User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


Happy National Hospitalist Day!
Hospitalists across the United States have been and continue to be a critical part of our nation’s response to COVID-19. On National Hospitalist Day, Thursday, March 4, 2021, the Society of Hospital Medicine invites you to celebrate the individuals and teams that make up the hospital medicine community.

On this special day, SHM encourages you to share your story, showcase your team’s efforts to improve patient care, express your pride for the specialty, or share how you are making a difference in your hospital and in the lives of patients.
Here are just a few of the ways you can celebrate:
- Register for our live roundtable, featuring Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and host of the Explore the Space podcast, and four hospitalist panelists, on March 4 at 7 p.m. ET/4 p.m. PT.
- Download shareable graphics, posters, Zoom backgrounds, and coloring book pages
- Enter our social media photo contest and follow the #HowWeHospitalist hashtag across all platforms
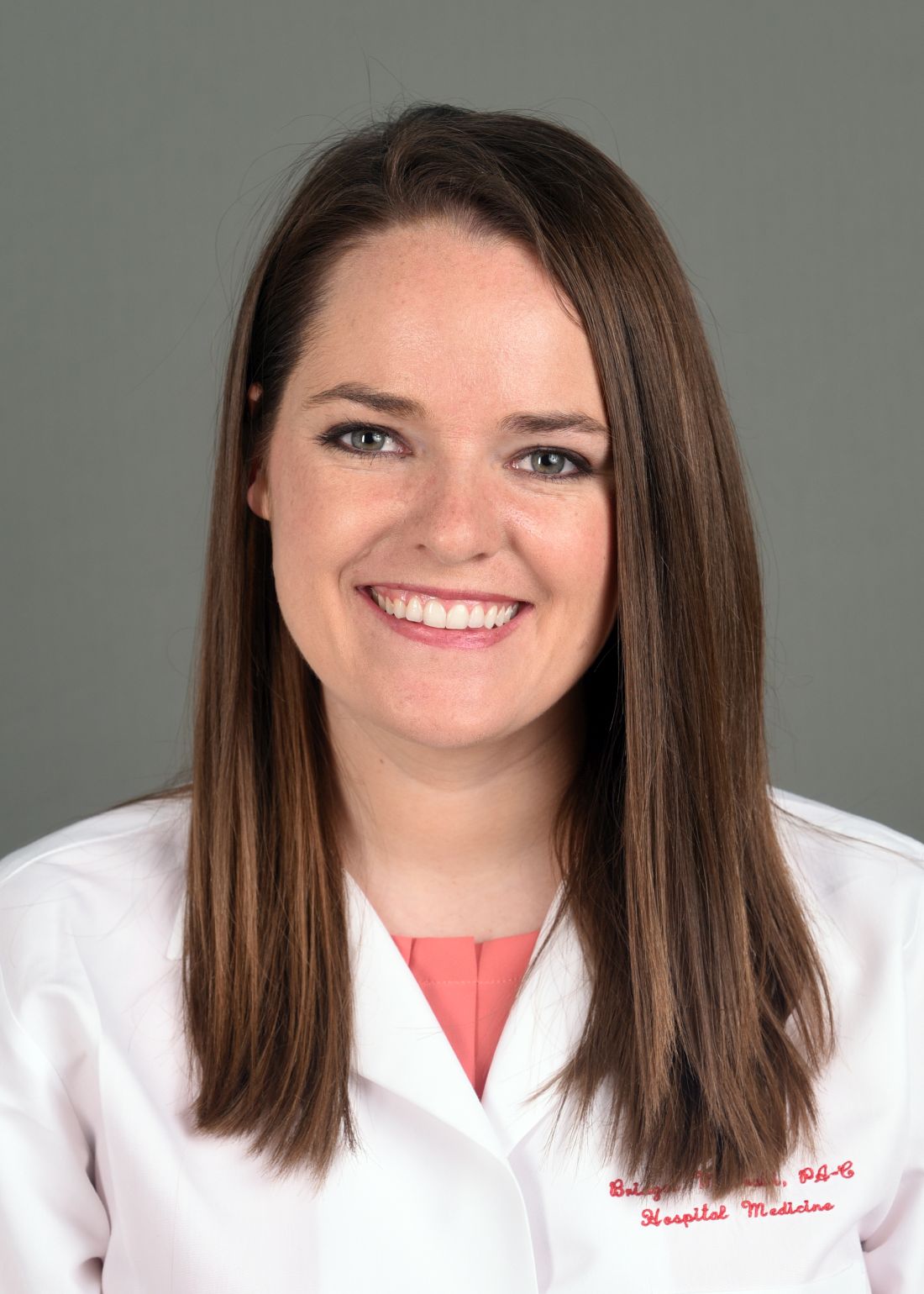
- Read special hospitalist profiles in the Hospitalist, including: Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM; Grace Huang, MD; Bridget McGrath, PA-C, FHM; and Harry Cho, MD, SFHM
Thank you for all you do and continue to do for hospital medicine. We hope you take some time today to celebrate you and your colleagues, as well as your commendable contributions to health care and the future of the specialty.
To learn more about National Hospitalist Day, visit hospitalmedicine.org/hospitalistday.
Hospitalists across the United States have been and continue to be a critical part of our nation’s response to COVID-19. On National Hospitalist Day, Thursday, March 4, 2021, the Society of Hospital Medicine invites you to celebrate the individuals and teams that make up the hospital medicine community.

On this special day, SHM encourages you to share your story, showcase your team’s efforts to improve patient care, express your pride for the specialty, or share how you are making a difference in your hospital and in the lives of patients.
Here are just a few of the ways you can celebrate:
- Register for our live roundtable, featuring Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and host of the Explore the Space podcast, and four hospitalist panelists, on March 4 at 7 p.m. ET/4 p.m. PT.
- Download shareable graphics, posters, Zoom backgrounds, and coloring book pages
- Enter our social media photo contest and follow the #HowWeHospitalist hashtag across all platforms
- Read special hospitalist profiles in the Hospitalist, including: Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM; Grace Huang, MD; Bridget McGrath, PA-C, FHM; and Harry Cho, MD, SFHM
Thank you for all you do and continue to do for hospital medicine. We hope you take some time today to celebrate you and your colleagues, as well as your commendable contributions to health care and the future of the specialty.
To learn more about National Hospitalist Day, visit hospitalmedicine.org/hospitalistday.
Hospitalists across the United States have been and continue to be a critical part of our nation’s response to COVID-19. On National Hospitalist Day, Thursday, March 4, 2021, the Society of Hospital Medicine invites you to celebrate the individuals and teams that make up the hospital medicine community.

On this special day, SHM encourages you to share your story, showcase your team’s efforts to improve patient care, express your pride for the specialty, or share how you are making a difference in your hospital and in the lives of patients.
Here are just a few of the ways you can celebrate:
- Register for our live roundtable, featuring Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and host of the Explore the Space podcast, and four hospitalist panelists, on March 4 at 7 p.m. ET/4 p.m. PT.
- Download shareable graphics, posters, Zoom backgrounds, and coloring book pages
- Enter our social media photo contest and follow the #HowWeHospitalist hashtag across all platforms
- Read special hospitalist profiles in the Hospitalist, including: Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM; Grace Huang, MD; Bridget McGrath, PA-C, FHM; and Harry Cho, MD, SFHM
Thank you for all you do and continue to do for hospital medicine. We hope you take some time today to celebrate you and your colleagues, as well as your commendable contributions to health care and the future of the specialty.
To learn more about National Hospitalist Day, visit hospitalmedicine.org/hospitalistday.
Owning all aspects of patient care: Bridget McGrath, PA-C, FHM
Editor’s note: This profile is part of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Bridget McGrath, PA-C, FHM, is a physician assistant and director of the nurse practitioner/physician assistant service line for the section of hospital medicine at the University of Chicago. She is a cochair of SHM’s NP/PA Special Interest Group.
Where did you receive your PA education/training? Was your intention always to be a PA?
I graduated from the PA program at Butler University, Indianapolis, in 2014. In college, whenever I shadowed a PA, I was always impressed that each one loved their job and said they would never change it. That universal passion for the PA profession really made an impression on me.
At what point in your PA education/training did you decide to practice hospital medicine? What about it appealed to you?
That occurred during my clinical rotation year at Butler. I had always thought I wanted to practice neonatology, but during my clinical rotation I really fell in love with adult medicine. I recall that during my clinical rotation, the preceptor said to me that the goal was not to have me understand every aspect of medicine, but to learn how to exist in a hospital setting. I was exposed to the breadth of hospital medicine practice and I fell in love with the complexity, the variety, and the environment itself.
I initially accepted a job as a med-peds hospitalist PA – which brought both of my passions together at that time – at Schneck Medical Center in Seymour, Ind. During that time, Schneck was a 100-bed rural community hospital which had recently been the recipient of the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. It was there that I was able to practice with a phenomenal group of physicians, nurses, and social workers who really took me under their wing and taught me how to be a hospitalist PA. I practiced at Schneck for 3 years, and then moved to the University of Chicago in 2017.
I am now the director of NP/PA services for the section of hospital medicine, overseeing a group of seven on our NP/PA team, within a larger group of about 60 physicians.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice?
Like many hospitalists, I enjoy the variety of medicine that hospitalists practice. One area that I find especially rewarding is my time in our transplant comanagement services. To be able to walk with patients on their transplant journey is very rewarding, and I am very appreciative of the mentoring I have received from some of my colleagues with a deeper understanding of transplant medicine.
In my administrative role, I have the privilege of helping to expand the professional education and training of my colleagues. I have a passion for medical education, and we have been working to develop interprofessional educational opportunities within our section. I have had time to think about the imprint of NPs and PAs in academic medicine, and how we can continue to meet the professional educational needs of our section while improving the care of our patients.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine?
The volume of diagnoses that we are expected to manage on a daily basis can be challenging. This challenges you to continue learning. The complexity of discharge planning, particularly for patients in underserved communities, can also be challenging. You have to make sure your patients are ready mentally, physically and emotionally for discharge. As a hospitalist, you are continuously thinking about how to optimize patients to leave your care. For example, patients have different insurance situations, different access to care at home – you are always managing the medical needs of your patient in the context of these other issues.
How does a hospitalist PA work differently from a PA in other care settings?
We are meant to be generalists. We serve as the main provider in owning our patients’ care. A hospitalist PA serves as a cog in the wheel, with connections to specialists, consultants, nurses, social workers, pharmacists, etc., and we are tasked with synthesizing all aspects of patient care to ensure the best outcome.
What has your experience taught you about how NPs and PAs can best fit into hospital medicine groups?
Each hospital medicine group will know how to best integrate their NPs and PAs based on the skillsets of their NPs and PAs, and the needs of the section and the hospital. I personally feel that the best way to utilize NPs and PAs is to allow them to own all aspects of patient care and work at the highest scope of practice. By doing this you empower the NP or PA to continue to develop their skill set and set a precedent of collaboration and respect for interprofessional care models within your section’s culture.
Scope of practice for an NP or PA is going to be based on a conglomeration of roles and bylaws. We are certified nationally, and our scope of practice is determined at the state level and the hospital by level. For the individual NP and PA, it really depends on the hospital medicine group, and how well a practice incorporates a sense of collegiality.
What kind of resources do hospitalist PAs need to succeed, either from SHM or from their own institutions?
There are a few key things that need to happen in order for hospital medicine groups to set up their NPs and PAs for success. The first is for PAs to have exposure to inpatient rotations during clinical rotations. A hospital medicine group also should have a very intentional onboarding process for NPs and PAs. They should also establish a culture of acceptance. To do this, they should utilize resources like SHM’s NP/PA Hospital Medicine Onboarding Toolkit and the SHM/American Academy of Physician Assistants Hospitalist Bootcamp On Demand.
Mentoring is also remarkably important. I have been incredibly blessed to have mentors that helped make me into the PA that I am. I could not have done what I did in the field without people taking a chance on me, and it is important to pass that on to the next generation of PAs.
How has COVID-19 changed the practice of hospital medicine, specifically for advanced practice providers?
The pandemic has demonstrated opportunities for teamwork and utilization of NPs and PAs. The COVID pandemic forced everyone to reflect on why they originally got into medicine – to help patients. I think there will be many doors opening for NPs and PAs, and many pathways for leadership.
The hospitalist leadership at the University of Chicago truly identified that we needed to make wellness a main priority during the beginning of the pandemic. We developed a wellness work group that I have been coleading.
What’s on the horizon for NPs and PAs in hospital medicine?
We are seeing significant increases in hospitalist program utilization, so this is a time where NPs and PAs can be advocates for our profession and articulate how we can use our backgrounds and training to build better care models in order to meet the needs of our patients.
I hope we will see more NPs and PAs assuming leadership roles to ensure that our voices are heard. We should also be advocating for more collaboration and teamwork with our MD and DO colleagues.
Do you have any advice for PA students interested in hospital medicine?
I always tell my students that they should be sponges – you are not expected to know everything as a hospitalist PA, but you are expected to continue learning in order to develop into the best PA you can be. Always be open to where your career path can take you. Hospital medicine is a relatively young field within medicine, and the diversity of our field is very exciting looking forward.
Editor’s note: This profile is part of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Bridget McGrath, PA-C, FHM, is a physician assistant and director of the nurse practitioner/physician assistant service line for the section of hospital medicine at the University of Chicago. She is a cochair of SHM’s NP/PA Special Interest Group.
Where did you receive your PA education/training? Was your intention always to be a PA?
I graduated from the PA program at Butler University, Indianapolis, in 2014. In college, whenever I shadowed a PA, I was always impressed that each one loved their job and said they would never change it. That universal passion for the PA profession really made an impression on me.
At what point in your PA education/training did you decide to practice hospital medicine? What about it appealed to you?
That occurred during my clinical rotation year at Butler. I had always thought I wanted to practice neonatology, but during my clinical rotation I really fell in love with adult medicine. I recall that during my clinical rotation, the preceptor said to me that the goal was not to have me understand every aspect of medicine, but to learn how to exist in a hospital setting. I was exposed to the breadth of hospital medicine practice and I fell in love with the complexity, the variety, and the environment itself.
I initially accepted a job as a med-peds hospitalist PA – which brought both of my passions together at that time – at Schneck Medical Center in Seymour, Ind. During that time, Schneck was a 100-bed rural community hospital which had recently been the recipient of the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. It was there that I was able to practice with a phenomenal group of physicians, nurses, and social workers who really took me under their wing and taught me how to be a hospitalist PA. I practiced at Schneck for 3 years, and then moved to the University of Chicago in 2017.
I am now the director of NP/PA services for the section of hospital medicine, overseeing a group of seven on our NP/PA team, within a larger group of about 60 physicians.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice?
Like many hospitalists, I enjoy the variety of medicine that hospitalists practice. One area that I find especially rewarding is my time in our transplant comanagement services. To be able to walk with patients on their transplant journey is very rewarding, and I am very appreciative of the mentoring I have received from some of my colleagues with a deeper understanding of transplant medicine.
In my administrative role, I have the privilege of helping to expand the professional education and training of my colleagues. I have a passion for medical education, and we have been working to develop interprofessional educational opportunities within our section. I have had time to think about the imprint of NPs and PAs in academic medicine, and how we can continue to meet the professional educational needs of our section while improving the care of our patients.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine?
The volume of diagnoses that we are expected to manage on a daily basis can be challenging. This challenges you to continue learning. The complexity of discharge planning, particularly for patients in underserved communities, can also be challenging. You have to make sure your patients are ready mentally, physically and emotionally for discharge. As a hospitalist, you are continuously thinking about how to optimize patients to leave your care. For example, patients have different insurance situations, different access to care at home – you are always managing the medical needs of your patient in the context of these other issues.
How does a hospitalist PA work differently from a PA in other care settings?
We are meant to be generalists. We serve as the main provider in owning our patients’ care. A hospitalist PA serves as a cog in the wheel, with connections to specialists, consultants, nurses, social workers, pharmacists, etc., and we are tasked with synthesizing all aspects of patient care to ensure the best outcome.
What has your experience taught you about how NPs and PAs can best fit into hospital medicine groups?
Each hospital medicine group will know how to best integrate their NPs and PAs based on the skillsets of their NPs and PAs, and the needs of the section and the hospital. I personally feel that the best way to utilize NPs and PAs is to allow them to own all aspects of patient care and work at the highest scope of practice. By doing this you empower the NP or PA to continue to develop their skill set and set a precedent of collaboration and respect for interprofessional care models within your section’s culture.
Scope of practice for an NP or PA is going to be based on a conglomeration of roles and bylaws. We are certified nationally, and our scope of practice is determined at the state level and the hospital by level. For the individual NP and PA, it really depends on the hospital medicine group, and how well a practice incorporates a sense of collegiality.
What kind of resources do hospitalist PAs need to succeed, either from SHM or from their own institutions?
There are a few key things that need to happen in order for hospital medicine groups to set up their NPs and PAs for success. The first is for PAs to have exposure to inpatient rotations during clinical rotations. A hospital medicine group also should have a very intentional onboarding process for NPs and PAs. They should also establish a culture of acceptance. To do this, they should utilize resources like SHM’s NP/PA Hospital Medicine Onboarding Toolkit and the SHM/American Academy of Physician Assistants Hospitalist Bootcamp On Demand.
