User login
Prediabetes linked to higher CVD and CKD rates
in a study of nearly 337,000 people included in the UK Biobank database.
The findings suggest that people with prediabetes have “heightened risk even without progression to type 2 diabetes,” Michael C. Honigberg, MD, said at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
“Hemoglobin A1c may be better considered as a continuous measure of risk rather than dichotomized” as either less than 6.5%, or 6.5% or higher, the usual threshold defining people with type 2 diabetes, said Dr. Honigberg, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
‘Prediabetes is not a benign entity’
“Our findings reinforce the notion that A1c represents a continuum of risk, with elevated risks observed, especially for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], at levels where some clinicians wouldn’t think twice about them. Prediabetes is not a benign entity in the middle-aged population we studied,” Dr. Honigberg said in an interview. “Risks are higher in individuals with type 2 diabetes,” he stressed, “however, prediabetes is so much more common that it appears to confer similar cardio, renal, and metabolic risks at a population level.”
Results from prior observational studies also showed elevated incidence rate of cardiovascular disease events in people with prediabetes, including a 2010 report based on data from about 11,000 U.S. residents, and in a more recent meta-analysis of 129 studies involving more than 10 million people. The new report by Dr. Honigberg “is the first to comprehensively evaluate diverse cardio-renal-metabolic outcomes across a range of A1c levels using a very large, contemporary database,” he noted. In addition, most prior reports did not include chronic kidney disease as an examined outcome.
The primary endpoint examined in the new analysis was the combined incidence during a median follow-up of just over 11 years of ASCVD events (coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, or peripheral artery disease), CKD, or heart failure among 336,709 adults in the UK Biobank who at baseline had none of these conditions nor type 1 diabetes.
The vast majority, 82%, were normoglycemic at baseline, based on having an A1c of less than 5.7%; 14% had prediabetes, with an A1c of 5.7%-6.4%; and 4% had type 2 diabetes based on an A1c of at least 6.5% or on insulin treatment. Patients averaged about 57 years of age, slightly more than half were women, and average body mass index was in the overweight category except for those with type 2 diabetes.
The primary endpoint, the combined incidence of ASCVD, CKD, and heart failure, was 24% among those with type 2 diabetes, 14% in those with prediabetes, and 8% in those who were normoglycemic at entry. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online. Most of these events involved ASCVD, which occurred in 11% of those in the prediabetes subgroup (roughly four-fifths of the events in this subgroup), and in 17% of those with type 2 diabetes (nearly three-quarters of the events in this subgroup).
In an analysis that adjusted for more than a dozen demographic and clinical factors, the presence of prediabetes linked with significant increases in the incidence rate of all three outcomes compared with people who were normoglycemic at baseline. The analysis also identified an A1c level of 5.0% as linked with the lowest incidence of each of the three adverse outcomes. And a very granular analysis suggested that a significantly elevated risk for ASCVD first appeared when A1c levels were in the range of 5.4%-5.7%; a significantly increased incidence of CKD became apparent once A1c was in the range of 6.2%-6.5%; and a significantly increased incidence of heart failure began to manifest once A1c levels reached at least 7.0%.
Need for comprehensive cardiometabolic risk management
The findings “highlight the importance of identifying and comprehensively managing cardiometabolic risk in people with prediabetes, including dietary modification, exercise, weight loss and obesity management, smoking cessation, and attention to hypertension and hypercholesterolemia,” Dr. Honigberg said. While these data cannot address the appropriateness of using novel drug interventions in people with prediabetes, they suggest that people with prediabetes should be the focus of future prevention trials testing agents such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“These data help us discuss risk with patients [with prediabetes], and reemphasize the importance of guideline-directed preventive care,” said Vijay Nambi, MD, PhD, a preventive cardiologist and lipid specialist at Baylor College of Medicine and the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston, who was not involved with the study.
An additional analysis reported by Dr. Honigberg examined the risk among people with prediabetes who also were current or former smokers and in the top tertile of the prediabetes study population for systolic blood pressure, high non-HDL cholesterol, and C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation). This very high-risk subgroup of people with prediabetes had incidence rates for ASCVD events and for heart failure that tracked identically to those with type 2 diabetes. However. the incidence rate for CKD in these high-risk people with prediabetes remained below that of patients with type 2 diabetes.
Dr. Honigberg had no disclosures. Dr. Nambi has received research funding from Amgen, Merck, and Roche.
in a study of nearly 337,000 people included in the UK Biobank database.
The findings suggest that people with prediabetes have “heightened risk even without progression to type 2 diabetes,” Michael C. Honigberg, MD, said at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
“Hemoglobin A1c may be better considered as a continuous measure of risk rather than dichotomized” as either less than 6.5%, or 6.5% or higher, the usual threshold defining people with type 2 diabetes, said Dr. Honigberg, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
‘Prediabetes is not a benign entity’
“Our findings reinforce the notion that A1c represents a continuum of risk, with elevated risks observed, especially for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], at levels where some clinicians wouldn’t think twice about them. Prediabetes is not a benign entity in the middle-aged population we studied,” Dr. Honigberg said in an interview. “Risks are higher in individuals with type 2 diabetes,” he stressed, “however, prediabetes is so much more common that it appears to confer similar cardio, renal, and metabolic risks at a population level.”
Results from prior observational studies also showed elevated incidence rate of cardiovascular disease events in people with prediabetes, including a 2010 report based on data from about 11,000 U.S. residents, and in a more recent meta-analysis of 129 studies involving more than 10 million people. The new report by Dr. Honigberg “is the first to comprehensively evaluate diverse cardio-renal-metabolic outcomes across a range of A1c levels using a very large, contemporary database,” he noted. In addition, most prior reports did not include chronic kidney disease as an examined outcome.
The primary endpoint examined in the new analysis was the combined incidence during a median follow-up of just over 11 years of ASCVD events (coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, or peripheral artery disease), CKD, or heart failure among 336,709 adults in the UK Biobank who at baseline had none of these conditions nor type 1 diabetes.
The vast majority, 82%, were normoglycemic at baseline, based on having an A1c of less than 5.7%; 14% had prediabetes, with an A1c of 5.7%-6.4%; and 4% had type 2 diabetes based on an A1c of at least 6.5% or on insulin treatment. Patients averaged about 57 years of age, slightly more than half were women, and average body mass index was in the overweight category except for those with type 2 diabetes.
The primary endpoint, the combined incidence of ASCVD, CKD, and heart failure, was 24% among those with type 2 diabetes, 14% in those with prediabetes, and 8% in those who were normoglycemic at entry. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online. Most of these events involved ASCVD, which occurred in 11% of those in the prediabetes subgroup (roughly four-fifths of the events in this subgroup), and in 17% of those with type 2 diabetes (nearly three-quarters of the events in this subgroup).
In an analysis that adjusted for more than a dozen demographic and clinical factors, the presence of prediabetes linked with significant increases in the incidence rate of all three outcomes compared with people who were normoglycemic at baseline. The analysis also identified an A1c level of 5.0% as linked with the lowest incidence of each of the three adverse outcomes. And a very granular analysis suggested that a significantly elevated risk for ASCVD first appeared when A1c levels were in the range of 5.4%-5.7%; a significantly increased incidence of CKD became apparent once A1c was in the range of 6.2%-6.5%; and a significantly increased incidence of heart failure began to manifest once A1c levels reached at least 7.0%.
Need for comprehensive cardiometabolic risk management
The findings “highlight the importance of identifying and comprehensively managing cardiometabolic risk in people with prediabetes, including dietary modification, exercise, weight loss and obesity management, smoking cessation, and attention to hypertension and hypercholesterolemia,” Dr. Honigberg said. While these data cannot address the appropriateness of using novel drug interventions in people with prediabetes, they suggest that people with prediabetes should be the focus of future prevention trials testing agents such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“These data help us discuss risk with patients [with prediabetes], and reemphasize the importance of guideline-directed preventive care,” said Vijay Nambi, MD, PhD, a preventive cardiologist and lipid specialist at Baylor College of Medicine and the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston, who was not involved with the study.
An additional analysis reported by Dr. Honigberg examined the risk among people with prediabetes who also were current or former smokers and in the top tertile of the prediabetes study population for systolic blood pressure, high non-HDL cholesterol, and C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation). This very high-risk subgroup of people with prediabetes had incidence rates for ASCVD events and for heart failure that tracked identically to those with type 2 diabetes. However. the incidence rate for CKD in these high-risk people with prediabetes remained below that of patients with type 2 diabetes.
Dr. Honigberg had no disclosures. Dr. Nambi has received research funding from Amgen, Merck, and Roche.
in a study of nearly 337,000 people included in the UK Biobank database.
The findings suggest that people with prediabetes have “heightened risk even without progression to type 2 diabetes,” Michael C. Honigberg, MD, said at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
“Hemoglobin A1c may be better considered as a continuous measure of risk rather than dichotomized” as either less than 6.5%, or 6.5% or higher, the usual threshold defining people with type 2 diabetes, said Dr. Honigberg, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
‘Prediabetes is not a benign entity’
“Our findings reinforce the notion that A1c represents a continuum of risk, with elevated risks observed, especially for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], at levels where some clinicians wouldn’t think twice about them. Prediabetes is not a benign entity in the middle-aged population we studied,” Dr. Honigberg said in an interview. “Risks are higher in individuals with type 2 diabetes,” he stressed, “however, prediabetes is so much more common that it appears to confer similar cardio, renal, and metabolic risks at a population level.”
Results from prior observational studies also showed elevated incidence rate of cardiovascular disease events in people with prediabetes, including a 2010 report based on data from about 11,000 U.S. residents, and in a more recent meta-analysis of 129 studies involving more than 10 million people. The new report by Dr. Honigberg “is the first to comprehensively evaluate diverse cardio-renal-metabolic outcomes across a range of A1c levels using a very large, contemporary database,” he noted. In addition, most prior reports did not include chronic kidney disease as an examined outcome.
The primary endpoint examined in the new analysis was the combined incidence during a median follow-up of just over 11 years of ASCVD events (coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, or peripheral artery disease), CKD, or heart failure among 336,709 adults in the UK Biobank who at baseline had none of these conditions nor type 1 diabetes.
The vast majority, 82%, were normoglycemic at baseline, based on having an A1c of less than 5.7%; 14% had prediabetes, with an A1c of 5.7%-6.4%; and 4% had type 2 diabetes based on an A1c of at least 6.5% or on insulin treatment. Patients averaged about 57 years of age, slightly more than half were women, and average body mass index was in the overweight category except for those with type 2 diabetes.
The primary endpoint, the combined incidence of ASCVD, CKD, and heart failure, was 24% among those with type 2 diabetes, 14% in those with prediabetes, and 8% in those who were normoglycemic at entry. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online. Most of these events involved ASCVD, which occurred in 11% of those in the prediabetes subgroup (roughly four-fifths of the events in this subgroup), and in 17% of those with type 2 diabetes (nearly three-quarters of the events in this subgroup).
In an analysis that adjusted for more than a dozen demographic and clinical factors, the presence of prediabetes linked with significant increases in the incidence rate of all three outcomes compared with people who were normoglycemic at baseline. The analysis also identified an A1c level of 5.0% as linked with the lowest incidence of each of the three adverse outcomes. And a very granular analysis suggested that a significantly elevated risk for ASCVD first appeared when A1c levels were in the range of 5.4%-5.7%; a significantly increased incidence of CKD became apparent once A1c was in the range of 6.2%-6.5%; and a significantly increased incidence of heart failure began to manifest once A1c levels reached at least 7.0%.
Need for comprehensive cardiometabolic risk management
The findings “highlight the importance of identifying and comprehensively managing cardiometabolic risk in people with prediabetes, including dietary modification, exercise, weight loss and obesity management, smoking cessation, and attention to hypertension and hypercholesterolemia,” Dr. Honigberg said. While these data cannot address the appropriateness of using novel drug interventions in people with prediabetes, they suggest that people with prediabetes should be the focus of future prevention trials testing agents such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
“These data help us discuss risk with patients [with prediabetes], and reemphasize the importance of guideline-directed preventive care,” said Vijay Nambi, MD, PhD, a preventive cardiologist and lipid specialist at Baylor College of Medicine and the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston, who was not involved with the study.
An additional analysis reported by Dr. Honigberg examined the risk among people with prediabetes who also were current or former smokers and in the top tertile of the prediabetes study population for systolic blood pressure, high non-HDL cholesterol, and C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation). This very high-risk subgroup of people with prediabetes had incidence rates for ASCVD events and for heart failure that tracked identically to those with type 2 diabetes. However. the incidence rate for CKD in these high-risk people with prediabetes remained below that of patients with type 2 diabetes.
Dr. Honigberg had no disclosures. Dr. Nambi has received research funding from Amgen, Merck, and Roche.
FROM ACC 2021
Mohs surgery favorable as monotherapy for early Merkel cell carcinomas
Pittsburgh.
The results compare favorably with the standard treatment approach, wide local excision with or without radiation, which has a local recurrence rate of 4.2%-31.7% because of incomplete excision or false negative margins, said Vitaly Terushkin, MD, a Mohs surgeon who presented the findings of the study, a retrospective chart review, at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
Mohs surgery as monotherapy offered “survival at least as good as historical controls treated with wide local excision plus radiation therapy, and because of the superior local control, Mohs surgery may obviate the need for adjuvant radiation and decrease the chance for additional surgery for the treatment of local recurrence,” said Dr. Terushkin, now in practice in the New York City area.
“We hope this data fuel additional studies with larger cohorts to continue to explore the value of Mohs for Merkel cell carcinoma,” he said.
The findings add to a growing body of literature supporting Mohs for many types of rare tumors. “Micrographic surgery or complete circumferential peripheral and deep margin analysis has been shown to be superior to wide local excision in a variety of tumors and clinical scenarios,” said Vishal Patel, MD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the cutaneous oncology program at George Washington University, Washington.
