User login
Dr. David Lieberman: A Groundbreaking Career in Gastroenterology
David Lieberman, MD, AGAF, spent much of his long career asking questions about everyday clinical practice in GI medicine and then researching ways to answer those questions.
“The answer to one question often leads to further questions. And I think that’s what makes this research so exciting and dynamic,” said Lieberman, professor emeritus with Oregon Health and Science University, where he served as chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology for 24 years.
He was also instrumental in creating a blood and tissue repository for colorectal cancer (CRC) research, and a national endoscopic database.
His groundbreaking GI research in colorectal cancer screening earned him AGA’s Julius Friedenwald Medal, a top career honor. “We started off with some questions about the role of specific screening tests like colonoscopy and stool-based tests for screening,” he said. This led to the first large study about the value of screening with colonoscopy, which set the stage for current screening guidelines. Assessing more than 3,000 asymptomatic adults, Lieberman and colleagues determined that colonoscopy was more effective than sigmoidoscopy in detecting advanced colonic neoplasms.
The next phase of research focused on how well GI doctors were performing colonoscopy, asking questions about the quality of the colonoscopies being performed, and what course of action to take in polyp discovery. “We did some work related to polyp surveillance, what happens after we take out polyps and some recommendations for the appropriate length of follow up afterwards,” he summarized.
Most recently, Lieberman has centered his research on program effectiveness. “If you’re doing high quality colonoscopy and you’re doing appropriate surveillance, how effective is that? And what are the potential problems that might impair effectiveness?”
Adherence and participation remain significant challenges, he said. “If people don’t get the tests done, then they’re not going to be effective. Or if they get part of it done, there can be issues.”
In an interview, Lieberman discussed the reasons why people resist CRC screening, and the new technologies and research underway to make screening options more palatable for reluctant patients.
What do you think are the biggest deterrents to getting screened for CRC?
Dr. Lieberman: The whole idea of dealing with a stool sample is not appealing to patients. The second issue, and this has been shown in many studies, is patients who are referred for colonoscopy may resist because they have heard stories about bowel preps and about colonoscopy itself. But there are many other reasons. I mean, there are issues with access to care that are important. What if you have a positive stool test and you need to get a colonoscopy? How do you get a colonoscopy? There are barriers in moving from one test to the other in a different setting. There are issues with having to take a day off work that’s potentially a financial hardship for some patients. If you’re taking care of elderly relatives or children or if you need transportation, that’s an issue for people.
So, there are many potential barriers, and we’ve been trying to work at a national level to try to understand these barriers and then develop tools to mitigate these problems and improve the overall participation in screening.
How has the field of GI changed since you started practicing medicine?
Dr. Lieberman: I think there have been many exciting changes in technology. The endoscopes we used when I started my career were called fiberoptic scopes. These were scopes that contained tiny glass fibers that ran the length of the scope, and they were good, but not great in terms of imaging, and sometimes they would break down. We now have digital imaging that far surpasses the quality there. We’ve come a long way in terms of things like CT scans, for example, and MRI imaging. The other big technology change has been the development of minimally invasive treatments. For example, if you have a gallstone that’s in your bile duct, we now have ways to remove that without sending the patient to surgery.
The second big change has been the assessment of quality. When I started my career in gastroenterology, we were doing a lot of things, but we didn’t necessarily know if we were doing them well. Most of us thought we were doing them well, of course, but nobody was really measuring quality. There were no quality benchmarks. And so if you don’t measure it, you don’t know. Where we are today in gastroenterology is we’re intensively concerned about quality and measuring quality in various aspects of what we do. And I think that’s a positive development.
What key achievements came out of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: This panel evolved because back in the early 2000s, each of the GI organizations were producing guidelines related to colon cancer screening and follow-up. And they were slightly different. This was an attempt to bring all the relevant groups together and try to align the guidelines and recommendations among the GI organizations so that there wouldn’t be a confusing message.
Over the history of this task force, which started around 2002, it’s been remarkably productive. The task force has really examined all aspects of colorectal cancer, including things like the bowel prep, quality of exams, high risk management, hereditary syndromes that can lead to the higher likelihood of developing colon cancer, polypectomy and polypectomy techniques, and screening and surveillance recommendations, which have evolved over time. It’s been, in my opinion, a remarkably productive task force and continues to this day. I’m so very proud of that group.
Could you give a status update on the blood and tissue repository you created for CRC research?
Dr. Lieberman: Our initial studies were part of a Veterans Affairs cooperative study, which is a mechanism of funding within the VA that allows us to work with multiple VA centers to collect data and information. At the very outset of this study, we were performing screening colonoscopies in individuals, and we decided to create a bio-repository that included blood samples, polyp tissue, and normal rectal tissue. The thinking was at some point we might be able to do some genomic studies that might help us predict which patients are most likely to develop colon polyps and colon cancer. All that happened in the 1990s. It was supported by the National Cancer Institute. We created this repository, which sat for a long period of time while we were waiting for the technology to develop and so that we could perform genomic studies in a cost-effective way.
We’re now at that point, which is really exciting. We’re beginning to look at this tissue and perform some genomic studies. Some of this data has been presented at national meetings. This was a precursor to creating a similar type of bio-repository in a larger VA cooperative study. CSP #577 Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer (CONFIRM) is a randomized study comparing two forms of screening, a fecal immunochemical test versus a colonoscopy. We’re in the process of enrolling 50,000 patients in that study. We have also created a blood and tissue repository, which we hope will be useful for future studies.
You lead the AGA CRC Task Force, which advances research and policy initiatives to improve screening rates and patient outcomes. What would you like to see in future GI research, particularly in colorectal cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: We have new blood tests coming along that are going to be very attractive to both patients and physicians. You can obtain a blood sample at a point of service and patients won’t have to deal with stool samples. We need to understand how those tests perform in clinical practice. If the test is abnormal, indicating a patient has a higher risk of colon cancer and should get a colonoscopy, are they getting that colonoscopy or not? And what are the barriers? And if it’s normal, then that patient should have a repeat test at an appropriate interval.
We know that the effectiveness of screening really depends on the participation of individuals in terms of completing the steps. We’ve published some work already on trying to understand the role of these blood tests. We expect that these tests will continue to improve over time.
We’re also working on trying to develop these risk stratification tools that could be used in clinical practice to help figure out the most appropriate test for a particular individual.
Let’s say you go to your doctor for colon cancer screening, and if we could determine that you are a low-risk individual, you may benefit best from having a non-invasive test, like a blood test or a stool test. Whereas if you’re a higher risk individual, you may need to have a more invasive screening test like colonoscopy.
This falls into a concept of personalized medicine where we’re trying to use all the information we have from the medical history, and maybe genomic information that I mentioned earlier, to try to determine who needs the most intensive screening and who might benefit from less intensive screening.
I think the most recent work is really focused on these gaps in screening. And the biggest gap are patients that get a non-invasive test, like a stool test, but do not get a colonoscopy that renders the program ineffective if they don’t get the colonoscopy. We’re trying to highlight that for primary care providers and make sure that everyone understands the importance of this follow-up. And then, trying to develop tools to help the primary care provider navigate that patient to a colonoscopy.
What do you think is the biggest misconception about your specialty?
Dr. Lieberman: If there’s a misconception, it’s that GI physicians are focused on procedures. I think a good GI provider should be holistic, and I think many are. What I mean by holistic is that many GI symptoms could be due to stress, medications, diet, or other aspects of behavior, and the remedy is not necessarily a procedure. I think that many GI physicians are really skilled at obtaining this information and trying to help guide the patient through some uncomfortable symptoms.
It means being more like an internist, spending time with the patient to take a detailed history and delve into many different possibilities that might be going on.
David Lieberman, MD, AGAF, spent much of his long career asking questions about everyday clinical practice in GI medicine and then researching ways to answer those questions.
“The answer to one question often leads to further questions. And I think that’s what makes this research so exciting and dynamic,” said Lieberman, professor emeritus with Oregon Health and Science University, where he served as chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology for 24 years.
He was also instrumental in creating a blood and tissue repository for colorectal cancer (CRC) research, and a national endoscopic database.
His groundbreaking GI research in colorectal cancer screening earned him AGA’s Julius Friedenwald Medal, a top career honor. “We started off with some questions about the role of specific screening tests like colonoscopy and stool-based tests for screening,” he said. This led to the first large study about the value of screening with colonoscopy, which set the stage for current screening guidelines. Assessing more than 3,000 asymptomatic adults, Lieberman and colleagues determined that colonoscopy was more effective than sigmoidoscopy in detecting advanced colonic neoplasms.
The next phase of research focused on how well GI doctors were performing colonoscopy, asking questions about the quality of the colonoscopies being performed, and what course of action to take in polyp discovery. “We did some work related to polyp surveillance, what happens after we take out polyps and some recommendations for the appropriate length of follow up afterwards,” he summarized.
Most recently, Lieberman has centered his research on program effectiveness. “If you’re doing high quality colonoscopy and you’re doing appropriate surveillance, how effective is that? And what are the potential problems that might impair effectiveness?”
Adherence and participation remain significant challenges, he said. “If people don’t get the tests done, then they’re not going to be effective. Or if they get part of it done, there can be issues.”
In an interview, Lieberman discussed the reasons why people resist CRC screening, and the new technologies and research underway to make screening options more palatable for reluctant patients.
What do you think are the biggest deterrents to getting screened for CRC?
Dr. Lieberman: The whole idea of dealing with a stool sample is not appealing to patients. The second issue, and this has been shown in many studies, is patients who are referred for colonoscopy may resist because they have heard stories about bowel preps and about colonoscopy itself. But there are many other reasons. I mean, there are issues with access to care that are important. What if you have a positive stool test and you need to get a colonoscopy? How do you get a colonoscopy? There are barriers in moving from one test to the other in a different setting. There are issues with having to take a day off work that’s potentially a financial hardship for some patients. If you’re taking care of elderly relatives or children or if you need transportation, that’s an issue for people.
So, there are many potential barriers, and we’ve been trying to work at a national level to try to understand these barriers and then develop tools to mitigate these problems and improve the overall participation in screening.
How has the field of GI changed since you started practicing medicine?
Dr. Lieberman: I think there have been many exciting changes in technology. The endoscopes we used when I started my career were called fiberoptic scopes. These were scopes that contained tiny glass fibers that ran the length of the scope, and they were good, but not great in terms of imaging, and sometimes they would break down. We now have digital imaging that far surpasses the quality there. We’ve come a long way in terms of things like CT scans, for example, and MRI imaging. The other big technology change has been the development of minimally invasive treatments. For example, if you have a gallstone that’s in your bile duct, we now have ways to remove that without sending the patient to surgery.
The second big change has been the assessment of quality. When I started my career in gastroenterology, we were doing a lot of things, but we didn’t necessarily know if we were doing them well. Most of us thought we were doing them well, of course, but nobody was really measuring quality. There were no quality benchmarks. And so if you don’t measure it, you don’t know. Where we are today in gastroenterology is we’re intensively concerned about quality and measuring quality in various aspects of what we do. And I think that’s a positive development.
What key achievements came out of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: This panel evolved because back in the early 2000s, each of the GI organizations were producing guidelines related to colon cancer screening and follow-up. And they were slightly different. This was an attempt to bring all the relevant groups together and try to align the guidelines and recommendations among the GI organizations so that there wouldn’t be a confusing message.
Over the history of this task force, which started around 2002, it’s been remarkably productive. The task force has really examined all aspects of colorectal cancer, including things like the bowel prep, quality of exams, high risk management, hereditary syndromes that can lead to the higher likelihood of developing colon cancer, polypectomy and polypectomy techniques, and screening and surveillance recommendations, which have evolved over time. It’s been, in my opinion, a remarkably productive task force and continues to this day. I’m so very proud of that group.
Could you give a status update on the blood and tissue repository you created for CRC research?
Dr. Lieberman: Our initial studies were part of a Veterans Affairs cooperative study, which is a mechanism of funding within the VA that allows us to work with multiple VA centers to collect data and information. At the very outset of this study, we were performing screening colonoscopies in individuals, and we decided to create a bio-repository that included blood samples, polyp tissue, and normal rectal tissue. The thinking was at some point we might be able to do some genomic studies that might help us predict which patients are most likely to develop colon polyps and colon cancer. All that happened in the 1990s. It was supported by the National Cancer Institute. We created this repository, which sat for a long period of time while we were waiting for the technology to develop and so that we could perform genomic studies in a cost-effective way.
We’re now at that point, which is really exciting. We’re beginning to look at this tissue and perform some genomic studies. Some of this data has been presented at national meetings. This was a precursor to creating a similar type of bio-repository in a larger VA cooperative study. CSP #577 Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer (CONFIRM) is a randomized study comparing two forms of screening, a fecal immunochemical test versus a colonoscopy. We’re in the process of enrolling 50,000 patients in that study. We have also created a blood and tissue repository, which we hope will be useful for future studies.
You lead the AGA CRC Task Force, which advances research and policy initiatives to improve screening rates and patient outcomes. What would you like to see in future GI research, particularly in colorectal cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: We have new blood tests coming along that are going to be very attractive to both patients and physicians. You can obtain a blood sample at a point of service and patients won’t have to deal with stool samples. We need to understand how those tests perform in clinical practice. If the test is abnormal, indicating a patient has a higher risk of colon cancer and should get a colonoscopy, are they getting that colonoscopy or not? And what are the barriers? And if it’s normal, then that patient should have a repeat test at an appropriate interval.
We know that the effectiveness of screening really depends on the participation of individuals in terms of completing the steps. We’ve published some work already on trying to understand the role of these blood tests. We expect that these tests will continue to improve over time.
We’re also working on trying to develop these risk stratification tools that could be used in clinical practice to help figure out the most appropriate test for a particular individual.
Let’s say you go to your doctor for colon cancer screening, and if we could determine that you are a low-risk individual, you may benefit best from having a non-invasive test, like a blood test or a stool test. Whereas if you’re a higher risk individual, you may need to have a more invasive screening test like colonoscopy.
This falls into a concept of personalized medicine where we’re trying to use all the information we have from the medical history, and maybe genomic information that I mentioned earlier, to try to determine who needs the most intensive screening and who might benefit from less intensive screening.
I think the most recent work is really focused on these gaps in screening. And the biggest gap are patients that get a non-invasive test, like a stool test, but do not get a colonoscopy that renders the program ineffective if they don’t get the colonoscopy. We’re trying to highlight that for primary care providers and make sure that everyone understands the importance of this follow-up. And then, trying to develop tools to help the primary care provider navigate that patient to a colonoscopy.
What do you think is the biggest misconception about your specialty?
Dr. Lieberman: If there’s a misconception, it’s that GI physicians are focused on procedures. I think a good GI provider should be holistic, and I think many are. What I mean by holistic is that many GI symptoms could be due to stress, medications, diet, or other aspects of behavior, and the remedy is not necessarily a procedure. I think that many GI physicians are really skilled at obtaining this information and trying to help guide the patient through some uncomfortable symptoms.
It means being more like an internist, spending time with the patient to take a detailed history and delve into many different possibilities that might be going on.
David Lieberman, MD, AGAF, spent much of his long career asking questions about everyday clinical practice in GI medicine and then researching ways to answer those questions.
“The answer to one question often leads to further questions. And I think that’s what makes this research so exciting and dynamic,” said Lieberman, professor emeritus with Oregon Health and Science University, where he served as chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology for 24 years.
He was also instrumental in creating a blood and tissue repository for colorectal cancer (CRC) research, and a national endoscopic database.
His groundbreaking GI research in colorectal cancer screening earned him AGA’s Julius Friedenwald Medal, a top career honor. “We started off with some questions about the role of specific screening tests like colonoscopy and stool-based tests for screening,” he said. This led to the first large study about the value of screening with colonoscopy, which set the stage for current screening guidelines. Assessing more than 3,000 asymptomatic adults, Lieberman and colleagues determined that colonoscopy was more effective than sigmoidoscopy in detecting advanced colonic neoplasms.
The next phase of research focused on how well GI doctors were performing colonoscopy, asking questions about the quality of the colonoscopies being performed, and what course of action to take in polyp discovery. “We did some work related to polyp surveillance, what happens after we take out polyps and some recommendations for the appropriate length of follow up afterwards,” he summarized.
Most recently, Lieberman has centered his research on program effectiveness. “If you’re doing high quality colonoscopy and you’re doing appropriate surveillance, how effective is that? And what are the potential problems that might impair effectiveness?”
Adherence and participation remain significant challenges, he said. “If people don’t get the tests done, then they’re not going to be effective. Or if they get part of it done, there can be issues.”
In an interview, Lieberman discussed the reasons why people resist CRC screening, and the new technologies and research underway to make screening options more palatable for reluctant patients.
What do you think are the biggest deterrents to getting screened for CRC?
Dr. Lieberman: The whole idea of dealing with a stool sample is not appealing to patients. The second issue, and this has been shown in many studies, is patients who are referred for colonoscopy may resist because they have heard stories about bowel preps and about colonoscopy itself. But there are many other reasons. I mean, there are issues with access to care that are important. What if you have a positive stool test and you need to get a colonoscopy? How do you get a colonoscopy? There are barriers in moving from one test to the other in a different setting. There are issues with having to take a day off work that’s potentially a financial hardship for some patients. If you’re taking care of elderly relatives or children or if you need transportation, that’s an issue for people.
So, there are many potential barriers, and we’ve been trying to work at a national level to try to understand these barriers and then develop tools to mitigate these problems and improve the overall participation in screening.
How has the field of GI changed since you started practicing medicine?
Dr. Lieberman: I think there have been many exciting changes in technology. The endoscopes we used when I started my career were called fiberoptic scopes. These were scopes that contained tiny glass fibers that ran the length of the scope, and they were good, but not great in terms of imaging, and sometimes they would break down. We now have digital imaging that far surpasses the quality there. We’ve come a long way in terms of things like CT scans, for example, and MRI imaging. The other big technology change has been the development of minimally invasive treatments. For example, if you have a gallstone that’s in your bile duct, we now have ways to remove that without sending the patient to surgery.
The second big change has been the assessment of quality. When I started my career in gastroenterology, we were doing a lot of things, but we didn’t necessarily know if we were doing them well. Most of us thought we were doing them well, of course, but nobody was really measuring quality. There were no quality benchmarks. And so if you don’t measure it, you don’t know. Where we are today in gastroenterology is we’re intensively concerned about quality and measuring quality in various aspects of what we do. And I think that’s a positive development.
What key achievements came out of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: This panel evolved because back in the early 2000s, each of the GI organizations were producing guidelines related to colon cancer screening and follow-up. And they were slightly different. This was an attempt to bring all the relevant groups together and try to align the guidelines and recommendations among the GI organizations so that there wouldn’t be a confusing message.
Over the history of this task force, which started around 2002, it’s been remarkably productive. The task force has really examined all aspects of colorectal cancer, including things like the bowel prep, quality of exams, high risk management, hereditary syndromes that can lead to the higher likelihood of developing colon cancer, polypectomy and polypectomy techniques, and screening and surveillance recommendations, which have evolved over time. It’s been, in my opinion, a remarkably productive task force and continues to this day. I’m so very proud of that group.
Could you give a status update on the blood and tissue repository you created for CRC research?
Dr. Lieberman: Our initial studies were part of a Veterans Affairs cooperative study, which is a mechanism of funding within the VA that allows us to work with multiple VA centers to collect data and information. At the very outset of this study, we were performing screening colonoscopies in individuals, and we decided to create a bio-repository that included blood samples, polyp tissue, and normal rectal tissue. The thinking was at some point we might be able to do some genomic studies that might help us predict which patients are most likely to develop colon polyps and colon cancer. All that happened in the 1990s. It was supported by the National Cancer Institute. We created this repository, which sat for a long period of time while we were waiting for the technology to develop and so that we could perform genomic studies in a cost-effective way.
We’re now at that point, which is really exciting. We’re beginning to look at this tissue and perform some genomic studies. Some of this data has been presented at national meetings. This was a precursor to creating a similar type of bio-repository in a larger VA cooperative study. CSP #577 Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer (CONFIRM) is a randomized study comparing two forms of screening, a fecal immunochemical test versus a colonoscopy. We’re in the process of enrolling 50,000 patients in that study. We have also created a blood and tissue repository, which we hope will be useful for future studies.
You lead the AGA CRC Task Force, which advances research and policy initiatives to improve screening rates and patient outcomes. What would you like to see in future GI research, particularly in colorectal cancer?
Dr. Lieberman: We have new blood tests coming along that are going to be very attractive to both patients and physicians. You can obtain a blood sample at a point of service and patients won’t have to deal with stool samples. We need to understand how those tests perform in clinical practice. If the test is abnormal, indicating a patient has a higher risk of colon cancer and should get a colonoscopy, are they getting that colonoscopy or not? And what are the barriers? And if it’s normal, then that patient should have a repeat test at an appropriate interval.
We know that the effectiveness of screening really depends on the participation of individuals in terms of completing the steps. We’ve published some work already on trying to understand the role of these blood tests. We expect that these tests will continue to improve over time.
We’re also working on trying to develop these risk stratification tools that could be used in clinical practice to help figure out the most appropriate test for a particular individual.
Let’s say you go to your doctor for colon cancer screening, and if we could determine that you are a low-risk individual, you may benefit best from having a non-invasive test, like a blood test or a stool test. Whereas if you’re a higher risk individual, you may need to have a more invasive screening test like colonoscopy.
This falls into a concept of personalized medicine where we’re trying to use all the information we have from the medical history, and maybe genomic information that I mentioned earlier, to try to determine who needs the most intensive screening and who might benefit from less intensive screening.
I think the most recent work is really focused on these gaps in screening. And the biggest gap are patients that get a non-invasive test, like a stool test, but do not get a colonoscopy that renders the program ineffective if they don’t get the colonoscopy. We’re trying to highlight that for primary care providers and make sure that everyone understands the importance of this follow-up. And then, trying to develop tools to help the primary care provider navigate that patient to a colonoscopy.
What do you think is the biggest misconception about your specialty?
Dr. Lieberman: If there’s a misconception, it’s that GI physicians are focused on procedures. I think a good GI provider should be holistic, and I think many are. What I mean by holistic is that many GI symptoms could be due to stress, medications, diet, or other aspects of behavior, and the remedy is not necessarily a procedure. I think that many GI physicians are really skilled at obtaining this information and trying to help guide the patient through some uncomfortable symptoms.
It means being more like an internist, spending time with the patient to take a detailed history and delve into many different possibilities that might be going on.
Approach to Weight Management in GI Practice
Introduction
The majority of patients in the United States are now overweight or obese, and as gastroenterologists we treat a number of conditions that are caused or worsened by obesity.1 Cirrhosis related to metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is now a leading indication for liver transplantation in the US2 and obesity is a clear risk factor for all major malignancies of the GI tract, including esophageal, gastric cardia, pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, colon, and rectum.3 Obesity is associated with dysbiosis and impacts barrier function: increasing permeability, abnormal gut bacterial translocation, and inflammation.4 It is more common than malnutrition in our patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where it impacts response to biologic drugs, increases the technical difficulty of surgeries, such as IPAA, and is associated with worse surgical outcomes.5 Furthermore, patients with obesity may be less likely to undergo preventative cancer screenings and are at increased risk related to sedation for endoscopic procedures.6 With over 40% of Americans suffering from obesity, and increasingly effective treatments available,
Understanding the Mechanisms of Obesity
There are complex orexigenic and anorexigenic brain pathways in the hypothalamus which control global energy balance.7 Obesity results when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. While overeating and a sedentary lifestyle are commonly blamed, there are a number of elements that contribute, including genetics, medical conditions, medications, psychosocial factors, and environmental components. For example, sleep loss contributes to weight gain by several mechanisms including increasing ghrelin and decreasing leptin levels, thereby increasing hunger and appetite, as well as by decreasing insulin sensitivity and increasing cortisol. Subjects exposed to sleep deprivation in research settings take in 550 kcal more the following day.8 Medications used commonly in GI practice including corticosteroids, antihistamines, propranolol, and amitriptyline, are obesogenic9 and cannabis can impact hypothalamic pathways to stimulate hunger.10
When patients diet or exercise to lose weight, as we have traditionally advised, there are strong hormonal changes and metabolic adaptations that occur to preserve the defended fat mass or “set point.” Loss of adipose tissue results in decreased production of leptin, a hormone that stimulates satiety pathways and inhibits orexigenic pathways, greatly increasing hunger and cravings. Increases in ghrelin production by the stomach decreases perceptions of fullness. With weight loss, energy requirements decrease, and muscles become more efficient, meaning fewer kcal are needed to maintain bodily processes.11 Eventually a plateau is reached, while motivation to diet and restraint around food wane, and hedonistic (reward) pathways are activated. These powerful factors result in the regain of lost weight within one year in the majority of patients.
Implementing Weight Management into GI Practice
Given the stigma and bias around obesity, patients often feel shame and vulnerability around the condition. It is important to have empathy in your approach, asking permission to discuss weight and using patient-first language (e.g. “patient with obesity” not “obese patient”). While BMI is predictive of health outcomes, it does not measure body fat percentage and may be misleading, such as in muscular individuals. Other measures of adiposity including waist circumference and body composition testing, such as with DEXA, may provide additional data. A BMI of 30 or above defines obesity, though newer definitions incorporate related symptoms, organ disfunction, and metabolic abnormalities into the term “clinical obesity.”12 Asian patients experience metabolic complications at a lower BMI, and therefore the definition of obese is 27.5kg/m2 in this population.
Begin by taking a weight history. Has this been a lifelong struggle or is there a particular life circumstance, such as working a third shift or recent pregnancy which precipitated weight gain? Patients should be asked about binge eating or eating late into the evening or waking at night to eat, as these disordered eating behaviors are managed with specific medications and behavioral therapies. Inquire about sleep duration and quality and refer for a sleep study if there is suspicion for obstructive sleep apnea. Other weight-related comorbidities including hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and MAFLD should be considered and merit a more aggressive approach, as does more severe obesity (class III, BMI ≥40). Questions about marijuana and alcohol use as well as review of the medication list for obesogenic medications can provide further insight into modifiable contributing factors.
Pillars of Weight Management
The internet is awash with trendy diet recommendations, and widespread misconceptions about obesity management are even ingrained into how physicians approach the disease. It is critical to remember that this is not a consequence of bad choices or lack of self-control. Exercise alone is insufficient to result in significant weight loss.13 Furthermore, whether it is through low fat, low carb, or intermittent fasting, weight loss will occur with calorie deficit.14 Evidence-based diet and lifestyle recommendations to lay the groundwork for success should be discussed at each visit (see Table 1). The Mediterranean diet is recommended for weight loss as well as for several GI disorders (i.e., MAFLD and IBD) and is the optimal eating strategy for cardiovascular health.15 Patients should be advised to engage in 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, such as brisk walking, and should incorporate resistance training to build muscle and maintain bone density.
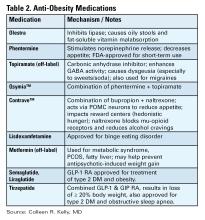
Anti-obesity Medications
There are a number of medications, either FDA approved or used off label, for treatment of obesity (see Table 2).16 All are indicated for patients with a BMI of ≥ 30 kg/m2 or for those with a BMI between 27-29 kg/m2 with weight-related comorbidities and should be used in combination with diet and lifestyle interventions. None are approved or safe in pregnancy. Mechanisms of action vary by type and include decreased appetite, increased energy expenditure, improved insulin sensitivity, and interfere with absorption.
The newest and most effective anti-obesity medications (AOM), the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) are derived from gut hormones secreted in the distal small bowel and colon in response to a meal, which function to delay gastric emptying, increase insulin release from the pancreas, and reduce hepatic gluconeogenesis. Central nervous system effects are not yet entirely understood, but function to decrease appetite and increase satiety. Initially developed for treatment of T2DM, observed weight reduction in patients treated with GLP-1 RA led to clinical trials for treatment of obesity. Semaglutide treatment resulted in weight reduction of 16.9% of total body weight (TBW), and one third of subjects lost ≥ 20% of TBW.17 Tirzepatide combines GLP-1 RA and a gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist, which also has an incretin effect and functions to slow gastric emptying. In the pivotal SURMOUNT trial, approximately 58% of patients achieved ≥20% loss of TBW18 with 15mg weekly dosing of tirzepatide. This class of drugs is a logical choice in patients with T2DM and obesity. Long-term treatment appears necessary, as patients typically regain two-thirds of lost weight within a year after GLP-1 RA are stopped.
Based on tumors observed in rodents, GLP-1 RA are contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN II) or medullary thyroid cancer. These tumors have not been observed in humans treated with GLP-1 RA. They should be used with caution in patients with history of pancreatitis, gastroparesis, or diabetic retinopathy, though a recent systematic review and meta-analysis suggests showed little to no increased risk for biliary events from GLP-1 RA.19 Side effects are most commonly gastrointestinal in nature (nausea, reflux, constipation or diarrhea) and are typically most severe with initiation of the drug and with dose escalation. Side effects can be mitigated by initiating these drugs at lowest doses and gradually titrating up (every four weeks) based on effectiveness and tolerability. Antisecretory, antiemetic, and laxative medications can also be used to help manage GLP-1 RA related side effects.
There is no reason to escalate to highest doses if patients are experiencing weight loss and reduction in food cravings at lower doses. Both semaglutide and tirzepatide are administered subcutaneously every seven days. Once patients have reached goal weight, they can either continue maintenance therapy at that same dose/interval, or if motivated to do so, may gradually reduce the weekly dose in a stepwise approach to determine the minimally effective dose to maintain weight loss. There are not yet published maintenance studies to guide this process. Currently the price of GLP-1 RA and inconsistent insurance coverage make them inaccessible to many patients. The manufacturers of both semaglutide and tirzepatide offer direct to consumer pricing and home delivery.
