User login
MD-IQ only
Do Statins Offset Venous Thrombosis Risk With Hormone Therapy?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This is Dr JoAnn Manson, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. I’d like to talk with you about a recent report in JAMA Network Open on the subject of whether statin therapy may be able to offset some of the excess risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) among women taking menopausal hormone therapy.
It’s an important issue because we know that menopausal hormone therapy, especially oral therapy, is linked to an excess risk for VTE, approximately doubling of risk in the randomized clinical trials. There is also emerging evidence from some randomized trials, such as the Jupiter trial, that step therapy may be linked to a reduction in risk. This may be related to anti-inflammatory or antithrombotic effects of statin therapy.
The authors made use of a very large administrative claims database, Optum Health, to look at more than 15 million annual members. They were able to identify 2000 women with a diagnostic code for VTE treatment. The women were between ages 50 and 64 years, and they were compared with 200,000 controls without VTE, matched in 10-to-1 fashion.
About 50% of the women were taking oral hormone therapy, and about 50% took non-oral transdermal or other non-oral formulations of hormone therapy. The odds ratio for VTE was 1.53 among the women who did not also have prescription records for statin therapy. They were able to look at prescribed prescriptions for both the hormone therapy and the statins. Among the women prescribed hormone therapy and also low- to intermediate-dose statins, the odds ratio was 1.29. So that was quite a mitigation of the elevated risk. Among the women taking high-intensity statins, the odds ratio was 1.06, and there was no significant elevation.
We do need more data and more research on this question. One approach would be a meta-analysis of all of the existing randomized trials of hormone therapy in recent years wherein there was increased uptake of statin therapy to look at this question not only for VTE but also for coronary heart disease, stroke, and other CVD outcomes to see whether statin therapy is associated with some attenuation of the excess risk. We also need a targeted randomized trial of statins vs placebo among women who have clear indications for hormone therapy but may be at some increased risk for VTE. That type of trial would be extremely helpful.
These include choosing a transdermal rather than an oral formulation of hormone therapy and using lower doses of hormone therapy. Also, women who are clear candidates for hormone therapy and also for statins, it’s obvious that statins could be co-prescribed. Even among women who are clear candidates for hormone therapy but only intermediate borderline candidates for statin therapy, the prescription of statins might be considered in that clinical scenario to try to mitigate that excess risk for VTE.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received study pill donation and infrastructure support from: Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This is Dr JoAnn Manson, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. I’d like to talk with you about a recent report in JAMA Network Open on the subject of whether statin therapy may be able to offset some of the excess risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) among women taking menopausal hormone therapy.
It’s an important issue because we know that menopausal hormone therapy, especially oral therapy, is linked to an excess risk for VTE, approximately doubling of risk in the randomized clinical trials. There is also emerging evidence from some randomized trials, such as the Jupiter trial, that step therapy may be linked to a reduction in risk. This may be related to anti-inflammatory or antithrombotic effects of statin therapy.
The authors made use of a very large administrative claims database, Optum Health, to look at more than 15 million annual members. They were able to identify 2000 women with a diagnostic code for VTE treatment. The women were between ages 50 and 64 years, and they were compared with 200,000 controls without VTE, matched in 10-to-1 fashion.
About 50% of the women were taking oral hormone therapy, and about 50% took non-oral transdermal or other non-oral formulations of hormone therapy. The odds ratio for VTE was 1.53 among the women who did not also have prescription records for statin therapy. They were able to look at prescribed prescriptions for both the hormone therapy and the statins. Among the women prescribed hormone therapy and also low- to intermediate-dose statins, the odds ratio was 1.29. So that was quite a mitigation of the elevated risk. Among the women taking high-intensity statins, the odds ratio was 1.06, and there was no significant elevation.
We do need more data and more research on this question. One approach would be a meta-analysis of all of the existing randomized trials of hormone therapy in recent years wherein there was increased uptake of statin therapy to look at this question not only for VTE but also for coronary heart disease, stroke, and other CVD outcomes to see whether statin therapy is associated with some attenuation of the excess risk. We also need a targeted randomized trial of statins vs placebo among women who have clear indications for hormone therapy but may be at some increased risk for VTE. That type of trial would be extremely helpful.
These include choosing a transdermal rather than an oral formulation of hormone therapy and using lower doses of hormone therapy. Also, women who are clear candidates for hormone therapy and also for statins, it’s obvious that statins could be co-prescribed. Even among women who are clear candidates for hormone therapy but only intermediate borderline candidates for statin therapy, the prescription of statins might be considered in that clinical scenario to try to mitigate that excess risk for VTE.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received study pill donation and infrastructure support from: Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This is Dr JoAnn Manson, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. I’d like to talk with you about a recent report in JAMA Network Open on the subject of whether statin therapy may be able to offset some of the excess risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) among women taking menopausal hormone therapy.
It’s an important issue because we know that menopausal hormone therapy, especially oral therapy, is linked to an excess risk for VTE, approximately doubling of risk in the randomized clinical trials. There is also emerging evidence from some randomized trials, such as the Jupiter trial, that step therapy may be linked to a reduction in risk. This may be related to anti-inflammatory or antithrombotic effects of statin therapy.
The authors made use of a very large administrative claims database, Optum Health, to look at more than 15 million annual members. They were able to identify 2000 women with a diagnostic code for VTE treatment. The women were between ages 50 and 64 years, and they were compared with 200,000 controls without VTE, matched in 10-to-1 fashion.
About 50% of the women were taking oral hormone therapy, and about 50% took non-oral transdermal or other non-oral formulations of hormone therapy. The odds ratio for VTE was 1.53 among the women who did not also have prescription records for statin therapy. They were able to look at prescribed prescriptions for both the hormone therapy and the statins. Among the women prescribed hormone therapy and also low- to intermediate-dose statins, the odds ratio was 1.29. So that was quite a mitigation of the elevated risk. Among the women taking high-intensity statins, the odds ratio was 1.06, and there was no significant elevation.
We do need more data and more research on this question. One approach would be a meta-analysis of all of the existing randomized trials of hormone therapy in recent years wherein there was increased uptake of statin therapy to look at this question not only for VTE but also for coronary heart disease, stroke, and other CVD outcomes to see whether statin therapy is associated with some attenuation of the excess risk. We also need a targeted randomized trial of statins vs placebo among women who have clear indications for hormone therapy but may be at some increased risk for VTE. That type of trial would be extremely helpful.
These include choosing a transdermal rather than an oral formulation of hormone therapy and using lower doses of hormone therapy. Also, women who are clear candidates for hormone therapy and also for statins, it’s obvious that statins could be co-prescribed. Even among women who are clear candidates for hormone therapy but only intermediate borderline candidates for statin therapy, the prescription of statins might be considered in that clinical scenario to try to mitigate that excess risk for VTE.
JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received study pill donation and infrastructure support from: Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnancy in rheumatic disease quadruples risk of cardiovascular events
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.
Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
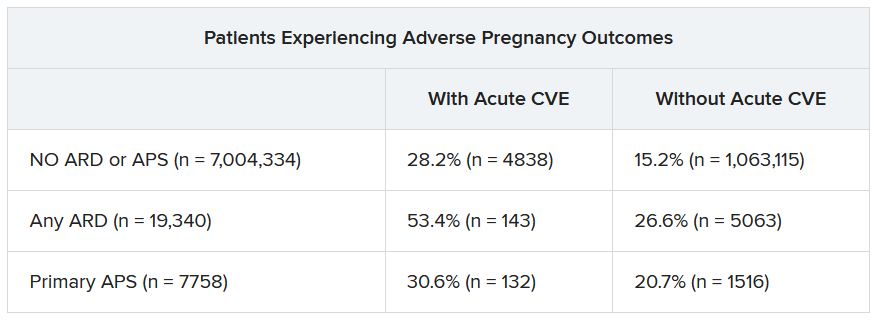
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.
Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.
Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2023
Review finds no CV or VTE risk signal with use of JAK inhibitors for skin indications
, results from a systematic literature review, and meta-analysis showed.
“There remains a knowledge gap regarding the risk of JAK inhibitor use and VTE and/or MACE in the dermatologic population,” researchers led by Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at New York University Langone Health, wrote in their study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology . “Pooled safety studies suggest that the risk of MACE and VTE may be lower in patients treated with JAK inhibitors for a dermatologic indication than the risk observed in the ORAL Surveillance study, which may be related to the younger age and better health status of those enrolled in trials for dermatologic indications.” The results of that study, which included patients with rheumatoid arthritis only, resulted in the addition of a boxed warning in the labels for topical and oral JAK inhibitors regarding the increased risk of MACE, VTE, serious infections, malignancies, and death .
For the review – thought to be the first to specifically evaluate these risks for dermatologic indications – the researchers searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception through April 1, 2023, for phase 3 dermatology randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to evaluate the risk of MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality with JAK inhibitors, compared with placebo or an active comparator in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases. They followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and used a random-effects model and the DerSimonian-Laird method to calculate adverse events with odds ratios.
The database search yielded 35 RCTs with a total of 20,651 patients. Their mean age was 38.5 years, 54% were male, and the mean follow-up time was 4.9 months. Of the 35 trials, most (21) involved patients with atopic dermatitis, followed by psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (9 trials), alopecia areata (3 trials) and vitiligo (2 trials).
The researchers found no significant difference between JAK inhibitors and placebo/active comparator in composite MACE and all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.57) or in VTE (OR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.26-1.04).
In a secondary analysis, which included additional psoriatic arthritis RCTs, no significant differences between the treatment and placebo/active comparator groups were observed. Similarly, subgroup analyses of oral versus topical JAK inhibitors and a sensitivity analysis that excluded pediatric trials showed no significant differences between patients exposed to JAK inhibitors and those not exposed.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the review, including the lack of access to patient-level data, the fact that most trials only included short-term follow-up, and that the findings have limited generalizability to an older patient population. “It remains unclear if the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are primarily due to patient level cardiovascular risk factors or are drug mediated,” they concluded. “Dermatologists should carefully select patients and assess baseline cardiovascular risk factors when considering JAK therapy. Cardiovascular risk assessment should continue for the duration of treatment.”
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study results, characterized the findings as reassuring to dermatologists who may be reluctant to initiate therapy with JAK inhibitors based on concerns about safety signals for MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality.
“These data systematically show that across medications and across conditions, there doesn’t appear to be an increased signal for these events during the short-term, placebo-controlled period which generally spans a few months in most studies,” he told this news organization. The findings, he added, “align well with our clinical experience to date for JAK inhibitor use in inflammatory skin disease. Short-term safety, particularly in relation to boxed warning events such MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality, have generally been favorable with real-world use. It’s good to have a rigorous statistical analysis to refer to when setting patient expectations.”
However, he noted that these data only examined short-term safety during the placebo or active comparator-controlled periods. “Considering that events like MACE or VTE may take many months or years to manifest, continued long-term data generation is needed to fully answer the question of risk,” he said.
Dr. Garshick disclosed that he received grants from Pfizer and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. Several other coauthors reported having advisory board roles and/or having received funding or support from several pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including those that develop JAK inhibitors.
, results from a systematic literature review, and meta-analysis showed.
“There remains a knowledge gap regarding the risk of JAK inhibitor use and VTE and/or MACE in the dermatologic population,” researchers led by Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at New York University Langone Health, wrote in their study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology . “Pooled safety studies suggest that the risk of MACE and VTE may be lower in patients treated with JAK inhibitors for a dermatologic indication than the risk observed in the ORAL Surveillance study, which may be related to the younger age and better health status of those enrolled in trials for dermatologic indications.” The results of that study, which included patients with rheumatoid arthritis only, resulted in the addition of a boxed warning in the labels for topical and oral JAK inhibitors regarding the increased risk of MACE, VTE, serious infections, malignancies, and death .
For the review – thought to be the first to specifically evaluate these risks for dermatologic indications – the researchers searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception through April 1, 2023, for phase 3 dermatology randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to evaluate the risk of MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality with JAK inhibitors, compared with placebo or an active comparator in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases. They followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and used a random-effects model and the DerSimonian-Laird method to calculate adverse events with odds ratios.
The database search yielded 35 RCTs with a total of 20,651 patients. Their mean age was 38.5 years, 54% were male, and the mean follow-up time was 4.9 months. Of the 35 trials, most (21) involved patients with atopic dermatitis, followed by psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (9 trials), alopecia areata (3 trials) and vitiligo (2 trials).
The researchers found no significant difference between JAK inhibitors and placebo/active comparator in composite MACE and all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.57) or in VTE (OR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.26-1.04).
In a secondary analysis, which included additional psoriatic arthritis RCTs, no significant differences between the treatment and placebo/active comparator groups were observed. Similarly, subgroup analyses of oral versus topical JAK inhibitors and a sensitivity analysis that excluded pediatric trials showed no significant differences between patients exposed to JAK inhibitors and those not exposed.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the review, including the lack of access to patient-level data, the fact that most trials only included short-term follow-up, and that the findings have limited generalizability to an older patient population. “It remains unclear if the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are primarily due to patient level cardiovascular risk factors or are drug mediated,” they concluded. “Dermatologists should carefully select patients and assess baseline cardiovascular risk factors when considering JAK therapy. Cardiovascular risk assessment should continue for the duration of treatment.”
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study results, characterized the findings as reassuring to dermatologists who may be reluctant to initiate therapy with JAK inhibitors based on concerns about safety signals for MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality.
“These data systematically show that across medications and across conditions, there doesn’t appear to be an increased signal for these events during the short-term, placebo-controlled period which generally spans a few months in most studies,” he told this news organization. The findings, he added, “align well with our clinical experience to date for JAK inhibitor use in inflammatory skin disease. Short-term safety, particularly in relation to boxed warning events such MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality, have generally been favorable with real-world use. It’s good to have a rigorous statistical analysis to refer to when setting patient expectations.”
However, he noted that these data only examined short-term safety during the placebo or active comparator-controlled periods. “Considering that events like MACE or VTE may take many months or years to manifest, continued long-term data generation is needed to fully answer the question of risk,” he said.
Dr. Garshick disclosed that he received grants from Pfizer and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. Several other coauthors reported having advisory board roles and/or having received funding or support from several pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including those that develop JAK inhibitors.
, results from a systematic literature review, and meta-analysis showed.
“There remains a knowledge gap regarding the risk of JAK inhibitor use and VTE and/or MACE in the dermatologic population,” researchers led by Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at New York University Langone Health, wrote in their study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology . “Pooled safety studies suggest that the risk of MACE and VTE may be lower in patients treated with JAK inhibitors for a dermatologic indication than the risk observed in the ORAL Surveillance study, which may be related to the younger age and better health status of those enrolled in trials for dermatologic indications.” The results of that study, which included patients with rheumatoid arthritis only, resulted in the addition of a boxed warning in the labels for topical and oral JAK inhibitors regarding the increased risk of MACE, VTE, serious infections, malignancies, and death .
For the review – thought to be the first to specifically evaluate these risks for dermatologic indications – the researchers searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception through April 1, 2023, for phase 3 dermatology randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to evaluate the risk of MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality with JAK inhibitors, compared with placebo or an active comparator in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases. They followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and used a random-effects model and the DerSimonian-Laird method to calculate adverse events with odds ratios.
The database search yielded 35 RCTs with a total of 20,651 patients. Their mean age was 38.5 years, 54% were male, and the mean follow-up time was 4.9 months. Of the 35 trials, most (21) involved patients with atopic dermatitis, followed by psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (9 trials), alopecia areata (3 trials) and vitiligo (2 trials).
The researchers found no significant difference between JAK inhibitors and placebo/active comparator in composite MACE and all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.57) or in VTE (OR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.26-1.04).
In a secondary analysis, which included additional psoriatic arthritis RCTs, no significant differences between the treatment and placebo/active comparator groups were observed. Similarly, subgroup analyses of oral versus topical JAK inhibitors and a sensitivity analysis that excluded pediatric trials showed no significant differences between patients exposed to JAK inhibitors and those not exposed.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the review, including the lack of access to patient-level data, the fact that most trials only included short-term follow-up, and that the findings have limited generalizability to an older patient population. “It remains unclear if the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are primarily due to patient level cardiovascular risk factors or are drug mediated,” they concluded. “Dermatologists should carefully select patients and assess baseline cardiovascular risk factors when considering JAK therapy. Cardiovascular risk assessment should continue for the duration of treatment.”
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study results, characterized the findings as reassuring to dermatologists who may be reluctant to initiate therapy with JAK inhibitors based on concerns about safety signals for MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality.
“These data systematically show that across medications and across conditions, there doesn’t appear to be an increased signal for these events during the short-term, placebo-controlled period which generally spans a few months in most studies,” he told this news organization. The findings, he added, “align well with our clinical experience to date for JAK inhibitor use in inflammatory skin disease. Short-term safety, particularly in relation to boxed warning events such MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality, have generally been favorable with real-world use. It’s good to have a rigorous statistical analysis to refer to when setting patient expectations.”