“When the entire margin is able to be evaluated over random bread-loafed sections, there is growing evidence that this leads to superior outcomes and disease specific mortality,” he said when asked for comment on the study results.
In all, 56 primary Merkel cell carcinomas were treated in the 53 patients from 2001 to 2019; about two-thirds of the patients had stage 1 tumors and the rest stage 2a.
They were treated with Mohs alone, without radiation. Average follow up was 4.6 years, with about a third of patients followed for 5 or more years.
The average age of the patients was 78 years, and just over half were men. In more than half the cases, tumors were located on the head and neck (62.5%), and the mean tumor size was 1.7 cm. Patients were negative for lymphadenopathy and declined lymph node biopsy.
Although there was no local recurrence, defined as tumor reemerging within or adjacent to the surgery site, 7 patients (12.7%) developed in-transit metastases, 13 (23.6%) developed nodal metastases, and 3 developed distant metastases.
The 5-year disease-specific survival rate was 91.2% for stage 1 and 68.6% for stage 2a patients, which compared favorably with historical controls treated with wide local excision with or without radiation, with reported 5-year disease-specific survival rates of 81%-87% for stage 1 disease and 63%-67% for stage 2. Although radiation wasn’t used in the study, Dr. Patel noted that more investigation is needed about the role of adjuvant radiation therapy after Mohs surgery “given recent publications showing improved outcomes in patients with narrow margin excision and postoperative radiation therapy.”
No external funding of the study was reported. Dr. Terushkin had no disclosures. Dr. Patel is a consultant for Sanofi, Regeneron, and Almirall.
Pittsburgh.
The results compare favorably with the standard treatment approach, wide local excision with or without radiation, which has a local recurrence rate of 4.2%-31.7% because of incomplete excision or false negative margins, said Vitaly Terushkin, MD, a Mohs surgeon who presented the findings of the study, a retrospective chart review, at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
Mohs surgery as monotherapy offered “survival at least as good as historical controls treated with wide local excision plus radiation therapy, and because of the superior local control, Mohs surgery may obviate the need for adjuvant radiation and decrease the chance for additional surgery for the treatment of local recurrence,” said Dr. Terushkin, now in practice in the New York City area.
“We hope this data fuel additional studies with larger cohorts to continue to explore the value of Mohs for Merkel cell carcinoma,” he said.
The findings add to a growing body of literature supporting Mohs for many types of rare tumors. “Micrographic surgery or complete circumferential peripheral and deep margin analysis has been shown to be superior to wide local excision in a variety of tumors and clinical scenarios,” said Vishal Patel, MD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the cutaneous oncology program at George Washington University, Washington.
“When the entire margin is able to be evaluated over random bread-loafed sections, there is growing evidence that this leads to superior outcomes and disease specific mortality,” he said when asked for comment on the study results.
In all, 56 primary Merkel cell carcinomas were treated in the 53 patients from 2001 to 2019; about two-thirds of the patients had stage 1 tumors and the rest stage 2a.
They were treated with Mohs alone, without radiation. Average follow up was 4.6 years, with about a third of patients followed for 5 or more years.
The average age of the patients was 78 years, and just over half were men. In more than half the cases, tumors were located on the head and neck (62.5%), and the mean tumor size was 1.7 cm. Patients were negative for lymphadenopathy and declined lymph node biopsy.
Although there was no local recurrence, defined as tumor reemerging within or adjacent to the surgery site, 7 patients (12.7%) developed in-transit metastases, 13 (23.6%) developed nodal metastases, and 3 developed distant metastases.
The 5-year disease-specific survival rate was 91.2% for stage 1 and 68.6% for stage 2a patients, which compared favorably with historical controls treated with wide local excision with or without radiation, with reported 5-year disease-specific survival rates of 81%-87% for stage 1 disease and 63%-67% for stage 2. Although radiation wasn’t used in the study, Dr. Patel noted that more investigation is needed about the role of adjuvant radiation therapy after Mohs surgery “given recent publications showing improved outcomes in patients with narrow margin excision and postoperative radiation therapy.”
No external funding of the study was reported. Dr. Terushkin had no disclosures. Dr. Patel is a consultant for Sanofi, Regeneron, and Almirall.
Pittsburgh.
The results compare favorably with the standard treatment approach, wide local excision with or without radiation, which has a local recurrence rate of 4.2%-31.7% because of incomplete excision or false negative margins, said Vitaly Terushkin, MD, a Mohs surgeon who presented the findings of the study, a retrospective chart review, at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
Mohs surgery as monotherapy offered “survival at least as good as historical controls treated with wide local excision plus radiation therapy, and because of the superior local control, Mohs surgery may obviate the need for adjuvant radiation and decrease the chance for additional surgery for the treatment of local recurrence,” said Dr. Terushkin, now in practice in the New York City area.
“We hope this data fuel additional studies with larger cohorts to continue to explore the value of Mohs for Merkel cell carcinoma,” he said.
The findings add to a growing body of literature supporting Mohs for many types of rare tumors. “Micrographic surgery or complete circumferential peripheral and deep margin analysis has been shown to be superior to wide local excision in a variety of tumors and clinical scenarios,” said Vishal Patel, MD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the cutaneous oncology program at George Washington University, Washington.
“When the entire margin is able to be evaluated over random bread-loafed sections, there is growing evidence that this leads to superior outcomes and disease specific mortality,” he said when asked for comment on the study results.
In all, 56 primary Merkel cell carcinomas were treated in the 53 patients from 2001 to 2019; about two-thirds of the patients had stage 1 tumors and the rest stage 2a.
They were treated with Mohs alone, without radiation. Average follow up was 4.6 years, with about a third of patients followed for 5 or more years.
The average age of the patients was 78 years, and just over half were men. In more than half the cases, tumors were located on the head and neck (62.5%), and the mean tumor size was 1.7 cm. Patients were negative for lymphadenopathy and declined lymph node biopsy.
Although there was no local recurrence, defined as tumor reemerging within or adjacent to the surgery site, 7 patients (12.7%) developed in-transit metastases, 13 (23.6%) developed nodal metastases, and 3 developed distant metastases.
The 5-year disease-specific survival rate was 91.2% for stage 1 and 68.6% for stage 2a patients, which compared favorably with historical controls treated with wide local excision with or without radiation, with reported 5-year disease-specific survival rates of 81%-87% for stage 1 disease and 63%-67% for stage 2. Although radiation wasn’t used in the study, Dr. Patel noted that more investigation is needed about the role of adjuvant radiation therapy after Mohs surgery “given recent publications showing improved outcomes in patients with narrow margin excision and postoperative radiation therapy.”
No external funding of the study was reported. Dr. Terushkin had no disclosures. Dr. Patel is a consultant for Sanofi, Regeneron, and Almirall.
FROM ACMS 2021
Noses can be electronic, and toilets can be smart
Cancer loses … by a nose
Since the human nose is unpredictable at best, we’ve learned to rely on animals for our detailed nozzle needs. But researchers have found the next best thing to man’s best friend to accurately identify cancers.
A team at the University of Pennsylvania has developed an electronic olfaction, or “e-nose,” that has a 95% accuracy rate in distinguishing benign and malignant pancreatic and ovarian cancer cells from a single blood sample. How?
The e-nose system is equipped with nanosensors that are able to detect the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by cells in a blood sample. Not only does this create an opportunity for an easier, noninvasive screening practice, but it’s fast. The e-nose can distinguish VOCs from healthy to cancerous blood cells in 20 minutes or less and is just as effective in picking up on early- and late-stage cancers.
The investigators hope that this innovative technology can pave the way for similar devices with other uses. Thanks to the e-nose, a handheld device is in development that may be able to sniff out the signature odor of people with COVID-19.
That’s one smart schnoz.
Do you think this is a (food) game?
Dieting and eating healthy is tough, even during the best of times, and it has not been the best of times. With all respect to Charles Dickens, it’s been the worst of times, full stop. Millions of people have spent the past year sitting around their homes doing nothing, and it’s only natural that many would let their discipline slide.
Naturally, the solution to unhealthy eating habits is to sit down and play with your phone. No, that’s not the joke, the Food Trainer app, available on all cellular devices near you, is designed to encourage healthy eating by turning it into a game of sorts. When users open the app, they’re presented with images of food, and they’re trained to tap on images of healthy food and pass on images of unhealthy ones. The process takes less than 5 minutes.
It sounds really simple, but in a study of more than 1,000 people, consumption of junk food fell by 1 point on an 8-point scale (ranging from four times per day to zero to one time per month), participants lost about half a kilogram (a little over one pound), and more healthy food was eaten. Those who used the app more regularly, along the lines of 10 times per month or more, saw greater benefits.
The authors did acknowledge that those who used the app more may have been more motivated to lose weight anyway, which perhaps limits the overall benefit, but reviews on Google Play were overall quite positive, and if there’s one great truth in this world, it’s that Internet reviewers are almost impossible to please. So perhaps this app is worth looking into if you’re like the LOTME staff and you’re up at the top end of that 8-point scale. What, pizza is delicious, who wouldn’t eat it four times a day? And you can also get it from your phone!
It’s time for a little mass kickin’
The universe, scientists tell us, is a big place. Really big. Chromosomes, scientists tell us, are small. Really small. But despite this very fundamental difference, the universe and chromosomes share a deep, dark secret: unexplained mass.
This being a medical publication, we’ll start with chromosomes. A group of researchers measured their mass with x-rays for the first time and found that “the 46 chromosomes in each of our cells weigh 242 picograms (trillionths of a gram). This is heavier than we would expect, and, if replicated, points to unexplained excess mass in chromosomes,” Ian K. Robinson, PhD, said in a written statement.
We’re not just talking about a bit of a beer belly here. “The chromosomes were about 20 times heavier than the DNA they contained,” according to the investigators.
Now to the universe. Here’s what CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Research, has to say about the mass of the universe: “Galaxies in our universe … are rotating with such speed that the gravity generated by their observable matter could not possibly hold them together. … which leads scientists to believe that something we cannot see is at work. They think something we have yet to detect directly is giving these galaxies extra mass.”
But wait, there’s more! “The matter we know and that makes up all stars and galaxies only accounts for 5% of the content of the universe!”
So chromosomes are about 20 times heavier than the DNA they contain, and the universe is about 20 times heavier than the matter that can be seen. Interesting.
We are, of course, happy to share this news with our readers, but there is one catch: Don’t tell Neil deGrasse Tyson. He’ll want to reclassify our genetic solar system into 45 chromosomes and one dwarf chromosome.
A photo finish for the Smart Toilet
We know that poop can tell us a lot about our health, but new research by scientists at Duke University is really on a roll. Their Smart Toilet has been created to help people keep an eye on their bowel health. The device takes pictures of poop after it is flushed and can tell whether the consistency is loose, bloody, or normal.
The Smart Toilet can really help people with issues such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease by helping them, and their doctors, keep tabs on their poop. “Typically, gastroenterologists have to rely on patient self-reported information about their stool to help determine the cause of their gastrointestinal health issues, which can be very unreliable,” study lead author Deborah Fisher said.
Not many people look too closely at their poop before it’s flushed, so the fecal photos can make a big difference. The Smart Toilet is installed into the pipes of a toilet and does its thing when the toilet is flushed, so there doesn’t seem to be much work on the patient’s end. Other than the, um, you know, usual work from the patient’s end.
Cancer loses … by a nose
Since the human nose is unpredictable at best, we’ve learned to rely on animals for our detailed nozzle needs. But researchers have found the next best thing to man’s best friend to accurately identify cancers.
A team at the University of Pennsylvania has developed an electronic olfaction, or “e-nose,” that has a 95% accuracy rate in distinguishing benign and malignant pancreatic and ovarian cancer cells from a single blood sample. How?
The e-nose system is equipped with nanosensors that are able to detect the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by cells in a blood sample. Not only does this create an opportunity for an easier, noninvasive screening practice, but it’s fast. The e-nose can distinguish VOCs from healthy to cancerous blood cells in 20 minutes or less and is just as effective in picking up on early- and late-stage cancers.
The investigators hope that this innovative technology can pave the way for similar devices with other uses. Thanks to the e-nose, a handheld device is in development that may be able to sniff out the signature odor of people with COVID-19.
That’s one smart schnoz.
Do you think this is a (food) game?
Dieting and eating healthy is tough, even during the best of times, and it has not been the best of times. With all respect to Charles Dickens, it’s been the worst of times, full stop. Millions of people have spent the past year sitting around their homes doing nothing, and it’s only natural that many would let their discipline slide.
Naturally, the solution to unhealthy eating habits is to sit down and play with your phone. No, that’s not the joke, the Food Trainer app, available on all cellular devices near you, is designed to encourage healthy eating by turning it into a game of sorts. When users open the app, they’re presented with images of food, and they’re trained to tap on images of healthy food and pass on images of unhealthy ones. The process takes less than 5 minutes.
It sounds really simple, but in a study of more than 1,000 people, consumption of junk food fell by 1 point on an 8-point scale (ranging from four times per day to zero to one time per month), participants lost about half a kilogram (a little over one pound), and more healthy food was eaten. Those who used the app more regularly, along the lines of 10 times per month or more, saw greater benefits.
The authors did acknowledge that those who used the app more may have been more motivated to lose weight anyway, which perhaps limits the overall benefit, but reviews on Google Play were overall quite positive, and if there’s one great truth in this world, it’s that Internet reviewers are almost impossible to please. So perhaps this app is worth looking into if you’re like the LOTME staff and you’re up at the top end of that 8-point scale. What, pizza is delicious, who wouldn’t eat it four times a day? And you can also get it from your phone!
