User login
A case-based framework for de-escalating conflict
Hospital medicine can be a demanding and fast-paced environment where resources are stretched thin, with both clinicians and patients stressed. A hospitalist’s role is dynamic, serving as an advocate, leader, or role model while working with interdisciplinary and diverse teams for the welfare of the patient. This constellation of pressures makes a degree of conflict inevitable.
Often, an unexpected scenario can render the hospitalist uncertain and yet the hospitalist’s response can escalate or deescalate conflict. The multiple roles that a hospitalist represents may buckle to the single role of advocating for themselves, a colleague, or a patient in a tense scenario. When this happens, many hospitalists feel disempowered to respond.
De-escalation is a practical skill that involves being calm, respectful, and open minded toward the other person, while also maintaining boundaries. Here we provide case-based tips and skills that highlight the role for de-escalation.
Questions to ask yourself in midst of conflict:
- How did the problematic behavior make you feel?
- What will be your approach in handling this?
- When should you address this?
- What is the outcome you are hoping to achieve?
- What is the outcome the other person is hoping to achieve?
Case 1
There is a female physician rounding with your team. Introductions were made at the start of a patient encounter. The patient repeatedly calls the female physician by her first name and refers to a male colleague as “doctor.”
Commentary: This scenario is commonly encountered by women who are physicians. They may be mistaken for the nurse, a technician, or a housekeeper. This exacerbates inequality and impostor syndrome as women can feel unheard, undervalued, and not recognized for their expertise and achievements. It can be challenging for a woman to reaffirm herself as she worries that the patient will not respect her or will think that she is being aggressive.
Approach: It is vital to interject by firmly reintroducing the female physician by her correct title. If you are the subject of this scenario, you may interject by firmly reintroducing yourself. If the patient or a colleague continues to refer to her by her first name, it is appropriate to say, “Please call her Dr. XYZ.” There is likely another female colleague or trainee nearby that will view this scenario as a model for setting boundaries.
To prevent similar future situations, consistently refer to all peers by their title in front of patients and peers in all professional settings (such as lectures, luncheons, etc.) to establish this as a cultural norm. Also, utilize hospital badges that clearly display roles in large letters.
Case 2
During sign out from a colleague, the colleague repeatedly refers to a patient hospitalized with sickle cell disease as a “frequent flyer” and “drug seeker,” and then remarks, “you know how these patients are.”
Commentary: A situation like this raises concerns about bias and stereotyping. Everyone has implicit bias. Recognizing and acknowledging when implicit bias affects objectivity in patient care is vital to providing appropriate care. It can be intimidating to broach this subject with a colleague as it may cause the colleague to become defensive and uncomfortable as revealing another person’s bias can be difficult. But physicians owe it to a patient’s wellbeing to remain objective and to prevent future colleagues from providing subpar care as a result.
Approach: In this case, saying, “Sometimes my previous experiences can affect my thinking. Will you explain what behaviors the patient has shown this admission that are concerning to you? This will allow me to grasp the complexity of the situation.” Another strategy is to share that there are new recommendations for how to use language about patients with sickle cell disease and patients who require opioids as a part of their treatment plan. Your hospitalist group could have a journal club on how bias affects patients and about the best practices in the care of people with sickle cell disease. A next step could be to build a quality improvement project to review the care of patients hospitalized for sickle cell disease or opioid use.
Case 3
You are conducting bedside rounds with your team. Your intern, a person of color, begins to present. The patient interjects by requesting that the intern leave as he “does not want a foreigner taking care” of him.
Commentary: Requests like this can be shocking. The team leader has a responsibility to immediately act to ensure the psychological safety of the team. Ideally, your response should set firm boundaries and expectations that support the learner as a valued and respected clinician and allow the intern to complete the presentation. In this scenario, regardless of the response the patient takes, it is vital to maintain a safe environment for the trainee. It is crucial to debrief with the team immediately after as an exchange of thoughts and emotions in a safe space can allow for everyone to feel welcome. Additionally, this debrief can provide insights to the team leader of how to address similar situations in the future. The opportunity to allow the intern to no longer follow the patient should be offered, and if the intern opts to no longer follow the patient, accommodations should be made.
Approach: “This physician is a member of the medical team, and we are all working together to provide you with the best care. Everyone on this team is an equal. We value diversity of our team members as it allows us to take care of all our patients. We respect you and expect respect for each member of the team. If you feel that you are unable to respect our team members right now, we will leave for now and return later.” To ensure the patient is provided with appropriate care, be sure to debrief with the patient’s nurse.
Conclusion
These scenarios represent some of the many complex interpersonal challenges hospitalists encounter. These approaches are suggestions that are open to improvement as de-escalation of a conflict is a critical and evolving skill and practice.
For more tips on managing conflict, consider reading “Crucial Conversations” by Kerry Patterson and colleagues. These skills can provide the tools we need to recenter ourselves when we are in the midst of these challenging situations.
Dr. Rawal is clinical assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. Dr. Ashford is assistant professor and program director in the department of internal medicine/pediatrics at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha. Dr. Lee and Dr. Barrett are based in the department of internal medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. This article is sponsored by the SHM Physicians in Training (PIT) committee, which submits quarterly content to The Hospitalist on topics relevant to trainees and early career hospitalists.
Hospital medicine can be a demanding and fast-paced environment where resources are stretched thin, with both clinicians and patients stressed. A hospitalist’s role is dynamic, serving as an advocate, leader, or role model while working with interdisciplinary and diverse teams for the welfare of the patient. This constellation of pressures makes a degree of conflict inevitable.
Often, an unexpected scenario can render the hospitalist uncertain and yet the hospitalist’s response can escalate or deescalate conflict. The multiple roles that a hospitalist represents may buckle to the single role of advocating for themselves, a colleague, or a patient in a tense scenario. When this happens, many hospitalists feel disempowered to respond.
De-escalation is a practical skill that involves being calm, respectful, and open minded toward the other person, while also maintaining boundaries. Here we provide case-based tips and skills that highlight the role for de-escalation.
Questions to ask yourself in midst of conflict:
- How did the problematic behavior make you feel?
- What will be your approach in handling this?
- When should you address this?
- What is the outcome you are hoping to achieve?
- What is the outcome the other person is hoping to achieve?
Case 1
There is a female physician rounding with your team. Introductions were made at the start of a patient encounter. The patient repeatedly calls the female physician by her first name and refers to a male colleague as “doctor.”
Commentary: This scenario is commonly encountered by women who are physicians. They may be mistaken for the nurse, a technician, or a housekeeper. This exacerbates inequality and impostor syndrome as women can feel unheard, undervalued, and not recognized for their expertise and achievements. It can be challenging for a woman to reaffirm herself as she worries that the patient will not respect her or will think that she is being aggressive.
Approach: It is vital to interject by firmly reintroducing the female physician by her correct title. If you are the subject of this scenario, you may interject by firmly reintroducing yourself. If the patient or a colleague continues to refer to her by her first name, it is appropriate to say, “Please call her Dr. XYZ.” There is likely another female colleague or trainee nearby that will view this scenario as a model for setting boundaries.
To prevent similar future situations, consistently refer to all peers by their title in front of patients and peers in all professional settings (such as lectures, luncheons, etc.) to establish this as a cultural norm. Also, utilize hospital badges that clearly display roles in large letters.
Case 2
During sign out from a colleague, the colleague repeatedly refers to a patient hospitalized with sickle cell disease as a “frequent flyer” and “drug seeker,” and then remarks, “you know how these patients are.”
Commentary: A situation like this raises concerns about bias and stereotyping. Everyone has implicit bias. Recognizing and acknowledging when implicit bias affects objectivity in patient care is vital to providing appropriate care. It can be intimidating to broach this subject with a colleague as it may cause the colleague to become defensive and uncomfortable as revealing another person’s bias can be difficult. But physicians owe it to a patient’s wellbeing to remain objective and to prevent future colleagues from providing subpar care as a result.
Approach: In this case, saying, “Sometimes my previous experiences can affect my thinking. Will you explain what behaviors the patient has shown this admission that are concerning to you? This will allow me to grasp the complexity of the situation.” Another strategy is to share that there are new recommendations for how to use language about patients with sickle cell disease and patients who require opioids as a part of their treatment plan. Your hospitalist group could have a journal club on how bias affects patients and about the best practices in the care of people with sickle cell disease. A next step could be to build a quality improvement project to review the care of patients hospitalized for sickle cell disease or opioid use.
Case 3
You are conducting bedside rounds with your team. Your intern, a person of color, begins to present. The patient interjects by requesting that the intern leave as he “does not want a foreigner taking care” of him.
Commentary: Requests like this can be shocking. The team leader has a responsibility to immediately act to ensure the psychological safety of the team. Ideally, your response should set firm boundaries and expectations that support the learner as a valued and respected clinician and allow the intern to complete the presentation. In this scenario, regardless of the response the patient takes, it is vital to maintain a safe environment for the trainee. It is crucial to debrief with the team immediately after as an exchange of thoughts and emotions in a safe space can allow for everyone to feel welcome. Additionally, this debrief can provide insights to the team leader of how to address similar situations in the future. The opportunity to allow the intern to no longer follow the patient should be offered, and if the intern opts to no longer follow the patient, accommodations should be made.
Approach: “This physician is a member of the medical team, and we are all working together to provide you with the best care. Everyone on this team is an equal. We value diversity of our team members as it allows us to take care of all our patients. We respect you and expect respect for each member of the team. If you feel that you are unable to respect our team members right now, we will leave for now and return later.” To ensure the patient is provided with appropriate care, be sure to debrief with the patient’s nurse.
Conclusion
These scenarios represent some of the many complex interpersonal challenges hospitalists encounter. These approaches are suggestions that are open to improvement as de-escalation of a conflict is a critical and evolving skill and practice.
For more tips on managing conflict, consider reading “Crucial Conversations” by Kerry Patterson and colleagues. These skills can provide the tools we need to recenter ourselves when we are in the midst of these challenging situations.
Dr. Rawal is clinical assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. Dr. Ashford is assistant professor and program director in the department of internal medicine/pediatrics at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha. Dr. Lee and Dr. Barrett are based in the department of internal medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. This article is sponsored by the SHM Physicians in Training (PIT) committee, which submits quarterly content to The Hospitalist on topics relevant to trainees and early career hospitalists.
Hospital medicine can be a demanding and fast-paced environment where resources are stretched thin, with both clinicians and patients stressed. A hospitalist’s role is dynamic, serving as an advocate, leader, or role model while working with interdisciplinary and diverse teams for the welfare of the patient. This constellation of pressures makes a degree of conflict inevitable.
Often, an unexpected scenario can render the hospitalist uncertain and yet the hospitalist’s response can escalate or deescalate conflict. The multiple roles that a hospitalist represents may buckle to the single role of advocating for themselves, a colleague, or a patient in a tense scenario. When this happens, many hospitalists feel disempowered to respond.
De-escalation is a practical skill that involves being calm, respectful, and open minded toward the other person, while also maintaining boundaries. Here we provide case-based tips and skills that highlight the role for de-escalation.
Questions to ask yourself in midst of conflict:
- How did the problematic behavior make you feel?
- What will be your approach in handling this?
- When should you address this?
- What is the outcome you are hoping to achieve?
- What is the outcome the other person is hoping to achieve?
Case 1
There is a female physician rounding with your team. Introductions were made at the start of a patient encounter. The patient repeatedly calls the female physician by her first name and refers to a male colleague as “doctor.”
Commentary: This scenario is commonly encountered by women who are physicians. They may be mistaken for the nurse, a technician, or a housekeeper. This exacerbates inequality and impostor syndrome as women can feel unheard, undervalued, and not recognized for their expertise and achievements. It can be challenging for a woman to reaffirm herself as she worries that the patient will not respect her or will think that she is being aggressive.
Approach: It is vital to interject by firmly reintroducing the female physician by her correct title. If you are the subject of this scenario, you may interject by firmly reintroducing yourself. If the patient or a colleague continues to refer to her by her first name, it is appropriate to say, “Please call her Dr. XYZ.” There is likely another female colleague or trainee nearby that will view this scenario as a model for setting boundaries.
To prevent similar future situations, consistently refer to all peers by their title in front of patients and peers in all professional settings (such as lectures, luncheons, etc.) to establish this as a cultural norm. Also, utilize hospital badges that clearly display roles in large letters.
Case 2
During sign out from a colleague, the colleague repeatedly refers to a patient hospitalized with sickle cell disease as a “frequent flyer” and “drug seeker,” and then remarks, “you know how these patients are.”
Commentary: A situation like this raises concerns about bias and stereotyping. Everyone has implicit bias. Recognizing and acknowledging when implicit bias affects objectivity in patient care is vital to providing appropriate care. It can be intimidating to broach this subject with a colleague as it may cause the colleague to become defensive and uncomfortable as revealing another person’s bias can be difficult. But physicians owe it to a patient’s wellbeing to remain objective and to prevent future colleagues from providing subpar care as a result.
Approach: In this case, saying, “Sometimes my previous experiences can affect my thinking. Will you explain what behaviors the patient has shown this admission that are concerning to you? This will allow me to grasp the complexity of the situation.” Another strategy is to share that there are new recommendations for how to use language about patients with sickle cell disease and patients who require opioids as a part of their treatment plan. Your hospitalist group could have a journal club on how bias affects patients and about the best practices in the care of people with sickle cell disease. A next step could be to build a quality improvement project to review the care of patients hospitalized for sickle cell disease or opioid use.
Case 3
You are conducting bedside rounds with your team. Your intern, a person of color, begins to present. The patient interjects by requesting that the intern leave as he “does not want a foreigner taking care” of him.
Commentary: Requests like this can be shocking. The team leader has a responsibility to immediately act to ensure the psychological safety of the team. Ideally, your response should set firm boundaries and expectations that support the learner as a valued and respected clinician and allow the intern to complete the presentation. In this scenario, regardless of the response the patient takes, it is vital to maintain a safe environment for the trainee. It is crucial to debrief with the team immediately after as an exchange of thoughts and emotions in a safe space can allow for everyone to feel welcome. Additionally, this debrief can provide insights to the team leader of how to address similar situations in the future. The opportunity to allow the intern to no longer follow the patient should be offered, and if the intern opts to no longer follow the patient, accommodations should be made.
Approach: “This physician is a member of the medical team, and we are all working together to provide you with the best care. Everyone on this team is an equal. We value diversity of our team members as it allows us to take care of all our patients. We respect you and expect respect for each member of the team. If you feel that you are unable to respect our team members right now, we will leave for now and return later.” To ensure the patient is provided with appropriate care, be sure to debrief with the patient’s nurse.
Conclusion
These scenarios represent some of the many complex interpersonal challenges hospitalists encounter. These approaches are suggestions that are open to improvement as de-escalation of a conflict is a critical and evolving skill and practice.
For more tips on managing conflict, consider reading “Crucial Conversations” by Kerry Patterson and colleagues. These skills can provide the tools we need to recenter ourselves when we are in the midst of these challenging situations.
Dr. Rawal is clinical assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. Dr. Ashford is assistant professor and program director in the department of internal medicine/pediatrics at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha. Dr. Lee and Dr. Barrett are based in the department of internal medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. This article is sponsored by the SHM Physicians in Training (PIT) committee, which submits quarterly content to The Hospitalist on topics relevant to trainees and early career hospitalists.
Vegetative Plaques on the Face
THE DIAGNOSIS: Vegetative Majocchi Granuloma
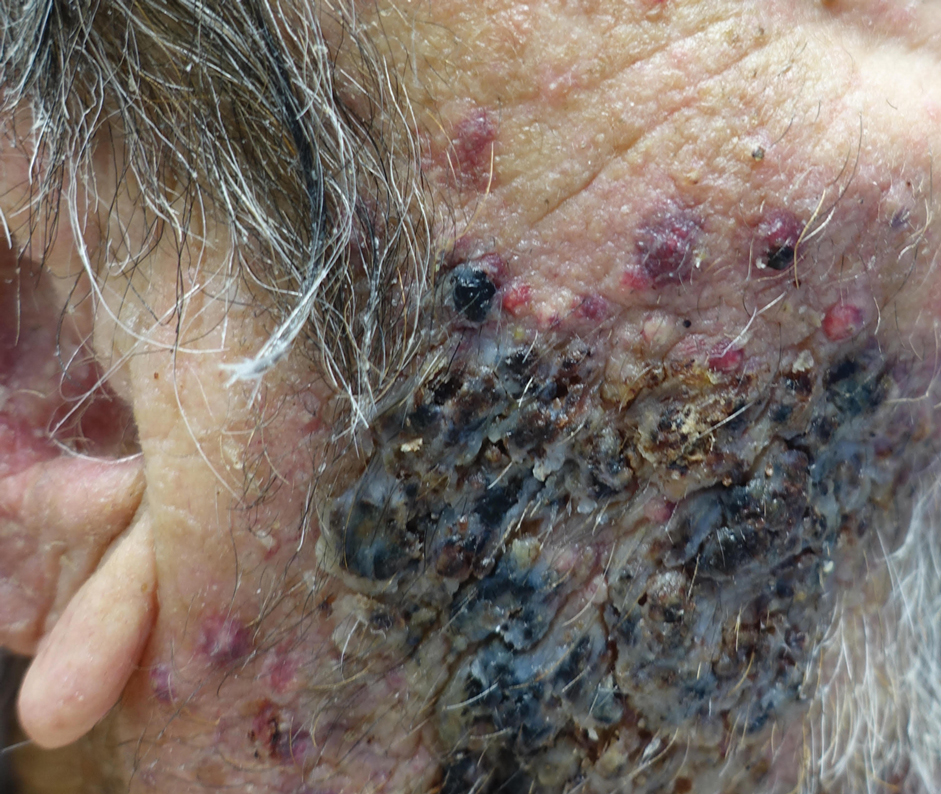
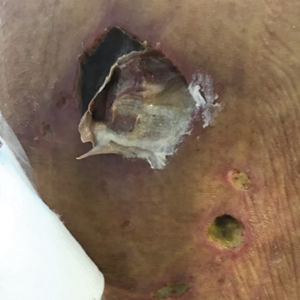
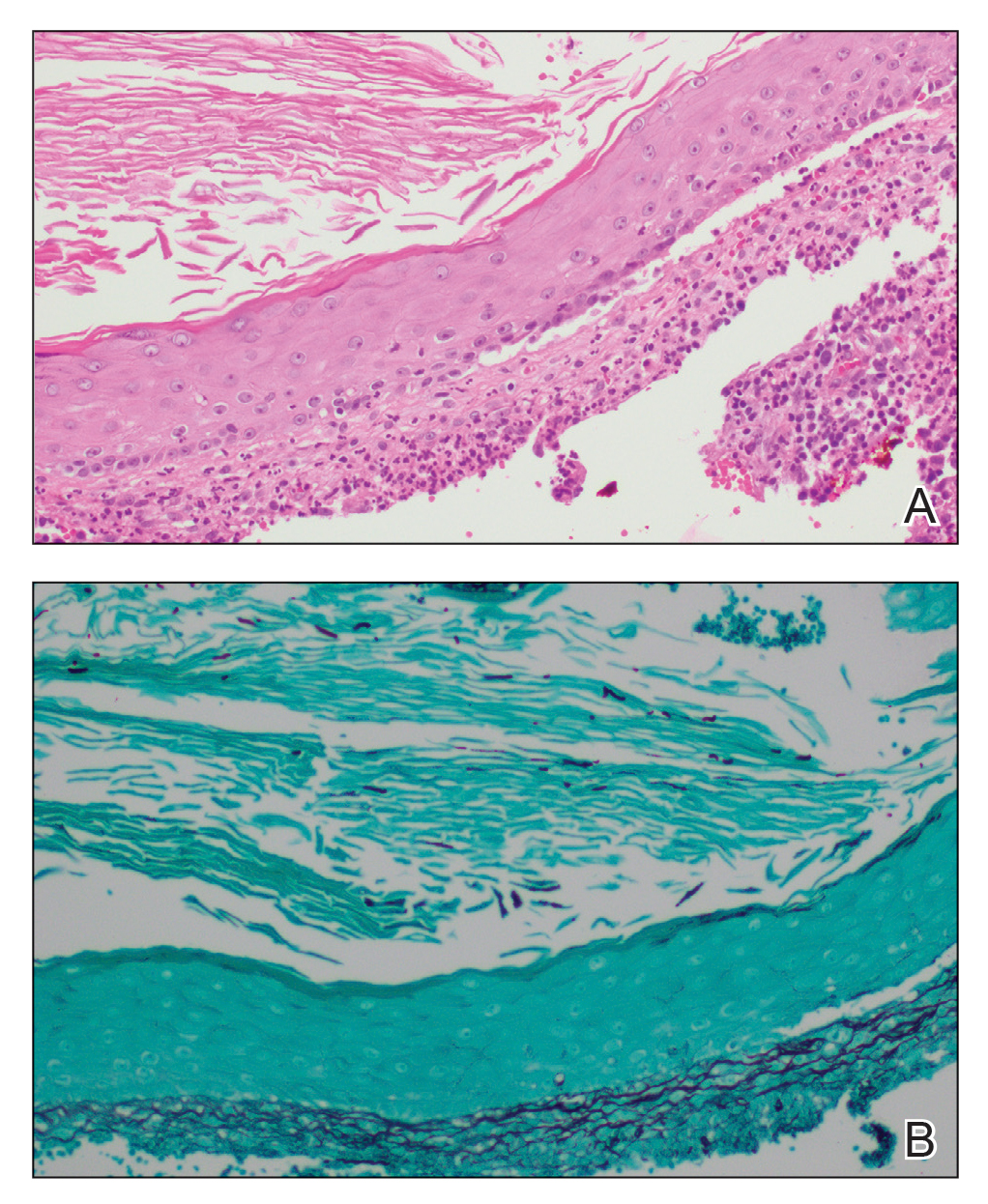
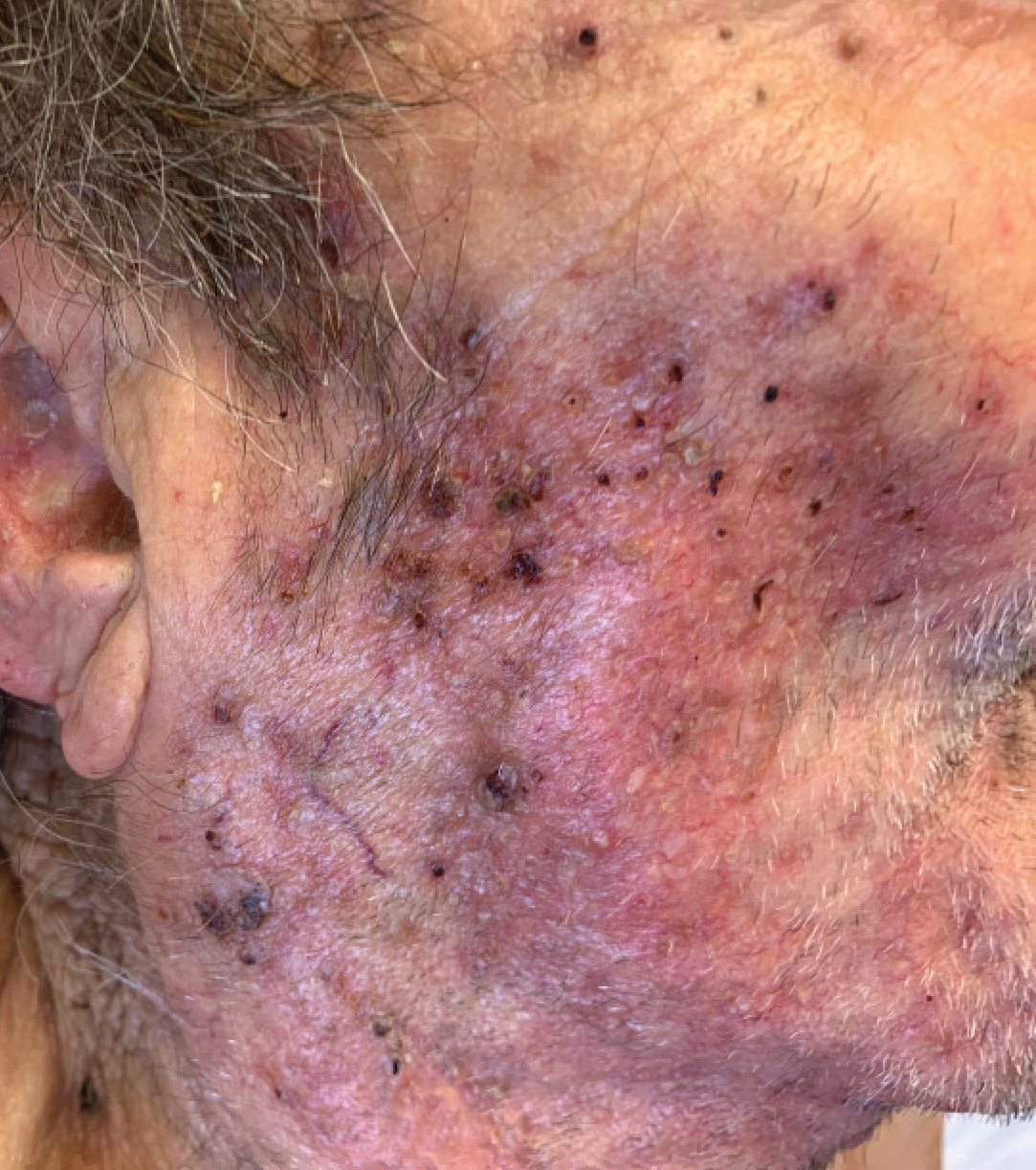
A biopsy and tissue culture showed acute dermal inflammation with granulomatous features and numerous fungal hyphae within the stratum corneum (Figure 1A), which were confirmed on GrocottGomori methenamine-silver staining (Figure 1B). Gram and Fite stains were negative for bacteria. A tissue culture speciated Trichophyton rubrum, which led to a diagnosis of deep dermatophyte infection (Majocchi granuloma) with a highly unusual clinical presentation of vegetative plaques. Predisposing factors included treatment with topical corticosteroids and possibly poor health and nutritional status at baseline. Our patient was treated with fluconazole 200 mg daily for 6 weeks, with near resolution of lesions at 3-week follow-up (Figure 2).
Dermatophytes are a common cause of superficial skin infections. The classic morphology consists of an annular scaly plaque; however, a wide variety of presentations have been observed (eg, verrucous, vesicular, pustular, granulomatous). Therefore, dermatophyte infections often mimic other dermatologic conditions, including atopic dermatitis, rosacea, psoriasis, bacterial abscess, erythema gyratum repens, lupus, granuloma annulare, cutaneous lymphoma, Hailey-Hailey disease, scarring alopecia, and syphilis.1
Notably, when dermatophytes grow downward along hair follicles causing deeper infection, disruption of the follicular wall can lead to an excessive inflammatory response with granulomatous features.2 Risk factors include cutaneous trauma, long-standing infection, immunocompromise, and treatment with topical corticosteroids.3 This disease evolution clinically appears as a nodule or infiltrated plaque, often without scale. The most well-known example is a kerion on the scalp. Elsewhere on the body, lesions often are termed Majocchi granulomas.2
Vegetative plaques, as seen in our patient, are a highly unusual morphology for deep tinea infection. Guanziroli et al4 reported a case of vegetative lesions on the forearm of a 67-year-old immunocompromised man that were successfully treated with a 3-month course of oral terbinafine after Trichophyton verrucosum was isolated. Skorepova et al5 reported a case of pyoderma vegetans triggered by recurrent Trichophyton mentagrophytes on the dorsal hands of a 64-year-old man with immunoglobulin deficiency of unknown etiology. The lesions were successfully treated with a prolonged course of doxycycline, topical triamcinolone, and intravenous immunoglobulin following 2 initial courses of terbinafine.
The differential diagnosis for vegetative lesions includes pemphigus vegetans, a vegetative variant of pyoderma gangrenosum; halogenoderma; and a variety of infections, including dimorphic fungi (histoplasmosis, blastomycosis), blastomycosislike pyoderma (bacterial), and candidiasis.6 These conditions usually can be distinguished based on histopathology. Clinically, pemphigus vegetans presents with pustules and vegetative lesions, as in our patient, but usually is more diffuse and favors the intertriginous areas. Histology likely would reveal foci of acantholysis and eosinophils. Vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum favors the trunk, particularly in sites of surgical trauma. In our patient, no lesions were present near the abdominal surgical sites, and there was no antecedent cribriform ulceration. Halogenoderma was a strong initial consideration given the localization, presence of large pustules, and history of numerous contrast computed tomography studies; however, our patient’s iodine levels were normal. Infectious etiologies including dimorphic fungi and blastomycosislike pyoderma generally are not restricted to the head and neck, and tissue culture helps exclude them. Vegetative lesions may occur in the setting of other infections, and tissue culture may be necessary to differentiate them if histopathology is not suggestive.
Deep dermatophyte infections require treatment with oral antifungals, as topicals do not penetrate adequately into the hair follicles. Exact regimens vary, but generally oral terbinafine or an oral azole (except ketoconazole) is administered for 2 to 6 weeks, with immunocompromise necessitating longer courses.
We present a rare case of vegetative Majocchi granuloma secondary to T rubrum infection. A dermatophyte infection should be included in the differential for vegetative lesions, especially in dense hair-bearing areas such as the beard. Treatment generally is straightforward with oral antifungals.
- Atzori L, Pau M, Aste N, et al. Dermatophyte infections mimicking other skin diseases: a 154-person case survey of tinea atypica in the district of Cagliari (Italy). Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:410-415.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karakas M. Majocchi’s granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457.
- Jevremovic L, Ilijin I, Kostic K, et al. Pyoderma vegetans—a case report. Serbian J Dermatol Venereol. 2017;9:22-28.
- Guanziroli E, Pavia G, Guttadauro A, et al. Deep dermatophytosis caused by Trichophyton verrucosum in an immunosuppressed patient: successful outcome with terbinafine. Mycopathologia. 2019;184:543-545.
- Skorepová M, Stuchlík D. Chronic pyoderma vegetans triggered by Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Mycoses. 2006;49:143-144.
- Reinholz M, Hermans C, Dietrich A, et al. A case of cutaneous vegetating candidiasis in a patient with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:537-539.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Vegetative Majocchi Granuloma
A biopsy and tissue culture showed acute dermal inflammation with granulomatous features and numerous fungal hyphae within the stratum corneum (Figure 1A), which were confirmed on GrocottGomori methenamine-silver staining (Figure 1B). Gram and Fite stains were negative for bacteria. A tissue culture speciated Trichophyton rubrum, which led to a diagnosis of deep dermatophyte infection (Majocchi granuloma) with a highly unusual clinical presentation of vegetative plaques. Predisposing factors included treatment with topical corticosteroids and possibly poor health and nutritional status at baseline. Our patient was treated with fluconazole 200 mg daily for 6 weeks, with near resolution of lesions at 3-week follow-up (Figure 2).


Dermatophytes are a common cause of superficial skin infections. The classic morphology consists of an annular scaly plaque; however, a wide variety of presentations have been observed (eg, verrucous, vesicular, pustular, granulomatous). Therefore, dermatophyte infections often mimic other dermatologic conditions, including atopic dermatitis, rosacea, psoriasis, bacterial abscess, erythema gyratum repens, lupus, granuloma annulare, cutaneous lymphoma, Hailey-Hailey disease, scarring alopecia, and syphilis.1
Notably, when dermatophytes grow downward along hair follicles causing deeper infection, disruption of the follicular wall can lead to an excessive inflammatory response with granulomatous features.2 Risk factors include cutaneous trauma, long-standing infection, immunocompromise, and treatment with topical corticosteroids.3 This disease evolution clinically appears as a nodule or infiltrated plaque, often without scale. The most well-known example is a kerion on the scalp. Elsewhere on the body, lesions often are termed Majocchi granulomas.2
Vegetative plaques, as seen in our patient, are a highly unusual morphology for deep tinea infection. Guanziroli et al4 reported a case of vegetative lesions on the forearm of a 67-year-old immunocompromised man that were successfully treated with a 3-month course of oral terbinafine after Trichophyton verrucosum was isolated. Skorepova et al5 reported a case of pyoderma vegetans triggered by recurrent Trichophyton mentagrophytes on the dorsal hands of a 64-year-old man with immunoglobulin deficiency of unknown etiology. The lesions were successfully treated with a prolonged course of doxycycline, topical triamcinolone, and intravenous immunoglobulin following 2 initial courses of terbinafine.
The differential diagnosis for vegetative lesions includes pemphigus vegetans, a vegetative variant of pyoderma gangrenosum; halogenoderma; and a variety of infections, including dimorphic fungi (histoplasmosis, blastomycosis), blastomycosislike pyoderma (bacterial), and candidiasis.6 These conditions usually can be distinguished based on histopathology. Clinically, pemphigus vegetans presents with pustules and vegetative lesions, as in our patient, but usually is more diffuse and favors the intertriginous areas. Histology likely would reveal foci of acantholysis and eosinophils. Vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum favors the trunk, particularly in sites of surgical trauma. In our patient, no lesions were present near the abdominal surgical sites, and there was no antecedent cribriform ulceration. Halogenoderma was a strong initial consideration given the localization, presence of large pustules, and history of numerous contrast computed tomography studies; however, our patient’s iodine levels were normal. Infectious etiologies including dimorphic fungi and blastomycosislike pyoderma generally are not restricted to the head and neck, and tissue culture helps exclude them. Vegetative lesions may occur in the setting of other infections, and tissue culture may be necessary to differentiate them if histopathology is not suggestive.
Deep dermatophyte infections require treatment with oral antifungals, as topicals do not penetrate adequately into the hair follicles. Exact regimens vary, but generally oral terbinafine or an oral azole (except ketoconazole) is administered for 2 to 6 weeks, with immunocompromise necessitating longer courses.
