User login
National Rosacea Society adds imprimatur to skin products
, according to a press release from the NRS.
The seal is meant to be a resource to easily identify skin care products and cosmetic products that have been evaluated as unlikely to cause rosacea flares or skin irritation, according to the press release.
Surveys conducted by the NRS indicate that 92% of rosacea patients report burning, stinging, or itching on their skin, 66% identified specific skin products as triggers for their symptoms, and 84% were “very interested” in skin care guidance.
Patients and clinicians can find a searchable list of currently approved products in the Seal of Acceptance section of the NRS website. New skin care and cosmetic products will be added to the list of those with the Seal of Acceptance on an ongoing basis.
Products under consideration to earn the Seal of Acceptance must be free of ingredients that can cause skin barrier disruption, flushing, burning, itching, or other unwanted neurosensory stimulation, according to the press release.
Each accepted product also must pass clinical testing to confirm safety and low risk for irritation and sensitization for individuals with rosacea. Applications for the Seal of Acceptance are reviewed anonymously by an independent panel of dermatologists. The NRS created the program under the guidance of Zoe D. Draelos, MD, a clinical and research dermatologist in High Point, North Carolina, who also serves on the NRS board of directors.
More information about products carrying the seal and how companies can apply to have their products considered to carry the seal is available at rosacea.org/seal-of-acceptance/.
, according to a press release from the NRS.
The seal is meant to be a resource to easily identify skin care products and cosmetic products that have been evaluated as unlikely to cause rosacea flares or skin irritation, according to the press release.
Surveys conducted by the NRS indicate that 92% of rosacea patients report burning, stinging, or itching on their skin, 66% identified specific skin products as triggers for their symptoms, and 84% were “very interested” in skin care guidance.
Patients and clinicians can find a searchable list of currently approved products in the Seal of Acceptance section of the NRS website. New skin care and cosmetic products will be added to the list of those with the Seal of Acceptance on an ongoing basis.
Products under consideration to earn the Seal of Acceptance must be free of ingredients that can cause skin barrier disruption, flushing, burning, itching, or other unwanted neurosensory stimulation, according to the press release.
Each accepted product also must pass clinical testing to confirm safety and low risk for irritation and sensitization for individuals with rosacea. Applications for the Seal of Acceptance are reviewed anonymously by an independent panel of dermatologists. The NRS created the program under the guidance of Zoe D. Draelos, MD, a clinical and research dermatologist in High Point, North Carolina, who also serves on the NRS board of directors.
More information about products carrying the seal and how companies can apply to have their products considered to carry the seal is available at rosacea.org/seal-of-acceptance/.
, according to a press release from the NRS.
The seal is meant to be a resource to easily identify skin care products and cosmetic products that have been evaluated as unlikely to cause rosacea flares or skin irritation, according to the press release.
Surveys conducted by the NRS indicate that 92% of rosacea patients report burning, stinging, or itching on their skin, 66% identified specific skin products as triggers for their symptoms, and 84% were “very interested” in skin care guidance.
Patients and clinicians can find a searchable list of currently approved products in the Seal of Acceptance section of the NRS website. New skin care and cosmetic products will be added to the list of those with the Seal of Acceptance on an ongoing basis.
Products under consideration to earn the Seal of Acceptance must be free of ingredients that can cause skin barrier disruption, flushing, burning, itching, or other unwanted neurosensory stimulation, according to the press release.
Each accepted product also must pass clinical testing to confirm safety and low risk for irritation and sensitization for individuals with rosacea. Applications for the Seal of Acceptance are reviewed anonymously by an independent panel of dermatologists. The NRS created the program under the guidance of Zoe D. Draelos, MD, a clinical and research dermatologist in High Point, North Carolina, who also serves on the NRS board of directors.
More information about products carrying the seal and how companies can apply to have their products considered to carry the seal is available at rosacea.org/seal-of-acceptance/.
New Injectable Weight Loss Drugs Pose Ethical Issues, Says Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s never been anything like the revolution in the treatment of obesity that we are now living through. Historically, there’s always been calorie counting and diets. Now, after a burst of interest in gastric bypass surgery, we have the amazing world of injectables. We all have heard about Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Wegovy.
These are being used by millions of Americans at this point, some on prescription for conditions like diabetes and some to bring about weight loss in prediabetes, or in some instances — as is often seen on American television — weight control or weight loss by people who just want to look better. Celebrities getting behind these injectables has really powered an explosion of use.
There still are ethical issues out there for practitioners. For one thing, there are some forms of semaglutide, a key ingredient in some of these injectables, that are made by compounding pharmacies. They’re not the name-brand prescription injectables made by large companies. They’re brewed up, if you will, by a specialty pharmacy trying to mimic the ingredient.
What we’ve seen in recent weeks is an explosion of overdoses. When a person uses one of these compounding pharmacies, usually in association with a spa or sometimes online sales of weight loss injectables, they’re not always certain about how to dose themselves, how much to give, and what to take. They could misread the instructions. The more that it’s up to them to determine the dose, the more there’s risk for error. Reports show as much as 1500% increases in poisoning of people who took, instead of a 10th of a milliliter, 10 mL of these compounded versions of the injectable drugs.
Everybody needs to be alert, and not only for adverse events from the prescription injectables. It is important to track that, make sure that people aren’t getting into trouble, and have contact with the FDA if you have a patient who reports some kind of adverse event they attribute to injectables.
It’s important to realize that there’s this generic, cheaper path, but it’s a more dangerous path. People need to know this if they’re going to try that route. Doctors should be aware of it. People should be ready to call the poison control center number in their area to make sure that they know what to do if they overdose on this stuff.
My own inclination is to try to discourage its use. I think it’s still too dangerous to have people self-dosing with ingredients that really are not yet FDA approved in terms of knowing that they’ve been tested in clinical trials.
The other big issue, aside from this Wild West world outside of prescribed injectables, is what to say to people who are obese or trying to manage their weight. I think people need to know all their options. It’s pretty easy to just say, “Let’s put you on one of these injectables” and prescribe it. For one thing, they may not be able to get it; there’s such huge demand that there are some shortages out there.
We don’t really know the long-term consequences of decades-long use of these drugs.
I think people should hear their options and maybe try something less invasive to begin with. If that doesn’t work, then move on to the injectables. It isn’t so clear to me — given the cost, some of the unknowns of long-term use, and some of the dangers of people sneaking around and trying to get things cheaper on the side — that going straight to injectables is our best answer.
I do think doctors should talk about weight with their patients, carefully, with the patient’s consent. Make sure there’s no stigma. Make sure we’re not doing anything to raise anxiety as we talk about this condition. After all, it is seen as a disease.
Then, maybe enter your way gradually into interventions, seeing if lifestyle change is possible. It’s cheap and easier to implement: better diet, better exercise, or calorie counting. Some people succeed. When they don’t, we should move on, but realize that we’ve got the equivalent of a black market. We need to encourage patients, if they use injectable weight loss drugs, to tell doctors so that they can be on alert about the dangers and risks of overdose.
Dr. Caplan is Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City. He disclosed an unpaid position with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use, and serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s never been anything like the revolution in the treatment of obesity that we are now living through. Historically, there’s always been calorie counting and diets. Now, after a burst of interest in gastric bypass surgery, we have the amazing world of injectables. We all have heard about Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Wegovy.
These are being used by millions of Americans at this point, some on prescription for conditions like diabetes and some to bring about weight loss in prediabetes, or in some instances — as is often seen on American television — weight control or weight loss by people who just want to look better. Celebrities getting behind these injectables has really powered an explosion of use.
There still are ethical issues out there for practitioners. For one thing, there are some forms of semaglutide, a key ingredient in some of these injectables, that are made by compounding pharmacies. They’re not the name-brand prescription injectables made by large companies. They’re brewed up, if you will, by a specialty pharmacy trying to mimic the ingredient.
What we’ve seen in recent weeks is an explosion of overdoses. When a person uses one of these compounding pharmacies, usually in association with a spa or sometimes online sales of weight loss injectables, they’re not always certain about how to dose themselves, how much to give, and what to take. They could misread the instructions. The more that it’s up to them to determine the dose, the more there’s risk for error. Reports show as much as 1500% increases in poisoning of people who took, instead of a 10th of a milliliter, 10 mL of these compounded versions of the injectable drugs.
Everybody needs to be alert, and not only for adverse events from the prescription injectables. It is important to track that, make sure that people aren’t getting into trouble, and have contact with the FDA if you have a patient who reports some kind of adverse event they attribute to injectables.
It’s important to realize that there’s this generic, cheaper path, but it’s a more dangerous path. People need to know this if they’re going to try that route. Doctors should be aware of it. People should be ready to call the poison control center number in their area to make sure that they know what to do if they overdose on this stuff.
My own inclination is to try to discourage its use. I think it’s still too dangerous to have people self-dosing with ingredients that really are not yet FDA approved in terms of knowing that they’ve been tested in clinical trials.
The other big issue, aside from this Wild West world outside of prescribed injectables, is what to say to people who are obese or trying to manage their weight. I think people need to know all their options. It’s pretty easy to just say, “Let’s put you on one of these injectables” and prescribe it. For one thing, they may not be able to get it; there’s such huge demand that there are some shortages out there.
We don’t really know the long-term consequences of decades-long use of these drugs.
I think people should hear their options and maybe try something less invasive to begin with. If that doesn’t work, then move on to the injectables. It isn’t so clear to me — given the cost, some of the unknowns of long-term use, and some of the dangers of people sneaking around and trying to get things cheaper on the side — that going straight to injectables is our best answer.
I do think doctors should talk about weight with their patients, carefully, with the patient’s consent. Make sure there’s no stigma. Make sure we’re not doing anything to raise anxiety as we talk about this condition. After all, it is seen as a disease.
Then, maybe enter your way gradually into interventions, seeing if lifestyle change is possible. It’s cheap and easier to implement: better diet, better exercise, or calorie counting. Some people succeed. When they don’t, we should move on, but realize that we’ve got the equivalent of a black market. We need to encourage patients, if they use injectable weight loss drugs, to tell doctors so that they can be on alert about the dangers and risks of overdose.
Dr. Caplan is Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City. He disclosed an unpaid position with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use, and serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s never been anything like the revolution in the treatment of obesity that we are now living through. Historically, there’s always been calorie counting and diets. Now, after a burst of interest in gastric bypass surgery, we have the amazing world of injectables. We all have heard about Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Wegovy.
These are being used by millions of Americans at this point, some on prescription for conditions like diabetes and some to bring about weight loss in prediabetes, or in some instances — as is often seen on American television — weight control or weight loss by people who just want to look better. Celebrities getting behind these injectables has really powered an explosion of use.
There still are ethical issues out there for practitioners. For one thing, there are some forms of semaglutide, a key ingredient in some of these injectables, that are made by compounding pharmacies. They’re not the name-brand prescription injectables made by large companies. They’re brewed up, if you will, by a specialty pharmacy trying to mimic the ingredient.
What we’ve seen in recent weeks is an explosion of overdoses. When a person uses one of these compounding pharmacies, usually in association with a spa or sometimes online sales of weight loss injectables, they’re not always certain about how to dose themselves, how much to give, and what to take. They could misread the instructions. The more that it’s up to them to determine the dose, the more there’s risk for error. Reports show as much as 1500% increases in poisoning of people who took, instead of a 10th of a milliliter, 10 mL of these compounded versions of the injectable drugs.
Everybody needs to be alert, and not only for adverse events from the prescription injectables. It is important to track that, make sure that people aren’t getting into trouble, and have contact with the FDA if you have a patient who reports some kind of adverse event they attribute to injectables.
It’s important to realize that there’s this generic, cheaper path, but it’s a more dangerous path. People need to know this if they’re going to try that route. Doctors should be aware of it. People should be ready to call the poison control center number in their area to make sure that they know what to do if they overdose on this stuff.
My own inclination is to try to discourage its use. I think it’s still too dangerous to have people self-dosing with ingredients that really are not yet FDA approved in terms of knowing that they’ve been tested in clinical trials.
The other big issue, aside from this Wild West world outside of prescribed injectables, is what to say to people who are obese or trying to manage their weight. I think people need to know all their options. It’s pretty easy to just say, “Let’s put you on one of these injectables” and prescribe it. For one thing, they may not be able to get it; there’s such huge demand that there are some shortages out there.
We don’t really know the long-term consequences of decades-long use of these drugs.
I think people should hear their options and maybe try something less invasive to begin with. If that doesn’t work, then move on to the injectables. It isn’t so clear to me — given the cost, some of the unknowns of long-term use, and some of the dangers of people sneaking around and trying to get things cheaper on the side — that going straight to injectables is our best answer.
I do think doctors should talk about weight with their patients, carefully, with the patient’s consent. Make sure there’s no stigma. Make sure we’re not doing anything to raise anxiety as we talk about this condition. After all, it is seen as a disease.
Then, maybe enter your way gradually into interventions, seeing if lifestyle change is possible. It’s cheap and easier to implement: better diet, better exercise, or calorie counting. Some people succeed. When they don’t, we should move on, but realize that we’ve got the equivalent of a black market. We need to encourage patients, if they use injectable weight loss drugs, to tell doctors so that they can be on alert about the dangers and risks of overdose.