However, he noted that these data only examined short-term safety during the placebo or active comparator-controlled periods. “Considering that events like MACE or VTE may take many months or years to manifest, continued long-term data generation is needed to fully answer the question of risk,” he said.
Dr. Garshick disclosed that he received grants from Pfizer and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. Several other coauthors reported having advisory board roles and/or having received funding or support from several pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including those that develop JAK inhibitors.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Supplemental oxygen fails to improve echocardiographic measures in PE patients
compared with ambient oxygen in a pilot study of 70 individuals.
Anticoagulation monotherapy is the standard of care for patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism (PE), but persistent short-term complication rates may approach 10%, wrote Deisy Barrios, MD, of Hospital Ramón y Cajal (IRYCIS), Madrid, and colleagues. Additional strategies are needed, and the use of supplemental oxygen in non-hypoxemic patients with intermediate-risk PE has not been explored, they said.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers recruited 36 women and 34 men who were non-hypoxemic with stable PE and intermediate risk, defined as echocardiographic RV enlargement. The study recruitment ended prematurely because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The mean age of the participants was 67.3 years. Patients were randomized within 24 hours of hospital admission to anticoagulation plus supplemental oxygen or anticoagulation alone. The groups were similar in echocardiographic mean RV end-diameter and RV/LV ratios at baseline.
The intervention patients received supplemental oxygen at a 35% concentration (7 L/min) continuously for 48 hours via a face mask, and through a nasal cannula during meal times.
The primary outcome was normalization of right ventricle size (defined as an RV/LV diameter ratio less than 1.0 from the subcostal or apical view) at 48 hours after randomization. Secondary outcomes included change in the right ventricle/left ventricle diameter as measured at 48 hours and 7 days after randomization compared to baseline.
The proportion of patients with an RV/LV ratio of 1.0 or less at 48 hours was not significantly different between the intervention and control groups (42.4% vs. 21.6%, P = .08). Similarly, the proportion of patients with an RV/LV ratio of 1.0 or less at 7 days was not significantly different between the groups (76% vs. 70%).
The between-group reduction in RV/LV ratio was significantly greater in the supplemental oxygen group vs. the control group from baseline to 48 hours (0.28 vs. 0.12 P = .02).
However, the within-group mean RV/LV ratio was significantly reduced in both the supplemental oxygen group and the control group compared to baseline at 48 hours and at 7 days after randomization.
None of the patients experienced hemodynamic collapse or recurrent venous thromboembolism during the follow-up period.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and open-label design, and lack of power to detect clinical outcomes, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that although supplemental oxygen had no significant impact of RV/LV normalization, “supplemental oxygen might increase the likelihood of reducing echocardiographic RV dilatation,” and the findings warrant a definitive clinical outcomes trial of supplemental oxygen vs. ambient air to improve outcomes in non-hypoxemic patients with intermediate-risk PE, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Dr. Barrios had no financial conflicts to disclose.
compared with ambient oxygen in a pilot study of 70 individuals.
Anticoagulation monotherapy is the standard of care for patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism (PE), but persistent short-term complication rates may approach 10%, wrote Deisy Barrios, MD, of Hospital Ramón y Cajal (IRYCIS), Madrid, and colleagues. Additional strategies are needed, and the use of supplemental oxygen in non-hypoxemic patients with intermediate-risk PE has not been explored, they said.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers recruited 36 women and 34 men who were non-hypoxemic with stable PE and intermediate risk, defined as echocardiographic RV enlargement. The study recruitment ended prematurely because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The mean age of the participants was 67.3 years. Patients were randomized within 24 hours of hospital admission to anticoagulation plus supplemental oxygen or anticoagulation alone. The groups were similar in echocardiographic mean RV end-diameter and RV/LV ratios at baseline.
The intervention patients received supplemental oxygen at a 35% concentration (7 L/min) continuously for 48 hours via a face mask, and through a nasal cannula during meal times.
The primary outcome was normalization of right ventricle size (defined as an RV/LV diameter ratio less than 1.0 from the subcostal or apical view) at 48 hours after randomization. Secondary outcomes included change in the right ventricle/left ventricle diameter as measured at 48 hours and 7 days after randomization compared to baseline.
The proportion of patients with an RV/LV ratio of 1.0 or less at 48 hours was not significantly different between the intervention and control groups (42.4% vs. 21.6%, P = .08). Similarly, the proportion of patients with an RV/LV ratio of 1.0 or less at 7 days was not significantly different between the groups (76% vs. 70%).
The between-group reduction in RV/LV ratio was significantly greater in the supplemental oxygen group vs. the control group from baseline to 48 hours (0.28 vs. 0.12 P = .02).
However, the within-group mean RV/LV ratio was significantly reduced in both the supplemental oxygen group and the control group compared to baseline at 48 hours and at 7 days after randomization.
None of the patients experienced hemodynamic collapse or recurrent venous thromboembolism during the follow-up period.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and open-label design, and lack of power to detect clinical outcomes, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that although supplemental oxygen had no significant impact of RV/LV normalization, “supplemental oxygen might increase the likelihood of reducing echocardiographic RV dilatation,” and the findings warrant a definitive clinical outcomes trial of supplemental oxygen vs. ambient air to improve outcomes in non-hypoxemic patients with intermediate-risk PE, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Dr. Barrios had no financial conflicts to disclose.
compared with ambient oxygen in a pilot study of 70 individuals.
Anticoagulation monotherapy is the standard of care for patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism (PE), but persistent short-term complication rates may approach 10%, wrote Deisy Barrios, MD, of Hospital Ramón y Cajal (IRYCIS), Madrid, and colleagues. Additional strategies are needed, and the use of supplemental oxygen in non-hypoxemic patients with intermediate-risk PE has not been explored, they said.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers recruited 36 women and 34 men who were non-hypoxemic with stable PE and intermediate risk, defined as echocardiographic RV enlargement. The study recruitment ended prematurely because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The mean age of the participants was 67.3 years. Patients were randomized within 24 hours of hospital admission to anticoagulation plus supplemental oxygen or anticoagulation alone. The groups were similar in echocardiographic mean RV end-diameter and RV/LV ratios at baseline.
The intervention patients received supplemental oxygen at a 35% concentration (7 L/min) continuously for 48 hours via a face mask, and through a nasal cannula during meal times.
The primary outcome was normalization of right ventricle size (defined as an RV/LV diameter ratio less than 1.0 from the subcostal or apical view) at 48 hours after randomization. Secondary outcomes included change in the right ventricle/left ventricle diameter as measured at 48 hours and 7 days after randomization compared to baseline.
The proportion of patients with an RV/LV ratio of 1.0 or less at 48 hours was not significantly different between the intervention and control groups (42.4% vs. 21.6%, P = .08). Similarly, the proportion of patients with an RV/LV ratio of 1.0 or less at 7 days was not significantly different between the groups (76% vs. 70%).
The between-group reduction in RV/LV ratio was significantly greater in the supplemental oxygen group vs. the control group from baseline to 48 hours (0.28 vs. 0.12 P = .02).
However, the within-group mean RV/LV ratio was significantly reduced in both the supplemental oxygen group and the control group compared to baseline at 48 hours and at 7 days after randomization.
None of the patients experienced hemodynamic collapse or recurrent venous thromboembolism during the follow-up period.
The findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and open-label design, and lack of power to detect clinical outcomes, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that although supplemental oxygen had no significant impact of RV/LV normalization, “supplemental oxygen might increase the likelihood of reducing echocardiographic RV dilatation,” and the findings warrant a definitive clinical outcomes trial of supplemental oxygen vs. ambient air to improve outcomes in non-hypoxemic patients with intermediate-risk PE, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Dr. Barrios had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST
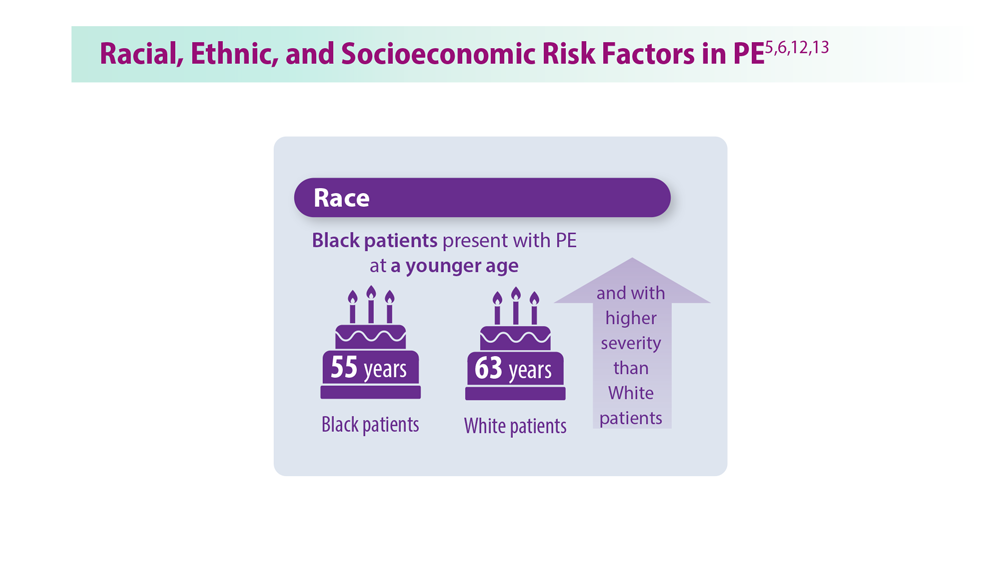
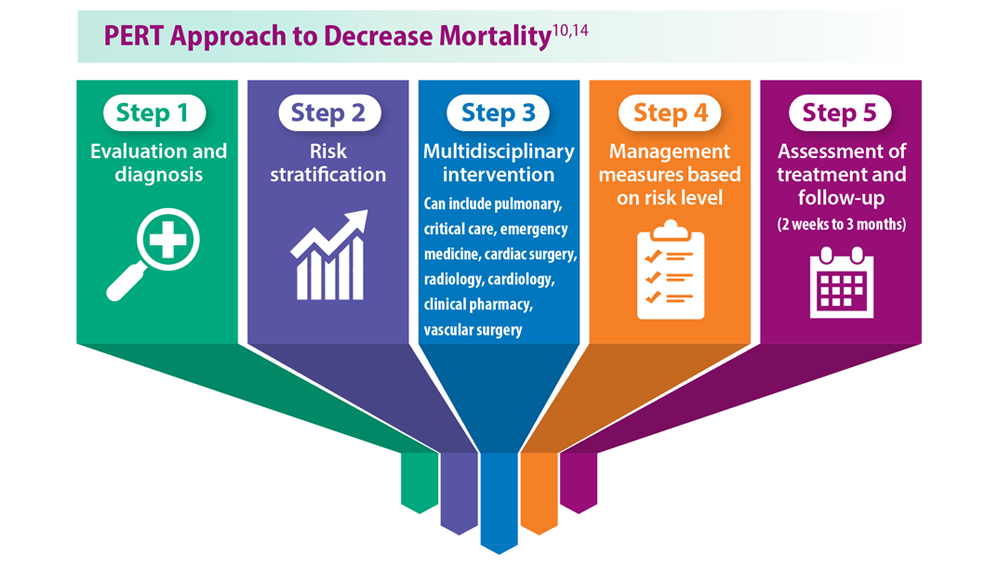
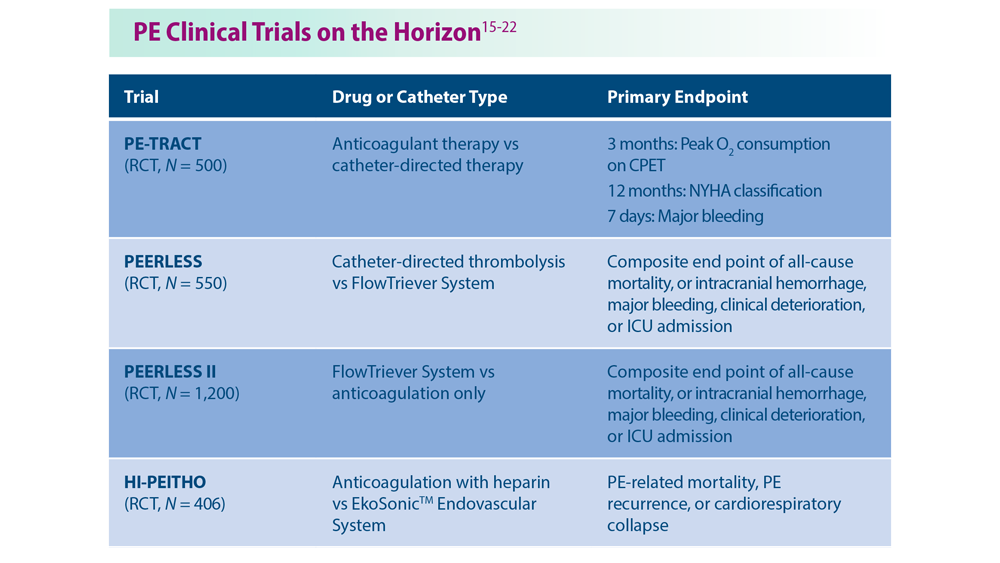
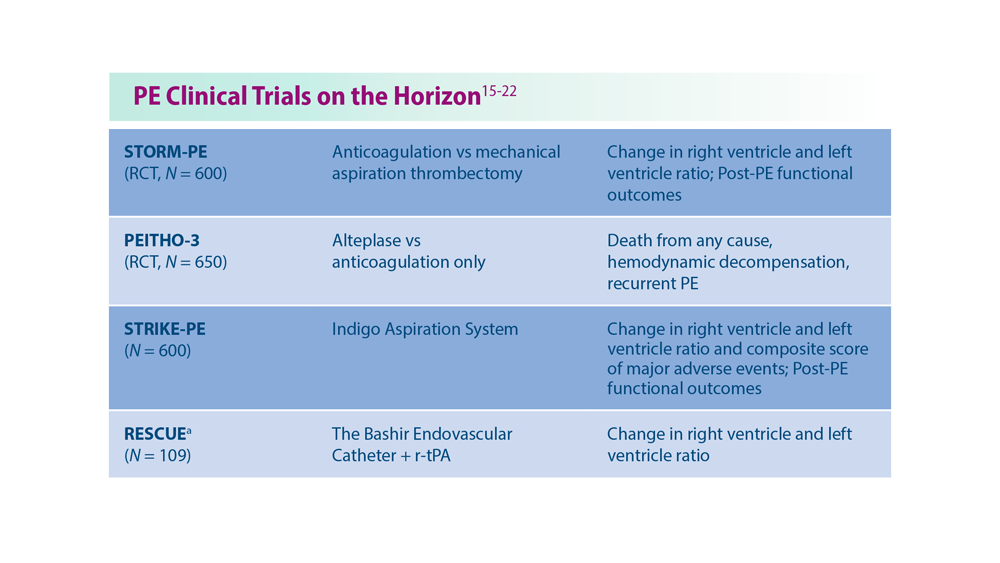
Decreasing Pulmonary Embolism-Related Mortality
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data and statistics on venous thromboembolism. Last reviewed June 28, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/data.html
- Becattini C et al. Chest. 2016;149(1):192-200. doi:10.1378/chest.15-0808
- Triantafyllou GA et al. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;42(2):183-198.doi:10.1055/s-0041-1722898
- Ng ACC et al. Respiration. 2013;85(5):408-416. doi:10.1159/000342024
- Phillips AR et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(17):e021818. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021818
- Wadhera RK et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(13):e021117. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021117
- Bashir R et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2022;15(23):2427-2436. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2022.09.011
- Patel NJ et al. Int J Cardiol. 2019;287:116-117. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.04.029
- Li X et al. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(10):838. doi:10.21037/atm-21-975
- Rivera-Lebron BN et al. Chest. 2021;159(1):347-355. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.07.065
- Noto JG, Rali P. Pulm Circ. 2022;12(1):e12021. doi:10.1002/pul2.12021
- Snyder DJ et al. Vasc Med. 2023;28(3):222-232. doi:10.1177/1358863X231157441
- Bikdeli B et al. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2023. doi:10.1055/s-0043-1764231
- Fleitas Sosa D et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2022;31(165):220023. doi:10.1183/16000617.0023-2022
- Pulmonary embolism - thrombus removal with catheter-directed therapy (PE-TRACT). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05591118
- The PEERLESS study (PEERLESS). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated Jun 23, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05111613
- Inari Medical, Inc. Inari Medical announces Peerless II, a randomized controlled trial evaluating clinical outcomes of the FlowTriever® system vs. anticoagulation in pulmonary embolism patients [press release]. Published May 22,2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://ir.inarimedical.com/news-releases/news-release-details/inari-medical-announces-peerless-ii-randomized-controlled-trial
- Ultrasound-facilitated, catheter-directed, thrombolysis in intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism (HI-PEITHO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04790370
- Comparison of two pulmonary embolism treatments. ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 31, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05684796
- Pulmonary Embolism International THrOmbolysis Study-3 (PEITHO-3).ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated June 8, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04430569
- Study of the long-term safety and outcomes of treating pulmonary embolism with the Indigo Aspiration System. ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04798261
- Bashir R et al. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2022;15(23):2427-2436. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2022.09.011
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data and statistics on venous thromboembolism. Last reviewed June 28, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/data.html
- Becattini C et al. Chest. 2016;149(1):192-200. doi:10.1378/chest.15-0808
- Triantafyllou GA et al. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;42(2):183-198.doi:10.1055/s-0041-1722898
- Ng ACC et al. Respiration. 2013;85(5):408-416. doi:10.1159/000342024
- Phillips AR et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(17):e021818. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021818
- Wadhera RK et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(13):e021117. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021117
- Bashir R et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2022;15(23):2427-2436. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2022.09.011
- Patel NJ et al. Int J Cardiol. 2019;287:116-117. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.04.029
- Li X et al. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(10):838. doi:10.21037/atm-21-975
- Rivera-Lebron BN et al. Chest. 2021;159(1):347-355. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.07.065
- Noto JG, Rali P. Pulm Circ. 2022;12(1):e12021. doi:10.1002/pul2.12021
- Snyder DJ et al. Vasc Med. 2023;28(3):222-232. doi:10.1177/1358863X231157441
- Bikdeli B et al. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2023. doi:10.1055/s-0043-1764231
- Fleitas Sosa D et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2022;31(165):220023. doi:10.1183/16000617.0023-2022
- Pulmonary embolism - thrombus removal with catheter-directed therapy (PE-TRACT). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05591118
- The PEERLESS study (PEERLESS). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated Jun 23, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05111613
- Inari Medical, Inc. Inari Medical announces Peerless II, a randomized controlled trial evaluating clinical outcomes of the FlowTriever® system vs. anticoagulation in pulmonary embolism patients [press release]. Published May 22,2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://ir.inarimedical.com/news-releases/news-release-details/inari-medical-announces-peerless-ii-randomized-controlled-trial
- Ultrasound-facilitated, catheter-directed, thrombolysis in intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism (HI-PEITHO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04790370
- Comparison of two pulmonary embolism treatments. ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 31, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05684796
- Pulmonary Embolism International THrOmbolysis Study-3 (PEITHO-3).ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated June 8, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04430569
- Study of the long-term safety and outcomes of treating pulmonary embolism with the Indigo Aspiration System. ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04798261
- Bashir R et al. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2022;15(23):2427-2436. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2022.09.011
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Data and statistics on venous thromboembolism. Last reviewed June 28, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/data.html
- Becattini C et al. Chest. 2016;149(1):192-200. doi:10.1378/chest.15-0808
- Triantafyllou GA et al. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;42(2):183-198.doi:10.1055/s-0041-1722898
- Ng ACC et al. Respiration. 2013;85(5):408-416. doi:10.1159/000342024
- Phillips AR et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(17):e021818. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021818
- Wadhera RK et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(13):e021117. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021117
- Bashir R et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2022;15(23):2427-2436. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2022.09.011
- Patel NJ et al. Int J Cardiol. 2019;287:116-117. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.04.029
- Li X et al. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(10):838. doi:10.21037/atm-21-975