We present a rare case of vegetative Majocchi granuloma secondary to T rubrum infection. A dermatophyte infection should be included in the differential for vegetative lesions, especially in dense hair-bearing areas such as the beard. Treatment generally is straightforward with oral antifungals.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Vegetative Majocchi Granuloma
A biopsy and tissue culture showed acute dermal inflammation with granulomatous features and numerous fungal hyphae within the stratum corneum (Figure 1A), which were confirmed on GrocottGomori methenamine-silver staining (Figure 1B). Gram and Fite stains were negative for bacteria. A tissue culture speciated Trichophyton rubrum, which led to a diagnosis of deep dermatophyte infection (Majocchi granuloma) with a highly unusual clinical presentation of vegetative plaques. Predisposing factors included treatment with topical corticosteroids and possibly poor health and nutritional status at baseline. Our patient was treated with fluconazole 200 mg daily for 6 weeks, with near resolution of lesions at 3-week follow-up (Figure 2).


Dermatophytes are a common cause of superficial skin infections. The classic morphology consists of an annular scaly plaque; however, a wide variety of presentations have been observed (eg, verrucous, vesicular, pustular, granulomatous). Therefore, dermatophyte infections often mimic other dermatologic conditions, including atopic dermatitis, rosacea, psoriasis, bacterial abscess, erythema gyratum repens, lupus, granuloma annulare, cutaneous lymphoma, Hailey-Hailey disease, scarring alopecia, and syphilis.1
Notably, when dermatophytes grow downward along hair follicles causing deeper infection, disruption of the follicular wall can lead to an excessive inflammatory response with granulomatous features.2 Risk factors include cutaneous trauma, long-standing infection, immunocompromise, and treatment with topical corticosteroids.3 This disease evolution clinically appears as a nodule or infiltrated plaque, often without scale. The most well-known example is a kerion on the scalp. Elsewhere on the body, lesions often are termed Majocchi granulomas.2
Vegetative plaques, as seen in our patient, are a highly unusual morphology for deep tinea infection. Guanziroli et al4 reported a case of vegetative lesions on the forearm of a 67-year-old immunocompromised man that were successfully treated with a 3-month course of oral terbinafine after Trichophyton verrucosum was isolated. Skorepova et al5 reported a case of pyoderma vegetans triggered by recurrent Trichophyton mentagrophytes on the dorsal hands of a 64-year-old man with immunoglobulin deficiency of unknown etiology. The lesions were successfully treated with a prolonged course of doxycycline, topical triamcinolone, and intravenous immunoglobulin following 2 initial courses of terbinafine.
The differential diagnosis for vegetative lesions includes pemphigus vegetans, a vegetative variant of pyoderma gangrenosum; halogenoderma; and a variety of infections, including dimorphic fungi (histoplasmosis, blastomycosis), blastomycosislike pyoderma (bacterial), and candidiasis.6 These conditions usually can be distinguished based on histopathology. Clinically, pemphigus vegetans presents with pustules and vegetative lesions, as in our patient, but usually is more diffuse and favors the intertriginous areas. Histology likely would reveal foci of acantholysis and eosinophils. Vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum favors the trunk, particularly in sites of surgical trauma. In our patient, no lesions were present near the abdominal surgical sites, and there was no antecedent cribriform ulceration. Halogenoderma was a strong initial consideration given the localization, presence of large pustules, and history of numerous contrast computed tomography studies; however, our patient’s iodine levels were normal. Infectious etiologies including dimorphic fungi and blastomycosislike pyoderma generally are not restricted to the head and neck, and tissue culture helps exclude them. Vegetative lesions may occur in the setting of other infections, and tissue culture may be necessary to differentiate them if histopathology is not suggestive.
Deep dermatophyte infections require treatment with oral antifungals, as topicals do not penetrate adequately into the hair follicles. Exact regimens vary, but generally oral terbinafine or an oral azole (except ketoconazole) is administered for 2 to 6 weeks, with immunocompromise necessitating longer courses.
We present a rare case of vegetative Majocchi granuloma secondary to T rubrum infection. A dermatophyte infection should be included in the differential for vegetative lesions, especially in dense hair-bearing areas such as the beard. Treatment generally is straightforward with oral antifungals.
- Atzori L, Pau M, Aste N, et al. Dermatophyte infections mimicking other skin diseases: a 154-person case survey of tinea atypica in the district of Cagliari (Italy). Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:410-415.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karakas M. Majocchi’s granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457.
- Jevremovic L, Ilijin I, Kostic K, et al. Pyoderma vegetans—a case report. Serbian J Dermatol Venereol. 2017;9:22-28.
- Guanziroli E, Pavia G, Guttadauro A, et al. Deep dermatophytosis caused by Trichophyton verrucosum in an immunosuppressed patient: successful outcome with terbinafine. Mycopathologia. 2019;184:543-545.
- Skorepová M, Stuchlík D. Chronic pyoderma vegetans triggered by Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Mycoses. 2006;49:143-144.
- Reinholz M, Hermans C, Dietrich A, et al. A case of cutaneous vegetating candidiasis in a patient with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:537-539.
- Atzori L, Pau M, Aste N, et al. Dermatophyte infections mimicking other skin diseases: a 154-person case survey of tinea atypica in the district of Cagliari (Italy). Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:410-415.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karakas M. Majocchi’s granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457.
- Jevremovic L, Ilijin I, Kostic K, et al. Pyoderma vegetans—a case report. Serbian J Dermatol Venereol. 2017;9:22-28.
- Guanziroli E, Pavia G, Guttadauro A, et al. Deep dermatophytosis caused by Trichophyton verrucosum in an immunosuppressed patient: successful outcome with terbinafine. Mycopathologia. 2019;184:543-545.
- Skorepová M, Stuchlík D. Chronic pyoderma vegetans triggered by Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Mycoses. 2006;49:143-144.
- Reinholz M, Hermans C, Dietrich A, et al. A case of cutaneous vegetating candidiasis in a patient with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:537-539.
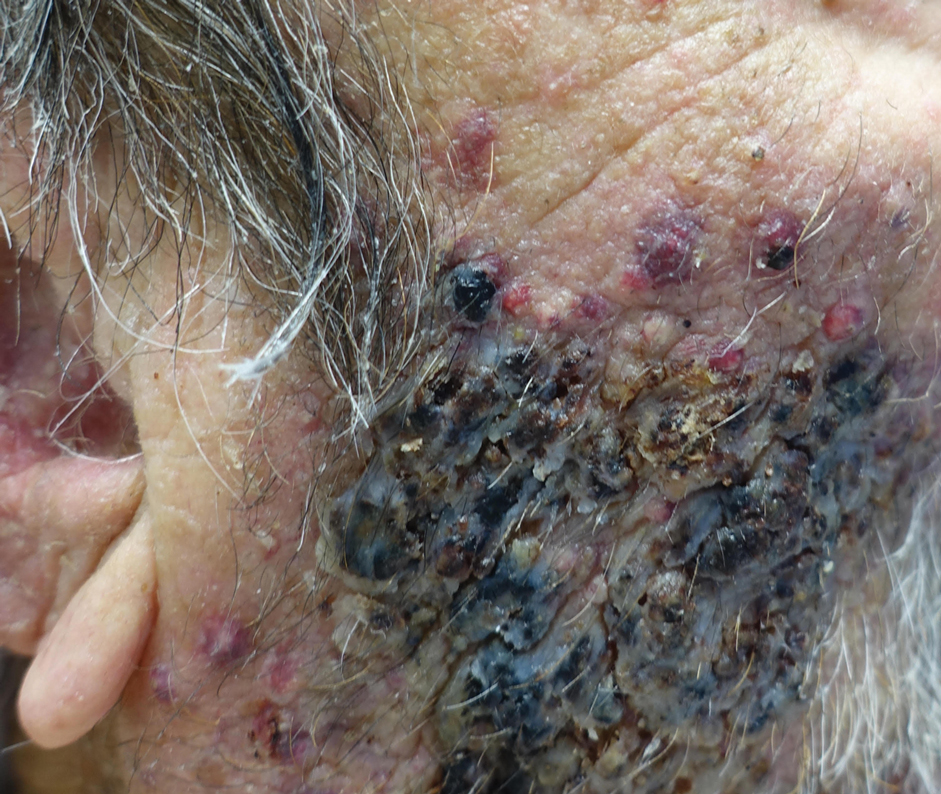
An 86-year-old man was admitted to the hospital for sigmoid colon perforation secondary to ischemic colitis. His medical history consisted of sequelae from atherosclerotic vascular disease. He had no known personal or family history of skin disease. His bowel perforation was surgically repaired, and his clinical status was stabilized, enabling transfer to a transitional care hospital. His course was complicated by delayed healing of the midline abdominal surgical wounds, leading to multiple computed tomography studies with iodinated contrast. One week following arrival at the transitional care hospital, he was noted to have a pustular rash on the face. He was empirically treated with topical steroids, mupirocin, and sulfacetamide. The rash did not improve, and the appearance changed, at which point dermatology was consulted. On evaluation, the patient was afebrile with a normal white blood cell count. Physical examination revealed gray-brown, moist, vegetative plaques on the cheeks with a few large pustules as well as similar-appearing lesions on the neck and upper chest. Attempted removal of a portion of the plaque left an erosion.
Widespread Necrotizing Purpura and Lucio Phenomenon as the First Diagnostic Presentation of Diffuse Nonnodular Lepromatous Leprosy
Case Report
A 70-year-old man living in Esna, Luxor, Egypt presented to the Department of Rheumatology and Rehabilitation with widespread gangrenous skin lesions associated with ulcers of 2 weeks’ duration. One year prior, the patient had an insidious onset of nocturnal fever, bilateral leg edema, and numbness and a tingling sensation in both hands. He presented some laboratory and radiologic investigations that were performed at another hospital prior to the current presentation, which revealed thrombocytopenia, mild splenomegaly, and generalized lymphadenopathy. An excisional left axillary lymph node biopsy was performed at another hospital prior to the current presentation, and the pathology report provided by the patient described a reactive, foamy, histiocyte-rich lesion, suggesting a diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. The patient had no diabetes or hypertension and no history of deep vein thrombosis, stroke, or unintentional weight loss. No medications were taken prior to the onset of the skin lesions, and his family history was irrelevant.
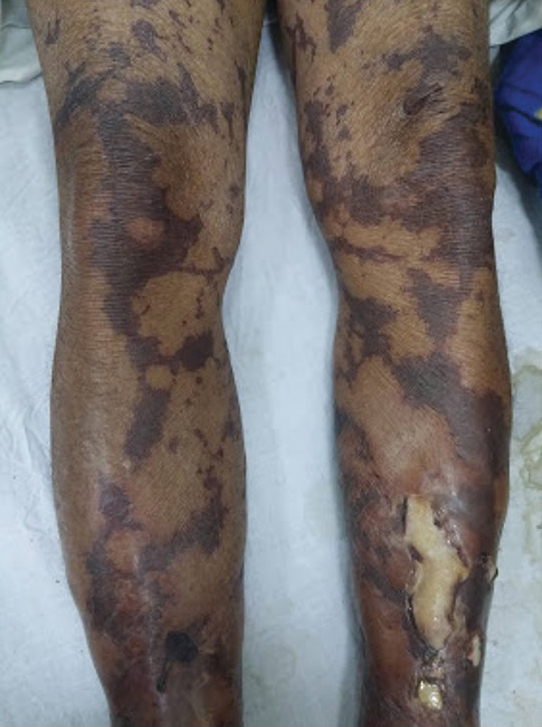
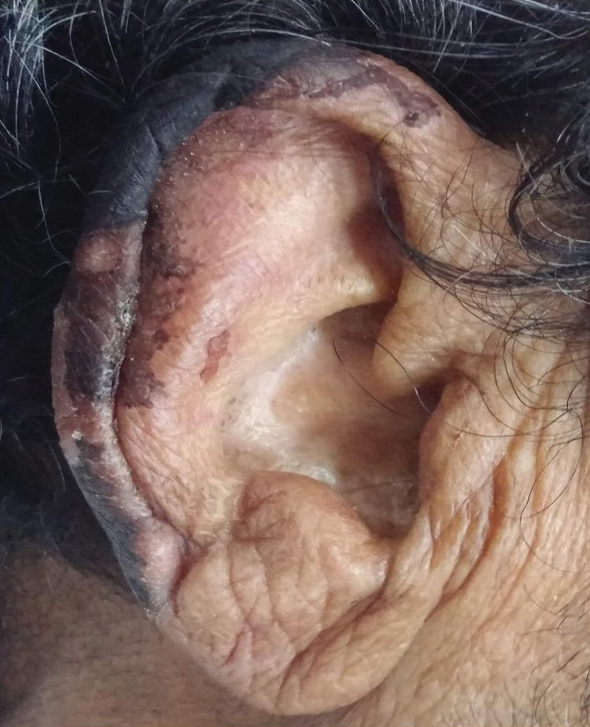
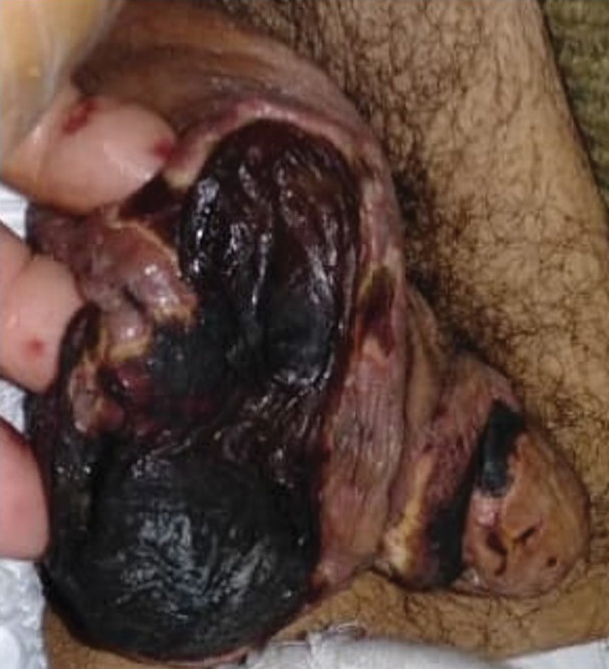
General examination at the current presentation revealed a fever (temperature, 101.3 °F [38.5 °C]), a normal heart rate (90 beats per minute), normal blood pressure (120/80 mmHg), normal respiratory rate (14 breaths per minute), accentuated heart sounds, and normal vesicular breathing without adventitious sounds. He had saddle nose, loss of the outer third of the eyebrows, and marked reduction in the density of the eyelashes (madarosis). Bilateral pitting edema of the legs also was present. Neurologic examination revealed hypoesthesia in a glove-and-stocking pattern, thickened peripheral nerves, and trophic changes over both hands; however, he had normal muscle power and deep reflexes. Joint examination revealed no abnormalities. Skin examination revealed widespread, reticulated, necrotizing, purpuric lesions on the arms, legs, abdomen, and ears, some associated with gangrenous ulcerations and hemorrhagic blisters. Scattered vasculitic ulcers and gangrenous patches were seen on the fingers. A gangrenous ulcer mimicking Fournier gangrene was seen involving the scrotal skin in addition to a gangrenous lesion on the glans penis (Figure 1–3). Unaffected skin appeared smooth, shiny, and edematous and showed no nodular lesions. Peripheral pulsations were intact.
Positive findings from a wide panel of laboratory investigations included an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (103 mm for the first hour [reference range, 0–22 mm]), high C-reactive protein (50.7 mg/L [reference range, up to 6 mg/L]), anemia (hemoglobin count, 7.3 g/dL [reference range, 13.5–17.5 g/dL]), thrombocytopenia (45×103/mm3 [reference range, 150×103/mm3), low serum albumin (2.3 g/dL [reference range, 3.4–5.4 g/dL]), elevated IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies (IgG, 21.4 IgG phospholipid [GPL] units [reference range, <10 IgG phospholipid (GPL) units]; IgM, 59.4 IgM phospholipid (MPL) units [reference range, <7 IgM phospholipid (MPL) units]), positive lupus anticoagulant panel test, elevated anti-β2 glycoprotein antibodies (IgG, 17.5
Nerve conduction velocity showed axonal sensory polyneuropathy. Motor nerve conduction studies for median and ulnar nerves were within normal range. Lower-limb nerves assessment was limited by the ulcerated areas and marked edema. Echocardiography was unremarkable. Arterial Doppler studies were only available for the upper limbs and were unremarkable.
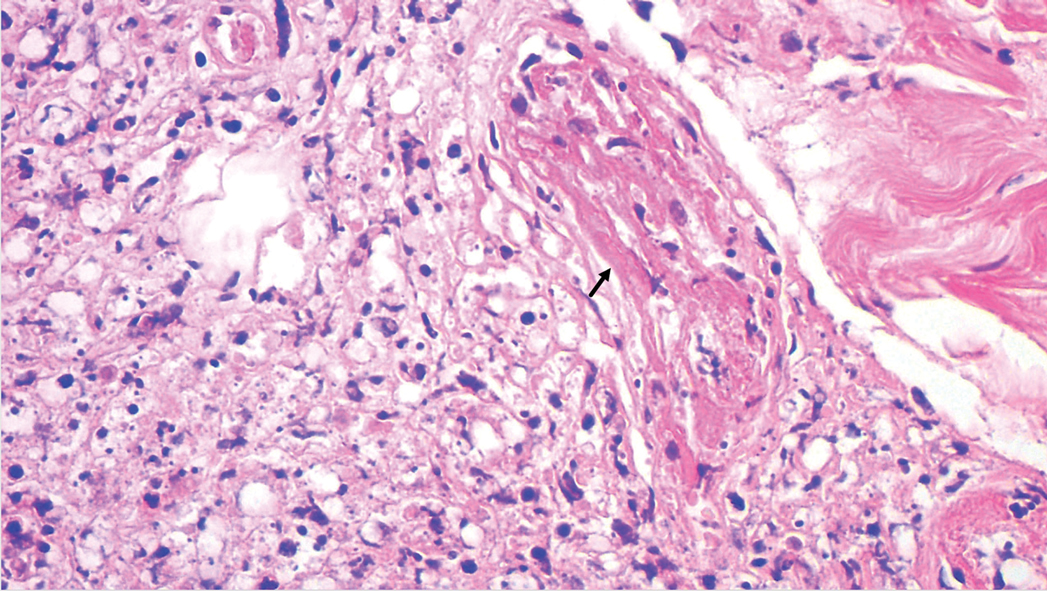
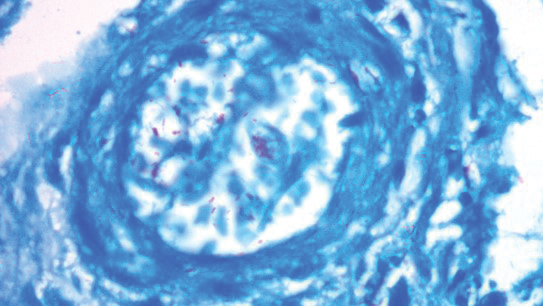
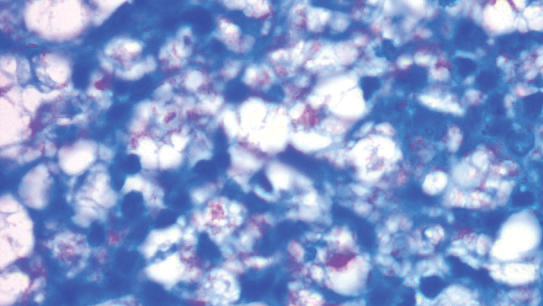
A punch biopsy was taken from one of the necrotizing purpuric lesions on the legs, and histopathologic examination revealed foci of epidermal necrosis and subepidermal separation and superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal infiltrates extending into the fat lobules. The infiltrates were mainly made up of foamy macrophages, and some contained globi (lepra cells), in addition to lymphocytes and many neutrophils with nuclear dust. Blood vessels in the superficial and deep dermis and in the subcutaneous fat showed fibrinoid necrosis in their walls with neutrophils infiltrating the walls and thrombi in the lumens (Figure 4). Modified Ziehl-Neelsen staining revealed clumps of acid-fast lepra bacilli inside vascular lumina and endothelial cell lining and within the foamy macrophages (Figure 5). Slit-skin smear examination was performed twice and yielded negative results. The slide and paraffin block of the already performed lymph node biopsy were retrieved. Examination revealed aggregates of foamy histiocytes surrounded by lymphocytes and plasma cells replacing normal lymphoid follicles. Modified Ziehl-Neelsen stain was performed, and clusters of acid-fast bacilli were detected within the foamy histiocytic infiltrate (Figure 6).
According to the results of the skin biopsy, the revised result of the lymph node biopsy, and the pattern of neurologic deficit together with clinical and laboratory correlation, the patient was diagnosed with diffuse nonnodular lepromatous leprosy presenting with Lucio phenomenon (Lucio leprosy) and associated with lepromatous lymphadenitis.
The patient received the following treatment: methylprednisolone 500 mg (intravenous pulse therapy) followed by daily oral administration of prednisolone 10 mg, rifampicin 300 mg, dapsone 100 mg, clofazimine 100 mg, acetylsalicylic acid 150 mg, and enoxaparin sodium 80 mg. In addition, the scrotal Fournier gangrene–like lesion was treated by surgical debridement followed by vacuum therapy. By the second week after treatment, the gangrenous lesions of the fingers developed a line of demarcation, and the skin infarctions started to recede.
Comment
Despite a decrease in its prevalence through a World Health Organization (WHO)–empowered eradication program, leprosy still represents a health problem in endemic areas.1,2 It is characterized by a wide range of immune responses to Mycobacterium leprae, displaying a spectrum of clinical and histopathologic manifestations that vary from the tuberculoid or paucibacillary pole with a strong cell-mediated immune response and fewer organisms to the lepromatous or multibacillary pole with weaker cell-mediated immune response and higher loads of organisms.3 In addition to its well-known cutaneous and neurologic manifestations, leprosy can present with a variety of manifestations, including constitutional symptoms, musculoskeletal manifestations, and serologic abnormalities; thus, leprosy can mimic rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, and vasculitis—a pitfall that may result in misdiagnosis as a rheumatologic disorder.3-7
The chronic course of leprosy can be disrupted by acute, immunologically mediated reactions known as lepra reactions, of which there are 3 types.8 Type I lepra reactions are cell mediated and occur mainly in patients with borderline disease, often representing an upgrade toward the tuberculoid pole; less often they represent a downgrade reaction. Nerves become painful and swollen with possible loss of function, and skin lesions become edematous and tender; sometimes arthritis develops.9 Type II lepra reactions, also known as erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL), occur in borderline lepromatous and lepromatous patients with a high bacillary load. They are characterized by fever, body aches, tender cutaneous/subcutaneous nodules that may ulcerate, possible bullous lesions, painful nerve swellings, swollen joints, iritis, lymphadenitis, glomerulonephritis, epididymo-orchitis, and hepatic affection. Both immune-complex and delayed hypersensitivity reactions play a role in ENL.8,10 The third reaction is a rare aggressive type known as Lucio phenomenon or Lucio leprosy, which presents with irregular-shaped, angulated, or stellar necrotizing purpuric lesions (hemorrhagic infacrtions) developing mainly on the extremities. The lesions evolve into ulcers that heal with atrophic scarring.2,11 Lucio phenomenon develops as a result of thrombotic vascular occlusion secondary to massive invasion of vascular endothelial cells by lepra bacilli.2,11-14 Involvement of the scrotal skin, such as in our patient, is rare.
Lucio phenomenon mainly is seen in Mexico and Central America, and few cases have been documented in Cuba, South America, the United States, India, Polynesia, South Africa, and Southeast Asia.15-17 It specifically occurs in patients with untreated, diffuse, nonnodular lepromatous leprosy (pure and primitive diffuse lepromatous leprosy (DLL)/diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapí). This type of leprosy was first described by Lucio and Alvarado18 in 1852 as a distinct form of lepromatous leprosy characterized by widespread and dense infiltration of the whole skin by lepra bacilli without the typical nodular lesions of leprosy, rendering its diagnosis challenging, especially in sporadic cases. Other manifestations of DLL include complete alopecia of the eyebrows and eyelashes, destructive rhinitis, and areas of anhidrosis and dyesthesia.2
Latapí and Chévez-Zomora19 defined Lucio phenomenon in 1948 as a form of histopathologic vasculitis restricted to patients with DLL. Histopathologically, in addition to the infiltration of the skin with acid-fast bacilli–laden foamy histiocytes, lesions of Lucio phenomenon show features of necrotizing (leukocytoclastic) vasculitis with fibrinoid necrosis20 or vascular thrombi with minimal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and no evidence of vasculitis.11 Medium to large vessels in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue show infiltration of their walls with a large number of macrophages laden with acid-fast bacilli.11 Cases with histopathologic features mimicking antiphospholipid syndrome with endothelial cell proliferation, thrombosis, and mild mononuclear cell infiltrate also may be seen.20 In all cases, ischemic epidermal necrosis is seen, as well as acid-fast bacilli, both singly and in clusters (globi) within endothelial cells and inside blood vessel lumina.
Although Lucio phenomenon initially was thought to be immune-complex mediated like ENL, it has been suggested that the main trigger is thrombotic vascular occlusion secondary to massive invasion of the vascular endothelial cells by the lepra bacilli, resulting in necrosis.14 Bacterial lipopolysaccharides promote the release of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor α, which in turn stimulate the production of prostaglandins, IL-6, and coagulation factor III, leading to vascular thrombosis and tissue necrosis.21,22 Moreover, antiphospholipid antibodies, which have been found to be induced in response to certain infectious agents in genetically predisposed individuals,23 have been reported in patients with leprosy, mainly in association with lepromatous leprosy. The reported prevalence of anticardiolipin antibodies ranged from 37% to 98%, whereas anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies ranged from 3% to 19%, and antiprothrombin antibodies ranged from 6% to 45%.24,25 Antiphospholipid antibodies have been reported to play a role in the pathogenesis of Lucio phenomenon.11,13,15,26 Our case supports this hypothesis with positive anticardiolipin antibodies, anti-β2 glycoprotein antibodies, and positive lupus anticoagulant.
In accordance with Curi et al,2 who reported 5 cases of DLL with Lucio phenomenon, our patient showed a similar presentation with positive inflammatory markers in association with a negative autoimmune profile (ANA, ANCA-C&P) and negative venereal disease research laboratory test. It is important to mention that a positive autoimmune profile (ANA, ANCA-C&P) can be present in leprotic patients, causing possible diagnostic confusion with collagen diseases.27,28
An interesting finding in our case was the negative slit-skin smear results. Although the specificity of slit-skin smear is 100%, as it directly demonstrates the presence of acid-fast bacilli,29 its sensitivity is low and varies from 10% to 50%.30 The detection of acid-fast bacilli in tissue sections is reported to be a better method for confirming the diagnosis of leprosy.31
The provisional impression of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in the lymph node biopsy in our patient was excluded upon detection of acid-fast bacilli in the foamy histiocytes infiltrating the lymph node; moreover, the normal serum lipids and serum ferritin argued against this diagnosis.32 Leprosy tends to involve the lymph nodes, particularly in borderline, borderline lepromatous, and lepromatous forms.33 The incidence of lymph node involvement accompanied by skin lesions with the presence of acid-fast bacilli in the lymph nodes is 92.2%.34
Our patient showed an excellent response to antileprotic treatment, which was administered according to the WHO multidrug therapy guidelines for multibacillary leprosy,35 combined with low-dose prednisolone, acetylsalicylic acid, and anticoagulant treatment. Thalidomide and high-dose prednisolone (60 mg/d) combined with antileprotic treatment also have been reported to be successful in managing recurrent infarctions in leprosy.36 The Fournier-like gangrenous ulcer of the scrotum was managed by surgical debridement and vacuum therapy.
It is noteworthy that the WHO elimination goal for leprosy was to reduce the prevalence to less than 1 case per 10,000 population. Egypt is among the first countries in North Africa and the Middle East regions to achieve this target supervised by the National Leprosy Control Program as early as 1994; this was further reduced to 0.33 cases per 10,000 population in 2004, and reduced again in 2009; however, certain foci showed a prevalence rate more than the elimination target, particularly in the cities of Qena (1.12) and Sohag (2.47).37 Esna, where our patient is from, is an endemic area in Egypt.38
Conclusion
1. World Health Organization. World Health Statistics: 2011. World Health Organization; 2011. https://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/EN_WHS2011_Full.pdf
2. Curi PF, Villaroel JS, Migliore N, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: report of five cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:1397-1401.
3. Shrestha B, Li YQ, Fu P. Leprosy mimics adult onset Still’s disease in a Chinese patient. Egypt Rheumatol. 2018;40:217-220.
4. Prasad S, Misra R, Aggarwal A, et al. Leprosy revealed in a rheumatology clinic: a case series. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013;16:129-133.
5. Chao G, Fang L, Lu C. Leprosy with ANA positive mistaken for connective tissue disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:645-648.
6. Chauhan S, Wakhlu A, Agarwal V. Arthritis in leprosy. Rheumatology. 2010;49:2237-2242.
7. Rath D, Bhargava S, Kundu BK. Leprosy mimicking common rheumatologic entities: a trial for the clinician in the era of biologics. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2014;2014:429698.
8. Cuevas J, Rodríguez-Peralto JL, Carrillo R, et al. Erythema nodosum leprosum: reactional leprosy. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:126-130.
9. Henriques CC, Lopéz B, Mestre T, et al. Leprosy and rheumatoid arthritis: consequence or association? BMJ Case Rep. 2012;13:1-4.
10. Vázquez-Botet M, Sánchez JL. Erythema nodosum leprosum. Int J Dermatol. 1987;26:436-437.
11. Nunzie E, Ortega Cabrera LV, Macanchi Moncayo FM, et al. Lucio leprosy with Lucio’s phenomenon, digital gangrene and anticardiolipin antibodies. Lepr Rev. 2014;85:194-200.
12. Salvi S, Chopra A. Leprosy in a rheumatology setting: a challenging mimic to expose. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:1557-1563.
13. Azulay-Abulafia L, Pereira SL, Hardmann D, et al. Lucio phenomenon. vasculitis or occlusive vasculopathy? Hautarzt. 2006;57:1101-1105.
14. Benard G, Sakai-Valente NY, Bianconcini Trindade MA. Concomittant Lucio phenomenon and erythema nodosum in a leprosy patient: clues for their distinct pathogenesis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:288-292.
15. Rocha RH, Emerich PS, Diniz LM, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: exuberant case report and review of Brazilian cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(suppl 5):S60-S63.
16. Costa IM, Kawano LB, Pereira CP, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:566-571.
17. Kumari R, Thappa DM, Basu D. A fatal case of Lucio phenomenon from India. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:10.
18. Lucio R, Alvarado I. Opúsculo Sobre el Mal de San Lázaro o Elefantiasis de los Griegos. M. Murguía; 1852.
19. Latapí F, Chévez-Zamora A. The “spotted” leprosy of Lucio: an introduction to its clinical and histological study. Int J Lepr. 1948;16:421-437.
20. Vargas OF. Diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapí: a histologic study. Lepr Rev. 2007;78:248-260.
21. Latapí FR, Chevez-Zamora A. La lepra manchada de Lucio. Rev Dermatol Mex. 1978;22:102-107.
22. Monteiro R, Abreu MA, Tiezzi MG, et al. Fenômeno de Lúcio: mais um caso relatado no Brasil. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:296-300.
23. Gharavi EE, Chaimovich H, Cucucrull E, et al. Induction of antiphospholipid antibodies by immunization with synthetic bacterial & viral peptides. Lupus. 1999;8:449-455.
24. de Larrañaga GF, Forastiero RR, Martinuzzo ME, et al. High prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in leprosy: evaluation of antigen reactivity. Lupus. 2000;9:594-600.
25. Loizou S, Singh S, Wypkema E, et al. Anticardiolipin, anti-beta(2)-glycoprotein I and antiprothrombin antibodies in black South African patients with infectious disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:1106-1111.
26. Akerkar SM, Bichile LS. Leprosy & gangrene: a rare association; role of antiphospholipid antibodies. BMC Infect Dis. 2005,5:74.
27. Horta-Baas G, Hernández-Cabrera MF, Barile-Fabris LA, et al. Multibacillary leprosy mimicking systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and literature review. Lupus. 2015;24:1095-1102.
28. Pradhan V, Badakere SS, Shankar KU. Increased incidence of cytoplasmic ANCA (cANCA) and other auto antibodies in leprosy patients from western India. Lepr Rev. 2004;75:50-56.
29. Oskam L. Diagnosis and classification of leprosy. Lepr Rev. 2002;73:17-26.
30. Rao PN. Recent advances in the control programs and therapy of leprosy. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2004;70:269-276.
31. Rao PN, Pratap D, Ramana Reddy AV, et al. Evaluation of leprosy patients with 1 to 5 skin lesions with relevance to their grouping into paucibacillary or multibacillary disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:207-210.
32. Rosado FGN, Kim AS. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. an update on diagnosis and pathogenesis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2013;139:713-727.
33. Kar HK, Mohanty HC, Mohanty GN, et al. Clinicopathological study of lymph node involvement in leprosy. Lepr India. 1983;55:725-738.
34. Gupta JC, Panda PK, Shrivastava KK, et al. A histopathologic study of lymph nodes in 43 cases of leprosy. Lepr India. 1978;50:196-203.
35. WHO Expert Committee on Leprosy. Seventh Report. World Health Organization; 1998. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42060/WHO_TRS_874.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
36. Misra DP, Parida JR, Chowdhury AC, et al. Lepra reaction with Lucio phenomenon mimicking cutaneous vasculitis. Case Rep Immunol. 2014;2014:641989.