It’s time for a little mass kickin’
The universe, scientists tell us, is a big place. Really big. Chromosomes, scientists tell us, are small. Really small. But despite this very fundamental difference, the universe and chromosomes share a deep, dark secret: unexplained mass.
This being a medical publication, we’ll start with chromosomes. A group of researchers measured their mass with x-rays for the first time and found that “the 46 chromosomes in each of our cells weigh 242 picograms (trillionths of a gram). This is heavier than we would expect, and, if replicated, points to unexplained excess mass in chromosomes,” Ian K. Robinson, PhD, said in a written statement.
We’re not just talking about a bit of a beer belly here. “The chromosomes were about 20 times heavier than the DNA they contained,” according to the investigators.
Now to the universe. Here’s what CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Research, has to say about the mass of the universe: “Galaxies in our universe … are rotating with such speed that the gravity generated by their observable matter could not possibly hold them together. … which leads scientists to believe that something we cannot see is at work. They think something we have yet to detect directly is giving these galaxies extra mass.”
But wait, there’s more! “The matter we know and that makes up all stars and galaxies only accounts for 5% of the content of the universe!”
So chromosomes are about 20 times heavier than the DNA they contain, and the universe is about 20 times heavier than the matter that can be seen. Interesting.
We are, of course, happy to share this news with our readers, but there is one catch: Don’t tell Neil deGrasse Tyson. He’ll want to reclassify our genetic solar system into 45 chromosomes and one dwarf chromosome.
A photo finish for the Smart Toilet
We know that poop can tell us a lot about our health, but new research by scientists at Duke University is really on a roll. Their Smart Toilet has been created to help people keep an eye on their bowel health. The device takes pictures of poop after it is flushed and can tell whether the consistency is loose, bloody, or normal.
The Smart Toilet can really help people with issues such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease by helping them, and their doctors, keep tabs on their poop. “Typically, gastroenterologists have to rely on patient self-reported information about their stool to help determine the cause of their gastrointestinal health issues, which can be very unreliable,” study lead author Deborah Fisher said.
Not many people look too closely at their poop before it’s flushed, so the fecal photos can make a big difference. The Smart Toilet is installed into the pipes of a toilet and does its thing when the toilet is flushed, so there doesn’t seem to be much work on the patient’s end. Other than the, um, you know, usual work from the patient’s end.
Cancer loses … by a nose
Since the human nose is unpredictable at best, we’ve learned to rely on animals for our detailed nozzle needs. But researchers have found the next best thing to man’s best friend to accurately identify cancers.
A team at the University of Pennsylvania has developed an electronic olfaction, or “e-nose,” that has a 95% accuracy rate in distinguishing benign and malignant pancreatic and ovarian cancer cells from a single blood sample. How?
The e-nose system is equipped with nanosensors that are able to detect the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by cells in a blood sample. Not only does this create an opportunity for an easier, noninvasive screening practice, but it’s fast. The e-nose can distinguish VOCs from healthy to cancerous blood cells in 20 minutes or less and is just as effective in picking up on early- and late-stage cancers.
The investigators hope that this innovative technology can pave the way for similar devices with other uses. Thanks to the e-nose, a handheld device is in development that may be able to sniff out the signature odor of people with COVID-19.
That’s one smart schnoz.
Do you think this is a (food) game?
Dieting and eating healthy is tough, even during the best of times, and it has not been the best of times. With all respect to Charles Dickens, it’s been the worst of times, full stop. Millions of people have spent the past year sitting around their homes doing nothing, and it’s only natural that many would let their discipline slide.
Naturally, the solution to unhealthy eating habits is to sit down and play with your phone. No, that’s not the joke, the Food Trainer app, available on all cellular devices near you, is designed to encourage healthy eating by turning it into a game of sorts. When users open the app, they’re presented with images of food, and they’re trained to tap on images of healthy food and pass on images of unhealthy ones. The process takes less than 5 minutes.
It sounds really simple, but in a study of more than 1,000 people, consumption of junk food fell by 1 point on an 8-point scale (ranging from four times per day to zero to one time per month), participants lost about half a kilogram (a little over one pound), and more healthy food was eaten. Those who used the app more regularly, along the lines of 10 times per month or more, saw greater benefits.
The authors did acknowledge that those who used the app more may have been more motivated to lose weight anyway, which perhaps limits the overall benefit, but reviews on Google Play were overall quite positive, and if there’s one great truth in this world, it’s that Internet reviewers are almost impossible to please. So perhaps this app is worth looking into if you’re like the LOTME staff and you’re up at the top end of that 8-point scale. What, pizza is delicious, who wouldn’t eat it four times a day? And you can also get it from your phone!
It’s time for a little mass kickin’
The universe, scientists tell us, is a big place. Really big. Chromosomes, scientists tell us, are small. Really small. But despite this very fundamental difference, the universe and chromosomes share a deep, dark secret: unexplained mass.
This being a medical publication, we’ll start with chromosomes. A group of researchers measured their mass with x-rays for the first time and found that “the 46 chromosomes in each of our cells weigh 242 picograms (trillionths of a gram). This is heavier than we would expect, and, if replicated, points to unexplained excess mass in chromosomes,” Ian K. Robinson, PhD, said in a written statement.
We’re not just talking about a bit of a beer belly here. “The chromosomes were about 20 times heavier than the DNA they contained,” according to the investigators.
Now to the universe. Here’s what CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Research, has to say about the mass of the universe: “Galaxies in our universe … are rotating with such speed that the gravity generated by their observable matter could not possibly hold them together. … which leads scientists to believe that something we cannot see is at work. They think something we have yet to detect directly is giving these galaxies extra mass.”
But wait, there’s more! “The matter we know and that makes up all stars and galaxies only accounts for 5% of the content of the universe!”
So chromosomes are about 20 times heavier than the DNA they contain, and the universe is about 20 times heavier than the matter that can be seen. Interesting.
We are, of course, happy to share this news with our readers, but there is one catch: Don’t tell Neil deGrasse Tyson. He’ll want to reclassify our genetic solar system into 45 chromosomes and one dwarf chromosome.
A photo finish for the Smart Toilet
We know that poop can tell us a lot about our health, but new research by scientists at Duke University is really on a roll. Their Smart Toilet has been created to help people keep an eye on their bowel health. The device takes pictures of poop after it is flushed and can tell whether the consistency is loose, bloody, or normal.
The Smart Toilet can really help people with issues such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease by helping them, and their doctors, keep tabs on their poop. “Typically, gastroenterologists have to rely on patient self-reported information about their stool to help determine the cause of their gastrointestinal health issues, which can be very unreliable,” study lead author Deborah Fisher said.
Not many people look too closely at their poop before it’s flushed, so the fecal photos can make a big difference. The Smart Toilet is installed into the pipes of a toilet and does its thing when the toilet is flushed, so there doesn’t seem to be much work on the patient’s end. Other than the, um, you know, usual work from the patient’s end.
Naomi Osaka withdraws from the French Open: When athletes struggle
In 2018, when Naomi Osaka won the U.S. Open by defeating Serena Williams, the trophy ceremony was painful to watch.
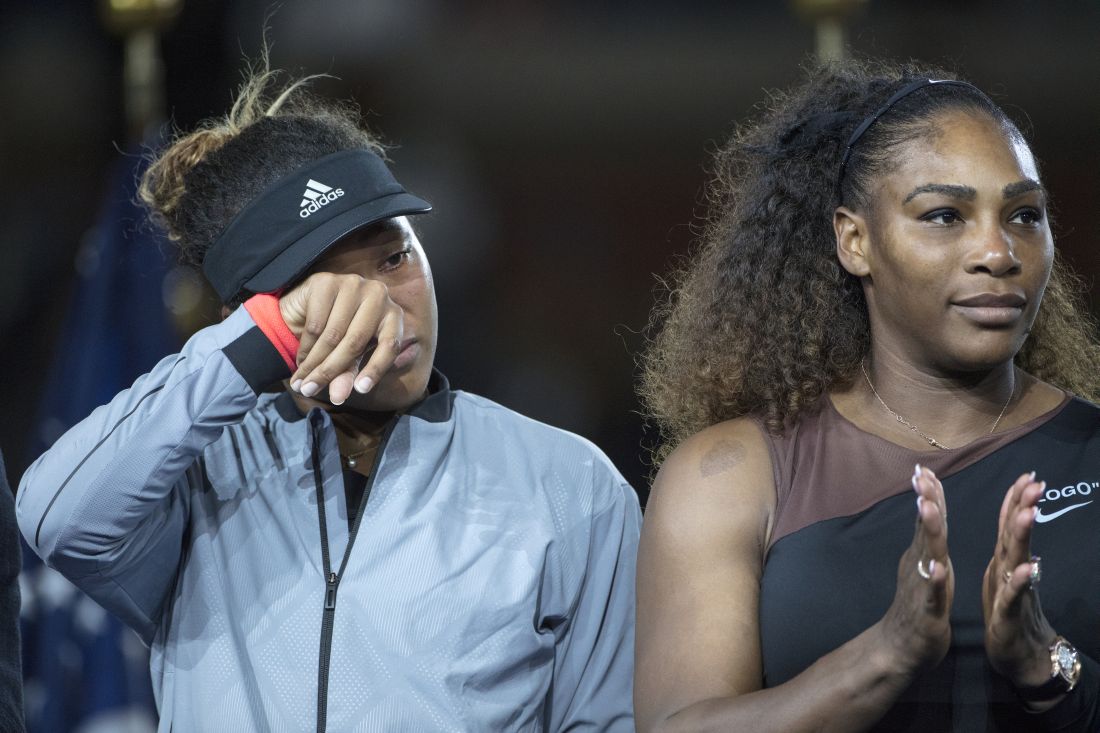

Ms. Williams had argued with an umpire over a controversial call, and the ceremony began with the crowd booing. Ms. Osaka, the victor, cried while Ms. Williams comforted her and quietly assured Ms. Osaka that the crowd was not booing at her. When asked how her dream of playing against Ms. Williams compared with the reality, the new champion, looking anything but victorious, responded: “Umm, I’m gonna sort of defer from your question, I’m sorry. I know that everyone was cheering for her, and I’m sorry it had to end like this.”
It was hardly the joyous moment it should have been in this young tennis player’s life.
Ms. Osaka, now 23, entered this year’s French Open as the Women’s Tennis Association’s second-ranked player and as the highest-paid female athlete of all time. She is known for her support of Black Lives Matter. Ms. Osaka announced that she would not be attending press conferences in an Instagram post days before the competition began. “If the organizations think they can keep saying, ‘do press or you’re going to get fined,’ and continue to ignore the mental health of the athletes that are the centerpiece of their cooperation then I just gotta laugh,” Ms. Osaka posted.
She was fined $15,000 on Sunday, May 30, when she did not appear at a press conference after winning her first match. Officials noted that she would be subjected to higher fines and expulsion from the tournament if she did not attend the mandatory media briefings. On June 1, Ms. Osaka withdrew from the French Open and explained her reasons on Instagram in a post where she announced that she has been struggling with depression and social anxiety and did not mean to become a distraction for the competition.
Psychiatrists weigh in
Sue Kim, MD, a psychiatrist who both plays and watches tennis, brought up Ms. Osaka’s resignation for discussion on the Maryland Psychiatric Society’s listserv. “[Ms.] Osaka put out on social media her depression and wanted to have rules reviewed and revised by the governing body of tennis, for future occasions. I feel it is so unfortunate and unfair and I am interested in hearing your opinions.”

Yusuke Sagawa, MD, a psychiatrist and tennis fan, wrote in: “During the COVID-19 pandemic, I rekindled my interest in tennis and I followed what transpired this past weekend. Naomi Osaka is an exceptionally shy and introverted person. I have noted that her speech is somewhat akin to (for lack of a better term) ‘Valley Girl’ talk, and from reading comments on tennis-related blogs, it appears she has garnered a significant amount of hatred as a result. Most of it is along the lines of people feeling her shyness and modesty is simply a masquerade.
“I have also seen YouTube videos of her signing autographs for fans. She is cooperative and pleasant, but clearly uncomfortable around large groups of people.
“Having seen many press conferences after a match,” Dr. Sagawa continued, “tennis journalists have a penchant for asking questions that are either personal or seemingly an attempt to stir up acrimony amongst players. Whatever the case, I truly do believe that this is not some sort of ruse on her part, and I hope that people come to her defense. It is disturbing to hear the comments already coming out from the ‘big names’ in the sport that have mostly been nonsupportive. Fortunately, there have also been a number of her contemporaries who have expressed this support for her.”
In the days following Ms. Osaka’s departure from the French Open, the situation has become more complex. as it is used in these types of communications.
Maryland psychiatrist Erik Roskes, MD, wrote: “I have followed this story from a distance and what strikes me is the intermixing of athleticism – which is presumably why we watch sports – and entertainment, the money-making part of it. The athletes are both athletes and entertainers, and [Ms.] Osaka seems to be unable to fully fulfill the latter part due to her unique traits. But like many, I wonder what if this had been Michael Phelps? Is there a gender issue at play?”
Stephanie Durruthy, MD, added: “[Ms.] Osaka brings complexity to the mental health conversations. There is no one answer to her current plight, but her being a person of color cannot be minimized. She magnified the race conversation in tennis to a higher level.
“When she was new to the Grand Slam scene, her Haitian, Japanese, and Black heritage became an issue with unending curiosity.
“[Ms.] Osaka used her platform during the 2020 U.S. Open to single-handedly highlight Black Lives Matter,” Dr. Durruthy continued. “Afterward, the tennis fans could not avoid seeing her face mask. In each match, she displayed another mask depicting the name of those killed. She described on social media her fears of being a Black person in America. The biases of gender and race are well described in the sports world.”