Dr. Caplan is Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City. He disclosed an unpaid position with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use, and serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Offsetting Side Effects of New Antiobesity Medications
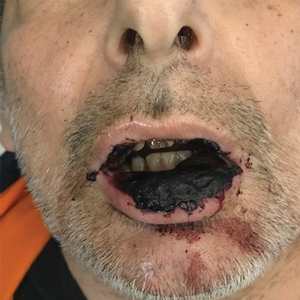
It’s 2 a.m. and my phone wakes me up with a start. My patient, Christine Z*, is vomiting uncontrollably, and Dr Google has diagnosed her with acute pancreatitis from semaglutide (Wegovy). Ten hours, several imaging studies, one blood draw, and many bags of fluids later, the verdict is in: Christine is alarmingly constipated. In fact, her entire large intestine is packed to the brim with stool. In residency, we called this diagnosis FOS, and I’ll leave it to your imagination to figure out what it stands for.
In retrospect, Christine mentions that upon raising her Wegovy dose, her bowel movements had become increasingly smaller and infrequent. This begs the question:
Proper nutrition always starts with drinking copious amounts of water. In general, I recommend a minimum of 64 ounces of water daily in patients taking incretins such as semaglutide (Wegovy for weight loss, Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes) or tirzepatide (Zepbound for weight loss, Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes). While these medications don’t directly dehydrate patients, they can increase the risk for dehydration due to severe nausea. Drinking copious amounts of water can prevent dehydration, preserve kidney function, and minimize fatigue and dizziness. In addition, fluids help soften bowel movements, making them easier to pass.
Occasionally incretins make it so easy for patients to drop pounds that their eating patterns become sloppier — more sweets and simple carbohydrates. I recommend a realistic and low glycemic index meal plan. While no foods are strictly contraindicated, processed, high-sugar, and fatty foods are likely to worsen side effects like nausea and gastrointestinal distress. Similarly, alcohol not only worsens nausea, but it’s also likely to exacerbate reflux by relaxing the sphincter that separates the stomach from the esophagus.
The next most important dietary advice is consuming sufficient fiber. In the majority of patients, increasing fiber intake relieves constipation. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. In practical terms, most fiber-rich foods contain a mixture of these two types. The general recommendation is 38 g/d for men and 25 g/d for women. The caveat to this advice is that a minority of patients, such as those with irritable bowel syndrome, may develop worsening constipation with increasing fiber.
To minimize side effects, some patients find it useful to eat five small meals throughout the day rather than three larger meals. In addition, I recommend eating slowly and stopping before the point of satiety. Finally, because weight loss of any kind is inevitably associated with muscle loss, I stress the importance of adequate protein. In general, I advise 25-30 g of protein per meal.
Christine eventually restarted her Wegovy after recovering from her grueling night in the emergency room. As this was her second go-around on Wegovy, she dug out my “guide to preventing side effects of incretins” and followed it to a T. So far, she’s feeling great.
*The patient’s name has been changed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s 2 a.m. and my phone wakes me up with a start. My patient, Christine Z*, is vomiting uncontrollably, and Dr Google has diagnosed her with acute pancreatitis from semaglutide (Wegovy). Ten hours, several imaging studies, one blood draw, and many bags of fluids later, the verdict is in: Christine is alarmingly constipated. In fact, her entire large intestine is packed to the brim with stool. In residency, we called this diagnosis FOS, and I’ll leave it to your imagination to figure out what it stands for.
In retrospect, Christine mentions that upon raising her Wegovy dose, her bowel movements had become increasingly smaller and infrequent. This begs the question:
Proper nutrition always starts with drinking copious amounts of water. In general, I recommend a minimum of 64 ounces of water daily in patients taking incretins such as semaglutide (Wegovy for weight loss, Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes) or tirzepatide (Zepbound for weight loss, Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes). While these medications don’t directly dehydrate patients, they can increase the risk for dehydration due to severe nausea. Drinking copious amounts of water can prevent dehydration, preserve kidney function, and minimize fatigue and dizziness. In addition, fluids help soften bowel movements, making them easier to pass.
Occasionally incretins make it so easy for patients to drop pounds that their eating patterns become sloppier — more sweets and simple carbohydrates. I recommend a realistic and low glycemic index meal plan. While no foods are strictly contraindicated, processed, high-sugar, and fatty foods are likely to worsen side effects like nausea and gastrointestinal distress. Similarly, alcohol not only worsens nausea, but it’s also likely to exacerbate reflux by relaxing the sphincter that separates the stomach from the esophagus.
The next most important dietary advice is consuming sufficient fiber. In the majority of patients, increasing fiber intake relieves constipation. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. In practical terms, most fiber-rich foods contain a mixture of these two types. The general recommendation is 38 g/d for men and 25 g/d for women. The caveat to this advice is that a minority of patients, such as those with irritable bowel syndrome, may develop worsening constipation with increasing fiber.
To minimize side effects, some patients find it useful to eat five small meals throughout the day rather than three larger meals. In addition, I recommend eating slowly and stopping before the point of satiety. Finally, because weight loss of any kind is inevitably associated with muscle loss, I stress the importance of adequate protein. In general, I advise 25-30 g of protein per meal.
Christine eventually restarted her Wegovy after recovering from her grueling night in the emergency room. As this was her second go-around on Wegovy, she dug out my “guide to preventing side effects of incretins” and followed it to a T. So far, she’s feeling great.
*The patient’s name has been changed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s 2 a.m. and my phone wakes me up with a start. My patient, Christine Z*, is vomiting uncontrollably, and Dr Google has diagnosed her with acute pancreatitis from semaglutide (Wegovy). Ten hours, several imaging studies, one blood draw, and many bags of fluids later, the verdict is in: Christine is alarmingly constipated. In fact, her entire large intestine is packed to the brim with stool. In residency, we called this diagnosis FOS, and I’ll leave it to your imagination to figure out what it stands for.
In retrospect, Christine mentions that upon raising her Wegovy dose, her bowel movements had become increasingly smaller and infrequent. This begs the question:
Proper nutrition always starts with drinking copious amounts of water. In general, I recommend a minimum of 64 ounces of water daily in patients taking incretins such as semaglutide (Wegovy for weight loss, Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes) or tirzepatide (Zepbound for weight loss, Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes). While these medications don’t directly dehydrate patients, they can increase the risk for dehydration due to severe nausea. Drinking copious amounts of water can prevent dehydration, preserve kidney function, and minimize fatigue and dizziness. In addition, fluids help soften bowel movements, making them easier to pass.
Occasionally incretins make it so easy for patients to drop pounds that their eating patterns become sloppier — more sweets and simple carbohydrates. I recommend a realistic and low glycemic index meal plan. While no foods are strictly contraindicated, processed, high-sugar, and fatty foods are likely to worsen side effects like nausea and gastrointestinal distress. Similarly, alcohol not only worsens nausea, but it’s also likely to exacerbate reflux by relaxing the sphincter that separates the stomach from the esophagus.
The next most important dietary advice is consuming sufficient fiber. In the majority of patients, increasing fiber intake relieves constipation. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. In practical terms, most fiber-rich foods contain a mixture of these two types. The general recommendation is 38 g/d for men and 25 g/d for women. The caveat to this advice is that a minority of patients, such as those with irritable bowel syndrome, may develop worsening constipation with increasing fiber.
To minimize side effects, some patients find it useful to eat five small meals throughout the day rather than three larger meals. In addition, I recommend eating slowly and stopping before the point of satiety. Finally, because weight loss of any kind is inevitably associated with muscle loss, I stress the importance of adequate protein. In general, I advise 25-30 g of protein per meal.
Christine eventually restarted her Wegovy after recovering from her grueling night in the emergency room. As this was her second go-around on Wegovy, she dug out my “guide to preventing side effects of incretins” and followed it to a T. So far, she’s feeling great.
*The patient’s name has been changed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
US Board Discloses Cheating, Grads Say Problem Is Rampant
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) program is invalidating scores attained by some examinees after an investigation revealed a pattern of anomalous exam performance associated with test-takers from Nepal.
In a January 31 announcement, the USMLE program said that officials are in the process of notifying examinees with results in question and that the examinees will be required to take validation exams. The program did not offer further details about its investigation or how the questionable performance was identified.
“The USMLE program regularly monitors and analyzes examinees’ test performances for unusual score patterns or variations, and other information that could raise questions about the validity of an examinee’s results,” the program said in a statement. “Highly irregular patterns can be indicative of prior unauthorized access to secure exam content.”
Some medical graduates say the action against students cheating on the USMLE is long overdue.
, particularly by groups within the international medical graduate (IMG) community, according to multiple IMGs who shared their concerns with this news organization. Sellers operate under pseudonyms across social media platforms and charge anywhere from $300 to $2000 for questions, Medscape research shows.
Facebook posts often advertise questions for sale, said Saqib Gul, MD, an IMG from Pakistan who has voiced concerns about the practice on social media.
“People make up fake profiles and tell others to [direct message] them for recalls,” he told this news organization. “There was a dedicated Facebook page that was doing this. In other cases, a couple of friends that took the exam remember a certain number of questions and write them down after the test.”
Ahmad Ozair, MD, an IMG from Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India, said that he has come across many groups online sharing or selling USMLE recalls. He first became suspicious when he saw several students, all from a few medical schools in Nepal, posting on social media about scoring in the 270 and 280-plus range.
“The statistical probability that you would have three or more candidates in the same year, scoring in the 99th percentile worldwide, belonging to a small geographical area is extremely low.”
Dr. Ozair, who now is studying public health at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said that the issue is important for “all stakeholders” who care about patient safety: “Would you want a doctor who has cheated on the medical licensing exam to take care of you?”
In an interview, USMLE program spokesman Joe Knickrehm said that the program relies on multiple processes to detect and respond to claims that exam integrity is being compromised. The process includes monitoring performance data, an anonymous tip line for reporting suspicious behavior, and a thorough investigative process.
“The USMLE program regularly monitors social media channels for comments relating to exam security and irregular behavior and will initiate an investigation if warranted,” Mr. Knickrehm told this news organization. “ The covert nature of this activity does not lend itself to a definitive statement regarding whether the problem has increased or decreased in recent years.”
Mr. Knickrehm said that the program’s STOPit app allows people to report suspicious behavior electronically to the USMLE program. Since its launch in 2021, the program has received more than 80 tips per year through the app, according to Mr. Knickrehm. Security violations are investigated by USMLE staff and reviewed by the USMLE Committee for Individualized Review (CIR). Anyone found to have engaged in irregular behavior by the CIR for activities undermining exam integrity are typically barred from access to the USMLE for multiple years.
How Easy Is It to Buy Recalls?
Two years ago, Dr B was approached by a former study partner who had just completed Step 2 of the USMLE. She asked whether Dr B wanted to buy recalled questions to help her pass.
“She paid this guy almost $2000 for recalls and told me if I pay this money, he’ll give me the recalls,” said Dr B, who asked to remain anonymous for fear of being associated with students cheating on the USMLE. “I told her I was not interested, and she said the guy would lower the price. I broke contact with her.”
Dr B, an IMG from Pakistan, was appalled. But she said that the episode was not the first time she has come across groups selling USMLE recalls or heard peers brag about having access to exam content.
“I am baffled at how many [groups] post on social media and brazenly advertise their ‘services,’” she told this news organization. “No one arrests them, their customers go on to score abnormally high on the boards, making it unachievable for people who take the honest route, plus giving IMGs a bad rep.”
Groups offering recalls are easily findable on sites such as Telegram and Signal. Telegram is a cloud-based messaging app that focuses on security, and Signal is an encrypted messaging service.
The website recallmastery.com purports to offer a range of USMLE recall packages, from a free, unsorted version to Step 1 and Step 2 packages that include “fresh updates,” and sections with “mostly repeated topics. Prices range from the free version to the $799 VIP package.
Another site called MedPox.com boasts 2024 Step 2 recalls, advertising “ actual exam questions to get HIGH scores.” The website’s owner states that the recalls were collected “by my friends,” and to message the them to be added to the “recalls group.”
A reporter was able to easily download a free version of alleged USMLE questions and answers from recallmastery.com. The document was a combination of typed and handwritten notes about medical questions, with red circles around recalled answers.
J. Bryan Carmody, MD, who blogs about medical education, reviewed a copy of the document. He said that the content appeared “credible” and was in fact recalled USMLE questions. However, the extent of which the question stem was recalled was incomplete at best, and there was little production value to the document, said Dr. Carmody, a nephrologist and associate professor of pediatrics at the Eastern Virgina Medical School in Norfolk.
The person selling the recall packages states on the website that the free version is not organized or sorted, but it allows viewers to “see how this works before paying for premium recalls.”
Mr. Knickrehm said that the program could not comment on the document, but that “whenever the USMLE program receives or locates information about a potential security violation, we investigate and take necessary action.”
When asked about the specific websites noted above, Knickrehm said that the program routinely monitors a wide array of websites, message boards, and chat rooms for USMLE-related materials. Though many sites advertise having USMLE recalls for sale, it’s more likely they are selling non-USMLE content, he said.
Using past content to cheat on medical exams is an old problem. In 2010, for example, the American Board of Internal Medicine suspended 139 physicians after they were caught cheating on the board exams. The scandal involved a vast cheating ring that included physicians memorizing questions and reproducing them after the tests. The board later sued a gastroenterologist for her part in the scandal.
In 2012, a CNN investigation exposed doctors who were memorizing test questions and creating sophisticated recall banks to cheat on radiology boards. The Association of American Medical Colleges sued a medical student in 2017 for attempting to secretly record content on the MCAT using spyglasses.
In recent years, Dr. Carmody said that he has received multiple messages and screenshots from concerned students and residents who were offered or encountered recalls.
“One thing that’s unclear is how legitimate the claims are,” he said. “Many of these recalls may be faulty or outdated. It could be someone who took the exam yesterday and has a photographic memory or it could be some sparsely recalled or mis-recalled information. Unless you’re willing to pay these people, you can’t inspect the quality, or even if you did, you wouldn’t know if the information was current or not.”