Mentoring is also remarkably important. I have been incredibly blessed to have mentors that helped make me into the PA that I am. I could not have done what I did in the field without people taking a chance on me, and it is important to pass that on to the next generation of PAs.
How has COVID-19 changed the practice of hospital medicine, specifically for advanced practice providers?
The pandemic has demonstrated opportunities for teamwork and utilization of NPs and PAs. The COVID pandemic forced everyone to reflect on why they originally got into medicine – to help patients. I think there will be many doors opening for NPs and PAs, and many pathways for leadership.
The hospitalist leadership at the University of Chicago truly identified that we needed to make wellness a main priority during the beginning of the pandemic. We developed a wellness work group that I have been coleading.
What’s on the horizon for NPs and PAs in hospital medicine?
We are seeing significant increases in hospitalist program utilization, so this is a time where NPs and PAs can be advocates for our profession and articulate how we can use our backgrounds and training to build better care models in order to meet the needs of our patients.
I hope we will see more NPs and PAs assuming leadership roles to ensure that our voices are heard. We should also be advocating for more collaboration and teamwork with our MD and DO colleagues.
Do you have any advice for PA students interested in hospital medicine?
I always tell my students that they should be sponges – you are not expected to know everything as a hospitalist PA, but you are expected to continue learning in order to develop into the best PA you can be. Always be open to where your career path can take you. Hospital medicine is a relatively young field within medicine, and the diversity of our field is very exciting looking forward.
Editor’s note: This profile is part of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Bridget McGrath, PA-C, FHM, is a physician assistant and director of the nurse practitioner/physician assistant service line for the section of hospital medicine at the University of Chicago. She is a cochair of SHM’s NP/PA Special Interest Group.
Where did you receive your PA education/training? Was your intention always to be a PA?
I graduated from the PA program at Butler University, Indianapolis, in 2014. In college, whenever I shadowed a PA, I was always impressed that each one loved their job and said they would never change it. That universal passion for the PA profession really made an impression on me.
At what point in your PA education/training did you decide to practice hospital medicine? What about it appealed to you?
That occurred during my clinical rotation year at Butler. I had always thought I wanted to practice neonatology, but during my clinical rotation I really fell in love with adult medicine. I recall that during my clinical rotation, the preceptor said to me that the goal was not to have me understand every aspect of medicine, but to learn how to exist in a hospital setting. I was exposed to the breadth of hospital medicine practice and I fell in love with the complexity, the variety, and the environment itself.
I initially accepted a job as a med-peds hospitalist PA – which brought both of my passions together at that time – at Schneck Medical Center in Seymour, Ind. During that time, Schneck was a 100-bed rural community hospital which had recently been the recipient of the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. It was there that I was able to practice with a phenomenal group of physicians, nurses, and social workers who really took me under their wing and taught me how to be a hospitalist PA. I practiced at Schneck for 3 years, and then moved to the University of Chicago in 2017.
I am now the director of NP/PA services for the section of hospital medicine, overseeing a group of seven on our NP/PA team, within a larger group of about 60 physicians.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice?
Like many hospitalists, I enjoy the variety of medicine that hospitalists practice. One area that I find especially rewarding is my time in our transplant comanagement services. To be able to walk with patients on their transplant journey is very rewarding, and I am very appreciative of the mentoring I have received from some of my colleagues with a deeper understanding of transplant medicine.
In my administrative role, I have the privilege of helping to expand the professional education and training of my colleagues. I have a passion for medical education, and we have been working to develop interprofessional educational opportunities within our section. I have had time to think about the imprint of NPs and PAs in academic medicine, and how we can continue to meet the professional educational needs of our section while improving the care of our patients.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine?
The volume of diagnoses that we are expected to manage on a daily basis can be challenging. This challenges you to continue learning. The complexity of discharge planning, particularly for patients in underserved communities, can also be challenging. You have to make sure your patients are ready mentally, physically and emotionally for discharge. As a hospitalist, you are continuously thinking about how to optimize patients to leave your care. For example, patients have different insurance situations, different access to care at home – you are always managing the medical needs of your patient in the context of these other issues.
How does a hospitalist PA work differently from a PA in other care settings?
We are meant to be generalists. We serve as the main provider in owning our patients’ care. A hospitalist PA serves as a cog in the wheel, with connections to specialists, consultants, nurses, social workers, pharmacists, etc., and we are tasked with synthesizing all aspects of patient care to ensure the best outcome.
What has your experience taught you about how NPs and PAs can best fit into hospital medicine groups?
Each hospital medicine group will know how to best integrate their NPs and PAs based on the skillsets of their NPs and PAs, and the needs of the section and the hospital. I personally feel that the best way to utilize NPs and PAs is to allow them to own all aspects of patient care and work at the highest scope of practice. By doing this you empower the NP or PA to continue to develop their skill set and set a precedent of collaboration and respect for interprofessional care models within your section’s culture.
Scope of practice for an NP or PA is going to be based on a conglomeration of roles and bylaws. We are certified nationally, and our scope of practice is determined at the state level and the hospital by level. For the individual NP and PA, it really depends on the hospital medicine group, and how well a practice incorporates a sense of collegiality.
What kind of resources do hospitalist PAs need to succeed, either from SHM or from their own institutions?
There are a few key things that need to happen in order for hospital medicine groups to set up their NPs and PAs for success. The first is for PAs to have exposure to inpatient rotations during clinical rotations. A hospital medicine group also should have a very intentional onboarding process for NPs and PAs. They should also establish a culture of acceptance. To do this, they should utilize resources like SHM’s NP/PA Hospital Medicine Onboarding Toolkit and the SHM/American Academy of Physician Assistants Hospitalist Bootcamp On Demand.
Mentoring is also remarkably important. I have been incredibly blessed to have mentors that helped make me into the PA that I am. I could not have done what I did in the field without people taking a chance on me, and it is important to pass that on to the next generation of PAs.
How has COVID-19 changed the practice of hospital medicine, specifically for advanced practice providers?
The pandemic has demonstrated opportunities for teamwork and utilization of NPs and PAs. The COVID pandemic forced everyone to reflect on why they originally got into medicine – to help patients. I think there will be many doors opening for NPs and PAs, and many pathways for leadership.
The hospitalist leadership at the University of Chicago truly identified that we needed to make wellness a main priority during the beginning of the pandemic. We developed a wellness work group that I have been coleading.
What’s on the horizon for NPs and PAs in hospital medicine?
We are seeing significant increases in hospitalist program utilization, so this is a time where NPs and PAs can be advocates for our profession and articulate how we can use our backgrounds and training to build better care models in order to meet the needs of our patients.
I hope we will see more NPs and PAs assuming leadership roles to ensure that our voices are heard. We should also be advocating for more collaboration and teamwork with our MD and DO colleagues.
Do you have any advice for PA students interested in hospital medicine?
I always tell my students that they should be sponges – you are not expected to know everything as a hospitalist PA, but you are expected to continue learning in order to develop into the best PA you can be. Always be open to where your career path can take you. Hospital medicine is a relatively young field within medicine, and the diversity of our field is very exciting looking forward.
Roundtable discussion: The Pluripotent Hospitalist
In honor of National Hospitalist Day, the Society of Hospital Medicine and the Explore the Space podcast are teaming up to bring you a roundtable discussion, featuring a diverse group of hospitalists from all stages in their careers, on Thursday, March 4, at 7 p.m. ET / 4 p.m. PT.
Registration is required. Sign up here.
Hosted by Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and founder, producer, and host of Explore the Space, the roundtable will include:
- Gurpreet Dhaliwal, MD, a clinician-educator and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. He studies, writes, and speaks about how doctors think – how they make diagnoses, how they develop diagnostic expertise, and what motivates them to improve their practice and the systems in which they work.
- Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She also serves as the pediatric editor of the Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly news magazine.
- Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, a clinician-researcher and clinical associate at the University of Chicago. Her research focuses on hospital-associated disability and she recently authored a perspectives piece in the Journal of Hospital Medicine with her mentor, Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, on why the COVID-19 pandemic might exacerbate this problem.
- Ndidi Unaka, MD, MEd, an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Unaka has served as the associate program director of the pediatric residency program since 2011. She is also the medical director of an inpatient unit that serves as the primary home.
For more information about SHM, please visit hospitalmedicine.org. To learn more about Explore the Space, please visit explorethespaceshow.com.
Register now.
In honor of National Hospitalist Day, the Society of Hospital Medicine and the Explore the Space podcast are teaming up to bring you a roundtable discussion, featuring a diverse group of hospitalists from all stages in their careers, on Thursday, March 4, at 7 p.m. ET / 4 p.m. PT.
Registration is required. Sign up here.
Hosted by Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and founder, producer, and host of Explore the Space, the roundtable will include:
- Gurpreet Dhaliwal, MD, a clinician-educator and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. He studies, writes, and speaks about how doctors think – how they make diagnoses, how they develop diagnostic expertise, and what motivates them to improve their practice and the systems in which they work.
- Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She also serves as the pediatric editor of the Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly news magazine.
- Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, a clinician-researcher and clinical associate at the University of Chicago. Her research focuses on hospital-associated disability and she recently authored a perspectives piece in the Journal of Hospital Medicine with her mentor, Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, on why the COVID-19 pandemic might exacerbate this problem.
- Ndidi Unaka, MD, MEd, an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Unaka has served as the associate program director of the pediatric residency program since 2011. She is also the medical director of an inpatient unit that serves as the primary home.
For more information about SHM, please visit hospitalmedicine.org. To learn more about Explore the Space, please visit explorethespaceshow.com.
Register now.
In honor of National Hospitalist Day, the Society of Hospital Medicine and the Explore the Space podcast are teaming up to bring you a roundtable discussion, featuring a diverse group of hospitalists from all stages in their careers, on Thursday, March 4, at 7 p.m. ET / 4 p.m. PT.
Registration is required. Sign up here.
Hosted by Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and founder, producer, and host of Explore the Space, the roundtable will include:
- Gurpreet Dhaliwal, MD, a clinician-educator and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. He studies, writes, and speaks about how doctors think – how they make diagnoses, how they develop diagnostic expertise, and what motivates them to improve their practice and the systems in which they work.
- Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She also serves as the pediatric editor of the Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly news magazine.
- Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, a clinician-researcher and clinical associate at the University of Chicago. Her research focuses on hospital-associated disability and she recently authored a perspectives piece in the Journal of Hospital Medicine with her mentor, Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, on why the COVID-19 pandemic might exacerbate this problem.
- Ndidi Unaka, MD, MEd, an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Unaka has served as the associate program director of the pediatric residency program since 2011. She is also the medical director of an inpatient unit that serves as the primary home.
For more information about SHM, please visit hospitalmedicine.org. To learn more about Explore the Space, please visit explorethespaceshow.com.
Register now.
Inpatient telemedicine can help address hospitalist pain points
COVID-19 has increased confidence in the technology
Since the advent of COVID-19, health care has seen an unprecedented rise in virtual health. Telemedicine has come to the forefront of our conversations, and there are many speculations around its future state. One such discussion is around the sustainability and expansion of inpatient telemedicine programs post COVID, and if – and how – it is going to be helpful for health care.
Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1
A patient presents to an emergency department of a small community hospital. He needs to be seen by a specialist, but (s)he is not available, so patient gets transferred out to the ED of a different hospital several miles away from his hometown.
He is evaluated in the second ED by the specialist, has repeat testing done – some of those tests were already completed at the first hospital. After evaluating him, the specialist recommends that he does not need to be admitted to the hospital and can be safely followed up as an outpatient. The patient does not require any further intervention and is discharged from the ED.
Scenario 2
Dr. N is a hospitalist in a rural hospital that does not have intensivist support at night. She works 7 on/7 off and is on call 24/7 during her “on” week. Dr. N cannot be physically present in the hospital 24/7. She receives messages from the hospital around the clock and feels that this call schedule is no longer sustainable. She doesn’t feel comfortable admitting patients in the ICU who come to the hospital at night without physically seeing them and without ICU backup. Therefore, some of the patients who are sick enough to be admitted in ICU for closer monitoring but can be potentially handled in this rural hospital get transferred out to a different hospital.
Dr. N has been asking the hospital to provide her intensivist back up at night and to give her some flexibility in the call schedule. However, from hospital’s perspective, the volume isn’t high enough to hire a dedicated nocturnist, and because the hospital is in the small rural area, it is having a hard time attracting more intensivists. After multiple conversations between both parties, Dr. N finally resigns.
Scenario 3
Dr. A is a specialist who is on call covering different hospitals and seeing patients in clinic. His call is getting busier. He has received many new consults and also has to follow up on his other patients in hospital who he saw a day prior.
Dr. A started receiving many pages from the hospitals – some of his patients and their families are anxiously waiting on him so that he can let them go home once he sees them, while some are waiting to know what the next steps and plan of action are. He ends up canceling some of his clinic patients who had scheduled an appointment with him 3, 4, or even 5 months ago. It’s already afternoon.
Dr. A now drives to one hospital, sees his new consults, orders tests which may or may not get results the same day, follows up on other patients, reviews their test results, modifies treatment plans for some while clearing other patients for discharge. He then drives to the other hospital and follows the same process. Some of the patients aren’t happy because of the long wait, a few couldn’t arrange for the ride to go home and ended up staying in hospital 1 extra night, while the ER is getting backlogged waiting on discharges.
These scenarios highlight some of the important and prevalent pain points in health care as shown in Figure 1.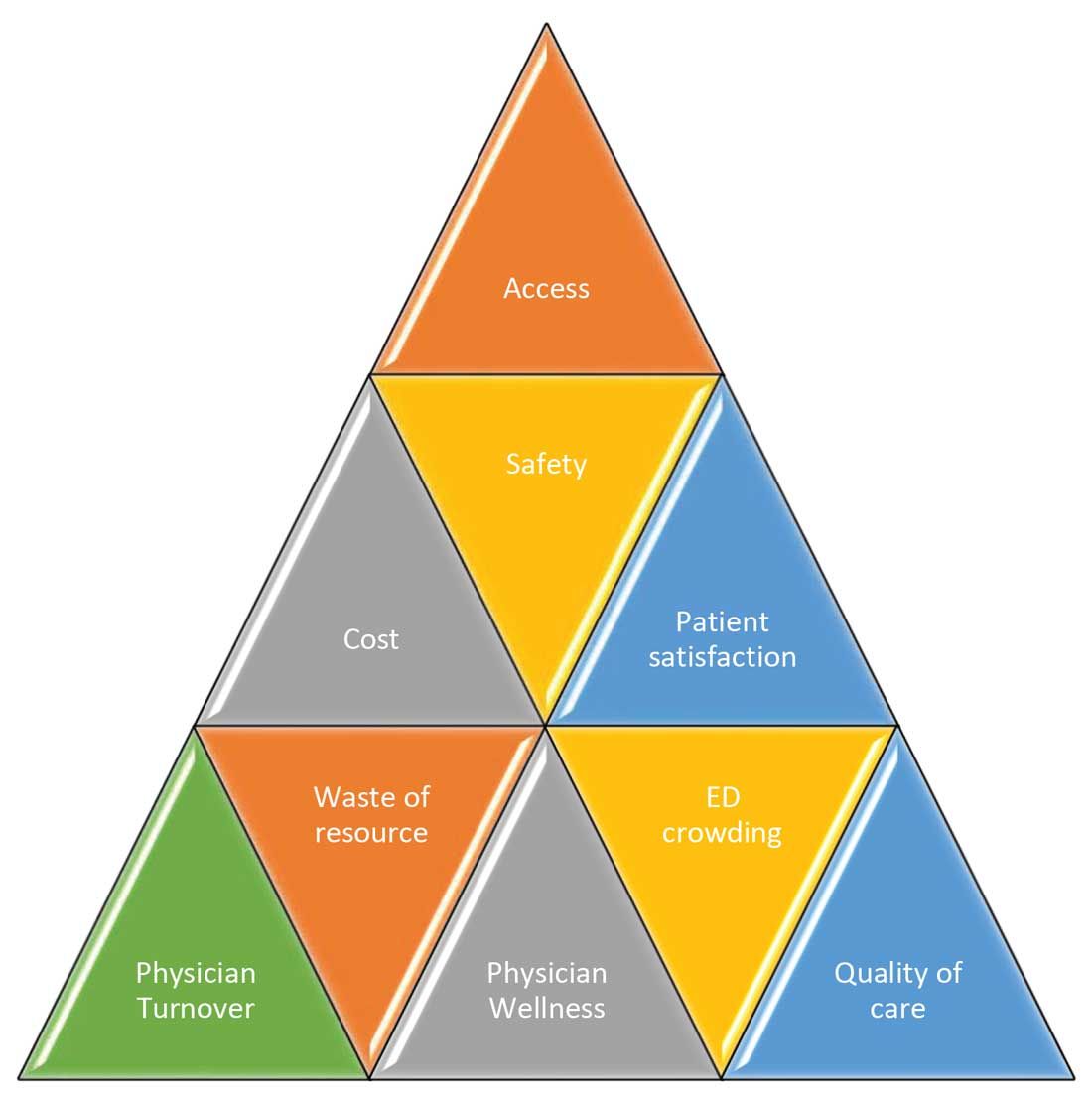
Scenario 1 and part of scenario 2 describe what is called potentially avoidable interfacility transfers. One study showed that around 8% of transferred patients (transferred from one ED to another) were discharged after ED evaluation in the second hospital, meaning they could have been retained locally without necessarily getting transferred if they could have been evaluated by the specialist.1
Transferring a patient from one hospital to another isn’t as simple as picking up a person from point A and dropping him off at point B. Rather it’s a very complicated, high-risk, capital-intensive, and time-consuming process that leads not only to excessive cost involved around transfer but also adds additional stress and burden on the patient and family. In these scenarios, having a specialist available via teleconsult could have eliminated much of this hassle and cost, allowing the patient to stay locally close to family and get access to necessary medical expertise from any part of the country in a timely manner.
