User login
Internists least likely to choose their specialty again, survey shows
Internists spent an average of 18.5 hours per week on paperwork, according to the Medscape Internist Compensation Report 2020. That number was surpassed only by intensivists, who spent 19.1 hours on such tasks.
Although that number was up $8,000 from last year, it was still less than half that of the top-earning specialists.
The top four specialties in terms of pay were the same this year as they were last year and ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000).
However, internists ranked in the middle of all physicians as to feeling fairly compensated. Just more than half (52%) reported they were fairly compensated, compared with 67% of oncologists, emergency medicine physicians, and radiologists, who were at the top of the ranking, and 44% of nephrologists, who were on the low end.
Also, just as last year, male internists earned 23% more than their female colleagues, which is a slightly smaller pay gap than the 31% gap seen overall.
COVID-19 reversing income gains
However, the compensation picture is changing for all physicians. This report reflects data gathered between Oct. 4, 2019, and Feb. 10, 2020. Since that time, the COVID-19 crisis has reversed income gains for physicians overall. A study from the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) indicates that more than half of medical practices reported a drop in revenue by early April of 55% and a drop in patient volume of 60%.
The MGMA noted, “Practices are struggling to stay afloat – and many fear that this is only the beginning.”
Specialty choice may vary
In the Medscape survey, internists were the physicians least likely to say they would choose their specialty again. Only 66% said they would choose it again, compared with the most enthusiastic specialists: orthopedists (97%), oncologists (96%), and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
However, three-fourths of internists (75%) said they would choose medicine again, which was a larger proportion than that reported by family physicians (74%), neurologists (73%), and plastic surgeons (72%).
This year’s Medscape survey is the first to ask about incentive bonuses. More than half of all physicians (56%) reported receiving one. Bonuses for internists ranked near the bottom, at an average of $27,000. Orthopedists averaged $96,000 bonuses, and family physicians received the least, at an average of $24,000.
Most internists (63%) said their bonus had no effect on the number of hours worked, which was similar to physicians in other specialties.
In good news, internists lost less money on claims that were denied or that required resubmission than most of their colleagues in other specialties. By comparison, internists reported losing 15% on such claims, and plastic surgeons lost almost twice that percentage (28%).
The survey authors noted, “One study found that, on average, 63% of denied claims are recoverable, but healthcare professionals spend about $118 per claim on appeals.”
Relationships with patients most rewarding
When asked about the most rewarding part of their job, internists ranked “gratitude/relationships with patients” at the top. In this survey, internists spent about the same amount of time with patients that all physicians spent with patients on average, 37.9 hours per week.
“Making good money at a job I like” was the fourth-biggest driver of satisfaction (only 11% said that was the most rewarding part), behind “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses” and “knowing that I’m making the world a better place.”
Some questions on the survey pertained to the use of advanced practice providers. More than half of internists (54%) reported their practice included nurse practitioners (NPs), and 36% included physician assistants (PAs); 37% employed neither.
Half of the internists who employed NPs and PAs said they had no effect on profitability, 44% said they increased it, and 6% said they decreased it. Physicians overall were split (47% each) on whether NPs and PAs increased profitability or had no effect on it.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Internists spent an average of 18.5 hours per week on paperwork, according to the Medscape Internist Compensation Report 2020. That number was surpassed only by intensivists, who spent 19.1 hours on such tasks.
Although that number was up $8,000 from last year, it was still less than half that of the top-earning specialists.
The top four specialties in terms of pay were the same this year as they were last year and ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000).
However, internists ranked in the middle of all physicians as to feeling fairly compensated. Just more than half (52%) reported they were fairly compensated, compared with 67% of oncologists, emergency medicine physicians, and radiologists, who were at the top of the ranking, and 44% of nephrologists, who were on the low end.
Also, just as last year, male internists earned 23% more than their female colleagues, which is a slightly smaller pay gap than the 31% gap seen overall.
COVID-19 reversing income gains
However, the compensation picture is changing for all physicians. This report reflects data gathered between Oct. 4, 2019, and Feb. 10, 2020. Since that time, the COVID-19 crisis has reversed income gains for physicians overall. A study from the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) indicates that more than half of medical practices reported a drop in revenue by early April of 55% and a drop in patient volume of 60%.
The MGMA noted, “Practices are struggling to stay afloat – and many fear that this is only the beginning.”
Specialty choice may vary
In the Medscape survey, internists were the physicians least likely to say they would choose their specialty again. Only 66% said they would choose it again, compared with the most enthusiastic specialists: orthopedists (97%), oncologists (96%), and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
However, three-fourths of internists (75%) said they would choose medicine again, which was a larger proportion than that reported by family physicians (74%), neurologists (73%), and plastic surgeons (72%).
This year’s Medscape survey is the first to ask about incentive bonuses. More than half of all physicians (56%) reported receiving one. Bonuses for internists ranked near the bottom, at an average of $27,000. Orthopedists averaged $96,000 bonuses, and family physicians received the least, at an average of $24,000.
Most internists (63%) said their bonus had no effect on the number of hours worked, which was similar to physicians in other specialties.
In good news, internists lost less money on claims that were denied or that required resubmission than most of their colleagues in other specialties. By comparison, internists reported losing 15% on such claims, and plastic surgeons lost almost twice that percentage (28%).
The survey authors noted, “One study found that, on average, 63% of denied claims are recoverable, but healthcare professionals spend about $118 per claim on appeals.”
Relationships with patients most rewarding
When asked about the most rewarding part of their job, internists ranked “gratitude/relationships with patients” at the top. In this survey, internists spent about the same amount of time with patients that all physicians spent with patients on average, 37.9 hours per week.
“Making good money at a job I like” was the fourth-biggest driver of satisfaction (only 11% said that was the most rewarding part), behind “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses” and “knowing that I’m making the world a better place.”
Some questions on the survey pertained to the use of advanced practice providers. More than half of internists (54%) reported their practice included nurse practitioners (NPs), and 36% included physician assistants (PAs); 37% employed neither.
Half of the internists who employed NPs and PAs said they had no effect on profitability, 44% said they increased it, and 6% said they decreased it. Physicians overall were split (47% each) on whether NPs and PAs increased profitability or had no effect on it.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Internists spent an average of 18.5 hours per week on paperwork, according to the Medscape Internist Compensation Report 2020. That number was surpassed only by intensivists, who spent 19.1 hours on such tasks.
Although that number was up $8,000 from last year, it was still less than half that of the top-earning specialists.
The top four specialties in terms of pay were the same this year as they were last year and ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000).
However, internists ranked in the middle of all physicians as to feeling fairly compensated. Just more than half (52%) reported they were fairly compensated, compared with 67% of oncologists, emergency medicine physicians, and radiologists, who were at the top of the ranking, and 44% of nephrologists, who were on the low end.
Also, just as last year, male internists earned 23% more than their female colleagues, which is a slightly smaller pay gap than the 31% gap seen overall.
COVID-19 reversing income gains
However, the compensation picture is changing for all physicians. This report reflects data gathered between Oct. 4, 2019, and Feb. 10, 2020. Since that time, the COVID-19 crisis has reversed income gains for physicians overall. A study from the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) indicates that more than half of medical practices reported a drop in revenue by early April of 55% and a drop in patient volume of 60%.
The MGMA noted, “Practices are struggling to stay afloat – and many fear that this is only the beginning.”
Specialty choice may vary
In the Medscape survey, internists were the physicians least likely to say they would choose their specialty again. Only 66% said they would choose it again, compared with the most enthusiastic specialists: orthopedists (97%), oncologists (96%), and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
However, three-fourths of internists (75%) said they would choose medicine again, which was a larger proportion than that reported by family physicians (74%), neurologists (73%), and plastic surgeons (72%).
This year’s Medscape survey is the first to ask about incentive bonuses. More than half of all physicians (56%) reported receiving one. Bonuses for internists ranked near the bottom, at an average of $27,000. Orthopedists averaged $96,000 bonuses, and family physicians received the least, at an average of $24,000.
Most internists (63%) said their bonus had no effect on the number of hours worked, which was similar to physicians in other specialties.
In good news, internists lost less money on claims that were denied or that required resubmission than most of their colleagues in other specialties. By comparison, internists reported losing 15% on such claims, and plastic surgeons lost almost twice that percentage (28%).
The survey authors noted, “One study found that, on average, 63% of denied claims are recoverable, but healthcare professionals spend about $118 per claim on appeals.”
Relationships with patients most rewarding
When asked about the most rewarding part of their job, internists ranked “gratitude/relationships with patients” at the top. In this survey, internists spent about the same amount of time with patients that all physicians spent with patients on average, 37.9 hours per week.
“Making good money at a job I like” was the fourth-biggest driver of satisfaction (only 11% said that was the most rewarding part), behind “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses” and “knowing that I’m making the world a better place.”
Some questions on the survey pertained to the use of advanced practice providers. More than half of internists (54%) reported their practice included nurse practitioners (NPs), and 36% included physician assistants (PAs); 37% employed neither.
Half of the internists who employed NPs and PAs said they had no effect on profitability, 44% said they increased it, and 6% said they decreased it. Physicians overall were split (47% each) on whether NPs and PAs increased profitability or had no effect on it.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Comparing COVID-19, flu death tolls ‘extremely dangerous’
The number of COVID-19 deaths cannot be directly compared to the number of seasonal influenza deaths because they are calculated differently, researchers say in a report released today.
Whereas COVID-19 death rates are determined from actual counts of people who have died, seasonal influenza death rates are estimated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) using population modeling algorithms, explains Jeremy Samuel Faust, MD, with Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Division of Health Policy and Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts.
The CDC estimates that between 24,000 and 62,000 people died from influenza during the 2019-2020 season (through April 4). At the time of the analysis (as of April 28), COVID-19 deaths had reached 65,000 in the United States.
But making that comparison “is extremely dangerous,” Faust told Medscape Medical News.
“COVID-19 is far more dangerous and is wreaking far more havoc than seasonal influenza ever has,” he said.
Faust coauthored the perspective article, published online in JAMA Internal Medicine, with Carlos del Rio, MD, Division of Infectious Diseases at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
The message and methodology of Faust’s and del Rio’s article are on target, according to Jonathan L. Temte, MD, PhD, who has been working in influenza surveillance for almost 25 years.
Current flu data draw on limited information from primary care practices and hospitals, said Dr. Temte, associate dean for public health and community engagement at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison. The estimates help bridge the gaps, he said, but the system is inherently vulnerable to error.
“Comparing them – as so many people in this country have done – to try to diminish the impact of SARS-CoV2 is not fair,” he said.
Estimated versus actual influenza deaths
The authors illustrate the difference in the way rates of death from influenza are calculated: “Between 2013-2014 and 2018-2019, the reported yearly estimated influenza deaths ranged from 23,000 to 61,000. Over that same time period, however, the number of counted influenza deaths was between 3,448 and 15,620 yearly.”
“It’s apparent [the CDC has] been overestimating,” Faust said. “If you publish a number on the higher end of the estimate, people might take your public health messages more seriously, such as, it’s important to get your yearly flu shot.”
He added that until influenza death rates started to be compared with COVID-19 rates, “there was never really a downside” to reporting estimates.
Dr. Temte said he doesn’t regard overestimating flu deaths as intentional but rather the result of a longstanding “bias against the elderly in this country” that the estimates are meant to account for.
For example, he says, reporting influenza deaths is mandatory when such deaths involve persons younger than 18 years but not when they involve adults.
Also, traditionally, influenza has been seen “as a cause of death in people with multiple comorbidities that was just part and parcel of wintertime,” Dr. Temte said.
“The likelihood of being tested for influenza goes down greatly when you’re older,” he said. “This is slowly changing.”
The CDC acknowledges on its website that it “does not know the exact number of people who have been sick and affected by influenza because influenza is not a reportable disease in most areas of the US.”
It adds that the burden is estimated through the US Influenza Surveillance System, which covers approximately 8.5% of the US population.
Comparing recorded deaths
It’s more accurate and meaningful to compare actual numbers of deaths for the diseases, Dr. Faust and Dr. del Rio say in their article.
When the authors made that comparison, they drew a stark contrast.
There were 15,455 recorded COVID-19 deaths in the week that ended April 21. The week before, the number of recorded deaths was 14,478, they found. (Those were the two most recent weeks before they submitted their article for publication.)
In comparison, counted deaths ranged from 351 to 1,626 during the peak week of the seven influenza seasons between 2013-2014 and 2019-2020. The average counted deaths for the peak week of the seven seasons was 752.4 (95% confidence interval, 558.8-946.1).
“These statistics on counted deaths suggest that the number of COVID-19 deaths for the week ending April 21 was 9.5-fold to 44.1-fold greater than the peak week of counted influenza deaths during the past seven influenza seasons in the US, with a 20.5-fold mean increase (95% CI, 16.3-27.7),” the authors write.
However, Natasha Chida, MD, MSPH, an infectious disease physician and assistant professor at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, said in an interview that the actual number of deaths doesn’t tell the complete flu story either. That count would miss people who later died from secondary complications associated with influenza, she said.
“There’s just no way to reliably count influenza deaths,” she said. “I think if we required it as a reported illness, that would be the ideal situation, but there’s so much flu every year that that probably would not be practical.”
She said she agrees that rates of influenza deaths and rates of COVID-19 deaths cannot be fairly compared.
What the authors don’t touch on, she said, is that flu season lasts 4 to 6 months a year, and just 3 months into the coronavirus pandemic, US deaths due to COVID-19 are already higher than those for seasonal influenza.
“Even if we look at it in the way that people who think we can compare flu and coronavirus do, it’s still not going to work out in their favor from a numbers standpoint,” she said.
The article clarifies the differences for “people who don’t live in the flu world,” she said.
“It is not accurate to compare the two for the reasons the authors described and also because they are very different diseases,” she added.
Real-life validation
Dr. Faust said in an interview that real-life experiences add external validity to their analysis.
Differences in the way deaths are calculated does not reflect frontline clinical conditions during the COVID-19 crisis, with hospitals stretched past their limits, ventilator shortages, and bodies stacking up in some overwhelmed facilities, the authors say.
