have other cardiovascular health benefits, such as decreasing LDL cholesterol, due to its very healthy nutrient profile. The exciting new finding reported by Cassidy et al. is that the effects of dietary flavonoids on lowering systolic blood pressure are modulated by the gut microbiome,” Dr. Kris-Etherton said.
“Further research needs to be done to confirm these findings and to identify how different foods affect specific gut bacteria that benefit cardiovascular health.”
The research was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. Cassidy and Dr. Jenkins have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kris-Etherton is a spokesperson for the AHA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stimulating jobs may help stave off dementia onset
Individuals with cognitively stimulating jobs are at a lower risk of developing dementia than their peers with less challenging employment, new research suggests.
Results from a large, multicohort study also showed an association between cognitive stimulation and lower levels of certain plasma proteins, providing possible clues on a protective biological mechanism.
“These new findings support the hypothesis that mental stimulation in adulthood may postpone the onset of dementia,” Mika Kivimäki, PhD, professor and director of the Whitehall II Study, department of epidemiology, University College London, said in an interview.
The results were published online Aug. 19, 2021, in the BMJ.
‘Work fast and hard’
Researchers assessed the association between workplace cognitive stimulation and dementia incidence in seven cohorts that included almost 108,000 men and women (mean age, 44.6 years). All were free of dementia at baseline.
Participants included civil servants, public sector employees, forestry workers, and others from the general working population.
Investigators separated the participants into three categories of workplace cognitive stimulation: “high,” which referred to both high job demand and high job control; “low,” which referred to low demands and low control; and “medium,” which referred to all other combinations of job demand and job control.
“Highly cognitively stimulating jobs require you to work fast and hard, learn new things, be creative, and have a high level of skill,” said Dr. Kivimäki.
The researchers controlled for low education, hypertension, smoking, obesity, depression, physical inactivity, diabetes, low social contact, excessive alcohol consumption, and traumatic brain injury. These represent 10 of the 12 dementia risk factors named by the 2020 Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention as having convincing evidence, Dr. Kivimäki noted.
Although the investigators had no data on the other two risk factors of hearing loss and air pollution, these are unlikely to be confounding factors, he said.
Follow-up for incident dementia varied from 13.7 to 30.1 years, depending on the cohort, and was 16.7 years in the total patient population. The mean age at dementia onset was 71.2 years.
Benefits across the life course
Results showed that incident dementia per 10,000 person years was 7.3 in the low–cognitive stimulation group and 4.8 in the high-stimulation group, for a difference of 2.5.
“These differences were relatively small because the incidence of dementia in this relatively young population was low,” Dr. Kivimäki said.
Compared with those with low stimulation, the adjusted hazard ratio for dementia for this with high stimulation was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.65-0.92).
The results were similar for men and women, and for those younger and older than 60 years. However, the link between workplace cognitive stimulation appeared stronger for Alzheimer’s disease than for other dementias.
There also appeared to be additive effects of higher cognitive stimulation in both childhood, as indicated by higher educational attainment, and adulthood, based on work characteristics, said Dr. Kivimäki.
“These findings support the benefits of cognitive stimulation across the life course, with education leading to higher peak cognitive performance and cognitive stimulation at work lowering age-related cognitive decline,” he added.
The findings don’t seem to be the result of workers with cognitive impairment remaining in unchallenging jobs, he noted. Separate analyses showed lower dementia incidence even when 10 years or more separated the assessment of cognitive stimulation and the dementia diagnosis.
“This suggests that the findings are unlikely to be biased due to reverse causation,” Dr. Kivimäki said.
Possible mechanism
Findings were similar when the researchers assessed effect from job changes. “This is probably because people in highly stimulating jobs are more likely to change to another highly stimulating job than to a low-stimulating job,” said Dr. Kivimäki. “Similarly, people with less stimulating jobs are seldom able to change to a substantially more stimulating job.”
As a dementia risk factor, low workplace stimulation is comparable with high alcohol intake and physical inactivity, but is weaker than education, diabetes, smoking, hypertension, and obesity, Dr. Kivimäki noted.
When asked about individuals with less cognitively stimulating jobs who are enormously stimulated outside work, he said that “previous large-scale studies have failed to find evidence that leisure time cognitive activity would significantly reduce risk of dementia.”
To explore potential underlying mechanisms, the investigators examined almost 5,000 plasma proteins in more than 2,200 individuals from one cohort in the Whitehall II study. They found six proteins were significantly lower among participants with high versus low cognitive stimulation.
In another analysis that included more than 13,500 participants from the Whitehall and another cohort, higher levels of three of these plasma proteins were associated with increased dementia risk – or conversely, lower protein levels with lower dementia risk.
The findings suggest a “novel plausible explanation” for the link between workplace cognitive stimulation and dementia risk, said Dr. Kivimäki.
He noted that higher levels of certain proteins prevent brain cells from forming new connections.
‘Some of the most compelling evidence to date’
In an accompanying editorial, Serhiy Dekhtyar, PhD, assistant professor (Docent), Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, noted that the study is “an important piece of work” and “some of the most compelling evidence to date” on the role of occupational cognitive stimulation in dementia risk.
The large-scale investigation in multiple cohorts and contexts has “advanced the field” and could help “explain previously mixed findings in the literature,” Dekhtyar said in an interview.
Importantly, the researchers provide “an indication of biological mechanisms potentially connecting work mental stimulation and dementia,” he added.
However, Dr. Dekhtyar noted that the difference of 2.5 incident cases of dementia per 10,000 person years of follow-up between the low and high mental-stimulation groups “is not especially large” – although it is comparable with other established risk factors for dementia.
He suspects the effect size would have been larger had the follow-up for dementia been longer.
Dr. Dekhtyar also raised the possibility that “innate cognition” might affect both educational and occupational attainment, and the subsequent dementia risk.
“Without taking this into account, we may inadvertently conclude that education or occupational stimulation help differentially preserve cognition into late life – when in reality, it may be initial differences in cognitive ability that are preserved throughout life,” he concluded.
Funding sources for the study included Nordic Research Programme on Health and Welfare (NordForsk), Medical Research Council, Wellcome Trust, Academy of Finland, and Helsinki Institute of Life Science. Dr. Kivimäki has received support from NordForsk, the UK Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, the Academy of Finland, and the Helsinki Institute of Life Science. Dr. Dekhtyar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with cognitively stimulating jobs are at a lower risk of developing dementia than their peers with less challenging employment, new research suggests.
