User login
Power-Washing Moves Beyond Home Improvement, Into Gastroenterology
Power-washing is no longer just for blasting grimy driveways and stripping flaky paint. It’s good for work inside the gut, too.
In a proof-of-concept study, a “novel systematically directed high-pressure liquid spray,” delivered via the ERBEJET flexible probe, showed promise for collecting cytology specimens from the stomachs of patients undergoing endoscopy for gastric cancer screening or surveillance, reported lead author Charles J. Lightdale, MD, of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, and colleagues.
“Systematic random biopsies (updated Sydney protocol) have been recommended to increase detection of gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) and dysplasia,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “However, random biopsies can be laborious, time consuming, costly, and susceptible to sampling error owing to the large surface area of the stomach.”
Power-washing, in contrast, with the pressure dial turned to 10 bar, involves spraying the gut in a systematic fashion “using sweeping and painting motions” to dislodge cells from the mucosa. These specimens are then suctioned from the resultant pools of liquid, mixed 1:1 with 10% formalin, and shipped to the lab.
Boom! Cytology!
Just to be sure, however, the nine patients involved in the study also underwent standard-of-care biopsy collection from areas of interest, followed by random sampling according to the updated Sydney protocol. Two of the patients were power-washed again 12 months later for endoscopic surveillance.
Power-washing added 7-10 minutes to standard endoscopy time and generated 60-100 mL of liquid for collection. Post suction, a closer look at the gastric mucosa revealed “scattered superficial erosions,” while blood loss was deemed “minimal.” The procedure appeared well tolerated, with no aspiration or esophageal reflux during endoscopy, or adverse events reported by patients after 1 week of follow-up.
Cytopathology samples were deemed satisfactory and yielded “multiple strips and large clusters of cells.” These were sufficient to diagnose GIM in three patients and reactive glandular changes with inflammation in one patient, with findings confirmed on biopsy. In contrast, the power-washed cells from one patient were “highly suspicious” for dysplasia, but biopsies were negative.
Although the study was too small for a reliable comparison with the Sydney protocol, Dr. Lightdale and colleagues concluded that the power-wash approach deserves further investigation.
“ and to reduce morbidity and mortality from gastric cancer,” they wrote.
The investigators predicted that power-washing is likely safe in most patients, although it may be unsuitable for those with noncorrectable coagulopathies or in patients who cannot stop anticoagulants. Postsurgical patients, on the other hand, should tolerate the procedure just fine.
Patients with risk of gastric cancer “might be an important group” for evaluating the power-wash procedure, the investigators wrote, noting that combining the approach with artificial intelligence could one day yield even better results.
In the meantime, Dr. Lightdale and colleagues — like so many weekend warriors wielding a power-washer — are going to see if a different nozzle will take their work to the next level.
“We are actively studying a catheter with a broader stream and the potential to increase efficiency and decrease procedure time,” they wrote. “Another catheter design might allow for simultaneous spray and suction, so that cytology samples from specific regions of the stomach could be separately analyzed.”
This study was funded by Dalio Philanthropies, the Price Family Foundation, and the Frederic and Patricia Salerno Foundation. The investigators disclosed relationships with Boston Scientific, Interscope, Medtronic, and others.
The optimal surveillance endoscopic modality for gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) is yet to be determined. Although the updated Sydney System, a comprehensive endoscopic biopsy protocol, has been advocated for GIM mapping, challenges are the heterogeneous distribution of GIM, suboptimal diagnostic accuracy of endoscopy to detect GIM, and the cost burden of multiple biopsies.
This study by Lightdale et al. demonstrated the technical feasibility and safety of obtaining cytology for the detection of gastric intestinal metaplasia by using a systemic endoscopy-guided high-pressure spray “power-wash” method. In this study, all cytophathology samples in nine subjects were deemed satisfactory for evaluation. All three subjects who were cytology positive for GIM on H&E stain and confirmed with positive immunohistochemistry (IHC) showed GIM on biopsy, and one subject had cells highly suspicious for dysplasia on cytology but biopsy was negative. Although all patients showed multiple superficial erosions after power-wash, bleeding was minimal and no adverse events related to power-wash were observed.