- Rivera-Lebron BN et al. Chest. 2021;159(1):347-355. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.07.065
- Noto JG, Rali P. Pulm Circ. 2022;12(1):e12021. doi:10.1002/pul2.12021
- Snyder DJ et al. Vasc Med. 2023;28(3):222-232. doi:10.1177/1358863X231157441
- Bikdeli B et al. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2023. doi:10.1055/s-0043-1764231
- Fleitas Sosa D et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2022;31(165):220023. doi:10.1183/16000617.0023-2022
- Pulmonary embolism - thrombus removal with catheter-directed therapy (PE-TRACT). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05591118
- The PEERLESS study (PEERLESS). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated Jun 23, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05111613
- Inari Medical, Inc. Inari Medical announces Peerless II, a randomized controlled trial evaluating clinical outcomes of the FlowTriever® system vs. anticoagulation in pulmonary embolism patients [press release]. Published May 22,2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://ir.inarimedical.com/news-releases/news-release-details/inari-medical-announces-peerless-ii-randomized-controlled-trial
- Ultrasound-facilitated, catheter-directed, thrombolysis in intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism (HI-PEITHO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated July 17, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04790370
- Comparison of two pulmonary embolism treatments. ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 31, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05684796
- Pulmonary Embolism International THrOmbolysis Study-3 (PEITHO-3).ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated June 8, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04430569
- Study of the long-term safety and outcomes of treating pulmonary embolism with the Indigo Aspiration System. ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04798261
- Bashir R et al. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2022;15(23):2427-2436. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2022.09.011
Longer edoxaban may benefit cancer patients with distal DVT
Patients with active cancer and newly diagnosed isolated distal deep vein thrombosis (DVT) who received 12 months of edoxaban (Savaysa) had fewer thrombotic events at 1 year than those who received 3 months of treatment, without significantly increased bleeding, in the ONCO-DVT trial.
However, lead author Yugo Yamashita, MD, of Kyoto University noted that caution is needed when determining anticoagulation strategies in individual patients with distal DVT, especially those with high risk for bleeding.
Dr. Yamashita presented the results at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, and the trial was simultaneously published in the journal Circulation.
“This is the first and only randomized trial to show the superiority of longer duration over shorter duration of anticoagulation therapy for reducing thrombotic events in cancer patients with isolated distal DVT,” he said in a press briefing.
The results provide support for 12 months of edoxaban in patients with active cancer and isolated distal DVD, he said in an email.
However, “considering the risk of bleeding associated with anticoagulation therapy, physicians should make the decision of anticoagulation strategies for these patients based on risk-benefit balance of anticoagulation therapy in individual patients,” he stressed.
The take-home message for clinicians is that, “if you find minor DVT in cancer patients, please be careful, because their thrombotic risk was not low” in this trial, Dr. Yamashita said.
The study was conducted in Japan, so whether or not the results are generalizable to other populations is not clear. “Subgroup analysis based on body weight did not show any signal of different effect,” he noted, which suggests that the main results could be applied to other populations, including the U.S. population. However, “generalizability of the current results should be carried out carefully.”
Caution needed when translating findings into clinical practice
The assigned discussant, Teresa Lopez-Fernandez, MD, from La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, who was co-chairperson of 2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology, noted that the optimal anticoagulation therapy strategy is unclear in patients with cancer and isolated distal DVT.
“2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology and [European Society for Medical Oncology] guidelines from this year,” she said, “are both in agreement that we need to prolong anticoagulation [therapy to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE)] when active cancer exists, and particularly in patients with metastatic cancer. The problem is that none of this text refers specifically to distal DVT.”
The ONCO-DVT trial sheds light on this, but there are a few points to consider when interpreting the findings.
Major bleeding was slightly increased in the 12-month vs 3-month edoxaban groups, although this was not statistically significant, she noted. Moreover, 75% of the patients were treated with low-dose edoxaban, mainly due to their low weight. Also, bleeding risk probably differs in different cancer types.
“These are important things that we need to keep in mind when we try to transfer this data to [inform] our clinical practice,” Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said.
She drew attention to a recent study based on RIETE registry data that suggests that “isolated distal DVT is a big problem for patients with cancer in comparison with noncancer patients, where it seems it’s a low-risk problem.”
The main takeaways from ONCO-DVT, Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said, are that it confirms that cancer-associated isolated distal DVT is a marker of poor prognosis, and it supports the need for extended anticoagulation in patients with active, ongoing cancer and isolated distal DVT.
However, “we need to be cautious to try to really understand what the bleeding risks of these patients are,” she said, “particularly because it is not always easy to transfer the results from an Asian population to other populations.”
There is also a need for further studies with other doses, with other novel oral anticoagulants, and in patients at high risk for bleeding, in clinical practice.
Dr. Yamashita said that the study suggests that there is a potential benefit of prolonged duration of anticoagulant therapy for some patients with isolated distal DVT, but not all patients should receive this dosing strategy, because some patients may be at high risk for bleeding or VTE recurrence. A subanalysis of data from ONCO-DVT study should shed further light on this.
“We need to individualize our risk stratification,” Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said, adding that notably, “a lot of patients in the 12-month group did not continue with the 12-month treatment,” which may have affected bleeding results. Dr. Yamashita agreed.
Study design and findings
From April 2019 to June 2022, the researchers enrolled and randomly assigned 604 patients with active cancer who had newly diagnosed isolated distal DVT, confirmed by ultrasonography, and were scheduled for DVT treatment with anticoagulation therapy, at 60 centers.
Active cancer was defined as a cancer diagnosis or cancer treatment (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.) within 6 months of randomization, or current recurrence, local invasion, distant metastases, or hematopoietic malignancy without complete remission.
The most common reasons for ultrasonography were elevated D-dimer levels (62%) and suspected DVT because of symptoms (20%).
The patients had a mean age of 70.8 years and 28% were men. The most common cancer sites were ovaries (14%), uterus (13%), lung (11%), colon (9%), and pancreas (8%), followed by stomach, blood, and breast (each 5%).
The patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive 12 months or 3 months of oral edoxaban at a dose of 60 mg once daily or 30 mg once daily in patients with body weight of 60 kg or less, creatinine clearance of 30-50 mL/minute, or concomitant treatment with a potent P-glycoprotein inhibitor.
After excluding 3 patients who withdrew consent, 601 patients were included in the intention-to-treat population: 296 patients in the 12-month edoxaban group and 305 patients in the 3-month edoxaban group.
About 70% of patients had a body weight of 60 kg or less and about 22% had a creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min. About three quarters received the lower dose of edoxaban.
In the 12-month edoxaban group, 223 patients completed the 1-year follow-up (66 patients had died and 7 were lost to follow-up). In the 3-month edoxaban group, 224 patients completed the 1-year follow-up (77 had died and 4 were lost to follow-up).
In the 12-month edoxaban group, 41% of the patients had discontinued treatment by 12 months. In the 3-month edoxaban group, 41% of patients had discontinued treatment by 3 months.
The primary endpoint – a symptomatic recurrent VTE event or VTE-related death – occurred in 3 of the 222 patients (1.2%) in the 12-month edoxaban group and in 22 of the 210 (8.5%) in the 3-month edoxaban group (odds ratio,0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.03-0.44, P < .001). There were no VTE-related deaths.
The major secondary endpoint – major bleeding, according to International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis criteria – occurred in 28 of the 210 patients (10.2%) in the 12-month edoxaban group and in 22 of the 217 (7.6%) in the 3-month edoxaban group (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 0.75-2.41, P = NS).
The researchers acknowledged that study limitations include an open-label design, a lower-than-expected primary endpoint rate, and less than high adherence to edoxaban, as well as the need for caution when generalizing the results to other populations.
The study was funded by Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Yamashita disclosed receiving lecture fees from Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Daiichi Sankyo, and grant support from Bayer Healthcare and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Lopez-Fernandez disclosed receiving speaker fees from Phillips, Janssen, Daiichi Sankyo, Myocardial Solutions, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Beigene, and Bayer not related to this study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with active cancer and newly diagnosed isolated distal deep vein thrombosis (DVT) who received 12 months of edoxaban (Savaysa) had fewer thrombotic events at 1 year than those who received 3 months of treatment, without significantly increased bleeding, in the ONCO-DVT trial.
However, lead author Yugo Yamashita, MD, of Kyoto University noted that caution is needed when determining anticoagulation strategies in individual patients with distal DVT, especially those with high risk for bleeding.
Dr. Yamashita presented the results at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, and the trial was simultaneously published in the journal Circulation.
“This is the first and only randomized trial to show the superiority of longer duration over shorter duration of anticoagulation therapy for reducing thrombotic events in cancer patients with isolated distal DVT,” he said in a press briefing.
The results provide support for 12 months of edoxaban in patients with active cancer and isolated distal DVD, he said in an email.
However, “considering the risk of bleeding associated with anticoagulation therapy, physicians should make the decision of anticoagulation strategies for these patients based on risk-benefit balance of anticoagulation therapy in individual patients,” he stressed.
The take-home message for clinicians is that, “if you find minor DVT in cancer patients, please be careful, because their thrombotic risk was not low” in this trial, Dr. Yamashita said.
The study was conducted in Japan, so whether or not the results are generalizable to other populations is not clear. “Subgroup analysis based on body weight did not show any signal of different effect,” he noted, which suggests that the main results could be applied to other populations, including the U.S. population. However, “generalizability of the current results should be carried out carefully.”
Caution needed when translating findings into clinical practice
The assigned discussant, Teresa Lopez-Fernandez, MD, from La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, who was co-chairperson of 2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology, noted that the optimal anticoagulation therapy strategy is unclear in patients with cancer and isolated distal DVT.
“2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology and [European Society for Medical Oncology] guidelines from this year,” she said, “are both in agreement that we need to prolong anticoagulation [therapy to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE)] when active cancer exists, and particularly in patients with metastatic cancer. The problem is that none of this text refers specifically to distal DVT.”
The ONCO-DVT trial sheds light on this, but there are a few points to consider when interpreting the findings.
Major bleeding was slightly increased in the 12-month vs 3-month edoxaban groups, although this was not statistically significant, she noted. Moreover, 75% of the patients were treated with low-dose edoxaban, mainly due to their low weight. Also, bleeding risk probably differs in different cancer types.
“These are important things that we need to keep in mind when we try to transfer this data to [inform] our clinical practice,” Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said.
She drew attention to a recent study based on RIETE registry data that suggests that “isolated distal DVT is a big problem for patients with cancer in comparison with noncancer patients, where it seems it’s a low-risk problem.”
The main takeaways from ONCO-DVT, Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said, are that it confirms that cancer-associated isolated distal DVT is a marker of poor prognosis, and it supports the need for extended anticoagulation in patients with active, ongoing cancer and isolated distal DVT.
However, “we need to be cautious to try to really understand what the bleeding risks of these patients are,” she said, “particularly because it is not always easy to transfer the results from an Asian population to other populations.”
There is also a need for further studies with other doses, with other novel oral anticoagulants, and in patients at high risk for bleeding, in clinical practice.
Dr. Yamashita said that the study suggests that there is a potential benefit of prolonged duration of anticoagulant therapy for some patients with isolated distal DVT, but not all patients should receive this dosing strategy, because some patients may be at high risk for bleeding or VTE recurrence. A subanalysis of data from ONCO-DVT study should shed further light on this.
“We need to individualize our risk stratification,” Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said, adding that notably, “a lot of patients in the 12-month group did not continue with the 12-month treatment,” which may have affected bleeding results. Dr. Yamashita agreed.
Study design and findings
From April 2019 to June 2022, the researchers enrolled and randomly assigned 604 patients with active cancer who had newly diagnosed isolated distal DVT, confirmed by ultrasonography, and were scheduled for DVT treatment with anticoagulation therapy, at 60 centers.
Active cancer was defined as a cancer diagnosis or cancer treatment (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.) within 6 months of randomization, or current recurrence, local invasion, distant metastases, or hematopoietic malignancy without complete remission.
The most common reasons for ultrasonography were elevated D-dimer levels (62%) and suspected DVT because of symptoms (20%).
The patients had a mean age of 70.8 years and 28% were men. The most common cancer sites were ovaries (14%), uterus (13%), lung (11%), colon (9%), and pancreas (8%), followed by stomach, blood, and breast (each 5%).
The patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive 12 months or 3 months of oral edoxaban at a dose of 60 mg once daily or 30 mg once daily in patients with body weight of 60 kg or less, creatinine clearance of 30-50 mL/minute, or concomitant treatment with a potent P-glycoprotein inhibitor.
After excluding 3 patients who withdrew consent, 601 patients were included in the intention-to-treat population: 296 patients in the 12-month edoxaban group and 305 patients in the 3-month edoxaban group.
About 70% of patients had a body weight of 60 kg or less and about 22% had a creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min. About three quarters received the lower dose of edoxaban.
In the 12-month edoxaban group, 223 patients completed the 1-year follow-up (66 patients had died and 7 were lost to follow-up). In the 3-month edoxaban group, 224 patients completed the 1-year follow-up (77 had died and 4 were lost to follow-up).
In the 12-month edoxaban group, 41% of the patients had discontinued treatment by 12 months. In the 3-month edoxaban group, 41% of patients had discontinued treatment by 3 months.
