User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Teriflunomide delays MS symptoms in radiologically isolated syndrome
BOSTON – , according to a double-blind, phase 3 trial presented in the Emerging Science session of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
“These data add to the evidence that early immunomodulation offers clinical benefit even in the presymptomatic phase of MS,” reported Christine Lebrun-Frenay, MD, PhD, head of inflammatory neurological disorders research unit, University of Nice, France. This is the second study to show a benefit from a disease-modifying therapy in asymptomatic RIS patients. The ARISE study, which was presented at the 2022 European Committee for Treatment and Research in MS and has now been published, compared 240 mg of twice-daily dimethyl fumarate with placebo. Dimethyl fumarate was associated with an 82% (hazard ratio, 0.18; P = .007) reduction in the risk of a first demyelinating event after 96 weeks of follow-up.
TERIS trial data
In the new study, called TERIS, the design and outcomes were similar to the ARISE study. Eighty-nine patients meeting standard criteria for RIS were randomized to 14 mg of once-daily teriflunomide or placebo. The majority (71%) were female, and the mean age was 39.8 years. At the time of RIS diagnosis, the mean age was 38 years. At study entry, standardized MRI studies were performed of the brain and spinal cord.
During 2 years of follow-up, 8 of 28 demyelinating events were observed in the active treatment group. The remaining 20 occurred in the placebo group. This translated to a 63% reduction (HR, 0.37; P = .018) in favor of teriflunomide. When graphed, the curves separated at about 6 months and then widened progressively over time.
Distinct from clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), which describes individuals who have a symptomatic episode consistent with a demyelinating event, RIS is based primarily on an MRI that shows lesions highly suggestive of MS. Neither confirms the MS diagnosis, but both are associated with a high likelihood of eventually meeting MS diagnostic criteria. The ARISE and TERIS studies now support therapy to delay demyelinating events.
“With more and more people having brain scans for various reasons, such as headache or head trauma, more of these cases are being discovered,” Dr. Lebrun-Frenay said.
Caution warranted when interpreting the findings
The data support the theory that treatment should begin early in patients with a high likelihood of developing symptomatic MS on the basis of brain lesions. It is logical to assume that preventing damage to the myelin will reduce or delay permanent symptoms and permanent neurologic impairment, but Dr. Lebrun-Frenay suggested that the available data from ARISE and TERIS are not practice changing even though both were multicenter double-blind trials.
“More data from larger groups of patients are needed to confirm the findings,” she said. She expressed concern about not adhering to strict criteria to diagnosis RIS.
“It is important that medical professionals are cautious,” she said, citing the risk of misdiagnosis of pathology of MRI that leads to treatment of patients with a low risk of developing symptomatic MS.
Teriflunomide and dimethyl fumarate, which have long been available as first-line therapies in relapsing-remitting MS, are generally well tolerated. In the TERIS and ARISE studies, mild or moderate events occurred more commonly in the active treatment than the placebo arms, but there were no serious adverse events. However, both can produce more serious adverse events, which, in the case of teriflunomide, include liver toxicity leading to injury and liver failure.
Challenging the traditional definition of MS
The author of the ARISE study, Darin T. Okuda, MD, a professor of neurology at the UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, indicated that his study, now reinforced by the TERIS study, challenges the definition of MS.
“Both ARISE and TERIS demonstrated a significant reduction in seminal clinical event rates related to inflammatory demyelination,” Dr. Okuda said in an interview. They provide evidence that patients are at high risk of the demyelinating events that characterize MS. Given the potential difficulty for accessing therapies of benefit, “how we define multiple sclerosis is highly important.”
“Individuals of younger age with abnormal spinal cord MRI studies along with other paraclinical features related to risk for a first event may be the most ideal group to treat,” he said. However, he agreed with Dr. Lebrun-Frenay that it is not yet clear which RIS patients are the most appropriate candidates.
“Gaining a more refined sense of who we should treat will require more work,” he said.
These data are likely to change the orientation toward RIS, according to Melina Hosseiny, MD, department of radiology, University of California, Los Angeles, Medical Center. She noted that the relationship between RIS and increased risk of MS has long been recognized, and the risk increases with specific features on imaging.
“Studies have shown that spinal cord lesions are associated with a greater than 50% chance of converting to MS,” said Dr. Hosseiny, who was the lead author of a review article on RIS. “Identifying such imaging findings can help identify patients who may benefit from disease-modifying medications.”
Dr. Lebrun-Frenay reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Okuda has financial relationships with Alexion, Biogen, Celgene, EMD Serono, Genzyme, TG Therapeutics, and VielaBio. Dr. Hosseiny reports no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – , according to a double-blind, phase 3 trial presented in the Emerging Science session of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
“These data add to the evidence that early immunomodulation offers clinical benefit even in the presymptomatic phase of MS,” reported Christine Lebrun-Frenay, MD, PhD, head of inflammatory neurological disorders research unit, University of Nice, France. This is the second study to show a benefit from a disease-modifying therapy in asymptomatic RIS patients. The ARISE study, which was presented at the 2022 European Committee for Treatment and Research in MS and has now been published, compared 240 mg of twice-daily dimethyl fumarate with placebo. Dimethyl fumarate was associated with an 82% (hazard ratio, 0.18; P = .007) reduction in the risk of a first demyelinating event after 96 weeks of follow-up.
TERIS trial data
In the new study, called TERIS, the design and outcomes were similar to the ARISE study. Eighty-nine patients meeting standard criteria for RIS were randomized to 14 mg of once-daily teriflunomide or placebo. The majority (71%) were female, and the mean age was 39.8 years. At the time of RIS diagnosis, the mean age was 38 years. At study entry, standardized MRI studies were performed of the brain and spinal cord.
During 2 years of follow-up, 8 of 28 demyelinating events were observed in the active treatment group. The remaining 20 occurred in the placebo group. This translated to a 63% reduction (HR, 0.37; P = .018) in favor of teriflunomide. When graphed, the curves separated at about 6 months and then widened progressively over time.
Distinct from clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), which describes individuals who have a symptomatic episode consistent with a demyelinating event, RIS is based primarily on an MRI that shows lesions highly suggestive of MS. Neither confirms the MS diagnosis, but both are associated with a high likelihood of eventually meeting MS diagnostic criteria. The ARISE and TERIS studies now support therapy to delay demyelinating events.
“With more and more people having brain scans for various reasons, such as headache or head trauma, more of these cases are being discovered,” Dr. Lebrun-Frenay said.
Caution warranted when interpreting the findings
The data support the theory that treatment should begin early in patients with a high likelihood of developing symptomatic MS on the basis of brain lesions. It is logical to assume that preventing damage to the myelin will reduce or delay permanent symptoms and permanent neurologic impairment, but Dr. Lebrun-Frenay suggested that the available data from ARISE and TERIS are not practice changing even though both were multicenter double-blind trials.
“More data from larger groups of patients are needed to confirm the findings,” she said. She expressed concern about not adhering to strict criteria to diagnosis RIS.
“It is important that medical professionals are cautious,” she said, citing the risk of misdiagnosis of pathology of MRI that leads to treatment of patients with a low risk of developing symptomatic MS.
Teriflunomide and dimethyl fumarate, which have long been available as first-line therapies in relapsing-remitting MS, are generally well tolerated. In the TERIS and ARISE studies, mild or moderate events occurred more commonly in the active treatment than the placebo arms, but there were no serious adverse events. However, both can produce more serious adverse events, which, in the case of teriflunomide, include liver toxicity leading to injury and liver failure.
Challenging the traditional definition of MS
The author of the ARISE study, Darin T. Okuda, MD, a professor of neurology at the UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, indicated that his study, now reinforced by the TERIS study, challenges the definition of MS.
“Both ARISE and TERIS demonstrated a significant reduction in seminal clinical event rates related to inflammatory demyelination,” Dr. Okuda said in an interview. They provide evidence that patients are at high risk of the demyelinating events that characterize MS. Given the potential difficulty for accessing therapies of benefit, “how we define multiple sclerosis is highly important.”
“Individuals of younger age with abnormal spinal cord MRI studies along with other paraclinical features related to risk for a first event may be the most ideal group to treat,” he said. However, he agreed with Dr. Lebrun-Frenay that it is not yet clear which RIS patients are the most appropriate candidates.
“Gaining a more refined sense of who we should treat will require more work,” he said.
These data are likely to change the orientation toward RIS, according to Melina Hosseiny, MD, department of radiology, University of California, Los Angeles, Medical Center. She noted that the relationship between RIS and increased risk of MS has long been recognized, and the risk increases with specific features on imaging.
“Studies have shown that spinal cord lesions are associated with a greater than 50% chance of converting to MS,” said Dr. Hosseiny, who was the lead author of a review article on RIS. “Identifying such imaging findings can help identify patients who may benefit from disease-modifying medications.”
Dr. Lebrun-Frenay reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Okuda has financial relationships with Alexion, Biogen, Celgene, EMD Serono, Genzyme, TG Therapeutics, and VielaBio. Dr. Hosseiny reports no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – , according to a double-blind, phase 3 trial presented in the Emerging Science session of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
“These data add to the evidence that early immunomodulation offers clinical benefit even in the presymptomatic phase of MS,” reported Christine Lebrun-Frenay, MD, PhD, head of inflammatory neurological disorders research unit, University of Nice, France. This is the second study to show a benefit from a disease-modifying therapy in asymptomatic RIS patients. The ARISE study, which was presented at the 2022 European Committee for Treatment and Research in MS and has now been published, compared 240 mg of twice-daily dimethyl fumarate with placebo. Dimethyl fumarate was associated with an 82% (hazard ratio, 0.18; P = .007) reduction in the risk of a first demyelinating event after 96 weeks of follow-up.
TERIS trial data
In the new study, called TERIS, the design and outcomes were similar to the ARISE study. Eighty-nine patients meeting standard criteria for RIS were randomized to 14 mg of once-daily teriflunomide or placebo. The majority (71%) were female, and the mean age was 39.8 years. At the time of RIS diagnosis, the mean age was 38 years. At study entry, standardized MRI studies were performed of the brain and spinal cord.
During 2 years of follow-up, 8 of 28 demyelinating events were observed in the active treatment group. The remaining 20 occurred in the placebo group. This translated to a 63% reduction (HR, 0.37; P = .018) in favor of teriflunomide. When graphed, the curves separated at about 6 months and then widened progressively over time.
Distinct from clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), which describes individuals who have a symptomatic episode consistent with a demyelinating event, RIS is based primarily on an MRI that shows lesions highly suggestive of MS. Neither confirms the MS diagnosis, but both are associated with a high likelihood of eventually meeting MS diagnostic criteria. The ARISE and TERIS studies now support therapy to delay demyelinating events.
“With more and more people having brain scans for various reasons, such as headache or head trauma, more of these cases are being discovered,” Dr. Lebrun-Frenay said.
Caution warranted when interpreting the findings
The data support the theory that treatment should begin early in patients with a high likelihood of developing symptomatic MS on the basis of brain lesions. It is logical to assume that preventing damage to the myelin will reduce or delay permanent symptoms and permanent neurologic impairment, but Dr. Lebrun-Frenay suggested that the available data from ARISE and TERIS are not practice changing even though both were multicenter double-blind trials.
“More data from larger groups of patients are needed to confirm the findings,” she said. She expressed concern about not adhering to strict criteria to diagnosis RIS.
“It is important that medical professionals are cautious,” she said, citing the risk of misdiagnosis of pathology of MRI that leads to treatment of patients with a low risk of developing symptomatic MS.
Teriflunomide and dimethyl fumarate, which have long been available as first-line therapies in relapsing-remitting MS, are generally well tolerated. In the TERIS and ARISE studies, mild or moderate events occurred more commonly in the active treatment than the placebo arms, but there were no serious adverse events. However, both can produce more serious adverse events, which, in the case of teriflunomide, include liver toxicity leading to injury and liver failure.
Challenging the traditional definition of MS
The author of the ARISE study, Darin T. Okuda, MD, a professor of neurology at the UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, indicated that his study, now reinforced by the TERIS study, challenges the definition of MS.
“Both ARISE and TERIS demonstrated a significant reduction in seminal clinical event rates related to inflammatory demyelination,” Dr. Okuda said in an interview. They provide evidence that patients are at high risk of the demyelinating events that characterize MS. Given the potential difficulty for accessing therapies of benefit, “how we define multiple sclerosis is highly important.”
“Individuals of younger age with abnormal spinal cord MRI studies along with other paraclinical features related to risk for a first event may be the most ideal group to treat,” he said. However, he agreed with Dr. Lebrun-Frenay that it is not yet clear which RIS patients are the most appropriate candidates.