Applying cytology for detection of GIM appears promising as the way of collecting samples from the large surface area of the stomach. As clinicians, however, we are still left with some challenges. Even if cells collected are suspicious for dysplasia/neoplasia by this power-wash method, it would not be useful unless we precisely localize the area as we can not provide a focal curative endoscopic treatment. It is critical to increase the yield of localization of cytology sampling. Further research is also needed to standardize the cytopathologic diagnostic criteria of GIM and cost-effectiveness of the cytology-based approach compared to the current gold-standard biopsy protocol for the diagnosis of GIM.
Yutaka Tomizawa, MD, MSc, is a therapeutic endoscopist and clinical associate professor of medicine, Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington, Seattle. He has no conflicts related to this report.
The optimal surveillance endoscopic modality for gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) is yet to be determined. Although the updated Sydney System, a comprehensive endoscopic biopsy protocol, has been advocated for GIM mapping, challenges are the heterogeneous distribution of GIM, suboptimal diagnostic accuracy of endoscopy to detect GIM, and the cost burden of multiple biopsies.
This study by Lightdale et al. demonstrated the technical feasibility and safety of obtaining cytology for the detection of gastric intestinal metaplasia by using a systemic endoscopy-guided high-pressure spray “power-wash” method. In this study, all cytophathology samples in nine subjects were deemed satisfactory for evaluation. All three subjects who were cytology positive for GIM on H&E stain and confirmed with positive immunohistochemistry (IHC) showed GIM on biopsy, and one subject had cells highly suspicious for dysplasia on cytology but biopsy was negative. Although all patients showed multiple superficial erosions after power-wash, bleeding was minimal and no adverse events related to power-wash were observed.
Applying cytology for detection of GIM appears promising as the way of collecting samples from the large surface area of the stomach. As clinicians, however, we are still left with some challenges. Even if cells collected are suspicious for dysplasia/neoplasia by this power-wash method, it would not be useful unless we precisely localize the area as we can not provide a focal curative endoscopic treatment. It is critical to increase the yield of localization of cytology sampling. Further research is also needed to standardize the cytopathologic diagnostic criteria of GIM and cost-effectiveness of the cytology-based approach compared to the current gold-standard biopsy protocol for the diagnosis of GIM.
Yutaka Tomizawa, MD, MSc, is a therapeutic endoscopist and clinical associate professor of medicine, Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington, Seattle. He has no conflicts related to this report.
The optimal surveillance endoscopic modality for gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) is yet to be determined. Although the updated Sydney System, a comprehensive endoscopic biopsy protocol, has been advocated for GIM mapping, challenges are the heterogeneous distribution of GIM, suboptimal diagnostic accuracy of endoscopy to detect GIM, and the cost burden of multiple biopsies.
This study by Lightdale et al. demonstrated the technical feasibility and safety of obtaining cytology for the detection of gastric intestinal metaplasia by using a systemic endoscopy-guided high-pressure spray “power-wash” method. In this study, all cytophathology samples in nine subjects were deemed satisfactory for evaluation. All three subjects who were cytology positive for GIM on H&E stain and confirmed with positive immunohistochemistry (IHC) showed GIM on biopsy, and one subject had cells highly suspicious for dysplasia on cytology but biopsy was negative. Although all patients showed multiple superficial erosions after power-wash, bleeding was minimal and no adverse events related to power-wash were observed.
Applying cytology for detection of GIM appears promising as the way of collecting samples from the large surface area of the stomach. As clinicians, however, we are still left with some challenges. Even if cells collected are suspicious for dysplasia/neoplasia by this power-wash method, it would not be useful unless we precisely localize the area as we can not provide a focal curative endoscopic treatment. It is critical to increase the yield of localization of cytology sampling. Further research is also needed to standardize the cytopathologic diagnostic criteria of GIM and cost-effectiveness of the cytology-based approach compared to the current gold-standard biopsy protocol for the diagnosis of GIM.
Yutaka Tomizawa, MD, MSc, is a therapeutic endoscopist and clinical associate professor of medicine, Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington, Seattle. He has no conflicts related to this report.
Power-washing is no longer just for blasting grimy driveways and stripping flaky paint. It’s good for work inside the gut, too.