‘As an IMG, There Is So Much at Stake’
Whether recall sellers — and those buying them — are more frequently IMGs has fostered heated debate on social media.
On a Reddit thread devoted to IMG issues, posters expressed frustration about being bombarded with recall advertisements and unwanted messages about buying USMLE questions while trying to find study materials. One poster called the practices a “huge slap to all those IMGs who are struggling day and night, just to get a good score.”
In an X thread about the same subject, however, some self-described IMGs took offense to claims that IMGs might score higher because they have access to recalls. The allegations are “incendiary” and “malign hardworking IMGs,” posters wrote.
When Dr. Gul spoke out online about the “biopsy” culture, he received multiple private messages from fellow IMGs telling him to remove his comments, he said.
“I received a lot of backlash on social media,” he told this news organization. “Some IMGs asked me to take down my posts because they thought I was making IMGs look bad, and it might prompt authorities to take action or shut down international examination centers for IMGs.”
Most of the IMGs who spoke to this news organization were afraid to be publicly identified. Several IMG advocates and IMG associations contacted for the story did not respond. One medical education expert said that his institution advised him to “steer clear” of commenting because the issue was “controversial.”
“As an IMG, there is so much at stake,” Dr B said. “Any association with shady operations like these is an absolute suicide. I’m personally afraid of any repercussions of the sort.”
USMLE officials declined to comment on whether the buying or selling of recalls appears to be more prevalent among the IMG community, saying it is “difficult to generalize this behavior as ‘prevalent’ simply due to the clandestine nature of this activity.”
Cheat-Proofing the USMLE
The USMLE program has taken several steps intended to prevent cheating, but more needs to be done, medical education advocates say.
For example, Dr. Carmody called the recent change in the attempt limit for taking USMLE exams from six to four times a good move.
“The reality is, if you’re taking a USMLE exam five-plus times, you’re far more likely to be memorizing questions and selling them for shady test prep operations than you are to be legitimately pursuing U.S. residency training or licensure,” he wrote on X.
The 2022 move to make USMLE Step 1 pass or fail is another positive change, said Dr. Gul, who added that US programs should also put less weight on test scores and focus more on clinical experience.
“Many programs in the US prioritize scores rather than clinical experiences in home countries,” he said. “If program directors would remove these criteria, probably the cheating practices would stop. Clinical practice matters. When a doctor gets matched, they have to be good at seeing and treating patients, not just good at sitting in front of a screen and taking an exam.”
Turning over questions more rapidly would help curb the practices, Dr. Carmody said. Another strategy is using math techniques to identify unusual deviations that suggest cheating, he said.
A blueprint for the strategy was created after a cheating scandal involving Canada’s Medical Council of Canada Qualifying Examination (MCCQE) in 2004. After learning which questions were circulated, MCCQE administrators evaluated exams by comparing answers of compromised questions with the answers of noncompromised questions.
“For a person who was not cheating, the error of performance should be pretty similar on those two groups of questions,” Dr. Carmody said. “But if you were given the questions in advance, you might have very poor performance on questions that had not been compromised, and very high performance on those that had been compromised. That disparity is very unlikely to occur just by chance alone.”
Based on his research, Dr. Ozair is working on an academic review paper about cheating on the USMLE and on the Medical Council of Canada Qualification Examination. He said that he hopes the paper will raise more awareness about the problem and drive more action.
He and others interviewed for this story shared that the websites they’ve reported to the USMLE program are still active and offering recalls to buyers.
“Even if they are not actually offering something tangible or true, appearance matters,” Dr. Ozair said. “I think it’s worth the USMLE sending cease and desist letters and getting these websites taken down. This would restore faith in the process and underscore that this issue is being taken seriously.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) program is invalidating scores attained by some examinees after an investigation revealed a pattern of anomalous exam performance associated with test-takers from Nepal.
In a January 31 announcement, the USMLE program said that officials are in the process of notifying examinees with results in question and that the examinees will be required to take validation exams. The program did not offer further details about its investigation or how the questionable performance was identified.
“The USMLE program regularly monitors and analyzes examinees’ test performances for unusual score patterns or variations, and other information that could raise questions about the validity of an examinee’s results,” the program said in a statement. “Highly irregular patterns can be indicative of prior unauthorized access to secure exam content.”
Some medical graduates say the action against students cheating on the USMLE is long overdue.
, particularly by groups within the international medical graduate (IMG) community, according to multiple IMGs who shared their concerns with this news organization. Sellers operate under pseudonyms across social media platforms and charge anywhere from $300 to $2000 for questions, Medscape research shows.
Facebook posts often advertise questions for sale, said Saqib Gul, MD, an IMG from Pakistan who has voiced concerns about the practice on social media.
“People make up fake profiles and tell others to [direct message] them for recalls,” he told this news organization. “There was a dedicated Facebook page that was doing this. In other cases, a couple of friends that took the exam remember a certain number of questions and write them down after the test.”
Ahmad Ozair, MD, an IMG from Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India, said that he has come across many groups online sharing or selling USMLE recalls. He first became suspicious when he saw several students, all from a few medical schools in Nepal, posting on social media about scoring in the 270 and 280-plus range.
“The statistical probability that you would have three or more candidates in the same year, scoring in the 99th percentile worldwide, belonging to a small geographical area is extremely low.”
Dr. Ozair, who now is studying public health at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said that the issue is important for “all stakeholders” who care about patient safety: “Would you want a doctor who has cheated on the medical licensing exam to take care of you?”
In an interview, USMLE program spokesman Joe Knickrehm said that the program relies on multiple processes to detect and respond to claims that exam integrity is being compromised. The process includes monitoring performance data, an anonymous tip line for reporting suspicious behavior, and a thorough investigative process.
“The USMLE program regularly monitors social media channels for comments relating to exam security and irregular behavior and will initiate an investigation if warranted,” Mr. Knickrehm told this news organization. “ The covert nature of this activity does not lend itself to a definitive statement regarding whether the problem has increased or decreased in recent years.”
Mr. Knickrehm said that the program’s STOPit app allows people to report suspicious behavior electronically to the USMLE program. Since its launch in 2021, the program has received more than 80 tips per year through the app, according to Mr. Knickrehm. Security violations are investigated by USMLE staff and reviewed by the USMLE Committee for Individualized Review (CIR). Anyone found to have engaged in irregular behavior by the CIR for activities undermining exam integrity are typically barred from access to the USMLE for multiple years.
How Easy Is It to Buy Recalls?
Two years ago, Dr B was approached by a former study partner who had just completed Step 2 of the USMLE. She asked whether Dr B wanted to buy recalled questions to help her pass.
“She paid this guy almost $2000 for recalls and told me if I pay this money, he’ll give me the recalls,” said Dr B, who asked to remain anonymous for fear of being associated with students cheating on the USMLE. “I told her I was not interested, and she said the guy would lower the price. I broke contact with her.”
Dr B, an IMG from Pakistan, was appalled. But she said that the episode was not the first time she has come across groups selling USMLE recalls or heard peers brag about having access to exam content.
“I am baffled at how many [groups] post on social media and brazenly advertise their ‘services,’” she told this news organization. “No one arrests them, their customers go on to score abnormally high on the boards, making it unachievable for people who take the honest route, plus giving IMGs a bad rep.”
Groups offering recalls are easily findable on sites such as Telegram and Signal. Telegram is a cloud-based messaging app that focuses on security, and Signal is an encrypted messaging service.
The website recallmastery.com purports to offer a range of USMLE recall packages, from a free, unsorted version to Step 1 and Step 2 packages that include “fresh updates,” and sections with “mostly repeated topics. Prices range from the free version to the $799 VIP package.
Another site called MedPox.com boasts 2024 Step 2 recalls, advertising “ actual exam questions to get HIGH scores.” The website’s owner states that the recalls were collected “by my friends,” and to message the them to be added to the “recalls group.”
A reporter was able to easily download a free version of alleged USMLE questions and answers from recallmastery.com. The document was a combination of typed and handwritten notes about medical questions, with red circles around recalled answers.
J. Bryan Carmody, MD, who blogs about medical education, reviewed a copy of the document. He said that the content appeared “credible” and was in fact recalled USMLE questions. However, the extent of which the question stem was recalled was incomplete at best, and there was little production value to the document, said Dr. Carmody, a nephrologist and associate professor of pediatrics at the Eastern Virgina Medical School in Norfolk.
The person selling the recall packages states on the website that the free version is not organized or sorted, but it allows viewers to “see how this works before paying for premium recalls.”
Mr. Knickrehm said that the program could not comment on the document, but that “whenever the USMLE program receives or locates information about a potential security violation, we investigate and take necessary action.”
When asked about the specific websites noted above, Knickrehm said that the program routinely monitors a wide array of websites, message boards, and chat rooms for USMLE-related materials. Though many sites advertise having USMLE recalls for sale, it’s more likely they are selling non-USMLE content, he said.
Using past content to cheat on medical exams is an old problem. In 2010, for example, the American Board of Internal Medicine suspended 139 physicians after they were caught cheating on the board exams. The scandal involved a vast cheating ring that included physicians memorizing questions and reproducing them after the tests. The board later sued a gastroenterologist for her part in the scandal.
In 2012, a CNN investigation exposed doctors who were memorizing test questions and creating sophisticated recall banks to cheat on radiology boards. The Association of American Medical Colleges sued a medical student in 2017 for attempting to secretly record content on the MCAT using spyglasses.
In recent years, Dr. Carmody said that he has received multiple messages and screenshots from concerned students and residents who were offered or encountered recalls.
“One thing that’s unclear is how legitimate the claims are,” he said. “Many of these recalls may be faulty or outdated. It could be someone who took the exam yesterday and has a photographic memory or it could be some sparsely recalled or mis-recalled information. Unless you’re willing to pay these people, you can’t inspect the quality, or even if you did, you wouldn’t know if the information was current or not.”
‘As an IMG, There Is So Much at Stake’
Whether recall sellers — and those buying them — are more frequently IMGs has fostered heated debate on social media.
On a Reddit thread devoted to IMG issues, posters expressed frustration about being bombarded with recall advertisements and unwanted messages about buying USMLE questions while trying to find study materials. One poster called the practices a “huge slap to all those IMGs who are struggling day and night, just to get a good score.”
In an X thread about the same subject, however, some self-described IMGs took offense to claims that IMGs might score higher because they have access to recalls. The allegations are “incendiary” and “malign hardworking IMGs,” posters wrote.
When Dr. Gul spoke out online about the “biopsy” culture, he received multiple private messages from fellow IMGs telling him to remove his comments, he said.
“I received a lot of backlash on social media,” he told this news organization. “Some IMGs asked me to take down my posts because they thought I was making IMGs look bad, and it might prompt authorities to take action or shut down international examination centers for IMGs.”
Most of the IMGs who spoke to this news organization were afraid to be publicly identified. Several IMG advocates and IMG associations contacted for the story did not respond. One medical education expert said that his institution advised him to “steer clear” of commenting because the issue was “controversial.”
“As an IMG, there is so much at stake,” Dr B said. “Any association with shady operations like these is an absolute suicide. I’m personally afraid of any repercussions of the sort.”
USMLE officials declined to comment on whether the buying or selling of recalls appears to be more prevalent among the IMG community, saying it is “difficult to generalize this behavior as ‘prevalent’ simply due to the clandestine nature of this activity.”
Cheat-Proofing the USMLE
The USMLE program has taken several steps intended to prevent cheating, but more needs to be done, medical education advocates say.
For example, Dr. Carmody called the recent change in the attempt limit for taking USMLE exams from six to four times a good move.
“The reality is, if you’re taking a USMLE exam five-plus times, you’re far more likely to be memorizing questions and selling them for shady test prep operations than you are to be legitimately pursuing U.S. residency training or licensure,” he wrote on X.
The 2022 move to make USMLE Step 1 pass or fail is another positive change, said Dr. Gul, who added that US programs should also put less weight on test scores and focus more on clinical experience.
“Many programs in the US prioritize scores rather than clinical experiences in home countries,” he said. “If program directors would remove these criteria, probably the cheating practices would stop. Clinical practice matters. When a doctor gets matched, they have to be good at seeing and treating patients, not just good at sitting in front of a screen and taking an exam.”
Turning over questions more rapidly would help curb the practices, Dr. Carmody said. Another strategy is using math techniques to identify unusual deviations that suggest cheating, he said.
A blueprint for the strategy was created after a cheating scandal involving Canada’s Medical Council of Canada Qualifying Examination (MCCQE) in 2004. After learning which questions were circulated, MCCQE administrators evaluated exams by comparing answers of compromised questions with the answers of noncompromised questions.
“For a person who was not cheating, the error of performance should be pretty similar on those two groups of questions,” Dr. Carmody said. “But if you were given the questions in advance, you might have very poor performance on questions that had not been compromised, and very high performance on those that had been compromised. That disparity is very unlikely to occur just by chance alone.”
Based on his research, Dr. Ozair is working on an academic review paper about cheating on the USMLE and on the Medical Council of Canada Qualification Examination. He said that he hopes the paper will raise more awareness about the problem and drive more action.
He and others interviewed for this story shared that the websites they’ve reported to the USMLE program are still active and offering recalls to buyers.
“Even if they are not actually offering something tangible or true, appearance matters,” Dr. Ozair said. “I think it’s worth the USMLE sending cease and desist letters and getting these websites taken down. This would restore faith in the process and underscore that this issue is being taken seriously.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) program is invalidating scores attained by some examinees after an investigation revealed a pattern of anomalous exam performance associated with test-takers from Nepal.