Bariatric Surgery
In patients with higher BMI (≥35kg/m2) or those with BMI ≥30kg/m2 and obesity-related metabolic disease and the desire to avoid lifelong medications or who fail or are intolerant of AOM, bariatric options should be considered.20 Sleeve gastrectomy has become the most performed surgery for treatment of obesity. It is a restrictive procedure, removing 80% of the stomach, but a drop in circulating levels of ghrelin afterwards also leads to decreased feelings of hunger. It results in weight loss of 25-30% TBW loss. It is not a good choice for patients who suffer from severe GERD, as this typically worsens afterwards; furthermore, de novo Barrett’s has been observed in nearly 6% of patients who undergo sleeve gastrectomy.21
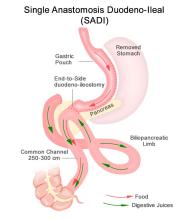
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a restrictive and malabsorptive procedure, resulting in 30-35% TBW loss. It has beneficial and immediate metabolic effects, including increased release of endogenous GLP-1, which leads to improvements in weight-related T2DM. The newer single anastomosis duodenal-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy (SADI-S) starts with a sleeve gastrectomy, making a smaller tube-shaped stomach. The duodenum is divided just after the stomach and then a loop of ileum is brought up and connected to the stomach (see Figure 1). This procedure is highly effective, with patients losing 75-95% of excess body weight and is becoming a preferred option for patients with greater BMI (≥50kg/m2). It is also an option for patients who have already had a sleeve gastrectomy and are seeking further weight loss. Because there is only one anastomosis, perioperative complications, such as anastomotic leaks, are reduced. The risk of micronutrient deficiencies is present with all malabsorptive procedures, and these patients must supplement with multivitamins, iron, vitamin D, and calcium.
Endoscopic Therapies
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) have been increasingly studied and utilized, and this less invasive option may be more appropriate for or attractive to many patients. Intragastric balloons, which reduce meal volume and delay gastric emptying, can be used short term only (six months) resulting in loss of about 6.9% of total body weight (TBW) greater than lifestyle modification (LM) alone, and may be considered in limited situations, such as need for pre-operative weight loss to reduce risks in very obese individuals.22
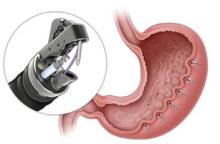
Endoscopic gastric remodeling (EGR), also known as endoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (ESG), is a purely restrictive procedure in which the stomach is cinched to resize and reshape using an endoscopic suturing device (see Figure 2).23 It is an option for patients with class 1 or 2 obesity, with data from a randomized controlled trial in this population demonstrating mean percentage of TBW loss of 13.6% at 52 weeks compared to 0.8% in those treated with LM alone.24 A recent meta-analysis of 21 observational studies, including patients with higher BMIs (32.5 to 49.9 kg/m2) showed pooled average weight loss of 17.3% TBW at 12 months with EGR.22 This procedure has potential advantages of fewer complications, quicker recovery, and much less new-onset GERD compared to laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Furthermore, it may be utilized in combination with AOMs to achieve optimum weight loss and metabolic outcomes.25,26 Potential adverse events include abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting (which may be severe), as well as rare instances of intra/extra luminal bleeding or abdominal abscess requiring drainage.22
Recent joint American/European Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines suggest the use of EBMTs plus lifestyle modification in patients with a BMI of ≥ 30 kg/m2, or with a BMI of 27.0-29.9 kg/m2 with at least 1 obesity-related comorbidity.22 Small bowel interventions including duodenal-jejunal bypass liner and duodenal mucosal resurfacing are being investigated for patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes but not yet commercially available.
Conclusion
Given the overlap of obesity with many GI disorders, it is entirely appropriate for gastroenterologists to consider it worthy of aggressive treatment, particularly in patients with MAFLD and other serious weight related comorbidities. With a compassionate and empathetic approach, and a number of highly effective medical, endoscopic, and surgical therapies now available, weight management has the potential to be extremely rewarding when implemented in GI practice.
Dr. Kelly is based in the Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, Massachusetts. She serves on the clinical advisory board for OpenBiome (unpaid) and has served on an advisory board for Eli Lilly and Company.
References
1. Hales CM, et al. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020 Feb:(360):1–8.
2. Pais R, et al. NAFLD and liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges. J Hepatol. 2016 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.033.
3. Lauby-Secretan B, et al. Body Fatness and Cancer--Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1606602.
4. Kim A. Dysbiosis: A Review Highlighting Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov-Dec. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000356.
5. Singh S, et al. Obesity in IBD: epidemiology, pathogenesis, disease course and treatment outcomes. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.181.
6. Sundararaman L, Goudra B. Sedation for GI Endoscopy in the Morbidly Obese: Challenges and Possible Solutions. J Clin Med. 2024 Aug. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164635.
7. Bombassaro B, et al. The hypothalamus as the central regulator of energy balance and its impact on current and future obesity treatments. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Nov. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2024-0082.
8. Beccuti G, Pannain S. Sleep and obesity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283479109.
9. Desalermos A, et al. Effect of Obesogenic Medications on Weight-Loss Outcomes in a Behavioral Weight-Management Program. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019 May. doi: 10.1002/oby.22444.
10. Lord MN, Noble EE. Hypothalamic cannabinoid signaling: Consequences for eating behavior. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024 Oct. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1251.
11. Farhana A, Rehman A. Metabolic Consequences of Weight Reduction. [Updated 2023 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572145/.
12. Rubino F, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(24)00316-4.
13. Cox CE. Role of Physical Activity for Weight Loss and Weight Maintenance. Diabetes Spectr. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.2337/ds17-0013.
14. Chaput JP, et al. Widespread misconceptions about obesity. Can Fam Physician. 2014 Nov. PMID: 25392431.
15. Muscogiuri G, et al. Mediterranean Diet and Obesity-related Disorders: What is the Evidence? Curr Obes Rep. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s13679-022-00481-1.
16. Gudzune KA, Kushner RF. Medications for Obesity: A Review. JAMA. 2024 Aug. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.10816.
17. Wilding JPH, et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032183.
18. Jastreboff AM, et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jun. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206038.
19. Chiang CH, et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.003.
20. Aderinto N, et al. Recent advances in bariatric surgery: a narrative review of weight loss procedures. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Nov. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001472.
21. Chandan S, et al. Risk of De Novo Barrett’s Esophagus Post Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies With Long-Term Follow-Up. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.06.041.
22. Jirapinyo P, et al. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy-European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline on primary endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for adults with obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2023.12.004.
23. Nduma BN, et al. Endoscopic Gastric Sleeve: A Review of Literature. Cureus. 2023 Mar. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36353.
24. Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for treatment of class 1 and 2 obesity (MERIT): a prospective, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01280-6.
25. Gala K, et al. Outcomes of concomitant antiobesity medication use with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty in clinical US settings. Obes Pillars. 2024 May. doi: 10.1016/j.obpill.2024.100112.
26. Chung CS, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty combined with anti-obesity medication for better control of weight and diabetes. Clin Endosc. 2025 May. doi: 10.5946/ce.2024.274.
Introduction
The majority of patients in the United States are now overweight or obese, and as gastroenterologists we treat a number of conditions that are caused or worsened by obesity.1 Cirrhosis related to metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is now a leading indication for liver transplantation in the US2 and obesity is a clear risk factor for all major malignancies of the GI tract, including esophageal, gastric cardia, pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, colon, and rectum.3 Obesity is associated with dysbiosis and impacts barrier function: increasing permeability, abnormal gut bacterial translocation, and inflammation.4 It is more common than malnutrition in our patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where it impacts response to biologic drugs, increases the technical difficulty of surgeries, such as IPAA, and is associated with worse surgical outcomes.5 Furthermore, patients with obesity may be less likely to undergo preventative cancer screenings and are at increased risk related to sedation for endoscopic procedures.6 With over 40% of Americans suffering from obesity, and increasingly effective treatments available,
Understanding the Mechanisms of Obesity
There are complex orexigenic and anorexigenic brain pathways in the hypothalamus which control global energy balance.7 Obesity results when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. While overeating and a sedentary lifestyle are commonly blamed, there are a number of elements that contribute, including genetics, medical conditions, medications, psychosocial factors, and environmental components. For example, sleep loss contributes to weight gain by several mechanisms including increasing ghrelin and decreasing leptin levels, thereby increasing hunger and appetite, as well as by decreasing insulin sensitivity and increasing cortisol. Subjects exposed to sleep deprivation in research settings take in 550 kcal more the following day.8 Medications used commonly in GI practice including corticosteroids, antihistamines, propranolol, and amitriptyline, are obesogenic9 and cannabis can impact hypothalamic pathways to stimulate hunger.10
When patients diet or exercise to lose weight, as we have traditionally advised, there are strong hormonal changes and metabolic adaptations that occur to preserve the defended fat mass or “set point.” Loss of adipose tissue results in decreased production of leptin, a hormone that stimulates satiety pathways and inhibits orexigenic pathways, greatly increasing hunger and cravings. Increases in ghrelin production by the stomach decreases perceptions of fullness. With weight loss, energy requirements decrease, and muscles become more efficient, meaning fewer kcal are needed to maintain bodily processes.11 Eventually a plateau is reached, while motivation to diet and restraint around food wane, and hedonistic (reward) pathways are activated. These powerful factors result in the regain of lost weight within one year in the majority of patients.
Implementing Weight Management into GI Practice
Given the stigma and bias around obesity, patients often feel shame and vulnerability around the condition. It is important to have empathy in your approach, asking permission to discuss weight and using patient-first language (e.g. “patient with obesity” not “obese patient”). While BMI is predictive of health outcomes, it does not measure body fat percentage and may be misleading, such as in muscular individuals. Other measures of adiposity including waist circumference and body composition testing, such as with DEXA, may provide additional data. A BMI of 30 or above defines obesity, though newer definitions incorporate related symptoms, organ disfunction, and metabolic abnormalities into the term “clinical obesity.”12 Asian patients experience metabolic complications at a lower BMI, and therefore the definition of obese is 27.5kg/m2 in this population.
Begin by taking a weight history. Has this been a lifelong struggle or is there a particular life circumstance, such as working a third shift or recent pregnancy which precipitated weight gain? Patients should be asked about binge eating or eating late into the evening or waking at night to eat, as these disordered eating behaviors are managed with specific medications and behavioral therapies. Inquire about sleep duration and quality and refer for a sleep study if there is suspicion for obstructive sleep apnea. Other weight-related comorbidities including hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and MAFLD should be considered and merit a more aggressive approach, as does more severe obesity (class III, BMI ≥40). Questions about marijuana and alcohol use as well as review of the medication list for obesogenic medications can provide further insight into modifiable contributing factors.
Pillars of Weight Management
The internet is awash with trendy diet recommendations, and widespread misconceptions about obesity management are even ingrained into how physicians approach the disease. It is critical to remember that this is not a consequence of bad choices or lack of self-control. Exercise alone is insufficient to result in significant weight loss.13 Furthermore, whether it is through low fat, low carb, or intermittent fasting, weight loss will occur with calorie deficit.14 Evidence-based diet and lifestyle recommendations to lay the groundwork for success should be discussed at each visit (see Table 1). The Mediterranean diet is recommended for weight loss as well as for several GI disorders (i.e., MAFLD and IBD) and is the optimal eating strategy for cardiovascular health.15 Patients should be advised to engage in 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, such as brisk walking, and should incorporate resistance training to build muscle and maintain bone density.
Anti-obesity Medications
There are a number of medications, either FDA approved or used off label, for treatment of obesity (see Table 2).16 All are indicated for patients with a BMI of ≥ 30 kg/m2 or for those with a BMI between 27-29 kg/m2 with weight-related comorbidities and should be used in combination with diet and lifestyle interventions. None are approved or safe in pregnancy. Mechanisms of action vary by type and include decreased appetite, increased energy expenditure, improved insulin sensitivity, and interfere with absorption.
The newest and most effective anti-obesity medications (AOM), the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) are derived from gut hormones secreted in the distal small bowel and colon in response to a meal, which function to delay gastric emptying, increase insulin release from the pancreas, and reduce hepatic gluconeogenesis. Central nervous system effects are not yet entirely understood, but function to decrease appetite and increase satiety. Initially developed for treatment of T2DM, observed weight reduction in patients treated with GLP-1 RA led to clinical trials for treatment of obesity. Semaglutide treatment resulted in weight reduction of 16.9% of total body weight (TBW), and one third of subjects lost ≥ 20% of TBW.17 Tirzepatide combines GLP-1 RA and a gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist, which also has an incretin effect and functions to slow gastric emptying. In the pivotal SURMOUNT trial, approximately 58% of patients achieved ≥20% loss of TBW18 with 15mg weekly dosing of tirzepatide. This class of drugs is a logical choice in patients with T2DM and obesity. Long-term treatment appears necessary, as patients typically regain two-thirds of lost weight within a year after GLP-1 RA are stopped.
Based on tumors observed in rodents, GLP-1 RA are contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN II) or medullary thyroid cancer. These tumors have not been observed in humans treated with GLP-1 RA. They should be used with caution in patients with history of pancreatitis, gastroparesis, or diabetic retinopathy, though a recent systematic review and meta-analysis suggests showed little to no increased risk for biliary events from GLP-1 RA.19 Side effects are most commonly gastrointestinal in nature (nausea, reflux, constipation or diarrhea) and are typically most severe with initiation of the drug and with dose escalation. Side effects can be mitigated by initiating these drugs at lowest doses and gradually titrating up (every four weeks) based on effectiveness and tolerability. Antisecretory, antiemetic, and laxative medications can also be used to help manage GLP-1 RA related side effects.
There is no reason to escalate to highest doses if patients are experiencing weight loss and reduction in food cravings at lower doses. Both semaglutide and tirzepatide are administered subcutaneously every seven days. Once patients have reached goal weight, they can either continue maintenance therapy at that same dose/interval, or if motivated to do so, may gradually reduce the weekly dose in a stepwise approach to determine the minimally effective dose to maintain weight loss. There are not yet published maintenance studies to guide this process. Currently the price of GLP-1 RA and inconsistent insurance coverage make them inaccessible to many patients. The manufacturers of both semaglutide and tirzepatide offer direct to consumer pricing and home delivery.
Bariatric Surgery
In patients with higher BMI (≥35kg/m2) or those with BMI ≥30kg/m2 and obesity-related metabolic disease and the desire to avoid lifelong medications or who fail or are intolerant of AOM, bariatric options should be considered.20 Sleeve gastrectomy has become the most performed surgery for treatment of obesity. It is a restrictive procedure, removing 80% of the stomach, but a drop in circulating levels of ghrelin afterwards also leads to decreased feelings of hunger. It results in weight loss of 25-30% TBW loss. It is not a good choice for patients who suffer from severe GERD, as this typically worsens afterwards; furthermore, de novo Barrett’s has been observed in nearly 6% of patients who undergo sleeve gastrectomy.21
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a restrictive and malabsorptive procedure, resulting in 30-35% TBW loss. It has beneficial and immediate metabolic effects, including increased release of endogenous GLP-1, which leads to improvements in weight-related T2DM. The newer single anastomosis duodenal-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy (SADI-S) starts with a sleeve gastrectomy, making a smaller tube-shaped stomach. The duodenum is divided just after the stomach and then a loop of ileum is brought up and connected to the stomach (see Figure 1). This procedure is highly effective, with patients losing 75-95% of excess body weight and is becoming a preferred option for patients with greater BMI (≥50kg/m2). It is also an option for patients who have already had a sleeve gastrectomy and are seeking further weight loss. Because there is only one anastomosis, perioperative complications, such as anastomotic leaks, are reduced. The risk of micronutrient deficiencies is present with all malabsorptive procedures, and these patients must supplement with multivitamins, iron, vitamin D, and calcium.
Endoscopic Therapies
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) have been increasingly studied and utilized, and this less invasive option may be more appropriate for or attractive to many patients. Intragastric balloons, which reduce meal volume and delay gastric emptying, can be used short term only (six months) resulting in loss of about 6.9% of total body weight (TBW) greater than lifestyle modification (LM) alone, and may be considered in limited situations, such as need for pre-operative weight loss to reduce risks in very obese individuals.22
Endoscopic gastric remodeling (EGR), also known as endoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (ESG), is a purely restrictive procedure in which the stomach is cinched to resize and reshape using an endoscopic suturing device (see Figure 2).23 It is an option for patients with class 1 or 2 obesity, with data from a randomized controlled trial in this population demonstrating mean percentage of TBW loss of 13.6% at 52 weeks compared to 0.8% in those treated with LM alone.24 A recent meta-analysis of 21 observational studies, including patients with higher BMIs (32.5 to 49.9 kg/m2) showed pooled average weight loss of 17.3% TBW at 12 months with EGR.22 This procedure has potential advantages of fewer complications, quicker recovery, and much less new-onset GERD compared to laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Furthermore, it may be utilized in combination with AOMs to achieve optimum weight loss and metabolic outcomes.25,26 Potential adverse events include abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting (which may be severe), as well as rare instances of intra/extra luminal bleeding or abdominal abscess requiring drainage.22
Recent joint American/European Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines suggest the use of EBMTs plus lifestyle modification in patients with a BMI of ≥ 30 kg/m2, or with a BMI of 27.0-29.9 kg/m2 with at least 1 obesity-related comorbidity.22 Small bowel interventions including duodenal-jejunal bypass liner and duodenal mucosal resurfacing are being investigated for patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes but not yet commercially available.
Conclusion
Given the overlap of obesity with many GI disorders, it is entirely appropriate for gastroenterologists to consider it worthy of aggressive treatment, particularly in patients with MAFLD and other serious weight related comorbidities. With a compassionate and empathetic approach, and a number of highly effective medical, endoscopic, and surgical therapies now available, weight management has the potential to be extremely rewarding when implemented in GI practice.
Dr. Kelly is based in the Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, Massachusetts. She serves on the clinical advisory board for OpenBiome (unpaid) and has served on an advisory board for Eli Lilly and Company.
References
1. Hales CM, et al. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020 Feb:(360):1–8.
2. Pais R, et al. NAFLD and liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges. J Hepatol. 2016 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.033.
3. Lauby-Secretan B, et al. Body Fatness and Cancer--Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1606602.
4. Kim A. Dysbiosis: A Review Highlighting Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov-Dec. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000356.
5. Singh S, et al. Obesity in IBD: epidemiology, pathogenesis, disease course and treatment outcomes. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.181.
6. Sundararaman L, Goudra B. Sedation for GI Endoscopy in the Morbidly Obese: Challenges and Possible Solutions. J Clin Med. 2024 Aug. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164635.
7. Bombassaro B, et al. The hypothalamus as the central regulator of energy balance and its impact on current and future obesity treatments. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Nov. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2024-0082.
8. Beccuti G, Pannain S. Sleep and obesity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283479109.
9. Desalermos A, et al. Effect of Obesogenic Medications on Weight-Loss Outcomes in a Behavioral Weight-Management Program. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019 May. doi: 10.1002/oby.22444.
10. Lord MN, Noble EE. Hypothalamic cannabinoid signaling: Consequences for eating behavior. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024 Oct. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1251.
11. Farhana A, Rehman A. Metabolic Consequences of Weight Reduction. [Updated 2023 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572145/.
12. Rubino F, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(24)00316-4.
13. Cox CE. Role of Physical Activity for Weight Loss and Weight Maintenance. Diabetes Spectr. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.2337/ds17-0013.
14. Chaput JP, et al. Widespread misconceptions about obesity. Can Fam Physician. 2014 Nov. PMID: 25392431.
15. Muscogiuri G, et al. Mediterranean Diet and Obesity-related Disorders: What is the Evidence? Curr Obes Rep. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s13679-022-00481-1.
16. Gudzune KA, Kushner RF. Medications for Obesity: A Review. JAMA. 2024 Aug. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.10816.
17. Wilding JPH, et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032183.
18. Jastreboff AM, et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jun. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206038.
19. Chiang CH, et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.003.
20. Aderinto N, et al. Recent advances in bariatric surgery: a narrative review of weight loss procedures. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Nov. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001472.
21. Chandan S, et al. Risk of De Novo Barrett’s Esophagus Post Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies With Long-Term Follow-Up. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.06.041.
22. Jirapinyo P, et al. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy-European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline on primary endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for adults with obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2023.12.004.
23. Nduma BN, et al. Endoscopic Gastric Sleeve: A Review of Literature. Cureus. 2023 Mar. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36353.
24. Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for treatment of class 1 and 2 obesity (MERIT): a prospective, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01280-6.
25. Gala K, et al. Outcomes of concomitant antiobesity medication use with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty in clinical US settings. Obes Pillars. 2024 May. doi: 10.1016/j.obpill.2024.100112.
26. Chung CS, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty combined with anti-obesity medication for better control of weight and diabetes. Clin Endosc. 2025 May. doi: 10.5946/ce.2024.274.
Introduction
The majority of patients in the United States are now overweight or obese, and as gastroenterologists we treat a number of conditions that are caused or worsened by obesity.1 Cirrhosis related to metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is now a leading indication for liver transplantation in the US2 and obesity is a clear risk factor for all major malignancies of the GI tract, including esophageal, gastric cardia, pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, colon, and rectum.3 Obesity is associated with dysbiosis and impacts barrier function: increasing permeability, abnormal gut bacterial translocation, and inflammation.4 It is more common than malnutrition in our patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where it impacts response to biologic drugs, increases the technical difficulty of surgeries, such as IPAA, and is associated with worse surgical outcomes.5 Furthermore, patients with obesity may be less likely to undergo preventative cancer screenings and are at increased risk related to sedation for endoscopic procedures.6 With over 40% of Americans suffering from obesity, and increasingly effective treatments available,
Understanding the Mechanisms of Obesity
There are complex orexigenic and anorexigenic brain pathways in the hypothalamus which control global energy balance.7 Obesity results when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. While overeating and a sedentary lifestyle are commonly blamed, there are a number of elements that contribute, including genetics, medical conditions, medications, psychosocial factors, and environmental components. For example, sleep loss contributes to weight gain by several mechanisms including increasing ghrelin and decreasing leptin levels, thereby increasing hunger and appetite, as well as by decreasing insulin sensitivity and increasing cortisol. Subjects exposed to sleep deprivation in research settings take in 550 kcal more the following day.8 Medications used commonly in GI practice including corticosteroids, antihistamines, propranolol, and amitriptyline, are obesogenic9 and cannabis can impact hypothalamic pathways to stimulate hunger.10
When patients diet or exercise to lose weight, as we have traditionally advised, there are strong hormonal changes and metabolic adaptations that occur to preserve the defended fat mass or “set point.” Loss of adipose tissue results in decreased production of leptin, a hormone that stimulates satiety pathways and inhibits orexigenic pathways, greatly increasing hunger and cravings. Increases in ghrelin production by the stomach decreases perceptions of fullness. With weight loss, energy requirements decrease, and muscles become more efficient, meaning fewer kcal are needed to maintain bodily processes.11 Eventually a plateau is reached, while motivation to diet and restraint around food wane, and hedonistic (reward) pathways are activated. These powerful factors result in the regain of lost weight within one year in the majority of patients.
Implementing Weight Management into GI Practice
Given the stigma and bias around obesity, patients often feel shame and vulnerability around the condition. It is important to have empathy in your approach, asking permission to discuss weight and using patient-first language (e.g. “patient with obesity” not “obese patient”). While BMI is predictive of health outcomes, it does not measure body fat percentage and may be misleading, such as in muscular individuals. Other measures of adiposity including waist circumference and body composition testing, such as with DEXA, may provide additional data. A BMI of 30 or above defines obesity, though newer definitions incorporate related symptoms, organ disfunction, and metabolic abnormalities into the term “clinical obesity.”12 Asian patients experience metabolic complications at a lower BMI, and therefore the definition of obese is 27.5kg/m2 in this population.
Begin by taking a weight history. Has this been a lifelong struggle or is there a particular life circumstance, such as working a third shift or recent pregnancy which precipitated weight gain? Patients should be asked about binge eating or eating late into the evening or waking at night to eat, as these disordered eating behaviors are managed with specific medications and behavioral therapies. Inquire about sleep duration and quality and refer for a sleep study if there is suspicion for obstructive sleep apnea. Other weight-related comorbidities including hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and MAFLD should be considered and merit a more aggressive approach, as does more severe obesity (class III, BMI ≥40). Questions about marijuana and alcohol use as well as review of the medication list for obesogenic medications can provide further insight into modifiable contributing factors.
Pillars of Weight Management
The internet is awash with trendy diet recommendations, and widespread misconceptions about obesity management are even ingrained into how physicians approach the disease. It is critical to remember that this is not a consequence of bad choices or lack of self-control. Exercise alone is insufficient to result in significant weight loss.13 Furthermore, whether it is through low fat, low carb, or intermittent fasting, weight loss will occur with calorie deficit.14 Evidence-based diet and lifestyle recommendations to lay the groundwork for success should be discussed at each visit (see Table 1). The Mediterranean diet is recommended for weight loss as well as for several GI disorders (i.e., MAFLD and IBD) and is the optimal eating strategy for cardiovascular health.15 Patients should be advised to engage in 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, such as brisk walking, and should incorporate resistance training to build muscle and maintain bone density.
Anti-obesity Medications
There are a number of medications, either FDA approved or used off label, for treatment of obesity (see Table 2).16 All are indicated for patients with a BMI of ≥ 30 kg/m2 or for those with a BMI between 27-29 kg/m2 with weight-related comorbidities and should be used in combination with diet and lifestyle interventions. None are approved or safe in pregnancy. Mechanisms of action vary by type and include decreased appetite, increased energy expenditure, improved insulin sensitivity, and interfere with absorption.
The newest and most effective anti-obesity medications (AOM), the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) are derived from gut hormones secreted in the distal small bowel and colon in response to a meal, which function to delay gastric emptying, increase insulin release from the pancreas, and reduce hepatic gluconeogenesis. Central nervous system effects are not yet entirely understood, but function to decrease appetite and increase satiety. Initially developed for treatment of T2DM, observed weight reduction in patients treated with GLP-1 RA led to clinical trials for treatment of obesity. Semaglutide treatment resulted in weight reduction of 16.9% of total body weight (TBW), and one third of subjects lost ≥ 20% of TBW.17 Tirzepatide combines GLP-1 RA and a gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist, which also has an incretin effect and functions to slow gastric emptying. In the pivotal SURMOUNT trial, approximately 58% of patients achieved ≥20% loss of TBW18 with 15mg weekly dosing of tirzepatide. This class of drugs is a logical choice in patients with T2DM and obesity. Long-term treatment appears necessary, as patients typically regain two-thirds of lost weight within a year after GLP-1 RA are stopped.
Based on tumors observed in rodents, GLP-1 RA are contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN II) or medullary thyroid cancer. These tumors have not been observed in humans treated with GLP-1 RA. They should be used with caution in patients with history of pancreatitis, gastroparesis, or diabetic retinopathy, though a recent systematic review and meta-analysis suggests showed little to no increased risk for biliary events from GLP-1 RA.19 Side effects are most commonly gastrointestinal in nature (nausea, reflux, constipation or diarrhea) and are typically most severe with initiation of the drug and with dose escalation. Side effects can be mitigated by initiating these drugs at lowest doses and gradually titrating up (every four weeks) based on effectiveness and tolerability. Antisecretory, antiemetic, and laxative medications can also be used to help manage GLP-1 RA related side effects.
There is no reason to escalate to highest doses if patients are experiencing weight loss and reduction in food cravings at lower doses. Both semaglutide and tirzepatide are administered subcutaneously every seven days. Once patients have reached goal weight, they can either continue maintenance therapy at that same dose/interval, or if motivated to do so, may gradually reduce the weekly dose in a stepwise approach to determine the minimally effective dose to maintain weight loss. There are not yet published maintenance studies to guide this process. Currently the price of GLP-1 RA and inconsistent insurance coverage make them inaccessible to many patients. The manufacturers of both semaglutide and tirzepatide offer direct to consumer pricing and home delivery.
Bariatric Surgery
In patients with higher BMI (≥35kg/m2) or those with BMI ≥30kg/m2 and obesity-related metabolic disease and the desire to avoid lifelong medications or who fail or are intolerant of AOM, bariatric options should be considered.20 Sleeve gastrectomy has become the most performed surgery for treatment of obesity. It is a restrictive procedure, removing 80% of the stomach, but a drop in circulating levels of ghrelin afterwards also leads to decreased feelings of hunger. It results in weight loss of 25-30% TBW loss. It is not a good choice for patients who suffer from severe GERD, as this typically worsens afterwards; furthermore, de novo Barrett’s has been observed in nearly 6% of patients who undergo sleeve gastrectomy.21
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a restrictive and malabsorptive procedure, resulting in 30-35% TBW loss. It has beneficial and immediate metabolic effects, including increased release of endogenous GLP-1, which leads to improvements in weight-related T2DM. The newer single anastomosis duodenal-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy (SADI-S) starts with a sleeve gastrectomy, making a smaller tube-shaped stomach. The duodenum is divided just after the stomach and then a loop of ileum is brought up and connected to the stomach (see Figure 1). This procedure is highly effective, with patients losing 75-95% of excess body weight and is becoming a preferred option for patients with greater BMI (≥50kg/m2). It is also an option for patients who have already had a sleeve gastrectomy and are seeking further weight loss. Because there is only one anastomosis, perioperative complications, such as anastomotic leaks, are reduced. The risk of micronutrient deficiencies is present with all malabsorptive procedures, and these patients must supplement with multivitamins, iron, vitamin D, and calcium.
Endoscopic Therapies
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) have been increasingly studied and utilized, and this less invasive option may be more appropriate for or attractive to many patients. Intragastric balloons, which reduce meal volume and delay gastric emptying, can be used short term only (six months) resulting in loss of about 6.9% of total body weight (TBW) greater than lifestyle modification (LM) alone, and may be considered in limited situations, such as need for pre-operative weight loss to reduce risks in very obese individuals.22
Endoscopic gastric remodeling (EGR), also known as endoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (ESG), is a purely restrictive procedure in which the stomach is cinched to resize and reshape using an endoscopic suturing device (see Figure 2).23 It is an option for patients with class 1 or 2 obesity, with data from a randomized controlled trial in this population demonstrating mean percentage of TBW loss of 13.6% at 52 weeks compared to 0.8% in those treated with LM alone.24 A recent meta-analysis of 21 observational studies, including patients with higher BMIs (32.5 to 49.9 kg/m2) showed pooled average weight loss of 17.3% TBW at 12 months with EGR.22 This procedure has potential advantages of fewer complications, quicker recovery, and much less new-onset GERD compared to laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Furthermore, it may be utilized in combination with AOMs to achieve optimum weight loss and metabolic outcomes.25,26 Potential adverse events include abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting (which may be severe), as well as rare instances of intra/extra luminal bleeding or abdominal abscess requiring drainage.22
Recent joint American/European Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines suggest the use of EBMTs plus lifestyle modification in patients with a BMI of ≥ 30 kg/m2, or with a BMI of 27.0-29.9 kg/m2 with at least 1 obesity-related comorbidity.22 Small bowel interventions including duodenal-jejunal bypass liner and duodenal mucosal resurfacing are being investigated for patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes but not yet commercially available.
Conclusion
Given the overlap of obesity with many GI disorders, it is entirely appropriate for gastroenterologists to consider it worthy of aggressive treatment, particularly in patients with MAFLD and other serious weight related comorbidities. With a compassionate and empathetic approach, and a number of highly effective medical, endoscopic, and surgical therapies now available, weight management has the potential to be extremely rewarding when implemented in GI practice.
