User login
Tackle obesity to drop risk for secondary cardiac event
Patients who had been hospitalized for heart attack or cardiovascular revascularization procedures commonly were overweight (46%) or had obesity (35%), but at a follow-up visit, few had lost weight or planned to do so, according to researchers who conduced a large European study.
The findings emphasize that obesity needs to be recognized as a disease that has to be optimally managed to lessen the risk for a secondary cardiovascular event, the authors stressed.
The study, by Dirk De Bacquer, PhD, professor, department of public health, Ghent (Belgium) University, and colleagues, was published recently in the European Heart Journal – Quality of Care and Clinical Outcomes.
The researchers analyzed data from more than 10,000 patients in the EUROASPIRE IV and V studies who were hospitalized for acute myocardial infarction (MI), coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and answered a survey 16 months later on average.
Although 20% of the patients with obesity had lost 5% or more of their initial weight, 16% had gained 5% or more of their initial weight.
Notably, “the discharge letter did not record the weight status in a quarter of [the patients with obesity] and a substantial proportion reported to have never been told by a healthcare professional [that they were] overweight,” the investigators wrote.
“It seems,” Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues noted, “that obesity is not considered by physicians as a serious medical problem, which requires attention, recommendations, and obvious advice on personal weight targets.”
However, “the benefits for patients who lost weight in our study, resulting in a healthier cardiovascular risk profile, are really worthwhile,” they pointed out.
Cardiovascular rehabilitation should include weight loss intervention
“The safest and most effective approach for managing body weight” in patients with coronary artery disease and obesity “is adopting a healthy eating pattern and increasing levels of physical activity,” they wrote.
Their findings that “patients who reported reducing their fat and sugar intake, consuming more fruit, vegetables, and fish and doing more regular physical activity, had significant weight loss,” support this.
Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues recommend that cardiovascular prevention and rehabilitation programs “should include weight loss intervention, including different forms of self-support, as a specific component of a comprehensive intervention to reduce total cardiovascular risk, extend life expectancy, and improve quality of life.”
Clinicians should “consider the incremental value of telehealth intervention as well as recently described pharmacological interventions,” they added, noting that the study did not look at these options or at metabolic surgery.
Invited to comment, one expert pointed out that two new observational studies of metabolic surgery in patients with obesity and coronary artery disease reported positive outcomes.
Another expert took issue with the “patient blaming” tone of the article and the lack of actionable ways to help patients lose weight.
Medical therapy or bariatric surgery as other options?
“The study demonstrated how prevalent obesity is in patients with heart disease“ and “confirmed how difficult it is to achieve weight loss, in particular, in patients with heart disease, where weight loss would be beneficial,” Erik Näslund, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Even though “current guidelines stress weight-loss counseling, some patients actually gained weight,” observed Dr. Näslund, of Danderyd Hospital and Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
On the other hand, patients who lost 5% or more of their initial weight had reduced comorbidities that are associated with cardiovascular disease.
“The best way to achieve long-term weight loss in patients with severe obesity is metabolic (bariatric) surgery,” noted Dr. Näslund, who was not involved in the study. “There are now two recent papers in the journal Circulation that demonstrate that metabolic surgery has a role in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with severe obesity” – one study from Dr. Näslund’s group (Circulation. 2021;143:1458-67), as previously reported, and one study from researchers in Ontario, Canada (Circulation. 2021;143:1468-80).
However, those were observational studies, and the findings would need to be confirmed in a randomized clinical trial before they could be used as recommended practice of care, he cautioned. In addition, most patients in the current study would not fulfill the minimum body weight criteria for metabolic surgery.
“Therefore, there is a need for intensified medical therapy for these patients,” as another treatment option, said Dr. Näslund.
“It would be interesting,” he speculated, “to study how the new glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist therapies could work in this setting as a weight loss agent and perhaps have a positive independent cardiovascular benefit.”
Obesity is a disease; clinicians need to be respectful
Meanwhile, Obesity Society fellow and spokesperson Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, said in an interview that she didn’t think the language and tone of the article was respectful for patients with obesity, and the researchers “talked about the old narrative of how we support patients with obesity.”
Lifestyle modification can be at the core of treatment, but medication or bariatric surgery may be other options to “help patients get to their best selves.
“Patients with obesity deserve to be cared for and treated with respect,” said Dr. Stanford, an obesity medicine physician scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Treatment needs to be individualized and clinicians need to listen to patient concerns. For example, a patient with obesity may not be able to follow advice to walk more. “I can barely stand up,” one patient with obesity and osteoarthritis told Dr. Stanford.
And patients’ insurance may not cover cardiac rehabilitation – especially patients from racial minorities or those with lower socioeconomic status, she noted.
“My feeling has always been that it is important to be respectful to all patients,” Dr. Näslund agreed. “I do agree that we need to recognize obesity as a chronic disease, and the paper in EHJ demonstrates this, as obesity was not registered in many of the discharge notes.
“If we as healthcare workers measured a weight of our patients the same way that we take a blood pressure,” he said, “perhaps the [stigma] of obesity would be reduced.”
Study findings
The researchers examined pooled data from EUROASPIRE IV (2012-13) and EUROASPIRE V (2016-17) surveys of patients who were overweight or had obesity who had been discharged from hospital after MI, CABG, or PCI to determine if they had received lifestyle advice for weight loss, if they had acted on this advice, and if losing weight altered their cardiovascular disease risk factors.
They identified 10,507 adult patients in 29 mainly European countries who had complete survey data.
The mean age of the patients was 63 at the time of their hospitalization; 25% were women. Many had hypertension (66%-88%), dyslipidemia (69%-80%), or diabetes (16%-37%).
The prevalence of obesity varied from 8% to 46% in men and from 18% to 57% in women, in different countries. Patients with obesity had a mean body weight of 97 kg (213 pounds).
One of the most “striking” findings was the “apparent lack of motivation” to lose weight, Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues wrote. Half of the patients with obesity had not attempted to lose weight in the month before the follow-up visit and most did not plan to do so in the following month.
Goal setting is an important aspect of behavior modification techniques, they wrote, yet 7% of the patients did not know their body weight and 21% did not have an optimal weight target.
Half of the patients had been advised to follow a cardiac rehabilitation program and two-thirds had been advised to follow dietary recommendations and move more.
Those who made positive dietary changes and were more physically active were more likely to lose at least 5% of their weight.
And patients who lost at least 5% of their initial weight were less likely to have hypertension, dyslipidemia, or diabetes compared with patients who had gained this much weight, which “is likely to translate into improved prognosis on the long term,” the authors wrote.
EUROASPIRE IV and V were supported through research grants to the European Society of Cardiology from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Emea Sarl, GlaxoSmithKline, Hoffmann-La Roche, and Merck, Sharp & Dohme (EUROASPIRE IV) and Amarin, Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, Ferrer, and Novo Nordisk (EUROASPIRE V). Dr. De Bacquer, Dr. Näslund, and Dr. Stanford have no disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who had been hospitalized for heart attack or cardiovascular revascularization procedures commonly were overweight (46%) or had obesity (35%), but at a follow-up visit, few had lost weight or planned to do so, according to researchers who conduced a large European study.
The findings emphasize that obesity needs to be recognized as a disease that has to be optimally managed to lessen the risk for a secondary cardiovascular event, the authors stressed.
The study, by Dirk De Bacquer, PhD, professor, department of public health, Ghent (Belgium) University, and colleagues, was published recently in the European Heart Journal – Quality of Care and Clinical Outcomes.
The researchers analyzed data from more than 10,000 patients in the EUROASPIRE IV and V studies who were hospitalized for acute myocardial infarction (MI), coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and answered a survey 16 months later on average.
Although 20% of the patients with obesity had lost 5% or more of their initial weight, 16% had gained 5% or more of their initial weight.
Notably, “the discharge letter did not record the weight status in a quarter of [the patients with obesity] and a substantial proportion reported to have never been told by a healthcare professional [that they were] overweight,” the investigators wrote.
“It seems,” Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues noted, “that obesity is not considered by physicians as a serious medical problem, which requires attention, recommendations, and obvious advice on personal weight targets.”
However, “the benefits for patients who lost weight in our study, resulting in a healthier cardiovascular risk profile, are really worthwhile,” they pointed out.
Cardiovascular rehabilitation should include weight loss intervention
“The safest and most effective approach for managing body weight” in patients with coronary artery disease and obesity “is adopting a healthy eating pattern and increasing levels of physical activity,” they wrote.
Their findings that “patients who reported reducing their fat and sugar intake, consuming more fruit, vegetables, and fish and doing more regular physical activity, had significant weight loss,” support this.
Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues recommend that cardiovascular prevention and rehabilitation programs “should include weight loss intervention, including different forms of self-support, as a specific component of a comprehensive intervention to reduce total cardiovascular risk, extend life expectancy, and improve quality of life.”
Clinicians should “consider the incremental value of telehealth intervention as well as recently described pharmacological interventions,” they added, noting that the study did not look at these options or at metabolic surgery.
Invited to comment, one expert pointed out that two new observational studies of metabolic surgery in patients with obesity and coronary artery disease reported positive outcomes.
Another expert took issue with the “patient blaming” tone of the article and the lack of actionable ways to help patients lose weight.
Medical therapy or bariatric surgery as other options?
“The study demonstrated how prevalent obesity is in patients with heart disease“ and “confirmed how difficult it is to achieve weight loss, in particular, in patients with heart disease, where weight loss would be beneficial,” Erik Näslund, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Even though “current guidelines stress weight-loss counseling, some patients actually gained weight,” observed Dr. Näslund, of Danderyd Hospital and Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
On the other hand, patients who lost 5% or more of their initial weight had reduced comorbidities that are associated with cardiovascular disease.
“The best way to achieve long-term weight loss in patients with severe obesity is metabolic (bariatric) surgery,” noted Dr. Näslund, who was not involved in the study. “There are now two recent papers in the journal Circulation that demonstrate that metabolic surgery has a role in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with severe obesity” – one study from Dr. Näslund’s group (Circulation. 2021;143:1458-67), as previously reported, and one study from researchers in Ontario, Canada (Circulation. 2021;143:1468-80).
However, those were observational studies, and the findings would need to be confirmed in a randomized clinical trial before they could be used as recommended practice of care, he cautioned. In addition, most patients in the current study would not fulfill the minimum body weight criteria for metabolic surgery.
“Therefore, there is a need for intensified medical therapy for these patients,” as another treatment option, said Dr. Näslund.
“It would be interesting,” he speculated, “to study how the new glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist therapies could work in this setting as a weight loss agent and perhaps have a positive independent cardiovascular benefit.”
Obesity is a disease; clinicians need to be respectful
Meanwhile, Obesity Society fellow and spokesperson Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, said in an interview that she didn’t think the language and tone of the article was respectful for patients with obesity, and the researchers “talked about the old narrative of how we support patients with obesity.”
Lifestyle modification can be at the core of treatment, but medication or bariatric surgery may be other options to “help patients get to their best selves.
“Patients with obesity deserve to be cared for and treated with respect,” said Dr. Stanford, an obesity medicine physician scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Treatment needs to be individualized and clinicians need to listen to patient concerns. For example, a patient with obesity may not be able to follow advice to walk more. “I can barely stand up,” one patient with obesity and osteoarthritis told Dr. Stanford.
And patients’ insurance may not cover cardiac rehabilitation – especially patients from racial minorities or those with lower socioeconomic status, she noted.
“My feeling has always been that it is important to be respectful to all patients,” Dr. Näslund agreed. “I do agree that we need to recognize obesity as a chronic disease, and the paper in EHJ demonstrates this, as obesity was not registered in many of the discharge notes.
“If we as healthcare workers measured a weight of our patients the same way that we take a blood pressure,” he said, “perhaps the [stigma] of obesity would be reduced.”
Study findings
The researchers examined pooled data from EUROASPIRE IV (2012-13) and EUROASPIRE V (2016-17) surveys of patients who were overweight or had obesity who had been discharged from hospital after MI, CABG, or PCI to determine if they had received lifestyle advice for weight loss, if they had acted on this advice, and if losing weight altered their cardiovascular disease risk factors.
They identified 10,507 adult patients in 29 mainly European countries who had complete survey data.
The mean age of the patients was 63 at the time of their hospitalization; 25% were women. Many had hypertension (66%-88%), dyslipidemia (69%-80%), or diabetes (16%-37%).
The prevalence of obesity varied from 8% to 46% in men and from 18% to 57% in women, in different countries. Patients with obesity had a mean body weight of 97 kg (213 pounds).
One of the most “striking” findings was the “apparent lack of motivation” to lose weight, Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues wrote. Half of the patients with obesity had not attempted to lose weight in the month before the follow-up visit and most did not plan to do so in the following month.
Goal setting is an important aspect of behavior modification techniques, they wrote, yet 7% of the patients did not know their body weight and 21% did not have an optimal weight target.
Half of the patients had been advised to follow a cardiac rehabilitation program and two-thirds had been advised to follow dietary recommendations and move more.
Those who made positive dietary changes and were more physically active were more likely to lose at least 5% of their weight.
And patients who lost at least 5% of their initial weight were less likely to have hypertension, dyslipidemia, or diabetes compared with patients who had gained this much weight, which “is likely to translate into improved prognosis on the long term,” the authors wrote.
EUROASPIRE IV and V were supported through research grants to the European Society of Cardiology from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Emea Sarl, GlaxoSmithKline, Hoffmann-La Roche, and Merck, Sharp & Dohme (EUROASPIRE IV) and Amarin, Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, Ferrer, and Novo Nordisk (EUROASPIRE V). Dr. De Bacquer, Dr. Näslund, and Dr. Stanford have no disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who had been hospitalized for heart attack or cardiovascular revascularization procedures commonly were overweight (46%) or had obesity (35%), but at a follow-up visit, few had lost weight or planned to do so, according to researchers who conduced a large European study.
The findings emphasize that obesity needs to be recognized as a disease that has to be optimally managed to lessen the risk for a secondary cardiovascular event, the authors stressed.
The study, by Dirk De Bacquer, PhD, professor, department of public health, Ghent (Belgium) University, and colleagues, was published recently in the European Heart Journal – Quality of Care and Clinical Outcomes.
The researchers analyzed data from more than 10,000 patients in the EUROASPIRE IV and V studies who were hospitalized for acute myocardial infarction (MI), coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and answered a survey 16 months later on average.
Although 20% of the patients with obesity had lost 5% or more of their initial weight, 16% had gained 5% or more of their initial weight.
Notably, “the discharge letter did not record the weight status in a quarter of [the patients with obesity] and a substantial proportion reported to have never been told by a healthcare professional [that they were] overweight,” the investigators wrote.
“It seems,” Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues noted, “that obesity is not considered by physicians as a serious medical problem, which requires attention, recommendations, and obvious advice on personal weight targets.”
However, “the benefits for patients who lost weight in our study, resulting in a healthier cardiovascular risk profile, are really worthwhile,” they pointed out.
Cardiovascular rehabilitation should include weight loss intervention
“The safest and most effective approach for managing body weight” in patients with coronary artery disease and obesity “is adopting a healthy eating pattern and increasing levels of physical activity,” they wrote.
Their findings that “patients who reported reducing their fat and sugar intake, consuming more fruit, vegetables, and fish and doing more regular physical activity, had significant weight loss,” support this.
Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues recommend that cardiovascular prevention and rehabilitation programs “should include weight loss intervention, including different forms of self-support, as a specific component of a comprehensive intervention to reduce total cardiovascular risk, extend life expectancy, and improve quality of life.”
Clinicians should “consider the incremental value of telehealth intervention as well as recently described pharmacological interventions,” they added, noting that the study did not look at these options or at metabolic surgery.
Invited to comment, one expert pointed out that two new observational studies of metabolic surgery in patients with obesity and coronary artery disease reported positive outcomes.
Another expert took issue with the “patient blaming” tone of the article and the lack of actionable ways to help patients lose weight.
Medical therapy or bariatric surgery as other options?
“The study demonstrated how prevalent obesity is in patients with heart disease“ and “confirmed how difficult it is to achieve weight loss, in particular, in patients with heart disease, where weight loss would be beneficial,” Erik Näslund, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Even though “current guidelines stress weight-loss counseling, some patients actually gained weight,” observed Dr. Näslund, of Danderyd Hospital and Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm.