The primary endpoint – a symptomatic recurrent VTE event or VTE-related death – occurred in 3 of the 222 patients (1.2%) in the 12-month edoxaban group and in 22 of the 210 (8.5%) in the 3-month edoxaban group (odds ratio,0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.03-0.44, P < .001). There were no VTE-related deaths.
The major secondary endpoint – major bleeding, according to International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis criteria – occurred in 28 of the 210 patients (10.2%) in the 12-month edoxaban group and in 22 of the 217 (7.6%) in the 3-month edoxaban group (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 0.75-2.41, P = NS).
The researchers acknowledged that study limitations include an open-label design, a lower-than-expected primary endpoint rate, and less than high adherence to edoxaban, as well as the need for caution when generalizing the results to other populations.
The study was funded by Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Yamashita disclosed receiving lecture fees from Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Daiichi Sankyo, and grant support from Bayer Healthcare and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Lopez-Fernandez disclosed receiving speaker fees from Phillips, Janssen, Daiichi Sankyo, Myocardial Solutions, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Beigene, and Bayer not related to this study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with active cancer and newly diagnosed isolated distal deep vein thrombosis (DVT) who received 12 months of edoxaban (Savaysa) had fewer thrombotic events at 1 year than those who received 3 months of treatment, without significantly increased bleeding, in the ONCO-DVT trial.
However, lead author Yugo Yamashita, MD, of Kyoto University noted that caution is needed when determining anticoagulation strategies in individual patients with distal DVT, especially those with high risk for bleeding.
Dr. Yamashita presented the results at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, and the trial was simultaneously published in the journal Circulation.
“This is the first and only randomized trial to show the superiority of longer duration over shorter duration of anticoagulation therapy for reducing thrombotic events in cancer patients with isolated distal DVT,” he said in a press briefing.
The results provide support for 12 months of edoxaban in patients with active cancer and isolated distal DVD, he said in an email.
However, “considering the risk of bleeding associated with anticoagulation therapy, physicians should make the decision of anticoagulation strategies for these patients based on risk-benefit balance of anticoagulation therapy in individual patients,” he stressed.
The take-home message for clinicians is that, “if you find minor DVT in cancer patients, please be careful, because their thrombotic risk was not low” in this trial, Dr. Yamashita said.
The study was conducted in Japan, so whether or not the results are generalizable to other populations is not clear. “Subgroup analysis based on body weight did not show any signal of different effect,” he noted, which suggests that the main results could be applied to other populations, including the U.S. population. However, “generalizability of the current results should be carried out carefully.”
Caution needed when translating findings into clinical practice
The assigned discussant, Teresa Lopez-Fernandez, MD, from La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, who was co-chairperson of 2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology, noted that the optimal anticoagulation therapy strategy is unclear in patients with cancer and isolated distal DVT.
“2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology and [European Society for Medical Oncology] guidelines from this year,” she said, “are both in agreement that we need to prolong anticoagulation [therapy to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE)] when active cancer exists, and particularly in patients with metastatic cancer. The problem is that none of this text refers specifically to distal DVT.”
The ONCO-DVT trial sheds light on this, but there are a few points to consider when interpreting the findings.
Major bleeding was slightly increased in the 12-month vs 3-month edoxaban groups, although this was not statistically significant, she noted. Moreover, 75% of the patients were treated with low-dose edoxaban, mainly due to their low weight. Also, bleeding risk probably differs in different cancer types.
“These are important things that we need to keep in mind when we try to transfer this data to [inform] our clinical practice,” Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said.
She drew attention to a recent study based on RIETE registry data that suggests that “isolated distal DVT is a big problem for patients with cancer in comparison with noncancer patients, where it seems it’s a low-risk problem.”
The main takeaways from ONCO-DVT, Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said, are that it confirms that cancer-associated isolated distal DVT is a marker of poor prognosis, and it supports the need for extended anticoagulation in patients with active, ongoing cancer and isolated distal DVT.
However, “we need to be cautious to try to really understand what the bleeding risks of these patients are,” she said, “particularly because it is not always easy to transfer the results from an Asian population to other populations.”
There is also a need for further studies with other doses, with other novel oral anticoagulants, and in patients at high risk for bleeding, in clinical practice.
Dr. Yamashita said that the study suggests that there is a potential benefit of prolonged duration of anticoagulant therapy for some patients with isolated distal DVT, but not all patients should receive this dosing strategy, because some patients may be at high risk for bleeding or VTE recurrence. A subanalysis of data from ONCO-DVT study should shed further light on this.
“We need to individualize our risk stratification,” Dr. Lopez-Fernandez said, adding that notably, “a lot of patients in the 12-month group did not continue with the 12-month treatment,” which may have affected bleeding results. Dr. Yamashita agreed.
Study design and findings
From April 2019 to June 2022, the researchers enrolled and randomly assigned 604 patients with active cancer who had newly diagnosed isolated distal DVT, confirmed by ultrasonography, and were scheduled for DVT treatment with anticoagulation therapy, at 60 centers.
Active cancer was defined as a cancer diagnosis or cancer treatment (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.) within 6 months of randomization, or current recurrence, local invasion, distant metastases, or hematopoietic malignancy without complete remission.
The most common reasons for ultrasonography were elevated D-dimer levels (62%) and suspected DVT because of symptoms (20%).
The patients had a mean age of 70.8 years and 28% were men. The most common cancer sites were ovaries (14%), uterus (13%), lung (11%), colon (9%), and pancreas (8%), followed by stomach, blood, and breast (each 5%).
The patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive 12 months or 3 months of oral edoxaban at a dose of 60 mg once daily or 30 mg once daily in patients with body weight of 60 kg or less, creatinine clearance of 30-50 mL/minute, or concomitant treatment with a potent P-glycoprotein inhibitor.
After excluding 3 patients who withdrew consent, 601 patients were included in the intention-to-treat population: 296 patients in the 12-month edoxaban group and 305 patients in the 3-month edoxaban group.
About 70% of patients had a body weight of 60 kg or less and about 22% had a creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min. About three quarters received the lower dose of edoxaban.
In the 12-month edoxaban group, 223 patients completed the 1-year follow-up (66 patients had died and 7 were lost to follow-up). In the 3-month edoxaban group, 224 patients completed the 1-year follow-up (77 had died and 4 were lost to follow-up).
In the 12-month edoxaban group, 41% of the patients had discontinued treatment by 12 months. In the 3-month edoxaban group, 41% of patients had discontinued treatment by 3 months.
The primary endpoint – a symptomatic recurrent VTE event or VTE-related death – occurred in 3 of the 222 patients (1.2%) in the 12-month edoxaban group and in 22 of the 210 (8.5%) in the 3-month edoxaban group (odds ratio,0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.03-0.44, P < .001). There were no VTE-related deaths.
The major secondary endpoint – major bleeding, according to International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis criteria – occurred in 28 of the 210 patients (10.2%) in the 12-month edoxaban group and in 22 of the 217 (7.6%) in the 3-month edoxaban group (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 0.75-2.41, P = NS).
The researchers acknowledged that study limitations include an open-label design, a lower-than-expected primary endpoint rate, and less than high adherence to edoxaban, as well as the need for caution when generalizing the results to other populations.
The study was funded by Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Yamashita disclosed receiving lecture fees from Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Daiichi Sankyo, and grant support from Bayer Healthcare and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Lopez-Fernandez disclosed receiving speaker fees from Phillips, Janssen, Daiichi Sankyo, Myocardial Solutions, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Beigene, and Bayer not related to this study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2023
Factor XI inhibitors: The promise of a truly safe anticoagulant?
The quest to find an anticoagulant that can prevent strokes, cardiovascular events, and venous thrombosis without significantly increasing risk of bleeding is something of a holy grail in cardiovascular medicine. Could the latest focus of interest in this field – the factor XI inhibitors – be the long–sought-after answer?
Topline results from the largest study so far of a factor XI inhibitor – released on Sep. 18 – are indeed very encouraging. The phase 2 AZALEA-TIMI 71 study was stopped early because of an “overwhelming” reduction in major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding shown with the factor XI inhibitor abelacimab (Anthos), compared with apixaban for patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Very few other data from this study have yet been released. Full results are due to be presented at the scientific sessions of the American Heart Association in November. Researchers in the field are optimistic that this new class of drugs may allow millions more patients who are at risk of thrombotic events but are concerned about bleeding risk to be treated, with a consequent reduction in strokes and possibly cardiovascular events as well.
Why factor XI?
In natural physiology, there are two ongoing processes: hemostasis – a set of actions that cause bleeding to stop after an injury – and thrombosis – a pathologic clotting process in which thrombus is formed and causes a stroke, MI, or deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
In patients prone to pathologic clotting, such as those with AFib, the balance of these two processes has shifted toward thrombosis, so anticoagulants are used to reduce the thrombotic risks. For many years, the only available oral anticoagulant was warfarin, a vitamin K antagonist that was very effective at preventing strokes but that comes with a high risk for bleeding, including intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) and fatal bleeding.
The introduction of the direct-acting anticoagulants (DOACs) a few years ago was a step forward in that these drugs have been shown to be as effective as warfarin but are associated with a lower risk of bleeding, particularly of ICH and fatal bleeding. But they still cause bleeding, and concerns over that risk of bleeding prevent millions of patients from taking these drugs and receiving protection against stroke.
John Alexander, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., a researcher active in this area, notes that “while the DOACs cause less bleeding than warfarin, they still cause two or three times more bleeding than placebo, and there is a huge, unmet need for safer anticoagulants that don’t cause as much bleeding. We are hopeful that factor XI inhibitors might be those anticoagulants.”
The lead investigator the AZALEA study, Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, explained why it is thought that factor XI inhibitors may be different.
“There’s a lot of different clotting factors, and most of them converge in a central pathway. The problem, therefore, with anticoagulants used to date that block one of these factors is that they prevent clotting but also cause bleeding.
“It has been discovered that factor XI has a really unique position in the cascade of how our body forms clots in that it seems to be important in clot formation, but it doesn’t seem to play a major role in our ability to heal and repair blood vessels.”
Another doctor involved in the field, Manesh Patel, MD, chief of cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, added, “We think that factor XI inhibitors may prevent the pathologic formation of thrombosis while allowing formation of thrombus for natural hemostasis to prevent bleeding. That is why they are so promising.”
This correlates with epidemiologic data suggesting that patients with a genetic factor XI deficiency have low rates of stroke and MI but don’t appear to bleed spontaneously, Dr. Patel notes.
Candidates in development
The pharmaceutical industry is on the case with several factor XI inhibitors now in clinical development. At present, three main candidates lead the field. These are abelacimab (Anthos), a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month; and two small molecules, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer), which are both given orally.
Phase 3 trials of these three factor XI inhibitors have recently started for a variety of thrombotic indications, including the prevention of stroke in patients with AFib, prevention of recurrent stroke in patients with ischemic stroke, and prevention of future cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Dr. Alexander, who has been involved in clinical trials of both milvexian and asundexian, commented: “We have pretty good data from a number of phase 2 trials now that these factor XI inhibitors at the doses used in these studies cause a lot less bleeding than therapeutic doses of DOACs and low-molecular-weight heparins.”
He pointed out that, in addition to the AZALEA trial with abelacimab, the phase 2 PACIFIC program of studies has shown less bleeding with asundexian than with apixaban in patients with AFib and a similar amount of bleeding as placebo in ACS/stroke patients on top of antiplatelet therapy. Milvexian has also shown similar results in the AXIOMATIC program of studies.
Dr. Ruff noted that the biggest need for new anticoagulants in general is in the AFib population. “Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common medical conditions in the world. Approximately one in every three people will develop AFib in their lifetime, and it is associated with more than a fivefold increased risk of stroke. But up to half of patients with AFib currently do not take anticoagulants because of concerns about bleeding risks, so these patients are being left unprotected from stroke risk.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that the AZALEA study was the largest and longest study of a factor XI inhibitor to date; 1,287 patients were followed for a median of 2 years.
“This was the first trial of long-term administration of factor XI inhibitor against a full-dose DOAC, and it was stopped because of an overwhelming reduction in a major bleeding with abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban,” he noted. “That is very encouraging. It looks like our quest to develop a safe anticoagulant with much lower rates of bleeding, compared with standard of care, seems to have been borne out. I think the field is very excited that we may finally have something that protects patients from thrombosis whilst being much safer than current agents.”
While all this sounds very promising, for these drugs to be successful, in addition to reducing bleeding risk, they will also have to be effective at preventing strokes and other thrombotic events.
“While we are pretty sure that factor XI inhibitors will cause less bleeding than current anticoagulants, what is unknown still is how effective they will be at preventing pathologic blood clots,” Dr. Alexander points out.
“We have some data from studies of these drugs in DVT prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery which suggest that they are effective in preventing blood clots in that scenario. But we don’t know yet about whether they can prevent pathologic blood clots that occur in AFib patients or in poststroke or post-ACS patients. Phase 3 studies are now underway with these three leading drug candidates which will answer some of these questions.”
Dr. Patel agrees that the efficacy data in the phase 3 trials will be key to the success of these drugs. “That is a very important part of the puzzle that is still missing,” he says.
Dr. Ruff notes that the AZALEA study will provide some data on efficacy. “But we already know that in the orthopedic surgery trials there was a 70%-80% reduction in VTE with abelacimab (at the 150-mg dose going forward) vs. prophylactic doses of low-molecular-weight heparin. And we know from the DOACs that the doses preventing clots on the venous side also translated into preventing strokes on the [AFib] side. So that is very encouraging,” Dr. Ruff adds.
Potential indications
The three leading factor XI inhibitors have slightly different phase 3 development programs.
Dr. Ruff notes that not every agent is being investigated in phase 3 trials for all the potential indications, but all three are going for the AFib indication. “This is by far the biggest population, the biggest market, and the biggest clinical need for these agents,” he says.
While the milvexian and asundexian trials are using an active comparator – pitting the factor XI inhibitors against apixaban in AFib patients – the Anthos LILAC trial is taking a slightly different approach and is comparing abelacimab with placebo in patients with AFib who are not currently taking an anticoagulant because of concerns about bleeding risk.
Janssen/BMS is conducting two other phase 3 trials of milvexian in their LIBREXIA phase 3 program. Those trials involve poststroke patients and ACS patients. Bayer is also involved in a poststroke trial of asundexian as part of its OCEANIC phase 3 program.
Dr. Ruff points out that anticoagulants currently do not have a large role in the poststroke or post-ACS population. “But the hope is that, if factor XI inhibitors are so safe, then there will be more enthusiasm about using an anticoagulant on top of antiplatelet therapy, which is the cornerstone of therapy in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.”
In addition to its phase 3 LILAC study in patients with AFib, Anthos is conducting two major phase 3 trials with abelacimab for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism.
Dr. Ruff notes that the indication of postsurgery or general prevention of VTE is not being pursued at present.
“The orthopedic surgery studies were done mainly for dose finding and proof of principle reasons,” he explains. “In orthopedic surgery the window for anticoagulation is quite short – a few weeks or months. And for the prevention of recurrent VTE in general in the community, those people are at a relatively low risk of bleeding, so there may not be much advantage of the factor XI inhibitors, whereas AFib patients and those with stroke or ACS are usually older and have a much higher bleeding risk. I think this is where the advantages of an anticoagulant with a lower bleeding risk are most needed.”
Dr. Alexander points out that to date anticoagulants have shown more efficacy in venous clotting, which appears to be more dependent on coagulation factors and less dependent on platelets. “Atrial fibrillation is a mix between venous and arterial clotting, but it has more similarities to venous, so I think AFib is a place where new anticoagulants such as the factor XI inhibitors are more likely to have success,” he suggests.
“So far, anticoagulants have had a less clear long-term role in the poststroke and post-ACS populations, so these indications may be a more difficult goal,” he added.
The phase 3 studies are just starting and will take a few years before results are known.
Differences between the agents
The three factor XI inhibitors also have some differences. Dr. Ruff points out that most important will be the safety and efficacy of the drugs in phase 3 trials.
“Early data suggest that the various agents being developed may not have equal inhibition of factor XI. The monoclonal antibody abelacimab may produce a higher degree of inhibition than the small molecules. But we don’t know if that matters or not – whether we need to achieve a certain threshold to prevent stroke. The efficacy and safety data from the phase 3 trials are what will primarily guide use.”
There are also differences in formulations and dosage. Abelacimab is administered by subcutaneous injection once a month and has a long duration of activity, whereas the small molecules are taken orally and their duration of action is much shorter.
Dr. Ruff notes: “If these drugs cause bleeding, having a long-acting drug like abelacimab could be a disadvantage because we wouldn’t be able to stop it. But if they are very safe with regard to bleeding, then having the drug hang around for a long time is not necessarily a disadvantage, and it may improve compliance. These older patients often miss doses, and with a shorter-acting drug, that will mean they will be unprotected from stroke risk for a period of time, so there is a trade-off here.”