Results from a large, multicohort study also showed an association between cognitive stimulation and lower levels of certain plasma proteins, providing possible clues on a protective biological mechanism.
“These new findings support the hypothesis that mental stimulation in adulthood may postpone the onset of dementia,” Mika Kivimäki, PhD, professor and director of the Whitehall II Study, department of epidemiology, University College London, said in an interview.
The results were published online Aug. 19, 2021, in the BMJ.
‘Work fast and hard’
Researchers assessed the association between workplace cognitive stimulation and dementia incidence in seven cohorts that included almost 108,000 men and women (mean age, 44.6 years). All were free of dementia at baseline.
Participants included civil servants, public sector employees, forestry workers, and others from the general working population.
Investigators separated the participants into three categories of workplace cognitive stimulation: “high,” which referred to both high job demand and high job control; “low,” which referred to low demands and low control; and “medium,” which referred to all other combinations of job demand and job control.
“Highly cognitively stimulating jobs require you to work fast and hard, learn new things, be creative, and have a high level of skill,” said Dr. Kivimäki.
The researchers controlled for low education, hypertension, smoking, obesity, depression, physical inactivity, diabetes, low social contact, excessive alcohol consumption, and traumatic brain injury. These represent 10 of the 12 dementia risk factors named by the 2020 Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention as having convincing evidence, Dr. Kivimäki noted.
Although the investigators had no data on the other two risk factors of hearing loss and air pollution, these are unlikely to be confounding factors, he said.
Follow-up for incident dementia varied from 13.7 to 30.1 years, depending on the cohort, and was 16.7 years in the total patient population. The mean age at dementia onset was 71.2 years.
Benefits across the life course
Results showed that incident dementia per 10,000 person years was 7.3 in the low–cognitive stimulation group and 4.8 in the high-stimulation group, for a difference of 2.5.
“These differences were relatively small because the incidence of dementia in this relatively young population was low,” Dr. Kivimäki said.
Compared with those with low stimulation, the adjusted hazard ratio for dementia for this with high stimulation was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.65-0.92).
The results were similar for men and women, and for those younger and older than 60 years. However, the link between workplace cognitive stimulation appeared stronger for Alzheimer’s disease than for other dementias.
There also appeared to be additive effects of higher cognitive stimulation in both childhood, as indicated by higher educational attainment, and adulthood, based on work characteristics, said Dr. Kivimäki.
“These findings support the benefits of cognitive stimulation across the life course, with education leading to higher peak cognitive performance and cognitive stimulation at work lowering age-related cognitive decline,” he added.
The findings don’t seem to be the result of workers with cognitive impairment remaining in unchallenging jobs, he noted. Separate analyses showed lower dementia incidence even when 10 years or more separated the assessment of cognitive stimulation and the dementia diagnosis.
“This suggests that the findings are unlikely to be biased due to reverse causation,” Dr. Kivimäki said.
Possible mechanism
Findings were similar when the researchers assessed effect from job changes. “This is probably because people in highly stimulating jobs are more likely to change to another highly stimulating job than to a low-stimulating job,” said Dr. Kivimäki. “Similarly, people with less stimulating jobs are seldom able to change to a substantially more stimulating job.”
As a dementia risk factor, low workplace stimulation is comparable with high alcohol intake and physical inactivity, but is weaker than education, diabetes, smoking, hypertension, and obesity, Dr. Kivimäki noted.
When asked about individuals with less cognitively stimulating jobs who are enormously stimulated outside work, he said that “previous large-scale studies have failed to find evidence that leisure time cognitive activity would significantly reduce risk of dementia.”
To explore potential underlying mechanisms, the investigators examined almost 5,000 plasma proteins in more than 2,200 individuals from one cohort in the Whitehall II study. They found six proteins were significantly lower among participants with high versus low cognitive stimulation.
In another analysis that included more than 13,500 participants from the Whitehall and another cohort, higher levels of three of these plasma proteins were associated with increased dementia risk – or conversely, lower protein levels with lower dementia risk.
The findings suggest a “novel plausible explanation” for the link between workplace cognitive stimulation and dementia risk, said Dr. Kivimäki.
He noted that higher levels of certain proteins prevent brain cells from forming new connections.
‘Some of the most compelling evidence to date’
In an accompanying editorial, Serhiy Dekhtyar, PhD, assistant professor (Docent), Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, noted that the study is “an important piece of work” and “some of the most compelling evidence to date” on the role of occupational cognitive stimulation in dementia risk.
The large-scale investigation in multiple cohorts and contexts has “advanced the field” and could help “explain previously mixed findings in the literature,” Dekhtyar said in an interview.
Importantly, the researchers provide “an indication of biological mechanisms potentially connecting work mental stimulation and dementia,” he added.
However, Dr. Dekhtyar noted that the difference of 2.5 incident cases of dementia per 10,000 person years of follow-up between the low and high mental-stimulation groups “is not especially large” – although it is comparable with other established risk factors for dementia.
He suspects the effect size would have been larger had the follow-up for dementia been longer.
Dr. Dekhtyar also raised the possibility that “innate cognition” might affect both educational and occupational attainment, and the subsequent dementia risk.
“Without taking this into account, we may inadvertently conclude that education or occupational stimulation help differentially preserve cognition into late life – when in reality, it may be initial differences in cognitive ability that are preserved throughout life,” he concluded.
Funding sources for the study included Nordic Research Programme on Health and Welfare (NordForsk), Medical Research Council, Wellcome Trust, Academy of Finland, and Helsinki Institute of Life Science. Dr. Kivimäki has received support from NordForsk, the UK Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, the Academy of Finland, and the Helsinki Institute of Life Science. Dr. Dekhtyar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with cognitively stimulating jobs are at a lower risk of developing dementia than their peers with less challenging employment, new research suggests.
Results from a large, multicohort study also showed an association between cognitive stimulation and lower levels of certain plasma proteins, providing possible clues on a protective biological mechanism.
“These new findings support the hypothesis that mental stimulation in adulthood may postpone the onset of dementia,” Mika Kivimäki, PhD, professor and director of the Whitehall II Study, department of epidemiology, University College London, said in an interview.