Dr. Temte said the external validation of the numbers also rings true in light of his own experience.
He said that, in the past 2 months, he has known two people who have had family members who died of COVID-19.
Conversely, “I would have to search long and hard to come up with people I have known or have been one degree of separation from” who have died from influenza, Dr. Temte said.
The authors, Dr. Temte, and Dr. Chida report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of COVID-19 deaths cannot be directly compared to the number of seasonal influenza deaths because they are calculated differently, researchers say in a report released today.
Whereas COVID-19 death rates are determined from actual counts of people who have died, seasonal influenza death rates are estimated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) using population modeling algorithms, explains Jeremy Samuel Faust, MD, with Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Division of Health Policy and Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts.
The CDC estimates that between 24,000 and 62,000 people died from influenza during the 2019-2020 season (through April 4). At the time of the analysis (as of April 28), COVID-19 deaths had reached 65,000 in the United States.
But making that comparison “is extremely dangerous,” Faust told Medscape Medical News.
“COVID-19 is far more dangerous and is wreaking far more havoc than seasonal influenza ever has,” he said.
Faust coauthored the perspective article, published online in JAMA Internal Medicine, with Carlos del Rio, MD, Division of Infectious Diseases at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
The message and methodology of Faust’s and del Rio’s article are on target, according to Jonathan L. Temte, MD, PhD, who has been working in influenza surveillance for almost 25 years.
Current flu data draw on limited information from primary care practices and hospitals, said Dr. Temte, associate dean for public health and community engagement at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison. The estimates help bridge the gaps, he said, but the system is inherently vulnerable to error.
“Comparing them – as so many people in this country have done – to try to diminish the impact of SARS-CoV2 is not fair,” he said.
Estimated versus actual influenza deaths
The authors illustrate the difference in the way rates of death from influenza are calculated: “Between 2013-2014 and 2018-2019, the reported yearly estimated influenza deaths ranged from 23,000 to 61,000. Over that same time period, however, the number of counted influenza deaths was between 3,448 and 15,620 yearly.”
“It’s apparent [the CDC has] been overestimating,” Faust said. “If you publish a number on the higher end of the estimate, people might take your public health messages more seriously, such as, it’s important to get your yearly flu shot.”
He added that until influenza death rates started to be compared with COVID-19 rates, “there was never really a downside” to reporting estimates.
Dr. Temte said he doesn’t regard overestimating flu deaths as intentional but rather the result of a longstanding “bias against the elderly in this country” that the estimates are meant to account for.
For example, he says, reporting influenza deaths is mandatory when such deaths involve persons younger than 18 years but not when they involve adults.
Also, traditionally, influenza has been seen “as a cause of death in people with multiple comorbidities that was just part and parcel of wintertime,” Dr. Temte said.
“The likelihood of being tested for influenza goes down greatly when you’re older,” he said. “This is slowly changing.”
The CDC acknowledges on its website that it “does not know the exact number of people who have been sick and affected by influenza because influenza is not a reportable disease in most areas of the US.”
It adds that the burden is estimated through the US Influenza Surveillance System, which covers approximately 8.5% of the US population.
Comparing recorded deaths
It’s more accurate and meaningful to compare actual numbers of deaths for the diseases, Dr. Faust and Dr. del Rio say in their article.
When the authors made that comparison, they drew a stark contrast.
There were 15,455 recorded COVID-19 deaths in the week that ended April 21. The week before, the number of recorded deaths was 14,478, they found. (Those were the two most recent weeks before they submitted their article for publication.)
In comparison, counted deaths ranged from 351 to 1,626 during the peak week of the seven influenza seasons between 2013-2014 and 2019-2020. The average counted deaths for the peak week of the seven seasons was 752.4 (95% confidence interval, 558.8-946.1).
“These statistics on counted deaths suggest that the number of COVID-19 deaths for the week ending April 21 was 9.5-fold to 44.1-fold greater than the peak week of counted influenza deaths during the past seven influenza seasons in the US, with a 20.5-fold mean increase (95% CI, 16.3-27.7),” the authors write.
However, Natasha Chida, MD, MSPH, an infectious disease physician and assistant professor at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, said in an interview that the actual number of deaths doesn’t tell the complete flu story either. That count would miss people who later died from secondary complications associated with influenza, she said.
“There’s just no way to reliably count influenza deaths,” she said. “I think if we required it as a reported illness, that would be the ideal situation, but there’s so much flu every year that that probably would not be practical.”
She said she agrees that rates of influenza deaths and rates of COVID-19 deaths cannot be fairly compared.
What the authors don’t touch on, she said, is that flu season lasts 4 to 6 months a year, and just 3 months into the coronavirus pandemic, US deaths due to COVID-19 are already higher than those for seasonal influenza.
“Even if we look at it in the way that people who think we can compare flu and coronavirus do, it’s still not going to work out in their favor from a numbers standpoint,” she said.
The article clarifies the differences for “people who don’t live in the flu world,” she said.
“It is not accurate to compare the two for the reasons the authors described and also because they are very different diseases,” she added.
Real-life validation
Dr. Faust said in an interview that real-life experiences add external validity to their analysis.
Differences in the way deaths are calculated does not reflect frontline clinical conditions during the COVID-19 crisis, with hospitals stretched past their limits, ventilator shortages, and bodies stacking up in some overwhelmed facilities, the authors say.
Dr. Temte said the external validation of the numbers also rings true in light of his own experience.
He said that, in the past 2 months, he has known two people who have had family members who died of COVID-19.
Conversely, “I would have to search long and hard to come up with people I have known or have been one degree of separation from” who have died from influenza, Dr. Temte said.
The authors, Dr. Temte, and Dr. Chida report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of COVID-19 deaths cannot be directly compared to the number of seasonal influenza deaths because they are calculated differently, researchers say in a report released today.
Whereas COVID-19 death rates are determined from actual counts of people who have died, seasonal influenza death rates are estimated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) using population modeling algorithms, explains Jeremy Samuel Faust, MD, with Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Division of Health Policy and Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts.
The CDC estimates that between 24,000 and 62,000 people died from influenza during the 2019-2020 season (through April 4). At the time of the analysis (as of April 28), COVID-19 deaths had reached 65,000 in the United States.
But making that comparison “is extremely dangerous,” Faust told Medscape Medical News.
“COVID-19 is far more dangerous and is wreaking far more havoc than seasonal influenza ever has,” he said.
Faust coauthored the perspective article, published online in JAMA Internal Medicine, with Carlos del Rio, MD, Division of Infectious Diseases at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
The message and methodology of Faust’s and del Rio’s article are on target, according to Jonathan L. Temte, MD, PhD, who has been working in influenza surveillance for almost 25 years.
Current flu data draw on limited information from primary care practices and hospitals, said Dr. Temte, associate dean for public health and community engagement at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison. The estimates help bridge the gaps, he said, but the system is inherently vulnerable to error.
“Comparing them – as so many people in this country have done – to try to diminish the impact of SARS-CoV2 is not fair,” he said.
Estimated versus actual influenza deaths
The authors illustrate the difference in the way rates of death from influenza are calculated: “Between 2013-2014 and 2018-2019, the reported yearly estimated influenza deaths ranged from 23,000 to 61,000. Over that same time period, however, the number of counted influenza deaths was between 3,448 and 15,620 yearly.”
“It’s apparent [the CDC has] been overestimating,” Faust said. “If you publish a number on the higher end of the estimate, people might take your public health messages more seriously, such as, it’s important to get your yearly flu shot.”
He added that until influenza death rates started to be compared with COVID-19 rates, “there was never really a downside” to reporting estimates.
Dr. Temte said he doesn’t regard overestimating flu deaths as intentional but rather the result of a longstanding “bias against the elderly in this country” that the estimates are meant to account for.
For example, he says, reporting influenza deaths is mandatory when such deaths involve persons younger than 18 years but not when they involve adults.
Also, traditionally, influenza has been seen “as a cause of death in people with multiple comorbidities that was just part and parcel of wintertime,” Dr. Temte said.
“The likelihood of being tested for influenza goes down greatly when you’re older,” he said. “This is slowly changing.”
The CDC acknowledges on its website that it “does not know the exact number of people who have been sick and affected by influenza because influenza is not a reportable disease in most areas of the US.”
It adds that the burden is estimated through the US Influenza Surveillance System, which covers approximately 8.5% of the US population.
Comparing recorded deaths
It’s more accurate and meaningful to compare actual numbers of deaths for the diseases, Dr. Faust and Dr. del Rio say in their article.
When the authors made that comparison, they drew a stark contrast.
There were 15,455 recorded COVID-19 deaths in the week that ended April 21. The week before, the number of recorded deaths was 14,478, they found. (Those were the two most recent weeks before they submitted their article for publication.)
In comparison, counted deaths ranged from 351 to 1,626 during the peak week of the seven influenza seasons between 2013-2014 and 2019-2020. The average counted deaths for the peak week of the seven seasons was 752.4 (95% confidence interval, 558.8-946.1).
“These statistics on counted deaths suggest that the number of COVID-19 deaths for the week ending April 21 was 9.5-fold to 44.1-fold greater than the peak week of counted influenza deaths during the past seven influenza seasons in the US, with a 20.5-fold mean increase (95% CI, 16.3-27.7),” the authors write.
However, Natasha Chida, MD, MSPH, an infectious disease physician and assistant professor at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, said in an interview that the actual number of deaths doesn’t tell the complete flu story either. That count would miss people who later died from secondary complications associated with influenza, she said.
“There’s just no way to reliably count influenza deaths,” she said. “I think if we required it as a reported illness, that would be the ideal situation, but there’s so much flu every year that that probably would not be practical.”
She said she agrees that rates of influenza deaths and rates of COVID-19 deaths cannot be fairly compared.
What the authors don’t touch on, she said, is that flu season lasts 4 to 6 months a year, and just 3 months into the coronavirus pandemic, US deaths due to COVID-19 are already higher than those for seasonal influenza.
“Even if we look at it in the way that people who think we can compare flu and coronavirus do, it’s still not going to work out in their favor from a numbers standpoint,” she said.
The article clarifies the differences for “people who don’t live in the flu world,” she said.
“It is not accurate to compare the two for the reasons the authors described and also because they are very different diseases,” she added.
Real-life validation
Dr. Faust said in an interview that real-life experiences add external validity to their analysis.
Differences in the way deaths are calculated does not reflect frontline clinical conditions during the COVID-19 crisis, with hospitals stretched past their limits, ventilator shortages, and bodies stacking up in some overwhelmed facilities, the authors say.
Dr. Temte said the external validation of the numbers also rings true in light of his own experience.
He said that, in the past 2 months, he has known two people who have had family members who died of COVID-19.
Conversely, “I would have to search long and hard to come up with people I have known or have been one degree of separation from” who have died from influenza, Dr. Temte said.
The authors, Dr. Temte, and Dr. Chida report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 will likely change docs’ incentive targets, bonuses: Survey
“Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., told Medscape Medical News.
“This amounts to salary reductions of 10% to 30%,” he said.
The COVID-19 crisis dramatically reversed the consistent upward trajectory of physician compensation, according to a Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) survey, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The survey, conducted April 7-8, found that practices have reported an average 55% drop in income. The report also found an average decrease in patient volume of 60%.
Before pandemic, salaries were rising
The pandemic interrupted a steady gain in compensation for this year compared to last, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020.
The report reflects data gathered from October 4, 2019, to February 10, 2020, and includes online survey responses from 17,000 physicians in more than 30 specialties.
Before the pandemic, primary care physician (PCP) pay was up 2.5%, to $243,000, from the previous year’s average of $237,000. Specialists saw a 1.5% increase, from $341,000 in 2019 to $346,000 this year.
Reported compensation for employed physicians included salary, bonus, and profit-sharing contributions. For those self-employed, compensation includes earnings after taxes and deductible business expenses before income tax.
This report reflects only full-time salaries. But most physicians work more than full time. The report notes that physicians overall spent 37.8 hours a week seeing patients. Add to that the 15.6 average hours spent on paperwork, and doctors are averaging 53.4 hours a week.
Administrative demands varied widely by specialty. Physicians in critical care, for example, spent the most hours on paperwork (19.1 per week), and ophthalmologists spent the least on those tasks, at 9.8.
Orthopedists top earners again
The top four specialties were the same this year as they were last year and were ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons, at $479,000, otolaryngologists, at $455,000, and cardiologists, at $438,000.
Pediatricians and public health/preventive medicine physicians made the least, at $232,000, followed by family physicians ($234,000) and diabetes/endocrinology specialists ($236,000).
Despite the low ranking, public health/preventive medicine providers had the biggest compensation increase of all physicians, up 11% from last year. Two specialties saw a decrease: otolaryngology salaries dropped 1%, and dermatology pay dropped 2%. Pay in gastroenterology and diabetes/endocrinology was virtually unchanged from last year.
Kentucky has highest pay
Ranked by state, physicians in Kentucky made the most on average ($346,000). Utah, Ohio, and North Carolina were new to the top 10 in physician pay this year, pushing out Connecticut, Arkansas, and Nevada.
More than half of all physicians receive incentive bonuses (58% of PCPs and 55% of specialists).
The average incentive bonus is 13% of salary, but that varies by specialty. Orthopedists got an average $96,000 bonus, whereas family physicians got $24,000.
According to the report, “Among physicians who have an incentive bonus, about a third of both PCPs and specialists say the prospect of an incentive bonus has encouraged them to work longer hours.”
Gender gap similar to previous year
Consistent with Medscape compensation reports over the past decade, this year’s report shows a large gender gap in pay. Among PCPs, men made 25% more than women ($264,000 vs. $212,000); among specialists, they made 31% more than their female colleagues ($375,000 vs. $286,000).
Some specialties report positive changes from growing awareness of the gap.
“Many organizations have been carefully analyzing their culture, transparency, and pay practices to make sure they aren’t unintentionally discriminating against any group of employees,” Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, pediatrician and CEO of MGMA, told Medscape Medical News.
She added that the growing physician shortage has given all physicians more leverage in salary demands and that increased recognition of the gender gap is giving women more confidence and more evidence to use in negotiations.