On the other hand, patients who lost 5% or more of their initial weight had reduced comorbidities that are associated with cardiovascular disease.
“The best way to achieve long-term weight loss in patients with severe obesity is metabolic (bariatric) surgery,” noted Dr. Näslund, who was not involved in the study. “There are now two recent papers in the journal Circulation that demonstrate that metabolic surgery has a role in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with severe obesity” – one study from Dr. Näslund’s group (Circulation. 2021;143:1458-67), as previously reported, and one study from researchers in Ontario, Canada (Circulation. 2021;143:1468-80).
However, those were observational studies, and the findings would need to be confirmed in a randomized clinical trial before they could be used as recommended practice of care, he cautioned. In addition, most patients in the current study would not fulfill the minimum body weight criteria for metabolic surgery.
“Therefore, there is a need for intensified medical therapy for these patients,” as another treatment option, said Dr. Näslund.
“It would be interesting,” he speculated, “to study how the new glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist therapies could work in this setting as a weight loss agent and perhaps have a positive independent cardiovascular benefit.”
Obesity is a disease; clinicians need to be respectful
Meanwhile, Obesity Society fellow and spokesperson Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, said in an interview that she didn’t think the language and tone of the article was respectful for patients with obesity, and the researchers “talked about the old narrative of how we support patients with obesity.”
Lifestyle modification can be at the core of treatment, but medication or bariatric surgery may be other options to “help patients get to their best selves.
“Patients with obesity deserve to be cared for and treated with respect,” said Dr. Stanford, an obesity medicine physician scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Treatment needs to be individualized and clinicians need to listen to patient concerns. For example, a patient with obesity may not be able to follow advice to walk more. “I can barely stand up,” one patient with obesity and osteoarthritis told Dr. Stanford.
And patients’ insurance may not cover cardiac rehabilitation – especially patients from racial minorities or those with lower socioeconomic status, she noted.
“My feeling has always been that it is important to be respectful to all patients,” Dr. Näslund agreed. “I do agree that we need to recognize obesity as a chronic disease, and the paper in EHJ demonstrates this, as obesity was not registered in many of the discharge notes.
“If we as healthcare workers measured a weight of our patients the same way that we take a blood pressure,” he said, “perhaps the [stigma] of obesity would be reduced.”
Study findings
The researchers examined pooled data from EUROASPIRE IV (2012-13) and EUROASPIRE V (2016-17) surveys of patients who were overweight or had obesity who had been discharged from hospital after MI, CABG, or PCI to determine if they had received lifestyle advice for weight loss, if they had acted on this advice, and if losing weight altered their cardiovascular disease risk factors.
They identified 10,507 adult patients in 29 mainly European countries who had complete survey data.
The mean age of the patients was 63 at the time of their hospitalization; 25% were women. Many had hypertension (66%-88%), dyslipidemia (69%-80%), or diabetes (16%-37%).
The prevalence of obesity varied from 8% to 46% in men and from 18% to 57% in women, in different countries. Patients with obesity had a mean body weight of 97 kg (213 pounds).
One of the most “striking” findings was the “apparent lack of motivation” to lose weight, Dr. De Bacquer and colleagues wrote. Half of the patients with obesity had not attempted to lose weight in the month before the follow-up visit and most did not plan to do so in the following month.
Goal setting is an important aspect of behavior modification techniques, they wrote, yet 7% of the patients did not know their body weight and 21% did not have an optimal weight target.
Half of the patients had been advised to follow a cardiac rehabilitation program and two-thirds had been advised to follow dietary recommendations and move more.
Those who made positive dietary changes and were more physically active were more likely to lose at least 5% of their weight.
And patients who lost at least 5% of their initial weight were less likely to have hypertension, dyslipidemia, or diabetes compared with patients who had gained this much weight, which “is likely to translate into improved prognosis on the long term,” the authors wrote.
EUROASPIRE IV and V were supported through research grants to the European Society of Cardiology from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Emea Sarl, GlaxoSmithKline, Hoffmann-La Roche, and Merck, Sharp & Dohme (EUROASPIRE IV) and Amarin, Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, Ferrer, and Novo Nordisk (EUROASPIRE V). Dr. De Bacquer, Dr. Näslund, and Dr. Stanford have no disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Plant-based lignan intake linked to lower CHD risk
Consumption of a plant-based diet rich in lignans is associated with a lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), new research suggests.
In a prospective cohort study that followed almost 214,108 men and women who were free of CHD and cancer at baseline, increased long-term intake of lignans, polyphenolic substances produced by plants, was associated with significantly lower risk of total CHD in both men and women.
The benefit was increased in participants with a greater intake of fiber, suggesting that synergistic effects between the two might exist in relation to CHD reduction.
The results were published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Lignan is an estrogen-like molecule, so it exerts some estrogenic effects which are cardioprotective. It also has anti-inflammatory properties,” first author Yang Hu, ScD, a research fellow at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
“Our results that showed an inverse association between lignan consumption and heart disease risk were expected, because it is known that lignans, which are predominantly from plant-based foods, like whole grains, fruit, vegetables, red wine, and coffee, are all associated with lower CHD risk,” Dr. Hu said.
What is novel about the current study is that it established a threshold for lignan consumption, above which there is no CHD benefit, he said.
“It is not a matter of the more you consume, the lower your risk. There is a certain amount of lignan you have to reach, after which there is no more benefit,” Dr. Hu said.
Dr. Hu and associates prospectively followed 214,108 men and women in three cohorts who did not have cardiovascular disease or cancer at baseline. The cohorts were the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, Nurses’ Health Study, and Nurses’ Health Study II.
Diets were assessed using the Food Frequency Questionnaire every 2-4 years at follow-up visits.
During 5.5 million person-years of follow-up, Dr. Hu and associates documented 10,244 CHD cases, including 6,283 nonfatal myocardial infarctions and 3,961 fatal CHD cases.
The results showed that higher total lignan intake, and all individual lignan intake as well, were associated with significantly lower risk of total CHD.
Participants with higher total lignan intake were older and had more favorable health and lifestyle profiles including lower body mass index, lower prevalence of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, high levels of physical activity, and better diet quality.
Overall, the pooled hazard ratios of CHD were 0.85 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-0.92) for total lignans, 0.76 (95% CI, 0.71-0.82) for matairesinol, 0.87 (95% CI, 0.81-0.93) for secoisolariciresinol, 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83-0.95) for pinoresinol, and 0.89 (95% CI: 0.83- 0.95) for lariciresinol (all P values for trend ≤ .003).
In addition, nonlinear relationships were found for total lignan, matairesinol, and secoisolariciresinol: The risk reduction plateaued at intakes above approximately 300 mcg/d for total lignan; 10 mcg/d for matairesinol, and 100 mcg/d for secoisolariciresinol.
The inverse associations for total lignan intake were more apparent among participants with higher total fiber intake.
In addition, lignan intake was more strongly associated with plasma concentrations of enterolactone when fiber intake was higher.
Dr. Hu said a next avenue of research will explore the synergistic association between lignans and fiber in further lowering CHD risk.
Lignans are exclusively metabolized by gut microbiota, Dr. Hu noted. “This opens another avenue of research because we can take further steps to see how the gut microbiota compositions and fiber interact with the production of lignans and how these might affect disease risk for other conditions, such as diabetes.”
An important study
“The evidence is building that there is an association between polyphenol intake and chronic disease, especially for CVD [cardiovascular disease],” David J.A. Jenkins, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Plant polyphenols may be important components of healthy plant-based diets that contribute to freedom from chronic diseases such as CVD, diabetes, and possibly cancer and so are associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality,” they wrote.
“I think this is an important study even though the results are not unexpected,” Dr. Jenkins, professor in the departments of medicine and nutritional sciences at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“We do know that plant polyphenols are important sources of antioxidants and may have many protective roles in preventing destruction of proteins and DNA destruction, so the results here reinforce very strongly the concept of plant foods and their importance in the diet,” he said.
The data reaffirmed the value of eating a variety of plant foods and eating them in a less processed form, because they have higher amounts of their phenolic compounds, Dr. Jenkins said.
“Things like wheat, oats, barley, [and] whole grain foods will have more phenolic components with them, as do fruits and vegetables,” he said.
Dr. Hu and Dr. Jenkins disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Aversion of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumption of a plant-based diet rich in lignans is associated with a lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), new research suggests.
In a prospective cohort study that followed almost 214,108 men and women who were free of CHD and cancer at baseline, increased long-term intake of lignans, polyphenolic substances produced by plants, was associated with significantly lower risk of total CHD in both men and women.
The benefit was increased in participants with a greater intake of fiber, suggesting that synergistic effects between the two might exist in relation to CHD reduction.
The results were published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Lignan is an estrogen-like molecule, so it exerts some estrogenic effects which are cardioprotective. It also has anti-inflammatory properties,” first author Yang Hu, ScD, a research fellow at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
“Our results that showed an inverse association between lignan consumption and heart disease risk were expected, because it is known that lignans, which are predominantly from plant-based foods, like whole grains, fruit, vegetables, red wine, and coffee, are all associated with lower CHD risk,” Dr. Hu said.
What is novel about the current study is that it established a threshold for lignan consumption, above which there is no CHD benefit, he said.
“It is not a matter of the more you consume, the lower your risk. There is a certain amount of lignan you have to reach, after which there is no more benefit,” Dr. Hu said.
Dr. Hu and associates prospectively followed 214,108 men and women in three cohorts who did not have cardiovascular disease or cancer at baseline. The cohorts were the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, Nurses’ Health Study, and Nurses’ Health Study II.
Diets were assessed using the Food Frequency Questionnaire every 2-4 years at follow-up visits.
During 5.5 million person-years of follow-up, Dr. Hu and associates documented 10,244 CHD cases, including 6,283 nonfatal myocardial infarctions and 3,961 fatal CHD cases.
The results showed that higher total lignan intake, and all individual lignan intake as well, were associated with significantly lower risk of total CHD.
Participants with higher total lignan intake were older and had more favorable health and lifestyle profiles including lower body mass index, lower prevalence of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, high levels of physical activity, and better diet quality.
Overall, the pooled hazard ratios of CHD were 0.85 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-0.92) for total lignans, 0.76 (95% CI, 0.71-0.82) for matairesinol, 0.87 (95% CI, 0.81-0.93) for secoisolariciresinol, 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83-0.95) for pinoresinol, and 0.89 (95% CI: 0.83- 0.95) for lariciresinol (all P values for trend ≤ .003).
In addition, nonlinear relationships were found for total lignan, matairesinol, and secoisolariciresinol: The risk reduction plateaued at intakes above approximately 300 mcg/d for total lignan; 10 mcg/d for matairesinol, and 100 mcg/d for secoisolariciresinol.
The inverse associations for total lignan intake were more apparent among participants with higher total fiber intake.
In addition, lignan intake was more strongly associated with plasma concentrations of enterolactone when fiber intake was higher.
Dr. Hu said a next avenue of research will explore the synergistic association between lignans and fiber in further lowering CHD risk.
Lignans are exclusively metabolized by gut microbiota, Dr. Hu noted. “This opens another avenue of research because we can take further steps to see how the gut microbiota compositions and fiber interact with the production of lignans and how these might affect disease risk for other conditions, such as diabetes.”
An important study
“The evidence is building that there is an association between polyphenol intake and chronic disease, especially for CVD [cardiovascular disease],” David J.A. Jenkins, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Plant polyphenols may be important components of healthy plant-based diets that contribute to freedom from chronic diseases such as CVD, diabetes, and possibly cancer and so are associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality,” they wrote.
“I think this is an important study even though the results are not unexpected,” Dr. Jenkins, professor in the departments of medicine and nutritional sciences at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“We do know that plant polyphenols are important sources of antioxidants and may have many protective roles in preventing destruction of proteins and DNA destruction, so the results here reinforce very strongly the concept of plant foods and their importance in the diet,” he said.
The data reaffirmed the value of eating a variety of plant foods and eating them in a less processed form, because they have higher amounts of their phenolic compounds, Dr. Jenkins said.
“Things like wheat, oats, barley, [and] whole grain foods will have more phenolic components with them, as do fruits and vegetables,” he said.
Dr. Hu and Dr. Jenkins disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Aversion of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumption of a plant-based diet rich in lignans is associated with a lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), new research suggests.
In a prospective cohort study that followed almost 214,108 men and women who were free of CHD and cancer at baseline, increased long-term intake of lignans, polyphenolic substances produced by plants, was associated with significantly lower risk of total CHD in both men and women.
The benefit was increased in participants with a greater intake of fiber, suggesting that synergistic effects between the two might exist in relation to CHD reduction.
The results were published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“Lignan is an estrogen-like molecule, so it exerts some estrogenic effects which are cardioprotective. It also has anti-inflammatory properties,” first author Yang Hu, ScD, a research fellow at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
“Our results that showed an inverse association between lignan consumption and heart disease risk were expected, because it is known that lignans, which are predominantly from plant-based foods, like whole grains, fruit, vegetables, red wine, and coffee, are all associated with lower CHD risk,” Dr. Hu said.
What is novel about the current study is that it established a threshold for lignan consumption, above which there is no CHD benefit, he said.
“It is not a matter of the more you consume, the lower your risk. There is a certain amount of lignan you have to reach, after which there is no more benefit,” Dr. Hu said.
Dr. Hu and associates prospectively followed 214,108 men and women in three cohorts who did not have cardiovascular disease or cancer at baseline. The cohorts were the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, Nurses’ Health Study, and Nurses’ Health Study II.
Diets were assessed using the Food Frequency Questionnaire every 2-4 years at follow-up visits.
During 5.5 million person-years of follow-up, Dr. Hu and associates documented 10,244 CHD cases, including 6,283 nonfatal myocardial infarctions and 3,961 fatal CHD cases.
The results showed that higher total lignan intake, and all individual lignan intake as well, were associated with significantly lower risk of total CHD.
Participants with higher total lignan intake were older and had more favorable health and lifestyle profiles including lower body mass index, lower prevalence of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, high levels of physical activity, and better diet quality.
Overall, the pooled hazard ratios of CHD were 0.85 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-0.92) for total lignans, 0.76 (95% CI, 0.71-0.82) for matairesinol, 0.87 (95% CI, 0.81-0.93) for secoisolariciresinol, 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83-0.95) for pinoresinol, and 0.89 (95% CI: 0.83- 0.95) for lariciresinol (all P values for trend ≤ .003).
In addition, nonlinear relationships were found for total lignan, matairesinol, and secoisolariciresinol: The risk reduction plateaued at intakes above approximately 300 mcg/d for total lignan; 10 mcg/d for matairesinol, and 100 mcg/d for secoisolariciresinol.
The inverse associations for total lignan intake were more apparent among participants with higher total fiber intake.
In addition, lignan intake was more strongly associated with plasma concentrations of enterolactone when fiber intake was higher.
Dr. Hu said a next avenue of research will explore the synergistic association between lignans and fiber in further lowering CHD risk.
Lignans are exclusively metabolized by gut microbiota, Dr. Hu noted. “This opens another avenue of research because we can take further steps to see how the gut microbiota compositions and fiber interact with the production of lignans and how these might affect disease risk for other conditions, such as diabetes.”
An important study
“The evidence is building that there is an association between polyphenol intake and chronic disease, especially for CVD [cardiovascular disease],” David J.A. Jenkins, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Plant polyphenols may be important components of healthy plant-based diets that contribute to freedom from chronic diseases such as CVD, diabetes, and possibly cancer and so are associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality,” they wrote.
“I think this is an important study even though the results are not unexpected,” Dr. Jenkins, professor in the departments of medicine and nutritional sciences at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“We do know that plant polyphenols are important sources of antioxidants and may have many protective roles in preventing destruction of proteins and DNA destruction, so the results here reinforce very strongly the concept of plant foods and their importance in the diet,” he said.
The data reaffirmed the value of eating a variety of plant foods and eating them in a less processed form, because they have higher amounts of their phenolic compounds, Dr. Jenkins said.