The results were published online Aug. 19, 2021, in the BMJ.
‘Work fast and hard’
Researchers assessed the association between workplace cognitive stimulation and dementia incidence in seven cohorts that included almost 108,000 men and women (mean age, 44.6 years). All were free of dementia at baseline.
Participants included civil servants, public sector employees, forestry workers, and others from the general working population.
Investigators separated the participants into three categories of workplace cognitive stimulation: “high,” which referred to both high job demand and high job control; “low,” which referred to low demands and low control; and “medium,” which referred to all other combinations of job demand and job control.
“Highly cognitively stimulating jobs require you to work fast and hard, learn new things, be creative, and have a high level of skill,” said Dr. Kivimäki.
The researchers controlled for low education, hypertension, smoking, obesity, depression, physical inactivity, diabetes, low social contact, excessive alcohol consumption, and traumatic brain injury. These represent 10 of the 12 dementia risk factors named by the 2020 Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention as having convincing evidence, Dr. Kivimäki noted.
Although the investigators had no data on the other two risk factors of hearing loss and air pollution, these are unlikely to be confounding factors, he said.
Follow-up for incident dementia varied from 13.7 to 30.1 years, depending on the cohort, and was 16.7 years in the total patient population. The mean age at dementia onset was 71.2 years.
Benefits across the life course
Results showed that incident dementia per 10,000 person years was 7.3 in the low–cognitive stimulation group and 4.8 in the high-stimulation group, for a difference of 2.5.
“These differences were relatively small because the incidence of dementia in this relatively young population was low,” Dr. Kivimäki said.
Compared with those with low stimulation, the adjusted hazard ratio for dementia for this with high stimulation was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.65-0.92).
The results were similar for men and women, and for those younger and older than 60 years. However, the link between workplace cognitive stimulation appeared stronger for Alzheimer’s disease than for other dementias.
There also appeared to be additive effects of higher cognitive stimulation in both childhood, as indicated by higher educational attainment, and adulthood, based on work characteristics, said Dr. Kivimäki.
“These findings support the benefits of cognitive stimulation across the life course, with education leading to higher peak cognitive performance and cognitive stimulation at work lowering age-related cognitive decline,” he added.
The findings don’t seem to be the result of workers with cognitive impairment remaining in unchallenging jobs, he noted. Separate analyses showed lower dementia incidence even when 10 years or more separated the assessment of cognitive stimulation and the dementia diagnosis.
“This suggests that the findings are unlikely to be biased due to reverse causation,” Dr. Kivimäki said.
Possible mechanism
Findings were similar when the researchers assessed effect from job changes. “This is probably because people in highly stimulating jobs are more likely to change to another highly stimulating job than to a low-stimulating job,” said Dr. Kivimäki. “Similarly, people with less stimulating jobs are seldom able to change to a substantially more stimulating job.”
As a dementia risk factor, low workplace stimulation is comparable with high alcohol intake and physical inactivity, but is weaker than education, diabetes, smoking, hypertension, and obesity, Dr. Kivimäki noted.
When asked about individuals with less cognitively stimulating jobs who are enormously stimulated outside work, he said that “previous large-scale studies have failed to find evidence that leisure time cognitive activity would significantly reduce risk of dementia.”
To explore potential underlying mechanisms, the investigators examined almost 5,000 plasma proteins in more than 2,200 individuals from one cohort in the Whitehall II study. They found six proteins were significantly lower among participants with high versus low cognitive stimulation.
In another analysis that included more than 13,500 participants from the Whitehall and another cohort, higher levels of three of these plasma proteins were associated with increased dementia risk – or conversely, lower protein levels with lower dementia risk.
The findings suggest a “novel plausible explanation” for the link between workplace cognitive stimulation and dementia risk, said Dr. Kivimäki.
He noted that higher levels of certain proteins prevent brain cells from forming new connections.
‘Some of the most compelling evidence to date’
In an accompanying editorial, Serhiy Dekhtyar, PhD, assistant professor (Docent), Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, noted that the study is “an important piece of work” and “some of the most compelling evidence to date” on the role of occupational cognitive stimulation in dementia risk.
The large-scale investigation in multiple cohorts and contexts has “advanced the field” and could help “explain previously mixed findings in the literature,” Dekhtyar said in an interview.
Importantly, the researchers provide “an indication of biological mechanisms potentially connecting work mental stimulation and dementia,” he added.
However, Dr. Dekhtyar noted that the difference of 2.5 incident cases of dementia per 10,000 person years of follow-up between the low and high mental-stimulation groups “is not especially large” – although it is comparable with other established risk factors for dementia.
He suspects the effect size would have been larger had the follow-up for dementia been longer.
Dr. Dekhtyar also raised the possibility that “innate cognition” might affect both educational and occupational attainment, and the subsequent dementia risk.
“Without taking this into account, we may inadvertently conclude that education or occupational stimulation help differentially preserve cognition into late life – when in reality, it may be initial differences in cognitive ability that are preserved throughout life,” he concluded.
Funding sources for the study included Nordic Research Programme on Health and Welfare (NordForsk), Medical Research Council, Wellcome Trust, Academy of Finland, and Helsinki Institute of Life Science. Dr. Kivimäki has received support from NordForsk, the UK Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, the Academy of Finland, and the Helsinki Institute of Life Science. Dr. Dekhtyar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CRP as a biomarker for community-acquired pneumonia
Background: In the United States, CAP was responsible for nearly 50,000 deaths in 2017. Prompt and accurate diagnosis promotes early treatment and avoids unnecessary antibiotic treatment for nonpneumonia lower respiratory tract infection patients. Diagnosis is based on signs and symptoms, as well as available imaging. Inflammatory markers such as CRP, white blood cell count, and procalcitonin are readily available in the ED and outpatient settings.
Study design: Bivariate meta-analysis.
Setting: A systematic review of literature was done via PubMed search to identify prospective studies evaluating the accuracy of biomarkers in patients with cough or suspected CAP.
Synopsis: Fourteen studies met the criteria to be included in the meta-analysis. Summary receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves generated reported area under the curve of 0.802 for CRP (95% confidence interval, 0.78-0.85), 0.777 for leukocytosis (95% CI, 0.74-0.81), and 0.771 for procalcitonin (95% CI, 0.74-0.81). The combination of CRP greater than 49.5 mg/L and procalcitonin greater than 0.1 mcg/L had a positive likelihood ratio of 2.24 and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.44.