In a proof-of-concept study, a “novel systematically directed high-pressure liquid spray,” delivered via the ERBEJET flexible probe, showed promise for collecting cytology specimens from the stomachs of patients undergoing endoscopy for gastric cancer screening or surveillance, reported lead author Charles J. Lightdale, MD, of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, and colleagues.
“Systematic random biopsies (updated Sydney protocol) have been recommended to increase detection of gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) and dysplasia,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “However, random biopsies can be laborious, time consuming, costly, and susceptible to sampling error owing to the large surface area of the stomach.”
Power-washing, in contrast, with the pressure dial turned to 10 bar, involves spraying the gut in a systematic fashion “using sweeping and painting motions” to dislodge cells from the mucosa. These specimens are then suctioned from the resultant pools of liquid, mixed 1:1 with 10% formalin, and shipped to the lab.
Boom! Cytology!
Just to be sure, however, the nine patients involved in the study also underwent standard-of-care biopsy collection from areas of interest, followed by random sampling according to the updated Sydney protocol. Two of the patients were power-washed again 12 months later for endoscopic surveillance.
Power-washing added 7-10 minutes to standard endoscopy time and generated 60-100 mL of liquid for collection. Post suction, a closer look at the gastric mucosa revealed “scattered superficial erosions,” while blood loss was deemed “minimal.” The procedure appeared well tolerated, with no aspiration or esophageal reflux during endoscopy, or adverse events reported by patients after 1 week of follow-up.
Cytopathology samples were deemed satisfactory and yielded “multiple strips and large clusters of cells.” These were sufficient to diagnose GIM in three patients and reactive glandular changes with inflammation in one patient, with findings confirmed on biopsy. In contrast, the power-washed cells from one patient were “highly suspicious” for dysplasia, but biopsies were negative.
Although the study was too small for a reliable comparison with the Sydney protocol, Dr. Lightdale and colleagues concluded that the power-wash approach deserves further investigation.
“ and to reduce morbidity and mortality from gastric cancer,” they wrote.
The investigators predicted that power-washing is likely safe in most patients, although it may be unsuitable for those with noncorrectable coagulopathies or in patients who cannot stop anticoagulants. Postsurgical patients, on the other hand, should tolerate the procedure just fine.
Patients with risk of gastric cancer “might be an important group” for evaluating the power-wash procedure, the investigators wrote, noting that combining the approach with artificial intelligence could one day yield even better results.
In the meantime, Dr. Lightdale and colleagues — like so many weekend warriors wielding a power-washer — are going to see if a different nozzle will take their work to the next level.
“We are actively studying a catheter with a broader stream and the potential to increase efficiency and decrease procedure time,” they wrote. “Another catheter design might allow for simultaneous spray and suction, so that cytology samples from specific regions of the stomach could be separately analyzed.”
This study was funded by Dalio Philanthropies, the Price Family Foundation, and the Frederic and Patricia Salerno Foundation. The investigators disclosed relationships with Boston Scientific, Interscope, Medtronic, and others.
Power-washing is no longer just for blasting grimy driveways and stripping flaky paint. It’s good for work inside the gut, too.
In a proof-of-concept study, a “novel systematically directed high-pressure liquid spray,” delivered via the ERBEJET flexible probe, showed promise for collecting cytology specimens from the stomachs of patients undergoing endoscopy for gastric cancer screening or surveillance, reported lead author Charles J. Lightdale, MD, of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, and colleagues.
“Systematic random biopsies (updated Sydney protocol) have been recommended to increase detection of gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) and dysplasia,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “However, random biopsies can be laborious, time consuming, costly, and susceptible to sampling error owing to the large surface area of the stomach.”
Power-washing, in contrast, with the pressure dial turned to 10 bar, involves spraying the gut in a systematic fashion “using sweeping and painting motions” to dislodge cells from the mucosa. These specimens are then suctioned from the resultant pools of liquid, mixed 1:1 with 10% formalin, and shipped to the lab.
Boom! Cytology!
Just to be sure, however, the nine patients involved in the study also underwent standard-of-care biopsy collection from areas of interest, followed by random sampling according to the updated Sydney protocol. Two of the patients were power-washed again 12 months later for endoscopic surveillance.