Dr. Kelly is based in the Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, Massachusetts. She serves on the clinical advisory board for OpenBiome (unpaid) and has served on an advisory board for Eli Lilly and Company.
References
1. Hales CM, et al. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020 Feb:(360):1–8.
2. Pais R, et al. NAFLD and liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges. J Hepatol. 2016 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.033.
3. Lauby-Secretan B, et al. Body Fatness and Cancer--Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsr1606602.
4. Kim A. Dysbiosis: A Review Highlighting Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov-Dec. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000356.
5. Singh S, et al. Obesity in IBD: epidemiology, pathogenesis, disease course and treatment outcomes. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.181.
6. Sundararaman L, Goudra B. Sedation for GI Endoscopy in the Morbidly Obese: Challenges and Possible Solutions. J Clin Med. 2024 Aug. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164635.
7. Bombassaro B, et al. The hypothalamus as the central regulator of energy balance and its impact on current and future obesity treatments. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Nov. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2024-0082.
8. Beccuti G, Pannain S. Sleep and obesity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283479109.
9. Desalermos A, et al. Effect of Obesogenic Medications on Weight-Loss Outcomes in a Behavioral Weight-Management Program. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019 May. doi: 10.1002/oby.22444.
10. Lord MN, Noble EE. Hypothalamic cannabinoid signaling: Consequences for eating behavior. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024 Oct. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1251.
11. Farhana A, Rehman A. Metabolic Consequences of Weight Reduction. [Updated 2023 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572145/.
12. Rubino F, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(24)00316-4.
13. Cox CE. Role of Physical Activity for Weight Loss and Weight Maintenance. Diabetes Spectr. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.2337/ds17-0013.
14. Chaput JP, et al. Widespread misconceptions about obesity. Can Fam Physician. 2014 Nov. PMID: 25392431.
15. Muscogiuri G, et al. Mediterranean Diet and Obesity-related Disorders: What is the Evidence? Curr Obes Rep. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s13679-022-00481-1.
16. Gudzune KA, Kushner RF. Medications for Obesity: A Review. JAMA. 2024 Aug. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.10816.
17. Wilding JPH, et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032183.
18. Jastreboff AM, et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jun. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206038.
19. Chiang CH, et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.003.
20. Aderinto N, et al. Recent advances in bariatric surgery: a narrative review of weight loss procedures. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Nov. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001472.
21. Chandan S, et al. Risk of De Novo Barrett’s Esophagus Post Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies With Long-Term Follow-Up. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.06.041.
22. Jirapinyo P, et al. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy-European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline on primary endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for adults with obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2023.12.004.
23. Nduma BN, et al. Endoscopic Gastric Sleeve: A Review of Literature. Cureus. 2023 Mar. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36353.
24. Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for treatment of class 1 and 2 obesity (MERIT): a prospective, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01280-6.
25. Gala K, et al. Outcomes of concomitant antiobesity medication use with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty in clinical US settings. Obes Pillars. 2024 May. doi: 10.1016/j.obpill.2024.100112.
26. Chung CS, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty combined with anti-obesity medication for better control of weight and diabetes. Clin Endosc. 2025 May. doi: 10.5946/ce.2024.274.
Colon Cleanses: How to Discourage Patients
Social media is rife with content promoting colon cleansing as a way to shed toxins and fix everything from chronic fatigue and overweight to weak immunity and skin problems.
Even doctors who aren’t hip to the latest TikTok trends may not be able to avoid the hype. That’s because patients are bringing up colon cleansing during their office visit.
“Patients often raise questions about colonics or detox teas, especially when these gain traction on social media platforms like TikTok,” said Tauseef Ali, MD, AGAF, medical executive director of SSM Health Digestive Care at St. Anthony Hospital in Oklahoma City. “Interest typically comes in waves, closely tied to the latest online trends.”
That means . And it’s not just patients who are asking.
“Sometimes we’ll get a message from primary care,” Mohammad Bilal, MD, associate professor of medicine and director of Bariatric and Third Space Endoscopy at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora, Colorado, told GI & Hepatology News. They’re getting the same questions from patients, and they want to know if colon cleansing that’s not connected with a colonoscopy exam has any benefits for overall health or specific health conditions.
The answer is no, and patients are more likely to believe that when physicians explain it using good information. Here is how Ali, Bilal, and professional organizations advise doctors to approach the issue.
What Exactly Is a Colon Cleanse?
Colon cleanses come in a variety of forms. Colonic irrigation, also called colon hydrotherapy, involves inserting a tube into the rectum and flushing out the colon with a large amount of fluid. Enemas do the same but use a small amount of liquid, and some product instructions tell the user to “hold it” for a designated amount of time before expelling colon contents.
Other cleanses, often called detoxing cleanses, are laxatives or herbal teas that users drink — and then stay close to the bathroom. Detox regimens and diets also are mentioned as a way to remove toxins from the body, improve health, and promote well-being.
Why Do Patients Use Them?
“Many patients describe a desire for ‘cleanliness,’ ‘detoxification,’ or to ‘feel lighter,’” Ali told GI & Hepatology News.
The claims on social media promote all of this and more — and well-known influencers make it all sound even more attractive.
“These motivations are often rooted in the cultural belief that the colon accumulates harmful toxins that must be flushed out,” Ali said. “This idea is not supported by scientific evidence. The body’s natural detox systems, primarily the liver and kidneys, already perform this function effectively.”
Bilal said that in recent years, he has noticed more awareness in general about the importance of gut health. “When there’s awareness, people often go to the other extreme,” he said.
Where Is the Evidence?
The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), part of the National Institutes of Health, warns on an information page that both cleansing and detox programs can be unsafe and falsely advertised.
While searches of medical literature turn up few studies, the NCCIH information points to a 2014 review that concluded that there is no compelling research to support the use of detox diets for managing weight or eliminating toxins. A 2017 review found juicing and detox regimens can cause weight loss initially but then lead to weight gain once a normal diet is resumed.
A systematic review of research on the safety and effectiveness of self-administered coffee enemas found nine case reports describing adverse events: seven reported colitis after the enema, and two reported more critical adverse events. All nine reports warned against the procedure. The researchers found no study reporting the effectiveness of coffee enemas.
The NCCIH information also notes that there is “limited clinical evidence validating colonic irrigation and insufficient evidence for its prescribed uses.”
Are Cleanses Regulated?
Some over-the-counter colon cleansing products are viewed as dietary supplements, giving the FDA authority to regulate them and take action under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994.
Certain products promoted as colon cleanses, such as laxatives, are regulated by the FDA as over-the-counter drugs and must meet safety and other requirements.
Colonic irrigation systems meant for cleansing before radiologic or endoscopic exams are class II devices — subject to 510(k) premarket notification requirements before marketing — whereas systems intended for other uses, such as routine colon cleansing for general well-being, are regarded as class III devices — subject to premarket approval requirements — according to an FDA spokesperson. To date, the FDA has not approved any colonic irrigation devices for the latter use, the spokesperson said.
For instance, the FDA warned consumers not to use a product promoted for colon cleansing after finding it contained tadalafil, the active ingredient in an FDA-approved drug for erectile dysfunction. The FDA has also issued numerous warning letters to the makers of colon cleansing devices, as they are not approved for this purpose.
The Federal Trade Commission can also take action specifically if the claims about the benefits and safety of products — including supplements, foods, over-the-counter drugs, or health equipment — are false, misleading, or not supported by science.
What Are the Dangers?
Cleanse and detox products come with many risks, including electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and infections, Ali said. With colonic irrigation, there is a risk for rectal perforation. Products also may disrupt the gut microbiome, and some can interact with medications or worsen underlying health conditions, he added.
“It’s important for patients to be aware of these risks before considering nonmedical ‘cleaning’ methods,” he said.
At worst, patients risk fatality, Ali noted. He recalled a young patient who began using a vegetable enema as a detox. As it was being administered, the colon ruptured. The patient was admitted as a medical emergency and required surgery. Fortunately, the patient survived, but the incident could have proven fatal, Ali said.
Educating Patients
Because patients often don’t think of herbal cleanses, detox teas, and over-the-counter powders as supplements, Ali said it’s important to ask them about everything they take.
One way to frame this question is to ask if they are consuming any over-the-counter supplements or any other remedies, he said, and perhaps ask directly about any cleanses they are doing.
When patients ask him about colon cleanses, Ali explains the difference between evidence-based colonoscopy preparation and unregulated “cleanses.” Most patients respond to that approach, he said. Indeed, AGA and other GI societies updated their recommendations on optimizing bowel preparation quality for colonoscopy.
“Still, the appeal of quick fixes of social media trends can sometimes outweigh medical advice,” Ali said. He depends on building trusted relationships and reinforcing the message over time and finds that helps patients make informed and healthier choices.
Bilal, too, explains to patients that cleanses are unnecessary and educates them about what to do instead:
- Eat a containing the recommended amount of (22-34 g, depending on age and gender).
- For , follow a bowel regimen advised by your doctor.
- If gastrointestinal issues persist, get a medical checkup.
- Get any unexplained constipation or checked out by a doctor.
Taking a careful history can pay off, Ali has found. He questioned a patient complaining of abdominal discomfort whose testing found unexpectedly elevated liver enzymes and found she had been using an herbal “cleanse tea” found online. Within 4 weeks of stopping it, her liver enzymes normalized. “Thankfully, she made a full recovery — and she never touched those remedies again,” he said.
Ali had no relevant disclosures. Bilal reported consulting for Boston Scientific, Cook Medical, and Steris.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Social media is rife with content promoting colon cleansing as a way to shed toxins and fix everything from chronic fatigue and overweight to weak immunity and skin problems.
Even doctors who aren’t hip to the latest TikTok trends may not be able to avoid the hype. That’s because patients are bringing up colon cleansing during their office visit.
“Patients often raise questions about colonics or detox teas, especially when these gain traction on social media platforms like TikTok,” said Tauseef Ali, MD, AGAF, medical executive director of SSM Health Digestive Care at St. Anthony Hospital in Oklahoma City. “Interest typically comes in waves, closely tied to the latest online trends.”
That means . And it’s not just patients who are asking.
“Sometimes we’ll get a message from primary care,” Mohammad Bilal, MD, associate professor of medicine and director of Bariatric and Third Space Endoscopy at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora, Colorado, told GI & Hepatology News. They’re getting the same questions from patients, and they want to know if colon cleansing that’s not connected with a colonoscopy exam has any benefits for overall health or specific health conditions.
The answer is no, and patients are more likely to believe that when physicians explain it using good information. Here is how Ali, Bilal, and professional organizations advise doctors to approach the issue.
What Exactly Is a Colon Cleanse?
Colon cleanses come in a variety of forms. Colonic irrigation, also called colon hydrotherapy, involves inserting a tube into the rectum and flushing out the colon with a large amount of fluid. Enemas do the same but use a small amount of liquid, and some product instructions tell the user to “hold it” for a designated amount of time before expelling colon contents.
Other cleanses, often called detoxing cleanses, are laxatives or herbal teas that users drink — and then stay close to the bathroom. Detox regimens and diets also are mentioned as a way to remove toxins from the body, improve health, and promote well-being.
Why Do Patients Use Them?
“Many patients describe a desire for ‘cleanliness,’ ‘detoxification,’ or to ‘feel lighter,’” Ali told GI & Hepatology News.
The claims on social media promote all of this and more — and well-known influencers make it all sound even more attractive.
“These motivations are often rooted in the cultural belief that the colon accumulates harmful toxins that must be flushed out,” Ali said. “This idea is not supported by scientific evidence. The body’s natural detox systems, primarily the liver and kidneys, already perform this function effectively.”
Bilal said that in recent years, he has noticed more awareness in general about the importance of gut health. “When there’s awareness, people often go to the other extreme,” he said.
Where Is the Evidence?
The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), part of the National Institutes of Health, warns on an information page that both cleansing and detox programs can be unsafe and falsely advertised.
While searches of medical literature turn up few studies, the NCCIH information points to a 2014 review that concluded that there is no compelling research to support the use of detox diets for managing weight or eliminating toxins. A 2017 review found juicing and detox regimens can cause weight loss initially but then lead to weight gain once a normal diet is resumed.
A systematic review of research on the safety and effectiveness of self-administered coffee enemas found nine case reports describing adverse events: seven reported colitis after the enema, and two reported more critical adverse events. All nine reports warned against the procedure. The researchers found no study reporting the effectiveness of coffee enemas.
The NCCIH information also notes that there is “limited clinical evidence validating colonic irrigation and insufficient evidence for its prescribed uses.”
Are Cleanses Regulated?
Some over-the-counter colon cleansing products are viewed as dietary supplements, giving the FDA authority to regulate them and take action under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994.
Certain products promoted as colon cleanses, such as laxatives, are regulated by the FDA as over-the-counter drugs and must meet safety and other requirements.
Colonic irrigation systems meant for cleansing before radiologic or endoscopic exams are class II devices — subject to 510(k) premarket notification requirements before marketing — whereas systems intended for other uses, such as routine colon cleansing for general well-being, are regarded as class III devices — subject to premarket approval requirements — according to an FDA spokesperson. To date, the FDA has not approved any colonic irrigation devices for the latter use, the spokesperson said.
For instance, the FDA warned consumers not to use a product promoted for colon cleansing after finding it contained tadalafil, the active ingredient in an FDA-approved drug for erectile dysfunction. The FDA has also issued numerous warning letters to the makers of colon cleansing devices, as they are not approved for this purpose.
The Federal Trade Commission can also take action specifically if the claims about the benefits and safety of products — including supplements, foods, over-the-counter drugs, or health equipment — are false, misleading, or not supported by science.
What Are the Dangers?
Cleanse and detox products come with many risks, including electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and infections, Ali said. With colonic irrigation, there is a risk for rectal perforation. Products also may disrupt the gut microbiome, and some can interact with medications or worsen underlying health conditions, he added.
“It’s important for patients to be aware of these risks before considering nonmedical ‘cleaning’ methods,” he said.
At worst, patients risk fatality, Ali noted. He recalled a young patient who began using a vegetable enema as a detox. As it was being administered, the colon ruptured. The patient was admitted as a medical emergency and required surgery. Fortunately, the patient survived, but the incident could have proven fatal, Ali said.
Educating Patients
Because patients often don’t think of herbal cleanses, detox teas, and over-the-counter powders as supplements, Ali said it’s important to ask them about everything they take.
One way to frame this question is to ask if they are consuming any over-the-counter supplements or any other remedies, he said, and perhaps ask directly about any cleanses they are doing.
When patients ask him about colon cleanses, Ali explains the difference between evidence-based colonoscopy preparation and unregulated “cleanses.” Most patients respond to that approach, he said. Indeed, AGA and other GI societies updated their recommendations on optimizing bowel preparation quality for colonoscopy.
“Still, the appeal of quick fixes of social media trends can sometimes outweigh medical advice,” Ali said. He depends on building trusted relationships and reinforcing the message over time and finds that helps patients make informed and healthier choices.
Bilal, too, explains to patients that cleanses are unnecessary and educates them about what to do instead:
- Eat a containing the recommended amount of (22-34 g, depending on age and gender).
- For , follow a bowel regimen advised by your doctor.
- If gastrointestinal issues persist, get a medical checkup.
- Get any unexplained constipation or checked out by a doctor.
Taking a careful history can pay off, Ali has found. He questioned a patient complaining of abdominal discomfort whose testing found unexpectedly elevated liver enzymes and found she had been using an herbal “cleanse tea” found online. Within 4 weeks of stopping it, her liver enzymes normalized. “Thankfully, she made a full recovery — and she never touched those remedies again,” he said.
Ali had no relevant disclosures. Bilal reported consulting for Boston Scientific, Cook Medical, and Steris.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Social media is rife with content promoting colon cleansing as a way to shed toxins and fix everything from chronic fatigue and overweight to weak immunity and skin problems.
Even doctors who aren’t hip to the latest TikTok trends may not be able to avoid the hype. That’s because patients are bringing up colon cleansing during their office visit.
“Patients often raise questions about colonics or detox teas, especially when these gain traction on social media platforms like TikTok,” said Tauseef Ali, MD, AGAF, medical executive director of SSM Health Digestive Care at St. Anthony Hospital in Oklahoma City. “Interest typically comes in waves, closely tied to the latest online trends.”
That means . And it’s not just patients who are asking.
“Sometimes we’ll get a message from primary care,” Mohammad Bilal, MD, associate professor of medicine and director of Bariatric and Third Space Endoscopy at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora, Colorado, told GI & Hepatology News. They’re getting the same questions from patients, and they want to know if colon cleansing that’s not connected with a colonoscopy exam has any benefits for overall health or specific health conditions.
The answer is no, and patients are more likely to believe that when physicians explain it using good information. Here is how Ali, Bilal, and professional organizations advise doctors to approach the issue.
What Exactly Is a Colon Cleanse?
Colon cleanses come in a variety of forms. Colonic irrigation, also called colon hydrotherapy, involves inserting a tube into the rectum and flushing out the colon with a large amount of fluid. Enemas do the same but use a small amount of liquid, and some product instructions tell the user to “hold it” for a designated amount of time before expelling colon contents.
Other cleanses, often called detoxing cleanses, are laxatives or herbal teas that users drink — and then stay close to the bathroom. Detox regimens and diets also are mentioned as a way to remove toxins from the body, improve health, and promote well-being.
Why Do Patients Use Them?
“Many patients describe a desire for ‘cleanliness,’ ‘detoxification,’ or to ‘feel lighter,’” Ali told GI & Hepatology News.
The claims on social media promote all of this and more — and well-known influencers make it all sound even more attractive.
“These motivations are often rooted in the cultural belief that the colon accumulates harmful toxins that must be flushed out,” Ali said. “This idea is not supported by scientific evidence. The body’s natural detox systems, primarily the liver and kidneys, already perform this function effectively.”
Bilal said that in recent years, he has noticed more awareness in general about the importance of gut health. “When there’s awareness, people often go to the other extreme,” he said.
Where Is the Evidence?
The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), part of the National Institutes of Health, warns on an information page that both cleansing and detox programs can be unsafe and falsely advertised.
While searches of medical literature turn up few studies, the NCCIH information points to a 2014 review that concluded that there is no compelling research to support the use of detox diets for managing weight or eliminating toxins. A 2017 review found juicing and detox regimens can cause weight loss initially but then lead to weight gain once a normal diet is resumed.
A systematic review of research on the safety and effectiveness of self-administered coffee enemas found nine case reports describing adverse events: seven reported colitis after the enema, and two reported more critical adverse events. All nine reports warned against the procedure. The researchers found no study reporting the effectiveness of coffee enemas.
The NCCIH information also notes that there is “limited clinical evidence validating colonic irrigation and insufficient evidence for its prescribed uses.”
Are Cleanses Regulated?
Some over-the-counter colon cleansing products are viewed as dietary supplements, giving the FDA authority to regulate them and take action under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994.
Certain products promoted as colon cleanses, such as laxatives, are regulated by the FDA as over-the-counter drugs and must meet safety and other requirements.
Colonic irrigation systems meant for cleansing before radiologic or endoscopic exams are class II devices — subject to 510(k) premarket notification requirements before marketing — whereas systems intended for other uses, such as routine colon cleansing for general well-being, are regarded as class III devices — subject to premarket approval requirements — according to an FDA spokesperson. To date, the FDA has not approved any colonic irrigation devices for the latter use, the spokesperson said.
For instance, the FDA warned consumers not to use a product promoted for colon cleansing after finding it contained tadalafil, the active ingredient in an FDA-approved drug for erectile dysfunction. The FDA has also issued numerous warning letters to the makers of colon cleansing devices, as they are not approved for this purpose.
The Federal Trade Commission can also take action specifically if the claims about the benefits and safety of products — including supplements, foods, over-the-counter drugs, or health equipment — are false, misleading, or not supported by science.
What Are the Dangers?
Cleanse and detox products come with many risks, including electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and infections, Ali said. With colonic irrigation, there is a risk for rectal perforation. Products also may disrupt the gut microbiome, and some can interact with medications or worsen underlying health conditions, he added.
“It’s important for patients to be aware of these risks before considering nonmedical ‘cleaning’ methods,” he said.
At worst, patients risk fatality, Ali noted. He recalled a young patient who began using a vegetable enema as a detox. As it was being administered, the colon ruptured. The patient was admitted as a medical emergency and required surgery. Fortunately, the patient survived, but the incident could have proven fatal, Ali said.
Educating Patients
Because patients often don’t think of herbal cleanses, detox teas, and over-the-counter powders as supplements, Ali said it’s important to ask them about everything they take.
One way to frame this question is to ask if they are consuming any over-the-counter supplements or any other remedies, he said, and perhaps ask directly about any cleanses they are doing.
When patients ask him about colon cleanses, Ali explains the difference between evidence-based colonoscopy preparation and unregulated “cleanses.” Most patients respond to that approach, he said. Indeed, AGA and other GI societies updated their recommendations on optimizing bowel preparation quality for colonoscopy.
“Still, the appeal of quick fixes of social media trends can sometimes outweigh medical advice,” Ali said. He depends on building trusted relationships and reinforcing the message over time and finds that helps patients make informed and healthier choices.
Bilal, too, explains to patients that cleanses are unnecessary and educates them about what to do instead:
- Eat a containing the recommended amount of (22-34 g, depending on age and gender).
- For , follow a bowel regimen advised by your doctor.
- If gastrointestinal issues persist, get a medical checkup.
- Get any unexplained constipation or checked out by a doctor.
Taking a careful history can pay off, Ali has found. He questioned a patient complaining of abdominal discomfort whose testing found unexpectedly elevated liver enzymes and found she had been using an herbal “cleanse tea” found online. Within 4 weeks of stopping it, her liver enzymes normalized. “Thankfully, she made a full recovery — and she never touched those remedies again,” he said.
Ali had no relevant disclosures. Bilal reported consulting for Boston Scientific, Cook Medical, and Steris.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AI in Gastroenterology and Endoscopy
Dear colleagues,
Since our last Perspectives feature on artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology and hepatology, the field has experienced remarkable growth in both innovation and clinical adoption. AI tools that were once conceptual are now entering everyday practice, with many more on the horizon poised to transform how we diagnose, treat, and manage patients.
Dr. Yuvaraj Singh, Dr. Alessandro Colletta, and Dr. Neil Marya discuss how purpose-built AI models can reduce diagnostic uncertainty in advanced endoscopy. From cholangioscopy systems that outperform standard ERCP sampling in distinguishing malignant biliary strictures to EUS-based platforms that differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer, they envision a near-term future in which machine intelligence enhances accuracy, accelerates decision-making, and refines interpretation—without replacing the clinician’s expertise.
Complementing this, Dr. Dennis Shung takes a broader view across the endoscopy unit and outpatient clinic. He highlights the promise of AI for polyp detection, digital biopsy, and automated reporting, while underscoring the importance of human oversight, workflow integration, and safeguards against misinformation. Dr. Shung also emphasizes the pivotal role professional societies can play in establishing clear standards, ethical boundaries, and trusted frameworks for AI deployment in GI practice.
We hope these perspectives spark practical conversations about when—and how—to integrate AI in your own practice. As always, we welcome your feedback and real-world experience. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
AI Models in Advanced Endoscopy
BY YUVARAJ SINGH, MD; ALESSANDRO COLLETTA, MD; NEIL MARYA, MD
As the adage goes, “if tumor is the rumor, then tissue is the issue, because cancer may be the answer.”
Establishing an accurate diagnosis is the essential first step toward curing or palliating malignancy. From detecting an early neoplastic lesion, to distinguishing between malignant and benign pathology, or to determining when and where to obtain tissue, endoscopists are frequently faced with the challenge of transforming diagnostic suspicion into certainty.
Artificial intelligence (AI), designed to replicate human cognition such as pattern recognition and decision-making, has emerged as a technology to assist gastroenterologists in addressing a variety of different tasks during endoscopy. AI research in gastrointestinal endoscopy has initially focused on computer-aided detection (CADe) of colorectal polyps. More recently, however, there has been increased emphasis on developing AI to assist advanced endoscopists.
For instance, in biliary endoscopy, AI is being explored to improve the notoriously challenging diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, where conventional tissue sampling often falls short of providing a definitive diagnosis. Similarly, in the pancreas, AI models are showing potential to differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a distinction with profound therapeutic implications. Even pancreatic cysts are beginning to benefit from AI models that refine risk stratification and guide management. Together, these advances underscore how AI is not merely an adjunct but a potentially massive catalyst for reimagining the diagnostic role of advanced endoscopists.
Classifying biliary strictures (MBS) accurately remains a challenge. Standard ERCP-based sampling techniques (forceps biopsy and brush cytology) are suboptimal diagnostic tools with false negative rates for detecting MBS of less than 50%. The diagnostic uncertainty related to biliary stricture classification carries significant consequences for patients. For example, patients with biliary cancer without positive cytology have treatments delayed until a malignant diagnosis is established.
Ancillary technologies to enhance ERCP-based tissue acquisition are still weighed down by low sensitivity and accuracy; even with ancillary use of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), diagnostic yield remains limited. EUS-FNA can help with distal biliary strictures, but this technique risks needle-tract seeding in cases of perihilar disease. Cholangioscopy allows for direct visualization and targeted sampling; however, cholangioscopy-guided forceps biopsies are burdened by low sensitivities.1 Additionally, physician interpretation of visual findings during cholangioscopy often suffers from poor interobserver agreement and poor accuracy.2
To improve the classification of biliary strictures, several groups have studied the application of AI for cholangioscopy footage of biliary pathology. In our lab, we trained an AI incorporating over 2.3 million cholangioscopy still images and nearly 20,000 expert-annotated frames to enhance its development. The AI closely mirrored expert labeling of cholangioscopy images of malignant pathology and, when tested on full cholangioscopy videos of indeterminate biliary strictures, the AI achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 91%—outperforming both brush cytology (63%) and forceps biopsy (61%).3
The results from this initial study were later validated across multiple centers. AI-assisted cholangioscopy could thus offer a reproducible, real-world solution to one of the most persistent diagnostic dilemmas advanced endoscopists face—helping clinicians act earlier and with greater confidence when evaluating indeterminate strictures.
Moving from the biliary tree to the pancreas, autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a benign fibro-inflammatory disease that often frustrates advanced endoscopists as it closely mimics the appearance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The stakes are high: despite modern diagnostic techniques, including advanced imaging, some patients with pancreatic resections for “suspected PDAC” are still found to have AIP on final pathology. Conventional tools to distinguish AIP from PDAC have gaps: serum IgG4 and EUS-guided biopsies are both specific but insensitive.
Using EUS videos and images of various pancreas pathologies at Mayo Clinic, we developed an AI to tackle this dilemma. After intensive training, the EUS AI achieved a greater accuracy for distinguishing AIP from PDAC than a group of expert Mayo clinic endosonographers.5 In practice, an EUS-AI can identify AIP patterns in real-time, guiding clinicians toward steroid trials or biopsies and reducing the need for unnecessary surgeries.
Looking ahead, there are multiple opportunities for integration of AI into advanced endoscopy practices. Ongoing research suggests that AI could soon assist with identification of pancreas cysts most at risk for malignant transformation, classification of high risk Barrett’s esophagus, and even help with rapid on-site assessment of cytologic specimens obtained during EUS. Beyond diagnosis, AI could likely play an important role in guiding therapeutic interventions. For example, an ERCP AI in the future may be able to provide cannulation assistance or an AI assistant could help endosonographers during deployments of lumen apposing metal stents.
By enhancing image interpretation and procedural consistency, AI has the potential to uphold the fundamental principle of primum non nocere, enabling us to intervene with precision while minimizing harm. AI can also bridge grey zones in clinical practice and narrow diagnostic uncertainty in real time. Importantly, these systems can help clinicians achieve expertise in a fraction of the time it traditionally takes to acquire comparable human proficiency, while offering wider availability across practice settings and reducing interobserver variability that has long challenged endoscopic interpretation.
Currently, adoption is limited by high bias risk, lack of external validation, and interpretability Still, the trajectory of AI suggests a future where these computer technologies will not only support but also elevate human expertise, reshaping the standards of care of diseases managed by advanced endoscopists.
Dr. Singh, Dr. Colletta, and Dr. Marya are based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts. Dr. Marya is a consultant for Boston Scientific, and has no other disclosures. Dr. Singh and Dr. Colletta have no disclosures.
References
1. Navaneethan U, et al. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.017.
2. Stassen PMC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement of digital single-operator cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary strictures. Gastrointest Endosc 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.027.
3. Marya NB, et al. Identification of patients with malignant biliary strictures using a cholangioscopy-based deep learning artificial intelligence (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.021.
4. Marya NB, et al. Multicenter validation of a cholangioscopy artificial intelligence system for the evaluation of biliary tract disease. Endoscopy. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1055/a-2650-0789.
5. Marya NB, et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322821.
AI in General GI and Endoscopy
BY DENNIS L. SHUNG, MD, MHS, PHD
The practice of gastroenterology is changing, but much of it will be rooted in the same – careful, focused attention on endoscopic procedures, and compassionate, attentive care in clinic. Artificial intelligence (AI), like the Industrial Revolution before, is going to transform our practice. This comes with upsides and downsides, and highlights the need for strong leadership from our societies to safeguard the technology for practitioners and patients.
What are the upsides?
AI has the potential to serve as a second set of eyes in detecting colon polyps, increasing the adenoma detection rate (ADR).1 AI can be applied to all areas of the gastrointestinal tract, providing digital biopsies, guiding resection, and ensuring quality, which are all now possible with powerful new endoscopy foundation models, such as GastroNet-5M.2
Additionally. the advent of automating the collection of data into reports may herald the end of our days as data entry clerks. Generative AI also has the potential to give us all the best information at our fingertips, suggesting guideline-based care, providing the most up to date evidence, and guiding the differential diagnosis. The potential for patient-facing AI systems could lead to better health literacy, more meaningful engagement, and improved patient satisfaction.3
What are the downsides?
For endoscopy, AI cannot make up for poor technique to ensure adequate mucosal exposure by the endoscopist, and an increase in AI-supported ADR does not yet convincingly translate into concrete gains in colorectal cancer-related mortality. For the foreseeable future, AI cannot make a connection with the patient in front of us, which is critical in diagnosing and treating patients.
Currently, AI appears to worsen loneliness4, and does not necessarily deepen the bonds or provide the positive touch that can heal, and which for many of us, was the reason we became physicians. Finally, as information proliferates, the information risk to patients and providers is growing – in the future, trusted sources to monitor, curate, and guide AI will be ever more important.