Scenario 2 talks about the recruitment and retention challenges in low-volume, low-resourced locations because of call schedule and the lack of specialty support. It is reported in one study that 19% of common hospitalist admissions happen between 7:00 p.m. and 7:00 a.m. Eighty percent of admissions occurred prior to midnight. Nonrural facilities averaged 6.69 hospitalist admissions per night in that study, whereas rural facilities averaged 1.35 admissions.2 It’s like a double-edged sword for such facilities. While having a dedicated nocturnist is not a sustainable model for these hospitals, not having adequate support at night impacts physician wellness, which is already costing hospitals billions of dollars as well as leading to physician turnover: It could cost a hospital somewhere between $500,000 and $1 million to replace just one physician.3 Hence, the potential exists for a telehospitalist program in these settings to address this dilemma.
Scenario 3 sheds light on the operational issues resulting in reduced patient satisfaction and lost revenues, both on the outpatient and inpatient sides by cancellation of office visits and ED backlog. Telemedicine use in these situations can improve the turnaround time of physicians who can see some of those patients while staying at one location as they wait on other patients to show up in the clinic or wait on the operation room crew, or the procedure kit etcetera, hence improving the length of stay, ED throughput, patient satisfaction, and quality of care. This also can improve overall workflow and the wellness of physicians.
One common outcome in all these scenarios is emergency department overcrowding. There have been multiple studies that suggest that ED overcrowding can result in increased costs, lost revenues, and poor clinical outcomes, including delayed administration of antibiotics, delayed administration of analgesics to suffering patients, increased hospital length of stay, and even increased mortality.4-6 A crowded ED limits the ability of an institution to accept referrals and increases medicolegal risks. (See Figure 2.)
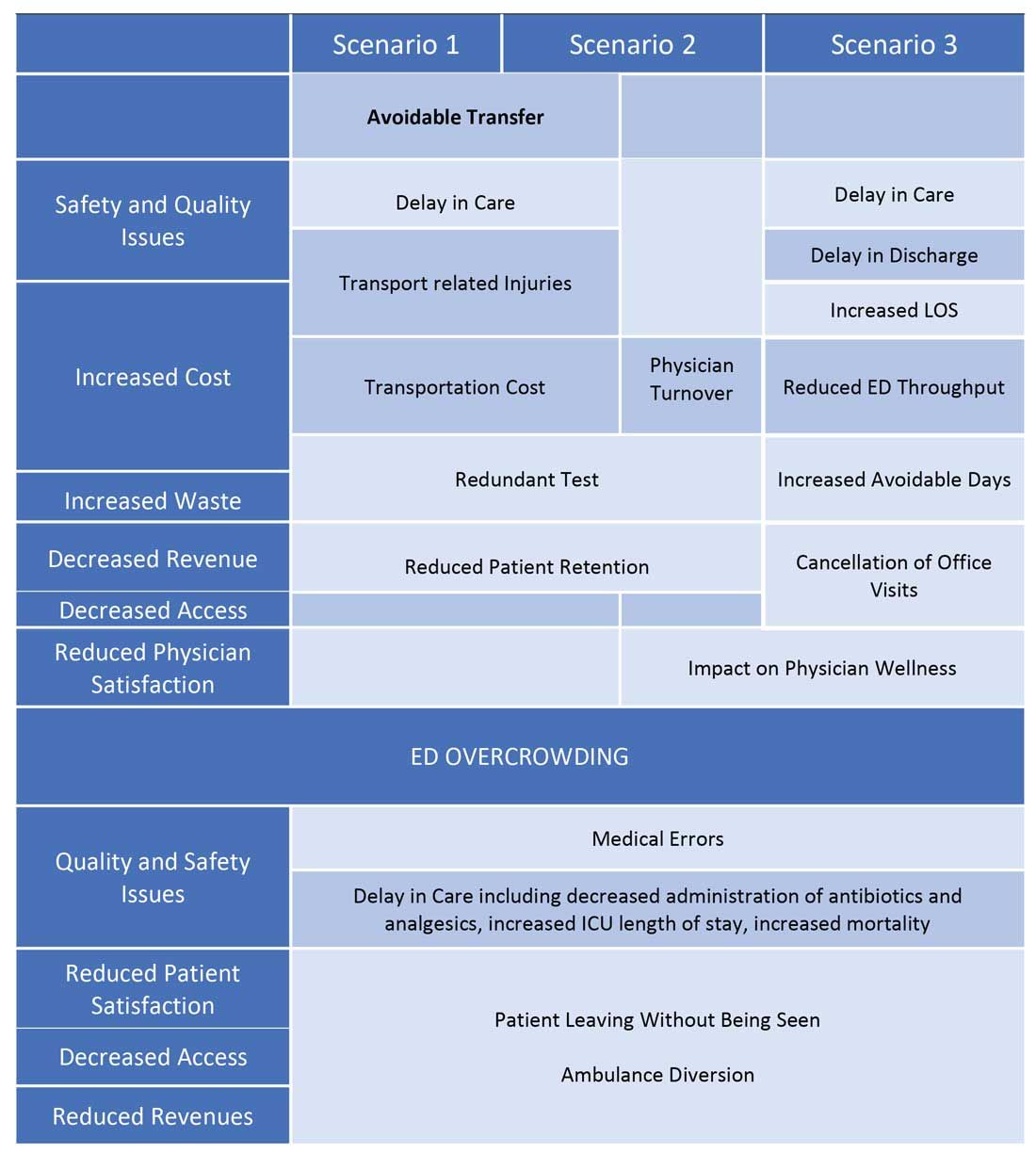
Another study showed that a 1-hour reduction in ED boarding time would result in over $9,000 of additional revenue by reducing ambulance diversion and the number of patients who left without being seen.7 Another found that using tele-emergency services can potentially result in net savings of $3,823 per avoided transfer, while accounting for the costs related to tele-emergency technology, hospital revenues, and patient-associated savings.8
There are other instances where gaps in staffing and cracks in workflow can have a negative impact on hospital operations. For example, the busier hospitals that do have a dedicated nocturnist also struggle with physician retention, since such hospitals have higher volumes and higher cross-coverage needs, and are therefore hard to manage by just one single physician at night. Since these are temporary surges, hiring another full-time nocturnist is not a viable option for the hospitals and is considered an expense in many places.
Similarly, during day shift, if a physician goes on vacation or there are surges in patient volumes, hiring a locum tenens hospitalist can be an expensive option, since the cost also includes travel and lodging. In many instances, hiring locum tenens in a given time frame is also not possible, and it leaves the physicians short staffed, fueling both physicians’ and patients’ dissatisfaction and leading to other operational and safety challenges, which I highlighted above.
Telemedicine services in these situations can provide cross-coverage while nocturnists can focus on admissions and other acute issues. Also, when physicians are on vacation or there is surge capacity (that can be forecast by using various predictive analytics models), hospitals can make plans accordingly and make use of telemedicine services. For example, Providence St. Joseph Health reported improvement in timeliness and efficiency of care after implementation of a telehospitalist program. Their 2-year study at a partner site showed a 59% improvement in patients admitted prior to midnight, about $547,000 improvement in first-day revenue capture, an increase in total revenue days and comparable patient experience scores, and a substantial increase in inpatient census and case mix index.9
Other institutions have successfully implemented some inpatient telemedicine programs – such as telepsych, telestroke, and tele-ICU – and some have also reported positive outcomes in terms of patient satisfaction, improved access, reduced length of stay in the ED, and improved quality metrics. Emory Healthcare in Atlanta reported $4.6 million savings in Medicare costs over a 15-month period from adopting a telemedicine model in the ICU, and a reduction in 60-day readmissions by 2.1%.10 Similarly, another study showed that one large health care center improved its direct contribution margins by 376% (from $7.9 million to $37.7 million) because of increased case volume, shorter lengths of stay, and higher case revenue relative to direct costs. When combined with a logistics center, they reported improved contribution margins by 665% (from $7.9 million to $60.6 million).11
There are barriers to the integration and implementation of inpatient telemedicine, including regulations, reimbursement, physician licensing, adoption of technology, and trust among staff and patients. However, I am cautiously optimistic that increased use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic has allowed patients, physicians, nurses, and health care workers and leaders to gain experience with this technology, which will help them gain confidence and reduce hesitation in adapting to this new digital platform. Ultimately, the extent to which telemedicine is able to positively impact patient care will revolve around overcoming these barriers, likely through an evolution of both the technology itself and the attitudes and regulations surrounding it.
I do not suggest that telemedicine should replace the in-person encounter, but it can be implemented and used successfully in addressing the pain points in U.S. health care. (See Figure 3.)
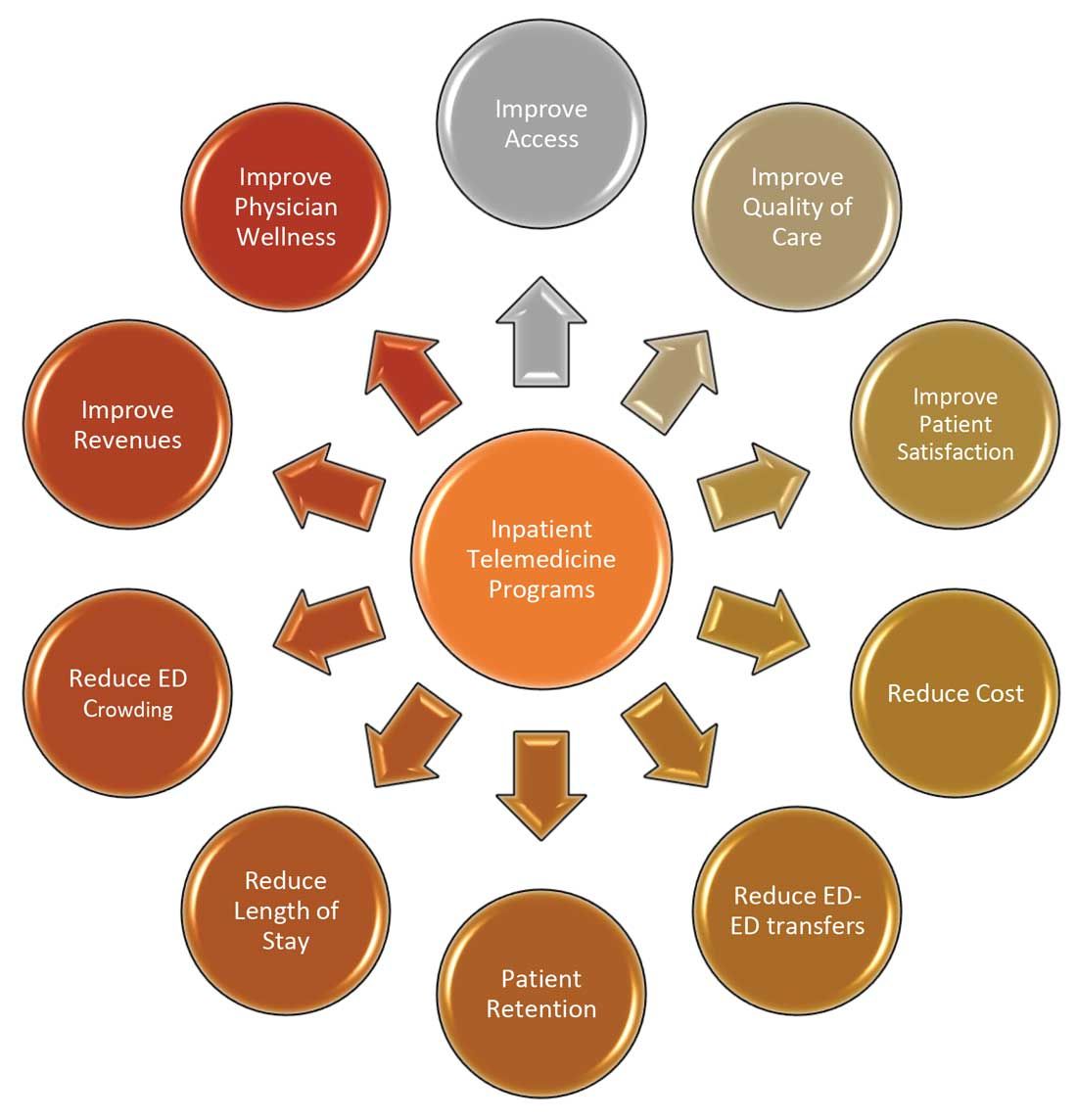
To that end, the purpose of this article is to spark discussion around different ways of implementing telemedicine in inpatient settings to solve many of the challenges that health care faces today.
Dr. Zia is an internal medicine board-certified physician, serving as a hospitalist and physician adviser in a medically underserved area. She has also served as interim medical director of the department of hospital medicine, and medical staff president, at SIH Herrin Hospital, in Herrin, Ill., part of Southern Illinois Healthcare. She has a special interest in improving access to health care in physician shortage areas.
References
1. Kindermann DR et al. Emergency department transfers and transfer relationships in United States hospitals. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Feb;22(2):157-65.
2. Sanders RB et al. New hospital telemedicine services: Potential market for a nighttime hospitalist service. Telemed J E Health. 2014 Oct 1;20(10):902-8.
3. Shanafelt T et al. The business case for investing in physician well-being. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(12):1826-32.
4. Pines JM et al. The impact of emergency department crowding measures on time to antibiotics for patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Emerg Med. 2007 Nov;50(5):510-6.
5. Pines JM and Hollander JE. Emergency department crowding is associated with poor care for patients with severe pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Jan;51(1):1-5.
6. Chalfin DB et al. Impact of delayed transfer of critically ill patients from the emergency department to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2007 Jun;35(6):1477-83.
7. Pines JM et al. The financial consequences of lost demand and reducing boarding in hospital emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2011 Oct;58(4):331-40.
8. Natafgi N et al. Using tele-emergency to avoid patient transfers in rural emergency. J Telemed Telecare. 2018 Apri;24(3):193-201.
9. Providence.org/telehealthhospitalistcasestudy.
10. Woodruff Health Sciences Center. CMS report: eICU program reduced hospital stays, saved millions, eased provider shortage. 2017 Apr 5.
11. Lilly CM et al. ICU telemedicine program financial outcomes. Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):286-97.
COVID-19 has increased confidence in the technology
COVID-19 has increased confidence in the technology
Since the advent of COVID-19, health care has seen an unprecedented rise in virtual health. Telemedicine has come to the forefront of our conversations, and there are many speculations around its future state. One such discussion is around the sustainability and expansion of inpatient telemedicine programs post COVID, and if – and how – it is going to be helpful for health care.
Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1
A patient presents to an emergency department of a small community hospital. He needs to be seen by a specialist, but (s)he is not available, so patient gets transferred out to the ED of a different hospital several miles away from his hometown.
He is evaluated in the second ED by the specialist, has repeat testing done – some of those tests were already completed at the first hospital. After evaluating him, the specialist recommends that he does not need to be admitted to the hospital and can be safely followed up as an outpatient. The patient does not require any further intervention and is discharged from the ED.
Scenario 2
Dr. N is a hospitalist in a rural hospital that does not have intensivist support at night. She works 7 on/7 off and is on call 24/7 during her “on” week. Dr. N cannot be physically present in the hospital 24/7. She receives messages from the hospital around the clock and feels that this call schedule is no longer sustainable. She doesn’t feel comfortable admitting patients in the ICU who come to the hospital at night without physically seeing them and without ICU backup. Therefore, some of the patients who are sick enough to be admitted in ICU for closer monitoring but can be potentially handled in this rural hospital get transferred out to a different hospital.
Dr. N has been asking the hospital to provide her intensivist back up at night and to give her some flexibility in the call schedule. However, from hospital’s perspective, the volume isn’t high enough to hire a dedicated nocturnist, and because the hospital is in the small rural area, it is having a hard time attracting more intensivists. After multiple conversations between both parties, Dr. N finally resigns.
Scenario 3
Dr. A is a specialist who is on call covering different hospitals and seeing patients in clinic. His call is getting busier. He has received many new consults and also has to follow up on his other patients in hospital who he saw a day prior.