Power-washing added 7-10 minutes to standard endoscopy time and generated 60-100 mL of liquid for collection. Post suction, a closer look at the gastric mucosa revealed “scattered superficial erosions,” while blood loss was deemed “minimal.” The procedure appeared well tolerated, with no aspiration or esophageal reflux during endoscopy, or adverse events reported by patients after 1 week of follow-up.
Cytopathology samples were deemed satisfactory and yielded “multiple strips and large clusters of cells.” These were sufficient to diagnose GIM in three patients and reactive glandular changes with inflammation in one patient, with findings confirmed on biopsy. In contrast, the power-washed cells from one patient were “highly suspicious” for dysplasia, but biopsies were negative.
Although the study was too small for a reliable comparison with the Sydney protocol, Dr. Lightdale and colleagues concluded that the power-wash approach deserves further investigation.
“ and to reduce morbidity and mortality from gastric cancer,” they wrote.
The investigators predicted that power-washing is likely safe in most patients, although it may be unsuitable for those with noncorrectable coagulopathies or in patients who cannot stop anticoagulants. Postsurgical patients, on the other hand, should tolerate the procedure just fine.
Patients with risk of gastric cancer “might be an important group” for evaluating the power-wash procedure, the investigators wrote, noting that combining the approach with artificial intelligence could one day yield even better results.