Lindsay Crouse wrote June 1 in the New York Times: “When Naomi Osaka dropped out of the French Open, after declining to attend media interviews that she said could trigger her anxiety, she wasn’t just protecting her mental health. She was sending a message to the establishment of one of the world’s most elite sports: I will not be controlled. This was a power move – and it packed more punch coming from a young woman of color. When the system hasn’t historically stood for you, why sacrifice yourself to uphold it? Especially when you have the power to change it instead.”
Professional sports are grueling on athletes, both physically and mentally. People will speculate about Ms. Osaka’s motives for refusing to participate in the media briefings that are mandated by her contract. Some will see it as manipulative, others as the desire of a young woman struggling with anxiety and depression to push back against a system that makes few allowances for those who suffer. As psychiatrists, we see how crippling these illnesses can be and admire those who achieve at these superhuman levels, often at the expense of their own well-being.
Dr. Kim, who started the MPS listserv discussion, ended it with: “I feel bad if Naomi Osaka needs to play a mental ‘illness’ card, as opposed to mental ‘wellness’ card.”
Let’s hope that Ms. Osaka’s withdrawal from the French Open sparks more conversation about how to accommodate athletes as they endeavor to meet both the demands of their contracts and when it might be more appropriate to be flexible for those with individual struggles.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “ Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care ” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, both in Baltimore.
In 2018, when Naomi Osaka won the U.S. Open by defeating Serena Williams, the trophy ceremony was painful to watch.

Ms. Williams had argued with an umpire over a controversial call, and the ceremony began with the crowd booing. Ms. Osaka, the victor, cried while Ms. Williams comforted her and quietly assured Ms. Osaka that the crowd was not booing at her. When asked how her dream of playing against Ms. Williams compared with the reality, the new champion, looking anything but victorious, responded: “Umm, I’m gonna sort of defer from your question, I’m sorry. I know that everyone was cheering for her, and I’m sorry it had to end like this.”
It was hardly the joyous moment it should have been in this young tennis player’s life.
Ms. Osaka, now 23, entered this year’s French Open as the Women’s Tennis Association’s second-ranked player and as the highest-paid female athlete of all time. She is known for her support of Black Lives Matter. Ms. Osaka announced that she would not be attending press conferences in an Instagram post days before the competition began. “If the organizations think they can keep saying, ‘do press or you’re going to get fined,’ and continue to ignore the mental health of the athletes that are the centerpiece of their cooperation then I just gotta laugh,” Ms. Osaka posted.
She was fined $15,000 on Sunday, May 30, when she did not appear at a press conference after winning her first match. Officials noted that she would be subjected to higher fines and expulsion from the tournament if she did not attend the mandatory media briefings. On June 1, Ms. Osaka withdrew from the French Open and explained her reasons on Instagram in a post where she announced that she has been struggling with depression and social anxiety and did not mean to become a distraction for the competition.
Psychiatrists weigh in
Sue Kim, MD, a psychiatrist who both plays and watches tennis, brought up Ms. Osaka’s resignation for discussion on the Maryland Psychiatric Society’s listserv. “[Ms.] Osaka put out on social media her depression and wanted to have rules reviewed and revised by the governing body of tennis, for future occasions. I feel it is so unfortunate and unfair and I am interested in hearing your opinions.”

Yusuke Sagawa, MD, a psychiatrist and tennis fan, wrote in: “During the COVID-19 pandemic, I rekindled my interest in tennis and I followed what transpired this past weekend. Naomi Osaka is an exceptionally shy and introverted person. I have noted that her speech is somewhat akin to (for lack of a better term) ‘Valley Girl’ talk, and from reading comments on tennis-related blogs, it appears she has garnered a significant amount of hatred as a result. Most of it is along the lines of people feeling her shyness and modesty is simply a masquerade.
“I have also seen YouTube videos of her signing autographs for fans. She is cooperative and pleasant, but clearly uncomfortable around large groups of people.
“Having seen many press conferences after a match,” Dr. Sagawa continued, “tennis journalists have a penchant for asking questions that are either personal or seemingly an attempt to stir up acrimony amongst players. Whatever the case, I truly do believe that this is not some sort of ruse on her part, and I hope that people come to her defense. It is disturbing to hear the comments already coming out from the ‘big names’ in the sport that have mostly been nonsupportive. Fortunately, there have also been a number of her contemporaries who have expressed this support for her.”
In the days following Ms. Osaka’s departure from the French Open, the situation has become more complex. as it is used in these types of communications.
Maryland psychiatrist Erik Roskes, MD, wrote: “I have followed this story from a distance and what strikes me is the intermixing of athleticism – which is presumably why we watch sports – and entertainment, the money-making part of it. The athletes are both athletes and entertainers, and [Ms.] Osaka seems to be unable to fully fulfill the latter part due to her unique traits. But like many, I wonder what if this had been Michael Phelps? Is there a gender issue at play?”
Stephanie Durruthy, MD, added: “[Ms.] Osaka brings complexity to the mental health conversations. There is no one answer to her current plight, but her being a person of color cannot be minimized. She magnified the race conversation in tennis to a higher level.
“When she was new to the Grand Slam scene, her Haitian, Japanese, and Black heritage became an issue with unending curiosity.
“[Ms.] Osaka used her platform during the 2020 U.S. Open to single-handedly highlight Black Lives Matter,” Dr. Durruthy continued. “Afterward, the tennis fans could not avoid seeing her face mask. In each match, she displayed another mask depicting the name of those killed. She described on social media her fears of being a Black person in America. The biases of gender and race are well described in the sports world.”
Lindsay Crouse wrote June 1 in the New York Times: “When Naomi Osaka dropped out of the French Open, after declining to attend media interviews that she said could trigger her anxiety, she wasn’t just protecting her mental health. She was sending a message to the establishment of one of the world’s most elite sports: I will not be controlled. This was a power move – and it packed more punch coming from a young woman of color. When the system hasn’t historically stood for you, why sacrifice yourself to uphold it? Especially when you have the power to change it instead.”
Professional sports are grueling on athletes, both physically and mentally. People will speculate about Ms. Osaka’s motives for refusing to participate in the media briefings that are mandated by her contract. Some will see it as manipulative, others as the desire of a young woman struggling with anxiety and depression to push back against a system that makes few allowances for those who suffer. As psychiatrists, we see how crippling these illnesses can be and admire those who achieve at these superhuman levels, often at the expense of their own well-being.
Dr. Kim, who started the MPS listserv discussion, ended it with: “I feel bad if Naomi Osaka needs to play a mental ‘illness’ card, as opposed to mental ‘wellness’ card.”
Let’s hope that Ms. Osaka’s withdrawal from the French Open sparks more conversation about how to accommodate athletes as they endeavor to meet both the demands of their contracts and when it might be more appropriate to be flexible for those with individual struggles.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “ Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care ” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, both in Baltimore.
In 2018, when Naomi Osaka won the U.S. Open by defeating Serena Williams, the trophy ceremony was painful to watch.

Ms. Williams had argued with an umpire over a controversial call, and the ceremony began with the crowd booing. Ms. Osaka, the victor, cried while Ms. Williams comforted her and quietly assured Ms. Osaka that the crowd was not booing at her. When asked how her dream of playing against Ms. Williams compared with the reality, the new champion, looking anything but victorious, responded: “Umm, I’m gonna sort of defer from your question, I’m sorry. I know that everyone was cheering for her, and I’m sorry it had to end like this.”
It was hardly the joyous moment it should have been in this young tennis player’s life.
Ms. Osaka, now 23, entered this year’s French Open as the Women’s Tennis Association’s second-ranked player and as the highest-paid female athlete of all time. She is known for her support of Black Lives Matter. Ms. Osaka announced that she would not be attending press conferences in an Instagram post days before the competition began. “If the organizations think they can keep saying, ‘do press or you’re going to get fined,’ and continue to ignore the mental health of the athletes that are the centerpiece of their cooperation then I just gotta laugh,” Ms. Osaka posted.
She was fined $15,000 on Sunday, May 30, when she did not appear at a press conference after winning her first match. Officials noted that she would be subjected to higher fines and expulsion from the tournament if she did not attend the mandatory media briefings. On June 1, Ms. Osaka withdrew from the French Open and explained her reasons on Instagram in a post where she announced that she has been struggling with depression and social anxiety and did not mean to become a distraction for the competition.
Psychiatrists weigh in
Sue Kim, MD, a psychiatrist who both plays and watches tennis, brought up Ms. Osaka’s resignation for discussion on the Maryland Psychiatric Society’s listserv. “[Ms.] Osaka put out on social media her depression and wanted to have rules reviewed and revised by the governing body of tennis, for future occasions. I feel it is so unfortunate and unfair and I am interested in hearing your opinions.”

Yusuke Sagawa, MD, a psychiatrist and tennis fan, wrote in: “During the COVID-19 pandemic, I rekindled my interest in tennis and I followed what transpired this past weekend. Naomi Osaka is an exceptionally shy and introverted person. I have noted that her speech is somewhat akin to (for lack of a better term) ‘Valley Girl’ talk, and from reading comments on tennis-related blogs, it appears she has garnered a significant amount of hatred as a result. Most of it is along the lines of people feeling her shyness and modesty is simply a masquerade.
“I have also seen YouTube videos of her signing autographs for fans. She is cooperative and pleasant, but clearly uncomfortable around large groups of people.
“Having seen many press conferences after a match,” Dr. Sagawa continued, “tennis journalists have a penchant for asking questions that are either personal or seemingly an attempt to stir up acrimony amongst players. Whatever the case, I truly do believe that this is not some sort of ruse on her part, and I hope that people come to her defense. It is disturbing to hear the comments already coming out from the ‘big names’ in the sport that have mostly been nonsupportive. Fortunately, there have also been a number of her contemporaries who have expressed this support for her.”
In the days following Ms. Osaka’s departure from the French Open, the situation has become more complex. as it is used in these types of communications.
Maryland psychiatrist Erik Roskes, MD, wrote: “I have followed this story from a distance and what strikes me is the intermixing of athleticism – which is presumably why we watch sports – and entertainment, the money-making part of it. The athletes are both athletes and entertainers, and [Ms.] Osaka seems to be unable to fully fulfill the latter part due to her unique traits. But like many, I wonder what if this had been Michael Phelps? Is there a gender issue at play?”
Stephanie Durruthy, MD, added: “[Ms.] Osaka brings complexity to the mental health conversations. There is no one answer to her current plight, but her being a person of color cannot be minimized. She magnified the race conversation in tennis to a higher level.
“When she was new to the Grand Slam scene, her Haitian, Japanese, and Black heritage became an issue with unending curiosity.
“[Ms.] Osaka used her platform during the 2020 U.S. Open to single-handedly highlight Black Lives Matter,” Dr. Durruthy continued. “Afterward, the tennis fans could not avoid seeing her face mask. In each match, she displayed another mask depicting the name of those killed. She described on social media her fears of being a Black person in America. The biases of gender and race are well described in the sports world.”
Lindsay Crouse wrote June 1 in the New York Times: “When Naomi Osaka dropped out of the French Open, after declining to attend media interviews that she said could trigger her anxiety, she wasn’t just protecting her mental health. She was sending a message to the establishment of one of the world’s most elite sports: I will not be controlled. This was a power move – and it packed more punch coming from a young woman of color. When the system hasn’t historically stood for you, why sacrifice yourself to uphold it? Especially when you have the power to change it instead.”
Professional sports are grueling on athletes, both physically and mentally. People will speculate about Ms. Osaka’s motives for refusing to participate in the media briefings that are mandated by her contract. Some will see it as manipulative, others as the desire of a young woman struggling with anxiety and depression to push back against a system that makes few allowances for those who suffer. As psychiatrists, we see how crippling these illnesses can be and admire those who achieve at these superhuman levels, often at the expense of their own well-being.
Dr. Kim, who started the MPS listserv discussion, ended it with: “I feel bad if Naomi Osaka needs to play a mental ‘illness’ card, as opposed to mental ‘wellness’ card.”
Let’s hope that Ms. Osaka’s withdrawal from the French Open sparks more conversation about how to accommodate athletes as they endeavor to meet both the demands of their contracts and when it might be more appropriate to be flexible for those with individual struggles.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “ Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care ” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, both in Baltimore.
Trastuzumab deruxtecan-related lung disease in MBC patients can occur anytime in first year
Although rates are generally low, interstitial lung disease (ILD) can occur at any point in the first year of treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
That’s according to a pooled analysis of three early clinical trials with the drug that was reported at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO): Breast Cancer virtual meeting.
Over a 5-year analysis period, the rate of any grade of ILD was 15.5%. The majority (79%) of those events were grade 1 or 2, observed pulmonologist Charles A. Powell, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, who presented the findings.
Of the 245 patients who were included in the analysis, 38 had an ILD event deemed related to treatment. A respective 9 (3.7%) and 21 (8.6%) had events graded as 1 or 2, 1 patient each (0.4%) had a grade 3 or 4 event, and 6 (2.4%) patients had a grade 5 event.
The timing of the first identified ILD event varied from 1.1 months to 20.8 months, given a median of 5.6 months overall. “This highlights an opportunity for more timely detection of ILD,” Dr. Powell suggested. He added that in almost all (97%) cases, ILD occurred before 12 months and the risk may even decrease over time “suggesting that the risk is not cumulative.”
He cautioned, however: “It is important to note that this analysis is exploratory and hypothesis generating in nature.”
ILD occurs with other cancer drugs
ILD is not just associated with T-DXd treatment, said the invited discussant for the trial, Harold J. Burstein, MD, PhD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
“It’s important for clinicians to remember that ILD/pneumonitis is an uncommon, but potentially very serious side effect that affects many breast cancer treatments,” he said.
