User login
Cases link vitiligoid lichen sclerosus and darker skin
, said Margaret H. Dennin, of the University of Chicago, and her associates.
Vitiligoid lichen sclerosus is a superficial variant of lichen sclerosus (LS), in which the lesion clinically appears to be vitiligo, but histologically is consistent with LS.
Seven dark-skinned girls aged 3-9 years had symptomatic (pruritus, pain, bleeding, constipation) depigmented patches of the vulvar or perianal region; three had purpuric lesions. None of the patients had atrophy or scarring, and they had no depigmentation anywhere else on their bodies. Follow-up was an average 2 years (range 3 months to 4 years).
Treatment with high-potency topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or both resulted in improvement or resolution of their symptoms in all cases, but there was mild or no improvement in the depigmentation. Biopsies were not performed because of the patients’ young age and the location of the lesions, the investigators said.
The term vitiligoid lichen sclerosus was first coined in 1961 by Borda et al. when depigmented patches, as seen in both conditions, constituted the clinical appearance, but lacked the inflammation, atrophy, and sclerosis of typical LS. Histologically, these lesions were like LS, “based on the presence of a thin band of papillary dermal sclerosis,” Ms. Dennin and her associates said. Borda et al. suggested that vitiligoid lichen sclerosus might be limited to dark-skinned people, and recent reports support this. Alternatively, it may be that the depigmentation simply is more obvious on dark-skinned people, and asymptomatic cases go unnoticed on lighter-skinned people, the investigators surmised.
Both vitiligo and LS are autoimmune cutaneous disorders, and they both often affect the anogenital region. The conditions “may be linked through a common autoimmune response from exposed intracellular or altered cell surface antigens on damaged melanocytes,” the investigators said. “Histologic evidence demonstrates that development of vitiligo involves a preceding lichenoid inflammatory reaction that may trigger an autoimmune reaction to melanocytes, decreasing their number. Evolving vitiligo with a lichenoid reaction may result in epitope spreading and the development of LS.”
The study is limited by its retrospective nature, small sample size, and lack of biopsies, the researchers noted. Larger studies are needed to look at the overlap of the conditions, and “understand the true prevalence of vitiligoid lichen sclerosus,” Ms. Dennin and her associates said.
Read more in Pediatric Dermatology (2018. doi: 10.1111/pde.13399).
, said Margaret H. Dennin, of the University of Chicago, and her associates.
Vitiligoid lichen sclerosus is a superficial variant of lichen sclerosus (LS), in which the lesion clinically appears to be vitiligo, but histologically is consistent with LS.
Seven dark-skinned girls aged 3-9 years had symptomatic (pruritus, pain, bleeding, constipation) depigmented patches of the vulvar or perianal region; three had purpuric lesions. None of the patients had atrophy or scarring, and they had no depigmentation anywhere else on their bodies. Follow-up was an average 2 years (range 3 months to 4 years).
Treatment with high-potency topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or both resulted in improvement or resolution of their symptoms in all cases, but there was mild or no improvement in the depigmentation. Biopsies were not performed because of the patients’ young age and the location of the lesions, the investigators said.
The term vitiligoid lichen sclerosus was first coined in 1961 by Borda et al. when depigmented patches, as seen in both conditions, constituted the clinical appearance, but lacked the inflammation, atrophy, and sclerosis of typical LS. Histologically, these lesions were like LS, “based on the presence of a thin band of papillary dermal sclerosis,” Ms. Dennin and her associates said. Borda et al. suggested that vitiligoid lichen sclerosus might be limited to dark-skinned people, and recent reports support this. Alternatively, it may be that the depigmentation simply is more obvious on dark-skinned people, and asymptomatic cases go unnoticed on lighter-skinned people, the investigators surmised.
Both vitiligo and LS are autoimmune cutaneous disorders, and they both often affect the anogenital region. The conditions “may be linked through a common autoimmune response from exposed intracellular or altered cell surface antigens on damaged melanocytes,” the investigators said. “Histologic evidence demonstrates that development of vitiligo involves a preceding lichenoid inflammatory reaction that may trigger an autoimmune reaction to melanocytes, decreasing their number. Evolving vitiligo with a lichenoid reaction may result in epitope spreading and the development of LS.”
The study is limited by its retrospective nature, small sample size, and lack of biopsies, the researchers noted. Larger studies are needed to look at the overlap of the conditions, and “understand the true prevalence of vitiligoid lichen sclerosus,” Ms. Dennin and her associates said.
Read more in Pediatric Dermatology (2018. doi: 10.1111/pde.13399).
, said Margaret H. Dennin, of the University of Chicago, and her associates.
Vitiligoid lichen sclerosus is a superficial variant of lichen sclerosus (LS), in which the lesion clinically appears to be vitiligo, but histologically is consistent with LS.
Seven dark-skinned girls aged 3-9 years had symptomatic (pruritus, pain, bleeding, constipation) depigmented patches of the vulvar or perianal region; three had purpuric lesions. None of the patients had atrophy or scarring, and they had no depigmentation anywhere else on their bodies. Follow-up was an average 2 years (range 3 months to 4 years).
Treatment with high-potency topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or both resulted in improvement or resolution of their symptoms in all cases, but there was mild or no improvement in the depigmentation. Biopsies were not performed because of the patients’ young age and the location of the lesions, the investigators said.
The term vitiligoid lichen sclerosus was first coined in 1961 by Borda et al. when depigmented patches, as seen in both conditions, constituted the clinical appearance, but lacked the inflammation, atrophy, and sclerosis of typical LS. Histologically, these lesions were like LS, “based on the presence of a thin band of papillary dermal sclerosis,” Ms. Dennin and her associates said. Borda et al. suggested that vitiligoid lichen sclerosus might be limited to dark-skinned people, and recent reports support this. Alternatively, it may be that the depigmentation simply is more obvious on dark-skinned people, and asymptomatic cases go unnoticed on lighter-skinned people, the investigators surmised.
Both vitiligo and LS are autoimmune cutaneous disorders, and they both often affect the anogenital region. The conditions “may be linked through a common autoimmune response from exposed intracellular or altered cell surface antigens on damaged melanocytes,” the investigators said. “Histologic evidence demonstrates that development of vitiligo involves a preceding lichenoid inflammatory reaction that may trigger an autoimmune reaction to melanocytes, decreasing their number. Evolving vitiligo with a lichenoid reaction may result in epitope spreading and the development of LS.”
The study is limited by its retrospective nature, small sample size, and lack of biopsies, the researchers noted. Larger studies are needed to look at the overlap of the conditions, and “understand the true prevalence of vitiligoid lichen sclerosus,” Ms. Dennin and her associates said.
Read more in Pediatric Dermatology (2018. doi: 10.1111/pde.13399).
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Local Depigmentation of a Tattoo
The Diagnosis: Dermatofibroma
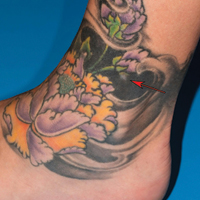
On dermoscopy, a central stellate, white, scarlike patch was seen (Figure). On both legs the patient had several additional brown 5- to 7-mm papules with similar dermoscopic features.
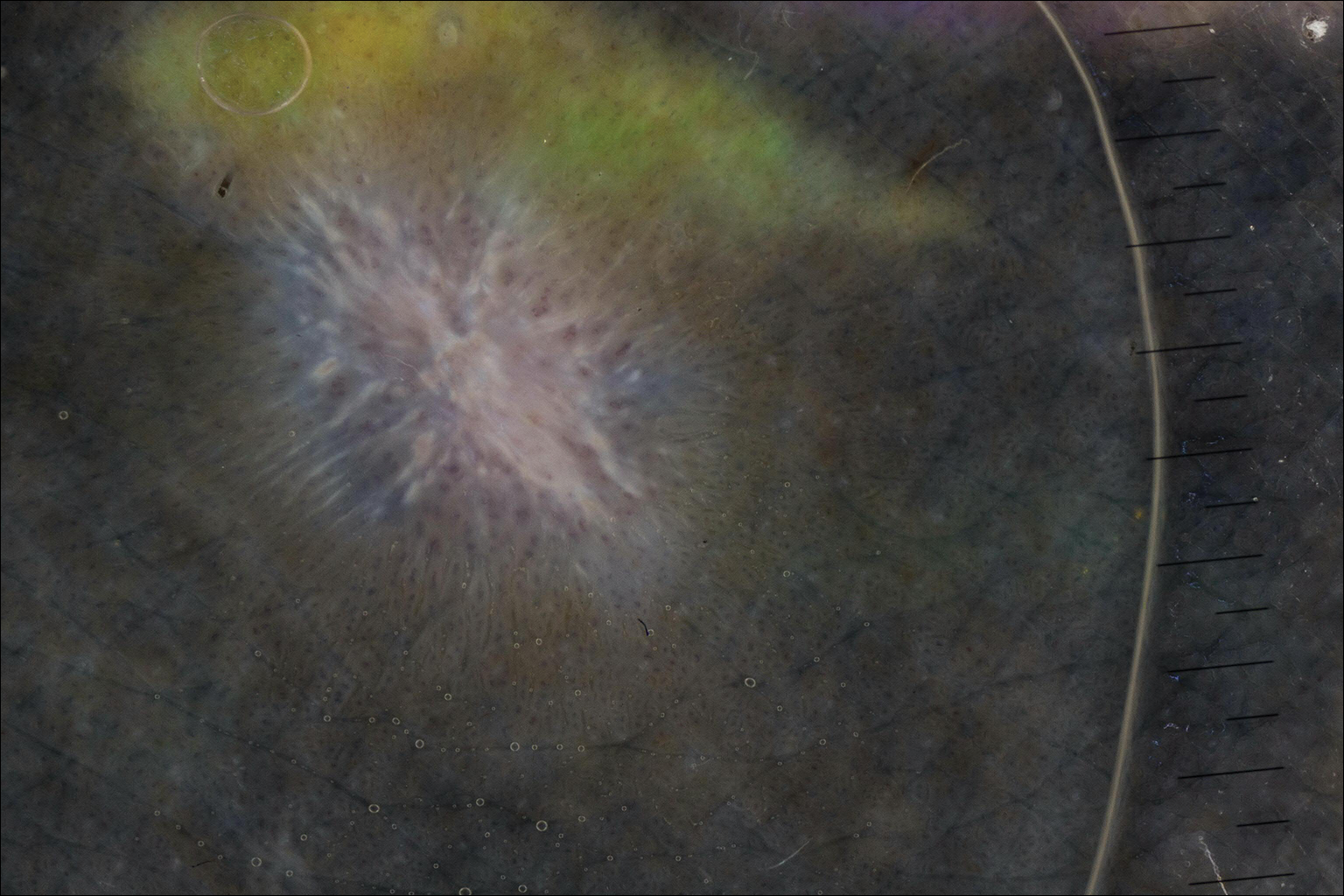
Dermatofibromas are common benign fibrosing tumors that appear as firm papules or plaques with variable color, commonly on the legs. Typically, lateral compression of a dermatofibroma causes downward displacement, called a positive dimple sign. On histology, fibroblasts and myofibroblasts can be seen as short intersecting fascicles with variable inflammatory cells and induction of adjacent structure hyperplasia. The etiology of dermatofibromas is unclear, though some are thought to be secondary to trauma or arthropod bites.1 Because these tumors are benign, the correct diagnosis can avoid unnecessary biopsies or other procedures.
The dermoscopic features of dermatofibromas have been well established.2 As perhaps the most easily identified structure, scarlike patches were seen in as many as 92% (22/24) of dermatofibromas in one study by Ferarri et al,3 while pigment networks also are commonly seen.2 In our case, given the surrounding dense tattoo deposition, it was difficult to ascertain any pigment network. However, the scarlike central patch was clearly apparent by dermoscopy.
Because dermatofibromas are hypothesized to be secondary to trauma, presumably applying tattoos also may cause dermatofibromas. Limited cases have described dermatofibromas arising in tattoos applied several months to years prior.4-6 No prior cases utilized dermoscopy. In our case, clinical examination and dermoscopy clearly demonstrated features consistent with a dermatofibroma, and the patient had more characteristic dermatofibromas scattered elsewhere on both legs. The patient was reassured that the lesions were benign and that the depigmentation was likely secondary to the process of dermatofibroma growth. She declined any treatment.
- Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
- Zaballos P, Puig S, Llambrich A, et al. Dermoscopy of dermatofibromas: a prospective morphological study of 412 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:75-83.
- Ferrari A, Soyer HP, Peris K, et al. Central white scarlike patch: a dermatoscopic clue for the diagnosis of dermatofibroma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:1123-1125.
- Kluger N, Cotten H, Magana C, et al. Dermatofibroma occurring within a tattoo: report of two cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:696-698.
- Lobato-Berezo A, Churruca-Grijelmo M, Martínez-Pérez M, et al. Dermatofibroma arising within a black tattoo [published online September 23, 2014]. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2014;2014:745304.
- Bittencourt Mde J, Miranda MF, Parijós AM, et al. Dermatofibroma in a black tattoo: report of a case. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:614-616.
The Diagnosis: Dermatofibroma
On dermoscopy, a central stellate, white, scarlike patch was seen (Figure). On both legs the patient had several additional brown 5- to 7-mm papules with similar dermoscopic features.

Dermatofibromas are common benign fibrosing tumors that appear as firm papules or plaques with variable color, commonly on the legs. Typically, lateral compression of a dermatofibroma causes downward displacement, called a positive dimple sign. On histology, fibroblasts and myofibroblasts can be seen as short intersecting fascicles with variable inflammatory cells and induction of adjacent structure hyperplasia. The etiology of dermatofibromas is unclear, though some are thought to be secondary to trauma or arthropod bites.1 Because these tumors are benign, the correct diagnosis can avoid unnecessary biopsies or other procedures.
The dermoscopic features of dermatofibromas have been well established.2 As perhaps the most easily identified structure, scarlike patches were seen in as many as 92% (22/24) of dermatofibromas in one study by Ferarri et al,3 while pigment networks also are commonly seen.2 In our case, given the surrounding dense tattoo deposition, it was difficult to ascertain any pigment network. However, the scarlike central patch was clearly apparent by dermoscopy.
Because dermatofibromas are hypothesized to be secondary to trauma, presumably applying tattoos also may cause dermatofibromas. Limited cases have described dermatofibromas arising in tattoos applied several months to years prior.4-6 No prior cases utilized dermoscopy. In our case, clinical examination and dermoscopy clearly demonstrated features consistent with a dermatofibroma, and the patient had more characteristic dermatofibromas scattered elsewhere on both legs. The patient was reassured that the lesions were benign and that the depigmentation was likely secondary to the process of dermatofibroma growth. She declined any treatment.
The Diagnosis: Dermatofibroma
On dermoscopy, a central stellate, white, scarlike patch was seen (Figure). On both legs the patient had several additional brown 5- to 7-mm papules with similar dermoscopic features.

Dermatofibromas are common benign fibrosing tumors that appear as firm papules or plaques with variable color, commonly on the legs. Typically, lateral compression of a dermatofibroma causes downward displacement, called a positive dimple sign. On histology, fibroblasts and myofibroblasts can be seen as short intersecting fascicles with variable inflammatory cells and induction of adjacent structure hyperplasia. The etiology of dermatofibromas is unclear, though some are thought to be secondary to trauma or arthropod bites.1 Because these tumors are benign, the correct diagnosis can avoid unnecessary biopsies or other procedures.
The dermoscopic features of dermatofibromas have been well established.2 As perhaps the most easily identified structure, scarlike patches were seen in as many as 92% (22/24) of dermatofibromas in one study by Ferarri et al,3 while pigment networks also are commonly seen.2 In our case, given the surrounding dense tattoo deposition, it was difficult to ascertain any pigment network. However, the scarlike central patch was clearly apparent by dermoscopy.
Because dermatofibromas are hypothesized to be secondary to trauma, presumably applying tattoos also may cause dermatofibromas. Limited cases have described dermatofibromas arising in tattoos applied several months to years prior.4-6 No prior cases utilized dermoscopy. In our case, clinical examination and dermoscopy clearly demonstrated features consistent with a dermatofibroma, and the patient had more characteristic dermatofibromas scattered elsewhere on both legs. The patient was reassured that the lesions were benign and that the depigmentation was likely secondary to the process of dermatofibroma growth. She declined any treatment.
- Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
- Zaballos P, Puig S, Llambrich A, et al. Dermoscopy of dermatofibromas: a prospective morphological study of 412 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:75-83.
- Ferrari A, Soyer HP, Peris K, et al. Central white scarlike patch: a dermatoscopic clue for the diagnosis of dermatofibroma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:1123-1125.
- Kluger N, Cotten H, Magana C, et al. Dermatofibroma occurring within a tattoo: report of two cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:696-698.
- Lobato-Berezo A, Churruca-Grijelmo M, Martínez-Pérez M, et al. Dermatofibroma arising within a black tattoo [published online September 23, 2014]. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2014;2014:745304.
- Bittencourt Mde J, Miranda MF, Parijós AM, et al. Dermatofibroma in a black tattoo: report of a case. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:614-616.
- Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
- Zaballos P, Puig S, Llambrich A, et al. Dermoscopy of dermatofibromas: a prospective morphological study of 412 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:75-83.
- Ferrari A, Soyer HP, Peris K, et al. Central white scarlike patch: a dermatoscopic clue for the diagnosis of dermatofibroma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:1123-1125.
- Kluger N, Cotten H, Magana C, et al. Dermatofibroma occurring within a tattoo: report of two cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:696-698.
- Lobato-Berezo A, Churruca-Grijelmo M, Martínez-Pérez M, et al. Dermatofibroma arising within a black tattoo [published online September 23, 2014]. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2014;2014:745304.
- Bittencourt Mde J, Miranda MF, Parijós AM, et al. Dermatofibroma in a black tattoo: report of a case. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:614-616.
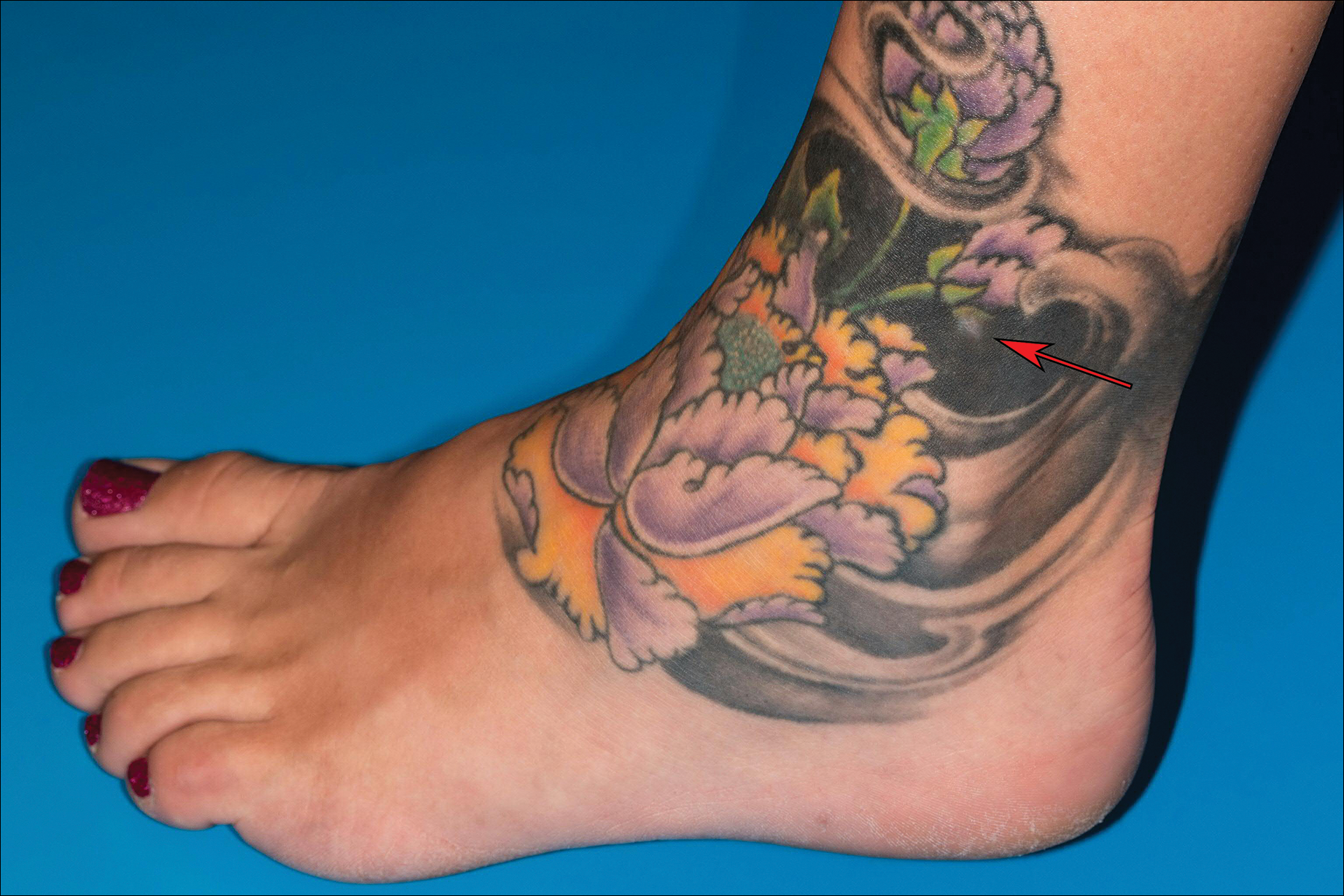
A 41-year-old woman presented with loss of pigment in a tattoo on the left ankle. The tattoo was initially placed several years prior to presentation. For an uncertain amount of time, she had noticed a small palpable whitish area with loss of tattoo pigment. There was no corresponding pain, pruritis, or other symptoms. Her dermatologic history was notable only for keratosis pilaris. Physical examination showed an approximately 7-mm whitish firm papule on the lateral aspect of the left ankle, clearly visible in an otherwise green-black area of the tattoo (arrow). The lesion displaced downward with lateral compression.
New frontier in TAVR is bicuspid disease
DENVER – Thirty-day transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) outcomes in real-world clinical practice using the Evolut R self-expanding valve were as good in patients treated for bicuspid disease as for tricuspid disease, according to a retrospective analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Therapy (STS/ACC TVT) national registry.
“I’ve always been insecure about whether we have the right technology to be able to treat bicuspid disease. This registry data is reassuring to me that we might. I think it may be time to do a prospective registry for low-surgical-risk patients with bicuspid disease and see if we can emulate these kinds of results,” said Dr. Popma, the director of interventional cardiology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
“I think that the one limitation to recruitment in our low-risk TAVR trial is patients with bicuspid disease. Probably 25%-30% of low-risk patients are bicuspid, so we can’t include them right now in our low-risk trial,” he added at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Even though TAVR for patients with bicuspid disease is off-label, operators do perform the procedure. All of these cases are captured in the STS/ACC TVT registry. Dr. Popma reported on 6,717 patients who underwent TAVR with placement of the Evolut R valve at 305 U.S. centers during 2014-2016. The purpose of this retrospective study was to compare 30-day outcomes in the 191 TAVR patients with native valve bicuspid disease with the outcomes in the 6,526 with tricuspid disease.
The two groups were evenly matched in terms of key baseline characteristics, including aortic valve mean gradient, severity of aortic, mitral, and tricuspid regurgitation, and comorbid conditions – with the exception of coronary artery disease, which was present in 48% of the bicuspid group versus 65% of those with tricuspid disease. Also, the bicuspid disease group was younger by an average of nearly 9 years, and their mean baseline left ventricular ejection fraction of 52.5% was lower than the LVEF of 55.5% seen in the tricuspid group.
Procedure time averaged 126 minutes in the bicuspid group and 116 in the tricuspid group. Femoral access was utilized in 87% of the bicuspid patients and in 92% of tricuspid patients. The device was implanted successfully in 97% of the bicuspid group and in 99% of the tricuspid group. More than one valve was required in 3.7% of the bicuspid disease group, a rate similar to that in the tricuspid group. Total hospital length of stay was roughly 6 days in both groups.