In the meantime, Dr. Lightdale and colleagues — like so many weekend warriors wielding a power-washer — are going to see if a different nozzle will take their work to the next level.
“We are actively studying a catheter with a broader stream and the potential to increase efficiency and decrease procedure time,” they wrote. “Another catheter design might allow for simultaneous spray and suction, so that cytology samples from specific regions of the stomach could be separately analyzed.”
This study was funded by Dalio Philanthropies, the Price Family Foundation, and the Frederic and Patricia Salerno Foundation. The investigators disclosed relationships with Boston Scientific, Interscope, Medtronic, and others.
FROM TECHNIQUES AND INNOVATIONS IN GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
Lichenoid Dermatosis on the Feet
The Diagnosis: Hypertrophic Lichen Planus
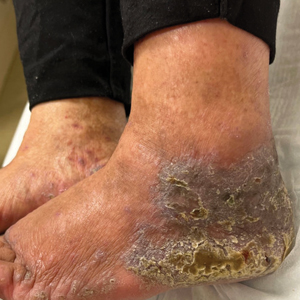
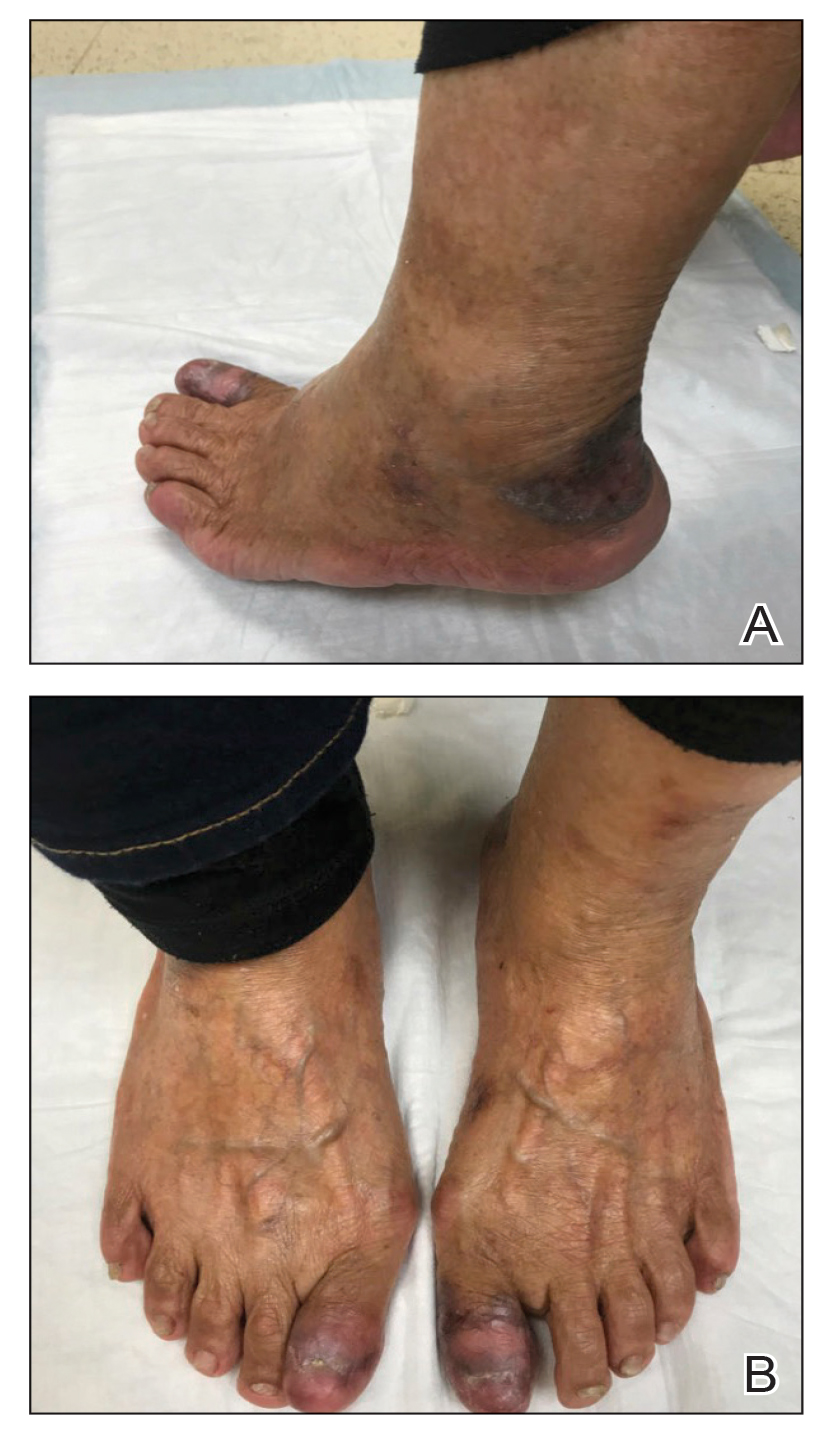
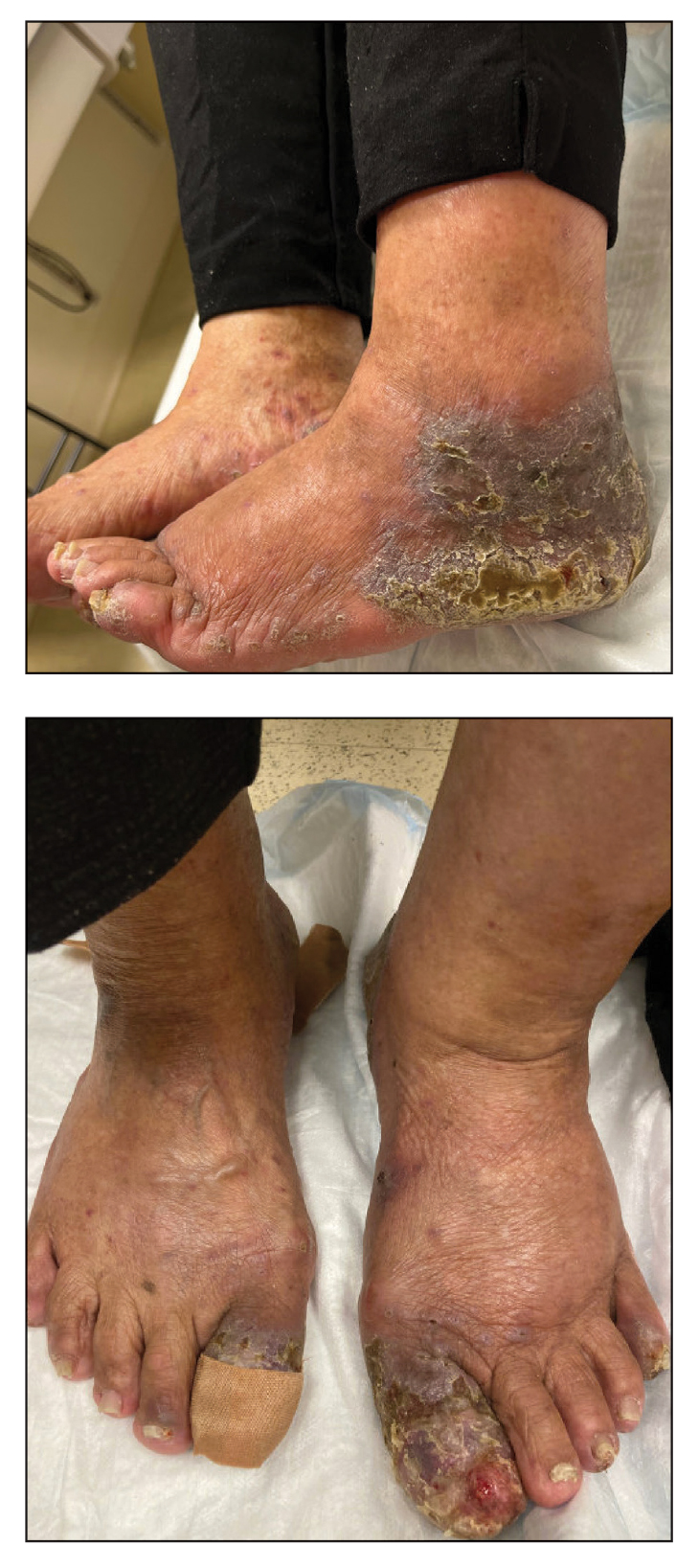
Two biopsies from the left lateral foot revealed hyperkeratosis, wedge-shaped hypergranulosis, irregular acanthosis, and a bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis with a classic sawtooth pattern of the rete ridges (Figure 1). Based on the clinical findings and histopathology, the patient was diagnosed with hypertrophic lichen planus (LP) and was treated with clobetasol ointment 0.05%, which resulted in progression of the symptoms. She experienced notable improvement 3 months after adding methotrexate 12.5 mg weekly (Figure 2).