“Gaining a more refined sense of who we should treat will require more work,” he said.
These data are likely to change the orientation toward RIS, according to Melina Hosseiny, MD, department of radiology, University of California, Los Angeles, Medical Center. She noted that the relationship between RIS and increased risk of MS has long been recognized, and the risk increases with specific features on imaging.
“Studies have shown that spinal cord lesions are associated with a greater than 50% chance of converting to MS,” said Dr. Hosseiny, who was the lead author of a review article on RIS. “Identifying such imaging findings can help identify patients who may benefit from disease-modifying medications.”
Dr. Lebrun-Frenay reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Okuda has financial relationships with Alexion, Biogen, Celgene, EMD Serono, Genzyme, TG Therapeutics, and VielaBio. Dr. Hosseiny reports no potential conflicts of interest.
AT AAN 2023
Plasma monitoring supports earlier osimertinib treatment in lung cancer patients
Previous studies have suggested that molecular progression of disease in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC, as measured by sequential plasma EGFR T790M, may precede radiological progression, as measured by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST).
However, the impact of these measures on timing of treatment changes and patient outcomes has not been examined, wrote Jordi Remon, MD, of Paris (France)–Saclay University and colleagues, in Annals of Oncology.
The European Organization for Research Treatment and Cancer Lung Cancer Group designed a phase 2 clinical trial known as APPLE to evaluate the use of sequential plasma EGFR T790M and determine the optimal sequencing for gefitinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC.
The researchers reported results from two randomized arms of the APPLE trial. In arm B, 52 patients received gefitinib until emergence of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) EGFR T790M mutation, based on the cobas EGFR test v2 (a real-time PCR test), or progression of disease based on Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). In arm C, 51 patients received gefitinib until disease progression based on RECIST. Both arms then switched to osimertinib. Patients randomized to a third arm (arm A) received osimertinib upfront until progression of disease based on RECIST, and they were not included in the current study.
The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) while receiving osimertinib at 18 months in patients who were originally randomized to gefitinib, then switched to osimertinib at the emergence of circulating tumor DNA. Secondary endpoints included PFS, overall response rate, overall survival, and brain PFS.
Patients entered the study between November 2017 and February 2020. A total of 75% and 65% of those in arms B and C, respectively, were female, approximately 65% had the mutation EGFR Del19, and approximately one-third had baseline brain metastases. In arm B, 17% of patients switched to osimertinib based on the emergence of ctDNA T790M mutation before progressive disease based on RECIST. The median time to molecular disease progression was 266 days.
More patients in arm B met the primary endpoint of PFS while receiving osimertinib at 18 months (67.2%) than in arm C (53.5%), after a median follow-up of 30 months.
As for secondary endpoints, the median PFS in the two arms was 22.0 months and 20.2 months, respectively. Median overall survival was 42.8 months in arm C and was not reached in arm B. The median brain PFS was 24.4 months for arm B and 21.4 months for arm C.
The benefits seen in the osimertinib patients may be due in part to the timing of the switch to correspond with molecular or radiological disease progression, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
In the future, more research is needed to determine whether molecular monitoring may impact patients’ outcomes, compared with monitoring based on radiological progression, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, mainly the rapid evolution in the treatment landscape of EGFR-mutant NSCLC, the researchers noted.
Osimertinib is currently considered the preferred first-line treatment by most physicians, they said. “The APPLE trial is the first prospective study supporting the role of dynamic adaptive strategies based on ctDNA monitoring in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC.”
The study was supported by AstraZeneca. Lead author Dr. Remon had no financial conflicts to disclose. Corresponding author Dr. Dziadziuszko disclosed honoraria for consultancy or lectures from AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, MSD, Takeda, Pfizer, Amgen, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Previous studies have suggested that molecular progression of disease in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC, as measured by sequential plasma EGFR T790M, may precede radiological progression, as measured by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST).
However, the impact of these measures on timing of treatment changes and patient outcomes has not been examined, wrote Jordi Remon, MD, of Paris (France)–Saclay University and colleagues, in Annals of Oncology.
The European Organization for Research Treatment and Cancer Lung Cancer Group designed a phase 2 clinical trial known as APPLE to evaluate the use of sequential plasma EGFR T790M and determine the optimal sequencing for gefitinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC.
The researchers reported results from two randomized arms of the APPLE trial. In arm B, 52 patients received gefitinib until emergence of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) EGFR T790M mutation, based on the cobas EGFR test v2 (a real-time PCR test), or progression of disease based on Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). In arm C, 51 patients received gefitinib until disease progression based on RECIST. Both arms then switched to osimertinib. Patients randomized to a third arm (arm A) received osimertinib upfront until progression of disease based on RECIST, and they were not included in the current study.
The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) while receiving osimertinib at 18 months in patients who were originally randomized to gefitinib, then switched to osimertinib at the emergence of circulating tumor DNA. Secondary endpoints included PFS, overall response rate, overall survival, and brain PFS.
Patients entered the study between November 2017 and February 2020. A total of 75% and 65% of those in arms B and C, respectively, were female, approximately 65% had the mutation EGFR Del19, and approximately one-third had baseline brain metastases. In arm B, 17% of patients switched to osimertinib based on the emergence of ctDNA T790M mutation before progressive disease based on RECIST. The median time to molecular disease progression was 266 days.
More patients in arm B met the primary endpoint of PFS while receiving osimertinib at 18 months (67.2%) than in arm C (53.5%), after a median follow-up of 30 months.
As for secondary endpoints, the median PFS in the two arms was 22.0 months and 20.2 months, respectively. Median overall survival was 42.8 months in arm C and was not reached in arm B. The median brain PFS was 24.4 months for arm B and 21.4 months for arm C.
The benefits seen in the osimertinib patients may be due in part to the timing of the switch to correspond with molecular or radiological disease progression, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
In the future, more research is needed to determine whether molecular monitoring may impact patients’ outcomes, compared with monitoring based on radiological progression, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, mainly the rapid evolution in the treatment landscape of EGFR-mutant NSCLC, the researchers noted.
Osimertinib is currently considered the preferred first-line treatment by most physicians, they said. “The APPLE trial is the first prospective study supporting the role of dynamic adaptive strategies based on ctDNA monitoring in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC.”
The study was supported by AstraZeneca. Lead author Dr. Remon had no financial conflicts to disclose. Corresponding author Dr. Dziadziuszko disclosed honoraria for consultancy or lectures from AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, MSD, Takeda, Pfizer, Amgen, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Previous studies have suggested that molecular progression of disease in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC, as measured by sequential plasma EGFR T790M, may precede radiological progression, as measured by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST).
However, the impact of these measures on timing of treatment changes and patient outcomes has not been examined, wrote Jordi Remon, MD, of Paris (France)–Saclay University and colleagues, in Annals of Oncology.
The European Organization for Research Treatment and Cancer Lung Cancer Group designed a phase 2 clinical trial known as APPLE to evaluate the use of sequential plasma EGFR T790M and determine the optimal sequencing for gefitinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC.
The researchers reported results from two randomized arms of the APPLE trial. In arm B, 52 patients received gefitinib until emergence of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) EGFR T790M mutation, based on the cobas EGFR test v2 (a real-time PCR test), or progression of disease based on Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). In arm C, 51 patients received gefitinib until disease progression based on RECIST. Both arms then switched to osimertinib. Patients randomized to a third arm (arm A) received osimertinib upfront until progression of disease based on RECIST, and they were not included in the current study.
The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) while receiving osimertinib at 18 months in patients who were originally randomized to gefitinib, then switched to osimertinib at the emergence of circulating tumor DNA. Secondary endpoints included PFS, overall response rate, overall survival, and brain PFS.
Patients entered the study between November 2017 and February 2020. A total of 75% and 65% of those in arms B and C, respectively, were female, approximately 65% had the mutation EGFR Del19, and approximately one-third had baseline brain metastases. In arm B, 17% of patients switched to osimertinib based on the emergence of ctDNA T790M mutation before progressive disease based on RECIST. The median time to molecular disease progression was 266 days.
More patients in arm B met the primary endpoint of PFS while receiving osimertinib at 18 months (67.2%) than in arm C (53.5%), after a median follow-up of 30 months.
As for secondary endpoints, the median PFS in the two arms was 22.0 months and 20.2 months, respectively. Median overall survival was 42.8 months in arm C and was not reached in arm B. The median brain PFS was 24.4 months for arm B and 21.4 months for arm C.
The benefits seen in the osimertinib patients may be due in part to the timing of the switch to correspond with molecular or radiological disease progression, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
In the future, more research is needed to determine whether molecular monitoring may impact patients’ outcomes, compared with monitoring based on radiological progression, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, mainly the rapid evolution in the treatment landscape of EGFR-mutant NSCLC, the researchers noted.
Osimertinib is currently considered the preferred first-line treatment by most physicians, they said. “The APPLE trial is the first prospective study supporting the role of dynamic adaptive strategies based on ctDNA monitoring in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC.”
The study was supported by AstraZeneca. Lead author Dr. Remon had no financial conflicts to disclose. Corresponding author Dr. Dziadziuszko disclosed honoraria for consultancy or lectures from AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, MSD, Takeda, Pfizer, Amgen, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
FROM ANNALS OF ONCOLOGY
Novel levodopa delivery system promises continuous dosing without surgery or pump
BOSTON – , according to an early clinical experience described in the Emerging Science session at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
On this device, the attenuation of levodopa fluctuations “translated into dramatic improvements in clinical behavior, including highly significant reductions in OFF time and an increase in ON time with no dyskinesias,” reported C. Warren Olanow, MD, who is a chairman emeritus of the department of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and now an employee of the company developing this new device.
A novel strategy
Numerous studies have demonstrated that reductions in the troughs of plasma levodopa associated with oral dosing result in longer ON time with fewer dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow, who explained this has led to strategies for numerous strategies to achieve continuous delivery. A device that delivers levodopa into the stomach through a surgically implanted catheter has already received regulatory approval. Other devices delivering levodopa subcutaneously are in development, but Dr. Olanow said each of these has had limitations.
“The problem with these approaches is they are associated with potentially serious side effects and they require the patient to wear a cumbersome device,” he explained. Relative to the subcutaneous delivery systems, which have been associated with injection site reactions that include painful nodules, and the surgically implanted devices, which also require an external pump, the latest strategy avoids both disadvantages.
Called DopaFuse, the experimental device is designed to deliver the levodopa and carbidopa into the mouth through a micropump within a wearable retainer. Dr. Olanow said that previous experimental studies demonstrated that small doses of levodopa delivered by mouth to the gastrointestinal system reduce levodopa plasma variability. This early clinical study supports that premise. Levodopa delivered into the mouth by way of a propellant in the retainer-mounted pump improved clinical endpoints.
Encouraging trial results
In the study, 16 patients between the ages of 30 and 75 with Parkinson’s disease were enrolled. On day 1, they received an oral dose of levodopa/carbidopa consistent with their current treatment. On day 2, levodopa/carbidopa was delivered through the retainer-mounted device at equivalent doses. On day 3, they received a single morning oral dose and the received the remainder of their levodopa/carbidopa regimen through the device. On days 4 to 14, they received treatment in the same schedule as day 3.
When pharmacokinetics of levodopa on day 3 were compared with those on day 1, the fluctuation index and coefficient of levodopa concentration variability was reduced to a degree that was highly statistically significant (P < .0001). This, in turn, correlated with “striking” reductions in OFF time with equally statistically significant improvement in ON time and ON time without dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow.
Relative to an OFF time of 3.2 hours on day 1, the OFF time of 1.6 hours on day 3 represented a 50% reduction (P < .0001). ON time improved from 12.8 hours to 14.5 hours (P < .001). ON time without dyskinesias improved numerically from 8.8 hours to 9.6 hours.
“There were also improvements in activities of daily living when patients were on DopaFuse, which is a hard endpoint to reach in a study with such a small sample size,” Dr. Olanow reported.
There were no serious adverse events. Three patients reported vomiting and two patients each reported headache, but these events were mild and all resolved within a day. Three patients reported buccal lesions, but these also resolved within a day.
“Some patients reported trouble with speaking in the beginning but at the end of the study, patients were reporting that it was easier to speak because of the motor improvements,” Dr. Olanow said.
Overall, the device was well tolerated by the subjects, providing the evidence for the next stages of clinical studies, reported Dr. Olanow.
“If this turns out to be what we hope it is, it will allow us to deliver levodopa without motor complications, without need for a surgical procedure, and without the risk of subcutaneous lesions,” Dr. Olanow said.