37. Amer A, Mansour A. Epidemiological study of leprosy in Egypt: 2005-2009. Egypt J Dermatol Venereol. 2014;34:70-73.
38. World Health Organization. Screening campaign aims to eliminate leprosy in Egypt. Published May 9, 2018. Accessed September 8, 2021. http://www.emro.who.int/egy/egypt-events/last-miless-activities-on-eliminating-leprosy-from-egypt.html
Case Report
A 70-year-old man living in Esna, Luxor, Egypt presented to the Department of Rheumatology and Rehabilitation with widespread gangrenous skin lesions associated with ulcers of 2 weeks’ duration. One year prior, the patient had an insidious onset of nocturnal fever, bilateral leg edema, and numbness and a tingling sensation in both hands. He presented some laboratory and radiologic investigations that were performed at another hospital prior to the current presentation, which revealed thrombocytopenia, mild splenomegaly, and generalized lymphadenopathy. An excisional left axillary lymph node biopsy was performed at another hospital prior to the current presentation, and the pathology report provided by the patient described a reactive, foamy, histiocyte-rich lesion, suggesting a diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. The patient had no diabetes or hypertension and no history of deep vein thrombosis, stroke, or unintentional weight loss. No medications were taken prior to the onset of the skin lesions, and his family history was irrelevant.
General examination at the current presentation revealed a fever (temperature, 101.3 °F [38.5 °C]), a normal heart rate (90 beats per minute), normal blood pressure (120/80 mmHg), normal respiratory rate (14 breaths per minute), accentuated heart sounds, and normal vesicular breathing without adventitious sounds. He had saddle nose, loss of the outer third of the eyebrows, and marked reduction in the density of the eyelashes (madarosis). Bilateral pitting edema of the legs also was present. Neurologic examination revealed hypoesthesia in a glove-and-stocking pattern, thickened peripheral nerves, and trophic changes over both hands; however, he had normal muscle power and deep reflexes. Joint examination revealed no abnormalities. Skin examination revealed widespread, reticulated, necrotizing, purpuric lesions on the arms, legs, abdomen, and ears, some associated with gangrenous ulcerations and hemorrhagic blisters. Scattered vasculitic ulcers and gangrenous patches were seen on the fingers. A gangrenous ulcer mimicking Fournier gangrene was seen involving the scrotal skin in addition to a gangrenous lesion on the glans penis (Figure 1–3). Unaffected skin appeared smooth, shiny, and edematous and showed no nodular lesions. Peripheral pulsations were intact.



Positive findings from a wide panel of laboratory investigations included an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (103 mm for the first hour [reference range, 0–22 mm]), high C-reactive protein (50.7 mg/L [reference range, up to 6 mg/L]), anemia (hemoglobin count, 7.3 g/dL [reference range, 13.5–17.5 g/dL]), thrombocytopenia (45×103/mm3 [reference range, 150×103/mm3), low serum albumin (2.3 g/dL [reference range, 3.4–5.4 g/dL]), elevated IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies (IgG, 21.4 IgG phospholipid [GPL] units [reference range, <10 IgG phospholipid (GPL) units]; IgM, 59.4 IgM phospholipid (MPL) units [reference range, <7 IgM phospholipid (MPL) units]), positive lupus anticoagulant panel test, elevated anti-β2 glycoprotein antibodies (IgG, 17.5
Nerve conduction velocity showed axonal sensory polyneuropathy. Motor nerve conduction studies for median and ulnar nerves were within normal range. Lower-limb nerves assessment was limited by the ulcerated areas and marked edema. Echocardiography was unremarkable. Arterial Doppler studies were only available for the upper limbs and were unremarkable.
A punch biopsy was taken from one of the necrotizing purpuric lesions on the legs, and histopathologic examination revealed foci of epidermal necrosis and subepidermal separation and superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal infiltrates extending into the fat lobules. The infiltrates were mainly made up of foamy macrophages, and some contained globi (lepra cells), in addition to lymphocytes and many neutrophils with nuclear dust. Blood vessels in the superficial and deep dermis and in the subcutaneous fat showed fibrinoid necrosis in their walls with neutrophils infiltrating the walls and thrombi in the lumens (Figure 4). Modified Ziehl-Neelsen staining revealed clumps of acid-fast lepra bacilli inside vascular lumina and endothelial cell lining and within the foamy macrophages (Figure 5). Slit-skin smear examination was performed twice and yielded negative results. The slide and paraffin block of the already performed lymph node biopsy were retrieved. Examination revealed aggregates of foamy histiocytes surrounded by lymphocytes and plasma cells replacing normal lymphoid follicles. Modified Ziehl-Neelsen stain was performed, and clusters of acid-fast bacilli were detected within the foamy histiocytic infiltrate (Figure 6).



According to the results of the skin biopsy, the revised result of the lymph node biopsy, and the pattern of neurologic deficit together with clinical and laboratory correlation, the patient was diagnosed with diffuse nonnodular lepromatous leprosy presenting with Lucio phenomenon (Lucio leprosy) and associated with lepromatous lymphadenitis.
The patient received the following treatment: methylprednisolone 500 mg (intravenous pulse therapy) followed by daily oral administration of prednisolone 10 mg, rifampicin 300 mg, dapsone 100 mg, clofazimine 100 mg, acetylsalicylic acid 150 mg, and enoxaparin sodium 80 mg. In addition, the scrotal Fournier gangrene–like lesion was treated by surgical debridement followed by vacuum therapy. By the second week after treatment, the gangrenous lesions of the fingers developed a line of demarcation, and the skin infarctions started to recede.
Comment
Despite a decrease in its prevalence through a World Health Organization (WHO)–empowered eradication program, leprosy still represents a health problem in endemic areas.1,2 It is characterized by a wide range of immune responses to Mycobacterium leprae, displaying a spectrum of clinical and histopathologic manifestations that vary from the tuberculoid or paucibacillary pole with a strong cell-mediated immune response and fewer organisms to the lepromatous or multibacillary pole with weaker cell-mediated immune response and higher loads of organisms.3 In addition to its well-known cutaneous and neurologic manifestations, leprosy can present with a variety of manifestations, including constitutional symptoms, musculoskeletal manifestations, and serologic abnormalities; thus, leprosy can mimic rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, and vasculitis—a pitfall that may result in misdiagnosis as a rheumatologic disorder.3-7
The chronic course of leprosy can be disrupted by acute, immunologically mediated reactions known as lepra reactions, of which there are 3 types.8 Type I lepra reactions are cell mediated and occur mainly in patients with borderline disease, often representing an upgrade toward the tuberculoid pole; less often they represent a downgrade reaction. Nerves become painful and swollen with possible loss of function, and skin lesions become edematous and tender; sometimes arthritis develops.9 Type II lepra reactions, also known as erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL), occur in borderline lepromatous and lepromatous patients with a high bacillary load. They are characterized by fever, body aches, tender cutaneous/subcutaneous nodules that may ulcerate, possible bullous lesions, painful nerve swellings, swollen joints, iritis, lymphadenitis, glomerulonephritis, epididymo-orchitis, and hepatic affection. Both immune-complex and delayed hypersensitivity reactions play a role in ENL.8,10 The third reaction is a rare aggressive type known as Lucio phenomenon or Lucio leprosy, which presents with irregular-shaped, angulated, or stellar necrotizing purpuric lesions (hemorrhagic infacrtions) developing mainly on the extremities. The lesions evolve into ulcers that heal with atrophic scarring.2,11 Lucio phenomenon develops as a result of thrombotic vascular occlusion secondary to massive invasion of vascular endothelial cells by lepra bacilli.2,11-14 Involvement of the scrotal skin, such as in our patient, is rare.
Lucio phenomenon mainly is seen in Mexico and Central America, and few cases have been documented in Cuba, South America, the United States, India, Polynesia, South Africa, and Southeast Asia.15-17 It specifically occurs in patients with untreated, diffuse, nonnodular lepromatous leprosy (pure and primitive diffuse lepromatous leprosy (DLL)/diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapí). This type of leprosy was first described by Lucio and Alvarado18 in 1852 as a distinct form of lepromatous leprosy characterized by widespread and dense infiltration of the whole skin by lepra bacilli without the typical nodular lesions of leprosy, rendering its diagnosis challenging, especially in sporadic cases. Other manifestations of DLL include complete alopecia of the eyebrows and eyelashes, destructive rhinitis, and areas of anhidrosis and dyesthesia.2
Latapí and Chévez-Zomora19 defined Lucio phenomenon in 1948 as a form of histopathologic vasculitis restricted to patients with DLL. Histopathologically, in addition to the infiltration of the skin with acid-fast bacilli–laden foamy histiocytes, lesions of Lucio phenomenon show features of necrotizing (leukocytoclastic) vasculitis with fibrinoid necrosis20 or vascular thrombi with minimal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and no evidence of vasculitis.11 Medium to large vessels in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue show infiltration of their walls with a large number of macrophages laden with acid-fast bacilli.11 Cases with histopathologic features mimicking antiphospholipid syndrome with endothelial cell proliferation, thrombosis, and mild mononuclear cell infiltrate also may be seen.20 In all cases, ischemic epidermal necrosis is seen, as well as acid-fast bacilli, both singly and in clusters (globi) within endothelial cells and inside blood vessel lumina.
Although Lucio phenomenon initially was thought to be immune-complex mediated like ENL, it has been suggested that the main trigger is thrombotic vascular occlusion secondary to massive invasion of the vascular endothelial cells by the lepra bacilli, resulting in necrosis.14 Bacterial lipopolysaccharides promote the release of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor α, which in turn stimulate the production of prostaglandins, IL-6, and coagulation factor III, leading to vascular thrombosis and tissue necrosis.21,22 Moreover, antiphospholipid antibodies, which have been found to be induced in response to certain infectious agents in genetically predisposed individuals,23 have been reported in patients with leprosy, mainly in association with lepromatous leprosy. The reported prevalence of anticardiolipin antibodies ranged from 37% to 98%, whereas anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies ranged from 3% to 19%, and antiprothrombin antibodies ranged from 6% to 45%.24,25 Antiphospholipid antibodies have been reported to play a role in the pathogenesis of Lucio phenomenon.11,13,15,26 Our case supports this hypothesis with positive anticardiolipin antibodies, anti-β2 glycoprotein antibodies, and positive lupus anticoagulant.
In accordance with Curi et al,2 who reported 5 cases of DLL with Lucio phenomenon, our patient showed a similar presentation with positive inflammatory markers in association with a negative autoimmune profile (ANA, ANCA-C&P) and negative venereal disease research laboratory test. It is important to mention that a positive autoimmune profile (ANA, ANCA-C&P) can be present in leprotic patients, causing possible diagnostic confusion with collagen diseases.27,28
An interesting finding in our case was the negative slit-skin smear results. Although the specificity of slit-skin smear is 100%, as it directly demonstrates the presence of acid-fast bacilli,29 its sensitivity is low and varies from 10% to 50%.30 The detection of acid-fast bacilli in tissue sections is reported to be a better method for confirming the diagnosis of leprosy.31
The provisional impression of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in the lymph node biopsy in our patient was excluded upon detection of acid-fast bacilli in the foamy histiocytes infiltrating the lymph node; moreover, the normal serum lipids and serum ferritin argued against this diagnosis.32 Leprosy tends to involve the lymph nodes, particularly in borderline, borderline lepromatous, and lepromatous forms.33 The incidence of lymph node involvement accompanied by skin lesions with the presence of acid-fast bacilli in the lymph nodes is 92.2%.34
Our patient showed an excellent response to antileprotic treatment, which was administered according to the WHO multidrug therapy guidelines for multibacillary leprosy,35 combined with low-dose prednisolone, acetylsalicylic acid, and anticoagulant treatment. Thalidomide and high-dose prednisolone (60 mg/d) combined with antileprotic treatment also have been reported to be successful in managing recurrent infarctions in leprosy.36 The Fournier-like gangrenous ulcer of the scrotum was managed by surgical debridement and vacuum therapy.
It is noteworthy that the WHO elimination goal for leprosy was to reduce the prevalence to less than 1 case per 10,000 population. Egypt is among the first countries in North Africa and the Middle East regions to achieve this target supervised by the National Leprosy Control Program as early as 1994; this was further reduced to 0.33 cases per 10,000 population in 2004, and reduced again in 2009; however, certain foci showed a prevalence rate more than the elimination target, particularly in the cities of Qena (1.12) and Sohag (2.47).37 Esna, where our patient is from, is an endemic area in Egypt.38
Conclusion
Case Report
A 70-year-old man living in Esna, Luxor, Egypt presented to the Department of Rheumatology and Rehabilitation with widespread gangrenous skin lesions associated with ulcers of 2 weeks’ duration. One year prior, the patient had an insidious onset of nocturnal fever, bilateral leg edema, and numbness and a tingling sensation in both hands. He presented some laboratory and radiologic investigations that were performed at another hospital prior to the current presentation, which revealed thrombocytopenia, mild splenomegaly, and generalized lymphadenopathy. An excisional left axillary lymph node biopsy was performed at another hospital prior to the current presentation, and the pathology report provided by the patient described a reactive, foamy, histiocyte-rich lesion, suggesting a diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. The patient had no diabetes or hypertension and no history of deep vein thrombosis, stroke, or unintentional weight loss. No medications were taken prior to the onset of the skin lesions, and his family history was irrelevant.
General examination at the current presentation revealed a fever (temperature, 101.3 °F [38.5 °C]), a normal heart rate (90 beats per minute), normal blood pressure (120/80 mmHg), normal respiratory rate (14 breaths per minute), accentuated heart sounds, and normal vesicular breathing without adventitious sounds. He had saddle nose, loss of the outer third of the eyebrows, and marked reduction in the density of the eyelashes (madarosis). Bilateral pitting edema of the legs also was present. Neurologic examination revealed hypoesthesia in a glove-and-stocking pattern, thickened peripheral nerves, and trophic changes over both hands; however, he had normal muscle power and deep reflexes. Joint examination revealed no abnormalities. Skin examination revealed widespread, reticulated, necrotizing, purpuric lesions on the arms, legs, abdomen, and ears, some associated with gangrenous ulcerations and hemorrhagic blisters. Scattered vasculitic ulcers and gangrenous patches were seen on the fingers. A gangrenous ulcer mimicking Fournier gangrene was seen involving the scrotal skin in addition to a gangrenous lesion on the glans penis (Figure 1–3). Unaffected skin appeared smooth, shiny, and edematous and showed no nodular lesions. Peripheral pulsations were intact.



Positive findings from a wide panel of laboratory investigations included an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (103 mm for the first hour [reference range, 0–22 mm]), high C-reactive protein (50.7 mg/L [reference range, up to 6 mg/L]), anemia (hemoglobin count, 7.3 g/dL [reference range, 13.5–17.5 g/dL]), thrombocytopenia (45×103/mm3 [reference range, 150×103/mm3), low serum albumin (2.3 g/dL [reference range, 3.4–5.4 g/dL]), elevated IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies (IgG, 21.4 IgG phospholipid [GPL] units [reference range, <10 IgG phospholipid (GPL) units]; IgM, 59.4 IgM phospholipid (MPL) units [reference range, <7 IgM phospholipid (MPL) units]), positive lupus anticoagulant panel test, elevated anti-β2 glycoprotein antibodies (IgG, 17.5
Nerve conduction velocity showed axonal sensory polyneuropathy. Motor nerve conduction studies for median and ulnar nerves were within normal range. Lower-limb nerves assessment was limited by the ulcerated areas and marked edema. Echocardiography was unremarkable. Arterial Doppler studies were only available for the upper limbs and were unremarkable.
A punch biopsy was taken from one of the necrotizing purpuric lesions on the legs, and histopathologic examination revealed foci of epidermal necrosis and subepidermal separation and superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal infiltrates extending into the fat lobules. The infiltrates were mainly made up of foamy macrophages, and some contained globi (lepra cells), in addition to lymphocytes and many neutrophils with nuclear dust. Blood vessels in the superficial and deep dermis and in the subcutaneous fat showed fibrinoid necrosis in their walls with neutrophils infiltrating the walls and thrombi in the lumens (Figure 4). Modified Ziehl-Neelsen staining revealed clumps of acid-fast lepra bacilli inside vascular lumina and endothelial cell lining and within the foamy macrophages (Figure 5). Slit-skin smear examination was performed twice and yielded negative results. The slide and paraffin block of the already performed lymph node biopsy were retrieved. Examination revealed aggregates of foamy histiocytes surrounded by lymphocytes and plasma cells replacing normal lymphoid follicles. Modified Ziehl-Neelsen stain was performed, and clusters of acid-fast bacilli were detected within the foamy histiocytic infiltrate (Figure 6).



According to the results of the skin biopsy, the revised result of the lymph node biopsy, and the pattern of neurologic deficit together with clinical and laboratory correlation, the patient was diagnosed with diffuse nonnodular lepromatous leprosy presenting with Lucio phenomenon (Lucio leprosy) and associated with lepromatous lymphadenitis.
The patient received the following treatment: methylprednisolone 500 mg (intravenous pulse therapy) followed by daily oral administration of prednisolone 10 mg, rifampicin 300 mg, dapsone 100 mg, clofazimine 100 mg, acetylsalicylic acid 150 mg, and enoxaparin sodium 80 mg. In addition, the scrotal Fournier gangrene–like lesion was treated by surgical debridement followed by vacuum therapy. By the second week after treatment, the gangrenous lesions of the fingers developed a line of demarcation, and the skin infarctions started to recede.
Comment
Despite a decrease in its prevalence through a World Health Organization (WHO)–empowered eradication program, leprosy still represents a health problem in endemic areas.1,2 It is characterized by a wide range of immune responses to Mycobacterium leprae, displaying a spectrum of clinical and histopathologic manifestations that vary from the tuberculoid or paucibacillary pole with a strong cell-mediated immune response and fewer organisms to the lepromatous or multibacillary pole with weaker cell-mediated immune response and higher loads of organisms.3 In addition to its well-known cutaneous and neurologic manifestations, leprosy can present with a variety of manifestations, including constitutional symptoms, musculoskeletal manifestations, and serologic abnormalities; thus, leprosy can mimic rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, and vasculitis—a pitfall that may result in misdiagnosis as a rheumatologic disorder.3-7
The chronic course of leprosy can be disrupted by acute, immunologically mediated reactions known as lepra reactions, of which there are 3 types.8 Type I lepra reactions are cell mediated and occur mainly in patients with borderline disease, often representing an upgrade toward the tuberculoid pole; less often they represent a downgrade reaction. Nerves become painful and swollen with possible loss of function, and skin lesions become edematous and tender; sometimes arthritis develops.9 Type II lepra reactions, also known as erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL), occur in borderline lepromatous and lepromatous patients with a high bacillary load. They are characterized by fever, body aches, tender cutaneous/subcutaneous nodules that may ulcerate, possible bullous lesions, painful nerve swellings, swollen joints, iritis, lymphadenitis, glomerulonephritis, epididymo-orchitis, and hepatic affection. Both immune-complex and delayed hypersensitivity reactions play a role in ENL.8,10 The third reaction is a rare aggressive type known as Lucio phenomenon or Lucio leprosy, which presents with irregular-shaped, angulated, or stellar necrotizing purpuric lesions (hemorrhagic infacrtions) developing mainly on the extremities. The lesions evolve into ulcers that heal with atrophic scarring.2,11 Lucio phenomenon develops as a result of thrombotic vascular occlusion secondary to massive invasion of vascular endothelial cells by lepra bacilli.2,11-14 Involvement of the scrotal skin, such as in our patient, is rare.
Lucio phenomenon mainly is seen in Mexico and Central America, and few cases have been documented in Cuba, South America, the United States, India, Polynesia, South Africa, and Southeast Asia.15-17 It specifically occurs in patients with untreated, diffuse, nonnodular lepromatous leprosy (pure and primitive diffuse lepromatous leprosy (DLL)/diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapí). This type of leprosy was first described by Lucio and Alvarado18 in 1852 as a distinct form of lepromatous leprosy characterized by widespread and dense infiltration of the whole skin by lepra bacilli without the typical nodular lesions of leprosy, rendering its diagnosis challenging, especially in sporadic cases. Other manifestations of DLL include complete alopecia of the eyebrows and eyelashes, destructive rhinitis, and areas of anhidrosis and dyesthesia.2
Latapí and Chévez-Zomora19 defined Lucio phenomenon in 1948 as a form of histopathologic vasculitis restricted to patients with DLL. Histopathologically, in addition to the infiltration of the skin with acid-fast bacilli–laden foamy histiocytes, lesions of Lucio phenomenon show features of necrotizing (leukocytoclastic) vasculitis with fibrinoid necrosis20 or vascular thrombi with minimal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and no evidence of vasculitis.11 Medium to large vessels in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue show infiltration of their walls with a large number of macrophages laden with acid-fast bacilli.11 Cases with histopathologic features mimicking antiphospholipid syndrome with endothelial cell proliferation, thrombosis, and mild mononuclear cell infiltrate also may be seen.20 In all cases, ischemic epidermal necrosis is seen, as well as acid-fast bacilli, both singly and in clusters (globi) within endothelial cells and inside blood vessel lumina.
Although Lucio phenomenon initially was thought to be immune-complex mediated like ENL, it has been suggested that the main trigger is thrombotic vascular occlusion secondary to massive invasion of the vascular endothelial cells by the lepra bacilli, resulting in necrosis.14 Bacterial lipopolysaccharides promote the release of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor α, which in turn stimulate the production of prostaglandins, IL-6, and coagulation factor III, leading to vascular thrombosis and tissue necrosis.21,22 Moreover, antiphospholipid antibodies, which have been found to be induced in response to certain infectious agents in genetically predisposed individuals,23 have been reported in patients with leprosy, mainly in association with lepromatous leprosy. The reported prevalence of anticardiolipin antibodies ranged from 37% to 98%, whereas anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies ranged from 3% to 19%, and antiprothrombin antibodies ranged from 6% to 45%.24,25 Antiphospholipid antibodies have been reported to play a role in the pathogenesis of Lucio phenomenon.11,13,15,26 Our case supports this hypothesis with positive anticardiolipin antibodies, anti-β2 glycoprotein antibodies, and positive lupus anticoagulant.
In accordance with Curi et al,2 who reported 5 cases of DLL with Lucio phenomenon, our patient showed a similar presentation with positive inflammatory markers in association with a negative autoimmune profile (ANA, ANCA-C&P) and negative venereal disease research laboratory test. It is important to mention that a positive autoimmune profile (ANA, ANCA-C&P) can be present in leprotic patients, causing possible diagnostic confusion with collagen diseases.27,28
An interesting finding in our case was the negative slit-skin smear results. Although the specificity of slit-skin smear is 100%, as it directly demonstrates the presence of acid-fast bacilli,29 its sensitivity is low and varies from 10% to 50%.30 The detection of acid-fast bacilli in tissue sections is reported to be a better method for confirming the diagnosis of leprosy.31
The provisional impression of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in the lymph node biopsy in our patient was excluded upon detection of acid-fast bacilli in the foamy histiocytes infiltrating the lymph node; moreover, the normal serum lipids and serum ferritin argued against this diagnosis.32 Leprosy tends to involve the lymph nodes, particularly in borderline, borderline lepromatous, and lepromatous forms.33 The incidence of lymph node involvement accompanied by skin lesions with the presence of acid-fast bacilli in the lymph nodes is 92.2%.34
Our patient showed an excellent response to antileprotic treatment, which was administered according to the WHO multidrug therapy guidelines for multibacillary leprosy,35 combined with low-dose prednisolone, acetylsalicylic acid, and anticoagulant treatment. Thalidomide and high-dose prednisolone (60 mg/d) combined with antileprotic treatment also have been reported to be successful in managing recurrent infarctions in leprosy.36 The Fournier-like gangrenous ulcer of the scrotum was managed by surgical debridement and vacuum therapy.
It is noteworthy that the WHO elimination goal for leprosy was to reduce the prevalence to less than 1 case per 10,000 population. Egypt is among the first countries in North Africa and the Middle East regions to achieve this target supervised by the National Leprosy Control Program as early as 1994; this was further reduced to 0.33 cases per 10,000 population in 2004, and reduced again in 2009; however, certain foci showed a prevalence rate more than the elimination target, particularly in the cities of Qena (1.12) and Sohag (2.47).37 Esna, where our patient is from, is an endemic area in Egypt.38
Conclusion
1. World Health Organization. World Health Statistics: 2011. World Health Organization; 2011. https://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/EN_WHS2011_Full.pdf
2. Curi PF, Villaroel JS, Migliore N, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: report of five cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:1397-1401.
3. Shrestha B, Li YQ, Fu P. Leprosy mimics adult onset Still’s disease in a Chinese patient. Egypt Rheumatol. 2018;40:217-220.
4. Prasad S, Misra R, Aggarwal A, et al. Leprosy revealed in a rheumatology clinic: a case series. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013;16:129-133.
5. Chao G, Fang L, Lu C. Leprosy with ANA positive mistaken for connective tissue disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:645-648.
6. Chauhan S, Wakhlu A, Agarwal V. Arthritis in leprosy. Rheumatology. 2010;49:2237-2242.
7. Rath D, Bhargava S, Kundu BK. Leprosy mimicking common rheumatologic entities: a trial for the clinician in the era of biologics. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2014;2014:429698.
8. Cuevas J, Rodríguez-Peralto JL, Carrillo R, et al. Erythema nodosum leprosum: reactional leprosy. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:126-130.
9. Henriques CC, Lopéz B, Mestre T, et al. Leprosy and rheumatoid arthritis: consequence or association? BMJ Case Rep. 2012;13:1-4.
10. Vázquez-Botet M, Sánchez JL. Erythema nodosum leprosum. Int J Dermatol. 1987;26:436-437.
11. Nunzie E, Ortega Cabrera LV, Macanchi Moncayo FM, et al. Lucio leprosy with Lucio’s phenomenon, digital gangrene and anticardiolipin antibodies. Lepr Rev. 2014;85:194-200.
12. Salvi S, Chopra A. Leprosy in a rheumatology setting: a challenging mimic to expose. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:1557-1563.
13. Azulay-Abulafia L, Pereira SL, Hardmann D, et al. Lucio phenomenon. vasculitis or occlusive vasculopathy? Hautarzt. 2006;57:1101-1105.
14. Benard G, Sakai-Valente NY, Bianconcini Trindade MA. Concomittant Lucio phenomenon and erythema nodosum in a leprosy patient: clues for their distinct pathogenesis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:288-292.
15. Rocha RH, Emerich PS, Diniz LM, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: exuberant case report and review of Brazilian cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(suppl 5):S60-S63.
16. Costa IM, Kawano LB, Pereira CP, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:566-571.
17. Kumari R, Thappa DM, Basu D. A fatal case of Lucio phenomenon from India. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:10.
18. Lucio R, Alvarado I. Opúsculo Sobre el Mal de San Lázaro o Elefantiasis de los Griegos. M. Murguía; 1852.
19. Latapí F, Chévez-Zamora A. The “spotted” leprosy of Lucio: an introduction to its clinical and histological study. Int J Lepr. 1948;16:421-437.
20. Vargas OF. Diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapí: a histologic study. Lepr Rev. 2007;78:248-260.
21. Latapí FR, Chevez-Zamora A. La lepra manchada de Lucio. Rev Dermatol Mex. 1978;22:102-107.
22. Monteiro R, Abreu MA, Tiezzi MG, et al. Fenômeno de Lúcio: mais um caso relatado no Brasil. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:296-300.
23. Gharavi EE, Chaimovich H, Cucucrull E, et al. Induction of antiphospholipid antibodies by immunization with synthetic bacterial & viral peptides. Lupus. 1999;8:449-455.
24. de Larrañaga GF, Forastiero RR, Martinuzzo ME, et al. High prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in leprosy: evaluation of antigen reactivity. Lupus. 2000;9:594-600.
25. Loizou S, Singh S, Wypkema E, et al. Anticardiolipin, anti-beta(2)-glycoprotein I and antiprothrombin antibodies in black South African patients with infectious disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:1106-1111.
26. Akerkar SM, Bichile LS. Leprosy & gangrene: a rare association; role of antiphospholipid antibodies. BMC Infect Dis. 2005,5:74.
27. Horta-Baas G, Hernández-Cabrera MF, Barile-Fabris LA, et al. Multibacillary leprosy mimicking systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and literature review. Lupus. 2015;24:1095-1102.
28. Pradhan V, Badakere SS, Shankar KU. Increased incidence of cytoplasmic ANCA (cANCA) and other auto antibodies in leprosy patients from western India. Lepr Rev. 2004;75:50-56.
29. Oskam L. Diagnosis and classification of leprosy. Lepr Rev. 2002;73:17-26.
30. Rao PN. Recent advances in the control programs and therapy of leprosy. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2004;70:269-276.
31. Rao PN, Pratap D, Ramana Reddy AV, et al. Evaluation of leprosy patients with 1 to 5 skin lesions with relevance to their grouping into paucibacillary or multibacillary disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:207-210.
32. Rosado FGN, Kim AS. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. an update on diagnosis and pathogenesis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2013;139:713-727.
33. Kar HK, Mohanty HC, Mohanty GN, et al. Clinicopathological study of lymph node involvement in leprosy. Lepr India. 1983;55:725-738.
34. Gupta JC, Panda PK, Shrivastava KK, et al. A histopathologic study of lymph nodes in 43 cases of leprosy. Lepr India. 1978;50:196-203.
35. WHO Expert Committee on Leprosy. Seventh Report. World Health Organization; 1998. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42060/WHO_TRS_874.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
36. Misra DP, Parida JR, Chowdhury AC, et al. Lepra reaction with Lucio phenomenon mimicking cutaneous vasculitis. Case Rep Immunol. 2014;2014:641989.
37. Amer A, Mansour A. Epidemiological study of leprosy in Egypt: 2005-2009. Egypt J Dermatol Venereol. 2014;34:70-73.
38. World Health Organization. Screening campaign aims to eliminate leprosy in Egypt. Published May 9, 2018. Accessed September 8, 2021. http://www.emro.who.int/egy/egypt-events/last-miless-activities-on-eliminating-leprosy-from-egypt.html
1. World Health Organization. World Health Statistics: 2011. World Health Organization; 2011. https://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/EN_WHS2011_Full.pdf
2. Curi PF, Villaroel JS, Migliore N, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: report of five cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:1397-1401.
3. Shrestha B, Li YQ, Fu P. Leprosy mimics adult onset Still’s disease in a Chinese patient. Egypt Rheumatol. 2018;40:217-220.
4. Prasad S, Misra R, Aggarwal A, et al. Leprosy revealed in a rheumatology clinic: a case series. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013;16:129-133.
5. Chao G, Fang L, Lu C. Leprosy with ANA positive mistaken for connective tissue disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:645-648.
6. Chauhan S, Wakhlu A, Agarwal V. Arthritis in leprosy. Rheumatology. 2010;49:2237-2242.
7. Rath D, Bhargava S, Kundu BK. Leprosy mimicking common rheumatologic entities: a trial for the clinician in the era of biologics. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2014;2014:429698.
8. Cuevas J, Rodríguez-Peralto JL, Carrillo R, et al. Erythema nodosum leprosum: reactional leprosy. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:126-130.
9. Henriques CC, Lopéz B, Mestre T, et al. Leprosy and rheumatoid arthritis: consequence or association? BMJ Case Rep. 2012;13:1-4.
10. Vázquez-Botet M, Sánchez JL. Erythema nodosum leprosum. Int J Dermatol. 1987;26:436-437.
11. Nunzie E, Ortega Cabrera LV, Macanchi Moncayo FM, et al. Lucio leprosy with Lucio’s phenomenon, digital gangrene and anticardiolipin antibodies. Lepr Rev. 2014;85:194-200.
12. Salvi S, Chopra A. Leprosy in a rheumatology setting: a challenging mimic to expose. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:1557-1563.
13. Azulay-Abulafia L, Pereira SL, Hardmann D, et al. Lucio phenomenon. vasculitis or occlusive vasculopathy? Hautarzt. 2006;57:1101-1105.
14. Benard G, Sakai-Valente NY, Bianconcini Trindade MA. Concomittant Lucio phenomenon and erythema nodosum in a leprosy patient: clues for their distinct pathogenesis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:288-292.
15. Rocha RH, Emerich PS, Diniz LM, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: exuberant case report and review of Brazilian cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(suppl 5):S60-S63.
16. Costa IM, Kawano LB, Pereira CP, et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:566-571.
17. Kumari R, Thappa DM, Basu D. A fatal case of Lucio phenomenon from India. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:10.
18. Lucio R, Alvarado I. Opúsculo Sobre el Mal de San Lázaro o Elefantiasis de los Griegos. M. Murguía; 1852.
19. Latapí F, Chévez-Zamora A. The “spotted” leprosy of Lucio: an introduction to its clinical and histological study. Int J Lepr. 1948;16:421-437.
20. Vargas OF. Diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapí: a histologic study. Lepr Rev. 2007;78:248-260.
21. Latapí FR, Chevez-Zamora A. La lepra manchada de Lucio. Rev Dermatol Mex. 1978;22:102-107.
22. Monteiro R, Abreu MA, Tiezzi MG, et al. Fenômeno de Lúcio: mais um caso relatado no Brasil. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:296-300.
23. Gharavi EE, Chaimovich H, Cucucrull E, et al. Induction of antiphospholipid antibodies by immunization with synthetic bacterial & viral peptides. Lupus. 1999;8:449-455.
24. de Larrañaga GF, Forastiero RR, Martinuzzo ME, et al. High prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in leprosy: evaluation of antigen reactivity. Lupus. 2000;9:594-600.
25. Loizou S, Singh S, Wypkema E, et al. Anticardiolipin, anti-beta(2)-glycoprotein I and antiprothrombin antibodies in black South African patients with infectious disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:1106-1111.
26. Akerkar SM, Bichile LS. Leprosy & gangrene: a rare association; role of antiphospholipid antibodies. BMC Infect Dis. 2005,5:74.