Dr. A started receiving many pages from the hospitals – some of his patients and their families are anxiously waiting on him so that he can let them go home once he sees them, while some are waiting to know what the next steps and plan of action are. He ends up canceling some of his clinic patients who had scheduled an appointment with him 3, 4, or even 5 months ago. It’s already afternoon.
Dr. A now drives to one hospital, sees his new consults, orders tests which may or may not get results the same day, follows up on other patients, reviews their test results, modifies treatment plans for some while clearing other patients for discharge. He then drives to the other hospital and follows the same process. Some of the patients aren’t happy because of the long wait, a few couldn’t arrange for the ride to go home and ended up staying in hospital 1 extra night, while the ER is getting backlogged waiting on discharges.
These scenarios highlight some of the important and prevalent pain points in health care as shown in Figure 1.
Scenario 1 and part of scenario 2 describe what is called potentially avoidable interfacility transfers. One study showed that around 8% of transferred patients (transferred from one ED to another) were discharged after ED evaluation in the second hospital, meaning they could have been retained locally without necessarily getting transferred if they could have been evaluated by the specialist.1
Transferring a patient from one hospital to another isn’t as simple as picking up a person from point A and dropping him off at point B. Rather it’s a very complicated, high-risk, capital-intensive, and time-consuming process that leads not only to excessive cost involved around transfer but also adds additional stress and burden on the patient and family. In these scenarios, having a specialist available via teleconsult could have eliminated much of this hassle and cost, allowing the patient to stay locally close to family and get access to necessary medical expertise from any part of the country in a timely manner.
Scenario 2 talks about the recruitment and retention challenges in low-volume, low-resourced locations because of call schedule and the lack of specialty support. It is reported in one study that 19% of common hospitalist admissions happen between 7:00 p.m. and 7:00 a.m. Eighty percent of admissions occurred prior to midnight. Nonrural facilities averaged 6.69 hospitalist admissions per night in that study, whereas rural facilities averaged 1.35 admissions.2 It’s like a double-edged sword for such facilities. While having a dedicated nocturnist is not a sustainable model for these hospitals, not having adequate support at night impacts physician wellness, which is already costing hospitals billions of dollars as well as leading to physician turnover: It could cost a hospital somewhere between $500,000 and $1 million to replace just one physician.3 Hence, the potential exists for a telehospitalist program in these settings to address this dilemma.
Scenario 3 sheds light on the operational issues resulting in reduced patient satisfaction and lost revenues, both on the outpatient and inpatient sides by cancellation of office visits and ED backlog. Telemedicine use in these situations can improve the turnaround time of physicians who can see some of those patients while staying at one location as they wait on other patients to show up in the clinic or wait on the operation room crew, or the procedure kit etcetera, hence improving the length of stay, ED throughput, patient satisfaction, and quality of care. This also can improve overall workflow and the wellness of physicians.
One common outcome in all these scenarios is emergency department overcrowding. There have been multiple studies that suggest that ED overcrowding can result in increased costs, lost revenues, and poor clinical outcomes, including delayed administration of antibiotics, delayed administration of analgesics to suffering patients, increased hospital length of stay, and even increased mortality.4-6 A crowded ED limits the ability of an institution to accept referrals and increases medicolegal risks. (See Figure 2.)

Another study showed that a 1-hour reduction in ED boarding time would result in over $9,000 of additional revenue by reducing ambulance diversion and the number of patients who left without being seen.7 Another found that using tele-emergency services can potentially result in net savings of $3,823 per avoided transfer, while accounting for the costs related to tele-emergency technology, hospital revenues, and patient-associated savings.8
There are other instances where gaps in staffing and cracks in workflow can have a negative impact on hospital operations. For example, the busier hospitals that do have a dedicated nocturnist also struggle with physician retention, since such hospitals have higher volumes and higher cross-coverage needs, and are therefore hard to manage by just one single physician at night. Since these are temporary surges, hiring another full-time nocturnist is not a viable option for the hospitals and is considered an expense in many places.
Similarly, during day shift, if a physician goes on vacation or there are surges in patient volumes, hiring a locum tenens hospitalist can be an expensive option, since the cost also includes travel and lodging. In many instances, hiring locum tenens in a given time frame is also not possible, and it leaves the physicians short staffed, fueling both physicians’ and patients’ dissatisfaction and leading to other operational and safety challenges, which I highlighted above.
Telemedicine services in these situations can provide cross-coverage while nocturnists can focus on admissions and other acute issues. Also, when physicians are on vacation or there is surge capacity (that can be forecast by using various predictive analytics models), hospitals can make plans accordingly and make use of telemedicine services. For example, Providence St. Joseph Health reported improvement in timeliness and efficiency of care after implementation of a telehospitalist program. Their 2-year study at a partner site showed a 59% improvement in patients admitted prior to midnight, about $547,000 improvement in first-day revenue capture, an increase in total revenue days and comparable patient experience scores, and a substantial increase in inpatient census and case mix index.9
Other institutions have successfully implemented some inpatient telemedicine programs – such as telepsych, telestroke, and tele-ICU – and some have also reported positive outcomes in terms of patient satisfaction, improved access, reduced length of stay in the ED, and improved quality metrics. Emory Healthcare in Atlanta reported $4.6 million savings in Medicare costs over a 15-month period from adopting a telemedicine model in the ICU, and a reduction in 60-day readmissions by 2.1%.10 Similarly, another study showed that one large health care center improved its direct contribution margins by 376% (from $7.9 million to $37.7 million) because of increased case volume, shorter lengths of stay, and higher case revenue relative to direct costs. When combined with a logistics center, they reported improved contribution margins by 665% (from $7.9 million to $60.6 million).11
There are barriers to the integration and implementation of inpatient telemedicine, including regulations, reimbursement, physician licensing, adoption of technology, and trust among staff and patients. However, I am cautiously optimistic that increased use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic has allowed patients, physicians, nurses, and health care workers and leaders to gain experience with this technology, which will help them gain confidence and reduce hesitation in adapting to this new digital platform. Ultimately, the extent to which telemedicine is able to positively impact patient care will revolve around overcoming these barriers, likely through an evolution of both the technology itself and the attitudes and regulations surrounding it.
I do not suggest that telemedicine should replace the in-person encounter, but it can be implemented and used successfully in addressing the pain points in U.S. health care. (See Figure 3.)

To that end, the purpose of this article is to spark discussion around different ways of implementing telemedicine in inpatient settings to solve many of the challenges that health care faces today.
Dr. Zia is an internal medicine board-certified physician, serving as a hospitalist and physician adviser in a medically underserved area. She has also served as interim medical director of the department of hospital medicine, and medical staff president, at SIH Herrin Hospital, in Herrin, Ill., part of Southern Illinois Healthcare. She has a special interest in improving access to health care in physician shortage areas.
References
1. Kindermann DR et al. Emergency department transfers and transfer relationships in United States hospitals. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Feb;22(2):157-65.
2. Sanders RB et al. New hospital telemedicine services: Potential market for a nighttime hospitalist service. Telemed J E Health. 2014 Oct 1;20(10):902-8.
3. Shanafelt T et al. The business case for investing in physician well-being. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(12):1826-32.
4. Pines JM et al. The impact of emergency department crowding measures on time to antibiotics for patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Emerg Med. 2007 Nov;50(5):510-6.
5. Pines JM and Hollander JE. Emergency department crowding is associated with poor care for patients with severe pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Jan;51(1):1-5.
6. Chalfin DB et al. Impact of delayed transfer of critically ill patients from the emergency department to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2007 Jun;35(6):1477-83.
7. Pines JM et al. The financial consequences of lost demand and reducing boarding in hospital emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2011 Oct;58(4):331-40.
8. Natafgi N et al. Using tele-emergency to avoid patient transfers in rural emergency. J Telemed Telecare. 2018 Apri;24(3):193-201.
9. Providence.org/telehealthhospitalistcasestudy.
10. Woodruff Health Sciences Center. CMS report: eICU program reduced hospital stays, saved millions, eased provider shortage. 2017 Apr 5.
11. Lilly CM et al. ICU telemedicine program financial outcomes. Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):286-97.
Since the advent of COVID-19, health care has seen an unprecedented rise in virtual health. Telemedicine has come to the forefront of our conversations, and there are many speculations around its future state. One such discussion is around the sustainability and expansion of inpatient telemedicine programs post COVID, and if – and how – it is going to be helpful for health care.
Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1
A patient presents to an emergency department of a small community hospital. He needs to be seen by a specialist, but (s)he is not available, so patient gets transferred out to the ED of a different hospital several miles away from his hometown.
He is evaluated in the second ED by the specialist, has repeat testing done – some of those tests were already completed at the first hospital. After evaluating him, the specialist recommends that he does not need to be admitted to the hospital and can be safely followed up as an outpatient. The patient does not require any further intervention and is discharged from the ED.
Scenario 2
Dr. N is a hospitalist in a rural hospital that does not have intensivist support at night. She works 7 on/7 off and is on call 24/7 during her “on” week. Dr. N cannot be physically present in the hospital 24/7. She receives messages from the hospital around the clock and feels that this call schedule is no longer sustainable. She doesn’t feel comfortable admitting patients in the ICU who come to the hospital at night without physically seeing them and without ICU backup. Therefore, some of the patients who are sick enough to be admitted in ICU for closer monitoring but can be potentially handled in this rural hospital get transferred out to a different hospital.
Dr. N has been asking the hospital to provide her intensivist back up at night and to give her some flexibility in the call schedule. However, from hospital’s perspective, the volume isn’t high enough to hire a dedicated nocturnist, and because the hospital is in the small rural area, it is having a hard time attracting more intensivists. After multiple conversations between both parties, Dr. N finally resigns.
Scenario 3
Dr. A is a specialist who is on call covering different hospitals and seeing patients in clinic. His call is getting busier. He has received many new consults and also has to follow up on his other patients in hospital who he saw a day prior.
Dr. A started receiving many pages from the hospitals – some of his patients and their families are anxiously waiting on him so that he can let them go home once he sees them, while some are waiting to know what the next steps and plan of action are. He ends up canceling some of his clinic patients who had scheduled an appointment with him 3, 4, or even 5 months ago. It’s already afternoon.
Dr. A now drives to one hospital, sees his new consults, orders tests which may or may not get results the same day, follows up on other patients, reviews their test results, modifies treatment plans for some while clearing other patients for discharge. He then drives to the other hospital and follows the same process. Some of the patients aren’t happy because of the long wait, a few couldn’t arrange for the ride to go home and ended up staying in hospital 1 extra night, while the ER is getting backlogged waiting on discharges.
These scenarios highlight some of the important and prevalent pain points in health care as shown in Figure 1.
Scenario 1 and part of scenario 2 describe what is called potentially avoidable interfacility transfers. One study showed that around 8% of transferred patients (transferred from one ED to another) were discharged after ED evaluation in the second hospital, meaning they could have been retained locally without necessarily getting transferred if they could have been evaluated by the specialist.1
Transferring a patient from one hospital to another isn’t as simple as picking up a person from point A and dropping him off at point B. Rather it’s a very complicated, high-risk, capital-intensive, and time-consuming process that leads not only to excessive cost involved around transfer but also adds additional stress and burden on the patient and family. In these scenarios, having a specialist available via teleconsult could have eliminated much of this hassle and cost, allowing the patient to stay locally close to family and get access to necessary medical expertise from any part of the country in a timely manner.
Scenario 2 talks about the recruitment and retention challenges in low-volume, low-resourced locations because of call schedule and the lack of specialty support. It is reported in one study that 19% of common hospitalist admissions happen between 7:00 p.m. and 7:00 a.m. Eighty percent of admissions occurred prior to midnight. Nonrural facilities averaged 6.69 hospitalist admissions per night in that study, whereas rural facilities averaged 1.35 admissions.2 It’s like a double-edged sword for such facilities. While having a dedicated nocturnist is not a sustainable model for these hospitals, not having adequate support at night impacts physician wellness, which is already costing hospitals billions of dollars as well as leading to physician turnover: It could cost a hospital somewhere between $500,000 and $1 million to replace just one physician.3 Hence, the potential exists for a telehospitalist program in these settings to address this dilemma.
Scenario 3 sheds light on the operational issues resulting in reduced patient satisfaction and lost revenues, both on the outpatient and inpatient sides by cancellation of office visits and ED backlog. Telemedicine use in these situations can improve the turnaround time of physicians who can see some of those patients while staying at one location as they wait on other patients to show up in the clinic or wait on the operation room crew, or the procedure kit etcetera, hence improving the length of stay, ED throughput, patient satisfaction, and quality of care. This also can improve overall workflow and the wellness of physicians.
One common outcome in all these scenarios is emergency department overcrowding. There have been multiple studies that suggest that ED overcrowding can result in increased costs, lost revenues, and poor clinical outcomes, including delayed administration of antibiotics, delayed administration of analgesics to suffering patients, increased hospital length of stay, and even increased mortality.4-6 A crowded ED limits the ability of an institution to accept referrals and increases medicolegal risks. (See Figure 2.)

Another study showed that a 1-hour reduction in ED boarding time would result in over $9,000 of additional revenue by reducing ambulance diversion and the number of patients who left without being seen.7 Another found that using tele-emergency services can potentially result in net savings of $3,823 per avoided transfer, while accounting for the costs related to tele-emergency technology, hospital revenues, and patient-associated savings.8
There are other instances where gaps in staffing and cracks in workflow can have a negative impact on hospital operations. For example, the busier hospitals that do have a dedicated nocturnist also struggle with physician retention, since such hospitals have higher volumes and higher cross-coverage needs, and are therefore hard to manage by just one single physician at night. Since these are temporary surges, hiring another full-time nocturnist is not a viable option for the hospitals and is considered an expense in many places.
Similarly, during day shift, if a physician goes on vacation or there are surges in patient volumes, hiring a locum tenens hospitalist can be an expensive option, since the cost also includes travel and lodging. In many instances, hiring locum tenens in a given time frame is also not possible, and it leaves the physicians short staffed, fueling both physicians’ and patients’ dissatisfaction and leading to other operational and safety challenges, which I highlighted above.
Telemedicine services in these situations can provide cross-coverage while nocturnists can focus on admissions and other acute issues. Also, when physicians are on vacation or there is surge capacity (that can be forecast by using various predictive analytics models), hospitals can make plans accordingly and make use of telemedicine services. For example, Providence St. Joseph Health reported improvement in timeliness and efficiency of care after implementation of a telehospitalist program. Their 2-year study at a partner site showed a 59% improvement in patients admitted prior to midnight, about $547,000 improvement in first-day revenue capture, an increase in total revenue days and comparable patient experience scores, and a substantial increase in inpatient census and case mix index.9
Other institutions have successfully implemented some inpatient telemedicine programs – such as telepsych, telestroke, and tele-ICU – and some have also reported positive outcomes in terms of patient satisfaction, improved access, reduced length of stay in the ED, and improved quality metrics. Emory Healthcare in Atlanta reported $4.6 million savings in Medicare costs over a 15-month period from adopting a telemedicine model in the ICU, and a reduction in 60-day readmissions by 2.1%.10 Similarly, another study showed that one large health care center improved its direct contribution margins by 376% (from $7.9 million to $37.7 million) because of increased case volume, shorter lengths of stay, and higher case revenue relative to direct costs. When combined with a logistics center, they reported improved contribution margins by 665% (from $7.9 million to $60.6 million).11
There are barriers to the integration and implementation of inpatient telemedicine, including regulations, reimbursement, physician licensing, adoption of technology, and trust among staff and patients. However, I am cautiously optimistic that increased use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic has allowed patients, physicians, nurses, and health care workers and leaders to gain experience with this technology, which will help them gain confidence and reduce hesitation in adapting to this new digital platform. Ultimately, the extent to which telemedicine is able to positively impact patient care will revolve around overcoming these barriers, likely through an evolution of both the technology itself and the attitudes and regulations surrounding it.
I do not suggest that telemedicine should replace the in-person encounter, but it can be implemented and used successfully in addressing the pain points in U.S. health care. (See Figure 3.)

To that end, the purpose of this article is to spark discussion around different ways of implementing telemedicine in inpatient settings to solve many of the challenges that health care faces today.
Dr. Zia is an internal medicine board-certified physician, serving as a hospitalist and physician adviser in a medically underserved area. She has also served as interim medical director of the department of hospital medicine, and medical staff president, at SIH Herrin Hospital, in Herrin, Ill., part of Southern Illinois Healthcare. She has a special interest in improving access to health care in physician shortage areas.
References
1. Kindermann DR et al. Emergency department transfers and transfer relationships in United States hospitals. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Feb;22(2):157-65.
2. Sanders RB et al. New hospital telemedicine services: Potential market for a nighttime hospitalist service. Telemed J E Health. 2014 Oct 1;20(10):902-8.
3. Shanafelt T et al. The business case for investing in physician well-being. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(12):1826-32.
4. Pines JM et al. The impact of emergency department crowding measures on time to antibiotics for patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Emerg Med. 2007 Nov;50(5):510-6.