More delivery strategies are needed
This device is in an early phase of development, but several specialists in Parkinson’s disease agreed that there is a need for more strategies to provide continuous levodopa in patients with advancing symptoms. Stuart Isaacson, MD, director, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center of Boca Raton, Fla., is among them.
“Novel delivery devices that can provide more continuous levodopa delivery would be an important therapeutic advance,” Dr. Isaacson said. He called levodopa “the cornerstone of treatment through the course of Parkinson’s disease,” but more physiologic dosing in advancing disease has been a challenge.
“While there are many therapies currently available to manage OFF time, many people living with Parkinson’s disease continue to spend only half of their waking day with good ON time,” he added.
The currently approved method of delivering continuous levodopa through a surgically placed catheter into the gastrointestinal system is effective, but has limitations, according to Aaron L. Ellenbogen, MD, a neurologist at Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, Mich.
“One of the challenges with the current treatment landscape of Parkinson’s disease is that medication can be absorbed variably through the gastrointestinal system,” he said. “As the disease progresses, this often becomes more troublesome.” Although this new device is likely to share this issue, Dr. Ellenbogen said that several devices might be useful to match patients with the one that works best for them.
Dr. Olanow is the founder and CEO of Clintrex Research Corporation, through which he also serves as chief medical officer of SynAgile, the company developing DopaFuse. Dr. Isaacson has financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that produce levodopa and levodopa delivery systems. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva.
BOSTON – , according to an early clinical experience described in the Emerging Science session at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
On this device, the attenuation of levodopa fluctuations “translated into dramatic improvements in clinical behavior, including highly significant reductions in OFF time and an increase in ON time with no dyskinesias,” reported C. Warren Olanow, MD, who is a chairman emeritus of the department of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and now an employee of the company developing this new device.
A novel strategy
Numerous studies have demonstrated that reductions in the troughs of plasma levodopa associated with oral dosing result in longer ON time with fewer dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow, who explained this has led to strategies for numerous strategies to achieve continuous delivery. A device that delivers levodopa into the stomach through a surgically implanted catheter has already received regulatory approval. Other devices delivering levodopa subcutaneously are in development, but Dr. Olanow said each of these has had limitations.
“The problem with these approaches is they are associated with potentially serious side effects and they require the patient to wear a cumbersome device,” he explained. Relative to the subcutaneous delivery systems, which have been associated with injection site reactions that include painful nodules, and the surgically implanted devices, which also require an external pump, the latest strategy avoids both disadvantages.
Called DopaFuse, the experimental device is designed to deliver the levodopa and carbidopa into the mouth through a micropump within a wearable retainer. Dr. Olanow said that previous experimental studies demonstrated that small doses of levodopa delivered by mouth to the gastrointestinal system reduce levodopa plasma variability. This early clinical study supports that premise. Levodopa delivered into the mouth by way of a propellant in the retainer-mounted pump improved clinical endpoints.
Encouraging trial results
In the study, 16 patients between the ages of 30 and 75 with Parkinson’s disease were enrolled. On day 1, they received an oral dose of levodopa/carbidopa consistent with their current treatment. On day 2, levodopa/carbidopa was delivered through the retainer-mounted device at equivalent doses. On day 3, they received a single morning oral dose and the received the remainder of their levodopa/carbidopa regimen through the device. On days 4 to 14, they received treatment in the same schedule as day 3.
When pharmacokinetics of levodopa on day 3 were compared with those on day 1, the fluctuation index and coefficient of levodopa concentration variability was reduced to a degree that was highly statistically significant (P < .0001). This, in turn, correlated with “striking” reductions in OFF time with equally statistically significant improvement in ON time and ON time without dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow.
Relative to an OFF time of 3.2 hours on day 1, the OFF time of 1.6 hours on day 3 represented a 50% reduction (P < .0001). ON time improved from 12.8 hours to 14.5 hours (P < .001). ON time without dyskinesias improved numerically from 8.8 hours to 9.6 hours.
“There were also improvements in activities of daily living when patients were on DopaFuse, which is a hard endpoint to reach in a study with such a small sample size,” Dr. Olanow reported.
There were no serious adverse events. Three patients reported vomiting and two patients each reported headache, but these events were mild and all resolved within a day. Three patients reported buccal lesions, but these also resolved within a day.
“Some patients reported trouble with speaking in the beginning but at the end of the study, patients were reporting that it was easier to speak because of the motor improvements,” Dr. Olanow said.
Overall, the device was well tolerated by the subjects, providing the evidence for the next stages of clinical studies, reported Dr. Olanow.
“If this turns out to be what we hope it is, it will allow us to deliver levodopa without motor complications, without need for a surgical procedure, and without the risk of subcutaneous lesions,” Dr. Olanow said.
More delivery strategies are needed
This device is in an early phase of development, but several specialists in Parkinson’s disease agreed that there is a need for more strategies to provide continuous levodopa in patients with advancing symptoms. Stuart Isaacson, MD, director, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center of Boca Raton, Fla., is among them.
“Novel delivery devices that can provide more continuous levodopa delivery would be an important therapeutic advance,” Dr. Isaacson said. He called levodopa “the cornerstone of treatment through the course of Parkinson’s disease,” but more physiologic dosing in advancing disease has been a challenge.
“While there are many therapies currently available to manage OFF time, many people living with Parkinson’s disease continue to spend only half of their waking day with good ON time,” he added.
The currently approved method of delivering continuous levodopa through a surgically placed catheter into the gastrointestinal system is effective, but has limitations, according to Aaron L. Ellenbogen, MD, a neurologist at Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, Mich.
“One of the challenges with the current treatment landscape of Parkinson’s disease is that medication can be absorbed variably through the gastrointestinal system,” he said. “As the disease progresses, this often becomes more troublesome.” Although this new device is likely to share this issue, Dr. Ellenbogen said that several devices might be useful to match patients with the one that works best for them.
Dr. Olanow is the founder and CEO of Clintrex Research Corporation, through which he also serves as chief medical officer of SynAgile, the company developing DopaFuse. Dr. Isaacson has financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that produce levodopa and levodopa delivery systems. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva.
BOSTON – , according to an early clinical experience described in the Emerging Science session at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
On this device, the attenuation of levodopa fluctuations “translated into dramatic improvements in clinical behavior, including highly significant reductions in OFF time and an increase in ON time with no dyskinesias,” reported C. Warren Olanow, MD, who is a chairman emeritus of the department of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and now an employee of the company developing this new device.
A novel strategy
Numerous studies have demonstrated that reductions in the troughs of plasma levodopa associated with oral dosing result in longer ON time with fewer dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow, who explained this has led to strategies for numerous strategies to achieve continuous delivery. A device that delivers levodopa into the stomach through a surgically implanted catheter has already received regulatory approval. Other devices delivering levodopa subcutaneously are in development, but Dr. Olanow said each of these has had limitations.
“The problem with these approaches is they are associated with potentially serious side effects and they require the patient to wear a cumbersome device,” he explained. Relative to the subcutaneous delivery systems, which have been associated with injection site reactions that include painful nodules, and the surgically implanted devices, which also require an external pump, the latest strategy avoids both disadvantages.
Called DopaFuse, the experimental device is designed to deliver the levodopa and carbidopa into the mouth through a micropump within a wearable retainer. Dr. Olanow said that previous experimental studies demonstrated that small doses of levodopa delivered by mouth to the gastrointestinal system reduce levodopa plasma variability. This early clinical study supports that premise. Levodopa delivered into the mouth by way of a propellant in the retainer-mounted pump improved clinical endpoints.
Encouraging trial results
In the study, 16 patients between the ages of 30 and 75 with Parkinson’s disease were enrolled. On day 1, they received an oral dose of levodopa/carbidopa consistent with their current treatment. On day 2, levodopa/carbidopa was delivered through the retainer-mounted device at equivalent doses. On day 3, they received a single morning oral dose and the received the remainder of their levodopa/carbidopa regimen through the device. On days 4 to 14, they received treatment in the same schedule as day 3.
When pharmacokinetics of levodopa on day 3 were compared with those on day 1, the fluctuation index and coefficient of levodopa concentration variability was reduced to a degree that was highly statistically significant (P < .0001). This, in turn, correlated with “striking” reductions in OFF time with equally statistically significant improvement in ON time and ON time without dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow.
Relative to an OFF time of 3.2 hours on day 1, the OFF time of 1.6 hours on day 3 represented a 50% reduction (P < .0001). ON time improved from 12.8 hours to 14.5 hours (P < .001). ON time without dyskinesias improved numerically from 8.8 hours to 9.6 hours.
“There were also improvements in activities of daily living when patients were on DopaFuse, which is a hard endpoint to reach in a study with such a small sample size,” Dr. Olanow reported.
There were no serious adverse events. Three patients reported vomiting and two patients each reported headache, but these events were mild and all resolved within a day. Three patients reported buccal lesions, but these also resolved within a day.
“Some patients reported trouble with speaking in the beginning but at the end of the study, patients were reporting that it was easier to speak because of the motor improvements,” Dr. Olanow said.
Overall, the device was well tolerated by the subjects, providing the evidence for the next stages of clinical studies, reported Dr. Olanow.
“If this turns out to be what we hope it is, it will allow us to deliver levodopa without motor complications, without need for a surgical procedure, and without the risk of subcutaneous lesions,” Dr. Olanow said.
More delivery strategies are needed
This device is in an early phase of development, but several specialists in Parkinson’s disease agreed that there is a need for more strategies to provide continuous levodopa in patients with advancing symptoms. Stuart Isaacson, MD, director, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center of Boca Raton, Fla., is among them.
“Novel delivery devices that can provide more continuous levodopa delivery would be an important therapeutic advance,” Dr. Isaacson said. He called levodopa “the cornerstone of treatment through the course of Parkinson’s disease,” but more physiologic dosing in advancing disease has been a challenge.
“While there are many therapies currently available to manage OFF time, many people living with Parkinson’s disease continue to spend only half of their waking day with good ON time,” he added.
The currently approved method of delivering continuous levodopa through a surgically placed catheter into the gastrointestinal system is effective, but has limitations, according to Aaron L. Ellenbogen, MD, a neurologist at Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, Mich.
“One of the challenges with the current treatment landscape of Parkinson’s disease is that medication can be absorbed variably through the gastrointestinal system,” he said. “As the disease progresses, this often becomes more troublesome.” Although this new device is likely to share this issue, Dr. Ellenbogen said that several devices might be useful to match patients with the one that works best for them.
Dr. Olanow is the founder and CEO of Clintrex Research Corporation, through which he also serves as chief medical officer of SynAgile, the company developing DopaFuse. Dr. Isaacson has financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that produce levodopa and levodopa delivery systems. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva.
FROM AAN 2023
Medical-level empathy? Yup, ChatGPT can fake that
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Surprising brain activity moments before death
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
All the participants in the study I am going to tell you about this week died. And three of them died twice. But their deaths provide us with a fascinating window into the complex electrochemistry of the dying brain. What we might be looking at, indeed, is the physiologic correlate of the near-death experience.
The concept of the near-death experience is culturally ubiquitous. And though the content seems to track along culture lines – Western Christians are more likely to report seeing guardian angels, while Hindus are more likely to report seeing messengers of the god of death – certain factors seem to transcend culture: an out-of-body experience; a feeling of peace; and, of course, the light at the end of the tunnel.
As a materialist, I won’t discuss the possibility that these commonalities reflect some metaphysical structure to the afterlife. More likely, it seems to me, is that the commonalities result from the fact that the experience is mediated by our brains, and our brains, when dying, may be more alike than different.
We are talking about this study, appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, by Jimo Borjigin and her team.
Dr. Borjigin studies the neural correlates of consciousness, perhaps one of the biggest questions in all of science today. To wit,
The study in question follows four unconscious patients –comatose patients, really – as life-sustaining support was withdrawn, up until the moment of death. Three had suffered severe anoxic brain injury in the setting of prolonged cardiac arrest. Though the heart was restarted, the brain damage was severe. The fourth had a large brain hemorrhage. All four patients were thus comatose and, though not brain-dead, unresponsive – with the lowest possible Glasgow Coma Scale score. No response to outside stimuli.
The families had made the decision to withdraw life support – to remove the breathing tube – but agreed to enroll their loved one in the study.
The team applied EEG leads to the head, EKG leads to the chest, and other monitoring equipment to observe the physiologic changes that occurred as the comatose and unresponsive patient died.