27. Horta-Baas G, Hernández-Cabrera MF, Barile-Fabris LA, et al. Multibacillary leprosy mimicking systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and literature review. Lupus. 2015;24:1095-1102.
28. Pradhan V, Badakere SS, Shankar KU. Increased incidence of cytoplasmic ANCA (cANCA) and other auto antibodies in leprosy patients from western India. Lepr Rev. 2004;75:50-56.
29. Oskam L. Diagnosis and classification of leprosy. Lepr Rev. 2002;73:17-26.
30. Rao PN. Recent advances in the control programs and therapy of leprosy. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2004;70:269-276.
31. Rao PN, Pratap D, Ramana Reddy AV, et al. Evaluation of leprosy patients with 1 to 5 skin lesions with relevance to their grouping into paucibacillary or multibacillary disease. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:207-210.
32. Rosado FGN, Kim AS. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. an update on diagnosis and pathogenesis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2013;139:713-727.
33. Kar HK, Mohanty HC, Mohanty GN, et al. Clinicopathological study of lymph node involvement in leprosy. Lepr India. 1983;55:725-738.
34. Gupta JC, Panda PK, Shrivastava KK, et al. A histopathologic study of lymph nodes in 43 cases of leprosy. Lepr India. 1978;50:196-203.
35. WHO Expert Committee on Leprosy. Seventh Report. World Health Organization; 1998. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42060/WHO_TRS_874.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
36. Misra DP, Parida JR, Chowdhury AC, et al. Lepra reaction with Lucio phenomenon mimicking cutaneous vasculitis. Case Rep Immunol. 2014;2014:641989.
37. Amer A, Mansour A. Epidemiological study of leprosy in Egypt: 2005-2009. Egypt J Dermatol Venereol. 2014;34:70-73.
38. World Health Organization. Screening campaign aims to eliminate leprosy in Egypt. Published May 9, 2018. Accessed September 8, 2021. http://www.emro.who.int/egy/egypt-events/last-miless-activities-on-eliminating-leprosy-from-egypt.html
Practice Points
- Leprosy is a great mimicker of many connective tissue diseases, including vasculitis.
- Antiphospholipid antibodies are involved in Lucio phenomenon.
- Prompt treatment is important in Lucio phenomenon to avoid morbidity and mortality.
Electrocuted by 11,000 volts, now a triple amputee ... and an MD
Bruce “BJ” Miller Jr., a 19-year-old Princeton (N.J.) University sophomore, was horsing around with friends near a train track in 1990 when they spotted a parked commuter train. They decided to climb over the train, and Mr. Miller was first up the ladder.
An explosion ripped through the air, and Mr. Miller was thrown on top of the train, his body smoking. His petrified friends called for an ambulance.
Clinging to life, Mr. Miller was airlifted to the burn unit at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, N.J..
Physicians saved Mr. Miller’s life, but they had to amputate both of his legs below the knees and his left arm below the elbow.
“With electricity, you burn from the inside out,” said Mr. Miller, now 50. “The voltage enters your body – in my case, the wrist – and runs around internally until it finds a way out. That is often the lower extremities as the ground tends to ground the current, but not always. In my case, the current tried to come through my chest – which is also burned and required skin grafting – but not enough to spare my legs. I think I had a half-dozen or so surgeries over the first month or 2 at the hospital.”
Waking up to a new body
Mr. Miller doesn’t remember much about the accident, but he recalls waking up a few days later in the ICU and feeling the need to use the bathroom. Disoriented, Mr. Miller pulled off his ventilator, climbed out of bed, and tried to walk forward, unaware of his injuries. His feet and legs had not yet been amputated. When the catheter line ran out of slack, he collapsed.
“Eventually, a nurse came rushing in, responding to the ventilator alarm bells going off,” Mr. Miller said. “My dad wasn’t far behind. It became clear to me then that this was not a dream and [I realized] what had happened and why I was in the hospital.”
For months, Mr. Miller lived in the burn unit, undergoing countless skin grafts and surgeries. Because viable and nonviable tissue take time to be revealed after burns, surgeons take the minimum amount of tissue during each operation to give damaged tissue a chance to heal, he explained. In Mr. Miller’s case, his feet were amputated first, and later, his legs.
“In those early days from the hospital bed, my mind turned to issues related to identity,” he said. “What do I do with myself?
Mr. Miller eventually moved to the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (now called The Shirley Ryan AbilityLab), where he started the grueling process of rebuilding his strength and learning to walk on prosthetic legs.
“Any one day was filled with a mix of optimism and good fight and 5 minutes later, exasperation, frustration, tons of pain, and insecurity about my body,” he said. “My family and friends held the gate for me in a way, but a lot of the work was up to me. I had to believe that I deserved this love, that I wanted to be alive, and that there was still something here for me.”
Mr. Miller didn’t have to look far for inspiration. His mom had lived with polio for most of her life and acquired post-polio syndrome as she grew older, he said. When he was a child, his mom walked with crutches, and she became wheelchair-dependent by the time he was a teenager.
After the first surgery to amputate his feet, Mr. Miller and his mom shared a deep discussion about his joining the ranks of “the disabled,” and how their connection was now even stronger.
“In this way, the injuries unlocked even more experiences to share between us, and more love to feel, and therefore some early sense of gain to complement all the losses happening,” he said. “She had taught me so much about living with disability and had given me all the tools I needed to refashion my sense of self.”
From burn patient to medical student
After returning to Princeton University and finishing his undergraduate degree, Mr. Miller decided to go into medicine. He wanted to use his experience to help patients and find ways to improve weaknesses in the health care system, he said. But he made a deal with himself that he wouldn’t become a doctor for the sake of becoming one; he would enter the vocation only if he could do the work and enjoy the job.
“I wasn’t sure if I could do it,” he said. “There weren’t a lot of triple amputees to point to, to say whether this was even mechanically possible, to get through the training. The medical institutions I spoke with knew they had some obligation by law to protect me, but there’s also an obligation that I need to be able to fulfill the competencies. This was uncharted water.”
Because his greatest physical challenge was standing for long periods, instructors at the University of California, San Francisco, made accommodations to alleviate the strain. His clinical rotations for example, were organized near his home to limit the need for travel. On surgical rotations, he was allowed to sit on a stool.
Medical training progressed smoothly until Mr. Miller completed a rotation in his chosen specialty, rehabilitation medicine. He didn’t enjoy it. The passion and meaning he hoped to find was missing. Disillusioned, and with his final year in medical school coming to an end, Mr. Miller dropped out of the Match program. Around the same time, his sister, Lisa, died by suicide.
“My whole family life was in shambles,” he said. “I felt like, ‘I can’t even help my sister, how am I going to help other people?’ ”
Mr. Miller earned his MD and moved to his parents’ home in Milwaukee after his sister’s death. He was close to giving up on medicine, but his deans convinced him to do a post-doc internship. It was as an intern at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, that he completed an elective in palliative care.
“I fell immediately in love with it the first day,” he said. “This was a field devoted to working with things you can’t change and dealing with a lack of control, what it’s like to live with these diagnoses. This was a place where I could dig into my experience and share that with patients and families. This was a place where my life story had something to offer.”
Creating a new form of palliative care
Dr. Miller went on to complete a fellowship at Harvard Medical School, Boston, in hospice and palliative medicine. He became a palliative care physician at UCSF Health, and later directed the Zen Hospice Project, a nonprofit dedicated to teaching mindfulness-based caregiving for professionals, family members, and caregivers.
Gayle Kojimoto, a program manager who worked with Dr. Miller at UCSF’s outpatient palliative care clinic for cancer patients, said Miller was a favorite among patients because of his authenticity and his ability to make them feel understood.
“Patients love him because he is 100% present with them,” said Ms. Kojimoto. “They feel like he can understand their suffering better than other docs. He’s open to hearing about their suffering, when others may not be, and he doesn’t judge them. Many patients have said that seeing him is better than seeing a therapist.”
In 2020, Dr. Miller cofounded Mettle Health, a first-of-its-kind company that aims to reframe the way people think about their well-being as it relates to chronic and serious illness. Mettle Health’s care team provides consultations on a range of topics, including practical, emotional, and existential issues. No physician referrals are needed.
When the pandemic started, Dr. Miller said he and his colleagues felt the moment was ripe for bringing palliative care online to increase access, while decreasing caregiver and clinician burnout.
“We set up Mettle Health as an online palliative care counseling and coaching business and we pulled it out of the healthcare system so that whether you’re a patient or a caregiver you don’t need to satisfy some insurance need to get this kind of care,” he said. “We also realized there are enough people writing prescriptions. The medical piece is relatively well tended to; it’s the psychosocial and spiritual issues, and the existential issues, that are so underdeveloped. We are a social service, not a medical service, and this allows us to complement existing structures of care rather than compete with them.”
Having Dr. Miller as a leader for Mettle Health is a huge driver for why people seek out the company, said Sonya Dolan, director of operations and cofounder of Mettle Health.
“His approach to working with patients, caregivers, and clinicians is something I think sets us apart and makes us special,” she said. “His way of thinking about serious illness and death and dying is incredibly unique and he has a way of talking about and humanizing something that’s scary for a lot of us.”
‘Surprised by how much I can still do’
Since the accident, Dr. Miller has come a long way in navigating his physical limitations. In the early years, Dr. Miller said he was determined to do as many activities as he still could. He skied, biked, and pushed himself to stand for long periods on his prosthetic legs.
“For years, I would force myself to do these things just to prove I could, but not really enjoy them,” he said. “I’d get out on the dance floor or put myself out in vulnerable social situations where I might fall. It was kind of brutal and difficult. But at about year 5 or so, I became much more at ease with myself and more at peace with myself.”
Today, Dr. Miller’s prosthetics make nearly all ambulatory activities possible, but he concentrates on the activities that bring him joy.
“Probably the thing I can still do that surprises people most, including myself, is riding a motorcycle,” he said. “As for my upper body, I’m thoroughly used to living with only one hand and I continue to be surprised at how much I can still do. With enough time and experimentation, I can usually find a way to do what I need/want to do. It took me awhile to figure out how to clap! Now I just pound my chest for the same effect!”
Dr. Miller is an animal-lover and said his pets and nature are a large part of his self-care. His dog Maysie travels nearly everywhere with him and his cats, the Muffin Man and Darkness, enjoy making guest appearances on his Zoom calls. The physician frequently visits the desert in southern Utah and said he loves the arts, architecture, and design.
Dr. Miller’s advice for others who are disabled and want to go into medicine? Live out loud with your truths and be open about your disabilities. Too often, disabled individuals hide their disabilities, lie about them, or shield the world from their story, he said.
“These are rich, ripe experiences that are incredibly valuable to someone who wants to go out and be of service in the world,” he said. “We should be proud of our experiences as disabled people. The creativity we’ve had to exercise, the workarounds we’ve had to employ, these should not be points of embarrassment, but points of pride. Anyone who wants to pursue clinical training of any kind should use these experiences explicitly. These are sources of strength, not something to be forgiven or tolerated or accommodated.”
The same goes for physicians who do not have disabilities but who have lived through hardship, pain, struggle, or adversity, he emphasized.
“Find a way to learn from them, find a way to own them,” he said. “Use them as a source of strength and the rest of the world will respond to you differently.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bruce “BJ” Miller Jr., a 19-year-old Princeton (N.J.) University sophomore, was horsing around with friends near a train track in 1990 when they spotted a parked commuter train. They decided to climb over the train, and Mr. Miller was first up the ladder.

An explosion ripped through the air, and Mr. Miller was thrown on top of the train, his body smoking. His petrified friends called for an ambulance.
Clinging to life, Mr. Miller was airlifted to the burn unit at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, N.J..
Physicians saved Mr. Miller’s life, but they had to amputate both of his legs below the knees and his left arm below the elbow.
“With electricity, you burn from the inside out,” said Mr. Miller, now 50. “The voltage enters your body – in my case, the wrist – and runs around internally until it finds a way out. That is often the lower extremities as the ground tends to ground the current, but not always. In my case, the current tried to come through my chest – which is also burned and required skin grafting – but not enough to spare my legs. I think I had a half-dozen or so surgeries over the first month or 2 at the hospital.”
Waking up to a new body
Mr. Miller doesn’t remember much about the accident, but he recalls waking up a few days later in the ICU and feeling the need to use the bathroom. Disoriented, Mr. Miller pulled off his ventilator, climbed out of bed, and tried to walk forward, unaware of his injuries. His feet and legs had not yet been amputated. When the catheter line ran out of slack, he collapsed.
“Eventually, a nurse came rushing in, responding to the ventilator alarm bells going off,” Mr. Miller said. “My dad wasn’t far behind. It became clear to me then that this was not a dream and [I realized] what had happened and why I was in the hospital.”
For months, Mr. Miller lived in the burn unit, undergoing countless skin grafts and surgeries. Because viable and nonviable tissue take time to be revealed after burns, surgeons take the minimum amount of tissue during each operation to give damaged tissue a chance to heal, he explained. In Mr. Miller’s case, his feet were amputated first, and later, his legs.
“In those early days from the hospital bed, my mind turned to issues related to identity,” he said. “What do I do with myself?
Mr. Miller eventually moved to the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (now called The Shirley Ryan AbilityLab), where he started the grueling process of rebuilding his strength and learning to walk on prosthetic legs.
“Any one day was filled with a mix of optimism and good fight and 5 minutes later, exasperation, frustration, tons of pain, and insecurity about my body,” he said. “My family and friends held the gate for me in a way, but a lot of the work was up to me. I had to believe that I deserved this love, that I wanted to be alive, and that there was still something here for me.”
Mr. Miller didn’t have to look far for inspiration. His mom had lived with polio for most of her life and acquired post-polio syndrome as she grew older, he said. When he was a child, his mom walked with crutches, and she became wheelchair-dependent by the time he was a teenager.
After the first surgery to amputate his feet, Mr. Miller and his mom shared a deep discussion about his joining the ranks of “the disabled,” and how their connection was now even stronger.
“In this way, the injuries unlocked even more experiences to share between us, and more love to feel, and therefore some early sense of gain to complement all the losses happening,” he said. “She had taught me so much about living with disability and had given me all the tools I needed to refashion my sense of self.”
From burn patient to medical student
After returning to Princeton University and finishing his undergraduate degree, Mr. Miller decided to go into medicine. He wanted to use his experience to help patients and find ways to improve weaknesses in the health care system, he said. But he made a deal with himself that he wouldn’t become a doctor for the sake of becoming one; he would enter the vocation only if he could do the work and enjoy the job.
“I wasn’t sure if I could do it,” he said. “There weren’t a lot of triple amputees to point to, to say whether this was even mechanically possible, to get through the training. The medical institutions I spoke with knew they had some obligation by law to protect me, but there’s also an obligation that I need to be able to fulfill the competencies. This was uncharted water.”
Because his greatest physical challenge was standing for long periods, instructors at the University of California, San Francisco, made accommodations to alleviate the strain. His clinical rotations for example, were organized near his home to limit the need for travel. On surgical rotations, he was allowed to sit on a stool.
Medical training progressed smoothly until Mr. Miller completed a rotation in his chosen specialty, rehabilitation medicine. He didn’t enjoy it. The passion and meaning he hoped to find was missing. Disillusioned, and with his final year in medical school coming to an end, Mr. Miller dropped out of the Match program. Around the same time, his sister, Lisa, died by suicide.
“My whole family life was in shambles,” he said. “I felt like, ‘I can’t even help my sister, how am I going to help other people?’ ”
Mr. Miller earned his MD and moved to his parents’ home in Milwaukee after his sister’s death. He was close to giving up on medicine, but his deans convinced him to do a post-doc internship. It was as an intern at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, that he completed an elective in palliative care.
“I fell immediately in love with it the first day,” he said. “This was a field devoted to working with things you can’t change and dealing with a lack of control, what it’s like to live with these diagnoses. This was a place where I could dig into my experience and share that with patients and families. This was a place where my life story had something to offer.”
Creating a new form of palliative care
Dr. Miller went on to complete a fellowship at Harvard Medical School, Boston, in hospice and palliative medicine. He became a palliative care physician at UCSF Health, and later directed the Zen Hospice Project, a nonprofit dedicated to teaching mindfulness-based caregiving for professionals, family members, and caregivers.
Gayle Kojimoto, a program manager who worked with Dr. Miller at UCSF’s outpatient palliative care clinic for cancer patients, said Miller was a favorite among patients because of his authenticity and his ability to make them feel understood.
“Patients love him because he is 100% present with them,” said Ms. Kojimoto. “They feel like he can understand their suffering better than other docs. He’s open to hearing about their suffering, when others may not be, and he doesn’t judge them. Many patients have said that seeing him is better than seeing a therapist.”
In 2020, Dr. Miller cofounded Mettle Health, a first-of-its-kind company that aims to reframe the way people think about their well-being as it relates to chronic and serious illness. Mettle Health’s care team provides consultations on a range of topics, including practical, emotional, and existential issues. No physician referrals are needed.
When the pandemic started, Dr. Miller said he and his colleagues felt the moment was ripe for bringing palliative care online to increase access, while decreasing caregiver and clinician burnout.
“We set up Mettle Health as an online palliative care counseling and coaching business and we pulled it out of the healthcare system so that whether you’re a patient or a caregiver you don’t need to satisfy some insurance need to get this kind of care,” he said. “We also realized there are enough people writing prescriptions. The medical piece is relatively well tended to; it’s the psychosocial and spiritual issues, and the existential issues, that are so underdeveloped. We are a social service, not a medical service, and this allows us to complement existing structures of care rather than compete with them.”
Having Dr. Miller as a leader for Mettle Health is a huge driver for why people seek out the company, said Sonya Dolan, director of operations and cofounder of Mettle Health.
“His approach to working with patients, caregivers, and clinicians is something I think sets us apart and makes us special,” she said. “His way of thinking about serious illness and death and dying is incredibly unique and he has a way of talking about and humanizing something that’s scary for a lot of us.”
‘Surprised by how much I can still do’
Since the accident, Dr. Miller has come a long way in navigating his physical limitations. In the early years, Dr. Miller said he was determined to do as many activities as he still could. He skied, biked, and pushed himself to stand for long periods on his prosthetic legs.
“For years, I would force myself to do these things just to prove I could, but not really enjoy them,” he said. “I’d get out on the dance floor or put myself out in vulnerable social situations where I might fall. It was kind of brutal and difficult. But at about year 5 or so, I became much more at ease with myself and more at peace with myself.”
Today, Dr. Miller’s prosthetics make nearly all ambulatory activities possible, but he concentrates on the activities that bring him joy.
“Probably the thing I can still do that surprises people most, including myself, is riding a motorcycle,” he said. “As for my upper body, I’m thoroughly used to living with only one hand and I continue to be surprised at how much I can still do. With enough time and experimentation, I can usually find a way to do what I need/want to do. It took me awhile to figure out how to clap! Now I just pound my chest for the same effect!”
Dr. Miller is an animal-lover and said his pets and nature are a large part of his self-care. His dog Maysie travels nearly everywhere with him and his cats, the Muffin Man and Darkness, enjoy making guest appearances on his Zoom calls. The physician frequently visits the desert in southern Utah and said he loves the arts, architecture, and design.
Dr. Miller’s advice for others who are disabled and want to go into medicine? Live out loud with your truths and be open about your disabilities. Too often, disabled individuals hide their disabilities, lie about them, or shield the world from their story, he said.
“These are rich, ripe experiences that are incredibly valuable to someone who wants to go out and be of service in the world,” he said. “We should be proud of our experiences as disabled people. The creativity we’ve had to exercise, the workarounds we’ve had to employ, these should not be points of embarrassment, but points of pride. Anyone who wants to pursue clinical training of any kind should use these experiences explicitly. These are sources of strength, not something to be forgiven or tolerated or accommodated.”
The same goes for physicians who do not have disabilities but who have lived through hardship, pain, struggle, or adversity, he emphasized.
“Find a way to learn from them, find a way to own them,” he said. “Use them as a source of strength and the rest of the world will respond to you differently.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bruce “BJ” Miller Jr., a 19-year-old Princeton (N.J.) University sophomore, was horsing around with friends near a train track in 1990 when they spotted a parked commuter train. They decided to climb over the train, and Mr. Miller was first up the ladder.

An explosion ripped through the air, and Mr. Miller was thrown on top of the train, his body smoking. His petrified friends called for an ambulance.
Clinging to life, Mr. Miller was airlifted to the burn unit at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, N.J..
Physicians saved Mr. Miller’s life, but they had to amputate both of his legs below the knees and his left arm below the elbow.
“With electricity, you burn from the inside out,” said Mr. Miller, now 50. “The voltage enters your body – in my case, the wrist – and runs around internally until it finds a way out. That is often the lower extremities as the ground tends to ground the current, but not always. In my case, the current tried to come through my chest – which is also burned and required skin grafting – but not enough to spare my legs. I think I had a half-dozen or so surgeries over the first month or 2 at the hospital.”
Waking up to a new body
Mr. Miller doesn’t remember much about the accident, but he recalls waking up a few days later in the ICU and feeling the need to use the bathroom. Disoriented, Mr. Miller pulled off his ventilator, climbed out of bed, and tried to walk forward, unaware of his injuries. His feet and legs had not yet been amputated. When the catheter line ran out of slack, he collapsed.
“Eventually, a nurse came rushing in, responding to the ventilator alarm bells going off,” Mr. Miller said. “My dad wasn’t far behind. It became clear to me then that this was not a dream and [I realized] what had happened and why I was in the hospital.”
For months, Mr. Miller lived in the burn unit, undergoing countless skin grafts and surgeries. Because viable and nonviable tissue take time to be revealed after burns, surgeons take the minimum amount of tissue during each operation to give damaged tissue a chance to heal, he explained. In Mr. Miller’s case, his feet were amputated first, and later, his legs.
“In those early days from the hospital bed, my mind turned to issues related to identity,” he said. “What do I do with myself?
Mr. Miller eventually moved to the Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (now called The Shirley Ryan AbilityLab), where he started the grueling process of rebuilding his strength and learning to walk on prosthetic legs.
“Any one day was filled with a mix of optimism and good fight and 5 minutes later, exasperation, frustration, tons of pain, and insecurity about my body,” he said. “My family and friends held the gate for me in a way, but a lot of the work was up to me. I had to believe that I deserved this love, that I wanted to be alive, and that there was still something here for me.”
Mr. Miller didn’t have to look far for inspiration. His mom had lived with polio for most of her life and acquired post-polio syndrome as she grew older, he said. When he was a child, his mom walked with crutches, and she became wheelchair-dependent by the time he was a teenager.
After the first surgery to amputate his feet, Mr. Miller and his mom shared a deep discussion about his joining the ranks of “the disabled,” and how their connection was now even stronger.
“In this way, the injuries unlocked even more experiences to share between us, and more love to feel, and therefore some early sense of gain to complement all the losses happening,” he said. “She had taught me so much about living with disability and had given me all the tools I needed to refashion my sense of self.”
From burn patient to medical student
After returning to Princeton University and finishing his undergraduate degree, Mr. Miller decided to go into medicine. He wanted to use his experience to help patients and find ways to improve weaknesses in the health care system, he said. But he made a deal with himself that he wouldn’t become a doctor for the sake of becoming one; he would enter the vocation only if he could do the work and enjoy the job.
“I wasn’t sure if I could do it,” he said. “There weren’t a lot of triple amputees to point to, to say whether this was even mechanically possible, to get through the training. The medical institutions I spoke with knew they had some obligation by law to protect me, but there’s also an obligation that I need to be able to fulfill the competencies. This was uncharted water.”
Because his greatest physical challenge was standing for long periods, instructors at the University of California, San Francisco, made accommodations to alleviate the strain. His clinical rotations for example, were organized near his home to limit the need for travel. On surgical rotations, he was allowed to sit on a stool.
Medical training progressed smoothly until Mr. Miller completed a rotation in his chosen specialty, rehabilitation medicine. He didn’t enjoy it. The passion and meaning he hoped to find was missing. Disillusioned, and with his final year in medical school coming to an end, Mr. Miller dropped out of the Match program. Around the same time, his sister, Lisa, died by suicide.
“My whole family life was in shambles,” he said. “I felt like, ‘I can’t even help my sister, how am I going to help other people?’ ”
Mr. Miller earned his MD and moved to his parents’ home in Milwaukee after his sister’s death. He was close to giving up on medicine, but his deans convinced him to do a post-doc internship. It was as an intern at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, that he completed an elective in palliative care.
“I fell immediately in love with it the first day,” he said. “This was a field devoted to working with things you can’t change and dealing with a lack of control, what it’s like to live with these diagnoses. This was a place where I could dig into my experience and share that with patients and families. This was a place where my life story had something to offer.”
Creating a new form of palliative care
Dr. Miller went on to complete a fellowship at Harvard Medical School, Boston, in hospice and palliative medicine. He became a palliative care physician at UCSF Health, and later directed the Zen Hospice Project, a nonprofit dedicated to teaching mindfulness-based caregiving for professionals, family members, and caregivers.
Gayle Kojimoto, a program manager who worked with Dr. Miller at UCSF’s outpatient palliative care clinic for cancer patients, said Miller was a favorite among patients because of his authenticity and his ability to make them feel understood.
“Patients love him because he is 100% present with them,” said Ms. Kojimoto. “They feel like he can understand their suffering better than other docs. He’s open to hearing about their suffering, when others may not be, and he doesn’t judge them. Many patients have said that seeing him is better than seeing a therapist.”
In 2020, Dr. Miller cofounded Mettle Health, a first-of-its-kind company that aims to reframe the way people think about their well-being as it relates to chronic and serious illness. Mettle Health’s care team provides consultations on a range of topics, including practical, emotional, and existential issues. No physician referrals are needed.
When the pandemic started, Dr. Miller said he and his colleagues felt the moment was ripe for bringing palliative care online to increase access, while decreasing caregiver and clinician burnout.
“We set up Mettle Health as an online palliative care counseling and coaching business and we pulled it out of the healthcare system so that whether you’re a patient or a caregiver you don’t need to satisfy some insurance need to get this kind of care,” he said. “We also realized there are enough people writing prescriptions. The medical piece is relatively well tended to; it’s the psychosocial and spiritual issues, and the existential issues, that are so underdeveloped. We are a social service, not a medical service, and this allows us to complement existing structures of care rather than compete with them.”
Having Dr. Miller as a leader for Mettle Health is a huge driver for why people seek out the company, said Sonya Dolan, director of operations and cofounder of Mettle Health.
“His approach to working with patients, caregivers, and clinicians is something I think sets us apart and makes us special,” she said. “His way of thinking about serious illness and death and dying is incredibly unique and he has a way of talking about and humanizing something that’s scary for a lot of us.”
‘Surprised by how much I can still do’
Since the accident, Dr. Miller has come a long way in navigating his physical limitations. In the early years, Dr. Miller said he was determined to do as many activities as he still could. He skied, biked, and pushed himself to stand for long periods on his prosthetic legs.
“For years, I would force myself to do these things just to prove I could, but not really enjoy them,” he said. “I’d get out on the dance floor or put myself out in vulnerable social situations where I might fall. It was kind of brutal and difficult. But at about year 5 or so, I became much more at ease with myself and more at peace with myself.”
Today, Dr. Miller’s prosthetics make nearly all ambulatory activities possible, but he concentrates on the activities that bring him joy.
“Probably the thing I can still do that surprises people most, including myself, is riding a motorcycle,” he said. “As for my upper body, I’m thoroughly used to living with only one hand and I continue to be surprised at how much I can still do. With enough time and experimentation, I can usually find a way to do what I need/want to do. It took me awhile to figure out how to clap! Now I just pound my chest for the same effect!”
Dr. Miller is an animal-lover and said his pets and nature are a large part of his self-care. His dog Maysie travels nearly everywhere with him and his cats, the Muffin Man and Darkness, enjoy making guest appearances on his Zoom calls. The physician frequently visits the desert in southern Utah and said he loves the arts, architecture, and design.
Dr. Miller’s advice for others who are disabled and want to go into medicine? Live out loud with your truths and be open about your disabilities. Too often, disabled individuals hide their disabilities, lie about them, or shield the world from their story, he said.
“These are rich, ripe experiences that are incredibly valuable to someone who wants to go out and be of service in the world,” he said. “We should be proud of our experiences as disabled people. The creativity we’ve had to exercise, the workarounds we’ve had to employ, these should not be points of embarrassment, but points of pride. Anyone who wants to pursue clinical training of any kind should use these experiences explicitly. These are sources of strength, not something to be forgiven or tolerated or accommodated.”
The same goes for physicians who do not have disabilities but who have lived through hardship, pain, struggle, or adversity, he emphasized.
“Find a way to learn from them, find a way to own them,” he said. “Use them as a source of strength and the rest of the world will respond to you differently.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AGILE: ‘Exciting’ survival results for IDH1-mutated AML
ATLANTA – Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) bearing mutations in IDH1 who could not withstand the rigors of intensive therapy had improved event-free and overall survival when they were treated with the combination of ivosidenib (Tibsovo) and azacitidine (Onureg, Vidaza), compared with azacitidine alone.
The results come from the phase 3 AGILE trial., reported Hartmut Döhner, MD, from Ulm (Germany) University Hospital.
Median overall survival was 24 months with the combination, compared with 7.9 months for azacitidine-placebo, translating into a hazard ratio for death with the IVO-AZA of 0.44 (P = .0005).
“The IVO-AZA combination was safe and tolerable, with fewer infections reported relative to placebo plus AZA. Additionally, the clinical benefit of the combination was supported by favorable health-related quality of life,” he said.
Dr. Döhner spoke at a press briefing prior to the presentation of the trial results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“I’m really excited by the results from the AGILE trial,” commented Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, chief of the division of hematology at the University of Miami’s Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, who moderated the briefing.
The results show “survival that’s three times longer for a combination of ivosidenib plus azacitidine versus azacitidine alone in a very distinct population of patients who have an IDH1 mutation,” he said.
“The question that will arise is, if the standard of care is now to give azacitidine and venetoclax [Venclexta] to patients who don’t receive intensive chemotherapy in the inpatient setting, where does this trial end? And I would answer [by saying] that the combination of azacitidine is not truly nonintensive therapy, and it’s probably on a spectrum between nonintensive and intensive therapy, and probably closer to seven plus three than a lot of people recognize,” Dr. Sekeres said.
The combination of ivosidenib and azacitidine may therefore be a better choice for treatment of older patients with IDH1-mutated AML – particularly those with comorbidities – who may not be able to tolerate venetoclax plus azacitidine, he added.
AGILE results
For the analysis presented at the meeting, there was a data cutoff in March 2021, at which point 146 patients out of a planned 200 had been enrolled and randomly assigned. They received treatment with either oral ivosidenib 500 mg daily plus azacitidine 75 mg/m2, delivered subcutaneously or intravenously, or azacitidine plus placebo.
In May 2021, after an interim analysis, the independent data-monitoring committee recommended a halt to the trial because of significant improvements in outcomes among patients assigned to the combination, and those data are reported at the meeting.
The median patient age was about 76 years in each group. Approximately 75% of patients in each arm had de novo AML, and about 25% had AML secondary to treatment, myelodysplastic syndrome, or myeloproliferative neoplasms. The majority of patients in each group had intermediate cytogenetic risk disease.
The analysis was by intention to treat, with patients who did not have complete remission (CR) by week 24 considered to have had an event on day 1 of randomization.
At the time of the interim analysis, with the longest follow-up out to 29 months (the investigators did not report median follow-up time for the study), there were significantly fewer study events – defined as treatment failure by week 24, relapse from remission, or death from any cause – in the ivosidenib/azacitidine combination, with a hazard ratio of 0.33 (P = .0011).
The EFS benefit and the overall survival benefit were consistent across subgroups, the researchers noted, including in patients with de novo disease, demographics, baseline cytogenetic risk status, World Health Organization AML classification, baseline white blood cell count, and baseline percentage of bone marrow blasts.
Clinical and hematologic responses also favored the combination, with a complete response (CR) rate of 34%, compared with 11% for azacitidine alone (odds ratio, 4.8; P < .0001), and respective overall response rates of 45% versus 14% (odds ratio, 7.2; P < .0001).
Health-related quality of life measures also trended better with the combination across all subscales, and were significantly better at day 1 of cycle 5 in the diarrhea and appetite loss domains.
Treatment-emergent adverse events included grade 2 or higher differentiation syndrome, which occurred in 14.1% of patients treated with IVO-AZA versus 8.2% treated with AZA alone. Grade 3 or higher QT interval prolongation was also more frequent with the combination, at 9.9% versus 4.1%.
Any-grade infections were less common with IVO-AZA, however, at 28.2% versus 49.3% with AZA alone. At the briefing, this news organization asked coinvestigator Stephane de Botton, MD, Gustave Roussy Cancer Center, Villejuif, France, whether he could explain this seemingly paradoxical result.
He replied that the combination results in greater production of neutrophils and therefore better protection against infections, compared with azacitidine alone.
The study was funded by Agios Pharmaceuticals, now a part of Servier Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Döhner disclosed consultancy and other relationships with various companies. Dr. Sekeres disclosed consulting/advising for Novartis, Takea/Millennium, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA – Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) bearing mutations in IDH1 who could not withstand the rigors of intensive therapy had improved event-free and overall survival when they were treated with the combination of ivosidenib (Tibsovo) and azacitidine (Onureg, Vidaza), compared with azacitidine alone.
The results come from the phase 3 AGILE trial., reported Hartmut Döhner, MD, from Ulm (Germany) University Hospital.
Median overall survival was 24 months with the combination, compared with 7.9 months for azacitidine-placebo, translating into a hazard ratio for death with the IVO-AZA of 0.44 (P = .0005).
“The IVO-AZA combination was safe and tolerable, with fewer infections reported relative to placebo plus AZA. Additionally, the clinical benefit of the combination was supported by favorable health-related quality of life,” he said.