In a January 31 announcement, the USMLE program said that officials are in the process of notifying examinees with results in question and that the examinees will be required to take validation exams. The program did not offer further details about its investigation or how the questionable performance was identified.
“The USMLE program regularly monitors and analyzes examinees’ test performances for unusual score patterns or variations, and other information that could raise questions about the validity of an examinee’s results,” the program said in a statement. “Highly irregular patterns can be indicative of prior unauthorized access to secure exam content.”
Some medical graduates say the action against students cheating on the USMLE is long overdue.
, particularly by groups within the international medical graduate (IMG) community, according to multiple IMGs who shared their concerns with this news organization. Sellers operate under pseudonyms across social media platforms and charge anywhere from $300 to $2000 for questions, Medscape research shows.
Facebook posts often advertise questions for sale, said Saqib Gul, MD, an IMG from Pakistan who has voiced concerns about the practice on social media.
“People make up fake profiles and tell others to [direct message] them for recalls,” he told this news organization. “There was a dedicated Facebook page that was doing this. In other cases, a couple of friends that took the exam remember a certain number of questions and write them down after the test.”
Ahmad Ozair, MD, an IMG from Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India, said that he has come across many groups online sharing or selling USMLE recalls. He first became suspicious when he saw several students, all from a few medical schools in Nepal, posting on social media about scoring in the 270 and 280-plus range.
“The statistical probability that you would have three or more candidates in the same year, scoring in the 99th percentile worldwide, belonging to a small geographical area is extremely low.”
Dr. Ozair, who now is studying public health at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said that the issue is important for “all stakeholders” who care about patient safety: “Would you want a doctor who has cheated on the medical licensing exam to take care of you?”
In an interview, USMLE program spokesman Joe Knickrehm said that the program relies on multiple processes to detect and respond to claims that exam integrity is being compromised. The process includes monitoring performance data, an anonymous tip line for reporting suspicious behavior, and a thorough investigative process.
“The USMLE program regularly monitors social media channels for comments relating to exam security and irregular behavior and will initiate an investigation if warranted,” Mr. Knickrehm told this news organization. “ The covert nature of this activity does not lend itself to a definitive statement regarding whether the problem has increased or decreased in recent years.”
Mr. Knickrehm said that the program’s STOPit app allows people to report suspicious behavior electronically to the USMLE program. Since its launch in 2021, the program has received more than 80 tips per year through the app, according to Mr. Knickrehm. Security violations are investigated by USMLE staff and reviewed by the USMLE Committee for Individualized Review (CIR). Anyone found to have engaged in irregular behavior by the CIR for activities undermining exam integrity are typically barred from access to the USMLE for multiple years.
How Easy Is It to Buy Recalls?
Two years ago, Dr B was approached by a former study partner who had just completed Step 2 of the USMLE. She asked whether Dr B wanted to buy recalled questions to help her pass.
“She paid this guy almost $2000 for recalls and told me if I pay this money, he’ll give me the recalls,” said Dr B, who asked to remain anonymous for fear of being associated with students cheating on the USMLE. “I told her I was not interested, and she said the guy would lower the price. I broke contact with her.”
Dr B, an IMG from Pakistan, was appalled. But she said that the episode was not the first time she has come across groups selling USMLE recalls or heard peers brag about having access to exam content.
“I am baffled at how many [groups] post on social media and brazenly advertise their ‘services,’” she told this news organization. “No one arrests them, their customers go on to score abnormally high on the boards, making it unachievable for people who take the honest route, plus giving IMGs a bad rep.”
Groups offering recalls are easily findable on sites such as Telegram and Signal. Telegram is a cloud-based messaging app that focuses on security, and Signal is an encrypted messaging service.
The website recallmastery.com purports to offer a range of USMLE recall packages, from a free, unsorted version to Step 1 and Step 2 packages that include “fresh updates,” and sections with “mostly repeated topics. Prices range from the free version to the $799 VIP package.
Another site called MedPox.com boasts 2024 Step 2 recalls, advertising “ actual exam questions to get HIGH scores.” The website’s owner states that the recalls were collected “by my friends,” and to message the them to be added to the “recalls group.”
A reporter was able to easily download a free version of alleged USMLE questions and answers from recallmastery.com. The document was a combination of typed and handwritten notes about medical questions, with red circles around recalled answers.
J. Bryan Carmody, MD, who blogs about medical education, reviewed a copy of the document. He said that the content appeared “credible” and was in fact recalled USMLE questions. However, the extent of which the question stem was recalled was incomplete at best, and there was little production value to the document, said Dr. Carmody, a nephrologist and associate professor of pediatrics at the Eastern Virgina Medical School in Norfolk.
The person selling the recall packages states on the website that the free version is not organized or sorted, but it allows viewers to “see how this works before paying for premium recalls.”
Mr. Knickrehm said that the program could not comment on the document, but that “whenever the USMLE program receives or locates information about a potential security violation, we investigate and take necessary action.”
When asked about the specific websites noted above, Knickrehm said that the program routinely monitors a wide array of websites, message boards, and chat rooms for USMLE-related materials. Though many sites advertise having USMLE recalls for sale, it’s more likely they are selling non-USMLE content, he said.
Using past content to cheat on medical exams is an old problem. In 2010, for example, the American Board of Internal Medicine suspended 139 physicians after they were caught cheating on the board exams. The scandal involved a vast cheating ring that included physicians memorizing questions and reproducing them after the tests. The board later sued a gastroenterologist for her part in the scandal.
In 2012, a CNN investigation exposed doctors who were memorizing test questions and creating sophisticated recall banks to cheat on radiology boards. The Association of American Medical Colleges sued a medical student in 2017 for attempting to secretly record content on the MCAT using spyglasses.
In recent years, Dr. Carmody said that he has received multiple messages and screenshots from concerned students and residents who were offered or encountered recalls.
“One thing that’s unclear is how legitimate the claims are,” he said. “Many of these recalls may be faulty or outdated. It could be someone who took the exam yesterday and has a photographic memory or it could be some sparsely recalled or mis-recalled information. Unless you’re willing to pay these people, you can’t inspect the quality, or even if you did, you wouldn’t know if the information was current or not.”
‘As an IMG, There Is So Much at Stake’
Whether recall sellers — and those buying them — are more frequently IMGs has fostered heated debate on social media.
On a Reddit thread devoted to IMG issues, posters expressed frustration about being bombarded with recall advertisements and unwanted messages about buying USMLE questions while trying to find study materials. One poster called the practices a “huge slap to all those IMGs who are struggling day and night, just to get a good score.”
In an X thread about the same subject, however, some self-described IMGs took offense to claims that IMGs might score higher because they have access to recalls. The allegations are “incendiary” and “malign hardworking IMGs,” posters wrote.
When Dr. Gul spoke out online about the “biopsy” culture, he received multiple private messages from fellow IMGs telling him to remove his comments, he said.
“I received a lot of backlash on social media,” he told this news organization. “Some IMGs asked me to take down my posts because they thought I was making IMGs look bad, and it might prompt authorities to take action or shut down international examination centers for IMGs.”
Most of the IMGs who spoke to this news organization were afraid to be publicly identified. Several IMG advocates and IMG associations contacted for the story did not respond. One medical education expert said that his institution advised him to “steer clear” of commenting because the issue was “controversial.”
“As an IMG, there is so much at stake,” Dr B said. “Any association with shady operations like these is an absolute suicide. I’m personally afraid of any repercussions of the sort.”
USMLE officials declined to comment on whether the buying or selling of recalls appears to be more prevalent among the IMG community, saying it is “difficult to generalize this behavior as ‘prevalent’ simply due to the clandestine nature of this activity.”
Cheat-Proofing the USMLE
The USMLE program has taken several steps intended to prevent cheating, but more needs to be done, medical education advocates say.
For example, Dr. Carmody called the recent change in the attempt limit for taking USMLE exams from six to four times a good move.
“The reality is, if you’re taking a USMLE exam five-plus times, you’re far more likely to be memorizing questions and selling them for shady test prep operations than you are to be legitimately pursuing U.S. residency training or licensure,” he wrote on X.
The 2022 move to make USMLE Step 1 pass or fail is another positive change, said Dr. Gul, who added that US programs should also put less weight on test scores and focus more on clinical experience.
“Many programs in the US prioritize scores rather than clinical experiences in home countries,” he said. “If program directors would remove these criteria, probably the cheating practices would stop. Clinical practice matters. When a doctor gets matched, they have to be good at seeing and treating patients, not just good at sitting in front of a screen and taking an exam.”
Turning over questions more rapidly would help curb the practices, Dr. Carmody said. Another strategy is using math techniques to identify unusual deviations that suggest cheating, he said.
A blueprint for the strategy was created after a cheating scandal involving Canada’s Medical Council of Canada Qualifying Examination (MCCQE) in 2004. After learning which questions were circulated, MCCQE administrators evaluated exams by comparing answers of compromised questions with the answers of noncompromised questions.
“For a person who was not cheating, the error of performance should be pretty similar on those two groups of questions,” Dr. Carmody said. “But if you were given the questions in advance, you might have very poor performance on questions that had not been compromised, and very high performance on those that had been compromised. That disparity is very unlikely to occur just by chance alone.”
Based on his research, Dr. Ozair is working on an academic review paper about cheating on the USMLE and on the Medical Council of Canada Qualification Examination. He said that he hopes the paper will raise more awareness about the problem and drive more action.
He and others interviewed for this story shared that the websites they’ve reported to the USMLE program are still active and offering recalls to buyers.
“Even if they are not actually offering something tangible or true, appearance matters,” Dr. Ozair said. “I think it’s worth the USMLE sending cease and desist letters and getting these websites taken down. This would restore faith in the process and underscore that this issue is being taken seriously.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiorespiratory Fitness May Cut Prostate Cancer Risk
Men with cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) who increased their CRF by more than 3% had a significantly lower risk of prostate cancer incidence, a large Swedish study found.
The prospective analysis, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, done in a cohort of nearly 58,000, was conducted by Kate A. Bolam, PhD, a clinical exercise physiologist at the Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences in Stockholm.
“The findings suggest that physicians could work toward supporting patients to understand what types of activities could improve their fitness and ways they can incorporate these activities into their lives in an enjoyable way, or at the very least refer patients on to an exercise specialist,” Dr. Bolam said in an interview.
Grouped by baseline CRF, the association between change in absolute CRF and prostate cancer incidence was significant only for participants with a moderate baseline CRF. Moreover, changes in both absolute and relative CRF were not associated with prostate cancer mortality.
The lack of mortality significance may be due to the relatively few deaths from prostate cancer in the cohort, Dr. Bolam said. “It may be we weren’t powered to detect anything with such low numbers. And it’s not likely men will die from prostate cancer but more likely from more common chronic diseases such as heart disease.” The authors noted that unlike the case with other common cancers, there are relatively few preventable risk factors with strong evidence for reducing overall prostate cancer risk. “Aside from developmental factors, being diagnosed with overweight or obesity are the main risk factors for developing advanced prostate cancer, but insufficient evidence exists to extend this conclusion to non-advanced prostate cancer,” they wrote.
There is evidence, however, that exercise reduces all-cause mortality risk across many cancer types, including prostate.
Study details
The cohort was drawn from Swedish national health-profile database figures from 1982 to 2019. Participants completed an occupational health profile assessment including at least two valid CRF tests on a cycle ergometer. During a mean follow-up of 6.7 years, 592 (1%) of 57,652 men (mean age 41.3 years, standard deviation 10.55) were diagnosed with prostate cancer, and in 46 (.08%) prostate cancer was the primary cause of death.
An increase in absolute CRF (as a percentage of liters per minute of cardiac output) was associated with a reduced incidence risk, with a hazard ratio of 0.98 (95% CI, 0.96-0.99). Grouping participants as having increased (+3%), stable (±3%), or decreased (−3%) CRF, the investigators found increased fitness was associated with an HR for prostate cancer incidence of 0.65 (95% CI, 0.49-0.86), vs decreased fitness.
According to the authors, this and similar investigations of mechanisms behind physical activity benefits will lead to more targeted prevention recommendations. The results highlight the importance of encouraging the general public to increase CRF or reach moderate fitness levels, Dr. Bolam’s group wrote. The group is planning a similar study in breast cancer.
This study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society. The authors declared no competing interests.
Men with cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) who increased their CRF by more than 3% had a significantly lower risk of prostate cancer incidence, a large Swedish study found.
The prospective analysis, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, done in a cohort of nearly 58,000, was conducted by Kate A. Bolam, PhD, a clinical exercise physiologist at the Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences in Stockholm.
“The findings suggest that physicians could work toward supporting patients to understand what types of activities could improve their fitness and ways they can incorporate these activities into their lives in an enjoyable way, or at the very least refer patients on to an exercise specialist,” Dr. Bolam said in an interview.
Grouped by baseline CRF, the association between change in absolute CRF and prostate cancer incidence was significant only for participants with a moderate baseline CRF. Moreover, changes in both absolute and relative CRF were not associated with prostate cancer mortality.
The lack of mortality significance may be due to the relatively few deaths from prostate cancer in the cohort, Dr. Bolam said. “It may be we weren’t powered to detect anything with such low numbers. And it’s not likely men will die from prostate cancer but more likely from more common chronic diseases such as heart disease.” The authors noted that unlike the case with other common cancers, there are relatively few preventable risk factors with strong evidence for reducing overall prostate cancer risk. “Aside from developmental factors, being diagnosed with overweight or obesity are the main risk factors for developing advanced prostate cancer, but insufficient evidence exists to extend this conclusion to non-advanced prostate cancer,” they wrote.