Three specialties have seen large increases in the past 5 years in the percentage of women physicians. Obstetrics/gynecology and pediatrics both saw increases from 50% in 2015 to 58% in 2020. Additionally, women now account for 54% of rheumatologists, up from 29% in 2015.
Would you choose your specialty again?
Of responding physicians who were asked if they would choose their specialty again, internists were least likely to say yes (66%), followed by nephrologists (69%) and family physicians (70%).
Orthopedists were most likely to say they would choose the same specialty (97%), followed by oncologists (96%) and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
Most physicians overall (77%) said they would choose medicine again.
Despite aggravations and pressures, in this survey and in previous years, physicians have indicated that the top rewards are “gratitude/relationships with patients,” “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses,” and “knowing that I make the world a better place.” From 24% to 27% ranked those rewards most important.
“Making good money at a job I like” came in fourth, at 12%.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., told Medscape Medical News.
“This amounts to salary reductions of 10% to 30%,” he said.
The COVID-19 crisis dramatically reversed the consistent upward trajectory of physician compensation, according to a Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) survey, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The survey, conducted April 7-8, found that practices have reported an average 55% drop in income. The report also found an average decrease in patient volume of 60%.
Before pandemic, salaries were rising
The pandemic interrupted a steady gain in compensation for this year compared to last, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020.
The report reflects data gathered from October 4, 2019, to February 10, 2020, and includes online survey responses from 17,000 physicians in more than 30 specialties.
Before the pandemic, primary care physician (PCP) pay was up 2.5%, to $243,000, from the previous year’s average of $237,000. Specialists saw a 1.5% increase, from $341,000 in 2019 to $346,000 this year.
Reported compensation for employed physicians included salary, bonus, and profit-sharing contributions. For those self-employed, compensation includes earnings after taxes and deductible business expenses before income tax.
This report reflects only full-time salaries. But most physicians work more than full time. The report notes that physicians overall spent 37.8 hours a week seeing patients. Add to that the 15.6 average hours spent on paperwork, and doctors are averaging 53.4 hours a week.
Administrative demands varied widely by specialty. Physicians in critical care, for example, spent the most hours on paperwork (19.1 per week), and ophthalmologists spent the least on those tasks, at 9.8.
Orthopedists top earners again
The top four specialties were the same this year as they were last year and were ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons, at $479,000, otolaryngologists, at $455,000, and cardiologists, at $438,000.
Pediatricians and public health/preventive medicine physicians made the least, at $232,000, followed by family physicians ($234,000) and diabetes/endocrinology specialists ($236,000).
Despite the low ranking, public health/preventive medicine providers had the biggest compensation increase of all physicians, up 11% from last year. Two specialties saw a decrease: otolaryngology salaries dropped 1%, and dermatology pay dropped 2%. Pay in gastroenterology and diabetes/endocrinology was virtually unchanged from last year.
Kentucky has highest pay
Ranked by state, physicians in Kentucky made the most on average ($346,000). Utah, Ohio, and North Carolina were new to the top 10 in physician pay this year, pushing out Connecticut, Arkansas, and Nevada.
More than half of all physicians receive incentive bonuses (58% of PCPs and 55% of specialists).
The average incentive bonus is 13% of salary, but that varies by specialty. Orthopedists got an average $96,000 bonus, whereas family physicians got $24,000.
According to the report, “Among physicians who have an incentive bonus, about a third of both PCPs and specialists say the prospect of an incentive bonus has encouraged them to work longer hours.”
Gender gap similar to previous year
Consistent with Medscape compensation reports over the past decade, this year’s report shows a large gender gap in pay. Among PCPs, men made 25% more than women ($264,000 vs. $212,000); among specialists, they made 31% more than their female colleagues ($375,000 vs. $286,000).
Some specialties report positive changes from growing awareness of the gap.
“Many organizations have been carefully analyzing their culture, transparency, and pay practices to make sure they aren’t unintentionally discriminating against any group of employees,” Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, pediatrician and CEO of MGMA, told Medscape Medical News.
She added that the growing physician shortage has given all physicians more leverage in salary demands and that increased recognition of the gender gap is giving women more confidence and more evidence to use in negotiations.
Three specialties have seen large increases in the past 5 years in the percentage of women physicians. Obstetrics/gynecology and pediatrics both saw increases from 50% in 2015 to 58% in 2020. Additionally, women now account for 54% of rheumatologists, up from 29% in 2015.
Would you choose your specialty again?
Of responding physicians who were asked if they would choose their specialty again, internists were least likely to say yes (66%), followed by nephrologists (69%) and family physicians (70%).
Orthopedists were most likely to say they would choose the same specialty (97%), followed by oncologists (96%) and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
Most physicians overall (77%) said they would choose medicine again.
Despite aggravations and pressures, in this survey and in previous years, physicians have indicated that the top rewards are “gratitude/relationships with patients,” “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses,” and “knowing that I make the world a better place.” From 24% to 27% ranked those rewards most important.
“Making good money at a job I like” came in fourth, at 12%.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., told Medscape Medical News.
“This amounts to salary reductions of 10% to 30%,” he said.
The COVID-19 crisis dramatically reversed the consistent upward trajectory of physician compensation, according to a Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) survey, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The survey, conducted April 7-8, found that practices have reported an average 55% drop in income. The report also found an average decrease in patient volume of 60%.
Before pandemic, salaries were rising
The pandemic interrupted a steady gain in compensation for this year compared to last, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020.
The report reflects data gathered from October 4, 2019, to February 10, 2020, and includes online survey responses from 17,000 physicians in more than 30 specialties.
Before the pandemic, primary care physician (PCP) pay was up 2.5%, to $243,000, from the previous year’s average of $237,000. Specialists saw a 1.5% increase, from $341,000 in 2019 to $346,000 this year.
Reported compensation for employed physicians included salary, bonus, and profit-sharing contributions. For those self-employed, compensation includes earnings after taxes and deductible business expenses before income tax.
This report reflects only full-time salaries. But most physicians work more than full time. The report notes that physicians overall spent 37.8 hours a week seeing patients. Add to that the 15.6 average hours spent on paperwork, and doctors are averaging 53.4 hours a week.
Administrative demands varied widely by specialty. Physicians in critical care, for example, spent the most hours on paperwork (19.1 per week), and ophthalmologists spent the least on those tasks, at 9.8.
Orthopedists top earners again
The top four specialties were the same this year as they were last year and were ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons, at $479,000, otolaryngologists, at $455,000, and cardiologists, at $438,000.
Pediatricians and public health/preventive medicine physicians made the least, at $232,000, followed by family physicians ($234,000) and diabetes/endocrinology specialists ($236,000).
Despite the low ranking, public health/preventive medicine providers had the biggest compensation increase of all physicians, up 11% from last year. Two specialties saw a decrease: otolaryngology salaries dropped 1%, and dermatology pay dropped 2%. Pay in gastroenterology and diabetes/endocrinology was virtually unchanged from last year.
Kentucky has highest pay
Ranked by state, physicians in Kentucky made the most on average ($346,000). Utah, Ohio, and North Carolina were new to the top 10 in physician pay this year, pushing out Connecticut, Arkansas, and Nevada.
More than half of all physicians receive incentive bonuses (58% of PCPs and 55% of specialists).
The average incentive bonus is 13% of salary, but that varies by specialty. Orthopedists got an average $96,000 bonus, whereas family physicians got $24,000.
According to the report, “Among physicians who have an incentive bonus, about a third of both PCPs and specialists say the prospect of an incentive bonus has encouraged them to work longer hours.”
Gender gap similar to previous year
Consistent with Medscape compensation reports over the past decade, this year’s report shows a large gender gap in pay. Among PCPs, men made 25% more than women ($264,000 vs. $212,000); among specialists, they made 31% more than their female colleagues ($375,000 vs. $286,000).
Some specialties report positive changes from growing awareness of the gap.
“Many organizations have been carefully analyzing their culture, transparency, and pay practices to make sure they aren’t unintentionally discriminating against any group of employees,” Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, pediatrician and CEO of MGMA, told Medscape Medical News.
She added that the growing physician shortage has given all physicians more leverage in salary demands and that increased recognition of the gender gap is giving women more confidence and more evidence to use in negotiations.
Three specialties have seen large increases in the past 5 years in the percentage of women physicians. Obstetrics/gynecology and pediatrics both saw increases from 50% in 2015 to 58% in 2020. Additionally, women now account for 54% of rheumatologists, up from 29% in 2015.
Would you choose your specialty again?
Of responding physicians who were asked if they would choose their specialty again, internists were least likely to say yes (66%), followed by nephrologists (69%) and family physicians (70%).
Orthopedists were most likely to say they would choose the same specialty (97%), followed by oncologists (96%) and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
Most physicians overall (77%) said they would choose medicine again.
Despite aggravations and pressures, in this survey and in previous years, physicians have indicated that the top rewards are “gratitude/relationships with patients,” “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses,” and “knowing that I make the world a better place.” From 24% to 27% ranked those rewards most important.
“Making good money at a job I like” came in fourth, at 12%.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA authorizes emergency use of remdesivir for COVID-19
The investigational antiviral drug, manufactured by Gilead Sciences Inc., was shown in a preliminary analysis of a National Institutes of Health (NIH) clinical trial to shorten recovery time in some patients, according to information presented during a White House press conference earlier this week. However, the results of the trial have not been published and little is known about how safe and effective it is in treating people in the hospital with COVID-19.
The emergency use authorization (EUA) designation means remdesivir can be distributed in the United States and administered intravenously by healthcare providers, as appropriate to treat severe disease. Those with severe disease, the FDA said in a press release, are patients with low blood oxygen levels or those who need oxygen therapy or more intensive support such as a mechanical ventilator.
“There’s tremendous interest among all parties to identify and arm ourselves with medicines to combat COVID-19, and through our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA is working around-the-clock and using every tool at our disposal to speed these efforts,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
The FDA writes, “Based on evaluation of the emergency use authorization criteria and the scientific evidence available, it was determined that it is reasonable to believe that remdesivir may be effective in treating COVID-19, and that, given there are no adequate, approved, or available alternative treatments, the known and potential benefits to treat this serious or life-threatening virus currently outweigh the known and potential risks of the drug’s use.”
The drug must be administered intravenously and the optimal dosing and duration are not yet known, the company said in a press release issued May 1.
In addition, Gilead advises that infusion-related reactions and liver transaminase elevations have been seen in patients treated with the drug.
“If signs and symptoms of a clinically significant infusion reaction occur, immediately discontinue administration of remdesivir and initiate appropriate treatment. Patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events. Monitor renal and hepatic function prior to initiating and daily during therapy with remdesivir; additionally monitor serum chemistries and hematology daily during therapy,” the company said.
Before granting the emergency use authorization, the FDA had allowed for study of the drug in clinical trials, as well as expanded access use for individual patients and through a multipatient expanded access program coordinated by Gilead.
“The EUA will be effective until the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of drugs and biologics for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is terminated and may be revised or revoked if it is determined the EUA no longer meets the statutory criteria for issuance,” the FDA said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational antiviral drug, manufactured by Gilead Sciences Inc., was shown in a preliminary analysis of a National Institutes of Health (NIH) clinical trial to shorten recovery time in some patients, according to information presented during a White House press conference earlier this week. However, the results of the trial have not been published and little is known about how safe and effective it is in treating people in the hospital with COVID-19.
The emergency use authorization (EUA) designation means remdesivir can be distributed in the United States and administered intravenously by healthcare providers, as appropriate to treat severe disease. Those with severe disease, the FDA said in a press release, are patients with low blood oxygen levels or those who need oxygen therapy or more intensive support such as a mechanical ventilator.
“There’s tremendous interest among all parties to identify and arm ourselves with medicines to combat COVID-19, and through our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA is working around-the-clock and using every tool at our disposal to speed these efforts,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
The FDA writes, “Based on evaluation of the emergency use authorization criteria and the scientific evidence available, it was determined that it is reasonable to believe that remdesivir may be effective in treating COVID-19, and that, given there are no adequate, approved, or available alternative treatments, the known and potential benefits to treat this serious or life-threatening virus currently outweigh the known and potential risks of the drug’s use.”
The drug must be administered intravenously and the optimal dosing and duration are not yet known, the company said in a press release issued May 1.
In addition, Gilead advises that infusion-related reactions and liver transaminase elevations have been seen in patients treated with the drug.
“If signs and symptoms of a clinically significant infusion reaction occur, immediately discontinue administration of remdesivir and initiate appropriate treatment. Patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events. Monitor renal and hepatic function prior to initiating and daily during therapy with remdesivir; additionally monitor serum chemistries and hematology daily during therapy,” the company said.
Before granting the emergency use authorization, the FDA had allowed for study of the drug in clinical trials, as well as expanded access use for individual patients and through a multipatient expanded access program coordinated by Gilead.
“The EUA will be effective until the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of drugs and biologics for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is terminated and may be revised or revoked if it is determined the EUA no longer meets the statutory criteria for issuance,” the FDA said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational antiviral drug, manufactured by Gilead Sciences Inc., was shown in a preliminary analysis of a National Institutes of Health (NIH) clinical trial to shorten recovery time in some patients, according to information presented during a White House press conference earlier this week. However, the results of the trial have not been published and little is known about how safe and effective it is in treating people in the hospital with COVID-19.
The emergency use authorization (EUA) designation means remdesivir can be distributed in the United States and administered intravenously by healthcare providers, as appropriate to treat severe disease. Those with severe disease, the FDA said in a press release, are patients with low blood oxygen levels or those who need oxygen therapy or more intensive support such as a mechanical ventilator.
“There’s tremendous interest among all parties to identify and arm ourselves with medicines to combat COVID-19, and through our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA is working around-the-clock and using every tool at our disposal to speed these efforts,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
The FDA writes, “Based on evaluation of the emergency use authorization criteria and the scientific evidence available, it was determined that it is reasonable to believe that remdesivir may be effective in treating COVID-19, and that, given there are no adequate, approved, or available alternative treatments, the known and potential benefits to treat this serious or life-threatening virus currently outweigh the known and potential risks of the drug’s use.”