That not only includes T-DXd, but other newer drugs such the cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors, as well as other older more established drugs including taxanes, cyclophosphamide and even the mTOR inhibitor everolimus.
“Both clinicians and patients need to be aware of this risk. It’s part of the differential diagnosis for any patient who develops either ground glass changes or other infiltrates on a CT scan, or who has symptoms,” Dr. Burstein added.
Investigating ILD in T-DXd trials
T-DXd (Enhertu) is an anti-HER2-antibody drug conjugate that contains a humanized anti-HER2 IgG1 monoclonal antibody akin to trastuzumab that is linked to DXd, a topoisomerase I inhibitor that is a derivative of exatecan.
It has been approved for use in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer after two other HER2 treatments fail in the United States and Europe, and after chemotherapy in Japan, noted Dr. Powell. This is largely due to the results from the phase 2, open-label DESTINY-Breast01 trial.
“In breast cancer, T-DXd continues to demonstrate clinically meaningful efficacy with a median duration of response of more than 20 months in a heavily pretreated population,” he said. Objective response rates seen in the DESTINY-Breast01 trial were around 60%, and the median progression-free survival was a little over 19 months.
To look at the issue of drug-related ILD events in patients treated with T-DXd for HER2-positive MBC, an independent adjudication committee was formed to look at all the imaging and clinical data from the DESTINY-Breast01 trial and two single-arm phase 1 trials (NCT02564900 and NCT03383692).
In all, data on 245 patients who had been treated with T-DXd at the approved dose of 5.4 mg/kg in those trials between August 2015 and June 2020 were analyzed.
Dealing with lung toxicity
“We are getting new drugs to improve the treatment of cancer, but they always come with a price in terms of toxicity,” observed David Cameron, MD, professor of medical oncology at Edinburgh University in Scotland. Dr. Cameron chaired the session.
“Several measures were taken to identify and mitigate ILD,” across all the T-DXd studies, Dr. Powell explained. As well as the independent adjudication committee, available guidelines were followed and updated on how to diagnose and treat drug-induced lung injuries, and a “safe use” campaign was run in 2019.
Many patients in the early MBC studies were recruited before these measures were in place, such as the use of systemic steroids to manage low-grade events.
The bottom line, however, is that if a patient develops ILD then treatment should be stopped, Dr. Powell said. “Patients with grade 1 events may restart once the ILD has resolved, but those with grade 2 to 4 events must discontinue treatment.”
Dr. Powell concluded: “The overall clinical data support the positive risk-benefit profile of T-DXd. Phase 3 randomized controlled trials in breast cancer are ongoing.”
ILD also seen in monarchE trial with abemaciclib
Data on ILD events seen in the phase 3 monarchE trial were also reported separately at the ESMO Breast Cancer virtual meeting. The analysis population included 2,971 patients who had been treated with the CDK 4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib (Verzenio) together with endocrine therapy and 2,800 who had received endocrine therapy alone in the early-stage, adjuvant advanced breast cancer setting.
Most ILD (97%) events that occurred were single occurrences, with any grade of ILD occurring in a higher percentage of patients treated with abemaciclib with endocrine therapy than endocrine therapy alone (2.9% vs. 1.2%). Grade 3 events occurred in a respective 0.4% and 0.0% of patients.
So who’s at risk?
The risk factors for ILD and pneumonitis are not well characterized with either of the two drugs discussed, Dr. Burstein observed.
“In the abemaciclib experience, it looked like obesity might be a predisposing factor, with trastuzumab deruxtecan, it looked like patients of Asian ancestry were greater risk, but we need more data to really understand who’s at jeopardy.”
Dr. Burstein observed: “This is something patients need to be aware of as they’re contemplating this treatment.”
While data to prove the benefit of the drug need to mature, Dr. Burstein “would likely discontinue therapy” if a patient were to develop ILD or pneumonitis and treat accordingly.
As for T-DXd, he said: “It’s important that patients know that lung disease is a potentially severe side effect of treatment and that any respiratory symptoms need to be jumped on quickly.”
While prospective studies are now needed, and the phase 3 data should help to better understand the risk of ILD with T-DXd, Dr. Burstein believes it will be important to develop algorithms to ensure the safe administration of the drug.
These algorithms should include “appropriate surveillance and monitoring, especially as we think about trying to move this drug forward into the early stage setting where we’re using it in women who have favorable prognosis, and potentially curative situations for breast cancer.”
The trastuzumab deruxtecan trials were cosponsored by Daiichi Sankyo and AstraZeneca. The monarchE trial was supported by Eli Lilly.
Dr. Powell acknowledged receiving personal fees for acting as an advisory or consultant to both companies as well as to Voluntis. Dr. Burstein had nothing to disclose, and Dr. Cameron had no relevant financial interests in the data being presented.
Although rates are generally low, interstitial lung disease (ILD) can occur at any point in the first year of treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
That’s according to a pooled analysis of three early clinical trials with the drug that was reported at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO): Breast Cancer virtual meeting.
Over a 5-year analysis period, the rate of any grade of ILD was 15.5%. The majority (79%) of those events were grade 1 or 2, observed pulmonologist Charles A. Powell, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, who presented the findings.
Of the 245 patients who were included in the analysis, 38 had an ILD event deemed related to treatment. A respective 9 (3.7%) and 21 (8.6%) had events graded as 1 or 2, 1 patient each (0.4%) had a grade 3 or 4 event, and 6 (2.4%) patients had a grade 5 event.
The timing of the first identified ILD event varied from 1.1 months to 20.8 months, given a median of 5.6 months overall. “This highlights an opportunity for more timely detection of ILD,” Dr. Powell suggested. He added that in almost all (97%) cases, ILD occurred before 12 months and the risk may even decrease over time “suggesting that the risk is not cumulative.”
He cautioned, however: “It is important to note that this analysis is exploratory and hypothesis generating in nature.”
ILD occurs with other cancer drugs
ILD is not just associated with T-DXd treatment, said the invited discussant for the trial, Harold J. Burstein, MD, PhD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
“It’s important for clinicians to remember that ILD/pneumonitis is an uncommon, but potentially very serious side effect that affects many breast cancer treatments,” he said.
That not only includes T-DXd, but other newer drugs such the cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors, as well as other older more established drugs including taxanes, cyclophosphamide and even the mTOR inhibitor everolimus.
“Both clinicians and patients need to be aware of this risk. It’s part of the differential diagnosis for any patient who develops either ground glass changes or other infiltrates on a CT scan, or who has symptoms,” Dr. Burstein added.
Investigating ILD in T-DXd trials
T-DXd (Enhertu) is an anti-HER2-antibody drug conjugate that contains a humanized anti-HER2 IgG1 monoclonal antibody akin to trastuzumab that is linked to DXd, a topoisomerase I inhibitor that is a derivative of exatecan.
It has been approved for use in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer after two other HER2 treatments fail in the United States and Europe, and after chemotherapy in Japan, noted Dr. Powell. This is largely due to the results from the phase 2, open-label DESTINY-Breast01 trial.
“In breast cancer, T-DXd continues to demonstrate clinically meaningful efficacy with a median duration of response of more than 20 months in a heavily pretreated population,” he said. Objective response rates seen in the DESTINY-Breast01 trial were around 60%, and the median progression-free survival was a little over 19 months.
To look at the issue of drug-related ILD events in patients treated with T-DXd for HER2-positive MBC, an independent adjudication committee was formed to look at all the imaging and clinical data from the DESTINY-Breast01 trial and two single-arm phase 1 trials (NCT02564900 and NCT03383692).
In all, data on 245 patients who had been treated with T-DXd at the approved dose of 5.4 mg/kg in those trials between August 2015 and June 2020 were analyzed.
Dealing with lung toxicity
“We are getting new drugs to improve the treatment of cancer, but they always come with a price in terms of toxicity,” observed David Cameron, MD, professor of medical oncology at Edinburgh University in Scotland. Dr. Cameron chaired the session.
“Several measures were taken to identify and mitigate ILD,” across all the T-DXd studies, Dr. Powell explained. As well as the independent adjudication committee, available guidelines were followed and updated on how to diagnose and treat drug-induced lung injuries, and a “safe use” campaign was run in 2019.
Many patients in the early MBC studies were recruited before these measures were in place, such as the use of systemic steroids to manage low-grade events.
The bottom line, however, is that if a patient develops ILD then treatment should be stopped, Dr. Powell said. “Patients with grade 1 events may restart once the ILD has resolved, but those with grade 2 to 4 events must discontinue treatment.”
Dr. Powell concluded: “The overall clinical data support the positive risk-benefit profile of T-DXd. Phase 3 randomized controlled trials in breast cancer are ongoing.”
ILD also seen in monarchE trial with abemaciclib
Data on ILD events seen in the phase 3 monarchE trial were also reported separately at the ESMO Breast Cancer virtual meeting. The analysis population included 2,971 patients who had been treated with the CDK 4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib (Verzenio) together with endocrine therapy and 2,800 who had received endocrine therapy alone in the early-stage, adjuvant advanced breast cancer setting.
Most ILD (97%) events that occurred were single occurrences, with any grade of ILD occurring in a higher percentage of patients treated with abemaciclib with endocrine therapy than endocrine therapy alone (2.9% vs. 1.2%). Grade 3 events occurred in a respective 0.4% and 0.0% of patients.
So who’s at risk?
The risk factors for ILD and pneumonitis are not well characterized with either of the two drugs discussed, Dr. Burstein observed.
“In the abemaciclib experience, it looked like obesity might be a predisposing factor, with trastuzumab deruxtecan, it looked like patients of Asian ancestry were greater risk, but we need more data to really understand who’s at jeopardy.”
Dr. Burstein observed: “This is something patients need to be aware of as they’re contemplating this treatment.”
While data to prove the benefit of the drug need to mature, Dr. Burstein “would likely discontinue therapy” if a patient were to develop ILD or pneumonitis and treat accordingly.
As for T-DXd, he said: “It’s important that patients know that lung disease is a potentially severe side effect of treatment and that any respiratory symptoms need to be jumped on quickly.”
While prospective studies are now needed, and the phase 3 data should help to better understand the risk of ILD with T-DXd, Dr. Burstein believes it will be important to develop algorithms to ensure the safe administration of the drug.
These algorithms should include “appropriate surveillance and monitoring, especially as we think about trying to move this drug forward into the early stage setting where we’re using it in women who have favorable prognosis, and potentially curative situations for breast cancer.”
The trastuzumab deruxtecan trials were cosponsored by Daiichi Sankyo and AstraZeneca. The monarchE trial was supported by Eli Lilly.
Dr. Powell acknowledged receiving personal fees for acting as an advisory or consultant to both companies as well as to Voluntis. Dr. Burstein had nothing to disclose, and Dr. Cameron had no relevant financial interests in the data being presented.
Although rates are generally low, interstitial lung disease (ILD) can occur at any point in the first year of treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
That’s according to a pooled analysis of three early clinical trials with the drug that was reported at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO): Breast Cancer virtual meeting.
Over a 5-year analysis period, the rate of any grade of ILD was 15.5%. The majority (79%) of those events were grade 1 or 2, observed pulmonologist Charles A. Powell, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, who presented the findings.
Of the 245 patients who were included in the analysis, 38 had an ILD event deemed related to treatment. A respective 9 (3.7%) and 21 (8.6%) had events graded as 1 or 2, 1 patient each (0.4%) had a grade 3 or 4 event, and 6 (2.4%) patients had a grade 5 event.
The timing of the first identified ILD event varied from 1.1 months to 20.8 months, given a median of 5.6 months overall. “This highlights an opportunity for more timely detection of ILD,” Dr. Powell suggested. He added that in almost all (97%) cases, ILD occurred before 12 months and the risk may even decrease over time “suggesting that the risk is not cumulative.”
He cautioned, however: “It is important to note that this analysis is exploratory and hypothesis generating in nature.”
ILD occurs with other cancer drugs
ILD is not just associated with T-DXd treatment, said the invited discussant for the trial, Harold J. Burstein, MD, PhD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
“It’s important for clinicians to remember that ILD/pneumonitis is an uncommon, but potentially very serious side effect that affects many breast cancer treatments,” he said.
That not only includes T-DXd, but other newer drugs such the cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors, as well as other older more established drugs including taxanes, cyclophosphamide and even the mTOR inhibitor everolimus.
“Both clinicians and patients need to be aware of this risk. It’s part of the differential diagnosis for any patient who develops either ground glass changes or other infiltrates on a CT scan, or who has symptoms,” Dr. Burstein added.
Investigating ILD in T-DXd trials
T-DXd (Enhertu) is an anti-HER2-antibody drug conjugate that contains a humanized anti-HER2 IgG1 monoclonal antibody akin to trastuzumab that is linked to DXd, a topoisomerase I inhibitor that is a derivative of exatecan.
It has been approved for use in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer after two other HER2 treatments fail in the United States and Europe, and after chemotherapy in Japan, noted Dr. Powell. This is largely due to the results from the phase 2, open-label DESTINY-Breast01 trial.
“In breast cancer, T-DXd continues to demonstrate clinically meaningful efficacy with a median duration of response of more than 20 months in a heavily pretreated population,” he said. Objective response rates seen in the DESTINY-Breast01 trial were around 60%, and the median progression-free survival was a little over 19 months.
To look at the issue of drug-related ILD events in patients treated with T-DXd for HER2-positive MBC, an independent adjudication committee was formed to look at all the imaging and clinical data from the DESTINY-Breast01 trial and two single-arm phase 1 trials (NCT02564900 and NCT03383692).
In all, data on 245 patients who had been treated with T-DXd at the approved dose of 5.4 mg/kg in those trials between August 2015 and June 2020 were analyzed.