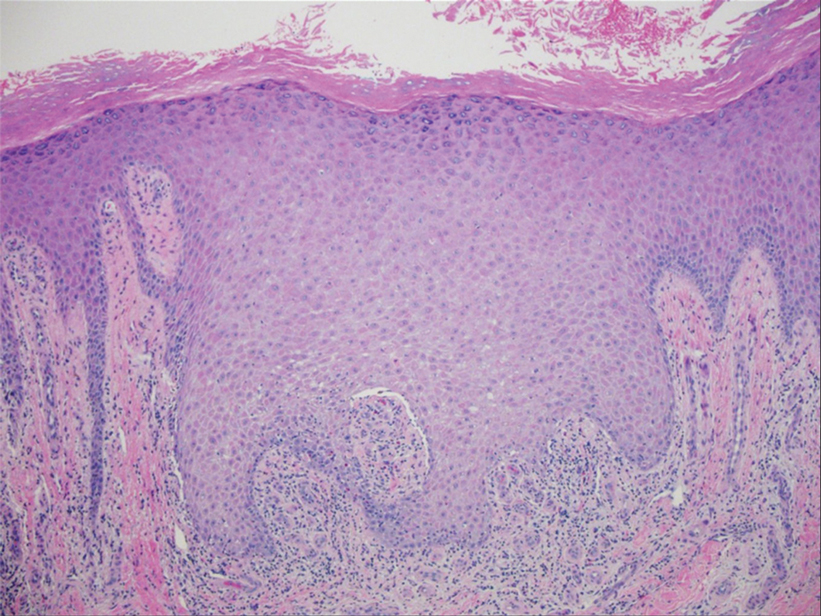
Lichen planus is an idiopathic chronic inflammatory condition of the skin and mucous membranes that classically manifests as pruritic violaceous papules and plaques, which commonly are found on the wrists, lower back, and ankles.1 The most common variants of LP are hypertrophic, linear, mucosal, actinic, follicular, pigmented, annular, atrophic, and guttate.2 The clinical presentation and biopsy results in our patient were consistent with the hypertrophic variant of LP, which is a chronic condition that most often manifests on the lower legs, especially around the ankles, as hyperkeratotic papules, plaques, and nodules.2,3 The exact pathophysiology of hypertrophic LP is unknown, but there is evidence that the immune system plays a role in its development and that the Koebner phenomenon may contribute to its exacerbation.4 There is a well-known association between LP and hepatitis. Patients with chronic LP may develop squamous cell carcinoma.4 The variants of LP can overlap and do not exist independent of one another. Recognizing the overlap in these variants allows for earlier diagnosis and therapeutic intervention of the disease process to limit disease progression and patient clinic visits and to improve patient quality of life.