The drug must be administered intravenously and the optimal dosing and duration are not yet known, the company said in a press release issued May 1.
In addition, Gilead advises that infusion-related reactions and liver transaminase elevations have been seen in patients treated with the drug.
“If signs and symptoms of a clinically significant infusion reaction occur, immediately discontinue administration of remdesivir and initiate appropriate treatment. Patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events. Monitor renal and hepatic function prior to initiating and daily during therapy with remdesivir; additionally monitor serum chemistries and hematology daily during therapy,” the company said.
Before granting the emergency use authorization, the FDA had allowed for study of the drug in clinical trials, as well as expanded access use for individual patients and through a multipatient expanded access program coordinated by Gilead.
“The EUA will be effective until the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of drugs and biologics for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is terminated and may be revised or revoked if it is determined the EUA no longer meets the statutory criteria for issuance,” the FDA said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hydroxychloroquine ineffective for COVID-19, VA study suggests
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) with or without azithromycin (AZ) is not associated with a lower risk of requiring mechanical ventilation, according to a retrospective study of Veterans Affairs patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
The study, which was posted on a preprint server April 21 and has not been peer reviewed, also showed an increased risk of death associated with COVID-19 patients treated with HCQ alone.
“These findings highlight the importance of awaiting the results of ongoing prospective, randomized controlled studies before widespread adoption of these drugs,” write Joseph Magagnoli with Dorn Research Institute at the Columbia (S.C.) VA Health Care System and the department of clinical pharmacy & outcomes sciences, University of South Carolina, and colleagues.
A spokesperson with the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, where several of coauthors practice, said that the authors declined to comment for this article before peer review is completed.
The new data are not the first to suggest no benefit with HCQ among patients with COVID-19. A randomized trial showed no benefit and more side effects among 75 patients in China treated with HCQ, compared with 75 who received standard of care alone, according to a preprint posted online April 14.
No benefit in ventilation, death rates
The current analysis included data from all 368 male patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and treated at Veterans Health Administration medical centers in the United States through April 11.
Patients were categorized into three groups: those treated with HCQ in addition to standard of care (n = 97); those treated with HCQ and the antibiotic azithromycin plus standard of care (n = 113); and those who received standard supportive care only (n = 158).
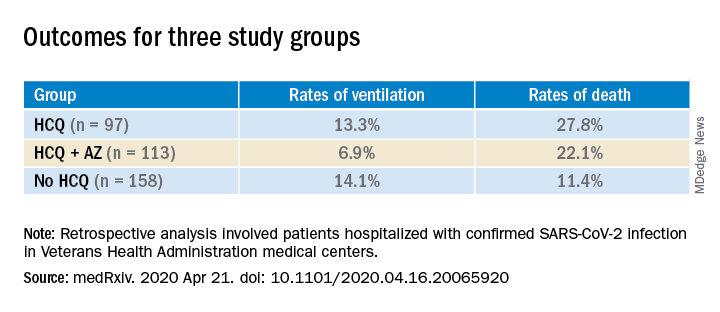
Compared with the no HCQ group, the risk of death from any cause was higher in the HCQ group (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-6.17; P = .03) but not in the HCQ+AZ group (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.56-2.32; P = .72).
The risk of ventilation was similar in the HCQ group (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 0.53-3.79; P = .48) and in the HCQ+AZ group (aHR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.16-1.12; P = .09), compared with the no-HCQ group.
This study provides another counterbalance to claims of HCQ efficacy, David R. Wessner, PhD, professor of biology and chair of the department of health and human values at Davidson (N.C.) College, said in an interview.
Interest in HCQ spiked after an open-label, nonrandomized, single-center study of COVID-19 patients in France suggested that hydroxychloroquine helped clear the virus and had a potential enhanced effect when combined with azithromycin.
But the 36-patient trial has since been called into question.
Wait for convincing data
Dr. Wessner, whose research focuses on viral pathogenesis, says that, although the current data don’t definitively answer the question of whether HCQ is effective in treating COVID-19, taking a “let’s try it and see” approach is not reasonable.
“Until we have good, prospective randomized trials, it’s hard to know what to make of this. But this is more evidence that there’s not a good reason to use [HCQ],” Dr. Wessner said. He points out that the small randomized trial from China shows that HCQ comes with potential harms.
Anecdotal evidence is often cited by those who promote HCQ as a potential treatment, but “those are one-off examples,” Wessner continued. “That doesn’t really tell us anything.”
Some HCQ proponents have said that trials finding no benefit are flawed in that the drug is given too late. However, Dr. Wessner says, there’s no way to prove or disprove that claim without randomized controlled trials.
Conflicting messages
Despite lack of clear evidence of benefit for patients with COVID-19, HCQ is recommended off-label by the Chinese National guideline, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization for the treatment of adult patients with COVID-19.
Conversely, the Infectious Diseases Society of America and a guideline panel convened by the National Institutes of Health each concluded recently that because of insufficient data, they could not recommend any specific treatments for patients with COVID-19.
The VA data for the current study came from the Veterans Affairs Informatics and Computing Infrastructure, which includes inpatient, outpatient and laboratory data and pharmacy claims.
The authors acknowledge some limitations, “including those inherent to all retrospective analyses such as nonrandomization of treatments.”
However, they note that they did adjust for potential confounders, including comorbidities, medications, and clinical and laboratory factors.
A coauthor, Jayakrishna Ambati, MD, is a cofounder of iVeena Holdings, iVeena Delivery Systems and Inflammasome Therapeutics, and has received consultancy fees from Allergan, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Immunovant, Janssen, Olix Pharmaceuticals, Retinal Solutions, and Saksin LifeSciences, all unrelated to this work. Dr. Ambati is named as an inventor on a patent application filed by the University of Virginia relating to COVID-19 but unrelated to this work. Another coauthor has received research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Portola Pharmaceuticals, and United Therapeutics, all unrelated to this work. The other authors and Dr. Wessner have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) with or without azithromycin (AZ) is not associated with a lower risk of requiring mechanical ventilation, according to a retrospective study of Veterans Affairs patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
The study, which was posted on a preprint server April 21 and has not been peer reviewed, also showed an increased risk of death associated with COVID-19 patients treated with HCQ alone.
“These findings highlight the importance of awaiting the results of ongoing prospective, randomized controlled studies before widespread adoption of these drugs,” write Joseph Magagnoli with Dorn Research Institute at the Columbia (S.C.) VA Health Care System and the department of clinical pharmacy & outcomes sciences, University of South Carolina, and colleagues.
A spokesperson with the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, where several of coauthors practice, said that the authors declined to comment for this article before peer review is completed.
The new data are not the first to suggest no benefit with HCQ among patients with COVID-19. A randomized trial showed no benefit and more side effects among 75 patients in China treated with HCQ, compared with 75 who received standard of care alone, according to a preprint posted online April 14.
No benefit in ventilation, death rates
The current analysis included data from all 368 male patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and treated at Veterans Health Administration medical centers in the United States through April 11.
Patients were categorized into three groups: those treated with HCQ in addition to standard of care (n = 97); those treated with HCQ and the antibiotic azithromycin plus standard of care (n = 113); and those who received standard supportive care only (n = 158).

Compared with the no HCQ group, the risk of death from any cause was higher in the HCQ group (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-6.17; P = .03) but not in the HCQ+AZ group (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.56-2.32; P = .72).
The risk of ventilation was similar in the HCQ group (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 0.53-3.79; P = .48) and in the HCQ+AZ group (aHR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.16-1.12; P = .09), compared with the no-HCQ group.
This study provides another counterbalance to claims of HCQ efficacy, David R. Wessner, PhD, professor of biology and chair of the department of health and human values at Davidson (N.C.) College, said in an interview.
Interest in HCQ spiked after an open-label, nonrandomized, single-center study of COVID-19 patients in France suggested that hydroxychloroquine helped clear the virus and had a potential enhanced effect when combined with azithromycin.
But the 36-patient trial has since been called into question.
Wait for convincing data
Dr. Wessner, whose research focuses on viral pathogenesis, says that, although the current data don’t definitively answer the question of whether HCQ is effective in treating COVID-19, taking a “let’s try it and see” approach is not reasonable.
“Until we have good, prospective randomized trials, it’s hard to know what to make of this. But this is more evidence that there’s not a good reason to use [HCQ],” Dr. Wessner said. He points out that the small randomized trial from China shows that HCQ comes with potential harms.
Anecdotal evidence is often cited by those who promote HCQ as a potential treatment, but “those are one-off examples,” Wessner continued. “That doesn’t really tell us anything.”
Some HCQ proponents have said that trials finding no benefit are flawed in that the drug is given too late. However, Dr. Wessner says, there’s no way to prove or disprove that claim without randomized controlled trials.
Conflicting messages
Despite lack of clear evidence of benefit for patients with COVID-19, HCQ is recommended off-label by the Chinese National guideline, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization for the treatment of adult patients with COVID-19.
Conversely, the Infectious Diseases Society of America and a guideline panel convened by the National Institutes of Health each concluded recently that because of insufficient data, they could not recommend any specific treatments for patients with COVID-19.
The VA data for the current study came from the Veterans Affairs Informatics and Computing Infrastructure, which includes inpatient, outpatient and laboratory data and pharmacy claims.
The authors acknowledge some limitations, “including those inherent to all retrospective analyses such as nonrandomization of treatments.”
However, they note that they did adjust for potential confounders, including comorbidities, medications, and clinical and laboratory factors.
A coauthor, Jayakrishna Ambati, MD, is a cofounder of iVeena Holdings, iVeena Delivery Systems and Inflammasome Therapeutics, and has received consultancy fees from Allergan, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Immunovant, Janssen, Olix Pharmaceuticals, Retinal Solutions, and Saksin LifeSciences, all unrelated to this work. Dr. Ambati is named as an inventor on a patent application filed by the University of Virginia relating to COVID-19 but unrelated to this work. Another coauthor has received research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Portola Pharmaceuticals, and United Therapeutics, all unrelated to this work. The other authors and Dr. Wessner have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) with or without azithromycin (AZ) is not associated with a lower risk of requiring mechanical ventilation, according to a retrospective study of Veterans Affairs patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
The study, which was posted on a preprint server April 21 and has not been peer reviewed, also showed an increased risk of death associated with COVID-19 patients treated with HCQ alone.
“These findings highlight the importance of awaiting the results of ongoing prospective, randomized controlled studies before widespread adoption of these drugs,” write Joseph Magagnoli with Dorn Research Institute at the Columbia (S.C.) VA Health Care System and the department of clinical pharmacy & outcomes sciences, University of South Carolina, and colleagues.
A spokesperson with the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, where several of coauthors practice, said that the authors declined to comment for this article before peer review is completed.
The new data are not the first to suggest no benefit with HCQ among patients with COVID-19. A randomized trial showed no benefit and more side effects among 75 patients in China treated with HCQ, compared with 75 who received standard of care alone, according to a preprint posted online April 14.
No benefit in ventilation, death rates
The current analysis included data from all 368 male patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and treated at Veterans Health Administration medical centers in the United States through April 11.
Patients were categorized into three groups: those treated with HCQ in addition to standard of care (n = 97); those treated with HCQ and the antibiotic azithromycin plus standard of care (n = 113); and those who received standard supportive care only (n = 158).

Compared with the no HCQ group, the risk of death from any cause was higher in the HCQ group (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-6.17; P = .03) but not in the HCQ+AZ group (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.56-2.32; P = .72).
The risk of ventilation was similar in the HCQ group (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 0.53-3.79; P = .48) and in the HCQ+AZ group (aHR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.16-1.12; P = .09), compared with the no-HCQ group.
This study provides another counterbalance to claims of HCQ efficacy, David R. Wessner, PhD, professor of biology and chair of the department of health and human values at Davidson (N.C.) College, said in an interview.
Interest in HCQ spiked after an open-label, nonrandomized, single-center study of COVID-19 patients in France suggested that hydroxychloroquine helped clear the virus and had a potential enhanced effect when combined with azithromycin.
But the 36-patient trial has since been called into question.
Wait for convincing data
Dr. Wessner, whose research focuses on viral pathogenesis, says that, although the current data don’t definitively answer the question of whether HCQ is effective in treating COVID-19, taking a “let’s try it and see” approach is not reasonable.
“Until we have good, prospective randomized trials, it’s hard to know what to make of this. But this is more evidence that there’s not a good reason to use [HCQ],” Dr. Wessner said. He points out that the small randomized trial from China shows that HCQ comes with potential harms.
Anecdotal evidence is often cited by those who promote HCQ as a potential treatment, but “those are one-off examples,” Wessner continued. “That doesn’t really tell us anything.”
Some HCQ proponents have said that trials finding no benefit are flawed in that the drug is given too late. However, Dr. Wessner says, there’s no way to prove or disprove that claim without randomized controlled trials.
Conflicting messages
Despite lack of clear evidence of benefit for patients with COVID-19, HCQ is recommended off-label by the Chinese National guideline, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization for the treatment of adult patients with COVID-19.
Conversely, the Infectious Diseases Society of America and a guideline panel convened by the National Institutes of Health each concluded recently that because of insufficient data, they could not recommend any specific treatments for patients with COVID-19.
The VA data for the current study came from the Veterans Affairs Informatics and Computing Infrastructure, which includes inpatient, outpatient and laboratory data and pharmacy claims.
The authors acknowledge some limitations, “including those inherent to all retrospective analyses such as nonrandomization of treatments.”
However, they note that they did adjust for potential confounders, including comorbidities, medications, and clinical and laboratory factors.
A coauthor, Jayakrishna Ambati, MD, is a cofounder of iVeena Holdings, iVeena Delivery Systems and Inflammasome Therapeutics, and has received consultancy fees from Allergan, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Immunovant, Janssen, Olix Pharmaceuticals, Retinal Solutions, and Saksin LifeSciences, all unrelated to this work. Dr. Ambati is named as an inventor on a patent application filed by the University of Virginia relating to COVID-19 but unrelated to this work. Another coauthor has received research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Portola Pharmaceuticals, and United Therapeutics, all unrelated to this work. The other authors and Dr. Wessner have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How to sanitize N95 masks for reuse: NIH study
Exposing contaminated N95 respirators to vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) or ultraviolet (UV) light appears to eliminate the SARS-CoV-2 virus from the material and preserve the integrity of the masks fit for up to three uses, a National Institutes of Health (NIH) study shows.