Rates of symptomatic improvement at 30 days were closely similar in the two groups. Preprocedurally, two-thirds of patients in both groups had a New York Heart Association class III; at 30 days, however, that was true for a mere 2.4% of the bicuspid patients and 10.3% of the tricuspid patients. By day 30, 52% of the bicuspid group and 48% of the tricuspid group were NYHA class I.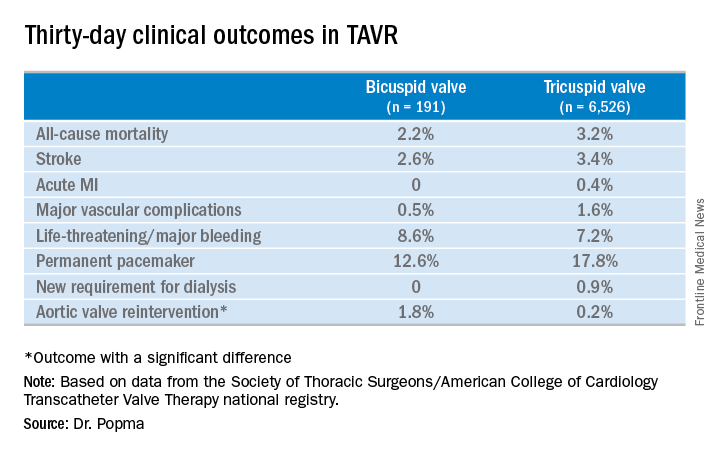
No or only trace aortic regurgitation was present at 30 days in 62% of the bicuspid group and in 61% of the tricuspid group, while mild aortic regurgitation was noted in 31% and 33%, respectively.
Thirty-day mean aortic valve gradient improved to a similar extent in the two groups: from a baseline of 47.2 mm Hg to 9.4 mm Hg in the bicuspid group and from 42.9 mm Hg to 7.5 mm Hg in the tricuspid group.
Dr. Popma noted that an earlier analysis he carried out comparing outcomes of TAVR using the earlier-generation CoreValve in bicuspid versus tricuspid disease showed suboptimal rates of paravalvular regurgitation and an increased need for multiple valves in the bicuspid group.
“The lesson is ‘Thank God we’ve got new technology!’ because the new technology has made a big difference for us,” the cardiologist observed. “We think that the advancement in the technique and the advancement in the valves is going to give us fairly comparable outcomes with Evolut in bicuspid and tricuspid patients.”
Discussant Hasan Jilaihawi, MD, a codirector of transcatheter valve therapy at New York University, pronounced the short-term outcomes in patients with bicuspid aortic valve disease “better than I would have expected,” adding that he, too, thinks it’s time for a prospective registry study of the Evolut valve in such patients.
Dr. Popma’s study was supported by Medtronic. He reported having received research grants from Medtronic and other medical device companies.
SOURCE: Popma JJ. TCT 2017.
DENVER – Thirty-day transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) outcomes in real-world clinical practice using the Evolut R self-expanding valve were as good in patients treated for bicuspid disease as for tricuspid disease, according to a retrospective analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Therapy (STS/ACC TVT) national registry.
“I’ve always been insecure about whether we have the right technology to be able to treat bicuspid disease. This registry data is reassuring to me that we might. I think it may be time to do a prospective registry for low-surgical-risk patients with bicuspid disease and see if we can emulate these kinds of results,” said Dr. Popma, the director of interventional cardiology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
“I think that the one limitation to recruitment in our low-risk TAVR trial is patients with bicuspid disease. Probably 25%-30% of low-risk patients are bicuspid, so we can’t include them right now in our low-risk trial,” he added at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Even though TAVR for patients with bicuspid disease is off-label, operators do perform the procedure. All of these cases are captured in the STS/ACC TVT registry. Dr. Popma reported on 6,717 patients who underwent TAVR with placement of the Evolut R valve at 305 U.S. centers during 2014-2016. The purpose of this retrospective study was to compare 30-day outcomes in the 191 TAVR patients with native valve bicuspid disease with the outcomes in the 6,526 with tricuspid disease.
The two groups were evenly matched in terms of key baseline characteristics, including aortic valve mean gradient, severity of aortic, mitral, and tricuspid regurgitation, and comorbid conditions – with the exception of coronary artery disease, which was present in 48% of the bicuspid group versus 65% of those with tricuspid disease. Also, the bicuspid disease group was younger by an average of nearly 9 years, and their mean baseline left ventricular ejection fraction of 52.5% was lower than the LVEF of 55.5% seen in the tricuspid group.
Procedure time averaged 126 minutes in the bicuspid group and 116 in the tricuspid group. Femoral access was utilized in 87% of the bicuspid patients and in 92% of tricuspid patients. The device was implanted successfully in 97% of the bicuspid group and in 99% of the tricuspid group. More than one valve was required in 3.7% of the bicuspid disease group, a rate similar to that in the tricuspid group. Total hospital length of stay was roughly 6 days in both groups.
Rates of symptomatic improvement at 30 days were closely similar in the two groups. Preprocedurally, two-thirds of patients in both groups had a New York Heart Association class III; at 30 days, however, that was true for a mere 2.4% of the bicuspid patients and 10.3% of the tricuspid patients. By day 30, 52% of the bicuspid group and 48% of the tricuspid group were NYHA class I.
No or only trace aortic regurgitation was present at 30 days in 62% of the bicuspid group and in 61% of the tricuspid group, while mild aortic regurgitation was noted in 31% and 33%, respectively.
Thirty-day mean aortic valve gradient improved to a similar extent in the two groups: from a baseline of 47.2 mm Hg to 9.4 mm Hg in the bicuspid group and from 42.9 mm Hg to 7.5 mm Hg in the tricuspid group.
Dr. Popma noted that an earlier analysis he carried out comparing outcomes of TAVR using the earlier-generation CoreValve in bicuspid versus tricuspid disease showed suboptimal rates of paravalvular regurgitation and an increased need for multiple valves in the bicuspid group.
“The lesson is ‘Thank God we’ve got new technology!’ because the new technology has made a big difference for us,” the cardiologist observed. “We think that the advancement in the technique and the advancement in the valves is going to give us fairly comparable outcomes with Evolut in bicuspid and tricuspid patients.”
Discussant Hasan Jilaihawi, MD, a codirector of transcatheter valve therapy at New York University, pronounced the short-term outcomes in patients with bicuspid aortic valve disease “better than I would have expected,” adding that he, too, thinks it’s time for a prospective registry study of the Evolut valve in such patients.
Dr. Popma’s study was supported by Medtronic. He reported having received research grants from Medtronic and other medical device companies.
SOURCE: Popma JJ. TCT 2017.
DENVER – Thirty-day transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) outcomes in real-world clinical practice using the Evolut R self-expanding valve were as good in patients treated for bicuspid disease as for tricuspid disease, according to a retrospective analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Therapy (STS/ACC TVT) national registry.
“I’ve always been insecure about whether we have the right technology to be able to treat bicuspid disease. This registry data is reassuring to me that we might. I think it may be time to do a prospective registry for low-surgical-risk patients with bicuspid disease and see if we can emulate these kinds of results,” said Dr. Popma, the director of interventional cardiology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
“I think that the one limitation to recruitment in our low-risk TAVR trial is patients with bicuspid disease. Probably 25%-30% of low-risk patients are bicuspid, so we can’t include them right now in our low-risk trial,” he added at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Even though TAVR for patients with bicuspid disease is off-label, operators do perform the procedure. All of these cases are captured in the STS/ACC TVT registry. Dr. Popma reported on 6,717 patients who underwent TAVR with placement of the Evolut R valve at 305 U.S. centers during 2014-2016. The purpose of this retrospective study was to compare 30-day outcomes in the 191 TAVR patients with native valve bicuspid disease with the outcomes in the 6,526 with tricuspid disease.
The two groups were evenly matched in terms of key baseline characteristics, including aortic valve mean gradient, severity of aortic, mitral, and tricuspid regurgitation, and comorbid conditions – with the exception of coronary artery disease, which was present in 48% of the bicuspid group versus 65% of those with tricuspid disease. Also, the bicuspid disease group was younger by an average of nearly 9 years, and their mean baseline left ventricular ejection fraction of 52.5% was lower than the LVEF of 55.5% seen in the tricuspid group.
Procedure time averaged 126 minutes in the bicuspid group and 116 in the tricuspid group. Femoral access was utilized in 87% of the bicuspid patients and in 92% of tricuspid patients. The device was implanted successfully in 97% of the bicuspid group and in 99% of the tricuspid group. More than one valve was required in 3.7% of the bicuspid disease group, a rate similar to that in the tricuspid group. Total hospital length of stay was roughly 6 days in both groups.
Rates of symptomatic improvement at 30 days were closely similar in the two groups. Preprocedurally, two-thirds of patients in both groups had a New York Heart Association class III; at 30 days, however, that was true for a mere 2.4% of the bicuspid patients and 10.3% of the tricuspid patients. By day 30, 52% of the bicuspid group and 48% of the tricuspid group were NYHA class I.
No or only trace aortic regurgitation was present at 30 days in 62% of the bicuspid group and in 61% of the tricuspid group, while mild aortic regurgitation was noted in 31% and 33%, respectively.
Thirty-day mean aortic valve gradient improved to a similar extent in the two groups: from a baseline of 47.2 mm Hg to 9.4 mm Hg in the bicuspid group and from 42.9 mm Hg to 7.5 mm Hg in the tricuspid group.
Dr. Popma noted that an earlier analysis he carried out comparing outcomes of TAVR using the earlier-generation CoreValve in bicuspid versus tricuspid disease showed suboptimal rates of paravalvular regurgitation and an increased need for multiple valves in the bicuspid group.
“The lesson is ‘Thank God we’ve got new technology!’ because the new technology has made a big difference for us,” the cardiologist observed. “We think that the advancement in the technique and the advancement in the valves is going to give us fairly comparable outcomes with Evolut in bicuspid and tricuspid patients.”
Discussant Hasan Jilaihawi, MD, a codirector of transcatheter valve therapy at New York University, pronounced the short-term outcomes in patients with bicuspid aortic valve disease “better than I would have expected,” adding that he, too, thinks it’s time for a prospective registry study of the Evolut valve in such patients.
Dr. Popma’s study was supported by Medtronic. He reported having received research grants from Medtronic and other medical device companies.
SOURCE: Popma JJ. TCT 2017.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Thirty-day clinical outcomes and symptomatic improvement were reassuringly similar both in TAVR patients who received the Evolut R valve for tricuspid disease and off-label for bicuspid disease.
Study details: This was a retrospective U.S. national registry study comparing 30-day outcomes in 191 TAVR patients with native valve bicuspid disease and 6,526 with tricuspid disease, all of whom underwent TAVR with placement of the Evolut R valve.
Disclosures: The study presenter reported having received research grants from Medtronic, the study sponsor, as well as other medical device companies.
Source: Popma JJ. TCT 2017.
Desmoplastic melanoma yields to checkpoint inhibitors
Desmoplastic melanoma, a rare chemotherapy-resistant cutaneous malignancy, appears to be particularly responsive to immunotherapy with inhibitors of programmed death 1 (PD-1) or PD ligand 1 (PD-L1), investigators found.
Of 60 patients with desmoplastic melanoma (DM) treated with pembrolizumab (Keytruda), nivolumab (Opdivo), or an experimental PD-L1 inhibitor (BMS 936559) and followed for a median of 22 months, 42 (70%) had an objective response to immunotherapy, including 19 patients (32%) with a complete response (CR), and 38% with a partial response, reported Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
Desmoplastic melanoma is frequently a consequence of DNA damage to cells exposed to ultraviolet light. The malignancy is characterized by spindle-shaped melanoma cells in dense, fibrous stroma. It is known to be resistant to conventional chemotherapy, and although DM tumors typically have high mutational loads, they generally lack driver mutations that could be treated with targeted agents, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, the mutational burden of DM tumors may make them good candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
“As recognition of neoantigens that result from somatic nonsynonymous mutations is associated with improved clinical responses to anti–PD-1 and anti–PD-L1 therapy, we hypothesized that patients with DM might respond well to anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 therapies, owing to their high mutational load,” Dr. Ribas and colleagues wrote.
To support their hypothesis, they identified 60 patients with DM from a retrospective review of pathology records on 1,058 patients with advanced melanoma treated with a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor at 10 international sites from 2011 through 2016. Four of the patients had received the CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy) in addition to anti–PD-1 agents.
Of the 60 patients, 35 (58%) had markers for a poor prognosis, either extrapulmonary visceral metastases or elevated lactate dehydrogenase levels.
The objective response rates were as noted before. Of the 23 patients with partial responses, 9 had tumor progression, whereas no patients with a CR had progression.
When the investigators looked at whole-exome sequencing results on 17 of the patients, they saw a high frequency of nonsynonymous mutations – in this instance, a change in the amino acid sequence of proteins from cytosine to thymine – “as part of a strong signature of ultraviolet light–induced DNA damage that is common to cutaneous melanoma.”
The most common driver mutations were in NF1, seen in 14 of the 17 cases. In contrast, targetable mutations in BRAF or RAS were absent.
Immunohistochemistry comparisons of samples from 19 cases of DM with 13 non-DM melanomas showed that the DM tumors had a significantly higher proportion of PD-L1–positive cells in the tumor parenchyma (P = .004). DM cells from invasive tumor margins showed increased CD8 cell density PD-L1 expression.
“Therefore, patients with advanced desmoplastic melanoma derive substantial clinical benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy, even though desmoplastic melanoma is defined by its dense desmoplastic fibrous stroma. The benefit is likely to result from the high mutational burden and a frequent preexisting adaptive immune response limited by PD-L1 expression,” Dr. Ribas and colleagues wrote.
The study was funded in part by the Grimaldi Family Fund, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, National Institutes of Health grants, the Ressler Family Fund, the Samuels Family Fund, and the Garcia-Corsini Family Fund. The authors reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ribas A et al. Nature. 2018 Jan 10. doi: 10.1038/nature25187.
Desmoplastic melanoma, a rare chemotherapy-resistant cutaneous malignancy, appears to be particularly responsive to immunotherapy with inhibitors of programmed death 1 (PD-1) or PD ligand 1 (PD-L1), investigators found.
Of 60 patients with desmoplastic melanoma (DM) treated with pembrolizumab (Keytruda), nivolumab (Opdivo), or an experimental PD-L1 inhibitor (BMS 936559) and followed for a median of 22 months, 42 (70%) had an objective response to immunotherapy, including 19 patients (32%) with a complete response (CR), and 38% with a partial response, reported Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
Desmoplastic melanoma is frequently a consequence of DNA damage to cells exposed to ultraviolet light. The malignancy is characterized by spindle-shaped melanoma cells in dense, fibrous stroma. It is known to be resistant to conventional chemotherapy, and although DM tumors typically have high mutational loads, they generally lack driver mutations that could be treated with targeted agents, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, the mutational burden of DM tumors may make them good candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
“As recognition of neoantigens that result from somatic nonsynonymous mutations is associated with improved clinical responses to anti–PD-1 and anti–PD-L1 therapy, we hypothesized that patients with DM might respond well to anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 therapies, owing to their high mutational load,” Dr. Ribas and colleagues wrote.
To support their hypothesis, they identified 60 patients with DM from a retrospective review of pathology records on 1,058 patients with advanced melanoma treated with a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor at 10 international sites from 2011 through 2016. Four of the patients had received the CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy) in addition to anti–PD-1 agents.
Of the 60 patients, 35 (58%) had markers for a poor prognosis, either extrapulmonary visceral metastases or elevated lactate dehydrogenase levels.
The objective response rates were as noted before. Of the 23 patients with partial responses, 9 had tumor progression, whereas no patients with a CR had progression.
When the investigators looked at whole-exome sequencing results on 17 of the patients, they saw a high frequency of nonsynonymous mutations – in this instance, a change in the amino acid sequence of proteins from cytosine to thymine – “as part of a strong signature of ultraviolet light–induced DNA damage that is common to cutaneous melanoma.”
The most common driver mutations were in NF1, seen in 14 of the 17 cases. In contrast, targetable mutations in BRAF or RAS were absent.
Immunohistochemistry comparisons of samples from 19 cases of DM with 13 non-DM melanomas showed that the DM tumors had a significantly higher proportion of PD-L1–positive cells in the tumor parenchyma (P = .004). DM cells from invasive tumor margins showed increased CD8 cell density PD-L1 expression.
“Therefore, patients with advanced desmoplastic melanoma derive substantial clinical benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy, even though desmoplastic melanoma is defined by its dense desmoplastic fibrous stroma. The benefit is likely to result from the high mutational burden and a frequent preexisting adaptive immune response limited by PD-L1 expression,” Dr. Ribas and colleagues wrote.
The study was funded in part by the Grimaldi Family Fund, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, National Institutes of Health grants, the Ressler Family Fund, the Samuels Family Fund, and the Garcia-Corsini Family Fund. The authors reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ribas A et al. Nature. 2018 Jan 10. doi: 10.1038/nature25187.
Desmoplastic melanoma, a rare chemotherapy-resistant cutaneous malignancy, appears to be particularly responsive to immunotherapy with inhibitors of programmed death 1 (PD-1) or PD ligand 1 (PD-L1), investigators found.
Of 60 patients with desmoplastic melanoma (DM) treated with pembrolizumab (Keytruda), nivolumab (Opdivo), or an experimental PD-L1 inhibitor (BMS 936559) and followed for a median of 22 months, 42 (70%) had an objective response to immunotherapy, including 19 patients (32%) with a complete response (CR), and 38% with a partial response, reported Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
Desmoplastic melanoma is frequently a consequence of DNA damage to cells exposed to ultraviolet light. The malignancy is characterized by spindle-shaped melanoma cells in dense, fibrous stroma. It is known to be resistant to conventional chemotherapy, and although DM tumors typically have high mutational loads, they generally lack driver mutations that could be treated with targeted agents, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, the mutational burden of DM tumors may make them good candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
“As recognition of neoantigens that result from somatic nonsynonymous mutations is associated with improved clinical responses to anti–PD-1 and anti–PD-L1 therapy, we hypothesized that patients with DM might respond well to anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 therapies, owing to their high mutational load,” Dr. Ribas and colleagues wrote.
To support their hypothesis, they identified 60 patients with DM from a retrospective review of pathology records on 1,058 patients with advanced melanoma treated with a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor at 10 international sites from 2011 through 2016. Four of the patients had received the CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy) in addition to anti–PD-1 agents.
Of the 60 patients, 35 (58%) had markers for a poor prognosis, either extrapulmonary visceral metastases or elevated lactate dehydrogenase levels.
The objective response rates were as noted before. Of the 23 patients with partial responses, 9 had tumor progression, whereas no patients with a CR had progression.
When the investigators looked at whole-exome sequencing results on 17 of the patients, they saw a high frequency of nonsynonymous mutations – in this instance, a change in the amino acid sequence of proteins from cytosine to thymine – “as part of a strong signature of ultraviolet light–induced DNA damage that is common to cutaneous melanoma.”
The most common driver mutations were in NF1, seen in 14 of the 17 cases. In contrast, targetable mutations in BRAF or RAS were absent.
Immunohistochemistry comparisons of samples from 19 cases of DM with 13 non-DM melanomas showed that the DM tumors had a significantly higher proportion of PD-L1–positive cells in the tumor parenchyma (P = .004). DM cells from invasive tumor margins showed increased CD8 cell density PD-L1 expression.
“Therefore, patients with advanced desmoplastic melanoma derive substantial clinical benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy, even though desmoplastic melanoma is defined by its dense desmoplastic fibrous stroma. The benefit is likely to result from the high mutational burden and a frequent preexisting adaptive immune response limited by PD-L1 expression,” Dr. Ribas and colleagues wrote.
The study was funded in part by the Grimaldi Family Fund, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, National Institutes of Health grants, the Ressler Family Fund, the Samuels Family Fund, and the Garcia-Corsini Family Fund. The authors reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ribas A et al. Nature. 2018 Jan 10. doi: 10.1038/nature25187.
FROM NATURE
Key clinical point: Desmoplastic melanoma (DM) has a high mutational load that may make it susceptible to anti–PD-1 and PD-L1 therapy.
Major finding: The objective response rate was 70%, including 32% complete and 38% partial responses.
Data source: A retrospective review of data on 60 patients with desmoplastic melanoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Disclosures: The study was funded in part by the Grimaldi Family Fund, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, National Institutes of Health grants, the Ressler Family Fund, the Samuels Family Fund, and the Garcia-Corsini Family Fund. The authors reported having no competing financial interests.
Source: Ribas A et al. Nature. 2018 Jan 10. doi: 10.1038/nature25187.
A trainee’s path to fighting addiction
When I came to this country, even before my current residency, I launched my addiction psychiatry career by researching nicotine addiction in schizophrenia patients. Those early experiences gave me a greater understanding of the health concerns and life experiences of people with addictions – and those more likely to develop them.
So imagine my excitement when I first became acquainted with the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry (AAAP). I first learned about the AAAP, its mission, and activities at the 2017 American Psychiatric Association’s annual meeting in San Diego.
Getting in and involved
After returning to New York, I took those next steps and joined up, which opened the AAAP gates so I could receive its newsletters and submission calls, gain access to resources such as The American Journal on Addictions, survey the various joinable task forces, as well as discover who might be available to me as a mentor as part of the AAAP’s mentor-mentee program.
Sometime during my third-year residency training, I received a member-email advertising the AAAP 28th Annual Meeting and Scientific Symposium, and soon after that, received another email calling for research submissions to be presented there, as well as an invitation to apply for a trainee travel scholarship that would defray the cost for and allow its fellows to attend the meeting in San Diego. That alone was enticing enough to apply. But even more enticing was the opportunity to showcase the addiction work I had been doing during my residency, as well as to meet other members at various levels of the AAAP to determine whether I wanted to become more involved.
Pursuing experiences
I did not think twice about applying for the poster presentation and the travel scholarship. The AAAP’s online application forms for both were easy to understand and very well structured, which greatly helped me with filling out and formatting my applications. Taking the initiative toward even these first AAAP offerings brought more positive echoes. I was thrilled when the poster I proposed was accepted, mostly because it would give me the chance to present my recent addiction psych work from a higher platform. A few weeks later, I was thrilled again when I received an AAAP email congratulating me on being awarded the San Diego 28th annual meeting travel scholarship, which would waive the annual membership and conference registration fees, in addition to defraying my travel costs. Pacific breezes, here I come. And there I went. (Thanks to my extremely supportive training director, who first nominated me for the award.)
On the ground at 2017 AAAP
The 28th AAAP annual meeting opened on a balmy December Thursday, and that’s the day I arrived. I attended many addiction workshops and symposiums, which featured premier figures in addiction psychiatry. Of the numerous trainee-specific events I attended, the most informative was the “Fellowship Forum: Exploring the Field of Addiction Psychiatry.” At this forum, I learned the true benefits of doing an addiction psychiatry fellowship, while meeting many of the fellowship program directors of top institutions. Having them all under one “roof” made it easy to compare and contrast the specific training they offered.
Then came what were, for me, major highlights of the AAAP 2017. After I delivered my poster presentation and shared my research, I was able to receive very close, constructive feedback from the field’s most experienced professionals. And, finally, I met my AAAP mentors face to face: Dr. Amy Yule of Harvard Medical School, Boston; Dr. Thomas Penders, of East Carolina University, Greenville, N.C.; and Dr. Cornel Stanciu of Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H.
One AAAP trainee’s takeaways
All AAAP trainees, fellows, presenters leave the meeting with their own conclusions, but my biggest takeaways were:
- Regarding barriers to buprenorphine, emerging research supports similar efficacy for long-acting injectable naltrexone.
- Various protocols for rapid implementation of naltrexone are being used, and these allow for smoother transition and shorter “washout” periods.
- We should not overlook the effects of tobacco use in our patient population – and should address it aggressively, regardless of psychiatric comorbidities.
- The cannabinoid CBD receptors that exist on the dopamine pathway strengthen and complicate their relationship with psychosis.
- , especially in rural and remote settings. The body of evidence supporting its efficacy is expanding.
- Synthetic cannabinoids are prevalent, and toxidromes exist – yet, trainees are not current on these.
The challenges facing those of us dedicated to fighting addiction have never been greater. I would urge more trainees and psychiatrists to join the AAAP in light of the opioid crisis and the potential fallout tied to marijuana legalization. I am grateful to have the opportunity to join my colleagues in this fight. Becoming part of the AAAP has led to a highly rewarding, career-enriching experience.
This article was updated 1/17/17.
Dr. Ahmed is a third-year resident in the department of psychiatry at Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, New York. Besides addiction psychiatry, his interests include public social psychiatry, health care policy, health disparities, and mental health stigma. Dr. Ahmed is a member of the American Psychiatric Association, the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology, and the American Association for Social Psychiatry.
When I came to this country, even before my current residency, I launched my addiction psychiatry career by researching nicotine addiction in schizophrenia patients. Those early experiences gave me a greater understanding of the health concerns and life experiences of people with addictions – and those more likely to develop them.