Black Swans
As AI begins to mature, there are risks that lurk beneath the surface. When regulatory bodies begin to look at AI-assisted diagnostics or therapeutics as the new standard of care, reimbursement models may adjust, and providers may be left behind. The rapid proliferation and haphazard adoption of AI could lead to overdependence and deskilling or result in weird and as yet unknown errors that are difficult to troubleshoot.
What is the role of the GI societies?
Specialty societies like AGA are taking leadership roles in determining the bounds of where AIs may tread, not just in providing information to their membership but also in digesting evidence and synthesizing recommendations. Societies must balance the real promise of AI in endoscopy with the practice realities for members, and provide living guidelines that reflect the consensus of members regarding scope of practice with the ability to update as new data become available.5
Societies also have a role as advocates for safety, taking ownership of high-quality content to prevent misinformation. AGA recently announced the development of a chat interface that will be focused on providing its members the highest quality information, and serve as a portal to identify and respond to its members’ information needs. By staying united rather than fragmenting, societies can maintain bounds to protect its members and their patients and advance areas where there is clinical need, together.
Dr. Shung is senior associate consultant, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, and director of clinical generative artificial intelligence and informatics, Department of Medicine, at Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
References
1. Soleymanjahi S, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Polyp Detection : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec. doi:10.7326/annals-24-00981.
2. Jong MR, et al. GastroNet-5M: A Multicenter Dataset for Developing Foundation Models in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.030.
3. Soroush A, et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicine and Impact on Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.03.038.
4. Mengying Fang C, et al. How AI and Human Behaviors Shape Psychosocial Effects of Extended Chatbot Use: A Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Study. arXiv e-prints. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.17473.
5. Sultan S, et al. AGA Living Clinical Practice Guideline on Computer-Aided Detection-Assisted Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Apr. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.002.
Dear colleagues,
Since our last Perspectives feature on artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology and hepatology, the field has experienced remarkable growth in both innovation and clinical adoption. AI tools that were once conceptual are now entering everyday practice, with many more on the horizon poised to transform how we diagnose, treat, and manage patients.
Dr. Yuvaraj Singh, Dr. Alessandro Colletta, and Dr. Neil Marya discuss how purpose-built AI models can reduce diagnostic uncertainty in advanced endoscopy. From cholangioscopy systems that outperform standard ERCP sampling in distinguishing malignant biliary strictures to EUS-based platforms that differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer, they envision a near-term future in which machine intelligence enhances accuracy, accelerates decision-making, and refines interpretation—without replacing the clinician’s expertise.
Complementing this, Dr. Dennis Shung takes a broader view across the endoscopy unit and outpatient clinic. He highlights the promise of AI for polyp detection, digital biopsy, and automated reporting, while underscoring the importance of human oversight, workflow integration, and safeguards against misinformation. Dr. Shung also emphasizes the pivotal role professional societies can play in establishing clear standards, ethical boundaries, and trusted frameworks for AI deployment in GI practice.
We hope these perspectives spark practical conversations about when—and how—to integrate AI in your own practice. As always, we welcome your feedback and real-world experience. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
AI Models in Advanced Endoscopy
BY YUVARAJ SINGH, MD; ALESSANDRO COLLETTA, MD; NEIL MARYA, MD
As the adage goes, “if tumor is the rumor, then tissue is the issue, because cancer may be the answer.”
Establishing an accurate diagnosis is the essential first step toward curing or palliating malignancy. From detecting an early neoplastic lesion, to distinguishing between malignant and benign pathology, or to determining when and where to obtain tissue, endoscopists are frequently faced with the challenge of transforming diagnostic suspicion into certainty.
Artificial intelligence (AI), designed to replicate human cognition such as pattern recognition and decision-making, has emerged as a technology to assist gastroenterologists in addressing a variety of different tasks during endoscopy. AI research in gastrointestinal endoscopy has initially focused on computer-aided detection (CADe) of colorectal polyps. More recently, however, there has been increased emphasis on developing AI to assist advanced endoscopists.
For instance, in biliary endoscopy, AI is being explored to improve the notoriously challenging diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, where conventional tissue sampling often falls short of providing a definitive diagnosis. Similarly, in the pancreas, AI models are showing potential to differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a distinction with profound therapeutic implications. Even pancreatic cysts are beginning to benefit from AI models that refine risk stratification and guide management. Together, these advances underscore how AI is not merely an adjunct but a potentially massive catalyst for reimagining the diagnostic role of advanced endoscopists.
Classifying biliary strictures (MBS) accurately remains a challenge. Standard ERCP-based sampling techniques (forceps biopsy and brush cytology) are suboptimal diagnostic tools with false negative rates for detecting MBS of less than 50%. The diagnostic uncertainty related to biliary stricture classification carries significant consequences for patients. For example, patients with biliary cancer without positive cytology have treatments delayed until a malignant diagnosis is established.
Ancillary technologies to enhance ERCP-based tissue acquisition are still weighed down by low sensitivity and accuracy; even with ancillary use of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), diagnostic yield remains limited. EUS-FNA can help with distal biliary strictures, but this technique risks needle-tract seeding in cases of perihilar disease. Cholangioscopy allows for direct visualization and targeted sampling; however, cholangioscopy-guided forceps biopsies are burdened by low sensitivities.1 Additionally, physician interpretation of visual findings during cholangioscopy often suffers from poor interobserver agreement and poor accuracy.2
To improve the classification of biliary strictures, several groups have studied the application of AI for cholangioscopy footage of biliary pathology. In our lab, we trained an AI incorporating over 2.3 million cholangioscopy still images and nearly 20,000 expert-annotated frames to enhance its development. The AI closely mirrored expert labeling of cholangioscopy images of malignant pathology and, when tested on full cholangioscopy videos of indeterminate biliary strictures, the AI achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 91%—outperforming both brush cytology (63%) and forceps biopsy (61%).3
The results from this initial study were later validated across multiple centers. AI-assisted cholangioscopy could thus offer a reproducible, real-world solution to one of the most persistent diagnostic dilemmas advanced endoscopists face—helping clinicians act earlier and with greater confidence when evaluating indeterminate strictures.
Moving from the biliary tree to the pancreas, autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a benign fibro-inflammatory disease that often frustrates advanced endoscopists as it closely mimics the appearance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The stakes are high: despite modern diagnostic techniques, including advanced imaging, some patients with pancreatic resections for “suspected PDAC” are still found to have AIP on final pathology. Conventional tools to distinguish AIP from PDAC have gaps: serum IgG4 and EUS-guided biopsies are both specific but insensitive.
Using EUS videos and images of various pancreas pathologies at Mayo Clinic, we developed an AI to tackle this dilemma. After intensive training, the EUS AI achieved a greater accuracy for distinguishing AIP from PDAC than a group of expert Mayo clinic endosonographers.5 In practice, an EUS-AI can identify AIP patterns in real-time, guiding clinicians toward steroid trials or biopsies and reducing the need for unnecessary surgeries.
Looking ahead, there are multiple opportunities for integration of AI into advanced endoscopy practices. Ongoing research suggests that AI could soon assist with identification of pancreas cysts most at risk for malignant transformation, classification of high risk Barrett’s esophagus, and even help with rapid on-site assessment of cytologic specimens obtained during EUS. Beyond diagnosis, AI could likely play an important role in guiding therapeutic interventions. For example, an ERCP AI in the future may be able to provide cannulation assistance or an AI assistant could help endosonographers during deployments of lumen apposing metal stents.
By enhancing image interpretation and procedural consistency, AI has the potential to uphold the fundamental principle of primum non nocere, enabling us to intervene with precision while minimizing harm. AI can also bridge grey zones in clinical practice and narrow diagnostic uncertainty in real time. Importantly, these systems can help clinicians achieve expertise in a fraction of the time it traditionally takes to acquire comparable human proficiency, while offering wider availability across practice settings and reducing interobserver variability that has long challenged endoscopic interpretation.
Currently, adoption is limited by high bias risk, lack of external validation, and interpretability Still, the trajectory of AI suggests a future where these computer technologies will not only support but also elevate human expertise, reshaping the standards of care of diseases managed by advanced endoscopists.
Dr. Singh, Dr. Colletta, and Dr. Marya are based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts. Dr. Marya is a consultant for Boston Scientific, and has no other disclosures. Dr. Singh and Dr. Colletta have no disclosures.
References
1. Navaneethan U, et al. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.017.
2. Stassen PMC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement of digital single-operator cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary strictures. Gastrointest Endosc 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.027.
3. Marya NB, et al. Identification of patients with malignant biliary strictures using a cholangioscopy-based deep learning artificial intelligence (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.021.
4. Marya NB, et al. Multicenter validation of a cholangioscopy artificial intelligence system for the evaluation of biliary tract disease. Endoscopy. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1055/a-2650-0789.
5. Marya NB, et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322821.
AI in General GI and Endoscopy
BY DENNIS L. SHUNG, MD, MHS, PHD
The practice of gastroenterology is changing, but much of it will be rooted in the same – careful, focused attention on endoscopic procedures, and compassionate, attentive care in clinic. Artificial intelligence (AI), like the Industrial Revolution before, is going to transform our practice. This comes with upsides and downsides, and highlights the need for strong leadership from our societies to safeguard the technology for practitioners and patients.
What are the upsides?
AI has the potential to serve as a second set of eyes in detecting colon polyps, increasing the adenoma detection rate (ADR).1 AI can be applied to all areas of the gastrointestinal tract, providing digital biopsies, guiding resection, and ensuring quality, which are all now possible with powerful new endoscopy foundation models, such as GastroNet-5M.2
Additionally. the advent of automating the collection of data into reports may herald the end of our days as data entry clerks. Generative AI also has the potential to give us all the best information at our fingertips, suggesting guideline-based care, providing the most up to date evidence, and guiding the differential diagnosis. The potential for patient-facing AI systems could lead to better health literacy, more meaningful engagement, and improved patient satisfaction.3
What are the downsides?
For endoscopy, AI cannot make up for poor technique to ensure adequate mucosal exposure by the endoscopist, and an increase in AI-supported ADR does not yet convincingly translate into concrete gains in colorectal cancer-related mortality. For the foreseeable future, AI cannot make a connection with the patient in front of us, which is critical in diagnosing and treating patients.
Currently, AI appears to worsen loneliness4, and does not necessarily deepen the bonds or provide the positive touch that can heal, and which for many of us, was the reason we became physicians. Finally, as information proliferates, the information risk to patients and providers is growing – in the future, trusted sources to monitor, curate, and guide AI will be ever more important.
Black Swans
As AI begins to mature, there are risks that lurk beneath the surface. When regulatory bodies begin to look at AI-assisted diagnostics or therapeutics as the new standard of care, reimbursement models may adjust, and providers may be left behind. The rapid proliferation and haphazard adoption of AI could lead to overdependence and deskilling or result in weird and as yet unknown errors that are difficult to troubleshoot.
What is the role of the GI societies?
Specialty societies like AGA are taking leadership roles in determining the bounds of where AIs may tread, not just in providing information to their membership but also in digesting evidence and synthesizing recommendations. Societies must balance the real promise of AI in endoscopy with the practice realities for members, and provide living guidelines that reflect the consensus of members regarding scope of practice with the ability to update as new data become available.5
Societies also have a role as advocates for safety, taking ownership of high-quality content to prevent misinformation. AGA recently announced the development of a chat interface that will be focused on providing its members the highest quality information, and serve as a portal to identify and respond to its members’ information needs. By staying united rather than fragmenting, societies can maintain bounds to protect its members and their patients and advance areas where there is clinical need, together.
Dr. Shung is senior associate consultant, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, and director of clinical generative artificial intelligence and informatics, Department of Medicine, at Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
References
1. Soleymanjahi S, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Polyp Detection : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec. doi:10.7326/annals-24-00981.
2. Jong MR, et al. GastroNet-5M: A Multicenter Dataset for Developing Foundation Models in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.030.
3. Soroush A, et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicine and Impact on Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.03.038.
4. Mengying Fang C, et al. How AI and Human Behaviors Shape Psychosocial Effects of Extended Chatbot Use: A Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Study. arXiv e-prints. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.17473.
5. Sultan S, et al. AGA Living Clinical Practice Guideline on Computer-Aided Detection-Assisted Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Apr. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.002.
Dear colleagues,
Since our last Perspectives feature on artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology and hepatology, the field has experienced remarkable growth in both innovation and clinical adoption. AI tools that were once conceptual are now entering everyday practice, with many more on the horizon poised to transform how we diagnose, treat, and manage patients.
Dr. Yuvaraj Singh, Dr. Alessandro Colletta, and Dr. Neil Marya discuss how purpose-built AI models can reduce diagnostic uncertainty in advanced endoscopy. From cholangioscopy systems that outperform standard ERCP sampling in distinguishing malignant biliary strictures to EUS-based platforms that differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer, they envision a near-term future in which machine intelligence enhances accuracy, accelerates decision-making, and refines interpretation—without replacing the clinician’s expertise.
Complementing this, Dr. Dennis Shung takes a broader view across the endoscopy unit and outpatient clinic. He highlights the promise of AI for polyp detection, digital biopsy, and automated reporting, while underscoring the importance of human oversight, workflow integration, and safeguards against misinformation. Dr. Shung also emphasizes the pivotal role professional societies can play in establishing clear standards, ethical boundaries, and trusted frameworks for AI deployment in GI practice.
We hope these perspectives spark practical conversations about when—and how—to integrate AI in your own practice. As always, we welcome your feedback and real-world experience. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
AI Models in Advanced Endoscopy
BY YUVARAJ SINGH, MD; ALESSANDRO COLLETTA, MD; NEIL MARYA, MD
As the adage goes, “if tumor is the rumor, then tissue is the issue, because cancer may be the answer.”
Establishing an accurate diagnosis is the essential first step toward curing or palliating malignancy. From detecting an early neoplastic lesion, to distinguishing between malignant and benign pathology, or to determining when and where to obtain tissue, endoscopists are frequently faced with the challenge of transforming diagnostic suspicion into certainty.
Artificial intelligence (AI), designed to replicate human cognition such as pattern recognition and decision-making, has emerged as a technology to assist gastroenterologists in addressing a variety of different tasks during endoscopy. AI research in gastrointestinal endoscopy has initially focused on computer-aided detection (CADe) of colorectal polyps. More recently, however, there has been increased emphasis on developing AI to assist advanced endoscopists.
For instance, in biliary endoscopy, AI is being explored to improve the notoriously challenging diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, where conventional tissue sampling often falls short of providing a definitive diagnosis. Similarly, in the pancreas, AI models are showing potential to differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a distinction with profound therapeutic implications. Even pancreatic cysts are beginning to benefit from AI models that refine risk stratification and guide management. Together, these advances underscore how AI is not merely an adjunct but a potentially massive catalyst for reimagining the diagnostic role of advanced endoscopists.
Classifying biliary strictures (MBS) accurately remains a challenge. Standard ERCP-based sampling techniques (forceps biopsy and brush cytology) are suboptimal diagnostic tools with false negative rates for detecting MBS of less than 50%. The diagnostic uncertainty related to biliary stricture classification carries significant consequences for patients. For example, patients with biliary cancer without positive cytology have treatments delayed until a malignant diagnosis is established.
Ancillary technologies to enhance ERCP-based tissue acquisition are still weighed down by low sensitivity and accuracy; even with ancillary use of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), diagnostic yield remains limited. EUS-FNA can help with distal biliary strictures, but this technique risks needle-tract seeding in cases of perihilar disease. Cholangioscopy allows for direct visualization and targeted sampling; however, cholangioscopy-guided forceps biopsies are burdened by low sensitivities.1 Additionally, physician interpretation of visual findings during cholangioscopy often suffers from poor interobserver agreement and poor accuracy.2
To improve the classification of biliary strictures, several groups have studied the application of AI for cholangioscopy footage of biliary pathology. In our lab, we trained an AI incorporating over 2.3 million cholangioscopy still images and nearly 20,000 expert-annotated frames to enhance its development. The AI closely mirrored expert labeling of cholangioscopy images of malignant pathology and, when tested on full cholangioscopy videos of indeterminate biliary strictures, the AI achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 91%—outperforming both brush cytology (63%) and forceps biopsy (61%).3
The results from this initial study were later validated across multiple centers. AI-assisted cholangioscopy could thus offer a reproducible, real-world solution to one of the most persistent diagnostic dilemmas advanced endoscopists face—helping clinicians act earlier and with greater confidence when evaluating indeterminate strictures.
Moving from the biliary tree to the pancreas, autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a benign fibro-inflammatory disease that often frustrates advanced endoscopists as it closely mimics the appearance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The stakes are high: despite modern diagnostic techniques, including advanced imaging, some patients with pancreatic resections for “suspected PDAC” are still found to have AIP on final pathology. Conventional tools to distinguish AIP from PDAC have gaps: serum IgG4 and EUS-guided biopsies are both specific but insensitive.
Using EUS videos and images of various pancreas pathologies at Mayo Clinic, we developed an AI to tackle this dilemma. After intensive training, the EUS AI achieved a greater accuracy for distinguishing AIP from PDAC than a group of expert Mayo clinic endosonographers.5 In practice, an EUS-AI can identify AIP patterns in real-time, guiding clinicians toward steroid trials or biopsies and reducing the need for unnecessary surgeries.
Looking ahead, there are multiple opportunities for integration of AI into advanced endoscopy practices. Ongoing research suggests that AI could soon assist with identification of pancreas cysts most at risk for malignant transformation, classification of high risk Barrett’s esophagus, and even help with rapid on-site assessment of cytologic specimens obtained during EUS. Beyond diagnosis, AI could likely play an important role in guiding therapeutic interventions. For example, an ERCP AI in the future may be able to provide cannulation assistance or an AI assistant could help endosonographers during deployments of lumen apposing metal stents.
By enhancing image interpretation and procedural consistency, AI has the potential to uphold the fundamental principle of primum non nocere, enabling us to intervene with precision while minimizing harm. AI can also bridge grey zones in clinical practice and narrow diagnostic uncertainty in real time. Importantly, these systems can help clinicians achieve expertise in a fraction of the time it traditionally takes to acquire comparable human proficiency, while offering wider availability across practice settings and reducing interobserver variability that has long challenged endoscopic interpretation.
Currently, adoption is limited by high bias risk, lack of external validation, and interpretability Still, the trajectory of AI suggests a future where these computer technologies will not only support but also elevate human expertise, reshaping the standards of care of diseases managed by advanced endoscopists.
Dr. Singh, Dr. Colletta, and Dr. Marya are based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts. Dr. Marya is a consultant for Boston Scientific, and has no other disclosures. Dr. Singh and Dr. Colletta have no disclosures.
References
1. Navaneethan U, et al. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.017.
2. Stassen PMC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement of digital single-operator cholangioscopy for indeterminate biliary strictures. Gastrointest Endosc 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.027.
3. Marya NB, et al. Identification of patients with malignant biliary strictures using a cholangioscopy-based deep learning artificial intelligence (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.021.
4. Marya NB, et al. Multicenter validation of a cholangioscopy artificial intelligence system for the evaluation of biliary tract disease. Endoscopy. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1055/a-2650-0789.
5. Marya NB, et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322821.
AI in General GI and Endoscopy
BY DENNIS L. SHUNG, MD, MHS, PHD
The practice of gastroenterology is changing, but much of it will be rooted in the same – careful, focused attention on endoscopic procedures, and compassionate, attentive care in clinic. Artificial intelligence (AI), like the Industrial Revolution before, is going to transform our practice. This comes with upsides and downsides, and highlights the need for strong leadership from our societies to safeguard the technology for practitioners and patients.
What are the upsides?
AI has the potential to serve as a second set of eyes in detecting colon polyps, increasing the adenoma detection rate (ADR).1 AI can be applied to all areas of the gastrointestinal tract, providing digital biopsies, guiding resection, and ensuring quality, which are all now possible with powerful new endoscopy foundation models, such as GastroNet-5M.2
Additionally. the advent of automating the collection of data into reports may herald the end of our days as data entry clerks. Generative AI also has the potential to give us all the best information at our fingertips, suggesting guideline-based care, providing the most up to date evidence, and guiding the differential diagnosis. The potential for patient-facing AI systems could lead to better health literacy, more meaningful engagement, and improved patient satisfaction.3
What are the downsides?
For endoscopy, AI cannot make up for poor technique to ensure adequate mucosal exposure by the endoscopist, and an increase in AI-supported ADR does not yet convincingly translate into concrete gains in colorectal cancer-related mortality. For the foreseeable future, AI cannot make a connection with the patient in front of us, which is critical in diagnosing and treating patients.
Currently, AI appears to worsen loneliness4, and does not necessarily deepen the bonds or provide the positive touch that can heal, and which for many of us, was the reason we became physicians. Finally, as information proliferates, the information risk to patients and providers is growing – in the future, trusted sources to monitor, curate, and guide AI will be ever more important.
Black Swans
As AI begins to mature, there are risks that lurk beneath the surface. When regulatory bodies begin to look at AI-assisted diagnostics or therapeutics as the new standard of care, reimbursement models may adjust, and providers may be left behind. The rapid proliferation and haphazard adoption of AI could lead to overdependence and deskilling or result in weird and as yet unknown errors that are difficult to troubleshoot.
What is the role of the GI societies?
Specialty societies like AGA are taking leadership roles in determining the bounds of where AIs may tread, not just in providing information to their membership but also in digesting evidence and synthesizing recommendations. Societies must balance the real promise of AI in endoscopy with the practice realities for members, and provide living guidelines that reflect the consensus of members regarding scope of practice with the ability to update as new data become available.5
Societies also have a role as advocates for safety, taking ownership of high-quality content to prevent misinformation. AGA recently announced the development of a chat interface that will be focused on providing its members the highest quality information, and serve as a portal to identify and respond to its members’ information needs. By staying united rather than fragmenting, societies can maintain bounds to protect its members and their patients and advance areas where there is clinical need, together.
Dr. Shung is senior associate consultant, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, and director of clinical generative artificial intelligence and informatics, Department of Medicine, at Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota. He has no disclosures in regard to this article.
References
1. Soleymanjahi S, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Polyp Detection : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec. doi:10.7326/annals-24-00981.
2. Jong MR, et al. GastroNet-5M: A Multicenter Dataset for Developing Foundation Models in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.030.
3. Soroush A, et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicine and Impact on Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.03.038.
4. Mengying Fang C, et al. How AI and Human Behaviors Shape Psychosocial Effects of Extended Chatbot Use: A Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Study. arXiv e-prints. 2025 Mar. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.17473.
5. Sultan S, et al. AGA Living Clinical Practice Guideline on Computer-Aided Detection-Assisted Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2025 Apr. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.002.
How Chronic Stress Disrupts the Gut Microbiome
Chronic psychological stress is common. A 2023 survey revealed that about one quarter of US adults reported high stress levels, and three quarters reported that chronic stress affects their daily lives.
Emerging evidence suggests that chronic stress not only exacts a high toll on mental health but also can wreak havoc on all levels of gastrointestinal (GI) functioning, all the way down to the microbiome.
Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, AGAF, gastroenterologist with NYU Langone Health and director of GI Outcomes Research, Gastroenterology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, said in an interview with GI & Hepatology News.
“This basically means that the normal balance of microorganisms that essentially we think are beneficial gets reduced, and the colonies considered to be more harmful proliferate,” she explained.
What Does the Science Tell Us?
Numerous studies published in the past 5 years have linked chronic stress to modest but reproducible shifts in the composition of the microbiome.
A study of frontline healthcare workers during COVID-19 revealed that the pandemic was associated with significant depression, anxiety, and stress, as well as gut dysbiosis that persisted for at least half a year.
Notably, healthcare workers had low gut alpha diversity, indicating a less resilient and diverse microbiome, a state often associated with dysbiosis and increased risk for various diseases and negative health outcomes.
A two-cohort study of healthy adults found higher alpha diversity in those reporting low stress levels. It also found a link between stress and enriched levels of Escherichia/Shigella, an overgrowth of which has been linked to various conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease.
In addition, a 2023 systematic review of human studies concluded that stress is associated with changes in specific genera — namely reductions in gut-healthy Lachnospira/Lachnospiraceae and Phascolarctobacterium, which produce beneficial short-chain fatty acids that support the health of the intestinal lining and modulate the immune system.
Stress during specific life stages also appears to alter the gut microbiome.
For example, in a study of postpartum women, those at an increased risk for parenting stress showed lower alpha diversity on the Shannon diversity index.
Research involving mother-child pairs tied adversity — such as maltreatment of the mother during her childhood, prenatal anxiety, and hardship in the child’s early life — to distinct microbiome profiles in 2-year-olds, supporting a stress-microbiome pathway relevant to socioemotional outcomes, the authors said.
Emerging evidence indicates a link between the gut microbiome and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
A recent systematic review found differences in gut microbial taxa between individuals with PTSD and trauma-exposed controls without PTSD. A separate analysis pointed to a potential causal impact of gut microbiomes on the development of PTSD.
Mechanisms Behind the Link
Stress interferes with the brain’s production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which controls anxiety, mood, sleep, and many other functions in the brain, Shaukat told GI & Hepatology News.
“But serotonin also crosses the blood-brain barrier, and actually, the gut has more serotonin receptors than the brain, so an imbalance of serotonin can actually affect the gut microbiome through signaling at the neurotransmitter level,” Shaukat explained.
Stress can also affect sleep, and sleep itself has regulatory properties for gut bacteria, Shaukat noted.
“Stress also lowers our immunity, and this can make the gut barrier susceptible or permeable to bacterial toxins that can pass through and breach the gut barrier and be released into the bloodstream, which can trigger inflammation,” Shaukat explained.
Implications for Patient Care
The gut-brain-microbiome axis remains an emerging field of study. “We’re learning more and more about this, and we need to because the microbial colonies are so diverse and we haven’t nailed it down yet,” Shaukat said.
In the meantime, what can clinicians tell patients?
Aside from managing stress, which “is easier said than done,” patients can improve their diet, Shaukat said.
“What we tell patients is to essentially increase their intake of gut-friendly foods that preferentially grow the bacterial colonies that are beneficial for us,” Shaukat said. This includes fermented foods, yogurt, kimchi, chia seeds, kombucha, pickled vegetables, and whole grains.
A recent randomized controlled trial of healthy adults found a “psychobiotic diet” — a diet high in prebiotic and fermented foods — was associated with less perceived stress and subtle beneficial shifts in microbial composition.
“These foods can help keep the gut in good health and may actually also reduce or mitigate some of the effects of stress,” Shaukat said.
“Eating well is something I think we should all think about and maybe prioritize when we’re going through a stressful situation or looking to kind of mitigate the effects of stress and the anxiety and depression it can cause,” she advised.
Shaukat said she also encourages patients to engage in regular physical activity, which benefits the gut microbiome by helping to regulate gut motility. Exercise can also boost mood and help relieve stress.
“A balanced Mediterranean diet and regular activity is truly the secret for gut health,” Shaukat said.
Patients may be tempted by the probiotic supplements lining drugstore shelves, but there “isn’t great evidence for probiotic supplements,” she said. “What we can get from dietary sources far outweighs what can be put in a pill.”
Shaukat disclosed having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic psychological stress is common. A 2023 survey revealed that about one quarter of US adults reported high stress levels, and three quarters reported that chronic stress affects their daily lives.
Emerging evidence suggests that chronic stress not only exacts a high toll on mental health but also can wreak havoc on all levels of gastrointestinal (GI) functioning, all the way down to the microbiome.
Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, AGAF, gastroenterologist with NYU Langone Health and director of GI Outcomes Research, Gastroenterology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, said in an interview with GI & Hepatology News.
“This basically means that the normal balance of microorganisms that essentially we think are beneficial gets reduced, and the colonies considered to be more harmful proliferate,” she explained.
What Does the Science Tell Us?
Numerous studies published in the past 5 years have linked chronic stress to modest but reproducible shifts in the composition of the microbiome.
A study of frontline healthcare workers during COVID-19 revealed that the pandemic was associated with significant depression, anxiety, and stress, as well as gut dysbiosis that persisted for at least half a year.
Notably, healthcare workers had low gut alpha diversity, indicating a less resilient and diverse microbiome, a state often associated with dysbiosis and increased risk for various diseases and negative health outcomes.
A two-cohort study of healthy adults found higher alpha diversity in those reporting low stress levels. It also found a link between stress and enriched levels of Escherichia/Shigella, an overgrowth of which has been linked to various conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease.
In addition, a 2023 systematic review of human studies concluded that stress is associated with changes in specific genera — namely reductions in gut-healthy Lachnospira/Lachnospiraceae and Phascolarctobacterium, which produce beneficial short-chain fatty acids that support the health of the intestinal lining and modulate the immune system.
Stress during specific life stages also appears to alter the gut microbiome.
For example, in a study of postpartum women, those at an increased risk for parenting stress showed lower alpha diversity on the Shannon diversity index.
Research involving mother-child pairs tied adversity — such as maltreatment of the mother during her childhood, prenatal anxiety, and hardship in the child’s early life — to distinct microbiome profiles in 2-year-olds, supporting a stress-microbiome pathway relevant to socioemotional outcomes, the authors said.
Emerging evidence indicates a link between the gut microbiome and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
A recent systematic review found differences in gut microbial taxa between individuals with PTSD and trauma-exposed controls without PTSD. A separate analysis pointed to a potential causal impact of gut microbiomes on the development of PTSD.
Mechanisms Behind the Link
Stress interferes with the brain’s production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which controls anxiety, mood, sleep, and many other functions in the brain, Shaukat told GI & Hepatology News.
“But serotonin also crosses the blood-brain barrier, and actually, the gut has more serotonin receptors than the brain, so an imbalance of serotonin can actually affect the gut microbiome through signaling at the neurotransmitter level,” Shaukat explained.
Stress can also affect sleep, and sleep itself has regulatory properties for gut bacteria, Shaukat noted.
“Stress also lowers our immunity, and this can make the gut barrier susceptible or permeable to bacterial toxins that can pass through and breach the gut barrier and be released into the bloodstream, which can trigger inflammation,” Shaukat explained.
Implications for Patient Care
The gut-brain-microbiome axis remains an emerging field of study. “We’re learning more and more about this, and we need to because the microbial colonies are so diverse and we haven’t nailed it down yet,” Shaukat said.
In the meantime, what can clinicians tell patients?
Aside from managing stress, which “is easier said than done,” patients can improve their diet, Shaukat said.
“What we tell patients is to essentially increase their intake of gut-friendly foods that preferentially grow the bacterial colonies that are beneficial for us,” Shaukat said. This includes fermented foods, yogurt, kimchi, chia seeds, kombucha, pickled vegetables, and whole grains.