“Things like wheat, oats, barley, [and] whole grain foods will have more phenolic components with them, as do fruits and vegetables,” he said.
Dr. Hu and Dr. Jenkins disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Aversion of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infusion shown effective for acquired von Willebrand disease
Acquired von Willebrand disease (aVWD) is a rare and serious condition associated with lymphoproliferative disorders, malignancy, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease. It is most commonly caused by monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), which acts to clear von Willebrand factor from the patient’s bloodstream. However, a continuous-infusion of plasma-derived von Willebrand factor (VWF) concentrate provided adequate hemostasis in aVWD resulting from MGUS, according to Kathryn E. Dane, PharmD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The infusion rapidly achieved target ristocetin cofactor activity with or without intravenous immunoglobulin in three patients, as detailed in the report published online in Blood Advances.
The three consecutive patients with aVWD were treated with plasma-derived VWF concentrate administered for periprocedural optimization (patient 1, an 85-year old woman) or to treat bleeding episodes (patient 2, an 88-year-old man; and patient 3, a 53-year-old woman). Factor VIII activity was measured via a 1-stage clotting test and von Willebrand factor activity was measured with a ristocetin cofactor assay.
Promising results
All three patients demonstrated increased VWF ristocetin cofactor and factor VIII activities within hours of initiation of the continuous infusion concentrate, according to the report.
“We hypothesize that the efficacy of CI VWF concentrate in aVWD may be related to continuous provision of VWF, allowing binding and neutralization of anti-VWF IgG antibodies, and providing adequate circulating unbound VWF for appropriate hemostatic efficacy,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no competing financial interests.
Acquired von Willebrand disease (aVWD) is a rare and serious condition associated with lymphoproliferative disorders, malignancy, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease. It is most commonly caused by monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), which acts to clear von Willebrand factor from the patient’s bloodstream. However, a continuous-infusion of plasma-derived von Willebrand factor (VWF) concentrate provided adequate hemostasis in aVWD resulting from MGUS, according to Kathryn E. Dane, PharmD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The infusion rapidly achieved target ristocetin cofactor activity with or without intravenous immunoglobulin in three patients, as detailed in the report published online in Blood Advances.
The three consecutive patients with aVWD were treated with plasma-derived VWF concentrate administered for periprocedural optimization (patient 1, an 85-year old woman) or to treat bleeding episodes (patient 2, an 88-year-old man; and patient 3, a 53-year-old woman). Factor VIII activity was measured via a 1-stage clotting test and von Willebrand factor activity was measured with a ristocetin cofactor assay.
Promising results
All three patients demonstrated increased VWF ristocetin cofactor and factor VIII activities within hours of initiation of the continuous infusion concentrate, according to the report.
“We hypothesize that the efficacy of CI VWF concentrate in aVWD may be related to continuous provision of VWF, allowing binding and neutralization of anti-VWF IgG antibodies, and providing adequate circulating unbound VWF for appropriate hemostatic efficacy,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no competing financial interests.
Acquired von Willebrand disease (aVWD) is a rare and serious condition associated with lymphoproliferative disorders, malignancy, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease. It is most commonly caused by monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), which acts to clear von Willebrand factor from the patient’s bloodstream. However, a continuous-infusion of plasma-derived von Willebrand factor (VWF) concentrate provided adequate hemostasis in aVWD resulting from MGUS, according to Kathryn E. Dane, PharmD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The infusion rapidly achieved target ristocetin cofactor activity with or without intravenous immunoglobulin in three patients, as detailed in the report published online in Blood Advances.
The three consecutive patients with aVWD were treated with plasma-derived VWF concentrate administered for periprocedural optimization (patient 1, an 85-year old woman) or to treat bleeding episodes (patient 2, an 88-year-old man; and patient 3, a 53-year-old woman). Factor VIII activity was measured via a 1-stage clotting test and von Willebrand factor activity was measured with a ristocetin cofactor assay.
Promising results
All three patients demonstrated increased VWF ristocetin cofactor and factor VIII activities within hours of initiation of the continuous infusion concentrate, according to the report.
“We hypothesize that the efficacy of CI VWF concentrate in aVWD may be related to continuous provision of VWF, allowing binding and neutralization of anti-VWF IgG antibodies, and providing adequate circulating unbound VWF for appropriate hemostatic efficacy,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no competing financial interests.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
He Needs More Than Lip Service for This Lesion
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “g”).
DISCUSSION
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lip—almost always the lower lip—is quite common and appears to be caused by several factors. These can include exposure to ultraviolet light, ionizing radiation, arsenic (through contaminated groundwater or certain medications), tobacco, and human papillomavirus.
Early on in its manifestation, this patient’s SCC could have been excised with margins, producing an excellent prognosis. But with the extended delay in diagnosis and apparent related adenopathy, the patient’s future looked much less certain. At the very least, he would face extensive surgery, possible lymph node dissection, and maybe chemo and radiation therapies. Metastasis to the brain and lung(s) were very real possibilities.
The history associated with this case is far from uncommon, since these cancers are often mistaken for infection, which further delays correct diagnosis and treatment. Compounding this problem—and for reasons unclear to this author—affected patients are often referred to the wrong specialist. The critical missing piece of information was a diagnosis, which could only have been obtained through an incisional biopsy. Only then could the patient be referred appropriately.
Fortunately, in this case, the patient ended up under the care of a head and neck surgeon who planned to address this tumor after imaging of the head, neck, and lungs was completed.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “g”).
DISCUSSION
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lip—almost always the lower lip—is quite common and appears to be caused by several factors. These can include exposure to ultraviolet light, ionizing radiation, arsenic (through contaminated groundwater or certain medications), tobacco, and human papillomavirus.
Early on in its manifestation, this patient’s SCC could have been excised with margins, producing an excellent prognosis. But with the extended delay in diagnosis and apparent related adenopathy, the patient’s future looked much less certain. At the very least, he would face extensive surgery, possible lymph node dissection, and maybe chemo and radiation therapies. Metastasis to the brain and lung(s) were very real possibilities.
The history associated with this case is far from uncommon, since these cancers are often mistaken for infection, which further delays correct diagnosis and treatment. Compounding this problem—and for reasons unclear to this author—affected patients are often referred to the wrong specialist. The critical missing piece of information was a diagnosis, which could only have been obtained through an incisional biopsy. Only then could the patient be referred appropriately.
Fortunately, in this case, the patient ended up under the care of a head and neck surgeon who planned to address this tumor after imaging of the head, neck, and lungs was completed.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “g”).
DISCUSSION
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lip—almost always the lower lip—is quite common and appears to be caused by several factors. These can include exposure to ultraviolet light, ionizing radiation, arsenic (through contaminated groundwater or certain medications), tobacco, and human papillomavirus.
Early on in its manifestation, this patient’s SCC could have been excised with margins, producing an excellent prognosis. But with the extended delay in diagnosis and apparent related adenopathy, the patient’s future looked much less certain. At the very least, he would face extensive surgery, possible lymph node dissection, and maybe chemo and radiation therapies. Metastasis to the brain and lung(s) were very real possibilities.
The history associated with this case is far from uncommon, since these cancers are often mistaken for infection, which further delays correct diagnosis and treatment. Compounding this problem—and for reasons unclear to this author—affected patients are often referred to the wrong specialist. The critical missing piece of information was a diagnosis, which could only have been obtained through an incisional biopsy. Only then could the patient be referred appropriately.
Fortunately, in this case, the patient ended up under the care of a head and neck surgeon who planned to address this tumor after imaging of the head, neck, and lungs was completed.
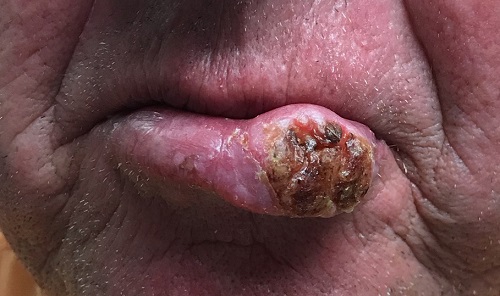
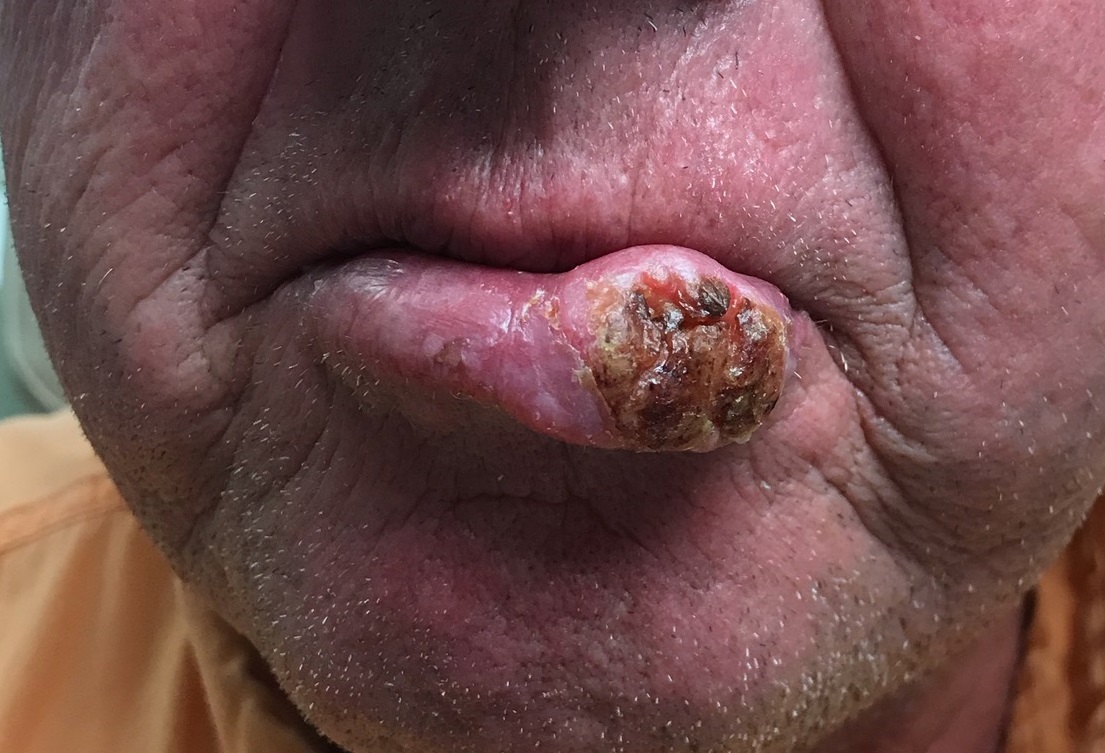
Several years ago, the patient developed what he thought was a cold sore, which waxed and waned but never quite healed. It grew considerably over time but caused no pain, so the patient and his wife assumed it was benign. A few times over the years, his primary care provider (PCP) prescribed oral antibiotics, then later acyclovir, to treat the lesion. When it became large enough to interfere with normal speech, the patient’s PCP referred him to a dentist, who in turn arranged an urgent consultation with dermatology.
The patient was retired but had spent more than 50 years working and recreating outdoors without any protection. For 40 of those adult years, he had smoked. His health was good in other respects.
The 3-cm warty mass on the vermillion surface of the lower lip, just to the left of center, was focally eroded and quite firm to touch. Palpation of local nodal locations revealed several fixed nontender nodes, most notably in the submental area. His sun-exposed skin was quite sun damaged, with stellate scarring, abundant dyschromia, telangiectasias, and marked solar atrophy.
A 5-mm punch biopsy was performed, showing poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma.
Colorectal polyps often recur after incomplete resection
When gastroenterologists resect polyps during colonoscopy, they may inadvertently leave some neoplastic tissue behind. Biopsies from resection margins sometimes contain polyp remnants, even after a lesion has been visibly removed, research has shown. But the significance of incomplete resection has been unclear.
A new study indicates that incomplete resection, compared with complete resection, substantially increases the likelihood that a polyp will be found during follow-up colonoscopy.
The evidence “strongly supports the hypothesis” that residual polyp tissue likely contributes to neoplastic polyp recurrence and, by extension, interval colorectal cancer, said study author Heiko Pohl, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Pohl is affiliated with the White River Junction Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Vermont and Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center and Dartmouth Geisel School of Medicine in Hanover, N.H.
Among 166 participants in the Complete Adenoma Resection (CARE) study who went on to have a surveillance colonoscopy in the following years, metachronous neoplasia was detected more often in colon segments where polyps had been incompletely resected, compared with colon segments with complete resections (52% vs. 23%), according to a study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
In addition, colon segments that had had incomplete resections in the CARE study were more likely to have polyps that were 10 mm or greater (18% vs. 3%). The 32 participants who had at least one incomplete resection during the original CARE study were three times more likely to have a polyp at follow-up, Dr. Pohl and coauthors found.
There were no instances of cancer or high-grade dysplasia during follow-up, however.
Key questions remain, including “Why do people get cancer after colonoscopy?” said Shai Friedland, MD, MS, who was not involved in the study. “Maybe it is because of these polyps that were not removed completely.”
On the other hand, lesions that are more difficult to see in the first place and more dangerous might be responsible when colorectal cancer does occur after colonoscopy, said Dr. Friedland, professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University and a gastroenterologist at Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System.
Although it is not surprising that polyp remnants may appear as polyps during follow-up examinations, the difference in polyp recurrence between groups “must be quite striking” for it to clearly be seen in this small study, Dr. Friedland said. The results suggest that there is a need to “redouble our efforts to make sure that we remove polyps completely and not just hope that they disappear after an incomplete job,” he added.
In the CARE study, which was conducted between 2009 and 2012 at two academic medical centers, researchers found that about 10% of neoplastic polyps with visibly complete removal may nonetheless be incompletely resected, based on the presence of neoplastic tissue in biopsies taken from resection margins.
The investigators focused on 5- to 20-mm nonpedunculated colorectal polyps that were removed during routine polypectomy using electrocautery snare resection.
Participants with incomplete polyp resections were encouraged to have a surveillance examination within 1 year, and those with complete resections received guideline-based surveillance recommendations. In the follow-up analysis, those with an incomplete resection had a median time to first examination of 17 months, and those with complete resections had a median time to first examination of 45 months.
“These results highlight the importance of achieving complete resection because the risk for subsequent advanced neoplasia detection statistically significantly increases without it,” Dr. Pohl said. “The large polyp size after incomplete resection within a generally short follow-up time may imply fast growth, even if none of the presumed recurrent polyps contained advanced histologic characteristics.”
Between-group differences in the participants and polyps could confound the observations, the authors noted. It is possible that endoscopists who did the follow-up colonoscopies looked harder for polyps in colon segments that had prior incomplete resections, on account of the initial study findings, they said. “It is also plausible that endoscopists with a greater incomplete resection rate would be more likely to miss polyps, which could then be detected at follow-up,” though detection and resection skills do not necessarily correlate, the investigators said.
With resection, the goal is to remove the polyp in one piece with clear margins, and researchers have known that the polyp removal techniques used in the study “are far from perfect,” Dr. Friedland said. One question is whether the field should focus on improving standard techniques, or incorporating newer, more advanced techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection, which is effective but may entail significant perforation risk when performed by someone who is not proficient, he said.
“One of the major focuses we had over the years is finding the polyps to prevent future cancer,” Dr. Pohl said in an interview. But the CARE study showed that “we do not do a good job of taking polyps off completely,” he added. The present analysis underscores that clinicians should do their best to remove polyps completely, even if they lack a way to confirm complete resection in routine practice, as is currently the case, Dr. Pohl said. To that end, clinicians should aim to refine their skills and techniques. Video evaluations with guidance from experts may prove helpful, he suggested. “We need to think hard about quality assessment,” Dr. Pohl said.
Dr. Pohl disclosed grants from Boston Scientific, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, and Steris outside of the study. Dr. Friedland had no disclosures.
When gastroenterologists resect polyps during colonoscopy, they may inadvertently leave some neoplastic tissue behind. Biopsies from resection margins sometimes contain polyp remnants, even after a lesion has been visibly removed, research has shown. But the significance of incomplete resection has been unclear.