The study had a some of limitations. The blinding of the person performing the index test to the reference standard and vice versa was not clear. Further, it was unclear if the person interpreting the reference standard was blinded to the index test in five studies and absent in one. Other limitations were inconsistent reporting of abnormal post hoc cutoffs and only two biomarkers being reported in a single study.
Combining a biomarker with signs and symptoms has the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy in the outpatient setting further. CRP was found to be most accurate regardless of the cutoff used; however, further studies without threshold effect will prove beneficial.
Bottom line: CRP is a more accurate and useful biomarker for outpatient CAP diagnosis than procalcitonin or leukocytosis.
Citation: Ebell MH et al. Accuracy of biomarkers for the diagnosis of adult community-acquired pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(3):195-206.
Dr. Castellanos is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: In the United States, CAP was responsible for nearly 50,000 deaths in 2017. Prompt and accurate diagnosis promotes early treatment and avoids unnecessary antibiotic treatment for nonpneumonia lower respiratory tract infection patients. Diagnosis is based on signs and symptoms, as well as available imaging. Inflammatory markers such as CRP, white blood cell count, and procalcitonin are readily available in the ED and outpatient settings.
Study design: Bivariate meta-analysis.
Setting: A systematic review of literature was done via PubMed search to identify prospective studies evaluating the accuracy of biomarkers in patients with cough or suspected CAP.
Synopsis: Fourteen studies met the criteria to be included in the meta-analysis. Summary receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves generated reported area under the curve of 0.802 for CRP (95% confidence interval, 0.78-0.85), 0.777 for leukocytosis (95% CI, 0.74-0.81), and 0.771 for procalcitonin (95% CI, 0.74-0.81). The combination of CRP greater than 49.5 mg/L and procalcitonin greater than 0.1 mcg/L had a positive likelihood ratio of 2.24 and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.44.
The study had a some of limitations. The blinding of the person performing the index test to the reference standard and vice versa was not clear. Further, it was unclear if the person interpreting the reference standard was blinded to the index test in five studies and absent in one. Other limitations were inconsistent reporting of abnormal post hoc cutoffs and only two biomarkers being reported in a single study.
Combining a biomarker with signs and symptoms has the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy in the outpatient setting further. CRP was found to be most accurate regardless of the cutoff used; however, further studies without threshold effect will prove beneficial.
Bottom line: CRP is a more accurate and useful biomarker for outpatient CAP diagnosis than procalcitonin or leukocytosis.
Citation: Ebell MH et al. Accuracy of biomarkers for the diagnosis of adult community-acquired pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(3):195-206.
Dr. Castellanos is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: In the United States, CAP was responsible for nearly 50,000 deaths in 2017. Prompt and accurate diagnosis promotes early treatment and avoids unnecessary antibiotic treatment for nonpneumonia lower respiratory tract infection patients. Diagnosis is based on signs and symptoms, as well as available imaging. Inflammatory markers such as CRP, white blood cell count, and procalcitonin are readily available in the ED and outpatient settings.
Study design: Bivariate meta-analysis.
Setting: A systematic review of literature was done via PubMed search to identify prospective studies evaluating the accuracy of biomarkers in patients with cough or suspected CAP.
Synopsis: Fourteen studies met the criteria to be included in the meta-analysis. Summary receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves generated reported area under the curve of 0.802 for CRP (95% confidence interval, 0.78-0.85), 0.777 for leukocytosis (95% CI, 0.74-0.81), and 0.771 for procalcitonin (95% CI, 0.74-0.81). The combination of CRP greater than 49.5 mg/L and procalcitonin greater than 0.1 mcg/L had a positive likelihood ratio of 2.24 and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.44.
The study had a some of limitations. The blinding of the person performing the index test to the reference standard and vice versa was not clear. Further, it was unclear if the person interpreting the reference standard was blinded to the index test in five studies and absent in one. Other limitations were inconsistent reporting of abnormal post hoc cutoffs and only two biomarkers being reported in a single study.
Combining a biomarker with signs and symptoms has the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy in the outpatient setting further. CRP was found to be most accurate regardless of the cutoff used; however, further studies without threshold effect will prove beneficial.
Bottom line: CRP is a more accurate and useful biomarker for outpatient CAP diagnosis than procalcitonin or leukocytosis.
Citation: Ebell MH et al. Accuracy of biomarkers for the diagnosis of adult community-acquired pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(3):195-206.
Dr. Castellanos is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Review eyes nail unit toxicities secondary to targeted cancer therapy
while damage to other nail unit anatomic areas can be wide-ranging.
Those are key findings from an evidence-based literature review published on July 21, 2021, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, as a letter to the editor. “Dermatologic toxicities are often the earliest-presenting and highest-incidence adverse events due to targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies,” corresponding author Anisha B. Patel, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues wrote. “Nail unit toxicities due to immunotherapy are caused by nonspecific immune activation. Targeted therapies, particularly mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibitors, lead to epidermal thinning of the nail folds and periungual tissue, increasing susceptibility to trauma and penetration by nail plate fragments. Although cutaneous toxicities have been well described, further characterization of nail unit toxicities is needed.”
The researchers searched the PubMed database using the terms nail, nail toxicity, nail dystrophy, paronychia, onycholysis, pyogenic granuloma, onychopathy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, and reviewed relevant articles for clinical presentation, diagnosis, incidence, outcomes, and references. They also proposed treatment algorithms for this patient population based on the existing literature and the authors’ collective clinical experience.
Dr. Patel and colleagues found that paronychia and periungual pyogenic granulomas were the most common nail unit toxicities caused by targeted therapy. “Damage to other nail unit anatomic areas includes drug induced or exacerbated lichen planus and psoriasis as well as pigmentary and neoplastic changes,” they wrote. “Onycholysis, onychoschizia, paronychia, psoriasis, lichen planus, and dermatomyositis have been reported with immune checkpoint inhibitors,” with the time of onset during the first week of treatment to several months after treatment has started.