5. Pines JM and Hollander JE. Emergency department crowding is associated with poor care for patients with severe pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Jan;51(1):1-5.
6. Chalfin DB et al. Impact of delayed transfer of critically ill patients from the emergency department to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2007 Jun;35(6):1477-83.
7. Pines JM et al. The financial consequences of lost demand and reducing boarding in hospital emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2011 Oct;58(4):331-40.
8. Natafgi N et al. Using tele-emergency to avoid patient transfers in rural emergency. J Telemed Telecare. 2018 Apri;24(3):193-201.
9. Providence.org/telehealthhospitalistcasestudy.
10. Woodruff Health Sciences Center. CMS report: eICU program reduced hospital stays, saved millions, eased provider shortage. 2017 Apr 5.
11. Lilly CM et al. ICU telemedicine program financial outcomes. Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):286-97.
Late-window stroke thrombolysis not linked to clot migration
In patients with acute ischemic stroke, the use of thrombolysis in the late window of 4.5-9 hours after symptom onset was not associated with an increase in clot migration that would cause reduced clot accessibility to endovascular therapy, a new analysis from the EXTEND trial shows.
“There was no significant difference in the incidence of clot migration leading to clot inaccessibility in patients who received placebo or (intravenous) thrombolysis,” the authors report.
“Our results found no convincing evidence against the use of bridging thrombolysis before endovascular therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke who present outside the 4.5-hour window,” they conclude.
“This information is important because it provides some comfort for neurointerventionists that IV thrombolysis does not unduly increase the risk of clot migration,” senior author, Bernard Yan, DMedSci, FRACP, told this news organization.
The study was published online in Stroke on Feb. 16.
The Australian researchers explain that endovascular thrombectomy is the standard of care in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke caused by large-vessel occlusion, and current treatment guidelines recommend bridging thrombolysis for all patients receiving thrombectomy within the 4.5-hour time window.
While thrombectomy is also recommended in selected patients up to 24 hours after onset of symptoms, it remains unclear whether thrombolysis pretreatment should be administered in this setting.
One of the issues that might affect use of thrombolysis is distal clot migration. As proximal clot location is a crucial factor determining suitability for endovascular clot retrieval, distal migration may prevent successful thrombectomy, they note.
“Clot migration can happen any time and makes life more difficult for the neurointerventionist who performs the endovascular clot retrieval,” added Dr. Yan, who is a neurologist and neurointerventionist at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, Australia.
In the current paper, the researchers report a retrospective analysis of data from the EXTEND trial of late thrombolysis, defined as 4.5-9 hours after symptom onset, to investigate the association between thrombolysis and clot migration leading to clot irretrievability.
The analysis included a total of 220 patients (109 patients in the placebo group and 111 in the thrombolysis group).
Results showed that retrievable clot was seen on baseline imaging in 69% of patients in the placebo group and 61% in the thrombolysis group. Clot resolution occurred in 28% of patients in the placebo group and 50% in the thrombolysis group.
No significant difference was observed in the incidence of clot migration leading to inaccessibility between groups. Clot migration from a retrievable to nonretrievable location occurred in 19% of the placebo group and 14% of the thrombolysis group, with an odds ratio for clot migration in the thrombolysis group of 0.70 (95% confidence interval, 0.35-1.44). This outcome was consistent across subgroups.
The researchers note that, to their knowledge, this is the first randomized controlled study to assess the effect of thrombolysis on clot migration and accessibility in an extended time window.
They acknowledge that a limitation of this study is that they only assessed clot migration from a retrievable to a nonretrievable location; therefore, the true frequency of any clot migration occurring was likely to be higher, and this could explain why other reports have found higher odds ratios of clot migration.
But they point out that they chose to limit their analysis in this way specifically to guide decision-making regarding bridging thrombolysis incorporating endovascular therapy in the extended time window.
“The findings of this study are highly relevant in the current clinical environment, where there are multiple ongoing trials looking at removing thrombolysis pretreatment within the 4.5-hour time window in thrombectomy patients,” the authors write.
“We have demonstrated that thrombolysis in the 4.5- to 9-hour window is not associated with reduced clot accessibility, and this information will be useful in future trial designs incorporating this extended time window,” they add.
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Michael Hill, MD, University of Calgary (Alta.), said: “Thrombus migration does happen and is likely part of the natural history of ischemic stroke, which may be influenced by therapeutics such as thrombolysis. This paper’s top-line result is that thrombus migration occurs in both treated and untreated groups – and therefore that this is really an observation of natural history.”
Dr. Hill says that, at present, patients should be treated with thrombolysis before endovascular therapy if they are eligible, and these results do not change that recommendation.
“The results of the ongoing trials comparing direct thrombectomy with thrombolysis plus thrombectomy will help to understand the potential clinical outcome relevance of this phenomenon,” he added.
The EXTEND trial was supported by grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization Flagship Program. Dr. Yan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with acute ischemic stroke, the use of thrombolysis in the late window of 4.5-9 hours after symptom onset was not associated with an increase in clot migration that would cause reduced clot accessibility to endovascular therapy, a new analysis from the EXTEND trial shows.
“There was no significant difference in the incidence of clot migration leading to clot inaccessibility in patients who received placebo or (intravenous) thrombolysis,” the authors report.
“Our results found no convincing evidence against the use of bridging thrombolysis before endovascular therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke who present outside the 4.5-hour window,” they conclude.
“This information is important because it provides some comfort for neurointerventionists that IV thrombolysis does not unduly increase the risk of clot migration,” senior author, Bernard Yan, DMedSci, FRACP, told this news organization.
The study was published online in Stroke on Feb. 16.
The Australian researchers explain that endovascular thrombectomy is the standard of care in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke caused by large-vessel occlusion, and current treatment guidelines recommend bridging thrombolysis for all patients receiving thrombectomy within the 4.5-hour time window.
While thrombectomy is also recommended in selected patients up to 24 hours after onset of symptoms, it remains unclear whether thrombolysis pretreatment should be administered in this setting.
One of the issues that might affect use of thrombolysis is distal clot migration. As proximal clot location is a crucial factor determining suitability for endovascular clot retrieval, distal migration may prevent successful thrombectomy, they note.
“Clot migration can happen any time and makes life more difficult for the neurointerventionist who performs the endovascular clot retrieval,” added Dr. Yan, who is a neurologist and neurointerventionist at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, Australia.
In the current paper, the researchers report a retrospective analysis of data from the EXTEND trial of late thrombolysis, defined as 4.5-9 hours after symptom onset, to investigate the association between thrombolysis and clot migration leading to clot irretrievability.
The analysis included a total of 220 patients (109 patients in the placebo group and 111 in the thrombolysis group).
Results showed that retrievable clot was seen on baseline imaging in 69% of patients in the placebo group and 61% in the thrombolysis group. Clot resolution occurred in 28% of patients in the placebo group and 50% in the thrombolysis group.
No significant difference was observed in the incidence of clot migration leading to inaccessibility between groups. Clot migration from a retrievable to nonretrievable location occurred in 19% of the placebo group and 14% of the thrombolysis group, with an odds ratio for clot migration in the thrombolysis group of 0.70 (95% confidence interval, 0.35-1.44). This outcome was consistent across subgroups.
The researchers note that, to their knowledge, this is the first randomized controlled study to assess the effect of thrombolysis on clot migration and accessibility in an extended time window.
They acknowledge that a limitation of this study is that they only assessed clot migration from a retrievable to a nonretrievable location; therefore, the true frequency of any clot migration occurring was likely to be higher, and this could explain why other reports have found higher odds ratios of clot migration.
But they point out that they chose to limit their analysis in this way specifically to guide decision-making regarding bridging thrombolysis incorporating endovascular therapy in the extended time window.
“The findings of this study are highly relevant in the current clinical environment, where there are multiple ongoing trials looking at removing thrombolysis pretreatment within the 4.5-hour time window in thrombectomy patients,” the authors write.
“We have demonstrated that thrombolysis in the 4.5- to 9-hour window is not associated with reduced clot accessibility, and this information will be useful in future trial designs incorporating this extended time window,” they add.
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Michael Hill, MD, University of Calgary (Alta.), said: “Thrombus migration does happen and is likely part of the natural history of ischemic stroke, which may be influenced by therapeutics such as thrombolysis. This paper’s top-line result is that thrombus migration occurs in both treated and untreated groups – and therefore that this is really an observation of natural history.”
Dr. Hill says that, at present, patients should be treated with thrombolysis before endovascular therapy if they are eligible, and these results do not change that recommendation.
“The results of the ongoing trials comparing direct thrombectomy with thrombolysis plus thrombectomy will help to understand the potential clinical outcome relevance of this phenomenon,” he added.
The EXTEND trial was supported by grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization Flagship Program. Dr. Yan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with acute ischemic stroke, the use of thrombolysis in the late window of 4.5-9 hours after symptom onset was not associated with an increase in clot migration that would cause reduced clot accessibility to endovascular therapy, a new analysis from the EXTEND trial shows.
“There was no significant difference in the incidence of clot migration leading to clot inaccessibility in patients who received placebo or (intravenous) thrombolysis,” the authors report.
“Our results found no convincing evidence against the use of bridging thrombolysis before endovascular therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke who present outside the 4.5-hour window,” they conclude.
“This information is important because it provides some comfort for neurointerventionists that IV thrombolysis does not unduly increase the risk of clot migration,” senior author, Bernard Yan, DMedSci, FRACP, told this news organization.
The study was published online in Stroke on Feb. 16.
The Australian researchers explain that endovascular thrombectomy is the standard of care in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke caused by large-vessel occlusion, and current treatment guidelines recommend bridging thrombolysis for all patients receiving thrombectomy within the 4.5-hour time window.
While thrombectomy is also recommended in selected patients up to 24 hours after onset of symptoms, it remains unclear whether thrombolysis pretreatment should be administered in this setting.
One of the issues that might affect use of thrombolysis is distal clot migration. As proximal clot location is a crucial factor determining suitability for endovascular clot retrieval, distal migration may prevent successful thrombectomy, they note.
“Clot migration can happen any time and makes life more difficult for the neurointerventionist who performs the endovascular clot retrieval,” added Dr. Yan, who is a neurologist and neurointerventionist at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, Australia.
In the current paper, the researchers report a retrospective analysis of data from the EXTEND trial of late thrombolysis, defined as 4.5-9 hours after symptom onset, to investigate the association between thrombolysis and clot migration leading to clot irretrievability.
The analysis included a total of 220 patients (109 patients in the placebo group and 111 in the thrombolysis group).
Results showed that retrievable clot was seen on baseline imaging in 69% of patients in the placebo group and 61% in the thrombolysis group. Clot resolution occurred in 28% of patients in the placebo group and 50% in the thrombolysis group.
No significant difference was observed in the incidence of clot migration leading to inaccessibility between groups. Clot migration from a retrievable to nonretrievable location occurred in 19% of the placebo group and 14% of the thrombolysis group, with an odds ratio for clot migration in the thrombolysis group of 0.70 (95% confidence interval, 0.35-1.44). This outcome was consistent across subgroups.
The researchers note that, to their knowledge, this is the first randomized controlled study to assess the effect of thrombolysis on clot migration and accessibility in an extended time window.
They acknowledge that a limitation of this study is that they only assessed clot migration from a retrievable to a nonretrievable location; therefore, the true frequency of any clot migration occurring was likely to be higher, and this could explain why other reports have found higher odds ratios of clot migration.
But they point out that they chose to limit their analysis in this way specifically to guide decision-making regarding bridging thrombolysis incorporating endovascular therapy in the extended time window.
“The findings of this study are highly relevant in the current clinical environment, where there are multiple ongoing trials looking at removing thrombolysis pretreatment within the 4.5-hour time window in thrombectomy patients,” the authors write.
“We have demonstrated that thrombolysis in the 4.5- to 9-hour window is not associated with reduced clot accessibility, and this information will be useful in future trial designs incorporating this extended time window,” they add.
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Michael Hill, MD, University of Calgary (Alta.), said: “Thrombus migration does happen and is likely part of the natural history of ischemic stroke, which may be influenced by therapeutics such as thrombolysis. This paper’s top-line result is that thrombus migration occurs in both treated and untreated groups – and therefore that this is really an observation of natural history.”
Dr. Hill says that, at present, patients should be treated with thrombolysis before endovascular therapy if they are eligible, and these results do not change that recommendation.
“The results of the ongoing trials comparing direct thrombectomy with thrombolysis plus thrombectomy will help to understand the potential clinical outcome relevance of this phenomenon,” he added.
The EXTEND trial was supported by grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization Flagship Program. Dr. Yan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier antibiotic initiation for sepsis did not lead to overuse
There has been a marked increase in the time to antibiotic administration for ICU patients with sepsis across Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals, but there is no evidence that they are being given inappropriately, according to new findings.
Accelerating time-to-antibiotics in sepsis means that patients will be treated earlier, but it could also result in more patients receiving antibiotics, including those without infection. This in turn may contribute to antimicrobial resistance.
“The time to antibiotics for sepsis accelerated across VA hospitals, and declined from 5.8 to 4.8 hours between 2013 and 2018,” said lead study author Sarah Seelye, PhD, data scientist at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Ann Arbor, Mich. “Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis.”
The results were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine, which was held virtually this year.
“Many hospitals have initiated programs like this to accelerate the use of antibiotics in patients with severe sepsis, but at the same time, there is growing concern that earlier antibiotic initiation may result in increased antibiotic treatment overall, including those without infection,” said Dr. Seelye. “However, to date, there is little evidence to support this claim.”
The goal of their study was to investigate whether hospital-level acceleration in antibiotic timing for sepsis was associated with increasing antibiotic use among patients hospitalized with potential infection.
They identified 1,101,239 hospitalizations for potential infection in 132 VA hospitals during the period from 2013 to 2018. Of these patients, 608,128 (55.2%) received antibiotics within 48 hours of presentation to the emergency department. A total of 117,435 (10.7%) met the criteria for sepsis.
Hospitals were classified into tertiles of antibiotic acceleration for sepsis: rapid, slow, and flat.
In the VA system, patients with severe sepsis began receiving faster antibiotic treatment in 2017, compared with earlier years. In 2017-2018 more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
In 2017-2018, more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
Hospitals categorized as rapid accelerators decreased their time to antibiotic initiation from 6.4 hours to 4.5 hours, while slow accelerators went from 5.6 to 4.6 hours from 2013 to 2018, and flat accelerators remained stable during the time period (5.3 hours down to 5.2 hours).
However, statistical analysis showed no real difference between the three groups in antibiotic prescribing.
“Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital-level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis,” said Dr. Seelye.
Weighing in on the study results, Craig M. Coopersmith, MD, professor of surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, noted that these results are very convincing, considering the size of the study and that it encompassed 132 different facilities.
“It’s difficult to say how generalizable these results are but they are definitely generalizable to all hospitals in the VA system,” he said. “In general, there are similarities between large health care systems, and it would be surprising if we found the opposite to be true in non-VA health systems.”
However, he emphasized that there is some possibility that the results would not be identical because different health care systems have different methods of providing care.
“This paper does show that you can get antibiotics into patients faster, which can be life saving, without inappropriately using them on everybody,” Dr. Coopersmith said.
He explained that there is more attention being paid now to antibiotic stewardship, compared with 10 or 15 years ago. “Given the choice of giving someone a single dose of antibiotics who may not need it, as opposed to withholding them from someone who is septic which is life threatening, the risk benefit ratio weighs heavily towards starting them early,” he said. “And then escalate rapidly.”
There has been a marked increase in the time to antibiotic administration for ICU patients with sepsis across Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals, but there is no evidence that they are being given inappropriately, according to new findings.
Accelerating time-to-antibiotics in sepsis means that patients will be treated earlier, but it could also result in more patients receiving antibiotics, including those without infection. This in turn may contribute to antimicrobial resistance.
“The time to antibiotics for sepsis accelerated across VA hospitals, and declined from 5.8 to 4.8 hours between 2013 and 2018,” said lead study author Sarah Seelye, PhD, data scientist at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Ann Arbor, Mich. “Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis.”
The results were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine, which was held virtually this year.
“Many hospitals have initiated programs like this to accelerate the use of antibiotics in patients with severe sepsis, but at the same time, there is growing concern that earlier antibiotic initiation may result in increased antibiotic treatment overall, including those without infection,” said Dr. Seelye. “However, to date, there is little evidence to support this claim.”
The goal of their study was to investigate whether hospital-level acceleration in antibiotic timing for sepsis was associated with increasing antibiotic use among patients hospitalized with potential infection.
They identified 1,101,239 hospitalizations for potential infection in 132 VA hospitals during the period from 2013 to 2018. Of these patients, 608,128 (55.2%) received antibiotics within 48 hours of presentation to the emergency department. A total of 117,435 (10.7%) met the criteria for sepsis.
Hospitals were classified into tertiles of antibiotic acceleration for sepsis: rapid, slow, and flat.