A new study indicates that incomplete resection, compared with complete resection, substantially increases the likelihood that a polyp will be found during follow-up colonoscopy.
The evidence “strongly supports the hypothesis” that residual polyp tissue likely contributes to neoplastic polyp recurrence and, by extension, interval colorectal cancer, said study author Heiko Pohl, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Pohl is affiliated with the White River Junction Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Vermont and Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center and Dartmouth Geisel School of Medicine in Hanover, N.H.
Among 166 participants in the Complete Adenoma Resection (CARE) study who went on to have a surveillance colonoscopy in the following years, metachronous neoplasia was detected more often in colon segments where polyps had been incompletely resected, compared with colon segments with complete resections (52% vs. 23%), according to a study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
In addition, colon segments that had had incomplete resections in the CARE study were more likely to have polyps that were 10 mm or greater (18% vs. 3%). The 32 participants who had at least one incomplete resection during the original CARE study were three times more likely to have a polyp at follow-up, Dr. Pohl and coauthors found.
There were no instances of cancer or high-grade dysplasia during follow-up, however.
Key questions remain, including “Why do people get cancer after colonoscopy?” said Shai Friedland, MD, MS, who was not involved in the study. “Maybe it is because of these polyps that were not removed completely.”
On the other hand, lesions that are more difficult to see in the first place and more dangerous might be responsible when colorectal cancer does occur after colonoscopy, said Dr. Friedland, professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University and a gastroenterologist at Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System.
Although it is not surprising that polyp remnants may appear as polyps during follow-up examinations, the difference in polyp recurrence between groups “must be quite striking” for it to clearly be seen in this small study, Dr. Friedland said. The results suggest that there is a need to “redouble our efforts to make sure that we remove polyps completely and not just hope that they disappear after an incomplete job,” he added.
In the CARE study, which was conducted between 2009 and 2012 at two academic medical centers, researchers found that about 10% of neoplastic polyps with visibly complete removal may nonetheless be incompletely resected, based on the presence of neoplastic tissue in biopsies taken from resection margins.
The investigators focused on 5- to 20-mm nonpedunculated colorectal polyps that were removed during routine polypectomy using electrocautery snare resection.
Participants with incomplete polyp resections were encouraged to have a surveillance examination within 1 year, and those with complete resections received guideline-based surveillance recommendations. In the follow-up analysis, those with an incomplete resection had a median time to first examination of 17 months, and those with complete resections had a median time to first examination of 45 months.
“These results highlight the importance of achieving complete resection because the risk for subsequent advanced neoplasia detection statistically significantly increases without it,” Dr. Pohl said. “The large polyp size after incomplete resection within a generally short follow-up time may imply fast growth, even if none of the presumed recurrent polyps contained advanced histologic characteristics.”
Between-group differences in the participants and polyps could confound the observations, the authors noted. It is possible that endoscopists who did the follow-up colonoscopies looked harder for polyps in colon segments that had prior incomplete resections, on account of the initial study findings, they said. “It is also plausible that endoscopists with a greater incomplete resection rate would be more likely to miss polyps, which could then be detected at follow-up,” though detection and resection skills do not necessarily correlate, the investigators said.
With resection, the goal is to remove the polyp in one piece with clear margins, and researchers have known that the polyp removal techniques used in the study “are far from perfect,” Dr. Friedland said. One question is whether the field should focus on improving standard techniques, or incorporating newer, more advanced techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection, which is effective but may entail significant perforation risk when performed by someone who is not proficient, he said.
“One of the major focuses we had over the years is finding the polyps to prevent future cancer,” Dr. Pohl said in an interview. But the CARE study showed that “we do not do a good job of taking polyps off completely,” he added. The present analysis underscores that clinicians should do their best to remove polyps completely, even if they lack a way to confirm complete resection in routine practice, as is currently the case, Dr. Pohl said. To that end, clinicians should aim to refine their skills and techniques. Video evaluations with guidance from experts may prove helpful, he suggested. “We need to think hard about quality assessment,” Dr. Pohl said.
Dr. Pohl disclosed grants from Boston Scientific, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, and Steris outside of the study. Dr. Friedland had no disclosures.
When gastroenterologists resect polyps during colonoscopy, they may inadvertently leave some neoplastic tissue behind. Biopsies from resection margins sometimes contain polyp remnants, even after a lesion has been visibly removed, research has shown. But the significance of incomplete resection has been unclear.
A new study indicates that incomplete resection, compared with complete resection, substantially increases the likelihood that a polyp will be found during follow-up colonoscopy.
The evidence “strongly supports the hypothesis” that residual polyp tissue likely contributes to neoplastic polyp recurrence and, by extension, interval colorectal cancer, said study author Heiko Pohl, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Pohl is affiliated with the White River Junction Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Vermont and Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center and Dartmouth Geisel School of Medicine in Hanover, N.H.
Among 166 participants in the Complete Adenoma Resection (CARE) study who went on to have a surveillance colonoscopy in the following years, metachronous neoplasia was detected more often in colon segments where polyps had been incompletely resected, compared with colon segments with complete resections (52% vs. 23%), according to a study in Annals of Internal Medicine.
In addition, colon segments that had had incomplete resections in the CARE study were more likely to have polyps that were 10 mm or greater (18% vs. 3%). The 32 participants who had at least one incomplete resection during the original CARE study were three times more likely to have a polyp at follow-up, Dr. Pohl and coauthors found.
There were no instances of cancer or high-grade dysplasia during follow-up, however.
Key questions remain, including “Why do people get cancer after colonoscopy?” said Shai Friedland, MD, MS, who was not involved in the study. “Maybe it is because of these polyps that were not removed completely.”
On the other hand, lesions that are more difficult to see in the first place and more dangerous might be responsible when colorectal cancer does occur after colonoscopy, said Dr. Friedland, professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University and a gastroenterologist at Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System.
Although it is not surprising that polyp remnants may appear as polyps during follow-up examinations, the difference in polyp recurrence between groups “must be quite striking” for it to clearly be seen in this small study, Dr. Friedland said. The results suggest that there is a need to “redouble our efforts to make sure that we remove polyps completely and not just hope that they disappear after an incomplete job,” he added.
In the CARE study, which was conducted between 2009 and 2012 at two academic medical centers, researchers found that about 10% of neoplastic polyps with visibly complete removal may nonetheless be incompletely resected, based on the presence of neoplastic tissue in biopsies taken from resection margins.
The investigators focused on 5- to 20-mm nonpedunculated colorectal polyps that were removed during routine polypectomy using electrocautery snare resection.
Participants with incomplete polyp resections were encouraged to have a surveillance examination within 1 year, and those with complete resections received guideline-based surveillance recommendations. In the follow-up analysis, those with an incomplete resection had a median time to first examination of 17 months, and those with complete resections had a median time to first examination of 45 months.
“These results highlight the importance of achieving complete resection because the risk for subsequent advanced neoplasia detection statistically significantly increases without it,” Dr. Pohl said. “The large polyp size after incomplete resection within a generally short follow-up time may imply fast growth, even if none of the presumed recurrent polyps contained advanced histologic characteristics.”
Between-group differences in the participants and polyps could confound the observations, the authors noted. It is possible that endoscopists who did the follow-up colonoscopies looked harder for polyps in colon segments that had prior incomplete resections, on account of the initial study findings, they said. “It is also plausible that endoscopists with a greater incomplete resection rate would be more likely to miss polyps, which could then be detected at follow-up,” though detection and resection skills do not necessarily correlate, the investigators said.
With resection, the goal is to remove the polyp in one piece with clear margins, and researchers have known that the polyp removal techniques used in the study “are far from perfect,” Dr. Friedland said. One question is whether the field should focus on improving standard techniques, or incorporating newer, more advanced techniques such as endoscopic submucosal dissection, which is effective but may entail significant perforation risk when performed by someone who is not proficient, he said.
“One of the major focuses we had over the years is finding the polyps to prevent future cancer,” Dr. Pohl said in an interview. But the CARE study showed that “we do not do a good job of taking polyps off completely,” he added. The present analysis underscores that clinicians should do their best to remove polyps completely, even if they lack a way to confirm complete resection in routine practice, as is currently the case, Dr. Pohl said. To that end, clinicians should aim to refine their skills and techniques. Video evaluations with guidance from experts may prove helpful, he suggested. “We need to think hard about quality assessment,” Dr. Pohl said.
Dr. Pohl disclosed grants from Boston Scientific, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, and Steris outside of the study. Dr. Friedland had no disclosures.
Medical residents need breastfeeding support too
As working mothers with babies in tow when the COVID-19 crisis struck, countless uncertainties threatened our already precarious work-life balance. We suddenly had many questions:
“If my daycare closes, what will I do for childcare?”
“How do I navigate diaper changes, feedings, and naps with my hectic remote work schedule?”
“If I’m constantly interrupted during the day, should I skip sleep to catch up on work and not let my colleagues down?”
As professionals who work closely with medical trainees, we knew our parenting dilemmas were being experienced even more acutely by our frontline worker colleagues.
Medical training is an increasingly common time to start a family. In a recent study, 34% of trainees in Harvard-affiliated residency programs became parents during training, and another 52% planned to do so. Trainees have higher breastfeeding initiation rates but lower continuation rates than the general population. Early nursing cessation among trainees is well documented nationally and is most often attributed to work-related barriers. These barriers range from insufficient time and limited access to facilities to a lack of support and discrimination by supervisors and peers.
This trend does not discriminate by specialty. Even among training programs known to be “family friendly,” the average duration of nursing is just 4.5 months. Residents of color are disproportionately affected by inadequate support. Studies show that Black parents breastfeed at lower rates than White parents. This has been largely attributed to structural racism and implicit bias, such as Black parents receiving less assistance initiating nursing after delivery. Adequate lactation support and inclusivity are also lacking for transgender parents who choose to breastfeed or chestfeed.
The very nature of residency training, which includes shifts that can span more than 24 hours, conflicts with many health-promoting behaviors like sleeping and eating well. However, its interference with lactation is correlated with gender. Women are disproportionately affected by the negative outcomes of unmet lactation goals. These include work-life imbalance, career dissatisfaction, and negative emotions. In a study of pediatric residents, one in four did not achieve their breastfeeding goals. Respondents reported feeling “sad, devastated, defeated, disappointed, guilty, embarrassed, frustrated, angry, like a failure, and inadequate.” Among physician mothers more broadly, discrimination related to pregnancy, parental leave, and nursing is associated with higher self-reported burnout.
Navigating nursing during residency training has more than just emotional and psychological consequences – it also has professional ones. Pursuing personal lactation goals can delay residency program completion and board certification, influence specialty selection, negatively impact research productivity, impede career advancement, and lead to misgivings about career choice.
Trainees and their families are not the only ones harmed by inadequate support in residency programs. Patients and their families are affected, too. Research suggests that physicians’ personal breastfeeding practices affect the advice they give to patients. Those who receive lactation support are more likely to help patients meet their own goals. In the previously mentioned study of pediatric residents, more than 90% of the 400 respondents said their own or their partner’s nursing experience affected their interaction with lactating patients in their clinic or hospital.
Increased lactation support is a straightforward, low-cost, high-impact intervention. It benefits trainee well-being, satisfaction, workflow, and future patient care. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education mandated in July 2019 that all residency programs provide adequate lactation facilities – including refrigeration capabilities and proximity for safe patient care. However, to our knowledge, rates of compliance with this new policy and citation for noncompliance have yet to be seen. Regardless, facilities alone are not enough. Residency programs should develop and enforce formal lactation policies.
Several institutions have successfully piloted such policies in recent years. One in particular from the University of Michigan’s surgery residency program inspired the development of a lactation policy within the internal medicine residency at our institution. These policies designate appropriate spaces at each clinical rotation site, clarify that residents are encouraged to take pumping breaks as needed – in coordination with clinical teams so as not to compromise patient care – and communicate support from supervisors.
Our program also established an informal peer mentoring program. Residents with experience pumping at work pair up with newer trainees. The policy benefits residents who wish to chestfeed or breastfeed, normalizes lactation, and empowers trainees by diminishing the need to ask for individual accommodations. It also costs the program nothing.
As more women enter medicine and more trainees become parents during residency, the need for support in this area will only continue to grow. The widespread lack of such resources, and the fact that clean and private facilities are only now being mandated, is symbolic. If even this basic need is rarely acknowledged or met, what other resident needs are being neglected?
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As working mothers with babies in tow when the COVID-19 crisis struck, countless uncertainties threatened our already precarious work-life balance. We suddenly had many questions:
“If my daycare closes, what will I do for childcare?”
“How do I navigate diaper changes, feedings, and naps with my hectic remote work schedule?”
“If I’m constantly interrupted during the day, should I skip sleep to catch up on work and not let my colleagues down?”
As professionals who work closely with medical trainees, we knew our parenting dilemmas were being experienced even more acutely by our frontline worker colleagues.
Medical training is an increasingly common time to start a family. In a recent study, 34% of trainees in Harvard-affiliated residency programs became parents during training, and another 52% planned to do so. Trainees have higher breastfeeding initiation rates but lower continuation rates than the general population. Early nursing cessation among trainees is well documented nationally and is most often attributed to work-related barriers. These barriers range from insufficient time and limited access to facilities to a lack of support and discrimination by supervisors and peers.
This trend does not discriminate by specialty. Even among training programs known to be “family friendly,” the average duration of nursing is just 4.5 months. Residents of color are disproportionately affected by inadequate support. Studies show that Black parents breastfeed at lower rates than White parents. This has been largely attributed to structural racism and implicit bias, such as Black parents receiving less assistance initiating nursing after delivery. Adequate lactation support and inclusivity are also lacking for transgender parents who choose to breastfeed or chestfeed.
The very nature of residency training, which includes shifts that can span more than 24 hours, conflicts with many health-promoting behaviors like sleeping and eating well. However, its interference with lactation is correlated with gender. Women are disproportionately affected by the negative outcomes of unmet lactation goals. These include work-life imbalance, career dissatisfaction, and negative emotions. In a study of pediatric residents, one in four did not achieve their breastfeeding goals. Respondents reported feeling “sad, devastated, defeated, disappointed, guilty, embarrassed, frustrated, angry, like a failure, and inadequate.” Among physician mothers more broadly, discrimination related to pregnancy, parental leave, and nursing is associated with higher self-reported burnout.
Navigating nursing during residency training has more than just emotional and psychological consequences – it also has professional ones. Pursuing personal lactation goals can delay residency program completion and board certification, influence specialty selection, negatively impact research productivity, impede career advancement, and lead to misgivings about career choice.
Trainees and their families are not the only ones harmed by inadequate support in residency programs. Patients and their families are affected, too. Research suggests that physicians’ personal breastfeeding practices affect the advice they give to patients. Those who receive lactation support are more likely to help patients meet their own goals. In the previously mentioned study of pediatric residents, more than 90% of the 400 respondents said their own or their partner’s nursing experience affected their interaction with lactating patients in their clinic or hospital.
Increased lactation support is a straightforward, low-cost, high-impact intervention. It benefits trainee well-being, satisfaction, workflow, and future patient care. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education mandated in July 2019 that all residency programs provide adequate lactation facilities – including refrigeration capabilities and proximity for safe patient care. However, to our knowledge, rates of compliance with this new policy and citation for noncompliance have yet to be seen. Regardless, facilities alone are not enough. Residency programs should develop and enforce formal lactation policies.
Several institutions have successfully piloted such policies in recent years. One in particular from the University of Michigan’s surgery residency program inspired the development of a lactation policy within the internal medicine residency at our institution. These policies designate appropriate spaces at each clinical rotation site, clarify that residents are encouraged to take pumping breaks as needed – in coordination with clinical teams so as not to compromise patient care – and communicate support from supervisors.
Our program also established an informal peer mentoring program. Residents with experience pumping at work pair up with newer trainees. The policy benefits residents who wish to chestfeed or breastfeed, normalizes lactation, and empowers trainees by diminishing the need to ask for individual accommodations. It also costs the program nothing.
As more women enter medicine and more trainees become parents during residency, the need for support in this area will only continue to grow. The widespread lack of such resources, and the fact that clean and private facilities are only now being mandated, is symbolic. If even this basic need is rarely acknowledged or met, what other resident needs are being neglected?
