User login
Pelvic organ prolapse surgery isn’t as ‘simple’ as you think
LAS VEGAS – Surgical repair of pelvic organ prolapse often may seem like an uncomplicated procedure. But many factors play roles into decisions, and surgeons around the world vary widely in how they handle the operations, Mark D. Walters, MD, told colleagues at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
“These prolapse repairs seem relatively simple at first, but they’re not simple at all,” he said.
Questions to ask prior to surgery
It’s important to first answer a number of questions, said Dr. Walters, professor and vice-chair of gynecology at the Cleveland Clinic. “When you see a patient like this, you may not realize how many decisions you’re making.”
These questions include:
- Is the patient sexually active or planning to be?
- Has she had a hysterectomy, and or is one necessary? If so, how should it be done? What does the patient think about a hysterectomy?
- Should the prolapse procedure be performed vaginally, open, laparoscopically, or robotically?
- Is adding a graft advisable? What kind?
- Should there be a sling to prevent stress urinary incontinence?”
Worldwide differences in surgical technique choice
Dr. Walters talked to colleagues from several nations and learned about these variations in surgical techniques.
Chinese surgeons use a variety of techniques with transvaginal mesh (TVM). Their use is more common in more populated cities because of the effect of medical education; native tissue procedures are more common in less-populated regions that are considered “backward.”
TVM with hysteropexy (“apical sling”) also is common in Latin America, while Middle Eastern surgeons have little training in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery.
In Europe, France embraces mesh surgery and laparoscopy, while the United Kingdom has “completely abandoned” mesh surgery, and the Netherlands rarely uses it in favor of vaginal procedures.
In the United States, he said, TVM is “discouraged” while a variety of other procedures are used.
What procedures should surgeons embrace? There are many topics of debate, Dr. Walters said, including type of transvaginal repair (native tissue or mesh-augmented or sacrocolpopexy?), repair of “defects” in the vagina (even if they’re nonsymptomatic?) and the removal of the uterus (yes or no?).
Dr. Walters pointed to several explanations for this variation, including lack of high-quality research, confirmation bias, economic conflicts – surgeons are in the business of surgery, after all – and lack of insight into what women prefer.
Consider patient choice
In a survey, Dr. Walters polled women in their 50s with this question: “How much do you value your uterus?” Three women, he said, had widely varied opinions on a scale of 1-10, with one at 10 and another at 0.
“A doctor doesn’t know this and doesn’t have a way to ask, and the doctor has [his/her] own opinion about the value of the uterus,” he said. “Shouldn’t we know what patients think?”
How to measure success
He offered these tips about measuring success:
- Focus on symptomatic cure more than clinical cure.
- Remember that perfect anatomic support isn’t linked to health-related quality of life, and some loss of anatomic support is normal.
- Understand that commonly used definitions of anatomic success often aren’t clinically relevant.
Dr. Walters’ disclosures: royalties (Elsevier, UpToDate), website/lecturer (International Academy of Pelvic Surgery), and website editor (Foundation for Female Health Awareness).
This meeting was jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
LAS VEGAS – Surgical repair of pelvic organ prolapse often may seem like an uncomplicated procedure. But many factors play roles into decisions, and surgeons around the world vary widely in how they handle the operations, Mark D. Walters, MD, told colleagues at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
“These prolapse repairs seem relatively simple at first, but they’re not simple at all,” he said.
Questions to ask prior to surgery
It’s important to first answer a number of questions, said Dr. Walters, professor and vice-chair of gynecology at the Cleveland Clinic. “When you see a patient like this, you may not realize how many decisions you’re making.”
These questions include:
- Is the patient sexually active or planning to be?
- Has she had a hysterectomy, and or is one necessary? If so, how should it be done? What does the patient think about a hysterectomy?
- Should the prolapse procedure be performed vaginally, open, laparoscopically, or robotically?
- Is adding a graft advisable? What kind?
- Should there be a sling to prevent stress urinary incontinence?”
Worldwide differences in surgical technique choice
Dr. Walters talked to colleagues from several nations and learned about these variations in surgical techniques.
Chinese surgeons use a variety of techniques with transvaginal mesh (TVM). Their use is more common in more populated cities because of the effect of medical education; native tissue procedures are more common in less-populated regions that are considered “backward.”
TVM with hysteropexy (“apical sling”) also is common in Latin America, while Middle Eastern surgeons have little training in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery.
In Europe, France embraces mesh surgery and laparoscopy, while the United Kingdom has “completely abandoned” mesh surgery, and the Netherlands rarely uses it in favor of vaginal procedures.
In the United States, he said, TVM is “discouraged” while a variety of other procedures are used.
What procedures should surgeons embrace? There are many topics of debate, Dr. Walters said, including type of transvaginal repair (native tissue or mesh-augmented or sacrocolpopexy?), repair of “defects” in the vagina (even if they’re nonsymptomatic?) and the removal of the uterus (yes or no?).
Dr. Walters pointed to several explanations for this variation, including lack of high-quality research, confirmation bias, economic conflicts – surgeons are in the business of surgery, after all – and lack of insight into what women prefer.
Consider patient choice
In a survey, Dr. Walters polled women in their 50s with this question: “How much do you value your uterus?” Three women, he said, had widely varied opinions on a scale of 1-10, with one at 10 and another at 0.
“A doctor doesn’t know this and doesn’t have a way to ask, and the doctor has [his/her] own opinion about the value of the uterus,” he said. “Shouldn’t we know what patients think?”
How to measure success
He offered these tips about measuring success:
- Focus on symptomatic cure more than clinical cure.
- Remember that perfect anatomic support isn’t linked to health-related quality of life, and some loss of anatomic support is normal.
- Understand that commonly used definitions of anatomic success often aren’t clinically relevant.
Dr. Walters’ disclosures: royalties (Elsevier, UpToDate), website/lecturer (International Academy of Pelvic Surgery), and website editor (Foundation for Female Health Awareness).
This meeting was jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
LAS VEGAS – Surgical repair of pelvic organ prolapse often may seem like an uncomplicated procedure. But many factors play roles into decisions, and surgeons around the world vary widely in how they handle the operations, Mark D. Walters, MD, told colleagues at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
“These prolapse repairs seem relatively simple at first, but they’re not simple at all,” he said.
Questions to ask prior to surgery
It’s important to first answer a number of questions, said Dr. Walters, professor and vice-chair of gynecology at the Cleveland Clinic. “When you see a patient like this, you may not realize how many decisions you’re making.”
These questions include:
- Is the patient sexually active or planning to be?
- Has she had a hysterectomy, and or is one necessary? If so, how should it be done? What does the patient think about a hysterectomy?
- Should the prolapse procedure be performed vaginally, open, laparoscopically, or robotically?
- Is adding a graft advisable? What kind?
- Should there be a sling to prevent stress urinary incontinence?”
Worldwide differences in surgical technique choice
Dr. Walters talked to colleagues from several nations and learned about these variations in surgical techniques.
Chinese surgeons use a variety of techniques with transvaginal mesh (TVM). Their use is more common in more populated cities because of the effect of medical education; native tissue procedures are more common in less-populated regions that are considered “backward.”
TVM with hysteropexy (“apical sling”) also is common in Latin America, while Middle Eastern surgeons have little training in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery.
In Europe, France embraces mesh surgery and laparoscopy, while the United Kingdom has “completely abandoned” mesh surgery, and the Netherlands rarely uses it in favor of vaginal procedures.
In the United States, he said, TVM is “discouraged” while a variety of other procedures are used.
What procedures should surgeons embrace? There are many topics of debate, Dr. Walters said, including type of transvaginal repair (native tissue or mesh-augmented or sacrocolpopexy?), repair of “defects” in the vagina (even if they’re nonsymptomatic?) and the removal of the uterus (yes or no?).
Dr. Walters pointed to several explanations for this variation, including lack of high-quality research, confirmation bias, economic conflicts – surgeons are in the business of surgery, after all – and lack of insight into what women prefer.
Consider patient choice
In a survey, Dr. Walters polled women in their 50s with this question: “How much do you value your uterus?” Three women, he said, had widely varied opinions on a scale of 1-10, with one at 10 and another at 0.
“A doctor doesn’t know this and doesn’t have a way to ask, and the doctor has [his/her] own opinion about the value of the uterus,” he said. “Shouldn’t we know what patients think?”
How to measure success
He offered these tips about measuring success:
- Focus on symptomatic cure more than clinical cure.
- Remember that perfect anatomic support isn’t linked to health-related quality of life, and some loss of anatomic support is normal.
- Understand that commonly used definitions of anatomic success often aren’t clinically relevant.
Dr. Walters’ disclosures: royalties (Elsevier, UpToDate), website/lecturer (International Academy of Pelvic Surgery), and website editor (Foundation for Female Health Awareness).
This meeting was jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PAGS 2019
Can insulin plus metformin improve pregnancy outcomes in women with type 2 diabetes?
WASHINGTON – Insulin is the preferred agent for type 2 diabetes in pregnant women, yet about a third of pregnancies still have an adverse outcome, according Kim Boggess, MD, who spoke at the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America.
“We are not where we need to be,” said Dr. Boggess, who is leading a trial that brings metformin, the first-line agent for type 2 diabetes outside of pregnancy, back into the picture for pregnant women – as an add-on to insulin.
It is an interesting twist, because pregnant women taking metformin for preexisting type 2 or gestational diabetes have been shown in some studies to require supplemental insulin, more than occasionally, to achieve target glycemic control.
This was the case in a small, randomized, controlled trial at Dr. Boggess’ institution, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, in which 43% of pregnant women with type 2 diabetes who were assigned to metformin required supplemental insulin (Am J Perinatol. 2013;30[6]:483-90). (0% vs. 36%, respectively) and fewer reports of glucose values less than 60 mg/dL (7.1% vs. 50%).
“I don’t consider this [need for supplemental insulin] ‘metformin failure,’ because studies that use metformin as monotherapy and that [show some patients] ultimately requiring insulin support ... also show that these women need less insulin,” she said. “What’s the risk of insulin alone? Hypoglycemia. So using less insulin could be a good thing.”
Other research suggests there may be less maternal weight gain, less neonatal hypoglycemia, fewer neonatal complications, and improved maternal glycemic control in patients treated with metformin, alone or with add-on insulin, than with insulin alone. “We’re starting to get a sense in the literature that, at least in the [pregnant] population with type 2 diabetes, there may be a role for metformin,” said Dr. Boggess, professor and program director for maternal-fetal medicine at the university.
Currently, the multisite MOMPOD trial (Medical Optimization of Management of T2DM Complicating Pregnancy) is randomizing 950 women to insulin plus 1,000 mg metformin twice daily or insulin plus placebo. The primary outcome of the trial is a composite of pregnancy loss, preterm birth, birth injury, neonatal hypoglycemia, or hyperbilirubinemia. Infant fat mass (within 72 hours of birth) is a secondary outcome, along with maternal safety and maternal side effects.
The MiTy (Metformin in Women with T2DM in Pregnancy) trial in Canada, with similar randomization arms and outcomes measures, is completed and undergoing analysis. “Hopefully we’ll [soon] be able to say whether the addition of adjuvant metformin to insulin to treat type 2 diabetes brings the perinatal adverse outcome rate down from 30%,” said Dr. Boggess.