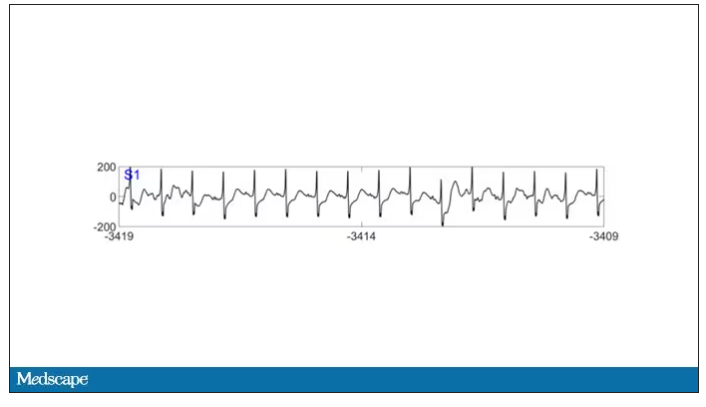
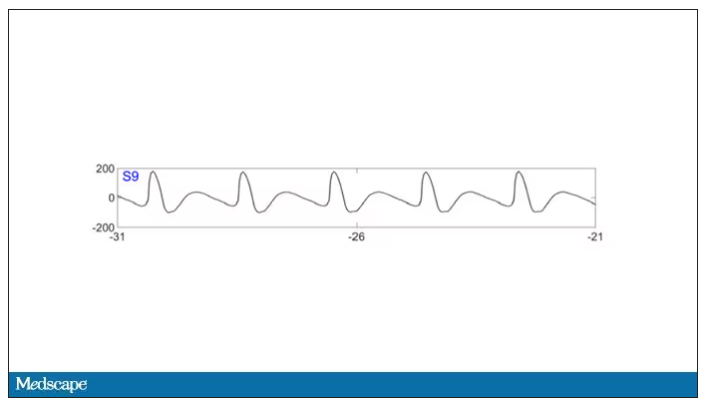
As the heart rhythm evolved from this:
To this:
And eventually stopped.
But this is a study about the brain, not the heart.
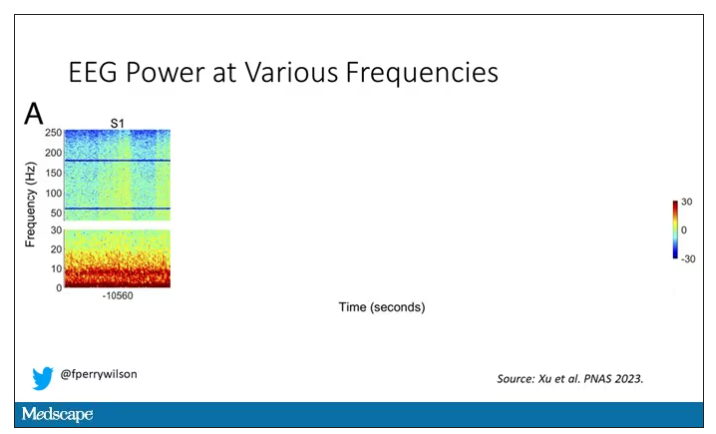
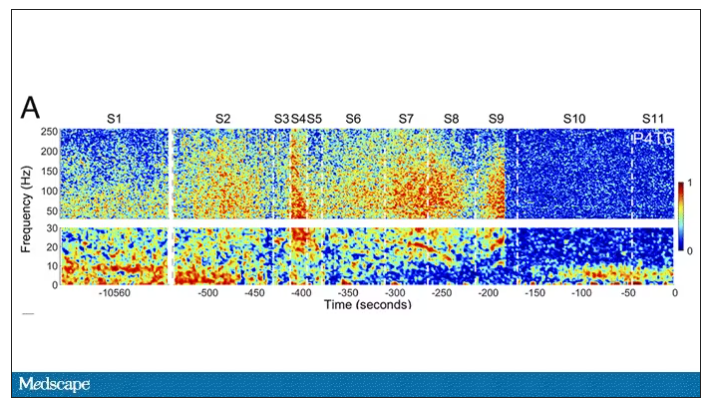
Prior to the withdrawal of life support, the brain electrical signals looked like this:
What you see is the EEG power at various frequencies, with red being higher. All the red was down at the low frequencies. Consciousness, at least as we understand it, is a higher-frequency phenomenon.
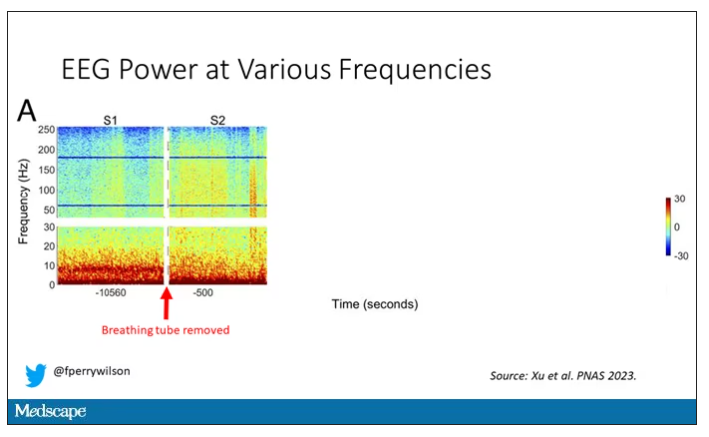
Right after the breathing tube was removed, the power didn’t change too much, but you can see some increased activity at the higher frequencies.
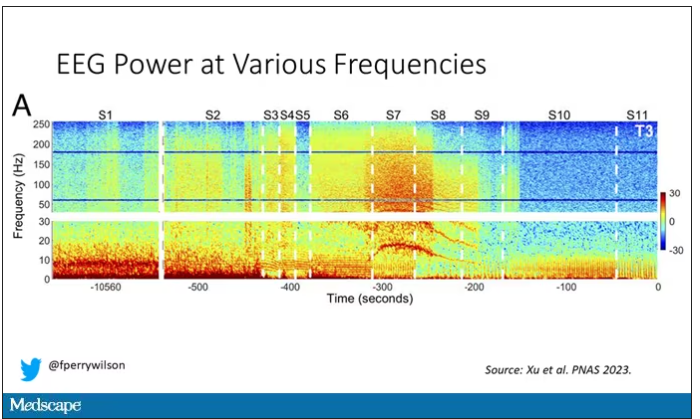
But in two of the four patients, something really surprising happened. Watch what happens as the brain gets closer and closer to death.
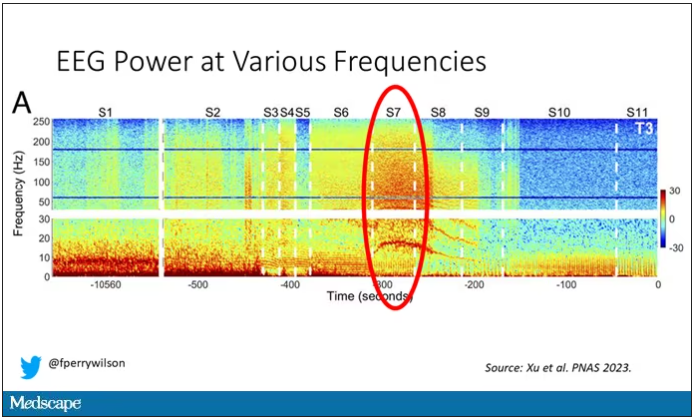
Here, about 300 seconds before death, there was a power surge at the high gamma frequencies.
This spike in power occurred in the somatosensory cortex and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, areas that are associated with conscious experience. It seems that this patient, 5 minutes before death, was experiencing something.
But I know what you’re thinking. This is a brain that is not receiving oxygen. Cells are going to become disordered quickly and start firing randomly – a last gasp, so to speak, before the end. Meaningless noise.
But connectivity mapping tells a different story. The signals seem to have structure.
Those high-frequency power surges increased connectivity in the posterior cortical “hot zone,” an area of the brain many researchers feel is necessary for conscious perception. This figure is not a map of raw brain electrical output like the one I showed before, but of coherence between brain regions in the consciousness hot zone. Those red areas indicate cross-talk – not the disordered scream of dying neurons, but a last set of messages passing back and forth from the parietal and posterior temporal lobes.
In fact, the electrical patterns of the brains in these patients looked very similar to the patterns seen in dreaming humans, as well as in patients with epilepsy who report sensations of out-of-body experiences.
It’s critical to realize two things here. First, these signals of consciousness were not present before life support was withdrawn. These comatose patients had minimal brain activity; there was no evidence that they were experiencing anything before the process of dying began. These brains are behaving fundamentally differently near death.
But second, we must realize that, although the brains of these individuals, in their last moments, appeared to be acting in a way that conscious brains act, we have no way of knowing if the patients were truly having a conscious experience. As I said, all the patients in the study died. Short of those metaphysics I alluded to earlier, we will have no way to ask them how they experienced their final moments.
Let’s be clear: This study doesn’t answer the question of what happens when we die. It says nothing about life after death or the existence or persistence of the soul. But what it does do is shed light on an incredibly difficult problem in neuroscience: the problem of consciousness. And as studies like this move forward, we may discover that the root of consciousness comes not from the breath of God or the energy of a living universe, but from very specific parts of the very complicated machine that is the brain, acting together to produce something transcendent. And to me, that is no less sublime.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
All the participants in the study I am going to tell you about this week died. And three of them died twice. But their deaths provide us with a fascinating window into the complex electrochemistry of the dying brain. What we might be looking at, indeed, is the physiologic correlate of the near-death experience.
The concept of the near-death experience is culturally ubiquitous. And though the content seems to track along culture lines – Western Christians are more likely to report seeing guardian angels, while Hindus are more likely to report seeing messengers of the god of death – certain factors seem to transcend culture: an out-of-body experience; a feeling of peace; and, of course, the light at the end of the tunnel.
As a materialist, I won’t discuss the possibility that these commonalities reflect some metaphysical structure to the afterlife. More likely, it seems to me, is that the commonalities result from the fact that the experience is mediated by our brains, and our brains, when dying, may be more alike than different.
We are talking about this study, appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, by Jimo Borjigin and her team.
Dr. Borjigin studies the neural correlates of consciousness, perhaps one of the biggest questions in all of science today. To wit,
The study in question follows four unconscious patients –comatose patients, really – as life-sustaining support was withdrawn, up until the moment of death. Three had suffered severe anoxic brain injury in the setting of prolonged cardiac arrest. Though the heart was restarted, the brain damage was severe. The fourth had a large brain hemorrhage. All four patients were thus comatose and, though not brain-dead, unresponsive – with the lowest possible Glasgow Coma Scale score. No response to outside stimuli.
The families had made the decision to withdraw life support – to remove the breathing tube – but agreed to enroll their loved one in the study.
The team applied EEG leads to the head, EKG leads to the chest, and other monitoring equipment to observe the physiologic changes that occurred as the comatose and unresponsive patient died.
As the heart rhythm evolved from this:
To this:
And eventually stopped.
But this is a study about the brain, not the heart.
Prior to the withdrawal of life support, the brain electrical signals looked like this:
What you see is the EEG power at various frequencies, with red being higher. All the red was down at the low frequencies. Consciousness, at least as we understand it, is a higher-frequency phenomenon.
Right after the breathing tube was removed, the power didn’t change too much, but you can see some increased activity at the higher frequencies.
But in two of the four patients, something really surprising happened. Watch what happens as the brain gets closer and closer to death.
Here, about 300 seconds before death, there was a power surge at the high gamma frequencies.
This spike in power occurred in the somatosensory cortex and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, areas that are associated with conscious experience. It seems that this patient, 5 minutes before death, was experiencing something.
But I know what you’re thinking. This is a brain that is not receiving oxygen. Cells are going to become disordered quickly and start firing randomly – a last gasp, so to speak, before the end. Meaningless noise.
But connectivity mapping tells a different story. The signals seem to have structure.
Those high-frequency power surges increased connectivity in the posterior cortical “hot zone,” an area of the brain many researchers feel is necessary for conscious perception. This figure is not a map of raw brain electrical output like the one I showed before, but of coherence between brain regions in the consciousness hot zone. Those red areas indicate cross-talk – not the disordered scream of dying neurons, but a last set of messages passing back and forth from the parietal and posterior temporal lobes.
In fact, the electrical patterns of the brains in these patients looked very similar to the patterns seen in dreaming humans, as well as in patients with epilepsy who report sensations of out-of-body experiences.
It’s critical to realize two things here. First, these signals of consciousness were not present before life support was withdrawn. These comatose patients had minimal brain activity; there was no evidence that they were experiencing anything before the process of dying began. These brains are behaving fundamentally differently near death.
But second, we must realize that, although the brains of these individuals, in their last moments, appeared to be acting in a way that conscious brains act, we have no way of knowing if the patients were truly having a conscious experience. As I said, all the patients in the study died. Short of those metaphysics I alluded to earlier, we will have no way to ask them how they experienced their final moments.