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As working mothers with babies in tow when the COVID-19 crisis struck, countless uncertainties threatened our already precarious work-life balance. We suddenly had many questions:
“If my daycare closes, what will I do for childcare?”
“How do I navigate diaper changes, feedings, and naps with my hectic remote work schedule?”
“If I’m constantly interrupted during the day, should I skip sleep to catch up on work and not let my colleagues down?”
As professionals who work closely with medical trainees, we knew our parenting dilemmas were being experienced even more acutely by our frontline worker colleagues.
Medical training is an increasingly common time to start a family. In a recent study, 34% of trainees in Harvard-affiliated residency programs became parents during training, and another 52% planned to do so. Trainees have higher breastfeeding initiation rates but lower continuation rates than the general population. Early nursing cessation among trainees is well documented nationally and is most often attributed to work-related barriers. These barriers range from insufficient time and limited access to facilities to a lack of support and discrimination by supervisors and peers.
This trend does not discriminate by specialty. Even among training programs known to be “family friendly,” the average duration of nursing is just 4.5 months. Residents of color are disproportionately affected by inadequate support. Studies show that Black parents breastfeed at lower rates than White parents. This has been largely attributed to structural racism and implicit bias, such as Black parents receiving less assistance initiating nursing after delivery. Adequate lactation support and inclusivity are also lacking for transgender parents who choose to breastfeed or chestfeed.
The very nature of residency training, which includes shifts that can span more than 24 hours, conflicts with many health-promoting behaviors like sleeping and eating well. However, its interference with lactation is correlated with gender. Women are disproportionately affected by the negative outcomes of unmet lactation goals. These include work-life imbalance, career dissatisfaction, and negative emotions. In a study of pediatric residents, one in four did not achieve their breastfeeding goals. Respondents reported feeling “sad, devastated, defeated, disappointed, guilty, embarrassed, frustrated, angry, like a failure, and inadequate.” Among physician mothers more broadly, discrimination related to pregnancy, parental leave, and nursing is associated with higher self-reported burnout.
Navigating nursing during residency training has more than just emotional and psychological consequences – it also has professional ones. Pursuing personal lactation goals can delay residency program completion and board certification, influence specialty selection, negatively impact research productivity, impede career advancement, and lead to misgivings about career choice.
Trainees and their families are not the only ones harmed by inadequate support in residency programs. Patients and their families are affected, too. Research suggests that physicians’ personal breastfeeding practices affect the advice they give to patients. Those who receive lactation support are more likely to help patients meet their own goals. In the previously mentioned study of pediatric residents, more than 90% of the 400 respondents said their own or their partner’s nursing experience affected their interaction with lactating patients in their clinic or hospital.
Increased lactation support is a straightforward, low-cost, high-impact intervention. It benefits trainee well-being, satisfaction, workflow, and future patient care. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education mandated in July 2019 that all residency programs provide adequate lactation facilities – including refrigeration capabilities and proximity for safe patient care. However, to our knowledge, rates of compliance with this new policy and citation for noncompliance have yet to be seen. Regardless, facilities alone are not enough. Residency programs should develop and enforce formal lactation policies.
Several institutions have successfully piloted such policies in recent years. One in particular from the University of Michigan’s surgery residency program inspired the development of a lactation policy within the internal medicine residency at our institution. These policies designate appropriate spaces at each clinical rotation site, clarify that residents are encouraged to take pumping breaks as needed – in coordination with clinical teams so as not to compromise patient care – and communicate support from supervisors.
Our program also established an informal peer mentoring program. Residents with experience pumping at work pair up with newer trainees. The policy benefits residents who wish to chestfeed or breastfeed, normalizes lactation, and empowers trainees by diminishing the need to ask for individual accommodations. It also costs the program nothing.
As more women enter medicine and more trainees become parents during residency, the need for support in this area will only continue to grow. The widespread lack of such resources, and the fact that clean and private facilities are only now being mandated, is symbolic. If even this basic need is rarely acknowledged or met, what other resident needs are being neglected?
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Achieving a ‘new sexual-health paradigm’ means expanding STI care
A vital aspect of expanding access and care for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the United States is broadening responsibility for this care across the health care system and other community resources, according to an article published online July 6 in Clinical Infectious Diseases. This expansion and decentralization of care are central to adopting the “new sexual health paradigm” recommended by a National Academies report that was published in March.
“STIs represent a sizable, longstanding, and growing public health challenge,” write Vincent Guilamo-Ramos, PhD, MPH, dean and professor at the Duke University School of Nursing and director of the Center for Latino Adolescent and Family Health (CLAFH) at Duke University, both in Durham, N.C., and his colleagues. Yet the limitations on the current STI workforce and limited federal funding and support for STI prevention and care mean it will take clinicians of all types from across the health care spectrum to meet the challenge, they explain.
“For too long, STI prevention and treatment has been perceived as the sole responsibility of a narrow workforce of specialized STI and HIV service providers,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his coauthor, Marco Thimm-Kaiser, MPH, associate in research at Duke University and epidemiologist at CLAFH, wrote in an email.
“However, the resources allocated to this STI specialty workforce have diminished over time, along with decreasing investments in the broader U.S. public health infrastructure,” they continued. “At the same time – and in part due to this underinvestment – STI rates have soared, reaching a record high for the sixth year in a row in 2019.”
Those factors led to the National Academies report, which recommends moving “away from the traditional, disease-focused perspective on STIs in favor of a holistic perspective of sexual health as an integral component of overall health and well-being,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote to this news organization.
In their article, the authors review the limitations in the STI workforce, the implications of those limitations for the broader health care industry, and what it will take for STI and HIV specialists as well as regulators to ensure it’s possible to achieve the paradigm shift recommended by the National Academies.
Currently, the biggest limitation is access to care, said Laura Mercer, MD, MBA, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and the ob.gyn. clerkship director at the University of Arizona, Phoenix. Dr. Mercer, who was not involved with the National Academies report or the analysis of it, said in an interview that it’s essential to emphasize “sexual health as a core element of routine primary and preventative care” to ensure it becomes more accessible to patients without the need to seek out specialty care.
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his colleagues drive home the importance of such a shift by noting that more than 200 million Americans live in counties with no practicing infectious disease physicians. The disparities are greatest in Southern states, which account for 40% of all reported STIs. The workforce shortage has continued to worsen alongside the deterioration of the clinical infrastructure supporting STI specialty services, the authors write.
Hence the need to expand accountability for care not only to primary-care physicians but also to nurses, pharmacists, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and behavioral health practitioners. Doing so also requires normalizing sexual health services across health care professions.
“Prevention is a crucial first step” to this, Dr. Mercer said. “This is particularly important as we recall that almost half of new sexually transmitted infections occur in teenagers. Destigmatizing sexual health and sexual health education will also help encourage patients of all ages to request and accept testing.”
Further, with primary care practitioners managing most STI testing and treatment, subspecialists can focus primarily on complex or refractory cases, she added. Ways to help broaden care include developing point-of-care testing for STIs and improving the accuracy of existing testing, she said.
“The goal is to make routine sexual health services accessible in a wide range of settings, such as in primary care, at pharmacies, and in community-based settings, and to draw on a broader workforce for delivery of sexual health services,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser said in an interview.
Kevin Ault, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology and director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said that many medical organizations, such as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, have long advocated incorporating sexual health into routine preventive care. He also noted that pharmacists have already become proactive in preventing STIs and could continue to do so.
“Vaccines for hepatitis and human papillomavirus are commonly available at pharmacies,” Dr. Ault said. He was not involved in the article by Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and colleagues or the original report. “Pharmacists could also fill a gap by administering injectable medications such as penicillin. States would have to approve changes in policy, but many states have already done this for expedited partner therapy.”
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser noted similar barriers that must be removed to broaden delivery of STI services.
“Unfortunately, too many highly trained health care providers who are well-positioned for the delivery of sexual health services face regulatory or administrative barriers to practice to the full scope of their training,” they wrote. “These barriers can have a particularly negative impact in medically underserved communities, where physician shortages are common and where novel, decentralized health care service delivery models that draw on nonphysician providers may hold the greatest promise.”
As more diverse health care practitioners take on these roles, ID and HIV specialists can provide their expertise in developing training and technical assistance to support generalists, Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote. They can also aid in aligning “clinical training curricula, licensing criteria, and practice guidelines with routine delivery of sexual health services.”
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his coauthors offer specific recommendations for professional training, licensing, and practice guidelines to help overcome the “insufficient knowledge, inadequate training, and absence of explicit protocols” that currently impede delivery of STI services in general practice settings.
Although the paradigm shift recommended by the National Academies is ambitious, it’s also necessary, and “none of the recommendations are out of reach,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser said in an interview. They pointed out how the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted how underresourced the health care workforce and infrastructure are and how great health care disparities are.
“There is momentum toward rebuilding the nation’s health and public health system in a more effective and efficient way,” they said, and many of the STI report’s recommendations “overlap with priorities for the broader health and public health system moving forward.”
Dr. Mercer also believes the recommendations are realistic, “but only the beginning,” she told this news organization. “Comprehensive sexual education to expand knowledge about STI prevention and public health campaigns to help destigmatize sexual health care in general will remain crucial,” she said.
Sexual education, expanded access, and destigmatizing sexual care are particularly important for reaching the populations most in need of care, such as adolescents and young adults, as well as ethnic, racial, sexual, and gender-minority youth.
“It cannot be overstated how important of a priority population adolescents and young adults are,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote. They noted that those aged 15-24 account for half of all STIs each year but represent only a quarter of the sexually active population. “Targeted efforts for STI prevention and treatment among adolescents and young adults are therefore essential for an overall successful strategy to address STIs and sexual health in the United States.”
The National Academies report was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Association of County and City Health Officials. Dr. Mercer, Dr. Ault, and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Guilamo-Ramos has received grants and personal fees from ViiV Health care.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A vital aspect of expanding access and care for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the United States is broadening responsibility for this care across the health care system and other community resources, according to an article published online July 6 in Clinical Infectious Diseases. This expansion and decentralization of care are central to adopting the “new sexual health paradigm” recommended by a National Academies report that was published in March.
“STIs represent a sizable, longstanding, and growing public health challenge,” write Vincent Guilamo-Ramos, PhD, MPH, dean and professor at the Duke University School of Nursing and director of the Center for Latino Adolescent and Family Health (CLAFH) at Duke University, both in Durham, N.C., and his colleagues. Yet the limitations on the current STI workforce and limited federal funding and support for STI prevention and care mean it will take clinicians of all types from across the health care spectrum to meet the challenge, they explain.
“For too long, STI prevention and treatment has been perceived as the sole responsibility of a narrow workforce of specialized STI and HIV service providers,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his coauthor, Marco Thimm-Kaiser, MPH, associate in research at Duke University and epidemiologist at CLAFH, wrote in an email.
“However, the resources allocated to this STI specialty workforce have diminished over time, along with decreasing investments in the broader U.S. public health infrastructure,” they continued. “At the same time – and in part due to this underinvestment – STI rates have soared, reaching a record high for the sixth year in a row in 2019.”
Those factors led to the National Academies report, which recommends moving “away from the traditional, disease-focused perspective on STIs in favor of a holistic perspective of sexual health as an integral component of overall health and well-being,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote to this news organization.
In their article, the authors review the limitations in the STI workforce, the implications of those limitations for the broader health care industry, and what it will take for STI and HIV specialists as well as regulators to ensure it’s possible to achieve the paradigm shift recommended by the National Academies.
Currently, the biggest limitation is access to care, said Laura Mercer, MD, MBA, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and the ob.gyn. clerkship director at the University of Arizona, Phoenix. Dr. Mercer, who was not involved with the National Academies report or the analysis of it, said in an interview that it’s essential to emphasize “sexual health as a core element of routine primary and preventative care” to ensure it becomes more accessible to patients without the need to seek out specialty care.
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his colleagues drive home the importance of such a shift by noting that more than 200 million Americans live in counties with no practicing infectious disease physicians. The disparities are greatest in Southern states, which account for 40% of all reported STIs. The workforce shortage has continued to worsen alongside the deterioration of the clinical infrastructure supporting STI specialty services, the authors write.
Hence the need to expand accountability for care not only to primary-care physicians but also to nurses, pharmacists, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and behavioral health practitioners. Doing so also requires normalizing sexual health services across health care professions.
“Prevention is a crucial first step” to this, Dr. Mercer said. “This is particularly important as we recall that almost half of new sexually transmitted infections occur in teenagers. Destigmatizing sexual health and sexual health education will also help encourage patients of all ages to request and accept testing.”
Further, with primary care practitioners managing most STI testing and treatment, subspecialists can focus primarily on complex or refractory cases, she added. Ways to help broaden care include developing point-of-care testing for STIs and improving the accuracy of existing testing, she said.
“The goal is to make routine sexual health services accessible in a wide range of settings, such as in primary care, at pharmacies, and in community-based settings, and to draw on a broader workforce for delivery of sexual health services,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser said in an interview.
Kevin Ault, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology and director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said that many medical organizations, such as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, have long advocated incorporating sexual health into routine preventive care. He also noted that pharmacists have already become proactive in preventing STIs and could continue to do so.
“Vaccines for hepatitis and human papillomavirus are commonly available at pharmacies,” Dr. Ault said. He was not involved in the article by Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and colleagues or the original report. “Pharmacists could also fill a gap by administering injectable medications such as penicillin. States would have to approve changes in policy, but many states have already done this for expedited partner therapy.”
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser noted similar barriers that must be removed to broaden delivery of STI services.
“Unfortunately, too many highly trained health care providers who are well-positioned for the delivery of sexual health services face regulatory or administrative barriers to practice to the full scope of their training,” they wrote. “These barriers can have a particularly negative impact in medically underserved communities, where physician shortages are common and where novel, decentralized health care service delivery models that draw on nonphysician providers may hold the greatest promise.”
As more diverse health care practitioners take on these roles, ID and HIV specialists can provide their expertise in developing training and technical assistance to support generalists, Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote. They can also aid in aligning “clinical training curricula, licensing criteria, and practice guidelines with routine delivery of sexual health services.”
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his coauthors offer specific recommendations for professional training, licensing, and practice guidelines to help overcome the “insufficient knowledge, inadequate training, and absence of explicit protocols” that currently impede delivery of STI services in general practice settings.
Although the paradigm shift recommended by the National Academies is ambitious, it’s also necessary, and “none of the recommendations are out of reach,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser said in an interview. They pointed out how the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted how underresourced the health care workforce and infrastructure are and how great health care disparities are.
“There is momentum toward rebuilding the nation’s health and public health system in a more effective and efficient way,” they said, and many of the STI report’s recommendations “overlap with priorities for the broader health and public health system moving forward.”
Dr. Mercer also believes the recommendations are realistic, “but only the beginning,” she told this news organization. “Comprehensive sexual education to expand knowledge about STI prevention and public health campaigns to help destigmatize sexual health care in general will remain crucial,” she said.
Sexual education, expanded access, and destigmatizing sexual care are particularly important for reaching the populations most in need of care, such as adolescents and young adults, as well as ethnic, racial, sexual, and gender-minority youth.
“It cannot be overstated how important of a priority population adolescents and young adults are,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote. They noted that those aged 15-24 account for half of all STIs each year but represent only a quarter of the sexually active population. “Targeted efforts for STI prevention and treatment among adolescents and young adults are therefore essential for an overall successful strategy to address STIs and sexual health in the United States.”
The National Academies report was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Association of County and City Health Officials. Dr. Mercer, Dr. Ault, and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Guilamo-Ramos has received grants and personal fees from ViiV Health care.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A vital aspect of expanding access and care for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the United States is broadening responsibility for this care across the health care system and other community resources, according to an article published online July 6 in Clinical Infectious Diseases. This expansion and decentralization of care are central to adopting the “new sexual health paradigm” recommended by a National Academies report that was published in March.