There is evidence, however, that exercise reduces all-cause mortality risk across many cancer types, including prostate.
Study details
The cohort was drawn from Swedish national health-profile database figures from 1982 to 2019. Participants completed an occupational health profile assessment including at least two valid CRF tests on a cycle ergometer. During a mean follow-up of 6.7 years, 592 (1%) of 57,652 men (mean age 41.3 years, standard deviation 10.55) were diagnosed with prostate cancer, and in 46 (.08%) prostate cancer was the primary cause of death.
An increase in absolute CRF (as a percentage of liters per minute of cardiac output) was associated with a reduced incidence risk, with a hazard ratio of 0.98 (95% CI, 0.96-0.99). Grouping participants as having increased (+3%), stable (±3%), or decreased (−3%) CRF, the investigators found increased fitness was associated with an HR for prostate cancer incidence of 0.65 (95% CI, 0.49-0.86), vs decreased fitness.
According to the authors, this and similar investigations of mechanisms behind physical activity benefits will lead to more targeted prevention recommendations. The results highlight the importance of encouraging the general public to increase CRF or reach moderate fitness levels, Dr. Bolam’s group wrote. The group is planning a similar study in breast cancer.
This study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society. The authors declared no competing interests.
Men with cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) who increased their CRF by more than 3% had a significantly lower risk of prostate cancer incidence, a large Swedish study found.
The prospective analysis, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, done in a cohort of nearly 58,000, was conducted by Kate A. Bolam, PhD, a clinical exercise physiologist at the Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences in Stockholm.
“The findings suggest that physicians could work toward supporting patients to understand what types of activities could improve their fitness and ways they can incorporate these activities into their lives in an enjoyable way, or at the very least refer patients on to an exercise specialist,” Dr. Bolam said in an interview.
Grouped by baseline CRF, the association between change in absolute CRF and prostate cancer incidence was significant only for participants with a moderate baseline CRF. Moreover, changes in both absolute and relative CRF were not associated with prostate cancer mortality.
The lack of mortality significance may be due to the relatively few deaths from prostate cancer in the cohort, Dr. Bolam said. “It may be we weren’t powered to detect anything with such low numbers. And it’s not likely men will die from prostate cancer but more likely from more common chronic diseases such as heart disease.” The authors noted that unlike the case with other common cancers, there are relatively few preventable risk factors with strong evidence for reducing overall prostate cancer risk. “Aside from developmental factors, being diagnosed with overweight or obesity are the main risk factors for developing advanced prostate cancer, but insufficient evidence exists to extend this conclusion to non-advanced prostate cancer,” they wrote.
There is evidence, however, that exercise reduces all-cause mortality risk across many cancer types, including prostate.
Study details
The cohort was drawn from Swedish national health-profile database figures from 1982 to 2019. Participants completed an occupational health profile assessment including at least two valid CRF tests on a cycle ergometer. During a mean follow-up of 6.7 years, 592 (1%) of 57,652 men (mean age 41.3 years, standard deviation 10.55) were diagnosed with prostate cancer, and in 46 (.08%) prostate cancer was the primary cause of death.
An increase in absolute CRF (as a percentage of liters per minute of cardiac output) was associated with a reduced incidence risk, with a hazard ratio of 0.98 (95% CI, 0.96-0.99). Grouping participants as having increased (+3%), stable (±3%), or decreased (−3%) CRF, the investigators found increased fitness was associated with an HR for prostate cancer incidence of 0.65 (95% CI, 0.49-0.86), vs decreased fitness.
According to the authors, this and similar investigations of mechanisms behind physical activity benefits will lead to more targeted prevention recommendations. The results highlight the importance of encouraging the general public to increase CRF or reach moderate fitness levels, Dr. Bolam’s group wrote. The group is planning a similar study in breast cancer.
This study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society. The authors declared no competing interests.
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE
Federal Bill Seeks AI Tools to Stop Medicare Fraud
A new Senate bill would require Medicare to test two tools routinely used by credit card companies to prevent fraud: Artificial intelligence (AI)-trained algorithms to detect suspicious activity and a system to quickly alert Medicare patients on whose behalf payment is being sought.
Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) recently introduced the Medicare Transaction Fraud Prevention Act, which calls for a 2-year test of this approach.
The experiment, targeted to start in 2025, would focus on durable medical equipment and clinical diagnostic laboratory tests and cover Medicare beneficiaries who receive electronic notices about claims.
The legislation would direct the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to test the use of predictive risk-scoring algorithms in finding fraud. The program would be modeled on the systems that credit card companies already use. Transactions could be scored from 1 (least risky) to 99 (most risky).
CMS would then check directly by email or phone call with selected Medicare enrollees about transactions considered to present a high risk for fraud.
Many consumers have benefited from this approach when used to check for fraud on their credit cards, Braun noted during a November hearing of the Senate Special Committee on Aging. Credit card companies often can intervene before a fraudulent transaction is cleared.
“There’s no reason we wouldn’t want to minimally at least mimic that,” Braun said at the hearing.
Asking Medicare enrollees to verify certain purchases could give CMS increased access to vital predictive data, test proof of concept, and save hundreds of millions of dollars, Braun said.
Concerns Raised
So far, Braun has only one cosponsor for the bill, Senator Bill Cassidy, MD (R-LA), and the bill has drawn some criticism.
Brett Meeks, executive director of the Health Innovation Alliance, a trade group representing technology companies, insurers, and consumer organizations, objected to requiring Medicare enrollees to verify flagged orders. CMS should internally root out fraud through technology, not burden seniors, Meeks told this news organization.
Meeks said he has been following the discussion about the use of AI in addressing Medicare fraud. Had a bill broadly targeted Medicare fraud through AI, his alliance might have backed it, he said. But the current proposed legislation has a narrower focus.
Focusing on durable medical equipment, for example, could have unintended consequences like denying power wheelchairs to people with debilitating conditions like multiple sclerosis, Meeks said.
But Braun’s bill won a quick nod of approval from a researcher who studies the use of AI to detect Medicare fraud. Taghi M. Khoshgoftaar, PhD, director of the Data Mining and Machine Learning Lab at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida, said he sees an advantage to Braun’s approach of involving Medicare enrollees in the protection of their benefits.
The bill does not authorize funding for the pilot project, and it’s unclear what it would cost.
Detecting Medicare Fraud
The federal government has stepped up Medicare fraud investigations in recent years, and more doctors are getting caught.
A study published in 2018 examined cases of physicians excluded from Medicare using data from the US Office of Inspector General (OIG) at the Department of Health and Human Services.
The OIG has the right to exclude clinicians from Medicare for fraud or other reasons. Chen and coauthors looked at Medicare physician exclusions from 2007 to 2017. They found that exclusions due to fraud increased an estimated 14% per year on average from a base level of 139 exclusions in 2007.
In 2019, CMS sought feedback on new ways to use AI to detect fraud. In a public request for information, the agency said Medicare scrutinizes fewer claims for payment than commercial insurers do.
About 99.7% of Medicare fee-for-service claims are processed and paid within 17 days without any medical review, CMS said at the time.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
A new Senate bill would require Medicare to test two tools routinely used by credit card companies to prevent fraud: Artificial intelligence (AI)-trained algorithms to detect suspicious activity and a system to quickly alert Medicare patients on whose behalf payment is being sought.
Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) recently introduced the Medicare Transaction Fraud Prevention Act, which calls for a 2-year test of this approach.
The experiment, targeted to start in 2025, would focus on durable medical equipment and clinical diagnostic laboratory tests and cover Medicare beneficiaries who receive electronic notices about claims.
The legislation would direct the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to test the use of predictive risk-scoring algorithms in finding fraud. The program would be modeled on the systems that credit card companies already use. Transactions could be scored from 1 (least risky) to 99 (most risky).
CMS would then check directly by email or phone call with selected Medicare enrollees about transactions considered to present a high risk for fraud.
Many consumers have benefited from this approach when used to check for fraud on their credit cards, Braun noted during a November hearing of the Senate Special Committee on Aging. Credit card companies often can intervene before a fraudulent transaction is cleared.
“There’s no reason we wouldn’t want to minimally at least mimic that,” Braun said at the hearing.
Asking Medicare enrollees to verify certain purchases could give CMS increased access to vital predictive data, test proof of concept, and save hundreds of millions of dollars, Braun said.
Concerns Raised
So far, Braun has only one cosponsor for the bill, Senator Bill Cassidy, MD (R-LA), and the bill has drawn some criticism.
Brett Meeks, executive director of the Health Innovation Alliance, a trade group representing technology companies, insurers, and consumer organizations, objected to requiring Medicare enrollees to verify flagged orders. CMS should internally root out fraud through technology, not burden seniors, Meeks told this news organization.
Meeks said he has been following the discussion about the use of AI in addressing Medicare fraud. Had a bill broadly targeted Medicare fraud through AI, his alliance might have backed it, he said. But the current proposed legislation has a narrower focus.
Focusing on durable medical equipment, for example, could have unintended consequences like denying power wheelchairs to people with debilitating conditions like multiple sclerosis, Meeks said.
But Braun’s bill won a quick nod of approval from a researcher who studies the use of AI to detect Medicare fraud. Taghi M. Khoshgoftaar, PhD, director of the Data Mining and Machine Learning Lab at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida, said he sees an advantage to Braun’s approach of involving Medicare enrollees in the protection of their benefits.
The bill does not authorize funding for the pilot project, and it’s unclear what it would cost.
Detecting Medicare Fraud
The federal government has stepped up Medicare fraud investigations in recent years, and more doctors are getting caught.
A study published in 2018 examined cases of physicians excluded from Medicare using data from the US Office of Inspector General (OIG) at the Department of Health and Human Services.
The OIG has the right to exclude clinicians from Medicare for fraud or other reasons. Chen and coauthors looked at Medicare physician exclusions from 2007 to 2017. They found that exclusions due to fraud increased an estimated 14% per year on average from a base level of 139 exclusions in 2007.
In 2019, CMS sought feedback on new ways to use AI to detect fraud. In a public request for information, the agency said Medicare scrutinizes fewer claims for payment than commercial insurers do.
About 99.7% of Medicare fee-for-service claims are processed and paid within 17 days without any medical review, CMS said at the time.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
A new Senate bill would require Medicare to test two tools routinely used by credit card companies to prevent fraud: Artificial intelligence (AI)-trained algorithms to detect suspicious activity and a system to quickly alert Medicare patients on whose behalf payment is being sought.
Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) recently introduced the Medicare Transaction Fraud Prevention Act, which calls for a 2-year test of this approach.
The experiment, targeted to start in 2025, would focus on durable medical equipment and clinical diagnostic laboratory tests and cover Medicare beneficiaries who receive electronic notices about claims.
The legislation would direct the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to test the use of predictive risk-scoring algorithms in finding fraud. The program would be modeled on the systems that credit card companies already use. Transactions could be scored from 1 (least risky) to 99 (most risky).
CMS would then check directly by email or phone call with selected Medicare enrollees about transactions considered to present a high risk for fraud.
Many consumers have benefited from this approach when used to check for fraud on their credit cards, Braun noted during a November hearing of the Senate Special Committee on Aging. Credit card companies often can intervene before a fraudulent transaction is cleared.
“There’s no reason we wouldn’t want to minimally at least mimic that,” Braun said at the hearing.
Asking Medicare enrollees to verify certain purchases could give CMS increased access to vital predictive data, test proof of concept, and save hundreds of millions of dollars, Braun said.
Concerns Raised
So far, Braun has only one cosponsor for the bill, Senator Bill Cassidy, MD (R-LA), and the bill has drawn some criticism.
Brett Meeks, executive director of the Health Innovation Alliance, a trade group representing technology companies, insurers, and consumer organizations, objected to requiring Medicare enrollees to verify flagged orders. CMS should internally root out fraud through technology, not burden seniors, Meeks told this news organization.
Meeks said he has been following the discussion about the use of AI in addressing Medicare fraud. Had a bill broadly targeted Medicare fraud through AI, his alliance might have backed it, he said. But the current proposed legislation has a narrower focus.
Focusing on durable medical equipment, for example, could have unintended consequences like denying power wheelchairs to people with debilitating conditions like multiple sclerosis, Meeks said.
But Braun’s bill won a quick nod of approval from a researcher who studies the use of AI to detect Medicare fraud. Taghi M. Khoshgoftaar, PhD, director of the Data Mining and Machine Learning Lab at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida, said he sees an advantage to Braun’s approach of involving Medicare enrollees in the protection of their benefits.
The bill does not authorize funding for the pilot project, and it’s unclear what it would cost.
Detecting Medicare Fraud
The federal government has stepped up Medicare fraud investigations in recent years, and more doctors are getting caught.
A study published in 2018 examined cases of physicians excluded from Medicare using data from the US Office of Inspector General (OIG) at the Department of Health and Human Services.
The OIG has the right to exclude clinicians from Medicare for fraud or other reasons. Chen and coauthors looked at Medicare physician exclusions from 2007 to 2017. They found that exclusions due to fraud increased an estimated 14% per year on average from a base level of 139 exclusions in 2007.
In 2019, CMS sought feedback on new ways to use AI to detect fraud. In a public request for information, the agency said Medicare scrutinizes fewer claims for payment than commercial insurers do.