So imagine my excitement when I first became acquainted with the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry (AAAP). I first learned about the AAAP, its mission, and activities at the 2017 American Psychiatric Association’s annual meeting in San Diego.
Getting in and involved
After returning to New York, I took those next steps and joined up, which opened the AAAP gates so I could receive its newsletters and submission calls, gain access to resources such as The American Journal on Addictions, survey the various joinable task forces, as well as discover who might be available to me as a mentor as part of the AAAP’s mentor-mentee program.
Sometime during my third-year residency training, I received a member-email advertising the AAAP 28th Annual Meeting and Scientific Symposium, and soon after that, received another email calling for research submissions to be presented there, as well as an invitation to apply for a trainee travel scholarship that would defray the cost for and allow its fellows to attend the meeting in San Diego. That alone was enticing enough to apply. But even more enticing was the opportunity to showcase the addiction work I had been doing during my residency, as well as to meet other members at various levels of the AAAP to determine whether I wanted to become more involved.
Pursuing experiences
I did not think twice about applying for the poster presentation and the travel scholarship. The AAAP’s online application forms for both were easy to understand and very well structured, which greatly helped me with filling out and formatting my applications. Taking the initiative toward even these first AAAP offerings brought more positive echoes. I was thrilled when the poster I proposed was accepted, mostly because it would give me the chance to present my recent addiction psych work from a higher platform. A few weeks later, I was thrilled again when I received an AAAP email congratulating me on being awarded the San Diego 28th annual meeting travel scholarship, which would waive the annual membership and conference registration fees, in addition to defraying my travel costs. Pacific breezes, here I come. And there I went. (Thanks to my extremely supportive training director, who first nominated me for the award.)
On the ground at 2017 AAAP
The 28th AAAP annual meeting opened on a balmy December Thursday, and that’s the day I arrived. I attended many addiction workshops and symposiums, which featured premier figures in addiction psychiatry. Of the numerous trainee-specific events I attended, the most informative was the “Fellowship Forum: Exploring the Field of Addiction Psychiatry.” At this forum, I learned the true benefits of doing an addiction psychiatry fellowship, while meeting many of the fellowship program directors of top institutions. Having them all under one “roof” made it easy to compare and contrast the specific training they offered.
Then came what were, for me, major highlights of the AAAP 2017. After I delivered my poster presentation and shared my research, I was able to receive very close, constructive feedback from the field’s most experienced professionals. And, finally, I met my AAAP mentors face to face: Dr. Amy Yule of Harvard Medical School, Boston; Dr. Thomas Penders, of East Carolina University, Greenville, N.C.; and Dr. Cornel Stanciu of Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H.
One AAAP trainee’s takeaways
All AAAP trainees, fellows, presenters leave the meeting with their own conclusions, but my biggest takeaways were:
- Regarding barriers to buprenorphine, emerging research supports similar efficacy for long-acting injectable naltrexone.
- Various protocols for rapid implementation of naltrexone are being used, and these allow for smoother transition and shorter “washout” periods.
- We should not overlook the effects of tobacco use in our patient population – and should address it aggressively, regardless of psychiatric comorbidities.
- The cannabinoid CBD receptors that exist on the dopamine pathway strengthen and complicate their relationship with psychosis.
- , especially in rural and remote settings. The body of evidence supporting its efficacy is expanding.
- Synthetic cannabinoids are prevalent, and toxidromes exist – yet, trainees are not current on these.
The challenges facing those of us dedicated to fighting addiction have never been greater. I would urge more trainees and psychiatrists to join the AAAP in light of the opioid crisis and the potential fallout tied to marijuana legalization. I am grateful to have the opportunity to join my colleagues in this fight. Becoming part of the AAAP has led to a highly rewarding, career-enriching experience.
This article was updated 1/17/17.
Dr. Ahmed is a third-year resident in the department of psychiatry at Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, New York. Besides addiction psychiatry, his interests include public social psychiatry, health care policy, health disparities, and mental health stigma. Dr. Ahmed is a member of the American Psychiatric Association, the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology, and the American Association for Social Psychiatry.
When I came to this country, even before my current residency, I launched my addiction psychiatry career by researching nicotine addiction in schizophrenia patients. Those early experiences gave me a greater understanding of the health concerns and life experiences of people with addictions – and those more likely to develop them.
So imagine my excitement when I first became acquainted with the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry (AAAP). I first learned about the AAAP, its mission, and activities at the 2017 American Psychiatric Association’s annual meeting in San Diego.
Getting in and involved
After returning to New York, I took those next steps and joined up, which opened the AAAP gates so I could receive its newsletters and submission calls, gain access to resources such as The American Journal on Addictions, survey the various joinable task forces, as well as discover who might be available to me as a mentor as part of the AAAP’s mentor-mentee program.
Sometime during my third-year residency training, I received a member-email advertising the AAAP 28th Annual Meeting and Scientific Symposium, and soon after that, received another email calling for research submissions to be presented there, as well as an invitation to apply for a trainee travel scholarship that would defray the cost for and allow its fellows to attend the meeting in San Diego. That alone was enticing enough to apply. But even more enticing was the opportunity to showcase the addiction work I had been doing during my residency, as well as to meet other members at various levels of the AAAP to determine whether I wanted to become more involved.
Pursuing experiences
I did not think twice about applying for the poster presentation and the travel scholarship. The AAAP’s online application forms for both were easy to understand and very well structured, which greatly helped me with filling out and formatting my applications. Taking the initiative toward even these first AAAP offerings brought more positive echoes. I was thrilled when the poster I proposed was accepted, mostly because it would give me the chance to present my recent addiction psych work from a higher platform. A few weeks later, I was thrilled again when I received an AAAP email congratulating me on being awarded the San Diego 28th annual meeting travel scholarship, which would waive the annual membership and conference registration fees, in addition to defraying my travel costs. Pacific breezes, here I come. And there I went. (Thanks to my extremely supportive training director, who first nominated me for the award.)
On the ground at 2017 AAAP
The 28th AAAP annual meeting opened on a balmy December Thursday, and that’s the day I arrived. I attended many addiction workshops and symposiums, which featured premier figures in addiction psychiatry. Of the numerous trainee-specific events I attended, the most informative was the “Fellowship Forum: Exploring the Field of Addiction Psychiatry.” At this forum, I learned the true benefits of doing an addiction psychiatry fellowship, while meeting many of the fellowship program directors of top institutions. Having them all under one “roof” made it easy to compare and contrast the specific training they offered.
Then came what were, for me, major highlights of the AAAP 2017. After I delivered my poster presentation and shared my research, I was able to receive very close, constructive feedback from the field’s most experienced professionals. And, finally, I met my AAAP mentors face to face: Dr. Amy Yule of Harvard Medical School, Boston; Dr. Thomas Penders, of East Carolina University, Greenville, N.C.; and Dr. Cornel Stanciu of Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H.
One AAAP trainee’s takeaways
All AAAP trainees, fellows, presenters leave the meeting with their own conclusions, but my biggest takeaways were:
- Regarding barriers to buprenorphine, emerging research supports similar efficacy for long-acting injectable naltrexone.
- Various protocols for rapid implementation of naltrexone are being used, and these allow for smoother transition and shorter “washout” periods.
- We should not overlook the effects of tobacco use in our patient population – and should address it aggressively, regardless of psychiatric comorbidities.
- The cannabinoid CBD receptors that exist on the dopamine pathway strengthen and complicate their relationship with psychosis.
- , especially in rural and remote settings. The body of evidence supporting its efficacy is expanding.
- Synthetic cannabinoids are prevalent, and toxidromes exist – yet, trainees are not current on these.
The challenges facing those of us dedicated to fighting addiction have never been greater. I would urge more trainees and psychiatrists to join the AAAP in light of the opioid crisis and the potential fallout tied to marijuana legalization. I am grateful to have the opportunity to join my colleagues in this fight. Becoming part of the AAAP has led to a highly rewarding, career-enriching experience.
This article was updated 1/17/17.
Dr. Ahmed is a third-year resident in the department of psychiatry at Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, New York. Besides addiction psychiatry, his interests include public social psychiatry, health care policy, health disparities, and mental health stigma. Dr. Ahmed is a member of the American Psychiatric Association, the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology, and the American Association for Social Psychiatry.
U.S. influenza activity widespread to start 2018
As far as the influenza virus is concerned, the new year started in the same way as the old one ended: with almost half of the states at the highest level of flu activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week ending Jan. 6, 2018, there were 23 states – including California, Illinois, and Texas – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, which was up from 22 for the last full week of 2017. Joining the 23 states in the “high” range were New Jersey and Ohio at level 9 and Colorado at level 8, the CDC’s influenza division reported Jan. 12.
Seven flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week ending Jan. 6, although one occurred during the week ending Dec. 16 and two were during the week ending Dec. 23. There have been a total of 20 pediatric deaths related to influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said. In 2016-2017, there were 110 pediatric deaths from the flu.
As far as the influenza virus is concerned, the new year started in the same way as the old one ended: with almost half of the states at the highest level of flu activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week ending Jan. 6, 2018, there were 23 states – including California, Illinois, and Texas – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, which was up from 22 for the last full week of 2017. Joining the 23 states in the “high” range were New Jersey and Ohio at level 9 and Colorado at level 8, the CDC’s influenza division reported Jan. 12.
Seven flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week ending Jan. 6, although one occurred during the week ending Dec. 16 and two were during the week ending Dec. 23. There have been a total of 20 pediatric deaths related to influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said. In 2016-2017, there were 110 pediatric deaths from the flu.
As far as the influenza virus is concerned, the new year started in the same way as the old one ended: with almost half of the states at the highest level of flu activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week ending Jan. 6, 2018, there were 23 states – including California, Illinois, and Texas – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, which was up from 22 for the last full week of 2017. Joining the 23 states in the “high” range were New Jersey and Ohio at level 9 and Colorado at level 8, the CDC’s influenza division reported Jan. 12.
Seven flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week ending Jan. 6, although one occurred during the week ending Dec. 16 and two were during the week ending Dec. 23. There have been a total of 20 pediatric deaths related to influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said. In 2016-2017, there were 110 pediatric deaths from the flu.
Vascular surgeons are top tier for burnout risk
CHICAGO – Vascular surgeons are solidly within the top tier of surgical subspecialists in terms of risk for burnout, Joan M. Anzia, MD, observed at a symposium on vascular surgery sponsored by Northwestern University.
Joining them in this unwelcome company with an elevated rate of lower quality of life are trauma surgeons, urologists, and otolaryngologists, according to the results of a 9-year-old national study of burnout and career satisfaction among American surgeons that has served as a wakeup call for the profession (Ann Surg. 2009 Sep;250[3]:463-71).
“This is where the biggest impact on burnout is going to be: institutional interventions to target the known drivers of burnout. Looking at nights on call, work compression, looking at the amount of time you guys spend in front of a computer documenting your EHR and your billing. Do you really need to do those things? You need help from midlevel professionals and others who can free you to practice at the top of your life, doing the work you love, which for most surgeons is being in the OR,” said Dr. Anzia, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and the departmental vice chair of education at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The Society for Vascular Surgery is one of many professional specialty organizations that are focusing on the burnout problem. They are joined by the Association of American Medical Colleges, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, the National Academy of Medicine, the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, the American Medical Association, and other interested groups.
“Since 2008, burnout rates in every specialty have increased by an average of an absolute 10%. That’s just remarkable, and it’s why people are very, very concerned,” noted the psychiatrist, who serves as the physician health liaison at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. In that capacity, she is frequently called upon to help physicians with the classic manifestations of burnout, including substance use disorders that arose as the practitioners tried to self-treat their burnout rather than seeking help.
“He reports only to the dean,” according to Dr. Anzia.
Why are vascular surgeons at such high risk for burnout? According to the Maslach Burnout Inventory, the leading psychological assessment tool for burnout, the syndrome has three main components: emotional exhaustion, a sense of loss of meaning in work, and feeling ineffective in one’s work. Studies show vascular surgeons often score high in all three domains.
Vascular surgeons’ work is extremely stressful. They average 20 hours per week in the OR, and almost 3 nights on call per week. They care for acutely ill patients and perform high-intensity, high-risk procedures in which unpredictable events are common.
“Work compression – not just workload, but facing multiple demands at once that you’re trying to balance – that’s one of the key drivers of burnout, and work compression is really common in vascular surgery,” Dr. Anzia noted.
In the national surgeon burnout study, younger surgeons and those with children still living at home were at increased risk for burnout. So were surgeons whose compensation was entirely based upon the Relative Value Unit system. The number of nights on call per week was another independent risk factor.
Dr. Shanafelt and his coinvestigators found that roughly 30% of respondent surgeons screened positive for depression, and 6.4% of the study population reported having suicidal thoughts within the past 12 months.
“We lose the equivalent of two to three medical school classes worth of physicians every year to suicide. And let me tell you: 98% of those folks, at the time they suicided, had major depression, which is eminently treatable. And the reason they weren’t treated was they, like most physicians, avoided treatment. They had difficulty accessing care. They were worried about stigma, life insurance, things like that. This is a huge problem which is mostly preventable, but we are not addressing it effectively,” Dr. Anzia said.
While institutional interventions aimed at the prevention of physician burnout such as spending less time on the electronic health record will have a major impact on the problem, thought leaders in medical education have come to realize that it also will be necessary to address the broader culture of medicine.
“There are so many implicit beliefs that every one of us grew up with, like ‘I work when I’m sick,’ or ‘I can work without sleep.’ All those things that we believe make us good physicians actually may not be entirely true,” the psychiatrist said.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
CHICAGO – Vascular surgeons are solidly within the top tier of surgical subspecialists in terms of risk for burnout, Joan M. Anzia, MD, observed at a symposium on vascular surgery sponsored by Northwestern University.
Joining them in this unwelcome company with an elevated rate of lower quality of life are trauma surgeons, urologists, and otolaryngologists, according to the results of a 9-year-old national study of burnout and career satisfaction among American surgeons that has served as a wakeup call for the profession (Ann Surg. 2009 Sep;250[3]:463-71).
“This is where the biggest impact on burnout is going to be: institutional interventions to target the known drivers of burnout. Looking at nights on call, work compression, looking at the amount of time you guys spend in front of a computer documenting your EHR and your billing. Do you really need to do those things? You need help from midlevel professionals and others who can free you to practice at the top of your life, doing the work you love, which for most surgeons is being in the OR,” said Dr. Anzia, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and the departmental vice chair of education at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The Society for Vascular Surgery is one of many professional specialty organizations that are focusing on the burnout problem. They are joined by the Association of American Medical Colleges, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, the National Academy of Medicine, the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, the American Medical Association, and other interested groups.
“Since 2008, burnout rates in every specialty have increased by an average of an absolute 10%. That’s just remarkable, and it’s why people are very, very concerned,” noted the psychiatrist, who serves as the physician health liaison at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. In that capacity, she is frequently called upon to help physicians with the classic manifestations of burnout, including substance use disorders that arose as the practitioners tried to self-treat their burnout rather than seeking help.
“He reports only to the dean,” according to Dr. Anzia.
Why are vascular surgeons at such high risk for burnout? According to the Maslach Burnout Inventory, the leading psychological assessment tool for burnout, the syndrome has three main components: emotional exhaustion, a sense of loss of meaning in work, and feeling ineffective in one’s work. Studies show vascular surgeons often score high in all three domains.
Vascular surgeons’ work is extremely stressful. They average 20 hours per week in the OR, and almost 3 nights on call per week. They care for acutely ill patients and perform high-intensity, high-risk procedures in which unpredictable events are common.
“Work compression – not just workload, but facing multiple demands at once that you’re trying to balance – that’s one of the key drivers of burnout, and work compression is really common in vascular surgery,” Dr. Anzia noted.
In the national surgeon burnout study, younger surgeons and those with children still living at home were at increased risk for burnout. So were surgeons whose compensation was entirely based upon the Relative Value Unit system. The number of nights on call per week was another independent risk factor.
Dr. Shanafelt and his coinvestigators found that roughly 30% of respondent surgeons screened positive for depression, and 6.4% of the study population reported having suicidal thoughts within the past 12 months.
“We lose the equivalent of two to three medical school classes worth of physicians every year to suicide. And let me tell you: 98% of those folks, at the time they suicided, had major depression, which is eminently treatable. And the reason they weren’t treated was they, like most physicians, avoided treatment. They had difficulty accessing care. They were worried about stigma, life insurance, things like that. This is a huge problem which is mostly preventable, but we are not addressing it effectively,” Dr. Anzia said.
While institutional interventions aimed at the prevention of physician burnout such as spending less time on the electronic health record will have a major impact on the problem, thought leaders in medical education have come to realize that it also will be necessary to address the broader culture of medicine.
“There are so many implicit beliefs that every one of us grew up with, like ‘I work when I’m sick,’ or ‘I can work without sleep.’ All those things that we believe make us good physicians actually may not be entirely true,” the psychiatrist said.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
CHICAGO – Vascular surgeons are solidly within the top tier of surgical subspecialists in terms of risk for burnout, Joan M. Anzia, MD, observed at a symposium on vascular surgery sponsored by Northwestern University.
Joining them in this unwelcome company with an elevated rate of lower quality of life are trauma surgeons, urologists, and otolaryngologists, according to the results of a 9-year-old national study of burnout and career satisfaction among American surgeons that has served as a wakeup call for the profession (Ann Surg. 2009 Sep;250[3]:463-71).
“This is where the biggest impact on burnout is going to be: institutional interventions to target the known drivers of burnout. Looking at nights on call, work compression, looking at the amount of time you guys spend in front of a computer documenting your EHR and your billing. Do you really need to do those things? You need help from midlevel professionals and others who can free you to practice at the top of your life, doing the work you love, which for most surgeons is being in the OR,” said Dr. Anzia, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and the departmental vice chair of education at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The Society for Vascular Surgery is one of many professional specialty organizations that are focusing on the burnout problem. They are joined by the Association of American Medical Colleges, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, the National Academy of Medicine, the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, the American Medical Association, and other interested groups.
“Since 2008, burnout rates in every specialty have increased by an average of an absolute 10%. That’s just remarkable, and it’s why people are very, very concerned,” noted the psychiatrist, who serves as the physician health liaison at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. In that capacity, she is frequently called upon to help physicians with the classic manifestations of burnout, including substance use disorders that arose as the practitioners tried to self-treat their burnout rather than seeking help.
“He reports only to the dean,” according to Dr. Anzia.
Why are vascular surgeons at such high risk for burnout? According to the Maslach Burnout Inventory, the leading psychological assessment tool for burnout, the syndrome has three main components: emotional exhaustion, a sense of loss of meaning in work, and feeling ineffective in one’s work. Studies show vascular surgeons often score high in all three domains.
Vascular surgeons’ work is extremely stressful. They average 20 hours per week in the OR, and almost 3 nights on call per week. They care for acutely ill patients and perform high-intensity, high-risk procedures in which unpredictable events are common.
“Work compression – not just workload, but facing multiple demands at once that you’re trying to balance – that’s one of the key drivers of burnout, and work compression is really common in vascular surgery,” Dr. Anzia noted.
In the national surgeon burnout study, younger surgeons and those with children still living at home were at increased risk for burnout. So were surgeons whose compensation was entirely based upon the Relative Value Unit system. The number of nights on call per week was another independent risk factor.
Dr. Shanafelt and his coinvestigators found that roughly 30% of respondent surgeons screened positive for depression, and 6.4% of the study population reported having suicidal thoughts within the past 12 months.
“We lose the equivalent of two to three medical school classes worth of physicians every year to suicide. And let me tell you: 98% of those folks, at the time they suicided, had major depression, which is eminently treatable. And the reason they weren’t treated was they, like most physicians, avoided treatment. They had difficulty accessing care. They were worried about stigma, life insurance, things like that. This is a huge problem which is mostly preventable, but we are not addressing it effectively,” Dr. Anzia said.
While institutional interventions aimed at the prevention of physician burnout such as spending less time on the electronic health record will have a major impact on the problem, thought leaders in medical education have come to realize that it also will be necessary to address the broader culture of medicine.
“There are so many implicit beliefs that every one of us grew up with, like ‘I work when I’m sick,’ or ‘I can work without sleep.’ All those things that we believe make us good physicians actually may not be entirely true,” the psychiatrist said.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE NORTHWESTERN VASCULAR SYMPOSIUM
Credentialing of Hospitalists in Ultrasound-Guided Bedside Procedures: A Position Statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine
The American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) changed its certification policy for bedside procedures over a decade ago.
Hospitalists increasingly perform bedside procedures with ultrasound guidance.
Therefore, the Society of Hospital Medicine (SHM) Education Committee convened a group of experts and conducted a systematic literature review in order to provide recommendations for credentialing hospitalist physicians in ultrasound-guided bedside procedures. These recommendations do not include training recommendations, aside from recommendations about remedial training for hospitalists who do not pass certification. Training is a means to competence but does not guarantee it. We believe that training recommendations ought to be considered separately.
METHODS
Working Group Formation
In January 2015, the SHM Board of Directors asked the SHM Education Committee to convene the POCUS Task Force. The purpose of the task force was to develop recommendations on ultrasound guidance for bedside procedures. The SHM Education Committee appointed 3 chairs of the task force: 1 senior member of the SHM Education Committee and 2 POCUS experts. The chairs assembled a task force of 31 members that included 5 working groups, a multispecialty peer review group, and a guideline methodologist (supplemental Appendix 1). Invitation was based on members’ past contributions to SHM POCUS-related activities, up-front commitment, and declared conflicts of interest. Working group members self-identified as “hospitalists,” whereas peer reviewers were nonhospitalists but nationally recognized POCUS physician-leaders specializing in emergency medicine, cardiology, critical care medicine, and anesthesiology. Task force membership was vetted by a chair of the SHM POCUS Task Force and the Director of Education before work began. This position statement was authored by the Credentialing Working Group together with the chairs of the other 4 working groups and a guideline methodologist.
Disclosures
Signed disclosure statements of all task force members were reviewed prior to inclusion on the task force (supplemental Appendix 2); no members received honoraria for participation. Industry representatives did not contribute to the development of the guidelines nor to any conference calls or meetings.
Literature Search Strategy
A literature search was conducted by a biomedical librarian. Records from 1979 to January of 2017 were searched in Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, and Google Scholar (supplemental Appendix 3). Search limiters were English language and adults. Articles were manually screened to exclude nonhuman or endoscopic ultrasound applications. Final article selection was based on working group consensus.
Draft Pathways
The Credentialing Working Group drafted initial and ongoing certification pathways (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The other 4 working groups from the task force were surveyed about the elements and overall appropriateness of these draft pathways. This survey and its results have already been published.12 The Credentialing Working Group then revised the certification pathways by using these survey results and codified individual aspects of these pathways into recommendations.
Development of Position Statement
Based on the Grading of Recommendation Assessment Development and Evaluation methodology, all final article selections were initially rated as either low-quality (observational studies) or unclassifiable (expert opinion).16 These initial ratings were downgraded further because of indirectness, because none of the articles involved the intervention of interest (a credentialing pathway) in a population of interest (hospitalists) measuring the outcomes of interest (patient-level outcomes).
First, the Credentialing Working Group drafted an initial position statement composed of recommendations for credentialing pathways and other general aspects of credentialing. All final article selections were incorporated as references in a draft of the position statement and compiled in a full-text compendium. Second, feedback was provided by the other 4 task force working groups, the task force peer reviewers, and the SHM Education Committee. Feedback was incorporated by the authors of this statement who were the Credentialing Working Group, the chairs of the other 4 working groups, and a guideline methodologist. Third, final suggestions from all members of the SHM POCUS Task Force and SHM Education Committee were incorporated before final approval by the SHM Board of Directors in September 2017.
RESULTS
A total of 1438 references were identified in the original search. Manual selection led to 101 articles, which were incorporated into the following 4 domains with 16 recommendations.
General Credentialing Process
Basic Cognitive Competence Can Be Certified with Written or Oral Examinations
The ABIM defines cognitive competence as having 3 abilities: “(1) to explain indications, contraindications, patient preparation methods, sterile techniques, pain management, proper techniques for handling specimens and fluids obtained, and test results; (2) to recognize and manage complications; and, (3) to clearly explain to a patient all facets of the procedure necessary to obtain informed consent.”1 These abilities can be assessed with written or oral examinations that may be integrated into simulation- or patient-based assessments.