Dr. Ruff says that the AZALEA phase 2 study will provide some data on patients being managed around procedures. “The hope is that these drugs are so safe that they will not have to be stopped for procedures. And then the compliance issue of a once-a-month dosing would be an advantage.”
Dr. Patel says he believes there is a place for different formations. “Some patients may prefer a once-monthly injection; others will prefer a daily tablet. It may come down to patient preference, but a lot will depend on the study results with the different agents,” he commented.
What effect could these drugs have?
If these drugs do show efficacy in these phase 3 trials, what difference will they make to clinical practice? The potential appears to be very large.
“If these drugs are as effective at preventing strokes as DOACs, they will be a huge breakthrough, and there is good reason to think they would replace the DOACs,” Dr. Alexander says. “It would be a really big deal to have an anticoagulant that causes almost no bleeding and could prevent clots as well as the DOACs. This would enable a lot more patients to receive protection against stroke.”
Dr. Alexander believes the surgery studies are hopeful. “They show that the factor XI inhibitors are doing something to prevent blood clots. The big question is whether they are as effective as what we already have for the prevention of stroke and if not, what is the trade-off with bleeding?”
He points out that, even if the factor XI inhibitors are not as effective as DOACs but are found to be much safer, they might still have a potential clinical role, especially for those patients who currently do not take an anticoagulant because of concerns regarding bleeding.
But Dr. Patel points out that there is always the issue of costs with new drugs. “New drugs are always expensive. The DOACS are just about to become generic, and there will inevitably be concerns about access to an expensive new therapy.”
Dr. Alexander adds: “Yes, costs could be an issue, but a safer drug will definitely help to get more patients treated and in preventing more strokes, which would be a great thing.”
Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an adviser to Bayer (asundexian) and Janssen (milvexian). Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer. Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AFib executive committee for BMS/Janssen, and has been on an advisory board for Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The quest to find an anticoagulant that can prevent strokes, cardiovascular events, and venous thrombosis without significantly increasing risk of bleeding is something of a holy grail in cardiovascular medicine. Could the latest focus of interest in this field – the factor XI inhibitors – be the long–sought-after answer?
Topline results from the largest study so far of a factor XI inhibitor – released on Sep. 18 – are indeed very encouraging. The phase 2 AZALEA-TIMI 71 study was stopped early because of an “overwhelming” reduction in major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding shown with the factor XI inhibitor abelacimab (Anthos), compared with apixaban for patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Very few other data from this study have yet been released. Full results are due to be presented at the scientific sessions of the American Heart Association in November. Researchers in the field are optimistic that this new class of drugs may allow millions more patients who are at risk of thrombotic events but are concerned about bleeding risk to be treated, with a consequent reduction in strokes and possibly cardiovascular events as well.
Why factor XI?
In natural physiology, there are two ongoing processes: hemostasis – a set of actions that cause bleeding to stop after an injury – and thrombosis – a pathologic clotting process in which thrombus is formed and causes a stroke, MI, or deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
In patients prone to pathologic clotting, such as those with AFib, the balance of these two processes has shifted toward thrombosis, so anticoagulants are used to reduce the thrombotic risks. For many years, the only available oral anticoagulant was warfarin, a vitamin K antagonist that was very effective at preventing strokes but that comes with a high risk for bleeding, including intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) and fatal bleeding.
The introduction of the direct-acting anticoagulants (DOACs) a few years ago was a step forward in that these drugs have been shown to be as effective as warfarin but are associated with a lower risk of bleeding, particularly of ICH and fatal bleeding. But they still cause bleeding, and concerns over that risk of bleeding prevent millions of patients from taking these drugs and receiving protection against stroke.
John Alexander, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., a researcher active in this area, notes that “while the DOACs cause less bleeding than warfarin, they still cause two or three times more bleeding than placebo, and there is a huge, unmet need for safer anticoagulants that don’t cause as much bleeding. We are hopeful that factor XI inhibitors might be those anticoagulants.”
The lead investigator the AZALEA study, Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, explained why it is thought that factor XI inhibitors may be different.
“There’s a lot of different clotting factors, and most of them converge in a central pathway. The problem, therefore, with anticoagulants used to date that block one of these factors is that they prevent clotting but also cause bleeding.
“It has been discovered that factor XI has a really unique position in the cascade of how our body forms clots in that it seems to be important in clot formation, but it doesn’t seem to play a major role in our ability to heal and repair blood vessels.”
Another doctor involved in the field, Manesh Patel, MD, chief of cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, added, “We think that factor XI inhibitors may prevent the pathologic formation of thrombosis while allowing formation of thrombus for natural hemostasis to prevent bleeding. That is why they are so promising.”
This correlates with epidemiologic data suggesting that patients with a genetic factor XI deficiency have low rates of stroke and MI but don’t appear to bleed spontaneously, Dr. Patel notes.
Candidates in development
The pharmaceutical industry is on the case with several factor XI inhibitors now in clinical development. At present, three main candidates lead the field. These are abelacimab (Anthos), a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month; and two small molecules, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer), which are both given orally.
Phase 3 trials of these three factor XI inhibitors have recently started for a variety of thrombotic indications, including the prevention of stroke in patients with AFib, prevention of recurrent stroke in patients with ischemic stroke, and prevention of future cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Dr. Alexander, who has been involved in clinical trials of both milvexian and asundexian, commented: “We have pretty good data from a number of phase 2 trials now that these factor XI inhibitors at the doses used in these studies cause a lot less bleeding than therapeutic doses of DOACs and low-molecular-weight heparins.”
He pointed out that, in addition to the AZALEA trial with abelacimab, the phase 2 PACIFIC program of studies has shown less bleeding with asundexian than with apixaban in patients with AFib and a similar amount of bleeding as placebo in ACS/stroke patients on top of antiplatelet therapy. Milvexian has also shown similar results in the AXIOMATIC program of studies.
Dr. Ruff noted that the biggest need for new anticoagulants in general is in the AFib population. “Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common medical conditions in the world. Approximately one in every three people will develop AFib in their lifetime, and it is associated with more than a fivefold increased risk of stroke. But up to half of patients with AFib currently do not take anticoagulants because of concerns about bleeding risks, so these patients are being left unprotected from stroke risk.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that the AZALEA study was the largest and longest study of a factor XI inhibitor to date; 1,287 patients were followed for a median of 2 years.
“This was the first trial of long-term administration of factor XI inhibitor against a full-dose DOAC, and it was stopped because of an overwhelming reduction in a major bleeding with abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban,” he noted. “That is very encouraging. It looks like our quest to develop a safe anticoagulant with much lower rates of bleeding, compared with standard of care, seems to have been borne out. I think the field is very excited that we may finally have something that protects patients from thrombosis whilst being much safer than current agents.”
While all this sounds very promising, for these drugs to be successful, in addition to reducing bleeding risk, they will also have to be effective at preventing strokes and other thrombotic events.
“While we are pretty sure that factor XI inhibitors will cause less bleeding than current anticoagulants, what is unknown still is how effective they will be at preventing pathologic blood clots,” Dr. Alexander points out.
“We have some data from studies of these drugs in DVT prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery which suggest that they are effective in preventing blood clots in that scenario. But we don’t know yet about whether they can prevent pathologic blood clots that occur in AFib patients or in poststroke or post-ACS patients. Phase 3 studies are now underway with these three leading drug candidates which will answer some of these questions.”
Dr. Patel agrees that the efficacy data in the phase 3 trials will be key to the success of these drugs. “That is a very important part of the puzzle that is still missing,” he says.
Dr. Ruff notes that the AZALEA study will provide some data on efficacy. “But we already know that in the orthopedic surgery trials there was a 70%-80% reduction in VTE with abelacimab (at the 150-mg dose going forward) vs. prophylactic doses of low-molecular-weight heparin. And we know from the DOACs that the doses preventing clots on the venous side also translated into preventing strokes on the [AFib] side. So that is very encouraging,” Dr. Ruff adds.
Potential indications
The three leading factor XI inhibitors have slightly different phase 3 development programs.
Dr. Ruff notes that not every agent is being investigated in phase 3 trials for all the potential indications, but all three are going for the AFib indication. “This is by far the biggest population, the biggest market, and the biggest clinical need for these agents,” he says.
While the milvexian and asundexian trials are using an active comparator – pitting the factor XI inhibitors against apixaban in AFib patients – the Anthos LILAC trial is taking a slightly different approach and is comparing abelacimab with placebo in patients with AFib who are not currently taking an anticoagulant because of concerns about bleeding risk.
Janssen/BMS is conducting two other phase 3 trials of milvexian in their LIBREXIA phase 3 program. Those trials involve poststroke patients and ACS patients. Bayer is also involved in a poststroke trial of asundexian as part of its OCEANIC phase 3 program.
Dr. Ruff points out that anticoagulants currently do not have a large role in the poststroke or post-ACS population. “But the hope is that, if factor XI inhibitors are so safe, then there will be more enthusiasm about using an anticoagulant on top of antiplatelet therapy, which is the cornerstone of therapy in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.”
In addition to its phase 3 LILAC study in patients with AFib, Anthos is conducting two major phase 3 trials with abelacimab for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism.
Dr. Ruff notes that the indication of postsurgery or general prevention of VTE is not being pursued at present.
“The orthopedic surgery studies were done mainly for dose finding and proof of principle reasons,” he explains. “In orthopedic surgery the window for anticoagulation is quite short – a few weeks or months. And for the prevention of recurrent VTE in general in the community, those people are at a relatively low risk of bleeding, so there may not be much advantage of the factor XI inhibitors, whereas AFib patients and those with stroke or ACS are usually older and have a much higher bleeding risk. I think this is where the advantages of an anticoagulant with a lower bleeding risk are most needed.”
Dr. Alexander points out that to date anticoagulants have shown more efficacy in venous clotting, which appears to be more dependent on coagulation factors and less dependent on platelets. “Atrial fibrillation is a mix between venous and arterial clotting, but it has more similarities to venous, so I think AFib is a place where new anticoagulants such as the factor XI inhibitors are more likely to have success,” he suggests.
“So far, anticoagulants have had a less clear long-term role in the poststroke and post-ACS populations, so these indications may be a more difficult goal,” he added.
The phase 3 studies are just starting and will take a few years before results are known.
Differences between the agents
The three factor XI inhibitors also have some differences. Dr. Ruff points out that most important will be the safety and efficacy of the drugs in phase 3 trials.
“Early data suggest that the various agents being developed may not have equal inhibition of factor XI. The monoclonal antibody abelacimab may produce a higher degree of inhibition than the small molecules. But we don’t know if that matters or not – whether we need to achieve a certain threshold to prevent stroke. The efficacy and safety data from the phase 3 trials are what will primarily guide use.”
There are also differences in formulations and dosage. Abelacimab is administered by subcutaneous injection once a month and has a long duration of activity, whereas the small molecules are taken orally and their duration of action is much shorter.
Dr. Ruff notes: “If these drugs cause bleeding, having a long-acting drug like abelacimab could be a disadvantage because we wouldn’t be able to stop it. But if they are very safe with regard to bleeding, then having the drug hang around for a long time is not necessarily a disadvantage, and it may improve compliance. These older patients often miss doses, and with a shorter-acting drug, that will mean they will be unprotected from stroke risk for a period of time, so there is a trade-off here.”
Dr. Ruff says that the AZALEA phase 2 study will provide some data on patients being managed around procedures. “The hope is that these drugs are so safe that they will not have to be stopped for procedures. And then the compliance issue of a once-a-month dosing would be an advantage.”
Dr. Patel says he believes there is a place for different formations. “Some patients may prefer a once-monthly injection; others will prefer a daily tablet. It may come down to patient preference, but a lot will depend on the study results with the different agents,” he commented.
What effect could these drugs have?
If these drugs do show efficacy in these phase 3 trials, what difference will they make to clinical practice? The potential appears to be very large.
“If these drugs are as effective at preventing strokes as DOACs, they will be a huge breakthrough, and there is good reason to think they would replace the DOACs,” Dr. Alexander says. “It would be a really big deal to have an anticoagulant that causes almost no bleeding and could prevent clots as well as the DOACs. This would enable a lot more patients to receive protection against stroke.”
Dr. Alexander believes the surgery studies are hopeful. “They show that the factor XI inhibitors are doing something to prevent blood clots. The big question is whether they are as effective as what we already have for the prevention of stroke and if not, what is the trade-off with bleeding?”
He points out that, even if the factor XI inhibitors are not as effective as DOACs but are found to be much safer, they might still have a potential clinical role, especially for those patients who currently do not take an anticoagulant because of concerns regarding bleeding.
But Dr. Patel points out that there is always the issue of costs with new drugs. “New drugs are always expensive. The DOACS are just about to become generic, and there will inevitably be concerns about access to an expensive new therapy.”
Dr. Alexander adds: “Yes, costs could be an issue, but a safer drug will definitely help to get more patients treated and in preventing more strokes, which would be a great thing.”
Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an adviser to Bayer (asundexian) and Janssen (milvexian). Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer. Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AFib executive committee for BMS/Janssen, and has been on an advisory board for Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The quest to find an anticoagulant that can prevent strokes, cardiovascular events, and venous thrombosis without significantly increasing risk of bleeding is something of a holy grail in cardiovascular medicine. Could the latest focus of interest in this field – the factor XI inhibitors – be the long–sought-after answer?
Topline results from the largest study so far of a factor XI inhibitor – released on Sep. 18 – are indeed very encouraging. The phase 2 AZALEA-TIMI 71 study was stopped early because of an “overwhelming” reduction in major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding shown with the factor XI inhibitor abelacimab (Anthos), compared with apixaban for patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Very few other data from this study have yet been released. Full results are due to be presented at the scientific sessions of the American Heart Association in November. Researchers in the field are optimistic that this new class of drugs may allow millions more patients who are at risk of thrombotic events but are concerned about bleeding risk to be treated, with a consequent reduction in strokes and possibly cardiovascular events as well.
Why factor XI?
In natural physiology, there are two ongoing processes: hemostasis – a set of actions that cause bleeding to stop after an injury – and thrombosis – a pathologic clotting process in which thrombus is formed and causes a stroke, MI, or deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
In patients prone to pathologic clotting, such as those with AFib, the balance of these two processes has shifted toward thrombosis, so anticoagulants are used to reduce the thrombotic risks. For many years, the only available oral anticoagulant was warfarin, a vitamin K antagonist that was very effective at preventing strokes but that comes with a high risk for bleeding, including intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) and fatal bleeding.
The introduction of the direct-acting anticoagulants (DOACs) a few years ago was a step forward in that these drugs have been shown to be as effective as warfarin but are associated with a lower risk of bleeding, particularly of ICH and fatal bleeding. But they still cause bleeding, and concerns over that risk of bleeding prevent millions of patients from taking these drugs and receiving protection against stroke.
John Alexander, MD, professor of medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., a researcher active in this area, notes that “while the DOACs cause less bleeding than warfarin, they still cause two or three times more bleeding than placebo, and there is a huge, unmet need for safer anticoagulants that don’t cause as much bleeding. We are hopeful that factor XI inhibitors might be those anticoagulants.”
The lead investigator the AZALEA study, Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, explained why it is thought that factor XI inhibitors may be different.
“There’s a lot of different clotting factors, and most of them converge in a central pathway. The problem, therefore, with anticoagulants used to date that block one of these factors is that they prevent clotting but also cause bleeding.
“It has been discovered that factor XI has a really unique position in the cascade of how our body forms clots in that it seems to be important in clot formation, but it doesn’t seem to play a major role in our ability to heal and repair blood vessels.”
Another doctor involved in the field, Manesh Patel, MD, chief of cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, added, “We think that factor XI inhibitors may prevent the pathologic formation of thrombosis while allowing formation of thrombus for natural hemostasis to prevent bleeding. That is why they are so promising.”
This correlates with epidemiologic data suggesting that patients with a genetic factor XI deficiency have low rates of stroke and MI but don’t appear to bleed spontaneously, Dr. Patel notes.
Candidates in development
The pharmaceutical industry is on the case with several factor XI inhibitors now in clinical development. At present, three main candidates lead the field. These are abelacimab (Anthos), a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month; and two small molecules, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer), which are both given orally.
Phase 3 trials of these three factor XI inhibitors have recently started for a variety of thrombotic indications, including the prevention of stroke in patients with AFib, prevention of recurrent stroke in patients with ischemic stroke, and prevention of future cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Dr. Alexander, who has been involved in clinical trials of both milvexian and asundexian, commented: “We have pretty good data from a number of phase 2 trials now that these factor XI inhibitors at the doses used in these studies cause a lot less bleeding than therapeutic doses of DOACs and low-molecular-weight heparins.”