According to National Cancer Institute criteria, nail adverse events associated with medical treatment include nail changes, discoloration, ridging, paronychia, and infection. The severity of nail loss, paronychia, and infection can be graded up to 3 (defined as “severe or medically significant but not life threatening”), while the remainder of nail toxicities may be categorized only as grade 1 (defined as “mild,” with “intervention not indicated”). “High-grade toxicities have been reported, especially with pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors,” the authors wrote, referring to a previous study.
The review includes treatment algorithms for paronychia, periungual pyogenic granuloma, nail lichen planus, and psoriasis. “Long-acting and nonselective immunosuppressants are reserved for dose-limiting toxicities, given their unknown effects on already-immunosuppressed patients with cancer and on cancer therapy,” the authors wrote. “A discussion with the oncology department is essential before starting an immunomodulator or immunosuppressant.”
To manage onycholysis, Dr. Patel and colleagues recommended trimming the onycholytic nail plate to its attachment point. “Partial avulsion is used to treat a refractory abscess or painful hemorrhage,” they wrote. “A Pseudomonas superinfection is treated twice daily with a topical antibiotic solution. Brittle nail syndrome is managed with emollients or the application of polyureaurethane, a 16% nail solution, or a hydrosoluble nail lacquer,” they wrote, adding that biotin supplementation is not recommended.
Jonathan Leventhal, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that nail toxicity from targeted cancer therapy is one of the most common reasons for consultation in his role as director of the Yale University oncodermatology program at Smilow Cancer Hospital, New Haven, Conn. “When severe, these reactions frequently impact patients’ quality of life,” he said.
“This study is helpful for all dermatologists caring for cancer patients,” with strengths that include “succinctly summarizing the most prevalent conditions and providing a clear and practical algorithm for approaching these nail toxicities,” he said. In addition to targeted agents and immunotherapy, “we commonly see nail toxicities from cytotoxic chemotherapy, which was not reviewed in this paper. Multidisciplinary evaluation and dermatologic involvement is certainly beneficial to make accurate diagnoses and promptly manage these conditions, helping patients stay on their oncologic therapies.”
The researchers reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Leventhal disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Regeneron, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and La Roche–Posay. He has also received research funding from Azitra and OnQuality.
while damage to other nail unit anatomic areas can be wide-ranging.
Those are key findings from an evidence-based literature review published on July 21, 2021, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, as a letter to the editor. “Dermatologic toxicities are often the earliest-presenting and highest-incidence adverse events due to targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies,” corresponding author Anisha B. Patel, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues wrote. “Nail unit toxicities due to immunotherapy are caused by nonspecific immune activation. Targeted therapies, particularly mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibitors, lead to epidermal thinning of the nail folds and periungual tissue, increasing susceptibility to trauma and penetration by nail plate fragments. Although cutaneous toxicities have been well described, further characterization of nail unit toxicities is needed.”
The researchers searched the PubMed database using the terms nail, nail toxicity, nail dystrophy, paronychia, onycholysis, pyogenic granuloma, onychopathy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, and reviewed relevant articles for clinical presentation, diagnosis, incidence, outcomes, and references. They also proposed treatment algorithms for this patient population based on the existing literature and the authors’ collective clinical experience.
Dr. Patel and colleagues found that paronychia and periungual pyogenic granulomas were the most common nail unit toxicities caused by targeted therapy. “Damage to other nail unit anatomic areas includes drug induced or exacerbated lichen planus and psoriasis as well as pigmentary and neoplastic changes,” they wrote. “Onycholysis, onychoschizia, paronychia, psoriasis, lichen planus, and dermatomyositis have been reported with immune checkpoint inhibitors,” with the time of onset during the first week of treatment to several months after treatment has started.
According to National Cancer Institute criteria, nail adverse events associated with medical treatment include nail changes, discoloration, ridging, paronychia, and infection. The severity of nail loss, paronychia, and infection can be graded up to 3 (defined as “severe or medically significant but not life threatening”), while the remainder of nail toxicities may be categorized only as grade 1 (defined as “mild,” with “intervention not indicated”). “High-grade toxicities have been reported, especially with pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors,” the authors wrote, referring to a previous study.
The review includes treatment algorithms for paronychia, periungual pyogenic granuloma, nail lichen planus, and psoriasis. “Long-acting and nonselective immunosuppressants are reserved for dose-limiting toxicities, given their unknown effects on already-immunosuppressed patients with cancer and on cancer therapy,” the authors wrote. “A discussion with the oncology department is essential before starting an immunomodulator or immunosuppressant.”
To manage onycholysis, Dr. Patel and colleagues recommended trimming the onycholytic nail plate to its attachment point. “Partial avulsion is used to treat a refractory abscess or painful hemorrhage,” they wrote. “A Pseudomonas superinfection is treated twice daily with a topical antibiotic solution. Brittle nail syndrome is managed with emollients or the application of polyureaurethane, a 16% nail solution, or a hydrosoluble nail lacquer,” they wrote, adding that biotin supplementation is not recommended.
Jonathan Leventhal, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that nail toxicity from targeted cancer therapy is one of the most common reasons for consultation in his role as director of the Yale University oncodermatology program at Smilow Cancer Hospital, New Haven, Conn. “When severe, these reactions frequently impact patients’ quality of life,” he said.
“This study is helpful for all dermatologists caring for cancer patients,” with strengths that include “succinctly summarizing the most prevalent conditions and providing a clear and practical algorithm for approaching these nail toxicities,” he said. In addition to targeted agents and immunotherapy, “we commonly see nail toxicities from cytotoxic chemotherapy, which was not reviewed in this paper. Multidisciplinary evaluation and dermatologic involvement is certainly beneficial to make accurate diagnoses and promptly manage these conditions, helping patients stay on their oncologic therapies.”
The researchers reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Leventhal disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Regeneron, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and La Roche–Posay. He has also received research funding from Azitra and OnQuality.
while damage to other nail unit anatomic areas can be wide-ranging.
Those are key findings from an evidence-based literature review published on July 21, 2021, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, as a letter to the editor. “Dermatologic toxicities are often the earliest-presenting and highest-incidence adverse events due to targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies,” corresponding author Anisha B. Patel, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues wrote. “Nail unit toxicities due to immunotherapy are caused by nonspecific immune activation. Targeted therapies, particularly mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibitors, lead to epidermal thinning of the nail folds and periungual tissue, increasing susceptibility to trauma and penetration by nail plate fragments. Although cutaneous toxicities have been well described, further characterization of nail unit toxicities is needed.”