In the VA system, patients with severe sepsis began receiving faster antibiotic treatment in 2017, compared with earlier years. In 2017-2018 more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
In 2017-2018, more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
Hospitals categorized as rapid accelerators decreased their time to antibiotic initiation from 6.4 hours to 4.5 hours, while slow accelerators went from 5.6 to 4.6 hours from 2013 to 2018, and flat accelerators remained stable during the time period (5.3 hours down to 5.2 hours).
However, statistical analysis showed no real difference between the three groups in antibiotic prescribing.
“Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital-level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis,” said Dr. Seelye.
Weighing in on the study results, Craig M. Coopersmith, MD, professor of surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, noted that these results are very convincing, considering the size of the study and that it encompassed 132 different facilities.
“It’s difficult to say how generalizable these results are but they are definitely generalizable to all hospitals in the VA system,” he said. “In general, there are similarities between large health care systems, and it would be surprising if we found the opposite to be true in non-VA health systems.”
However, he emphasized that there is some possibility that the results would not be identical because different health care systems have different methods of providing care.
“This paper does show that you can get antibiotics into patients faster, which can be life saving, without inappropriately using them on everybody,” Dr. Coopersmith said.
He explained that there is more attention being paid now to antibiotic stewardship, compared with 10 or 15 years ago. “Given the choice of giving someone a single dose of antibiotics who may not need it, as opposed to withholding them from someone who is septic which is life threatening, the risk benefit ratio weighs heavily towards starting them early,” he said. “And then escalate rapidly.”
There has been a marked increase in the time to antibiotic administration for ICU patients with sepsis across Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals, but there is no evidence that they are being given inappropriately, according to new findings.
Accelerating time-to-antibiotics in sepsis means that patients will be treated earlier, but it could also result in more patients receiving antibiotics, including those without infection. This in turn may contribute to antimicrobial resistance.
“The time to antibiotics for sepsis accelerated across VA hospitals, and declined from 5.8 to 4.8 hours between 2013 and 2018,” said lead study author Sarah Seelye, PhD, data scientist at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Ann Arbor, Mich. “Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis.”
The results were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine, which was held virtually this year.
“Many hospitals have initiated programs like this to accelerate the use of antibiotics in patients with severe sepsis, but at the same time, there is growing concern that earlier antibiotic initiation may result in increased antibiotic treatment overall, including those without infection,” said Dr. Seelye. “However, to date, there is little evidence to support this claim.”
The goal of their study was to investigate whether hospital-level acceleration in antibiotic timing for sepsis was associated with increasing antibiotic use among patients hospitalized with potential infection.
They identified 1,101,239 hospitalizations for potential infection in 132 VA hospitals during the period from 2013 to 2018. Of these patients, 608,128 (55.2%) received antibiotics within 48 hours of presentation to the emergency department. A total of 117,435 (10.7%) met the criteria for sepsis.
Hospitals were classified into tertiles of antibiotic acceleration for sepsis: rapid, slow, and flat.
In the VA system, patients with severe sepsis began receiving faster antibiotic treatment in 2017, compared with earlier years. In 2017-2018 more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
In 2017-2018, more than 20% of sepsis patients had received their first treatment within 2 hours, compared with 14% in 2013-1014.
Hospitals categorized as rapid accelerators decreased their time to antibiotic initiation from 6.4 hours to 4.5 hours, while slow accelerators went from 5.6 to 4.6 hours from 2013 to 2018, and flat accelerators remained stable during the time period (5.3 hours down to 5.2 hours).
However, statistical analysis showed no real difference between the three groups in antibiotic prescribing.
“Despite this, there was no evidence between hospital-level antibiotic acceleration in sepsis and antibiotic use among all patients with potential sepsis,” said Dr. Seelye.
Weighing in on the study results, Craig M. Coopersmith, MD, professor of surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, noted that these results are very convincing, considering the size of the study and that it encompassed 132 different facilities.
“It’s difficult to say how generalizable these results are but they are definitely generalizable to all hospitals in the VA system,” he said. “In general, there are similarities between large health care systems, and it would be surprising if we found the opposite to be true in non-VA health systems.”
However, he emphasized that there is some possibility that the results would not be identical because different health care systems have different methods of providing care.
“This paper does show that you can get antibiotics into patients faster, which can be life saving, without inappropriately using them on everybody,” Dr. Coopersmith said.
He explained that there is more attention being paid now to antibiotic stewardship, compared with 10 or 15 years ago. “Given the choice of giving someone a single dose of antibiotics who may not need it, as opposed to withholding them from someone who is septic which is life threatening, the risk benefit ratio weighs heavily towards starting them early,” he said. “And then escalate rapidly.”
FROM CCC50
Study clarifies who gets post–COVID-19 interstitial lung disease
A study of post–COVID-19 patients in the United Kingdom who developed severe lung inflammation after they left the hospital may provide greater clarity on which patients are most likely to have persistent lung dysfunction.
In addition to pinpointing those most at risk, the findings showed that conventional corticosteroid treatment is highly effective in improving lung function and reducing symptoms.
Researchers from Guy’s and St. Thomas’ National Health Foundation Trust in London reported that a small percentage of patients – 4.8%, or 35 of 837 patients in the study – had severe persistent interstitial lung disease (ILD), mostly organizing pneumonia, 4 weeks after discharge. Of these patients, 30 received steroid treatment, all of whom showed improvement in lung function.
Lead author Katherine Jane Myall, MRCP, and colleagues wrote that the most common radiologic finding in acute COVID-19 is bilateral ground-glass opacification, and findings of organizing pneumonia are common. However, no reports exist of the role of inflammatory infiltrates during recovery from COVID-19 or of the effectiveness of treatments for persistent ILD. “The long-term respiratory morbidity remains unclear,” Dr. Myall and colleagues wrote.
The study findings are significant because they quantify the degree of lung disease that patients have after COVID-19, said Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, a pulmonologist and critical care specialist at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif. He added that the disease course and presentation followed the pattern of organizing pneumonia in some patients, and traditional corticosteroid therapy seemed to resolve symptoms and improve lung function.
“This is a really important piece to get out there because it describes what a lot of us are worried about in patients with post-COVID lung disease and about what type of lung disease they have. It offers a potential treatment,” he said.
Dr. Myall and colleagues noted that even a “relatively small proportion” of patients with persistent, severe ILD – as reported in this study – pose “a significant disease burden.” They added: “Prompt therapy may avoid potentially permanent fibrosis and functional impairment.”
The single-center, prospective, observational study followed discharged patients with telephone calls 4 weeks after discharge to determine their status. At that point, 39% of the study cohort (n = 325) reported ongoing symptoms.
The patients had outpatient examinations at 6 weeks post discharge, at which time 42.9% (n = 138) had no signs or symptoms of persistent disease; 33.8% (n = 110) had symptoms but no radiologic findings and received referrals to other departments; and 24% (n = 77) were referred to the post-COVID lung disease multidisciplinary team. A total of 59 were diagnosed with persistent post-COVID interstitial change, 35 of whom had organizing pneumonia, hence the rationale for using steroids in this group, Dr. Myall and colleagues stated.
The 30 patients treated with corticosteroids received a maximum initial dose of 0.5 mg/kg prednisolone, which was rapidly weaned over 3 weeks. Some patients received lower doses depending on their comorbidities.
Treatment resulted in an average relative increase in transfer factor of 31.6% (P < .001) and forced vital capacity of 9.6% (P = .014), along with significant improvement in symptoms and x-ray signs.
The study identified some key characteristics of the patients who had persistent post–COVID-19 inflammatory ILD. They were mostly male (71.5%) and overweight with an average body mass index of 28.3, but only 26% were obese. Most had at least one comorbidity, with the most common being diabetes and asthma (22.9%). Their average hospital stay was 16.9 days, 82.9% required oxygen, 55% were in the ICU, and 46% needed invasive mechanical ventilation.
The patients most vulnerable to ILD and organizing pneumonia were the “sicker” of the whole cohort, Dr. Gupta said. “In one sense, it’s reassuring that this is not just happening in anyone; this is happening in patients who had the worst course and were hospitalized in the ICU for the most part.”
The study shows that identifying these patients early on and initiating steroid therapy could avoid persistent lung injury and scarring, Dr. Gupta said.
The London researchers noted that theirs wasn’t a radiologic study, so CT scans weren’t formally scored before and after treatment. They also acknowledged vagueness about imaging and clinical findings representing “nothing other than slow ongoing recovery.”
Patients with post–COVID-19 ILD will require ongoing follow-up to better understand the disease course, Dr. Myall and colleagues stated, although they predicted organizing pneumonia is unlikely to recur once it resolves.
Dr. Myall and coauthors had no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Gupta disclosed he is also an employee and shareholder at Genentech.
A study of post–COVID-19 patients in the United Kingdom who developed severe lung inflammation after they left the hospital may provide greater clarity on which patients are most likely to have persistent lung dysfunction.
In addition to pinpointing those most at risk, the findings showed that conventional corticosteroid treatment is highly effective in improving lung function and reducing symptoms.
Researchers from Guy’s and St. Thomas’ National Health Foundation Trust in London reported that a small percentage of patients – 4.8%, or 35 of 837 patients in the study – had severe persistent interstitial lung disease (ILD), mostly organizing pneumonia, 4 weeks after discharge. Of these patients, 30 received steroid treatment, all of whom showed improvement in lung function.
Lead author Katherine Jane Myall, MRCP, and colleagues wrote that the most common radiologic finding in acute COVID-19 is bilateral ground-glass opacification, and findings of organizing pneumonia are common. However, no reports exist of the role of inflammatory infiltrates during recovery from COVID-19 or of the effectiveness of treatments for persistent ILD. “The long-term respiratory morbidity remains unclear,” Dr. Myall and colleagues wrote.
The study findings are significant because they quantify the degree of lung disease that patients have after COVID-19, said Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, a pulmonologist and critical care specialist at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif. He added that the disease course and presentation followed the pattern of organizing pneumonia in some patients, and traditional corticosteroid therapy seemed to resolve symptoms and improve lung function.
“This is a really important piece to get out there because it describes what a lot of us are worried about in patients with post-COVID lung disease and about what type of lung disease they have. It offers a potential treatment,” he said.
Dr. Myall and colleagues noted that even a “relatively small proportion” of patients with persistent, severe ILD – as reported in this study – pose “a significant disease burden.” They added: “Prompt therapy may avoid potentially permanent fibrosis and functional impairment.”
The single-center, prospective, observational study followed discharged patients with telephone calls 4 weeks after discharge to determine their status. At that point, 39% of the study cohort (n = 325) reported ongoing symptoms.
The patients had outpatient examinations at 6 weeks post discharge, at which time 42.9% (n = 138) had no signs or symptoms of persistent disease; 33.8% (n = 110) had symptoms but no radiologic findings and received referrals to other departments; and 24% (n = 77) were referred to the post-COVID lung disease multidisciplinary team. A total of 59 were diagnosed with persistent post-COVID interstitial change, 35 of whom had organizing pneumonia, hence the rationale for using steroids in this group, Dr. Myall and colleagues stated.
The 30 patients treated with corticosteroids received a maximum initial dose of 0.5 mg/kg prednisolone, which was rapidly weaned over 3 weeks. Some patients received lower doses depending on their comorbidities.
Treatment resulted in an average relative increase in transfer factor of 31.6% (P < .001) and forced vital capacity of 9.6% (P = .014), along with significant improvement in symptoms and x-ray signs.
The study identified some key characteristics of the patients who had persistent post–COVID-19 inflammatory ILD. They were mostly male (71.5%) and overweight with an average body mass index of 28.3, but only 26% were obese. Most had at least one comorbidity, with the most common being diabetes and asthma (22.9%). Their average hospital stay was 16.9 days, 82.9% required oxygen, 55% were in the ICU, and 46% needed invasive mechanical ventilation.
The patients most vulnerable to ILD and organizing pneumonia were the “sicker” of the whole cohort, Dr. Gupta said. “In one sense, it’s reassuring that this is not just happening in anyone; this is happening in patients who had the worst course and were hospitalized in the ICU for the most part.”
The study shows that identifying these patients early on and initiating steroid therapy could avoid persistent lung injury and scarring, Dr. Gupta said.
The London researchers noted that theirs wasn’t a radiologic study, so CT scans weren’t formally scored before and after treatment. They also acknowledged vagueness about imaging and clinical findings representing “nothing other than slow ongoing recovery.”
Patients with post–COVID-19 ILD will require ongoing follow-up to better understand the disease course, Dr. Myall and colleagues stated, although they predicted organizing pneumonia is unlikely to recur once it resolves.
Dr. Myall and coauthors had no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Gupta disclosed he is also an employee and shareholder at Genentech.
A study of post–COVID-19 patients in the United Kingdom who developed severe lung inflammation after they left the hospital may provide greater clarity on which patients are most likely to have persistent lung dysfunction.
In addition to pinpointing those most at risk, the findings showed that conventional corticosteroid treatment is highly effective in improving lung function and reducing symptoms.
Researchers from Guy’s and St. Thomas’ National Health Foundation Trust in London reported that a small percentage of patients – 4.8%, or 35 of 837 patients in the study – had severe persistent interstitial lung disease (ILD), mostly organizing pneumonia, 4 weeks after discharge. Of these patients, 30 received steroid treatment, all of whom showed improvement in lung function.
Lead author Katherine Jane Myall, MRCP, and colleagues wrote that the most common radiologic finding in acute COVID-19 is bilateral ground-glass opacification, and findings of organizing pneumonia are common. However, no reports exist of the role of inflammatory infiltrates during recovery from COVID-19 or of the effectiveness of treatments for persistent ILD. “The long-term respiratory morbidity remains unclear,” Dr. Myall and colleagues wrote.
The study findings are significant because they quantify the degree of lung disease that patients have after COVID-19, said Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, a pulmonologist and critical care specialist at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif. He added that the disease course and presentation followed the pattern of organizing pneumonia in some patients, and traditional corticosteroid therapy seemed to resolve symptoms and improve lung function.
“This is a really important piece to get out there because it describes what a lot of us are worried about in patients with post-COVID lung disease and about what type of lung disease they have. It offers a potential treatment,” he said.
Dr. Myall and colleagues noted that even a “relatively small proportion” of patients with persistent, severe ILD – as reported in this study – pose “a significant disease burden.” They added: “Prompt therapy may avoid potentially permanent fibrosis and functional impairment.”
The single-center, prospective, observational study followed discharged patients with telephone calls 4 weeks after discharge to determine their status. At that point, 39% of the study cohort (n = 325) reported ongoing symptoms.
The patients had outpatient examinations at 6 weeks post discharge, at which time 42.9% (n = 138) had no signs or symptoms of persistent disease; 33.8% (n = 110) had symptoms but no radiologic findings and received referrals to other departments; and 24% (n = 77) were referred to the post-COVID lung disease multidisciplinary team. A total of 59 were diagnosed with persistent post-COVID interstitial change, 35 of whom had organizing pneumonia, hence the rationale for using steroids in this group, Dr. Myall and colleagues stated.
The 30 patients treated with corticosteroids received a maximum initial dose of 0.5 mg/kg prednisolone, which was rapidly weaned over 3 weeks. Some patients received lower doses depending on their comorbidities.
Treatment resulted in an average relative increase in transfer factor of 31.6% (P < .001) and forced vital capacity of 9.6% (P = .014), along with significant improvement in symptoms and x-ray signs.
The study identified some key characteristics of the patients who had persistent post–COVID-19 inflammatory ILD. They were mostly male (71.5%) and overweight with an average body mass index of 28.3, but only 26% were obese. Most had at least one comorbidity, with the most common being diabetes and asthma (22.9%). Their average hospital stay was 16.9 days, 82.9% required oxygen, 55% were in the ICU, and 46% needed invasive mechanical ventilation.
The patients most vulnerable to ILD and organizing pneumonia were the “sicker” of the whole cohort, Dr. Gupta said. “In one sense, it’s reassuring that this is not just happening in anyone; this is happening in patients who had the worst course and were hospitalized in the ICU for the most part.”
The study shows that identifying these patients early on and initiating steroid therapy could avoid persistent lung injury and scarring, Dr. Gupta said.
The London researchers noted that theirs wasn’t a radiologic study, so CT scans weren’t formally scored before and after treatment. They also acknowledged vagueness about imaging and clinical findings representing “nothing other than slow ongoing recovery.”
Patients with post–COVID-19 ILD will require ongoing follow-up to better understand the disease course, Dr. Myall and colleagues stated, although they predicted organizing pneumonia is unlikely to recur once it resolves.
Dr. Myall and coauthors had no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Gupta disclosed he is also an employee and shareholder at Genentech.
FROM ANNALS OF THE AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY
A ‘hospitalist plus’: Grace C. Huang, MD
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Grace C. Huang, MD, is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Dr. Huang currently serves as vice chair for career development and mentoring in the department of medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess as well as director of the Office of Academic Careers and Faculty Development, and codirector of the Beth Israel Deaconess Academy of Medical Educators. She is also director of the Rabkin Fellowship in Medical Education, a program for Harvard Medical School faculty designed to help develop the skills needed to launch or advance academic careers in medical education or academic leadership.