“STIs represent a sizable, longstanding, and growing public health challenge,” write Vincent Guilamo-Ramos, PhD, MPH, dean and professor at the Duke University School of Nursing and director of the Center for Latino Adolescent and Family Health (CLAFH) at Duke University, both in Durham, N.C., and his colleagues. Yet the limitations on the current STI workforce and limited federal funding and support for STI prevention and care mean it will take clinicians of all types from across the health care spectrum to meet the challenge, they explain.
“For too long, STI prevention and treatment has been perceived as the sole responsibility of a narrow workforce of specialized STI and HIV service providers,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his coauthor, Marco Thimm-Kaiser, MPH, associate in research at Duke University and epidemiologist at CLAFH, wrote in an email.
“However, the resources allocated to this STI specialty workforce have diminished over time, along with decreasing investments in the broader U.S. public health infrastructure,” they continued. “At the same time – and in part due to this underinvestment – STI rates have soared, reaching a record high for the sixth year in a row in 2019.”
Those factors led to the National Academies report, which recommends moving “away from the traditional, disease-focused perspective on STIs in favor of a holistic perspective of sexual health as an integral component of overall health and well-being,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote to this news organization.
In their article, the authors review the limitations in the STI workforce, the implications of those limitations for the broader health care industry, and what it will take for STI and HIV specialists as well as regulators to ensure it’s possible to achieve the paradigm shift recommended by the National Academies.
Currently, the biggest limitation is access to care, said Laura Mercer, MD, MBA, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and the ob.gyn. clerkship director at the University of Arizona, Phoenix. Dr. Mercer, who was not involved with the National Academies report or the analysis of it, said in an interview that it’s essential to emphasize “sexual health as a core element of routine primary and preventative care” to ensure it becomes more accessible to patients without the need to seek out specialty care.
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his colleagues drive home the importance of such a shift by noting that more than 200 million Americans live in counties with no practicing infectious disease physicians. The disparities are greatest in Southern states, which account for 40% of all reported STIs. The workforce shortage has continued to worsen alongside the deterioration of the clinical infrastructure supporting STI specialty services, the authors write.
Hence the need to expand accountability for care not only to primary-care physicians but also to nurses, pharmacists, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and behavioral health practitioners. Doing so also requires normalizing sexual health services across health care professions.
“Prevention is a crucial first step” to this, Dr. Mercer said. “This is particularly important as we recall that almost half of new sexually transmitted infections occur in teenagers. Destigmatizing sexual health and sexual health education will also help encourage patients of all ages to request and accept testing.”
Further, with primary care practitioners managing most STI testing and treatment, subspecialists can focus primarily on complex or refractory cases, she added. Ways to help broaden care include developing point-of-care testing for STIs and improving the accuracy of existing testing, she said.
“The goal is to make routine sexual health services accessible in a wide range of settings, such as in primary care, at pharmacies, and in community-based settings, and to draw on a broader workforce for delivery of sexual health services,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser said in an interview.
Kevin Ault, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology and director of clinical and translational research at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said that many medical organizations, such as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, have long advocated incorporating sexual health into routine preventive care. He also noted that pharmacists have already become proactive in preventing STIs and could continue to do so.
“Vaccines for hepatitis and human papillomavirus are commonly available at pharmacies,” Dr. Ault said. He was not involved in the article by Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and colleagues or the original report. “Pharmacists could also fill a gap by administering injectable medications such as penicillin. States would have to approve changes in policy, but many states have already done this for expedited partner therapy.”
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser noted similar barriers that must be removed to broaden delivery of STI services.
“Unfortunately, too many highly trained health care providers who are well-positioned for the delivery of sexual health services face regulatory or administrative barriers to practice to the full scope of their training,” they wrote. “These barriers can have a particularly negative impact in medically underserved communities, where physician shortages are common and where novel, decentralized health care service delivery models that draw on nonphysician providers may hold the greatest promise.”
As more diverse health care practitioners take on these roles, ID and HIV specialists can provide their expertise in developing training and technical assistance to support generalists, Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote. They can also aid in aligning “clinical training curricula, licensing criteria, and practice guidelines with routine delivery of sexual health services.”
Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and his coauthors offer specific recommendations for professional training, licensing, and practice guidelines to help overcome the “insufficient knowledge, inadequate training, and absence of explicit protocols” that currently impede delivery of STI services in general practice settings.
Although the paradigm shift recommended by the National Academies is ambitious, it’s also necessary, and “none of the recommendations are out of reach,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser said in an interview. They pointed out how the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted how underresourced the health care workforce and infrastructure are and how great health care disparities are.
“There is momentum toward rebuilding the nation’s health and public health system in a more effective and efficient way,” they said, and many of the STI report’s recommendations “overlap with priorities for the broader health and public health system moving forward.”
Dr. Mercer also believes the recommendations are realistic, “but only the beginning,” she told this news organization. “Comprehensive sexual education to expand knowledge about STI prevention and public health campaigns to help destigmatize sexual health care in general will remain crucial,” she said.
Sexual education, expanded access, and destigmatizing sexual care are particularly important for reaching the populations most in need of care, such as adolescents and young adults, as well as ethnic, racial, sexual, and gender-minority youth.
“It cannot be overstated how important of a priority population adolescents and young adults are,” Dr. Guilamo-Ramos and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser wrote. They noted that those aged 15-24 account for half of all STIs each year but represent only a quarter of the sexually active population. “Targeted efforts for STI prevention and treatment among adolescents and young adults are therefore essential for an overall successful strategy to address STIs and sexual health in the United States.”
The National Academies report was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Association of County and City Health Officials. Dr. Mercer, Dr. Ault, and Mr. Thimm-Kaiser have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Guilamo-Ramos has received grants and personal fees from ViiV Health care.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with diabetes more likely to be hospitalized, especially with foot infection
People with diabetes are at increased risk of hospitalization for infection, as well as infection-related mortality, shows a large U.S. study that suggests the risk is even higher in younger and Black individuals.
Michael Fang, PhD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues studied more than 12,000 participants in a community cohort study who were followed for an average of 24 years, between 1987-1989 and 2019.
Participants with diabetes faced a 67% increase risk of infection-related hospitalization, compared with those without diabetes.
Of particular note, the risk of hospitalization with foot infection was almost sixfold higher for people with diabetes than those without.
The research, published in Diabetologia on August 4, also suggests that diabetes may be associated with a 72% increased risk of infection-related mortality, although the absolute numbers were small.
Dr. Fang explained to this news organization that they focused on infection-related hospitalization and mortality “because these are comprehensively tracked in administrative data and ... are the most severe types of outcomes.”
However, this is probably just the tip of the iceberg, as people with diabetes are “likely at increased risk for milder infection too,” which can have a “significant adverse impact on people’s well-being and quality of life.”
As a result of their findings, the authors call for “broader guidance on infection prevention and management” in people with diabetes. To achieve this, Dr. Fang said, “we need to better understand why diabetes is associated with an increased risk of infection-related complications.”
“One likely factor is glycemic control: Emerging research suggests patients with diabetes with better glycemic control may be at significantly lower risk of infection-related complications.”
He continued that, in younger patients, a factor for worse outcomes could be that “diabetes tends to be more aggressive when it emerges early in life,” while in Black patients “there is research highlighting Black-White differences in glycemic control, access to care, and beliefs around vaccines.”
Overall, their findings – coupled with recent data showing that diabetes is an important risk factor for adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection – paint “a common picture,” Dr. Fang said.
“People with diabetes are much more susceptible to infection-related complications, including COVID-related hospitalization and mortality,” which suggests people with diabetes “may need to be especially cautious.”
Adds to existing literature; amputations begin with infections
Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, chief scientific and medical officer for the American Diabetes Association (ADA), said the study “does add to the existing literature by having followed a larger number of people over time and linking them to serious complications from infections.”
“Sadly, we have seen this play out in real-time during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
“One of the sobering bits of data is the significant health disparities that exist in Black Americans and the fact that foot infections remain a significant problem,” he said in an interview.
“Given that amputation rates for [Black Americans] are three times higher than White Americans, amputations begin with infections,” Dr. Gabbay added, noting the ADA “has been taking a strong stand to prevent amputations and address the inequities in health that exist.”
Jamie Hartmann-Boyce, PhD, from the University of Oxford, U.K., who was not involved in the study, commented that diabetes is a “well-known risk factor for worse outcomes from all kinds of infection,” which is why they “are prioritized for flu vaccination every year.”
She told this news organization that the current study “further confirms that people with diabetes are more likely to be hospitalized for infection of any type and most markedly for foot infection.”
“These new data further highlight the need for public health interventions to prevent type 2 diabetes, and for preventive health care in people with diabetes, including access to diabetes medications and support and to vaccinations to prevent infection,” added Dr. Hartmann-Boyce, who is a senior research fellow in health behaviors.
Diabetes is thought to be associated with susceptibility to infection via mechanisms such as impaired neutrophil functioning and humoral immune responses, and studies have shown a link with both common and rare infections.
However, the authors point out that “most” of those included “small clinical populations and were cross-sectional or had short follow-up.”
Guidelines for diabetes management, they note, also “pay less attention” to infectious diseases than they do to the prevention of micro- and macrovascular complications.
ARIC data mined for infections in those with diabetes
The team analyzed data from the ongoing U.S. community-based Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored cohort was comprised of adults aged 45-64 years from four U.S. communities, recruited between 1987 and 1989 for clinical examinations, medical interviews, and laboratory tests, repeated over five more visits up to 2018-2019.
For the current analysis, the team included 12,739 individuals with a mean age of 54.5 years, of whom 54.3% were female and 24.7% were Black.
Patients were defined as having diabetes if their baseline fasting blood glucose was greater than or equal to 7 mmol/L, or nonfasting glucose was greater than or equal to 11.1 mmol/l, they self-reported a diagnosis of diabetes by a physician, or they were taking glucose-lowering medication at the first study visit. The researchers weren’t able to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
In total, 1,485 individuals had diabetes at baseline. They were more likely to be older, Black, have a low socioeconomic status, and have worse cardiometabolic health than participants without diabetes.
Over an average follow-up of 23.8 years, there were 4,229 incident hospitalizations for infection, at an overall rate of 15.9 per 1,000 person-years.
Individuals with diabetes at baseline had a higher rate of hospitalizations than those without, at 25.4 per 1,000 person-years versus 15.2 per 1,000 person-years.
After taking into account sociodemographic characteristics, socioeconomic status, and cardiometabolic risk factors, this equated to a hazard ratio for hospitalization with any infection of 1.67 (P < .001).
The risk of hospitalization for any infection was significantly higher for younger patients with diabetes, defined as aged less than 55 years (P = .005), and for Black patients (P < .001).
While the increased risk was generally consistent across infection types, it was markedly increased for foot infection, at a hazard ratio of 5.99 (P < .001).
Overall, there were few deaths due to infection in the study, at just 362. The risk of infection mortality was nevertheless significantly increased in people with diabetes, at an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.72 (P < .001).
Dr. Fang has reported being supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Selvin has reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Selvin is an associate editor for Diabetologia and had no role in the peer review of the manuscript.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with diabetes are at increased risk of hospitalization for infection, as well as infection-related mortality, shows a large U.S. study that suggests the risk is even higher in younger and Black individuals.
Michael Fang, PhD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues studied more than 12,000 participants in a community cohort study who were followed for an average of 24 years, between 1987-1989 and 2019.
Participants with diabetes faced a 67% increase risk of infection-related hospitalization, compared with those without diabetes.
Of particular note, the risk of hospitalization with foot infection was almost sixfold higher for people with diabetes than those without.
The research, published in Diabetologia on August 4, also suggests that diabetes may be associated with a 72% increased risk of infection-related mortality, although the absolute numbers were small.
Dr. Fang explained to this news organization that they focused on infection-related hospitalization and mortality “because these are comprehensively tracked in administrative data and ... are the most severe types of outcomes.”
However, this is probably just the tip of the iceberg, as people with diabetes are “likely at increased risk for milder infection too,” which can have a “significant adverse impact on people’s well-being and quality of life.”
As a result of their findings, the authors call for “broader guidance on infection prevention and management” in people with diabetes. To achieve this, Dr. Fang said, “we need to better understand why diabetes is associated with an increased risk of infection-related complications.”
“One likely factor is glycemic control: Emerging research suggests patients with diabetes with better glycemic control may be at significantly lower risk of infection-related complications.”
He continued that, in younger patients, a factor for worse outcomes could be that “diabetes tends to be more aggressive when it emerges early in life,” while in Black patients “there is research highlighting Black-White differences in glycemic control, access to care, and beliefs around vaccines.”
Overall, their findings – coupled with recent data showing that diabetes is an important risk factor for adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection – paint “a common picture,” Dr. Fang said.
“People with diabetes are much more susceptible to infection-related complications, including COVID-related hospitalization and mortality,” which suggests people with diabetes “may need to be especially cautious.”
Adds to existing literature; amputations begin with infections
Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, chief scientific and medical officer for the American Diabetes Association (ADA), said the study “does add to the existing literature by having followed a larger number of people over time and linking them to serious complications from infections.”
“Sadly, we have seen this play out in real-time during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
“One of the sobering bits of data is the significant health disparities that exist in Black Americans and the fact that foot infections remain a significant problem,” he said in an interview.
“Given that amputation rates for [Black Americans] are three times higher than White Americans, amputations begin with infections,” Dr. Gabbay added, noting the ADA “has been taking a strong stand to prevent amputations and address the inequities in health that exist.”
Jamie Hartmann-Boyce, PhD, from the University of Oxford, U.K., who was not involved in the study, commented that diabetes is a “well-known risk factor for worse outcomes from all kinds of infection,” which is why they “are prioritized for flu vaccination every year.”
She told this news organization that the current study “further confirms that people with diabetes are more likely to be hospitalized for infection of any type and most markedly for foot infection.”
“These new data further highlight the need for public health interventions to prevent type 2 diabetes, and for preventive health care in people with diabetes, including access to diabetes medications and support and to vaccinations to prevent infection,” added Dr. Hartmann-Boyce, who is a senior research fellow in health behaviors.
Diabetes is thought to be associated with susceptibility to infection via mechanisms such as impaired neutrophil functioning and humoral immune responses, and studies have shown a link with both common and rare infections.
However, the authors point out that “most” of those included “small clinical populations and were cross-sectional or had short follow-up.”
Guidelines for diabetes management, they note, also “pay less attention” to infectious diseases than they do to the prevention of micro- and macrovascular complications.
ARIC data mined for infections in those with diabetes
The team analyzed data from the ongoing U.S. community-based Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored cohort was comprised of adults aged 45-64 years from four U.S. communities, recruited between 1987 and 1989 for clinical examinations, medical interviews, and laboratory tests, repeated over five more visits up to 2018-2019.
For the current analysis, the team included 12,739 individuals with a mean age of 54.5 years, of whom 54.3% were female and 24.7% were Black.
Patients were defined as having diabetes if their baseline fasting blood glucose was greater than or equal to 7 mmol/L, or nonfasting glucose was greater than or equal to 11.1 mmol/l, they self-reported a diagnosis of diabetes by a physician, or they were taking glucose-lowering medication at the first study visit. The researchers weren’t able to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
In total, 1,485 individuals had diabetes at baseline. They were more likely to be older, Black, have a low socioeconomic status, and have worse cardiometabolic health than participants without diabetes.
Over an average follow-up of 23.8 years, there were 4,229 incident hospitalizations for infection, at an overall rate of 15.9 per 1,000 person-years.
Individuals with diabetes at baseline had a higher rate of hospitalizations than those without, at 25.4 per 1,000 person-years versus 15.2 per 1,000 person-years.
After taking into account sociodemographic characteristics, socioeconomic status, and cardiometabolic risk factors, this equated to a hazard ratio for hospitalization with any infection of 1.67 (P < .001).
The risk of hospitalization for any infection was significantly higher for younger patients with diabetes, defined as aged less than 55 years (P = .005), and for Black patients (P < .001).
While the increased risk was generally consistent across infection types, it was markedly increased for foot infection, at a hazard ratio of 5.99 (P < .001).
Overall, there were few deaths due to infection in the study, at just 362. The risk of infection mortality was nevertheless significantly increased in people with diabetes, at an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.72 (P < .001).