Dealing with lung toxicity
“We are getting new drugs to improve the treatment of cancer, but they always come with a price in terms of toxicity,” observed David Cameron, MD, professor of medical oncology at Edinburgh University in Scotland. Dr. Cameron chaired the session.
“Several measures were taken to identify and mitigate ILD,” across all the T-DXd studies, Dr. Powell explained. As well as the independent adjudication committee, available guidelines were followed and updated on how to diagnose and treat drug-induced lung injuries, and a “safe use” campaign was run in 2019.
Many patients in the early MBC studies were recruited before these measures were in place, such as the use of systemic steroids to manage low-grade events.
The bottom line, however, is that if a patient develops ILD then treatment should be stopped, Dr. Powell said. “Patients with grade 1 events may restart once the ILD has resolved, but those with grade 2 to 4 events must discontinue treatment.”
Dr. Powell concluded: “The overall clinical data support the positive risk-benefit profile of T-DXd. Phase 3 randomized controlled trials in breast cancer are ongoing.”
ILD also seen in monarchE trial with abemaciclib
Data on ILD events seen in the phase 3 monarchE trial were also reported separately at the ESMO Breast Cancer virtual meeting. The analysis population included 2,971 patients who had been treated with the CDK 4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib (Verzenio) together with endocrine therapy and 2,800 who had received endocrine therapy alone in the early-stage, adjuvant advanced breast cancer setting.
Most ILD (97%) events that occurred were single occurrences, with any grade of ILD occurring in a higher percentage of patients treated with abemaciclib with endocrine therapy than endocrine therapy alone (2.9% vs. 1.2%). Grade 3 events occurred in a respective 0.4% and 0.0% of patients.
So who’s at risk?
The risk factors for ILD and pneumonitis are not well characterized with either of the two drugs discussed, Dr. Burstein observed.
“In the abemaciclib experience, it looked like obesity might be a predisposing factor, with trastuzumab deruxtecan, it looked like patients of Asian ancestry were greater risk, but we need more data to really understand who’s at jeopardy.”
Dr. Burstein observed: “This is something patients need to be aware of as they’re contemplating this treatment.”
While data to prove the benefit of the drug need to mature, Dr. Burstein “would likely discontinue therapy” if a patient were to develop ILD or pneumonitis and treat accordingly.
As for T-DXd, he said: “It’s important that patients know that lung disease is a potentially severe side effect of treatment and that any respiratory symptoms need to be jumped on quickly.”
While prospective studies are now needed, and the phase 3 data should help to better understand the risk of ILD with T-DXd, Dr. Burstein believes it will be important to develop algorithms to ensure the safe administration of the drug.
These algorithms should include “appropriate surveillance and monitoring, especially as we think about trying to move this drug forward into the early stage setting where we’re using it in women who have favorable prognosis, and potentially curative situations for breast cancer.”
The trastuzumab deruxtecan trials were cosponsored by Daiichi Sankyo and AstraZeneca. The monarchE trial was supported by Eli Lilly.
Dr. Powell acknowledged receiving personal fees for acting as an advisory or consultant to both companies as well as to Voluntis. Dr. Burstein had nothing to disclose, and Dr. Cameron had no relevant financial interests in the data being presented.
FROM ESMO BREAST CANCER 2021
Urticarial Vasculitis Successfully Treated With Omalizumab
To the Editor:
Urticarial vasculitis (UV) is a clinicopathologic entity. It manifests as an eruption of erythematous wheals that clinically resemble urticaria, but the lesions of UV last longer, may leave residual hyperpigmentation, and may or may not be pruritic.1 Therapies most often employed include oral antihistamines and systemic immunosuppressant drugs such as corticosteroids, dapsone, colchicine, or hydroxychloroquine.2 We present a woman with UV who successfully was treated with omalizumab.
A 49-year-old woman presented to our outpatient clinic with generalized pruritic skin rashes of 2 years’ duration. She also described swelling on the upper eyelids 2 times monthly. She used several antihistamines (up to 4 times daily) and was taking systemic corticosteroids and antidepressants. Physical examination revealed generalized erythematous and edematous papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities (Figure 1). At follow-up a few days later, we observed that the lesions were lasting for more than 24 hours, but there was no residual pigmentation. According to clinical concerns and the association with angioedema, we initially thought the diagnosis was chronic urticaria and angioedema. The patient had no extracutaneous manifestations such as fever, arthralgia, or lymphadenopathy. Routine laboratory examinations including antinuclear antibodies were within reference range. She had normal C3 and C4 levels and an elevated total IgE level (344 IU/mL [reference range, 0–170 IU/mL]). Because the IgE level was elevated and she had no response to the highest dosages of antihistamines, we decided to start omalizumab therapy. Prior to starting omalizumab, we performed a skin biopsy for histopathologic and direct immunofluorescence examinations for UV, as the duration of the lesions was more than 24 hours. Histopathologic examination revealed lymphocytes within the vessel wall and perivascular lymphocytic infiltration with eosinophils (Figure 2). On direct immunofluorescence, perivascular IgA deposition was observed (Figure 3). Histopathologic findings were associated with lymphocytic vasculitis. Systemic involvement was not detected on detailed laboratory and radiologic examinations.
After the first application of omalizumab, the lesions disappeared within a few days. She was treated with subcutaneous omalizumab 300 mg every 4 weeks for 6 months, and we did not observe any adverse effects related to the drug. There was no relapse after therapy cessation.
Omalizumab is a recombinant humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody that is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria.3-5 Studies have suggested that omalizumab might play an important role in the treatment of other potentially IgE-mediated disease processes including allergic asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, nasal polyposis, and severe ocular allergies.6 The proposed mechanism of action of omalizumab includes reduction of free IgE through the reversible formation of tiny, biologically inert complexes; targeting IgE-expressing B cells; and inhibiting production of IgE. Because it reduces free IgE, omalizumab has been used in normal IgE or hyper-IgE situations. Omalizumab also induces eosinophil apoptosis; increases IL-2, IL-3, tumor necrosis factor α, and IFN-γ; and reduces IL-4.7 A number of off-label uses have been described such as atopic dermatitis, bullous pemphigoid, hyper-IgE syndrome, cutaneous mastocytosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangitis.8 There are no clinical studies of omalizumab for UV, and only a few case reports have shown that omalizumab also might be beneficial for this condition.2-4 Diez et al4 reported 3 cases of women aged 28, 51, and 54 years with spontaneous chronic urticaria with autoimmune and pressure components as well as vasculitis whose symptoms completely improved after starting omalizumab. Kai et al3 successfully treated a patient with normocomplementemic UV with omalizumab and suggested that omalizumab markedly improved the patient’s quality of life with chronic urticaria and UV. Ghazanfar and Thomsen2 reported the case of a 68-year-old man diagnosed with histopathologically confirmed leukocytoclastic vasculitis. He had used systemic corticosteroid therapy and dapsone without notable improvement. The patient was switched to subcutaneous omalizumab 300 mg once every 4 weeks; after 1 month, he observed complete remission of the UV and symptoms.2
Our case suggests that omalizumab has a beneficial effect on patients with UV. Omalizumab may be effective in UV through its reduction of IgE, as in chronic urticaria, and through downstream effects on cellular activation mechanisms (possibly a reduction in chemotaxis or immune complex formation). However, the mechanism of action of omalizumab for UV remains, in part, unresolved. It is not known whether omalizumab is efficacious against both normocomplementemic and hypocomplementemic UV. Further studies with a greater number of patients are needed to confirm the effects of omalizumab for vasculitic patients.
- Chang S, Carr W. Urticarial vasculitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007;28:97-100.
- Ghazanfar MN, Thomsen SF. Omalizumab for urticarial vasculitis: case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2015:576893.
- Kai AC, Flohr C, Grattan CE. Improvement in quality of life impairment followed by relapse with 6-monthly periodic administration of omalizumab for severe treatment-refractory chronic urticaria and urticarial vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:651-652.
- Diez LS, Tamayo LM, Cardona R. Omalizumab: therapeutic option in chronic spontaneous urticaria difficult to control with associated vasculitis, report of three cases. Biomedica. 2013;33:503-512.
- Maurer M, Rosen K, Hsieh HJ. Omalizumab for chronic urticaria. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2530.
- Ben Shoshan M. Omalizumab: not only for asthma. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008;2:191-201.
- Fueyo-Casado A, Campos-Munoz L, Gonzalez-Guerra E, et al. Effectiveness of omalizumab in a case of urticarial vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. Published March 1, 2017. doi:10.1111/ced.13076
- Chia JC, Mydlarski PR. Dermatologic uses of omalizumab. J Dermatol Treat. Published November 7, 2016. doi:10.1080/09546634.2016.1249819
To the Editor:
Urticarial vasculitis (UV) is a clinicopathologic entity. It manifests as an eruption of erythematous wheals that clinically resemble urticaria, but the lesions of UV last longer, may leave residual hyperpigmentation, and may or may not be pruritic.1 Therapies most often employed include oral antihistamines and systemic immunosuppressant drugs such as corticosteroids, dapsone, colchicine, or hydroxychloroquine.2 We present a woman with UV who successfully was treated with omalizumab.
A 49-year-old woman presented to our outpatient clinic with generalized pruritic skin rashes of 2 years’ duration. She also described swelling on the upper eyelids 2 times monthly. She used several antihistamines (up to 4 times daily) and was taking systemic corticosteroids and antidepressants. Physical examination revealed generalized erythematous and edematous papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities (Figure 1). At follow-up a few days later, we observed that the lesions were lasting for more than 24 hours, but there was no residual pigmentation. According to clinical concerns and the association with angioedema, we initially thought the diagnosis was chronic urticaria and angioedema. The patient had no extracutaneous manifestations such as fever, arthralgia, or lymphadenopathy. Routine laboratory examinations including antinuclear antibodies were within reference range. She had normal C3 and C4 levels and an elevated total IgE level (344 IU/mL [reference range, 0–170 IU/mL]). Because the IgE level was elevated and she had no response to the highest dosages of antihistamines, we decided to start omalizumab therapy. Prior to starting omalizumab, we performed a skin biopsy for histopathologic and direct immunofluorescence examinations for UV, as the duration of the lesions was more than 24 hours. Histopathologic examination revealed lymphocytes within the vessel wall and perivascular lymphocytic infiltration with eosinophils (Figure 2). On direct immunofluorescence, perivascular IgA deposition was observed (Figure 3). Histopathologic findings were associated with lymphocytic vasculitis. Systemic involvement was not detected on detailed laboratory and radiologic examinations.
After the first application of omalizumab, the lesions disappeared within a few days. She was treated with subcutaneous omalizumab 300 mg every 4 weeks for 6 months, and we did not observe any adverse effects related to the drug. There was no relapse after therapy cessation.
Omalizumab is a recombinant humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody that is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria.3-5 Studies have suggested that omalizumab might play an important role in the treatment of other potentially IgE-mediated disease processes including allergic asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, nasal polyposis, and severe ocular allergies.6 The proposed mechanism of action of omalizumab includes reduction of free IgE through the reversible formation of tiny, biologically inert complexes; targeting IgE-expressing B cells; and inhibiting production of IgE. Because it reduces free IgE, omalizumab has been used in normal IgE or hyper-IgE situations. Omalizumab also induces eosinophil apoptosis; increases IL-2, IL-3, tumor necrosis factor α, and IFN-γ; and reduces IL-4.7 A number of off-label uses have been described such as atopic dermatitis, bullous pemphigoid, hyper-IgE syndrome, cutaneous mastocytosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangitis.8 There are no clinical studies of omalizumab for UV, and only a few case reports have shown that omalizumab also might be beneficial for this condition.2-4 Diez et al4 reported 3 cases of women aged 28, 51, and 54 years with spontaneous chronic urticaria with autoimmune and pressure components as well as vasculitis whose symptoms completely improved after starting omalizumab. Kai et al3 successfully treated a patient with normocomplementemic UV with omalizumab and suggested that omalizumab markedly improved the patient’s quality of life with chronic urticaria and UV. Ghazanfar and Thomsen2 reported the case of a 68-year-old man diagnosed with histopathologically confirmed leukocytoclastic vasculitis. He had used systemic corticosteroid therapy and dapsone without notable improvement. The patient was switched to subcutaneous omalizumab 300 mg once every 4 weeks; after 1 month, he observed complete remission of the UV and symptoms.2
Our case suggests that omalizumab has a beneficial effect on patients with UV. Omalizumab may be effective in UV through its reduction of IgE, as in chronic urticaria, and through downstream effects on cellular activation mechanisms (possibly a reduction in chemotaxis or immune complex formation). However, the mechanism of action of omalizumab for UV remains, in part, unresolved. It is not known whether omalizumab is efficacious against both normocomplementemic and hypocomplementemic UV. Further studies with a greater number of patients are needed to confirm the effects of omalizumab for vasculitic patients.
To the Editor:
Urticarial vasculitis (UV) is a clinicopathologic entity. It manifests as an eruption of erythematous wheals that clinically resemble urticaria, but the lesions of UV last longer, may leave residual hyperpigmentation, and may or may not be pruritic.1 Therapies most often employed include oral antihistamines and systemic immunosuppressant drugs such as corticosteroids, dapsone, colchicine, or hydroxychloroquine.2 We present a woman with UV who successfully was treated with omalizumab.