Metformin is the recommended first-line agent for type 2 diabetes in nonpregnant adults. But during pregnancy, insulin, which does not cross the placenta, is the preferred agent, according to recommendations of the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, she noted. Lingering in the background is the fact that the long-term effects of in utero metformin exposure on offspring – and of exposure to any oral hypoglycemic agent – are unknown, she said*
A majority of the adverse pregnancy outcomes that occur in the context of type 2 diabetes involve macrosomia. “It’s a big deal,” Dr. Boggess said, that results in numerous maternal and infant risks and complications. “We also know that the in utero environment that contributes to, or causes, macrosomia predisposes to childhood obesity and obesity later on.”
Diabetes is the “leading risk factor” for adverse pregnancy outcomes today, said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers distinguished professor and dean of the University of Maryland School of Medicine. In the United States, 11% of women aged 20 years and older have diabetes, and the disease affects more than 1% of all pregnancies, he said.
The MOMPOD trial is sponsored by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Boggess reported no conflicts of interest.
* This article was updated 1/2/2020.
WASHINGTON – Insulin is the preferred agent for type 2 diabetes in pregnant women, yet about a third of pregnancies still have an adverse outcome, according Kim Boggess, MD, who spoke at the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America.
“We are not where we need to be,” said Dr. Boggess, who is leading a trial that brings metformin, the first-line agent for type 2 diabetes outside of pregnancy, back into the picture for pregnant women – as an add-on to insulin.
It is an interesting twist, because pregnant women taking metformin for preexisting type 2 or gestational diabetes have been shown in some studies to require supplemental insulin, more than occasionally, to achieve target glycemic control.
This was the case in a small, randomized, controlled trial at Dr. Boggess’ institution, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, in which 43% of pregnant women with type 2 diabetes who were assigned to metformin required supplemental insulin (Am J Perinatol. 2013;30[6]:483-90). (0% vs. 36%, respectively) and fewer reports of glucose values less than 60 mg/dL (7.1% vs. 50%).
“I don’t consider this [need for supplemental insulin] ‘metformin failure,’ because studies that use metformin as monotherapy and that [show some patients] ultimately requiring insulin support ... also show that these women need less insulin,” she said. “What’s the risk of insulin alone? Hypoglycemia. So using less insulin could be a good thing.”
Other research suggests there may be less maternal weight gain, less neonatal hypoglycemia, fewer neonatal complications, and improved maternal glycemic control in patients treated with metformin, alone or with add-on insulin, than with insulin alone. “We’re starting to get a sense in the literature that, at least in the [pregnant] population with type 2 diabetes, there may be a role for metformin,” said Dr. Boggess, professor and program director for maternal-fetal medicine at the university.
Currently, the multisite MOMPOD trial (Medical Optimization of Management of T2DM Complicating Pregnancy) is randomizing 950 women to insulin plus 1,000 mg metformin twice daily or insulin plus placebo. The primary outcome of the trial is a composite of pregnancy loss, preterm birth, birth injury, neonatal hypoglycemia, or hyperbilirubinemia. Infant fat mass (within 72 hours of birth) is a secondary outcome, along with maternal safety and maternal side effects.
The MiTy (Metformin in Women with T2DM in Pregnancy) trial in Canada, with similar randomization arms and outcomes measures, is completed and undergoing analysis. “Hopefully we’ll [soon] be able to say whether the addition of adjuvant metformin to insulin to treat type 2 diabetes brings the perinatal adverse outcome rate down from 30%,” said Dr. Boggess.
Metformin is the recommended first-line agent for type 2 diabetes in nonpregnant adults. But during pregnancy, insulin, which does not cross the placenta, is the preferred agent, according to recommendations of the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, she noted. Lingering in the background is the fact that the long-term effects of in utero metformin exposure on offspring – and of exposure to any oral hypoglycemic agent – are unknown, she said*
A majority of the adverse pregnancy outcomes that occur in the context of type 2 diabetes involve macrosomia. “It’s a big deal,” Dr. Boggess said, that results in numerous maternal and infant risks and complications. “We also know that the in utero environment that contributes to, or causes, macrosomia predisposes to childhood obesity and obesity later on.”
Diabetes is the “leading risk factor” for adverse pregnancy outcomes today, said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers distinguished professor and dean of the University of Maryland School of Medicine. In the United States, 11% of women aged 20 years and older have diabetes, and the disease affects more than 1% of all pregnancies, he said.
The MOMPOD trial is sponsored by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Boggess reported no conflicts of interest.
* This article was updated 1/2/2020.
WASHINGTON – Insulin is the preferred agent for type 2 diabetes in pregnant women, yet about a third of pregnancies still have an adverse outcome, according Kim Boggess, MD, who spoke at the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America.
“We are not where we need to be,” said Dr. Boggess, who is leading a trial that brings metformin, the first-line agent for type 2 diabetes outside of pregnancy, back into the picture for pregnant women – as an add-on to insulin.
It is an interesting twist, because pregnant women taking metformin for preexisting type 2 or gestational diabetes have been shown in some studies to require supplemental insulin, more than occasionally, to achieve target glycemic control.
This was the case in a small, randomized, controlled trial at Dr. Boggess’ institution, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, in which 43% of pregnant women with type 2 diabetes who were assigned to metformin required supplemental insulin (Am J Perinatol. 2013;30[6]:483-90). (0% vs. 36%, respectively) and fewer reports of glucose values less than 60 mg/dL (7.1% vs. 50%).
“I don’t consider this [need for supplemental insulin] ‘metformin failure,’ because studies that use metformin as monotherapy and that [show some patients] ultimately requiring insulin support ... also show that these women need less insulin,” she said. “What’s the risk of insulin alone? Hypoglycemia. So using less insulin could be a good thing.”
Other research suggests there may be less maternal weight gain, less neonatal hypoglycemia, fewer neonatal complications, and improved maternal glycemic control in patients treated with metformin, alone or with add-on insulin, than with insulin alone. “We’re starting to get a sense in the literature that, at least in the [pregnant] population with type 2 diabetes, there may be a role for metformin,” said Dr. Boggess, professor and program director for maternal-fetal medicine at the university.
Currently, the multisite MOMPOD trial (Medical Optimization of Management of T2DM Complicating Pregnancy) is randomizing 950 women to insulin plus 1,000 mg metformin twice daily or insulin plus placebo. The primary outcome of the trial is a composite of pregnancy loss, preterm birth, birth injury, neonatal hypoglycemia, or hyperbilirubinemia. Infant fat mass (within 72 hours of birth) is a secondary outcome, along with maternal safety and maternal side effects.
The MiTy (Metformin in Women with T2DM in Pregnancy) trial in Canada, with similar randomization arms and outcomes measures, is completed and undergoing analysis. “Hopefully we’ll [soon] be able to say whether the addition of adjuvant metformin to insulin to treat type 2 diabetes brings the perinatal adverse outcome rate down from 30%,” said Dr. Boggess.
Metformin is the recommended first-line agent for type 2 diabetes in nonpregnant adults. But during pregnancy, insulin, which does not cross the placenta, is the preferred agent, according to recommendations of the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, she noted. Lingering in the background is the fact that the long-term effects of in utero metformin exposure on offspring – and of exposure to any oral hypoglycemic agent – are unknown, she said*
A majority of the adverse pregnancy outcomes that occur in the context of type 2 diabetes involve macrosomia. “It’s a big deal,” Dr. Boggess said, that results in numerous maternal and infant risks and complications. “We also know that the in utero environment that contributes to, or causes, macrosomia predisposes to childhood obesity and obesity later on.”
Diabetes is the “leading risk factor” for adverse pregnancy outcomes today, said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers distinguished professor and dean of the University of Maryland School of Medicine. In the United States, 11% of women aged 20 years and older have diabetes, and the disease affects more than 1% of all pregnancies, he said.
The MOMPOD trial is sponsored by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Boggess reported no conflicts of interest.
* This article was updated 1/2/2020.
REPORTING FROM DPSG-NA 2019
Vitamin E acetate confirmed as likely source of EVALI
Vitamin E acetate was found in fluid from the lungs of 94% of patients with electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, data from a convenience sample of 51 patients indicate. The findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cases of electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention starting in early 2019, and numbers rose throughout the year, “which suggests new or increased exposure to one or more toxicants from the use of e-cigarette products,” wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the National Center for Environmental Health at the CDC, and colleagues.
To further investigate potential toxins in patients with EVALI, the researchers examined bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid from 51 EVALI patients and 99 healthy controls.
After the researchers used isotope dilution mass spectrometry on the samples, 48 of the 51 patients (94%) showed vitamin E acetate in their BAL samples. No other potential toxins – including plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes – were identified. The samples of one patient each showed coconut oil and limonene.
A total of 47 of 51 patients for whom complete laboratory data were available either reported vaping tetrahydrocannabinol products within 90 days of becoming ill, or showed tetrahydrocannabinol or its metabolites in their BAL fluid. In addition, 30 of 47 patients showed nicotine or nicotine metabolites in their BAL fluid.
The average age of the patients was 23 years, 69% were male. Overall, 25 were confirmed EVALI cases and 26 were probable cases, and probable cases included the three patients who showed no vitamin E acetate.
The safety of inhaling vitamin E acetate, which is a common ingredient in dietary supplements and skin care creams, has not been well studied. It could contribute to lung injury when heated in e-cigarette products by splitting the acetate to create the reactive compound and potential lung irritant ketene, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility that vitamin E acetate is a marker for exposure to other toxicants, a lack of data on the impact of heating vitamin e acetate, and the inability to assess the timing of the vitamin E acetate exposure compared to BAL sample collection, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that vitamin E acetate may play a role in EVALI because of the high detection rate in patients from across the United States, the biologically possible potential for lung injury from vitamin e acetate, and the timing of the rise of EVALI and the use of vitamin E acetate in vaping products, they concluded.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and The Ohio State University Pelotonia intramural research program. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
Vitamin E acetate was found in fluid from the lungs of 94% of patients with electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, data from a convenience sample of 51 patients indicate. The findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cases of electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention starting in early 2019, and numbers rose throughout the year, “which suggests new or increased exposure to one or more toxicants from the use of e-cigarette products,” wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the National Center for Environmental Health at the CDC, and colleagues.
To further investigate potential toxins in patients with EVALI, the researchers examined bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid from 51 EVALI patients and 99 healthy controls.
After the researchers used isotope dilution mass spectrometry on the samples, 48 of the 51 patients (94%) showed vitamin E acetate in their BAL samples. No other potential toxins – including plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes – were identified. The samples of one patient each showed coconut oil and limonene.
A total of 47 of 51 patients for whom complete laboratory data were available either reported vaping tetrahydrocannabinol products within 90 days of becoming ill, or showed tetrahydrocannabinol or its metabolites in their BAL fluid. In addition, 30 of 47 patients showed nicotine or nicotine metabolites in their BAL fluid.
The average age of the patients was 23 years, 69% were male. Overall, 25 were confirmed EVALI cases and 26 were probable cases, and probable cases included the three patients who showed no vitamin E acetate.