About 99.7% of Medicare fee-for-service claims are processed and paid within 17 days without any medical review, CMS said at the time.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Methotrexate-Induced Mucositis in a Patient With Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
To the Editor:
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) is an uncommon peripheral T-cell lymphoma that accounts for 1% to 2% of all forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and usually affects middle-aged individuals.1 It primarily appears on the skin and mimics an inflammatory dermatosis, leading to diagnostic and therapeutic delays.2 No gold-standard treatment has been identified for AITL; the prognosis often remains poor, with a 5-year progression-free survival rate of approximately 25%.3 Because of the rarity of AITL and the unmet need of a standard-of-care treatment regimen, relapsing and remitting disease is common and continues to challenge clinicians.
Methotrexate (MTX), a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor used to treat many autoimmune diseases, is prescribed at a higher dosage (>500 mg/m2) to manage cancers, including refractory AITL.4 In blocking dihydrofolate reductase, MTX reduces the folate pool, with the possible adverse effect of bone marrow suppression. Another important toxic effect is acute kidney injury, which may be due to an overdose of MTX or a patient’s predisposition to chronic kidney failure.4
A 50-year-old man was admitted to our inpatient clinic for evaluation of acute oral and genital mucositis. He had a 5-year history of AITL. He was previously treated by hematology with 3 lines of chemotherapy for multiple supradiaphragmatic and subdiaphragmatic localizations of lymphoma, without success. Six days prior to the current presentation, the hematologist started high-dose (3.5 g/m2) intravenous MTX therapy. Five days later, the patient developed transfusion-resistant pancytopenia and fever (maximum body temperature, 102.7°F [39.3°C]).
Physical examination at the current presentation revealed massive necrosis of the lower lip (Figure, A) and partial necrosis of the upper lip. Severe purulent balanoposthitis, causing penile edema and phimosis, complicated the clinical condition. Analysis of a specimen from a cutaneous swab of the penis showed infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterococcus faecalis. Considering the clinical presentation and time of onset of signs and symptoms, a diagnosis of acute MTX-induced mucositis was made.
Rescue therapy was started immediately, including high-dose intravenous leucovorin (120 mg 4 times daily), oral sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (800 mg/160 mg 3 times daily for 3 days per week), and oral levofloxacin (500 mg/d). After 4 days of treatment, the patient was afebrile. Mucositis of the lips had almost resolved (Figure, B), and balanoposthitis also improved after this rescue therapy. Methotrexate was not resumed because rituximab had been started.
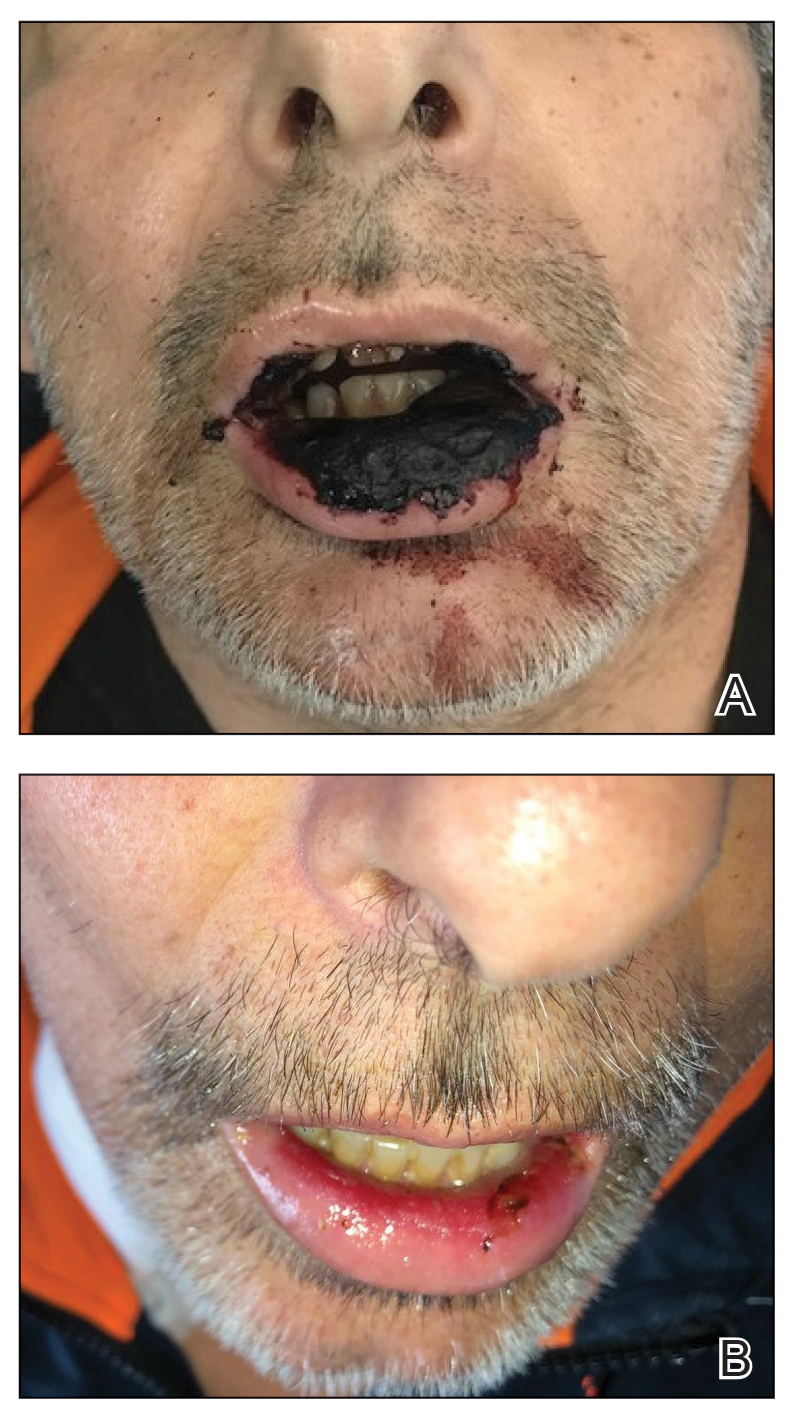
Methotrexate-induced mucositis is a rare severe skin manifestation of MTX toxicity. Prolonged renal toxicity from MTX can predispose a patient to massive myelosuppression, multiorgan failure, and mucositis.5 Pancytopenia manifests during the first 10 days of treatment. Because accumulation of MTX is higher in mucosal epithelial cells than in bone marrow stem cells, mucositis usually occurs during the first 7 days of administration, prior to onset of pancytopenia.
Skin involvement usually manifests as oral and genital mucositis due to direct toxicity against epithelial cells, with a pattern of severe keratinocyte necrosis on histopathology, known as MTX-induced epidermal necrosis.6 The principal condition in the differential diagnosis is Stevens-Johnson syndrome—including its severe form, toxic epidermal necrolysis—characterized by widespread blistering and more extensive skin detachment caused by an immune-mediated cytotoxic T-cell drug-specific reaction.7
To prevent MTX toxicity, liver and renal function should be assessed and a complete blood cell count should be performed before starting therapy. These tests should be repeated during treatment to monitor for MTX toxicity.
Leucovorin (folinic acid) counteracts MTX-induced epidermal necrosis by neutralizing the effect of MTX, including antitumoral effectiveness of the drug.8 For that reason, leucovorin cannot be started prophylactically.
The main challenges that we encountered in our patient's case were the rarity of reports of AITL in the literature and failure of 3 different lines of chemotherapy previously, which meant that MTX could not possibly be suspended because the drug represented the last therapeutic option. Our case confirms that timely clinical diagnosis and a rapid combined approach consisting of discontinuation of MTX and initiation of leucovorin rescue therapy represents an effective strategy to prevent further toxicity and to alleviate mucositis, even in patients with this rare subset of lymphoma.
- Swarup S, Kopel J, Thein, KZ, et al. Sequential complications of hypercalcemia, necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis, and aplastic anemia occurring in one patient with angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma. Am J Med Sci. 2021;361:375-382. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2020.09.003
- Wang L, Lee HY, Koh HY, et al. Cutaneous presentation of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: a harbinger of poor prognosis? Skinmed. 2016;14:469-471.
- Kameoka Y, Takahashi N, Itou S, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and prognostic factors for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2015;101:536-542. doi:10.1007/s12185-015-1763-7
- Howard SC, McCormick J, Pui C-H, et al. Preventing and managing toxicities of high-dose methotrexate. Oncologist. 2016;21:1471-1482. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0164
- Bhojwani D, Sabin ND, Pei D, et al. Methotrexate-induced neurotoxicity and leukoencephalopathy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:949-959. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.53.0808
- Yélamos O, Català A, Vilarrasa E, et al. Acute severe methotrexate toxicity in patients with psoriasis: a case series and discussion. Dermatology. 2014;229:306-309. doi:10.1159/000366501
- Delyon J, Ortonne N, Benayoun E, et al. Low-dose methotrexate-induced skin toxicity: keratinocyte dystrophy as a histologic marker.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:484-490. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.06.015
- Chen T-J, Chung W-H, Chen C-B, et al. Methotrexate-induced epidermal necrosis: a case series of 24 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:247-255.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.021
To the Editor:
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) is an uncommon peripheral T-cell lymphoma that accounts for 1% to 2% of all forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and usually affects middle-aged individuals.1 It primarily appears on the skin and mimics an inflammatory dermatosis, leading to diagnostic and therapeutic delays.2 No gold-standard treatment has been identified for AITL; the prognosis often remains poor, with a 5-year progression-free survival rate of approximately 25%.3 Because of the rarity of AITL and the unmet need of a standard-of-care treatment regimen, relapsing and remitting disease is common and continues to challenge clinicians.
Methotrexate (MTX), a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor used to treat many autoimmune diseases, is prescribed at a higher dosage (>500 mg/m2) to manage cancers, including refractory AITL.4 In blocking dihydrofolate reductase, MTX reduces the folate pool, with the possible adverse effect of bone marrow suppression. Another important toxic effect is acute kidney injury, which may be due to an overdose of MTX or a patient’s predisposition to chronic kidney failure.4
A 50-year-old man was admitted to our inpatient clinic for evaluation of acute oral and genital mucositis. He had a 5-year history of AITL. He was previously treated by hematology with 3 lines of chemotherapy for multiple supradiaphragmatic and subdiaphragmatic localizations of lymphoma, without success. Six days prior to the current presentation, the hematologist started high-dose (3.5 g/m2) intravenous MTX therapy. Five days later, the patient developed transfusion-resistant pancytopenia and fever (maximum body temperature, 102.7°F [39.3°C]).
Physical examination at the current presentation revealed massive necrosis of the lower lip (Figure, A) and partial necrosis of the upper lip. Severe purulent balanoposthitis, causing penile edema and phimosis, complicated the clinical condition. Analysis of a specimen from a cutaneous swab of the penis showed infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterococcus faecalis. Considering the clinical presentation and time of onset of signs and symptoms, a diagnosis of acute MTX-induced mucositis was made.
Rescue therapy was started immediately, including high-dose intravenous leucovorin (120 mg 4 times daily), oral sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (800 mg/160 mg 3 times daily for 3 days per week), and oral levofloxacin (500 mg/d). After 4 days of treatment, the patient was afebrile. Mucositis of the lips had almost resolved (Figure, B), and balanoposthitis also improved after this rescue therapy. Methotrexate was not resumed because rituximab had been started.

Methotrexate-induced mucositis is a rare severe skin manifestation of MTX toxicity. Prolonged renal toxicity from MTX can predispose a patient to massive myelosuppression, multiorgan failure, and mucositis.5 Pancytopenia manifests during the first 10 days of treatment. Because accumulation of MTX is higher in mucosal epithelial cells than in bone marrow stem cells, mucositis usually occurs during the first 7 days of administration, prior to onset of pancytopenia.
Skin involvement usually manifests as oral and genital mucositis due to direct toxicity against epithelial cells, with a pattern of severe keratinocyte necrosis on histopathology, known as MTX-induced epidermal necrosis.6 The principal condition in the differential diagnosis is Stevens-Johnson syndrome—including its severe form, toxic epidermal necrolysis—characterized by widespread blistering and more extensive skin detachment caused by an immune-mediated cytotoxic T-cell drug-specific reaction.7
To prevent MTX toxicity, liver and renal function should be assessed and a complete blood cell count should be performed before starting therapy. These tests should be repeated during treatment to monitor for MTX toxicity.
Leucovorin (folinic acid) counteracts MTX-induced epidermal necrosis by neutralizing the effect of MTX, including antitumoral effectiveness of the drug.8 For that reason, leucovorin cannot be started prophylactically.
The main challenges that we encountered in our patient's case were the rarity of reports of AITL in the literature and failure of 3 different lines of chemotherapy previously, which meant that MTX could not possibly be suspended because the drug represented the last therapeutic option. Our case confirms that timely clinical diagnosis and a rapid combined approach consisting of discontinuation of MTX and initiation of leucovorin rescue therapy represents an effective strategy to prevent further toxicity and to alleviate mucositis, even in patients with this rare subset of lymphoma.
To the Editor:
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) is an uncommon peripheral T-cell lymphoma that accounts for 1% to 2% of all forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and usually affects middle-aged individuals.1 It primarily appears on the skin and mimics an inflammatory dermatosis, leading to diagnostic and therapeutic delays.2 No gold-standard treatment has been identified for AITL; the prognosis often remains poor, with a 5-year progression-free survival rate of approximately 25%.3 Because of the rarity of AITL and the unmet need of a standard-of-care treatment regimen, relapsing and remitting disease is common and continues to challenge clinicians.