Additionally, Dr. Huang is the editor in chief of MedEdPORTAL, a MEDLINE-indexed, open-access journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
At what point in your training did you decide to practice hospital medicine, and what about it appealed to you?
I trained at a point in time where it was rare for people to aspire to go in to hospital medicine. It just wasn’t that common, and there were so few examples of what a career trajectory in hospital medicine would look like. So I don’t know that I actively chose to go into hospital medicine; I chose it because it was what I knew how to do, based on my residency experience.
But it is really easy and authentic for me now to share about what makes hospital medicine such a vibrant career choice. I’m doing a lot of things in my job other than hospital medicine, but when I am on service, it reminds me acutely what it means to stay connected to why I became a doctor. The practice of hospital medicine means to be there at the most intense time of many people’s lives, to shoulder the responsibility of knowing that what I say to my patients will be remembered forever, and to be challenged by some of medicine’s hardest problems.
Hospital medicine has a way of putting you at the nexus of individual, family, society, government, and planet. But it also means that, even while I am witness to disease, suffering, broken relationships, social injustice, and environmental issues, I get a privileged look at what it means to comfort, to identify what really matters to people, to understand what gives us dignity as human beings. Lastly, I always come back to the fact that working as a team has made my clinical job so much more enriching; it’s not trench warfare, but you do create bonds quickly with learners, colleagues, and other health professionals in such an intense, fast-paced environment.
What is your current role at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center?
At Beth Israel Deaconess, I’m holding four different jobs. It’s sometimes hard for me to keep track of them, but they all center on career and faculty development. I’m a vice chair for career development within the department of medicine, and I also have an institutional role for faculty development for clinicians, educators, and researchers. I provide academic promotion support for the faculty, provide ad hoc mentorship, and run professional development programming. I also direct a year-long medical education fellowship. On the side, I am the editor in chief for a medical education journal.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice and research?
Being a generalist means I love a lot of areas of clinical practice. I’m not sure there’s a particular area that I enjoy more than others. I love teaching specific topics – antibiotics, pharmacology, direct oral anticoagulants, the microbiology of common infections. I love thinking about how the heart and kidney battle for dominance each day and being the mediator. I have a particular interest in high-value care and lab ordering (or the fact that we should do much less of it). I love complex diagnostic problems and mapping them out on paper for my team.
The research that I’ve been doing over the past 20 years has focused on how we train internists and internists-to-be to do bedside procedures. It stemmed from my own ineptitude in doing procedures, and it caused me to question the age-old approach we took in sticking needles into patients without standardized training, supervision, or safety measures.
I’ve been proud of the small role I’ve been able to play in influencing how residents are taught to do procedures, and now I’m working with others to focus on how we should teach procedures to hospitalists, who don’t do procedures on a regular basis, and aren’t under the same expectations for ongoing skill development.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine, and what are the most rewarding?
The intensity is probably what’s hardest for me about hospital medicine. At this point in my career, if I’m on service for a week, it takes me just as long to recover. It’s the cognitive load of needing to keep track of details that can make a big difference, the rapidity at which patients can deteriorate, the need to change course in an instant because of new information, and wanting to be mentally present and available for my patients and my learners.
It’s also hard to see suffering up close and personal and to leave feeling helpless to change the course of severe illness or to optimize care within the constraints of the health care system. This is why I do – and have to – extract satisfaction from the smallest of wins and brief moments of connection. Like seeing a patient turn the corner after being on the brink. Or gaining trust from an initially upset family member. Getting a copy of the eulogy from the daughter of my patient. A phone call from a patient I cared for 18 months ago, thanking me for my care. Visiting patients in the hospital socially that I had gotten to know over the years.
How has COVID-19 impacted hospitalist practice, and what changes will outlast the pandemic?
What you read in the lay press has put a spotlight on hospital-based work. What has been shared resonates with my own experience – the loss of connection from visitor restrictions, the isolation patients experience when everyone is wearing personal protective equipment, the worsening of everything that was already hard to begin with, like health care disparities, mental health, access to community supports, financial challenges, the disproportionate burden on unpaid caregivers, etc.
After the pandemic is “over,” I hope that we will retain a sense of intentionality how we address limited resources, the importance of social connection, the structural racism that has disadvantaged patients and physicians of color.
How will hospital medicine as a field change in the next decade or 2?
The hospitalist model has already influenced other specialties, like ob.gyn., neurology, and cardiology, and I expect that to continue. Hospitalists have already become leaders at the highest levels, and we will see them in higher numbers throughout health care leadership.
Are there any particular mentors who have been influential in your journey as a hospitalist?
Because I’m one of the older hospitalists in my group, there were fewer mentors, other than my boss, Joe Li, MD, SFHM, [section chief in hospital medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess], who has been an amazing role model. I think also of my colleagues as peer mentors, who continue to push me to be a better doctor. Whether it means remaining curious during the physical exam, or inspiring me with their excitement about clinical cases.
Do you have any advice for students and residents interested in hospital medicine?
When I talk to trainees about career development as a hospitalist, I encourage them to think about what will make them a “Hospitalist Plus.” Whether that Plus is teaching, research, or leadership, being a hospitalist gives you an opportunity to extend your impact as a physician into related realm.
I look around at our hospital medicine group, and every person has their Plus. We have educators, quality improvement leaders, a health services researcher, a health policy expert, a textbook editor – everyone brings special expertise to the group. My Plus now is much bigger than my footprint as a hospitalist, but I would never have gotten here had I not chosen a career path that would allow me to explore the farthest reaches of my potential as a physician.
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Grace C. Huang, MD, is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Dr. Huang currently serves as vice chair for career development and mentoring in the department of medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess as well as director of the Office of Academic Careers and Faculty Development, and codirector of the Beth Israel Deaconess Academy of Medical Educators. She is also director of the Rabkin Fellowship in Medical Education, a program for Harvard Medical School faculty designed to help develop the skills needed to launch or advance academic careers in medical education or academic leadership.
Additionally, Dr. Huang is the editor in chief of MedEdPORTAL, a MEDLINE-indexed, open-access journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
At what point in your training did you decide to practice hospital medicine, and what about it appealed to you?
I trained at a point in time where it was rare for people to aspire to go in to hospital medicine. It just wasn’t that common, and there were so few examples of what a career trajectory in hospital medicine would look like. So I don’t know that I actively chose to go into hospital medicine; I chose it because it was what I knew how to do, based on my residency experience.
But it is really easy and authentic for me now to share about what makes hospital medicine such a vibrant career choice. I’m doing a lot of things in my job other than hospital medicine, but when I am on service, it reminds me acutely what it means to stay connected to why I became a doctor. The practice of hospital medicine means to be there at the most intense time of many people’s lives, to shoulder the responsibility of knowing that what I say to my patients will be remembered forever, and to be challenged by some of medicine’s hardest problems.
Hospital medicine has a way of putting you at the nexus of individual, family, society, government, and planet. But it also means that, even while I am witness to disease, suffering, broken relationships, social injustice, and environmental issues, I get a privileged look at what it means to comfort, to identify what really matters to people, to understand what gives us dignity as human beings. Lastly, I always come back to the fact that working as a team has made my clinical job so much more enriching; it’s not trench warfare, but you do create bonds quickly with learners, colleagues, and other health professionals in such an intense, fast-paced environment.
What is your current role at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center?
At Beth Israel Deaconess, I’m holding four different jobs. It’s sometimes hard for me to keep track of them, but they all center on career and faculty development. I’m a vice chair for career development within the department of medicine, and I also have an institutional role for faculty development for clinicians, educators, and researchers. I provide academic promotion support for the faculty, provide ad hoc mentorship, and run professional development programming. I also direct a year-long medical education fellowship. On the side, I am the editor in chief for a medical education journal.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice and research?
Being a generalist means I love a lot of areas of clinical practice. I’m not sure there’s a particular area that I enjoy more than others. I love teaching specific topics – antibiotics, pharmacology, direct oral anticoagulants, the microbiology of common infections. I love thinking about how the heart and kidney battle for dominance each day and being the mediator. I have a particular interest in high-value care and lab ordering (or the fact that we should do much less of it). I love complex diagnostic problems and mapping them out on paper for my team.
The research that I’ve been doing over the past 20 years has focused on how we train internists and internists-to-be to do bedside procedures. It stemmed from my own ineptitude in doing procedures, and it caused me to question the age-old approach we took in sticking needles into patients without standardized training, supervision, or safety measures.
I’ve been proud of the small role I’ve been able to play in influencing how residents are taught to do procedures, and now I’m working with others to focus on how we should teach procedures to hospitalists, who don’t do procedures on a regular basis, and aren’t under the same expectations for ongoing skill development.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine, and what are the most rewarding?
The intensity is probably what’s hardest for me about hospital medicine. At this point in my career, if I’m on service for a week, it takes me just as long to recover. It’s the cognitive load of needing to keep track of details that can make a big difference, the rapidity at which patients can deteriorate, the need to change course in an instant because of new information, and wanting to be mentally present and available for my patients and my learners.
It’s also hard to see suffering up close and personal and to leave feeling helpless to change the course of severe illness or to optimize care within the constraints of the health care system. This is why I do – and have to – extract satisfaction from the smallest of wins and brief moments of connection. Like seeing a patient turn the corner after being on the brink. Or gaining trust from an initially upset family member. Getting a copy of the eulogy from the daughter of my patient. A phone call from a patient I cared for 18 months ago, thanking me for my care. Visiting patients in the hospital socially that I had gotten to know over the years.
How has COVID-19 impacted hospitalist practice, and what changes will outlast the pandemic?
What you read in the lay press has put a spotlight on hospital-based work. What has been shared resonates with my own experience – the loss of connection from visitor restrictions, the isolation patients experience when everyone is wearing personal protective equipment, the worsening of everything that was already hard to begin with, like health care disparities, mental health, access to community supports, financial challenges, the disproportionate burden on unpaid caregivers, etc.
After the pandemic is “over,” I hope that we will retain a sense of intentionality how we address limited resources, the importance of social connection, the structural racism that has disadvantaged patients and physicians of color.
How will hospital medicine as a field change in the next decade or 2?
The hospitalist model has already influenced other specialties, like ob.gyn., neurology, and cardiology, and I expect that to continue. Hospitalists have already become leaders at the highest levels, and we will see them in higher numbers throughout health care leadership.
Are there any particular mentors who have been influential in your journey as a hospitalist?
Because I’m one of the older hospitalists in my group, there were fewer mentors, other than my boss, Joe Li, MD, SFHM, [section chief in hospital medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess], who has been an amazing role model. I think also of my colleagues as peer mentors, who continue to push me to be a better doctor. Whether it means remaining curious during the physical exam, or inspiring me with their excitement about clinical cases.
Do you have any advice for students and residents interested in hospital medicine?
When I talk to trainees about career development as a hospitalist, I encourage them to think about what will make them a “Hospitalist Plus.” Whether that Plus is teaching, research, or leadership, being a hospitalist gives you an opportunity to extend your impact as a physician into related realm.
I look around at our hospital medicine group, and every person has their Plus. We have educators, quality improvement leaders, a health services researcher, a health policy expert, a textbook editor – everyone brings special expertise to the group. My Plus now is much bigger than my footprint as a hospitalist, but I would never have gotten here had I not chosen a career path that would allow me to explore the farthest reaches of my potential as a physician.
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Grace C. Huang, MD, is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Dr. Huang currently serves as vice chair for career development and mentoring in the department of medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess as well as director of the Office of Academic Careers and Faculty Development, and codirector of the Beth Israel Deaconess Academy of Medical Educators. She is also director of the Rabkin Fellowship in Medical Education, a program for Harvard Medical School faculty designed to help develop the skills needed to launch or advance academic careers in medical education or academic leadership.
Additionally, Dr. Huang is the editor in chief of MedEdPORTAL, a MEDLINE-indexed, open-access journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
At what point in your training did you decide to practice hospital medicine, and what about it appealed to you?
I trained at a point in time where it was rare for people to aspire to go in to hospital medicine. It just wasn’t that common, and there were so few examples of what a career trajectory in hospital medicine would look like. So I don’t know that I actively chose to go into hospital medicine; I chose it because it was what I knew how to do, based on my residency experience.
But it is really easy and authentic for me now to share about what makes hospital medicine such a vibrant career choice. I’m doing a lot of things in my job other than hospital medicine, but when I am on service, it reminds me acutely what it means to stay connected to why I became a doctor. The practice of hospital medicine means to be there at the most intense time of many people’s lives, to shoulder the responsibility of knowing that what I say to my patients will be remembered forever, and to be challenged by some of medicine’s hardest problems.
Hospital medicine has a way of putting you at the nexus of individual, family, society, government, and planet. But it also means that, even while I am witness to disease, suffering, broken relationships, social injustice, and environmental issues, I get a privileged look at what it means to comfort, to identify what really matters to people, to understand what gives us dignity as human beings. Lastly, I always come back to the fact that working as a team has made my clinical job so much more enriching; it’s not trench warfare, but you do create bonds quickly with learners, colleagues, and other health professionals in such an intense, fast-paced environment.
What is your current role at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center?
At Beth Israel Deaconess, I’m holding four different jobs. It’s sometimes hard for me to keep track of them, but they all center on career and faculty development. I’m a vice chair for career development within the department of medicine, and I also have an institutional role for faculty development for clinicians, educators, and researchers. I provide academic promotion support for the faculty, provide ad hoc mentorship, and run professional development programming. I also direct a year-long medical education fellowship. On the side, I am the editor in chief for a medical education journal.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice and research?
Being a generalist means I love a lot of areas of clinical practice. I’m not sure there’s a particular area that I enjoy more than others. I love teaching specific topics – antibiotics, pharmacology, direct oral anticoagulants, the microbiology of common infections. I love thinking about how the heart and kidney battle for dominance each day and being the mediator. I have a particular interest in high-value care and lab ordering (or the fact that we should do much less of it). I love complex diagnostic problems and mapping them out on paper for my team.
The research that I’ve been doing over the past 20 years has focused on how we train internists and internists-to-be to do bedside procedures. It stemmed from my own ineptitude in doing procedures, and it caused me to question the age-old approach we took in sticking needles into patients without standardized training, supervision, or safety measures.
I’ve been proud of the small role I’ve been able to play in influencing how residents are taught to do procedures, and now I’m working with others to focus on how we should teach procedures to hospitalists, who don’t do procedures on a regular basis, and aren’t under the same expectations for ongoing skill development.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine, and what are the most rewarding?
The intensity is probably what’s hardest for me about hospital medicine. At this point in my career, if I’m on service for a week, it takes me just as long to recover. It’s the cognitive load of needing to keep track of details that can make a big difference, the rapidity at which patients can deteriorate, the need to change course in an instant because of new information, and wanting to be mentally present and available for my patients and my learners.
It’s also hard to see suffering up close and personal and to leave feeling helpless to change the course of severe illness or to optimize care within the constraints of the health care system. This is why I do – and have to – extract satisfaction from the smallest of wins and brief moments of connection. Like seeing a patient turn the corner after being on the brink. Or gaining trust from an initially upset family member. Getting a copy of the eulogy from the daughter of my patient. A phone call from a patient I cared for 18 months ago, thanking me for my care. Visiting patients in the hospital socially that I had gotten to know over the years.
How has COVID-19 impacted hospitalist practice, and what changes will outlast the pandemic?
What you read in the lay press has put a spotlight on hospital-based work. What has been shared resonates with my own experience – the loss of connection from visitor restrictions, the isolation patients experience when everyone is wearing personal protective equipment, the worsening of everything that was already hard to begin with, like health care disparities, mental health, access to community supports, financial challenges, the disproportionate burden on unpaid caregivers, etc.
After the pandemic is “over,” I hope that we will retain a sense of intentionality how we address limited resources, the importance of social connection, the structural racism that has disadvantaged patients and physicians of color.
How will hospital medicine as a field change in the next decade or 2?
The hospitalist model has already influenced other specialties, like ob.gyn., neurology, and cardiology, and I expect that to continue. Hospitalists have already become leaders at the highest levels, and we will see them in higher numbers throughout health care leadership.
Are there any particular mentors who have been influential in your journey as a hospitalist?
Because I’m one of the older hospitalists in my group, there were fewer mentors, other than my boss, Joe Li, MD, SFHM, [section chief in hospital medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess], who has been an amazing role model. I think also of my colleagues as peer mentors, who continue to push me to be a better doctor. Whether it means remaining curious during the physical exam, or inspiring me with their excitement about clinical cases.
Do you have any advice for students and residents interested in hospital medicine?
When I talk to trainees about career development as a hospitalist, I encourage them to think about what will make them a “Hospitalist Plus.” Whether that Plus is teaching, research, or leadership, being a hospitalist gives you an opportunity to extend your impact as a physician into related realm.
I look around at our hospital medicine group, and every person has their Plus. We have educators, quality improvement leaders, a health services researcher, a health policy expert, a textbook editor – everyone brings special expertise to the group. My Plus now is much bigger than my footprint as a hospitalist, but I would never have gotten here had I not chosen a career path that would allow me to explore the farthest reaches of my potential as a physician.