The safety of inhaling vitamin E acetate, which is a common ingredient in dietary supplements and skin care creams, has not been well studied. It could contribute to lung injury when heated in e-cigarette products by splitting the acetate to create the reactive compound and potential lung irritant ketene, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility that vitamin E acetate is a marker for exposure to other toxicants, a lack of data on the impact of heating vitamin e acetate, and the inability to assess the timing of the vitamin E acetate exposure compared to BAL sample collection, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that vitamin E acetate may play a role in EVALI because of the high detection rate in patients from across the United States, the biologically possible potential for lung injury from vitamin e acetate, and the timing of the rise of EVALI and the use of vitamin E acetate in vaping products, they concluded.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and The Ohio State University Pelotonia intramural research program. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
Vitamin E acetate was found in fluid from the lungs of 94% of patients with electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, data from a convenience sample of 51 patients indicate. The findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Cases of electronic cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention starting in early 2019, and numbers rose throughout the year, “which suggests new or increased exposure to one or more toxicants from the use of e-cigarette products,” wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the National Center for Environmental Health at the CDC, and colleagues.
To further investigate potential toxins in patients with EVALI, the researchers examined bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid from 51 EVALI patients and 99 healthy controls.
After the researchers used isotope dilution mass spectrometry on the samples, 48 of the 51 patients (94%) showed vitamin E acetate in their BAL samples. No other potential toxins – including plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes – were identified. The samples of one patient each showed coconut oil and limonene.
A total of 47 of 51 patients for whom complete laboratory data were available either reported vaping tetrahydrocannabinol products within 90 days of becoming ill, or showed tetrahydrocannabinol or its metabolites in their BAL fluid. In addition, 30 of 47 patients showed nicotine or nicotine metabolites in their BAL fluid.
The average age of the patients was 23 years, 69% were male. Overall, 25 were confirmed EVALI cases and 26 were probable cases, and probable cases included the three patients who showed no vitamin E acetate.
The safety of inhaling vitamin E acetate, which is a common ingredient in dietary supplements and skin care creams, has not been well studied. It could contribute to lung injury when heated in e-cigarette products by splitting the acetate to create the reactive compound and potential lung irritant ketene, the researchers said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the possibility that vitamin E acetate is a marker for exposure to other toxicants, a lack of data on the impact of heating vitamin e acetate, and the inability to assess the timing of the vitamin E acetate exposure compared to BAL sample collection, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that vitamin E acetate may play a role in EVALI because of the high detection rate in patients from across the United States, the biologically possible potential for lung injury from vitamin e acetate, and the timing of the rise of EVALI and the use of vitamin E acetate in vaping products, they concluded.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and The Ohio State University Pelotonia intramural research program. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
FDA panel okays teprotumumab for thyroid eye disease
TED is a rare autoimmune disease that causes the eyes to bulge (proptosis) and can lead to blindness. It is also known as thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy, Graves ophthalmopathy, and Graves orbitopathy. Current treatment is aimed at relief of symptoms and includes corticosteroids and orbital decompression.
“TED can affect patients both physically and emotionally, limiting their ability to perform everyday activities like driving, working, reading, sleeping, and participating in social activities,” Jeff Todd, president and chief executive officer, Prevent Blindness, said in a news release.
“As an organization dedicated to helping patients with vision impairment and those who are at significant risk, we are extremely encouraged by today’s vote and hopeful this will change the future of TED treatment by giving patients an option that has been shown to improve the painful and vision-threatening aspects of the disease,” Mr. Todd said.
Teprotumumab was granted fast-track status in April 2015 and breakthrough therapy designation in July 2016. It received orphan drug designation on June 19, 2019. If approved, it would be the first approved treatment for this indication.
All 12 members of the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee of the FDA voted to recommend approval of teprotumumab.
“It’s clearly a pleasure to participate in seeing a drug being designed and moving forward in a clinical trial for a disease that really has not been treatable for us in the past,” said voting committee member Timothy Murray, MD, MBA, of the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami.
Efficacy demonstrated
The FDA advisory committee considered data from two randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies that were similar in design and that demonstrated efficacy.
The studies included a total of 171 patients, fewer than 90 of whom were treated with teprotumumab, the agency explained in a briefing document. “This is a considerably smaller database than the common safety database of greater than 300 patients treated with a course of therapy,” it observed.
The study required that patients have proptosis but did not require that they have “progressive forward motion of the globe,” it noted.
The primary objective – a reduction in proptosis of 2 or more mm – was met in 82% of patients who received teprotumumab, compared with 16% of those who received placebo.
Review study No. 1 (TED01RV) was a phase 2 study, and review study No. 2 (OPTIC) was a phase 3 study. Both trials included a 24-week treatment period during which participants received teprotumumab or placebo intravenously every 3 weeks for a total of eight doses. Patients in both studies underwent a follow-up period during which they received no further treatment.
Some patients experienced a reduction in proptosis as early as 6 weeks after they received the first infusion. In an extension of TED01RV, that reduction extended for at least 4 weeks after the last infusion. For about 60% of responders, no relapse had occurred by week 72. The extension of OPTIC and an open-label treatment period for those with no response to placebo or teprotumumab are ongoing.
“I welcome the addition of this drug to our armamentarium to treat this horrible, horrible disease,” said temporary voting committee member John F. Stamler, MD, PhD, clinical instructor, ophthalmology and visual sciences, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
Adverse events
Teprotumumab inhibits the insulinlike growth factor–1 receptor, which can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate glucose, particularly in patients with diabetes. In the study, some patients with diabetes required additional insulin for glycemic control.
In three study participants whose baseline fasting blood glucose levels were normal, blood glucose levels were found to be elevated at one or more visits during the treatment period. None had a history of diabetes mellitus, but for two, baseline hemoglobin A1c levels were elevated.
Five or more patients reported loss of hearing (hypoacusis), and others reported tinnitus. One of them experienced a spontaneous return of hearing the day after the hypoacusis developed, whereas for others, hearing did not return until after teprotumumab treatment was completed. The mechanism of action for hearing loss is unclear.
Panel members felt the potential for hearing loss is important and that patients should receive some type of monitoring, but they did not all agree on when that testing should occur or who should be responsible for getting it done.
“It strikes me that, if this drug were approved, there would be centers that would be interested in undertaking independent studies of hearing loss in treated patients, and that that could be done outside the sponsor’s responsibility and probably would be of interest to independent investigators,” noted committee chairperson James Chodosh, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Benefits outweigh risks
More than one-third of patients (36%) experienced gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea and diarrhea (12% each) and abdominal pain (5%). None of the cases caused any patient to discontinue the study drug.
The overall incidence of muscle spasms was more than three times higher in the teprotumumab group (32%) than in the placebo group (9.5%).
One patient stopped taking teprotumumab after being hospitalized for Escherichia coli sepsis and dehydration, and another participant stopped after experiencing an episode of inflammatory bowel disease. It is not clear whether there is a causal association between teprotumumab and inflammatory bowel disease.
No study participants died.
Panel members expressed concern about safety in the longer term or in patients who receive multiple courses of teprotumumab, but they felt the potential benefits from teprotumumab outweigh the risks. The committee also wanted more information about the effects of teprotumumab with respect to glucose control, hearing loss, and other outcomes that are very important to patients, such as alopecia.
The panel favored including diarrhea in the list of adverse events in the label and felt that there should be a warning about inflammatory bowel disease.
“We’re finally going to be able to get a lot of people some help,” concluded voting committee member Sidney Gicheru, MD, LaserCare Eye Center, Irving, Texas.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
TED is a rare autoimmune disease that causes the eyes to bulge (proptosis) and can lead to blindness. It is also known as thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy, Graves ophthalmopathy, and Graves orbitopathy. Current treatment is aimed at relief of symptoms and includes corticosteroids and orbital decompression.
“TED can affect patients both physically and emotionally, limiting their ability to perform everyday activities like driving, working, reading, sleeping, and participating in social activities,” Jeff Todd, president and chief executive officer, Prevent Blindness, said in a news release.
“As an organization dedicated to helping patients with vision impairment and those who are at significant risk, we are extremely encouraged by today’s vote and hopeful this will change the future of TED treatment by giving patients an option that has been shown to improve the painful and vision-threatening aspects of the disease,” Mr. Todd said.
Teprotumumab was granted fast-track status in April 2015 and breakthrough therapy designation in July 2016. It received orphan drug designation on June 19, 2019. If approved, it would be the first approved treatment for this indication.
All 12 members of the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee of the FDA voted to recommend approval of teprotumumab.
“It’s clearly a pleasure to participate in seeing a drug being designed and moving forward in a clinical trial for a disease that really has not been treatable for us in the past,” said voting committee member Timothy Murray, MD, MBA, of the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami.
Efficacy demonstrated
The FDA advisory committee considered data from two randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies that were similar in design and that demonstrated efficacy.
The studies included a total of 171 patients, fewer than 90 of whom were treated with teprotumumab, the agency explained in a briefing document. “This is a considerably smaller database than the common safety database of greater than 300 patients treated with a course of therapy,” it observed.
The study required that patients have proptosis but did not require that they have “progressive forward motion of the globe,” it noted.
The primary objective – a reduction in proptosis of 2 or more mm – was met in 82% of patients who received teprotumumab, compared with 16% of those who received placebo.
Review study No. 1 (TED01RV) was a phase 2 study, and review study No. 2 (OPTIC) was a phase 3 study. Both trials included a 24-week treatment period during which participants received teprotumumab or placebo intravenously every 3 weeks for a total of eight doses. Patients in both studies underwent a follow-up period during which they received no further treatment.
Some patients experienced a reduction in proptosis as early as 6 weeks after they received the first infusion. In an extension of TED01RV, that reduction extended for at least 4 weeks after the last infusion. For about 60% of responders, no relapse had occurred by week 72. The extension of OPTIC and an open-label treatment period for those with no response to placebo or teprotumumab are ongoing.
“I welcome the addition of this drug to our armamentarium to treat this horrible, horrible disease,” said temporary voting committee member John F. Stamler, MD, PhD, clinical instructor, ophthalmology and visual sciences, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
Adverse events
Teprotumumab inhibits the insulinlike growth factor–1 receptor, which can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate glucose, particularly in patients with diabetes. In the study, some patients with diabetes required additional insulin for glycemic control.
In three study participants whose baseline fasting blood glucose levels were normal, blood glucose levels were found to be elevated at one or more visits during the treatment period. None had a history of diabetes mellitus, but for two, baseline hemoglobin A1c levels were elevated.
Five or more patients reported loss of hearing (hypoacusis), and others reported tinnitus. One of them experienced a spontaneous return of hearing the day after the hypoacusis developed, whereas for others, hearing did not return until after teprotumumab treatment was completed. The mechanism of action for hearing loss is unclear.
Panel members felt the potential for hearing loss is important and that patients should receive some type of monitoring, but they did not all agree on when that testing should occur or who should be responsible for getting it done.
“It strikes me that, if this drug were approved, there would be centers that would be interested in undertaking independent studies of hearing loss in treated patients, and that that could be done outside the sponsor’s responsibility and probably would be of interest to independent investigators,” noted committee chairperson James Chodosh, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Benefits outweigh risks
More than one-third of patients (36%) experienced gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea and diarrhea (12% each) and abdominal pain (5%). None of the cases caused any patient to discontinue the study drug.
The overall incidence of muscle spasms was more than three times higher in the teprotumumab group (32%) than in the placebo group (9.5%).
One patient stopped taking teprotumumab after being hospitalized for Escherichia coli sepsis and dehydration, and another participant stopped after experiencing an episode of inflammatory bowel disease. It is not clear whether there is a causal association between teprotumumab and inflammatory bowel disease.