A recent randomized controlled trial of healthy adults found a “psychobiotic diet” — a diet high in prebiotic and fermented foods — was associated with less perceived stress and subtle beneficial shifts in microbial composition.
“These foods can help keep the gut in good health and may actually also reduce or mitigate some of the effects of stress,” Shaukat said.
“Eating well is something I think we should all think about and maybe prioritize when we’re going through a stressful situation or looking to kind of mitigate the effects of stress and the anxiety and depression it can cause,” she advised.
Shaukat said she also encourages patients to engage in regular physical activity, which benefits the gut microbiome by helping to regulate gut motility. Exercise can also boost mood and help relieve stress.
“A balanced Mediterranean diet and regular activity is truly the secret for gut health,” Shaukat said.
Patients may be tempted by the probiotic supplements lining drugstore shelves, but there “isn’t great evidence for probiotic supplements,” she said. “What we can get from dietary sources far outweighs what can be put in a pill.”
Shaukat disclosed having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic psychological stress is common. A 2023 survey revealed that about one quarter of US adults reported high stress levels, and three quarters reported that chronic stress affects their daily lives.
Emerging evidence suggests that chronic stress not only exacts a high toll on mental health but also can wreak havoc on all levels of gastrointestinal (GI) functioning, all the way down to the microbiome.
Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, AGAF, gastroenterologist with NYU Langone Health and director of GI Outcomes Research, Gastroenterology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, said in an interview with GI & Hepatology News.
“This basically means that the normal balance of microorganisms that essentially we think are beneficial gets reduced, and the colonies considered to be more harmful proliferate,” she explained.
What Does the Science Tell Us?
Numerous studies published in the past 5 years have linked chronic stress to modest but reproducible shifts in the composition of the microbiome.
A study of frontline healthcare workers during COVID-19 revealed that the pandemic was associated with significant depression, anxiety, and stress, as well as gut dysbiosis that persisted for at least half a year.
Notably, healthcare workers had low gut alpha diversity, indicating a less resilient and diverse microbiome, a state often associated with dysbiosis and increased risk for various diseases and negative health outcomes.
A two-cohort study of healthy adults found higher alpha diversity in those reporting low stress levels. It also found a link between stress and enriched levels of Escherichia/Shigella, an overgrowth of which has been linked to various conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease.
In addition, a 2023 systematic review of human studies concluded that stress is associated with changes in specific genera — namely reductions in gut-healthy Lachnospira/Lachnospiraceae and Phascolarctobacterium, which produce beneficial short-chain fatty acids that support the health of the intestinal lining and modulate the immune system.
Stress during specific life stages also appears to alter the gut microbiome.
For example, in a study of postpartum women, those at an increased risk for parenting stress showed lower alpha diversity on the Shannon diversity index.
Research involving mother-child pairs tied adversity — such as maltreatment of the mother during her childhood, prenatal anxiety, and hardship in the child’s early life — to distinct microbiome profiles in 2-year-olds, supporting a stress-microbiome pathway relevant to socioemotional outcomes, the authors said.
Emerging evidence indicates a link between the gut microbiome and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
A recent systematic review found differences in gut microbial taxa between individuals with PTSD and trauma-exposed controls without PTSD. A separate analysis pointed to a potential causal impact of gut microbiomes on the development of PTSD.
Mechanisms Behind the Link
Stress interferes with the brain’s production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which controls anxiety, mood, sleep, and many other functions in the brain, Shaukat told GI & Hepatology News.
“But serotonin also crosses the blood-brain barrier, and actually, the gut has more serotonin receptors than the brain, so an imbalance of serotonin can actually affect the gut microbiome through signaling at the neurotransmitter level,” Shaukat explained.
Stress can also affect sleep, and sleep itself has regulatory properties for gut bacteria, Shaukat noted.
“Stress also lowers our immunity, and this can make the gut barrier susceptible or permeable to bacterial toxins that can pass through and breach the gut barrier and be released into the bloodstream, which can trigger inflammation,” Shaukat explained.
Implications for Patient Care
The gut-brain-microbiome axis remains an emerging field of study. “We’re learning more and more about this, and we need to because the microbial colonies are so diverse and we haven’t nailed it down yet,” Shaukat said.
In the meantime, what can clinicians tell patients?
Aside from managing stress, which “is easier said than done,” patients can improve their diet, Shaukat said.
“What we tell patients is to essentially increase their intake of gut-friendly foods that preferentially grow the bacterial colonies that are beneficial for us,” Shaukat said. This includes fermented foods, yogurt, kimchi, chia seeds, kombucha, pickled vegetables, and whole grains.
A recent randomized controlled trial of healthy adults found a “psychobiotic diet” — a diet high in prebiotic and fermented foods — was associated with less perceived stress and subtle beneficial shifts in microbial composition.
“These foods can help keep the gut in good health and may actually also reduce or mitigate some of the effects of stress,” Shaukat said.
“Eating well is something I think we should all think about and maybe prioritize when we’re going through a stressful situation or looking to kind of mitigate the effects of stress and the anxiety and depression it can cause,” she advised.
Shaukat said she also encourages patients to engage in regular physical activity, which benefits the gut microbiome by helping to regulate gut motility. Exercise can also boost mood and help relieve stress.
“A balanced Mediterranean diet and regular activity is truly the secret for gut health,” Shaukat said.
Patients may be tempted by the probiotic supplements lining drugstore shelves, but there “isn’t great evidence for probiotic supplements,” she said. “What we can get from dietary sources far outweighs what can be put in a pill.”
Shaukat disclosed having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Common Meds Can Secretly Wreck Your Patients’ Microbiome
Effective ways to combat harmful viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasitic worms have driven major advances in medicine and contributed to a significant increase in human life expectancy over the past century. However, as knowledge about the role of these microorganisms in promoting and maintaining health deepens, there is a need for a new look at the impact of these treatments.
The list of drugs that can directly alter the gut microbiota is long. In addition to antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, anthelmintics, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), laxatives, oral antidiabetics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, statins, chemotherapeutics, and immunosuppressants can trigger dysbiosis.
A 2020 study published in Nature Communications, which analyzed the impact of common medications on the composition and metabolic function of the gut bacteria, showed that , most notably antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, laxatives, and metformin.
“There are still no protocols aimed at preserving the microbiota during pharmacological treatment. Future research should identify biomarkers of drug-induced dysbiosis and potentially adapt live biotherapeutics to counteract it,” said Maria Júlia Segantini, MD, a coloproctologist at the University of São Paulo, Brazil.
Known Facts
Antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and anthelmintics eliminate pathogens but can also disrupt the microbiota across the gut, skin, mouth, lungs, and genitourinary tract.
“This ecosystem is part of the innate immune system and helps to balance inflammation and homeostasis. Loss of microbial diversity alters interspecies interactions and changes nutrient availability, which can undermine the ability to fend off pathogens,” said Segantini, noting the role of microbiota in vitamin K and B-complex production.
“The microbiome may lose its ability to prevent pathogens from taking hold. This is due to the loss of microbial diversity, changes in interactions between species, and the availability of nutrients,” she added.
Antibiotics, as is well known, eliminate bacterial species indiscriminately, reduce the presence of beneficial bacteria in the gut, and, therefore, favor the growth of opportunistic pathogenic microorganisms. However, in addition to their direct effects on microorganisms, different medications can alter the intestinal microbiota through various mechanisms linked to their specific actions. Here are some examples:
Proton pump inhibitors: These can facilitate the translocation of bacteria from the mouth to the intestine and affect the metabolic functions of the intestinal microbiota. “In users of these medications, there may be an enrichment of pathways related to carbohydrate metabolism, such as glycolysis and pyruvate metabolism, indicating possible changes in intestinal metabolism,” Segantini explained.
NSAIDs: NSAIDs can modify the function and composition of the intestinal microbiota, favor the growth of pathogenic species, and reduce the diversity of preexisting bacteria by reducing the presence of beneficial commensal bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. “This is due to changes in the permeability of the intestinal wall, due to the inhibition of prostaglandins that help maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, enteropathy induced by NSAIDs, and drug interactions,” said Segantini.
Laxatives: Accelerated intestinal transit using laxatives impairs the quality of the microbiota and alters bile acid. Osmotic agents, such as lactulose and polyethylene glycol, may decrease resistance to infection.
“Studies in animal models indicate that polyethylene glycol can increase the proportion of Bacteroides and reduce the abundance of Bacteroidales bacteria, with lasting repercussions on the intestinal microbiota. Stimulant laxatives, in addition to causing an acceleration of the evacuation flow, can lead to a decrease in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are important for intestinal health,” Segantini explained.
Chemotherapeutics: Chemotherapeutic agents can significantly influence the intestinal microbiota and affect its composition, diversity, and functionality, which in turn can affect the efficacy of treatment and the occurrence of adverse effects. “5-fluorouracil led to a decrease in the abundance of beneficial anaerobic genera, such as Blautia, and an increase in opportunistic pathogens, such as Staphylococcus and Escherichia coli, during chemotherapy. In addition, it can lead to an increase in the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria while reducing Firmicutes and Actinobacteria. These changes can affect the function of the intestinal barrier and the immune response. Other problems related to chemotherapy-induced dysbiosis are the adverse effects themselves, such as diarrhea and mucositis,” said Segantini.
Statins: Animal studies suggest that treatment with statins, including atorvastatin, may alter the composition of the gut microbiota. “These changes include the reduction of beneficial bacteria, such as Akkermansia muciniphila, and the increase in intestinal pathogens, resulting in intestinal dysbiosis. The use of statins can affect the diversity of the intestinal microbiota, although the results vary according to the type of statin and the clinical context.”
“Statins can activate intestinal nuclear receptors, such as pregnane X receptors, which modulate the expression of genes involved in bile metabolism and the inflammatory response. This activation can contribute to changes in the intestinal microbiota and associated metabolic processes. Although statins play a fundamental role in reducing cardiovascular risk, their interactions with the intestinal microbiota can influence the efficacy of treatment and the profile of adverse effects,” said Segantini.
Immunosuppressants: The use of immunosuppressants, such as corticosteroids, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate, has been associated with changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. “Immunosuppressant-induced dysbiosis can compromise the intestinal barrier, increase permeability, and facilitate bacterial translocation. This can result in opportunistic infections by pathogens and post-transplant complications, such as graft rejection and post-transplant diabetes,” Segantini stated.
“Alteration of the gut microbiota by immunosuppressants may influence the host’s immune response. For example, tacrolimus has been associated with an increase in the abundance of Allobaculum, Bacteroides, and Lactobacillus, in addition to elevated levels of regulatory T cells in the colonic mucosa and circulation, suggesting a role in modulating gut immunity,” she said.
Antipsychotics: Antipsychotics can affect gut microbiota in several ways, influencing bacterial composition and diversity, which may contribute to adverse metabolic and gastrointestinal effects.
“Olanzapine, for example, has been shown in rodent studies to increase the abundance of Firmicutes and reduce that of Bacteroidetes, resulting in a higher Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, which is associated with weight gain and dyslipidemia,” said Segantini.
She stated that risperidone increased the abundance of Firmicutes and decreased that of Bacteroidetes in animal models, correlating with weight gain and reduced basal metabolic rate. “Fecal transfer from risperidone-treated mice to naive mice resulted in decreased metabolic rate, suggesting that the gut microbiota would mediate these effects.”
Treatment with aripiprazole increased microbial diversity and the abundance of Clostridium, Peptoclostridium, Intestinibacter, and Christensenellaceae, in addition to promoting increased intestinal permeability in animal models.
“Therefore, the use of these medications can lead to metabolic changes, such as weight gain, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. This is due to a decrease in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are important for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier. Another change frequently observed in clinical practice is constipation induced by these medications. This functional change can also generate changes in the intestinal microbiota,” she said.
Oral antidiabetic agents: Oral antidiabetic agents influence the intestinal microbiota in different ways, depending on the therapeutic class. However, not all drug interactions in the microbiome are harmful. Liraglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria associated with metabolism.
“Exenatide, another GLP-1 agonist, has varied effects and can increase both beneficial and inflammatory bacteria,” explained Álvaro Delgado, MD, a gastroenterologist at Hospital Alemão Oswaldo Cruz in São Paulo, Brazil.
“In humans, an increase in bacteria such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii has been observed, with positive effects. However, more studies are needed to evaluate the clinical impacts,” he said, and that, in animal models, these changes caused by GLP-1 agonists are linked to metabolic changes, such as greater glucose tolerance.
Metformin has been linked to increased abundance of A muciniphila, a beneficial bacterium that degrades mucin and produces short-chain fatty acids. “These bacteria are associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation,” he said.
Segantini stated that studies in mice have shown that vildagliptin also plays a positive role in altering the composition of the intestinal microbiota, increasing the abundance of Lactobacillus and Roseburia, and reducing Oscillibacter. “This same beneficial effect is seen with the use of sitagliptin,” she said.
Studies in animal models have also indicated that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin increase the populations of short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria, such as Bacteroides and Odoribacter, and reduce the populations of lipopolysaccharide-producing bacteria, such as Oscillibacter.
“There are still not many studies regarding the use of sulfonylureas on the intestinal microbiota, so their action on the microbiota is still controversial,” said Segantini.
Antivirals: Antiviral treatment can influence gut microbiota in complex ways, depending on the type of infection and medication used.
“Although many studies focus on the effects of viral infection on the microbiota, there is evidence that antiviral treatment can also restore the healthy composition of the microbiota, promoting additional benefits to gut and immune health,” said Segantini.
In mice with chronic hepatitis B, entecavir restored the alpha diversity of the gut microbiota, which was reduced due to infection. In addition, the recovery of beneficial bacteria, such as Akkermansia and Blautia, was observed, which was associated with the protection of the intestinal barrier and reduction of hepatic inflammation.
Studies have indicated that tenofovir may aid in the recovery of intestinal dysbiosis induced by chronic hepatitis B virus infection and promote the restoration of a healthy microbial composition.
“Specifically, an increase in Collinsella and Bifidobacterium, bacteria associated with the production of short-chain fatty acids and modulation of the immune response, was observed,” said Segantini.
The use of antiretrovirals, such as lopinavir and ritonavir, has been associated with changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in patients living with HIV.
“A decrease in Lachnospira, Butyricicoccus, Oscillospira, and Prevotella, bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids that are important in intestinal health and in modulating the immune response, was observed.”
Antifungals: As a side effect, antifungals also eliminate commensal fungi, which “share intestinal niches with microbiota bacteria, balancing their immunological functions. When modified, they culminate in dysbiosis, worsening of inflammatory pathologies — such as colitis and allergic diseases — and can increase bacterial translocation,” said Segantini.
For example, fluconazole reduces the abundance of Candida spp. while promoting the growth of fungi such as Aspergillus, Wallemia, and Epicoccum.
“A relative increase in Firmicutes and Proteobacteria and a decrease in Bacteroidetes, Deferribacteres, Patescibacteria, and Tenericutes were also observed,” she explained.
Anthelmintics: These also affect the intestinal bacterial and fungal microbiota and alter the modulation of the immune response, in addition to having specific effects depending on the type of drug used.
Clinical Advice
Symptoms of dysbiosis include abdominal distension, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea, pain, fatigue, and mood swings. “The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, since tests such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, which indicate metabolites of bacteria associated with dysbiosis, specific stool tests, and microbiota mapping with GI-MAP [Gastrointestinal Microbial Assay Plus], for example, are expensive, difficult to access, and often inconclusive for diagnosis and for assessing the cause of the microbiota alteration,” explained Fernando Seefelder Flaquer, MD, a gastroenterologist at Albert Einstein Israelite Hospital in São Paulo.
When caused by medication, dysbiosis tends to be reversed naturally after discontinuation of the drug. “However, in medications with a high chance of altering the microbiota, probiotics can be used as prevention,” said Flaquer.
“To avoid problems, it is important to use antibiotics with caution and prefer, when possible, those with a reduced spectrum,” advised Delgado.
“Supplementation with probiotics and prebiotics can help maintain the balance of the microbiota, but it should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, as its indications are still restricted at present.”
Currently, dysbiosis management relies on nutritional support and lifestyle modifications. “Physical exercise, management of psychological changes, and use of probiotics and prebiotics. In specific cases, individualized treatment may even require the administration of some types of antibiotics,” explained Segantini.
Although fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) has been widely discussed and increasingly studied, it should still be approached with caution. While promising, FMT remains experimental for most conditions, and its use outside research settings should be carefully considered, particularly in patients who are immunocompromised or have compromised intestinal barriers.
“Currently, the treatment has stood out as promising for cases of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection, being the only consolidated clinical indication,” said Segantini.
Science Hype
The interest in gut microbiome research has undoubtedly driven important scientific advances, but it also risks exaggeration. While the field holds enormous promise, much of the research remains in its early stages.
“The indiscriminate use of probiotics and reliance on microbiota analysis tests for personalized probiotic prescriptions are growing concerns,” Delgado warned. “We need to bridge the gap between basic science and clinical application. When that translation happens, it could revolutionize care for many diseases.”
Flaquer emphasized a broader issue: “There has been an overvaluation of dysbiosis and microbiota-focused treatments as cure-alls for a wide range of conditions — often subjective or lacking solid scientific correlation — such as depression, anxiety, fatigue, cancer, and even autism.”
With ongoing advances in microbiome research, understanding the impact of this complex ecosystem on human health has become essential across all medical specialties. In pediatrics, for instance, microbiota plays a critical role in immune and metabolic development, particularly in preventing conditions such as allergies and obesity.
In digestive surgery, preoperative use of probiotics has been shown to reduce complications and enhance postoperative recovery. Neurological research has highlighted the gut-brain axis as a potential factor in the development of neurodegenerative diseases. In gynecology, regulating the vaginal microbiota is key to preventing infections and complications during pregnancy.
“Given the connections between the microbiota and both intestinal and systemic diseases, every medical specialist should understand how it relates to the conditions they treat daily,” concluded Flaquer.
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition.
Effective ways to combat harmful viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasitic worms have driven major advances in medicine and contributed to a significant increase in human life expectancy over the past century. However, as knowledge about the role of these microorganisms in promoting and maintaining health deepens, there is a need for a new look at the impact of these treatments.
The list of drugs that can directly alter the gut microbiota is long. In addition to antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, anthelmintics, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), laxatives, oral antidiabetics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, statins, chemotherapeutics, and immunosuppressants can trigger dysbiosis.
A 2020 study published in Nature Communications, which analyzed the impact of common medications on the composition and metabolic function of the gut bacteria, showed that , most notably antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, laxatives, and metformin.
“There are still no protocols aimed at preserving the microbiota during pharmacological treatment. Future research should identify biomarkers of drug-induced dysbiosis and potentially adapt live biotherapeutics to counteract it,” said Maria Júlia Segantini, MD, a coloproctologist at the University of São Paulo, Brazil.
Known Facts
Antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and anthelmintics eliminate pathogens but can also disrupt the microbiota across the gut, skin, mouth, lungs, and genitourinary tract.
“This ecosystem is part of the innate immune system and helps to balance inflammation and homeostasis. Loss of microbial diversity alters interspecies interactions and changes nutrient availability, which can undermine the ability to fend off pathogens,” said Segantini, noting the role of microbiota in vitamin K and B-complex production.
“The microbiome may lose its ability to prevent pathogens from taking hold. This is due to the loss of microbial diversity, changes in interactions between species, and the availability of nutrients,” she added.
Antibiotics, as is well known, eliminate bacterial species indiscriminately, reduce the presence of beneficial bacteria in the gut, and, therefore, favor the growth of opportunistic pathogenic microorganisms. However, in addition to their direct effects on microorganisms, different medications can alter the intestinal microbiota through various mechanisms linked to their specific actions. Here are some examples:
Proton pump inhibitors: These can facilitate the translocation of bacteria from the mouth to the intestine and affect the metabolic functions of the intestinal microbiota. “In users of these medications, there may be an enrichment of pathways related to carbohydrate metabolism, such as glycolysis and pyruvate metabolism, indicating possible changes in intestinal metabolism,” Segantini explained.
NSAIDs: NSAIDs can modify the function and composition of the intestinal microbiota, favor the growth of pathogenic species, and reduce the diversity of preexisting bacteria by reducing the presence of beneficial commensal bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. “This is due to changes in the permeability of the intestinal wall, due to the inhibition of prostaglandins that help maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, enteropathy induced by NSAIDs, and drug interactions,” said Segantini.
Laxatives: Accelerated intestinal transit using laxatives impairs the quality of the microbiota and alters bile acid. Osmotic agents, such as lactulose and polyethylene glycol, may decrease resistance to infection.
“Studies in animal models indicate that polyethylene glycol can increase the proportion of Bacteroides and reduce the abundance of Bacteroidales bacteria, with lasting repercussions on the intestinal microbiota. Stimulant laxatives, in addition to causing an acceleration of the evacuation flow, can lead to a decrease in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are important for intestinal health,” Segantini explained.
Chemotherapeutics: Chemotherapeutic agents can significantly influence the intestinal microbiota and affect its composition, diversity, and functionality, which in turn can affect the efficacy of treatment and the occurrence of adverse effects. “5-fluorouracil led to a decrease in the abundance of beneficial anaerobic genera, such as Blautia, and an increase in opportunistic pathogens, such as Staphylococcus and Escherichia coli, during chemotherapy. In addition, it can lead to an increase in the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria while reducing Firmicutes and Actinobacteria. These changes can affect the function of the intestinal barrier and the immune response. Other problems related to chemotherapy-induced dysbiosis are the adverse effects themselves, such as diarrhea and mucositis,” said Segantini.
Statins: Animal studies suggest that treatment with statins, including atorvastatin, may alter the composition of the gut microbiota. “These changes include the reduction of beneficial bacteria, such as Akkermansia muciniphila, and the increase in intestinal pathogens, resulting in intestinal dysbiosis. The use of statins can affect the diversity of the intestinal microbiota, although the results vary according to the type of statin and the clinical context.”
“Statins can activate intestinal nuclear receptors, such as pregnane X receptors, which modulate the expression of genes involved in bile metabolism and the inflammatory response. This activation can contribute to changes in the intestinal microbiota and associated metabolic processes. Although statins play a fundamental role in reducing cardiovascular risk, their interactions with the intestinal microbiota can influence the efficacy of treatment and the profile of adverse effects,” said Segantini.
Immunosuppressants: The use of immunosuppressants, such as corticosteroids, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate, has been associated with changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. “Immunosuppressant-induced dysbiosis can compromise the intestinal barrier, increase permeability, and facilitate bacterial translocation. This can result in opportunistic infections by pathogens and post-transplant complications, such as graft rejection and post-transplant diabetes,” Segantini stated.
“Alteration of the gut microbiota by immunosuppressants may influence the host’s immune response. For example, tacrolimus has been associated with an increase in the abundance of Allobaculum, Bacteroides, and Lactobacillus, in addition to elevated levels of regulatory T cells in the colonic mucosa and circulation, suggesting a role in modulating gut immunity,” she said.
Antipsychotics: Antipsychotics can affect gut microbiota in several ways, influencing bacterial composition and diversity, which may contribute to adverse metabolic and gastrointestinal effects.
“Olanzapine, for example, has been shown in rodent studies to increase the abundance of Firmicutes and reduce that of Bacteroidetes, resulting in a higher Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, which is associated with weight gain and dyslipidemia,” said Segantini.
She stated that risperidone increased the abundance of Firmicutes and decreased that of Bacteroidetes in animal models, correlating with weight gain and reduced basal metabolic rate. “Fecal transfer from risperidone-treated mice to naive mice resulted in decreased metabolic rate, suggesting that the gut microbiota would mediate these effects.”
Treatment with aripiprazole increased microbial diversity and the abundance of Clostridium, Peptoclostridium, Intestinibacter, and Christensenellaceae, in addition to promoting increased intestinal permeability in animal models.
“Therefore, the use of these medications can lead to metabolic changes, such as weight gain, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. This is due to a decrease in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are important for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier. Another change frequently observed in clinical practice is constipation induced by these medications. This functional change can also generate changes in the intestinal microbiota,” she said.
Oral antidiabetic agents: Oral antidiabetic agents influence the intestinal microbiota in different ways, depending on the therapeutic class. However, not all drug interactions in the microbiome are harmful. Liraglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria associated with metabolism.
“Exenatide, another GLP-1 agonist, has varied effects and can increase both beneficial and inflammatory bacteria,” explained Álvaro Delgado, MD, a gastroenterologist at Hospital Alemão Oswaldo Cruz in São Paulo, Brazil.
“In humans, an increase in bacteria such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii has been observed, with positive effects. However, more studies are needed to evaluate the clinical impacts,” he said, and that, in animal models, these changes caused by GLP-1 agonists are linked to metabolic changes, such as greater glucose tolerance.
Metformin has been linked to increased abundance of A muciniphila, a beneficial bacterium that degrades mucin and produces short-chain fatty acids. “These bacteria are associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation,” he said.
Segantini stated that studies in mice have shown that vildagliptin also plays a positive role in altering the composition of the intestinal microbiota, increasing the abundance of Lactobacillus and Roseburia, and reducing Oscillibacter. “This same beneficial effect is seen with the use of sitagliptin,” she said.
Studies in animal models have also indicated that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin increase the populations of short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria, such as Bacteroides and Odoribacter, and reduce the populations of lipopolysaccharide-producing bacteria, such as Oscillibacter.
“There are still not many studies regarding the use of sulfonylureas on the intestinal microbiota, so their action on the microbiota is still controversial,” said Segantini.
Antivirals: Antiviral treatment can influence gut microbiota in complex ways, depending on the type of infection and medication used.
“Although many studies focus on the effects of viral infection on the microbiota, there is evidence that antiviral treatment can also restore the healthy composition of the microbiota, promoting additional benefits to gut and immune health,” said Segantini.
In mice with chronic hepatitis B, entecavir restored the alpha diversity of the gut microbiota, which was reduced due to infection. In addition, the recovery of beneficial bacteria, such as Akkermansia and Blautia, was observed, which was associated with the protection of the intestinal barrier and reduction of hepatic inflammation.
Studies have indicated that tenofovir may aid in the recovery of intestinal dysbiosis induced by chronic hepatitis B virus infection and promote the restoration of a healthy microbial composition.
“Specifically, an increase in Collinsella and Bifidobacterium, bacteria associated with the production of short-chain fatty acids and modulation of the immune response, was observed,” said Segantini.
The use of antiretrovirals, such as lopinavir and ritonavir, has been associated with changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in patients living with HIV.
“A decrease in Lachnospira, Butyricicoccus, Oscillospira, and Prevotella, bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids that are important in intestinal health and in modulating the immune response, was observed.”
Antifungals: As a side effect, antifungals also eliminate commensal fungi, which “share intestinal niches with microbiota bacteria, balancing their immunological functions. When modified, they culminate in dysbiosis, worsening of inflammatory pathologies — such as colitis and allergic diseases — and can increase bacterial translocation,” said Segantini.
For example, fluconazole reduces the abundance of Candida spp. while promoting the growth of fungi such as Aspergillus, Wallemia, and Epicoccum.
“A relative increase in Firmicutes and Proteobacteria and a decrease in Bacteroidetes, Deferribacteres, Patescibacteria, and Tenericutes were also observed,” she explained.
Anthelmintics: These also affect the intestinal bacterial and fungal microbiota and alter the modulation of the immune response, in addition to having specific effects depending on the type of drug used.
Clinical Advice
Symptoms of dysbiosis include abdominal distension, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea, pain, fatigue, and mood swings. “The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, since tests such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, which indicate metabolites of bacteria associated with dysbiosis, specific stool tests, and microbiota mapping with GI-MAP [Gastrointestinal Microbial Assay Plus], for example, are expensive, difficult to access, and often inconclusive for diagnosis and for assessing the cause of the microbiota alteration,” explained Fernando Seefelder Flaquer, MD, a gastroenterologist at Albert Einstein Israelite Hospital in São Paulo.
When caused by medication, dysbiosis tends to be reversed naturally after discontinuation of the drug. “However, in medications with a high chance of altering the microbiota, probiotics can be used as prevention,” said Flaquer.
“To avoid problems, it is important to use antibiotics with caution and prefer, when possible, those with a reduced spectrum,” advised Delgado.
“Supplementation with probiotics and prebiotics can help maintain the balance of the microbiota, but it should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, as its indications are still restricted at present.”
Currently, dysbiosis management relies on nutritional support and lifestyle modifications. “Physical exercise, management of psychological changes, and use of probiotics and prebiotics. In specific cases, individualized treatment may even require the administration of some types of antibiotics,” explained Segantini.
Although fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) has been widely discussed and increasingly studied, it should still be approached with caution. While promising, FMT remains experimental for most conditions, and its use outside research settings should be carefully considered, particularly in patients who are immunocompromised or have compromised intestinal barriers.
“Currently, the treatment has stood out as promising for cases of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection, being the only consolidated clinical indication,” said Segantini.
Science Hype
The interest in gut microbiome research has undoubtedly driven important scientific advances, but it also risks exaggeration. While the field holds enormous promise, much of the research remains in its early stages.
“The indiscriminate use of probiotics and reliance on microbiota analysis tests for personalized probiotic prescriptions are growing concerns,” Delgado warned. “We need to bridge the gap between basic science and clinical application. When that translation happens, it could revolutionize care for many diseases.”
Flaquer emphasized a broader issue: “There has been an overvaluation of dysbiosis and microbiota-focused treatments as cure-alls for a wide range of conditions — often subjective or lacking solid scientific correlation — such as depression, anxiety, fatigue, cancer, and even autism.”
With ongoing advances in microbiome research, understanding the impact of this complex ecosystem on human health has become essential across all medical specialties. In pediatrics, for instance, microbiota plays a critical role in immune and metabolic development, particularly in preventing conditions such as allergies and obesity.
In digestive surgery, preoperative use of probiotics has been shown to reduce complications and enhance postoperative recovery. Neurological research has highlighted the gut-brain axis as a potential factor in the development of neurodegenerative diseases. In gynecology, regulating the vaginal microbiota is key to preventing infections and complications during pregnancy.
“Given the connections between the microbiota and both intestinal and systemic diseases, every medical specialist should understand how it relates to the conditions they treat daily,” concluded Flaquer.
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition.
Effective ways to combat harmful viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasitic worms have driven major advances in medicine and contributed to a significant increase in human life expectancy over the past century. However, as knowledge about the role of these microorganisms in promoting and maintaining health deepens, there is a need for a new look at the impact of these treatments.