Dry heat (70° C) was also found to eliminate the virus on masks but was effective for two uses instead of three.
Robert Fischer, PhD, with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in Hamilton, Montana, and colleagues posted the findings on a preprint server on April 15. The paper has not yet been peer reviewed.
Four methods tested
Fischer and colleagues compared four methods for decontaminating the masks, which are designed for one-time use: UV radiation (260-285 nm); 70° C dry heat; 70% ethanol spray; and VHP.
For each method, the researchers compared the rate at which SARS-CoV-2 is inactivated on N95 filter fabric to that on stainless steel.
All four methods eliminated detectable SARS-CoV-2 virus from the fabric test samples, though the time needed for decontamination varied. VHP was the quickest, requiring 10 minutes. Dry heat and UV light each required approximately 60 minutes. Ethanol required an intermediate amount of time.
To test durability over three uses, the researchers treated intact, clean masks with the same decontamination method and assessed function via quantitative fit testing.
Volunteers from the Rocky Mountain laboratory wore the masks for 2 hours to test fit and seal.
The researchers found that masks that had been decontaminated with ethanol spray did not function effectively after decontamination, and they did not recommend use of that method.
By contrast, masks decontaminated with UV and VHP could be used up to three times and function properly. Masks decontaminated with dry heat could be used two times before function declined.
“Our results indicate that N95 respirators can be decontaminated and reused in times of shortage for up to three times for UV and HPV, and up to two times for dry heat,” the authors write. “However, utmost care should be given to ensure the proper functioning of the N95 respirator after each decontamination using readily available qualitative fit testing tools and to ensure that treatments are carried out for sufficient time to achieve desired risk-reduction.”
Reassurance for clinicians
The results will reassure clinicians, many of whom are already using these decontamination methods, Ravina Kullar, PharmD, MPH, an infectious disease expert with the Infectious Diseases Society of America, told Medscape Medical News.
Kullar, who is also an adjunct faculty member at the David Geffen School of Medicine of the University of California, Los Angeles, said the most widely used methods have been UV light and VPH.
UV light has been used for years to decontaminate rooms, she said. She also said that so far, supplies of hydrogen peroxide are adequate.
A shortcoming of the study, Kullar said, is that it tested the masks for only 2 hours, whereas in clinical practice, they are being worn for much longer periods.
After the study is peer reviewed, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) may update its recommendations, she said.
So far, she noted, the CDC has not approved any method for decontaminating masks, “but it has said that it does not object to using these sterilizers, disinfectants, devices, and air purifiers for effectively killing this virus.”
Safe, multiple use of the masks is critical in the COVID-19 crisis, she said.
“We have to look at other mechanisms to keep these N95 respirators in use when there’s such a shortage,” she said.
Integrity of the fit was an important factor in the study.
“All health care workers have to go through a fitting to have that mask fitted appropriately. That’s why these N95s are only approved for health care professionals, not the lay public,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health; the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency; the University of California, Los Angeles; the US National Science Foundation; and the US Department of Defense.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exposing contaminated N95 respirators to vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) or ultraviolet (UV) light appears to eliminate the SARS-CoV-2 virus from the material and preserve the integrity of the masks fit for up to three uses, a National Institutes of Health (NIH) study shows.
Dry heat (70° C) was also found to eliminate the virus on masks but was effective for two uses instead of three.
Robert Fischer, PhD, with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in Hamilton, Montana, and colleagues posted the findings on a preprint server on April 15. The paper has not yet been peer reviewed.
Four methods tested
Fischer and colleagues compared four methods for decontaminating the masks, which are designed for one-time use: UV radiation (260-285 nm); 70° C dry heat; 70% ethanol spray; and VHP.
For each method, the researchers compared the rate at which SARS-CoV-2 is inactivated on N95 filter fabric to that on stainless steel.
All four methods eliminated detectable SARS-CoV-2 virus from the fabric test samples, though the time needed for decontamination varied. VHP was the quickest, requiring 10 minutes. Dry heat and UV light each required approximately 60 minutes. Ethanol required an intermediate amount of time.
To test durability over three uses, the researchers treated intact, clean masks with the same decontamination method and assessed function via quantitative fit testing.
Volunteers from the Rocky Mountain laboratory wore the masks for 2 hours to test fit and seal.
The researchers found that masks that had been decontaminated with ethanol spray did not function effectively after decontamination, and they did not recommend use of that method.
By contrast, masks decontaminated with UV and VHP could be used up to three times and function properly. Masks decontaminated with dry heat could be used two times before function declined.
“Our results indicate that N95 respirators can be decontaminated and reused in times of shortage for up to three times for UV and HPV, and up to two times for dry heat,” the authors write. “However, utmost care should be given to ensure the proper functioning of the N95 respirator after each decontamination using readily available qualitative fit testing tools and to ensure that treatments are carried out for sufficient time to achieve desired risk-reduction.”
Reassurance for clinicians
The results will reassure clinicians, many of whom are already using these decontamination methods, Ravina Kullar, PharmD, MPH, an infectious disease expert with the Infectious Diseases Society of America, told Medscape Medical News.
Kullar, who is also an adjunct faculty member at the David Geffen School of Medicine of the University of California, Los Angeles, said the most widely used methods have been UV light and VPH.
UV light has been used for years to decontaminate rooms, she said. She also said that so far, supplies of hydrogen peroxide are adequate.
A shortcoming of the study, Kullar said, is that it tested the masks for only 2 hours, whereas in clinical practice, they are being worn for much longer periods.
After the study is peer reviewed, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) may update its recommendations, she said.
So far, she noted, the CDC has not approved any method for decontaminating masks, “but it has said that it does not object to using these sterilizers, disinfectants, devices, and air purifiers for effectively killing this virus.”
Safe, multiple use of the masks is critical in the COVID-19 crisis, she said.
“We have to look at other mechanisms to keep these N95 respirators in use when there’s such a shortage,” she said.
Integrity of the fit was an important factor in the study.
“All health care workers have to go through a fitting to have that mask fitted appropriately. That’s why these N95s are only approved for health care professionals, not the lay public,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health; the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency; the University of California, Los Angeles; the US National Science Foundation; and the US Department of Defense.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exposing contaminated N95 respirators to vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) or ultraviolet (UV) light appears to eliminate the SARS-CoV-2 virus from the material and preserve the integrity of the masks fit for up to three uses, a National Institutes of Health (NIH) study shows.
Dry heat (70° C) was also found to eliminate the virus on masks but was effective for two uses instead of three.
Robert Fischer, PhD, with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in Hamilton, Montana, and colleagues posted the findings on a preprint server on April 15. The paper has not yet been peer reviewed.
Four methods tested
Fischer and colleagues compared four methods for decontaminating the masks, which are designed for one-time use: UV radiation (260-285 nm); 70° C dry heat; 70% ethanol spray; and VHP.
For each method, the researchers compared the rate at which SARS-CoV-2 is inactivated on N95 filter fabric to that on stainless steel.
All four methods eliminated detectable SARS-CoV-2 virus from the fabric test samples, though the time needed for decontamination varied. VHP was the quickest, requiring 10 minutes. Dry heat and UV light each required approximately 60 minutes. Ethanol required an intermediate amount of time.
To test durability over three uses, the researchers treated intact, clean masks with the same decontamination method and assessed function via quantitative fit testing.
Volunteers from the Rocky Mountain laboratory wore the masks for 2 hours to test fit and seal.
The researchers found that masks that had been decontaminated with ethanol spray did not function effectively after decontamination, and they did not recommend use of that method.
By contrast, masks decontaminated with UV and VHP could be used up to three times and function properly. Masks decontaminated with dry heat could be used two times before function declined.
“Our results indicate that N95 respirators can be decontaminated and reused in times of shortage for up to three times for UV and HPV, and up to two times for dry heat,” the authors write. “However, utmost care should be given to ensure the proper functioning of the N95 respirator after each decontamination using readily available qualitative fit testing tools and to ensure that treatments are carried out for sufficient time to achieve desired risk-reduction.”
Reassurance for clinicians
The results will reassure clinicians, many of whom are already using these decontamination methods, Ravina Kullar, PharmD, MPH, an infectious disease expert with the Infectious Diseases Society of America, told Medscape Medical News.
Kullar, who is also an adjunct faculty member at the David Geffen School of Medicine of the University of California, Los Angeles, said the most widely used methods have been UV light and VPH.
UV light has been used for years to decontaminate rooms, she said. She also said that so far, supplies of hydrogen peroxide are adequate.
A shortcoming of the study, Kullar said, is that it tested the masks for only 2 hours, whereas in clinical practice, they are being worn for much longer periods.
After the study is peer reviewed, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) may update its recommendations, she said.
So far, she noted, the CDC has not approved any method for decontaminating masks, “but it has said that it does not object to using these sterilizers, disinfectants, devices, and air purifiers for effectively killing this virus.”
Safe, multiple use of the masks is critical in the COVID-19 crisis, she said.
“We have to look at other mechanisms to keep these N95 respirators in use when there’s such a shortage,” she said.
Integrity of the fit was an important factor in the study.
“All health care workers have to go through a fitting to have that mask fitted appropriately. That’s why these N95s are only approved for health care professionals, not the lay public,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health; the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency; the University of California, Los Angeles; the US National Science Foundation; and the US Department of Defense.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No hydroxychloroquine benefit in small, randomized COVID-19 trial
However, two experts caution that, because of confounding, the trial is unable to answer convincingly the question of whether HCQ can benefit COVID-19 patients.
Wei Tang, with the Departments of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine at Ruijin Hospital, in Shanghai, China, and colleagues enrolled patients with COVID-19 from 16 treatment centers in China in February. They posted their findings on the medRxiv preprint server, but their paper has not been peer reviewed. A coauthor told Medscape Medical News the work has been submitted to a journal.
The overall 28-day negative conversion rate of SARS-CoV-2, which was the primary endpoint, was similar in the two 75-patient treatment groups. The Kaplan-Meier estimate for negative conversion rate was 85.4% in the HCQ plus standard of care (SOC) arm, vs 81.3% in the SOC-only group (P = .341). Negative conversion rates for the two groups were similar at days 4, 7, 10, 14, and 21.
Adverse events were reported in 8.8% of patients in the control group compared with 30% in the HCQ group. Diarrhea was the most common side effect, occurring in 10% of patients in the HCQ group vs none in the control group. Two patients in the HCQ arm had serious adverse events; one experienced disease progression, and the other experienced upper respiratory tract infection.
Patients in the HCQ group received a high loading dose of 1200 mg daily for 3 days followed by a maintenance dose of 800 mg daily for the remaining days. Total duration was 2 weeks for patients with mild or moderate disease and 3 weeks for those with severe disease.
No Difference in Relief of Symptoms
The two arms were similar in alleviation of symptoms by day 28: 59.9% with HCQ plus SOC vs 66.6% with SOC alone.
However, the researchers said that in a post hoc analysis, they found a significant reduction of symptoms after adjusting for the confounding effects of antiviral agents (hazard ratio, 8.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.09 – 71.3).
In addition, Tang and colleagues report a significantly greater reduction of C-reactive protein (CRP), a biomarker for inflammation, from baseline to day 28 in the HCQ group in comparison with the control group (6.986 vs 2.723 mg/L).
The authors suggest the alleviation of symptoms may come from HCQ’s anti-inflammatory effects.
The mean age of the patients was 46 years, and 55% were male. Almost all patients had mild or moderate disease; two had severe disease.
Experts Say Study Arms May Not Have Been Comparable
J. Michelle Kahlenberg, MD, PhD, research professor of rheumatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told Medscape Medical News that it’s important to note that in the post hoc analysis, 89% of the patients in this trial were receiving other therapy in addition to HCQ.
“When [the researchers] say they saw improvement in symptoms when they removed the confounders, what they actually did was remove the patients from the analysis that got antivirals, and that left 14 patients in each arm,” Kahlenberg said.
Moreover, Kahlenberg noted, 20% of patients who received HCQ had mild symptoms, whereas only 9% of those in the SOC group did.
“We don’t know how those patients played out in the post hoc analysis — whether it was the patients who were really mild that didn’t get the antivirals that were left in the hydroxychloroquine group and that’s why they had a slightly faster resolution of symptoms,” she said.
She said that in this study, the researchers calculated CRP in milligrams per liter, whereas in the United States, it is measured in milligrams per deciliter. The conversion highlights the fact that the reduction in CRP was not terribly noteworthy, she said.
“The patients with COVID who tend to tank and have cytokine storms ― their CRP is much higher,” she said. “So the small improvement in CRP wasn’t that exciting.
“I don’t think this gets us anywhere closer to an answer. It’s another muddy study,” she said.
Similarly, Christopher V. Plowe, MD, MPH, director of the Global Health Institute at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, told Medscape Medical News he sees no convincing answers in this study.
Plowe, professor of medicine, molecular genetics, microbiology, and global health at Duke, also noted differences between the two groups at enrollment.
For example, the HCQ group had more than three times the number of patients with shortness of breath (22.1% vs 5.9%); more with sputum production (16.2 vs 5.9%); and more with cough (51.5% vs 38.2%). In addition, the average age was 4 years higher in the HCQ group.
“It makes me wonder whether the randomization was truly random,” Plowe said.
Plowe also questioned the authors’ statement that they didn’t see cardiac arrhythmia events, such as prolonged QT intervals. “I can’t see any evidence that they did an EKG on anybody,” he said.
“This study leaves the door open to the possibility that hydroxychloroquine may have a clinical benefit. If there is a benefit, it seems to be related to the drug’s anti-inflammatory properties. If that’s the case, I’m not sure this particular drug, as opposed to others, would be the way to go,” Plowe said.
Mixed Results in Other Studies
“Our negative results on the anti-viral efficacy of HCQ obtained in this trial are on the contrary to the encouraging in-vitro results and to the recently reported promising results from a non-randomized trial with 36 COVID-19 patients,” the authors write.