He pointed out that, in addition to the AZALEA trial with abelacimab, the phase 2 PACIFIC program of studies has shown less bleeding with asundexian than with apixaban in patients with AFib and a similar amount of bleeding as placebo in ACS/stroke patients on top of antiplatelet therapy. Milvexian has also shown similar results in the AXIOMATIC program of studies.
Dr. Ruff noted that the biggest need for new anticoagulants in general is in the AFib population. “Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common medical conditions in the world. Approximately one in every three people will develop AFib in their lifetime, and it is associated with more than a fivefold increased risk of stroke. But up to half of patients with AFib currently do not take anticoagulants because of concerns about bleeding risks, so these patients are being left unprotected from stroke risk.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that the AZALEA study was the largest and longest study of a factor XI inhibitor to date; 1,287 patients were followed for a median of 2 years.
“This was the first trial of long-term administration of factor XI inhibitor against a full-dose DOAC, and it was stopped because of an overwhelming reduction in a major bleeding with abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban,” he noted. “That is very encouraging. It looks like our quest to develop a safe anticoagulant with much lower rates of bleeding, compared with standard of care, seems to have been borne out. I think the field is very excited that we may finally have something that protects patients from thrombosis whilst being much safer than current agents.”
While all this sounds very promising, for these drugs to be successful, in addition to reducing bleeding risk, they will also have to be effective at preventing strokes and other thrombotic events.
“While we are pretty sure that factor XI inhibitors will cause less bleeding than current anticoagulants, what is unknown still is how effective they will be at preventing pathologic blood clots,” Dr. Alexander points out.
“We have some data from studies of these drugs in DVT prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery which suggest that they are effective in preventing blood clots in that scenario. But we don’t know yet about whether they can prevent pathologic blood clots that occur in AFib patients or in poststroke or post-ACS patients. Phase 3 studies are now underway with these three leading drug candidates which will answer some of these questions.”
Dr. Patel agrees that the efficacy data in the phase 3 trials will be key to the success of these drugs. “That is a very important part of the puzzle that is still missing,” he says.
Dr. Ruff notes that the AZALEA study will provide some data on efficacy. “But we already know that in the orthopedic surgery trials there was a 70%-80% reduction in VTE with abelacimab (at the 150-mg dose going forward) vs. prophylactic doses of low-molecular-weight heparin. And we know from the DOACs that the doses preventing clots on the venous side also translated into preventing strokes on the [AFib] side. So that is very encouraging,” Dr. Ruff adds.
Potential indications
The three leading factor XI inhibitors have slightly different phase 3 development programs.
Dr. Ruff notes that not every agent is being investigated in phase 3 trials for all the potential indications, but all three are going for the AFib indication. “This is by far the biggest population, the biggest market, and the biggest clinical need for these agents,” he says.
While the milvexian and asundexian trials are using an active comparator – pitting the factor XI inhibitors against apixaban in AFib patients – the Anthos LILAC trial is taking a slightly different approach and is comparing abelacimab with placebo in patients with AFib who are not currently taking an anticoagulant because of concerns about bleeding risk.
Janssen/BMS is conducting two other phase 3 trials of milvexian in their LIBREXIA phase 3 program. Those trials involve poststroke patients and ACS patients. Bayer is also involved in a poststroke trial of asundexian as part of its OCEANIC phase 3 program.
Dr. Ruff points out that anticoagulants currently do not have a large role in the poststroke or post-ACS population. “But the hope is that, if factor XI inhibitors are so safe, then there will be more enthusiasm about using an anticoagulant on top of antiplatelet therapy, which is the cornerstone of therapy in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.”
In addition to its phase 3 LILAC study in patients with AFib, Anthos is conducting two major phase 3 trials with abelacimab for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism.
Dr. Ruff notes that the indication of postsurgery or general prevention of VTE is not being pursued at present.
“The orthopedic surgery studies were done mainly for dose finding and proof of principle reasons,” he explains. “In orthopedic surgery the window for anticoagulation is quite short – a few weeks or months. And for the prevention of recurrent VTE in general in the community, those people are at a relatively low risk of bleeding, so there may not be much advantage of the factor XI inhibitors, whereas AFib patients and those with stroke or ACS are usually older and have a much higher bleeding risk. I think this is where the advantages of an anticoagulant with a lower bleeding risk are most needed.”
Dr. Alexander points out that to date anticoagulants have shown more efficacy in venous clotting, which appears to be more dependent on coagulation factors and less dependent on platelets. “Atrial fibrillation is a mix between venous and arterial clotting, but it has more similarities to venous, so I think AFib is a place where new anticoagulants such as the factor XI inhibitors are more likely to have success,” he suggests.
“So far, anticoagulants have had a less clear long-term role in the poststroke and post-ACS populations, so these indications may be a more difficult goal,” he added.
The phase 3 studies are just starting and will take a few years before results are known.
Differences between the agents
The three factor XI inhibitors also have some differences. Dr. Ruff points out that most important will be the safety and efficacy of the drugs in phase 3 trials.
“Early data suggest that the various agents being developed may not have equal inhibition of factor XI. The monoclonal antibody abelacimab may produce a higher degree of inhibition than the small molecules. But we don’t know if that matters or not – whether we need to achieve a certain threshold to prevent stroke. The efficacy and safety data from the phase 3 trials are what will primarily guide use.”
There are also differences in formulations and dosage. Abelacimab is administered by subcutaneous injection once a month and has a long duration of activity, whereas the small molecules are taken orally and their duration of action is much shorter.
Dr. Ruff notes: “If these drugs cause bleeding, having a long-acting drug like abelacimab could be a disadvantage because we wouldn’t be able to stop it. But if they are very safe with regard to bleeding, then having the drug hang around for a long time is not necessarily a disadvantage, and it may improve compliance. These older patients often miss doses, and with a shorter-acting drug, that will mean they will be unprotected from stroke risk for a period of time, so there is a trade-off here.”
Dr. Ruff says that the AZALEA phase 2 study will provide some data on patients being managed around procedures. “The hope is that these drugs are so safe that they will not have to be stopped for procedures. And then the compliance issue of a once-a-month dosing would be an advantage.”
Dr. Patel says he believes there is a place for different formations. “Some patients may prefer a once-monthly injection; others will prefer a daily tablet. It may come down to patient preference, but a lot will depend on the study results with the different agents,” he commented.
What effect could these drugs have?
If these drugs do show efficacy in these phase 3 trials, what difference will they make to clinical practice? The potential appears to be very large.
“If these drugs are as effective at preventing strokes as DOACs, they will be a huge breakthrough, and there is good reason to think they would replace the DOACs,” Dr. Alexander says. “It would be a really big deal to have an anticoagulant that causes almost no bleeding and could prevent clots as well as the DOACs. This would enable a lot more patients to receive protection against stroke.”
Dr. Alexander believes the surgery studies are hopeful. “They show that the factor XI inhibitors are doing something to prevent blood clots. The big question is whether they are as effective as what we already have for the prevention of stroke and if not, what is the trade-off with bleeding?”
He points out that, even if the factor XI inhibitors are not as effective as DOACs but are found to be much safer, they might still have a potential clinical role, especially for those patients who currently do not take an anticoagulant because of concerns regarding bleeding.
But Dr. Patel points out that there is always the issue of costs with new drugs. “New drugs are always expensive. The DOACS are just about to become generic, and there will inevitably be concerns about access to an expensive new therapy.”
Dr. Alexander adds: “Yes, costs could be an issue, but a safer drug will definitely help to get more patients treated and in preventing more strokes, which would be a great thing.”
Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an adviser to Bayer (asundexian) and Janssen (milvexian). Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer. Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AFib executive committee for BMS/Janssen, and has been on an advisory board for Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Steady VKA therapy beats switch to NOAC in frail AFib patients: FRAIL-AF
Switching frail patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) from anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) resulted in more bleeding without any reduction in thromboembolic complications or all-cause mortality, randomized trial results show.
The study, FRAIL-AF, is the first randomized NOAC trial to exclusively include frail older patients, said lead author Linda P.T. Joosten, MD, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care in Utrecht, the Netherlands, and these unexpected findings provide evidence that goes beyond what is currently available.
“Data from the FRAIL-AF trial showed that switching from a VKA to a NOAC should not be considered without a clear indication in frail older patients with AF[ib], as switching to a NOAC leads to 69% more bleeding,” she concluded, without any benefit on secondary clinical endpoints, including thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality.
“The results turned out different than we expected,” Dr. Joosten said. “The hypothesis of this superiority trial was that switching from VKA therapy to a NOAC would result in less bleeding. However, we observed the opposite. After the interim analysis, the data and safety monitoring board advised to stop inclusion because switching from a VKA to a NOAC was clearly contraindicated with a hazard ratio of 1.69 and a highly significant P value of .001.”
Results of FRAIL-AF were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published online in the journal Circulation.
Session moderator Renate B. Schnabel, MD, interventional cardiologist with University Heart & Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), congratulated the researchers on these “astonishing” data.
“The thing I want to emphasize here is that, in the absence of randomized controlled trial data, we should be very cautious in extrapolating data from the landmark trials to populations not enrolled in those, and to rely on observational data only,” Dr. Schnabel told Dr. Joosten. “We need randomized controlled trials that sometimes give astonishing results.”
Frailty a clinical syndrome
Frailty is “a lot more than just aging, multiple comorbidities and polypharmacy,” Dr. Joosten explained. “It’s really a clinical syndrome, with people with a high biological vulnerability, dependency on significant others, and a reduced capacity to resist stressors, all leading to a reduced homeostatic reserve.”
Frailty is common in the community, with a prevalence of about 12%, she noted, “and even more important, AF[ib] in frail older people is very common, with a prevalence of 18%. And “without any doubt, we have to adequately anticoagulate frail AF[ib] patients, as they have a high stroke risk, with an incidence of 12.4% per year,” Dr. Joosten noted, compared with 3.9% per year among nonfrail AFib patients.
NOACs are preferred over VKAs in nonfrail AFib patients, after four major trials, RE-LY with dabigatran, ROCKET-AF with rivaroxaban, ARISTOTLE with apixaban, and ENGAGE-AF with edoxaban, showed that NOAC treatment resulted in less major bleeding while stroke risk was comparable with treatment with warfarin, she noted.
The 2023 European Heart Rhythm Association consensus document on management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome concludes that the advantages of NOACs relative to VKAs are “likely consistent” in frail and nonfrail AFib patients, but the level of evidence is low.
So it’s unknown if NOACs are preferred over VKAs in frail AFib patients, “and it’s even more questionable whether patients on VKAs should switch to NOAC therapy,” Dr. Joosten said.
This new trial aimed to answer the question of whether switching frail AFib patients currently managed on a VKA to a NOAC would reduce bleeding. FRAIL-AF was a pragmatic, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled superiority trial.
Older AFib patients were deemed frail if they were aged 75 years or older and had a score of 3 or more on the validated Groningen Frailty Indicator (GFI). Patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or with valvular AFib were excluded.
Eligible patients were then assigned randomly to switch from their international normalized ratio (INR)–guided VKA treatment with either 1 mg acenocoumarol or 3 mg phenprocoumon, to a NOAC, or to continue VKA treatment. They were followed for 12 months for the primary outcome – major bleeding or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding complication, whichever came first – accounting for death as a competing risk.
A total of 1,330 patients were randomly assigned between January 2018 and June 2022. Their mean age was 83 years, and they had a median GFI of 4. After randomization, 6 patients in the switch-to-NOAC arm, and 1 in the continue-VKA arm were found to have exclusion criteria, so in the end, 662 patients were switched from a VKA to NOAC, while 661 continued on VKA therapy. The choice of NOAC was made by the treating physician.
Major bleeding was defined as a fatal bleeding; bleeding in a critical area or organ; bleeding leading to transfusion; and/or bleeding leading to a fall in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more. Nonmajor bleeding was bleeding not considered major but requiring face-to-face consultation, hospitalization or increased level of care, or medical intervention.
After a prespecified futility analysis planned after 163 primary outcome events, the trial was halted when it was seen that there were 101 primary outcome events in the switch arm compared to 62 in the continue arm, Dr. Joosten said. The difference appeared to be driven by clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding.
Secondary outcomes of thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality were similar between the groups.
Completely different patients
Discussant at the meeting for the presentation was Isabelle C. Van Gelder, MD, University Medical Centre Groningen (the Netherlands). She said the results are important and relevant because it “provides data on an important gap of knowledge in our AF[ib] guidelines, and a note for all the cardiologists – this study was not done in the hospital. This trial was done in general practitioner practices, so that’s important to consider.”
Comparing FRAIL-AF patients with those of the four previous NOAC trials, “you see that enormous difference in age,” with an average age of 83 years versus 70-73 years in those trials. “These are completely different patients than have been included previously,” she said.
That GFI score of 4 or more includes patients on four or more different types of medication, as well as memory complaints, an inability to walk around the house, and problems with vision or hearing.
The finding of a 69% increase in bleeding with NOACs in FRAIL-AF was “completely unexpected, and I think that we as cardiologists and as NOAC believers did not expect it at all, but it is as clear as it is.” The curves don’t diverge immediately, but rather after 3 months or thereafter, “so it has nothing to do with the switching process. So why did it occur?”
The Netherlands has dedicated thrombosis services that might improve time in therapeutic range for VKA patients, but there is no real difference in TTRs in FRAIL-AF versus the other NOAC trials, Dr. Van Gelder noted.
The most likely suspect in her view is frailty itself, in particular the tendency for patients to be on a high number of medications. A previous study showed, for example, that polypharmacy could be used as a proxy for the effect of frailty on bleeding risk; patients on 10 or more medications had a higher risk for bleeding on treatment with rivaroxaban versus those on 4 or fewer medications.
“Therefore, in my view, why was there such a high risk of bleeding? It’s because these are other patients than we are normally used to treat, we as cardiologists,” although general practitioners see these patients all the time. “It’s all about frailty.”
NOACs are still relatively new drugs, with possible unknown interactions, she added. Because of their frailty and polypharmacy, these patients may benefit from INR control, Dr. Van Gelder speculated. “Therefore, I agree with them that we should be careful; if such old, frail patients survive on VKA, do not change medications and do not switch!”
The study was supported by the Dutch government with additional and unrestricted educational grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS-Pfizer, Bayer, and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Joosten reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Switching frail patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) from anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) resulted in more bleeding without any reduction in thromboembolic complications or all-cause mortality, randomized trial results show.
The study, FRAIL-AF, is the first randomized NOAC trial to exclusively include frail older patients, said lead author Linda P.T. Joosten, MD, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care in Utrecht, the Netherlands, and these unexpected findings provide evidence that goes beyond what is currently available.
“Data from the FRAIL-AF trial showed that switching from a VKA to a NOAC should not be considered without a clear indication in frail older patients with AF[ib], as switching to a NOAC leads to 69% more bleeding,” she concluded, without any benefit on secondary clinical endpoints, including thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality.
“The results turned out different than we expected,” Dr. Joosten said. “The hypothesis of this superiority trial was that switching from VKA therapy to a NOAC would result in less bleeding. However, we observed the opposite. After the interim analysis, the data and safety monitoring board advised to stop inclusion because switching from a VKA to a NOAC was clearly contraindicated with a hazard ratio of 1.69 and a highly significant P value of .001.”
Results of FRAIL-AF were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published online in the journal Circulation.
Session moderator Renate B. Schnabel, MD, interventional cardiologist with University Heart & Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), congratulated the researchers on these “astonishing” data.
“The thing I want to emphasize here is that, in the absence of randomized controlled trial data, we should be very cautious in extrapolating data from the landmark trials to populations not enrolled in those, and to rely on observational data only,” Dr. Schnabel told Dr. Joosten. “We need randomized controlled trials that sometimes give astonishing results.”
Frailty a clinical syndrome
Frailty is “a lot more than just aging, multiple comorbidities and polypharmacy,” Dr. Joosten explained. “It’s really a clinical syndrome, with people with a high biological vulnerability, dependency on significant others, and a reduced capacity to resist stressors, all leading to a reduced homeostatic reserve.”
Frailty is common in the community, with a prevalence of about 12%, she noted, “and even more important, AF[ib] in frail older people is very common, with a prevalence of 18%. And “without any doubt, we have to adequately anticoagulate frail AF[ib] patients, as they have a high stroke risk, with an incidence of 12.4% per year,” Dr. Joosten noted, compared with 3.9% per year among nonfrail AFib patients.
NOACs are preferred over VKAs in nonfrail AFib patients, after four major trials, RE-LY with dabigatran, ROCKET-AF with rivaroxaban, ARISTOTLE with apixaban, and ENGAGE-AF with edoxaban, showed that NOAC treatment resulted in less major bleeding while stroke risk was comparable with treatment with warfarin, she noted.
The 2023 European Heart Rhythm Association consensus document on management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome concludes that the advantages of NOACs relative to VKAs are “likely consistent” in frail and nonfrail AFib patients, but the level of evidence is low.