The researchers searched the PubMed database using the terms nail, nail toxicity, nail dystrophy, paronychia, onycholysis, pyogenic granuloma, onychopathy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, and reviewed relevant articles for clinical presentation, diagnosis, incidence, outcomes, and references. They also proposed treatment algorithms for this patient population based on the existing literature and the authors’ collective clinical experience.
Dr. Patel and colleagues found that paronychia and periungual pyogenic granulomas were the most common nail unit toxicities caused by targeted therapy. “Damage to other nail unit anatomic areas includes drug induced or exacerbated lichen planus and psoriasis as well as pigmentary and neoplastic changes,” they wrote. “Onycholysis, onychoschizia, paronychia, psoriasis, lichen planus, and dermatomyositis have been reported with immune checkpoint inhibitors,” with the time of onset during the first week of treatment to several months after treatment has started.
According to National Cancer Institute criteria, nail adverse events associated with medical treatment include nail changes, discoloration, ridging, paronychia, and infection. The severity of nail loss, paronychia, and infection can be graded up to 3 (defined as “severe or medically significant but not life threatening”), while the remainder of nail toxicities may be categorized only as grade 1 (defined as “mild,” with “intervention not indicated”). “High-grade toxicities have been reported, especially with pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors,” the authors wrote, referring to a previous study.
The review includes treatment algorithms for paronychia, periungual pyogenic granuloma, nail lichen planus, and psoriasis. “Long-acting and nonselective immunosuppressants are reserved for dose-limiting toxicities, given their unknown effects on already-immunosuppressed patients with cancer and on cancer therapy,” the authors wrote. “A discussion with the oncology department is essential before starting an immunomodulator or immunosuppressant.”
To manage onycholysis, Dr. Patel and colleagues recommended trimming the onycholytic nail plate to its attachment point. “Partial avulsion is used to treat a refractory abscess or painful hemorrhage,” they wrote. “A Pseudomonas superinfection is treated twice daily with a topical antibiotic solution. Brittle nail syndrome is managed with emollients or the application of polyureaurethane, a 16% nail solution, or a hydrosoluble nail lacquer,” they wrote, adding that biotin supplementation is not recommended.
Jonathan Leventhal, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that nail toxicity from targeted cancer therapy is one of the most common reasons for consultation in his role as director of the Yale University oncodermatology program at Smilow Cancer Hospital, New Haven, Conn. “When severe, these reactions frequently impact patients’ quality of life,” he said.
“This study is helpful for all dermatologists caring for cancer patients,” with strengths that include “succinctly summarizing the most prevalent conditions and providing a clear and practical algorithm for approaching these nail toxicities,” he said. In addition to targeted agents and immunotherapy, “we commonly see nail toxicities from cytotoxic chemotherapy, which was not reviewed in this paper. Multidisciplinary evaluation and dermatologic involvement is certainly beneficial to make accurate diagnoses and promptly manage these conditions, helping patients stay on their oncologic therapies.”
The researchers reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Leventhal disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Regeneron, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and La Roche–Posay. He has also received research funding from Azitra and OnQuality.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
US Preventive Services Task Force lowers diabetes screening age for overweight
The United States Preventive Services Task Force has updated its recommendation on the age of screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in the primary care setting – lowering the age from 40 to 35 years for asymptomatic patients who are overweight or obese and encouraging greater interventions when patients do show a risk.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes and offering or referring patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions has a moderate net benefit,” the task force concludes in its recommendation, published Aug. 24 in JAMA.
“Clinicians should offer or refer patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions,” they write.
Experts commenting on the issue strongly emphasize that it’s not just the screening, but the subsequent intervention that is needed to make a difference.
“If young adults newly identified with abnormal glucose metabolism do not receive the needed intensive behavioral change support, screening may provide no benefit,” write Richard W. Grant, MD, MPH, and colleagues in an editorial published with the recommendation.
“Given the role of our obesogenic and physically inactive society in the shift toward earlier onset of diabetes, efforts to increase screening and recognition of abnormal glucose metabolism must be coupled with robust public health measures to address the underlying contributors.”
BMI cutoff lower for at-risk ethnic populations
The recommendation, which updates the task force’s 2015 guideline, carries a “B” classification, meaning the USPSTF has high certainty that the net benefit is moderate. It now specifies screening from age 35to 70 for persons classified as overweight (body mass index at least 25) or obese (BMI at least 30) and recommends referral to preventive interventions when patients are found to have prediabetes.
In addition to recommendations of lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, the task force also endorses the diabetes drug metformin as a beneficial intervention in the prevention or delay of diabetes, while noting fewer overall health benefits from metformin than from the lifestyle changes.
A lower BMI cutoff of at least 23 is recommended for diabetes screening of Asian Americans, and, importantly, screening for prediabetes and diabetes should be considered at an even earlier age if the patient is from a population with a disproportionately high prevalence of diabetes, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Hispanic/Latino, the task force recommends.
Screening tests should include fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, or an oral glucose tolerance test. Although screening every 3 years “may be a reasonable approach for adults with normal blood glucose levels,” the task force adds that “the optimal screening interval for adults with an initial normal glucose test result is uncertain.”
Data review: Few with prediabetes know they have it
The need for the update was prompted by troubling data showing increasing diabetes rates despite early signs that can and should be identified and acted upon in the primary care setting to prevent disease progression.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for instance, show that while 13% of all U.S. adults 18 years or older have diabetes and 35% meet criteria for prediabetes, as many as 21% of those with diabetes were not aware of or did not report having the disease. Furthermore, only a small fraction – 15% of those with prediabetes – said they had been told by a health professional that they had this condition, the task force notes.
The task force’s final recommendation was based on a systematic review of evidence regarding the screening of asymptomatic, nonpregnant adults and the harms and benefits of interventions, such as physical activity, behavioral counseling, or pharmacotherapy.
Among key evidence supporting the lower age was a 2014 study showing that the number of people necessary to obtain one positive test for diabetes with screening sharply drops from 80 among those aged 30-34 years to just 31 among those aged 36-39.