Dr. Fang has reported being supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Selvin has reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Selvin is an associate editor for Diabetologia and had no role in the peer review of the manuscript.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with diabetes are at increased risk of hospitalization for infection, as well as infection-related mortality, shows a large U.S. study that suggests the risk is even higher in younger and Black individuals.
Michael Fang, PhD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues studied more than 12,000 participants in a community cohort study who were followed for an average of 24 years, between 1987-1989 and 2019.
Participants with diabetes faced a 67% increase risk of infection-related hospitalization, compared with those without diabetes.
Of particular note, the risk of hospitalization with foot infection was almost sixfold higher for people with diabetes than those without.
The research, published in Diabetologia on August 4, also suggests that diabetes may be associated with a 72% increased risk of infection-related mortality, although the absolute numbers were small.
Dr. Fang explained to this news organization that they focused on infection-related hospitalization and mortality “because these are comprehensively tracked in administrative data and ... are the most severe types of outcomes.”
However, this is probably just the tip of the iceberg, as people with diabetes are “likely at increased risk for milder infection too,” which can have a “significant adverse impact on people’s well-being and quality of life.”
As a result of their findings, the authors call for “broader guidance on infection prevention and management” in people with diabetes. To achieve this, Dr. Fang said, “we need to better understand why diabetes is associated with an increased risk of infection-related complications.”
“One likely factor is glycemic control: Emerging research suggests patients with diabetes with better glycemic control may be at significantly lower risk of infection-related complications.”
He continued that, in younger patients, a factor for worse outcomes could be that “diabetes tends to be more aggressive when it emerges early in life,” while in Black patients “there is research highlighting Black-White differences in glycemic control, access to care, and beliefs around vaccines.”
Overall, their findings – coupled with recent data showing that diabetes is an important risk factor for adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection – paint “a common picture,” Dr. Fang said.
“People with diabetes are much more susceptible to infection-related complications, including COVID-related hospitalization and mortality,” which suggests people with diabetes “may need to be especially cautious.”
Adds to existing literature; amputations begin with infections
Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, chief scientific and medical officer for the American Diabetes Association (ADA), said the study “does add to the existing literature by having followed a larger number of people over time and linking them to serious complications from infections.”
“Sadly, we have seen this play out in real-time during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
“One of the sobering bits of data is the significant health disparities that exist in Black Americans and the fact that foot infections remain a significant problem,” he said in an interview.
“Given that amputation rates for [Black Americans] are three times higher than White Americans, amputations begin with infections,” Dr. Gabbay added, noting the ADA “has been taking a strong stand to prevent amputations and address the inequities in health that exist.”
Jamie Hartmann-Boyce, PhD, from the University of Oxford, U.K., who was not involved in the study, commented that diabetes is a “well-known risk factor for worse outcomes from all kinds of infection,” which is why they “are prioritized for flu vaccination every year.”
She told this news organization that the current study “further confirms that people with diabetes are more likely to be hospitalized for infection of any type and most markedly for foot infection.”
“These new data further highlight the need for public health interventions to prevent type 2 diabetes, and for preventive health care in people with diabetes, including access to diabetes medications and support and to vaccinations to prevent infection,” added Dr. Hartmann-Boyce, who is a senior research fellow in health behaviors.
Diabetes is thought to be associated with susceptibility to infection via mechanisms such as impaired neutrophil functioning and humoral immune responses, and studies have shown a link with both common and rare infections.
However, the authors point out that “most” of those included “small clinical populations and were cross-sectional or had short follow-up.”
Guidelines for diabetes management, they note, also “pay less attention” to infectious diseases than they do to the prevention of micro- and macrovascular complications.
ARIC data mined for infections in those with diabetes
The team analyzed data from the ongoing U.S. community-based Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study.
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored cohort was comprised of adults aged 45-64 years from four U.S. communities, recruited between 1987 and 1989 for clinical examinations, medical interviews, and laboratory tests, repeated over five more visits up to 2018-2019.
For the current analysis, the team included 12,739 individuals with a mean age of 54.5 years, of whom 54.3% were female and 24.7% were Black.
Patients were defined as having diabetes if their baseline fasting blood glucose was greater than or equal to 7 mmol/L, or nonfasting glucose was greater than or equal to 11.1 mmol/l, they self-reported a diagnosis of diabetes by a physician, or they were taking glucose-lowering medication at the first study visit. The researchers weren’t able to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
In total, 1,485 individuals had diabetes at baseline. They were more likely to be older, Black, have a low socioeconomic status, and have worse cardiometabolic health than participants without diabetes.
Over an average follow-up of 23.8 years, there were 4,229 incident hospitalizations for infection, at an overall rate of 15.9 per 1,000 person-years.
Individuals with diabetes at baseline had a higher rate of hospitalizations than those without, at 25.4 per 1,000 person-years versus 15.2 per 1,000 person-years.
After taking into account sociodemographic characteristics, socioeconomic status, and cardiometabolic risk factors, this equated to a hazard ratio for hospitalization with any infection of 1.67 (P < .001).
The risk of hospitalization for any infection was significantly higher for younger patients with diabetes, defined as aged less than 55 years (P = .005), and for Black patients (P < .001).
While the increased risk was generally consistent across infection types, it was markedly increased for foot infection, at a hazard ratio of 5.99 (P < .001).
Overall, there were few deaths due to infection in the study, at just 362. The risk of infection mortality was nevertheless significantly increased in people with diabetes, at an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.72 (P < .001).
Dr. Fang has reported being supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Selvin has reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Selvin is an associate editor for Diabetologia and had no role in the peer review of the manuscript.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Better CNS control in children with ALL: ‘Goldilocks’ approach
Treatment of central nervous system involvement in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) needs to be based on risk, and should no longer be applied in a one-size-fits all approach, say experts writing in an editorial published July 29 in the journal Blood.
“Because cure rates now exceed 90%, using neurotoxic drugs in non–risk-adapted protocols is unacceptable and a paradigm shift in treating CNS ALL is required,” write pediatric leukemia researchers Christina Halsey, PhD, of the University of Glasgow and Gabriele Escherich, MD, of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany).
“We want to reach a Goldilocks point: not too much, not too little, but just right for every child,” they write.
The problem is that “the absence of clinically useful biomarkers prevents accurate risk stratification, resulting in universal use of intensive CNS-directed therapy. This therapy is likely to overtreat many children, exposing them to an unnecessary risk of toxicity,” including long-term cognitive deficits in 20%-40% of them, they point out.
The editorial accompanied a new study in which investigators in China focused on improving CNS control in children with ALL, which the editorialists said was step in the right direction.
In the Chinese Children’s Cancer Group ALL-2015 trial, investigators found that prephase dexamethasone, delayed intrathecal therapy, intravenous anesthesia to reduce traumatic lumbar punctures, and flow cytometry to accurately ascertain initial CNS involvement may improve CNS control.
The trial included 7,640 consecutive children up to age 18 treated from 2015 to 2019 across 20 major medical centers in China. Children received conventional remission induction and subsequent risk-directed therapy, including 16-22 triple intrathecal treatments. Prophylactic cranial irradiation was not used.
The 5-year event-free survival was 80.3% and overall survival 91.1%. The cumulative risk of isolated CNS relapse was 1.9% and of any CNS relapse 2.7%, comparable to reports from other major study groups, both with and without cranial radiation.
“We attributed our relatively good CNS control to the prephase treatment with dexamethasone, which reduced leukemia cells in blood and the CNS, and to the delayed intrathecal therapy until all (or a large proportion) of circulating leukemic blasts were cleared, thus reducing the consequence of traumatic lumbar puncture with blasts,” said the investigators, led by Jingyan Tang, MD, a hematologist/oncologist at the Shanghai (China) Children’s Medical Center.
“This approach of delayed administration of initial intrathecal therapy after prephase steroid treatment, if confirmed successful by additional studies, can be adopted readily,” they say.
The editorialists concur. The low rates of CNS relapse, despite omission of radiotherapy and inclusion of high-risk subgroups, “might suggest a potential protective effect of steroids before diagnostic lumbar puncture,” they said.
“However, flow cytometry is not sensitive enough to track disease response over time. In the bone marrow, minimal residual disease (MRD) is used to identify children at high or low risk of relapse and modify therapy accordingly. We desperately need a minimal residual disease equivalent for CNS leukemia to allow us to tailor therapy,” Dr. Halsey and Dr. Escherich say.
It’s not surprising that the use of anesthesia led to fewer traumatic lumbar punctures than in “frightened child[ren] undergoing such a painful procedure without anesthesia,” the study team notes. Its correlation with lower CNS relapses is probably because drug delivery was more accurate in sedated children, the editorialists add.
Female sex was also protective against relapse in cases where general anesthesia wasn’t used for lumbar puncture. “One could speculate that it is more difficult to restrict male patients than female patients for successful intrathecal therapy if they were not undergoing anesthesia during the procedure,” the investigators write.
“Unfortunately,” the editorialists add, rapid adoption of anesthesia for lumbar punctures “is tempered by the recent observation that repeated general anesthesia in children with ALL is associated with increased neurotoxicity.”
The work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Cancer Institute, and others. The study authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment of central nervous system involvement in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) needs to be based on risk, and should no longer be applied in a one-size-fits all approach, say experts writing in an editorial published July 29 in the journal Blood.
“Because cure rates now exceed 90%, using neurotoxic drugs in non–risk-adapted protocols is unacceptable and a paradigm shift in treating CNS ALL is required,” write pediatric leukemia researchers Christina Halsey, PhD, of the University of Glasgow and Gabriele Escherich, MD, of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany).
“We want to reach a Goldilocks point: not too much, not too little, but just right for every child,” they write.
The problem is that “the absence of clinically useful biomarkers prevents accurate risk stratification, resulting in universal use of intensive CNS-directed therapy. This therapy is likely to overtreat many children, exposing them to an unnecessary risk of toxicity,” including long-term cognitive deficits in 20%-40% of them, they point out.
The editorial accompanied a new study in which investigators in China focused on improving CNS control in children with ALL, which the editorialists said was step in the right direction.
In the Chinese Children’s Cancer Group ALL-2015 trial, investigators found that prephase dexamethasone, delayed intrathecal therapy, intravenous anesthesia to reduce traumatic lumbar punctures, and flow cytometry to accurately ascertain initial CNS involvement may improve CNS control.
The trial included 7,640 consecutive children up to age 18 treated from 2015 to 2019 across 20 major medical centers in China. Children received conventional remission induction and subsequent risk-directed therapy, including 16-22 triple intrathecal treatments. Prophylactic cranial irradiation was not used.
The 5-year event-free survival was 80.3% and overall survival 91.1%. The cumulative risk of isolated CNS relapse was 1.9% and of any CNS relapse 2.7%, comparable to reports from other major study groups, both with and without cranial radiation.
“We attributed our relatively good CNS control to the prephase treatment with dexamethasone, which reduced leukemia cells in blood and the CNS, and to the delayed intrathecal therapy until all (or a large proportion) of circulating leukemic blasts were cleared, thus reducing the consequence of traumatic lumbar puncture with blasts,” said the investigators, led by Jingyan Tang, MD, a hematologist/oncologist at the Shanghai (China) Children’s Medical Center.
“This approach of delayed administration of initial intrathecal therapy after prephase steroid treatment, if confirmed successful by additional studies, can be adopted readily,” they say.
The editorialists concur. The low rates of CNS relapse, despite omission of radiotherapy and inclusion of high-risk subgroups, “might suggest a potential protective effect of steroids before diagnostic lumbar puncture,” they said.
“However, flow cytometry is not sensitive enough to track disease response over time. In the bone marrow, minimal residual disease (MRD) is used to identify children at high or low risk of relapse and modify therapy accordingly. We desperately need a minimal residual disease equivalent for CNS leukemia to allow us to tailor therapy,” Dr. Halsey and Dr. Escherich say.
It’s not surprising that the use of anesthesia led to fewer traumatic lumbar punctures than in “frightened child[ren] undergoing such a painful procedure without anesthesia,” the study team notes. Its correlation with lower CNS relapses is probably because drug delivery was more accurate in sedated children, the editorialists add.
Female sex was also protective against relapse in cases where general anesthesia wasn’t used for lumbar puncture. “One could speculate that it is more difficult to restrict male patients than female patients for successful intrathecal therapy if they were not undergoing anesthesia during the procedure,” the investigators write.
“Unfortunately,” the editorialists add, rapid adoption of anesthesia for lumbar punctures “is tempered by the recent observation that repeated general anesthesia in children with ALL is associated with increased neurotoxicity.”
The work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Cancer Institute, and others. The study authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment of central nervous system involvement in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) needs to be based on risk, and should no longer be applied in a one-size-fits all approach, say experts writing in an editorial published July 29 in the journal Blood.
“Because cure rates now exceed 90%, using neurotoxic drugs in non–risk-adapted protocols is unacceptable and a paradigm shift in treating CNS ALL is required,” write pediatric leukemia researchers Christina Halsey, PhD, of the University of Glasgow and Gabriele Escherich, MD, of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany).
“We want to reach a Goldilocks point: not too much, not too little, but just right for every child,” they write.
The problem is that “the absence of clinically useful biomarkers prevents accurate risk stratification, resulting in universal use of intensive CNS-directed therapy. This therapy is likely to overtreat many children, exposing them to an unnecessary risk of toxicity,” including long-term cognitive deficits in 20%-40% of them, they point out.
The editorial accompanied a new study in which investigators in China focused on improving CNS control in children with ALL, which the editorialists said was step in the right direction.
In the Chinese Children’s Cancer Group ALL-2015 trial, investigators found that prephase dexamethasone, delayed intrathecal therapy, intravenous anesthesia to reduce traumatic lumbar punctures, and flow cytometry to accurately ascertain initial CNS involvement may improve CNS control.
The trial included 7,640 consecutive children up to age 18 treated from 2015 to 2019 across 20 major medical centers in China. Children received conventional remission induction and subsequent risk-directed therapy, including 16-22 triple intrathecal treatments. Prophylactic cranial irradiation was not used.
The 5-year event-free survival was 80.3% and overall survival 91.1%. The cumulative risk of isolated CNS relapse was 1.9% and of any CNS relapse 2.7%, comparable to reports from other major study groups, both with and without cranial radiation.
“We attributed our relatively good CNS control to the prephase treatment with dexamethasone, which reduced leukemia cells in blood and the CNS, and to the delayed intrathecal therapy until all (or a large proportion) of circulating leukemic blasts were cleared, thus reducing the consequence of traumatic lumbar puncture with blasts,” said the investigators, led by Jingyan Tang, MD, a hematologist/oncologist at the Shanghai (China) Children’s Medical Center.
“This approach of delayed administration of initial intrathecal therapy after prephase steroid treatment, if confirmed successful by additional studies, can be adopted readily,” they say.
The editorialists concur. The low rates of CNS relapse, despite omission of radiotherapy and inclusion of high-risk subgroups, “might suggest a potential protective effect of steroids before diagnostic lumbar puncture,” they said.
“However, flow cytometry is not sensitive enough to track disease response over time. In the bone marrow, minimal residual disease (MRD) is used to identify children at high or low risk of relapse and modify therapy accordingly. We desperately need a minimal residual disease equivalent for CNS leukemia to allow us to tailor therapy,” Dr. Halsey and Dr. Escherich say.
It’s not surprising that the use of anesthesia led to fewer traumatic lumbar punctures than in “frightened child[ren] undergoing such a painful procedure without anesthesia,” the study team notes. Its correlation with lower CNS relapses is probably because drug delivery was more accurate in sedated children, the editorialists add.
Female sex was also protective against relapse in cases where general anesthesia wasn’t used for lumbar puncture. “One could speculate that it is more difficult to restrict male patients than female patients for successful intrathecal therapy if they were not undergoing anesthesia during the procedure,” the investigators write.
“Unfortunately,” the editorialists add, rapid adoption of anesthesia for lumbar punctures “is tempered by the recent observation that repeated general anesthesia in children with ALL is associated with increased neurotoxicity.”
The work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Cancer Institute, and others. The study authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Global youth depression and anxiety doubled during pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic doubled international rates of child and adolescent psychological disorders, according to results of a meta-analysis.