Let’s be clear: This study doesn’t answer the question of what happens when we die. It says nothing about life after death or the existence or persistence of the soul. But what it does do is shed light on an incredibly difficult problem in neuroscience: the problem of consciousness. And as studies like this move forward, we may discover that the root of consciousness comes not from the breath of God or the energy of a living universe, but from very specific parts of the very complicated machine that is the brain, acting together to produce something transcendent. And to me, that is no less sublime.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
All the participants in the study I am going to tell you about this week died. And three of them died twice. But their deaths provide us with a fascinating window into the complex electrochemistry of the dying brain. What we might be looking at, indeed, is the physiologic correlate of the near-death experience.
The concept of the near-death experience is culturally ubiquitous. And though the content seems to track along culture lines – Western Christians are more likely to report seeing guardian angels, while Hindus are more likely to report seeing messengers of the god of death – certain factors seem to transcend culture: an out-of-body experience; a feeling of peace; and, of course, the light at the end of the tunnel.
As a materialist, I won’t discuss the possibility that these commonalities reflect some metaphysical structure to the afterlife. More likely, it seems to me, is that the commonalities result from the fact that the experience is mediated by our brains, and our brains, when dying, may be more alike than different.
We are talking about this study, appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, by Jimo Borjigin and her team.
Dr. Borjigin studies the neural correlates of consciousness, perhaps one of the biggest questions in all of science today. To wit,
The study in question follows four unconscious patients –comatose patients, really – as life-sustaining support was withdrawn, up until the moment of death. Three had suffered severe anoxic brain injury in the setting of prolonged cardiac arrest. Though the heart was restarted, the brain damage was severe. The fourth had a large brain hemorrhage. All four patients were thus comatose and, though not brain-dead, unresponsive – with the lowest possible Glasgow Coma Scale score. No response to outside stimuli.
The families had made the decision to withdraw life support – to remove the breathing tube – but agreed to enroll their loved one in the study.
The team applied EEG leads to the head, EKG leads to the chest, and other monitoring equipment to observe the physiologic changes that occurred as the comatose and unresponsive patient died.
As the heart rhythm evolved from this:
To this:
And eventually stopped.
But this is a study about the brain, not the heart.
Prior to the withdrawal of life support, the brain electrical signals looked like this:
What you see is the EEG power at various frequencies, with red being higher. All the red was down at the low frequencies. Consciousness, at least as we understand it, is a higher-frequency phenomenon.
Right after the breathing tube was removed, the power didn’t change too much, but you can see some increased activity at the higher frequencies.
But in two of the four patients, something really surprising happened. Watch what happens as the brain gets closer and closer to death.
Here, about 300 seconds before death, there was a power surge at the high gamma frequencies.
This spike in power occurred in the somatosensory cortex and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, areas that are associated with conscious experience. It seems that this patient, 5 minutes before death, was experiencing something.
But I know what you’re thinking. This is a brain that is not receiving oxygen. Cells are going to become disordered quickly and start firing randomly – a last gasp, so to speak, before the end. Meaningless noise.
But connectivity mapping tells a different story. The signals seem to have structure.
Those high-frequency power surges increased connectivity in the posterior cortical “hot zone,” an area of the brain many researchers feel is necessary for conscious perception. This figure is not a map of raw brain electrical output like the one I showed before, but of coherence between brain regions in the consciousness hot zone. Those red areas indicate cross-talk – not the disordered scream of dying neurons, but a last set of messages passing back and forth from the parietal and posterior temporal lobes.
In fact, the electrical patterns of the brains in these patients looked very similar to the patterns seen in dreaming humans, as well as in patients with epilepsy who report sensations of out-of-body experiences.
It’s critical to realize two things here. First, these signals of consciousness were not present before life support was withdrawn. These comatose patients had minimal brain activity; there was no evidence that they were experiencing anything before the process of dying began. These brains are behaving fundamentally differently near death.
But second, we must realize that, although the brains of these individuals, in their last moments, appeared to be acting in a way that conscious brains act, we have no way of knowing if the patients were truly having a conscious experience. As I said, all the patients in the study died. Short of those metaphysics I alluded to earlier, we will have no way to ask them how they experienced their final moments.
Let’s be clear: This study doesn’t answer the question of what happens when we die. It says nothing about life after death or the existence or persistence of the soul. But what it does do is shed light on an incredibly difficult problem in neuroscience: the problem of consciousness. And as studies like this move forward, we may discover that the root of consciousness comes not from the breath of God or the energy of a living universe, but from very specific parts of the very complicated machine that is the brain, acting together to produce something transcendent. And to me, that is no less sublime.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
AHA backs screening for cognitive impairment after stroke
Screening for cognitive impairment should be part of multidisciplinary care for stroke survivors, the American Heart Association says in a new scientific statement.
“Cognitive impairment after stroke is very common, is associated with other post-stroke outcomes, and often has significant impact on the quality of life,” Nada El Husseini, MD, MHSc, chair of the scientific statement writing group, told this news organization.
“It is important to screen stroke survivors for cognitive impairment as well as for associated comorbidities such as mood and sleep disorders,” said Dr. El Husseini, associate professor of neurology at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C.
The scientific statement was published online in Stroke. It’s the first to specifically focus on the cognitive impairment resulting from an overt stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic).
‘Actionable’ considerations for care
The writing group performed a “scoping” review of the literature on the prevalence, diagnosis, and management of poststroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) to provide a framework for “actionable considerations” for clinical practice as well as to highlight gaps needing additional studies, Dr. El Husseini explained.
PSCI, ranging from mild to severe, occurs in up to 60% of stroke survivors in the first year after stroke; yet, it is often underreported and underdiagnosed, the writing group notes.
Up to 20% of stroke survivors who experience mild cognitive impairment fully recover cognitive function, and cognitive recovery is most likely within the first 6 months after a stroke.
However, improvement in cognitive impairment without return to prestroke levels is more frequent than is complete recovery. As many as one in three stroke survivors may develop dementia within 5 years of stroke.
The writing group also notes that PSCI is often associated with other conditions, including physical disability, sleep disorders, behavioral and personality changes, depression, and other neuropsychological changes – each of which may contribute to lower quality of life.
Currently, there is no “gold standard” for cognitive screening following stroke, but several brief cognitive screening tests, including the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, are widely used to identify cognitive impairment after stroke.
The statement also highlights the importance of assessing cognitive changes over time after stroke. Stroke survivors who experience unexplained difficulties with cognitive-related activities of daily living, following care instructions, or providing a reliable health history may be candidates for additional cognitive screening.
Manage risk factors to prevent repeat stroke
“Anticipatory guidance regarding home and driving safety and, return to work (if applicable) along with interdisciplinary collaboration among different medical and ancillary specialists in the diagnosis and management of cognitive impairment is key for the holistic care of stroke survivors,” Dr. El Husseini told this news organization.
The multidisciplinary poststroke health care team could include neurologists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, nurses, neuropsychologists, gerontologists, and primary care providers.
“Because recurrent stroke is strongly associated with the development of cognitive impairment and dementia, prevention of recurrent strokes should be sought to decrease that risk,” Dr. El Husseini said. This includes addressing stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and atrial fibrillation.
The writing group says research is needed in the future to determine how cognitive impairment develops after stroke and the impact of nonbrain factors, including infection, frailty, and social factors.
Further research is also needed to determine best practices for cognitive screening after stroke, including the development and use of screening instruments that consider demographic, cultural, and linguistic factors in determining “normal” function.
“Perhaps the most pressing need, however, is the development of effective and culturally relevant treatments for poststroke cognitive impairment,” Dr. El Husseini said in a news release.
“We hope to see big enough clinical trials that assess various techniques, medications, and lifestyle changes in diverse groups of patients that may help improve cognitive function,” she added.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Stroke Council, the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, the Council on Hypertension, and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health.
Screening for cognitive impairment should be part of multidisciplinary care for stroke survivors, the American Heart Association says in a new scientific statement.
“Cognitive impairment after stroke is very common, is associated with other post-stroke outcomes, and often has significant impact on the quality of life,” Nada El Husseini, MD, MHSc, chair of the scientific statement writing group, told this news organization.
“It is important to screen stroke survivors for cognitive impairment as well as for associated comorbidities such as mood and sleep disorders,” said Dr. El Husseini, associate professor of neurology at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C.
The scientific statement was published online in Stroke. It’s the first to specifically focus on the cognitive impairment resulting from an overt stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic).
‘Actionable’ considerations for care
The writing group performed a “scoping” review of the literature on the prevalence, diagnosis, and management of poststroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) to provide a framework for “actionable considerations” for clinical practice as well as to highlight gaps needing additional studies, Dr. El Husseini explained.
PSCI, ranging from mild to severe, occurs in up to 60% of stroke survivors in the first year after stroke; yet, it is often underreported and underdiagnosed, the writing group notes.
Up to 20% of stroke survivors who experience mild cognitive impairment fully recover cognitive function, and cognitive recovery is most likely within the first 6 months after a stroke.
However, improvement in cognitive impairment without return to prestroke levels is more frequent than is complete recovery. As many as one in three stroke survivors may develop dementia within 5 years of stroke.
The writing group also notes that PSCI is often associated with other conditions, including physical disability, sleep disorders, behavioral and personality changes, depression, and other neuropsychological changes – each of which may contribute to lower quality of life.
Currently, there is no “gold standard” for cognitive screening following stroke, but several brief cognitive screening tests, including the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, are widely used to identify cognitive impairment after stroke.
The statement also highlights the importance of assessing cognitive changes over time after stroke. Stroke survivors who experience unexplained difficulties with cognitive-related activities of daily living, following care instructions, or providing a reliable health history may be candidates for additional cognitive screening.
Manage risk factors to prevent repeat stroke
“Anticipatory guidance regarding home and driving safety and, return to work (if applicable) along with interdisciplinary collaboration among different medical and ancillary specialists in the diagnosis and management of cognitive impairment is key for the holistic care of stroke survivors,” Dr. El Husseini told this news organization.
The multidisciplinary poststroke health care team could include neurologists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, nurses, neuropsychologists, gerontologists, and primary care providers.
“Because recurrent stroke is strongly associated with the development of cognitive impairment and dementia, prevention of recurrent strokes should be sought to decrease that risk,” Dr. El Husseini said. This includes addressing stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and atrial fibrillation.
The writing group says research is needed in the future to determine how cognitive impairment develops after stroke and the impact of nonbrain factors, including infection, frailty, and social factors.
Further research is also needed to determine best practices for cognitive screening after stroke, including the development and use of screening instruments that consider demographic, cultural, and linguistic factors in determining “normal” function.
“Perhaps the most pressing need, however, is the development of effective and culturally relevant treatments for poststroke cognitive impairment,” Dr. El Husseini said in a news release.
“We hope to see big enough clinical trials that assess various techniques, medications, and lifestyle changes in diverse groups of patients that may help improve cognitive function,” she added.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Stroke Council, the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, the Council on Hypertension, and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health.
Screening for cognitive impairment should be part of multidisciplinary care for stroke survivors, the American Heart Association says in a new scientific statement.
“Cognitive impairment after stroke is very common, is associated with other post-stroke outcomes, and often has significant impact on the quality of life,” Nada El Husseini, MD, MHSc, chair of the scientific statement writing group, told this news organization.
“It is important to screen stroke survivors for cognitive impairment as well as for associated comorbidities such as mood and sleep disorders,” said Dr. El Husseini, associate professor of neurology at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C.
The scientific statement was published online in Stroke. It’s the first to specifically focus on the cognitive impairment resulting from an overt stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic).
‘Actionable’ considerations for care
The writing group performed a “scoping” review of the literature on the prevalence, diagnosis, and management of poststroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) to provide a framework for “actionable considerations” for clinical practice as well as to highlight gaps needing additional studies, Dr. El Husseini explained.
PSCI, ranging from mild to severe, occurs in up to 60% of stroke survivors in the first year after stroke; yet, it is often underreported and underdiagnosed, the writing group notes.
Up to 20% of stroke survivors who experience mild cognitive impairment fully recover cognitive function, and cognitive recovery is most likely within the first 6 months after a stroke.
However, improvement in cognitive impairment without return to prestroke levels is more frequent than is complete recovery. As many as one in three stroke survivors may develop dementia within 5 years of stroke.
The writing group also notes that PSCI is often associated with other conditions, including physical disability, sleep disorders, behavioral and personality changes, depression, and other neuropsychological changes – each of which may contribute to lower quality of life.