The differential diagnosis for hyperkeratotic plaques of the feet and ankles can be broad and may include keratosis lichenoides chronica, palmoplantar keratoderma, palmoplantar psoriasis, or lichen amyloidosis. These conditions are classified based on various criteria that include extent of disease manifestations, morphology of palmoplantar skin involvement, inheritance patterns, and molecular pathogenesis.5 Keratosis lichenoides chronica is a rare dermatosis that presents as a distinctive seborrheic dermatitis–like facial eruption. The facial eruption is accompanied by violaceous papular and nodular lesions that appear on the extremities and trunk, typically arranged in a linear or reticular pattern.6 Palmoplantar keratoderma represents a group of acquired and hereditary conditions that are characterized by excessive thickening of the palms and soles.5 Palmoplantar psoriasis is a variant of psoriasis that affects the palms and soles and can manifest as hyperkeratosis, pustular, or mixed morphology.7 Lichen amyloidosis is a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis that manifests as multiple pruritic, firm, hyperpigmented, hyperkeratotic papules on the shins that later coalesce in a rippled pattern.8,9
The first-line treatment for hypertrophic LP is topical corticosteroids. Alternative therapies include mycophenolate mofetil, acitretin, and intralesional corticosteroid injections.4 Treatment is similar for all of the LP variants.
- Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen planus. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Namazi MR, Bahmani M. Diagnosis: hypertrophic lichen planus. Ann Saudi Med. 2008;28:1-2. doi:10.5144/0256-4947.2008.222
- Riahi RR, Cohen PR. Hypertrophic lichen planus mimicking verrucous lupus erythematosus. Cureus. 2018;10:e3555. doi:10.7759 /cureus.3555
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149. doi:10.1016/j .ijwd.2015.04.001
- Has C, Technau-Hafsi K. Palmoplantar keratodermas: clinical and genetic aspects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:123-139; quiz 140. doi:10.1111/ddg.12930
- Konstantinov KN, Søndergaard J, Izuno G, et al. Keratosis lichenoides chronica. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38(2 Pt 2):306-309. doi:10.1016 /s0190-9622(98)70570-5
- Miceli A, Schmieder GJ. Palmoplantar psoriasis. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Tay CH, Dacosta JL. Lichen amyloidosis—clinical study of 40 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1970;82:129-136.
- Salim T, Shenoi SD, Balachandran C, et al. Lichen amyloidosis: a study of clinical, histopathologic and immunofluorescence findings in 30 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:166-169.
The Diagnosis: Hypertrophic Lichen Planus
Two biopsies from the left lateral foot revealed hyperkeratosis, wedge-shaped hypergranulosis, irregular acanthosis, and a bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis with a classic sawtooth pattern of the rete ridges (Figure 1). Based on the clinical findings and histopathology, the patient was diagnosed with hypertrophic lichen planus (LP) and was treated with clobetasol ointment 0.05%, which resulted in progression of the symptoms. She experienced notable improvement 3 months after adding methotrexate 12.5 mg weekly (Figure 2).