No study participants died.
Panel members expressed concern about safety in the longer term or in patients who receive multiple courses of teprotumumab, but they felt the potential benefits from teprotumumab outweigh the risks. The committee also wanted more information about the effects of teprotumumab with respect to glucose control, hearing loss, and other outcomes that are very important to patients, such as alopecia.
The panel favored including diarrhea in the list of adverse events in the label and felt that there should be a warning about inflammatory bowel disease.
“We’re finally going to be able to get a lot of people some help,” concluded voting committee member Sidney Gicheru, MD, LaserCare Eye Center, Irving, Texas.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
TED is a rare autoimmune disease that causes the eyes to bulge (proptosis) and can lead to blindness. It is also known as thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy, Graves ophthalmopathy, and Graves orbitopathy. Current treatment is aimed at relief of symptoms and includes corticosteroids and orbital decompression.
“TED can affect patients both physically and emotionally, limiting their ability to perform everyday activities like driving, working, reading, sleeping, and participating in social activities,” Jeff Todd, president and chief executive officer, Prevent Blindness, said in a news release.
“As an organization dedicated to helping patients with vision impairment and those who are at significant risk, we are extremely encouraged by today’s vote and hopeful this will change the future of TED treatment by giving patients an option that has been shown to improve the painful and vision-threatening aspects of the disease,” Mr. Todd said.
Teprotumumab was granted fast-track status in April 2015 and breakthrough therapy designation in July 2016. It received orphan drug designation on June 19, 2019. If approved, it would be the first approved treatment for this indication.
All 12 members of the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee of the FDA voted to recommend approval of teprotumumab.
“It’s clearly a pleasure to participate in seeing a drug being designed and moving forward in a clinical trial for a disease that really has not been treatable for us in the past,” said voting committee member Timothy Murray, MD, MBA, of the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami.
Efficacy demonstrated
The FDA advisory committee considered data from two randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies that were similar in design and that demonstrated efficacy.
The studies included a total of 171 patients, fewer than 90 of whom were treated with teprotumumab, the agency explained in a briefing document. “This is a considerably smaller database than the common safety database of greater than 300 patients treated with a course of therapy,” it observed.
The study required that patients have proptosis but did not require that they have “progressive forward motion of the globe,” it noted.
The primary objective – a reduction in proptosis of 2 or more mm – was met in 82% of patients who received teprotumumab, compared with 16% of those who received placebo.
Review study No. 1 (TED01RV) was a phase 2 study, and review study No. 2 (OPTIC) was a phase 3 study. Both trials included a 24-week treatment period during which participants received teprotumumab or placebo intravenously every 3 weeks for a total of eight doses. Patients in both studies underwent a follow-up period during which they received no further treatment.
Some patients experienced a reduction in proptosis as early as 6 weeks after they received the first infusion. In an extension of TED01RV, that reduction extended for at least 4 weeks after the last infusion. For about 60% of responders, no relapse had occurred by week 72. The extension of OPTIC and an open-label treatment period for those with no response to placebo or teprotumumab are ongoing.
“I welcome the addition of this drug to our armamentarium to treat this horrible, horrible disease,” said temporary voting committee member John F. Stamler, MD, PhD, clinical instructor, ophthalmology and visual sciences, University of Iowa, Iowa City.
Adverse events
Teprotumumab inhibits the insulinlike growth factor–1 receptor, which can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate glucose, particularly in patients with diabetes. In the study, some patients with diabetes required additional insulin for glycemic control.
In three study participants whose baseline fasting blood glucose levels were normal, blood glucose levels were found to be elevated at one or more visits during the treatment period. None had a history of diabetes mellitus, but for two, baseline hemoglobin A1c levels were elevated.
Five or more patients reported loss of hearing (hypoacusis), and others reported tinnitus. One of them experienced a spontaneous return of hearing the day after the hypoacusis developed, whereas for others, hearing did not return until after teprotumumab treatment was completed. The mechanism of action for hearing loss is unclear.
Panel members felt the potential for hearing loss is important and that patients should receive some type of monitoring, but they did not all agree on when that testing should occur or who should be responsible for getting it done.
“It strikes me that, if this drug were approved, there would be centers that would be interested in undertaking independent studies of hearing loss in treated patients, and that that could be done outside the sponsor’s responsibility and probably would be of interest to independent investigators,” noted committee chairperson James Chodosh, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts Eye and Ear and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Benefits outweigh risks
More than one-third of patients (36%) experienced gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea and diarrhea (12% each) and abdominal pain (5%). None of the cases caused any patient to discontinue the study drug.
The overall incidence of muscle spasms was more than three times higher in the teprotumumab group (32%) than in the placebo group (9.5%).
One patient stopped taking teprotumumab after being hospitalized for Escherichia coli sepsis and dehydration, and another participant stopped after experiencing an episode of inflammatory bowel disease. It is not clear whether there is a causal association between teprotumumab and inflammatory bowel disease.
No study participants died.
Panel members expressed concern about safety in the longer term or in patients who receive multiple courses of teprotumumab, but they felt the potential benefits from teprotumumab outweigh the risks. The committee also wanted more information about the effects of teprotumumab with respect to glucose control, hearing loss, and other outcomes that are very important to patients, such as alopecia.
The panel favored including diarrhea in the list of adverse events in the label and felt that there should be a warning about inflammatory bowel disease.
“We’re finally going to be able to get a lot of people some help,” concluded voting committee member Sidney Gicheru, MD, LaserCare Eye Center, Irving, Texas.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Influenza activity continues to be unusually high
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.
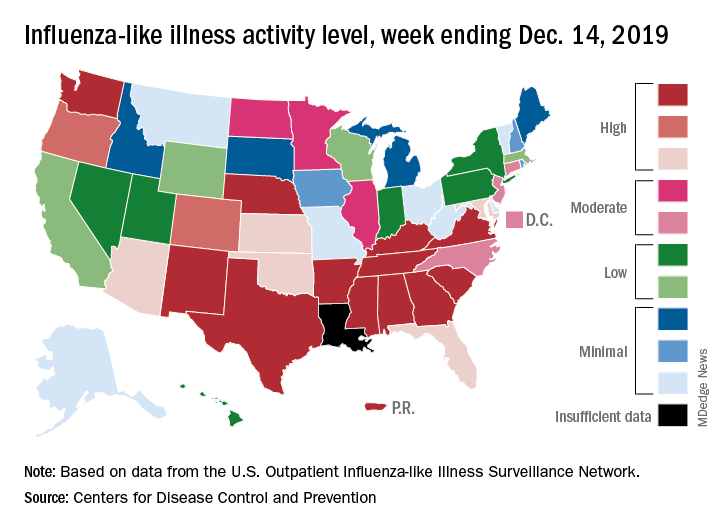
which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.

which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.

which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
LOXO-305: Next-gen BTK inhibitor safe and effective in B-cell malignancies
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
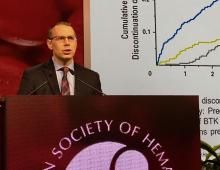
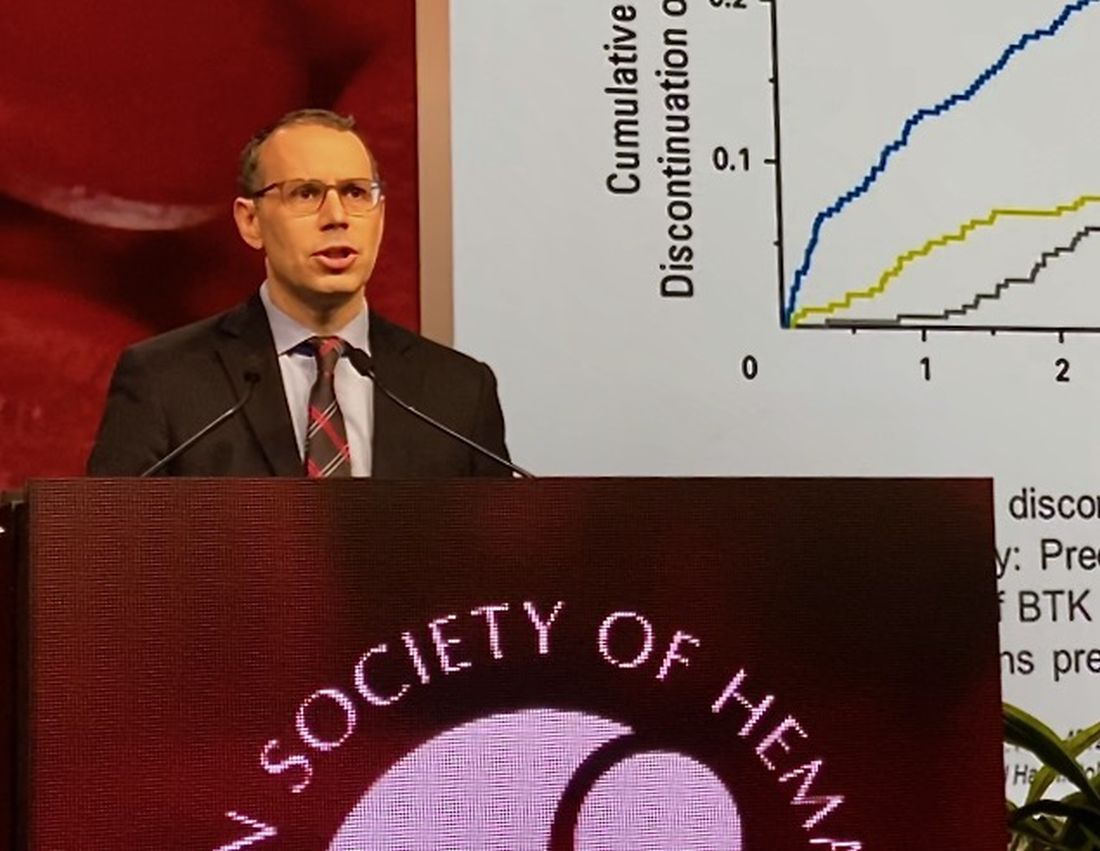
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
First autoimmune epilepsy RCT supports IVIG therapy
BALTIMORE –
Although the numbers of enrolled subjects was small, it was the first double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial in autoimmune epilepsy, the start of a level 1 evidence base. Until now, treatment has been based mostly on case reports and expert opinion. “We’ve clearly shown that immunotherapy works and that treating early makes a difference, much more so than antiseizure medications,” said lead author Divyanshu Dubey, MBBS, from the Mayo Clinic.
The lack of data has meant that “we couldn’t get insurance approval for IVIG, so people have generally leaned towards” high-dose intravenous steroids, which are problematic because LGI-1 antibody epilepsy is a disease of older people, in whom osteoporosis, underlying infections, and other problems complicate steroid use, Dr. Dubey said.
The trial also included three people with contactin-associated-protein-like-2 (CASPR2) antibody epilepsy, but they all wound up in the placebo arm, “so it’s hard to say anything about them,” Dr. Dubey said at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting. The work was published shortly before the meeting (Ann Neurol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1002/ana.25655).
CASPR2 and LGI-1 are proteins found in brain cells; attack by antibodies triggers encephalitis and tens to hundreds of seizures per day. The seizures tend to diminish with time, but the cognitive damage caused by the encephalitis does not. “We’ve seen patients end up in nursing homes diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease” because the conditions weren’t recognized and treated, Dr. Dubey said.