Minimum Thresholds of Experience to Trigger the Timing of a Patient-Based Assessment Should Be Determined by Empirical Methods
Learning curves are highly variable22-25 and even plateaus may not herald basic competence.26 Expert opinion
Hospitalists Should Formally Log All of Their Attempted Procedures, Ideally in an Electronic Medical Record
Simple self-reported numbers of procedures performed often misrepresent actual experience33,34 and do not include periprocedural complications.35,36 Thus, hospitalists should report their experience with logs of all attempted procedures, both successful and unsuccessful. Such logs must include information about supervising providers (if applicable) and patient outcomes, including periprocedural adverse events,37 but they must also remain compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Health Information Technology Service Should Routinely Pull Collations of All Attempted Procedures from Comprehensive Electronic Medical Records
Active surveillance may reduce complications by identifying hospitalists who may benefit from further training.38 In order to facilitate active surveillance systems, documentation (such as a procedure note) should be both integrated into an electronic medical record and protocol driven,39 including procedure technique, ultrasound findings, and any safety events (both near misses and adverse events).
Multiple interacting factors, including environment, patients, baseline skills, training, experience, and skills decay, affect manual competence. Certifications that are based solely on reaching minimum thresholds of experience, even when accurate, are not valid reflections of manual competence,15,40-43 and neither are those based on self-perception.44 Patient-based assessments are, thus, necessary to ensure manual competence.45-48
Certification Assessments of Manual Competence Should Combine 2 Types of Structured Instruments: Checklists and Overall Scores
Assessments based on direct observation are more reliable when formally structured.49,50 Though checklists used in observed structured clinical examinations capture many important manual skills,51-56 they do not completely reflect a hospitalist’s manual competence;57 situations may occur in which a hospitalist meets all the individual items on a checklist but cannot perform an entire procedure with basic competence. Therefore, checklists should be paired with overall scores.58-61 Both checklists and overall scores ought to be obtained from reliable and valid instruments.
Certification Assessments Should Include Feedback
Assessments without feedback are missed learning opportunities.62 Both simulation-63 and patient-based assessments should provide feedback in real time to reinforce effective behaviors and remedy faulty ones.
If Remedial Training is Needed, Simulator-Based Training Can Supplement but Not Replace Patient-Based Training
Supervised simulator-based training allows hospitalists to master basic components of a procedure64 (including orientation to equipment, sequence of operations, dexterity, ultrasound anatomy, and real-time guidance technique) while improving both cognitive and manual skills.42,43,65-71 In addition to their role in basic training (which is outside the scope of this position statement), simulators can be useful for remedial training. To be sufficient for hospitalists who do not pass their patient-based assessments, however, remedial training that begins with simulation must also include patient-based training and assessment.72-75
Initial Credentialing Process
A Minimum Threshold of Experience Should Be Reached before Patient-Based Assessments are Conducted (Figure 1)
Initial Certification Assessments Should Ideally Begin on Simulators
Simulators allow the assurance of safe manual skills, including proper needle insertion techniques and disposal of sharp objects.3,79 If simulators are not available, however, then patient-based training and assessments can still be performed under direct observation. Safe performance of ultrasound-guided procedures during patient-based assessments (without preceding simulator-based assessments) is sufficient to certify manual competence.
Ongoing Credentialing
Certification to Perform Ultrasound-Guided Procedures Should Be Routinely Re-Evaluated During Ongoing Credentialing (Figure 2)
Observed Patient-Based Assessments Should Occur When a Periprocedural Safety Event Occurs that is Potentially Caused by “Provider Error”
Safety events include both near misses and adverse events. Information about both is ideally “flagged” and “pushed” to hospitalist group leaders by active surveillance and reporting systems. Once reviewed, if a safety event is considered to potentially have been caused by provider error (including knowledge- and skill-based errors),83 then the provider who performed the procedure should undergo an observed patient-based assessment.
Simulation-Based Practice Can Supplement Patient-Based Experience for Ongoing Credentialing
When hospitalists do not achieve a minimum threshold of patient-based experience since the antecedent certification, simulation-based training can supplement their patient-based experience.
Credentialing Infrastructure
Hospitalists Themselves Should Not Bear the Financial Costs of Developing and Maintaining Training and Certification Programs for Ultrasound-Guided Procedures
Equipment and personnel costs
Assessors Should Be Unbiased Expert Providers Who Have Demonstrated Mastery in Performance of the Procedure Being Assessed and Regularly Perform It in a Similar Practice Environment
Assessors should be expert providers who regularly perform the ultrasound-guided procedure in a similar practice environment.9,89-94 For example, providers who are not hospitalists but who are experts in an ultrasound-guided procedure and commonly perform it on the hospital wards would be acceptable assessors. However, a radiologist who only performs that procedure in a fully-staffed interventional radiology suite with fluoroscopy or computed tomography guidance would not be an acceptable assessor. More than 1 assessor may balance idiosyncratic assessments;95 but when assessments are well structured, additional assessors are generally not needed.18
If Intramural Assessors Are Not Available, Extramural Assessors May Be Considered
Intramural assessors are generally preferred because of familiarity with the local practice environment, including the available procedure kits and typical patient characteristics. Nevertheless, extramural assessors27,77,85,96 may theoretically provide even more valid assessments than intramural ones because extramural assessors are neither influenced by relationships with local hospitalists nor biased by local hospitalists’ skills.
DISCUSSION
There are no high-quality randomized trials in support of a single credentialing pathway over any other.94,102 The credentialing pathways at the center of this position statement are based on expert opinion. Our methods can be criticized straightaway, therefore, for reliance on the experience and expertise of our working group and task force. Any position statement written without high-quality supportive evidence would be appropriately subject to the same criticism. Without evidence in support of an overall pathway, we codified specific aspects of the pathways into 16 individual recommendations.
Patient-level outcomes do not back these recommendations. Consider, for example, our recommendation that certification assessments be made from structured instruments and not simply from an assessor’s gestalt. Here, the basis is not improved patient-level outcomes from a trial (such as reduced complications or increased procedural success) but improved psychometric performance from reliability studies. The body of evidence for our recommendations is similarly indirect, mostly because the outcomes studied are more proximate and, thus, less meaningful than patient-level outcomes, which are the outcomes of greatest interest but are woefully understudied for clinical competence.17,97,103
The need for high-quality evidence is most pronounced in distinguishing how recommendations should be modified for various settings. Wide variations in resources and patient-mix will make some recommendations impracticable, meaning that they could not be carried out with available resources. For example, our recommendation that credentialing decisions should ultimately rely on certifications made by assessors during patient-based assessments may not be practicable at small, rural hospitals. Such hospitals may not have access to local assessors, and they may not admit enough patients who need the types of ultrasound-guided procedures for which hospitalists seek certification (especially given the need to coordinate the schedules of patients, procedure-performing hospitalists, and assessors).
Regardless of whether some or all hospitalists at a particular hospital are expected to perform bedside procedures, technology may help to improve the practicability of our recommendations. For example, simulators may evolve to replace actual patient-level experience in achieving minimum thresholds. Certification assessments of manual skills may even someday occur entirely on simulators. Real-time high-definition video streaming enhanced with multiple cameras may allow for remote assessments. Until such advances mature, high-quality patient-level data should be sought through additional research to refine our current recommendations.
We hope that these recommendations will improve how basic competence in ultrasound-guided bedside procedures is assessed. Our ultimate goal is to improve how hospitalists perform these procedures. Patient safety is, therefore, considered paramount to cost. Nevertheless, the hospital administrative leaders and privileging committee members on our Task Force concluded that many hospitals have been seeking guidance on credentialing for bedside procedures, and the likely difficulties of implementing our recommendations (including cost) would not be prohibitive at most hospitals, especially given recognition that these recommendations can be tailored to each setting.
Acknowledgments
Collaborators from SHM POCUS Task Force are Saaid Abdel-Ghani, Michael Blaivas, Dan Brotman, Carolina Candotti, Jagriti Chadha, Joel Cho, Ria Dancel, Ricardo Franco, Richard Hoppmann, Susan Hunt, Venkat Kalidindi, Ketino Kobaidze, Josh Lenchus, Benji Mathews, Satyen Nichani, Vicki Noble, Martin Perez, Nitin Puri, Aliaksei Pustavoitau, Sophia Rodgers, Gerard Salame, Daniel Schnobrich, Kirk Spencer, Vivek Tayal, Jeff Bates, Anjali Bhagra, Kreegan Reierson, Robert Arntfield, Paul Mayo, Loretta Grikis.
Disclosure
Brian P. Lucas received funding from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development and Dartmouth SYNERGY, National Institutes of Health, and National Center for Translational Science (UL1TR001086). Nilam Soni received funding from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI) Partnered Evaluation Initiative (HX002263-01A1). The contents of this publication do not represent the views of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
1. American Board of Internal Medicine. Policies and procedures for certification. Philadelphia: American Board of Internal Medicine; 2006.
2. Nichani S, Fitterman N, Lukela M, Crocker J; Society of Hospital Medicine. The Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine 2017 Revision. Section 2: Procedures. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(4 Suppl 1):S44-S54 PubMed
3. Lucas BP, Asbury JK, Franco-Sadud R. Training future hospitalists with simulators: a needed step toward accessible, expertly performed bedside procedures. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):395-396. PubMed
4. Schnobrich DJ, Gladding S, Olson APJ, Duran-Nelson A. Point-of-care ultrasound in internal medicine: a national survey of educational leadership. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(3):498-502. PubMed
5. Brown GM, Otremba M, Devine LA, Gray C, Millington SJ, Ma IW. Defining competencies for ultrasound-guided bedside procedures: consensus opinions from Canadian physicians. J Ultrasound Med. 2016;35(1):129-141. PubMed
6. Vaisman A, Cram P. Procedural competence among faculty in academic health centers: challenges and future directions. Acad Med. 2017;92(1):31-34. PubMed
7. Kreisman RD. With ED ultrasound, credentialing is at issue. ED Legal Letter. 2010;21:102-103.
8. Goudie AM. Credentialing a new skill: what should the standard be for emergency department ultrasound in Australasia? Emerg Med Australas. 2010;22:263-264. PubMed
9. Maizel J, Guyomarc HL, Henon P, et al. Residents learning ultrasound-guided catheterization are not sufficiently skilled to use landmarks. Crit Care. 2014;18(1):R36. doi:10.1186/cc13741. PubMed
10. American College of Emergency Physicians. Ultrasound guidelines: emergency, point-of-care, and clinical ultrasound guidelines in medicine. Ann Emerg Med. 2017;69(5):e27-e54. PubMed
11. Amini R, Adhikari S, Fiorello A. Ultrasound competency assessment in emergency medicine residency programs. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21(7):799-801. PubMed
12. Jensen T, Soni NJ, Tierney DM, Lucas BP. Hospital privileging practices for bedside procedures: a survey of hospitalist experts. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(10):836-839. PubMed
13. Chang W. Is hospitalist proficiency in bedside procedures in decline? The Hospitalist. 2012. http://www.the-hospitalist.org/hospitalist/article/125236/patient-safety/hospitalist-proficiency-bedside-procedures-decline. Accessed September 30, 2017.
14. Barsuk JH, Feinglass J, Kozmic SE, Hohmann SF, Ganger D, Wayne DB. Specialties Performing Paracentesis Procedures at University Hospitals: Implications for Training and Certification. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(3):162-168. PubMed
15. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Feinglass J, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Residents’ Procedural Experience Does Not Ensure Competence: A Research Synthesis. J Grad Med Educ. 2017;9(2):201-208. PubMed
16. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schunemann HJ, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):401-406. PubMed
17. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, et al. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence—indirectness. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(12):1303-1310. PubMed
18. Miller GE. The assessment of clinical skills/competence/performance. Acad Med. 1990;65(9 Suppl):S63-S67. PubMed
19. Grover S, Currier PF, Elinoff JM, Mouchantaf KJ, Katz JT, McMahon GT. Development of a test to evaluate residents knowledge of medical procedures. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):430-432. PubMed
20. Millington SJ, Wong RY, Kassen BO, Roberts JM, Ma IWY. Improving internal medicine residents’ performance, knowledge, and confidence in central venous catheterization using simulators. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):410-416. PubMed
21. Lenchus JD, Carvalho CM, Ferreri K, et al. Filling the void: defining invasive bedside procedural competency for internal medicine residents. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(4):605-612. PubMed
22. Heegeman DJ, Kieke B Jr. Learning curves, credentialing, and the need for ultrasound fellowships. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10:404-405. PubMed
23. Jang TB, Ruggeri W, Dyne P, Kaji AH. The learning curve of resident physicians using emergency ultrasonography for cholelithaisis and cholecystitis. Acad Emerg Med. 2010;17(11):1247-1252. PubMed
24. Akhtar MI, Hamid M. Ultrasound guided central venous access; a review of literature. Anaesth Pain Intensive Care. 2015;19:317-322.
25. Bahl A, Yunker A. Assessment of the numbers–based model for evaluation of resident competency in emergency ultrasound core applications. J Emerg Med Trauma Acute Care. 2015;2015(5). doi:10.5339/jemtac.2015.5
26. Cazes N, Desmots F, Geffroy Y, Renard A, Leyral J, Chaumoitre K. Emergency ultrasound: a prospective study on sufficient adequate training for military doctors. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94(11):1109-1115. PubMed
27. Arntfield RT, Millington SJ, Ainsworth CD, et al. Canadian recommendations for critical care ultrasound training and competency for the Canadian critical care society. Can Respir J. 2014;21(16):341-345.
28. Bolsin S, Colson M. The use of the Cusum technique in the assessment of trainee competence in new procedures. Int J Qual Health Care. 2000;12(5):433-438. PubMed
29. de Oliveira Filho GR, Helayel PE, da Conceição DB, Garzel IS, Pavei P, Ceccon MS. Learning curves and mathematical models for interventional ultrasound basic skills. Anaesth Analg. 2008;106(2):568-573. PubMed
30. Starkie T, Drake EJ. Assessment of procedural skills training and performance in anesthesia using cumulative sum analysis (cusum). Can J Anaesth. 2013;60(12):1228-1239. PubMed
31. Tierney D. Competency cut-point identification derived from a mastery learning cohort approach: A hybrid model. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:S19.
32. Rankin JH, Elkhunovich MA, Rangarajan V, Chilstrom M, Mailhot T. Learning Curves for Ultrasound Assessment of Lumbar Puncture Insertion Sites: When is Competency Established? J Emerg Med. 2016;51(1):55-62. PubMed
33. Klasko SK, Cummings RV, Glazerman LR. Resident data collection: Do the numbers add up? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172(4 Pt 1):1312-1316. PubMed
34. Tierney D. Development & analysis of a mobile POCUS tracking tool. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41(suppl 4):S31.
35. Sethi MV, Zimmer J, Ure B, Lacher M. Prospective assessment of complications on a daily basis is essential to determine morbidity and mortality in routine pediatric surgery. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51(4):630-633. PubMed
36. Fisher JC, Kuenzler KA, Tomita SS, Sinha P, Shah P, Ginsburg HB. Increased capture of pediatric surgical complications utilizing a novel case-log web application to enhance quality improvement. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52(1):166-171. PubMed
37. Rethans JJ, Norcini JJ, Barón-Maldonado M, et al. The relationship between competence and performance: implications for assessing practice performance. Med Educ. 2002;36(10):901-909. PubMed
38. Duncan DR, Morgenthaler TI, Ryu JH, Daniels CE. Reducing iatrogenic risk in thoracentesis: establishing best practice via experiential training in a zero-risk environment. Chest. 2009;135(5):1315-1320. PubMed
39. Society of Critical Care Medicine Ultrasound Certification Task Force. Recommendations for achieving and maintaining competence and credentialing in critical care ultrasound with focused cardiac ultrasound and advanced critical care echocardiography. http://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/Documents/Critical%20Care%20Ultrasound.pdf Published 2013. Accessed February 2, 2017.
40. Carraccio C, Wolfsthal SD, Englander R, Ferentz K, Martin C. Shifting paradigms: from Flexner to competencies. Acad Med. 2002;77(5):361-367. PubMed
41. Clark EG, Paparello JJ, Wayne DB, et al. Use of a national continuing medical education meeting to provide simulation-based training in temporary hemodialysis catheter insertion skills: a pre-test post-test study. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2014;1:25-31. PubMed
42. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Caprio T, McGaghie WC, Simuni T, Wayne DB. Simulation-based education with mastery learning improves residents’ lumbar puncture skills. Neurology. 2012;79(2):132-137. PubMed
43. Barsuk JH, McGaghie WC, Cohen ER, O’Leary KJ, Wayne DB. Simulation-based mastery learning reduces complications during central venous catheter insertion in a medical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(10):2697-2701. PubMed
44. Davis DA, Mazmanian PE, Fordis M, Van Harrison R, Thorpe KE, Perrier L. Accuracy of physician self-assessment compared with observed measures of competence: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1094-1102. PubMed
45. Shah J, Darzi A. Surgical skills assessment: an ongoing debate. BJU Int. 2001;88(7):655-660. PubMed
46. Lamperti M, Bodenham AR, Pittiruti M, et al. International evidence-based recommendations on ultrasound-guided vascular access. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(7):1105-1117. PubMed
47. Tolsgaard MG, Todsen T, Sorensen JL, et al. International multispecialty consensus on how to evaluate ultrasound competence: a Delphi consensus survey. PLOS One. 2013;8(2):e57687. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057687 PubMed
48. Moureau N, Laperti M, Kelly LJ, et al. Evidence-based consensus on the insertion of central venous access devices: definition of minimal requirements for training. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110(3):347-356. PubMed
49. Feldman LS, Hagarty S, Ghitulescu G, Stanbridge D, Fried GM. Relationship between objective assessment of technical skills and subjective in-training evaluations in surgical residents. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198(1):105-110. PubMed
50. Baker S, Willey B, Mitchell C. The attempt to standardize technical and analytic competence in sonography education. J Diagn Med Sonogr. 2011;27(5):203-211.
51. Tolsgaard MG, Ringsted C, Dreisler E, et al. Reliable and valid assessment of ultrasound operator competence in obstetrics and gynecology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014;43(4):437-443. PubMed
52. Rice J, Crichlow A, Baker M, et al. An assessment tool for the placement of ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous access. J Grad Med Educ. 2016;8(2):202-207. PubMed
53. Hartman N, Wittler M, Askew K, Hiestand B, Manthey D. Validation of a performance checklist for ultrasound-guided internal jubular central lines for use in procedural instruction and assessment. Postgrad Med J. 2017;93(1096):67-70. PubMed
54. Primdahl SC, Todsen T, Clemmesen L, et al. Rating scale for the assessment of competence in ultrasound-guided peripheral vascular access—a Delphi Consensus Study. J Vasc Access. 2016;17(5):440-445.
55. Berg D, Berg K, Riesenberg LA, et al. The development of a validated checklist for thoracentesis: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2013;28(3):220-226. PubMed
56. Berg K, Riesenberg LA, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for radial arterial line placement: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2014;29(3):242-246. PubMed
57. Walzak A, Bacchus M, Schaefer MP, et al. Diagnosing technical competence in six bedside procedures: comparing checklists and a global rating scale in the assessment of resident performance. Acad Med. 2015;90(8):1100-1108. PubMed
58. Riesenberg LA, Berg K, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for femoral venous catheterization: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2014;29(5):445-450. PubMed
59. Riesenberg LA, Berg K, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for paracentesis: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2013;28(3):227-231. PubMed
60. Huang GC, Newman LR, Schwartzstein RM, et al. Procedural competence in internal medicine residents: validity of a central venous catheter insertion assessment instrument. Acad Med. 2009;84(8):1127-1134. PubMed
61. Salamonsen M, McGrath D, Steiler G, et al. A new instrument to assess physician skill at thoracic ultrasound, including pleural effusion markup. Chest. 2013;144(3):930-934. PubMed
62. Boniface K, Yarris LM. Emergency ultrasound: Leveling the training and assessment landscape. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21(7):803-805. PubMed
63. Boyle E, O’Keeffe D, Naughton P, Hill A, McDonnell C, Moneley D. The importance of expert feedback during endovascular simulator training. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54(1):240-248.e1. PubMed
64. Langhan TS, Rigby IJ, Walker IW, Howes D, Donnon T, Lord JA. Simulation-based training in critical resuscitation procedures improves residents’ competence. CJEM. 2009;11(6):535-539. PubMed
65. Barsuk JH, McGaghie WC, Cohen ER, Balachandran JS, Wayne DB. Use of simulation-based mastery learning to improve the quality of central venous catheter placement in a medical intensive care unit. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):397-403. PubMed
66. Lenchus JD. End of the “see one, do one, teach one” era: the next generation of invasive bedside procedural instruction. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2010;110(6):340-346. PubMed
67. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Vozenilek JA, O’Connor LM, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Simulation-based education with mastery learning improves paracentesis skills. J Grad Med Educ. 2012;4(1):23-27. PubMed
68. McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Cohen ER, Barsuk JH, Wayne DB. Does simulation-based medical education with deliberate practice yield better results than traditional clinical education? A meta-analytic comparative review of the evidence. Acad Med. 2011;86(6):706-711. PubMed
69. Ross JG. Simulation and psychomotor skill acquisition: A review of the literature. Clin Simul Nurs. 2012;8(9):e429-e435.
70. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Potts S, et al. Dissemination of a simulation-based mastery learning intervention reduces central line-associated bloodstream infections. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(9):749-756. PubMed
71. McSparron JI, Michaud GC, Gordan PL, et al. Simulation for skills-based education in pulmonary and critical care medicine. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(4):579-586. PubMed
72. Kneebone RL, Scott W, Darzi A, Horrocks M. Simulation and clinical practice: strengthening the relationship. Med Educ. 2004;38(10):1095-1102. PubMed
73. Mema B, Harris I. The barriers and facilitators to transfer of ultrasound-guided central venous line skills from simulation to practice: exploring perceptions of learners and supervisors. Teach Learn Med. 2016;28(2):115-124. PubMed
74. Castanelli DJ. The rise of simulation in technical skills teaching and the implications for training novices in anaestheia. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2009;37(6):903-910. PubMed
75. McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Barsuk JH, Wayne DB. A critical review of simulation-based mastery learning with translational outcomes. Med Educ. 2014;48(4):375-385. PubMed
76. Langlois SLP. Focused ultrasound training for clinicians. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(5 suppl):S138-S143.
77. Price S, Via G, Sloth E, et al. Echocardiography practice, training and accreditation in the intesive care: document for the World Interactive Network Focused on Critical Ultrasound (WINFOCUS). Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008;6:49-83. PubMed
78. Blehar DJ, Barton B, Gaspari RJ. Learning curves in emergency ultrasound education. Acad Emerg Med. 2015;22(5):574-582. PubMed
79. Ault MJ, Rosen BT, Ault B. The use of tissue models for vascular access training. Phase I of the procedural patient safety initiative. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(5):514-517. PubMed
80. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Long-term retention of central venous catheter insertion skills after simulation-based mastery learning. Acad Med. 2010;85(10 Suppl):S9-S12. PubMed
81. Sliman Sean, Amundson S, Shaw D, Phan JN, Waalen J, Kimura B. Recently-acquired cardiac ultrasound skills are rapidly lost when not used: implications for competency in physician imaging. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(13S):1569.
82. Kessler CS, Leone KA. The current state of core competency assessment in emergency medicine and a future research agenda: recommendations of the working group on assessment of observable learner performance. Acad Emerg Med. 2012;19(12):1354-1359. PubMed
83. Chang A, Schyve PM, Croteau RJ, O’Leary DS, Loeb JM. The JCAHO patient safety event taxonomy: a standardized terminology and classification schema for near misses and adverse events. Int J Qual Health Care. 2005;17(2):95-105. PubMed
84. Sawyer T, White M, Zaveri P, et al. Learn, see, practice, prove, do, maintain: an evidence-based pedagogical framework for procedural skill training in medicine. Acad Med. 2015;90(8):1025-1033. PubMed
85. Das D, Kapoor M, Brown C, Ndubuisi A, Gupta S. Current status of emergency department attending physician ultrasound credentialing and quality assurance in the United States. Crit Ultrasound J. 2016;8(1):6-12. PubMed
86. Ndubuisi AK, Gupta S, Brown C, Das D. Current status and future issues in emergency department attending physician ultrasound credentialing. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;64(45):S27-S28.