Opportunistic universal screening of eligible people aged 35 and older would yield a ratio of 1 out of just 15 to spot a positive test, the authors of that study reported.
In addition, a large cohort study in more than 77,000 people with prediabetes strongly links the risk of developing diabetes with increases in A1c level and with increasing BMI.
ADA recommendations differ
The new recommendations differ from American Diabetes Association guidelines, which call for diabetes screening at all ages for people who are overweight or obese and who have one or more risk factors, such as physical inactivity or a first-degree relative with diabetes. If results are normal, repeat screening at least every 3 years is recommended.
The ADA further recommends universal screening for all adults 45 years and older, regardless of their risk factors.
For the screening of adults over 45, the ADA recommends using a fasting plasma glucose level, 2-hour plasma glucose level during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, or A1c level, regardless of risk factors.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology also recommends universal screening for prediabetes and diabetes for all adults 45 years or older, regardless of risk factors, and also advises screening those who have risk factors for diabetes regardless of age.
Screening of little benefit without behavior change support
In an interview, Dr. Grant added that broad efforts are essential as those at the practice level have clearly not succeeded.
“The medical model of individual counseling and referral has not really been effective, and so we really need to think in terms of large-scale public health action,” said Dr. Grant, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland.
His editorial details the sweeping, multifactorial efforts that are needed.
“To turn this recommendation into action – that is, to translate screening activities into improved clinical outcomes – change is needed at the patient-clinician level (recognizing and encouraging eligible individuals to be screened), health care system level (reducing screening barriers and ensuring access to robust lifestyle programs), and societal level (applying effective public health interventions to reduce obesity and increase exercise),” they write.
A top priority has to be a focus on individuals of diverse backgrounds and issues such as access to healthy programs in minority communities, Dr. Grant noted.
“Newly diagnosed adults are more likely to be African-American and Latinx,” he said.
“We really need to invest in healthier communities for low-income, non-White communities to reverse the persistent health care disparities in these communities.”
While the challenges may appear daunting, history shows they are not necessarily insurmountable – as evidenced in the campaign to discourage tobacco smoking.
“National smoking cessation efforts are one example of a mostly successful public health campaign that has made a difference in health behaviors,” Grant noted.
The recommendation is also posted on the USPSTF web site .
Dr. Grant reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force has updated its recommendation on the age of screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in the primary care setting – lowering the age from 40 to 35 years for asymptomatic patients who are overweight or obese and encouraging greater interventions when patients do show a risk.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes and offering or referring patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions has a moderate net benefit,” the task force concludes in its recommendation, published Aug. 24 in JAMA.
“Clinicians should offer or refer patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions,” they write.
Experts commenting on the issue strongly emphasize that it’s not just the screening, but the subsequent intervention that is needed to make a difference.
“If young adults newly identified with abnormal glucose metabolism do not receive the needed intensive behavioral change support, screening may provide no benefit,” write Richard W. Grant, MD, MPH, and colleagues in an editorial published with the recommendation.
“Given the role of our obesogenic and physically inactive society in the shift toward earlier onset of diabetes, efforts to increase screening and recognition of abnormal glucose metabolism must be coupled with robust public health measures to address the underlying contributors.”
BMI cutoff lower for at-risk ethnic populations
The recommendation, which updates the task force’s 2015 guideline, carries a “B” classification, meaning the USPSTF has high certainty that the net benefit is moderate. It now specifies screening from age 35to 70 for persons classified as overweight (body mass index at least 25) or obese (BMI at least 30) and recommends referral to preventive interventions when patients are found to have prediabetes.
In addition to recommendations of lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, the task force also endorses the diabetes drug metformin as a beneficial intervention in the prevention or delay of diabetes, while noting fewer overall health benefits from metformin than from the lifestyle changes.
A lower BMI cutoff of at least 23 is recommended for diabetes screening of Asian Americans, and, importantly, screening for prediabetes and diabetes should be considered at an even earlier age if the patient is from a population with a disproportionately high prevalence of diabetes, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Hispanic/Latino, the task force recommends.
Screening tests should include fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, or an oral glucose tolerance test. Although screening every 3 years “may be a reasonable approach for adults with normal blood glucose levels,” the task force adds that “the optimal screening interval for adults with an initial normal glucose test result is uncertain.”
Data review: Few with prediabetes know they have it
The need for the update was prompted by troubling data showing increasing diabetes rates despite early signs that can and should be identified and acted upon in the primary care setting to prevent disease progression.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for instance, show that while 13% of all U.S. adults 18 years or older have diabetes and 35% meet criteria for prediabetes, as many as 21% of those with diabetes were not aware of or did not report having the disease. Furthermore, only a small fraction – 15% of those with prediabetes – said they had been told by a health professional that they had this condition, the task force notes.
The task force’s final recommendation was based on a systematic review of evidence regarding the screening of asymptomatic, nonpregnant adults and the harms and benefits of interventions, such as physical activity, behavioral counseling, or pharmacotherapy.
Among key evidence supporting the lower age was a 2014 study showing that the number of people necessary to obtain one positive test for diabetes with screening sharply drops from 80 among those aged 30-34 years to just 31 among those aged 36-39.
Opportunistic universal screening of eligible people aged 35 and older would yield a ratio of 1 out of just 15 to spot a positive test, the authors of that study reported.
In addition, a large cohort study in more than 77,000 people with prediabetes strongly links the risk of developing diabetes with increases in A1c level and with increasing BMI.
ADA recommendations differ
The new recommendations differ from American Diabetes Association guidelines, which call for diabetes screening at all ages for people who are overweight or obese and who have one or more risk factors, such as physical inactivity or a first-degree relative with diabetes. If results are normal, repeat screening at least every 3 years is recommended.
The ADA further recommends universal screening for all adults 45 years and older, regardless of their risk factors.
For the screening of adults over 45, the ADA recommends using a fasting plasma glucose level, 2-hour plasma glucose level during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, or A1c level, regardless of risk factors.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology also recommends universal screening for prediabetes and diabetes for all adults 45 years or older, regardless of risk factors, and also advises screening those who have risk factors for diabetes regardless of age.
Screening of little benefit without behavior change support
In an interview, Dr. Grant added that broad efforts are essential as those at the practice level have clearly not succeeded.