He and his team chose LGI-1 and CASPR2 epilepsy because of the potentially devastating consequences and because they are among the most common autoimmune epilepsies for which antibodies have been identified. There was also a hope that positive results might open up insurance coverage.
The trial randomized eight people to IVIG 0.5 g/kg on day 1; 1 g/kg on day 2; and 0.6 g/kg once at 3 and 5 weeks. Nine others were randomized to volume-matched IV saline placebo on the same schedule. After enrollment of 17 patients (LGI1-IgG, 14; CASPR2-IgG, 3) over 34 months, the study was terminated because of slow enrollment.
Although none of the LGI-1 subjects in the placebo group responded, two CASPR2 patients did, yielding an IVIG response rate of 75% versus 22% (2/9) in the placebo arm after week 5 (odds ratio, 10.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-98.9; P = .044).
Two of the LGI-1 subjects in the IVIG arm were completely seizure free after treatment. Results in both arms, meanwhile, did not correlate with concomitant antiseizure medications among those who were on them.
All eight IVIG patients showed stabilization or improvement in cognitive function, compared with two of five in the placebo arm, as gauged by Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status scores. Patients in the IVIG arm gained a median of 3 points, while patients in the placebo arm lost a median of 1 point (P = .077).
At week 5, six patients with persistent seizures who were in the placebo group were switched to the IVIG regimen after unblinding; four (67%) reported more than a 50% reduction in seizures.
Responses did not correlate with LGI-1/CASPR2-IgG1-4 subclass, and there were no IVIG-associated adverse events. One IVIG patients fell because of a faciobrachial dystonic seizure, a classic sign of LGI-1 disease. Antibodies were not measured in the trial because they “do not correlate with severity of autoimmune epilepsy,” Dr. Dubey said.
The original plan was to enroll 30 subjects, but the investigators terminated the study after 18 because of slow enrollment. With knowledge of autoimmune epilepsy growing at Mayo, it was increasingly difficult to find immunotherapy-naive patients, he said.
All the subjects were between 60 and 70 years old, and the majority in both arms were men, which was not surprising because the conditions skew male, Dr. Dubey said. None of the patients had underlying tumors, which are known triggers of autoimmune epilepsy.
This work was funded by Grifols Shared Services, a maker of IVIG, and Option Care, a provider of home infusion equipment. Dr. Dubey said the company had no active role in the trial, but that the lack of insurance coverage for IVIG in autoimmune epilepsy was one of the drivers of the study. He disclosed research support from Grifols; another investigator is a consultant.
SOURCE: Dubey D et al. AES 2019, Abstract 1.292.
BALTIMORE –
Although the numbers of enrolled subjects was small, it was the first double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial in autoimmune epilepsy, the start of a level 1 evidence base. Until now, treatment has been based mostly on case reports and expert opinion. “We’ve clearly shown that immunotherapy works and that treating early makes a difference, much more so than antiseizure medications,” said lead author Divyanshu Dubey, MBBS, from the Mayo Clinic.
The lack of data has meant that “we couldn’t get insurance approval for IVIG, so people have generally leaned towards” high-dose intravenous steroids, which are problematic because LGI-1 antibody epilepsy is a disease of older people, in whom osteoporosis, underlying infections, and other problems complicate steroid use, Dr. Dubey said.
The trial also included three people with contactin-associated-protein-like-2 (CASPR2) antibody epilepsy, but they all wound up in the placebo arm, “so it’s hard to say anything about them,” Dr. Dubey said at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting. The work was published shortly before the meeting (Ann Neurol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1002/ana.25655).
CASPR2 and LGI-1 are proteins found in brain cells; attack by antibodies triggers encephalitis and tens to hundreds of seizures per day. The seizures tend to diminish with time, but the cognitive damage caused by the encephalitis does not. “We’ve seen patients end up in nursing homes diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease” because the conditions weren’t recognized and treated, Dr. Dubey said.
He and his team chose LGI-1 and CASPR2 epilepsy because of the potentially devastating consequences and because they are among the most common autoimmune epilepsies for which antibodies have been identified. There was also a hope that positive results might open up insurance coverage.
The trial randomized eight people to IVIG 0.5 g/kg on day 1; 1 g/kg on day 2; and 0.6 g/kg once at 3 and 5 weeks. Nine others were randomized to volume-matched IV saline placebo on the same schedule. After enrollment of 17 patients (LGI1-IgG, 14; CASPR2-IgG, 3) over 34 months, the study was terminated because of slow enrollment.
Although none of the LGI-1 subjects in the placebo group responded, two CASPR2 patients did, yielding an IVIG response rate of 75% versus 22% (2/9) in the placebo arm after week 5 (odds ratio, 10.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-98.9; P = .044).
Two of the LGI-1 subjects in the IVIG arm were completely seizure free after treatment. Results in both arms, meanwhile, did not correlate with concomitant antiseizure medications among those who were on them.
All eight IVIG patients showed stabilization or improvement in cognitive function, compared with two of five in the placebo arm, as gauged by Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status scores. Patients in the IVIG arm gained a median of 3 points, while patients in the placebo arm lost a median of 1 point (P = .077).
At week 5, six patients with persistent seizures who were in the placebo group were switched to the IVIG regimen after unblinding; four (67%) reported more than a 50% reduction in seizures.
Responses did not correlate with LGI-1/CASPR2-IgG1-4 subclass, and there were no IVIG-associated adverse events. One IVIG patients fell because of a faciobrachial dystonic seizure, a classic sign of LGI-1 disease. Antibodies were not measured in the trial because they “do not correlate with severity of autoimmune epilepsy,” Dr. Dubey said.
The original plan was to enroll 30 subjects, but the investigators terminated the study after 18 because of slow enrollment. With knowledge of autoimmune epilepsy growing at Mayo, it was increasingly difficult to find immunotherapy-naive patients, he said.
All the subjects were between 60 and 70 years old, and the majority in both arms were men, which was not surprising because the conditions skew male, Dr. Dubey said. None of the patients had underlying tumors, which are known triggers of autoimmune epilepsy.
This work was funded by Grifols Shared Services, a maker of IVIG, and Option Care, a provider of home infusion equipment. Dr. Dubey said the company had no active role in the trial, but that the lack of insurance coverage for IVIG in autoimmune epilepsy was one of the drivers of the study. He disclosed research support from Grifols; another investigator is a consultant.
SOURCE: Dubey D et al. AES 2019, Abstract 1.292.
BALTIMORE –
Although the numbers of enrolled subjects was small, it was the first double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial in autoimmune epilepsy, the start of a level 1 evidence base. Until now, treatment has been based mostly on case reports and expert opinion. “We’ve clearly shown that immunotherapy works and that treating early makes a difference, much more so than antiseizure medications,” said lead author Divyanshu Dubey, MBBS, from the Mayo Clinic.
The lack of data has meant that “we couldn’t get insurance approval for IVIG, so people have generally leaned towards” high-dose intravenous steroids, which are problematic because LGI-1 antibody epilepsy is a disease of older people, in whom osteoporosis, underlying infections, and other problems complicate steroid use, Dr. Dubey said.
The trial also included three people with contactin-associated-protein-like-2 (CASPR2) antibody epilepsy, but they all wound up in the placebo arm, “so it’s hard to say anything about them,” Dr. Dubey said at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting. The work was published shortly before the meeting (Ann Neurol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1002/ana.25655).
CASPR2 and LGI-1 are proteins found in brain cells; attack by antibodies triggers encephalitis and tens to hundreds of seizures per day. The seizures tend to diminish with time, but the cognitive damage caused by the encephalitis does not. “We’ve seen patients end up in nursing homes diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease” because the conditions weren’t recognized and treated, Dr. Dubey said.
He and his team chose LGI-1 and CASPR2 epilepsy because of the potentially devastating consequences and because they are among the most common autoimmune epilepsies for which antibodies have been identified. There was also a hope that positive results might open up insurance coverage.
The trial randomized eight people to IVIG 0.5 g/kg on day 1; 1 g/kg on day 2; and 0.6 g/kg once at 3 and 5 weeks. Nine others were randomized to volume-matched IV saline placebo on the same schedule. After enrollment of 17 patients (LGI1-IgG, 14; CASPR2-IgG, 3) over 34 months, the study was terminated because of slow enrollment.
Although none of the LGI-1 subjects in the placebo group responded, two CASPR2 patients did, yielding an IVIG response rate of 75% versus 22% (2/9) in the placebo arm after week 5 (odds ratio, 10.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-98.9; P = .044).
Two of the LGI-1 subjects in the IVIG arm were completely seizure free after treatment. Results in both arms, meanwhile, did not correlate with concomitant antiseizure medications among those who were on them.
All eight IVIG patients showed stabilization or improvement in cognitive function, compared with two of five in the placebo arm, as gauged by Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status scores. Patients in the IVIG arm gained a median of 3 points, while patients in the placebo arm lost a median of 1 point (P = .077).
At week 5, six patients with persistent seizures who were in the placebo group were switched to the IVIG regimen after unblinding; four (67%) reported more than a 50% reduction in seizures.
Responses did not correlate with LGI-1/CASPR2-IgG1-4 subclass, and there were no IVIG-associated adverse events. One IVIG patients fell because of a faciobrachial dystonic seizure, a classic sign of LGI-1 disease. Antibodies were not measured in the trial because they “do not correlate with severity of autoimmune epilepsy,” Dr. Dubey said.
The original plan was to enroll 30 subjects, but the investigators terminated the study after 18 because of slow enrollment. With knowledge of autoimmune epilepsy growing at Mayo, it was increasingly difficult to find immunotherapy-naive patients, he said.
All the subjects were between 60 and 70 years old, and the majority in both arms were men, which was not surprising because the conditions skew male, Dr. Dubey said. None of the patients had underlying tumors, which are known triggers of autoimmune epilepsy.
This work was funded by Grifols Shared Services, a maker of IVIG, and Option Care, a provider of home infusion equipment. Dr. Dubey said the company had no active role in the trial, but that the lack of insurance coverage for IVIG in autoimmune epilepsy was one of the drivers of the study. He disclosed research support from Grifols; another investigator is a consultant.
SOURCE: Dubey D et al. AES 2019, Abstract 1.292.