However, the 36-patient trial to which they refer has since been called into question, as previously reported by Retraction Watch.
Despite lack of clear evidence of benefit, HCQ is recommended off label for the treatment of COVID-19 by the Chinese National guideline, and the US Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization for the treatment of adult patients with COVID-19.
By contrast, the Infectious Diseases Society of America recently concluded that because of insufficient data, they could not recommend any particular treatment for patients with COVID-19.
The work was supported by the Emergent Projects of National Science and Technology; the National Natural Science Foundation of China; the National Key Research and Development Program of China; the Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty; the National Innovative Research Team of High-Level Local Universities in Shanghai; the Shanghai Key Discipline for Respiratory Diseases; the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for Significant New Drugs Development; and Key Projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program. The authors, Kahlenberg, and Plowe have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, two experts caution that, because of confounding, the trial is unable to answer convincingly the question of whether HCQ can benefit COVID-19 patients.
Wei Tang, with the Departments of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine at Ruijin Hospital, in Shanghai, China, and colleagues enrolled patients with COVID-19 from 16 treatment centers in China in February. They posted their findings on the medRxiv preprint server, but their paper has not been peer reviewed. A coauthor told Medscape Medical News the work has been submitted to a journal.
The overall 28-day negative conversion rate of SARS-CoV-2, which was the primary endpoint, was similar in the two 75-patient treatment groups. The Kaplan-Meier estimate for negative conversion rate was 85.4% in the HCQ plus standard of care (SOC) arm, vs 81.3% in the SOC-only group (P = .341). Negative conversion rates for the two groups were similar at days 4, 7, 10, 14, and 21.
Adverse events were reported in 8.8% of patients in the control group compared with 30% in the HCQ group. Diarrhea was the most common side effect, occurring in 10% of patients in the HCQ group vs none in the control group. Two patients in the HCQ arm had serious adverse events; one experienced disease progression, and the other experienced upper respiratory tract infection.
Patients in the HCQ group received a high loading dose of 1200 mg daily for 3 days followed by a maintenance dose of 800 mg daily for the remaining days. Total duration was 2 weeks for patients with mild or moderate disease and 3 weeks for those with severe disease.
No Difference in Relief of Symptoms
The two arms were similar in alleviation of symptoms by day 28: 59.9% with HCQ plus SOC vs 66.6% with SOC alone.
However, the researchers said that in a post hoc analysis, they found a significant reduction of symptoms after adjusting for the confounding effects of antiviral agents (hazard ratio, 8.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.09 – 71.3).
In addition, Tang and colleagues report a significantly greater reduction of C-reactive protein (CRP), a biomarker for inflammation, from baseline to day 28 in the HCQ group in comparison with the control group (6.986 vs 2.723 mg/L).
The authors suggest the alleviation of symptoms may come from HCQ’s anti-inflammatory effects.
The mean age of the patients was 46 years, and 55% were male. Almost all patients had mild or moderate disease; two had severe disease.
Experts Say Study Arms May Not Have Been Comparable
J. Michelle Kahlenberg, MD, PhD, research professor of rheumatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told Medscape Medical News that it’s important to note that in the post hoc analysis, 89% of the patients in this trial were receiving other therapy in addition to HCQ.
“When [the researchers] say they saw improvement in symptoms when they removed the confounders, what they actually did was remove the patients from the analysis that got antivirals, and that left 14 patients in each arm,” Kahlenberg said.
Moreover, Kahlenberg noted, 20% of patients who received HCQ had mild symptoms, whereas only 9% of those in the SOC group did.
“We don’t know how those patients played out in the post hoc analysis — whether it was the patients who were really mild that didn’t get the antivirals that were left in the hydroxychloroquine group and that’s why they had a slightly faster resolution of symptoms,” she said.
She said that in this study, the researchers calculated CRP in milligrams per liter, whereas in the United States, it is measured in milligrams per deciliter. The conversion highlights the fact that the reduction in CRP was not terribly noteworthy, she said.
“The patients with COVID who tend to tank and have cytokine storms ― their CRP is much higher,” she said. “So the small improvement in CRP wasn’t that exciting.
“I don’t think this gets us anywhere closer to an answer. It’s another muddy study,” she said.
Similarly, Christopher V. Plowe, MD, MPH, director of the Global Health Institute at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, told Medscape Medical News he sees no convincing answers in this study.
Plowe, professor of medicine, molecular genetics, microbiology, and global health at Duke, also noted differences between the two groups at enrollment.
For example, the HCQ group had more than three times the number of patients with shortness of breath (22.1% vs 5.9%); more with sputum production (16.2 vs 5.9%); and more with cough (51.5% vs 38.2%). In addition, the average age was 4 years higher in the HCQ group.
“It makes me wonder whether the randomization was truly random,” Plowe said.
Plowe also questioned the authors’ statement that they didn’t see cardiac arrhythmia events, such as prolonged QT intervals. “I can’t see any evidence that they did an EKG on anybody,” he said.
“This study leaves the door open to the possibility that hydroxychloroquine may have a clinical benefit. If there is a benefit, it seems to be related to the drug’s anti-inflammatory properties. If that’s the case, I’m not sure this particular drug, as opposed to others, would be the way to go,” Plowe said.
Mixed Results in Other Studies
“Our negative results on the anti-viral efficacy of HCQ obtained in this trial are on the contrary to the encouraging in-vitro results and to the recently reported promising results from a non-randomized trial with 36 COVID-19 patients,” the authors write.
However, the 36-patient trial to which they refer has since been called into question, as previously reported by Retraction Watch.
Despite lack of clear evidence of benefit, HCQ is recommended off label for the treatment of COVID-19 by the Chinese National guideline, and the US Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization for the treatment of adult patients with COVID-19.
By contrast, the Infectious Diseases Society of America recently concluded that because of insufficient data, they could not recommend any particular treatment for patients with COVID-19.
The work was supported by the Emergent Projects of National Science and Technology; the National Natural Science Foundation of China; the National Key Research and Development Program of China; the Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty; the National Innovative Research Team of High-Level Local Universities in Shanghai; the Shanghai Key Discipline for Respiratory Diseases; the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for Significant New Drugs Development; and Key Projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program. The authors, Kahlenberg, and Plowe have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, two experts caution that, because of confounding, the trial is unable to answer convincingly the question of whether HCQ can benefit COVID-19 patients.
Wei Tang, with the Departments of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine at Ruijin Hospital, in Shanghai, China, and colleagues enrolled patients with COVID-19 from 16 treatment centers in China in February. They posted their findings on the medRxiv preprint server, but their paper has not been peer reviewed. A coauthor told Medscape Medical News the work has been submitted to a journal.
The overall 28-day negative conversion rate of SARS-CoV-2, which was the primary endpoint, was similar in the two 75-patient treatment groups. The Kaplan-Meier estimate for negative conversion rate was 85.4% in the HCQ plus standard of care (SOC) arm, vs 81.3% in the SOC-only group (P = .341). Negative conversion rates for the two groups were similar at days 4, 7, 10, 14, and 21.
Adverse events were reported in 8.8% of patients in the control group compared with 30% in the HCQ group. Diarrhea was the most common side effect, occurring in 10% of patients in the HCQ group vs none in the control group. Two patients in the HCQ arm had serious adverse events; one experienced disease progression, and the other experienced upper respiratory tract infection.
Patients in the HCQ group received a high loading dose of 1200 mg daily for 3 days followed by a maintenance dose of 800 mg daily for the remaining days. Total duration was 2 weeks for patients with mild or moderate disease and 3 weeks for those with severe disease.
No Difference in Relief of Symptoms
The two arms were similar in alleviation of symptoms by day 28: 59.9% with HCQ plus SOC vs 66.6% with SOC alone.
However, the researchers said that in a post hoc analysis, they found a significant reduction of symptoms after adjusting for the confounding effects of antiviral agents (hazard ratio, 8.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.09 – 71.3).
In addition, Tang and colleagues report a significantly greater reduction of C-reactive protein (CRP), a biomarker for inflammation, from baseline to day 28 in the HCQ group in comparison with the control group (6.986 vs 2.723 mg/L).
The authors suggest the alleviation of symptoms may come from HCQ’s anti-inflammatory effects.
The mean age of the patients was 46 years, and 55% were male. Almost all patients had mild or moderate disease; two had severe disease.
Experts Say Study Arms May Not Have Been Comparable
J. Michelle Kahlenberg, MD, PhD, research professor of rheumatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told Medscape Medical News that it’s important to note that in the post hoc analysis, 89% of the patients in this trial were receiving other therapy in addition to HCQ.
“When [the researchers] say they saw improvement in symptoms when they removed the confounders, what they actually did was remove the patients from the analysis that got antivirals, and that left 14 patients in each arm,” Kahlenberg said.
Moreover, Kahlenberg noted, 20% of patients who received HCQ had mild symptoms, whereas only 9% of those in the SOC group did.
“We don’t know how those patients played out in the post hoc analysis — whether it was the patients who were really mild that didn’t get the antivirals that were left in the hydroxychloroquine group and that’s why they had a slightly faster resolution of symptoms,” she said.
She said that in this study, the researchers calculated CRP in milligrams per liter, whereas in the United States, it is measured in milligrams per deciliter. The conversion highlights the fact that the reduction in CRP was not terribly noteworthy, she said.
“The patients with COVID who tend to tank and have cytokine storms ― their CRP is much higher,” she said. “So the small improvement in CRP wasn’t that exciting.
“I don’t think this gets us anywhere closer to an answer. It’s another muddy study,” she said.
Similarly, Christopher V. Plowe, MD, MPH, director of the Global Health Institute at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, told Medscape Medical News he sees no convincing answers in this study.
Plowe, professor of medicine, molecular genetics, microbiology, and global health at Duke, also noted differences between the two groups at enrollment.
For example, the HCQ group had more than three times the number of patients with shortness of breath (22.1% vs 5.9%); more with sputum production (16.2 vs 5.9%); and more with cough (51.5% vs 38.2%). In addition, the average age was 4 years higher in the HCQ group.
“It makes me wonder whether the randomization was truly random,” Plowe said.
Plowe also questioned the authors’ statement that they didn’t see cardiac arrhythmia events, such as prolonged QT intervals. “I can’t see any evidence that they did an EKG on anybody,” he said.
“This study leaves the door open to the possibility that hydroxychloroquine may have a clinical benefit. If there is a benefit, it seems to be related to the drug’s anti-inflammatory properties. If that’s the case, I’m not sure this particular drug, as opposed to others, would be the way to go,” Plowe said.
Mixed Results in Other Studies
“Our negative results on the anti-viral efficacy of HCQ obtained in this trial are on the contrary to the encouraging in-vitro results and to the recently reported promising results from a non-randomized trial with 36 COVID-19 patients,” the authors write.
However, the 36-patient trial to which they refer has since been called into question, as previously reported by Retraction Watch.
Despite lack of clear evidence of benefit, HCQ is recommended off label for the treatment of COVID-19 by the Chinese National guideline, and the US Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization for the treatment of adult patients with COVID-19.
By contrast, the Infectious Diseases Society of America recently concluded that because of insufficient data, they could not recommend any particular treatment for patients with COVID-19.
The work was supported by the Emergent Projects of National Science and Technology; the National Natural Science Foundation of China; the National Key Research and Development Program of China; the Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty; the National Innovative Research Team of High-Level Local Universities in Shanghai; the Shanghai Key Discipline for Respiratory Diseases; the National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for Significant New Drugs Development; and Key Projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program. The authors, Kahlenberg, and Plowe have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
See acute hepatitis? Consider COVID-19, N.Y. case suggests
A woman presented to the emergency department with high liver enzyme levels and dark urine. She developed fever on day 2 of care, and then tested positive for the new coronavirus, researchers at Northwell Health, in Hempstead, New York, report.
The authors say the case, published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, is the first documented instance of a patient with COVID-19 presenting with acute hepatitis as the primary symptom before developing respiratory symptoms.
Prior data show that the most common early indications of COVID-19 are respiratory symptoms with fever, shortness of breath, sore throat, and cough, and with imaging results consistent with pneumonia. However, liver enzyme abnormalities are not uncommon in the disease course.
“In patients who are now presenting with acute hepatitis, people need to think of COVID,” senior author David Bernstein, MD, chief of the Division of Hepatology at Northwell Health, told Medscape Medical News.
In addition to Bernstein, Praneet Wander, MD, also in Northwell’s hepatology division, and Marcia Epstein, MD, with Northwell’s Department of Infectious Disease, authored the case report.
Bernstein said Northwell currently has the largest number of COVID-19 cases in the nation and that many patients are presenting with abnormal liver test results and COVID-19 symptoms.
He said that anecdotally, colleagues elsewhere in the United States are also reporting the connection.
“It seems to be that the liver enzyme elevations are part and parcel of this disease,” he said.
Case Details
According to the case report, the 59-year-old woman, who lives alone, came to the emergency department with a chief complaint of dark urine. She was given a face mask and was isolated, per protocol.
“She denied cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain,” the authors wrote. She denied having been in contact with someone who was sick.
She had well-controlled HIV, and recent outpatient liver test results were normal. Eighteen hours after she came to the ED, she was admitted, owing to concern regarding rising liver enzyme levels in conjunction with her being HIV positive.
On presentation, her temperature was 98.9° F. There were no skin indications, lungs were normal, and “there was no jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, hepatomegaly or splenomegaly.”
Liver enzyme levels were as follows: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), 1230 (IU/L); alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 697 IU/L (normal for both is < 50 IU/L); alkaline phosphatase, 141 IU/L (normal, < 125 IU/L).
The patient tested negative for hepatitis A, B, C, E, cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus. A respiratory viral panel and autoimmune markers were normal.
Fever Appeared on Day 2
She was admitted, and 18 hours after she came to the ED, she developed a fever of 102.2° F. A chest x-ray showed interstitial opacities in both lungs.
Nasopharyngeal samples were taken, and polymerase chain reaction test results were positive for the novel coronavirus. The patient was placed on 3 L of oxygen.
On post admission day 4, a 5-day course of hydroxychloroquine (200 mg twice a day) was initiated.