Dr. Döhner spoke at a press briefing prior to the presentation of the trial results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“I’m really excited by the results from the AGILE trial,” commented Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, chief of the division of hematology at the University of Miami’s Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, who moderated the briefing.
The results show “survival that’s three times longer for a combination of ivosidenib plus azacitidine versus azacitidine alone in a very distinct population of patients who have an IDH1 mutation,” he said.
“The question that will arise is, if the standard of care is now to give azacitidine and venetoclax [Venclexta] to patients who don’t receive intensive chemotherapy in the inpatient setting, where does this trial end? And I would answer [by saying] that the combination of azacitidine is not truly nonintensive therapy, and it’s probably on a spectrum between nonintensive and intensive therapy, and probably closer to seven plus three than a lot of people recognize,” Dr. Sekeres said.
The combination of ivosidenib and azacitidine may therefore be a better choice for treatment of older patients with IDH1-mutated AML – particularly those with comorbidities – who may not be able to tolerate venetoclax plus azacitidine, he added.
AGILE results
For the analysis presented at the meeting, there was a data cutoff in March 2021, at which point 146 patients out of a planned 200 had been enrolled and randomly assigned. They received treatment with either oral ivosidenib 500 mg daily plus azacitidine 75 mg/m2, delivered subcutaneously or intravenously, or azacitidine plus placebo.
In May 2021, after an interim analysis, the independent data-monitoring committee recommended a halt to the trial because of significant improvements in outcomes among patients assigned to the combination, and those data are reported at the meeting.
The median patient age was about 76 years in each group. Approximately 75% of patients in each arm had de novo AML, and about 25% had AML secondary to treatment, myelodysplastic syndrome, or myeloproliferative neoplasms. The majority of patients in each group had intermediate cytogenetic risk disease.
The analysis was by intention to treat, with patients who did not have complete remission (CR) by week 24 considered to have had an event on day 1 of randomization.
At the time of the interim analysis, with the longest follow-up out to 29 months (the investigators did not report median follow-up time for the study), there were significantly fewer study events – defined as treatment failure by week 24, relapse from remission, or death from any cause – in the ivosidenib/azacitidine combination, with a hazard ratio of 0.33 (P = .0011).
The EFS benefit and the overall survival benefit were consistent across subgroups, the researchers noted, including in patients with de novo disease, demographics, baseline cytogenetic risk status, World Health Organization AML classification, baseline white blood cell count, and baseline percentage of bone marrow blasts.
Clinical and hematologic responses also favored the combination, with a complete response (CR) rate of 34%, compared with 11% for azacitidine alone (odds ratio, 4.8; P < .0001), and respective overall response rates of 45% versus 14% (odds ratio, 7.2; P < .0001).
Health-related quality of life measures also trended better with the combination across all subscales, and were significantly better at day 1 of cycle 5 in the diarrhea and appetite loss domains.
Treatment-emergent adverse events included grade 2 or higher differentiation syndrome, which occurred in 14.1% of patients treated with IVO-AZA versus 8.2% treated with AZA alone. Grade 3 or higher QT interval prolongation was also more frequent with the combination, at 9.9% versus 4.1%.
Any-grade infections were less common with IVO-AZA, however, at 28.2% versus 49.3% with AZA alone. At the briefing, this news organization asked coinvestigator Stephane de Botton, MD, Gustave Roussy Cancer Center, Villejuif, France, whether he could explain this seemingly paradoxical result.
He replied that the combination results in greater production of neutrophils and therefore better protection against infections, compared with azacitidine alone.
The study was funded by Agios Pharmaceuticals, now a part of Servier Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Döhner disclosed consultancy and other relationships with various companies. Dr. Sekeres disclosed consulting/advising for Novartis, Takea/Millennium, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATLANTA – Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) bearing mutations in IDH1 who could not withstand the rigors of intensive therapy had improved event-free and overall survival when they were treated with the combination of ivosidenib (Tibsovo) and azacitidine (Onureg, Vidaza), compared with azacitidine alone.
The results come from the phase 3 AGILE trial., reported Hartmut Döhner, MD, from Ulm (Germany) University Hospital.
Median overall survival was 24 months with the combination, compared with 7.9 months for azacitidine-placebo, translating into a hazard ratio for death with the IVO-AZA of 0.44 (P = .0005).
“The IVO-AZA combination was safe and tolerable, with fewer infections reported relative to placebo plus AZA. Additionally, the clinical benefit of the combination was supported by favorable health-related quality of life,” he said.
Dr. Döhner spoke at a press briefing prior to the presentation of the trial results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“I’m really excited by the results from the AGILE trial,” commented Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, chief of the division of hematology at the University of Miami’s Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, who moderated the briefing.
The results show “survival that’s three times longer for a combination of ivosidenib plus azacitidine versus azacitidine alone in a very distinct population of patients who have an IDH1 mutation,” he said.
“The question that will arise is, if the standard of care is now to give azacitidine and venetoclax [Venclexta] to patients who don’t receive intensive chemotherapy in the inpatient setting, where does this trial end? And I would answer [by saying] that the combination of azacitidine is not truly nonintensive therapy, and it’s probably on a spectrum between nonintensive and intensive therapy, and probably closer to seven plus three than a lot of people recognize,” Dr. Sekeres said.
The combination of ivosidenib and azacitidine may therefore be a better choice for treatment of older patients with IDH1-mutated AML – particularly those with comorbidities – who may not be able to tolerate venetoclax plus azacitidine, he added.
AGILE results
For the analysis presented at the meeting, there was a data cutoff in March 2021, at which point 146 patients out of a planned 200 had been enrolled and randomly assigned. They received treatment with either oral ivosidenib 500 mg daily plus azacitidine 75 mg/m2, delivered subcutaneously or intravenously, or azacitidine plus placebo.
In May 2021, after an interim analysis, the independent data-monitoring committee recommended a halt to the trial because of significant improvements in outcomes among patients assigned to the combination, and those data are reported at the meeting.
The median patient age was about 76 years in each group. Approximately 75% of patients in each arm had de novo AML, and about 25% had AML secondary to treatment, myelodysplastic syndrome, or myeloproliferative neoplasms. The majority of patients in each group had intermediate cytogenetic risk disease.
The analysis was by intention to treat, with patients who did not have complete remission (CR) by week 24 considered to have had an event on day 1 of randomization.
At the time of the interim analysis, with the longest follow-up out to 29 months (the investigators did not report median follow-up time for the study), there were significantly fewer study events – defined as treatment failure by week 24, relapse from remission, or death from any cause – in the ivosidenib/azacitidine combination, with a hazard ratio of 0.33 (P = .0011).
The EFS benefit and the overall survival benefit were consistent across subgroups, the researchers noted, including in patients with de novo disease, demographics, baseline cytogenetic risk status, World Health Organization AML classification, baseline white blood cell count, and baseline percentage of bone marrow blasts.
Clinical and hematologic responses also favored the combination, with a complete response (CR) rate of 34%, compared with 11% for azacitidine alone (odds ratio, 4.8; P < .0001), and respective overall response rates of 45% versus 14% (odds ratio, 7.2; P < .0001).
Health-related quality of life measures also trended better with the combination across all subscales, and were significantly better at day 1 of cycle 5 in the diarrhea and appetite loss domains.
Treatment-emergent adverse events included grade 2 or higher differentiation syndrome, which occurred in 14.1% of patients treated with IVO-AZA versus 8.2% treated with AZA alone. Grade 3 or higher QT interval prolongation was also more frequent with the combination, at 9.9% versus 4.1%.
Any-grade infections were less common with IVO-AZA, however, at 28.2% versus 49.3% with AZA alone. At the briefing, this news organization asked coinvestigator Stephane de Botton, MD, Gustave Roussy Cancer Center, Villejuif, France, whether he could explain this seemingly paradoxical result.
He replied that the combination results in greater production of neutrophils and therefore better protection against infections, compared with azacitidine alone.
The study was funded by Agios Pharmaceuticals, now a part of Servier Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Döhner disclosed consultancy and other relationships with various companies. Dr. Sekeres disclosed consulting/advising for Novartis, Takea/Millennium, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASH 2021
Rare GU cancers: Overcoming obstacles through collaboration, novel trial design
In a field of poor outcomes, few standards of care, and small populations of patients scattered across the world, investigators studying rare genitourinary (GU) cancers are gaining ground through international collaboration and novel trial design.
Fundamental clinical questions in the area remain unanswered, including the value of conventional treatments, such as chemotherapy and surgery, vs. emerging immunotherapy combinations.
Managing patients with rare GU cancers presents a variety of challenges, as does conducting research in the field, according to Philippe E. Spiess, MD, MS, FACS, assistant chief of surgical services and senior member in the department of GU oncology at Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa.
“Unfortunately, there are limited resources for patients – from an education, from a patient advocacy, and ultimately also from a research standpoint,” Dr. Spiess said in an interview, noting difficulties in attaining funding and reaching meaningful endpoints.
The Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors
Last year Dr. Spiess teamed up with Andrea Necchi, MD, of the department of medical oncology at Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, to found the Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors (GSRGT), the first organization of its kind.
“We’ve formally established a society and gotten some of the world leaders [in the field] … to work with us in developing educational tools and patient advocacy efforts to really promote and improve the care of patients impacted with rare cancers,” Dr. Spiess said.
He went on to highlight the truly global makeup of GSRGT, which includes members from leading centers in North America, South America, Europe, and India, and described it as a “grass-roots” organization that he and Dr. Necchi privately funded without financial backing from pharmaceutical companies.
The first GSRGT summit took place in 2020; it focused on penile and testis cancers and was attended by more than 350 participants. The second summit, planned for March 2022, in a virtual format, will focus on rare kidney cancers and upper tract cancers.
“We’ll definitely be having a lot of important conversations about important unmet needs, and some of the important clinical trials that patients and clinicians should be aware of,” Dr. Spiess said.
Dr. Spiess is currently involved in the International Penile Advanced Cancer Trial(InPACT), which is aiming to enroll 200 patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. The randomized study will compare outcomes across patients treated with standard surgery alone, neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus surgery, and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery.
“I think this is going to be a landmark study because it’s going to give really baseline high-quality data on the effectiveness of these therapies,” Dr. Spiess said.
Results are expected in 2024.
Basket trials open doors for patients in need
Other investigators are testing immunotherapy combinations in patients with rare GU tumors via nonrandomized basket trials, which widen inclusion criteria and improve local availability.
According to Bradley McGregor, MD, clinical director of the Lank Center for GU Oncology at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, early results from these trials are promising, both in terms of therapeutic efficacy and the approach itself.
“Patients [with rare GU tumors] would come to us saying, ‘Well, what can we do? What trial?’,” Dr. McGregor said. “But really, there was no trial to get them on.”Basket trials are therefore needed, he said, as they accelerate progress in the field and help meet patient needs.
“For some of these relatively rare diseases … there is no standard of care,” Dr. McGregor said. “And low incidence makes it challenging to conduct a dedicated clinical trial. Those patients are left with minimal therapeutic options. … We look to provide care for that unmet need.”Andrea B. Apolo, MD, described similar experiences as head of the bladder cancer section of the GU malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute (NCI), Bethesda, Md.
“I’ve been at the NCI for the past 10 years and I’ve gotten a lot of referrals for rare tumors,” Dr. Apolo said. “[These patients] have tried all available standard of care options, and therefore are often looking for clinical trials and new drugs – any kind of therapy that may be effective for their disease.”This call for help, along with a growing scientific curiosity, motivated Dr. Apolo to design trials that would include patients who had nowhere else to go.
“I became very interested in … understanding more about the mechanism of tumorigenesis and understanding rare tumors, biologically, within the lab,” she said, “but also clinically, in terms of finding more effective therapies.”
Both Dr. McGregor and Dr. Apolo are currently conducting basket trials for patients with rare GU tumors. While Dr. McGregor is testing a combination of PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab and CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab, Dr. Apolo is exploring the benefit of cabozantinib, a targeted therapy, given with either nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab.
When asked about these trials, Dr. Spiess said that “basket trials are important because they may give us an understanding of some potentially useful therapies or combinations;” however, he also pointed out their limitations, noting that they may inaccurately characterize the efficacy of given therapies over a broad array of disease entities even if they are of similar histology. As an example, he noted “very different” genomic profiles across squamous cell carcinomas of the pelvis depending on exact anatomical location, suggesting that these differences may affect responses to therapy, citing a recent study in European Urology that he conducted with Dr. Necchi.1
“[Basket trials] are probably not going to be the be-all-end-all,” Dr. Spiess said. “It really requires a global initiative to do these types of studies, which the Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors will allow.”
Exploring immunotherapy combinations
Despite the potential limitations, recent basket trials involving immunotherapy regimens have been associated with overall response rates, in some subgroups, that exceed 35%.2,3
In comparison with previous trials, many of which had response rates in the single digits, or no responses at all, these results are, in Dr. McGregor’s words, “very thought provoking.”Most rare GU malignancies fall into one of four categories: bladder cancer variant histology (BCVH), adrenal tumors, penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC), and chemotherapy-refractory germ cell tumors (CRGCT). Among these, BCVH has the strongest evidence supporting clinical use of immunotherapy, based on U.S. approval for urothelial histology, according to Dr. McGregor.4Data supporting immunotherapy for the remaining disease subtypes are scarce. Although pembrolizumab is approved for patients with solid tumors that exhibit microsatellite instability (MSI), MSI is uncommon among patients with rare GU cancers; estimated incidence rates are less than 10%.4
“As such, clinical trials to address this unmet need are imperative,” Dr. McGregor wrote in a recent review article.4
According to Dr. McGregor, programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in rare GU tumors may be relatively common in some disease subtypes, such as PSCC, which has a PD-L1 expression rate of up to 60%.4
But rare GU tumor trials involving a single checkpoint inhibitor have produced limited results, if any.
The largest trial for adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC), for example, which included 50 patients, showed that avelumab resulted in an objective response rate (ORR) of just 6%.5
Pembrolizumab was slightly more effective for ACC, based on a trial involving 39 patients, which returned an ORR of 23%, and another trial involving 15 patients that had a 15% ORR.6,7
Two other trials, which tested single-agent pembrolizumab or durvalumab in patients with CRGCT, resulted in no responses at all, whereas a trial testing pembrolizumab alone for penile squamous cell carcinoma was terminated in 2020, citing poor accrual.8,9 Still, the durvalumab trial for CRGCT, led by Dr. Necchi, did offer a glimpse at what might be possible with a combination of immunotherapies. Although no responses were observed among 11 patients who received durvalumab alone, an efficacy signal was observed in a second cohort of 11 patients who were given durvalumab in combination with the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremilimumab.9
Out of those 11 patients, 1 had a partial response, and another achieved stable disease.
In light of these findings, and more that have been published since then, the clinical trial landscape for rare GU tumors is shifting toward a combination immunotherapy approach, according to Dr. McGregor.4
Nivolumab and ipilimumab
Dr. McGregor is leading a phase II trial (NCT03333616) testing a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with a variety of advanced rare GU malignancies, including bladder and upper tract carcinoma of variant histology (BUTCVH), adrenal tumors, CRGCT, PSCC, and prostate cancer of variant histology (PCVH).
“When trials are designed, these patients are often forgotten,” Dr. McGregor noted. “We said, let’s do a trial for all rare GU tumors and just sort of assess and look for a signal, and, hopefully, find a signal that we can then take to the next level.”
Along with appropriate disease phenotype, trial eligibility depended upon an ECOG performance status of 0-2 and no prior exposure to checkpoint inhibitors. Treatment-naive patients were allowed. All participants received nivolumab 3 mg/kg and ipilimumab 1 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by maintenance nivolumab at a dose of 480 mg every 4 weeks.
Most recent results, published in Cancer, included data from 55 patients, including 19 with BUTCVH, 18 with adrenal tumors, and 18 with other tumors.3 After a median follow-up of 9.9 months, 28 patients (51%) received all four doses of the regimen, 25 of whom received maintenance therapy with a median of four cycles.
Overall, nine patients (16%) responded to therapy, six of whom (67%) maintained their response for at least 9 months. Two responses were complete, and seven were partial. Median progression-free survival was 2.8 months.
Twenty-two patients (39%) had grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events, approximately one-quarter (23%) needed high-dose steroids, and a slightly greater proportion (27%) discontinued the regimen because of adverse events. Three patients exhibited grade 5 toxicity, and one patient death was treatment related. A closer look at the efficacy data suggested that one disease subgroup benefited much more than the others. The overall response rate among 19 patients with BUTCVH was 37%, compared with 6% in the other two cohorts.
“A response rate of 37% compares quite favorably to anything we’ve seen to date,” Dr. McGregor said. “It’s remarkable that [this response] was seen across histologies – we saw this in urachal, we saw this in adenocarcinoma – we really saw this across the board. This is very, very, very intriguing data.”
The phase II trial is ongoing at multiple centers across the country, including the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center, Boston, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, the Moores Cancer Center at University of California Health, San Diego, the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, and the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We accrued this trial in just under 18 months,” Dr. McGregor said. “I think this shows that with a well-designed trial, we can actually study these diseases and improve outcomes in these patients.” According to Dr. McGregor, the current findings deserve further investigation, potentially including expansion of the BUTCVH cohort. Recruitment is ongoing for a fourth cohort involving patients with tumors that exhibit neuroendocrine differentiation.
Cabozantinib and nivolumab with or without ipilimumab
Dr. Apolo is leading a similar basket trial (NCT02496208) that is testing cabozantinib plus nivolumab with or without ipilimumab.
“What we’re doing is using immunotherapy and a targeted therapy that work in standard urothelial carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Apolo said. “But really, we don’t know the activity in these rare GU tumors. … There’s still so much we don’t understand about what the driving mutations are, and how we can best target them.”
Most recent data, published in Journal of Clinical Oncology, include 122 patients with metastatic GU tumors, including urothelial carcinoma, clear cell renal cell carcinoma, bladder adenocarcinoma, and other rare GU cancers.2
Among these patients, 54 were in the phase I dose-finding cohort (eight escalating doses) and 64 were in the dose-expansion cohorts.
After a median follow-up of 40.4 months, 64 patients received the dual combination, whereas 56 received the triplet regimen. The ORR for 108 evaluable patients was 38%, including 12 complete responses (11.1%) and 29 partial responses (26.9%). The largest disease cohort, for urothelial carcinoma, included 33 patients and was associated with an ORR of 42.4%, with a complete response rate of 21.2%. Objective response rate was highest for squamous bladder cancer (85.7%; n = 7), followed by clear cell renal carcinoma (62.5%; n = 16), renal medullary cancer (50%; n = 2), penile cancer (44.4%; n = 9), small cell bladder cancer (33.1%; n = 3), bladder adenocarcinoma (20%; n = 15), and prostate cancer (11.1%; n = 9). No responses were seen in six patients with germ cell tumors.
Adding ipilimumab appeared to have a minimal impact on toxicity. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) occurred in 84% of patients in the dual combination group, compared with 80% receiving the triplet regimen. Most common AEs were hypophosphatemia (16-25%), lipase elevation (20%), fatigue (18-20%), ALT elevation (5-14%), AST elevation (9-11%), diarrhea (9-11%), and thromboembolic event (4-11%). One patient taking the triplet regimen had grade 5 pneumonitis.
These positive phase I results have paved the way for the phase II ICONIC trial (NCT03866382), a national study available through the Alliance Cooperative Group. The trial is currently recruiting, with an estimated enrollment of 224 patients with rare GU tumors.
The ICONIC trial is just one of several studies that Dr. Apolo is conducting for patients with rare GU cancer. “I have several bladder cancer trials where I’m accepting rare GU tumors to enroll,” she said, noting that efficacy signals in these exploratory cohorts may be pursued with expansion studies like ICONIC.
This inclusive strategy is uncovering promising new treatments for some rare GU malignancies, but the rarest of the rare tumor types remain challenging to study, Dr. Apolo said, because very small sample sizes can preclude significant data. “Although we do have the referral base at the NCI, we still get a small number of a lot of rare tumors,” Dr. Apolo said. “What I end up having, a lot of time, are small subsets of rare tumors – I’ll have 4 of one kind, 10 of another.” This situation means that sometimes, time and resources must be focused where they are needed most.
“Sometimes I actually have to decide which are the more common rare tumors so I can study them in a larger cohort,” Dr. Apolo said. “It can have more clinical impact within the community of that rare tumor.” Dr. Apolo described the inherent conflict involved in this decision, but also, its ultimate necessity.
“It’s what you don’t want to do, but you end up doing,” she said. “Because you want to be inclusive and include the rare, rare tumor, but sometimes you just can’t get enough numbers to see if there’s actually a difference [in efficacy]. If it doesn’t work in one patient, does that mean it doesn’t work at all? You need more numbers to really test the efficacy of therapy.”
From clinical trials to clinical practice
To accrue the number of patients needed for practice-altering findings, both Dr. McGregor and Dr. Apolo emphasized the importance of institutional support and collaborative trial designs.
“The FDA is a great ally,” Dr. McGregor said. “They’re acutely aware of the challenges facing patients with rare malignancies – not just GU malignancies. They’re continuing to evaluate the best way to move these drugs forward for those patients. … They’re constantly working with investigators, with industry, looking at data and trying to determine at what threshold these will be practice-changing studies.”
Dr. McGregor suggested that larger trials could shift national guideline recommendations toward combination immunotherapies for patients with rare GU tumors, which would lead to inclusion in compendia, and from there, broader clinical usage.
“At end of the day, luckily, we’re not dealing with drugs that aren’t available,” Dr. McGregor said. “These are drugs that are readily available, approved by the FDA in other settings.”
Dr. Apolo also described strong support from the NCI.
“The NCI really encourages the conduction and enrollment of these rare GU tumor trials, because they understand that the NCI is a really good place to study these rare tumors,” she said. “We have unique resources that make it feasible to conduct some of these trials.”
Dr. Apolo also praised the Alliance Cooperative Group for helping expand patient access to rare GU tumor trials.
“[The Alliance Cooperative Group] makes trials available at community centers across the country,” Dr. Apolo said. “Patients don’t have to travel to the NCI, and they can get the same therapies.”
Still, Dr. Apolo recommended that, when possible, clinicians refer patients with newly diagnosed, rare GU tumors to centers that see a higher number of such cases.
“It’s hard to keep up with all the different treatments that are available right now for different cancers,” Dr. Apolo said. “And sometimes for the rare tumors, there may be great opportunities within a clinical trial that a cancer center may have available that may not be available locally in the community.”
For patients who would like to learn more about rare bladder cancers, Dr. Apolo recommended a visit to the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network (BCAN) website (bcan.org).
“I’m a big fan of these patient-centered advocacy networks,” Dr. Apolo said. “I like BCAN a lot. It’s a patient-run organization for patients with bladder cancer. With them, I have done a couple of webinars for rare bladder tumors that Ive had some patients tell me are very helpful. They’re a terrific organization that really provides not only emotional support but also educational support for patients that have a diagnosis of bladder cancer and now, rare bladder tumors.” Dr. Spiess offered similar advice for clinicians managing patients with rare GU tumors. He emphasized the key role played by patient advocacy groups, and recommended referral to institutions specializing in specific GU tumor types. For example, he recommended that patients with penile cancer be treated at Moffitt (Tampa) or MD Anderson (Houston), as these centers have the greatest relevant experience. Dr. McGregor disclosed relationships with Bayer, Astellas, Nektar, and others. Dr. Apolo and Dr. Spiess disclosed no conflicts of interest.
References
1.Necchi A et al. Eur Urol. 2021 June;79:S929-30.
2.Apolo AB et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(6_suppl):3.
3.McGregor BA et al. Cancer. 2021 Mar 15;127(6):840-9.
4.McGregor BA and Sonpavde GP. Eur Urol Focus. 2020;6(1):14-16.5.Le Tourneau C et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Oct 22;6(1):111.6.Naing A et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(1).
7.Raj N et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(1):71-80.
8.Adra N et al. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):209-14.
9.Necchi A et al. Eur Urol. 2019;75(1):201-3.
In a field of poor outcomes, few standards of care, and small populations of patients scattered across the world, investigators studying rare genitourinary (GU) cancers are gaining ground through international collaboration and novel trial design.
Fundamental clinical questions in the area remain unanswered, including the value of conventional treatments, such as chemotherapy and surgery, vs. emerging immunotherapy combinations.
Managing patients with rare GU cancers presents a variety of challenges, as does conducting research in the field, according to Philippe E. Spiess, MD, MS, FACS, assistant chief of surgical services and senior member in the department of GU oncology at Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa.
“Unfortunately, there are limited resources for patients – from an education, from a patient advocacy, and ultimately also from a research standpoint,” Dr. Spiess said in an interview, noting difficulties in attaining funding and reaching meaningful endpoints.
The Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors
Last year Dr. Spiess teamed up with Andrea Necchi, MD, of the department of medical oncology at Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, to found the Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors (GSRGT), the first organization of its kind.
“We’ve formally established a society and gotten some of the world leaders [in the field] … to work with us in developing educational tools and patient advocacy efforts to really promote and improve the care of patients impacted with rare cancers,” Dr. Spiess said.
He went on to highlight the truly global makeup of GSRGT, which includes members from leading centers in North America, South America, Europe, and India, and described it as a “grass-roots” organization that he and Dr. Necchi privately funded without financial backing from pharmaceutical companies.
The first GSRGT summit took place in 2020; it focused on penile and testis cancers and was attended by more than 350 participants. The second summit, planned for March 2022, in a virtual format, will focus on rare kidney cancers and upper tract cancers.
“We’ll definitely be having a lot of important conversations about important unmet needs, and some of the important clinical trials that patients and clinicians should be aware of,” Dr. Spiess said.
Dr. Spiess is currently involved in the International Penile Advanced Cancer Trial(InPACT), which is aiming to enroll 200 patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. The randomized study will compare outcomes across patients treated with standard surgery alone, neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus surgery, and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery.
“I think this is going to be a landmark study because it’s going to give really baseline high-quality data on the effectiveness of these therapies,” Dr. Spiess said.
Results are expected in 2024.
Basket trials open doors for patients in need
Other investigators are testing immunotherapy combinations in patients with rare GU tumors via nonrandomized basket trials, which widen inclusion criteria and improve local availability.
According to Bradley McGregor, MD, clinical director of the Lank Center for GU Oncology at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, early results from these trials are promising, both in terms of therapeutic efficacy and the approach itself.
“Patients [with rare GU tumors] would come to us saying, ‘Well, what can we do? What trial?’,” Dr. McGregor said. “But really, there was no trial to get them on.”Basket trials are therefore needed, he said, as they accelerate progress in the field and help meet patient needs.
“For some of these relatively rare diseases … there is no standard of care,” Dr. McGregor said. “And low incidence makes it challenging to conduct a dedicated clinical trial. Those patients are left with minimal therapeutic options. … We look to provide care for that unmet need.”Andrea B. Apolo, MD, described similar experiences as head of the bladder cancer section of the GU malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute (NCI), Bethesda, Md.
“I’ve been at the NCI for the past 10 years and I’ve gotten a lot of referrals for rare tumors,” Dr. Apolo said. “[These patients] have tried all available standard of care options, and therefore are often looking for clinical trials and new drugs – any kind of therapy that may be effective for their disease.”This call for help, along with a growing scientific curiosity, motivated Dr. Apolo to design trials that would include patients who had nowhere else to go.
“I became very interested in … understanding more about the mechanism of tumorigenesis and understanding rare tumors, biologically, within the lab,” she said, “but also clinically, in terms of finding more effective therapies.”
Both Dr. McGregor and Dr. Apolo are currently conducting basket trials for patients with rare GU tumors. While Dr. McGregor is testing a combination of PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab and CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab, Dr. Apolo is exploring the benefit of cabozantinib, a targeted therapy, given with either nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab.
When asked about these trials, Dr. Spiess said that “basket trials are important because they may give us an understanding of some potentially useful therapies or combinations;” however, he also pointed out their limitations, noting that they may inaccurately characterize the efficacy of given therapies over a broad array of disease entities even if they are of similar histology. As an example, he noted “very different” genomic profiles across squamous cell carcinomas of the pelvis depending on exact anatomical location, suggesting that these differences may affect responses to therapy, citing a recent study in European Urology that he conducted with Dr. Necchi.1
“[Basket trials] are probably not going to be the be-all-end-all,” Dr. Spiess said. “It really requires a global initiative to do these types of studies, which the Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors will allow.”
Exploring immunotherapy combinations
Despite the potential limitations, recent basket trials involving immunotherapy regimens have been associated with overall response rates, in some subgroups, that exceed 35%.2,3
In comparison with previous trials, many of which had response rates in the single digits, or no responses at all, these results are, in Dr. McGregor’s words, “very thought provoking.”Most rare GU malignancies fall into one of four categories: bladder cancer variant histology (BCVH), adrenal tumors, penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC), and chemotherapy-refractory germ cell tumors (CRGCT). Among these, BCVH has the strongest evidence supporting clinical use of immunotherapy, based on U.S. approval for urothelial histology, according to Dr. McGregor.4Data supporting immunotherapy for the remaining disease subtypes are scarce. Although pembrolizumab is approved for patients with solid tumors that exhibit microsatellite instability (MSI), MSI is uncommon among patients with rare GU cancers; estimated incidence rates are less than 10%.4
“As such, clinical trials to address this unmet need are imperative,” Dr. McGregor wrote in a recent review article.4
According to Dr. McGregor, programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in rare GU tumors may be relatively common in some disease subtypes, such as PSCC, which has a PD-L1 expression rate of up to 60%.4
But rare GU tumor trials involving a single checkpoint inhibitor have produced limited results, if any.
The largest trial for adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC), for example, which included 50 patients, showed that avelumab resulted in an objective response rate (ORR) of just 6%.5
Pembrolizumab was slightly more effective for ACC, based on a trial involving 39 patients, which returned an ORR of 23%, and another trial involving 15 patients that had a 15% ORR.6,7
Two other trials, which tested single-agent pembrolizumab or durvalumab in patients with CRGCT, resulted in no responses at all, whereas a trial testing pembrolizumab alone for penile squamous cell carcinoma was terminated in 2020, citing poor accrual.8,9 Still, the durvalumab trial for CRGCT, led by Dr. Necchi, did offer a glimpse at what might be possible with a combination of immunotherapies. Although no responses were observed among 11 patients who received durvalumab alone, an efficacy signal was observed in a second cohort of 11 patients who were given durvalumab in combination with the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremilimumab.9
Out of those 11 patients, 1 had a partial response, and another achieved stable disease.
In light of these findings, and more that have been published since then, the clinical trial landscape for rare GU tumors is shifting toward a combination immunotherapy approach, according to Dr. McGregor.4
Nivolumab and ipilimumab
Dr. McGregor is leading a phase II trial (NCT03333616) testing a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with a variety of advanced rare GU malignancies, including bladder and upper tract carcinoma of variant histology (BUTCVH), adrenal tumors, CRGCT, PSCC, and prostate cancer of variant histology (PCVH).
“When trials are designed, these patients are often forgotten,” Dr. McGregor noted. “We said, let’s do a trial for all rare GU tumors and just sort of assess and look for a signal, and, hopefully, find a signal that we can then take to the next level.”
Along with appropriate disease phenotype, trial eligibility depended upon an ECOG performance status of 0-2 and no prior exposure to checkpoint inhibitors. Treatment-naive patients were allowed. All participants received nivolumab 3 mg/kg and ipilimumab 1 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by maintenance nivolumab at a dose of 480 mg every 4 weeks.
Most recent results, published in Cancer, included data from 55 patients, including 19 with BUTCVH, 18 with adrenal tumors, and 18 with other tumors.3 After a median follow-up of 9.9 months, 28 patients (51%) received all four doses of the regimen, 25 of whom received maintenance therapy with a median of four cycles.
Overall, nine patients (16%) responded to therapy, six of whom (67%) maintained their response for at least 9 months. Two responses were complete, and seven were partial. Median progression-free survival was 2.8 months.
Twenty-two patients (39%) had grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events, approximately one-quarter (23%) needed high-dose steroids, and a slightly greater proportion (27%) discontinued the regimen because of adverse events. Three patients exhibited grade 5 toxicity, and one patient death was treatment related. A closer look at the efficacy data suggested that one disease subgroup benefited much more than the others. The overall response rate among 19 patients with BUTCVH was 37%, compared with 6% in the other two cohorts.
“A response rate of 37% compares quite favorably to anything we’ve seen to date,” Dr. McGregor said. “It’s remarkable that [this response] was seen across histologies – we saw this in urachal, we saw this in adenocarcinoma – we really saw this across the board. This is very, very, very intriguing data.”
The phase II trial is ongoing at multiple centers across the country, including the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center, Boston, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, the Moores Cancer Center at University of California Health, San Diego, the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, and the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We accrued this trial in just under 18 months,” Dr. McGregor said. “I think this shows that with a well-designed trial, we can actually study these diseases and improve outcomes in these patients.” According to Dr. McGregor, the current findings deserve further investigation, potentially including expansion of the BUTCVH cohort. Recruitment is ongoing for a fourth cohort involving patients with tumors that exhibit neuroendocrine differentiation.
Cabozantinib and nivolumab with or without ipilimumab
Dr. Apolo is leading a similar basket trial (NCT02496208) that is testing cabozantinib plus nivolumab with or without ipilimumab.
“What we’re doing is using immunotherapy and a targeted therapy that work in standard urothelial carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Apolo said. “But really, we don’t know the activity in these rare GU tumors. … There’s still so much we don’t understand about what the driving mutations are, and how we can best target them.”
Most recent data, published in Journal of Clinical Oncology, include 122 patients with metastatic GU tumors, including urothelial carcinoma, clear cell renal cell carcinoma, bladder adenocarcinoma, and other rare GU cancers.2
Among these patients, 54 were in the phase I dose-finding cohort (eight escalating doses) and 64 were in the dose-expansion cohorts.