The list of drugs that can directly alter the gut microbiota is long. In addition to antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, anthelmintics, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), laxatives, oral antidiabetics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, statins, chemotherapeutics, and immunosuppressants can trigger dysbiosis.
A 2020 study published in Nature Communications, which analyzed the impact of common medications on the composition and metabolic function of the gut bacteria, showed that , most notably antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, laxatives, and metformin.
“There are still no protocols aimed at preserving the microbiota during pharmacological treatment. Future research should identify biomarkers of drug-induced dysbiosis and potentially adapt live biotherapeutics to counteract it,” said Maria Júlia Segantini, MD, a coloproctologist at the University of São Paulo, Brazil.
Known Facts
Antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and anthelmintics eliminate pathogens but can also disrupt the microbiota across the gut, skin, mouth, lungs, and genitourinary tract.
“This ecosystem is part of the innate immune system and helps to balance inflammation and homeostasis. Loss of microbial diversity alters interspecies interactions and changes nutrient availability, which can undermine the ability to fend off pathogens,” said Segantini, noting the role of microbiota in vitamin K and B-complex production.
“The microbiome may lose its ability to prevent pathogens from taking hold. This is due to the loss of microbial diversity, changes in interactions between species, and the availability of nutrients,” she added.
Antibiotics, as is well known, eliminate bacterial species indiscriminately, reduce the presence of beneficial bacteria in the gut, and, therefore, favor the growth of opportunistic pathogenic microorganisms. However, in addition to their direct effects on microorganisms, different medications can alter the intestinal microbiota through various mechanisms linked to their specific actions. Here are some examples:
Proton pump inhibitors: These can facilitate the translocation of bacteria from the mouth to the intestine and affect the metabolic functions of the intestinal microbiota. “In users of these medications, there may be an enrichment of pathways related to carbohydrate metabolism, such as glycolysis and pyruvate metabolism, indicating possible changes in intestinal metabolism,” Segantini explained.
NSAIDs: NSAIDs can modify the function and composition of the intestinal microbiota, favor the growth of pathogenic species, and reduce the diversity of preexisting bacteria by reducing the presence of beneficial commensal bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. “This is due to changes in the permeability of the intestinal wall, due to the inhibition of prostaglandins that help maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, enteropathy induced by NSAIDs, and drug interactions,” said Segantini.
Laxatives: Accelerated intestinal transit using laxatives impairs the quality of the microbiota and alters bile acid. Osmotic agents, such as lactulose and polyethylene glycol, may decrease resistance to infection.
“Studies in animal models indicate that polyethylene glycol can increase the proportion of Bacteroides and reduce the abundance of Bacteroidales bacteria, with lasting repercussions on the intestinal microbiota. Stimulant laxatives, in addition to causing an acceleration of the evacuation flow, can lead to a decrease in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are important for intestinal health,” Segantini explained.
Chemotherapeutics: Chemotherapeutic agents can significantly influence the intestinal microbiota and affect its composition, diversity, and functionality, which in turn can affect the efficacy of treatment and the occurrence of adverse effects. “5-fluorouracil led to a decrease in the abundance of beneficial anaerobic genera, such as Blautia, and an increase in opportunistic pathogens, such as Staphylococcus and Escherichia coli, during chemotherapy. In addition, it can lead to an increase in the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria while reducing Firmicutes and Actinobacteria. These changes can affect the function of the intestinal barrier and the immune response. Other problems related to chemotherapy-induced dysbiosis are the adverse effects themselves, such as diarrhea and mucositis,” said Segantini.
Statins: Animal studies suggest that treatment with statins, including atorvastatin, may alter the composition of the gut microbiota. “These changes include the reduction of beneficial bacteria, such as Akkermansia muciniphila, and the increase in intestinal pathogens, resulting in intestinal dysbiosis. The use of statins can affect the diversity of the intestinal microbiota, although the results vary according to the type of statin and the clinical context.”
“Statins can activate intestinal nuclear receptors, such as pregnane X receptors, which modulate the expression of genes involved in bile metabolism and the inflammatory response. This activation can contribute to changes in the intestinal microbiota and associated metabolic processes. Although statins play a fundamental role in reducing cardiovascular risk, their interactions with the intestinal microbiota can influence the efficacy of treatment and the profile of adverse effects,” said Segantini.
Immunosuppressants: The use of immunosuppressants, such as corticosteroids, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate, has been associated with changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. “Immunosuppressant-induced dysbiosis can compromise the intestinal barrier, increase permeability, and facilitate bacterial translocation. This can result in opportunistic infections by pathogens and post-transplant complications, such as graft rejection and post-transplant diabetes,” Segantini stated.
“Alteration of the gut microbiota by immunosuppressants may influence the host’s immune response. For example, tacrolimus has been associated with an increase in the abundance of Allobaculum, Bacteroides, and Lactobacillus, in addition to elevated levels of regulatory T cells in the colonic mucosa and circulation, suggesting a role in modulating gut immunity,” she said.
Antipsychotics: Antipsychotics can affect gut microbiota in several ways, influencing bacterial composition and diversity, which may contribute to adverse metabolic and gastrointestinal effects.
“Olanzapine, for example, has been shown in rodent studies to increase the abundance of Firmicutes and reduce that of Bacteroidetes, resulting in a higher Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, which is associated with weight gain and dyslipidemia,” said Segantini.
She stated that risperidone increased the abundance of Firmicutes and decreased that of Bacteroidetes in animal models, correlating with weight gain and reduced basal metabolic rate. “Fecal transfer from risperidone-treated mice to naive mice resulted in decreased metabolic rate, suggesting that the gut microbiota would mediate these effects.”
Treatment with aripiprazole increased microbial diversity and the abundance of Clostridium, Peptoclostridium, Intestinibacter, and Christensenellaceae, in addition to promoting increased intestinal permeability in animal models.
“Therefore, the use of these medications can lead to metabolic changes, such as weight gain, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. This is due to a decrease in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are important for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier. Another change frequently observed in clinical practice is constipation induced by these medications. This functional change can also generate changes in the intestinal microbiota,” she said.
Oral antidiabetic agents: Oral antidiabetic agents influence the intestinal microbiota in different ways, depending on the therapeutic class. However, not all drug interactions in the microbiome are harmful. Liraglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria associated with metabolism.
“Exenatide, another GLP-1 agonist, has varied effects and can increase both beneficial and inflammatory bacteria,” explained Álvaro Delgado, MD, a gastroenterologist at Hospital Alemão Oswaldo Cruz in São Paulo, Brazil.
“In humans, an increase in bacteria such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii has been observed, with positive effects. However, more studies are needed to evaluate the clinical impacts,” he said, and that, in animal models, these changes caused by GLP-1 agonists are linked to metabolic changes, such as greater glucose tolerance.
Metformin has been linked to increased abundance of A muciniphila, a beneficial bacterium that degrades mucin and produces short-chain fatty acids. “These bacteria are associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation,” he said.
Segantini stated that studies in mice have shown that vildagliptin also plays a positive role in altering the composition of the intestinal microbiota, increasing the abundance of Lactobacillus and Roseburia, and reducing Oscillibacter. “This same beneficial effect is seen with the use of sitagliptin,” she said.
Studies in animal models have also indicated that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin increase the populations of short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria, such as Bacteroides and Odoribacter, and reduce the populations of lipopolysaccharide-producing bacteria, such as Oscillibacter.
“There are still not many studies regarding the use of sulfonylureas on the intestinal microbiota, so their action on the microbiota is still controversial,” said Segantini.
Antivirals: Antiviral treatment can influence gut microbiota in complex ways, depending on the type of infection and medication used.
“Although many studies focus on the effects of viral infection on the microbiota, there is evidence that antiviral treatment can also restore the healthy composition of the microbiota, promoting additional benefits to gut and immune health,” said Segantini.
In mice with chronic hepatitis B, entecavir restored the alpha diversity of the gut microbiota, which was reduced due to infection. In addition, the recovery of beneficial bacteria, such as Akkermansia and Blautia, was observed, which was associated with the protection of the intestinal barrier and reduction of hepatic inflammation.
Studies have indicated that tenofovir may aid in the recovery of intestinal dysbiosis induced by chronic hepatitis B virus infection and promote the restoration of a healthy microbial composition.
“Specifically, an increase in Collinsella and Bifidobacterium, bacteria associated with the production of short-chain fatty acids and modulation of the immune response, was observed,” said Segantini.
The use of antiretrovirals, such as lopinavir and ritonavir, has been associated with changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in patients living with HIV.
“A decrease in Lachnospira, Butyricicoccus, Oscillospira, and Prevotella, bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids that are important in intestinal health and in modulating the immune response, was observed.”
Antifungals: As a side effect, antifungals also eliminate commensal fungi, which “share intestinal niches with microbiota bacteria, balancing their immunological functions. When modified, they culminate in dysbiosis, worsening of inflammatory pathologies — such as colitis and allergic diseases — and can increase bacterial translocation,” said Segantini.
For example, fluconazole reduces the abundance of Candida spp. while promoting the growth of fungi such as Aspergillus, Wallemia, and Epicoccum.
“A relative increase in Firmicutes and Proteobacteria and a decrease in Bacteroidetes, Deferribacteres, Patescibacteria, and Tenericutes were also observed,” she explained.
Anthelmintics: These also affect the intestinal bacterial and fungal microbiota and alter the modulation of the immune response, in addition to having specific effects depending on the type of drug used.
Clinical Advice
Symptoms of dysbiosis include abdominal distension, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea, pain, fatigue, and mood swings. “The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, since tests such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, which indicate metabolites of bacteria associated with dysbiosis, specific stool tests, and microbiota mapping with GI-MAP [Gastrointestinal Microbial Assay Plus], for example, are expensive, difficult to access, and often inconclusive for diagnosis and for assessing the cause of the microbiota alteration,” explained Fernando Seefelder Flaquer, MD, a gastroenterologist at Albert Einstein Israelite Hospital in São Paulo.
When caused by medication, dysbiosis tends to be reversed naturally after discontinuation of the drug. “However, in medications with a high chance of altering the microbiota, probiotics can be used as prevention,” said Flaquer.
“To avoid problems, it is important to use antibiotics with caution and prefer, when possible, those with a reduced spectrum,” advised Delgado.
“Supplementation with probiotics and prebiotics can help maintain the balance of the microbiota, but it should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, as its indications are still restricted at present.”
Currently, dysbiosis management relies on nutritional support and lifestyle modifications. “Physical exercise, management of psychological changes, and use of probiotics and prebiotics. In specific cases, individualized treatment may even require the administration of some types of antibiotics,” explained Segantini.
Although fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) has been widely discussed and increasingly studied, it should still be approached with caution. While promising, FMT remains experimental for most conditions, and its use outside research settings should be carefully considered, particularly in patients who are immunocompromised or have compromised intestinal barriers.
“Currently, the treatment has stood out as promising for cases of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection, being the only consolidated clinical indication,” said Segantini.
Science Hype
The interest in gut microbiome research has undoubtedly driven important scientific advances, but it also risks exaggeration. While the field holds enormous promise, much of the research remains in its early stages.
“The indiscriminate use of probiotics and reliance on microbiota analysis tests for personalized probiotic prescriptions are growing concerns,” Delgado warned. “We need to bridge the gap between basic science and clinical application. When that translation happens, it could revolutionize care for many diseases.”
Flaquer emphasized a broader issue: “There has been an overvaluation of dysbiosis and microbiota-focused treatments as cure-alls for a wide range of conditions — often subjective or lacking solid scientific correlation — such as depression, anxiety, fatigue, cancer, and even autism.”
With ongoing advances in microbiome research, understanding the impact of this complex ecosystem on human health has become essential across all medical specialties. In pediatrics, for instance, microbiota plays a critical role in immune and metabolic development, particularly in preventing conditions such as allergies and obesity.
In digestive surgery, preoperative use of probiotics has been shown to reduce complications and enhance postoperative recovery. Neurological research has highlighted the gut-brain axis as a potential factor in the development of neurodegenerative diseases. In gynecology, regulating the vaginal microbiota is key to preventing infections and complications during pregnancy.
“Given the connections between the microbiota and both intestinal and systemic diseases, every medical specialist should understand how it relates to the conditions they treat daily,” concluded Flaquer.
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition.
Ostomy Innovation Grabs ‘Shark Tank’ Win
The “Shark Tank” winning innovation at the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Tech Summit in Chicago this April has “life-altering” potential for ostomy patients, according to one of the judges, and eliminates the need for constant pouch wear.
The innovation is called Twistomy and it is designed to replace current ostomy-pouch systems that can cause leaks, odor, skin irritation, embarrassment, and social and emotional distress. The AGA Committee for GI Innovation and Technology (CGIT) organizes the annual Tech Summit.
Twistomy’s winning design includes a flexible ring and sleeve, which are inserted into the stoma and secured on the outside with a set of rings that make up the housing unit attached to a standard wafer. The housing unit twists the sleeve closed, allowing the user to control fecal output. For evacuation, the user attaches a pouch, untwists the sleeve, evacuates cleanly and effectively, and then discards the pouch.
Twistomy cofounders Devon Horton, BS, senior bioengineer, and Lily Williams, BS, biomedical researcher and engineer, both work for the department of surgery at University of Colorado, Denver.
Horton said in an interview that when he was approached with the idea to create a better ostomy solution for a senior-year capstone project he was intrigued because the traditional ostomy system “has not changed in more than 70 years. It was crazy that no one had done anything to change that.”
The Twistomy team also won the Grand Prize this spring at the Emerging Medical Innovation Valuation Competition at the Design of Medical Devices Conference held at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Witnessing the Struggle as a CNA
Horton also works as a certified nursing assistant at an inpatient unit at University of Colorado Hospital and the ostomy patients he sees there every shift help drive his passion to find a better solution.
He hears the emotional stories of people who manage their ostomy daily.
“Many express feelings of depression and anxiety, feeling isolated with their severe inability to go out and do things because of the fear of the noise the stoma makes, or the crinkling of the plastic bag in a yoga class,” he said. “We want to help them regain that control of quality of life.”
They also hope to cut down on the ostomy management time. “Initial user testing [for Twistomy] was less than 75 seconds to insert and assemble,” he said. “I did an interview with a patient yesterday who said they probably spend an hour a day managing their ostomy,” including cleaning and replacing.
Horton and Williams have a patent on the device and currently use three-dimensional printing for the prototypes.
Williams said they are now conducting consumer discovery studies through the National Science Foundation and are interviewing 30 stakeholders — “anyone who has a relationship with an ostomy,” whether a colorectal surgeon, a gastrointestinal nurse, ostomy patients, or insurers.
Those interviews will help in refining the device so they can start consulting with manufacturers and work toward approval as a Class II medical device from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Williams said.
Saving Healthcare Costs
Another potential benefit for Twistomy is its ability to cut healthcare costs, Horton said. Traditional ostomies are prone to leakage, which can lead to peristomal skin complications.
He pointed to a National Institutes of Health analysis that found that on average peristomal skin complications caused upwards of $80,000 more per ostomy patient in increased healthcare costs over a 3-month period than for those without the complications.
“With Twistomy, we are reducing leakage most likely to zero,” Horton said. “We set out to say if we could reduce [infections] by half or a little less than half, we can cut out those tens of thousands of dollars that insurance companies and payers are spending.”
Permanent and Temporary Ostomy Markets
He pointed out that not all ostomies are permanent ostomies, adding that the reversal rate “is about 65%.” Often those reversal surgeries cannot take place until peristomal skin complications have been healed.
“We’re not only hoping to market to the permanent stoma patients, but the patients with temporary stomas as well,” he said.
The team estimates it will need $4 million–$6 million in funding for manufacturing and consultation costs as well as costs involved in seeking FDA approval.
Horton and Williams project the housing unit cost will be $399 based on known out-of-pocket expenses for patients with ostomy care products and the unit would be replaced annually. Disposable elements would be an additional cost.
Assuming insurance acceptance of the product, he said, “With about an 80/20 insurance coverage, typical for many patients, it would be about $100 in out-of-pocket expenses per month to use our device, which is around the lower end of what a lot of patients are spending out of pocket.”
One of the Tech Summit judges, Somaya Albhaisi, MD, a gastroenterology/hepatology fellow at University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview that the Shark Tank results were unanimous among the five judges and Twistomy also took the fan favorite vote.
She said the teams were judged on quality of pitch, potential clinical impact, and feasibility of business plan. Teams got 5-7 minutes to pitch and answered questions afterward.
“Deep Understanding” of Patient Need
“They combined smart engineering with deep understanding of patient need, which is restoring control, dignity, and quality of life for ostomy users while also reducing healthcare costs. It is rare to see a solution this scalable and impactful. It was a deeply empathetic solution overall.” She noted that nearly 1 million people in the United States currently use an ostomy.
Ostomy users’ quality of life is compromised, and they often have mental health challenges, Albhaisi said. This innovation appears to offer easy use, more dignity and control.
The other four Shark Tank finalists were:
- AI Lumen, which developed a retroview camera system, which attaches to the colonoscope and enhances imaging to detect hidden polyps that may evade conventional endoscopes.
- Amplified Sciences, which developed an ultrasensitive diagnostic platform that detects biomarker activities in minute volumes of fluid from pancreatic cystic lesions, helping to stratify patients into low risk or potential malignancy, reducing unneeded surgeries, costs, and comorbidities.
- KITE Endoscopic Innovations, which designed the Dynaflex TruCut needle to offer a simpler endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)–guided biopsy procedure with fewer needle passes, deeper insights into tumor pathology, and more tissue for geonomic analysis.
- MicroSteer, which designed a device to facilitate semiautomated endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) by decoupling the dissecting knife from the endoscope, enhancing safety and effectiveness during the procedure.
The Twistomy Team “Surprised Everyone”
The competitors’ scores were “very close,” one of the judges, Kevin Berliner, said in an interview. “The Twistomy team surprised everyone — the judges and the crowd — with their succinct, informative, and impactful pitch. That presentation disparity was the tiebreaker for me,” said Berliner, who works for Medtronic, a sponsor of the competition, in Chicago.
He said Horton and Williams were the youngest presenters and had the earliest stage pitch they judged, but they “outpresented other competitors in clarity, simplification, and storytelling.”
Also impressive was their description of their “commercially viable path to success” and their plan for the challenges ahead, he said.
Those challenges to get Twistomy to market center “on the ongoing changing climate we have with research funds lately,” Horton said. “We’re giving it an estimate of 3-5 years.”
Horton, Williams, Albhaisi, and Berliner reported no relevant financial relationships.
The “Shark Tank” winning innovation at the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Tech Summit in Chicago this April has “life-altering” potential for ostomy patients, according to one of the judges, and eliminates the need for constant pouch wear.
The innovation is called Twistomy and it is designed to replace current ostomy-pouch systems that can cause leaks, odor, skin irritation, embarrassment, and social and emotional distress. The AGA Committee for GI Innovation and Technology (CGIT) organizes the annual Tech Summit.
Twistomy’s winning design includes a flexible ring and sleeve, which are inserted into the stoma and secured on the outside with a set of rings that make up the housing unit attached to a standard wafer. The housing unit twists the sleeve closed, allowing the user to control fecal output. For evacuation, the user attaches a pouch, untwists the sleeve, evacuates cleanly and effectively, and then discards the pouch.
Twistomy cofounders Devon Horton, BS, senior bioengineer, and Lily Williams, BS, biomedical researcher and engineer, both work for the department of surgery at University of Colorado, Denver.
Horton said in an interview that when he was approached with the idea to create a better ostomy solution for a senior-year capstone project he was intrigued because the traditional ostomy system “has not changed in more than 70 years. It was crazy that no one had done anything to change that.”
The Twistomy team also won the Grand Prize this spring at the Emerging Medical Innovation Valuation Competition at the Design of Medical Devices Conference held at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Witnessing the Struggle as a CNA
Horton also works as a certified nursing assistant at an inpatient unit at University of Colorado Hospital and the ostomy patients he sees there every shift help drive his passion to find a better solution.
He hears the emotional stories of people who manage their ostomy daily.
“Many express feelings of depression and anxiety, feeling isolated with their severe inability to go out and do things because of the fear of the noise the stoma makes, or the crinkling of the plastic bag in a yoga class,” he said. “We want to help them regain that control of quality of life.”
They also hope to cut down on the ostomy management time. “Initial user testing [for Twistomy] was less than 75 seconds to insert and assemble,” he said. “I did an interview with a patient yesterday who said they probably spend an hour a day managing their ostomy,” including cleaning and replacing.
Horton and Williams have a patent on the device and currently use three-dimensional printing for the prototypes.
Williams said they are now conducting consumer discovery studies through the National Science Foundation and are interviewing 30 stakeholders — “anyone who has a relationship with an ostomy,” whether a colorectal surgeon, a gastrointestinal nurse, ostomy patients, or insurers.
Those interviews will help in refining the device so they can start consulting with manufacturers and work toward approval as a Class II medical device from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Williams said.
Saving Healthcare Costs
Another potential benefit for Twistomy is its ability to cut healthcare costs, Horton said. Traditional ostomies are prone to leakage, which can lead to peristomal skin complications.
He pointed to a National Institutes of Health analysis that found that on average peristomal skin complications caused upwards of $80,000 more per ostomy patient in increased healthcare costs over a 3-month period than for those without the complications.
“With Twistomy, we are reducing leakage most likely to zero,” Horton said. “We set out to say if we could reduce [infections] by half or a little less than half, we can cut out those tens of thousands of dollars that insurance companies and payers are spending.”
Permanent and Temporary Ostomy Markets
He pointed out that not all ostomies are permanent ostomies, adding that the reversal rate “is about 65%.” Often those reversal surgeries cannot take place until peristomal skin complications have been healed.
“We’re not only hoping to market to the permanent stoma patients, but the patients with temporary stomas as well,” he said.
The team estimates it will need $4 million–$6 million in funding for manufacturing and consultation costs as well as costs involved in seeking FDA approval.
Horton and Williams project the housing unit cost will be $399 based on known out-of-pocket expenses for patients with ostomy care products and the unit would be replaced annually. Disposable elements would be an additional cost.
Assuming insurance acceptance of the product, he said, “With about an 80/20 insurance coverage, typical for many patients, it would be about $100 in out-of-pocket expenses per month to use our device, which is around the lower end of what a lot of patients are spending out of pocket.”
One of the Tech Summit judges, Somaya Albhaisi, MD, a gastroenterology/hepatology fellow at University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview that the Shark Tank results were unanimous among the five judges and Twistomy also took the fan favorite vote.
She said the teams were judged on quality of pitch, potential clinical impact, and feasibility of business plan. Teams got 5-7 minutes to pitch and answered questions afterward.
“Deep Understanding” of Patient Need
“They combined smart engineering with deep understanding of patient need, which is restoring control, dignity, and quality of life for ostomy users while also reducing healthcare costs. It is rare to see a solution this scalable and impactful. It was a deeply empathetic solution overall.” She noted that nearly 1 million people in the United States currently use an ostomy.
Ostomy users’ quality of life is compromised, and they often have mental health challenges, Albhaisi said. This innovation appears to offer easy use, more dignity and control.
The other four Shark Tank finalists were:
- AI Lumen, which developed a retroview camera system, which attaches to the colonoscope and enhances imaging to detect hidden polyps that may evade conventional endoscopes.
- Amplified Sciences, which developed an ultrasensitive diagnostic platform that detects biomarker activities in minute volumes of fluid from pancreatic cystic lesions, helping to stratify patients into low risk or potential malignancy, reducing unneeded surgeries, costs, and comorbidities.
- KITE Endoscopic Innovations, which designed the Dynaflex TruCut needle to offer a simpler endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)–guided biopsy procedure with fewer needle passes, deeper insights into tumor pathology, and more tissue for geonomic analysis.
- MicroSteer, which designed a device to facilitate semiautomated endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) by decoupling the dissecting knife from the endoscope, enhancing safety and effectiveness during the procedure.
The Twistomy Team “Surprised Everyone”
The competitors’ scores were “very close,” one of the judges, Kevin Berliner, said in an interview. “The Twistomy team surprised everyone — the judges and the crowd — with their succinct, informative, and impactful pitch. That presentation disparity was the tiebreaker for me,” said Berliner, who works for Medtronic, a sponsor of the competition, in Chicago.
He said Horton and Williams were the youngest presenters and had the earliest stage pitch they judged, but they “outpresented other competitors in clarity, simplification, and storytelling.”
Also impressive was their description of their “commercially viable path to success” and their plan for the challenges ahead, he said.
Those challenges to get Twistomy to market center “on the ongoing changing climate we have with research funds lately,” Horton said. “We’re giving it an estimate of 3-5 years.”
Horton, Williams, Albhaisi, and Berliner reported no relevant financial relationships.
The “Shark Tank” winning innovation at the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Tech Summit in Chicago this April has “life-altering” potential for ostomy patients, according to one of the judges, and eliminates the need for constant pouch wear.
The innovation is called Twistomy and it is designed to replace current ostomy-pouch systems that can cause leaks, odor, skin irritation, embarrassment, and social and emotional distress. The AGA Committee for GI Innovation and Technology (CGIT) organizes the annual Tech Summit.
Twistomy’s winning design includes a flexible ring and sleeve, which are inserted into the stoma and secured on the outside with a set of rings that make up the housing unit attached to a standard wafer. The housing unit twists the sleeve closed, allowing the user to control fecal output. For evacuation, the user attaches a pouch, untwists the sleeve, evacuates cleanly and effectively, and then discards the pouch.
Twistomy cofounders Devon Horton, BS, senior bioengineer, and Lily Williams, BS, biomedical researcher and engineer, both work for the department of surgery at University of Colorado, Denver.
Horton said in an interview that when he was approached with the idea to create a better ostomy solution for a senior-year capstone project he was intrigued because the traditional ostomy system “has not changed in more than 70 years. It was crazy that no one had done anything to change that.”
The Twistomy team also won the Grand Prize this spring at the Emerging Medical Innovation Valuation Competition at the Design of Medical Devices Conference held at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Witnessing the Struggle as a CNA
Horton also works as a certified nursing assistant at an inpatient unit at University of Colorado Hospital and the ostomy patients he sees there every shift help drive his passion to find a better solution.
He hears the emotional stories of people who manage their ostomy daily.
“Many express feelings of depression and anxiety, feeling isolated with their severe inability to go out and do things because of the fear of the noise the stoma makes, or the crinkling of the plastic bag in a yoga class,” he said. “We want to help them regain that control of quality of life.”
They also hope to cut down on the ostomy management time. “Initial user testing [for Twistomy] was less than 75 seconds to insert and assemble,” he said. “I did an interview with a patient yesterday who said they probably spend an hour a day managing their ostomy,” including cleaning and replacing.
Horton and Williams have a patent on the device and currently use three-dimensional printing for the prototypes.
Williams said they are now conducting consumer discovery studies through the National Science Foundation and are interviewing 30 stakeholders — “anyone who has a relationship with an ostomy,” whether a colorectal surgeon, a gastrointestinal nurse, ostomy patients, or insurers.
Those interviews will help in refining the device so they can start consulting with manufacturers and work toward approval as a Class II medical device from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Williams said.
Saving Healthcare Costs
Another potential benefit for Twistomy is its ability to cut healthcare costs, Horton said. Traditional ostomies are prone to leakage, which can lead to peristomal skin complications.
He pointed to a National Institutes of Health analysis that found that on average peristomal skin complications caused upwards of $80,000 more per ostomy patient in increased healthcare costs over a 3-month period than for those without the complications.
“With Twistomy, we are reducing leakage most likely to zero,” Horton said. “We set out to say if we could reduce [infections] by half or a little less than half, we can cut out those tens of thousands of dollars that insurance companies and payers are spending.”
Permanent and Temporary Ostomy Markets
He pointed out that not all ostomies are permanent ostomies, adding that the reversal rate “is about 65%.” Often those reversal surgeries cannot take place until peristomal skin complications have been healed.
“We’re not only hoping to market to the permanent stoma patients, but the patients with temporary stomas as well,” he said.
The team estimates it will need $4 million–$6 million in funding for manufacturing and consultation costs as well as costs involved in seeking FDA approval.
Horton and Williams project the housing unit cost will be $399 based on known out-of-pocket expenses for patients with ostomy care products and the unit would be replaced annually. Disposable elements would be an additional cost.
Assuming insurance acceptance of the product, he said, “With about an 80/20 insurance coverage, typical for many patients, it would be about $100 in out-of-pocket expenses per month to use our device, which is around the lower end of what a lot of patients are spending out of pocket.”
One of the Tech Summit judges, Somaya Albhaisi, MD, a gastroenterology/hepatology fellow at University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said in an interview that the Shark Tank results were unanimous among the five judges and Twistomy also took the fan favorite vote.
She said the teams were judged on quality of pitch, potential clinical impact, and feasibility of business plan. Teams got 5-7 minutes to pitch and answered questions afterward.
“Deep Understanding” of Patient Need
“They combined smart engineering with deep understanding of patient need, which is restoring control, dignity, and quality of life for ostomy users while also reducing healthcare costs. It is rare to see a solution this scalable and impactful. It was a deeply empathetic solution overall.” She noted that nearly 1 million people in the United States currently use an ostomy.
Ostomy users’ quality of life is compromised, and they often have mental health challenges, Albhaisi said. This innovation appears to offer easy use, more dignity and control.
The other four Shark Tank finalists were:
- AI Lumen, which developed a retroview camera system, which attaches to the colonoscope and enhances imaging to detect hidden polyps that may evade conventional endoscopes.
- Amplified Sciences, which developed an ultrasensitive diagnostic platform that detects biomarker activities in minute volumes of fluid from pancreatic cystic lesions, helping to stratify patients into low risk or potential malignancy, reducing unneeded surgeries, costs, and comorbidities.
- KITE Endoscopic Innovations, which designed the Dynaflex TruCut needle to offer a simpler endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)–guided biopsy procedure with fewer needle passes, deeper insights into tumor pathology, and more tissue for geonomic analysis.
- MicroSteer, which designed a device to facilitate semiautomated endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) by decoupling the dissecting knife from the endoscope, enhancing safety and effectiveness during the procedure.
The Twistomy Team “Surprised Everyone”
The competitors’ scores were “very close,” one of the judges, Kevin Berliner, said in an interview. “The Twistomy team surprised everyone — the judges and the crowd — with their succinct, informative, and impactful pitch. That presentation disparity was the tiebreaker for me,” said Berliner, who works for Medtronic, a sponsor of the competition, in Chicago.
He said Horton and Williams were the youngest presenters and had the earliest stage pitch they judged, but they “outpresented other competitors in clarity, simplification, and storytelling.”
Also impressive was their description of their “commercially viable path to success” and their plan for the challenges ahead, he said.