Currently, there is no “gold standard” for cognitive screening following stroke, but several brief cognitive screening tests, including the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, are widely used to identify cognitive impairment after stroke.
The statement also highlights the importance of assessing cognitive changes over time after stroke. Stroke survivors who experience unexplained difficulties with cognitive-related activities of daily living, following care instructions, or providing a reliable health history may be candidates for additional cognitive screening.
Manage risk factors to prevent repeat stroke
“Anticipatory guidance regarding home and driving safety and, return to work (if applicable) along with interdisciplinary collaboration among different medical and ancillary specialists in the diagnosis and management of cognitive impairment is key for the holistic care of stroke survivors,” Dr. El Husseini told this news organization.
The multidisciplinary poststroke health care team could include neurologists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, nurses, neuropsychologists, gerontologists, and primary care providers.
“Because recurrent stroke is strongly associated with the development of cognitive impairment and dementia, prevention of recurrent strokes should be sought to decrease that risk,” Dr. El Husseini said. This includes addressing stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and atrial fibrillation.
The writing group says research is needed in the future to determine how cognitive impairment develops after stroke and the impact of nonbrain factors, including infection, frailty, and social factors.
Further research is also needed to determine best practices for cognitive screening after stroke, including the development and use of screening instruments that consider demographic, cultural, and linguistic factors in determining “normal” function.
“Perhaps the most pressing need, however, is the development of effective and culturally relevant treatments for poststroke cognitive impairment,” Dr. El Husseini said in a news release.
“We hope to see big enough clinical trials that assess various techniques, medications, and lifestyle changes in diverse groups of patients that may help improve cognitive function,” she added.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Stroke Council, the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, the Council on Hypertension, and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health.
U.S. incidence, prevalence of myasthenia gravis is rising
, an analysis of new claims data shows. Investigators speculate the rise of this rare disorder may be due to “increased diagnosis and more awareness of the disease over time, which has been shown in several studies,” study investigator Ema Rodrigues, DSc, MPH, with Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Boston.
Dr. Rodrigues presented her research at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Myasthenia gravis is a rare neuromuscular disease characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue caused by the binding of autoantibodies at the neuromuscular junction. It affects the voluntary muscles of the body, especially those that control the eyes, mouth, throat, and limbs.
In Europe, the incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis has increased for the past several decades. In the United States, increasing prevalence has also been observed, but recent estimates are lacking, making it tough to gauge the true burden of disease, Dr. Rodrigues explained.
Claims-based analysis
To investigate, Dr. Rodrigues and colleagues analyzed claims data (commercial, Medicare, and Medicaid) and electronic health records representing over 300 million patients in the United States from 2011 to present.
They calculated sex- and age-specific incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis for the year 2021 using U.S. Census data.
Prevalent patients were identified as having one or more myasthenia gravis records in 2021 and two or more myasthenia gravis records, at least 30 days apart, from 2016 to 2021. This cohort had 78,225 patients.
Incident patients were identified as those with a myasthenia gravis record in 2021 and no previous myasthenia gravis record from 2019 to 2020. This cohort had 4,214 patients.
For both the prevalent and incident cohort, the distribution of male and female patients was roughly 50/50, with a slightly higher proportion of females in the incident cohort, Dr. Rodrigues reported.
When looking at age groups, there were “very few pediatric patients,” she noted, with less than 1% of the patients under the age of 12. The highest proportion of patients were 65 years or older. The mean age was 67 in the prevalent cohort and 68 in the incident cohort.
In 2021, the overall incidence of myasthenia gravis was 3.2 per 100,000 with similar estimates for males and females (3.2 vs. 3.1 per 100,000, respectively).
Total prevalence was estimated to be 37.0 per 100,000 with sex-specific estimates being comparable at 37.3 and 36.7 per 100,000 for males and females, respectively.
The incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis increased with age, ranging from 0.3 and 0.4 per 100,000, respectively, in children younger than age 2 years, to 10.2 and 116.8 per 100,000, respectively, in people 65 and older.
These estimates are “significantly higher” than those from a prior U.S. analysis from 2003, Dr. Rodrigues told attendees, but they are quite similar to the estimates that were reported in Sweden in 2020.
A limitation of the analysis is that patients who do not seek care regularly may have not been identified due to inclusion criteria, potentially leading to underestimates. Also, no information was available on the myasthenia gravis subtype (ocular vs. generalized).
Underestimated burden
Reached for comment, Richard J. Nowak, MD, MS, director of the Yale Myasthenia Gravis Clinic, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., noted that the new report, “albeit limited as a claims-based analysis, presents modern data on incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis in the United States.”
“It suggests that the current estimates of myasthenia gravis in the United States are too low and that the true impact/burden of myasthenia gravis is greater. While we are unable to verify the accuracy of the diagnosis, the total myasthenia gravis population is likely to be about 100,000, which is higher than prior estimates.”
“This, in fact, might be driven by greater disease awareness and increased diagnosis along with decreased mortality and longer life expectancy,” Dr. Nowak said.
“Anecdotally, we are most certainly seeing patients with new-onset myasthenia gravis in their 70s, 80s, and even 90s in recent years. The EXPLORE-MG registry published data from a tertiary center on age of onset breakdown showing myasthenia gravis can present at any age,” Dr. Nowak added.
Funding for the study was provided by Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease. Dr. Rodrigues receives compensation and owns stock as an employee of Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Diseases. Dr. Nowak has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, an analysis of new claims data shows. Investigators speculate the rise of this rare disorder may be due to “increased diagnosis and more awareness of the disease over time, which has been shown in several studies,” study investigator Ema Rodrigues, DSc, MPH, with Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Boston.
Dr. Rodrigues presented her research at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Myasthenia gravis is a rare neuromuscular disease characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue caused by the binding of autoantibodies at the neuromuscular junction. It affects the voluntary muscles of the body, especially those that control the eyes, mouth, throat, and limbs.
In Europe, the incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis has increased for the past several decades. In the United States, increasing prevalence has also been observed, but recent estimates are lacking, making it tough to gauge the true burden of disease, Dr. Rodrigues explained.
Claims-based analysis
To investigate, Dr. Rodrigues and colleagues analyzed claims data (commercial, Medicare, and Medicaid) and electronic health records representing over 300 million patients in the United States from 2011 to present.
They calculated sex- and age-specific incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis for the year 2021 using U.S. Census data.
Prevalent patients were identified as having one or more myasthenia gravis records in 2021 and two or more myasthenia gravis records, at least 30 days apart, from 2016 to 2021. This cohort had 78,225 patients.
Incident patients were identified as those with a myasthenia gravis record in 2021 and no previous myasthenia gravis record from 2019 to 2020. This cohort had 4,214 patients.
For both the prevalent and incident cohort, the distribution of male and female patients was roughly 50/50, with a slightly higher proportion of females in the incident cohort, Dr. Rodrigues reported.
When looking at age groups, there were “very few pediatric patients,” she noted, with less than 1% of the patients under the age of 12. The highest proportion of patients were 65 years or older. The mean age was 67 in the prevalent cohort and 68 in the incident cohort.
In 2021, the overall incidence of myasthenia gravis was 3.2 per 100,000 with similar estimates for males and females (3.2 vs. 3.1 per 100,000, respectively).
Total prevalence was estimated to be 37.0 per 100,000 with sex-specific estimates being comparable at 37.3 and 36.7 per 100,000 for males and females, respectively.
The incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis increased with age, ranging from 0.3 and 0.4 per 100,000, respectively, in children younger than age 2 years, to 10.2 and 116.8 per 100,000, respectively, in people 65 and older.
These estimates are “significantly higher” than those from a prior U.S. analysis from 2003, Dr. Rodrigues told attendees, but they are quite similar to the estimates that were reported in Sweden in 2020.
A limitation of the analysis is that patients who do not seek care regularly may have not been identified due to inclusion criteria, potentially leading to underestimates. Also, no information was available on the myasthenia gravis subtype (ocular vs. generalized).
Underestimated burden
Reached for comment, Richard J. Nowak, MD, MS, director of the Yale Myasthenia Gravis Clinic, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., noted that the new report, “albeit limited as a claims-based analysis, presents modern data on incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis in the United States.”
“It suggests that the current estimates of myasthenia gravis in the United States are too low and that the true impact/burden of myasthenia gravis is greater. While we are unable to verify the accuracy of the diagnosis, the total myasthenia gravis population is likely to be about 100,000, which is higher than prior estimates.”
“This, in fact, might be driven by greater disease awareness and increased diagnosis along with decreased mortality and longer life expectancy,” Dr. Nowak said.
“Anecdotally, we are most certainly seeing patients with new-onset myasthenia gravis in their 70s, 80s, and even 90s in recent years. The EXPLORE-MG registry published data from a tertiary center on age of onset breakdown showing myasthenia gravis can present at any age,” Dr. Nowak added.
Funding for the study was provided by Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease. Dr. Rodrigues receives compensation and owns stock as an employee of Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Diseases. Dr. Nowak has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, an analysis of new claims data shows. Investigators speculate the rise of this rare disorder may be due to “increased diagnosis and more awareness of the disease over time, which has been shown in several studies,” study investigator Ema Rodrigues, DSc, MPH, with Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Boston.
Dr. Rodrigues presented her research at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Myasthenia gravis is a rare neuromuscular disease characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue caused by the binding of autoantibodies at the neuromuscular junction. It affects the voluntary muscles of the body, especially those that control the eyes, mouth, throat, and limbs.
In Europe, the incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis has increased for the past several decades. In the United States, increasing prevalence has also been observed, but recent estimates are lacking, making it tough to gauge the true burden of disease, Dr. Rodrigues explained.
Claims-based analysis
To investigate, Dr. Rodrigues and colleagues analyzed claims data (commercial, Medicare, and Medicaid) and electronic health records representing over 300 million patients in the United States from 2011 to present.
They calculated sex- and age-specific incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis for the year 2021 using U.S. Census data.
Prevalent patients were identified as having one or more myasthenia gravis records in 2021 and two or more myasthenia gravis records, at least 30 days apart, from 2016 to 2021. This cohort had 78,225 patients.
Incident patients were identified as those with a myasthenia gravis record in 2021 and no previous myasthenia gravis record from 2019 to 2020. This cohort had 4,214 patients.
For both the prevalent and incident cohort, the distribution of male and female patients was roughly 50/50, with a slightly higher proportion of females in the incident cohort, Dr. Rodrigues reported.
When looking at age groups, there were “very few pediatric patients,” she noted, with less than 1% of the patients under the age of 12. The highest proportion of patients were 65 years or older. The mean age was 67 in the prevalent cohort and 68 in the incident cohort.
In 2021, the overall incidence of myasthenia gravis was 3.2 per 100,000 with similar estimates for males and females (3.2 vs. 3.1 per 100,000, respectively).
Total prevalence was estimated to be 37.0 per 100,000 with sex-specific estimates being comparable at 37.3 and 36.7 per 100,000 for males and females, respectively.
The incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis increased with age, ranging from 0.3 and 0.4 per 100,000, respectively, in children younger than age 2 years, to 10.2 and 116.8 per 100,000, respectively, in people 65 and older.
These estimates are “significantly higher” than those from a prior U.S. analysis from 2003, Dr. Rodrigues told attendees, but they are quite similar to the estimates that were reported in Sweden in 2020.
A limitation of the analysis is that patients who do not seek care regularly may have not been identified due to inclusion criteria, potentially leading to underestimates. Also, no information was available on the myasthenia gravis subtype (ocular vs. generalized).
Underestimated burden
Reached for comment, Richard J. Nowak, MD, MS, director of the Yale Myasthenia Gravis Clinic, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., noted that the new report, “albeit limited as a claims-based analysis, presents modern data on incidence and prevalence of myasthenia gravis in the United States.”
“It suggests that the current estimates of myasthenia gravis in the United States are too low and that the true impact/burden of myasthenia gravis is greater. While we are unable to verify the accuracy of the diagnosis, the total myasthenia gravis population is likely to be about 100,000, which is higher than prior estimates.”
“This, in fact, might be driven by greater disease awareness and increased diagnosis along with decreased mortality and longer life expectancy,” Dr. Nowak said.
“Anecdotally, we are most certainly seeing patients with new-onset myasthenia gravis in their 70s, 80s, and even 90s in recent years. The EXPLORE-MG registry published data from a tertiary center on age of onset breakdown showing myasthenia gravis can present at any age,” Dr. Nowak added.
Funding for the study was provided by Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease. Dr. Rodrigues receives compensation and owns stock as an employee of Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Diseases. Dr. Nowak has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
From AAN 2023
Head-to-head comparison of migraine meds reveals top options
BOSTON – , a new real-world analysis of data on more than 3 million migraine attacks shows.