After a median follow-up of 40.4 months, 64 patients received the dual combination, whereas 56 received the triplet regimen. The ORR for 108 evaluable patients was 38%, including 12 complete responses (11.1%) and 29 partial responses (26.9%). The largest disease cohort, for urothelial carcinoma, included 33 patients and was associated with an ORR of 42.4%, with a complete response rate of 21.2%. Objective response rate was highest for squamous bladder cancer (85.7%; n = 7), followed by clear cell renal carcinoma (62.5%; n = 16), renal medullary cancer (50%; n = 2), penile cancer (44.4%; n = 9), small cell bladder cancer (33.1%; n = 3), bladder adenocarcinoma (20%; n = 15), and prostate cancer (11.1%; n = 9). No responses were seen in six patients with germ cell tumors.
Adding ipilimumab appeared to have a minimal impact on toxicity. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) occurred in 84% of patients in the dual combination group, compared with 80% receiving the triplet regimen. Most common AEs were hypophosphatemia (16-25%), lipase elevation (20%), fatigue (18-20%), ALT elevation (5-14%), AST elevation (9-11%), diarrhea (9-11%), and thromboembolic event (4-11%). One patient taking the triplet regimen had grade 5 pneumonitis.
These positive phase I results have paved the way for the phase II ICONIC trial (NCT03866382), a national study available through the Alliance Cooperative Group. The trial is currently recruiting, with an estimated enrollment of 224 patients with rare GU tumors.
The ICONIC trial is just one of several studies that Dr. Apolo is conducting for patients with rare GU cancer. “I have several bladder cancer trials where I’m accepting rare GU tumors to enroll,” she said, noting that efficacy signals in these exploratory cohorts may be pursued with expansion studies like ICONIC.
This inclusive strategy is uncovering promising new treatments for some rare GU malignancies, but the rarest of the rare tumor types remain challenging to study, Dr. Apolo said, because very small sample sizes can preclude significant data. “Although we do have the referral base at the NCI, we still get a small number of a lot of rare tumors,” Dr. Apolo said. “What I end up having, a lot of time, are small subsets of rare tumors – I’ll have 4 of one kind, 10 of another.” This situation means that sometimes, time and resources must be focused where they are needed most.
“Sometimes I actually have to decide which are the more common rare tumors so I can study them in a larger cohort,” Dr. Apolo said. “It can have more clinical impact within the community of that rare tumor.” Dr. Apolo described the inherent conflict involved in this decision, but also, its ultimate necessity.
“It’s what you don’t want to do, but you end up doing,” she said. “Because you want to be inclusive and include the rare, rare tumor, but sometimes you just can’t get enough numbers to see if there’s actually a difference [in efficacy]. If it doesn’t work in one patient, does that mean it doesn’t work at all? You need more numbers to really test the efficacy of therapy.”
From clinical trials to clinical practice
To accrue the number of patients needed for practice-altering findings, both Dr. McGregor and Dr. Apolo emphasized the importance of institutional support and collaborative trial designs.
“The FDA is a great ally,” Dr. McGregor said. “They’re acutely aware of the challenges facing patients with rare malignancies – not just GU malignancies. They’re continuing to evaluate the best way to move these drugs forward for those patients. … They’re constantly working with investigators, with industry, looking at data and trying to determine at what threshold these will be practice-changing studies.”
Dr. McGregor suggested that larger trials could shift national guideline recommendations toward combination immunotherapies for patients with rare GU tumors, which would lead to inclusion in compendia, and from there, broader clinical usage.
“At end of the day, luckily, we’re not dealing with drugs that aren’t available,” Dr. McGregor said. “These are drugs that are readily available, approved by the FDA in other settings.”
Dr. Apolo also described strong support from the NCI.
“The NCI really encourages the conduction and enrollment of these rare GU tumor trials, because they understand that the NCI is a really good place to study these rare tumors,” she said. “We have unique resources that make it feasible to conduct some of these trials.”
Dr. Apolo also praised the Alliance Cooperative Group for helping expand patient access to rare GU tumor trials.
“[The Alliance Cooperative Group] makes trials available at community centers across the country,” Dr. Apolo said. “Patients don’t have to travel to the NCI, and they can get the same therapies.”
Still, Dr. Apolo recommended that, when possible, clinicians refer patients with newly diagnosed, rare GU tumors to centers that see a higher number of such cases.
“It’s hard to keep up with all the different treatments that are available right now for different cancers,” Dr. Apolo said. “And sometimes for the rare tumors, there may be great opportunities within a clinical trial that a cancer center may have available that may not be available locally in the community.”
For patients who would like to learn more about rare bladder cancers, Dr. Apolo recommended a visit to the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network (BCAN) website (bcan.org).
“I’m a big fan of these patient-centered advocacy networks,” Dr. Apolo said. “I like BCAN a lot. It’s a patient-run organization for patients with bladder cancer. With them, I have done a couple of webinars for rare bladder tumors that Ive had some patients tell me are very helpful. They’re a terrific organization that really provides not only emotional support but also educational support for patients that have a diagnosis of bladder cancer and now, rare bladder tumors.” Dr. Spiess offered similar advice for clinicians managing patients with rare GU tumors. He emphasized the key role played by patient advocacy groups, and recommended referral to institutions specializing in specific GU tumor types. For example, he recommended that patients with penile cancer be treated at Moffitt (Tampa) or MD Anderson (Houston), as these centers have the greatest relevant experience. Dr. McGregor disclosed relationships with Bayer, Astellas, Nektar, and others. Dr. Apolo and Dr. Spiess disclosed no conflicts of interest.
References
1.Necchi A et al. Eur Urol. 2021 June;79:S929-30.
2.Apolo AB et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(6_suppl):3.
3.McGregor BA et al. Cancer. 2021 Mar 15;127(6):840-9.
4.McGregor BA and Sonpavde GP. Eur Urol Focus. 2020;6(1):14-16.5.Le Tourneau C et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Oct 22;6(1):111.6.Naing A et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(1).
7.Raj N et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(1):71-80.
8.Adra N et al. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):209-14.
9.Necchi A et al. Eur Urol. 2019;75(1):201-3.
In a field of poor outcomes, few standards of care, and small populations of patients scattered across the world, investigators studying rare genitourinary (GU) cancers are gaining ground through international collaboration and novel trial design.
Fundamental clinical questions in the area remain unanswered, including the value of conventional treatments, such as chemotherapy and surgery, vs. emerging immunotherapy combinations.
Managing patients with rare GU cancers presents a variety of challenges, as does conducting research in the field, according to Philippe E. Spiess, MD, MS, FACS, assistant chief of surgical services and senior member in the department of GU oncology at Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa.
“Unfortunately, there are limited resources for patients – from an education, from a patient advocacy, and ultimately also from a research standpoint,” Dr. Spiess said in an interview, noting difficulties in attaining funding and reaching meaningful endpoints.
The Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors
Last year Dr. Spiess teamed up with Andrea Necchi, MD, of the department of medical oncology at Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, to found the Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors (GSRGT), the first organization of its kind.
“We’ve formally established a society and gotten some of the world leaders [in the field] … to work with us in developing educational tools and patient advocacy efforts to really promote and improve the care of patients impacted with rare cancers,” Dr. Spiess said.
He went on to highlight the truly global makeup of GSRGT, which includes members from leading centers in North America, South America, Europe, and India, and described it as a “grass-roots” organization that he and Dr. Necchi privately funded without financial backing from pharmaceutical companies.
The first GSRGT summit took place in 2020; it focused on penile and testis cancers and was attended by more than 350 participants. The second summit, planned for March 2022, in a virtual format, will focus on rare kidney cancers and upper tract cancers.
“We’ll definitely be having a lot of important conversations about important unmet needs, and some of the important clinical trials that patients and clinicians should be aware of,” Dr. Spiess said.
Dr. Spiess is currently involved in the International Penile Advanced Cancer Trial(InPACT), which is aiming to enroll 200 patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. The randomized study will compare outcomes across patients treated with standard surgery alone, neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus surgery, and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery.
“I think this is going to be a landmark study because it’s going to give really baseline high-quality data on the effectiveness of these therapies,” Dr. Spiess said.
Results are expected in 2024.
Basket trials open doors for patients in need
Other investigators are testing immunotherapy combinations in patients with rare GU tumors via nonrandomized basket trials, which widen inclusion criteria and improve local availability.
According to Bradley McGregor, MD, clinical director of the Lank Center for GU Oncology at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, early results from these trials are promising, both in terms of therapeutic efficacy and the approach itself.
“Patients [with rare GU tumors] would come to us saying, ‘Well, what can we do? What trial?’,” Dr. McGregor said. “But really, there was no trial to get them on.”Basket trials are therefore needed, he said, as they accelerate progress in the field and help meet patient needs.
“For some of these relatively rare diseases … there is no standard of care,” Dr. McGregor said. “And low incidence makes it challenging to conduct a dedicated clinical trial. Those patients are left with minimal therapeutic options. … We look to provide care for that unmet need.”Andrea B. Apolo, MD, described similar experiences as head of the bladder cancer section of the GU malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute (NCI), Bethesda, Md.
“I’ve been at the NCI for the past 10 years and I’ve gotten a lot of referrals for rare tumors,” Dr. Apolo said. “[These patients] have tried all available standard of care options, and therefore are often looking for clinical trials and new drugs – any kind of therapy that may be effective for their disease.”This call for help, along with a growing scientific curiosity, motivated Dr. Apolo to design trials that would include patients who had nowhere else to go.
“I became very interested in … understanding more about the mechanism of tumorigenesis and understanding rare tumors, biologically, within the lab,” she said, “but also clinically, in terms of finding more effective therapies.”
Both Dr. McGregor and Dr. Apolo are currently conducting basket trials for patients with rare GU tumors. While Dr. McGregor is testing a combination of PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab and CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab, Dr. Apolo is exploring the benefit of cabozantinib, a targeted therapy, given with either nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab.
When asked about these trials, Dr. Spiess said that “basket trials are important because they may give us an understanding of some potentially useful therapies or combinations;” however, he also pointed out their limitations, noting that they may inaccurately characterize the efficacy of given therapies over a broad array of disease entities even if they are of similar histology. As an example, he noted “very different” genomic profiles across squamous cell carcinomas of the pelvis depending on exact anatomical location, suggesting that these differences may affect responses to therapy, citing a recent study in European Urology that he conducted with Dr. Necchi.1
“[Basket trials] are probably not going to be the be-all-end-all,” Dr. Spiess said. “It really requires a global initiative to do these types of studies, which the Global Society of Rare Genitourinary Tumors will allow.”
Exploring immunotherapy combinations
Despite the potential limitations, recent basket trials involving immunotherapy regimens have been associated with overall response rates, in some subgroups, that exceed 35%.2,3
In comparison with previous trials, many of which had response rates in the single digits, or no responses at all, these results are, in Dr. McGregor’s words, “very thought provoking.”Most rare GU malignancies fall into one of four categories: bladder cancer variant histology (BCVH), adrenal tumors, penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC), and chemotherapy-refractory germ cell tumors (CRGCT). Among these, BCVH has the strongest evidence supporting clinical use of immunotherapy, based on U.S. approval for urothelial histology, according to Dr. McGregor.4Data supporting immunotherapy for the remaining disease subtypes are scarce. Although pembrolizumab is approved for patients with solid tumors that exhibit microsatellite instability (MSI), MSI is uncommon among patients with rare GU cancers; estimated incidence rates are less than 10%.4
“As such, clinical trials to address this unmet need are imperative,” Dr. McGregor wrote in a recent review article.4
According to Dr. McGregor, programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in rare GU tumors may be relatively common in some disease subtypes, such as PSCC, which has a PD-L1 expression rate of up to 60%.4
But rare GU tumor trials involving a single checkpoint inhibitor have produced limited results, if any.
The largest trial for adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC), for example, which included 50 patients, showed that avelumab resulted in an objective response rate (ORR) of just 6%.5
Pembrolizumab was slightly more effective for ACC, based on a trial involving 39 patients, which returned an ORR of 23%, and another trial involving 15 patients that had a 15% ORR.6,7
Two other trials, which tested single-agent pembrolizumab or durvalumab in patients with CRGCT, resulted in no responses at all, whereas a trial testing pembrolizumab alone for penile squamous cell carcinoma was terminated in 2020, citing poor accrual.8,9 Still, the durvalumab trial for CRGCT, led by Dr. Necchi, did offer a glimpse at what might be possible with a combination of immunotherapies. Although no responses were observed among 11 patients who received durvalumab alone, an efficacy signal was observed in a second cohort of 11 patients who were given durvalumab in combination with the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremilimumab.9
Out of those 11 patients, 1 had a partial response, and another achieved stable disease.
In light of these findings, and more that have been published since then, the clinical trial landscape for rare GU tumors is shifting toward a combination immunotherapy approach, according to Dr. McGregor.4
Nivolumab and ipilimumab
Dr. McGregor is leading a phase II trial (NCT03333616) testing a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with a variety of advanced rare GU malignancies, including bladder and upper tract carcinoma of variant histology (BUTCVH), adrenal tumors, CRGCT, PSCC, and prostate cancer of variant histology (PCVH).
“When trials are designed, these patients are often forgotten,” Dr. McGregor noted. “We said, let’s do a trial for all rare GU tumors and just sort of assess and look for a signal, and, hopefully, find a signal that we can then take to the next level.”
Along with appropriate disease phenotype, trial eligibility depended upon an ECOG performance status of 0-2 and no prior exposure to checkpoint inhibitors. Treatment-naive patients were allowed. All participants received nivolumab 3 mg/kg and ipilimumab 1 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by maintenance nivolumab at a dose of 480 mg every 4 weeks.
Most recent results, published in Cancer, included data from 55 patients, including 19 with BUTCVH, 18 with adrenal tumors, and 18 with other tumors.3 After a median follow-up of 9.9 months, 28 patients (51%) received all four doses of the regimen, 25 of whom received maintenance therapy with a median of four cycles.
Overall, nine patients (16%) responded to therapy, six of whom (67%) maintained their response for at least 9 months. Two responses were complete, and seven were partial. Median progression-free survival was 2.8 months.
Twenty-two patients (39%) had grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events, approximately one-quarter (23%) needed high-dose steroids, and a slightly greater proportion (27%) discontinued the regimen because of adverse events. Three patients exhibited grade 5 toxicity, and one patient death was treatment related. A closer look at the efficacy data suggested that one disease subgroup benefited much more than the others. The overall response rate among 19 patients with BUTCVH was 37%, compared with 6% in the other two cohorts.
“A response rate of 37% compares quite favorably to anything we’ve seen to date,” Dr. McGregor said. “It’s remarkable that [this response] was seen across histologies – we saw this in urachal, we saw this in adenocarcinoma – we really saw this across the board. This is very, very, very intriguing data.”
The phase II trial is ongoing at multiple centers across the country, including the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center, Boston, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, the Moores Cancer Center at University of California Health, San Diego, the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, and the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“We accrued this trial in just under 18 months,” Dr. McGregor said. “I think this shows that with a well-designed trial, we can actually study these diseases and improve outcomes in these patients.” According to Dr. McGregor, the current findings deserve further investigation, potentially including expansion of the BUTCVH cohort. Recruitment is ongoing for a fourth cohort involving patients with tumors that exhibit neuroendocrine differentiation.
Cabozantinib and nivolumab with or without ipilimumab
Dr. Apolo is leading a similar basket trial (NCT02496208) that is testing cabozantinib plus nivolumab with or without ipilimumab.
“What we’re doing is using immunotherapy and a targeted therapy that work in standard urothelial carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Apolo said. “But really, we don’t know the activity in these rare GU tumors. … There’s still so much we don’t understand about what the driving mutations are, and how we can best target them.”
Most recent data, published in Journal of Clinical Oncology, include 122 patients with metastatic GU tumors, including urothelial carcinoma, clear cell renal cell carcinoma, bladder adenocarcinoma, and other rare GU cancers.2
Among these patients, 54 were in the phase I dose-finding cohort (eight escalating doses) and 64 were in the dose-expansion cohorts.
After a median follow-up of 40.4 months, 64 patients received the dual combination, whereas 56 received the triplet regimen. The ORR for 108 evaluable patients was 38%, including 12 complete responses (11.1%) and 29 partial responses (26.9%). The largest disease cohort, for urothelial carcinoma, included 33 patients and was associated with an ORR of 42.4%, with a complete response rate of 21.2%. Objective response rate was highest for squamous bladder cancer (85.7%; n = 7), followed by clear cell renal carcinoma (62.5%; n = 16), renal medullary cancer (50%; n = 2), penile cancer (44.4%; n = 9), small cell bladder cancer (33.1%; n = 3), bladder adenocarcinoma (20%; n = 15), and prostate cancer (11.1%; n = 9). No responses were seen in six patients with germ cell tumors.
Adding ipilimumab appeared to have a minimal impact on toxicity. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) occurred in 84% of patients in the dual combination group, compared with 80% receiving the triplet regimen. Most common AEs were hypophosphatemia (16-25%), lipase elevation (20%), fatigue (18-20%), ALT elevation (5-14%), AST elevation (9-11%), diarrhea (9-11%), and thromboembolic event (4-11%). One patient taking the triplet regimen had grade 5 pneumonitis.
These positive phase I results have paved the way for the phase II ICONIC trial (NCT03866382), a national study available through the Alliance Cooperative Group. The trial is currently recruiting, with an estimated enrollment of 224 patients with rare GU tumors.
The ICONIC trial is just one of several studies that Dr. Apolo is conducting for patients with rare GU cancer. “I have several bladder cancer trials where I’m accepting rare GU tumors to enroll,” she said, noting that efficacy signals in these exploratory cohorts may be pursued with expansion studies like ICONIC.
This inclusive strategy is uncovering promising new treatments for some rare GU malignancies, but the rarest of the rare tumor types remain challenging to study, Dr. Apolo said, because very small sample sizes can preclude significant data. “Although we do have the referral base at the NCI, we still get a small number of a lot of rare tumors,” Dr. Apolo said. “What I end up having, a lot of time, are small subsets of rare tumors – I’ll have 4 of one kind, 10 of another.” This situation means that sometimes, time and resources must be focused where they are needed most.
“Sometimes I actually have to decide which are the more common rare tumors so I can study them in a larger cohort,” Dr. Apolo said. “It can have more clinical impact within the community of that rare tumor.” Dr. Apolo described the inherent conflict involved in this decision, but also, its ultimate necessity.
“It’s what you don’t want to do, but you end up doing,” she said. “Because you want to be inclusive and include the rare, rare tumor, but sometimes you just can’t get enough numbers to see if there’s actually a difference [in efficacy]. If it doesn’t work in one patient, does that mean it doesn’t work at all? You need more numbers to really test the efficacy of therapy.”
From clinical trials to clinical practice
To accrue the number of patients needed for practice-altering findings, both Dr. McGregor and Dr. Apolo emphasized the importance of institutional support and collaborative trial designs.
“The FDA is a great ally,” Dr. McGregor said. “They’re acutely aware of the challenges facing patients with rare malignancies – not just GU malignancies. They’re continuing to evaluate the best way to move these drugs forward for those patients. … They’re constantly working with investigators, with industry, looking at data and trying to determine at what threshold these will be practice-changing studies.”
Dr. McGregor suggested that larger trials could shift national guideline recommendations toward combination immunotherapies for patients with rare GU tumors, which would lead to inclusion in compendia, and from there, broader clinical usage.
“At end of the day, luckily, we’re not dealing with drugs that aren’t available,” Dr. McGregor said. “These are drugs that are readily available, approved by the FDA in other settings.”
Dr. Apolo also described strong support from the NCI.
“The NCI really encourages the conduction and enrollment of these rare GU tumor trials, because they understand that the NCI is a really good place to study these rare tumors,” she said. “We have unique resources that make it feasible to conduct some of these trials.”
Dr. Apolo also praised the Alliance Cooperative Group for helping expand patient access to rare GU tumor trials.
“[The Alliance Cooperative Group] makes trials available at community centers across the country,” Dr. Apolo said. “Patients don’t have to travel to the NCI, and they can get the same therapies.”
Still, Dr. Apolo recommended that, when possible, clinicians refer patients with newly diagnosed, rare GU tumors to centers that see a higher number of such cases.
“It’s hard to keep up with all the different treatments that are available right now for different cancers,” Dr. Apolo said. “And sometimes for the rare tumors, there may be great opportunities within a clinical trial that a cancer center may have available that may not be available locally in the community.”
For patients who would like to learn more about rare bladder cancers, Dr. Apolo recommended a visit to the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network (BCAN) website (bcan.org).
“I’m a big fan of these patient-centered advocacy networks,” Dr. Apolo said. “I like BCAN a lot. It’s a patient-run organization for patients with bladder cancer. With them, I have done a couple of webinars for rare bladder tumors that Ive had some patients tell me are very helpful. They’re a terrific organization that really provides not only emotional support but also educational support for patients that have a diagnosis of bladder cancer and now, rare bladder tumors.” Dr. Spiess offered similar advice for clinicians managing patients with rare GU tumors. He emphasized the key role played by patient advocacy groups, and recommended referral to institutions specializing in specific GU tumor types. For example, he recommended that patients with penile cancer be treated at Moffitt (Tampa) or MD Anderson (Houston), as these centers have the greatest relevant experience. Dr. McGregor disclosed relationships with Bayer, Astellas, Nektar, and others. Dr. Apolo and Dr. Spiess disclosed no conflicts of interest.
References
1.Necchi A et al. Eur Urol. 2021 June;79:S929-30.
2.Apolo AB et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(6_suppl):3.
3.McGregor BA et al. Cancer. 2021 Mar 15;127(6):840-9.
4.McGregor BA and Sonpavde GP. Eur Urol Focus. 2020;6(1):14-16.5.Le Tourneau C et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Oct 22;6(1):111.6.Naing A et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(1).
7.Raj N et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(1):71-80.
8.Adra N et al. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(1):209-14.
9.Necchi A et al. Eur Urol. 2019;75(1):201-3.
D-dimer thresholds rule out PE in meta-analysis
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
What the Future May Hold for Covid-19 Survivors
What the Future May Hold for Covid-19 Survivors
More than 3 million Americans1 have been hospitalized with Covid-19, and
And these are just the patients with severe Covid: those who were never hospitalized are also showing deleterious effects from the effects of their illness.
Covid in the ICU
What we know is that prior to Covid, 10% of all patients were admitted to ICU with acute respiratory distress syndrome4 (ARDS), despite receiving such life-saving measures as mechanical ventilation, medication, and supportive nutrition. Those who do survive face a long journey.4 Besides the specific respiratory recovery needed in those with ARDS, patients who have spent time in the ICU can develop multiple non-respiratory complications, including muscle wasting, generalized weakness, and delirium. The physical, cognitive, and psychological impairments that follow an ICU stay are termed postintensive care syndrome (PICS). PICS is an underrecognized phenomenon that describes the immense complications of an ICU stay for any reason. Recognition of this entity, and education of patients, is particularly important now as we face an ongoing pandemic which is creating a burgeoning number of ICU graduates.
PICS
Cognitive dysfunction is one hallmark of PICS. Delirium is a common complication of any hospitalization, with critically ill patients particularly susceptible given the severity of their illness and their exposure to medications such as sedatives. However, persistent global cognitive impairment is unique to PICS. Up to
The second aspect of PICS is its psychological component. In the Hopkins study,5
The final component of PICS is physical impairment. Those who are critically ill commonly suffer intensive care unit
Covid in the ICU
Estimates of the incidence of PICS due to Covid are evolving. A report on 1700 Covid hospitalized patients in Wuhan, China demonstrated a large prevalence of residual symptoms at 6 months. The most common symptoms were fatigue and weakness (63%), insomnia (26%), and anxiety or depression (
As more centers track the progress of their ICU graduates over time, we can better understand the profound impact of critical illness on our Covid patients and better educate our patients and families on what to expect. One might be able to gain some clues from what is known regarding the prior coronavirus epidemics, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). In these diseases, a meta-analysis showed significant rates of
Additional issues
What is particularly unique to Covid is the prevalence of long-term symptoms in those who were never hospitalized for Covid. Recent estimates of non-hospitalized patients who had Covid are showing at least 25% of them have had long-lasting effects, including stomach pain and respiratory
Financially
Conclusion
The long-term effects of hospitalization from Covid argues further for continued work on increasing the vaccination rate of our population. Even with Delta variant, vaccines decrease the risk of hospitalization and death by more than a factor of
- CDC. Covid Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#new-hospital-admissions
- CDC. Covid Data Tracker. Trends total death. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_totaldeaths_currenthospitaladmissions|tot_deaths|sum_inpatient_beds_used_covid_7DayAvg
- Johns Hopkins. Weekly hospital trends. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/hospitalization-7-day-trend
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al.; LUNG SAFE Investigators; ESICM Trials Group. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016 Feb 23;315(8):788-800
- Ramona O. Hopkins, Lindell K. Weaver, Dave Collingridge, et al. Two-Year Cognitive, Emotional, and Quality-of-Life Outcomes in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Amer J Resp Crit Care Med. 2005; (171):4.
- Stevens, Robert D, Marshall, Scott A, Cornblath, David R, et al. A framework for diagnosing and classifying intensive care unit-acquired weakness, Critic Care Medic. 2009; (37)10: S299-S308.
- Chaolin Huang, Lixue Huang, Yeming Wang, et al. 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from om hospital: a cohort study. The Lancet 2021; 397(10270): 220-232.
- Gamberini L, Mazzoli CA, Sintonen H, et al.; ICU-RER COVID-19 Collaboration. Quality of life of COVID-19 critically ill survivors after ICU discharge: 90 days follow-up. Qual Life Res. 2021 Oct;30(10):2805-2817.
- Chopra V, Flanders SA, O'Malley M, et al. Sixty-Day Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Apr;174(4):576-578.
- The Writing Committee for the COMEBAC Study Group. Four-Month Clinical Status of a Cohort of Patients After Hospitalization for COVID-19. JAMA. 2021;325(15):1525–1534.
- Ahmed H, Patel K, Greenwood DC, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreaks after hospitalisation or ICU admission: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2020 May 31;52(5): jrm00063.
- Logue JK, Franko NM, McCulloch DJ, et al. Sequelae in Adults at 6 Months After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2): e210830.
- Brenda Goodman. Major study will investigate long-haul Covid-19. WebMD News Brief. Sept. 15, 2021. https://www.webmd.com/lung/news/20210915/major-study-will-investigate-long-haul-covid
- Vineet Chopra, Scott A. Flanders, Megan O’Malley, et al. Sixty-Day Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. Letters. 2021; Apr.
- Yuping Tsai, Tara M. Vogt, Fangjun Zhou. Patient Characteristics and Costs Associated With COVID-19–Related Medical Care Among Medicare Fee-for-Service Beneficiaries. Ann Intern Med. 2021; Aug.
- Lavery AM, Preston LE, Ko JY, et al. Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Discharged and Experiencing Same-Hospital Readmission — United States, March–August 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020; 69:1695–1699.
- Scobie HM, Johnson AG, Suthar AB, et al. Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status — 13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4–July 17, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70:1284–1290.
What the Future May Hold for Covid-19 Survivors
More than 3 million Americans1 have been hospitalized with Covid-19, and
And these are just the patients with severe Covid: those who were never hospitalized are also showing deleterious effects from the effects of their illness.
Covid in the ICU
What we know is that prior to Covid, 10% of all patients were admitted to ICU with acute respiratory distress syndrome4 (ARDS), despite receiving such life-saving measures as mechanical ventilation, medication, and supportive nutrition. Those who do survive face a long journey.4 Besides the specific respiratory recovery needed in those with ARDS, patients who have spent time in the ICU can develop multiple non-respiratory complications, including muscle wasting, generalized weakness, and delirium. The physical, cognitive, and psychological impairments that follow an ICU stay are termed postintensive care syndrome (PICS). PICS is an underrecognized phenomenon that describes the immense complications of an ICU stay for any reason. Recognition of this entity, and education of patients, is particularly important now as we face an ongoing pandemic which is creating a burgeoning number of ICU graduates.
PICS
Cognitive dysfunction is one hallmark of PICS. Delirium is a common complication of any hospitalization, with critically ill patients particularly susceptible given the severity of their illness and their exposure to medications such as sedatives. However, persistent global cognitive impairment is unique to PICS. Up to
The second aspect of PICS is its psychological component. In the Hopkins study,5
The final component of PICS is physical impairment. Those who are critically ill commonly suffer intensive care unit
Covid in the ICU
Estimates of the incidence of PICS due to Covid are evolving. A report on 1700 Covid hospitalized patients in Wuhan, China demonstrated a large prevalence of residual symptoms at 6 months. The most common symptoms were fatigue and weakness (63%), insomnia (26%), and anxiety or depression (
As more centers track the progress of their ICU graduates over time, we can better understand the profound impact of critical illness on our Covid patients and better educate our patients and families on what to expect. One might be able to gain some clues from what is known regarding the prior coronavirus epidemics, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). In these diseases, a meta-analysis showed significant rates of
Additional issues
What is particularly unique to Covid is the prevalence of long-term symptoms in those who were never hospitalized for Covid. Recent estimates of non-hospitalized patients who had Covid are showing at least 25% of them have had long-lasting effects, including stomach pain and respiratory
Financially
Conclusion
The long-term effects of hospitalization from Covid argues further for continued work on increasing the vaccination rate of our population. Even with Delta variant, vaccines decrease the risk of hospitalization and death by more than a factor of
What the Future May Hold for Covid-19 Survivors
More than 3 million Americans1 have been hospitalized with Covid-19, and
And these are just the patients with severe Covid: those who were never hospitalized are also showing deleterious effects from the effects of their illness.
Covid in the ICU
What we know is that prior to Covid, 10% of all patients were admitted to ICU with acute respiratory distress syndrome4 (ARDS), despite receiving such life-saving measures as mechanical ventilation, medication, and supportive nutrition. Those who do survive face a long journey.4 Besides the specific respiratory recovery needed in those with ARDS, patients who have spent time in the ICU can develop multiple non-respiratory complications, including muscle wasting, generalized weakness, and delirium. The physical, cognitive, and psychological impairments that follow an ICU stay are termed postintensive care syndrome (PICS). PICS is an underrecognized phenomenon that describes the immense complications of an ICU stay for any reason. Recognition of this entity, and education of patients, is particularly important now as we face an ongoing pandemic which is creating a burgeoning number of ICU graduates.
PICS
Cognitive dysfunction is one hallmark of PICS. Delirium is a common complication of any hospitalization, with critically ill patients particularly susceptible given the severity of their illness and their exposure to medications such as sedatives. However, persistent global cognitive impairment is unique to PICS. Up to
The second aspect of PICS is its psychological component. In the Hopkins study,5
The final component of PICS is physical impairment. Those who are critically ill commonly suffer intensive care unit
Covid in the ICU
Estimates of the incidence of PICS due to Covid are evolving. A report on 1700 Covid hospitalized patients in Wuhan, China demonstrated a large prevalence of residual symptoms at 6 months. The most common symptoms were fatigue and weakness (63%), insomnia (26%), and anxiety or depression (
As more centers track the progress of their ICU graduates over time, we can better understand the profound impact of critical illness on our Covid patients and better educate our patients and families on what to expect. One might be able to gain some clues from what is known regarding the prior coronavirus epidemics, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). In these diseases, a meta-analysis showed significant rates of
Additional issues
What is particularly unique to Covid is the prevalence of long-term symptoms in those who were never hospitalized for Covid. Recent estimates of non-hospitalized patients who had Covid are showing at least 25% of them have had long-lasting effects, including stomach pain and respiratory
Financially
Conclusion
The long-term effects of hospitalization from Covid argues further for continued work on increasing the vaccination rate of our population. Even with Delta variant, vaccines decrease the risk of hospitalization and death by more than a factor of
- CDC. Covid Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#new-hospital-admissions
- CDC. Covid Data Tracker. Trends total death. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_totaldeaths_currenthospitaladmissions|tot_deaths|sum_inpatient_beds_used_covid_7DayAvg
- Johns Hopkins. Weekly hospital trends. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/hospitalization-7-day-trend
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al.; LUNG SAFE Investigators; ESICM Trials Group. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016 Feb 23;315(8):788-800
- Ramona O. Hopkins, Lindell K. Weaver, Dave Collingridge, et al. Two-Year Cognitive, Emotional, and Quality-of-Life Outcomes in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Amer J Resp Crit Care Med. 2005; (171):4.
- Stevens, Robert D, Marshall, Scott A, Cornblath, David R, et al. A framework for diagnosing and classifying intensive care unit-acquired weakness, Critic Care Medic. 2009; (37)10: S299-S308.
- Chaolin Huang, Lixue Huang, Yeming Wang, et al. 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from om hospital: a cohort study. The Lancet 2021; 397(10270): 220-232.
- Gamberini L, Mazzoli CA, Sintonen H, et al.; ICU-RER COVID-19 Collaboration. Quality of life of COVID-19 critically ill survivors after ICU discharge: 90 days follow-up. Qual Life Res. 2021 Oct;30(10):2805-2817.
- Chopra V, Flanders SA, O'Malley M, et al. Sixty-Day Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Apr;174(4):576-578.
- The Writing Committee for the COMEBAC Study Group. Four-Month Clinical Status of a Cohort of Patients After Hospitalization for COVID-19. JAMA. 2021;325(15):1525–1534.
- Ahmed H, Patel K, Greenwood DC, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreaks after hospitalisation or ICU admission: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2020 May 31;52(5): jrm00063.
- Logue JK, Franko NM, McCulloch DJ, et al. Sequelae in Adults at 6 Months After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2): e210830.
- Brenda Goodman. Major study will investigate long-haul Covid-19. WebMD News Brief. Sept. 15, 2021. https://www.webmd.com/lung/news/20210915/major-study-will-investigate-long-haul-covid
- Vineet Chopra, Scott A. Flanders, Megan O’Malley, et al. Sixty-Day Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. Letters. 2021; Apr.