87. Tandy Tk, Hoffenberg S. Emergency department ultrasound services by emergency physicians: model for gaining hospital approval. Ann Emerg Med. 1997;29(3):367-374. PubMed
88. Lewiss RE, Saul T, Del Rios M. Acquiring credentials in bedside ultrasound: a cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open. 2013;3:e003502. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003502 PubMed
89. Lanoix R. Credentialing issues in emergency ultrasonography. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1997;15(4):913-920. PubMed
90. Scalea T, Rodriquez A, Chiu WC, et al. Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST): results from an international consensus conference. J Trauma. 1999;46(3):466-472. PubMed
91. Hertzberg BS, Kliewer MA, Bowie JD, et al. Physician training requirements in sonography: how many cases are needed for competence? AJR. 2000;174(5):1221-1227. PubMed
92. Blaivas M, Theodoro DL, Sierzenski P. Proliferation of ultrasound fellowships in emergency medicine: how do we ensure future experts are expertly trained? Acad Emerg Med. 2002;9(8):863-864. PubMed
93. Bodenham AR. Editorial II: Ultrasound imaging by anaesthetists: training and accreditation issues. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96(4):414-417. PubMed
94. Williamson JP, Twaddell SH, Lee YCG, et al. Thoracic ultrasound recognition of competence: A position paper of the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand. Respirology. 2017;22(2):405-408. PubMed
95. Harrison G. Summative clinical competency assessment: a survey of ultrasound practitioners’ views. Ultrasound. 2015;23(1):11-17. PubMed
96. Evans LV, Morse JL, Hamann CJ, Osborne M, Lin Z, D'Onofrio G. The development of an independent rater system to assess residents' competence in invasive procedures. Acad Med. 2009;84(8):1135-1143. PubMed
97. Wass V, Van der Vleuten C, Shatzer J, Jones R. Assessment of clinical competence. Lancet. 2001;357(9260):945-949. PubMed
98. Arntfield RT. The utility of remote supervision with feedback as a method to deliver high-volume critical care ultrasound training. J Crit Care. 2015;30(2):441.e1-e6. PubMed
99. Akhtar S, Theodoro D, Gaspari R, et al. Resident training in emergency ultrasound: consensus recommendations from the 2008 Council of Emergency Residency Directors Conference. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16:S32-S36. PubMed
100. Yu E. The assessment of technical skills in a cardiology training program: is the ITER sufficient? Can J Cardiol. 2000;16(4):457-462. PubMed
101. Todsen T, Tolsgaard MG, Olsen BH, et al. Reliable and valid assessment of point-of-care ultrasonography. Ann Surg. 2015;261(2):309-315. PubMed
102. Stein JC, Nobay F. Emergency department ultrasound credentialing: a sample policy and procedure. J Emerg Med. 2009;37(2):153-159. PubMed
103. Chen FM. Burstin H, Huntington J. The importance of clinical outcomes in medical education research. Med Educ. 2005;39(4):350-351. PubMed
104. Dressler DD, Pistoria MJ, Budnitz TL, McKean SCW, Amin AN. Core competencies in hospital medicine: development and methodology. J Hosp Med. 2006;1:48-56. PubMed
105. ten Cate O. Nuts and bolts of entrustable professional activities. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(1):157-158. PubMed
106. Castillo J, Caruana CJ, Wainwright D. The changing concept of competence and categorisation of learning outcomes in Europe: Implications for the design of higher education radiography curricula at the European level. Radiography. 2011;17(3):230-234.
107. Goldstein SR. Accreditation, certification: why all the confusion? Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110(6):1396-1398. PubMed
108. Moore CL. Credentialing and reimbursement in point-of-care ultrasound. Clin Pediatr Emerg Med. 2011;12(1):73-77. PubMed
109. ten Cate O, Scheele F. Competency-based postgraduate training: can we bridge the gap between theory and clinical practice? Acad Med. 2007;82(6):542-547. PubMed
110. Abuhamad AZ, Benacerraf BR, Woletz P, Burke BL. The accreditation of ultrasound practices: impact on compliance with minimum performance guidelines. J Ultrasound Med. 2004;23(8):1023-1029. PubMed
The American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) changed its certification policy for bedside procedures over a decade ago.
Hospitalists increasingly perform bedside procedures with ultrasound guidance.
Therefore, the Society of Hospital Medicine (SHM) Education Committee convened a group of experts and conducted a systematic literature review in order to provide recommendations for credentialing hospitalist physicians in ultrasound-guided bedside procedures. These recommendations do not include training recommendations, aside from recommendations about remedial training for hospitalists who do not pass certification. Training is a means to competence but does not guarantee it. We believe that training recommendations ought to be considered separately.
METHODS
Working Group Formation
In January 2015, the SHM Board of Directors asked the SHM Education Committee to convene the POCUS Task Force. The purpose of the task force was to develop recommendations on ultrasound guidance for bedside procedures. The SHM Education Committee appointed 3 chairs of the task force: 1 senior member of the SHM Education Committee and 2 POCUS experts. The chairs assembled a task force of 31 members that included 5 working groups, a multispecialty peer review group, and a guideline methodologist (supplemental Appendix 1). Invitation was based on members’ past contributions to SHM POCUS-related activities, up-front commitment, and declared conflicts of interest. Working group members self-identified as “hospitalists,” whereas peer reviewers were nonhospitalists but nationally recognized POCUS physician-leaders specializing in emergency medicine, cardiology, critical care medicine, and anesthesiology. Task force membership was vetted by a chair of the SHM POCUS Task Force and the Director of Education before work began. This position statement was authored by the Credentialing Working Group together with the chairs of the other 4 working groups and a guideline methodologist.
Disclosures
Signed disclosure statements of all task force members were reviewed prior to inclusion on the task force (supplemental Appendix 2); no members received honoraria for participation. Industry representatives did not contribute to the development of the guidelines nor to any conference calls or meetings.
Literature Search Strategy
A literature search was conducted by a biomedical librarian. Records from 1979 to January of 2017 were searched in Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, and Google Scholar (supplemental Appendix 3). Search limiters were English language and adults. Articles were manually screened to exclude nonhuman or endoscopic ultrasound applications. Final article selection was based on working group consensus.
Draft Pathways
The Credentialing Working Group drafted initial and ongoing certification pathways (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The other 4 working groups from the task force were surveyed about the elements and overall appropriateness of these draft pathways. This survey and its results have already been published.12 The Credentialing Working Group then revised the certification pathways by using these survey results and codified individual aspects of these pathways into recommendations.
Development of Position Statement
Based on the Grading of Recommendation Assessment Development and Evaluation methodology, all final article selections were initially rated as either low-quality (observational studies) or unclassifiable (expert opinion).16 These initial ratings were downgraded further because of indirectness, because none of the articles involved the intervention of interest (a credentialing pathway) in a population of interest (hospitalists) measuring the outcomes of interest (patient-level outcomes).
First, the Credentialing Working Group drafted an initial position statement composed of recommendations for credentialing pathways and other general aspects of credentialing. All final article selections were incorporated as references in a draft of the position statement and compiled in a full-text compendium. Second, feedback was provided by the other 4 task force working groups, the task force peer reviewers, and the SHM Education Committee. Feedback was incorporated by the authors of this statement who were the Credentialing Working Group, the chairs of the other 4 working groups, and a guideline methodologist. Third, final suggestions from all members of the SHM POCUS Task Force and SHM Education Committee were incorporated before final approval by the SHM Board of Directors in September 2017.
RESULTS
A total of 1438 references were identified in the original search. Manual selection led to 101 articles, which were incorporated into the following 4 domains with 16 recommendations.
General Credentialing Process
Basic Cognitive Competence Can Be Certified with Written or Oral Examinations
The ABIM defines cognitive competence as having 3 abilities: “(1) to explain indications, contraindications, patient preparation methods, sterile techniques, pain management, proper techniques for handling specimens and fluids obtained, and test results; (2) to recognize and manage complications; and, (3) to clearly explain to a patient all facets of the procedure necessary to obtain informed consent.”1 These abilities can be assessed with written or oral examinations that may be integrated into simulation- or patient-based assessments.
Minimum Thresholds of Experience to Trigger the Timing of a Patient-Based Assessment Should Be Determined by Empirical Methods
Learning curves are highly variable22-25 and even plateaus may not herald basic competence.26 Expert opinion
Hospitalists Should Formally Log All of Their Attempted Procedures, Ideally in an Electronic Medical Record
Simple self-reported numbers of procedures performed often misrepresent actual experience33,34 and do not include periprocedural complications.35,36 Thus, hospitalists should report their experience with logs of all attempted procedures, both successful and unsuccessful. Such logs must include information about supervising providers (if applicable) and patient outcomes, including periprocedural adverse events,37 but they must also remain compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Health Information Technology Service Should Routinely Pull Collations of All Attempted Procedures from Comprehensive Electronic Medical Records
Active surveillance may reduce complications by identifying hospitalists who may benefit from further training.38 In order to facilitate active surveillance systems, documentation (such as a procedure note) should be both integrated into an electronic medical record and protocol driven,39 including procedure technique, ultrasound findings, and any safety events (both near misses and adverse events).
Multiple interacting factors, including environment, patients, baseline skills, training, experience, and skills decay, affect manual competence. Certifications that are based solely on reaching minimum thresholds of experience, even when accurate, are not valid reflections of manual competence,15,40-43 and neither are those based on self-perception.44 Patient-based assessments are, thus, necessary to ensure manual competence.45-48
Certification Assessments of Manual Competence Should Combine 2 Types of Structured Instruments: Checklists and Overall Scores
Assessments based on direct observation are more reliable when formally structured.49,50 Though checklists used in observed structured clinical examinations capture many important manual skills,51-56 they do not completely reflect a hospitalist’s manual competence;57 situations may occur in which a hospitalist meets all the individual items on a checklist but cannot perform an entire procedure with basic competence. Therefore, checklists should be paired with overall scores.58-61 Both checklists and overall scores ought to be obtained from reliable and valid instruments.
Certification Assessments Should Include Feedback
Assessments without feedback are missed learning opportunities.62 Both simulation-63 and patient-based assessments should provide feedback in real time to reinforce effective behaviors and remedy faulty ones.
If Remedial Training is Needed, Simulator-Based Training Can Supplement but Not Replace Patient-Based Training
Supervised simulator-based training allows hospitalists to master basic components of a procedure64 (including orientation to equipment, sequence of operations, dexterity, ultrasound anatomy, and real-time guidance technique) while improving both cognitive and manual skills.42,43,65-71 In addition to their role in basic training (which is outside the scope of this position statement), simulators can be useful for remedial training. To be sufficient for hospitalists who do not pass their patient-based assessments, however, remedial training that begins with simulation must also include patient-based training and assessment.72-75
Initial Credentialing Process
A Minimum Threshold of Experience Should Be Reached before Patient-Based Assessments are Conducted (Figure 1)
Initial Certification Assessments Should Ideally Begin on Simulators
Simulators allow the assurance of safe manual skills, including proper needle insertion techniques and disposal of sharp objects.3,79 If simulators are not available, however, then patient-based training and assessments can still be performed under direct observation. Safe performance of ultrasound-guided procedures during patient-based assessments (without preceding simulator-based assessments) is sufficient to certify manual competence.
Ongoing Credentialing
Certification to Perform Ultrasound-Guided Procedures Should Be Routinely Re-Evaluated During Ongoing Credentialing (Figure 2)
Observed Patient-Based Assessments Should Occur When a Periprocedural Safety Event Occurs that is Potentially Caused by “Provider Error”
Safety events include both near misses and adverse events. Information about both is ideally “flagged” and “pushed” to hospitalist group leaders by active surveillance and reporting systems. Once reviewed, if a safety event is considered to potentially have been caused by provider error (including knowledge- and skill-based errors),83 then the provider who performed the procedure should undergo an observed patient-based assessment.
Simulation-Based Practice Can Supplement Patient-Based Experience for Ongoing Credentialing
When hospitalists do not achieve a minimum threshold of patient-based experience since the antecedent certification, simulation-based training can supplement their patient-based experience.
Credentialing Infrastructure
Hospitalists Themselves Should Not Bear the Financial Costs of Developing and Maintaining Training and Certification Programs for Ultrasound-Guided Procedures
Equipment and personnel costs
Assessors Should Be Unbiased Expert Providers Who Have Demonstrated Mastery in Performance of the Procedure Being Assessed and Regularly Perform It in a Similar Practice Environment
Assessors should be expert providers who regularly perform the ultrasound-guided procedure in a similar practice environment.9,89-94 For example, providers who are not hospitalists but who are experts in an ultrasound-guided procedure and commonly perform it on the hospital wards would be acceptable assessors. However, a radiologist who only performs that procedure in a fully-staffed interventional radiology suite with fluoroscopy or computed tomography guidance would not be an acceptable assessor. More than 1 assessor may balance idiosyncratic assessments;95 but when assessments are well structured, additional assessors are generally not needed.18
If Intramural Assessors Are Not Available, Extramural Assessors May Be Considered
Intramural assessors are generally preferred because of familiarity with the local practice environment, including the available procedure kits and typical patient characteristics. Nevertheless, extramural assessors27,77,85,96 may theoretically provide even more valid assessments than intramural ones because extramural assessors are neither influenced by relationships with local hospitalists nor biased by local hospitalists’ skills.
DISCUSSION
There are no high-quality randomized trials in support of a single credentialing pathway over any other.94,102 The credentialing pathways at the center of this position statement are based on expert opinion. Our methods can be criticized straightaway, therefore, for reliance on the experience and expertise of our working group and task force. Any position statement written without high-quality supportive evidence would be appropriately subject to the same criticism. Without evidence in support of an overall pathway, we codified specific aspects of the pathways into 16 individual recommendations.
Patient-level outcomes do not back these recommendations. Consider, for example, our recommendation that certification assessments be made from structured instruments and not simply from an assessor’s gestalt. Here, the basis is not improved patient-level outcomes from a trial (such as reduced complications or increased procedural success) but improved psychometric performance from reliability studies. The body of evidence for our recommendations is similarly indirect, mostly because the outcomes studied are more proximate and, thus, less meaningful than patient-level outcomes, which are the outcomes of greatest interest but are woefully understudied for clinical competence.17,97,103
The need for high-quality evidence is most pronounced in distinguishing how recommendations should be modified for various settings. Wide variations in resources and patient-mix will make some recommendations impracticable, meaning that they could not be carried out with available resources. For example, our recommendation that credentialing decisions should ultimately rely on certifications made by assessors during patient-based assessments may not be practicable at small, rural hospitals. Such hospitals may not have access to local assessors, and they may not admit enough patients who need the types of ultrasound-guided procedures for which hospitalists seek certification (especially given the need to coordinate the schedules of patients, procedure-performing hospitalists, and assessors).
Regardless of whether some or all hospitalists at a particular hospital are expected to perform bedside procedures, technology may help to improve the practicability of our recommendations. For example, simulators may evolve to replace actual patient-level experience in achieving minimum thresholds. Certification assessments of manual skills may even someday occur entirely on simulators. Real-time high-definition video streaming enhanced with multiple cameras may allow for remote assessments. Until such advances mature, high-quality patient-level data should be sought through additional research to refine our current recommendations.
We hope that these recommendations will improve how basic competence in ultrasound-guided bedside procedures is assessed. Our ultimate goal is to improve how hospitalists perform these procedures. Patient safety is, therefore, considered paramount to cost. Nevertheless, the hospital administrative leaders and privileging committee members on our Task Force concluded that many hospitals have been seeking guidance on credentialing for bedside procedures, and the likely difficulties of implementing our recommendations (including cost) would not be prohibitive at most hospitals, especially given recognition that these recommendations can be tailored to each setting.
Acknowledgments
Collaborators from SHM POCUS Task Force are Saaid Abdel-Ghani, Michael Blaivas, Dan Brotman, Carolina Candotti, Jagriti Chadha, Joel Cho, Ria Dancel, Ricardo Franco, Richard Hoppmann, Susan Hunt, Venkat Kalidindi, Ketino Kobaidze, Josh Lenchus, Benji Mathews, Satyen Nichani, Vicki Noble, Martin Perez, Nitin Puri, Aliaksei Pustavoitau, Sophia Rodgers, Gerard Salame, Daniel Schnobrich, Kirk Spencer, Vivek Tayal, Jeff Bates, Anjali Bhagra, Kreegan Reierson, Robert Arntfield, Paul Mayo, Loretta Grikis.
Disclosure
Brian P. Lucas received funding from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development and Dartmouth SYNERGY, National Institutes of Health, and National Center for Translational Science (UL1TR001086). Nilam Soni received funding from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI) Partnered Evaluation Initiative (HX002263-01A1). The contents of this publication do not represent the views of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
The American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) changed its certification policy for bedside procedures over a decade ago.
Hospitalists increasingly perform bedside procedures with ultrasound guidance.
Therefore, the Society of Hospital Medicine (SHM) Education Committee convened a group of experts and conducted a systematic literature review in order to provide recommendations for credentialing hospitalist physicians in ultrasound-guided bedside procedures. These recommendations do not include training recommendations, aside from recommendations about remedial training for hospitalists who do not pass certification. Training is a means to competence but does not guarantee it. We believe that training recommendations ought to be considered separately.
METHODS
Working Group Formation
In January 2015, the SHM Board of Directors asked the SHM Education Committee to convene the POCUS Task Force. The purpose of the task force was to develop recommendations on ultrasound guidance for bedside procedures. The SHM Education Committee appointed 3 chairs of the task force: 1 senior member of the SHM Education Committee and 2 POCUS experts. The chairs assembled a task force of 31 members that included 5 working groups, a multispecialty peer review group, and a guideline methodologist (supplemental Appendix 1). Invitation was based on members’ past contributions to SHM POCUS-related activities, up-front commitment, and declared conflicts of interest. Working group members self-identified as “hospitalists,” whereas peer reviewers were nonhospitalists but nationally recognized POCUS physician-leaders specializing in emergency medicine, cardiology, critical care medicine, and anesthesiology. Task force membership was vetted by a chair of the SHM POCUS Task Force and the Director of Education before work began. This position statement was authored by the Credentialing Working Group together with the chairs of the other 4 working groups and a guideline methodologist.
Disclosures
Signed disclosure statements of all task force members were reviewed prior to inclusion on the task force (supplemental Appendix 2); no members received honoraria for participation. Industry representatives did not contribute to the development of the guidelines nor to any conference calls or meetings.
Literature Search Strategy
A literature search was conducted by a biomedical librarian. Records from 1979 to January of 2017 were searched in Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, and Google Scholar (supplemental Appendix 3). Search limiters were English language and adults. Articles were manually screened to exclude nonhuman or endoscopic ultrasound applications. Final article selection was based on working group consensus.
Draft Pathways
The Credentialing Working Group drafted initial and ongoing certification pathways (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The other 4 working groups from the task force were surveyed about the elements and overall appropriateness of these draft pathways. This survey and its results have already been published.12 The Credentialing Working Group then revised the certification pathways by using these survey results and codified individual aspects of these pathways into recommendations.
Development of Position Statement
Based on the Grading of Recommendation Assessment Development and Evaluation methodology, all final article selections were initially rated as either low-quality (observational studies) or unclassifiable (expert opinion).16 These initial ratings were downgraded further because of indirectness, because none of the articles involved the intervention of interest (a credentialing pathway) in a population of interest (hospitalists) measuring the outcomes of interest (patient-level outcomes).
First, the Credentialing Working Group drafted an initial position statement composed of recommendations for credentialing pathways and other general aspects of credentialing. All final article selections were incorporated as references in a draft of the position statement and compiled in a full-text compendium. Second, feedback was provided by the other 4 task force working groups, the task force peer reviewers, and the SHM Education Committee. Feedback was incorporated by the authors of this statement who were the Credentialing Working Group, the chairs of the other 4 working groups, and a guideline methodologist. Third, final suggestions from all members of the SHM POCUS Task Force and SHM Education Committee were incorporated before final approval by the SHM Board of Directors in September 2017.
RESULTS
A total of 1438 references were identified in the original search. Manual selection led to 101 articles, which were incorporated into the following 4 domains with 16 recommendations.
General Credentialing Process
Basic Cognitive Competence Can Be Certified with Written or Oral Examinations
The ABIM defines cognitive competence as having 3 abilities: “(1) to explain indications, contraindications, patient preparation methods, sterile techniques, pain management, proper techniques for handling specimens and fluids obtained, and test results; (2) to recognize and manage complications; and, (3) to clearly explain to a patient all facets of the procedure necessary to obtain informed consent.”1 These abilities can be assessed with written or oral examinations that may be integrated into simulation- or patient-based assessments.
Minimum Thresholds of Experience to Trigger the Timing of a Patient-Based Assessment Should Be Determined by Empirical Methods
Learning curves are highly variable22-25 and even plateaus may not herald basic competence.26 Expert opinion
Hospitalists Should Formally Log All of Their Attempted Procedures, Ideally in an Electronic Medical Record
Simple self-reported numbers of procedures performed often misrepresent actual experience33,34 and do not include periprocedural complications.35,36 Thus, hospitalists should report their experience with logs of all attempted procedures, both successful and unsuccessful. Such logs must include information about supervising providers (if applicable) and patient outcomes, including periprocedural adverse events,37 but they must also remain compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Health Information Technology Service Should Routinely Pull Collations of All Attempted Procedures from Comprehensive Electronic Medical Records
Active surveillance may reduce complications by identifying hospitalists who may benefit from further training.38 In order to facilitate active surveillance systems, documentation (such as a procedure note) should be both integrated into an electronic medical record and protocol driven,39 including procedure technique, ultrasound findings, and any safety events (both near misses and adverse events).
Multiple interacting factors, including environment, patients, baseline skills, training, experience, and skills decay, affect manual competence. Certifications that are based solely on reaching minimum thresholds of experience, even when accurate, are not valid reflections of manual competence,15,40-43 and neither are those based on self-perception.44 Patient-based assessments are, thus, necessary to ensure manual competence.45-48
Certification Assessments of Manual Competence Should Combine 2 Types of Structured Instruments: Checklists and Overall Scores
Assessments based on direct observation are more reliable when formally structured.49,50 Though checklists used in observed structured clinical examinations capture many important manual skills,51-56 they do not completely reflect a hospitalist’s manual competence;57 situations may occur in which a hospitalist meets all the individual items on a checklist but cannot perform an entire procedure with basic competence. Therefore, checklists should be paired with overall scores.58-61 Both checklists and overall scores ought to be obtained from reliable and valid instruments.
Certification Assessments Should Include Feedback
Assessments without feedback are missed learning opportunities.62 Both simulation-63 and patient-based assessments should provide feedback in real time to reinforce effective behaviors and remedy faulty ones.
If Remedial Training is Needed, Simulator-Based Training Can Supplement but Not Replace Patient-Based Training
Supervised simulator-based training allows hospitalists to master basic components of a procedure64 (including orientation to equipment, sequence of operations, dexterity, ultrasound anatomy, and real-time guidance technique) while improving both cognitive and manual skills.42,43,65-71 In addition to their role in basic training (which is outside the scope of this position statement), simulators can be useful for remedial training. To be sufficient for hospitalists who do not pass their patient-based assessments, however, remedial training that begins with simulation must also include patient-based training and assessment.72-75
Initial Credentialing Process
A Minimum Threshold of Experience Should Be Reached before Patient-Based Assessments are Conducted (Figure 1)
Initial Certification Assessments Should Ideally Begin on Simulators
Simulators allow the assurance of safe manual skills, including proper needle insertion techniques and disposal of sharp objects.3,79 If simulators are not available, however, then patient-based training and assessments can still be performed under direct observation. Safe performance of ultrasound-guided procedures during patient-based assessments (without preceding simulator-based assessments) is sufficient to certify manual competence.
Ongoing Credentialing
Certification to Perform Ultrasound-Guided Procedures Should Be Routinely Re-Evaluated During Ongoing Credentialing (Figure 2)
Observed Patient-Based Assessments Should Occur When a Periprocedural Safety Event Occurs that is Potentially Caused by “Provider Error”
Safety events include both near misses and adverse events. Information about both is ideally “flagged” and “pushed” to hospitalist group leaders by active surveillance and reporting systems. Once reviewed, if a safety event is considered to potentially have been caused by provider error (including knowledge- and skill-based errors),83 then the provider who performed the procedure should undergo an observed patient-based assessment.
Simulation-Based Practice Can Supplement Patient-Based Experience for Ongoing Credentialing
When hospitalists do not achieve a minimum threshold of patient-based experience since the antecedent certification, simulation-based training can supplement their patient-based experience.
Credentialing Infrastructure
Hospitalists Themselves Should Not Bear the Financial Costs of Developing and Maintaining Training and Certification Programs for Ultrasound-Guided Procedures
Equipment and personnel costs
Assessors Should Be Unbiased Expert Providers Who Have Demonstrated Mastery in Performance of the Procedure Being Assessed and Regularly Perform It in a Similar Practice Environment
Assessors should be expert providers who regularly perform the ultrasound-guided procedure in a similar practice environment.9,89-94 For example, providers who are not hospitalists but who are experts in an ultrasound-guided procedure and commonly perform it on the hospital wards would be acceptable assessors. However, a radiologist who only performs that procedure in a fully-staffed interventional radiology suite with fluoroscopy or computed tomography guidance would not be an acceptable assessor. More than 1 assessor may balance idiosyncratic assessments;95 but when assessments are well structured, additional assessors are generally not needed.18
If Intramural Assessors Are Not Available, Extramural Assessors May Be Considered
Intramural assessors are generally preferred because of familiarity with the local practice environment, including the available procedure kits and typical patient characteristics. Nevertheless, extramural assessors27,77,85,96 may theoretically provide even more valid assessments than intramural ones because extramural assessors are neither influenced by relationships with local hospitalists nor biased by local hospitalists’ skills.