The findings “align with results of clinical trials and recommendations from clinical treatment guidelines” and provide insights to complement clinical practice, said study investigator Chia-Chun Chiang, MD, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The findings were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The power of big data
Despite a wide variety of acute migraine medications that are available, large-scale, head-to-head comparisons of treatment effectiveness from real-world patient experience reports are lacking, Dr. Chiang explained.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that simultaneously compared multiple acute migraine medications using a Big Data analysis approach based on real-world patient-provided data,” she said.
The researchers extracted more than 10 million self-reported migraine attack records from a migraine smartphone app called Migraine Buddy, where users can document whether a treatment was helpful, somewhat helpful, unsure, or unhelpful.
They analyzed 25 acute medications among seven classes: acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), triptans, combination analgesics (acetaminophen/aspirin/caffeine), ergots, antiemetics, and opioids. The newer gepants and ditan medication classes of medications were not included because of the relatively lower numbers of usage when data was extracted (2014-2020).
The researchers employed a two-level nested logistic regression model to analyze the odds of treatment effectiveness of each medication by adjusting concurrent medications and the covariance within the same user.
The final analysis included more than 3.1 million migraine attacks among 278,000 users globally.
Using ibuprofen as the reference, triptans, ergots, and antiemetics had the highest efficacy with mean odds ratios of 4.8, 3.02, and 2.67, respectively, followed by opioids (OR, 2.49), NSAIDs (OR, 1.94), combination analgesics (OR, 1.69), others (OR, 1.49), and acetaminophen (OR, 0.83).
Individual medications with the highest patient-reported effectiveness were eletriptan (Relpax; OR, 6.1), zolmitriptan (Zomig; OR, 5.7) and sumatriptan (Zecuity; OR, 5.2).
This migraine medication comparative effectiveness analysis, based on patient-reported outcomes, “supports and complements the treatment recommendations from national headache societies based on randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses and strongly supports the use of triptans,” Dr. Chiang said.
End of trial-and-error?
Commenting on this research, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher in Boston, said “This is a great study of Big Data in that it shows the power of the smartphone to collect real-world data and smart researchers like at Mayo Clinic to analyze them.”
“The study sheds light on how different therapeutics compare with each other. The next iteration of this line of research, I would hope, would be to determine if particular medications are effective for a particular migraine population, and even down to individuals with migraine,” said Dr. Lakhan, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“Once those models are appropriately built, long gone will be the era of trial-and-error medicine,” Dr. Lakhan added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Chiang has served as a consultant for Satsuma. Dr. Lakhan reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – , a new real-world analysis of data on more than 3 million migraine attacks shows.
The findings “align with results of clinical trials and recommendations from clinical treatment guidelines” and provide insights to complement clinical practice, said study investigator Chia-Chun Chiang, MD, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The findings were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The power of big data
Despite a wide variety of acute migraine medications that are available, large-scale, head-to-head comparisons of treatment effectiveness from real-world patient experience reports are lacking, Dr. Chiang explained.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that simultaneously compared multiple acute migraine medications using a Big Data analysis approach based on real-world patient-provided data,” she said.
The researchers extracted more than 10 million self-reported migraine attack records from a migraine smartphone app called Migraine Buddy, where users can document whether a treatment was helpful, somewhat helpful, unsure, or unhelpful.
They analyzed 25 acute medications among seven classes: acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), triptans, combination analgesics (acetaminophen/aspirin/caffeine), ergots, antiemetics, and opioids. The newer gepants and ditan medication classes of medications were not included because of the relatively lower numbers of usage when data was extracted (2014-2020).
The researchers employed a two-level nested logistic regression model to analyze the odds of treatment effectiveness of each medication by adjusting concurrent medications and the covariance within the same user.
The final analysis included more than 3.1 million migraine attacks among 278,000 users globally.
Using ibuprofen as the reference, triptans, ergots, and antiemetics had the highest efficacy with mean odds ratios of 4.8, 3.02, and 2.67, respectively, followed by opioids (OR, 2.49), NSAIDs (OR, 1.94), combination analgesics (OR, 1.69), others (OR, 1.49), and acetaminophen (OR, 0.83).
Individual medications with the highest patient-reported effectiveness were eletriptan (Relpax; OR, 6.1), zolmitriptan (Zomig; OR, 5.7) and sumatriptan (Zecuity; OR, 5.2).
This migraine medication comparative effectiveness analysis, based on patient-reported outcomes, “supports and complements the treatment recommendations from national headache societies based on randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses and strongly supports the use of triptans,” Dr. Chiang said.
End of trial-and-error?
Commenting on this research, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher in Boston, said “This is a great study of Big Data in that it shows the power of the smartphone to collect real-world data and smart researchers like at Mayo Clinic to analyze them.”
“The study sheds light on how different therapeutics compare with each other. The next iteration of this line of research, I would hope, would be to determine if particular medications are effective for a particular migraine population, and even down to individuals with migraine,” said Dr. Lakhan, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“Once those models are appropriately built, long gone will be the era of trial-and-error medicine,” Dr. Lakhan added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Chiang has served as a consultant for Satsuma. Dr. Lakhan reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – , a new real-world analysis of data on more than 3 million migraine attacks shows.
The findings “align with results of clinical trials and recommendations from clinical treatment guidelines” and provide insights to complement clinical practice, said study investigator Chia-Chun Chiang, MD, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The findings were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The power of big data
Despite a wide variety of acute migraine medications that are available, large-scale, head-to-head comparisons of treatment effectiveness from real-world patient experience reports are lacking, Dr. Chiang explained.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that simultaneously compared multiple acute migraine medications using a Big Data analysis approach based on real-world patient-provided data,” she said.
The researchers extracted more than 10 million self-reported migraine attack records from a migraine smartphone app called Migraine Buddy, where users can document whether a treatment was helpful, somewhat helpful, unsure, or unhelpful.
They analyzed 25 acute medications among seven classes: acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), triptans, combination analgesics (acetaminophen/aspirin/caffeine), ergots, antiemetics, and opioids. The newer gepants and ditan medication classes of medications were not included because of the relatively lower numbers of usage when data was extracted (2014-2020).
The researchers employed a two-level nested logistic regression model to analyze the odds of treatment effectiveness of each medication by adjusting concurrent medications and the covariance within the same user.
The final analysis included more than 3.1 million migraine attacks among 278,000 users globally.
Using ibuprofen as the reference, triptans, ergots, and antiemetics had the highest efficacy with mean odds ratios of 4.8, 3.02, and 2.67, respectively, followed by opioids (OR, 2.49), NSAIDs (OR, 1.94), combination analgesics (OR, 1.69), others (OR, 1.49), and acetaminophen (OR, 0.83).
Individual medications with the highest patient-reported effectiveness were eletriptan (Relpax; OR, 6.1), zolmitriptan (Zomig; OR, 5.7) and sumatriptan (Zecuity; OR, 5.2).
This migraine medication comparative effectiveness analysis, based on patient-reported outcomes, “supports and complements the treatment recommendations from national headache societies based on randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses and strongly supports the use of triptans,” Dr. Chiang said.
End of trial-and-error?
Commenting on this research, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher in Boston, said “This is a great study of Big Data in that it shows the power of the smartphone to collect real-world data and smart researchers like at Mayo Clinic to analyze them.”
“The study sheds light on how different therapeutics compare with each other. The next iteration of this line of research, I would hope, would be to determine if particular medications are effective for a particular migraine population, and even down to individuals with migraine,” said Dr. Lakhan, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“Once those models are appropriately built, long gone will be the era of trial-and-error medicine,” Dr. Lakhan added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Chiang has served as a consultant for Satsuma. Dr. Lakhan reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAN 2023
Oral antiamyloid shows disease-modifying potential Phase 3 trial underway
BOSTON – , represented by positive changes in plasma and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Use of the drug, ALZ-801 (Alzheon), led to a significant reduction of plasma phosphorylated–tau 181 (p-tau181) , a marker of amyloid-induced neuronal injury in Alzheimer’s disease, as well as slowing of hippocampal atrophy and stabilization of cognition.
“The 12-month results of our phase 2 trial support the finding that ALZ-801 blocks misfolding of amyloid monomers and subsequent formation of neurotoxic amyloid oligomers, the key initial step in the amyloid aggregation cascade, which leads to a rapid and sustained reduction of brain neurodegeneration as measured by plasma p-tau181,” John Hey, PhD, Alzheon’s chief scientific officer, said in a statement.
“The severalfold greater reduction on the p-tau181 biomarker in plasma compared to plaque-clearing antiamyloid antibodies, combined with preservation of brain hippocampal volume and their positive correlations with cognitive benefits, further validate the disease-modifying effects of ALZ-801 in Alzheimer’s patients,” Dr. Hey added.
The results were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
ALZ-801 is an optimized prodrug of tramiprosate that has been shown to inhibit amyloid-beta 42 aggregation into toxic oligomers.
The ongoing phase 2 study is evaluating the effects of oral ALZ-801 (265 mg twice daily) on biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology for 84 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have either the APOE4/4 or APOE3/4 genotype. These genotypes represent the majority of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
The mean age of the cohort was 69 years, and 51% are women; 70% had mild cognitive impairment, and 30% had mild Alzheimer’s disease. The mean Mini-Mental State Examination score for the cohort was 26.0. Roughly half were taking a cholinesterase inhibitor.
Significant plasma p-tau181 reduction was observed at 13 weeks. Levels were reduced by 41% by 52 weeks (P = .016). There was also a significant 5% reduction in plasma amyloid-beta 42 and 40 at 52 weeks (P = .002 and P = .005, respectively), Dr. Hey reported.
After 12 months of treatment, hippocampal atrophy was reduced by about 23%, and expansion of ventricular volume was reduced by about 15%, both in comparison with matched controls from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Composite cognitive z-score improved significantly at 13 and 26 weeks and remained above baseline at 52 weeks in comparison with matched ADNI controls. “These are very promising data,” Dr. Hey told conference attendees.
He noted that the safety profile of ALZ-801 remains favorable and consistent with prior safety data. Common adverse events were mild nausea and SARS-CoV-2 infection. There were no drug-related serious events or amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-E).
The phase 3 APOLLOE4 study of ALZ-801 is underway. This double-blind, randomized study is comparing oral ALZ-801 with placebo over 78 weeks for roughly 300 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have the APOE4/4 genotype. APOLLOE4 is expected to be completed in mid 2024.
The APOLLOE4 study is supported by a $47 million grant from the National Institute on Aging. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted ALZ-801 fast-track designation.
More accessible option?
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, noted that the “biggest difference between this drug and others is that it is taken orally, rather than delivered through an infusion. This is important and valuable for reducing patient and caregiver burden and increasing ease of use and access.”
It’s also noteworthy that ALZ-801 was not associated with ARIA-E, “which has been reported in other antiamyloid trials and can occasionally be serious,” Dr. Griffin said.
Overall, he said the results are “encouraging, but more work is needed. If studies results continue to be positive, this treatment may provide a more accessible option for people who are at higher risk of ARIA,” Dr. Griffin said.
The study was funded by Alzheon. Dr. Hey is an employee of Alzheon and holds stock in the company. Dr. Griffin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – , represented by positive changes in plasma and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Use of the drug, ALZ-801 (Alzheon), led to a significant reduction of plasma phosphorylated–tau 181 (p-tau181) , a marker of amyloid-induced neuronal injury in Alzheimer’s disease, as well as slowing of hippocampal atrophy and stabilization of cognition.
“The 12-month results of our phase 2 trial support the finding that ALZ-801 blocks misfolding of amyloid monomers and subsequent formation of neurotoxic amyloid oligomers, the key initial step in the amyloid aggregation cascade, which leads to a rapid and sustained reduction of brain neurodegeneration as measured by plasma p-tau181,” John Hey, PhD, Alzheon’s chief scientific officer, said in a statement.
“The severalfold greater reduction on the p-tau181 biomarker in plasma compared to plaque-clearing antiamyloid antibodies, combined with preservation of brain hippocampal volume and their positive correlations with cognitive benefits, further validate the disease-modifying effects of ALZ-801 in Alzheimer’s patients,” Dr. Hey added.
The results were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
ALZ-801 is an optimized prodrug of tramiprosate that has been shown to inhibit amyloid-beta 42 aggregation into toxic oligomers.