Those challenges to get Twistomy to market center “on the ongoing changing climate we have with research funds lately,” Horton said. “We’re giving it an estimate of 3-5 years.”
Horton, Williams, Albhaisi, and Berliner reported no relevant financial relationships.
Don’t Overlook Processed Meat as Colorectal Cancer Risk Factor
Even though older adults are more likely to be diagnosed with colorectal cancer (CRC),
Many are familiar with the modifiable risk factors of obesity, smoking, and alcohol consumption, but the impact of processed meat — a common element of the Western diet —often remains underappreciated.
But the data are clear: Processed meat, defined as meat that has been altered through methods such as salting, curing, fermentation, or smoking to enhance flavor or preservation, has been linked to an increased risk for CRC.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer, part of the World Health Organization, analyzed over 800 global studies and classified processed meats as carcinogenic to humans, whereas red meat was deemed “probably” carcinogenic. Their findings were later published in The Lancet Oncology, confirming that the strongest epidemiological evidence linked processed meat consumption to CRC.
“While I routinely counsel my patients about lifestyle and dietary risk factors for CRC, including processed meat, I’m not sure how often this is specifically mentioned by physicians in practice,” Peter S. Liang, MD, MPH, an assistant professor and researcher focused on CRC prevention at NYU Langone Health in New York City, and an AGA spokesperson, told GI & Hepatology News.
David A. Johnson, MD, chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School and Old Dominion University, both in Norfolk, Virginia, concurred.
Many healthcare providers may not fully recognize the risks posed by processed meat in relation to CRC to counsel their patients, Johnson said. “In my experience, there is not a widespread awareness.”
Understanding the Carcinogenic Risks
The excess risk for CRC per gram of intake is higher for processed meat than for red meat. However, the threshold for harmful consumption varies among studies, and many group red and processed meat together in their analyses.
For example, a 2020 prospective analysis of UK Biobank data reported that a 70 g/d higher intake of red and processed meat was associated with a 32% and 40% greater risk for CRC and colon cancer, respectively.
More recently, a 2025 prospective study examined the associations between CRC and 97 dietary factors in 542,778 women. Investigators found that, aside from alcohol, red and processed meat were the only other dietary factors positively associated with CRC, with a 30 g/d intake increasing the risk for CRC by 8%.
Although the World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) and the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) recommend limiting red meat consumption to no more than three portions a week, their guidance on processed meat is simpler and more restrictive: Consume very little, if any.
The risk for CRC associated with processed meats is likely due to a naturally occurring element in the meat and carcinogenic compounds that are added or created during its preparation, Johnson said.
Large bodies of evidence support the association between certain compounds in processed meat and cancer, added Ulrike Peters, PhD, MPH, professor and associate director of the Public Health Sciences Division at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
These compounds include:
- Heterocyclic amines: Prevalent in charred and well-done meat, these chemicals are created from the reaction at high temperatures between creatine/creatinine, amino acids, and sugars.
- Nitrates/nitrites: Widely used in the curing of meat (eg, sausages, ham, bacon) to give products their pink coloring and savory flavor, these inorganic compounds bind with amines to produce N-nitrosamines, among the most potent genotoxic carcinogens.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Generated during high-temperature cooking and smoking, these compounds can induce DNA damage in the colon.
- Heme iron: This type of iron, abundant in red and processed meats, promotes formation of carcinogenic N-nitroso compounds and oxidative damage to intestinal tissue.
Peters said that the compounds may work synergistically to increase the risk for CRC through various mechanisms, including DNA damage, inflammation, and altered gut microbiota.
While it would be useful to study whether the different meat-processing methods — for example, smoking vs salting — affect CRC risk differently, “practically, this is difficult because there’s so much overlap,” Liang noted.
Risk Mitigation
Lifestyle factors likely play a crucial role in the risk for CRC. For example, a study of European migrants to Australia found that those from countries with lower CRC incidences tended to develop a higher risk for CRC the longer they resided in Australia due to the dietary change.
Understanding how to mitigate these risk factors is becoming increasingly important with the rates of early-onset CRC projected to double by 2030 in the United States, a trend that is also being observed globally.
“With early-onset CRC, it’s becoming quite clear that there’s no single risk factor that’s driving this increase,” Liang said. “We need to look at the risk factors that we know cause CRC in older adults and see which have become more common over time.”
The consumption of processed meats is one such factor that’s been implicated, particularly for early-onset CRC. The average global consumption of all types of meat per capita has increased significantly over the last 50 years. A 2022 report estimated that global mean processed meat consumption was 17 g/d, with significantly higher rates in high-income regions. This number is expected to rise, with the global processed meat market projected to grow from $318 billion in 2023 to $429 billion by 2029. Given this, the importance of counseling patients to reduce their meat intake is further underscored.
Another strategy for mitigating the risks around processed meat is specifically identifying those patients who may be most vulnerable.
In 2024, Peters and colleagues published findings from their genome-wide gene-environment interaction analysis comparing a large population with CRC and healthy control individuals. The research identified two novel biomarkers that support the role of red and processed meat with an increased risk for CRC and may explain the higher risk in certain population subgroups. They are working on genetic risk prediction models that will incorporate these genetic markers but must first ensure robust validation through larger studies.
“This approach aligns with precision medicine principles, allowing for more personalized prevention strategies, though we’re not quite there yet in terms of clinical application,” Peters said.
Another knowledge gap that future research efforts could address is how dietary factors influence survival outcomes after a diagnosis of CRC.
“The existing guidelines primarily focus on cancer prevention, with strong evidence linking processed meat consumption to increased CRC risk. However, the impact of dietary choices on survival after CRC diagnosis remains poorly understood,” Peters said. “This distinction between prevention and survival is crucial, as biological mechanisms and optimal dietary interventions may differ significantly between these two contexts.”
Well-designed studies investigating the relationship between dietary patterns and CRC survival outcomes would enable the development of evidence-based nutritional recommendations specifically tailored for CRC survivors, Peters said. In addition, she called for well-designed studies that compare levels of processed meat consumption between cohorts of patients with early-onset CRC and healthy counterparts.
“This would help establish whether there’s a true causal relationship rather than just correlation,” Peters said.
Simple Strategies to Dietary Changes
With a 2024 study finding that greater adherence to WCRF/AICR Cancer Prevention Recommendations, including reducing processed meat consumption, was linked to a 14% reduction in CRC risk, physicians should emphasize the benefits of adopting dietary and lifestyle recommendations to patients.
Johnson advised simple strategies to encourage any needed dietary changes.
“Pay attention to what you eat, proportions, and variation of meal menus. Those are good starter points,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “None of these recommendations related to meats should be absolute, but reduction can be the target.”
Liang stressed the importance of repeated, nonjudgmental discussions.
“Research shows that physician recommendation is one of the strongest motivators in preventive health, so even if it doesn’t work the first few times, we have to continue delivering the message that can improve our patients’ health.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Even though older adults are more likely to be diagnosed with colorectal cancer (CRC),
Many are familiar with the modifiable risk factors of obesity, smoking, and alcohol consumption, but the impact of processed meat — a common element of the Western diet —often remains underappreciated.
But the data are clear: Processed meat, defined as meat that has been altered through methods such as salting, curing, fermentation, or smoking to enhance flavor or preservation, has been linked to an increased risk for CRC.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer, part of the World Health Organization, analyzed over 800 global studies and classified processed meats as carcinogenic to humans, whereas red meat was deemed “probably” carcinogenic. Their findings were later published in The Lancet Oncology, confirming that the strongest epidemiological evidence linked processed meat consumption to CRC.
“While I routinely counsel my patients about lifestyle and dietary risk factors for CRC, including processed meat, I’m not sure how often this is specifically mentioned by physicians in practice,” Peter S. Liang, MD, MPH, an assistant professor and researcher focused on CRC prevention at NYU Langone Health in New York City, and an AGA spokesperson, told GI & Hepatology News.
David A. Johnson, MD, chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School and Old Dominion University, both in Norfolk, Virginia, concurred.
Many healthcare providers may not fully recognize the risks posed by processed meat in relation to CRC to counsel their patients, Johnson said. “In my experience, there is not a widespread awareness.”
Understanding the Carcinogenic Risks
The excess risk for CRC per gram of intake is higher for processed meat than for red meat. However, the threshold for harmful consumption varies among studies, and many group red and processed meat together in their analyses.
For example, a 2020 prospective analysis of UK Biobank data reported that a 70 g/d higher intake of red and processed meat was associated with a 32% and 40% greater risk for CRC and colon cancer, respectively.
More recently, a 2025 prospective study examined the associations between CRC and 97 dietary factors in 542,778 women. Investigators found that, aside from alcohol, red and processed meat were the only other dietary factors positively associated with CRC, with a 30 g/d intake increasing the risk for CRC by 8%.
Although the World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) and the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) recommend limiting red meat consumption to no more than three portions a week, their guidance on processed meat is simpler and more restrictive: Consume very little, if any.
The risk for CRC associated with processed meats is likely due to a naturally occurring element in the meat and carcinogenic compounds that are added or created during its preparation, Johnson said.
Large bodies of evidence support the association between certain compounds in processed meat and cancer, added Ulrike Peters, PhD, MPH, professor and associate director of the Public Health Sciences Division at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
These compounds include:
- Heterocyclic amines: Prevalent in charred and well-done meat, these chemicals are created from the reaction at high temperatures between creatine/creatinine, amino acids, and sugars.
- Nitrates/nitrites: Widely used in the curing of meat (eg, sausages, ham, bacon) to give products their pink coloring and savory flavor, these inorganic compounds bind with amines to produce N-nitrosamines, among the most potent genotoxic carcinogens.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Generated during high-temperature cooking and smoking, these compounds can induce DNA damage in the colon.
- Heme iron: This type of iron, abundant in red and processed meats, promotes formation of carcinogenic N-nitroso compounds and oxidative damage to intestinal tissue.
Peters said that the compounds may work synergistically to increase the risk for CRC through various mechanisms, including DNA damage, inflammation, and altered gut microbiota.
While it would be useful to study whether the different meat-processing methods — for example, smoking vs salting — affect CRC risk differently, “practically, this is difficult because there’s so much overlap,” Liang noted.
Risk Mitigation
Lifestyle factors likely play a crucial role in the risk for CRC. For example, a study of European migrants to Australia found that those from countries with lower CRC incidences tended to develop a higher risk for CRC the longer they resided in Australia due to the dietary change.
Understanding how to mitigate these risk factors is becoming increasingly important with the rates of early-onset CRC projected to double by 2030 in the United States, a trend that is also being observed globally.
“With early-onset CRC, it’s becoming quite clear that there’s no single risk factor that’s driving this increase,” Liang said. “We need to look at the risk factors that we know cause CRC in older adults and see which have become more common over time.”
The consumption of processed meats is one such factor that’s been implicated, particularly for early-onset CRC. The average global consumption of all types of meat per capita has increased significantly over the last 50 years. A 2022 report estimated that global mean processed meat consumption was 17 g/d, with significantly higher rates in high-income regions. This number is expected to rise, with the global processed meat market projected to grow from $318 billion in 2023 to $429 billion by 2029. Given this, the importance of counseling patients to reduce their meat intake is further underscored.
Another strategy for mitigating the risks around processed meat is specifically identifying those patients who may be most vulnerable.
In 2024, Peters and colleagues published findings from their genome-wide gene-environment interaction analysis comparing a large population with CRC and healthy control individuals. The research identified two novel biomarkers that support the role of red and processed meat with an increased risk for CRC and may explain the higher risk in certain population subgroups. They are working on genetic risk prediction models that will incorporate these genetic markers but must first ensure robust validation through larger studies.
“This approach aligns with precision medicine principles, allowing for more personalized prevention strategies, though we’re not quite there yet in terms of clinical application,” Peters said.
Another knowledge gap that future research efforts could address is how dietary factors influence survival outcomes after a diagnosis of CRC.
“The existing guidelines primarily focus on cancer prevention, with strong evidence linking processed meat consumption to increased CRC risk. However, the impact of dietary choices on survival after CRC diagnosis remains poorly understood,” Peters said. “This distinction between prevention and survival is crucial, as biological mechanisms and optimal dietary interventions may differ significantly between these two contexts.”
Well-designed studies investigating the relationship between dietary patterns and CRC survival outcomes would enable the development of evidence-based nutritional recommendations specifically tailored for CRC survivors, Peters said. In addition, she called for well-designed studies that compare levels of processed meat consumption between cohorts of patients with early-onset CRC and healthy counterparts.
“This would help establish whether there’s a true causal relationship rather than just correlation,” Peters said.
Simple Strategies to Dietary Changes
With a 2024 study finding that greater adherence to WCRF/AICR Cancer Prevention Recommendations, including reducing processed meat consumption, was linked to a 14% reduction in CRC risk, physicians should emphasize the benefits of adopting dietary and lifestyle recommendations to patients.
Johnson advised simple strategies to encourage any needed dietary changes.
“Pay attention to what you eat, proportions, and variation of meal menus. Those are good starter points,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “None of these recommendations related to meats should be absolute, but reduction can be the target.”
Liang stressed the importance of repeated, nonjudgmental discussions.
“Research shows that physician recommendation is one of the strongest motivators in preventive health, so even if it doesn’t work the first few times, we have to continue delivering the message that can improve our patients’ health.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Even though older adults are more likely to be diagnosed with colorectal cancer (CRC),
Many are familiar with the modifiable risk factors of obesity, smoking, and alcohol consumption, but the impact of processed meat — a common element of the Western diet —often remains underappreciated.
But the data are clear: Processed meat, defined as meat that has been altered through methods such as salting, curing, fermentation, or smoking to enhance flavor or preservation, has been linked to an increased risk for CRC.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer, part of the World Health Organization, analyzed over 800 global studies and classified processed meats as carcinogenic to humans, whereas red meat was deemed “probably” carcinogenic. Their findings were later published in The Lancet Oncology, confirming that the strongest epidemiological evidence linked processed meat consumption to CRC.
“While I routinely counsel my patients about lifestyle and dietary risk factors for CRC, including processed meat, I’m not sure how often this is specifically mentioned by physicians in practice,” Peter S. Liang, MD, MPH, an assistant professor and researcher focused on CRC prevention at NYU Langone Health in New York City, and an AGA spokesperson, told GI & Hepatology News.
David A. Johnson, MD, chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School and Old Dominion University, both in Norfolk, Virginia, concurred.
Many healthcare providers may not fully recognize the risks posed by processed meat in relation to CRC to counsel their patients, Johnson said. “In my experience, there is not a widespread awareness.”
Understanding the Carcinogenic Risks
The excess risk for CRC per gram of intake is higher for processed meat than for red meat. However, the threshold for harmful consumption varies among studies, and many group red and processed meat together in their analyses.
For example, a 2020 prospective analysis of UK Biobank data reported that a 70 g/d higher intake of red and processed meat was associated with a 32% and 40% greater risk for CRC and colon cancer, respectively.
More recently, a 2025 prospective study examined the associations between CRC and 97 dietary factors in 542,778 women. Investigators found that, aside from alcohol, red and processed meat were the only other dietary factors positively associated with CRC, with a 30 g/d intake increasing the risk for CRC by 8%.
Although the World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) and the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) recommend limiting red meat consumption to no more than three portions a week, their guidance on processed meat is simpler and more restrictive: Consume very little, if any.
The risk for CRC associated with processed meats is likely due to a naturally occurring element in the meat and carcinogenic compounds that are added or created during its preparation, Johnson said.
Large bodies of evidence support the association between certain compounds in processed meat and cancer, added Ulrike Peters, PhD, MPH, professor and associate director of the Public Health Sciences Division at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
These compounds include:
- Heterocyclic amines: Prevalent in charred and well-done meat, these chemicals are created from the reaction at high temperatures between creatine/creatinine, amino acids, and sugars.
- Nitrates/nitrites: Widely used in the curing of meat (eg, sausages, ham, bacon) to give products their pink coloring and savory flavor, these inorganic compounds bind with amines to produce N-nitrosamines, among the most potent genotoxic carcinogens.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Generated during high-temperature cooking and smoking, these compounds can induce DNA damage in the colon.
- Heme iron: This type of iron, abundant in red and processed meats, promotes formation of carcinogenic N-nitroso compounds and oxidative damage to intestinal tissue.
Peters said that the compounds may work synergistically to increase the risk for CRC through various mechanisms, including DNA damage, inflammation, and altered gut microbiota.
While it would be useful to study whether the different meat-processing methods — for example, smoking vs salting — affect CRC risk differently, “practically, this is difficult because there’s so much overlap,” Liang noted.
Risk Mitigation
Lifestyle factors likely play a crucial role in the risk for CRC. For example, a study of European migrants to Australia found that those from countries with lower CRC incidences tended to develop a higher risk for CRC the longer they resided in Australia due to the dietary change.
Understanding how to mitigate these risk factors is becoming increasingly important with the rates of early-onset CRC projected to double by 2030 in the United States, a trend that is also being observed globally.
“With early-onset CRC, it’s becoming quite clear that there’s no single risk factor that’s driving this increase,” Liang said. “We need to look at the risk factors that we know cause CRC in older adults and see which have become more common over time.”
The consumption of processed meats is one such factor that’s been implicated, particularly for early-onset CRC. The average global consumption of all types of meat per capita has increased significantly over the last 50 years. A 2022 report estimated that global mean processed meat consumption was 17 g/d, with significantly higher rates in high-income regions. This number is expected to rise, with the global processed meat market projected to grow from $318 billion in 2023 to $429 billion by 2029. Given this, the importance of counseling patients to reduce their meat intake is further underscored.
Another strategy for mitigating the risks around processed meat is specifically identifying those patients who may be most vulnerable.
In 2024, Peters and colleagues published findings from their genome-wide gene-environment interaction analysis comparing a large population with CRC and healthy control individuals. The research identified two novel biomarkers that support the role of red and processed meat with an increased risk for CRC and may explain the higher risk in certain population subgroups. They are working on genetic risk prediction models that will incorporate these genetic markers but must first ensure robust validation through larger studies.
“This approach aligns with precision medicine principles, allowing for more personalized prevention strategies, though we’re not quite there yet in terms of clinical application,” Peters said.
Another knowledge gap that future research efforts could address is how dietary factors influence survival outcomes after a diagnosis of CRC.
“The existing guidelines primarily focus on cancer prevention, with strong evidence linking processed meat consumption to increased CRC risk. However, the impact of dietary choices on survival after CRC diagnosis remains poorly understood,” Peters said. “This distinction between prevention and survival is crucial, as biological mechanisms and optimal dietary interventions may differ significantly between these two contexts.”
Well-designed studies investigating the relationship between dietary patterns and CRC survival outcomes would enable the development of evidence-based nutritional recommendations specifically tailored for CRC survivors, Peters said. In addition, she called for well-designed studies that compare levels of processed meat consumption between cohorts of patients with early-onset CRC and healthy counterparts.
“This would help establish whether there’s a true causal relationship rather than just correlation,” Peters said.
Simple Strategies to Dietary Changes
With a 2024 study finding that greater adherence to WCRF/AICR Cancer Prevention Recommendations, including reducing processed meat consumption, was linked to a 14% reduction in CRC risk, physicians should emphasize the benefits of adopting dietary and lifestyle recommendations to patients.
Johnson advised simple strategies to encourage any needed dietary changes.
“Pay attention to what you eat, proportions, and variation of meal menus. Those are good starter points,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “None of these recommendations related to meats should be absolute, but reduction can be the target.”
Liang stressed the importance of repeated, nonjudgmental discussions.
“Research shows that physician recommendation is one of the strongest motivators in preventive health, so even if it doesn’t work the first few times, we have to continue delivering the message that can improve our patients’ health.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A Common Pancreatic Condition That Few Have Heard Of
— a disorder experienced by roughly one fifth of the world’s population. Although it is more common than type 2 diabetes, pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer combined, it has remained relatively obscure.
By contrast, fatty liver — once called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and recently renamed metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) — is well-known.
“When it comes to diseases of the liver and pancreas, the liver is the big brother that has gotten all the attention, while the pancreas is the neglected little stepbrother that’s not sufficiently profiled in most medical textbooks and gets very little attention,” Max Petrov, MD, MPH, PhD, professor of pancreatology, University of Auckland, New Zealand, said in an interview. “The phenomenon of fatty pancreas has been observed for decades, but it is underappreciated and underrecognized.”
As early as 1926, fat depositions were identified during autopsies, but the condition remained relatively unknown, Mohammad Bilal, MD, associate professor of medicine-gastroenterology, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, said in an interview. “Fortunately, FPD has recently been receiving more focus.”
Generally, healthy individuals have small amounts of fat in their pancreas. IPFD is defined as “the diffuse presence of fat in the pancreas, measured on a continuous scale,” and FPD refers to IPFD above the upper limit of normal. While there is no clear consensus as to what the normal range is, studies suggest it’s a pancreatic fat content ranging from 1.8% to 10.4%.
FPD’s “most important implication is that it can be a precursor for more challenging and burdensome diseases of the pancreas,” Petrov said.
Fatty changes in the pancreas affect both its endocrine and exocrine systems. FPD is associated with type 2 diabetes, the most common disease of the endocrine pancreas, as well as pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, the most common diseases of the exocrine pancreas. It’s also implicated in the development of carotid atherosclerosis, pancreatic fistula following surgery, and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI).
A ‘Pandora’s Box’
Up to half of people with fatty pancreas are lean. The condition isn’t merely caused by an overflow of fat from the liver into the pancreas in people who consume more calories than they burn, Petrov said. Neither robust postmortem nor biopsy studies have found a statistically significant association between fatty deposition in the pancreas and liver fat.
Compared with the way people accumulate liver fat, the development of FPD is more complex, Petrov said.
“Hepatic fat is a relatively simple process: Lipid droplets accumulate in the hepatocytes; but, in the pancreas, there are several ways by which fat may accumulate,” he said.
One relates to the location of the pancreas within visceral, retroperitoneal fat, Petrov said. That fat can migrate and build up between pancreatic lobules.
Fat also can accumulate inside the lobes. This process can involve a buildup of fat droplets in acinar and stellate cells on the exocrine side and in the islets of Langerhans on the endocrine side. Additionally, when functional pancreatic cells die, particularly acinar cells, adult stem cells may replace them with adipocytes. Transformation of acinar cells into fat cells — a process called acinar-to-adipocyte transdifferentiation — also may be a way fat accumulates inside the lobes, Petrov said.
The accumulation of fat is a response to a wide array of insults to the pancreas over time. For example, obesity and metabolic syndrome lead to the accumulation of adipocytes and fat infiltration, whereas alcohol abuse and viral infections may lead to the death of acinar cells, which produce digestive enzymes.
Ultimately, the negative changes produced by excess fat in the pancreas are the origin of all common noninherited pancreatic diseases, bringing them under one umbrella, Petrov maintained. He dubbed this hypothesis PANcreatic Diseases Originating from intRapancreatic fAt (PANDORA).
The type of cells involved has implications for which disease may arise. For example, fat infiltration in stellate cells may promote pancreatic cancer, whereas its accumulation in the islets of Langerhans, which produce insulin and glucagon, is associated with type 2 diabetes.
The PANDORA hypothesis has eight foundational principles:
- Fatty pancreas is a key driver of pancreatic diseases in most people.
- Inflammation within the pancreatic microenvironment results from overwhelming lipotoxicity fueled by fatty pancreas.
- Aberrant communication between acinar cells involving lipid droplets drives acute pancreatitis.
- The pancreas responds to lipotoxicity with fibrosis and calcification — the hallmarks of chronic pancreatitis.
- Fat deposition affects signaling between stellate cells and other components of the microenvironment in ways that raise the risk for pancreatic cancer.
- The development of diabetes of the exocrine pancreas and EPI is affected by the presence of fatty pancreas.
- The higher risk for pancreatic disease in older adults is influenced by fatty pancreas.
- The multipronged nature of intrapancreatic fat deposition accounts for the common development of one pancreatic disease after another.
The idea that all common pancreatic diseases are the result of pathways emanating from FPD could “explain the bidirectional relationship between diabetes and pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer,” Petrov said.
Risk Factors, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
A variety of risk factors are involved in the accumulation of fat that may lead to pancreatic diseases, including aging, cholelithiasis, dyslipidemia, drugs/toxins (eg, steroids), genetic predisposition, iron overload, diet (eg, fatty foods, ultraprocessed foods), heavy alcohol use, overweight/obesity, pancreatic duct obstruction, tobacco use, viral infection (eg, hepatitis B, COVID-19), severe malnutrition, prediabetes, and dysglycemia.
Petrov described FPD as a “silent disease” that’s often asymptomatic, with its presence emerging as an incidental finding during abdominal ultrasonography for other reasons. However, patients may sometimes experience stomach pain or nausea if they have concurrent diseases of the pancreas, he said.
There are no currently available lab tests that can definitively detect the presence of FPD. Rather, the gold standard for a noninvasive diagnosis of FPD is MRI, with CT as the second-best choice, Petrov said.
In countries where advanced imaging is not available, a low-cost alternative might be a simple abdominal ultrasound, but it is not definitive, he said. “It’s operator-dependent and can be subjective.”
Some risk factors, such as derangements of glucose and lipid metabolism, especially in the presence of heavy alcohol use and a high-fat diet, can “be detected on lab tests,” Petrov said. “This, in combination with the abdominal ultrasound, might suggest the patients will benefit from deeper investigation, including MRI.”
Because the exocrine pancreas helps with digestion of fatty food, intralobular fatty deposits or replacement of pancreatic exocrine cells with adipose cells can lead to steatorrhea, Bilal said.
“Fat within the stool or oily diarrhea is a clue to the presence of FPD,” Bilal said.
Although this symptom isn’t unique to FPD and is found in other types of pancreatic conditions, its presence suggests that further investigation for FPD is warranted, he added.
Common-Sense Treatment Approaches
At present, there are no US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments for FPD, Petrov said.
“What might be recommended is something along the lines of treatment of MASLD — appropriate diet and physical activity,” he said. Petrov hopes that as the disease entity garners more research attention, more clinical drug trials will be initiated, and new medications are found and approved.
Petrov suggested that there could be a “theoretical rationale” for the use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) as a treatment, given their effectiveness in multiple conditions, including MASLD, but no human trials have robustly shown specific benefits of these drugs for FPD.
Petrov added that, to date, 12 classes of drugs have been investigated for reducing IPFD: biguanides, sulfonylureas, GLP-1 RAs, thiazolidinediones, dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, statins, fibrates, pancreatic lipase inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, somatostatin receptor agonists, and antioxidants.
Of these, most have shown promise in preclinical animal models. But only thiazolidinediones, GLP-1 RAs, DPP-4 inhibitors, and somatostatin receptor agonists have been investigated in randomized controlled trials in humans. The findings have been inconsistent, with the active treatment often not achieving statistically significant improvements.
“At this stage of our knowledge, we can’t recommend a specific pharmacotherapy,” Petrov said. But we can suggest dietary changes, such as saturated fat reduction, alcohol reduction, smoking cessation, reduction in consumption of ultraprocessed food, physical exercise, and addressing obesity and other drivers of metabolic disease.
Bilal, who is also a spokesperson for AGA, suggested that pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy, often used to treat pancreatic EPI, may treat some symptoms of FPD such as diarrhea.
Bariatric surgery has shown promise for FPD, in that it can decrease the patient’s body mass and potentially reduce the fat in the pancreas as well as it can improve metabolic diseases and hyperlipidemia. One study showed that it significantly decreased IPFD, fatty acid uptake, and blood flow, and these improvements were associated with more favorable glucose homeostasis and beta-cell function.
However, bariatric surgery is only appropriate for certain patients; is associated with potentially adverse sequelae including malnutrition, anemia, and digestive tract stenosis; and is currently not indicated for FPD.
Bilal advises clinicians to “keep an eye on FPD” if it’s detected incidentally and to screen patients more carefully for MASLD, metabolic disease, and diabetes.
“Although there are no consensus guidelines and recommendations for managing FPD at present, these common-sense approaches will benefit the patient’s overall health and hopefully will have a beneficial impact on pancreatic health as well,” he said.
Petrov reported no relevant financial relationships. Bilal reported being a consultant for Boston Scientific, Steris Endoscopy, and Cook Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
— a disorder experienced by roughly one fifth of the world’s population. Although it is more common than type 2 diabetes, pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer combined, it has remained relatively obscure.
By contrast, fatty liver — once called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and recently renamed metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) — is well-known.
“When it comes to diseases of the liver and pancreas, the liver is the big brother that has gotten all the attention, while the pancreas is the neglected little stepbrother that’s not sufficiently profiled in most medical textbooks and gets very little attention,” Max Petrov, MD, MPH, PhD, professor of pancreatology, University of Auckland, New Zealand, said in an interview. “The phenomenon of fatty pancreas has been observed for decades, but it is underappreciated and underrecognized.”
As early as 1926, fat depositions were identified during autopsies, but the condition remained relatively unknown, Mohammad Bilal, MD, associate professor of medicine-gastroenterology, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, said in an interview. “Fortunately, FPD has recently been receiving more focus.”
Generally, healthy individuals have small amounts of fat in their pancreas. IPFD is defined as “the diffuse presence of fat in the pancreas, measured on a continuous scale,” and FPD refers to IPFD above the upper limit of normal. While there is no clear consensus as to what the normal range is, studies suggest it’s a pancreatic fat content ranging from 1.8% to 10.4%.
FPD’s “most important implication is that it can be a precursor for more challenging and burdensome diseases of the pancreas,” Petrov said.
Fatty changes in the pancreas affect both its endocrine and exocrine systems. FPD is associated with type 2 diabetes, the most common disease of the endocrine pancreas, as well as pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, the most common diseases of the exocrine pancreas. It’s also implicated in the development of carotid atherosclerosis, pancreatic fistula following surgery, and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI).
A ‘Pandora’s Box’
Up to half of people with fatty pancreas are lean. The condition isn’t merely caused by an overflow of fat from the liver into the pancreas in people who consume more calories than they burn, Petrov said. Neither robust postmortem nor biopsy studies have found a statistically significant association between fatty deposition in the pancreas and liver fat.
Compared with the way people accumulate liver fat, the development of FPD is more complex, Petrov said.
“Hepatic fat is a relatively simple process: Lipid droplets accumulate in the hepatocytes; but, in the pancreas, there are several ways by which fat may accumulate,” he said.
One relates to the location of the pancreas within visceral, retroperitoneal fat, Petrov said. That fat can migrate and build up between pancreatic lobules.