DISCUSSION
There are no high-quality randomized trials in support of a single credentialing pathway over any other.94,102 The credentialing pathways at the center of this position statement are based on expert opinion. Our methods can be criticized straightaway, therefore, for reliance on the experience and expertise of our working group and task force. Any position statement written without high-quality supportive evidence would be appropriately subject to the same criticism. Without evidence in support of an overall pathway, we codified specific aspects of the pathways into 16 individual recommendations.
Patient-level outcomes do not back these recommendations. Consider, for example, our recommendation that certification assessments be made from structured instruments and not simply from an assessor’s gestalt. Here, the basis is not improved patient-level outcomes from a trial (such as reduced complications or increased procedural success) but improved psychometric performance from reliability studies. The body of evidence for our recommendations is similarly indirect, mostly because the outcomes studied are more proximate and, thus, less meaningful than patient-level outcomes, which are the outcomes of greatest interest but are woefully understudied for clinical competence.17,97,103
The need for high-quality evidence is most pronounced in distinguishing how recommendations should be modified for various settings. Wide variations in resources and patient-mix will make some recommendations impracticable, meaning that they could not be carried out with available resources. For example, our recommendation that credentialing decisions should ultimately rely on certifications made by assessors during patient-based assessments may not be practicable at small, rural hospitals. Such hospitals may not have access to local assessors, and they may not admit enough patients who need the types of ultrasound-guided procedures for which hospitalists seek certification (especially given the need to coordinate the schedules of patients, procedure-performing hospitalists, and assessors).
Regardless of whether some or all hospitalists at a particular hospital are expected to perform bedside procedures, technology may help to improve the practicability of our recommendations. For example, simulators may evolve to replace actual patient-level experience in achieving minimum thresholds. Certification assessments of manual skills may even someday occur entirely on simulators. Real-time high-definition video streaming enhanced with multiple cameras may allow for remote assessments. Until such advances mature, high-quality patient-level data should be sought through additional research to refine our current recommendations.
We hope that these recommendations will improve how basic competence in ultrasound-guided bedside procedures is assessed. Our ultimate goal is to improve how hospitalists perform these procedures. Patient safety is, therefore, considered paramount to cost. Nevertheless, the hospital administrative leaders and privileging committee members on our Task Force concluded that many hospitals have been seeking guidance on credentialing for bedside procedures, and the likely difficulties of implementing our recommendations (including cost) would not be prohibitive at most hospitals, especially given recognition that these recommendations can be tailored to each setting.
Acknowledgments
Collaborators from SHM POCUS Task Force are Saaid Abdel-Ghani, Michael Blaivas, Dan Brotman, Carolina Candotti, Jagriti Chadha, Joel Cho, Ria Dancel, Ricardo Franco, Richard Hoppmann, Susan Hunt, Venkat Kalidindi, Ketino Kobaidze, Josh Lenchus, Benji Mathews, Satyen Nichani, Vicki Noble, Martin Perez, Nitin Puri, Aliaksei Pustavoitau, Sophia Rodgers, Gerard Salame, Daniel Schnobrich, Kirk Spencer, Vivek Tayal, Jeff Bates, Anjali Bhagra, Kreegan Reierson, Robert Arntfield, Paul Mayo, Loretta Grikis.
Disclosure
Brian P. Lucas received funding from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development and Dartmouth SYNERGY, National Institutes of Health, and National Center for Translational Science (UL1TR001086). Nilam Soni received funding from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI) Partnered Evaluation Initiative (HX002263-01A1). The contents of this publication do not represent the views of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
1. American Board of Internal Medicine. Policies and procedures for certification. Philadelphia: American Board of Internal Medicine; 2006.
2. Nichani S, Fitterman N, Lukela M, Crocker J; Society of Hospital Medicine. The Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine 2017 Revision. Section 2: Procedures. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(4 Suppl 1):S44-S54 PubMed
3. Lucas BP, Asbury JK, Franco-Sadud R. Training future hospitalists with simulators: a needed step toward accessible, expertly performed bedside procedures. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):395-396. PubMed
4. Schnobrich DJ, Gladding S, Olson APJ, Duran-Nelson A. Point-of-care ultrasound in internal medicine: a national survey of educational leadership. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(3):498-502. PubMed
5. Brown GM, Otremba M, Devine LA, Gray C, Millington SJ, Ma IW. Defining competencies for ultrasound-guided bedside procedures: consensus opinions from Canadian physicians. J Ultrasound Med. 2016;35(1):129-141. PubMed
6. Vaisman A, Cram P. Procedural competence among faculty in academic health centers: challenges and future directions. Acad Med. 2017;92(1):31-34. PubMed
7. Kreisman RD. With ED ultrasound, credentialing is at issue. ED Legal Letter. 2010;21:102-103.
8. Goudie AM. Credentialing a new skill: what should the standard be for emergency department ultrasound in Australasia? Emerg Med Australas. 2010;22:263-264. PubMed
9. Maizel J, Guyomarc HL, Henon P, et al. Residents learning ultrasound-guided catheterization are not sufficiently skilled to use landmarks. Crit Care. 2014;18(1):R36. doi:10.1186/cc13741. PubMed
10. American College of Emergency Physicians. Ultrasound guidelines: emergency, point-of-care, and clinical ultrasound guidelines in medicine. Ann Emerg Med. 2017;69(5):e27-e54. PubMed
11. Amini R, Adhikari S, Fiorello A. Ultrasound competency assessment in emergency medicine residency programs. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21(7):799-801. PubMed
12. Jensen T, Soni NJ, Tierney DM, Lucas BP. Hospital privileging practices for bedside procedures: a survey of hospitalist experts. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(10):836-839. PubMed
13. Chang W. Is hospitalist proficiency in bedside procedures in decline? The Hospitalist. 2012. http://www.the-hospitalist.org/hospitalist/article/125236/patient-safety/hospitalist-proficiency-bedside-procedures-decline. Accessed September 30, 2017.
14. Barsuk JH, Feinglass J, Kozmic SE, Hohmann SF, Ganger D, Wayne DB. Specialties Performing Paracentesis Procedures at University Hospitals: Implications for Training and Certification. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(3):162-168. PubMed
15. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Feinglass J, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Residents’ Procedural Experience Does Not Ensure Competence: A Research Synthesis. J Grad Med Educ. 2017;9(2):201-208. PubMed
16. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schunemann HJ, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):401-406. PubMed
17. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, et al. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence—indirectness. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(12):1303-1310. PubMed
18. Miller GE. The assessment of clinical skills/competence/performance. Acad Med. 1990;65(9 Suppl):S63-S67. PubMed
19. Grover S, Currier PF, Elinoff JM, Mouchantaf KJ, Katz JT, McMahon GT. Development of a test to evaluate residents knowledge of medical procedures. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):430-432. PubMed
20. Millington SJ, Wong RY, Kassen BO, Roberts JM, Ma IWY. Improving internal medicine residents’ performance, knowledge, and confidence in central venous catheterization using simulators. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):410-416. PubMed
21. Lenchus JD, Carvalho CM, Ferreri K, et al. Filling the void: defining invasive bedside procedural competency for internal medicine residents. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(4):605-612. PubMed
22. Heegeman DJ, Kieke B Jr. Learning curves, credentialing, and the need for ultrasound fellowships. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10:404-405. PubMed
23. Jang TB, Ruggeri W, Dyne P, Kaji AH. The learning curve of resident physicians using emergency ultrasonography for cholelithaisis and cholecystitis. Acad Emerg Med. 2010;17(11):1247-1252. PubMed
24. Akhtar MI, Hamid M. Ultrasound guided central venous access; a review of literature. Anaesth Pain Intensive Care. 2015;19:317-322.
25. Bahl A, Yunker A. Assessment of the numbers–based model for evaluation of resident competency in emergency ultrasound core applications. J Emerg Med Trauma Acute Care. 2015;2015(5). doi:10.5339/jemtac.2015.5
26. Cazes N, Desmots F, Geffroy Y, Renard A, Leyral J, Chaumoitre K. Emergency ultrasound: a prospective study on sufficient adequate training for military doctors. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94(11):1109-1115. PubMed
27. Arntfield RT, Millington SJ, Ainsworth CD, et al. Canadian recommendations for critical care ultrasound training and competency for the Canadian critical care society. Can Respir J. 2014;21(16):341-345.
28. Bolsin S, Colson M. The use of the Cusum technique in the assessment of trainee competence in new procedures. Int J Qual Health Care. 2000;12(5):433-438. PubMed
29. de Oliveira Filho GR, Helayel PE, da Conceição DB, Garzel IS, Pavei P, Ceccon MS. Learning curves and mathematical models for interventional ultrasound basic skills. Anaesth Analg. 2008;106(2):568-573. PubMed
30. Starkie T, Drake EJ. Assessment of procedural skills training and performance in anesthesia using cumulative sum analysis (cusum). Can J Anaesth. 2013;60(12):1228-1239. PubMed
31. Tierney D. Competency cut-point identification derived from a mastery learning cohort approach: A hybrid model. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:S19.
32. Rankin JH, Elkhunovich MA, Rangarajan V, Chilstrom M, Mailhot T. Learning Curves for Ultrasound Assessment of Lumbar Puncture Insertion Sites: When is Competency Established? J Emerg Med. 2016;51(1):55-62. PubMed
33. Klasko SK, Cummings RV, Glazerman LR. Resident data collection: Do the numbers add up? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172(4 Pt 1):1312-1316. PubMed
34. Tierney D. Development & analysis of a mobile POCUS tracking tool. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41(suppl 4):S31.
35. Sethi MV, Zimmer J, Ure B, Lacher M. Prospective assessment of complications on a daily basis is essential to determine morbidity and mortality in routine pediatric surgery. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51(4):630-633. PubMed
36. Fisher JC, Kuenzler KA, Tomita SS, Sinha P, Shah P, Ginsburg HB. Increased capture of pediatric surgical complications utilizing a novel case-log web application to enhance quality improvement. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52(1):166-171. PubMed
37. Rethans JJ, Norcini JJ, Barón-Maldonado M, et al. The relationship between competence and performance: implications for assessing practice performance. Med Educ. 2002;36(10):901-909. PubMed
38. Duncan DR, Morgenthaler TI, Ryu JH, Daniels CE. Reducing iatrogenic risk in thoracentesis: establishing best practice via experiential training in a zero-risk environment. Chest. 2009;135(5):1315-1320. PubMed
39. Society of Critical Care Medicine Ultrasound Certification Task Force. Recommendations for achieving and maintaining competence and credentialing in critical care ultrasound with focused cardiac ultrasound and advanced critical care echocardiography. http://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/Documents/Critical%20Care%20Ultrasound.pdf Published 2013. Accessed February 2, 2017.
40. Carraccio C, Wolfsthal SD, Englander R, Ferentz K, Martin C. Shifting paradigms: from Flexner to competencies. Acad Med. 2002;77(5):361-367. PubMed
41. Clark EG, Paparello JJ, Wayne DB, et al. Use of a national continuing medical education meeting to provide simulation-based training in temporary hemodialysis catheter insertion skills: a pre-test post-test study. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2014;1:25-31. PubMed
42. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Caprio T, McGaghie WC, Simuni T, Wayne DB. Simulation-based education with mastery learning improves residents’ lumbar puncture skills. Neurology. 2012;79(2):132-137. PubMed
43. Barsuk JH, McGaghie WC, Cohen ER, O’Leary KJ, Wayne DB. Simulation-based mastery learning reduces complications during central venous catheter insertion in a medical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(10):2697-2701. PubMed
44. Davis DA, Mazmanian PE, Fordis M, Van Harrison R, Thorpe KE, Perrier L. Accuracy of physician self-assessment compared with observed measures of competence: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1094-1102. PubMed
45. Shah J, Darzi A. Surgical skills assessment: an ongoing debate. BJU Int. 2001;88(7):655-660. PubMed
46. Lamperti M, Bodenham AR, Pittiruti M, et al. International evidence-based recommendations on ultrasound-guided vascular access. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(7):1105-1117. PubMed
47. Tolsgaard MG, Todsen T, Sorensen JL, et al. International multispecialty consensus on how to evaluate ultrasound competence: a Delphi consensus survey. PLOS One. 2013;8(2):e57687. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057687 PubMed
48. Moureau N, Laperti M, Kelly LJ, et al. Evidence-based consensus on the insertion of central venous access devices: definition of minimal requirements for training. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110(3):347-356. PubMed
49. Feldman LS, Hagarty S, Ghitulescu G, Stanbridge D, Fried GM. Relationship between objective assessment of technical skills and subjective in-training evaluations in surgical residents. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198(1):105-110. PubMed
50. Baker S, Willey B, Mitchell C. The attempt to standardize technical and analytic competence in sonography education. J Diagn Med Sonogr. 2011;27(5):203-211.
51. Tolsgaard MG, Ringsted C, Dreisler E, et al. Reliable and valid assessment of ultrasound operator competence in obstetrics and gynecology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014;43(4):437-443. PubMed
52. Rice J, Crichlow A, Baker M, et al. An assessment tool for the placement of ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous access. J Grad Med Educ. 2016;8(2):202-207. PubMed
53. Hartman N, Wittler M, Askew K, Hiestand B, Manthey D. Validation of a performance checklist for ultrasound-guided internal jubular central lines for use in procedural instruction and assessment. Postgrad Med J. 2017;93(1096):67-70. PubMed
54. Primdahl SC, Todsen T, Clemmesen L, et al. Rating scale for the assessment of competence in ultrasound-guided peripheral vascular access—a Delphi Consensus Study. J Vasc Access. 2016;17(5):440-445.
55. Berg D, Berg K, Riesenberg LA, et al. The development of a validated checklist for thoracentesis: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2013;28(3):220-226. PubMed
56. Berg K, Riesenberg LA, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for radial arterial line placement: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2014;29(3):242-246. PubMed
57. Walzak A, Bacchus M, Schaefer MP, et al. Diagnosing technical competence in six bedside procedures: comparing checklists and a global rating scale in the assessment of resident performance. Acad Med. 2015;90(8):1100-1108. PubMed
58. Riesenberg LA, Berg K, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for femoral venous catheterization: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2014;29(5):445-450. PubMed
59. Riesenberg LA, Berg K, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for paracentesis: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2013;28(3):227-231. PubMed
60. Huang GC, Newman LR, Schwartzstein RM, et al. Procedural competence in internal medicine residents: validity of a central venous catheter insertion assessment instrument. Acad Med. 2009;84(8):1127-1134. PubMed
61. Salamonsen M, McGrath D, Steiler G, et al. A new instrument to assess physician skill at thoracic ultrasound, including pleural effusion markup. Chest. 2013;144(3):930-934. PubMed
62. Boniface K, Yarris LM. Emergency ultrasound: Leveling the training and assessment landscape. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21(7):803-805. PubMed
63. Boyle E, O’Keeffe D, Naughton P, Hill A, McDonnell C, Moneley D. The importance of expert feedback during endovascular simulator training. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54(1):240-248.e1. PubMed
64. Langhan TS, Rigby IJ, Walker IW, Howes D, Donnon T, Lord JA. Simulation-based training in critical resuscitation procedures improves residents’ competence. CJEM. 2009;11(6):535-539. PubMed
65. Barsuk JH, McGaghie WC, Cohen ER, Balachandran JS, Wayne DB. Use of simulation-based mastery learning to improve the quality of central venous catheter placement in a medical intensive care unit. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):397-403. PubMed
66. Lenchus JD. End of the “see one, do one, teach one” era: the next generation of invasive bedside procedural instruction. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2010;110(6):340-346. PubMed
67. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Vozenilek JA, O’Connor LM, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Simulation-based education with mastery learning improves paracentesis skills. J Grad Med Educ. 2012;4(1):23-27. PubMed
68. McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Cohen ER, Barsuk JH, Wayne DB. Does simulation-based medical education with deliberate practice yield better results than traditional clinical education? A meta-analytic comparative review of the evidence. Acad Med. 2011;86(6):706-711. PubMed
69. Ross JG. Simulation and psychomotor skill acquisition: A review of the literature. Clin Simul Nurs. 2012;8(9):e429-e435.
70. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Potts S, et al. Dissemination of a simulation-based mastery learning intervention reduces central line-associated bloodstream infections. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(9):749-756. PubMed
71. McSparron JI, Michaud GC, Gordan PL, et al. Simulation for skills-based education in pulmonary and critical care medicine. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(4):579-586. PubMed
72. Kneebone RL, Scott W, Darzi A, Horrocks M. Simulation and clinical practice: strengthening the relationship. Med Educ. 2004;38(10):1095-1102. PubMed
73. Mema B, Harris I. The barriers and facilitators to transfer of ultrasound-guided central venous line skills from simulation to practice: exploring perceptions of learners and supervisors. Teach Learn Med. 2016;28(2):115-124. PubMed
74. Castanelli DJ. The rise of simulation in technical skills teaching and the implications for training novices in anaestheia. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2009;37(6):903-910. PubMed
75. McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Barsuk JH, Wayne DB. A critical review of simulation-based mastery learning with translational outcomes. Med Educ. 2014;48(4):375-385. PubMed
76. Langlois SLP. Focused ultrasound training for clinicians. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(5 suppl):S138-S143.
77. Price S, Via G, Sloth E, et al. Echocardiography practice, training and accreditation in the intesive care: document for the World Interactive Network Focused on Critical Ultrasound (WINFOCUS). Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008;6:49-83. PubMed
78. Blehar DJ, Barton B, Gaspari RJ. Learning curves in emergency ultrasound education. Acad Emerg Med. 2015;22(5):574-582. PubMed
79. Ault MJ, Rosen BT, Ault B. The use of tissue models for vascular access training. Phase I of the procedural patient safety initiative. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(5):514-517. PubMed
80. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Long-term retention of central venous catheter insertion skills after simulation-based mastery learning. Acad Med. 2010;85(10 Suppl):S9-S12. PubMed
81. Sliman Sean, Amundson S, Shaw D, Phan JN, Waalen J, Kimura B. Recently-acquired cardiac ultrasound skills are rapidly lost when not used: implications for competency in physician imaging. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(13S):1569.
82. Kessler CS, Leone KA. The current state of core competency assessment in emergency medicine and a future research agenda: recommendations of the working group on assessment of observable learner performance. Acad Emerg Med. 2012;19(12):1354-1359. PubMed
83. Chang A, Schyve PM, Croteau RJ, O’Leary DS, Loeb JM. The JCAHO patient safety event taxonomy: a standardized terminology and classification schema for near misses and adverse events. Int J Qual Health Care. 2005;17(2):95-105. PubMed
84. Sawyer T, White M, Zaveri P, et al. Learn, see, practice, prove, do, maintain: an evidence-based pedagogical framework for procedural skill training in medicine. Acad Med. 2015;90(8):1025-1033. PubMed
85. Das D, Kapoor M, Brown C, Ndubuisi A, Gupta S. Current status of emergency department attending physician ultrasound credentialing and quality assurance in the United States. Crit Ultrasound J. 2016;8(1):6-12. PubMed
86. Ndubuisi AK, Gupta S, Brown C, Das D. Current status and future issues in emergency department attending physician ultrasound credentialing. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;64(45):S27-S28.
87. Tandy Tk, Hoffenberg S. Emergency department ultrasound services by emergency physicians: model for gaining hospital approval. Ann Emerg Med. 1997;29(3):367-374. PubMed
88. Lewiss RE, Saul T, Del Rios M. Acquiring credentials in bedside ultrasound: a cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open. 2013;3:e003502. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003502 PubMed
89. Lanoix R. Credentialing issues in emergency ultrasonography. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1997;15(4):913-920. PubMed
90. Scalea T, Rodriquez A, Chiu WC, et al. Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST): results from an international consensus conference. J Trauma. 1999;46(3):466-472. PubMed
91. Hertzberg BS, Kliewer MA, Bowie JD, et al. Physician training requirements in sonography: how many cases are needed for competence? AJR. 2000;174(5):1221-1227. PubMed
92. Blaivas M, Theodoro DL, Sierzenski P. Proliferation of ultrasound fellowships in emergency medicine: how do we ensure future experts are expertly trained? Acad Emerg Med. 2002;9(8):863-864. PubMed
93. Bodenham AR. Editorial II: Ultrasound imaging by anaesthetists: training and accreditation issues. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96(4):414-417. PubMed
94. Williamson JP, Twaddell SH, Lee YCG, et al. Thoracic ultrasound recognition of competence: A position paper of the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand. Respirology. 2017;22(2):405-408. PubMed
95. Harrison G. Summative clinical competency assessment: a survey of ultrasound practitioners’ views. Ultrasound. 2015;23(1):11-17. PubMed
96. Evans LV, Morse JL, Hamann CJ, Osborne M, Lin Z, D'Onofrio G. The development of an independent rater system to assess residents' competence in invasive procedures. Acad Med. 2009;84(8):1135-1143. PubMed
97. Wass V, Van der Vleuten C, Shatzer J, Jones R. Assessment of clinical competence. Lancet. 2001;357(9260):945-949. PubMed
98. Arntfield RT. The utility of remote supervision with feedback as a method to deliver high-volume critical care ultrasound training. J Crit Care. 2015;30(2):441.e1-e6. PubMed
99. Akhtar S, Theodoro D, Gaspari R, et al. Resident training in emergency ultrasound: consensus recommendations from the 2008 Council of Emergency Residency Directors Conference. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16:S32-S36. PubMed
100. Yu E. The assessment of technical skills in a cardiology training program: is the ITER sufficient? Can J Cardiol. 2000;16(4):457-462. PubMed
101. Todsen T, Tolsgaard MG, Olsen BH, et al. Reliable and valid assessment of point-of-care ultrasonography. Ann Surg. 2015;261(2):309-315. PubMed
102. Stein JC, Nobay F. Emergency department ultrasound credentialing: a sample policy and procedure. J Emerg Med. 2009;37(2):153-159. PubMed
103. Chen FM. Burstin H, Huntington J. The importance of clinical outcomes in medical education research. Med Educ. 2005;39(4):350-351. PubMed
104. Dressler DD, Pistoria MJ, Budnitz TL, McKean SCW, Amin AN. Core competencies in hospital medicine: development and methodology. J Hosp Med. 2006;1:48-56. PubMed
105. ten Cate O. Nuts and bolts of entrustable professional activities. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(1):157-158. PubMed
106. Castillo J, Caruana CJ, Wainwright D. The changing concept of competence and categorisation of learning outcomes in Europe: Implications for the design of higher education radiography curricula at the European level. Radiography. 2011;17(3):230-234.
107. Goldstein SR. Accreditation, certification: why all the confusion? Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110(6):1396-1398. PubMed
108. Moore CL. Credentialing and reimbursement in point-of-care ultrasound. Clin Pediatr Emerg Med. 2011;12(1):73-77. PubMed
109. ten Cate O, Scheele F. Competency-based postgraduate training: can we bridge the gap between theory and clinical practice? Acad Med. 2007;82(6):542-547. PubMed
110. Abuhamad AZ, Benacerraf BR, Woletz P, Burke BL. The accreditation of ultrasound practices: impact on compliance with minimum performance guidelines. J Ultrasound Med. 2004;23(8):1023-1029. PubMed
1. American Board of Internal Medicine. Policies and procedures for certification. Philadelphia: American Board of Internal Medicine; 2006.