- Yuping Tsai, Tara M. Vogt, Fangjun Zhou. Patient Characteristics and Costs Associated With COVID-19–Related Medical Care Among Medicare Fee-for-Service Beneficiaries. Ann Intern Med. 2021; Aug.
- Lavery AM, Preston LE, Ko JY, et al. Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Discharged and Experiencing Same-Hospital Readmission — United States, March–August 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020; 69:1695–1699.
- Scobie HM, Johnson AG, Suthar AB, et al. Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status — 13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4–July 17, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70:1284–1290.
- CDC. Covid Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#new-hospital-admissions
- CDC. Covid Data Tracker. Trends total death. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#trends_totaldeaths_currenthospitaladmissions|tot_deaths|sum_inpatient_beds_used_covid_7DayAvg
- Johns Hopkins. Weekly hospital trends. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/hospitalization-7-day-trend
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al.; LUNG SAFE Investigators; ESICM Trials Group. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016 Feb 23;315(8):788-800
- Ramona O. Hopkins, Lindell K. Weaver, Dave Collingridge, et al. Two-Year Cognitive, Emotional, and Quality-of-Life Outcomes in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Amer J Resp Crit Care Med. 2005; (171):4.
- Stevens, Robert D, Marshall, Scott A, Cornblath, David R, et al. A framework for diagnosing and classifying intensive care unit-acquired weakness, Critic Care Medic. 2009; (37)10: S299-S308.
- Chaolin Huang, Lixue Huang, Yeming Wang, et al. 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from om hospital: a cohort study. The Lancet 2021; 397(10270): 220-232.
- Gamberini L, Mazzoli CA, Sintonen H, et al.; ICU-RER COVID-19 Collaboration. Quality of life of COVID-19 critically ill survivors after ICU discharge: 90 days follow-up. Qual Life Res. 2021 Oct;30(10):2805-2817.
- Chopra V, Flanders SA, O'Malley M, et al. Sixty-Day Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Apr;174(4):576-578.
- The Writing Committee for the COMEBAC Study Group. Four-Month Clinical Status of a Cohort of Patients After Hospitalization for COVID-19. JAMA. 2021;325(15):1525–1534.
- Ahmed H, Patel K, Greenwood DC, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreaks after hospitalisation or ICU admission: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2020 May 31;52(5): jrm00063.
- Logue JK, Franko NM, McCulloch DJ, et al. Sequelae in Adults at 6 Months After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2): e210830.
- Brenda Goodman. Major study will investigate long-haul Covid-19. WebMD News Brief. Sept. 15, 2021. https://www.webmd.com/lung/news/20210915/major-study-will-investigate-long-haul-covid
- Vineet Chopra, Scott A. Flanders, Megan O’Malley, et al. Sixty-Day Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. Letters. 2021; Apr.
- Yuping Tsai, Tara M. Vogt, Fangjun Zhou. Patient Characteristics and Costs Associated With COVID-19–Related Medical Care Among Medicare Fee-for-Service Beneficiaries. Ann Intern Med. 2021; Aug.
- Lavery AM, Preston LE, Ko JY, et al. Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Discharged and Experiencing Same-Hospital Readmission — United States, March–August 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020; 69:1695–1699.
- Scobie HM, Johnson AG, Suthar AB, et al. Monitoring Incidence of COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, by Vaccination Status — 13 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4–July 17, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70:1284–1290.
Yoga effective adjunct therapy in recurrent vasovagal syncope
Yoga added to conventional therapy for vasovagal syncope (VVS), when patients faint after a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life, new research suggests.
A small, open-label trial conducted in New Delhi showed that participants practicing yoga reported an improvement in VVS symptoms after only 6 weeks, with a reduction of 1.82 events at 12 months. All those practicing yoga also showed significantly improved quality of life (QoL) scores by the end of the trial.
“Yoga as add-on therapy in VVS is superior to medical therapy in reducing syncopal and presyncopal events and in improving the QoL,” report Gautam Sharma, MD, DM, Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues. “It may be useful to integrate a cost-effective and safe intervention such as yoga into the management of VVS.”
Results of the LIVE-Yoga study were published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Vasovagal syncope is a common and non–life-threatening condition, but given the severity and frequency of recurrence it can result in significant deterioration in a patient’s quality of life, the authors note. “Existing management therapies have been largely ineffective,” they write.
Recent trials have suggested some efficacy for yoga in diseases of autonomic imbalance, suggesting a possible use in VVS. To find out, the researchers enrolled adults with VVS between the ages of 15-70 years who had a positive head-up tilt test (HUTT) and at least two syncope or presyncope events within 3 months of enrollment. They also needed to be willing and able to practice yoga. Those with structural heart disease, accelerated hypertension, and underlying neurologic disorders were not included in the study.
A total of 55 patients were randomly assigned to receive either a specialized yoga training program in addition to guideline-based therapy, or guideline-based therapy alone. Standard care included physical counterpressure maneuvers, avoidance of known triggers, increased salt and water intake, and drug therapy or pacing at the discretion of the treating physician.
The primary outcome was a composite of the number of episodes of syncope and presyncope at 12 months.
Secondary outcomes including QoL, assessed using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Brief Field questionnaire (WHOQoL-BREF) and the Syncope Functional Status Questionnaire (SFSQ) at 12 months, a head-up tilt test, and heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
For the first 2 weeks, patients in the intervention group were enrolled in eight supervised yoga sessions conducted at the Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences. For the remainder of the trial, they continued a daily yoga practice at home at least 5 days a week.
The yoga module created for participants was designed with a view to the pathophysiology of VVS and featured postures, breathing, and relaxation techniques. Yoga classes were taught by qualified therapists under the guidance of physicians.
In addition to a booklet with a pictorial of the yoga regimen, participants received twice-monthly calls from the yoga center to encourage compliance. Results show that all participants adhered to their yoga routine for more than 80% of the 12-month trial.
At 12 months, the mean number of syncopal or presyncopal events was 0.7 ± 0.7 with the yoga intervention versus 2.52 ± 1.93 among patients in the control arm (P < .05). The reduction in events started as early as 6 weeks and continued to separate out to 12 months, the researchers note.
Thirteen of 30 (43.3%) intervention patients and 4 of 25 (16%) control patients remained event-free at 12 months, a statistically significant difference (P = .02). There was a trend toward fewer positive head-up tilt tests between groups that did not reach significance, and there was no difference in heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
No adverse events as a result of the yoga practice were reported, and no patient started drug therapy or received pacing therapy during the trial, they note.
The researchers point out that yoga postures can enhance vascular and muscle tone, especially in the lower limbs.
“Yoga breathing and relaxation techniques have been shown to increase vagal tone and improve autonomic balance, which could potentially curtail the sympathetic overdrive phase and interrupt the activation of the c-mechanoreceptors, which is a critical step in the syncope cascade,” they note.
“We postulate that positive effects of yoga in this study could be related to a multidimensional effect of this intervention acting through both central and peripheral mechanisms, including physical, psychological, and autonomic pathways,” the authors conclude.
Comprehensive regimen
Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, medical director for the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kansas, says these results are in line with previous research indicating the benefits of yoga in improving cardiovascular function.
“All of this clearly shows that when you [include] a systematic diet of yoga for a reasonable amount of time to improve the plasticity of parasympathetic inputs into the chest and thereby the cardiovascular system ... you can help patients to improve their symptoms,” he said in an interview.
He already prescribes yoga in his own practice as part of a comprehensive therapeutic regimen, he said. “We have a handful of practitioners all around the city who work with us,” Dr. Lakkireddy said.
Both he and the study authors point the economic burden of VVS both in management and in loss of patient productivity. “A low-cost intervention in the form of yoga, which essentially requires only a mat, can reduce both direct and indirect costs significantly,” note the authors.
The trial was supported under the extramural research (EMR) scheme by the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Yoga added to conventional therapy for vasovagal syncope (VVS), when patients faint after a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life, new research suggests.
A small, open-label trial conducted in New Delhi showed that participants practicing yoga reported an improvement in VVS symptoms after only 6 weeks, with a reduction of 1.82 events at 12 months. All those practicing yoga also showed significantly improved quality of life (QoL) scores by the end of the trial.
“Yoga as add-on therapy in VVS is superior to medical therapy in reducing syncopal and presyncopal events and in improving the QoL,” report Gautam Sharma, MD, DM, Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues. “It may be useful to integrate a cost-effective and safe intervention such as yoga into the management of VVS.”
Results of the LIVE-Yoga study were published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Vasovagal syncope is a common and non–life-threatening condition, but given the severity and frequency of recurrence it can result in significant deterioration in a patient’s quality of life, the authors note. “Existing management therapies have been largely ineffective,” they write.
Recent trials have suggested some efficacy for yoga in diseases of autonomic imbalance, suggesting a possible use in VVS. To find out, the researchers enrolled adults with VVS between the ages of 15-70 years who had a positive head-up tilt test (HUTT) and at least two syncope or presyncope events within 3 months of enrollment. They also needed to be willing and able to practice yoga. Those with structural heart disease, accelerated hypertension, and underlying neurologic disorders were not included in the study.
A total of 55 patients were randomly assigned to receive either a specialized yoga training program in addition to guideline-based therapy, or guideline-based therapy alone. Standard care included physical counterpressure maneuvers, avoidance of known triggers, increased salt and water intake, and drug therapy or pacing at the discretion of the treating physician.
The primary outcome was a composite of the number of episodes of syncope and presyncope at 12 months.
Secondary outcomes including QoL, assessed using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Brief Field questionnaire (WHOQoL-BREF) and the Syncope Functional Status Questionnaire (SFSQ) at 12 months, a head-up tilt test, and heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
For the first 2 weeks, patients in the intervention group were enrolled in eight supervised yoga sessions conducted at the Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences. For the remainder of the trial, they continued a daily yoga practice at home at least 5 days a week.
The yoga module created for participants was designed with a view to the pathophysiology of VVS and featured postures, breathing, and relaxation techniques. Yoga classes were taught by qualified therapists under the guidance of physicians.
In addition to a booklet with a pictorial of the yoga regimen, participants received twice-monthly calls from the yoga center to encourage compliance. Results show that all participants adhered to their yoga routine for more than 80% of the 12-month trial.
At 12 months, the mean number of syncopal or presyncopal events was 0.7 ± 0.7 with the yoga intervention versus 2.52 ± 1.93 among patients in the control arm (P < .05). The reduction in events started as early as 6 weeks and continued to separate out to 12 months, the researchers note.
Thirteen of 30 (43.3%) intervention patients and 4 of 25 (16%) control patients remained event-free at 12 months, a statistically significant difference (P = .02). There was a trend toward fewer positive head-up tilt tests between groups that did not reach significance, and there was no difference in heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
No adverse events as a result of the yoga practice were reported, and no patient started drug therapy or received pacing therapy during the trial, they note.
The researchers point out that yoga postures can enhance vascular and muscle tone, especially in the lower limbs.
“Yoga breathing and relaxation techniques have been shown to increase vagal tone and improve autonomic balance, which could potentially curtail the sympathetic overdrive phase and interrupt the activation of the c-mechanoreceptors, which is a critical step in the syncope cascade,” they note.
“We postulate that positive effects of yoga in this study could be related to a multidimensional effect of this intervention acting through both central and peripheral mechanisms, including physical, psychological, and autonomic pathways,” the authors conclude.
Comprehensive regimen
Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, medical director for the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kansas, says these results are in line with previous research indicating the benefits of yoga in improving cardiovascular function.
“All of this clearly shows that when you [include] a systematic diet of yoga for a reasonable amount of time to improve the plasticity of parasympathetic inputs into the chest and thereby the cardiovascular system ... you can help patients to improve their symptoms,” he said in an interview.
He already prescribes yoga in his own practice as part of a comprehensive therapeutic regimen, he said. “We have a handful of practitioners all around the city who work with us,” Dr. Lakkireddy said.
Both he and the study authors point the economic burden of VVS both in management and in loss of patient productivity. “A low-cost intervention in the form of yoga, which essentially requires only a mat, can reduce both direct and indirect costs significantly,” note the authors.
The trial was supported under the extramural research (EMR) scheme by the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Yoga added to conventional therapy for vasovagal syncope (VVS), when patients faint after a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life, new research suggests.
A small, open-label trial conducted in New Delhi showed that participants practicing yoga reported an improvement in VVS symptoms after only 6 weeks, with a reduction of 1.82 events at 12 months. All those practicing yoga also showed significantly improved quality of life (QoL) scores by the end of the trial.
“Yoga as add-on therapy in VVS is superior to medical therapy in reducing syncopal and presyncopal events and in improving the QoL,” report Gautam Sharma, MD, DM, Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues. “It may be useful to integrate a cost-effective and safe intervention such as yoga into the management of VVS.”
Results of the LIVE-Yoga study were published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Vasovagal syncope is a common and non–life-threatening condition, but given the severity and frequency of recurrence it can result in significant deterioration in a patient’s quality of life, the authors note. “Existing management therapies have been largely ineffective,” they write.
Recent trials have suggested some efficacy for yoga in diseases of autonomic imbalance, suggesting a possible use in VVS. To find out, the researchers enrolled adults with VVS between the ages of 15-70 years who had a positive head-up tilt test (HUTT) and at least two syncope or presyncope events within 3 months of enrollment. They also needed to be willing and able to practice yoga. Those with structural heart disease, accelerated hypertension, and underlying neurologic disorders were not included in the study.
A total of 55 patients were randomly assigned to receive either a specialized yoga training program in addition to guideline-based therapy, or guideline-based therapy alone. Standard care included physical counterpressure maneuvers, avoidance of known triggers, increased salt and water intake, and drug therapy or pacing at the discretion of the treating physician.
The primary outcome was a composite of the number of episodes of syncope and presyncope at 12 months.
Secondary outcomes including QoL, assessed using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Brief Field questionnaire (WHOQoL-BREF) and the Syncope Functional Status Questionnaire (SFSQ) at 12 months, a head-up tilt test, and heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
For the first 2 weeks, patients in the intervention group were enrolled in eight supervised yoga sessions conducted at the Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences. For the remainder of the trial, they continued a daily yoga practice at home at least 5 days a week.
The yoga module created for participants was designed with a view to the pathophysiology of VVS and featured postures, breathing, and relaxation techniques. Yoga classes were taught by qualified therapists under the guidance of physicians.
In addition to a booklet with a pictorial of the yoga regimen, participants received twice-monthly calls from the yoga center to encourage compliance. Results show that all participants adhered to their yoga routine for more than 80% of the 12-month trial.
At 12 months, the mean number of syncopal or presyncopal events was 0.7 ± 0.7 with the yoga intervention versus 2.52 ± 1.93 among patients in the control arm (P < .05). The reduction in events started as early as 6 weeks and continued to separate out to 12 months, the researchers note.
Thirteen of 30 (43.3%) intervention patients and 4 of 25 (16%) control patients remained event-free at 12 months, a statistically significant difference (P = .02). There was a trend toward fewer positive head-up tilt tests between groups that did not reach significance, and there was no difference in heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
No adverse events as a result of the yoga practice were reported, and no patient started drug therapy or received pacing therapy during the trial, they note.
The researchers point out that yoga postures can enhance vascular and muscle tone, especially in the lower limbs.
“Yoga breathing and relaxation techniques have been shown to increase vagal tone and improve autonomic balance, which could potentially curtail the sympathetic overdrive phase and interrupt the activation of the c-mechanoreceptors, which is a critical step in the syncope cascade,” they note.
“We postulate that positive effects of yoga in this study could be related to a multidimensional effect of this intervention acting through both central and peripheral mechanisms, including physical, psychological, and autonomic pathways,” the authors conclude.
Comprehensive regimen
Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, medical director for the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kansas, says these results are in line with previous research indicating the benefits of yoga in improving cardiovascular function.
“All of this clearly shows that when you [include] a systematic diet of yoga for a reasonable amount of time to improve the plasticity of parasympathetic inputs into the chest and thereby the cardiovascular system ... you can help patients to improve their symptoms,” he said in an interview.
He already prescribes yoga in his own practice as part of a comprehensive therapeutic regimen, he said. “We have a handful of practitioners all around the city who work with us,” Dr. Lakkireddy said.
Both he and the study authors point the economic burden of VVS both in management and in loss of patient productivity. “A low-cost intervention in the form of yoga, which essentially requires only a mat, can reduce both direct and indirect costs significantly,” note the authors.
The trial was supported under the extramural research (EMR) scheme by the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Fatal Case of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Anti-MDA5–Positive Dermatomyositis
To the Editor:
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy characterized by bilateral, symmetrical, proximal muscle weakness and classic cutaneous manifestations.1 Patients with antibodies directed against melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5, MDA5, have a distinct presentation due to vasculopathy with more severe cutaneous ulcerations, palmar papules, alopecia, and an elevated risk of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease.2 A ferritin level greater than 1600 ng/mL portends an increased risk for pulmonary disease and therefore can be of prognostic value.3 Further, patients with anti-MDA5 DM are at a lower risk of malignancy and are more likely to test negative for antinuclear antibodies in comparison to other patients with DM.2,4
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), also known as hemophagocytic syndrome, is a potentially lethal condition whereby uncontrolled activation of histiocytes in the reticuloendothelial system causes hemophagocytosis and a hyperinflammatory state. Patients present with fever, splenomegaly, cytopenia, and hyperferritinemia.5 Autoimmune‐associated hemophagocytic syndrome (AAHS) describes HLH that develops in association with autoimmune conditions, most commonly systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still disease. Cases reported in association with DM exist but are few in number, and there is no standard-of-care treatment.6 We report a case of a woman with anti-MDA5 DM complicated by HLH and DM-associated liver injury.
A 50-year-old woman presented as a direct admit from the rheumatology clinic for diffuse muscle weakness of 8 months’ duration, 40-pound unintentional weight loss, pruritic rash, bilateral joint pains, dry eyes, dry mouth, and altered mental status. Four months prior, she presented to an outside hospital and was given a diagnosis of probable Sjögren syndrome and autoimmune hepatitis vs drug-induced liver injury. At that time, a workup was notable for antibodies against Sjögren syndrome–related antigen A, anti–smooth muscle antibodies, and transaminitis. Ultrasonography of the right upper quadrant revealed hepatic steatosis. The patient was started on oral prednisone and pilocarpine but had been off all medications for 1 month when she presented to our hospital.
On hospital admission, physical examination revealed a violaceous heliotrope rash; a v-sign on the chest; shawl sign; palmar papules with pits at the fingertips; and periungual erythema and ulcerations along the metacarpophalangeal joints, elbows, lateral feet, and upper eyelids (Figure 1). Laboratory workup showed the following results: white blood cell count, 4100/μL (reference range, 4000–11,000/μL); hemoglobin, 11.6 g/dL (reference range, 12–16 g/dL); platelet count, 100,000/μL (reference range, 150,000–450,000/μL); lactate dehydrogenase, 510 U/L (reference range, 80–225 U/L); alkaline phosphatase (ALP), 766 U/L (reference range, 30–120 U/L); alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 88 U/L (reference range, 10–40 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase (AST), 544 U/L (reference range, 10–40 U/L); total bilirubin, 4.2 mg/dL (reference range, 0.3–1.0 mg/dL); direct bilirubin, 3.7 mg/dL (reference range, 0.1–0.3 mg/dL); aldolase, 20.2 U/L (reference range, 1–7.5 U/L), creatine kinase, 180 U/L (reference range, 30–135 U/L); γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT), 2743 U/L (reference range, 8–40 U/L); high sensitivity C-reactive protein, 122.9 mg/L (low-risk reference range, <1.0 mg/L); triglycerides, 534 mg/dL (reference range, <150 mg/dL); ferritin, 3784 ng/mL (reference range, 24–307 ng/mL); antinuclear antibody, negative titer; antimitochondrial antibody, negative titer; soluble IL-2 receptor (CD25), 7000 U/mL (reference range, 189–846 U/mL); anti-Sjögren syndrome–related antigen A antibody, positive.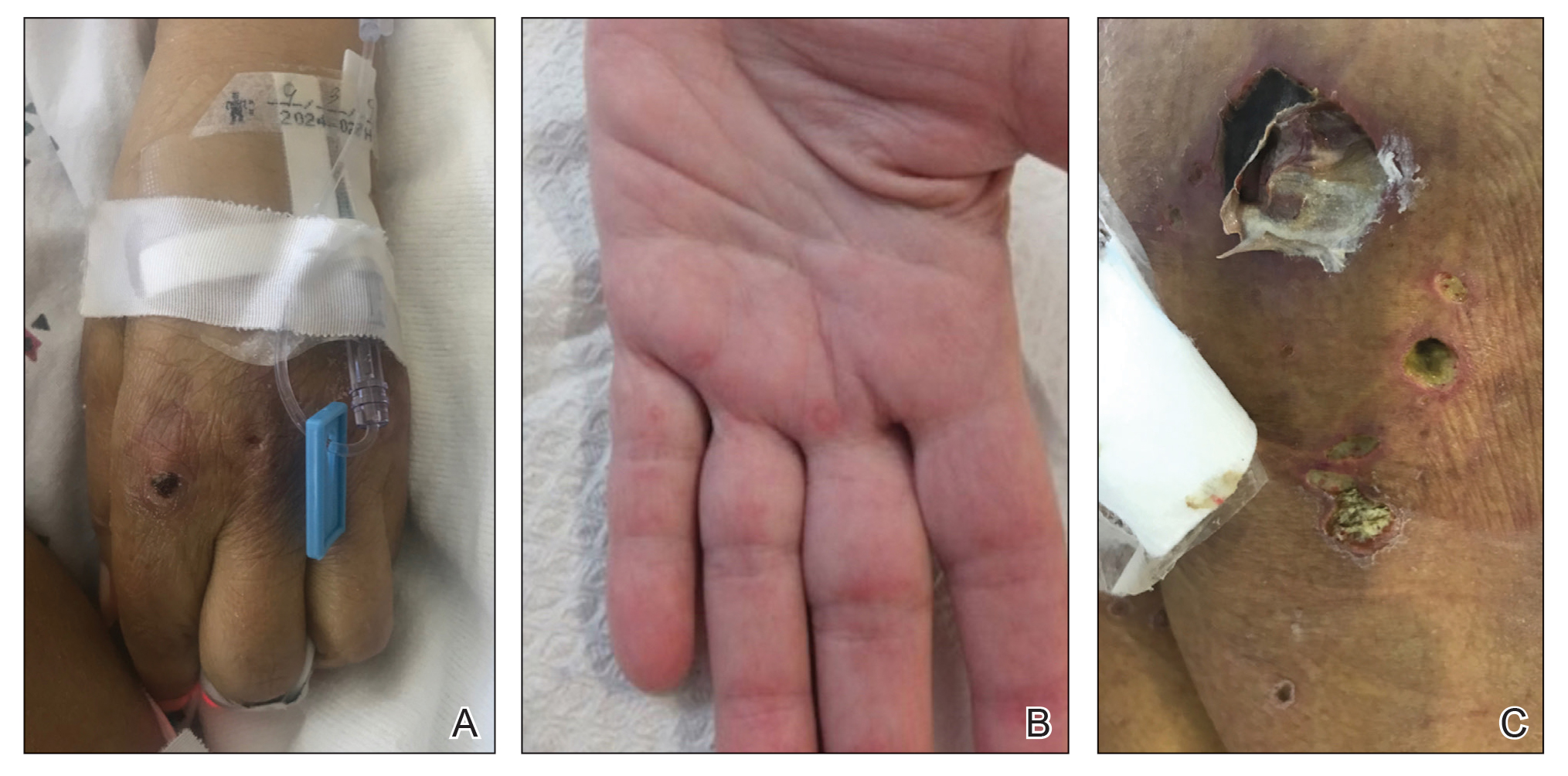
Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulders showed diffuse soft-tissue edema. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated parabronchial thickening and parenchymal bands suggestive of DM. An age-appropriate malignancy workup was negative, and results from a liver biopsy showed diffuse steatosis with no histologic evidence of autoimmune hepatitis. Punch biopsy results from a plaque on the left knee revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis with increased dermal mucin on colloidal iron staining, indicative of connective tissue disease (Figure 2). The patient was treated with intravenous (IV) methylprednisolone 250 mg twice daily for 2 days followed by oral prednisone 50 mg daily with IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) 0.4 mg/kg daily for 5 days. The patient’s symptoms improved, and she was discharged on oral prednisone 50 mg and mycophenolate mofetil 1000 mg twice daily with a plan for outpatient IVIG.
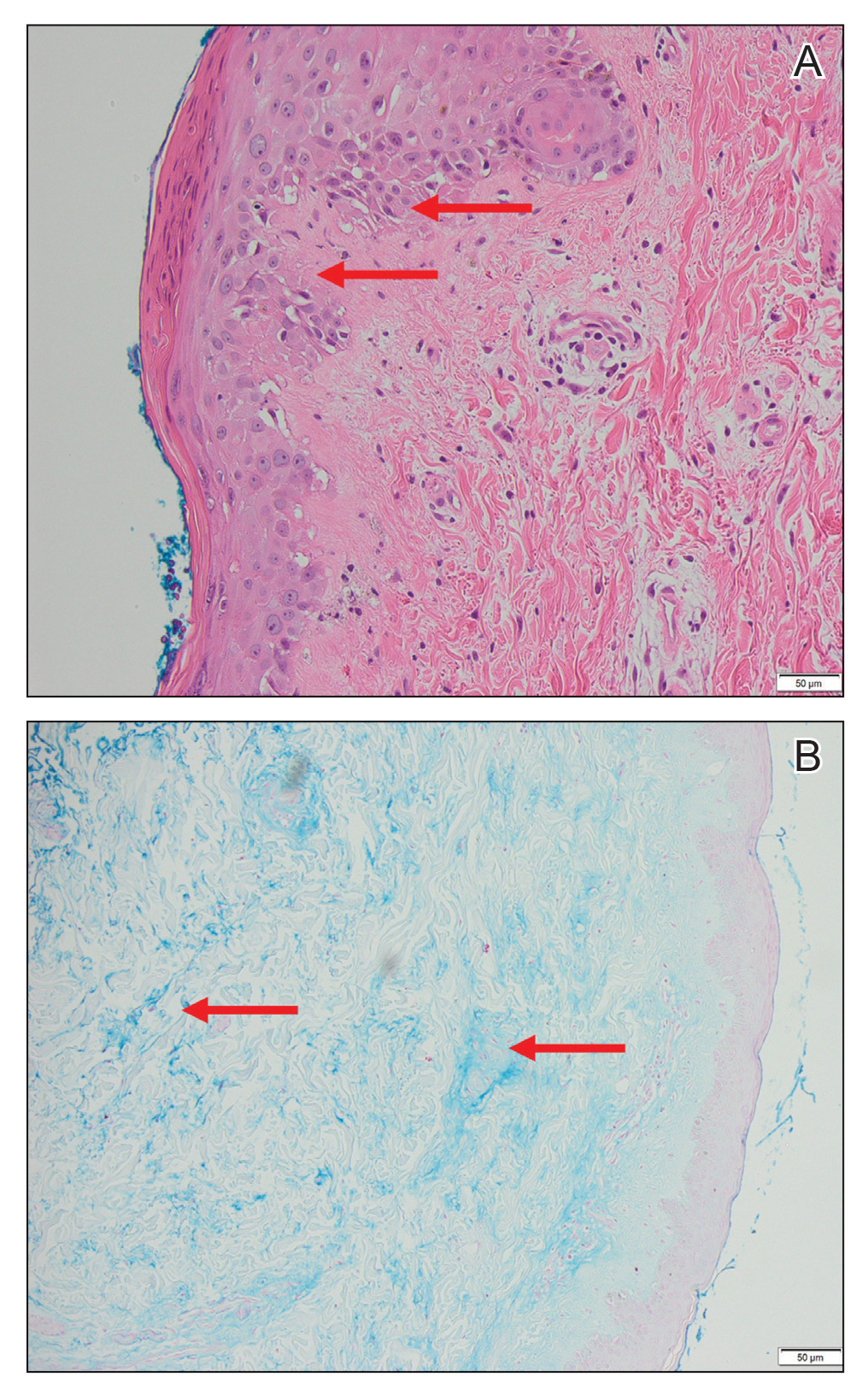
Two days after discharge, the patient was re-admitted for worsening muscle weakness; recalcitrant rash; new-onset hypophonia, dysphagia, and odynophagia; and intermittent fevers. Myositis panel results were positive for MDA5. Additionally, workup for HLH, which was initiated during the first hospital admission, revealed that she met 6 of 8 diagnostic criteria: intermittent fevers (maximum temperature, 38.2 °C), splenomegaly (12.6 cm on CT scan of abdomen), cytopenia in 2 cell lines (anemia, thrombocytopenia), hypertriglyceridemia, hyperferritinemia, and elevated IL-2 receptor (CD25). Based on these findings, the patient was diagnosed with anti-MDA5 DM associated with HLH.
The patient was started on IV methylprednisolone 1000 mg daily and received 1 rituximab infusion. Two days later, she experienced worsening fever with tachycardia, and a chest radiograph showed bibasilar infiltrates concerning for aspiration pneumonia, with sputum cultures growing Staphylococcus aureus. Due to the infection, the dosage of methylprednisolone was decreased to 16 mg 3 times daily and rituximab was stopped. The hematology department was consulted for the patient’s HLH, and due to her profound weakness and sepsis, the decision was made to hold initiation of etoposide, which, in addition to glucocorticoids, is considered first-line therapy for HLH. She subsequently experienced worsening hypoxia requiring intubation and received a second course of IVIG. Two days later, CT of the chest revealed progressive ground-glass opacities in the lower lobes of the lungs. The patient was then started on plasmapheresis every other day, hydroxychloroquine 200 mg daily, and IV methylprednisolone 1000 mg daily. Over the subsequent 6 days, she developed worsening renal failure, liver dysfunction, profound thrombocytopenia (13/μL), and acidemia. After extensive discussion with her family, the patient was transitioned to comfort care, and she died 33 days after the initial admission to our hospital.
Our case is a collection of several rare presentations: anti-MDA5 DM, with HLH and AAHS as complications of anti-MDA5 DM, and DM-associated liver injury. Anti-MDA5 DM is frequently refractory to conventional therapy, including high-dose glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, oral tacrolimus, and cyclosporine, and there currently is no single treatment algorithm.2 Lake and colleagues7 highlighted the importance of personalizing treatment of anti-MDA5 DM, as it can be one of the most aggressive rheumatologic diseases. We initially chose to treat our patient with high-dose methylprednisolone, IVIG, and rituximab. Kampylafka et al8 performed a retrospective analysis of the use of IVIG for DM as compared to standard therapy and demonstrated improved muscle and cutaneous involvement from a collection of 50 patients. Case reports have specifically revealed efficacy for the use of IVIG in patients with anti-MDA5 DM.9,10 Additionally, rituximab—an anti–B lymphocyte therapy—has been shown to be an effective supplemental therapy for cases of aggressive anti-MDA5 DM with associated interstitial lung disease, especially when conventional therapy has failed.11,12 Our patient’s sepsis secondary to S aureus pneumonia limited her to only receiving 1 dose of rituximab.
One promising treatment approach for anti-MDA5 DM recently published by Tsuji et al13 involves the use of combination therapy. In this prospective multicenter trial, patients were initially treated with a combination of high-dose glucocorticoids, oral tacrolimus, and IV cyclophosphamide. Plasmapheresis was then started for patients without symptomatic improvement. This method was compared to the more traditional step-up approach of high-dose steroids followed by another immunosuppressant. At 1-year follow-up, the combination therapy group demonstrated an 85% survival rate compared to 33% of historical controls.13
We suspect that our patient developed HLH and AAHS secondary to her underlying anti-MDA5 DM. Kumakura and Murakawa6 reported that among 116 cases of AAHS, 6.9% of cases were associated with DM, most commonly anti-Jo-1 DM. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with anti-MDA5 DM has been described in only a few cases.14-16 The diagnosis of HLH is critical, as the treatments for HLH and DM differ. Both diseases manifest with hyperferritinemia—greater than 500 ng/mL in the case of HLH and 3784 ng/mL in our patient. Therefore, HLH can be easily overlooked. It is possible the rates of HLH associated with anti-MDA5 DM are higher than reported given their similar presentations.
Analogous to our case, Fujita et al15 reported a case of HLH associated with anti-MDA5 DM successfully treated with IV cyclophosphamide pulse therapy and plasmapheresis. The rationale for using plasmapheresis in anti-MDA5 DM is based on its success in patients with other antibody-mediated conditions such as Goodpasture syndrome and granulomatosis with polyangiitis.7 It is thought to expedite response to traditional treatment, and in the case described by Fujita et al,15 the patient received plasmapheresis 6 times total over the course of 9 days. The patient’s clinical symptoms, as well as platelet levels, liver enzymes, and ferritin value, improved.15 Our patient received 3 days of plasmapheresis with no improvement when the decision was made to discontinue plasmapheresis given her worsening clinical state.