Methotrexate (MTX), a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor used to treat many autoimmune diseases, is prescribed at a higher dosage (>500 mg/m2) to manage cancers, including refractory AITL.4 In blocking dihydrofolate reductase, MTX reduces the folate pool, with the possible adverse effect of bone marrow suppression. Another important toxic effect is acute kidney injury, which may be due to an overdose of MTX or a patient’s predisposition to chronic kidney failure.4
A 50-year-old man was admitted to our inpatient clinic for evaluation of acute oral and genital mucositis. He had a 5-year history of AITL. He was previously treated by hematology with 3 lines of chemotherapy for multiple supradiaphragmatic and subdiaphragmatic localizations of lymphoma, without success. Six days prior to the current presentation, the hematologist started high-dose (3.5 g/m2) intravenous MTX therapy. Five days later, the patient developed transfusion-resistant pancytopenia and fever (maximum body temperature, 102.7°F [39.3°C]).
Physical examination at the current presentation revealed massive necrosis of the lower lip (Figure, A) and partial necrosis of the upper lip. Severe purulent balanoposthitis, causing penile edema and phimosis, complicated the clinical condition. Analysis of a specimen from a cutaneous swab of the penis showed infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterococcus faecalis. Considering the clinical presentation and time of onset of signs and symptoms, a diagnosis of acute MTX-induced mucositis was made.
Rescue therapy was started immediately, including high-dose intravenous leucovorin (120 mg 4 times daily), oral sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (800 mg/160 mg 3 times daily for 3 days per week), and oral levofloxacin (500 mg/d). After 4 days of treatment, the patient was afebrile. Mucositis of the lips had almost resolved (Figure, B), and balanoposthitis also improved after this rescue therapy. Methotrexate was not resumed because rituximab had been started.

Methotrexate-induced mucositis is a rare severe skin manifestation of MTX toxicity. Prolonged renal toxicity from MTX can predispose a patient to massive myelosuppression, multiorgan failure, and mucositis.5 Pancytopenia manifests during the first 10 days of treatment. Because accumulation of MTX is higher in mucosal epithelial cells than in bone marrow stem cells, mucositis usually occurs during the first 7 days of administration, prior to onset of pancytopenia.
Skin involvement usually manifests as oral and genital mucositis due to direct toxicity against epithelial cells, with a pattern of severe keratinocyte necrosis on histopathology, known as MTX-induced epidermal necrosis.6 The principal condition in the differential diagnosis is Stevens-Johnson syndrome—including its severe form, toxic epidermal necrolysis—characterized by widespread blistering and more extensive skin detachment caused by an immune-mediated cytotoxic T-cell drug-specific reaction.7
To prevent MTX toxicity, liver and renal function should be assessed and a complete blood cell count should be performed before starting therapy. These tests should be repeated during treatment to monitor for MTX toxicity.
Leucovorin (folinic acid) counteracts MTX-induced epidermal necrosis by neutralizing the effect of MTX, including antitumoral effectiveness of the drug.8 For that reason, leucovorin cannot be started prophylactically.
The main challenges that we encountered in our patient's case were the rarity of reports of AITL in the literature and failure of 3 different lines of chemotherapy previously, which meant that MTX could not possibly be suspended because the drug represented the last therapeutic option. Our case confirms that timely clinical diagnosis and a rapid combined approach consisting of discontinuation of MTX and initiation of leucovorin rescue therapy represents an effective strategy to prevent further toxicity and to alleviate mucositis, even in patients with this rare subset of lymphoma.
- Swarup S, Kopel J, Thein, KZ, et al. Sequential complications of hypercalcemia, necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis, and aplastic anemia occurring in one patient with angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma. Am J Med Sci. 2021;361:375-382. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2020.09.003
- Wang L, Lee HY, Koh HY, et al. Cutaneous presentation of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: a harbinger of poor prognosis? Skinmed. 2016;14:469-471.
- Kameoka Y, Takahashi N, Itou S, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and prognostic factors for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2015;101:536-542. doi:10.1007/s12185-015-1763-7
- Howard SC, McCormick J, Pui C-H, et al. Preventing and managing toxicities of high-dose methotrexate. Oncologist. 2016;21:1471-1482. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0164
- Bhojwani D, Sabin ND, Pei D, et al. Methotrexate-induced neurotoxicity and leukoencephalopathy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:949-959. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.53.0808
- Yélamos O, Català A, Vilarrasa E, et al. Acute severe methotrexate toxicity in patients with psoriasis: a case series and discussion. Dermatology. 2014;229:306-309. doi:10.1159/000366501
- Delyon J, Ortonne N, Benayoun E, et al. Low-dose methotrexate-induced skin toxicity: keratinocyte dystrophy as a histologic marker.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:484-490. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.06.015
- Chen T-J, Chung W-H, Chen C-B, et al. Methotrexate-induced epidermal necrosis: a case series of 24 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:247-255.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.021
- Swarup S, Kopel J, Thein, KZ, et al. Sequential complications of hypercalcemia, necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis, and aplastic anemia occurring in one patient with angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma. Am J Med Sci. 2021;361:375-382. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2020.09.003
- Wang L, Lee HY, Koh HY, et al. Cutaneous presentation of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: a harbinger of poor prognosis? Skinmed. 2016;14:469-471.
- Kameoka Y, Takahashi N, Itou S, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and prognostic factors for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2015;101:536-542. doi:10.1007/s12185-015-1763-7
- Howard SC, McCormick J, Pui C-H, et al. Preventing and managing toxicities of high-dose methotrexate. Oncologist. 2016;21:1471-1482. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0164
- Bhojwani D, Sabin ND, Pei D, et al. Methotrexate-induced neurotoxicity and leukoencephalopathy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:949-959. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.53.0808
- Yélamos O, Català A, Vilarrasa E, et al. Acute severe methotrexate toxicity in patients with psoriasis: a case series and discussion. Dermatology. 2014;229:306-309. doi:10.1159/000366501
- Delyon J, Ortonne N, Benayoun E, et al. Low-dose methotrexate-induced skin toxicity: keratinocyte dystrophy as a histologic marker.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:484-490. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.06.015
- Chen T-J, Chung W-H, Chen C-B, et al. Methotrexate-induced epidermal necrosis: a case series of 24 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:247-255.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.021
PRACTICE POINTS
- Methotrexate (MTX), a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor used to treat many autoimmune diseases, is prescribed to manage cancers such as refractory angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma.
- Dermatologists should be aware of the potential mucocutaneous adverse effects of high-dosage MTX.
- To prevent MTX toxicity, liver and renal function should be assessed and a complete blood cell count should be performed before starting therapy.
Total Abstinence Not the Only Treatment Goal in SUD
In patients with stimulant use disorder (SUD), even slight reductions in drug use can lessen depression and reduce cravings, a new analysis showed.
Abstinence has long been the overall goal of SUD treatment, the investigators noted. The findings from this pooled analysis of randomized clinical trials support what investigators noted was a growing recognition that reducing stimulant use can lead to better outcomes.
“This study provides evidence that reducing the overall use of drugs is important and clinically meaningful,” study author Mehdi Farokhnia, MD, MPH, of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, North Bethesda, Maryland, wrote in a press release. “This shift may open opportunities for medication development that can help individuals achieve these improved outcomes, even if complete abstinence is not immediately achievable or wanted.”
The findings were published online on January 10, 2024, in Addiction.
Not the Only Indicator of Success
To compare clinical indicators of improvement among those with SUDs who achieved abstinence or reduced their use, investigators pooled data from 13 randomized clinical trials with more than 2000 patients seeking treatment for cocaine or methamphetamine use disorders at centers in the United States from 2001 to 2017.
The trials used similar study protocols, including similar eligibility criteria, recruitment methods, and outcome measures. Participants were 18 or older and met criteria for methamphetamine or cocaine dependence at the beginning of each trial.
Among the participants, 1196 sought treatment for cocaine use disorder and 866 for methamphetamine use disorder. Of those, just 1487 had outcomes available by the end of the trial.
Most participants had no change in the level of use or increased their use through the trial (68%) or transitioned from low (1-4 days a month) to high (5 or more days a month) frequency use.
Nearly one third of participants (32%) stopped or reduced drug use, including 18% who cut down on stimulant use and 14% who abstained altogether.
Participants using methamphetamine were more likely to be in the abstinence vs reduced use category (21.3% vs 13.9%, respectively), whereas participants using cocaine were less likely to be in the abstinence vs reduced use category (9.1% vs 20.9%).
Those who reached abstinence showed better clinical improvement than those who reduced use on most clinical measures (P < .009).
However, there were no significant differences between groups on the Addiction Severity Index (ASI) psychiatric problems subscale and cravings for secondary drugs.
“Our findings suggest that reduced frequency of stimulant use is also associated with improved psychosocial functioning,” the authors wrote. “These findings suggest the need to re-evaluate the traditional approach of exclusively relying on total abstinence as the only indicator of successful treatment, a goal that may not be achievable for all patients, especially after one treatment episode.”
Those who reduced drug intake showed a significant association with nearly all clinical indicators of improvement (P < .010) compared with those who didn’t, except for the ASI psychiatric problems subscale and family/social relationship domains of the Problem Free Functioning scale, and HIV risk behavior.
Study limitations included short follow-up time in most trials and follow-up measures were based only on urine drug screens. There were also a substantial number of missing assessment points.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Health. There were no reported disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with stimulant use disorder (SUD), even slight reductions in drug use can lessen depression and reduce cravings, a new analysis showed.
Abstinence has long been the overall goal of SUD treatment, the investigators noted. The findings from this pooled analysis of randomized clinical trials support what investigators noted was a growing recognition that reducing stimulant use can lead to better outcomes.
“This study provides evidence that reducing the overall use of drugs is important and clinically meaningful,” study author Mehdi Farokhnia, MD, MPH, of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, North Bethesda, Maryland, wrote in a press release. “This shift may open opportunities for medication development that can help individuals achieve these improved outcomes, even if complete abstinence is not immediately achievable or wanted.”
The findings were published online on January 10, 2024, in Addiction.
Not the Only Indicator of Success
To compare clinical indicators of improvement among those with SUDs who achieved abstinence or reduced their use, investigators pooled data from 13 randomized clinical trials with more than 2000 patients seeking treatment for cocaine or methamphetamine use disorders at centers in the United States from 2001 to 2017.
The trials used similar study protocols, including similar eligibility criteria, recruitment methods, and outcome measures. Participants were 18 or older and met criteria for methamphetamine or cocaine dependence at the beginning of each trial.
Among the participants, 1196 sought treatment for cocaine use disorder and 866 for methamphetamine use disorder. Of those, just 1487 had outcomes available by the end of the trial.
Most participants had no change in the level of use or increased their use through the trial (68%) or transitioned from low (1-4 days a month) to high (5 or more days a month) frequency use.
Nearly one third of participants (32%) stopped or reduced drug use, including 18% who cut down on stimulant use and 14% who abstained altogether.
Participants using methamphetamine were more likely to be in the abstinence vs reduced use category (21.3% vs 13.9%, respectively), whereas participants using cocaine were less likely to be in the abstinence vs reduced use category (9.1% vs 20.9%).
Those who reached abstinence showed better clinical improvement than those who reduced use on most clinical measures (P < .009).
However, there were no significant differences between groups on the Addiction Severity Index (ASI) psychiatric problems subscale and cravings for secondary drugs.
“Our findings suggest that reduced frequency of stimulant use is also associated with improved psychosocial functioning,” the authors wrote. “These findings suggest the need to re-evaluate the traditional approach of exclusively relying on total abstinence as the only indicator of successful treatment, a goal that may not be achievable for all patients, especially after one treatment episode.”
Those who reduced drug intake showed a significant association with nearly all clinical indicators of improvement (P < .010) compared with those who didn’t, except for the ASI psychiatric problems subscale and family/social relationship domains of the Problem Free Functioning scale, and HIV risk behavior.
Study limitations included short follow-up time in most trials and follow-up measures were based only on urine drug screens. There were also a substantial number of missing assessment points.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Health. There were no reported disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with stimulant use disorder (SUD), even slight reductions in drug use can lessen depression and reduce cravings, a new analysis showed.
Abstinence has long been the overall goal of SUD treatment, the investigators noted. The findings from this pooled analysis of randomized clinical trials support what investigators noted was a growing recognition that reducing stimulant use can lead to better outcomes.
“This study provides evidence that reducing the overall use of drugs is important and clinically meaningful,” study author Mehdi Farokhnia, MD, MPH, of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, North Bethesda, Maryland, wrote in a press release. “This shift may open opportunities for medication development that can help individuals achieve these improved outcomes, even if complete abstinence is not immediately achievable or wanted.”
The findings were published online on January 10, 2024, in Addiction.
Not the Only Indicator of Success
To compare clinical indicators of improvement among those with SUDs who achieved abstinence or reduced their use, investigators pooled data from 13 randomized clinical trials with more than 2000 patients seeking treatment for cocaine or methamphetamine use disorders at centers in the United States from 2001 to 2017.
The trials used similar study protocols, including similar eligibility criteria, recruitment methods, and outcome measures. Participants were 18 or older and met criteria for methamphetamine or cocaine dependence at the beginning of each trial.
Among the participants, 1196 sought treatment for cocaine use disorder and 866 for methamphetamine use disorder. Of those, just 1487 had outcomes available by the end of the trial.
Most participants had no change in the level of use or increased their use through the trial (68%) or transitioned from low (1-4 days a month) to high (5 or more days a month) frequency use.
Nearly one third of participants (32%) stopped or reduced drug use, including 18% who cut down on stimulant use and 14% who abstained altogether.
Participants using methamphetamine were more likely to be in the abstinence vs reduced use category (21.3% vs 13.9%, respectively), whereas participants using cocaine were less likely to be in the abstinence vs reduced use category (9.1% vs 20.9%).