“The medical model of individual counseling and referral has not really been effective, and so we really need to think in terms of large-scale public health action,” said Dr. Grant, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland.
His editorial details the sweeping, multifactorial efforts that are needed.
“To turn this recommendation into action – that is, to translate screening activities into improved clinical outcomes – change is needed at the patient-clinician level (recognizing and encouraging eligible individuals to be screened), health care system level (reducing screening barriers and ensuring access to robust lifestyle programs), and societal level (applying effective public health interventions to reduce obesity and increase exercise),” they write.
A top priority has to be a focus on individuals of diverse backgrounds and issues such as access to healthy programs in minority communities, Dr. Grant noted.
“Newly diagnosed adults are more likely to be African-American and Latinx,” he said.
“We really need to invest in healthier communities for low-income, non-White communities to reverse the persistent health care disparities in these communities.”
While the challenges may appear daunting, history shows they are not necessarily insurmountable – as evidenced in the campaign to discourage tobacco smoking.
“National smoking cessation efforts are one example of a mostly successful public health campaign that has made a difference in health behaviors,” Grant noted.
The recommendation is also posted on the USPSTF web site .
Dr. Grant reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force has updated its recommendation on the age of screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in the primary care setting – lowering the age from 40 to 35 years for asymptomatic patients who are overweight or obese and encouraging greater interventions when patients do show a risk.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes and offering or referring patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions has a moderate net benefit,” the task force concludes in its recommendation, published Aug. 24 in JAMA.
“Clinicians should offer or refer patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions,” they write.
Experts commenting on the issue strongly emphasize that it’s not just the screening, but the subsequent intervention that is needed to make a difference.
“If young adults newly identified with abnormal glucose metabolism do not receive the needed intensive behavioral change support, screening may provide no benefit,” write Richard W. Grant, MD, MPH, and colleagues in an editorial published with the recommendation.
“Given the role of our obesogenic and physically inactive society in the shift toward earlier onset of diabetes, efforts to increase screening and recognition of abnormal glucose metabolism must be coupled with robust public health measures to address the underlying contributors.”
BMI cutoff lower for at-risk ethnic populations
The recommendation, which updates the task force’s 2015 guideline, carries a “B” classification, meaning the USPSTF has high certainty that the net benefit is moderate. It now specifies screening from age 35to 70 for persons classified as overweight (body mass index at least 25) or obese (BMI at least 30) and recommends referral to preventive interventions when patients are found to have prediabetes.
In addition to recommendations of lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, the task force also endorses the diabetes drug metformin as a beneficial intervention in the prevention or delay of diabetes, while noting fewer overall health benefits from metformin than from the lifestyle changes.
A lower BMI cutoff of at least 23 is recommended for diabetes screening of Asian Americans, and, importantly, screening for prediabetes and diabetes should be considered at an even earlier age if the patient is from a population with a disproportionately high prevalence of diabetes, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Hispanic/Latino, the task force recommends.
Screening tests should include fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, or an oral glucose tolerance test. Although screening every 3 years “may be a reasonable approach for adults with normal blood glucose levels,” the task force adds that “the optimal screening interval for adults with an initial normal glucose test result is uncertain.”
Data review: Few with prediabetes know they have it
The need for the update was prompted by troubling data showing increasing diabetes rates despite early signs that can and should be identified and acted upon in the primary care setting to prevent disease progression.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for instance, show that while 13% of all U.S. adults 18 years or older have diabetes and 35% meet criteria for prediabetes, as many as 21% of those with diabetes were not aware of or did not report having the disease. Furthermore, only a small fraction – 15% of those with prediabetes – said they had been told by a health professional that they had this condition, the task force notes.
The task force’s final recommendation was based on a systematic review of evidence regarding the screening of asymptomatic, nonpregnant adults and the harms and benefits of interventions, such as physical activity, behavioral counseling, or pharmacotherapy.
Among key evidence supporting the lower age was a 2014 study showing that the number of people necessary to obtain one positive test for diabetes with screening sharply drops from 80 among those aged 30-34 years to just 31 among those aged 36-39.
Opportunistic universal screening of eligible people aged 35 and older would yield a ratio of 1 out of just 15 to spot a positive test, the authors of that study reported.
In addition, a large cohort study in more than 77,000 people with prediabetes strongly links the risk of developing diabetes with increases in A1c level and with increasing BMI.
ADA recommendations differ
The new recommendations differ from American Diabetes Association guidelines, which call for diabetes screening at all ages for people who are overweight or obese and who have one or more risk factors, such as physical inactivity or a first-degree relative with diabetes. If results are normal, repeat screening at least every 3 years is recommended.
The ADA further recommends universal screening for all adults 45 years and older, regardless of their risk factors.
For the screening of adults over 45, the ADA recommends using a fasting plasma glucose level, 2-hour plasma glucose level during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, or A1c level, regardless of risk factors.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology also recommends universal screening for prediabetes and diabetes for all adults 45 years or older, regardless of risk factors, and also advises screening those who have risk factors for diabetes regardless of age.
Screening of little benefit without behavior change support
In an interview, Dr. Grant added that broad efforts are essential as those at the practice level have clearly not succeeded.
“The medical model of individual counseling and referral has not really been effective, and so we really need to think in terms of large-scale public health action,” said Dr. Grant, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland.
His editorial details the sweeping, multifactorial efforts that are needed.
“To turn this recommendation into action – that is, to translate screening activities into improved clinical outcomes – change is needed at the patient-clinician level (recognizing and encouraging eligible individuals to be screened), health care system level (reducing screening barriers and ensuring access to robust lifestyle programs), and societal level (applying effective public health interventions to reduce obesity and increase exercise),” they write.
A top priority has to be a focus on individuals of diverse backgrounds and issues such as access to healthy programs in minority communities, Dr. Grant noted.
“Newly diagnosed adults are more likely to be African-American and Latinx,” he said.
“We really need to invest in healthier communities for low-income, non-White communities to reverse the persistent health care disparities in these communities.”
While the challenges may appear daunting, history shows they are not necessarily insurmountable – as evidenced in the campaign to discourage tobacco smoking.
“National smoking cessation efforts are one example of a mostly successful public health campaign that has made a difference in health behaviors,” Grant noted.
The recommendation is also posted on the USPSTF web site .
Dr. Grant reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
FROM JAMA