Neurologic disorders ubiquitous and rising in the U.S.
, according to new findings derived from the 2017 Global Burden of Disease study.
The authors of the analysis, led by Valery Feigin, MD, PhD, of New Zealand’s National Institute for Stroke and Applied Neurosciences, and published in the February 2021 issue of JAMA Neurology, looked at prevalence, incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years for 14 neurological disorders across 50 states between 1990 and 2017. The diseases included in the analysis were stroke, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, headaches, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injuries, brain and other nervous system cancers, meningitis, encephalitis, and tetanus.
Tracking the burden of neurologic diseases
Dr. Feigin and colleagues estimated that a full 60% of the U.S. population lives with one or more of these disorders, a figure much greater than previous estimates for neurological disease burden nationwide. Tension-type headache and migraine were the most prevalent in the analysis by Dr. Feigin and colleagues. During the study period, they found, prevalence, incidence, and disability burden of nearly all the included disorders increased, with the exception of brain and spinal cord injuries, meningitis, and encephalitis.
The researchers attributed most of the rise in noncommunicable neurological diseases to population aging. An age-standardized analysis found trends for stroke and Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias to be declining or flat. Age-standardized stroke incidence dropped by 16% from 1990 to 2017, while stroke mortality declined by nearly a third, and stroke disability by a quarter. Age-standardized incidence of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias dropped by 12%, and their prevalence by 13%, during the study period, though dementia mortality and disability were seen increasing.
The authors surmised that the age-standardized declines in stroke and dementias could reflect that “primary prevention of these disorders are beginning to show an influence.” With dementia, which is linked to cognitive reserve and education, “improving educational levels of cohort reaching the age groups at greatest risk of disease may also be contributing to a modest decline over time,” Dr. Feigin and his colleagues wrote.
Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis, meanwhile, were both seen rising in incidence, prevalence, and disability adjusted life years (DALYs) even with age-standardized figures. The United States saw comparatively more disability in 2017 from dementias, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, and headache disorders, which together comprised 6.7% of DALYs, compared with 4.4% globally; these also accounted for a higher share of mortality in the U.S. than worldwide. The authors attributed at least some of the difference to better case ascertainment in the U.S.
Regional variations
The researchers also reported variations in disease burden by state and region. While previous studies have identified a “stroke belt” concentrated in North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, the new findings point to stroke disability highest in Alabama, Arkansas, and Mississippi, and mortality highest in Alabama, Mississippi, and South Carolina. The researchers noted increases in dementia mortality in these states, “likely attributable to the reciprocal association between stroke and dementia.”
Northern states saw higher burdens of multiple sclerosis compared with the rest of the country, while eastern states had higher rates of Parkinson’s disease.
Such regional and state-by state variations, Dr. Feigin and colleagues wrote in their analysis, “may be associated with differences in the case ascertainment, as well as access to health care; racial/ethnic, genetic, and socioeconomic diversity; quality and comprehensiveness of preventive strategies; and risk factor distribution.”
The researchers noted as a limitation of their study that the 14 diseases captured were not an exhaustive list of neurological conditions; chronic lower back pain, a condition included in a previous major study of the burden of neurological disease in the United States, was omitted, as were restless legs syndrome and peripheral neuropathy. The researchers cited changes to coding practice in the U.S. and accuracy of medical claims data as potential limitations of their analysis. The Global Burden of Disease study is funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and several of Dr. Feigin’s coauthors reported financial relationships with industry.
Time to adjust the stroke belt?
Amelia Boehme, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health in New York, said in an interview that the current study added to recent findings showing surprising local variability in stroke prevalence, incidence, and mortality. “What we had always conceptually thought of as the ‘stroke belt’ isn’t necessarily the case,” Dr. Boehme said, but is rather subject to local, county-by-county variations. “Looking at the data here in conjunction with what previous authors have found, it raises some questions as to whether or not state-level data is giving a completely accurate picture, and whether we need to start looking at the county level and adjust for populations and age.” Importantly, Dr. Boehme said, data collected in the Global Burden of Disease study tends to be exceptionally rigorous and systematic, adding weight to Dr. Feigin and colleagues’ suggestions that prevention efforts may be making a dent in stroke and dementia.
“More data is always needed before we start to say we’re seeing things change,” Dr. Boehme noted. “But any glimmer of optimism is welcome, especially with regard to interventions that have been put in place, to allow us to build on those interventions.”
Dr. Boehme disclosed no financial conflicts of interest.
, according to new findings derived from the 2017 Global Burden of Disease study.
The authors of the analysis, led by Valery Feigin, MD, PhD, of New Zealand’s National Institute for Stroke and Applied Neurosciences, and published in the February 2021 issue of JAMA Neurology, looked at prevalence, incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years for 14 neurological disorders across 50 states between 1990 and 2017. The diseases included in the analysis were stroke, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, headaches, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injuries, brain and other nervous system cancers, meningitis, encephalitis, and tetanus.
Tracking the burden of neurologic diseases
Dr. Feigin and colleagues estimated that a full 60% of the U.S. population lives with one or more of these disorders, a figure much greater than previous estimates for neurological disease burden nationwide. Tension-type headache and migraine were the most prevalent in the analysis by Dr. Feigin and colleagues. During the study period, they found, prevalence, incidence, and disability burden of nearly all the included disorders increased, with the exception of brain and spinal cord injuries, meningitis, and encephalitis.
The researchers attributed most of the rise in noncommunicable neurological diseases to population aging. An age-standardized analysis found trends for stroke and Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias to be declining or flat. Age-standardized stroke incidence dropped by 16% from 1990 to 2017, while stroke mortality declined by nearly a third, and stroke disability by a quarter. Age-standardized incidence of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias dropped by 12%, and their prevalence by 13%, during the study period, though dementia mortality and disability were seen increasing.
The authors surmised that the age-standardized declines in stroke and dementias could reflect that “primary prevention of these disorders are beginning to show an influence.” With dementia, which is linked to cognitive reserve and education, “improving educational levels of cohort reaching the age groups at greatest risk of disease may also be contributing to a modest decline over time,” Dr. Feigin and his colleagues wrote.
Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis, meanwhile, were both seen rising in incidence, prevalence, and disability adjusted life years (DALYs) even with age-standardized figures. The United States saw comparatively more disability in 2017 from dementias, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, and headache disorders, which together comprised 6.7% of DALYs, compared with 4.4% globally; these also accounted for a higher share of mortality in the U.S. than worldwide. The authors attributed at least some of the difference to better case ascertainment in the U.S.
Regional variations
The researchers also reported variations in disease burden by state and region. While previous studies have identified a “stroke belt” concentrated in North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, the new findings point to stroke disability highest in Alabama, Arkansas, and Mississippi, and mortality highest in Alabama, Mississippi, and South Carolina. The researchers noted increases in dementia mortality in these states, “likely attributable to the reciprocal association between stroke and dementia.”
Northern states saw higher burdens of multiple sclerosis compared with the rest of the country, while eastern states had higher rates of Parkinson’s disease.
Such regional and state-by state variations, Dr. Feigin and colleagues wrote in their analysis, “may be associated with differences in the case ascertainment, as well as access to health care; racial/ethnic, genetic, and socioeconomic diversity; quality and comprehensiveness of preventive strategies; and risk factor distribution.”
The researchers noted as a limitation of their study that the 14 diseases captured were not an exhaustive list of neurological conditions; chronic lower back pain, a condition included in a previous major study of the burden of neurological disease in the United States, was omitted, as were restless legs syndrome and peripheral neuropathy. The researchers cited changes to coding practice in the U.S. and accuracy of medical claims data as potential limitations of their analysis. The Global Burden of Disease study is funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and several of Dr. Feigin’s coauthors reported financial relationships with industry.
Time to adjust the stroke belt?
Amelia Boehme, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health in New York, said in an interview that the current study added to recent findings showing surprising local variability in stroke prevalence, incidence, and mortality. “What we had always conceptually thought of as the ‘stroke belt’ isn’t necessarily the case,” Dr. Boehme said, but is rather subject to local, county-by-county variations. “Looking at the data here in conjunction with what previous authors have found, it raises some questions as to whether or not state-level data is giving a completely accurate picture, and whether we need to start looking at the county level and adjust for populations and age.” Importantly, Dr. Boehme said, data collected in the Global Burden of Disease study tends to be exceptionally rigorous and systematic, adding weight to Dr. Feigin and colleagues’ suggestions that prevention efforts may be making a dent in stroke and dementia.
“More data is always needed before we start to say we’re seeing things change,” Dr. Boehme noted. “But any glimmer of optimism is welcome, especially with regard to interventions that have been put in place, to allow us to build on those interventions.”
Dr. Boehme disclosed no financial conflicts of interest.
, according to new findings derived from the 2017 Global Burden of Disease study.
The authors of the analysis, led by Valery Feigin, MD, PhD, of New Zealand’s National Institute for Stroke and Applied Neurosciences, and published in the February 2021 issue of JAMA Neurology, looked at prevalence, incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years for 14 neurological disorders across 50 states between 1990 and 2017. The diseases included in the analysis were stroke, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, headaches, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injuries, brain and other nervous system cancers, meningitis, encephalitis, and tetanus.
Tracking the burden of neurologic diseases
Dr. Feigin and colleagues estimated that a full 60% of the U.S. population lives with one or more of these disorders, a figure much greater than previous estimates for neurological disease burden nationwide. Tension-type headache and migraine were the most prevalent in the analysis by Dr. Feigin and colleagues. During the study period, they found, prevalence, incidence, and disability burden of nearly all the included disorders increased, with the exception of brain and spinal cord injuries, meningitis, and encephalitis.
The researchers attributed most of the rise in noncommunicable neurological diseases to population aging. An age-standardized analysis found trends for stroke and Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias to be declining or flat. Age-standardized stroke incidence dropped by 16% from 1990 to 2017, while stroke mortality declined by nearly a third, and stroke disability by a quarter. Age-standardized incidence of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias dropped by 12%, and their prevalence by 13%, during the study period, though dementia mortality and disability were seen increasing.
The authors surmised that the age-standardized declines in stroke and dementias could reflect that “primary prevention of these disorders are beginning to show an influence.” With dementia, which is linked to cognitive reserve and education, “improving educational levels of cohort reaching the age groups at greatest risk of disease may also be contributing to a modest decline over time,” Dr. Feigin and his colleagues wrote.
Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis, meanwhile, were both seen rising in incidence, prevalence, and disability adjusted life years (DALYs) even with age-standardized figures. The United States saw comparatively more disability in 2017 from dementias, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, motor neuron disease, and headache disorders, which together comprised 6.7% of DALYs, compared with 4.4% globally; these also accounted for a higher share of mortality in the U.S. than worldwide. The authors attributed at least some of the difference to better case ascertainment in the U.S.
Regional variations
The researchers also reported variations in disease burden by state and region. While previous studies have identified a “stroke belt” concentrated in North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, the new findings point to stroke disability highest in Alabama, Arkansas, and Mississippi, and mortality highest in Alabama, Mississippi, and South Carolina. The researchers noted increases in dementia mortality in these states, “likely attributable to the reciprocal association between stroke and dementia.”
Northern states saw higher burdens of multiple sclerosis compared with the rest of the country, while eastern states had higher rates of Parkinson’s disease.
Such regional and state-by state variations, Dr. Feigin and colleagues wrote in their analysis, “may be associated with differences in the case ascertainment, as well as access to health care; racial/ethnic, genetic, and socioeconomic diversity; quality and comprehensiveness of preventive strategies; and risk factor distribution.”
The researchers noted as a limitation of their study that the 14 diseases captured were not an exhaustive list of neurological conditions; chronic lower back pain, a condition included in a previous major study of the burden of neurological disease in the United States, was omitted, as were restless legs syndrome and peripheral neuropathy. The researchers cited changes to coding practice in the U.S. and accuracy of medical claims data as potential limitations of their analysis. The Global Burden of Disease study is funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and several of Dr. Feigin’s coauthors reported financial relationships with industry.
Time to adjust the stroke belt?
Amelia Boehme, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health in New York, said in an interview that the current study added to recent findings showing surprising local variability in stroke prevalence, incidence, and mortality. “What we had always conceptually thought of as the ‘stroke belt’ isn’t necessarily the case,” Dr. Boehme said, but is rather subject to local, county-by-county variations. “Looking at the data here in conjunction with what previous authors have found, it raises some questions as to whether or not state-level data is giving a completely accurate picture, and whether we need to start looking at the county level and adjust for populations and age.” Importantly, Dr. Boehme said, data collected in the Global Burden of Disease study tends to be exceptionally rigorous and systematic, adding weight to Dr. Feigin and colleagues’ suggestions that prevention efforts may be making a dent in stroke and dementia.
“More data is always needed before we start to say we’re seeing things change,” Dr. Boehme noted. “But any glimmer of optimism is welcome, especially with regard to interventions that have been put in place, to allow us to build on those interventions.”
Dr. Boehme disclosed no financial conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Decline in children’s COVID-19 cases slows
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children declined for the sixth consecutive week, but the drop was the smallest yet, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
That drop of almost 6,400 cases, or 9.0%, falls short of the declines recorded in any the previous 5 weeks, which ranged from 18,000 to 46,000 cases and 15.3% to 28.7%, based on data from the heath departments of 49 states (excluding New York), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is up to almost 3.17 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all age groups. That cumulative proportion was unchanged from the previous week, which has occurred only three other times over the course of the pandemic, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Despite the 6-week decline in new cases, however, the cumulative rate continued to climb, rising from 4,124 cases per 100,000 children to 4,209 for the week of Feb. 19-25. The states, not surprisingly, fall on both sides of that national tally. The lowest rates can be found in Hawaii (1,040 per 100,000 children), Vermont (2,111 per 100,000), and Maine (2,394), while the highest rates were recorded in North Dakota (8,580), Tennessee (7,851), and Rhode Island (7,223), the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new child deaths, nine, stayed in single digits for a second consecutive week, although it was up from six deaths reported a week earlier. Total COVID-19–related deaths in children now number 256, which represents just 0.06% of coronavirus deaths for all ages among the 43 states (along with New York City and Guam) reporting such data.
Among those jurisdictions, Texas (40), Arizona (27), and New York City (23) have reported the most deaths in children, while nine states and the District of Columbia have reported no deaths yet, the AAP and CHA noted.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children declined for the sixth consecutive week, but the drop was the smallest yet, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

That drop of almost 6,400 cases, or 9.0%, falls short of the declines recorded in any the previous 5 weeks, which ranged from 18,000 to 46,000 cases and 15.3% to 28.7%, based on data from the heath departments of 49 states (excluding New York), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is up to almost 3.17 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all age groups. That cumulative proportion was unchanged from the previous week, which has occurred only three other times over the course of the pandemic, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Despite the 6-week decline in new cases, however, the cumulative rate continued to climb, rising from 4,124 cases per 100,000 children to 4,209 for the week of Feb. 19-25. The states, not surprisingly, fall on both sides of that national tally. The lowest rates can be found in Hawaii (1,040 per 100,000 children), Vermont (2,111 per 100,000), and Maine (2,394), while the highest rates were recorded in North Dakota (8,580), Tennessee (7,851), and Rhode Island (7,223), the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new child deaths, nine, stayed in single digits for a second consecutive week, although it was up from six deaths reported a week earlier. Total COVID-19–related deaths in children now number 256, which represents just 0.06% of coronavirus deaths for all ages among the 43 states (along with New York City and Guam) reporting such data.
Among those jurisdictions, Texas (40), Arizona (27), and New York City (23) have reported the most deaths in children, while nine states and the District of Columbia have reported no deaths yet, the AAP and CHA noted.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children declined for the sixth consecutive week, but the drop was the smallest yet, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

That drop of almost 6,400 cases, or 9.0%, falls short of the declines recorded in any the previous 5 weeks, which ranged from 18,000 to 46,000 cases and 15.3% to 28.7%, based on data from the heath departments of 49 states (excluding New York), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is up to almost 3.17 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all age groups. That cumulative proportion was unchanged from the previous week, which has occurred only three other times over the course of the pandemic, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Despite the 6-week decline in new cases, however, the cumulative rate continued to climb, rising from 4,124 cases per 100,000 children to 4,209 for the week of Feb. 19-25. The states, not surprisingly, fall on both sides of that national tally. The lowest rates can be found in Hawaii (1,040 per 100,000 children), Vermont (2,111 per 100,000), and Maine (2,394), while the highest rates were recorded in North Dakota (8,580), Tennessee (7,851), and Rhode Island (7,223), the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new child deaths, nine, stayed in single digits for a second consecutive week, although it was up from six deaths reported a week earlier. Total COVID-19–related deaths in children now number 256, which represents just 0.06% of coronavirus deaths for all ages among the 43 states (along with New York City and Guam) reporting such data.
Among those jurisdictions, Texas (40), Arizona (27), and New York City (23) have reported the most deaths in children, while nine states and the District of Columbia have reported no deaths yet, the AAP and CHA noted.