Those who reached abstinence showed better clinical improvement than those who reduced use on most clinical measures (P < .009).
However, there were no significant differences between groups on the Addiction Severity Index (ASI) psychiatric problems subscale and cravings for secondary drugs.
“Our findings suggest that reduced frequency of stimulant use is also associated with improved psychosocial functioning,” the authors wrote. “These findings suggest the need to re-evaluate the traditional approach of exclusively relying on total abstinence as the only indicator of successful treatment, a goal that may not be achievable for all patients, especially after one treatment episode.”
Those who reduced drug intake showed a significant association with nearly all clinical indicators of improvement (P < .010) compared with those who didn’t, except for the ASI psychiatric problems subscale and family/social relationship domains of the Problem Free Functioning scale, and HIV risk behavior.
Study limitations included short follow-up time in most trials and follow-up measures were based only on urine drug screens. There were also a substantial number of missing assessment points.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Health. There were no reported disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Social Frailty Linked to Risk for Predementia Syndrome
TOPLINE:
Social frailty, the lack of resources to meet basic social needs, is associated with an increased risk for motoric cognitive risk syndrome (MCR), a predementia syndrome characterized by cognitive complaints and slow gait, results of a large, population-based study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study used 2011 (Round 1) to 2018 (Round 8) data on a discovery sample of 4657 individuals without MCR or dementia at baseline from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a longitudinal survey of older adult Medicare beneficiaries.
- Researchers also collected data on 3075 newly recruited individuals in Round 5 and followed to Round 8 as an independent validation sample to create a pooled sample of 7732 older adults, mean age 76.06, without MCR at baseline.
- Social frailty, assessed at baseline, included five social items: Going out less, not feeling confident, rarely visiting friends/family, not talking with others, and without live-in partner/spouse (researchers divided participants into normal [zero to one items] and social frailty [two to five items] groups).
- Individuals were considered to have MCR if they had both subjective cognitive complaints and slow gait speed (greater than 1 standard deviation below age-specific level) without dementia or mobility disability.
- Covariates included demographic and lifestyle data, presence of depression and/or anxiety symptoms, and number of chronic diseases.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up period of 4 years, 10.35% individuals were diagnosed with MCR.
- After the researchers controlled for confounding factors, those with social frailty had an increased risk for MCR compared with the normal group (pooled sample: hazard ratio [HR], 1.57; 95% CI, 1.34-1.84; P < .001).
- Each additional unfavorable social item was associated with an increased risk for MCR (pooled sample: HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.22-1.43; P < .001).
- Results of stratified analyses across subgroups suggested individuals with social frailty had a significantly higher risk for incident MCR than that of those without social frailty, regardless of socioeconomic status, lifestyle factors, chronic diseases, and mental health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest assessing social frailty using simple questions “is an efficient tool for detecting older individuals with a high risk of MCR,” the authors wrote. They noted that the addition of such a tool in clinical practice may facilitate “timely implementation of prevention strategies.”
SOURCE:
The research was led by Hui Zhang, Human Phenome Institute, Zhangjiang Fudan International Innovation Centre, Fudan University, Shanghai, China. It was published online on January 29, 2024, in Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational, so the association between social frailty and MCR is merely correlational. Due to the lack of genetic information in NHATS data, researchers didn’t evaluate the effect of genetic factors such as apolipoprotein E on the association between social frailty and MCR. Social frailty was assessed at a single time point. In addition, the researchers were unable examine the time sequence between social frailty and MCR and so could not determine the cause of this association.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Youth Science Fund, Shanghai Rising-Star Program, Shanghai Municipal Health Commission and Key Discipline Construction Project of Pudong Health, and Family Planning Commission of Shanghai. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Social frailty, the lack of resources to meet basic social needs, is associated with an increased risk for motoric cognitive risk syndrome (MCR), a predementia syndrome characterized by cognitive complaints and slow gait, results of a large, population-based study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study used 2011 (Round 1) to 2018 (Round 8) data on a discovery sample of 4657 individuals without MCR or dementia at baseline from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a longitudinal survey of older adult Medicare beneficiaries.
- Researchers also collected data on 3075 newly recruited individuals in Round 5 and followed to Round 8 as an independent validation sample to create a pooled sample of 7732 older adults, mean age 76.06, without MCR at baseline.
- Social frailty, assessed at baseline, included five social items: Going out less, not feeling confident, rarely visiting friends/family, not talking with others, and without live-in partner/spouse (researchers divided participants into normal [zero to one items] and social frailty [two to five items] groups).
- Individuals were considered to have MCR if they had both subjective cognitive complaints and slow gait speed (greater than 1 standard deviation below age-specific level) without dementia or mobility disability.
- Covariates included demographic and lifestyle data, presence of depression and/or anxiety symptoms, and number of chronic diseases.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up period of 4 years, 10.35% individuals were diagnosed with MCR.
- After the researchers controlled for confounding factors, those with social frailty had an increased risk for MCR compared with the normal group (pooled sample: hazard ratio [HR], 1.57; 95% CI, 1.34-1.84; P < .001).
- Each additional unfavorable social item was associated with an increased risk for MCR (pooled sample: HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.22-1.43; P < .001).
- Results of stratified analyses across subgroups suggested individuals with social frailty had a significantly higher risk for incident MCR than that of those without social frailty, regardless of socioeconomic status, lifestyle factors, chronic diseases, and mental health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest assessing social frailty using simple questions “is an efficient tool for detecting older individuals with a high risk of MCR,” the authors wrote. They noted that the addition of such a tool in clinical practice may facilitate “timely implementation of prevention strategies.”
SOURCE:
The research was led by Hui Zhang, Human Phenome Institute, Zhangjiang Fudan International Innovation Centre, Fudan University, Shanghai, China. It was published online on January 29, 2024, in Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational, so the association between social frailty and MCR is merely correlational. Due to the lack of genetic information in NHATS data, researchers didn’t evaluate the effect of genetic factors such as apolipoprotein E on the association between social frailty and MCR. Social frailty was assessed at a single time point. In addition, the researchers were unable examine the time sequence between social frailty and MCR and so could not determine the cause of this association.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Youth Science Fund, Shanghai Rising-Star Program, Shanghai Municipal Health Commission and Key Discipline Construction Project of Pudong Health, and Family Planning Commission of Shanghai. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Social frailty, the lack of resources to meet basic social needs, is associated with an increased risk for motoric cognitive risk syndrome (MCR), a predementia syndrome characterized by cognitive complaints and slow gait, results of a large, population-based study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study used 2011 (Round 1) to 2018 (Round 8) data on a discovery sample of 4657 individuals without MCR or dementia at baseline from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a longitudinal survey of older adult Medicare beneficiaries.
- Researchers also collected data on 3075 newly recruited individuals in Round 5 and followed to Round 8 as an independent validation sample to create a pooled sample of 7732 older adults, mean age 76.06, without MCR at baseline.
- Social frailty, assessed at baseline, included five social items: Going out less, not feeling confident, rarely visiting friends/family, not talking with others, and without live-in partner/spouse (researchers divided participants into normal [zero to one items] and social frailty [two to five items] groups).
- Individuals were considered to have MCR if they had both subjective cognitive complaints and slow gait speed (greater than 1 standard deviation below age-specific level) without dementia or mobility disability.
- Covariates included demographic and lifestyle data, presence of depression and/or anxiety symptoms, and number of chronic diseases.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up period of 4 years, 10.35% individuals were diagnosed with MCR.
- After the researchers controlled for confounding factors, those with social frailty had an increased risk for MCR compared with the normal group (pooled sample: hazard ratio [HR], 1.57; 95% CI, 1.34-1.84; P < .001).
- Each additional unfavorable social item was associated with an increased risk for MCR (pooled sample: HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.22-1.43; P < .001).
- Results of stratified analyses across subgroups suggested individuals with social frailty had a significantly higher risk for incident MCR than that of those without social frailty, regardless of socioeconomic status, lifestyle factors, chronic diseases, and mental health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest assessing social frailty using simple questions “is an efficient tool for detecting older individuals with a high risk of MCR,” the authors wrote. They noted that the addition of such a tool in clinical practice may facilitate “timely implementation of prevention strategies.”
SOURCE:
The research was led by Hui Zhang, Human Phenome Institute, Zhangjiang Fudan International Innovation Centre, Fudan University, Shanghai, China. It was published online on January 29, 2024, in Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational, so the association between social frailty and MCR is merely correlational. Due to the lack of genetic information in NHATS data, researchers didn’t evaluate the effect of genetic factors such as apolipoprotein E on the association between social frailty and MCR. Social frailty was assessed at a single time point. In addition, the researchers were unable examine the time sequence between social frailty and MCR and so could not determine the cause of this association.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Youth Science Fund, Shanghai Rising-Star Program, Shanghai Municipal Health Commission and Key Discipline Construction Project of Pudong Health, and Family Planning Commission of Shanghai. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cold Water Swimming Eased Menstrual, Perimenopause Symptoms
TOPLINE:
Women with menstrual or perimenopausal symptoms can relieve common physical and psychological issues through cold water swimming, a new study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Symptoms of menstrual cycles and perimenopause vary widely but frequently include mood swings, anxiety, depression, fatigue, hot flashes, and sleep disturbances.
- This is the first investigation of whether cold water swimming has an impact on these symptoms.
- Researchers conducted a 42-question online survey of 1114 women who were regularly swam in cold water. More than two-thirds of respondents (68.1%) were between 45 and 59 years of age.
- Some of the data included responses by women who were perimenopausal but still had menstrual symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- Women who swam more frequently and for longer reported more beneficial effects than women who swam less often or for less time per swim.
- Reduction of psychological and vasomotor symptoms were most often cited by cold-water swimmers.
- Perimenopausal women who swam regularly in winter and summer saw greater reduction in anxiety and hot flashes than did those who swam in the other seasons.
IN PRACTICE:
“Teaching women to swim safely and encouraging them to swim regularly may have a benefit on the debilitating symptoms associated with the perimenopause,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers from University College, London, and published online in Post Reproductive Health. The corresponding author is Joyce Harper, PhD, professor of reproductive science at EGA Institute for Women’s Health, University College London, England.
LIMITATIONS:
This was an observational study, with no control group. The underlying cause of improved psychological symptoms of perimenopause were not fully evaluated owing to unaccounted multiple variables. Use of an online survey may introduce sampling bias and not align with the population of all menstruating or perimenopausal women. Participants were primarily White and highly educated.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Harper disclosed giving paid talks on menopause to businesses and at conferences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with menstrual or perimenopausal symptoms can relieve common physical and psychological issues through cold water swimming, a new study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Symptoms of menstrual cycles and perimenopause vary widely but frequently include mood swings, anxiety, depression, fatigue, hot flashes, and sleep disturbances.
- This is the first investigation of whether cold water swimming has an impact on these symptoms.
- Researchers conducted a 42-question online survey of 1114 women who were regularly swam in cold water. More than two-thirds of respondents (68.1%) were between 45 and 59 years of age.
- Some of the data included responses by women who were perimenopausal but still had menstrual symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- Women who swam more frequently and for longer reported more beneficial effects than women who swam less often or for less time per swim.
- Reduction of psychological and vasomotor symptoms were most often cited by cold-water swimmers.
- Perimenopausal women who swam regularly in winter and summer saw greater reduction in anxiety and hot flashes than did those who swam in the other seasons.
IN PRACTICE:
“Teaching women to swim safely and encouraging them to swim regularly may have a benefit on the debilitating symptoms associated with the perimenopause,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers from University College, London, and published online in Post Reproductive Health. The corresponding author is Joyce Harper, PhD, professor of reproductive science at EGA Institute for Women’s Health, University College London, England.
LIMITATIONS:
This was an observational study, with no control group. The underlying cause of improved psychological symptoms of perimenopause were not fully evaluated owing to unaccounted multiple variables. Use of an online survey may introduce sampling bias and not align with the population of all menstruating or perimenopausal women. Participants were primarily White and highly educated.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Harper disclosed giving paid talks on menopause to businesses and at conferences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Women with menstrual or perimenopausal symptoms can relieve common physical and psychological issues through cold water swimming, a new study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Symptoms of menstrual cycles and perimenopause vary widely but frequently include mood swings, anxiety, depression, fatigue, hot flashes, and sleep disturbances.
- This is the first investigation of whether cold water swimming has an impact on these symptoms.
- Researchers conducted a 42-question online survey of 1114 women who were regularly swam in cold water. More than two-thirds of respondents (68.1%) were between 45 and 59 years of age.
- Some of the data included responses by women who were perimenopausal but still had menstrual symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- Women who swam more frequently and for longer reported more beneficial effects than women who swam less often or for less time per swim.
- Reduction of psychological and vasomotor symptoms were most often cited by cold-water swimmers.
- Perimenopausal women who swam regularly in winter and summer saw greater reduction in anxiety and hot flashes than did those who swam in the other seasons.
IN PRACTICE:
“Teaching women to swim safely and encouraging them to swim regularly may have a benefit on the debilitating symptoms associated with the perimenopause,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers from University College, London, and published online in Post Reproductive Health. The corresponding author is Joyce Harper, PhD, professor of reproductive science at EGA Institute for Women’s Health, University College London, England.
LIMITATIONS:
This was an observational study, with no control group. The underlying cause of improved psychological symptoms of perimenopause were not fully evaluated owing to unaccounted multiple variables. Use of an online survey may introduce sampling bias and not align with the population of all menstruating or perimenopausal women. Participants were primarily White and highly educated.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Harper disclosed giving paid talks on menopause to businesses and at conferences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.