The ongoing phase 2 study is evaluating the effects of oral ALZ-801 (265 mg twice daily) on biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology for 84 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have either the APOE4/4 or APOE3/4 genotype. These genotypes represent the majority of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
The mean age of the cohort was 69 years, and 51% are women; 70% had mild cognitive impairment, and 30% had mild Alzheimer’s disease. The mean Mini-Mental State Examination score for the cohort was 26.0. Roughly half were taking a cholinesterase inhibitor.
Significant plasma p-tau181 reduction was observed at 13 weeks. Levels were reduced by 41% by 52 weeks (P = .016). There was also a significant 5% reduction in plasma amyloid-beta 42 and 40 at 52 weeks (P = .002 and P = .005, respectively), Dr. Hey reported.
After 12 months of treatment, hippocampal atrophy was reduced by about 23%, and expansion of ventricular volume was reduced by about 15%, both in comparison with matched controls from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Composite cognitive z-score improved significantly at 13 and 26 weeks and remained above baseline at 52 weeks in comparison with matched ADNI controls. “These are very promising data,” Dr. Hey told conference attendees.
He noted that the safety profile of ALZ-801 remains favorable and consistent with prior safety data. Common adverse events were mild nausea and SARS-CoV-2 infection. There were no drug-related serious events or amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-E).
The phase 3 APOLLOE4 study of ALZ-801 is underway. This double-blind, randomized study is comparing oral ALZ-801 with placebo over 78 weeks for roughly 300 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have the APOE4/4 genotype. APOLLOE4 is expected to be completed in mid 2024.
The APOLLOE4 study is supported by a $47 million grant from the National Institute on Aging. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted ALZ-801 fast-track designation.
More accessible option?
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, noted that the “biggest difference between this drug and others is that it is taken orally, rather than delivered through an infusion. This is important and valuable for reducing patient and caregiver burden and increasing ease of use and access.”
It’s also noteworthy that ALZ-801 was not associated with ARIA-E, “which has been reported in other antiamyloid trials and can occasionally be serious,” Dr. Griffin said.
Overall, he said the results are “encouraging, but more work is needed. If studies results continue to be positive, this treatment may provide a more accessible option for people who are at higher risk of ARIA,” Dr. Griffin said.
The study was funded by Alzheon. Dr. Hey is an employee of Alzheon and holds stock in the company. Dr. Griffin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – , represented by positive changes in plasma and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Use of the drug, ALZ-801 (Alzheon), led to a significant reduction of plasma phosphorylated–tau 181 (p-tau181) , a marker of amyloid-induced neuronal injury in Alzheimer’s disease, as well as slowing of hippocampal atrophy and stabilization of cognition.
“The 12-month results of our phase 2 trial support the finding that ALZ-801 blocks misfolding of amyloid monomers and subsequent formation of neurotoxic amyloid oligomers, the key initial step in the amyloid aggregation cascade, which leads to a rapid and sustained reduction of brain neurodegeneration as measured by plasma p-tau181,” John Hey, PhD, Alzheon’s chief scientific officer, said in a statement.
“The severalfold greater reduction on the p-tau181 biomarker in plasma compared to plaque-clearing antiamyloid antibodies, combined with preservation of brain hippocampal volume and their positive correlations with cognitive benefits, further validate the disease-modifying effects of ALZ-801 in Alzheimer’s patients,” Dr. Hey added.
The results were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
ALZ-801 is an optimized prodrug of tramiprosate that has been shown to inhibit amyloid-beta 42 aggregation into toxic oligomers.
The ongoing phase 2 study is evaluating the effects of oral ALZ-801 (265 mg twice daily) on biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology for 84 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have either the APOE4/4 or APOE3/4 genotype. These genotypes represent the majority of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
The mean age of the cohort was 69 years, and 51% are women; 70% had mild cognitive impairment, and 30% had mild Alzheimer’s disease. The mean Mini-Mental State Examination score for the cohort was 26.0. Roughly half were taking a cholinesterase inhibitor.
Significant plasma p-tau181 reduction was observed at 13 weeks. Levels were reduced by 41% by 52 weeks (P = .016). There was also a significant 5% reduction in plasma amyloid-beta 42 and 40 at 52 weeks (P = .002 and P = .005, respectively), Dr. Hey reported.
After 12 months of treatment, hippocampal atrophy was reduced by about 23%, and expansion of ventricular volume was reduced by about 15%, both in comparison with matched controls from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Composite cognitive z-score improved significantly at 13 and 26 weeks and remained above baseline at 52 weeks in comparison with matched ADNI controls. “These are very promising data,” Dr. Hey told conference attendees.
He noted that the safety profile of ALZ-801 remains favorable and consistent with prior safety data. Common adverse events were mild nausea and SARS-CoV-2 infection. There were no drug-related serious events or amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-E).
The phase 3 APOLLOE4 study of ALZ-801 is underway. This double-blind, randomized study is comparing oral ALZ-801 with placebo over 78 weeks for roughly 300 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have the APOE4/4 genotype. APOLLOE4 is expected to be completed in mid 2024.
The APOLLOE4 study is supported by a $47 million grant from the National Institute on Aging. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted ALZ-801 fast-track designation.
More accessible option?
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, noted that the “biggest difference between this drug and others is that it is taken orally, rather than delivered through an infusion. This is important and valuable for reducing patient and caregiver burden and increasing ease of use and access.”
It’s also noteworthy that ALZ-801 was not associated with ARIA-E, “which has been reported in other antiamyloid trials and can occasionally be serious,” Dr. Griffin said.
Overall, he said the results are “encouraging, but more work is needed. If studies results continue to be positive, this treatment may provide a more accessible option for people who are at higher risk of ARIA,” Dr. Griffin said.
The study was funded by Alzheon. Dr. Hey is an employee of Alzheon and holds stock in the company. Dr. Griffin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAN 2023
CPAP not only solution for sleep apnea
Although continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are the gold standard in the management of sleep apnea, several other treatments should be considered.
“Just because you have a hammer doesn’t mean everything is a nail,” Kimberly Hardin, MD, professor of clinical internal medicine at University of California, Davis, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
“Sleep has been underestimated in the health arena for many, many years,” said Dr. Hardin, who likened sound sleep to the “sixth vital sign.” “We know that sleep plays an integral role in our health.”
Surgical options include nasal surgery and maxillomandibular advancement surgery, also known as double-jaw surgery. Such procedures should be considered only for patients who are unwilling or unable to use CPAP or other nonsurgical treatments.
Sleep apnea occurs in 4% of adult men and 2% of adult women aged 30-60. Most commonly, obstructive sleep apnea involves the cessation or significant decrease in airflow while sleeping. The Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) is the number of times a patient experiences apnea or hypopnea during one night divided by the hours of sleep. Normal sleep AHI is fewer than five events per hour on average; mild sleep apnea is five to 14 events; moderate, 15-29; and severe, at least 30 events.
To identify sleep apnea, physicians have several tools at their disposal, starting with preliminary questionnaires that query patients as to whether they are having trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or are tired during the day. Additional assessment tools include sleep lab testing and at-home testing.
At-home testing has come to include more than the common devices that are worn around the chest and nose for a night.
“It’s not very fun looking,” Dr. Hardin said of the weighty, obtrusive monitoring devices. “So lots of folks have come up with some new ways of doing things.”
These new options incorporate headbands, wrist and finger devices, arterial tonometry, and sleep rings.
Studies show that U.S. adults do not get enough sleep, and poor-quality sleep is as inadequate as insufficient sleep. Barely a third of adults get the minimum 7 hours recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to report sleeping 7-9 hours and are more likely to report sleeping 6 or fewer hours than are non-Hispanic White and Hispanic adults.
Dr. Hardin said doctors can advise patients to keep their bedrooms quiet, dark, and cool with no TVs or electronics, to maintain regular wake and sleep times, and to stop consuming caffeine late in the day.
Insufficient or poor sleep can have wide-ranging implications on medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, obesity, immunodeficiency, cognitive function, mental health, and, ultimately, mortality, according to Dr. Hardin.
“Some people say, ‘Oh, never mind, I can sleep when I’m dead,’ “ Dr. Hardin said. But such a mentality can have a bearing on life expectancy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are the gold standard in the management of sleep apnea, several other treatments should be considered.
“Just because you have a hammer doesn’t mean everything is a nail,” Kimberly Hardin, MD, professor of clinical internal medicine at University of California, Davis, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
“Sleep has been underestimated in the health arena for many, many years,” said Dr. Hardin, who likened sound sleep to the “sixth vital sign.” “We know that sleep plays an integral role in our health.”
Surgical options include nasal surgery and maxillomandibular advancement surgery, also known as double-jaw surgery. Such procedures should be considered only for patients who are unwilling or unable to use CPAP or other nonsurgical treatments.
Sleep apnea occurs in 4% of adult men and 2% of adult women aged 30-60. Most commonly, obstructive sleep apnea involves the cessation or significant decrease in airflow while sleeping. The Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) is the number of times a patient experiences apnea or hypopnea during one night divided by the hours of sleep. Normal sleep AHI is fewer than five events per hour on average; mild sleep apnea is five to 14 events; moderate, 15-29; and severe, at least 30 events.
To identify sleep apnea, physicians have several tools at their disposal, starting with preliminary questionnaires that query patients as to whether they are having trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or are tired during the day. Additional assessment tools include sleep lab testing and at-home testing.
At-home testing has come to include more than the common devices that are worn around the chest and nose for a night.
“It’s not very fun looking,” Dr. Hardin said of the weighty, obtrusive monitoring devices. “So lots of folks have come up with some new ways of doing things.”
These new options incorporate headbands, wrist and finger devices, arterial tonometry, and sleep rings.
Studies show that U.S. adults do not get enough sleep, and poor-quality sleep is as inadequate as insufficient sleep. Barely a third of adults get the minimum 7 hours recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to report sleeping 7-9 hours and are more likely to report sleeping 6 or fewer hours than are non-Hispanic White and Hispanic adults.
Dr. Hardin said doctors can advise patients to keep their bedrooms quiet, dark, and cool with no TVs or electronics, to maintain regular wake and sleep times, and to stop consuming caffeine late in the day.
Insufficient or poor sleep can have wide-ranging implications on medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, obesity, immunodeficiency, cognitive function, mental health, and, ultimately, mortality, according to Dr. Hardin.
“Some people say, ‘Oh, never mind, I can sleep when I’m dead,’ “ Dr. Hardin said. But such a mentality can have a bearing on life expectancy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are the gold standard in the management of sleep apnea, several other treatments should be considered.
“Just because you have a hammer doesn’t mean everything is a nail,” Kimberly Hardin, MD, professor of clinical internal medicine at University of California, Davis, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
“Sleep has been underestimated in the health arena for many, many years,” said Dr. Hardin, who likened sound sleep to the “sixth vital sign.” “We know that sleep plays an integral role in our health.”
Surgical options include nasal surgery and maxillomandibular advancement surgery, also known as double-jaw surgery. Such procedures should be considered only for patients who are unwilling or unable to use CPAP or other nonsurgical treatments.
Sleep apnea occurs in 4% of adult men and 2% of adult women aged 30-60. Most commonly, obstructive sleep apnea involves the cessation or significant decrease in airflow while sleeping. The Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) is the number of times a patient experiences apnea or hypopnea during one night divided by the hours of sleep. Normal sleep AHI is fewer than five events per hour on average; mild sleep apnea is five to 14 events; moderate, 15-29; and severe, at least 30 events.
To identify sleep apnea, physicians have several tools at their disposal, starting with preliminary questionnaires that query patients as to whether they are having trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or are tired during the day. Additional assessment tools include sleep lab testing and at-home testing.
At-home testing has come to include more than the common devices that are worn around the chest and nose for a night.
“It’s not very fun looking,” Dr. Hardin said of the weighty, obtrusive monitoring devices. “So lots of folks have come up with some new ways of doing things.”
These new options incorporate headbands, wrist and finger devices, arterial tonometry, and sleep rings.
Studies show that U.S. adults do not get enough sleep, and poor-quality sleep is as inadequate as insufficient sleep. Barely a third of adults get the minimum 7 hours recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Hispanic Black adults are less likely to report sleeping 7-9 hours and are more likely to report sleeping 6 or fewer hours than are non-Hispanic White and Hispanic adults.
Dr. Hardin said doctors can advise patients to keep their bedrooms quiet, dark, and cool with no TVs or electronics, to maintain regular wake and sleep times, and to stop consuming caffeine late in the day.
Insufficient or poor sleep can have wide-ranging implications on medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, obesity, immunodeficiency, cognitive function, mental health, and, ultimately, mortality, according to Dr. Hardin.
“Some people say, ‘Oh, never mind, I can sleep when I’m dead,’ “ Dr. Hardin said. But such a mentality can have a bearing on life expectancy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2023