REPORTING FROM AES 2019
Survival data reported from largest CAR T trial in B-cell lymphoma
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Developing a career in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders
The role of diet and nutrition is becoming increasingly recognized in the cause, management, and prevention of disease. Despite the clear importance of the role of nutrition in the field of medicine, among health professionals, formal training in nutrition support is lacking. A lack of nutrition training has been recognized in multiple subspecialty fields1 and is highlighted by a shortage of physicians trained to manage disease-related malnutrition.2 Gastroenterologists, in particular, have a special responsibility related to nutrition in disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and are in a unique position to recognize and manage disorders of maldigestion and malabsorption. Unfortunately, surveys of both U.S. and Canadian fellows have demonstrated deficiencies in the training of nutrition support and management of enteral and parenteral nutrition (PN).3,4
Current status of nutrition training
The impact of diet and nutrition on health and disease is universally recognized but unfortunately lagging with respect to formal training at all levels of medical education. A survey of program directors from primary care, surgery, and anesthesia showed only 26% of respondent programs had a formal curriculum in nutrition education.1 Specific to gastroenterology, a majority of trainees and recent graduates perceived that nutrition education was an important aspect of their training; however, only 50% of respondents had training in nutrition support with 36% reporting mandatory training.3
The Gastroenterology Core Curriculum, most recently updated in 2007 – and sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the American Gastroenterological Association – includes six domains of nutrition training within the training track: nutrition assessment, basic nutrition requirements, specific gastrointestinal disorders and other allied diseases, enteral nutrition, PN, and diet therapy. Level 1 training is expected for all gastroenterology fellows. Level 2 is comprised, on average, of an additional 12 months with described objectives, either occurring outside of a standard gastroenterology fellowship or coinciding with a dedicated third year of training. Although training durations for level 1 are not defined, level 2 recommends at least 6 months of experience working with an inpatient nutrition support team (NST) and the management of outpatients in nutrition and weight management clinics.5
Role of a nutrition support team
Training in nutrition is a heterogeneous field, with a wide range that covers understanding metabolism in health and disease, micronutrient and macronutrient requirements, nutrient digestion and absorption, and the best route and provision of nutrition support. Therefore, a critical aspect of education includes access to a dedicated NST. Such teams were common and necessary in the late 1900s with the inception of specialized nutrition therapy. However, with an increase in the use of home infusion therapies, NSTs were dismantled in favor of shifting responsibility to decentralized home infusion companies. A dedicated NST often will include some combination of pharmacists with an interest in the safe compounding of parenteral formulas, nurses with experience in the home management of intravenous therapies and catheters, and dietitians with dedicated interests in intestinal failure, recognition of malnutrition, and provision of calories. Collectively, a highly functioning NST also provides dedicated multidisciplinary training to health professionals of varying backgrounds.
My entry into the field of nutrition support
Entering a fellowship in gastroenterology should be pursued with an open mind. We all have varying experiences in the management of patients with gastrointestinal conditions, both in the inpatient and outpatient arenas through residency training. My early experiences in fellowship at the University of Chicago centered on the management of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and with research interests related to the clinical course of IBD. I was also fortunate to be part of a fellowship program offering both level 1 and level 2 training with a longstanding track record of graduating fellows responsible for the running of NSTs at their local institutions. Categorical fellows spend 3 months of training on a rotation with combined inpatient and outpatient responsibilities focusing on the management of patients with intestinal failure, inpatient management of complications from PN support, and an outpatient clinic focused on small-bowel disorders (celiac disease, small-bowel bleeding, and intestinal malabsorption). This experience led me to pursue level 2 training at Northwestern University with a combined focus on small-bowel diseases and enteroscopy.
These collective experiences in fellowship and postfellowship training grounded my ideas on the role of nutrition pervading many gastrointestinal conditions from acute and chronic pancreatitis and IBD to rare conditions such as enteropathy associated with immune deficiencies and autoimmune enteropathy. Now, as a junior faculty member with a focus in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders, my clinical responsibilities include a dedicated half-day in the management of outpatients (parenteral and enteral nutrition), inpatient rounding with our dedicated NST focusing on the initiation of PN, management of home PN complications, and dedicated procedural time focusing on enteral access techniques (percutaneous gastrostomy/jejunostomy tubes) and small-bowel enteroscopy. To my surprise, entry into the field of nutrition support and small-bowel disorders has been filled with excitement and a growing list of collaborations and opportunities. While initial work in the management of PN has been in existence since the 1970s and earlier with respect to the development of safe administration techniques, most of my current work transcends specialties as we develop appropriateness criteria related to PN support in collaboration with a wide range of specialties that include surgery, oncology, and palliative care.
Seeking opportunities for additional training
As the field of gastroenterology grows outward in various directions, mastery of subjects has led to subspecialization in specific areas including interventional gastroenterology, pancreatology, IBD, and motility disorders. The field is primed for broader access to specialty training in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders. Exposure to dedicated training in nutrition and nutrition-related disorders is vital as part of a categorical fellowship, but can also be complemented via visiting observerships, access to formal level 2 training programs, and external programs related to promoting nutrition education.
Since 2001, formal nutrition fellowship programs offering level 2 training have been compiled by the National Board of Physician Nutrition Specialists, although attraction of interested fellows has been lacking.2 The Nestlé Nutrition Institute Clinical Nutrition Fellowship, endorsed by the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition and the AGA, is an ongoing program that pairs interested trainees with expert program faculty through onsite clinical rotations lasting a total of 4 weeks.2 Attendance at national and international conferences can supplement a fellows training in nutrition, and an increased focus on nutrition lectures should be a priority of meeting education committees to increase the exposure of trainees to leaders in the field.
Conclusion
A career in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders is incredibly rewarding as it incorporates the basic physiologic processes of digestion and absorption with a wide array of pathologic conditions. Incorporation of the basic principles of intestinal absorption allows for a greater understanding of the role of the low–fermentable oligo-, di-, monosaccharides and polyols (FODMAP) diet in the management of irritable bowel syndrome to the varying principles of diets currently under study for the management of IBD. Outside of this spectrum, working with an NST allows for the management of complex cases of malnutrition resulting from disorders ranging from cancer to various postsurgical intestinal alterations. Although observerships and external training programs allow for an introduction into the field, formal level 2 training, combining both work with a NST and small-bowel enteroscopy, allows for exposure to the full range of disorders of the small bowel. As patients continue to seek disease management options rooted in diet, the demand for gastroenterologists with subspecialty training in nutritional disorders will continue to grow and will require further support across training programs to incorporate additional training into categorical fellowships.
References
1. Daley BJ et al. JPEN J Paren Enteral Nutr. 2016;40(1):95-9. doi: 10.1177/0148607115571155.
2. Kiraly LN et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2014;29(3):332-7. doi: 10.1177/0884533614525212.
3. Hu J et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2018 Apr;33(2):191-7. doi: 10.1177/0884533617700852.
4. Scolapio JS et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008 Feb;42(2):122-7. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181595b6a.
5. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases et al. The Gastroenterology Core Curriculum, 3rd ed. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(5):2012-8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.079.
Dr. Micic is assistant professor of medicine, department of internal medicine, section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, University of Chicago.
The role of diet and nutrition is becoming increasingly recognized in the cause, management, and prevention of disease. Despite the clear importance of the role of nutrition in the field of medicine, among health professionals, formal training in nutrition support is lacking. A lack of nutrition training has been recognized in multiple subspecialty fields1 and is highlighted by a shortage of physicians trained to manage disease-related malnutrition.2 Gastroenterologists, in particular, have a special responsibility related to nutrition in disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and are in a unique position to recognize and manage disorders of maldigestion and malabsorption. Unfortunately, surveys of both U.S. and Canadian fellows have demonstrated deficiencies in the training of nutrition support and management of enteral and parenteral nutrition (PN).3,4
Current status of nutrition training
The impact of diet and nutrition on health and disease is universally recognized but unfortunately lagging with respect to formal training at all levels of medical education. A survey of program directors from primary care, surgery, and anesthesia showed only 26% of respondent programs had a formal curriculum in nutrition education.1 Specific to gastroenterology, a majority of trainees and recent graduates perceived that nutrition education was an important aspect of their training; however, only 50% of respondents had training in nutrition support with 36% reporting mandatory training.3
The Gastroenterology Core Curriculum, most recently updated in 2007 – and sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the American Gastroenterological Association – includes six domains of nutrition training within the training track: nutrition assessment, basic nutrition requirements, specific gastrointestinal disorders and other allied diseases, enteral nutrition, PN, and diet therapy. Level 1 training is expected for all gastroenterology fellows. Level 2 is comprised, on average, of an additional 12 months with described objectives, either occurring outside of a standard gastroenterology fellowship or coinciding with a dedicated third year of training. Although training durations for level 1 are not defined, level 2 recommends at least 6 months of experience working with an inpatient nutrition support team (NST) and the management of outpatients in nutrition and weight management clinics.5
Role of a nutrition support team
Training in nutrition is a heterogeneous field, with a wide range that covers understanding metabolism in health and disease, micronutrient and macronutrient requirements, nutrient digestion and absorption, and the best route and provision of nutrition support. Therefore, a critical aspect of education includes access to a dedicated NST. Such teams were common and necessary in the late 1900s with the inception of specialized nutrition therapy. However, with an increase in the use of home infusion therapies, NSTs were dismantled in favor of shifting responsibility to decentralized home infusion companies. A dedicated NST often will include some combination of pharmacists with an interest in the safe compounding of parenteral formulas, nurses with experience in the home management of intravenous therapies and catheters, and dietitians with dedicated interests in intestinal failure, recognition of malnutrition, and provision of calories. Collectively, a highly functioning NST also provides dedicated multidisciplinary training to health professionals of varying backgrounds.
My entry into the field of nutrition support
Entering a fellowship in gastroenterology should be pursued with an open mind. We all have varying experiences in the management of patients with gastrointestinal conditions, both in the inpatient and outpatient arenas through residency training. My early experiences in fellowship at the University of Chicago centered on the management of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and with research interests related to the clinical course of IBD. I was also fortunate to be part of a fellowship program offering both level 1 and level 2 training with a longstanding track record of graduating fellows responsible for the running of NSTs at their local institutions. Categorical fellows spend 3 months of training on a rotation with combined inpatient and outpatient responsibilities focusing on the management of patients with intestinal failure, inpatient management of complications from PN support, and an outpatient clinic focused on small-bowel disorders (celiac disease, small-bowel bleeding, and intestinal malabsorption). This experience led me to pursue level 2 training at Northwestern University with a combined focus on small-bowel diseases and enteroscopy.
These collective experiences in fellowship and postfellowship training grounded my ideas on the role of nutrition pervading many gastrointestinal conditions from acute and chronic pancreatitis and IBD to rare conditions such as enteropathy associated with immune deficiencies and autoimmune enteropathy. Now, as a junior faculty member with a focus in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders, my clinical responsibilities include a dedicated half-day in the management of outpatients (parenteral and enteral nutrition), inpatient rounding with our dedicated NST focusing on the initiation of PN, management of home PN complications, and dedicated procedural time focusing on enteral access techniques (percutaneous gastrostomy/jejunostomy tubes) and small-bowel enteroscopy. To my surprise, entry into the field of nutrition support and small-bowel disorders has been filled with excitement and a growing list of collaborations and opportunities. While initial work in the management of PN has been in existence since the 1970s and earlier with respect to the development of safe administration techniques, most of my current work transcends specialties as we develop appropriateness criteria related to PN support in collaboration with a wide range of specialties that include surgery, oncology, and palliative care.
Seeking opportunities for additional training
As the field of gastroenterology grows outward in various directions, mastery of subjects has led to subspecialization in specific areas including interventional gastroenterology, pancreatology, IBD, and motility disorders. The field is primed for broader access to specialty training in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders. Exposure to dedicated training in nutrition and nutrition-related disorders is vital as part of a categorical fellowship, but can also be complemented via visiting observerships, access to formal level 2 training programs, and external programs related to promoting nutrition education.
Since 2001, formal nutrition fellowship programs offering level 2 training have been compiled by the National Board of Physician Nutrition Specialists, although attraction of interested fellows has been lacking.2 The Nestlé Nutrition Institute Clinical Nutrition Fellowship, endorsed by the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition and the AGA, is an ongoing program that pairs interested trainees with expert program faculty through onsite clinical rotations lasting a total of 4 weeks.2 Attendance at national and international conferences can supplement a fellows training in nutrition, and an increased focus on nutrition lectures should be a priority of meeting education committees to increase the exposure of trainees to leaders in the field.