The patient was discharged to home on hospital day 8. The serum bilirubin level was 0.6 mg/dL; AST, 114 IU/L; ALT, 227 IU/L; and alkaline phosphatase, 259 IU/L.
According to Bernstein, it’s hard to tell in what order COVID-19 symptoms occur because people are staying home with other complaints. They may only present to the emergency department after they develop more typical COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
In this case, the patient noticed a darkening of her urine, “but if she had come the next day, she would have had fever. I think we just happened to catch it early,” Bernstein said.
He added that he saw no connection between the underlying HIV and her liver abnormalities or COVID-19 diagnosis.
Bernstein notes that most COVID-19 patients are not admitted, and he said he worries that a COVID-19 test might not be on the radar of providers in the outpatient setting when a patient presents with elevated liver enzymes levels.
If elevated liver enzyme levels can predict disease course, the information could alter how and where the disease is treated, Bernstein said.
“This is a first report. We’re really right now in the beginning of learning,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A woman presented to the emergency department with high liver enzyme levels and dark urine. She developed fever on day 2 of care, and then tested positive for the new coronavirus, researchers at Northwell Health, in Hempstead, New York, report.
The authors say the case, published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, is the first documented instance of a patient with COVID-19 presenting with acute hepatitis as the primary symptom before developing respiratory symptoms.
Prior data show that the most common early indications of COVID-19 are respiratory symptoms with fever, shortness of breath, sore throat, and cough, and with imaging results consistent with pneumonia. However, liver enzyme abnormalities are not uncommon in the disease course.
“In patients who are now presenting with acute hepatitis, people need to think of COVID,” senior author David Bernstein, MD, chief of the Division of Hepatology at Northwell Health, told Medscape Medical News.
In addition to Bernstein, Praneet Wander, MD, also in Northwell’s hepatology division, and Marcia Epstein, MD, with Northwell’s Department of Infectious Disease, authored the case report.
Bernstein said Northwell currently has the largest number of COVID-19 cases in the nation and that many patients are presenting with abnormal liver test results and COVID-19 symptoms.
He said that anecdotally, colleagues elsewhere in the United States are also reporting the connection.
“It seems to be that the liver enzyme elevations are part and parcel of this disease,” he said.
Case Details
According to the case report, the 59-year-old woman, who lives alone, came to the emergency department with a chief complaint of dark urine. She was given a face mask and was isolated, per protocol.
“She denied cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain,” the authors wrote. She denied having been in contact with someone who was sick.
She had well-controlled HIV, and recent outpatient liver test results were normal. Eighteen hours after she came to the ED, she was admitted, owing to concern regarding rising liver enzyme levels in conjunction with her being HIV positive.
On presentation, her temperature was 98.9° F. There were no skin indications, lungs were normal, and “there was no jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, hepatomegaly or splenomegaly.”
Liver enzyme levels were as follows: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), 1230 (IU/L); alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 697 IU/L (normal for both is < 50 IU/L); alkaline phosphatase, 141 IU/L (normal, < 125 IU/L).
The patient tested negative for hepatitis A, B, C, E, cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus. A respiratory viral panel and autoimmune markers were normal.
Fever Appeared on Day 2
She was admitted, and 18 hours after she came to the ED, she developed a fever of 102.2° F. A chest x-ray showed interstitial opacities in both lungs.
Nasopharyngeal samples were taken, and polymerase chain reaction test results were positive for the novel coronavirus. The patient was placed on 3 L of oxygen.
On post admission day 4, a 5-day course of hydroxychloroquine (200 mg twice a day) was initiated.
The patient was discharged to home on hospital day 8. The serum bilirubin level was 0.6 mg/dL; AST, 114 IU/L; ALT, 227 IU/L; and alkaline phosphatase, 259 IU/L.
According to Bernstein, it’s hard to tell in what order COVID-19 symptoms occur because people are staying home with other complaints. They may only present to the emergency department after they develop more typical COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
In this case, the patient noticed a darkening of her urine, “but if she had come the next day, she would have had fever. I think we just happened to catch it early,” Bernstein said.
He added that he saw no connection between the underlying HIV and her liver abnormalities or COVID-19 diagnosis.
Bernstein notes that most COVID-19 patients are not admitted, and he said he worries that a COVID-19 test might not be on the radar of providers in the outpatient setting when a patient presents with elevated liver enzymes levels.
If elevated liver enzyme levels can predict disease course, the information could alter how and where the disease is treated, Bernstein said.
“This is a first report. We’re really right now in the beginning of learning,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A woman presented to the emergency department with high liver enzyme levels and dark urine. She developed fever on day 2 of care, and then tested positive for the new coronavirus, researchers at Northwell Health, in Hempstead, New York, report.
The authors say the case, published online in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, is the first documented instance of a patient with COVID-19 presenting with acute hepatitis as the primary symptom before developing respiratory symptoms.
Prior data show that the most common early indications of COVID-19 are respiratory symptoms with fever, shortness of breath, sore throat, and cough, and with imaging results consistent with pneumonia. However, liver enzyme abnormalities are not uncommon in the disease course.
“In patients who are now presenting with acute hepatitis, people need to think of COVID,” senior author David Bernstein, MD, chief of the Division of Hepatology at Northwell Health, told Medscape Medical News.
In addition to Bernstein, Praneet Wander, MD, also in Northwell’s hepatology division, and Marcia Epstein, MD, with Northwell’s Department of Infectious Disease, authored the case report.
Bernstein said Northwell currently has the largest number of COVID-19 cases in the nation and that many patients are presenting with abnormal liver test results and COVID-19 symptoms.
He said that anecdotally, colleagues elsewhere in the United States are also reporting the connection.
“It seems to be that the liver enzyme elevations are part and parcel of this disease,” he said.
Case Details
According to the case report, the 59-year-old woman, who lives alone, came to the emergency department with a chief complaint of dark urine. She was given a face mask and was isolated, per protocol.
“She denied cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain,” the authors wrote. She denied having been in contact with someone who was sick.
She had well-controlled HIV, and recent outpatient liver test results were normal. Eighteen hours after she came to the ED, she was admitted, owing to concern regarding rising liver enzyme levels in conjunction with her being HIV positive.
On presentation, her temperature was 98.9° F. There were no skin indications, lungs were normal, and “there was no jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, hepatomegaly or splenomegaly.”
Liver enzyme levels were as follows: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), 1230 (IU/L); alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 697 IU/L (normal for both is < 50 IU/L); alkaline phosphatase, 141 IU/L (normal, < 125 IU/L).
The patient tested negative for hepatitis A, B, C, E, cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus. A respiratory viral panel and autoimmune markers were normal.
Fever Appeared on Day 2
She was admitted, and 18 hours after she came to the ED, she developed a fever of 102.2° F. A chest x-ray showed interstitial opacities in both lungs.
Nasopharyngeal samples were taken, and polymerase chain reaction test results were positive for the novel coronavirus. The patient was placed on 3 L of oxygen.
On post admission day 4, a 5-day course of hydroxychloroquine (200 mg twice a day) was initiated.
The patient was discharged to home on hospital day 8. The serum bilirubin level was 0.6 mg/dL; AST, 114 IU/L; ALT, 227 IU/L; and alkaline phosphatase, 259 IU/L.
According to Bernstein, it’s hard to tell in what order COVID-19 symptoms occur because people are staying home with other complaints. They may only present to the emergency department after they develop more typical COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
In this case, the patient noticed a darkening of her urine, “but if she had come the next day, she would have had fever. I think we just happened to catch it early,” Bernstein said.
He added that he saw no connection between the underlying HIV and her liver abnormalities or COVID-19 diagnosis.
Bernstein notes that most COVID-19 patients are not admitted, and he said he worries that a COVID-19 test might not be on the radar of providers in the outpatient setting when a patient presents with elevated liver enzymes levels.
If elevated liver enzyme levels can predict disease course, the information could alter how and where the disease is treated, Bernstein said.
“This is a first report. We’re really right now in the beginning of learning,” he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. lifts visa halt to boost COVID-19 physician workforce
New information from the US State Department indicates that it is lifting the suspension on visas for foreign-trained medical professionals, a move that has promise for boosting the US physician workforce battling COVID-19.
The move may also help physicians extend their visas.
The communication late last week follows a March 18 announcement that, because of COVID-19, the United States was suspending routine processing of immigrant and nonimmigrant visas, including the J and H visas, at embassies and consulates worldwide.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG) appealed to the State Department to lift the suspension, noting that 4222 graduates of medical schools outside the United States who had matched into residencies in the United States and were ready to start on July 1 would not get the visas most of them need to begin training.
The State Department lifted the suspensions and issued this update:
“We encourage medical professionals with an approved US non-immigrant or immigrant visa petition (I-129, I-140, or similar) or a certificate of eligibility in an approved exchange visitor program (DS-2019), particularly those working to treat or mitigate the effects of COVID-19, to review the website of their nearest embassy or consulate for procedures to request a visa appointment.”
The State Department also issued guidance for foreign medical professionals already in the United States:
“J-1 Alien Physicians (medical residents) may consult with their program sponsor, ECFMG, to extend their programs in the United States. Generally, a J-1 program for a foreign medical resident can be extended one year at a time for up to seven years.
“Note that the expiration date on a US visa does not determine how long one can be in the United States. The way to confirm one’s required departure date is here : https://i94.cbp.dhs.gov/I94/#/home.
“Those who need to extend their stay or adjust their visa status must apply with USCIS (US Citizenship and Immigration Services).”
Complications Still Exist
ECFMG’s CEO, William W. Pinsky, MD, told Medscape Medical News that, although they welcomed the news from the State Department, there are still unanswered questions.
ECFMG explained that J-1 visas are currently granted only 30 days before the residency program begins.
However, travel to the United States may still be difficult in June, Pinsky said, and physicians may need to be quarantined for 2 weeks upon arrival.
“We’re still having some discussion with the Department of State on whether that regulation could be relaxed and they could come in earlier,” he said.
He cautioned that even after a J-1 visa application is made, the physician’s home country has to endorse the application.
Pinsky said he did not yet know whether that would be a problem.
He also said that, in response to New York’s plea for more healthcare workers, ECFMG is offering to verify education and licensing credentials for physicians educated outside the United States at no cost.
Individual hospitals and regulatory authorities can decide whether there may be roles in some capacity for physicians who have graduated from medical school, even if they have not completed residency or have not been licensed, he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New information from the US State Department indicates that it is lifting the suspension on visas for foreign-trained medical professionals, a move that has promise for boosting the US physician workforce battling COVID-19.
The move may also help physicians extend their visas.
The communication late last week follows a March 18 announcement that, because of COVID-19, the United States was suspending routine processing of immigrant and nonimmigrant visas, including the J and H visas, at embassies and consulates worldwide.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG) appealed to the State Department to lift the suspension, noting that 4222 graduates of medical schools outside the United States who had matched into residencies in the United States and were ready to start on July 1 would not get the visas most of them need to begin training.
The State Department lifted the suspensions and issued this update:
“We encourage medical professionals with an approved US non-immigrant or immigrant visa petition (I-129, I-140, or similar) or a certificate of eligibility in an approved exchange visitor program (DS-2019), particularly those working to treat or mitigate the effects of COVID-19, to review the website of their nearest embassy or consulate for procedures to request a visa appointment.”
The State Department also issued guidance for foreign medical professionals already in the United States:
“J-1 Alien Physicians (medical residents) may consult with their program sponsor, ECFMG, to extend their programs in the United States. Generally, a J-1 program for a foreign medical resident can be extended one year at a time for up to seven years.
“Note that the expiration date on a US visa does not determine how long one can be in the United States. The way to confirm one’s required departure date is here : https://i94.cbp.dhs.gov/I94/#/home.
“Those who need to extend their stay or adjust their visa status must apply with USCIS (US Citizenship and Immigration Services).”
Complications Still Exist
ECFMG’s CEO, William W. Pinsky, MD, told Medscape Medical News that, although they welcomed the news from the State Department, there are still unanswered questions.
ECFMG explained that J-1 visas are currently granted only 30 days before the residency program begins.
However, travel to the United States may still be difficult in June, Pinsky said, and physicians may need to be quarantined for 2 weeks upon arrival.
“We’re still having some discussion with the Department of State on whether that regulation could be relaxed and they could come in earlier,” he said.
He cautioned that even after a J-1 visa application is made, the physician’s home country has to endorse the application.
Pinsky said he did not yet know whether that would be a problem.
He also said that, in response to New York’s plea for more healthcare workers, ECFMG is offering to verify education and licensing credentials for physicians educated outside the United States at no cost.
Individual hospitals and regulatory authorities can decide whether there may be roles in some capacity for physicians who have graduated from medical school, even if they have not completed residency or have not been licensed, he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New information from the US State Department indicates that it is lifting the suspension on visas for foreign-trained medical professionals, a move that has promise for boosting the US physician workforce battling COVID-19.
The move may also help physicians extend their visas.
The communication late last week follows a March 18 announcement that, because of COVID-19, the United States was suspending routine processing of immigrant and nonimmigrant visas, including the J and H visas, at embassies and consulates worldwide.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG) appealed to the State Department to lift the suspension, noting that 4222 graduates of medical schools outside the United States who had matched into residencies in the United States and were ready to start on July 1 would not get the visas most of them need to begin training.
The State Department lifted the suspensions and issued this update:
“We encourage medical professionals with an approved US non-immigrant or immigrant visa petition (I-129, I-140, or similar) or a certificate of eligibility in an approved exchange visitor program (DS-2019), particularly those working to treat or mitigate the effects of COVID-19, to review the website of their nearest embassy or consulate for procedures to request a visa appointment.”
The State Department also issued guidance for foreign medical professionals already in the United States:
“J-1 Alien Physicians (medical residents) may consult with their program sponsor, ECFMG, to extend their programs in the United States. Generally, a J-1 program for a foreign medical resident can be extended one year at a time for up to seven years.
“Note that the expiration date on a US visa does not determine how long one can be in the United States. The way to confirm one’s required departure date is here : https://i94.cbp.dhs.gov/I94/#/home.