Additionally, our patient had elevated hepatic enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT), and results of a liver biopsy demonstrated diffuse steatosis. We speculate her transaminitis was a complication of anti-MDA5 DM. Hepatocellular damage accompanying DM has been investigated in multiple studies and is most often defined as an elevated ALT.17-20 Improvement in ALT levels has been seen with DM treatment. However, investigators note that creatine kinase (CK) values often do not correlate with the resolution of the transaminitis, suggesting that CK denotes muscle damage whereas ALT represents separate liver damage.18-21
Nagashima et al22 highlighted that among 50 patients with DM without malignancy, only 20% presented with a transaminitis or elevated bilirubin. However, among those with liver injury, all were positive for antibodies against MDA5.22 The patients with anti-MDA5 DM liver dysfunction had higher ALT, ALP, and GGT levels compared to those without liver dysfunction. Similarly, in a retrospective review of 14 patients with anti-MDA5 DM, Gono and colleagues3 found elevated GGT levels and lower CK levels in comparison to patients with anti-aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetase DM. Although liver enzymes can be elevated in patients with DM secondary to muscle damage, the authors argue that the specificity of GGT to the liver suggests intrinsic liver damage.3
The mechanism behind liver disease in anti-MDA5 DM is unclear, but it is hypothesized to be similar to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.22 Other studies have revealed drug-induced hepatitis, hepatic congestion, nonspecific reactive hepatitis, metastatic liver tumor, primary biliary cholangitis, and autoimmune hepatitis as the etiology behind liver disease in their patients with DM.17-19 Liver biopsy results from patients with anti-MDA5 DM most commonly reveal hepatic steatosis, as seen in our patient, as well as hepatocyte ballooning and increased pigmented macrophages.22
We presented a case of anti-MDA5 DM complicated by HLH. Our patient had a fatal outcome despite aggressive treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone, IVIG, rituximab, and plasmapheresis. It is accepted that anti-MDA5 DM affects the lungs and skin, and our patient’s presentation also suggests liver involvement. In our case, onset of symptoms to fatality was approximately 1 year. It is essential to consider the diagnosis of HLH in all cases of anti-MDA5 DM given clinical disease overlap. Our patient could have benefited from earlier disease recognition and thus earlier aggressive therapy.
1. Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:344-347.
2. Kurtzman DJB, Vleugels RA. Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) dermatomyositis: a concise review with an emphasis on distinctive clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:776-785.
3. Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Satoh T, et al. Clinical manifestation and prognostic factor in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-associated interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:1713-1719.
4. Fiorentino D, Chung L, Zwerner J, et al. The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:25-34.
5. Sepulveda FE, de Saint Basile G. Hemophagocytic syndrome: primary forms and predisposing conditions. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;49:20-26.
6. Kumakura S, Murakawa Y. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in adults. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66:2297-2307.
7. Lake M, George G, Summer R. Time to personalize the treatment of anti-MDA-5 associated lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:E52.
8. Kampylafka EI, Kosmidis ML, Panagiotakos DB, et al. The effect of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment on patients with dermatomyositis: a 4-year follow-up study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30:397-401.
9. Koguchi-Yoshioka H, Okiyama N, Iwamoto K, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin contributes to the control of antimelanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibody-associated dermatomyositis with palmar violaceous macules/papules. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1442-1446.
10. Hamada-Ode K, Taniguchi Y, Kimata T, et al. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonitis accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2015;2:83-85.
11. So H, Wong VTL, Lao VWN, et al. Rituximab for refractory rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease related to anti-MDA5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:1983-1989.
12. Koichi Y, Aya Y, Megumi U, et al. A case of anti-MDA5-positive rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in a patient with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis ameliorated by rituximab, in addition to standard immunosuppressive treatment. Mod Rheumatol. 2017;27:536-540.
13. Tsuji H, Nakashima R, Hosono Y, et al. Multicenter prospective study of the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive therapy with high-dose glucocorticoid, tacrolimus, and cyclophosphamide in interstitial lung diseases accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72:488-498.
14. Honda M, Moriyama M, Kondo M, et al. Three cases of autoimmune-associated haemophagocytic syndrome in dermatomyositis with anti-MDA5 autoantibody. Scand J Rheumatol. 2020;49:244-246.
15. Fujita Y, Fukui S, Suzuki T, et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis complicated by autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome that was successfully treated with immunosuppressive therapy and plasmapheresis. Intern Med. 2018;57:3473-3478.
16. Gono T, Miyake K, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Hyperferritinaemia and macrophage activation in a patient with interstitial lung disease with clinically amyopathic DM. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:1336-1338.
17. Wada T, Abe G, Kudou, T, et al. Liver damage in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Kitasato Med Journal. 2016;46:40-46.
18. Takahashi A, Abe K, Yokokawa J, et al. Clinical features of liver dysfunction in collagen diseases. Hepatol Res. 2010;40:1092-1097.
19. Matsumoto T, Kobayashi S, Shimizu H, et al. The liver in collagen diseases: pathologic study of 160 cases with particular reference to hepatic arteritis, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis and nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Liver. 2000;20:366-373.
20. Shi Q, Niu J, Huang X, et al. Do muscle enzyme changes forecast liver injury in polymyositis/dermatomyositis patients treated with methylprednisolone and methotrexate? Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46:266-269.
21. Noda S, Asano Y, Tamaki Z, et al. A case of dermatomyositis with “liver disease associated with rheumatoid diseases” positive for anti-liver-kidney microsome-1 antibody. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:941-943.
22. Nagashima T, Kamata Y, Iwamoto M, et al. Liver dysfunction in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive patients with dermatomyositis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39:901-909.
To the Editor:
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy characterized by bilateral, symmetrical, proximal muscle weakness and classic cutaneous manifestations.1 Patients with antibodies directed against melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5, MDA5, have a distinct presentation due to vasculopathy with more severe cutaneous ulcerations, palmar papules, alopecia, and an elevated risk of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease.2 A ferritin level greater than 1600 ng/mL portends an increased risk for pulmonary disease and therefore can be of prognostic value.3 Further, patients with anti-MDA5 DM are at a lower risk of malignancy and are more likely to test negative for antinuclear antibodies in comparison to other patients with DM.2,4
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), also known as hemophagocytic syndrome, is a potentially lethal condition whereby uncontrolled activation of histiocytes in the reticuloendothelial system causes hemophagocytosis and a hyperinflammatory state. Patients present with fever, splenomegaly, cytopenia, and hyperferritinemia.5 Autoimmune‐associated hemophagocytic syndrome (AAHS) describes HLH that develops in association with autoimmune conditions, most commonly systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still disease. Cases reported in association with DM exist but are few in number, and there is no standard-of-care treatment.6 We report a case of a woman with anti-MDA5 DM complicated by HLH and DM-associated liver injury.
A 50-year-old woman presented as a direct admit from the rheumatology clinic for diffuse muscle weakness of 8 months’ duration, 40-pound unintentional weight loss, pruritic rash, bilateral joint pains, dry eyes, dry mouth, and altered mental status. Four months prior, she presented to an outside hospital and was given a diagnosis of probable Sjögren syndrome and autoimmune hepatitis vs drug-induced liver injury. At that time, a workup was notable for antibodies against Sjögren syndrome–related antigen A, anti–smooth muscle antibodies, and transaminitis. Ultrasonography of the right upper quadrant revealed hepatic steatosis. The patient was started on oral prednisone and pilocarpine but had been off all medications for 1 month when she presented to our hospital.
On hospital admission, physical examination revealed a violaceous heliotrope rash; a v-sign on the chest; shawl sign; palmar papules with pits at the fingertips; and periungual erythema and ulcerations along the metacarpophalangeal joints, elbows, lateral feet, and upper eyelids (Figure 1). Laboratory workup showed the following results: white blood cell count, 4100/μL (reference range, 4000–11,000/μL); hemoglobin, 11.6 g/dL (reference range, 12–16 g/dL); platelet count, 100,000/μL (reference range, 150,000–450,000/μL); lactate dehydrogenase, 510 U/L (reference range, 80–225 U/L); alkaline phosphatase (ALP), 766 U/L (reference range, 30–120 U/L); alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 88 U/L (reference range, 10–40 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase (AST), 544 U/L (reference range, 10–40 U/L); total bilirubin, 4.2 mg/dL (reference range, 0.3–1.0 mg/dL); direct bilirubin, 3.7 mg/dL (reference range, 0.1–0.3 mg/dL); aldolase, 20.2 U/L (reference range, 1–7.5 U/L), creatine kinase, 180 U/L (reference range, 30–135 U/L); γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT), 2743 U/L (reference range, 8–40 U/L); high sensitivity C-reactive protein, 122.9 mg/L (low-risk reference range, <1.0 mg/L); triglycerides, 534 mg/dL (reference range, <150 mg/dL); ferritin, 3784 ng/mL (reference range, 24–307 ng/mL); antinuclear antibody, negative titer; antimitochondrial antibody, negative titer; soluble IL-2 receptor (CD25), 7000 U/mL (reference range, 189–846 U/mL); anti-Sjögren syndrome–related antigen A antibody, positive.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulders showed diffuse soft-tissue edema. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated parabronchial thickening and parenchymal bands suggestive of DM. An age-appropriate malignancy workup was negative, and results from a liver biopsy showed diffuse steatosis with no histologic evidence of autoimmune hepatitis. Punch biopsy results from a plaque on the left knee revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis with increased dermal mucin on colloidal iron staining, indicative of connective tissue disease (Figure 2). The patient was treated with intravenous (IV) methylprednisolone 250 mg twice daily for 2 days followed by oral prednisone 50 mg daily with IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) 0.4 mg/kg daily for 5 days. The patient’s symptoms improved, and she was discharged on oral prednisone 50 mg and mycophenolate mofetil 1000 mg twice daily with a plan for outpatient IVIG.

Two days after discharge, the patient was re-admitted for worsening muscle weakness; recalcitrant rash; new-onset hypophonia, dysphagia, and odynophagia; and intermittent fevers. Myositis panel results were positive for MDA5. Additionally, workup for HLH, which was initiated during the first hospital admission, revealed that she met 6 of 8 diagnostic criteria: intermittent fevers (maximum temperature, 38.2 °C), splenomegaly (12.6 cm on CT scan of abdomen), cytopenia in 2 cell lines (anemia, thrombocytopenia), hypertriglyceridemia, hyperferritinemia, and elevated IL-2 receptor (CD25). Based on these findings, the patient was diagnosed with anti-MDA5 DM associated with HLH.
The patient was started on IV methylprednisolone 1000 mg daily and received 1 rituximab infusion. Two days later, she experienced worsening fever with tachycardia, and a chest radiograph showed bibasilar infiltrates concerning for aspiration pneumonia, with sputum cultures growing Staphylococcus aureus. Due to the infection, the dosage of methylprednisolone was decreased to 16 mg 3 times daily and rituximab was stopped. The hematology department was consulted for the patient’s HLH, and due to her profound weakness and sepsis, the decision was made to hold initiation of etoposide, which, in addition to glucocorticoids, is considered first-line therapy for HLH. She subsequently experienced worsening hypoxia requiring intubation and received a second course of IVIG. Two days later, CT of the chest revealed progressive ground-glass opacities in the lower lobes of the lungs. The patient was then started on plasmapheresis every other day, hydroxychloroquine 200 mg daily, and IV methylprednisolone 1000 mg daily. Over the subsequent 6 days, she developed worsening renal failure, liver dysfunction, profound thrombocytopenia (13/μL), and acidemia. After extensive discussion with her family, the patient was transitioned to comfort care, and she died 33 days after the initial admission to our hospital.
Our case is a collection of several rare presentations: anti-MDA5 DM, with HLH and AAHS as complications of anti-MDA5 DM, and DM-associated liver injury. Anti-MDA5 DM is frequently refractory to conventional therapy, including high-dose glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, oral tacrolimus, and cyclosporine, and there currently is no single treatment algorithm.2 Lake and colleagues7 highlighted the importance of personalizing treatment of anti-MDA5 DM, as it can be one of the most aggressive rheumatologic diseases. We initially chose to treat our patient with high-dose methylprednisolone, IVIG, and rituximab. Kampylafka et al8 performed a retrospective analysis of the use of IVIG for DM as compared to standard therapy and demonstrated improved muscle and cutaneous involvement from a collection of 50 patients. Case reports have specifically revealed efficacy for the use of IVIG in patients with anti-MDA5 DM.9,10 Additionally, rituximab—an anti–B lymphocyte therapy—has been shown to be an effective supplemental therapy for cases of aggressive anti-MDA5 DM with associated interstitial lung disease, especially when conventional therapy has failed.11,12 Our patient’s sepsis secondary to S aureus pneumonia limited her to only receiving 1 dose of rituximab.
One promising treatment approach for anti-MDA5 DM recently published by Tsuji et al13 involves the use of combination therapy. In this prospective multicenter trial, patients were initially treated with a combination of high-dose glucocorticoids, oral tacrolimus, and IV cyclophosphamide. Plasmapheresis was then started for patients without symptomatic improvement. This method was compared to the more traditional step-up approach of high-dose steroids followed by another immunosuppressant. At 1-year follow-up, the combination therapy group demonstrated an 85% survival rate compared to 33% of historical controls.13
We suspect that our patient developed HLH and AAHS secondary to her underlying anti-MDA5 DM. Kumakura and Murakawa6 reported that among 116 cases of AAHS, 6.9% of cases were associated with DM, most commonly anti-Jo-1 DM. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with anti-MDA5 DM has been described in only a few cases.14-16 The diagnosis of HLH is critical, as the treatments for HLH and DM differ. Both diseases manifest with hyperferritinemia—greater than 500 ng/mL in the case of HLH and 3784 ng/mL in our patient. Therefore, HLH can be easily overlooked. It is possible the rates of HLH associated with anti-MDA5 DM are higher than reported given their similar presentations.
Analogous to our case, Fujita et al15 reported a case of HLH associated with anti-MDA5 DM successfully treated with IV cyclophosphamide pulse therapy and plasmapheresis. The rationale for using plasmapheresis in anti-MDA5 DM is based on its success in patients with other antibody-mediated conditions such as Goodpasture syndrome and granulomatosis with polyangiitis.7 It is thought to expedite response to traditional treatment, and in the case described by Fujita et al,15 the patient received plasmapheresis 6 times total over the course of 9 days. The patient’s clinical symptoms, as well as platelet levels, liver enzymes, and ferritin value, improved.15 Our patient received 3 days of plasmapheresis with no improvement when the decision was made to discontinue plasmapheresis given her worsening clinical state.
Additionally, our patient had elevated hepatic enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT), and results of a liver biopsy demonstrated diffuse steatosis. We speculate her transaminitis was a complication of anti-MDA5 DM. Hepatocellular damage accompanying DM has been investigated in multiple studies and is most often defined as an elevated ALT.17-20 Improvement in ALT levels has been seen with DM treatment. However, investigators note that creatine kinase (CK) values often do not correlate with the resolution of the transaminitis, suggesting that CK denotes muscle damage whereas ALT represents separate liver damage.18-21
Nagashima et al22 highlighted that among 50 patients with DM without malignancy, only 20% presented with a transaminitis or elevated bilirubin. However, among those with liver injury, all were positive for antibodies against MDA5.22 The patients with anti-MDA5 DM liver dysfunction had higher ALT, ALP, and GGT levels compared to those without liver dysfunction. Similarly, in a retrospective review of 14 patients with anti-MDA5 DM, Gono and colleagues3 found elevated GGT levels and lower CK levels in comparison to patients with anti-aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetase DM. Although liver enzymes can be elevated in patients with DM secondary to muscle damage, the authors argue that the specificity of GGT to the liver suggests intrinsic liver damage.3
The mechanism behind liver disease in anti-MDA5 DM is unclear, but it is hypothesized to be similar to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.22 Other studies have revealed drug-induced hepatitis, hepatic congestion, nonspecific reactive hepatitis, metastatic liver tumor, primary biliary cholangitis, and autoimmune hepatitis as the etiology behind liver disease in their patients with DM.17-19 Liver biopsy results from patients with anti-MDA5 DM most commonly reveal hepatic steatosis, as seen in our patient, as well as hepatocyte ballooning and increased pigmented macrophages.22
We presented a case of anti-MDA5 DM complicated by HLH. Our patient had a fatal outcome despite aggressive treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone, IVIG, rituximab, and plasmapheresis. It is accepted that anti-MDA5 DM affects the lungs and skin, and our patient’s presentation also suggests liver involvement. In our case, onset of symptoms to fatality was approximately 1 year. It is essential to consider the diagnosis of HLH in all cases of anti-MDA5 DM given clinical disease overlap. Our patient could have benefited from earlier disease recognition and thus earlier aggressive therapy.
To the Editor:
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy characterized by bilateral, symmetrical, proximal muscle weakness and classic cutaneous manifestations.1 Patients with antibodies directed against melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5, MDA5, have a distinct presentation due to vasculopathy with more severe cutaneous ulcerations, palmar papules, alopecia, and an elevated risk of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease.2 A ferritin level greater than 1600 ng/mL portends an increased risk for pulmonary disease and therefore can be of prognostic value.3 Further, patients with anti-MDA5 DM are at a lower risk of malignancy and are more likely to test negative for antinuclear antibodies in comparison to other patients with DM.2,4
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), also known as hemophagocytic syndrome, is a potentially lethal condition whereby uncontrolled activation of histiocytes in the reticuloendothelial system causes hemophagocytosis and a hyperinflammatory state. Patients present with fever, splenomegaly, cytopenia, and hyperferritinemia.5 Autoimmune‐associated hemophagocytic syndrome (AAHS) describes HLH that develops in association with autoimmune conditions, most commonly systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still disease. Cases reported in association with DM exist but are few in number, and there is no standard-of-care treatment.6 We report a case of a woman with anti-MDA5 DM complicated by HLH and DM-associated liver injury.
A 50-year-old woman presented as a direct admit from the rheumatology clinic for diffuse muscle weakness of 8 months’ duration, 40-pound unintentional weight loss, pruritic rash, bilateral joint pains, dry eyes, dry mouth, and altered mental status. Four months prior, she presented to an outside hospital and was given a diagnosis of probable Sjögren syndrome and autoimmune hepatitis vs drug-induced liver injury. At that time, a workup was notable for antibodies against Sjögren syndrome–related antigen A, anti–smooth muscle antibodies, and transaminitis. Ultrasonography of the right upper quadrant revealed hepatic steatosis. The patient was started on oral prednisone and pilocarpine but had been off all medications for 1 month when she presented to our hospital.
On hospital admission, physical examination revealed a violaceous heliotrope rash; a v-sign on the chest; shawl sign; palmar papules with pits at the fingertips; and periungual erythema and ulcerations along the metacarpophalangeal joints, elbows, lateral feet, and upper eyelids (Figure 1). Laboratory workup showed the following results: white blood cell count, 4100/μL (reference range, 4000–11,000/μL); hemoglobin, 11.6 g/dL (reference range, 12–16 g/dL); platelet count, 100,000/μL (reference range, 150,000–450,000/μL); lactate dehydrogenase, 510 U/L (reference range, 80–225 U/L); alkaline phosphatase (ALP), 766 U/L (reference range, 30–120 U/L); alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 88 U/L (reference range, 10–40 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase (AST), 544 U/L (reference range, 10–40 U/L); total bilirubin, 4.2 mg/dL (reference range, 0.3–1.0 mg/dL); direct bilirubin, 3.7 mg/dL (reference range, 0.1–0.3 mg/dL); aldolase, 20.2 U/L (reference range, 1–7.5 U/L), creatine kinase, 180 U/L (reference range, 30–135 U/L); γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT), 2743 U/L (reference range, 8–40 U/L); high sensitivity C-reactive protein, 122.9 mg/L (low-risk reference range, <1.0 mg/L); triglycerides, 534 mg/dL (reference range, <150 mg/dL); ferritin, 3784 ng/mL (reference range, 24–307 ng/mL); antinuclear antibody, negative titer; antimitochondrial antibody, negative titer; soluble IL-2 receptor (CD25), 7000 U/mL (reference range, 189–846 U/mL); anti-Sjögren syndrome–related antigen A antibody, positive.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulders showed diffuse soft-tissue edema. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest demonstrated parabronchial thickening and parenchymal bands suggestive of DM. An age-appropriate malignancy workup was negative, and results from a liver biopsy showed diffuse steatosis with no histologic evidence of autoimmune hepatitis. Punch biopsy results from a plaque on the left knee revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis with increased dermal mucin on colloidal iron staining, indicative of connective tissue disease (Figure 2). The patient was treated with intravenous (IV) methylprednisolone 250 mg twice daily for 2 days followed by oral prednisone 50 mg daily with IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) 0.4 mg/kg daily for 5 days. The patient’s symptoms improved, and she was discharged on oral prednisone 50 mg and mycophenolate mofetil 1000 mg twice daily with a plan for outpatient IVIG.

Two days after discharge, the patient was re-admitted for worsening muscle weakness; recalcitrant rash; new-onset hypophonia, dysphagia, and odynophagia; and intermittent fevers. Myositis panel results were positive for MDA5. Additionally, workup for HLH, which was initiated during the first hospital admission, revealed that she met 6 of 8 diagnostic criteria: intermittent fevers (maximum temperature, 38.2 °C), splenomegaly (12.6 cm on CT scan of abdomen), cytopenia in 2 cell lines (anemia, thrombocytopenia), hypertriglyceridemia, hyperferritinemia, and elevated IL-2 receptor (CD25). Based on these findings, the patient was diagnosed with anti-MDA5 DM associated with HLH.
The patient was started on IV methylprednisolone 1000 mg daily and received 1 rituximab infusion. Two days later, she experienced worsening fever with tachycardia, and a chest radiograph showed bibasilar infiltrates concerning for aspiration pneumonia, with sputum cultures growing Staphylococcus aureus. Due to the infection, the dosage of methylprednisolone was decreased to 16 mg 3 times daily and rituximab was stopped. The hematology department was consulted for the patient’s HLH, and due to her profound weakness and sepsis, the decision was made to hold initiation of etoposide, which, in addition to glucocorticoids, is considered first-line therapy for HLH. She subsequently experienced worsening hypoxia requiring intubation and received a second course of IVIG. Two days later, CT of the chest revealed progressive ground-glass opacities in the lower lobes of the lungs. The patient was then started on plasmapheresis every other day, hydroxychloroquine 200 mg daily, and IV methylprednisolone 1000 mg daily. Over the subsequent 6 days, she developed worsening renal failure, liver dysfunction, profound thrombocytopenia (13/μL), and acidemia. After extensive discussion with her family, the patient was transitioned to comfort care, and she died 33 days after the initial admission to our hospital.
Our case is a collection of several rare presentations: anti-MDA5 DM, with HLH and AAHS as complications of anti-MDA5 DM, and DM-associated liver injury. Anti-MDA5 DM is frequently refractory to conventional therapy, including high-dose glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, oral tacrolimus, and cyclosporine, and there currently is no single treatment algorithm.2 Lake and colleagues7 highlighted the importance of personalizing treatment of anti-MDA5 DM, as it can be one of the most aggressive rheumatologic diseases. We initially chose to treat our patient with high-dose methylprednisolone, IVIG, and rituximab. Kampylafka et al8 performed a retrospective analysis of the use of IVIG for DM as compared to standard therapy and demonstrated improved muscle and cutaneous involvement from a collection of 50 patients. Case reports have specifically revealed efficacy for the use of IVIG in patients with anti-MDA5 DM.9,10 Additionally, rituximab—an anti–B lymphocyte therapy—has been shown to be an effective supplemental therapy for cases of aggressive anti-MDA5 DM with associated interstitial lung disease, especially when conventional therapy has failed.11,12 Our patient’s sepsis secondary to S aureus pneumonia limited her to only receiving 1 dose of rituximab.
One promising treatment approach for anti-MDA5 DM recently published by Tsuji et al13 involves the use of combination therapy. In this prospective multicenter trial, patients were initially treated with a combination of high-dose glucocorticoids, oral tacrolimus, and IV cyclophosphamide. Plasmapheresis was then started for patients without symptomatic improvement. This method was compared to the more traditional step-up approach of high-dose steroids followed by another immunosuppressant. At 1-year follow-up, the combination therapy group demonstrated an 85% survival rate compared to 33% of historical controls.13
We suspect that our patient developed HLH and AAHS secondary to her underlying anti-MDA5 DM. Kumakura and Murakawa6 reported that among 116 cases of AAHS, 6.9% of cases were associated with DM, most commonly anti-Jo-1 DM. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with anti-MDA5 DM has been described in only a few cases.14-16 The diagnosis of HLH is critical, as the treatments for HLH and DM differ. Both diseases manifest with hyperferritinemia—greater than 500 ng/mL in the case of HLH and 3784 ng/mL in our patient. Therefore, HLH can be easily overlooked. It is possible the rates of HLH associated with anti-MDA5 DM are higher than reported given their similar presentations.
Analogous to our case, Fujita et al15 reported a case of HLH associated with anti-MDA5 DM successfully treated with IV cyclophosphamide pulse therapy and plasmapheresis. The rationale for using plasmapheresis in anti-MDA5 DM is based on its success in patients with other antibody-mediated conditions such as Goodpasture syndrome and granulomatosis with polyangiitis.7 It is thought to expedite response to traditional treatment, and in the case described by Fujita et al,15 the patient received plasmapheresis 6 times total over the course of 9 days. The patient’s clinical symptoms, as well as platelet levels, liver enzymes, and ferritin value, improved.15 Our patient received 3 days of plasmapheresis with no improvement when the decision was made to discontinue plasmapheresis given her worsening clinical state.
Additionally, our patient had elevated hepatic enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT), and results of a liver biopsy demonstrated diffuse steatosis. We speculate her transaminitis was a complication of anti-MDA5 DM. Hepatocellular damage accompanying DM has been investigated in multiple studies and is most often defined as an elevated ALT.17-20 Improvement in ALT levels has been seen with DM treatment. However, investigators note that creatine kinase (CK) values often do not correlate with the resolution of the transaminitis, suggesting that CK denotes muscle damage whereas ALT represents separate liver damage.18-21
Nagashima et al22 highlighted that among 50 patients with DM without malignancy, only 20% presented with a transaminitis or elevated bilirubin. However, among those with liver injury, all were positive for antibodies against MDA5.22 The patients with anti-MDA5 DM liver dysfunction had higher ALT, ALP, and GGT levels compared to those without liver dysfunction. Similarly, in a retrospective review of 14 patients with anti-MDA5 DM, Gono and colleagues3 found elevated GGT levels and lower CK levels in comparison to patients with anti-aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetase DM. Although liver enzymes can be elevated in patients with DM secondary to muscle damage, the authors argue that the specificity of GGT to the liver suggests intrinsic liver damage.3
The mechanism behind liver disease in anti-MDA5 DM is unclear, but it is hypothesized to be similar to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.22 Other studies have revealed drug-induced hepatitis, hepatic congestion, nonspecific reactive hepatitis, metastatic liver tumor, primary biliary cholangitis, and autoimmune hepatitis as the etiology behind liver disease in their patients with DM.17-19 Liver biopsy results from patients with anti-MDA5 DM most commonly reveal hepatic steatosis, as seen in our patient, as well as hepatocyte ballooning and increased pigmented macrophages.22
We presented a case of anti-MDA5 DM complicated by HLH. Our patient had a fatal outcome despite aggressive treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone, IVIG, rituximab, and plasmapheresis. It is accepted that anti-MDA5 DM affects the lungs and skin, and our patient’s presentation also suggests liver involvement. In our case, onset of symptoms to fatality was approximately 1 year. It is essential to consider the diagnosis of HLH in all cases of anti-MDA5 DM given clinical disease overlap. Our patient could have benefited from earlier disease recognition and thus earlier aggressive therapy.
1. Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:344-347.
2. Kurtzman DJB, Vleugels RA. Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) dermatomyositis: a concise review with an emphasis on distinctive clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:776-785.
3. Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Satoh T, et al. Clinical manifestation and prognostic factor in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-associated interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:1713-1719.
4. Fiorentino D, Chung L, Zwerner J, et al. The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:25-34.
5. Sepulveda FE, de Saint Basile G. Hemophagocytic syndrome: primary forms and predisposing conditions. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;49:20-26.
6. Kumakura S, Murakawa Y. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in adults. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66:2297-2307.
7. Lake M, George G, Summer R. Time to personalize the treatment of anti-MDA-5 associated lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:E52.
8. Kampylafka EI, Kosmidis ML, Panagiotakos DB, et al. The effect of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment on patients with dermatomyositis: a 4-year follow-up study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30:397-401.
9. Koguchi-Yoshioka H, Okiyama N, Iwamoto K, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin contributes to the control of antimelanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibody-associated dermatomyositis with palmar violaceous macules/papules. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1442-1446.
10. Hamada-Ode K, Taniguchi Y, Kimata T, et al. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonitis accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2015;2:83-85.
11. So H, Wong VTL, Lao VWN, et al. Rituximab for refractory rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease related to anti-MDA5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:1983-1989.
12. Koichi Y, Aya Y, Megumi U, et al. A case of anti-MDA5-positive rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in a patient with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis ameliorated by rituximab, in addition to standard immunosuppressive treatment. Mod Rheumatol. 2017;27:536-540.
13. Tsuji H, Nakashima R, Hosono Y, et al. Multicenter prospective study of the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive therapy with high-dose glucocorticoid, tacrolimus, and cyclophosphamide in interstitial lung diseases accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72:488-498.
14. Honda M, Moriyama M, Kondo M, et al. Three cases of autoimmune-associated haemophagocytic syndrome in dermatomyositis with anti-MDA5 autoantibody. Scand J Rheumatol. 2020;49:244-246.
15. Fujita Y, Fukui S, Suzuki T, et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis complicated by autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome that was successfully treated with immunosuppressive therapy and plasmapheresis. Intern Med. 2018;57:3473-3478.
16. Gono T, Miyake K, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Hyperferritinaemia and macrophage activation in a patient with interstitial lung disease with clinically amyopathic DM. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:1336-1338.
17. Wada T, Abe G, Kudou, T, et al. Liver damage in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Kitasato Med Journal. 2016;46:40-46.
18. Takahashi A, Abe K, Yokokawa J, et al. Clinical features of liver dysfunction in collagen diseases. Hepatol Res. 2010;40:1092-1097.
19. Matsumoto T, Kobayashi S, Shimizu H, et al. The liver in collagen diseases: pathologic study of 160 cases with particular reference to hepatic arteritis, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis and nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Liver. 2000;20:366-373.
20. Shi Q, Niu J, Huang X, et al. Do muscle enzyme changes forecast liver injury in polymyositis/dermatomyositis patients treated with methylprednisolone and methotrexate? Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46:266-269.
21. Noda S, Asano Y, Tamaki Z, et al. A case of dermatomyositis with “liver disease associated with rheumatoid diseases” positive for anti-liver-kidney microsome-1 antibody. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:941-943.
22. Nagashima T, Kamata Y, Iwamoto M, et al. Liver dysfunction in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive patients with dermatomyositis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39:901-909.
1. Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:344-347.
2. Kurtzman DJB, Vleugels RA. Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) dermatomyositis: a concise review with an emphasis on distinctive clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:776-785.
3. Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Satoh T, et al. Clinical manifestation and prognostic factor in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-associated interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:1713-1719.
4. Fiorentino D, Chung L, Zwerner J, et al. The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:25-34.
5. Sepulveda FE, de Saint Basile G. Hemophagocytic syndrome: primary forms and predisposing conditions. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;49:20-26.
6. Kumakura S, Murakawa Y. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in adults. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66:2297-2307.
7. Lake M, George G, Summer R. Time to personalize the treatment of anti-MDA-5 associated lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:E52.
8. Kampylafka EI, Kosmidis ML, Panagiotakos DB, et al. The effect of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment on patients with dermatomyositis: a 4-year follow-up study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30:397-401.
9. Koguchi-Yoshioka H, Okiyama N, Iwamoto K, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin contributes to the control of antimelanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibody-associated dermatomyositis with palmar violaceous macules/papules. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177:1442-1446.
10. Hamada-Ode K, Taniguchi Y, Kimata T, et al. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonitis accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2015;2:83-85.
11. So H, Wong VTL, Lao VWN, et al. Rituximab for refractory rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease related to anti-MDA5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:1983-1989.
12. Koichi Y, Aya Y, Megumi U, et al. A case of anti-MDA5-positive rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in a patient with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis ameliorated by rituximab, in addition to standard immunosuppressive treatment. Mod Rheumatol. 2017;27:536-540.
13. Tsuji H, Nakashima R, Hosono Y, et al. Multicenter prospective study of the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive therapy with high-dose glucocorticoid, tacrolimus, and cyclophosphamide in interstitial lung diseases accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5-positive dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72:488-498.
14. Honda M, Moriyama M, Kondo M, et al. Three cases of autoimmune-associated haemophagocytic syndrome in dermatomyositis with anti-MDA5 autoantibody. Scand J Rheumatol. 2020;49:244-246.
15. Fujita Y, Fukui S, Suzuki T, et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis complicated by autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome that was successfully treated with immunosuppressive therapy and plasmapheresis. Intern Med. 2018;57:3473-3478.
16. Gono T, Miyake K, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Hyperferritinaemia and macrophage activation in a patient with interstitial lung disease with clinically amyopathic DM. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:1336-1338.
17. Wada T, Abe G, Kudou, T, et al. Liver damage in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Kitasato Med Journal. 2016;46:40-46.
18. Takahashi A, Abe K, Yokokawa J, et al. Clinical features of liver dysfunction in collagen diseases. Hepatol Res. 2010;40:1092-1097.
19. Matsumoto T, Kobayashi S, Shimizu H, et al. The liver in collagen diseases: pathologic study of 160 cases with particular reference to hepatic arteritis, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis and nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Liver. 2000;20:366-373.
20. Shi Q, Niu J, Huang X, et al. Do muscle enzyme changes forecast liver injury in polymyositis/dermatomyositis patients treated with methylprednisolone and methotrexate? Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46:266-269.
21. Noda S, Asano Y, Tamaki Z, et al. A case of dermatomyositis with “liver disease associated with rheumatoid diseases” positive for anti-liver-kidney microsome-1 antibody. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:941-943.
22. Nagashima T, Kamata Y, Iwamoto M, et al. Liver dysfunction in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive patients with dermatomyositis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39:901-909.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Anti-MDA5 (melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 antibody)–positive dermatomyositis associated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis is a rare and aggressive condition associated with a poor prognosis, and there is no standard treatment.
- Dermatomyositis-associated liver injury is not well defined.