Conclusion
A career in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders is incredibly rewarding as it incorporates the basic physiologic processes of digestion and absorption with a wide array of pathologic conditions. Incorporation of the basic principles of intestinal absorption allows for a greater understanding of the role of the low–fermentable oligo-, di-, monosaccharides and polyols (FODMAP) diet in the management of irritable bowel syndrome to the varying principles of diets currently under study for the management of IBD. Outside of this spectrum, working with an NST allows for the management of complex cases of malnutrition resulting from disorders ranging from cancer to various postsurgical intestinal alterations. Although observerships and external training programs allow for an introduction into the field, formal level 2 training, combining both work with a NST and small-bowel enteroscopy, allows for exposure to the full range of disorders of the small bowel. As patients continue to seek disease management options rooted in diet, the demand for gastroenterologists with subspecialty training in nutritional disorders will continue to grow and will require further support across training programs to incorporate additional training into categorical fellowships.
References
1. Daley BJ et al. JPEN J Paren Enteral Nutr. 2016;40(1):95-9. doi: 10.1177/0148607115571155.
2. Kiraly LN et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2014;29(3):332-7. doi: 10.1177/0884533614525212.
3. Hu J et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2018 Apr;33(2):191-7. doi: 10.1177/0884533617700852.
4. Scolapio JS et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008 Feb;42(2):122-7. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181595b6a.
5. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases et al. The Gastroenterology Core Curriculum, 3rd ed. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(5):2012-8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.079.
Dr. Micic is assistant professor of medicine, department of internal medicine, section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, University of Chicago.
The role of diet and nutrition is becoming increasingly recognized in the cause, management, and prevention of disease. Despite the clear importance of the role of nutrition in the field of medicine, among health professionals, formal training in nutrition support is lacking. A lack of nutrition training has been recognized in multiple subspecialty fields1 and is highlighted by a shortage of physicians trained to manage disease-related malnutrition.2 Gastroenterologists, in particular, have a special responsibility related to nutrition in disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and are in a unique position to recognize and manage disorders of maldigestion and malabsorption. Unfortunately, surveys of both U.S. and Canadian fellows have demonstrated deficiencies in the training of nutrition support and management of enteral and parenteral nutrition (PN).3,4
Current status of nutrition training
The impact of diet and nutrition on health and disease is universally recognized but unfortunately lagging with respect to formal training at all levels of medical education. A survey of program directors from primary care, surgery, and anesthesia showed only 26% of respondent programs had a formal curriculum in nutrition education.1 Specific to gastroenterology, a majority of trainees and recent graduates perceived that nutrition education was an important aspect of their training; however, only 50% of respondents had training in nutrition support with 36% reporting mandatory training.3
The Gastroenterology Core Curriculum, most recently updated in 2007 – and sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the American Gastroenterological Association – includes six domains of nutrition training within the training track: nutrition assessment, basic nutrition requirements, specific gastrointestinal disorders and other allied diseases, enteral nutrition, PN, and diet therapy. Level 1 training is expected for all gastroenterology fellows. Level 2 is comprised, on average, of an additional 12 months with described objectives, either occurring outside of a standard gastroenterology fellowship or coinciding with a dedicated third year of training. Although training durations for level 1 are not defined, level 2 recommends at least 6 months of experience working with an inpatient nutrition support team (NST) and the management of outpatients in nutrition and weight management clinics.5
Role of a nutrition support team
Training in nutrition is a heterogeneous field, with a wide range that covers understanding metabolism in health and disease, micronutrient and macronutrient requirements, nutrient digestion and absorption, and the best route and provision of nutrition support. Therefore, a critical aspect of education includes access to a dedicated NST. Such teams were common and necessary in the late 1900s with the inception of specialized nutrition therapy. However, with an increase in the use of home infusion therapies, NSTs were dismantled in favor of shifting responsibility to decentralized home infusion companies. A dedicated NST often will include some combination of pharmacists with an interest in the safe compounding of parenteral formulas, nurses with experience in the home management of intravenous therapies and catheters, and dietitians with dedicated interests in intestinal failure, recognition of malnutrition, and provision of calories. Collectively, a highly functioning NST also provides dedicated multidisciplinary training to health professionals of varying backgrounds.
My entry into the field of nutrition support
Entering a fellowship in gastroenterology should be pursued with an open mind. We all have varying experiences in the management of patients with gastrointestinal conditions, both in the inpatient and outpatient arenas through residency training. My early experiences in fellowship at the University of Chicago centered on the management of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and with research interests related to the clinical course of IBD. I was also fortunate to be part of a fellowship program offering both level 1 and level 2 training with a longstanding track record of graduating fellows responsible for the running of NSTs at their local institutions. Categorical fellows spend 3 months of training on a rotation with combined inpatient and outpatient responsibilities focusing on the management of patients with intestinal failure, inpatient management of complications from PN support, and an outpatient clinic focused on small-bowel disorders (celiac disease, small-bowel bleeding, and intestinal malabsorption). This experience led me to pursue level 2 training at Northwestern University with a combined focus on small-bowel diseases and enteroscopy.
These collective experiences in fellowship and postfellowship training grounded my ideas on the role of nutrition pervading many gastrointestinal conditions from acute and chronic pancreatitis and IBD to rare conditions such as enteropathy associated with immune deficiencies and autoimmune enteropathy. Now, as a junior faculty member with a focus in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders, my clinical responsibilities include a dedicated half-day in the management of outpatients (parenteral and enteral nutrition), inpatient rounding with our dedicated NST focusing on the initiation of PN, management of home PN complications, and dedicated procedural time focusing on enteral access techniques (percutaneous gastrostomy/jejunostomy tubes) and small-bowel enteroscopy. To my surprise, entry into the field of nutrition support and small-bowel disorders has been filled with excitement and a growing list of collaborations and opportunities. While initial work in the management of PN has been in existence since the 1970s and earlier with respect to the development of safe administration techniques, most of my current work transcends specialties as we develop appropriateness criteria related to PN support in collaboration with a wide range of specialties that include surgery, oncology, and palliative care.
Seeking opportunities for additional training
As the field of gastroenterology grows outward in various directions, mastery of subjects has led to subspecialization in specific areas including interventional gastroenterology, pancreatology, IBD, and motility disorders. The field is primed for broader access to specialty training in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders. Exposure to dedicated training in nutrition and nutrition-related disorders is vital as part of a categorical fellowship, but can also be complemented via visiting observerships, access to formal level 2 training programs, and external programs related to promoting nutrition education.
Since 2001, formal nutrition fellowship programs offering level 2 training have been compiled by the National Board of Physician Nutrition Specialists, although attraction of interested fellows has been lacking.2 The Nestlé Nutrition Institute Clinical Nutrition Fellowship, endorsed by the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition and the AGA, is an ongoing program that pairs interested trainees with expert program faculty through onsite clinical rotations lasting a total of 4 weeks.2 Attendance at national and international conferences can supplement a fellows training in nutrition, and an increased focus on nutrition lectures should be a priority of meeting education committees to increase the exposure of trainees to leaders in the field.
Conclusion
A career in nutrition support and small-bowel disorders is incredibly rewarding as it incorporates the basic physiologic processes of digestion and absorption with a wide array of pathologic conditions. Incorporation of the basic principles of intestinal absorption allows for a greater understanding of the role of the low–fermentable oligo-, di-, monosaccharides and polyols (FODMAP) diet in the management of irritable bowel syndrome to the varying principles of diets currently under study for the management of IBD. Outside of this spectrum, working with an NST allows for the management of complex cases of malnutrition resulting from disorders ranging from cancer to various postsurgical intestinal alterations. Although observerships and external training programs allow for an introduction into the field, formal level 2 training, combining both work with a NST and small-bowel enteroscopy, allows for exposure to the full range of disorders of the small bowel. As patients continue to seek disease management options rooted in diet, the demand for gastroenterologists with subspecialty training in nutritional disorders will continue to grow and will require further support across training programs to incorporate additional training into categorical fellowships.
References
1. Daley BJ et al. JPEN J Paren Enteral Nutr. 2016;40(1):95-9. doi: 10.1177/0148607115571155.
2. Kiraly LN et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2014;29(3):332-7. doi: 10.1177/0884533614525212.
3. Hu J et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2018 Apr;33(2):191-7. doi: 10.1177/0884533617700852.
4. Scolapio JS et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008 Feb;42(2):122-7. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181595b6a.
5. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases et al. The Gastroenterology Core Curriculum, 3rd ed. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(5):2012-8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.079.
Dr. Micic is assistant professor of medicine, department of internal medicine, section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, University of Chicago.
Pitfalls in physician-patient communication via patient access support portals
Technology can be used to enhance communication, increase patient safety, and improve overall patient care. For example, many physicians have arranged for remote access to medical records and established a unique system of communication via a patient access support portal. A patient portal is a secure online website that provides patients 24-hour, on-demand access to their health information. Patient portals, while popular and oftentimes quite helpful, are not without drawbacks. Communication by electronic means with your patient can be viewed by some as impersonal and can make patients less tolerant to what they perceive to be a mistake, error, or unwanted outcome. A decrease in face-to-face contact and communication with your patient also gives you less time to resolve any conflict or disagreement. While communication via a patient access support portal has the potential to free up medical staff for direct patient care, such communication also carries liability risk.
Patient access support portal
A physician’s legal responsibility to communicate in a timely and accurate manner does not change, irrespective of the form of communication. However, communication via a patient access portal does have some unique features that must be considered by the practitioner. Practitioners must remember that any communication via the patient portal creates a permanent record, which can and will be used in the event of litigation. For example, when responding to a patient inquiry about a specific complaint, treatment provided, or test result, it will be presumed that the physician had access to the patient’s full medical record and that the full record will be utilized in making a response. Accessing the patient’s chart will leave an audit trail that will provide what is known as metadata, which in the context of electronic medical records, is what allows technicians to verify that the patient record was accessed, and it provides details as to when, and for how long it was accessed. These records are frequently pursued in litigation, so you must understand that parties can often re-create an intricate and accurate timeline of events. While state courts are divided on the issue of whether metadata contained within electronic medical records is discoverable, recent federal court decisions have held that such data is discoverable pursuant to the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. Thus, once a patient has communicated with you via the portal, you will be responsible for responding in an appropriate and prompt fashion. For these reasons, it is imperative that you create an agreement with your patients as to how the portal will be used and clearly set forth the rules for such use.
Patient portal policies and procedures
In creating patient portal user agreements (See "Sample User Agreement," attached below), it is crucial that an agreement clearly identify the policies and procedures for use. A patient portal user agreement should:
- Set forth the rules and regulations for portal use.
- Include a verification procedure that requires the patients to confirm that they have the legal capacity to consent to the terms of use. This is especially important when treating patients with mental disability, elderly patients with dementia, minors, and any other individuals who may not legally consent.
- Include a verification procedure that requires the patients to confirm that they understand and agree to abide by the user agreement rules.
- Include a detailed list that informs users of the risks and benefits of communicating via the patient portal.
- Stress that communication through the patient portal is for nonemergent matters only.