Fat also can accumulate inside the lobes. This process can involve a buildup of fat droplets in acinar and stellate cells on the exocrine side and in the islets of Langerhans on the endocrine side. Additionally, when functional pancreatic cells die, particularly acinar cells, adult stem cells may replace them with adipocytes. Transformation of acinar cells into fat cells — a process called acinar-to-adipocyte transdifferentiation — also may be a way fat accumulates inside the lobes, Petrov said.
The accumulation of fat is a response to a wide array of insults to the pancreas over time. For example, obesity and metabolic syndrome lead to the accumulation of adipocytes and fat infiltration, whereas alcohol abuse and viral infections may lead to the death of acinar cells, which produce digestive enzymes.
Ultimately, the negative changes produced by excess fat in the pancreas are the origin of all common noninherited pancreatic diseases, bringing them under one umbrella, Petrov maintained. He dubbed this hypothesis PANcreatic Diseases Originating from intRapancreatic fAt (PANDORA).
The type of cells involved has implications for which disease may arise. For example, fat infiltration in stellate cells may promote pancreatic cancer, whereas its accumulation in the islets of Langerhans, which produce insulin and glucagon, is associated with type 2 diabetes.
The PANDORA hypothesis has eight foundational principles:
- Fatty pancreas is a key driver of pancreatic diseases in most people.
- Inflammation within the pancreatic microenvironment results from overwhelming lipotoxicity fueled by fatty pancreas.
- Aberrant communication between acinar cells involving lipid droplets drives acute pancreatitis.
- The pancreas responds to lipotoxicity with fibrosis and calcification — the hallmarks of chronic pancreatitis.
- Fat deposition affects signaling between stellate cells and other components of the microenvironment in ways that raise the risk for pancreatic cancer.
- The development of diabetes of the exocrine pancreas and EPI is affected by the presence of fatty pancreas.
- The higher risk for pancreatic disease in older adults is influenced by fatty pancreas.
- The multipronged nature of intrapancreatic fat deposition accounts for the common development of one pancreatic disease after another.
The idea that all common pancreatic diseases are the result of pathways emanating from FPD could “explain the bidirectional relationship between diabetes and pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer,” Petrov said.
Risk Factors, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
A variety of risk factors are involved in the accumulation of fat that may lead to pancreatic diseases, including aging, cholelithiasis, dyslipidemia, drugs/toxins (eg, steroids), genetic predisposition, iron overload, diet (eg, fatty foods, ultraprocessed foods), heavy alcohol use, overweight/obesity, pancreatic duct obstruction, tobacco use, viral infection (eg, hepatitis B, COVID-19), severe malnutrition, prediabetes, and dysglycemia.
Petrov described FPD as a “silent disease” that’s often asymptomatic, with its presence emerging as an incidental finding during abdominal ultrasonography for other reasons. However, patients may sometimes experience stomach pain or nausea if they have concurrent diseases of the pancreas, he said.
There are no currently available lab tests that can definitively detect the presence of FPD. Rather, the gold standard for a noninvasive diagnosis of FPD is MRI, with CT as the second-best choice, Petrov said.
In countries where advanced imaging is not available, a low-cost alternative might be a simple abdominal ultrasound, but it is not definitive, he said. “It’s operator-dependent and can be subjective.”
Some risk factors, such as derangements of glucose and lipid metabolism, especially in the presence of heavy alcohol use and a high-fat diet, can “be detected on lab tests,” Petrov said. “This, in combination with the abdominal ultrasound, might suggest the patients will benefit from deeper investigation, including MRI.”
Because the exocrine pancreas helps with digestion of fatty food, intralobular fatty deposits or replacement of pancreatic exocrine cells with adipose cells can lead to steatorrhea, Bilal said.
“Fat within the stool or oily diarrhea is a clue to the presence of FPD,” Bilal said.
Although this symptom isn’t unique to FPD and is found in other types of pancreatic conditions, its presence suggests that further investigation for FPD is warranted, he added.
Common-Sense Treatment Approaches
At present, there are no US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments for FPD, Petrov said.
“What might be recommended is something along the lines of treatment of MASLD — appropriate diet and physical activity,” he said. Petrov hopes that as the disease entity garners more research attention, more clinical drug trials will be initiated, and new medications are found and approved.
Petrov suggested that there could be a “theoretical rationale” for the use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) as a treatment, given their effectiveness in multiple conditions, including MASLD, but no human trials have robustly shown specific benefits of these drugs for FPD.
Petrov added that, to date, 12 classes of drugs have been investigated for reducing IPFD: biguanides, sulfonylureas, GLP-1 RAs, thiazolidinediones, dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, statins, fibrates, pancreatic lipase inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, somatostatin receptor agonists, and antioxidants.
Of these, most have shown promise in preclinical animal models. But only thiazolidinediones, GLP-1 RAs, DPP-4 inhibitors, and somatostatin receptor agonists have been investigated in randomized controlled trials in humans. The findings have been inconsistent, with the active treatment often not achieving statistically significant improvements.
“At this stage of our knowledge, we can’t recommend a specific pharmacotherapy,” Petrov said. But we can suggest dietary changes, such as saturated fat reduction, alcohol reduction, smoking cessation, reduction in consumption of ultraprocessed food, physical exercise, and addressing obesity and other drivers of metabolic disease.
Bilal, who is also a spokesperson for AGA, suggested that pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy, often used to treat pancreatic EPI, may treat some symptoms of FPD such as diarrhea.
Bariatric surgery has shown promise for FPD, in that it can decrease the patient’s body mass and potentially reduce the fat in the pancreas as well as it can improve metabolic diseases and hyperlipidemia. One study showed that it significantly decreased IPFD, fatty acid uptake, and blood flow, and these improvements were associated with more favorable glucose homeostasis and beta-cell function.
However, bariatric surgery is only appropriate for certain patients; is associated with potentially adverse sequelae including malnutrition, anemia, and digestive tract stenosis; and is currently not indicated for FPD.
Bilal advises clinicians to “keep an eye on FPD” if it’s detected incidentally and to screen patients more carefully for MASLD, metabolic disease, and diabetes.
“Although there are no consensus guidelines and recommendations for managing FPD at present, these common-sense approaches will benefit the patient’s overall health and hopefully will have a beneficial impact on pancreatic health as well,” he said.
Petrov reported no relevant financial relationships. Bilal reported being a consultant for Boston Scientific, Steris Endoscopy, and Cook Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
— a disorder experienced by roughly one fifth of the world’s population. Although it is more common than type 2 diabetes, pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer combined, it has remained relatively obscure.
By contrast, fatty liver — once called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and recently renamed metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) — is well-known.
“When it comes to diseases of the liver and pancreas, the liver is the big brother that has gotten all the attention, while the pancreas is the neglected little stepbrother that’s not sufficiently profiled in most medical textbooks and gets very little attention,” Max Petrov, MD, MPH, PhD, professor of pancreatology, University of Auckland, New Zealand, said in an interview. “The phenomenon of fatty pancreas has been observed for decades, but it is underappreciated and underrecognized.”
As early as 1926, fat depositions were identified during autopsies, but the condition remained relatively unknown, Mohammad Bilal, MD, associate professor of medicine-gastroenterology, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, said in an interview. “Fortunately, FPD has recently been receiving more focus.”
Generally, healthy individuals have small amounts of fat in their pancreas. IPFD is defined as “the diffuse presence of fat in the pancreas, measured on a continuous scale,” and FPD refers to IPFD above the upper limit of normal. While there is no clear consensus as to what the normal range is, studies suggest it’s a pancreatic fat content ranging from 1.8% to 10.4%.
FPD’s “most important implication is that it can be a precursor for more challenging and burdensome diseases of the pancreas,” Petrov said.
Fatty changes in the pancreas affect both its endocrine and exocrine systems. FPD is associated with type 2 diabetes, the most common disease of the endocrine pancreas, as well as pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, the most common diseases of the exocrine pancreas. It’s also implicated in the development of carotid atherosclerosis, pancreatic fistula following surgery, and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI).
A ‘Pandora’s Box’
Up to half of people with fatty pancreas are lean. The condition isn’t merely caused by an overflow of fat from the liver into the pancreas in people who consume more calories than they burn, Petrov said. Neither robust postmortem nor biopsy studies have found a statistically significant association between fatty deposition in the pancreas and liver fat.
Compared with the way people accumulate liver fat, the development of FPD is more complex, Petrov said.
“Hepatic fat is a relatively simple process: Lipid droplets accumulate in the hepatocytes; but, in the pancreas, there are several ways by which fat may accumulate,” he said.
One relates to the location of the pancreas within visceral, retroperitoneal fat, Petrov said. That fat can migrate and build up between pancreatic lobules.
Fat also can accumulate inside the lobes. This process can involve a buildup of fat droplets in acinar and stellate cells on the exocrine side and in the islets of Langerhans on the endocrine side. Additionally, when functional pancreatic cells die, particularly acinar cells, adult stem cells may replace them with adipocytes. Transformation of acinar cells into fat cells — a process called acinar-to-adipocyte transdifferentiation — also may be a way fat accumulates inside the lobes, Petrov said.
The accumulation of fat is a response to a wide array of insults to the pancreas over time. For example, obesity and metabolic syndrome lead to the accumulation of adipocytes and fat infiltration, whereas alcohol abuse and viral infections may lead to the death of acinar cells, which produce digestive enzymes.
Ultimately, the negative changes produced by excess fat in the pancreas are the origin of all common noninherited pancreatic diseases, bringing them under one umbrella, Petrov maintained. He dubbed this hypothesis PANcreatic Diseases Originating from intRapancreatic fAt (PANDORA).
The type of cells involved has implications for which disease may arise. For example, fat infiltration in stellate cells may promote pancreatic cancer, whereas its accumulation in the islets of Langerhans, which produce insulin and glucagon, is associated with type 2 diabetes.
The PANDORA hypothesis has eight foundational principles:
- Fatty pancreas is a key driver of pancreatic diseases in most people.
- Inflammation within the pancreatic microenvironment results from overwhelming lipotoxicity fueled by fatty pancreas.
- Aberrant communication between acinar cells involving lipid droplets drives acute pancreatitis.
- The pancreas responds to lipotoxicity with fibrosis and calcification — the hallmarks of chronic pancreatitis.
- Fat deposition affects signaling between stellate cells and other components of the microenvironment in ways that raise the risk for pancreatic cancer.
- The development of diabetes of the exocrine pancreas and EPI is affected by the presence of fatty pancreas.
- The higher risk for pancreatic disease in older adults is influenced by fatty pancreas.
- The multipronged nature of intrapancreatic fat deposition accounts for the common development of one pancreatic disease after another.
The idea that all common pancreatic diseases are the result of pathways emanating from FPD could “explain the bidirectional relationship between diabetes and pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer,” Petrov said.
Risk Factors, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
A variety of risk factors are involved in the accumulation of fat that may lead to pancreatic diseases, including aging, cholelithiasis, dyslipidemia, drugs/toxins (eg, steroids), genetic predisposition, iron overload, diet (eg, fatty foods, ultraprocessed foods), heavy alcohol use, overweight/obesity, pancreatic duct obstruction, tobacco use, viral infection (eg, hepatitis B, COVID-19), severe malnutrition, prediabetes, and dysglycemia.
Petrov described FPD as a “silent disease” that’s often asymptomatic, with its presence emerging as an incidental finding during abdominal ultrasonography for other reasons. However, patients may sometimes experience stomach pain or nausea if they have concurrent diseases of the pancreas, he said.
There are no currently available lab tests that can definitively detect the presence of FPD. Rather, the gold standard for a noninvasive diagnosis of FPD is MRI, with CT as the second-best choice, Petrov said.
In countries where advanced imaging is not available, a low-cost alternative might be a simple abdominal ultrasound, but it is not definitive, he said. “It’s operator-dependent and can be subjective.”
Some risk factors, such as derangements of glucose and lipid metabolism, especially in the presence of heavy alcohol use and a high-fat diet, can “be detected on lab tests,” Petrov said. “This, in combination with the abdominal ultrasound, might suggest the patients will benefit from deeper investigation, including MRI.”
Because the exocrine pancreas helps with digestion of fatty food, intralobular fatty deposits or replacement of pancreatic exocrine cells with adipose cells can lead to steatorrhea, Bilal said.
“Fat within the stool or oily diarrhea is a clue to the presence of FPD,” Bilal said.
Although this symptom isn’t unique to FPD and is found in other types of pancreatic conditions, its presence suggests that further investigation for FPD is warranted, he added.
Common-Sense Treatment Approaches
At present, there are no US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments for FPD, Petrov said.
“What might be recommended is something along the lines of treatment of MASLD — appropriate diet and physical activity,” he said. Petrov hopes that as the disease entity garners more research attention, more clinical drug trials will be initiated, and new medications are found and approved.
Petrov suggested that there could be a “theoretical rationale” for the use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) as a treatment, given their effectiveness in multiple conditions, including MASLD, but no human trials have robustly shown specific benefits of these drugs for FPD.
Petrov added that, to date, 12 classes of drugs have been investigated for reducing IPFD: biguanides, sulfonylureas, GLP-1 RAs, thiazolidinediones, dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, statins, fibrates, pancreatic lipase inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, somatostatin receptor agonists, and antioxidants.
Of these, most have shown promise in preclinical animal models. But only thiazolidinediones, GLP-1 RAs, DPP-4 inhibitors, and somatostatin receptor agonists have been investigated in randomized controlled trials in humans. The findings have been inconsistent, with the active treatment often not achieving statistically significant improvements.
“At this stage of our knowledge, we can’t recommend a specific pharmacotherapy,” Petrov said. But we can suggest dietary changes, such as saturated fat reduction, alcohol reduction, smoking cessation, reduction in consumption of ultraprocessed food, physical exercise, and addressing obesity and other drivers of metabolic disease.
Bilal, who is also a spokesperson for AGA, suggested that pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy, often used to treat pancreatic EPI, may treat some symptoms of FPD such as diarrhea.
Bariatric surgery has shown promise for FPD, in that it can decrease the patient’s body mass and potentially reduce the fat in the pancreas as well as it can improve metabolic diseases and hyperlipidemia. One study showed that it significantly decreased IPFD, fatty acid uptake, and blood flow, and these improvements were associated with more favorable glucose homeostasis and beta-cell function.
However, bariatric surgery is only appropriate for certain patients; is associated with potentially adverse sequelae including malnutrition, anemia, and digestive tract stenosis; and is currently not indicated for FPD.
Bilal advises clinicians to “keep an eye on FPD” if it’s detected incidentally and to screen patients more carefully for MASLD, metabolic disease, and diabetes.
“Although there are no consensus guidelines and recommendations for managing FPD at present, these common-sense approaches will benefit the patient’s overall health and hopefully will have a beneficial impact on pancreatic health as well,” he said.
Petrov reported no relevant financial relationships. Bilal reported being a consultant for Boston Scientific, Steris Endoscopy, and Cook Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Identifying Pancreatic Cancer Remains Elusive: Here’s Why
Now, a growing body of evidence indicates that this deadly cancer has been steadily on the rise, particularly in younger individuals who may not even realize they are at risk.
A recent survey, for instance, found that 33% of 1000 respondents younger than 50 years believe that only older adults are at risk for pancreatic cancer, and more than half said they wouldn’t even recognize the early signs and symptoms, which include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain that radiates to the back, nausea, and vomiting.
These survey findings allude to a bigger challenge: Identifying the disease remains elusive against a backdrop of these increasing rates and nonspecific risks and symptoms.
Currently, only about 15% of pancreatic cancers are caught at a localized, resectable stage, when 5-year survival rates are highest at 44%. But most are found later, after symptoms arise, and at this point, the 5-year survival odds plummet —16% for regional disease, 3% for distant, and 1% for stage IV.
“This disease is too often a silent killer, with no symptoms until it has progressed to less treatable stages,” said survey coauthor Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, PhD, in the division of gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition at Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus.
Rising Rates
Since 2001, rates of pancreatic cancer have steadily increased by about 1% annually, and this increase appears greater among younger individuals, especially women.
A recent study in Gastroenterology, for instance, found that, while overall rates of pancreatic cancer among people aged 15-34 years remained low (0.3% in women and 0.2% in men) between 2001 and 2018, the average annual percent change in this age group was considerably higher than that for older individuals — 6.45% for women and 2.97% for men compared with 1.11% for women aged 55 years and 1.17% for men aged 55 years. Another recent analysis, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, reported similar increased rates in men and women aged 15-39 years between 2011 and 2019.
Although more than 90% of cases do occur in those 55 years or older, “we’re now seeing this disease in people who are in their 40s much more regularly,” Cruz-Monserrate said. “This is a concerning trend — and more research is needed to learn why.”
But it’s early days. Studies so far indicate that early onset pancreatic cancer tends to be even more aggressive, but the “underlying reason is not yet clear,” researcher wrote in a 2025 review.
Some evidence indicates younger individuals may have distinct molecular characteristics, whereas other research shows younger and older patients have similar genetic profiles. Younger patients may also be more likely to smoke, drink more, and delay seeking medical attention as well as experience delays in being diagnosed by physicians, the authors explained.
Catching It Early
Given the rising rates, early detection is especially important.
There are some known genetic and medical risk factors for pancreatic cancer. About 10% of these cancers are linked to heredity risk or genetic markers, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 or Lynch syndrome. People with chronic pancreatitis, type 2 diabetes, obesity, or with a family history of pancreatic cancer face an elevated risk.
Lifestyle factors can play a role as well. Alcohol consumption, a poor diet that includes red or processed meat, and smoking increase people’s risk for pancreatic cancer. In fact, smoking leads to a twofold higher risk, compared with not smoking.
However, uncovering pancreatic cancer from these factors alone can be like “finding a needle in a haystack,” said Srinivas Gaddam, MD, head of the pancreatic cancer screening and early detection program at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
One strategy to help detect the disease earlier would be to screen more.
The latest guidance from the American Cancer Society suggests that people with a genetic predisposition or a family history of pancreatic cancer could benefit from annual surveillance with endoscopic ultrasound or MRI.
But the US Preventive Services Task Force currently recommends against routine screening of average-risk asymptomatic adults (JAMA. 2019;322[5]:438-444). The task force found no evidence that screening for pancreatic cancer improves disease-specific morbidity or mortality or all-cause mortality.
“The absolute incidence in younger people is far too small to make screening beneficial,” explained The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology editors in a 2023 editorial.
In fact, more screening could lead to overdiagnosis, a concern reinforced by the recent study in Annals of Internal Medicine. That analysis found that much of the observed increase in early-onset pancreatic cancer stemmed from the detection of more small, early-stage endocrine cancer, rather than pancreatic adenocarcinoma, whereas mortality from the disease remained stable over the study period.
Recent findings do “suggest the potential for overdiagnosis and overtreatment, particularly in cases of indolent pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors,” Gaddam said.
Gaddam has observed an increase in both adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors in the clinic and in his research, especially in women younger than 50 years, but he noted these early onset diagnoses do remain rare.
Staying Vigilant
As the understanding of pancreatic cancer risks and symptoms evolves, ensuring that patients, especially younger individuals, recognize the warning signs, without causing alarm, remains a challenge.
The disease “presents more advanced in younger patients, but symptoms are so nonspecific,” said Randall Brand, MD, AGAF, director of the gastrointestinal malignancy early detection, diagnosis, and prevention program at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pennsylvania. Given that, “I am not sure how to best highlight a communication approach that would not cause undue stress to the patient and our healthcare resources.”
Gaddam agreed that it’s tough to pinpoint or communicate straightforward risks or symptoms to the general public without potentially leading to unnecessary screening.
At a minimum, however, clinicians can share more general risk-mitigating strategies with their patients.
Communicating such strategies may be especially important for younger patients, given that the recent survey found almost 40% of younger adults believe there’s nothing they can do to change their risk for pancreatic cancer.
However, Cruz-Monserrate explained, adults of all ages can lower their risks through regular exercise, limited alcohol and tobacco use, and a healthy diet with less red meat or processed meat.
Ultimately, for clinicians, given how difficult it is now to identify pancreatic cancer early, we have to “follow their good clinical judgment when alarming features, such as weight loss or nuances of pancreatic pain arise, and then get good imaging,” Gaddam said.
Cruz-Monserrate, Brand, and Gaddam reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now, a growing body of evidence indicates that this deadly cancer has been steadily on the rise, particularly in younger individuals who may not even realize they are at risk.
A recent survey, for instance, found that 33% of 1000 respondents younger than 50 years believe that only older adults are at risk for pancreatic cancer, and more than half said they wouldn’t even recognize the early signs and symptoms, which include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain that radiates to the back, nausea, and vomiting.
These survey findings allude to a bigger challenge: Identifying the disease remains elusive against a backdrop of these increasing rates and nonspecific risks and symptoms.
Currently, only about 15% of pancreatic cancers are caught at a localized, resectable stage, when 5-year survival rates are highest at 44%. But most are found later, after symptoms arise, and at this point, the 5-year survival odds plummet —16% for regional disease, 3% for distant, and 1% for stage IV.
“This disease is too often a silent killer, with no symptoms until it has progressed to less treatable stages,” said survey coauthor Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, PhD, in the division of gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition at Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus.
Rising Rates
Since 2001, rates of pancreatic cancer have steadily increased by about 1% annually, and this increase appears greater among younger individuals, especially women.
A recent study in Gastroenterology, for instance, found that, while overall rates of pancreatic cancer among people aged 15-34 years remained low (0.3% in women and 0.2% in men) between 2001 and 2018, the average annual percent change in this age group was considerably higher than that for older individuals — 6.45% for women and 2.97% for men compared with 1.11% for women aged 55 years and 1.17% for men aged 55 years. Another recent analysis, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, reported similar increased rates in men and women aged 15-39 years between 2011 and 2019.
Although more than 90% of cases do occur in those 55 years or older, “we’re now seeing this disease in people who are in their 40s much more regularly,” Cruz-Monserrate said. “This is a concerning trend — and more research is needed to learn why.”
But it’s early days. Studies so far indicate that early onset pancreatic cancer tends to be even more aggressive, but the “underlying reason is not yet clear,” researcher wrote in a 2025 review.
Some evidence indicates younger individuals may have distinct molecular characteristics, whereas other research shows younger and older patients have similar genetic profiles. Younger patients may also be more likely to smoke, drink more, and delay seeking medical attention as well as experience delays in being diagnosed by physicians, the authors explained.
Catching It Early
Given the rising rates, early detection is especially important.
There are some known genetic and medical risk factors for pancreatic cancer. About 10% of these cancers are linked to heredity risk or genetic markers, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 or Lynch syndrome. People with chronic pancreatitis, type 2 diabetes, obesity, or with a family history of pancreatic cancer face an elevated risk.
Lifestyle factors can play a role as well. Alcohol consumption, a poor diet that includes red or processed meat, and smoking increase people’s risk for pancreatic cancer. In fact, smoking leads to a twofold higher risk, compared with not smoking.
However, uncovering pancreatic cancer from these factors alone can be like “finding a needle in a haystack,” said Srinivas Gaddam, MD, head of the pancreatic cancer screening and early detection program at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
One strategy to help detect the disease earlier would be to screen more.
The latest guidance from the American Cancer Society suggests that people with a genetic predisposition or a family history of pancreatic cancer could benefit from annual surveillance with endoscopic ultrasound or MRI.
But the US Preventive Services Task Force currently recommends against routine screening of average-risk asymptomatic adults (JAMA. 2019;322[5]:438-444). The task force found no evidence that screening for pancreatic cancer improves disease-specific morbidity or mortality or all-cause mortality.
“The absolute incidence in younger people is far too small to make screening beneficial,” explained The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology editors in a 2023 editorial.
In fact, more screening could lead to overdiagnosis, a concern reinforced by the recent study in Annals of Internal Medicine. That analysis found that much of the observed increase in early-onset pancreatic cancer stemmed from the detection of more small, early-stage endocrine cancer, rather than pancreatic adenocarcinoma, whereas mortality from the disease remained stable over the study period.
Recent findings do “suggest the potential for overdiagnosis and overtreatment, particularly in cases of indolent pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors,” Gaddam said.
Gaddam has observed an increase in both adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors in the clinic and in his research, especially in women younger than 50 years, but he noted these early onset diagnoses do remain rare.
Staying Vigilant
As the understanding of pancreatic cancer risks and symptoms evolves, ensuring that patients, especially younger individuals, recognize the warning signs, without causing alarm, remains a challenge.
The disease “presents more advanced in younger patients, but symptoms are so nonspecific,” said Randall Brand, MD, AGAF, director of the gastrointestinal malignancy early detection, diagnosis, and prevention program at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pennsylvania. Given that, “I am not sure how to best highlight a communication approach that would not cause undue stress to the patient and our healthcare resources.”
Gaddam agreed that it’s tough to pinpoint or communicate straightforward risks or symptoms to the general public without potentially leading to unnecessary screening.
At a minimum, however, clinicians can share more general risk-mitigating strategies with their patients.
Communicating such strategies may be especially important for younger patients, given that the recent survey found almost 40% of younger adults believe there’s nothing they can do to change their risk for pancreatic cancer.
However, Cruz-Monserrate explained, adults of all ages can lower their risks through regular exercise, limited alcohol and tobacco use, and a healthy diet with less red meat or processed meat.
Ultimately, for clinicians, given how difficult it is now to identify pancreatic cancer early, we have to “follow their good clinical judgment when alarming features, such as weight loss or nuances of pancreatic pain arise, and then get good imaging,” Gaddam said.
Cruz-Monserrate, Brand, and Gaddam reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now, a growing body of evidence indicates that this deadly cancer has been steadily on the rise, particularly in younger individuals who may not even realize they are at risk.
A recent survey, for instance, found that 33% of 1000 respondents younger than 50 years believe that only older adults are at risk for pancreatic cancer, and more than half said they wouldn’t even recognize the early signs and symptoms, which include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain that radiates to the back, nausea, and vomiting.
These survey findings allude to a bigger challenge: Identifying the disease remains elusive against a backdrop of these increasing rates and nonspecific risks and symptoms.
Currently, only about 15% of pancreatic cancers are caught at a localized, resectable stage, when 5-year survival rates are highest at 44%. But most are found later, after symptoms arise, and at this point, the 5-year survival odds plummet —16% for regional disease, 3% for distant, and 1% for stage IV.
“This disease is too often a silent killer, with no symptoms until it has progressed to less treatable stages,” said survey coauthor Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, PhD, in the division of gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition at Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus.
Rising Rates
Since 2001, rates of pancreatic cancer have steadily increased by about 1% annually, and this increase appears greater among younger individuals, especially women.
A recent study in Gastroenterology, for instance, found that, while overall rates of pancreatic cancer among people aged 15-34 years remained low (0.3% in women and 0.2% in men) between 2001 and 2018, the average annual percent change in this age group was considerably higher than that for older individuals — 6.45% for women and 2.97% for men compared with 1.11% for women aged 55 years and 1.17% for men aged 55 years. Another recent analysis, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, reported similar increased rates in men and women aged 15-39 years between 2011 and 2019.
Although more than 90% of cases do occur in those 55 years or older, “we’re now seeing this disease in people who are in their 40s much more regularly,” Cruz-Monserrate said. “This is a concerning trend — and more research is needed to learn why.”
But it’s early days. Studies so far indicate that early onset pancreatic cancer tends to be even more aggressive, but the “underlying reason is not yet clear,” researcher wrote in a 2025 review.
Some evidence indicates younger individuals may have distinct molecular characteristics, whereas other research shows younger and older patients have similar genetic profiles. Younger patients may also be more likely to smoke, drink more, and delay seeking medical attention as well as experience delays in being diagnosed by physicians, the authors explained.
Catching It Early
Given the rising rates, early detection is especially important.
There are some known genetic and medical risk factors for pancreatic cancer. About 10% of these cancers are linked to heredity risk or genetic markers, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 or Lynch syndrome. People with chronic pancreatitis, type 2 diabetes, obesity, or with a family history of pancreatic cancer face an elevated risk.
Lifestyle factors can play a role as well. Alcohol consumption, a poor diet that includes red or processed meat, and smoking increase people’s risk for pancreatic cancer. In fact, smoking leads to a twofold higher risk, compared with not smoking.
However, uncovering pancreatic cancer from these factors alone can be like “finding a needle in a haystack,” said Srinivas Gaddam, MD, head of the pancreatic cancer screening and early detection program at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
One strategy to help detect the disease earlier would be to screen more.
The latest guidance from the American Cancer Society suggests that people with a genetic predisposition or a family history of pancreatic cancer could benefit from annual surveillance with endoscopic ultrasound or MRI.
But the US Preventive Services Task Force currently recommends against routine screening of average-risk asymptomatic adults (JAMA. 2019;322[5]:438-444). The task force found no evidence that screening for pancreatic cancer improves disease-specific morbidity or mortality or all-cause mortality.
“The absolute incidence in younger people is far too small to make screening beneficial,” explained The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology editors in a 2023 editorial.
In fact, more screening could lead to overdiagnosis, a concern reinforced by the recent study in Annals of Internal Medicine. That analysis found that much of the observed increase in early-onset pancreatic cancer stemmed from the detection of more small, early-stage endocrine cancer, rather than pancreatic adenocarcinoma, whereas mortality from the disease remained stable over the study period.
Recent findings do “suggest the potential for overdiagnosis and overtreatment, particularly in cases of indolent pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors,” Gaddam said.
Gaddam has observed an increase in both adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors in the clinic and in his research, especially in women younger than 50 years, but he noted these early onset diagnoses do remain rare.
Staying Vigilant
As the understanding of pancreatic cancer risks and symptoms evolves, ensuring that patients, especially younger individuals, recognize the warning signs, without causing alarm, remains a challenge.
The disease “presents more advanced in younger patients, but symptoms are so nonspecific,” said Randall Brand, MD, AGAF, director of the gastrointestinal malignancy early detection, diagnosis, and prevention program at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pennsylvania. Given that, “I am not sure how to best highlight a communication approach that would not cause undue stress to the patient and our healthcare resources.”
Gaddam agreed that it’s tough to pinpoint or communicate straightforward risks or symptoms to the general public without potentially leading to unnecessary screening.
At a minimum, however, clinicians can share more general risk-mitigating strategies with their patients.
Communicating such strategies may be especially important for younger patients, given that the recent survey found almost 40% of younger adults believe there’s nothing they can do to change their risk for pancreatic cancer.
However, Cruz-Monserrate explained, adults of all ages can lower their risks through regular exercise, limited alcohol and tobacco use, and a healthy diet with less red meat or processed meat.
Ultimately, for clinicians, given how difficult it is now to identify pancreatic cancer early, we have to “follow their good clinical judgment when alarming features, such as weight loss or nuances of pancreatic pain arise, and then get good imaging,” Gaddam said.
Cruz-Monserrate, Brand, and Gaddam reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.