2. Nichani S, Fitterman N, Lukela M, Crocker J; Society of Hospital Medicine. The Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine 2017 Revision. Section 2: Procedures. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(4 Suppl 1):S44-S54 PubMed
3. Lucas BP, Asbury JK, Franco-Sadud R. Training future hospitalists with simulators: a needed step toward accessible, expertly performed bedside procedures. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):395-396. PubMed
4. Schnobrich DJ, Gladding S, Olson APJ, Duran-Nelson A. Point-of-care ultrasound in internal medicine: a national survey of educational leadership. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(3):498-502. PubMed
5. Brown GM, Otremba M, Devine LA, Gray C, Millington SJ, Ma IW. Defining competencies for ultrasound-guided bedside procedures: consensus opinions from Canadian physicians. J Ultrasound Med. 2016;35(1):129-141. PubMed
6. Vaisman A, Cram P. Procedural competence among faculty in academic health centers: challenges and future directions. Acad Med. 2017;92(1):31-34. PubMed
7. Kreisman RD. With ED ultrasound, credentialing is at issue. ED Legal Letter. 2010;21:102-103.
8. Goudie AM. Credentialing a new skill: what should the standard be for emergency department ultrasound in Australasia? Emerg Med Australas. 2010;22:263-264. PubMed
9. Maizel J, Guyomarc HL, Henon P, et al. Residents learning ultrasound-guided catheterization are not sufficiently skilled to use landmarks. Crit Care. 2014;18(1):R36. doi:10.1186/cc13741. PubMed
10. American College of Emergency Physicians. Ultrasound guidelines: emergency, point-of-care, and clinical ultrasound guidelines in medicine. Ann Emerg Med. 2017;69(5):e27-e54. PubMed
11. Amini R, Adhikari S, Fiorello A. Ultrasound competency assessment in emergency medicine residency programs. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21(7):799-801. PubMed
12. Jensen T, Soni NJ, Tierney DM, Lucas BP. Hospital privileging practices for bedside procedures: a survey of hospitalist experts. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(10):836-839. PubMed
13. Chang W. Is hospitalist proficiency in bedside procedures in decline? The Hospitalist. 2012. http://www.the-hospitalist.org/hospitalist/article/125236/patient-safety/hospitalist-proficiency-bedside-procedures-decline. Accessed September 30, 2017.
14. Barsuk JH, Feinglass J, Kozmic SE, Hohmann SF, Ganger D, Wayne DB. Specialties Performing Paracentesis Procedures at University Hospitals: Implications for Training and Certification. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(3):162-168. PubMed
15. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Feinglass J, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Residents’ Procedural Experience Does Not Ensure Competence: A Research Synthesis. J Grad Med Educ. 2017;9(2):201-208. PubMed
16. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schunemann HJ, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):401-406. PubMed
17. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, et al. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence—indirectness. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(12):1303-1310. PubMed
18. Miller GE. The assessment of clinical skills/competence/performance. Acad Med. 1990;65(9 Suppl):S63-S67. PubMed
19. Grover S, Currier PF, Elinoff JM, Mouchantaf KJ, Katz JT, McMahon GT. Development of a test to evaluate residents knowledge of medical procedures. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):430-432. PubMed
20. Millington SJ, Wong RY, Kassen BO, Roberts JM, Ma IWY. Improving internal medicine residents’ performance, knowledge, and confidence in central venous catheterization using simulators. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):410-416. PubMed
21. Lenchus JD, Carvalho CM, Ferreri K, et al. Filling the void: defining invasive bedside procedural competency for internal medicine residents. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(4):605-612. PubMed
22. Heegeman DJ, Kieke B Jr. Learning curves, credentialing, and the need for ultrasound fellowships. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10:404-405. PubMed
23. Jang TB, Ruggeri W, Dyne P, Kaji AH. The learning curve of resident physicians using emergency ultrasonography for cholelithaisis and cholecystitis. Acad Emerg Med. 2010;17(11):1247-1252. PubMed
24. Akhtar MI, Hamid M. Ultrasound guided central venous access; a review of literature. Anaesth Pain Intensive Care. 2015;19:317-322.
25. Bahl A, Yunker A. Assessment of the numbers–based model for evaluation of resident competency in emergency ultrasound core applications. J Emerg Med Trauma Acute Care. 2015;2015(5). doi:10.5339/jemtac.2015.5
26. Cazes N, Desmots F, Geffroy Y, Renard A, Leyral J, Chaumoitre K. Emergency ultrasound: a prospective study on sufficient adequate training for military doctors. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94(11):1109-1115. PubMed
27. Arntfield RT, Millington SJ, Ainsworth CD, et al. Canadian recommendations for critical care ultrasound training and competency for the Canadian critical care society. Can Respir J. 2014;21(16):341-345.
28. Bolsin S, Colson M. The use of the Cusum technique in the assessment of trainee competence in new procedures. Int J Qual Health Care. 2000;12(5):433-438. PubMed
29. de Oliveira Filho GR, Helayel PE, da Conceição DB, Garzel IS, Pavei P, Ceccon MS. Learning curves and mathematical models for interventional ultrasound basic skills. Anaesth Analg. 2008;106(2):568-573. PubMed
30. Starkie T, Drake EJ. Assessment of procedural skills training and performance in anesthesia using cumulative sum analysis (cusum). Can J Anaesth. 2013;60(12):1228-1239. PubMed
31. Tierney D. Competency cut-point identification derived from a mastery learning cohort approach: A hybrid model. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:S19.
32. Rankin JH, Elkhunovich MA, Rangarajan V, Chilstrom M, Mailhot T. Learning Curves for Ultrasound Assessment of Lumbar Puncture Insertion Sites: When is Competency Established? J Emerg Med. 2016;51(1):55-62. PubMed
33. Klasko SK, Cummings RV, Glazerman LR. Resident data collection: Do the numbers add up? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172(4 Pt 1):1312-1316. PubMed
34. Tierney D. Development & analysis of a mobile POCUS tracking tool. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41(suppl 4):S31.
35. Sethi MV, Zimmer J, Ure B, Lacher M. Prospective assessment of complications on a daily basis is essential to determine morbidity and mortality in routine pediatric surgery. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51(4):630-633. PubMed
36. Fisher JC, Kuenzler KA, Tomita SS, Sinha P, Shah P, Ginsburg HB. Increased capture of pediatric surgical complications utilizing a novel case-log web application to enhance quality improvement. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52(1):166-171. PubMed
37. Rethans JJ, Norcini JJ, Barón-Maldonado M, et al. The relationship between competence and performance: implications for assessing practice performance. Med Educ. 2002;36(10):901-909. PubMed
38. Duncan DR, Morgenthaler TI, Ryu JH, Daniels CE. Reducing iatrogenic risk in thoracentesis: establishing best practice via experiential training in a zero-risk environment. Chest. 2009;135(5):1315-1320. PubMed
39. Society of Critical Care Medicine Ultrasound Certification Task Force. Recommendations for achieving and maintaining competence and credentialing in critical care ultrasound with focused cardiac ultrasound and advanced critical care echocardiography. http://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/Documents/Critical%20Care%20Ultrasound.pdf Published 2013. Accessed February 2, 2017.
40. Carraccio C, Wolfsthal SD, Englander R, Ferentz K, Martin C. Shifting paradigms: from Flexner to competencies. Acad Med. 2002;77(5):361-367. PubMed
41. Clark EG, Paparello JJ, Wayne DB, et al. Use of a national continuing medical education meeting to provide simulation-based training in temporary hemodialysis catheter insertion skills: a pre-test post-test study. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2014;1:25-31. PubMed
42. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Caprio T, McGaghie WC, Simuni T, Wayne DB. Simulation-based education with mastery learning improves residents’ lumbar puncture skills. Neurology. 2012;79(2):132-137. PubMed
43. Barsuk JH, McGaghie WC, Cohen ER, O’Leary KJ, Wayne DB. Simulation-based mastery learning reduces complications during central venous catheter insertion in a medical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(10):2697-2701. PubMed
44. Davis DA, Mazmanian PE, Fordis M, Van Harrison R, Thorpe KE, Perrier L. Accuracy of physician self-assessment compared with observed measures of competence: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1094-1102. PubMed
45. Shah J, Darzi A. Surgical skills assessment: an ongoing debate. BJU Int. 2001;88(7):655-660. PubMed
46. Lamperti M, Bodenham AR, Pittiruti M, et al. International evidence-based recommendations on ultrasound-guided vascular access. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(7):1105-1117. PubMed
47. Tolsgaard MG, Todsen T, Sorensen JL, et al. International multispecialty consensus on how to evaluate ultrasound competence: a Delphi consensus survey. PLOS One. 2013;8(2):e57687. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057687 PubMed
48. Moureau N, Laperti M, Kelly LJ, et al. Evidence-based consensus on the insertion of central venous access devices: definition of minimal requirements for training. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110(3):347-356. PubMed
49. Feldman LS, Hagarty S, Ghitulescu G, Stanbridge D, Fried GM. Relationship between objective assessment of technical skills and subjective in-training evaluations in surgical residents. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198(1):105-110. PubMed
50. Baker S, Willey B, Mitchell C. The attempt to standardize technical and analytic competence in sonography education. J Diagn Med Sonogr. 2011;27(5):203-211.
51. Tolsgaard MG, Ringsted C, Dreisler E, et al. Reliable and valid assessment of ultrasound operator competence in obstetrics and gynecology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014;43(4):437-443. PubMed
52. Rice J, Crichlow A, Baker M, et al. An assessment tool for the placement of ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous access. J Grad Med Educ. 2016;8(2):202-207. PubMed
53. Hartman N, Wittler M, Askew K, Hiestand B, Manthey D. Validation of a performance checklist for ultrasound-guided internal jubular central lines for use in procedural instruction and assessment. Postgrad Med J. 2017;93(1096):67-70. PubMed
54. Primdahl SC, Todsen T, Clemmesen L, et al. Rating scale for the assessment of competence in ultrasound-guided peripheral vascular access—a Delphi Consensus Study. J Vasc Access. 2016;17(5):440-445.
55. Berg D, Berg K, Riesenberg LA, et al. The development of a validated checklist for thoracentesis: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2013;28(3):220-226. PubMed
56. Berg K, Riesenberg LA, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for radial arterial line placement: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2014;29(3):242-246. PubMed
57. Walzak A, Bacchus M, Schaefer MP, et al. Diagnosing technical competence in six bedside procedures: comparing checklists and a global rating scale in the assessment of resident performance. Acad Med. 2015;90(8):1100-1108. PubMed
58. Riesenberg LA, Berg K, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for femoral venous catheterization: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2014;29(5):445-450. PubMed
59. Riesenberg LA, Berg K, Berg D, et al. The development of a validated checklist for paracentesis: preliminary results. Am J Med Qual. 2013;28(3):227-231. PubMed
60. Huang GC, Newman LR, Schwartzstein RM, et al. Procedural competence in internal medicine residents: validity of a central venous catheter insertion assessment instrument. Acad Med. 2009;84(8):1127-1134. PubMed
61. Salamonsen M, McGrath D, Steiler G, et al. A new instrument to assess physician skill at thoracic ultrasound, including pleural effusion markup. Chest. 2013;144(3):930-934. PubMed
62. Boniface K, Yarris LM. Emergency ultrasound: Leveling the training and assessment landscape. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21(7):803-805. PubMed
63. Boyle E, O’Keeffe D, Naughton P, Hill A, McDonnell C, Moneley D. The importance of expert feedback during endovascular simulator training. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54(1):240-248.e1. PubMed
64. Langhan TS, Rigby IJ, Walker IW, Howes D, Donnon T, Lord JA. Simulation-based training in critical resuscitation procedures improves residents’ competence. CJEM. 2009;11(6):535-539. PubMed
65. Barsuk JH, McGaghie WC, Cohen ER, Balachandran JS, Wayne DB. Use of simulation-based mastery learning to improve the quality of central venous catheter placement in a medical intensive care unit. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(7):397-403. PubMed
66. Lenchus JD. End of the “see one, do one, teach one” era: the next generation of invasive bedside procedural instruction. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2010;110(6):340-346. PubMed
67. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Vozenilek JA, O’Connor LM, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Simulation-based education with mastery learning improves paracentesis skills. J Grad Med Educ. 2012;4(1):23-27. PubMed
68. McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Cohen ER, Barsuk JH, Wayne DB. Does simulation-based medical education with deliberate practice yield better results than traditional clinical education? A meta-analytic comparative review of the evidence. Acad Med. 2011;86(6):706-711. PubMed
69. Ross JG. Simulation and psychomotor skill acquisition: A review of the literature. Clin Simul Nurs. 2012;8(9):e429-e435.
70. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, Potts S, et al. Dissemination of a simulation-based mastery learning intervention reduces central line-associated bloodstream infections. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(9):749-756. PubMed
71. McSparron JI, Michaud GC, Gordan PL, et al. Simulation for skills-based education in pulmonary and critical care medicine. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(4):579-586. PubMed
72. Kneebone RL, Scott W, Darzi A, Horrocks M. Simulation and clinical practice: strengthening the relationship. Med Educ. 2004;38(10):1095-1102. PubMed
73. Mema B, Harris I. The barriers and facilitators to transfer of ultrasound-guided central venous line skills from simulation to practice: exploring perceptions of learners and supervisors. Teach Learn Med. 2016;28(2):115-124. PubMed
74. Castanelli DJ. The rise of simulation in technical skills teaching and the implications for training novices in anaestheia. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2009;37(6):903-910. PubMed
75. McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Barsuk JH, Wayne DB. A critical review of simulation-based mastery learning with translational outcomes. Med Educ. 2014;48(4):375-385. PubMed
76. Langlois SLP. Focused ultrasound training for clinicians. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(5 suppl):S138-S143.
77. Price S, Via G, Sloth E, et al. Echocardiography practice, training and accreditation in the intesive care: document for the World Interactive Network Focused on Critical Ultrasound (WINFOCUS). Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008;6:49-83. PubMed
78. Blehar DJ, Barton B, Gaspari RJ. Learning curves in emergency ultrasound education. Acad Emerg Med. 2015;22(5):574-582. PubMed
79. Ault MJ, Rosen BT, Ault B. The use of tissue models for vascular access training. Phase I of the procedural patient safety initiative. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(5):514-517. PubMed
80. Barsuk JH, Cohen ER, McGaghie WC, Wayne DB. Long-term retention of central venous catheter insertion skills after simulation-based mastery learning. Acad Med. 2010;85(10 Suppl):S9-S12. PubMed
81. Sliman Sean, Amundson S, Shaw D, Phan JN, Waalen J, Kimura B. Recently-acquired cardiac ultrasound skills are rapidly lost when not used: implications for competency in physician imaging. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(13S):1569.
82. Kessler CS, Leone KA. The current state of core competency assessment in emergency medicine and a future research agenda: recommendations of the working group on assessment of observable learner performance. Acad Emerg Med. 2012;19(12):1354-1359. PubMed
83. Chang A, Schyve PM, Croteau RJ, O’Leary DS, Loeb JM. The JCAHO patient safety event taxonomy: a standardized terminology and classification schema for near misses and adverse events. Int J Qual Health Care. 2005;17(2):95-105. PubMed
84. Sawyer T, White M, Zaveri P, et al. Learn, see, practice, prove, do, maintain: an evidence-based pedagogical framework for procedural skill training in medicine. Acad Med. 2015;90(8):1025-1033. PubMed
85. Das D, Kapoor M, Brown C, Ndubuisi A, Gupta S. Current status of emergency department attending physician ultrasound credentialing and quality assurance in the United States. Crit Ultrasound J. 2016;8(1):6-12. PubMed
86. Ndubuisi AK, Gupta S, Brown C, Das D. Current status and future issues in emergency department attending physician ultrasound credentialing. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;64(45):S27-S28.
87. Tandy Tk, Hoffenberg S. Emergency department ultrasound services by emergency physicians: model for gaining hospital approval. Ann Emerg Med. 1997;29(3):367-374. PubMed
88. Lewiss RE, Saul T, Del Rios M. Acquiring credentials in bedside ultrasound: a cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open. 2013;3:e003502. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003502 PubMed
89. Lanoix R. Credentialing issues in emergency ultrasonography. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1997;15(4):913-920. PubMed
90. Scalea T, Rodriquez A, Chiu WC, et al. Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST): results from an international consensus conference. J Trauma. 1999;46(3):466-472. PubMed
91. Hertzberg BS, Kliewer MA, Bowie JD, et al. Physician training requirements in sonography: how many cases are needed for competence? AJR. 2000;174(5):1221-1227. PubMed
92. Blaivas M, Theodoro DL, Sierzenski P. Proliferation of ultrasound fellowships in emergency medicine: how do we ensure future experts are expertly trained? Acad Emerg Med. 2002;9(8):863-864. PubMed
93. Bodenham AR. Editorial II: Ultrasound imaging by anaesthetists: training and accreditation issues. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96(4):414-417. PubMed
94. Williamson JP, Twaddell SH, Lee YCG, et al. Thoracic ultrasound recognition of competence: A position paper of the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand. Respirology. 2017;22(2):405-408. PubMed
95. Harrison G. Summative clinical competency assessment: a survey of ultrasound practitioners’ views. Ultrasound. 2015;23(1):11-17. PubMed
96. Evans LV, Morse JL, Hamann CJ, Osborne M, Lin Z, D'Onofrio G. The development of an independent rater system to assess residents' competence in invasive procedures. Acad Med. 2009;84(8):1135-1143. PubMed
97. Wass V, Van der Vleuten C, Shatzer J, Jones R. Assessment of clinical competence. Lancet. 2001;357(9260):945-949. PubMed
98. Arntfield RT. The utility of remote supervision with feedback as a method to deliver high-volume critical care ultrasound training. J Crit Care. 2015;30(2):441.e1-e6. PubMed
99. Akhtar S, Theodoro D, Gaspari R, et al. Resident training in emergency ultrasound: consensus recommendations from the 2008 Council of Emergency Residency Directors Conference. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16:S32-S36. PubMed
100. Yu E. The assessment of technical skills in a cardiology training program: is the ITER sufficient? Can J Cardiol. 2000;16(4):457-462. PubMed
101. Todsen T, Tolsgaard MG, Olsen BH, et al. Reliable and valid assessment of point-of-care ultrasonography. Ann Surg. 2015;261(2):309-315. PubMed
102. Stein JC, Nobay F. Emergency department ultrasound credentialing: a sample policy and procedure. J Emerg Med. 2009;37(2):153-159. PubMed
103. Chen FM. Burstin H, Huntington J. The importance of clinical outcomes in medical education research. Med Educ. 2005;39(4):350-351. PubMed
104. Dressler DD, Pistoria MJ, Budnitz TL, McKean SCW, Amin AN. Core competencies in hospital medicine: development and methodology. J Hosp Med. 2006;1:48-56. PubMed
105. ten Cate O. Nuts and bolts of entrustable professional activities. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(1):157-158. PubMed
106. Castillo J, Caruana CJ, Wainwright D. The changing concept of competence and categorisation of learning outcomes in Europe: Implications for the design of higher education radiography curricula at the European level. Radiography. 2011;17(3):230-234.
107. Goldstein SR. Accreditation, certification: why all the confusion? Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110(6):1396-1398. PubMed
108. Moore CL. Credentialing and reimbursement in point-of-care ultrasound. Clin Pediatr Emerg Med. 2011;12(1):73-77. PubMed
109. ten Cate O, Scheele F. Competency-based postgraduate training: can we bridge the gap between theory and clinical practice? Acad Med. 2007;82(6):542-547. PubMed
110. Abuhamad AZ, Benacerraf BR, Woletz P, Burke BL. The accreditation of ultrasound practices: impact on compliance with minimum performance guidelines. J Ultrasound Med. 2004;23(8):1023-1029. PubMed
© 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine
Bariatric surgery comes with some risk of complications
that should acknowledged by clinicians and understood by patients, a large cohort study has shown.
Gunn Signe Jakobsen, MD, of Vestfold Hospital Trust, Tønsberg, Norway, and her colleagues wrote in an article published in JAMA, “Few studies report long-term complication rates. ... No large-scale clinical practice–based study has compared the long-term association of bariatric surgery and specialized medical obesity treatment with obesity-related somatic and mental comorbidities, nor the irrespective complication rates.”
The investigators compared outcomes from 932 patients who underwent bariatric surgery and 956 who underwent specialized medical treatment that involved either individual or group lifestyle intervention programs. The study population included 1,249 women and 639 men with an average age of 44 years and an average baseline body mass index of 44 kg/m2.
The surgery patients were more likely than the medical treatment patients to have hypertension remission (absolute risk 32% vs. 12%, respectively), and less likely to develop new-onset hypertension (absolute risk 4% vs. 12%, respectively). Diabetes remission was significantly higher among surgery patients, compared with medical treatment patients (58% vs. 13%) as was the likelihood of dyslipidemia remission (43% vs. 13%). Surgery patients also were less likely to develop new-onset diabetes or dyslipidemia than the medical treatment patients.
However, more patients who underwent bariatric surgery had low ferritin levels, compared with the medical treatment patients (26% vs. 12%). The surgery patients were significantly more likely than the medical treatment patients to develop new-onset depression (adjusted relative risk, 1.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-1.7), anxiety and sleep disorders (aRR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.2-1.5), and treatment with opioids (aRR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.2-1.4). In addition, bariatric patients were more likely to have at least one additional gastrointestinal surgical procedure (aRR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.7-2.4), an operation for intestinal obstruction (aRR, 10.5; 95% CI, 5.1-21.5), abdominal pain (aRR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.6-2.3), and gastroduodenal ulcers (aRR, 3.4; 95% CI 2.0-5.6).
The study was limited by several factors, including selection bias of younger, heavier patients in the bariatric surgery group, the lack of data on actual weight loss, incomplete laboratory data, and a relatively homogeneous white population, the researchers noted. However, the nearly 100% follow-up over approximately 6 years adds to the strength of the findings, which suggest that “the risk for complications should be considered in the decision-making process,” for obese patients considering bariatric surgery, they said.
Dr. Jakobsen was supported by the Vestfold Hospital Trust, with no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Jakobsen G et al. JAMA. 2018 Jan 16;319(3):291-301.
that should acknowledged by clinicians and understood by patients, a large cohort study has shown.
Gunn Signe Jakobsen, MD, of Vestfold Hospital Trust, Tønsberg, Norway, and her colleagues wrote in an article published in JAMA, “Few studies report long-term complication rates. ... No large-scale clinical practice–based study has compared the long-term association of bariatric surgery and specialized medical obesity treatment with obesity-related somatic and mental comorbidities, nor the irrespective complication rates.”
The investigators compared outcomes from 932 patients who underwent bariatric surgery and 956 who underwent specialized medical treatment that involved either individual or group lifestyle intervention programs. The study population included 1,249 women and 639 men with an average age of 44 years and an average baseline body mass index of 44 kg/m2.
The surgery patients were more likely than the medical treatment patients to have hypertension remission (absolute risk 32% vs. 12%, respectively), and less likely to develop new-onset hypertension (absolute risk 4% vs. 12%, respectively). Diabetes remission was significantly higher among surgery patients, compared with medical treatment patients (58% vs. 13%) as was the likelihood of dyslipidemia remission (43% vs. 13%). Surgery patients also were less likely to develop new-onset diabetes or dyslipidemia than the medical treatment patients.
However, more patients who underwent bariatric surgery had low ferritin levels, compared with the medical treatment patients (26% vs. 12%). The surgery patients were significantly more likely than the medical treatment patients to develop new-onset depression (adjusted relative risk, 1.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-1.7), anxiety and sleep disorders (aRR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.2-1.5), and treatment with opioids (aRR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.2-1.4). In addition, bariatric patients were more likely to have at least one additional gastrointestinal surgical procedure (aRR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.7-2.4), an operation for intestinal obstruction (aRR, 10.5; 95% CI, 5.1-21.5), abdominal pain (aRR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.6-2.3), and gastroduodenal ulcers (aRR, 3.4; 95% CI 2.0-5.6).
The study was limited by several factors, including selection bias of younger, heavier patients in the bariatric surgery group, the lack of data on actual weight loss, incomplete laboratory data, and a relatively homogeneous white population, the researchers noted. However, the nearly 100% follow-up over approximately 6 years adds to the strength of the findings, which suggest that “the risk for complications should be considered in the decision-making process,” for obese patients considering bariatric surgery, they said.
Dr. Jakobsen was supported by the Vestfold Hospital Trust, with no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Jakobsen G et al. JAMA. 2018 Jan 16;319(3):291-301.
that should acknowledged by clinicians and understood by patients, a large cohort study has shown.
Gunn Signe Jakobsen, MD, of Vestfold Hospital Trust, Tønsberg, Norway, and her colleagues wrote in an article published in JAMA, “Few studies report long-term complication rates. ... No large-scale clinical practice–based study has compared the long-term association of bariatric surgery and specialized medical obesity treatment with obesity-related somatic and mental comorbidities, nor the irrespective complication rates.”
The investigators compared outcomes from 932 patients who underwent bariatric surgery and 956 who underwent specialized medical treatment that involved either individual or group lifestyle intervention programs. The study population included 1,249 women and 639 men with an average age of 44 years and an average baseline body mass index of 44 kg/m2.