“Those who need to extend their stay or adjust their visa status must apply with USCIS (US Citizenship and Immigration Services).”
Complications Still Exist
ECFMG’s CEO, William W. Pinsky, MD, told Medscape Medical News that, although they welcomed the news from the State Department, there are still unanswered questions.
ECFMG explained that J-1 visas are currently granted only 30 days before the residency program begins.
However, travel to the United States may still be difficult in June, Pinsky said, and physicians may need to be quarantined for 2 weeks upon arrival.
“We’re still having some discussion with the Department of State on whether that regulation could be relaxed and they could come in earlier,” he said.
He cautioned that even after a J-1 visa application is made, the physician’s home country has to endorse the application.
Pinsky said he did not yet know whether that would be a problem.
He also said that, in response to New York’s plea for more healthcare workers, ECFMG is offering to verify education and licensing credentials for physicians educated outside the United States at no cost.
Individual hospitals and regulatory authorities can decide whether there may be roles in some capacity for physicians who have graduated from medical school, even if they have not completed residency or have not been licensed, he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dawn of new lupus nephritis treatment after AURORA trial
The calcineurin inhibitor is the first novel agent to demonstrate effectiveness in the treatment of people with lupus nephritis, a disease that can lead to irreversible kidney damage, kidney failure, and even death.
“We believe that voclosporin – as an add-on therapy – will help more patients achieve remission,” said Keisha Gibson, MD, MPH, chief of pediatric nephrology at the UNC Kidney Center in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, who led the study and presented the findings during a virtual session at the National Kidney Foundation 2020 Spring Clinical Meetings.
The burden that lupus places on patients and the health system is high, she reported. Patients with lupus and uncontrolled kidney disease frequently have complications that require hospitalization, can suffer complete or partial loss of income, and can become temporarily disabled. And up to 50% of lupus patients will develop lupus nephritis.
“When we are lucky and see early treatment responses in our patients, we know that their long-term outcomes, measured by proteinuria reduction, are quite good,” said Gibson. “Unfortunately, in 10% to 30% of patients, despite standard-of-care therapies, we see progression to end-stage kidney disease within 15 years of diagnosis. This confers a huge cost to overall health and quality of life, and is an excess burden to the healthcare system.
“It is clear that one of the biggest risk factors for these patients who have kidney disease that is progressing to kidney failure is an inability to control the inflammation and chronic damage from uncontrolled disease,” she told Medscape Medical News.
“While there have certainly been a few advances in the care of patients with lupus disease, I believe that this therapy may help move the needle, specifically for patients with kidney involvement from their lupus disease,” she added.
Renal Response Much Higher With Voclosporin
The typical standard of care for patients with active lupus and kidney disease is either a combination of cyclophosphamide plus steroids or a combination of mycophenolate mofetil plus steroids.
The global, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial compared the effectiveness and safety of twice-daily oral voclosporin 23.7 mg with placebo. All 357 study participants also received mycophenolate 2 g daily and rapidly tapered low-dose oral corticosteroids.
At 1 year, the renal response rate was higher in the voclosporin group than in the placebo group (40.8% vs 22.5%; odds ratio, 2.65; P < .001).
“AURORA patients achieved low levels of protein twice as quickly as patients on standard of care,” the researchers write in their abstract. Median time to the achievement of a urine protein to creatinine ratio below 0.5 mg/mg was significantly and clinically better with voclosporin than with placebo (169 vs 372 days; log rank P < .001).
And voclosporin was well tolerated. The percentage of serious adverse events was similar in the voclosporin and placebo groups (20.8% vs 21.3%), with infection being the most common serious event (10.1% vs 11.2%).
In the voclosporin group, there were no significant differences between baseline and 1 year estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR), blood pressure, lipid levels, or sugar levels.
And there were fewer deaths in the voclosporin group than in the placebo group (1 vs 5).
Benefits were seen in all subgroups, including age, sex, race, biopsy class, geographic region of origin, and mycophenolate exposure at screening, Gibson reported.
Promise of a New Treatment
The promise of a new treatment is exciting for the field, said Joseph Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer of the National Kidney Foundation.
However, it’s important to note that “this study is applicable only to patients with lupus nephritis with preserved kidney function,” he added.
An “eGFR less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was implied as an exclusion criteria, so I would say it certainly doesn’t apply to patients with impaired kidney function,” he said, pointing out that this will be clearer when the final data are published.
The study cohort was heterogeneous; 86% of participants had class 3 or 4 biopsy findings and 14% had class 5, so the superiority of voclosporin is convincing, he said.
“We look forward to full publication and more details,” he told Medscape Medical News. “They do have an extension study, and it will be interesting to see how that plays out.”
Voclosporin was granted Fast Track designation by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2016, and these positive phase 3 results mean that a New Drug Application will likely be filed in the next few months. If approved, the drug could be on the market by 2021, according to a press release from Aurinia.
Nephrologists are familiar with calcineurin inhibitors, so it will be interesting to see, given the success of this trial, if voclosporin has a potential role in other kidney diseases, “such as minimal change disease,” said Vassalotti.
He added that there are concerns, unrelated to the AURORA trial, about the supply of hydroxychloroquine, which is also used for the treatment of lupus nephritis. “An overarching concern is that the supply will be limited now that the drug is being studied and used as prophylaxis after exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and as a treatment for COVID-19, creating challenges for patients with lupus nephritis trying to obtain their needed medication,” he said.
Gibson reports no relevant financial relationships. Two coauthors work for the drugmaker, Aurinia. Vassalotti reports no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The calcineurin inhibitor is the first novel agent to demonstrate effectiveness in the treatment of people with lupus nephritis, a disease that can lead to irreversible kidney damage, kidney failure, and even death.
“We believe that voclosporin – as an add-on therapy – will help more patients achieve remission,” said Keisha Gibson, MD, MPH, chief of pediatric nephrology at the UNC Kidney Center in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, who led the study and presented the findings during a virtual session at the National Kidney Foundation 2020 Spring Clinical Meetings.
The burden that lupus places on patients and the health system is high, she reported. Patients with lupus and uncontrolled kidney disease frequently have complications that require hospitalization, can suffer complete or partial loss of income, and can become temporarily disabled. And up to 50% of lupus patients will develop lupus nephritis.
“When we are lucky and see early treatment responses in our patients, we know that their long-term outcomes, measured by proteinuria reduction, are quite good,” said Gibson. “Unfortunately, in 10% to 30% of patients, despite standard-of-care therapies, we see progression to end-stage kidney disease within 15 years of diagnosis. This confers a huge cost to overall health and quality of life, and is an excess burden to the healthcare system.
“It is clear that one of the biggest risk factors for these patients who have kidney disease that is progressing to kidney failure is an inability to control the inflammation and chronic damage from uncontrolled disease,” she told Medscape Medical News.
“While there have certainly been a few advances in the care of patients with lupus disease, I believe that this therapy may help move the needle, specifically for patients with kidney involvement from their lupus disease,” she added.
Renal Response Much Higher With Voclosporin
The typical standard of care for patients with active lupus and kidney disease is either a combination of cyclophosphamide plus steroids or a combination of mycophenolate mofetil plus steroids.
The global, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial compared the effectiveness and safety of twice-daily oral voclosporin 23.7 mg with placebo. All 357 study participants also received mycophenolate 2 g daily and rapidly tapered low-dose oral corticosteroids.
At 1 year, the renal response rate was higher in the voclosporin group than in the placebo group (40.8% vs 22.5%; odds ratio, 2.65; P < .001).
“AURORA patients achieved low levels of protein twice as quickly as patients on standard of care,” the researchers write in their abstract. Median time to the achievement of a urine protein to creatinine ratio below 0.5 mg/mg was significantly and clinically better with voclosporin than with placebo (169 vs 372 days; log rank P < .001).
And voclosporin was well tolerated. The percentage of serious adverse events was similar in the voclosporin and placebo groups (20.8% vs 21.3%), with infection being the most common serious event (10.1% vs 11.2%).
In the voclosporin group, there were no significant differences between baseline and 1 year estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR), blood pressure, lipid levels, or sugar levels.
And there were fewer deaths in the voclosporin group than in the placebo group (1 vs 5).
Benefits were seen in all subgroups, including age, sex, race, biopsy class, geographic region of origin, and mycophenolate exposure at screening, Gibson reported.
Promise of a New Treatment
The promise of a new treatment is exciting for the field, said Joseph Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer of the National Kidney Foundation.
However, it’s important to note that “this study is applicable only to patients with lupus nephritis with preserved kidney function,” he added.
An “eGFR less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was implied as an exclusion criteria, so I would say it certainly doesn’t apply to patients with impaired kidney function,” he said, pointing out that this will be clearer when the final data are published.
The study cohort was heterogeneous; 86% of participants had class 3 or 4 biopsy findings and 14% had class 5, so the superiority of voclosporin is convincing, he said.
“We look forward to full publication and more details,” he told Medscape Medical News. “They do have an extension study, and it will be interesting to see how that plays out.”
Voclosporin was granted Fast Track designation by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2016, and these positive phase 3 results mean that a New Drug Application will likely be filed in the next few months. If approved, the drug could be on the market by 2021, according to a press release from Aurinia.
Nephrologists are familiar with calcineurin inhibitors, so it will be interesting to see, given the success of this trial, if voclosporin has a potential role in other kidney diseases, “such as minimal change disease,” said Vassalotti.
He added that there are concerns, unrelated to the AURORA trial, about the supply of hydroxychloroquine, which is also used for the treatment of lupus nephritis. “An overarching concern is that the supply will be limited now that the drug is being studied and used as prophylaxis after exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and as a treatment for COVID-19, creating challenges for patients with lupus nephritis trying to obtain their needed medication,” he said.
Gibson reports no relevant financial relationships. Two coauthors work for the drugmaker, Aurinia. Vassalotti reports no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The calcineurin inhibitor is the first novel agent to demonstrate effectiveness in the treatment of people with lupus nephritis, a disease that can lead to irreversible kidney damage, kidney failure, and even death.
“We believe that voclosporin – as an add-on therapy – will help more patients achieve remission,” said Keisha Gibson, MD, MPH, chief of pediatric nephrology at the UNC Kidney Center in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, who led the study and presented the findings during a virtual session at the National Kidney Foundation 2020 Spring Clinical Meetings.
The burden that lupus places on patients and the health system is high, she reported. Patients with lupus and uncontrolled kidney disease frequently have complications that require hospitalization, can suffer complete or partial loss of income, and can become temporarily disabled. And up to 50% of lupus patients will develop lupus nephritis.
“When we are lucky and see early treatment responses in our patients, we know that their long-term outcomes, measured by proteinuria reduction, are quite good,” said Gibson. “Unfortunately, in 10% to 30% of patients, despite standard-of-care therapies, we see progression to end-stage kidney disease within 15 years of diagnosis. This confers a huge cost to overall health and quality of life, and is an excess burden to the healthcare system.
“It is clear that one of the biggest risk factors for these patients who have kidney disease that is progressing to kidney failure is an inability to control the inflammation and chronic damage from uncontrolled disease,” she told Medscape Medical News.
“While there have certainly been a few advances in the care of patients with lupus disease, I believe that this therapy may help move the needle, specifically for patients with kidney involvement from their lupus disease,” she added.
Renal Response Much Higher With Voclosporin
The typical standard of care for patients with active lupus and kidney disease is either a combination of cyclophosphamide plus steroids or a combination of mycophenolate mofetil plus steroids.
The global, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial compared the effectiveness and safety of twice-daily oral voclosporin 23.7 mg with placebo. All 357 study participants also received mycophenolate 2 g daily and rapidly tapered low-dose oral corticosteroids.
At 1 year, the renal response rate was higher in the voclosporin group than in the placebo group (40.8% vs 22.5%; odds ratio, 2.65; P < .001).
“AURORA patients achieved low levels of protein twice as quickly as patients on standard of care,” the researchers write in their abstract. Median time to the achievement of a urine protein to creatinine ratio below 0.5 mg/mg was significantly and clinically better with voclosporin than with placebo (169 vs 372 days; log rank P < .001).
And voclosporin was well tolerated. The percentage of serious adverse events was similar in the voclosporin and placebo groups (20.8% vs 21.3%), with infection being the most common serious event (10.1% vs 11.2%).
In the voclosporin group, there were no significant differences between baseline and 1 year estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR), blood pressure, lipid levels, or sugar levels.
And there were fewer deaths in the voclosporin group than in the placebo group (1 vs 5).
Benefits were seen in all subgroups, including age, sex, race, biopsy class, geographic region of origin, and mycophenolate exposure at screening, Gibson reported.
Promise of a New Treatment
The promise of a new treatment is exciting for the field, said Joseph Vassalotti, MD, chief medical officer of the National Kidney Foundation.
However, it’s important to note that “this study is applicable only to patients with lupus nephritis with preserved kidney function,” he added.
An “eGFR less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was implied as an exclusion criteria, so I would say it certainly doesn’t apply to patients with impaired kidney function,” he said, pointing out that this will be clearer when the final data are published.
The study cohort was heterogeneous; 86% of participants had class 3 or 4 biopsy findings and 14% had class 5, so the superiority of voclosporin is convincing, he said.
“We look forward to full publication and more details,” he told Medscape Medical News. “They do have an extension study, and it will be interesting to see how that plays out.”
Voclosporin was granted Fast Track designation by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2016, and these positive phase 3 results mean that a New Drug Application will likely be filed in the next few months. If approved, the drug could be on the market by 2021, according to a press release from Aurinia.
Nephrologists are familiar with calcineurin inhibitors, so it will be interesting to see, given the success of this trial, if voclosporin has a potential role in other kidney diseases, “such as minimal change disease,” said Vassalotti.
He added that there are concerns, unrelated to the AURORA trial, about the supply of hydroxychloroquine, which is also used for the treatment of lupus nephritis. “An overarching concern is that the supply will be limited now that the drug is being studied and used as prophylaxis after exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and as a treatment for COVID-19, creating challenges for patients with lupus nephritis trying to obtain their needed medication,” he said.
Gibson reports no relevant financial relationships. Two coauthors work for the drugmaker, Aurinia. Vassalotti reports no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.