A 49-year-old woman presented to our outpatient clinic with generalized pruritic skin rashes of 2 years’ duration. She also described swelling on the upper eyelids 2 times monthly. She used several antihistamines (up to 4 times daily) and was taking systemic corticosteroids and antidepressants. Physical examination revealed generalized erythematous and edematous papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities (Figure 1). At follow-up a few days later, we observed that the lesions were lasting for more than 24 hours, but there was no residual pigmentation. According to clinical concerns and the association with angioedema, we initially thought the diagnosis was chronic urticaria and angioedema. The patient had no extracutaneous manifestations such as fever, arthralgia, or lymphadenopathy. Routine laboratory examinations including antinuclear antibodies were within reference range. She had normal C3 and C4 levels and an elevated total IgE level (344 IU/mL [reference range, 0–170 IU/mL]). Because the IgE level was elevated and she had no response to the highest dosages of antihistamines, we decided to start omalizumab therapy. Prior to starting omalizumab, we performed a skin biopsy for histopathologic and direct immunofluorescence examinations for UV, as the duration of the lesions was more than 24 hours. Histopathologic examination revealed lymphocytes within the vessel wall and perivascular lymphocytic infiltration with eosinophils (Figure 2). On direct immunofluorescence, perivascular IgA deposition was observed (Figure 3). Histopathologic findings were associated with lymphocytic vasculitis. Systemic involvement was not detected on detailed laboratory and radiologic examinations.
After the first application of omalizumab, the lesions disappeared within a few days. She was treated with subcutaneous omalizumab 300 mg every 4 weeks for 6 months, and we did not observe any adverse effects related to the drug. There was no relapse after therapy cessation.
Omalizumab is a recombinant humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody that is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria.3-5 Studies have suggested that omalizumab might play an important role in the treatment of other potentially IgE-mediated disease processes including allergic asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, nasal polyposis, and severe ocular allergies.6 The proposed mechanism of action of omalizumab includes reduction of free IgE through the reversible formation of tiny, biologically inert complexes; targeting IgE-expressing B cells; and inhibiting production of IgE. Because it reduces free IgE, omalizumab has been used in normal IgE or hyper-IgE situations. Omalizumab also induces eosinophil apoptosis; increases IL-2, IL-3, tumor necrosis factor α, and IFN-γ; and reduces IL-4.7 A number of off-label uses have been described such as atopic dermatitis, bullous pemphigoid, hyper-IgE syndrome, cutaneous mastocytosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangitis.8 There are no clinical studies of omalizumab for UV, and only a few case reports have shown that omalizumab also might be beneficial for this condition.2-4 Diez et al4 reported 3 cases of women aged 28, 51, and 54 years with spontaneous chronic urticaria with autoimmune and pressure components as well as vasculitis whose symptoms completely improved after starting omalizumab. Kai et al3 successfully treated a patient with normocomplementemic UV with omalizumab and suggested that omalizumab markedly improved the patient’s quality of life with chronic urticaria and UV. Ghazanfar and Thomsen2 reported the case of a 68-year-old man diagnosed with histopathologically confirmed leukocytoclastic vasculitis. He had used systemic corticosteroid therapy and dapsone without notable improvement. The patient was switched to subcutaneous omalizumab 300 mg once every 4 weeks; after 1 month, he observed complete remission of the UV and symptoms.2
Our case suggests that omalizumab has a beneficial effect on patients with UV. Omalizumab may be effective in UV through its reduction of IgE, as in chronic urticaria, and through downstream effects on cellular activation mechanisms (possibly a reduction in chemotaxis or immune complex formation). However, the mechanism of action of omalizumab for UV remains, in part, unresolved. It is not known whether omalizumab is efficacious against both normocomplementemic and hypocomplementemic UV. Further studies with a greater number of patients are needed to confirm the effects of omalizumab for vasculitic patients.
- Chang S, Carr W. Urticarial vasculitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007;28:97-100.
- Ghazanfar MN, Thomsen SF. Omalizumab for urticarial vasculitis: case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2015:576893.
- Kai AC, Flohr C, Grattan CE. Improvement in quality of life impairment followed by relapse with 6-monthly periodic administration of omalizumab for severe treatment-refractory chronic urticaria and urticarial vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:651-652.
- Diez LS, Tamayo LM, Cardona R. Omalizumab: therapeutic option in chronic spontaneous urticaria difficult to control with associated vasculitis, report of three cases. Biomedica. 2013;33:503-512.
- Maurer M, Rosen K, Hsieh HJ. Omalizumab for chronic urticaria. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2530.
- Ben Shoshan M. Omalizumab: not only for asthma. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008;2:191-201.
- Fueyo-Casado A, Campos-Munoz L, Gonzalez-Guerra E, et al. Effectiveness of omalizumab in a case of urticarial vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. Published March 1, 2017. doi:10.1111/ced.13076
- Chia JC, Mydlarski PR. Dermatologic uses of omalizumab. J Dermatol Treat. Published November 7, 2016. doi:10.1080/09546634.2016.1249819
- Chang S, Carr W. Urticarial vasculitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007;28:97-100.
- Ghazanfar MN, Thomsen SF. Omalizumab for urticarial vasculitis: case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2015:576893.
- Kai AC, Flohr C, Grattan CE. Improvement in quality of life impairment followed by relapse with 6-monthly periodic administration of omalizumab for severe treatment-refractory chronic urticaria and urticarial vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:651-652.
- Diez LS, Tamayo LM, Cardona R. Omalizumab: therapeutic option in chronic spontaneous urticaria difficult to control with associated vasculitis, report of three cases. Biomedica. 2013;33:503-512.
- Maurer M, Rosen K, Hsieh HJ. Omalizumab for chronic urticaria. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2530.
- Ben Shoshan M. Omalizumab: not only for asthma. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008;2:191-201.
- Fueyo-Casado A, Campos-Munoz L, Gonzalez-Guerra E, et al. Effectiveness of omalizumab in a case of urticarial vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. Published March 1, 2017. doi:10.1111/ced.13076
- Chia JC, Mydlarski PR. Dermatologic uses of omalizumab. J Dermatol Treat. Published November 7, 2016. doi:10.1080/09546634.2016.1249819
Practice Points
- The differential diagnosis of urticaria and urticarial vasculitis may be complicated.
- Omalizumab is an effective urticaria treatment and also can be an alternative treatment choice in resistant urticarial vasculitis.
FDA expands rimegepant indication to include migraine prevention
Last year, rimegepant became the first calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, available in a fast-acting orally disintegrating tablet, to be approved for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
Rimegepant is currently the only migraine medication approved to both treat acute migraine attacks and help prevent future migraine attacks.
The new indication allows for use of rimegepant for preventive treatment in adults with episodic migraine (more than 15 migraine days per month). Rimegepant may be used for up to 18 doses per month, which includes both acute and preventive therapy.
In a phase 2/3 study, oral rimegepant was superior to placebo in reducing monthly migraine days. About half of adults who took rimegepant experienced a 50% or greater reduction in the number of days of moderate to severe migraines per month.
The most common adverse effects of rimegepant therapy were nausea (2.7%) and stomach pain or indigestion (2.4%).
The FDA approval of rimegepant for the preventive treatment of migraine, along with its acute treatment indication, is “one of the most ground-breaking things to happen to migraine treatment in my 40 years of practicing headache medicine,” Peter J. Goadsby, MD, PhD, an investigator in the prevention study, said in a company news release.
“To have one medication patients can use to treat and prevent migraine will likely change the treatment paradigm for many of the millions of people who live with migraine,” said Dr. Goadsby, professor of neurology, University of California, Los Angeles and King’s College, London.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, rimegepant became the first calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, available in a fast-acting orally disintegrating tablet, to be approved for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
Rimegepant is currently the only migraine medication approved to both treat acute migraine attacks and help prevent future migraine attacks.
The new indication allows for use of rimegepant for preventive treatment in adults with episodic migraine (more than 15 migraine days per month). Rimegepant may be used for up to 18 doses per month, which includes both acute and preventive therapy.
In a phase 2/3 study, oral rimegepant was superior to placebo in reducing monthly migraine days. About half of adults who took rimegepant experienced a 50% or greater reduction in the number of days of moderate to severe migraines per month.
The most common adverse effects of rimegepant therapy were nausea (2.7%) and stomach pain or indigestion (2.4%).
The FDA approval of rimegepant for the preventive treatment of migraine, along with its acute treatment indication, is “one of the most ground-breaking things to happen to migraine treatment in my 40 years of practicing headache medicine,” Peter J. Goadsby, MD, PhD, an investigator in the prevention study, said in a company news release.
“To have one medication patients can use to treat and prevent migraine will likely change the treatment paradigm for many of the millions of people who live with migraine,” said Dr. Goadsby, professor of neurology, University of California, Los Angeles and King’s College, London.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, rimegepant became the first calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, available in a fast-acting orally disintegrating tablet, to be approved for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
Rimegepant is currently the only migraine medication approved to both treat acute migraine attacks and help prevent future migraine attacks.
The new indication allows for use of rimegepant for preventive treatment in adults with episodic migraine (more than 15 migraine days per month). Rimegepant may be used for up to 18 doses per month, which includes both acute and preventive therapy.
In a phase 2/3 study, oral rimegepant was superior to placebo in reducing monthly migraine days. About half of adults who took rimegepant experienced a 50% or greater reduction in the number of days of moderate to severe migraines per month.
The most common adverse effects of rimegepant therapy were nausea (2.7%) and stomach pain or indigestion (2.4%).
The FDA approval of rimegepant for the preventive treatment of migraine, along with its acute treatment indication, is “one of the most ground-breaking things to happen to migraine treatment in my 40 years of practicing headache medicine,” Peter J. Goadsby, MD, PhD, an investigator in the prevention study, said in a company news release.
“To have one medication patients can use to treat and prevent migraine will likely change the treatment paradigm for many of the millions of people who live with migraine,” said Dr. Goadsby, professor of neurology, University of California, Los Angeles and King’s College, London.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Subclinical myocarditis found in some athletes post COVID
Myocarditis is present in a small percentage of competitive athletes after COVID-19 infection, even in those without symptoms, new research suggests.
In a cohort study of 1,597 competitive collegiate athletes undergoing comprehensive cardiovascular testing in the United States, the prevalence of clinical myocarditis based on a symptom-based screening strategy was only 0.31%.
But screening with cardiac MRI increased the prevalence of clinical and subclinical myocarditis by a factor of 7.4, to 2.3%, the authors reported.
The findings are published online May 27, 2021, in JAMA Cardiology.
“It was the largest study to evaluate college athletes who have had COVID with extensive cardiac testing, including MRI, and this gave us a very objective look at the cardiac findings, as they were not purely based upon a subjective evaluation of symptoms,” lead investigator Curt J. Daniels, MD, professor at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
“Unfortunately, our study showed that athletes can be asymptomatic, or at least not report symptoms. This is a very subjective feature, and we don’t know if they don’t report symptoms because they didn’t want to get tested. That is why we took a very objective approach,” Dr. Daniels said.
The finding that more than half of the asymptomatic athletes had myocarditis, or as the investigators called it, “subclinical myocarditis,” was a surprise, he acknowledged.
“More than half of the athletes found to have myocarditis reported no symptoms, and yes, that was a surprise, because prior to this study, the protocols that had been published stated that you had to have symptoms to even enter into the protocol for cardiac MRI. But, as our ... paper shows, if we had followed that protocol, we only would have found about 5 cases of myocarditis, as opposed to the total of 37 we found with cardiac MRI,” Dr. Daniels said.
In October 2020, the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Council recommended that cardiac MRI be limited to athletes who exhibited symptoms as part of their guide to ensuring a safe return to play.
As reported by this news organization the council recommended a tiered approach to screening based on the presence of symptoms, followed by electrocardiography, injury biomarkers, and echocardiography. Any abnormalities detected were to be further characterized by the selective use of cardiac MRI.
At the time, there were relatively few data to support the recommendations, and all stakeholders called for larger datasets to better drive informed recommendations in the future.
In the current study, Dr. Daniels and associates conducted comprehensive cardiac screening – including ECG, troponin testing, echocardiography, and cardiac MRI – of 1,597 college athlete survivors of COVID-19.
The athletes were part of the Big Ten athletic conference, which consists of 13 major American universities.
Cardiac MRI revealed that 37 (2.3%) of these athletes demonstrated diagnostic criteria for COVID-19 myocarditis; of these, 20 had no cardiovascular symptoms and had normal ECGs, echocardiography, and troponin test results.
“These patients would not have been identified without CMR imaging. If we were going according to the older protocol, we would not have made this discovery. Cardiac MRI is the most sensitive and specific test for myocardial inflammation, there is no argument about that,” Dr. Daniels said.
The catch is, cardiac MRI is expensive and often difficult to access, especially in remote, rural, or other underserviced areas.
“You can’t get an MRI for every person who has had COVID, it’s just not feasible,” Dr. Daniels said. “We are not advocating that everybody get an MRI. But we do hope that our study creates awareness among clinicians and athletes themselves that if you’ve had COVID, even if you’re asymptomatic, there may be some heart changes. So be aware when you start to exercise again, if you have any symptoms, pause and seek medical care.”
Kudos to the sports cardiology community
In an accompanying editorial, James E. Udelson, MD, Ethan J. Rowin, MD, and Barry J. Maron, MD, from the CardioVascular Center at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, applauded the sports cardiology community for its diligence in acquiring and publishing data about the post–COVID-19 prevalence of cardiac abnormalities in competitive athletes.
“It is a real tribute to the sports cardiology community. There has been an amazing growth of information, and they not only gathered this information, they analyzed and published it, starting out with a study of 29 or 30 athletes, and now thousands,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
At the start of the pandemic, it appeared that 15%-20% of athletes had myocarditis, and athletic conferences were discussing canceling sports events.
However, with greater numbers comes a more accurate picture of the extent of the problem.
“Once you get thousands of subjects in these studies, you can hone in on what the real number is, so now we understand that if you screen everybody with a cardiac MRI, 1%, 2%, or 3% will have some evidence of what looks like myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Udelson agreed that doing cardiac imaging in everyone is not feasible.