The surgery patients were more likely than the medical treatment patients to have hypertension remission (absolute risk 32% vs. 12%, respectively), and less likely to develop new-onset hypertension (absolute risk 4% vs. 12%, respectively). Diabetes remission was significantly higher among surgery patients, compared with medical treatment patients (58% vs. 13%) as was the likelihood of dyslipidemia remission (43% vs. 13%). Surgery patients also were less likely to develop new-onset diabetes or dyslipidemia than the medical treatment patients.
However, more patients who underwent bariatric surgery had low ferritin levels, compared with the medical treatment patients (26% vs. 12%). The surgery patients were significantly more likely than the medical treatment patients to develop new-onset depression (adjusted relative risk, 1.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-1.7), anxiety and sleep disorders (aRR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.2-1.5), and treatment with opioids (aRR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.2-1.4). In addition, bariatric patients were more likely to have at least one additional gastrointestinal surgical procedure (aRR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.7-2.4), an operation for intestinal obstruction (aRR, 10.5; 95% CI, 5.1-21.5), abdominal pain (aRR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.6-2.3), and gastroduodenal ulcers (aRR, 3.4; 95% CI 2.0-5.6).
The study was limited by several factors, including selection bias of younger, heavier patients in the bariatric surgery group, the lack of data on actual weight loss, incomplete laboratory data, and a relatively homogeneous white population, the researchers noted. However, the nearly 100% follow-up over approximately 6 years adds to the strength of the findings, which suggest that “the risk for complications should be considered in the decision-making process,” for obese patients considering bariatric surgery, they said.
Dr. Jakobsen was supported by the Vestfold Hospital Trust, with no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Jakobsen G et al. JAMA. 2018 Jan 16;319(3):291-301.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Bariatric surgery was associated with reduced hypertension but more complications, including iron deficiency and ulcers.
Major finding: Obese adults who had bariatric surgery were at greater risk for new-onset depression (aRR, 1.5), anxiety and sleep disorders (aRR, 1.3), and ulcers (aRR 3.4).
Study details: A cohort study of 1,888 adults treated with bariatric surgery or medical therapy.
Disclosures: Dr. Jakobsen was supported by the Vestfold Hospital Trust, with no financial conflicts to disclose.
Source: Jakobsen G et al. JAMA. 2018 Jan 16;319(3):291-301.
You are an integral part of the epilepsy care team
CHICAGO – While neurologists treat children’s seizure conditions, you or an emergency physician usually sees the child first and must determine whether a seizure has occurred and how to proceed.
Knowing the characteristics of seizures – and their imitators – helps you appropriately evaluate and treat these children, said Sucheta Joshi, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Linda C. Laux, MD, the medical director of the Comprehensive Epilepsy Center at the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago. You also must consider the long-term management and well-being of a child with epilepsy.
A primer on seizures
Abnormal electrical discharges in the brain cause seizures, and various acute conditions can cause them, including fevers, infections, trauma, and metabolic abnormalities. But an epilepsy diagnosis requires at least two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 1 day apart. More than two dozen different epilepsy syndromes exist, determined based on age of onset, seizure type, the child’s development, and EEG patterns.
You also should be aware of what seizure imitators to rule out: movement disorders such as tics and Sandifer’s syndrome, daydreaming and inattention, fainting, migraines, panic attacks, psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES), self-stimulatory behaviors, periods of the child holding her breath, and sleep parasomnias, such as night terrors, sleepwalking, and sleep myoclonus.
“It’s often difficult to tell if it’s a seizure or a nonepileptic paroxysmal event,” said Dr. Joshi. An interictal EEG can be helpful, but “there’s no reliable test to differentiate the two.”
Knowing the environment where the incident occurred, what provoking factors might have been present, what the seizure looked like, how long it lasted, and what happened afterward can help you differentiate paroxysmal spells from seizures.
Febrile seizures
About 4% of all children experience febrile seizures, particularly between 6 months and 6 years of age, Dr. Joshi said. The two types are simple and complex. A simple febrile seizure is generalized and brief, lasting less than 15 minutes, and is not followed by another within 24 hours. The child may have a family history of epilepsy but appear normal. Complex febrile seizures are focal, last more than 15 minutes, and occur more than once within 24 hours.
Although antipyretics may help the child feel better, fever control won’t always prevent seizures. Rectal or sometimes oral diazepam can prevent recurrent prolonged febrile seizures if necessary. You also may consider oral clonazepam as a rescue medication.
However, children with only simple febrile seizures are at no greater risk of developing epilepsy by age 7 years than are children in the general population, about 1%, according to the AAP’s clinical practice guideline for long-term management of children with simple febrile seizures (Pediatrics. 2008 Jun;121(6):1281-6.)
If a child has a family history of epilepsy, has their first febrile before 12 months of age, and has multiple simple febrile seizures, however, their risk of epilepsy more than doubles. An estimated 2.4% of these children will develop epilepsy by age 25 years.
“No study has demonstrated that successful treatment of simple febrile seizures can prevent this later development of epilepsy, and there currently is no evidence that simple febrile seizures cause structural damage to the brain,” the practice guideline states. “Indeed, it is most likely that the increased risk of epilepsy in this population is the result of genetic predisposition.”
Determining seizure causes
If the child’s seizure is not clearly febrile with a known cause, you should run through other possibilities. Did the child have head trauma? A central nervous system infection? Are metabolic abnormalities present, such as renal or hepatic disease or an electrolyte abnormality? Has the patient ingested something, such as a recreational drug or other toxic substance?
Lab work is unlikely to offer much information without clinical signs or symptoms present, but you may consider glucose, electrolytes, serum alcohol level, and a toxicology drug screen on a case-by-case basis: A child’s first unprovoked seizure should not lead to a lumbar puncture, Dr. Laux said. But if you suspect a CNS infection or the child is under 6 months old and does not return to baseline, you should consider a lumbar puncture. Modest increases in cerebrospinal fluid cell count (pleocytosis) occur after a seizure, but a “CSF above 20 WBC/mm3 or above 10 PMN/mm3 should not be attributed to a seizure,” she said.
An outpatient EEG, preferably performed within 24-48 hours, shows abnormalities 70% of the time after a seizure, but a normal EEG cannot rule out a seizure. EEG data also may suggest recurrence risk or a specific epilepsy syndrome and long-term prognosis.
Epilepsy management
After a second unprovoked seizure occurrs more than 24 hours after the first, you should diagnose new onset epilepsy, order an EEG and head MRI, and refer the child to a neurologist. Metabolic or genetic tests may be indicated depending on signs and symptoms.
Managing epilepsy requires much more than just treating seizures, Dr. Laux emphasized, so you play an important role in educating the family, considering safety issues, monitoring bone and reproductive health, and considering the condition’s effect on learning and mental, behavioral, and physical health.
Children with epilepsy and normal cognitive development have no greater rate of injuries than children without epilepsy, but risk increases as seizures increase, and if the child has ADHD, intellectual disability, or generalized-onset seizures, that can lead to falls.
Still, children with epilepsy can play contact sports such as soccer or volleyball without worrying it will cause a seizure. They also should always wear a helmet while bicycling, rollerblading, skating, and using scooters or anything else with wheels.
Swimming, water sports, harnessed rock climbing, horseback riding, and gymnastics also are fine with appropriate supervision. Showers are preferred to baths because of the risk of drowning should a seizure occur in the bathtub. Bathing and swimming require a specified supervisor.
Unsafe activities include free climbing, sky-diving, hang-gliding, and scuba diving. Parents should supervise their children around irons, hairdryers, curling irons, stove tops, camp fires, BBQs, and playground equipment. TV and video games are fine if children do not sit close to the screen and have ambient light in the room.
A teen with uncontrolled seizures should not drive, and pediatricians should be aware of their state’s laws related to epilepsy and driving (www.epilepsy.com/driving-laws). Pennsylvania, California, Delaware, Nevada, New Jersey, and Oregon, for example, have physician reporting laws.
Physical health and learning differences
Epilepsy increases risk of poor bone mineralization, and seizures can lead to falls and fractures. You therefore should keep tabs on the child’s vitamin D intake, physical activity levels, neuromotor dysfunction, and overall nutrition. Vitamin D insufficiency is more common in those with epilepsy than in the general population, particularly females and those with obesity. Evidence suggests both anticonvulsants and epilepsy syndromes contribute to low vitamin D levels, so daily supplements may be wise.
Antiepileptic drugs also reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraception, and teens with epilepsy already have a higher risk for unplanned pregnancy. You should ensure that sexually active female teens get folic acid daily and educate them on valproate’s increased risk of causing birth defects. For pregnant teens, levetiracetam and lamotrigine present less risk to a fetus.
You should ask about the patient’s school performance and consider requesting an Individualized Education Plan or a 504 plan at school if it seems needed. Even in youths with a normal IQ and well-managed seizures, lower academic achievement and difficulties with memory and behavior are more likely. Risk increases in disorganized or unsupportive homes and with comorbidities. ADHD occurs in 38% of children with epilepsy, but stimulants such as methylphenidate are not contraindicated with epilepsy medications.
Epilepsy affects the whole family: About half of all mothers of children with epilepsy have depression – which can adversely affect her children – and risk increases for younger moms with lower education and income. Siblings have added burdens, too: In one study, 95% of siblings had witnessed a seizure, and 79% believed their siblings suffered during seizures. More than two-thirds (68%) say their sibling with epilepsy gets more attention, and 42% feel responsible for their sibling, often restricting their own activities. You should be considering all these factors in managing the well-being of a child with epilepsy.
Dr. Joshi summed up the complex management of epilepsy with an acrostic that may be helpful to share with parents:
• Education
• Parenting
• Independence (including driving)
• Learning
• Eating (nutrition and bone health)
• Pharmacotherapy (anticonvulsants)
• School
• You (the child’s caretakers).
Dr. Joshi and Dr. Laux reported having no relevant financial disclosures and no external funding.
CHICAGO – While neurologists treat children’s seizure conditions, you or an emergency physician usually sees the child first and must determine whether a seizure has occurred and how to proceed.
Knowing the characteristics of seizures – and their imitators – helps you appropriately evaluate and treat these children, said Sucheta Joshi, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Linda C. Laux, MD, the medical director of the Comprehensive Epilepsy Center at the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago. You also must consider the long-term management and well-being of a child with epilepsy.
A primer on seizures
Abnormal electrical discharges in the brain cause seizures, and various acute conditions can cause them, including fevers, infections, trauma, and metabolic abnormalities. But an epilepsy diagnosis requires at least two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 1 day apart. More than two dozen different epilepsy syndromes exist, determined based on age of onset, seizure type, the child’s development, and EEG patterns.
You also should be aware of what seizure imitators to rule out: movement disorders such as tics and Sandifer’s syndrome, daydreaming and inattention, fainting, migraines, panic attacks, psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES), self-stimulatory behaviors, periods of the child holding her breath, and sleep parasomnias, such as night terrors, sleepwalking, and sleep myoclonus.
“It’s often difficult to tell if it’s a seizure or a nonepileptic paroxysmal event,” said Dr. Joshi. An interictal EEG can be helpful, but “there’s no reliable test to differentiate the two.”
Knowing the environment where the incident occurred, what provoking factors might have been present, what the seizure looked like, how long it lasted, and what happened afterward can help you differentiate paroxysmal spells from seizures.
Febrile seizures
About 4% of all children experience febrile seizures, particularly between 6 months and 6 years of age, Dr. Joshi said. The two types are simple and complex. A simple febrile seizure is generalized and brief, lasting less than 15 minutes, and is not followed by another within 24 hours. The child may have a family history of epilepsy but appear normal. Complex febrile seizures are focal, last more than 15 minutes, and occur more than once within 24 hours.
Although antipyretics may help the child feel better, fever control won’t always prevent seizures. Rectal or sometimes oral diazepam can prevent recurrent prolonged febrile seizures if necessary. You also may consider oral clonazepam as a rescue medication.
However, children with only simple febrile seizures are at no greater risk of developing epilepsy by age 7 years than are children in the general population, about 1%, according to the AAP’s clinical practice guideline for long-term management of children with simple febrile seizures (Pediatrics. 2008 Jun;121(6):1281-6.)
If a child has a family history of epilepsy, has their first febrile before 12 months of age, and has multiple simple febrile seizures, however, their risk of epilepsy more than doubles. An estimated 2.4% of these children will develop epilepsy by age 25 years.
“No study has demonstrated that successful treatment of simple febrile seizures can prevent this later development of epilepsy, and there currently is no evidence that simple febrile seizures cause structural damage to the brain,” the practice guideline states. “Indeed, it is most likely that the increased risk of epilepsy in this population is the result of genetic predisposition.”
Determining seizure causes
If the child’s seizure is not clearly febrile with a known cause, you should run through other possibilities. Did the child have head trauma? A central nervous system infection? Are metabolic abnormalities present, such as renal or hepatic disease or an electrolyte abnormality? Has the patient ingested something, such as a recreational drug or other toxic substance?
Lab work is unlikely to offer much information without clinical signs or symptoms present, but you may consider glucose, electrolytes, serum alcohol level, and a toxicology drug screen on a case-by-case basis: A child’s first unprovoked seizure should not lead to a lumbar puncture, Dr. Laux said. But if you suspect a CNS infection or the child is under 6 months old and does not return to baseline, you should consider a lumbar puncture. Modest increases in cerebrospinal fluid cell count (pleocytosis) occur after a seizure, but a “CSF above 20 WBC/mm3 or above 10 PMN/mm3 should not be attributed to a seizure,” she said.
An outpatient EEG, preferably performed within 24-48 hours, shows abnormalities 70% of the time after a seizure, but a normal EEG cannot rule out a seizure. EEG data also may suggest recurrence risk or a specific epilepsy syndrome and long-term prognosis.
Epilepsy management
After a second unprovoked seizure occurrs more than 24 hours after the first, you should diagnose new onset epilepsy, order an EEG and head MRI, and refer the child to a neurologist. Metabolic or genetic tests may be indicated depending on signs and symptoms.
Managing epilepsy requires much more than just treating seizures, Dr. Laux emphasized, so you play an important role in educating the family, considering safety issues, monitoring bone and reproductive health, and considering the condition’s effect on learning and mental, behavioral, and physical health.
Children with epilepsy and normal cognitive development have no greater rate of injuries than children without epilepsy, but risk increases as seizures increase, and if the child has ADHD, intellectual disability, or generalized-onset seizures, that can lead to falls.
Still, children with epilepsy can play contact sports such as soccer or volleyball without worrying it will cause a seizure. They also should always wear a helmet while bicycling, rollerblading, skating, and using scooters or anything else with wheels.
Swimming, water sports, harnessed rock climbing, horseback riding, and gymnastics also are fine with appropriate supervision. Showers are preferred to baths because of the risk of drowning should a seizure occur in the bathtub. Bathing and swimming require a specified supervisor.
Unsafe activities include free climbing, sky-diving, hang-gliding, and scuba diving. Parents should supervise their children around irons, hairdryers, curling irons, stove tops, camp fires, BBQs, and playground equipment. TV and video games are fine if children do not sit close to the screen and have ambient light in the room.
A teen with uncontrolled seizures should not drive, and pediatricians should be aware of their state’s laws related to epilepsy and driving (www.epilepsy.com/driving-laws). Pennsylvania, California, Delaware, Nevada, New Jersey, and Oregon, for example, have physician reporting laws.
Physical health and learning differences
Epilepsy increases risk of poor bone mineralization, and seizures can lead to falls and fractures. You therefore should keep tabs on the child’s vitamin D intake, physical activity levels, neuromotor dysfunction, and overall nutrition. Vitamin D insufficiency is more common in those with epilepsy than in the general population, particularly females and those with obesity. Evidence suggests both anticonvulsants and epilepsy syndromes contribute to low vitamin D levels, so daily supplements may be wise.
Antiepileptic drugs also reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraception, and teens with epilepsy already have a higher risk for unplanned pregnancy. You should ensure that sexually active female teens get folic acid daily and educate them on valproate’s increased risk of causing birth defects. For pregnant teens, levetiracetam and lamotrigine present less risk to a fetus.
You should ask about the patient’s school performance and consider requesting an Individualized Education Plan or a 504 plan at school if it seems needed. Even in youths with a normal IQ and well-managed seizures, lower academic achievement and difficulties with memory and behavior are more likely. Risk increases in disorganized or unsupportive homes and with comorbidities. ADHD occurs in 38% of children with epilepsy, but stimulants such as methylphenidate are not contraindicated with epilepsy medications.
Epilepsy affects the whole family: About half of all mothers of children with epilepsy have depression – which can adversely affect her children – and risk increases for younger moms with lower education and income. Siblings have added burdens, too: In one study, 95% of siblings had witnessed a seizure, and 79% believed their siblings suffered during seizures. More than two-thirds (68%) say their sibling with epilepsy gets more attention, and 42% feel responsible for their sibling, often restricting their own activities. You should be considering all these factors in managing the well-being of a child with epilepsy.
Dr. Joshi summed up the complex management of epilepsy with an acrostic that may be helpful to share with parents:
• Education
• Parenting
• Independence (including driving)
• Learning
• Eating (nutrition and bone health)
• Pharmacotherapy (anticonvulsants)
• School
• You (the child’s caretakers).
Dr. Joshi and Dr. Laux reported having no relevant financial disclosures and no external funding.
CHICAGO – While neurologists treat children’s seizure conditions, you or an emergency physician usually sees the child first and must determine whether a seizure has occurred and how to proceed.
Knowing the characteristics of seizures – and their imitators – helps you appropriately evaluate and treat these children, said Sucheta Joshi, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Linda C. Laux, MD, the medical director of the Comprehensive Epilepsy Center at the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago. You also must consider the long-term management and well-being of a child with epilepsy.
A primer on seizures
Abnormal electrical discharges in the brain cause seizures, and various acute conditions can cause them, including fevers, infections, trauma, and metabolic abnormalities. But an epilepsy diagnosis requires at least two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 1 day apart. More than two dozen different epilepsy syndromes exist, determined based on age of onset, seizure type, the child’s development, and EEG patterns.
You also should be aware of what seizure imitators to rule out: movement disorders such as tics and Sandifer’s syndrome, daydreaming and inattention, fainting, migraines, panic attacks, psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES), self-stimulatory behaviors, periods of the child holding her breath, and sleep parasomnias, such as night terrors, sleepwalking, and sleep myoclonus.
“It’s often difficult to tell if it’s a seizure or a nonepileptic paroxysmal event,” said Dr. Joshi. An interictal EEG can be helpful, but “there’s no reliable test to differentiate the two.”
Knowing the environment where the incident occurred, what provoking factors might have been present, what the seizure looked like, how long it lasted, and what happened afterward can help you differentiate paroxysmal spells from seizures.
Febrile seizures
About 4% of all children experience febrile seizures, particularly between 6 months and 6 years of age, Dr. Joshi said. The two types are simple and complex. A simple febrile seizure is generalized and brief, lasting less than 15 minutes, and is not followed by another within 24 hours. The child may have a family history of epilepsy but appear normal. Complex febrile seizures are focal, last more than 15 minutes, and occur more than once within 24 hours.
Although antipyretics may help the child feel better, fever control won’t always prevent seizures. Rectal or sometimes oral diazepam can prevent recurrent prolonged febrile seizures if necessary. You also may consider oral clonazepam as a rescue medication.
However, children with only simple febrile seizures are at no greater risk of developing epilepsy by age 7 years than are children in the general population, about 1%, according to the AAP’s clinical practice guideline for long-term management of children with simple febrile seizures (Pediatrics. 2008 Jun;121(6):1281-6.)
If a child has a family history of epilepsy, has their first febrile before 12 months of age, and has multiple simple febrile seizures, however, their risk of epilepsy more than doubles. An estimated 2.4% of these children will develop epilepsy by age 25 years.
“No study has demonstrated that successful treatment of simple febrile seizures can prevent this later development of epilepsy, and there currently is no evidence that simple febrile seizures cause structural damage to the brain,” the practice guideline states. “Indeed, it is most likely that the increased risk of epilepsy in this population is the result of genetic predisposition.”
Determining seizure causes
If the child’s seizure is not clearly febrile with a known cause, you should run through other possibilities. Did the child have head trauma? A central nervous system infection? Are metabolic abnormalities present, such as renal or hepatic disease or an electrolyte abnormality? Has the patient ingested something, such as a recreational drug or other toxic substance?
Lab work is unlikely to offer much information without clinical signs or symptoms present, but you may consider glucose, electrolytes, serum alcohol level, and a toxicology drug screen on a case-by-case basis: A child’s first unprovoked seizure should not lead to a lumbar puncture, Dr. Laux said. But if you suspect a CNS infection or the child is under 6 months old and does not return to baseline, you should consider a lumbar puncture. Modest increases in cerebrospinal fluid cell count (pleocytosis) occur after a seizure, but a “CSF above 20 WBC/mm3 or above 10 PMN/mm3 should not be attributed to a seizure,” she said.
An outpatient EEG, preferably performed within 24-48 hours, shows abnormalities 70% of the time after a seizure, but a normal EEG cannot rule out a seizure. EEG data also may suggest recurrence risk or a specific epilepsy syndrome and long-term prognosis.
Epilepsy management
After a second unprovoked seizure occurrs more than 24 hours after the first, you should diagnose new onset epilepsy, order an EEG and head MRI, and refer the child to a neurologist. Metabolic or genetic tests may be indicated depending on signs and symptoms.
Managing epilepsy requires much more than just treating seizures, Dr. Laux emphasized, so you play an important role in educating the family, considering safety issues, monitoring bone and reproductive health, and considering the condition’s effect on learning and mental, behavioral, and physical health.
Children with epilepsy and normal cognitive development have no greater rate of injuries than children without epilepsy, but risk increases as seizures increase, and if the child has ADHD, intellectual disability, or generalized-onset seizures, that can lead to falls.
Still, children with epilepsy can play contact sports such as soccer or volleyball without worrying it will cause a seizure. They also should always wear a helmet while bicycling, rollerblading, skating, and using scooters or anything else with wheels.
Swimming, water sports, harnessed rock climbing, horseback riding, and gymnastics also are fine with appropriate supervision. Showers are preferred to baths because of the risk of drowning should a seizure occur in the bathtub. Bathing and swimming require a specified supervisor.
Unsafe activities include free climbing, sky-diving, hang-gliding, and scuba diving. Parents should supervise their children around irons, hairdryers, curling irons, stove tops, camp fires, BBQs, and playground equipment. TV and video games are fine if children do not sit close to the screen and have ambient light in the room.
A teen with uncontrolled seizures should not drive, and pediatricians should be aware of their state’s laws related to epilepsy and driving (www.epilepsy.com/driving-laws). Pennsylvania, California, Delaware, Nevada, New Jersey, and Oregon, for example, have physician reporting laws.
Physical health and learning differences
Epilepsy increases risk of poor bone mineralization, and seizures can lead to falls and fractures. You therefore should keep tabs on the child’s vitamin D intake, physical activity levels, neuromotor dysfunction, and overall nutrition. Vitamin D insufficiency is more common in those with epilepsy than in the general population, particularly females and those with obesity. Evidence suggests both anticonvulsants and epilepsy syndromes contribute to low vitamin D levels, so daily supplements may be wise.
Antiepileptic drugs also reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraception, and teens with epilepsy already have a higher risk for unplanned pregnancy. You should ensure that sexually active female teens get folic acid daily and educate them on valproate’s increased risk of causing birth defects. For pregnant teens, levetiracetam and lamotrigine present less risk to a fetus.
You should ask about the patient’s school performance and consider requesting an Individualized Education Plan or a 504 plan at school if it seems needed. Even in youths with a normal IQ and well-managed seizures, lower academic achievement and difficulties with memory and behavior are more likely. Risk increases in disorganized or unsupportive homes and with comorbidities. ADHD occurs in 38% of children with epilepsy, but stimulants such as methylphenidate are not contraindicated with epilepsy medications.
Epilepsy affects the whole family: About half of all mothers of children with epilepsy have depression – which can adversely affect her children – and risk increases for younger moms with lower education and income. Siblings have added burdens, too: In one study, 95% of siblings had witnessed a seizure, and 79% believed their siblings suffered during seizures. More than two-thirds (68%) say their sibling with epilepsy gets more attention, and 42% feel responsible for their sibling, often restricting their own activities. You should be considering all these factors in managing the well-being of a child with epilepsy.
Dr. Joshi summed up the complex management of epilepsy with an acrostic that may be helpful to share with parents:
• Education
• Parenting
• Independence (including driving)
• Learning
• Eating (nutrition and bone health)
• Pharmacotherapy (anticonvulsants)
• School
• You (the child’s caretakers).
Dr. Joshi and Dr. Laux reported having no relevant financial disclosures and no external funding.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 2017