So it’s unknown if NOACs are preferred over VKAs in frail AFib patients, “and it’s even more questionable whether patients on VKAs should switch to NOAC therapy,” Dr. Joosten said.
This new trial aimed to answer the question of whether switching frail AFib patients currently managed on a VKA to a NOAC would reduce bleeding. FRAIL-AF was a pragmatic, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled superiority trial.
Older AFib patients were deemed frail if they were aged 75 years or older and had a score of 3 or more on the validated Groningen Frailty Indicator (GFI). Patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or with valvular AFib were excluded.
Eligible patients were then assigned randomly to switch from their international normalized ratio (INR)–guided VKA treatment with either 1 mg acenocoumarol or 3 mg phenprocoumon, to a NOAC, or to continue VKA treatment. They were followed for 12 months for the primary outcome – major bleeding or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding complication, whichever came first – accounting for death as a competing risk.
A total of 1,330 patients were randomly assigned between January 2018 and June 2022. Their mean age was 83 years, and they had a median GFI of 4. After randomization, 6 patients in the switch-to-NOAC arm, and 1 in the continue-VKA arm were found to have exclusion criteria, so in the end, 662 patients were switched from a VKA to NOAC, while 661 continued on VKA therapy. The choice of NOAC was made by the treating physician.
Major bleeding was defined as a fatal bleeding; bleeding in a critical area or organ; bleeding leading to transfusion; and/or bleeding leading to a fall in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more. Nonmajor bleeding was bleeding not considered major but requiring face-to-face consultation, hospitalization or increased level of care, or medical intervention.
After a prespecified futility analysis planned after 163 primary outcome events, the trial was halted when it was seen that there were 101 primary outcome events in the switch arm compared to 62 in the continue arm, Dr. Joosten said. The difference appeared to be driven by clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding.
Secondary outcomes of thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality were similar between the groups.
Completely different patients
Discussant at the meeting for the presentation was Isabelle C. Van Gelder, MD, University Medical Centre Groningen (the Netherlands). She said the results are important and relevant because it “provides data on an important gap of knowledge in our AF[ib] guidelines, and a note for all the cardiologists – this study was not done in the hospital. This trial was done in general practitioner practices, so that’s important to consider.”
Comparing FRAIL-AF patients with those of the four previous NOAC trials, “you see that enormous difference in age,” with an average age of 83 years versus 70-73 years in those trials. “These are completely different patients than have been included previously,” she said.
That GFI score of 4 or more includes patients on four or more different types of medication, as well as memory complaints, an inability to walk around the house, and problems with vision or hearing.
The finding of a 69% increase in bleeding with NOACs in FRAIL-AF was “completely unexpected, and I think that we as cardiologists and as NOAC believers did not expect it at all, but it is as clear as it is.” The curves don’t diverge immediately, but rather after 3 months or thereafter, “so it has nothing to do with the switching process. So why did it occur?”
The Netherlands has dedicated thrombosis services that might improve time in therapeutic range for VKA patients, but there is no real difference in TTRs in FRAIL-AF versus the other NOAC trials, Dr. Van Gelder noted.
The most likely suspect in her view is frailty itself, in particular the tendency for patients to be on a high number of medications. A previous study showed, for example, that polypharmacy could be used as a proxy for the effect of frailty on bleeding risk; patients on 10 or more medications had a higher risk for bleeding on treatment with rivaroxaban versus those on 4 or fewer medications.
“Therefore, in my view, why was there such a high risk of bleeding? It’s because these are other patients than we are normally used to treat, we as cardiologists,” although general practitioners see these patients all the time. “It’s all about frailty.”
NOACs are still relatively new drugs, with possible unknown interactions, she added. Because of their frailty and polypharmacy, these patients may benefit from INR control, Dr. Van Gelder speculated. “Therefore, I agree with them that we should be careful; if such old, frail patients survive on VKA, do not change medications and do not switch!”
The study was supported by the Dutch government with additional and unrestricted educational grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS-Pfizer, Bayer, and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Joosten reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Switching frail patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) from anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) resulted in more bleeding without any reduction in thromboembolic complications or all-cause mortality, randomized trial results show.
The study, FRAIL-AF, is the first randomized NOAC trial to exclusively include frail older patients, said lead author Linda P.T. Joosten, MD, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care in Utrecht, the Netherlands, and these unexpected findings provide evidence that goes beyond what is currently available.
“Data from the FRAIL-AF trial showed that switching from a VKA to a NOAC should not be considered without a clear indication in frail older patients with AF[ib], as switching to a NOAC leads to 69% more bleeding,” she concluded, without any benefit on secondary clinical endpoints, including thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality.
“The results turned out different than we expected,” Dr. Joosten said. “The hypothesis of this superiority trial was that switching from VKA therapy to a NOAC would result in less bleeding. However, we observed the opposite. After the interim analysis, the data and safety monitoring board advised to stop inclusion because switching from a VKA to a NOAC was clearly contraindicated with a hazard ratio of 1.69 and a highly significant P value of .001.”
Results of FRAIL-AF were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published online in the journal Circulation.
Session moderator Renate B. Schnabel, MD, interventional cardiologist with University Heart & Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), congratulated the researchers on these “astonishing” data.
“The thing I want to emphasize here is that, in the absence of randomized controlled trial data, we should be very cautious in extrapolating data from the landmark trials to populations not enrolled in those, and to rely on observational data only,” Dr. Schnabel told Dr. Joosten. “We need randomized controlled trials that sometimes give astonishing results.”
Frailty a clinical syndrome
Frailty is “a lot more than just aging, multiple comorbidities and polypharmacy,” Dr. Joosten explained. “It’s really a clinical syndrome, with people with a high biological vulnerability, dependency on significant others, and a reduced capacity to resist stressors, all leading to a reduced homeostatic reserve.”
Frailty is common in the community, with a prevalence of about 12%, she noted, “and even more important, AF[ib] in frail older people is very common, with a prevalence of 18%. And “without any doubt, we have to adequately anticoagulate frail AF[ib] patients, as they have a high stroke risk, with an incidence of 12.4% per year,” Dr. Joosten noted, compared with 3.9% per year among nonfrail AFib patients.
NOACs are preferred over VKAs in nonfrail AFib patients, after four major trials, RE-LY with dabigatran, ROCKET-AF with rivaroxaban, ARISTOTLE with apixaban, and ENGAGE-AF with edoxaban, showed that NOAC treatment resulted in less major bleeding while stroke risk was comparable with treatment with warfarin, she noted.
The 2023 European Heart Rhythm Association consensus document on management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome concludes that the advantages of NOACs relative to VKAs are “likely consistent” in frail and nonfrail AFib patients, but the level of evidence is low.
So it’s unknown if NOACs are preferred over VKAs in frail AFib patients, “and it’s even more questionable whether patients on VKAs should switch to NOAC therapy,” Dr. Joosten said.
This new trial aimed to answer the question of whether switching frail AFib patients currently managed on a VKA to a NOAC would reduce bleeding. FRAIL-AF was a pragmatic, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled superiority trial.
Older AFib patients were deemed frail if they were aged 75 years or older and had a score of 3 or more on the validated Groningen Frailty Indicator (GFI). Patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or with valvular AFib were excluded.
Eligible patients were then assigned randomly to switch from their international normalized ratio (INR)–guided VKA treatment with either 1 mg acenocoumarol or 3 mg phenprocoumon, to a NOAC, or to continue VKA treatment. They were followed for 12 months for the primary outcome – major bleeding or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding complication, whichever came first – accounting for death as a competing risk.
A total of 1,330 patients were randomly assigned between January 2018 and June 2022. Their mean age was 83 years, and they had a median GFI of 4. After randomization, 6 patients in the switch-to-NOAC arm, and 1 in the continue-VKA arm were found to have exclusion criteria, so in the end, 662 patients were switched from a VKA to NOAC, while 661 continued on VKA therapy. The choice of NOAC was made by the treating physician.
Major bleeding was defined as a fatal bleeding; bleeding in a critical area or organ; bleeding leading to transfusion; and/or bleeding leading to a fall in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more. Nonmajor bleeding was bleeding not considered major but requiring face-to-face consultation, hospitalization or increased level of care, or medical intervention.
After a prespecified futility analysis planned after 163 primary outcome events, the trial was halted when it was seen that there were 101 primary outcome events in the switch arm compared to 62 in the continue arm, Dr. Joosten said. The difference appeared to be driven by clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding.
Secondary outcomes of thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality were similar between the groups.
Completely different patients
Discussant at the meeting for the presentation was Isabelle C. Van Gelder, MD, University Medical Centre Groningen (the Netherlands). She said the results are important and relevant because it “provides data on an important gap of knowledge in our AF[ib] guidelines, and a note for all the cardiologists – this study was not done in the hospital. This trial was done in general practitioner practices, so that’s important to consider.”
Comparing FRAIL-AF patients with those of the four previous NOAC trials, “you see that enormous difference in age,” with an average age of 83 years versus 70-73 years in those trials. “These are completely different patients than have been included previously,” she said.
That GFI score of 4 or more includes patients on four or more different types of medication, as well as memory complaints, an inability to walk around the house, and problems with vision or hearing.
The finding of a 69% increase in bleeding with NOACs in FRAIL-AF was “completely unexpected, and I think that we as cardiologists and as NOAC believers did not expect it at all, but it is as clear as it is.” The curves don’t diverge immediately, but rather after 3 months or thereafter, “so it has nothing to do with the switching process. So why did it occur?”
The Netherlands has dedicated thrombosis services that might improve time in therapeutic range for VKA patients, but there is no real difference in TTRs in FRAIL-AF versus the other NOAC trials, Dr. Van Gelder noted.
The most likely suspect in her view is frailty itself, in particular the tendency for patients to be on a high number of medications. A previous study showed, for example, that polypharmacy could be used as a proxy for the effect of frailty on bleeding risk; patients on 10 or more medications had a higher risk for bleeding on treatment with rivaroxaban versus those on 4 or fewer medications.
“Therefore, in my view, why was there such a high risk of bleeding? It’s because these are other patients than we are normally used to treat, we as cardiologists,” although general practitioners see these patients all the time. “It’s all about frailty.”
NOACs are still relatively new drugs, with possible unknown interactions, she added. Because of their frailty and polypharmacy, these patients may benefit from INR control, Dr. Van Gelder speculated. “Therefore, I agree with them that we should be careful; if such old, frail patients survive on VKA, do not change medications and do not switch!”
The study was supported by the Dutch government with additional and unrestricted educational grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS-Pfizer, Bayer, and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Joosten reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2023
Medicare announces 10 drugs targeted for price cuts in 2026
People on Medicare may in 2026 see prices drop for 10 medicines, including pricey diabetes, cancer, blood clot, and arthritis treatments, if advocates for federal drug-price negotiations can implement their plans amid tough opposition.
It’s unclear at this time, though, how these negotiations will play out. The Chamber of Commerce has sided with pharmaceutical companies in bids to block direct Medicare negotiation of drug prices. Many influential Republicans in Congress oppose this plan, which has deep support from both Democrats and AARP.
While facing strong opposition to negotiations, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services sought in its announcement to illustrate the high costs of the selected medicines.
CMS provided data on total Part D costs for selected medicines for the period from June 2022 to May 2023, along with tallies of the number of people taking these drugs. The 10 selected medicines are as follows:
- Eliquis (generic name: apixaban), used to prevent and treat serious blood clots. It is taken by about 3.7 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $16.4 billion.
- Jardiance (generic name: empagliflozin), used for diabetes and heart failure. It is taken by almost 1.6 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $7.06 billion.
- Xarelto (generic name: rivaroxaban), used for blood clots. It is taken by about 1.3 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $6 billion.
- Januvia (generic name: sitagliptin), used for diabetes. It is taken by about 869,00 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $4.1 billion.
- Farxiga (generic name: dapagliflozin), used for diabetes, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. It is taken by about 799,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is almost $3.3 billion.
- Entresto (generic name: sacubitril/valsartan), used to treat heart failure. It is taken by 587,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.9 billion.
- Enbrel( generic name: etanercept), used for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. It is taken by 48,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.8 billion.
- Imbruvica (generic name: ibrutinib), used to treat some blood cancers. It is taken by about 20,000 people in Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.7 billion.
- Stelara (generic name: ustekinumab), used to treat plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or certain bowel conditions (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis). It is used by about 22,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.6 billion.
- Fiasp; Fiasp FlexTouch; Fiasp PenFill; NovoLog; NovoLog FlexPen; NovoLog PenFill. These are forms of insulin used to treat diabetes. They are used by about 777,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.6 billion.
A vocal critic of Medicare drug negotiations, Joel White, president of the Council for Affordable Health Coverage, called the announcement of the 10 drugs selected for negotiation “a hollow victory lap.” A former Republican staffer on the House Ways and Means Committee, Mr. White aided with the development of the Medicare Part D plans and has kept tabs on the pharmacy programs since its launch in 2006.
“No one’s costs will go down now or for years because of this announcement” about Part D negotiations, Mr. White said in a statement.
According to its website, CAHC includes among its members the American Academy of Ophthalmology as well as some patient groups, drugmakers, such as Johnson & Johnson, and insurers and industry groups, such as the National Association of Manufacturers.
Separately, the influential Chamber of Commerce is making a strong push to at least delay the implementation of the Medicare Part D drug negotiations. On Aug. 28, the chamber released a letter sent to the Biden administration, raising concerns about a “rush” to implement the provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act.
The chamber also has filed suit to challenge the drug negotiation provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act, requesting that the court issue a preliminary injunction by Oct. 1, 2023.
Other pending legal challenges to direct Medicare drug negotiations include suits filed by Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca, according to an email from Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. PhRMA also said it is a party to a case.
In addition, the three congressional Republicans with most direct influence over Medicare policy issued on Aug. 29 a joint statement outlining their objections to the planned negotiations on drug prices.
This drug-negotiation proposal is “an unworkable, legally dubious scheme that will lead to higher prices for new drugs coming to market, stifle the development of new cures, and destroy jobs,” said House Energy and Commerce Committee Chair Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-Wash.), House Ways and Means Committee Chair Jason Smith (R-Mo.), and Senate Finance Committee Ranking Member Mike Crapo (R-Idaho).
Democrats were equally firm and vocal in their support of the negotiations. Senate Finance Chairman Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) issued a statement on Aug. 29 that said the release of the list of the 10 drugs selected for Medicare drug negotiations is part of a “seismic shift in the relationship between Big Pharma, the federal government, and seniors who are counting on lower prices.
“I will be following the negotiation process closely and will fight any attempt by Big Pharma to undo or undermine the progress that’s been made,” Mr. Wyden said.
In addition, AARP issued a statement of its continued support for Medicare drug negotiations.
“The No. 1 reason seniors skip or ration their prescriptions is because they can’t afford them. This must stop,” said AARP executive vice president and chief advocacy and engagement officer Nancy LeaMond in the statement. “The big drug companies and their allies continue suing to overturn the Medicare drug price negotiation program to keep up their price gouging. We can’t allow seniors to be Big Pharma’s cash machine anymore.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People on Medicare may in 2026 see prices drop for 10 medicines, including pricey diabetes, cancer, blood clot, and arthritis treatments, if advocates for federal drug-price negotiations can implement their plans amid tough opposition.
It’s unclear at this time, though, how these negotiations will play out. The Chamber of Commerce has sided with pharmaceutical companies in bids to block direct Medicare negotiation of drug prices. Many influential Republicans in Congress oppose this plan, which has deep support from both Democrats and AARP.
While facing strong opposition to negotiations, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services sought in its announcement to illustrate the high costs of the selected medicines.
CMS provided data on total Part D costs for selected medicines for the period from June 2022 to May 2023, along with tallies of the number of people taking these drugs. The 10 selected medicines are as follows:
- Eliquis (generic name: apixaban), used to prevent and treat serious blood clots. It is taken by about 3.7 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $16.4 billion.
- Jardiance (generic name: empagliflozin), used for diabetes and heart failure. It is taken by almost 1.6 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $7.06 billion.
- Xarelto (generic name: rivaroxaban), used for blood clots. It is taken by about 1.3 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $6 billion.
- Januvia (generic name: sitagliptin), used for diabetes. It is taken by about 869,00 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $4.1 billion.
- Farxiga (generic name: dapagliflozin), used for diabetes, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. It is taken by about 799,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is almost $3.3 billion.
- Entresto (generic name: sacubitril/valsartan), used to treat heart failure. It is taken by 587,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.9 billion.
- Enbrel( generic name: etanercept), used for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. It is taken by 48,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.8 billion.
- Imbruvica (generic name: ibrutinib), used to treat some blood cancers. It is taken by about 20,000 people in Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.7 billion.