- Set forth permissible topics for use, such as communicating with the physician or staff, obtaining test results or records, and setting, changing, or canceling appointments.
- Clearly indicate certain topics that should not be discussed via the patient portal, including mental health issues.
- Reiterate that communication via the patient portal is only one option, and that all other standard methods of communication remain available. In doing so, provide office telephone numbers, hotlines, and email addresses for convenience.
- Inform the patients that they should call the office with any questions or concerns regarding use of the patient portal.
- Include a statement that the patient should call 911 or proceed directly to the nearest hospital for any and all urgent or emergent medical matters.
Other considerations
There are, however, equally critical considerations to be made that go beyond the core details of the user agreement. For instance, use of the patient access portal should be limited to only current or active patients, and you should stress to patients the importance of keeping their contact information updated and accurate. This is especially vital in situations in which a patient is unresponsive to communication via the portal, as your staff will need to follow up via other means of communication. It is also imperative to ensure the patient portal is programmed to promptly alert you or your staff following an inquiry from the patient as the patient will likely expect an immediate response.
Notably, communication via the patient portal must still comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This means that only authorized users are able to access records within the patient portal. To ensure compliance with HIPAA, all users should be instructed in the appropriate practices of maintaining patient privacy. This includes barring the use of shared passwords amongst multiple individuals, requiring that users enable an auto log-off setting, and programming work stations to turn off automatically after brief periods of nonuse. Further, all communications in the patient portal should be encrypted to prevent the patient’s sensitive information from being accessed in the event of an attempted security breach.
Finally, depending upon the practice, there may be instances in which someone other than the patient’s physician would be reading and responding to patient queries. In these situations, the patient should be informed of such potential. This way, if the communication is intended only for the physician, the patient will be afforded the opportunity to call the physician directly rather than communicate via the patient portal.
While the use of patient access portals is becoming far more prevalent, as they offer many practical benefits ranging from increased convenience and efficiency to enhanced patient care, they also carry the potential for increased liability exposure. As such, it is vital that physicians weigh all potential risks and benefits that are inherent in the use of patient access portals prior to making the decision to implement such technology.
Mr. Mills is an equity partner in Cunningham, Meyer & Vedrine, Chicago.
Technology can be used to enhance communication, increase patient safety, and improve overall patient care. For example, many physicians have arranged for remote access to medical records and established a unique system of communication via a patient access support portal. A patient portal is a secure online website that provides patients 24-hour, on-demand access to their health information. Patient portals, while popular and oftentimes quite helpful, are not without drawbacks. Communication by electronic means with your patient can be viewed by some as impersonal and can make patients less tolerant to what they perceive to be a mistake, error, or unwanted outcome. A decrease in face-to-face contact and communication with your patient also gives you less time to resolve any conflict or disagreement. While communication via a patient access support portal has the potential to free up medical staff for direct patient care, such communication also carries liability risk.
Patient access support portal
A physician’s legal responsibility to communicate in a timely and accurate manner does not change, irrespective of the form of communication. However, communication via a patient access portal does have some unique features that must be considered by the practitioner. Practitioners must remember that any communication via the patient portal creates a permanent record, which can and will be used in the event of litigation. For example, when responding to a patient inquiry about a specific complaint, treatment provided, or test result, it will be presumed that the physician had access to the patient’s full medical record and that the full record will be utilized in making a response. Accessing the patient’s chart will leave an audit trail that will provide what is known as metadata, which in the context of electronic medical records, is what allows technicians to verify that the patient record was accessed, and it provides details as to when, and for how long it was accessed. These records are frequently pursued in litigation, so you must understand that parties can often re-create an intricate and accurate timeline of events. While state courts are divided on the issue of whether metadata contained within electronic medical records is discoverable, recent federal court decisions have held that such data is discoverable pursuant to the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. Thus, once a patient has communicated with you via the portal, you will be responsible for responding in an appropriate and prompt fashion. For these reasons, it is imperative that you create an agreement with your patients as to how the portal will be used and clearly set forth the rules for such use.
Patient portal policies and procedures
In creating patient portal user agreements (See "Sample User Agreement," attached below), it is crucial that an agreement clearly identify the policies and procedures for use. A patient portal user agreement should:
- Set forth the rules and regulations for portal use.
- Include a verification procedure that requires the patients to confirm that they have the legal capacity to consent to the terms of use. This is especially important when treating patients with mental disability, elderly patients with dementia, minors, and any other individuals who may not legally consent.
- Include a verification procedure that requires the patients to confirm that they understand and agree to abide by the user agreement rules.
- Include a detailed list that informs users of the risks and benefits of communicating via the patient portal.
- Stress that communication through the patient portal is for nonemergent matters only.
- Set forth permissible topics for use, such as communicating with the physician or staff, obtaining test results or records, and setting, changing, or canceling appointments.
- Clearly indicate certain topics that should not be discussed via the patient portal, including mental health issues.
- Reiterate that communication via the patient portal is only one option, and that all other standard methods of communication remain available. In doing so, provide office telephone numbers, hotlines, and email addresses for convenience.
- Inform the patients that they should call the office with any questions or concerns regarding use of the patient portal.
- Include a statement that the patient should call 911 or proceed directly to the nearest hospital for any and all urgent or emergent medical matters.
Other considerations
There are, however, equally critical considerations to be made that go beyond the core details of the user agreement. For instance, use of the patient access portal should be limited to only current or active patients, and you should stress to patients the importance of keeping their contact information updated and accurate. This is especially vital in situations in which a patient is unresponsive to communication via the portal, as your staff will need to follow up via other means of communication. It is also imperative to ensure the patient portal is programmed to promptly alert you or your staff following an inquiry from the patient as the patient will likely expect an immediate response.
Notably, communication via the patient portal must still comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This means that only authorized users are able to access records within the patient portal. To ensure compliance with HIPAA, all users should be instructed in the appropriate practices of maintaining patient privacy. This includes barring the use of shared passwords amongst multiple individuals, requiring that users enable an auto log-off setting, and programming work stations to turn off automatically after brief periods of nonuse. Further, all communications in the patient portal should be encrypted to prevent the patient’s sensitive information from being accessed in the event of an attempted security breach.
Finally, depending upon the practice, there may be instances in which someone other than the patient’s physician would be reading and responding to patient queries. In these situations, the patient should be informed of such potential. This way, if the communication is intended only for the physician, the patient will be afforded the opportunity to call the physician directly rather than communicate via the patient portal.
While the use of patient access portals is becoming far more prevalent, as they offer many practical benefits ranging from increased convenience and efficiency to enhanced patient care, they also carry the potential for increased liability exposure. As such, it is vital that physicians weigh all potential risks and benefits that are inherent in the use of patient access portals prior to making the decision to implement such technology.
Mr. Mills is an equity partner in Cunningham, Meyer & Vedrine, Chicago.
Technology can be used to enhance communication, increase patient safety, and improve overall patient care. For example, many physicians have arranged for remote access to medical records and established a unique system of communication via a patient access support portal. A patient portal is a secure online website that provides patients 24-hour, on-demand access to their health information. Patient portals, while popular and oftentimes quite helpful, are not without drawbacks. Communication by electronic means with your patient can be viewed by some as impersonal and can make patients less tolerant to what they perceive to be a mistake, error, or unwanted outcome. A decrease in face-to-face contact and communication with your patient also gives you less time to resolve any conflict or disagreement. While communication via a patient access support portal has the potential to free up medical staff for direct patient care, such communication also carries liability risk.
Patient access support portal
A physician’s legal responsibility to communicate in a timely and accurate manner does not change, irrespective of the form of communication. However, communication via a patient access portal does have some unique features that must be considered by the practitioner. Practitioners must remember that any communication via the patient portal creates a permanent record, which can and will be used in the event of litigation. For example, when responding to a patient inquiry about a specific complaint, treatment provided, or test result, it will be presumed that the physician had access to the patient’s full medical record and that the full record will be utilized in making a response. Accessing the patient’s chart will leave an audit trail that will provide what is known as metadata, which in the context of electronic medical records, is what allows technicians to verify that the patient record was accessed, and it provides details as to when, and for how long it was accessed. These records are frequently pursued in litigation, so you must understand that parties can often re-create an intricate and accurate timeline of events. While state courts are divided on the issue of whether metadata contained within electronic medical records is discoverable, recent federal court decisions have held that such data is discoverable pursuant to the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. Thus, once a patient has communicated with you via the portal, you will be responsible for responding in an appropriate and prompt fashion. For these reasons, it is imperative that you create an agreement with your patients as to how the portal will be used and clearly set forth the rules for such use.
Patient portal policies and procedures
In creating patient portal user agreements (See "Sample User Agreement," attached below), it is crucial that an agreement clearly identify the policies and procedures for use. A patient portal user agreement should:
- Set forth the rules and regulations for portal use.
- Include a verification procedure that requires the patients to confirm that they have the legal capacity to consent to the terms of use. This is especially important when treating patients with mental disability, elderly patients with dementia, minors, and any other individuals who may not legally consent.
- Include a verification procedure that requires the patients to confirm that they understand and agree to abide by the user agreement rules.
- Include a detailed list that informs users of the risks and benefits of communicating via the patient portal.
- Stress that communication through the patient portal is for nonemergent matters only.
- Set forth permissible topics for use, such as communicating with the physician or staff, obtaining test results or records, and setting, changing, or canceling appointments.
- Clearly indicate certain topics that should not be discussed via the patient portal, including mental health issues.
- Reiterate that communication via the patient portal is only one option, and that all other standard methods of communication remain available. In doing so, provide office telephone numbers, hotlines, and email addresses for convenience.
- Inform the patients that they should call the office with any questions or concerns regarding use of the patient portal.
- Include a statement that the patient should call 911 or proceed directly to the nearest hospital for any and all urgent or emergent medical matters.
Other considerations
There are, however, equally critical considerations to be made that go beyond the core details of the user agreement. For instance, use of the patient access portal should be limited to only current or active patients, and you should stress to patients the importance of keeping their contact information updated and accurate. This is especially vital in situations in which a patient is unresponsive to communication via the portal, as your staff will need to follow up via other means of communication. It is also imperative to ensure the patient portal is programmed to promptly alert you or your staff following an inquiry from the patient as the patient will likely expect an immediate response.
Notably, communication via the patient portal must still comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This means that only authorized users are able to access records within the patient portal. To ensure compliance with HIPAA, all users should be instructed in the appropriate practices of maintaining patient privacy. This includes barring the use of shared passwords amongst multiple individuals, requiring that users enable an auto log-off setting, and programming work stations to turn off automatically after brief periods of nonuse. Further, all communications in the patient portal should be encrypted to prevent the patient’s sensitive information from being accessed in the event of an attempted security breach.
Finally, depending upon the practice, there may be instances in which someone other than the patient’s physician would be reading and responding to patient queries. In these situations, the patient should be informed of such potential. This way, if the communication is intended only for the physician, the patient will be afforded the opportunity to call the physician directly rather than communicate via the patient portal.
While the use of patient access portals is becoming far more prevalent, as they offer many practical benefits ranging from increased convenience and efficiency to enhanced patient care, they also carry the potential for increased liability exposure. As such, it is vital that physicians weigh all potential risks and benefits that are inherent in the use of patient access portals prior to making the decision to implement such technology.
Mr. Mills is an equity partner in Cunningham, Meyer & Vedrine, Chicago.