In the first year of the pandemic, an estimated one in four youth across various regions of the globe experienced clinically elevated depression symptoms, while one in five experienced clinically elevated anxiety symptoms. These pooled estimates, which increased over time, are double prepandemic estimates, according to Nicole Racine, PhD, RPsych, a clinical psychologist at the University of Calgary (Alta.) and colleagues.
Their meta-analysis of 29 studies, comprising 80,879 young people worldwide aged 18 years or less, found pooled prevalence estimates of clinically elevated youth depression and anxiety of 25.2% (95% confidence interval, 21.2%-29.7%) and 20.5% (95% CI, 17.2%-24.4%), respectively.
“The prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms during COVID-19 [has] doubled, compared with prepandemic estimates, and moderator analyses revealed that prevalence rates were higher when collected later in the pandemic, in older adolescents, and in girls,” the researchers write online in JAMA Pediatrics.
Prepandemic estimates of clinically significant generalized anxiety and depressive symptoms in large youth cohorts were approximately 11.6% and 12.9%, respectively, the authors say.
The increases revealed in these international findings have implications for targeted mental health resource planning.
“One difficulty in the literature is that there are large discrepancies on the prevalence of child depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic, with published rates between 2% and 68%,” corresponding author Sheri Madigan, PhD, RPsych, of the University of Calgary department of psychology, said in an interview. “By conducting a synthesis of the 29 studies on over 80,000 children, we were able to determine that, on average across these studies, 25% of youth are experiencing depression and 20% are experiencing anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
The cohort
The mean age in the combined global cohort was 13 years (range 4.1-17.6 ), and the mean proportion of females was 52.7% (standard deviation) 12.3%). The findings were based on international data published from Jan. 1, 2020, to Feb. 16, 2021, in studies conducted in the Middle East (n = 1), Europe (n = 4), South America (n = 2), North America (n = 6), and East Asia (n = 16). Notably absent were data from most of Latin America and the Middle East, Africa, South East Asia, and the Pacific Islands.
As the year progressed, the prevalence of depressive symptoms rose (b = .26; 95% CI, .06-46) with the number of months elapsed. Prevalence rates also rose as both age (b = 0.08, 95% CI, 0.01-0.15), and the percentage of females in samples increased (b = .03; 95% CI, 0.01-0.05).
The authors surmise that this cumulative worsening might be because of prolonged social isolation, family financial difficulties, missed milestones, and school disruptions, which are compounded over time. A second possibility is that studies conducted in the earlier months of the pandemic were more likely to be conducted in East Asia, where the self-reported prevalence of mental health symptoms tends to be lower.
The findings highlight an urgent need for intervention and recovery efforts and also indicate the need to consider individual differences when determining targets for intervention, including age, sex, and exposure to COVID-19 stressors), they add.
Even more concerning, recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest that the pandemic spurred an increase in suspected suicide attempts by teenage girls. In the United Kingdom, acute mental health presentations to emergency care tripled over 2019 at one pediatric facility during the pandemic.
The authors attribute the toll on the psychological well-being of the world’s young people to pandemic-mandated restrictions. Those entailed loss of peer interactions, social isolation, and reduced contact with support figures such as teachers, and, “In addition, schools are often a primary location for receiving psychological services, with 80% of children relying on school-based services to address their mental health needs.” For many children, these services were rendered unavailable owing to school closures, Dr. Madigan and associates write.
In the context of clinical practice, doctors play a critical role. “With school closures, the physician’s office may be the only mental health checkpoint for youth,” Dr. Madigan said “So I recommend that family physicians screen for, and/or ask children and youth, about their mental health.”
On the home front, emerging research suggests that a predictable home environment can protect children’s mental well-being, with less depression and fewer behavioral problems observed in families adhering to regular routines during COVID-19. “Thus, a tangible solution to help mitigate the adverse effects of COVID-19 on youth is working with children and families to implement consistent and predictable routines around schoolwork, sleep, screen use, and physical activity,” the authors write.
They also point to the need for research on the long-term effects of the pandemic on mental health, including studies in order to “augment understanding of the implications of this crisis on the mental health trajectories of today’s children and youth.”
In an accompanying editorial, Tami D. Benton, MD, psychiatrist-in-chief at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues, who were not involved in the meta-analysis, note certain limitations to the study. First, the included studies are based on self- or parent-reported symptoms. Second, the studies, more than half of which (55.2%) were done in China, may not be generalizable to all regions of the world, where 90% of children live in low- or middle-income countries.
Still, they write,“The increased mental health needs identified in the meta-analysis call for immediate action for every country. Our responses must consider the range of child mental health infrastructures available, which vary across countries, with some having well-developed and coordinated mental health services, while others have informal, limited, underfunded, or fragmented systems of care.”
Empirically supported and culturally appropriate intervention strategies for children and families according to countries and communities will be crucial, they stress.
“This meta-analysis provides the most complete evidence to date on the toll the COVID-19 pandemic has taken on child and adolescent mental health,” said Katie A. McLaughlin, PhD, a professor of psychology at Harvard University in Boston, who was not involved in the study. “The results confirm the substantial increases in symptoms of youth depression and anxiety that many clinicians and researchers have observed during the pandemic and highlight the critical need for greater investments in mental health services for children and adolescents.”
This study received no specific funding other than research support to the investigators from nonprivate entities. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Benton and associates and Dr. McLaughlin declared no competing interests.
The COVID-19 pandemic doubled international rates of child and adolescent psychological disorders, according to results of a meta-analysis.
In the first year of the pandemic, an estimated one in four youth across various regions of the globe experienced clinically elevated depression symptoms, while one in five experienced clinically elevated anxiety symptoms. These pooled estimates, which increased over time, are double prepandemic estimates, according to Nicole Racine, PhD, RPsych, a clinical psychologist at the University of Calgary (Alta.) and colleagues.
Their meta-analysis of 29 studies, comprising 80,879 young people worldwide aged 18 years or less, found pooled prevalence estimates of clinically elevated youth depression and anxiety of 25.2% (95% confidence interval, 21.2%-29.7%) and 20.5% (95% CI, 17.2%-24.4%), respectively.
“The prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms during COVID-19 [has] doubled, compared with prepandemic estimates, and moderator analyses revealed that prevalence rates were higher when collected later in the pandemic, in older adolescents, and in girls,” the researchers write online in JAMA Pediatrics.
Prepandemic estimates of clinically significant generalized anxiety and depressive symptoms in large youth cohorts were approximately 11.6% and 12.9%, respectively, the authors say.
The increases revealed in these international findings have implications for targeted mental health resource planning.
“One difficulty in the literature is that there are large discrepancies on the prevalence of child depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic, with published rates between 2% and 68%,” corresponding author Sheri Madigan, PhD, RPsych, of the University of Calgary department of psychology, said in an interview. “By conducting a synthesis of the 29 studies on over 80,000 children, we were able to determine that, on average across these studies, 25% of youth are experiencing depression and 20% are experiencing anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
The cohort
The mean age in the combined global cohort was 13 years (range 4.1-17.6 ), and the mean proportion of females was 52.7% (standard deviation) 12.3%). The findings were based on international data published from Jan. 1, 2020, to Feb. 16, 2021, in studies conducted in the Middle East (n = 1), Europe (n = 4), South America (n = 2), North America (n = 6), and East Asia (n = 16). Notably absent were data from most of Latin America and the Middle East, Africa, South East Asia, and the Pacific Islands.
As the year progressed, the prevalence of depressive symptoms rose (b = .26; 95% CI, .06-46) with the number of months elapsed. Prevalence rates also rose as both age (b = 0.08, 95% CI, 0.01-0.15), and the percentage of females in samples increased (b = .03; 95% CI, 0.01-0.05).
The authors surmise that this cumulative worsening might be because of prolonged social isolation, family financial difficulties, missed milestones, and school disruptions, which are compounded over time. A second possibility is that studies conducted in the earlier months of the pandemic were more likely to be conducted in East Asia, where the self-reported prevalence of mental health symptoms tends to be lower.
The findings highlight an urgent need for intervention and recovery efforts and also indicate the need to consider individual differences when determining targets for intervention, including age, sex, and exposure to COVID-19 stressors), they add.
Even more concerning, recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest that the pandemic spurred an increase in suspected suicide attempts by teenage girls. In the United Kingdom, acute mental health presentations to emergency care tripled over 2019 at one pediatric facility during the pandemic.
The authors attribute the toll on the psychological well-being of the world’s young people to pandemic-mandated restrictions. Those entailed loss of peer interactions, social isolation, and reduced contact with support figures such as teachers, and, “In addition, schools are often a primary location for receiving psychological services, with 80% of children relying on school-based services to address their mental health needs.” For many children, these services were rendered unavailable owing to school closures, Dr. Madigan and associates write.
In the context of clinical practice, doctors play a critical role. “With school closures, the physician’s office may be the only mental health checkpoint for youth,” Dr. Madigan said “So I recommend that family physicians screen for, and/or ask children and youth, about their mental health.”
On the home front, emerging research suggests that a predictable home environment can protect children’s mental well-being, with less depression and fewer behavioral problems observed in families adhering to regular routines during COVID-19. “Thus, a tangible solution to help mitigate the adverse effects of COVID-19 on youth is working with children and families to implement consistent and predictable routines around schoolwork, sleep, screen use, and physical activity,” the authors write.
They also point to the need for research on the long-term effects of the pandemic on mental health, including studies in order to “augment understanding of the implications of this crisis on the mental health trajectories of today’s children and youth.”
In an accompanying editorial, Tami D. Benton, MD, psychiatrist-in-chief at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues, who were not involved in the meta-analysis, note certain limitations to the study. First, the included studies are based on self- or parent-reported symptoms. Second, the studies, more than half of which (55.2%) were done in China, may not be generalizable to all regions of the world, where 90% of children live in low- or middle-income countries.
Still, they write,“The increased mental health needs identified in the meta-analysis call for immediate action for every country. Our responses must consider the range of child mental health infrastructures available, which vary across countries, with some having well-developed and coordinated mental health services, while others have informal, limited, underfunded, or fragmented systems of care.”
Empirically supported and culturally appropriate intervention strategies for children and families according to countries and communities will be crucial, they stress.
“This meta-analysis provides the most complete evidence to date on the toll the COVID-19 pandemic has taken on child and adolescent mental health,” said Katie A. McLaughlin, PhD, a professor of psychology at Harvard University in Boston, who was not involved in the study. “The results confirm the substantial increases in symptoms of youth depression and anxiety that many clinicians and researchers have observed during the pandemic and highlight the critical need for greater investments in mental health services for children and adolescents.”
This study received no specific funding other than research support to the investigators from nonprivate entities. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Benton and associates and Dr. McLaughlin declared no competing interests.
The COVID-19 pandemic doubled international rates of child and adolescent psychological disorders, according to results of a meta-analysis.
In the first year of the pandemic, an estimated one in four youth across various regions of the globe experienced clinically elevated depression symptoms, while one in five experienced clinically elevated anxiety symptoms. These pooled estimates, which increased over time, are double prepandemic estimates, according to Nicole Racine, PhD, RPsych, a clinical psychologist at the University of Calgary (Alta.) and colleagues.
Their meta-analysis of 29 studies, comprising 80,879 young people worldwide aged 18 years or less, found pooled prevalence estimates of clinically elevated youth depression and anxiety of 25.2% (95% confidence interval, 21.2%-29.7%) and 20.5% (95% CI, 17.2%-24.4%), respectively.
“The prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms during COVID-19 [has] doubled, compared with prepandemic estimates, and moderator analyses revealed that prevalence rates were higher when collected later in the pandemic, in older adolescents, and in girls,” the researchers write online in JAMA Pediatrics.
Prepandemic estimates of clinically significant generalized anxiety and depressive symptoms in large youth cohorts were approximately 11.6% and 12.9%, respectively, the authors say.
The increases revealed in these international findings have implications for targeted mental health resource planning.
“One difficulty in the literature is that there are large discrepancies on the prevalence of child depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic, with published rates between 2% and 68%,” corresponding author Sheri Madigan, PhD, RPsych, of the University of Calgary department of psychology, said in an interview. “By conducting a synthesis of the 29 studies on over 80,000 children, we were able to determine that, on average across these studies, 25% of youth are experiencing depression and 20% are experiencing anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
The cohort
The mean age in the combined global cohort was 13 years (range 4.1-17.6 ), and the mean proportion of females was 52.7% (standard deviation) 12.3%). The findings were based on international data published from Jan. 1, 2020, to Feb. 16, 2021, in studies conducted in the Middle East (n = 1), Europe (n = 4), South America (n = 2), North America (n = 6), and East Asia (n = 16). Notably absent were data from most of Latin America and the Middle East, Africa, South East Asia, and the Pacific Islands.
As the year progressed, the prevalence of depressive symptoms rose (b = .26; 95% CI, .06-46) with the number of months elapsed. Prevalence rates also rose as both age (b = 0.08, 95% CI, 0.01-0.15), and the percentage of females in samples increased (b = .03; 95% CI, 0.01-0.05).
The authors surmise that this cumulative worsening might be because of prolonged social isolation, family financial difficulties, missed milestones, and school disruptions, which are compounded over time. A second possibility is that studies conducted in the earlier months of the pandemic were more likely to be conducted in East Asia, where the self-reported prevalence of mental health symptoms tends to be lower.
The findings highlight an urgent need for intervention and recovery efforts and also indicate the need to consider individual differences when determining targets for intervention, including age, sex, and exposure to COVID-19 stressors), they add.
Even more concerning, recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest that the pandemic spurred an increase in suspected suicide attempts by teenage girls. In the United Kingdom, acute mental health presentations to emergency care tripled over 2019 at one pediatric facility during the pandemic.
The authors attribute the toll on the psychological well-being of the world’s young people to pandemic-mandated restrictions. Those entailed loss of peer interactions, social isolation, and reduced contact with support figures such as teachers, and, “In addition, schools are often a primary location for receiving psychological services, with 80% of children relying on school-based services to address their mental health needs.” For many children, these services were rendered unavailable owing to school closures, Dr. Madigan and associates write.
In the context of clinical practice, doctors play a critical role. “With school closures, the physician’s office may be the only mental health checkpoint for youth,” Dr. Madigan said “So I recommend that family physicians screen for, and/or ask children and youth, about their mental health.”
On the home front, emerging research suggests that a predictable home environment can protect children’s mental well-being, with less depression and fewer behavioral problems observed in families adhering to regular routines during COVID-19. “Thus, a tangible solution to help mitigate the adverse effects of COVID-19 on youth is working with children and families to implement consistent and predictable routines around schoolwork, sleep, screen use, and physical activity,” the authors write.
They also point to the need for research on the long-term effects of the pandemic on mental health, including studies in order to “augment understanding of the implications of this crisis on the mental health trajectories of today’s children and youth.”
In an accompanying editorial, Tami D. Benton, MD, psychiatrist-in-chief at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues, who were not involved in the meta-analysis, note certain limitations to the study. First, the included studies are based on self- or parent-reported symptoms. Second, the studies, more than half of which (55.2%) were done in China, may not be generalizable to all regions of the world, where 90% of children live in low- or middle-income countries.
Still, they write,“The increased mental health needs identified in the meta-analysis call for immediate action for every country. Our responses must consider the range of child mental health infrastructures available, which vary across countries, with some having well-developed and coordinated mental health services, while others have informal, limited, underfunded, or fragmented systems of care.”
Empirically supported and culturally appropriate intervention strategies for children and families according to countries and communities will be crucial, they stress.
“This meta-analysis provides the most complete evidence to date on the toll the COVID-19 pandemic has taken on child and adolescent mental health,” said Katie A. McLaughlin, PhD, a professor of psychology at Harvard University in Boston, who was not involved in the study. “The results confirm the substantial increases in symptoms of youth depression and anxiety that many clinicians and researchers have observed during the pandemic and highlight the critical need for greater investments in mental health services for children and adolescents.”
This study received no specific funding other than research support to the investigators from nonprivate entities. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Benton and associates and Dr. McLaughlin declared no competing interests.