- Stelara (generic name: ustekinumab), used to treat plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or certain bowel conditions (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis). It is used by about 22,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.6 billion.
- Fiasp; Fiasp FlexTouch; Fiasp PenFill; NovoLog; NovoLog FlexPen; NovoLog PenFill. These are forms of insulin used to treat diabetes. They are used by about 777,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.6 billion.
A vocal critic of Medicare drug negotiations, Joel White, president of the Council for Affordable Health Coverage, called the announcement of the 10 drugs selected for negotiation “a hollow victory lap.” A former Republican staffer on the House Ways and Means Committee, Mr. White aided with the development of the Medicare Part D plans and has kept tabs on the pharmacy programs since its launch in 2006.
“No one’s costs will go down now or for years because of this announcement” about Part D negotiations, Mr. White said in a statement.
According to its website, CAHC includes among its members the American Academy of Ophthalmology as well as some patient groups, drugmakers, such as Johnson & Johnson, and insurers and industry groups, such as the National Association of Manufacturers.
Separately, the influential Chamber of Commerce is making a strong push to at least delay the implementation of the Medicare Part D drug negotiations. On Aug. 28, the chamber released a letter sent to the Biden administration, raising concerns about a “rush” to implement the provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act.
The chamber also has filed suit to challenge the drug negotiation provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act, requesting that the court issue a preliminary injunction by Oct. 1, 2023.
Other pending legal challenges to direct Medicare drug negotiations include suits filed by Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca, according to an email from Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. PhRMA also said it is a party to a case.
In addition, the three congressional Republicans with most direct influence over Medicare policy issued on Aug. 29 a joint statement outlining their objections to the planned negotiations on drug prices.
This drug-negotiation proposal is “an unworkable, legally dubious scheme that will lead to higher prices for new drugs coming to market, stifle the development of new cures, and destroy jobs,” said House Energy and Commerce Committee Chair Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-Wash.), House Ways and Means Committee Chair Jason Smith (R-Mo.), and Senate Finance Committee Ranking Member Mike Crapo (R-Idaho).
Democrats were equally firm and vocal in their support of the negotiations. Senate Finance Chairman Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) issued a statement on Aug. 29 that said the release of the list of the 10 drugs selected for Medicare drug negotiations is part of a “seismic shift in the relationship between Big Pharma, the federal government, and seniors who are counting on lower prices.
“I will be following the negotiation process closely and will fight any attempt by Big Pharma to undo or undermine the progress that’s been made,” Mr. Wyden said.
In addition, AARP issued a statement of its continued support for Medicare drug negotiations.
“The No. 1 reason seniors skip or ration their prescriptions is because they can’t afford them. This must stop,” said AARP executive vice president and chief advocacy and engagement officer Nancy LeaMond in the statement. “The big drug companies and their allies continue suing to overturn the Medicare drug price negotiation program to keep up their price gouging. We can’t allow seniors to be Big Pharma’s cash machine anymore.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People on Medicare may in 2026 see prices drop for 10 medicines, including pricey diabetes, cancer, blood clot, and arthritis treatments, if advocates for federal drug-price negotiations can implement their plans amid tough opposition.
It’s unclear at this time, though, how these negotiations will play out. The Chamber of Commerce has sided with pharmaceutical companies in bids to block direct Medicare negotiation of drug prices. Many influential Republicans in Congress oppose this plan, which has deep support from both Democrats and AARP.
While facing strong opposition to negotiations, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services sought in its announcement to illustrate the high costs of the selected medicines.
CMS provided data on total Part D costs for selected medicines for the period from June 2022 to May 2023, along with tallies of the number of people taking these drugs. The 10 selected medicines are as follows:
- Eliquis (generic name: apixaban), used to prevent and treat serious blood clots. It is taken by about 3.7 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $16.4 billion.
- Jardiance (generic name: empagliflozin), used for diabetes and heart failure. It is taken by almost 1.6 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $7.06 billion.
- Xarelto (generic name: rivaroxaban), used for blood clots. It is taken by about 1.3 million people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $6 billion.
- Januvia (generic name: sitagliptin), used for diabetes. It is taken by about 869,00 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $4.1 billion.
- Farxiga (generic name: dapagliflozin), used for diabetes, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. It is taken by about 799,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is almost $3.3 billion.
- Entresto (generic name: sacubitril/valsartan), used to treat heart failure. It is taken by 587,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.9 billion.
- Enbrel( generic name: etanercept), used for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. It is taken by 48,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.8 billion.
- Imbruvica (generic name: ibrutinib), used to treat some blood cancers. It is taken by about 20,000 people in Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.7 billion.
- Stelara (generic name: ustekinumab), used to treat plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or certain bowel conditions (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis). It is used by about 22,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.6 billion.
- Fiasp; Fiasp FlexTouch; Fiasp PenFill; NovoLog; NovoLog FlexPen; NovoLog PenFill. These are forms of insulin used to treat diabetes. They are used by about 777,000 people through Part D plans. The estimated cost is $2.6 billion.
A vocal critic of Medicare drug negotiations, Joel White, president of the Council for Affordable Health Coverage, called the announcement of the 10 drugs selected for negotiation “a hollow victory lap.” A former Republican staffer on the House Ways and Means Committee, Mr. White aided with the development of the Medicare Part D plans and has kept tabs on the pharmacy programs since its launch in 2006.
“No one’s costs will go down now or for years because of this announcement” about Part D negotiations, Mr. White said in a statement.
According to its website, CAHC includes among its members the American Academy of Ophthalmology as well as some patient groups, drugmakers, such as Johnson & Johnson, and insurers and industry groups, such as the National Association of Manufacturers.
Separately, the influential Chamber of Commerce is making a strong push to at least delay the implementation of the Medicare Part D drug negotiations. On Aug. 28, the chamber released a letter sent to the Biden administration, raising concerns about a “rush” to implement the provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act.
The chamber also has filed suit to challenge the drug negotiation provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act, requesting that the court issue a preliminary injunction by Oct. 1, 2023.
Other pending legal challenges to direct Medicare drug negotiations include suits filed by Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca, according to an email from Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. PhRMA also said it is a party to a case.
In addition, the three congressional Republicans with most direct influence over Medicare policy issued on Aug. 29 a joint statement outlining their objections to the planned negotiations on drug prices.
This drug-negotiation proposal is “an unworkable, legally dubious scheme that will lead to higher prices for new drugs coming to market, stifle the development of new cures, and destroy jobs,” said House Energy and Commerce Committee Chair Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-Wash.), House Ways and Means Committee Chair Jason Smith (R-Mo.), and Senate Finance Committee Ranking Member Mike Crapo (R-Idaho).
Democrats were equally firm and vocal in their support of the negotiations. Senate Finance Chairman Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) issued a statement on Aug. 29 that said the release of the list of the 10 drugs selected for Medicare drug negotiations is part of a “seismic shift in the relationship between Big Pharma, the federal government, and seniors who are counting on lower prices.
“I will be following the negotiation process closely and will fight any attempt by Big Pharma to undo or undermine the progress that’s been made,” Mr. Wyden said.
In addition, AARP issued a statement of its continued support for Medicare drug negotiations.
“The No. 1 reason seniors skip or ration their prescriptions is because they can’t afford them. This must stop,” said AARP executive vice president and chief advocacy and engagement officer Nancy LeaMond in the statement. “The big drug companies and their allies continue suing to overturn the Medicare drug price negotiation program to keep up their price gouging. We can’t allow seniors to be Big Pharma’s cash machine anymore.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated Beers Criteria highlights
Every 4 years, an interprofessional panel of experts from the American Geriatrics Society provides updated guidelines on safe prescribing of medications in older adults, known as the Beers Criteria. A 2023 update was released in May 2023 after panel review of more 1,500 clinical trials and research studies published since the last update.
Anticoagulants
Notable changes to the 2023 guidelines include updated recommendations for anticoagulation. Warfarin should be avoided as initial therapy for venous thromboembolism or nonvalvular atrial fibrillation unless there are contraindications to direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) or other substantial barriers to use.
Rivaroxaban should also be avoided, and dabigatran used with caution in favor of apixaban, which is felt to have a better safety profile in older adults. Rivaroxaban may be considered if once daily dosing is deemed to be more clinically appropriate. Financial barriers regarding drug coverage and formulary options were acknowledged as a significant barrier to equitable access to preferred direct oral anticoagulants in older adults.
Diabetes medication
Regarding diabetes management, short-acting sulfonylureas should be avoided in addition to long-acting sulfonylureas, because of the increased risk of hypoglycemia, and cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in older adults. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as an entire class are recommended to be used with caution, as older adults are at higher risk of euglycemic ketoacidosis and urogenital infections, particularly in women in the first month of initiating treatment.
Like DOACs, the panel acknowledged that financial considerations may lead to limited options for oral diabetic treatment. In circumstances where a sulfonylurea is used, short-acting forms are preferred over long acting to reduce the risk of prolonged hypoglycemia.
Aspirin for primary prevention
Alongside the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guideline update in 2022 regarding aspirin for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and stroke, the Beer’s Criteria recommend against initiation of aspirin for primary prevention in older adults. Ticagrelor and prasugrel should be used with caution because of the increased risk of major bleeding in older adults over the age of 75, compared with clopidogrel. If prasugrel is used, a lower dose of 5 mg is recommended, in line with guidelines by the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association.
Pain medication
For pain management, the Beer’s Criteria updated recommendations to avoid NSAIDs, particularly when used in combination with steroids or anticoagulants. The panel highlights that even short-term use of NSAIDs is high risk when used in combination with steroids or anticoagulants. If no other alternatives are possible, patients should be placed on a proton pump inhibitor or misoprostol while taking NSAIDs.
Baclofen should be avoided in older adults with renal insufficiency (estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2) because of the increased risk of encephalopathy, and when used, should be given at the lowest effective dose with close monitoring for mental status changes.
Androgen and estrogen replacement therapy
For androgen replacement therapy, the panel notes that testosterone supplementation should be avoided because of cardiovascular risks unless there is confirmed hypogonadism. The panel revised their recommendation on the basis of emerging data that a history of prostate cancer is not an absolute contraindication for exogenous testosterone. A risk versus benefit discussion about exogenous testosterone should be had with a medical oncologist or urologist in those with a history of prostate cancer.
Regarding estrogen, systemic formulations should not be initiated in women over the age of 60 because of increased risk of cardiovascular events, venous thromboembolism, and dementia. In women with a history of breast cancer, vaginal estrogens are generally felt to be safe to use at low doses, such as less than 25 mcg twice weekly.
Dr. Wang is a geriatrician and general internist at Harborview Medical Center, Seattle.
Every 4 years, an interprofessional panel of experts from the American Geriatrics Society provides updated guidelines on safe prescribing of medications in older adults, known as the Beers Criteria. A 2023 update was released in May 2023 after panel review of more 1,500 clinical trials and research studies published since the last update.
Anticoagulants
Notable changes to the 2023 guidelines include updated recommendations for anticoagulation. Warfarin should be avoided as initial therapy for venous thromboembolism or nonvalvular atrial fibrillation unless there are contraindications to direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) or other substantial barriers to use.
Rivaroxaban should also be avoided, and dabigatran used with caution in favor of apixaban, which is felt to have a better safety profile in older adults. Rivaroxaban may be considered if once daily dosing is deemed to be more clinically appropriate. Financial barriers regarding drug coverage and formulary options were acknowledged as a significant barrier to equitable access to preferred direct oral anticoagulants in older adults.
Diabetes medication
Regarding diabetes management, short-acting sulfonylureas should be avoided in addition to long-acting sulfonylureas, because of the increased risk of hypoglycemia, and cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in older adults. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as an entire class are recommended to be used with caution, as older adults are at higher risk of euglycemic ketoacidosis and urogenital infections, particularly in women in the first month of initiating treatment.
Like DOACs, the panel acknowledged that financial considerations may lead to limited options for oral diabetic treatment. In circumstances where a sulfonylurea is used, short-acting forms are preferred over long acting to reduce the risk of prolonged hypoglycemia.
Aspirin for primary prevention
Alongside the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guideline update in 2022 regarding aspirin for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and stroke, the Beer’s Criteria recommend against initiation of aspirin for primary prevention in older adults. Ticagrelor and prasugrel should be used with caution because of the increased risk of major bleeding in older adults over the age of 75, compared with clopidogrel. If prasugrel is used, a lower dose of 5 mg is recommended, in line with guidelines by the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association.
Pain medication
For pain management, the Beer’s Criteria updated recommendations to avoid NSAIDs, particularly when used in combination with steroids or anticoagulants. The panel highlights that even short-term use of NSAIDs is high risk when used in combination with steroids or anticoagulants. If no other alternatives are possible, patients should be placed on a proton pump inhibitor or misoprostol while taking NSAIDs.
Baclofen should be avoided in older adults with renal insufficiency (estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2) because of the increased risk of encephalopathy, and when used, should be given at the lowest effective dose with close monitoring for mental status changes.
Androgen and estrogen replacement therapy
For androgen replacement therapy, the panel notes that testosterone supplementation should be avoided because of cardiovascular risks unless there is confirmed hypogonadism. The panel revised their recommendation on the basis of emerging data that a history of prostate cancer is not an absolute contraindication for exogenous testosterone. A risk versus benefit discussion about exogenous testosterone should be had with a medical oncologist or urologist in those with a history of prostate cancer.
Regarding estrogen, systemic formulations should not be initiated in women over the age of 60 because of increased risk of cardiovascular events, venous thromboembolism, and dementia. In women with a history of breast cancer, vaginal estrogens are generally felt to be safe to use at low doses, such as less than 25 mcg twice weekly.
Dr. Wang is a geriatrician and general internist at Harborview Medical Center, Seattle.
Every 4 years, an interprofessional panel of experts from the American Geriatrics Society provides updated guidelines on safe prescribing of medications in older adults, known as the Beers Criteria. A 2023 update was released in May 2023 after panel review of more 1,500 clinical trials and research studies published since the last update.
Anticoagulants
Notable changes to the 2023 guidelines include updated recommendations for anticoagulation. Warfarin should be avoided as initial therapy for venous thromboembolism or nonvalvular atrial fibrillation unless there are contraindications to direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) or other substantial barriers to use.
Rivaroxaban should also be avoided, and dabigatran used with caution in favor of apixaban, which is felt to have a better safety profile in older adults. Rivaroxaban may be considered if once daily dosing is deemed to be more clinically appropriate. Financial barriers regarding drug coverage and formulary options were acknowledged as a significant barrier to equitable access to preferred direct oral anticoagulants in older adults.
Diabetes medication
Regarding diabetes management, short-acting sulfonylureas should be avoided in addition to long-acting sulfonylureas, because of the increased risk of hypoglycemia, and cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in older adults. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as an entire class are recommended to be used with caution, as older adults are at higher risk of euglycemic ketoacidosis and urogenital infections, particularly in women in the first month of initiating treatment.
Like DOACs, the panel acknowledged that financial considerations may lead to limited options for oral diabetic treatment. In circumstances where a sulfonylurea is used, short-acting forms are preferred over long acting to reduce the risk of prolonged hypoglycemia.
Aspirin for primary prevention
Alongside the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guideline update in 2022 regarding aspirin for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and stroke, the Beer’s Criteria recommend against initiation of aspirin for primary prevention in older adults. Ticagrelor and prasugrel should be used with caution because of the increased risk of major bleeding in older adults over the age of 75, compared with clopidogrel. If prasugrel is used, a lower dose of 5 mg is recommended, in line with guidelines by the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association.
Pain medication
For pain management, the Beer’s Criteria updated recommendations to avoid NSAIDs, particularly when used in combination with steroids or anticoagulants. The panel highlights that even short-term use of NSAIDs is high risk when used in combination with steroids or anticoagulants. If no other alternatives are possible, patients should be placed on a proton pump inhibitor or misoprostol while taking NSAIDs.
Baclofen should be avoided in older adults with renal insufficiency (estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2) because of the increased risk of encephalopathy, and when used, should be given at the lowest effective dose with close monitoring for mental status changes.
Androgen and estrogen replacement therapy
For androgen replacement therapy, the panel notes that testosterone supplementation should be avoided because of cardiovascular risks unless there is confirmed hypogonadism. The panel revised their recommendation on the basis of emerging data that a history of prostate cancer is not an absolute contraindication for exogenous testosterone. A risk versus benefit discussion about exogenous testosterone should be had with a medical oncologist or urologist in those with a history of prostate cancer.
Regarding estrogen, systemic formulations should not be initiated in women over the age of 60 because of increased risk of cardiovascular events, venous thromboembolism, and dementia. In women with a history of breast cancer, vaginal estrogens are generally felt to be safe to use at low doses, such as less than 25 mcg twice weekly.
Dr. Wang is a geriatrician and general internist at Harborview Medical Center, Seattle.