“This study looked at a very large number of people who all had an MRI, but that doesn’t mean everyone should have them. If you just do an echo, an EKG, and a troponin test, and if everything is normal, which is kind of what current recommendations are, this paper tells us that we are going to miss one or two people out of a hundred, and that might be okay,” he said. “So, if you are at a huge university that has a large medical center and you want to screen all your athletes with MRI, great. But if you’re at a high school in a remote area, you know that the alternative, not having an MRI, isn’t so bad, either.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocarditis is present in a small percentage of competitive athletes after COVID-19 infection, even in those without symptoms, new research suggests.
In a cohort study of 1,597 competitive collegiate athletes undergoing comprehensive cardiovascular testing in the United States, the prevalence of clinical myocarditis based on a symptom-based screening strategy was only 0.31%.
But screening with cardiac MRI increased the prevalence of clinical and subclinical myocarditis by a factor of 7.4, to 2.3%, the authors reported.
The findings are published online May 27, 2021, in JAMA Cardiology.
“It was the largest study to evaluate college athletes who have had COVID with extensive cardiac testing, including MRI, and this gave us a very objective look at the cardiac findings, as they were not purely based upon a subjective evaluation of symptoms,” lead investigator Curt J. Daniels, MD, professor at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
“Unfortunately, our study showed that athletes can be asymptomatic, or at least not report symptoms. This is a very subjective feature, and we don’t know if they don’t report symptoms because they didn’t want to get tested. That is why we took a very objective approach,” Dr. Daniels said.
The finding that more than half of the asymptomatic athletes had myocarditis, or as the investigators called it, “subclinical myocarditis,” was a surprise, he acknowledged.
“More than half of the athletes found to have myocarditis reported no symptoms, and yes, that was a surprise, because prior to this study, the protocols that had been published stated that you had to have symptoms to even enter into the protocol for cardiac MRI. But, as our ... paper shows, if we had followed that protocol, we only would have found about 5 cases of myocarditis, as opposed to the total of 37 we found with cardiac MRI,” Dr. Daniels said.
In October 2020, the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Council recommended that cardiac MRI be limited to athletes who exhibited symptoms as part of their guide to ensuring a safe return to play.
As reported by this news organization the council recommended a tiered approach to screening based on the presence of symptoms, followed by electrocardiography, injury biomarkers, and echocardiography. Any abnormalities detected were to be further characterized by the selective use of cardiac MRI.
At the time, there were relatively few data to support the recommendations, and all stakeholders called for larger datasets to better drive informed recommendations in the future.
In the current study, Dr. Daniels and associates conducted comprehensive cardiac screening – including ECG, troponin testing, echocardiography, and cardiac MRI – of 1,597 college athlete survivors of COVID-19.
The athletes were part of the Big Ten athletic conference, which consists of 13 major American universities.
Cardiac MRI revealed that 37 (2.3%) of these athletes demonstrated diagnostic criteria for COVID-19 myocarditis; of these, 20 had no cardiovascular symptoms and had normal ECGs, echocardiography, and troponin test results.
“These patients would not have been identified without CMR imaging. If we were going according to the older protocol, we would not have made this discovery. Cardiac MRI is the most sensitive and specific test for myocardial inflammation, there is no argument about that,” Dr. Daniels said.
The catch is, cardiac MRI is expensive and often difficult to access, especially in remote, rural, or other underserviced areas.
“You can’t get an MRI for every person who has had COVID, it’s just not feasible,” Dr. Daniels said. “We are not advocating that everybody get an MRI. But we do hope that our study creates awareness among clinicians and athletes themselves that if you’ve had COVID, even if you’re asymptomatic, there may be some heart changes. So be aware when you start to exercise again, if you have any symptoms, pause and seek medical care.”
Kudos to the sports cardiology community
In an accompanying editorial, James E. Udelson, MD, Ethan J. Rowin, MD, and Barry J. Maron, MD, from the CardioVascular Center at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, applauded the sports cardiology community for its diligence in acquiring and publishing data about the post–COVID-19 prevalence of cardiac abnormalities in competitive athletes.
“It is a real tribute to the sports cardiology community. There has been an amazing growth of information, and they not only gathered this information, they analyzed and published it, starting out with a study of 29 or 30 athletes, and now thousands,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
At the start of the pandemic, it appeared that 15%-20% of athletes had myocarditis, and athletic conferences were discussing canceling sports events.
However, with greater numbers comes a more accurate picture of the extent of the problem.
“Once you get thousands of subjects in these studies, you can hone in on what the real number is, so now we understand that if you screen everybody with a cardiac MRI, 1%, 2%, or 3% will have some evidence of what looks like myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Udelson agreed that doing cardiac imaging in everyone is not feasible.
“This study looked at a very large number of people who all had an MRI, but that doesn’t mean everyone should have them. If you just do an echo, an EKG, and a troponin test, and if everything is normal, which is kind of what current recommendations are, this paper tells us that we are going to miss one or two people out of a hundred, and that might be okay,” he said. “So, if you are at a huge university that has a large medical center and you want to screen all your athletes with MRI, great. But if you’re at a high school in a remote area, you know that the alternative, not having an MRI, isn’t so bad, either.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocarditis is present in a small percentage of competitive athletes after COVID-19 infection, even in those without symptoms, new research suggests.
In a cohort study of 1,597 competitive collegiate athletes undergoing comprehensive cardiovascular testing in the United States, the prevalence of clinical myocarditis based on a symptom-based screening strategy was only 0.31%.
But screening with cardiac MRI increased the prevalence of clinical and subclinical myocarditis by a factor of 7.4, to 2.3%, the authors reported.
The findings are published online May 27, 2021, in JAMA Cardiology.
“It was the largest study to evaluate college athletes who have had COVID with extensive cardiac testing, including MRI, and this gave us a very objective look at the cardiac findings, as they were not purely based upon a subjective evaluation of symptoms,” lead investigator Curt J. Daniels, MD, professor at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
“Unfortunately, our study showed that athletes can be asymptomatic, or at least not report symptoms. This is a very subjective feature, and we don’t know if they don’t report symptoms because they didn’t want to get tested. That is why we took a very objective approach,” Dr. Daniels said.
The finding that more than half of the asymptomatic athletes had myocarditis, or as the investigators called it, “subclinical myocarditis,” was a surprise, he acknowledged.
“More than half of the athletes found to have myocarditis reported no symptoms, and yes, that was a surprise, because prior to this study, the protocols that had been published stated that you had to have symptoms to even enter into the protocol for cardiac MRI. But, as our ... paper shows, if we had followed that protocol, we only would have found about 5 cases of myocarditis, as opposed to the total of 37 we found with cardiac MRI,” Dr. Daniels said.
In October 2020, the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Council recommended that cardiac MRI be limited to athletes who exhibited symptoms as part of their guide to ensuring a safe return to play.
As reported by this news organization the council recommended a tiered approach to screening based on the presence of symptoms, followed by electrocardiography, injury biomarkers, and echocardiography. Any abnormalities detected were to be further characterized by the selective use of cardiac MRI.
At the time, there were relatively few data to support the recommendations, and all stakeholders called for larger datasets to better drive informed recommendations in the future.
In the current study, Dr. Daniels and associates conducted comprehensive cardiac screening – including ECG, troponin testing, echocardiography, and cardiac MRI – of 1,597 college athlete survivors of COVID-19.
The athletes were part of the Big Ten athletic conference, which consists of 13 major American universities.
Cardiac MRI revealed that 37 (2.3%) of these athletes demonstrated diagnostic criteria for COVID-19 myocarditis; of these, 20 had no cardiovascular symptoms and had normal ECGs, echocardiography, and troponin test results.
“These patients would not have been identified without CMR imaging. If we were going according to the older protocol, we would not have made this discovery. Cardiac MRI is the most sensitive and specific test for myocardial inflammation, there is no argument about that,” Dr. Daniels said.
The catch is, cardiac MRI is expensive and often difficult to access, especially in remote, rural, or other underserviced areas.
“You can’t get an MRI for every person who has had COVID, it’s just not feasible,” Dr. Daniels said. “We are not advocating that everybody get an MRI. But we do hope that our study creates awareness among clinicians and athletes themselves that if you’ve had COVID, even if you’re asymptomatic, there may be some heart changes. So be aware when you start to exercise again, if you have any symptoms, pause and seek medical care.”
Kudos to the sports cardiology community
In an accompanying editorial, James E. Udelson, MD, Ethan J. Rowin, MD, and Barry J. Maron, MD, from the CardioVascular Center at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, applauded the sports cardiology community for its diligence in acquiring and publishing data about the post–COVID-19 prevalence of cardiac abnormalities in competitive athletes.
“It is a real tribute to the sports cardiology community. There has been an amazing growth of information, and they not only gathered this information, they analyzed and published it, starting out with a study of 29 or 30 athletes, and now thousands,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
At the start of the pandemic, it appeared that 15%-20% of athletes had myocarditis, and athletic conferences were discussing canceling sports events.
However, with greater numbers comes a more accurate picture of the extent of the problem.
“Once you get thousands of subjects in these studies, you can hone in on what the real number is, so now we understand that if you screen everybody with a cardiac MRI, 1%, 2%, or 3% will have some evidence of what looks like myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Udelson agreed that doing cardiac imaging in everyone is not feasible.
“This study looked at a very large number of people who all had an MRI, but that doesn’t mean everyone should have them. If you just do an echo, an EKG, and a troponin test, and if everything is normal, which is kind of what current recommendations are, this paper tells us that we are going to miss one or two people out of a hundred, and that might be okay,” he said. “So, if you are at a huge university that has a large medical center and you want to screen all your athletes with MRI, great. But if you’re at a high school in a remote area, you know that the alternative, not having an MRI, isn’t so bad, either.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
High-flow nasal cannula improves dyspnea in palliative care patients with respiratory failure
Background: For patients receiving palliative care who develop respiratory distress, conventional oxygen therapy may not adequately relieve symptoms of dyspnea, and noninvasive ventilation may not promote comfort. Few randomized controlled trials have investigated the use of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) for treatment of palliative care patients who present to the hospital with respiratory distress.
Study design: Randomized crossover study.
Setting: Emergency department of a single institution.
Synopsis: Forty-eight palliative care patients who presented to the ED with acute dyspnea were enrolled and randomized to receive HFNC for 1 hour, followed by conventional oxygen therapy for 1 hour, or vice versa. The authors found that patients using HFNC reported significantly less dyspnea on a breathlessness severity scale, compared with patients using conventional oxygen therapy. Additionally, patients using HFNC had significantly lower respiratory rates, and HFNC use was associated with significantly lower need for morphine in a 1-hour period. The study was limited because of its single institution and small sample size, and therefore the results may not be generalizable to other patient populations.
Bottom line: Treatment with a high-flow nasal cannula may improve symptoms of acute dysp-nea in palliative patients when compared with conventional oxygen therapy.
Citation: Ruangsomboon O et al. High-flow nasal cannula versus conventional oxygen therapy in relieving dyspnea in emergency palliative patients with do-not-intubate status: A randomized crossover study. Ann Emerg Med. 2019 Dec 18. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2019.09.009.
Dr. Halford is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and instructor in medicine, Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Background: For patients receiving palliative care who develop respiratory distress, conventional oxygen therapy may not adequately relieve symptoms of dyspnea, and noninvasive ventilation may not promote comfort. Few randomized controlled trials have investigated the use of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) for treatment of palliative care patients who present to the hospital with respiratory distress.
Study design: Randomized crossover study.
Setting: Emergency department of a single institution.
Synopsis: Forty-eight palliative care patients who presented to the ED with acute dyspnea were enrolled and randomized to receive HFNC for 1 hour, followed by conventional oxygen therapy for 1 hour, or vice versa. The authors found that patients using HFNC reported significantly less dyspnea on a breathlessness severity scale, compared with patients using conventional oxygen therapy. Additionally, patients using HFNC had significantly lower respiratory rates, and HFNC use was associated with significantly lower need for morphine in a 1-hour period. The study was limited because of its single institution and small sample size, and therefore the results may not be generalizable to other patient populations.
Bottom line: Treatment with a high-flow nasal cannula may improve symptoms of acute dysp-nea in palliative patients when compared with conventional oxygen therapy.
Citation: Ruangsomboon O et al. High-flow nasal cannula versus conventional oxygen therapy in relieving dyspnea in emergency palliative patients with do-not-intubate status: A randomized crossover study. Ann Emerg Med. 2019 Dec 18. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2019.09.009.
Dr. Halford is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and instructor in medicine, Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Background: For patients receiving palliative care who develop respiratory distress, conventional oxygen therapy may not adequately relieve symptoms of dyspnea, and noninvasive ventilation may not promote comfort. Few randomized controlled trials have investigated the use of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) for treatment of palliative care patients who present to the hospital with respiratory distress.
Study design: Randomized crossover study.
Setting: Emergency department of a single institution.
Synopsis: Forty-eight palliative care patients who presented to the ED with acute dyspnea were enrolled and randomized to receive HFNC for 1 hour, followed by conventional oxygen therapy for 1 hour, or vice versa. The authors found that patients using HFNC reported significantly less dyspnea on a breathlessness severity scale, compared with patients using conventional oxygen therapy. Additionally, patients using HFNC had significantly lower respiratory rates, and HFNC use was associated with significantly lower need for morphine in a 1-hour period. The study was limited because of its single institution and small sample size, and therefore the results may not be generalizable to other patient populations.
Bottom line: Treatment with a high-flow nasal cannula may improve symptoms of acute dysp-nea in palliative patients when compared with conventional oxygen therapy.
Citation: Ruangsomboon O et al. High-flow nasal cannula versus conventional oxygen therapy in relieving dyspnea in emergency palliative patients with do-not-intubate status: A randomized crossover study. Ann Emerg Med. 2019 Dec 18. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2019.09.009.
Dr. Halford is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and instructor in medicine, Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.