Lichen planus is an idiopathic chronic inflammatory condition of the skin and mucous membranes that classically manifests as pruritic violaceous papules and plaques, which commonly are found on the wrists, lower back, and ankles.1 The most common variants of LP are hypertrophic, linear, mucosal, actinic, follicular, pigmented, annular, atrophic, and guttate.2 The clinical presentation and biopsy results in our patient were consistent with the hypertrophic variant of LP, which is a chronic condition that most often manifests on the lower legs, especially around the ankles, as hyperkeratotic papules, plaques, and nodules.2,3 The exact pathophysiology of hypertrophic LP is unknown, but there is evidence that the immune system plays a role in its development and that the Koebner phenomenon may contribute to its exacerbation.4 There is a well-known association between LP and hepatitis. Patients with chronic LP may develop squamous cell carcinoma.4 The variants of LP can overlap and do not exist independent of one another. Recognizing the overlap in these variants allows for earlier diagnosis and therapeutic intervention of the disease process to limit disease progression and patient clinic visits and to improve patient quality of life.

The differential diagnosis for hyperkeratotic plaques of the feet and ankles can be broad and may include keratosis lichenoides chronica, palmoplantar keratoderma, palmoplantar psoriasis, or lichen amyloidosis. These conditions are classified based on various criteria that include extent of disease manifestations, morphology of palmoplantar skin involvement, inheritance patterns, and molecular pathogenesis.5 Keratosis lichenoides chronica is a rare dermatosis that presents as a distinctive seborrheic dermatitis–like facial eruption. The facial eruption is accompanied by violaceous papular and nodular lesions that appear on the extremities and trunk, typically arranged in a linear or reticular pattern.6 Palmoplantar keratoderma represents a group of acquired and hereditary conditions that are characterized by excessive thickening of the palms and soles.5 Palmoplantar psoriasis is a variant of psoriasis that affects the palms and soles and can manifest as hyperkeratosis, pustular, or mixed morphology.7 Lichen amyloidosis is a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis that manifests as multiple pruritic, firm, hyperpigmented, hyperkeratotic papules on the shins that later coalesce in a rippled pattern.8,9
The first-line treatment for hypertrophic LP is topical corticosteroids. Alternative therapies include mycophenolate mofetil, acitretin, and intralesional corticosteroid injections.4 Treatment is similar for all of the LP variants.
The Diagnosis: Hypertrophic Lichen Planus
Two biopsies from the left lateral foot revealed hyperkeratosis, wedge-shaped hypergranulosis, irregular acanthosis, and a bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis with a classic sawtooth pattern of the rete ridges (Figure 1). Based on the clinical findings and histopathology, the patient was diagnosed with hypertrophic lichen planus (LP) and was treated with clobetasol ointment 0.05%, which resulted in progression of the symptoms. She experienced notable improvement 3 months after adding methotrexate 12.5 mg weekly (Figure 2).

Lichen planus is an idiopathic chronic inflammatory condition of the skin and mucous membranes that classically manifests as pruritic violaceous papules and plaques, which commonly are found on the wrists, lower back, and ankles.1 The most common variants of LP are hypertrophic, linear, mucosal, actinic, follicular, pigmented, annular, atrophic, and guttate.2 The clinical presentation and biopsy results in our patient were consistent with the hypertrophic variant of LP, which is a chronic condition that most often manifests on the lower legs, especially around the ankles, as hyperkeratotic papules, plaques, and nodules.2,3 The exact pathophysiology of hypertrophic LP is unknown, but there is evidence that the immune system plays a role in its development and that the Koebner phenomenon may contribute to its exacerbation.4 There is a well-known association between LP and hepatitis. Patients with chronic LP may develop squamous cell carcinoma.4 The variants of LP can overlap and do not exist independent of one another. Recognizing the overlap in these variants allows for earlier diagnosis and therapeutic intervention of the disease process to limit disease progression and patient clinic visits and to improve patient quality of life.

The differential diagnosis for hyperkeratotic plaques of the feet and ankles can be broad and may include keratosis lichenoides chronica, palmoplantar keratoderma, palmoplantar psoriasis, or lichen amyloidosis. These conditions are classified based on various criteria that include extent of disease manifestations, morphology of palmoplantar skin involvement, inheritance patterns, and molecular pathogenesis.5 Keratosis lichenoides chronica is a rare dermatosis that presents as a distinctive seborrheic dermatitis–like facial eruption. The facial eruption is accompanied by violaceous papular and nodular lesions that appear on the extremities and trunk, typically arranged in a linear or reticular pattern.6 Palmoplantar keratoderma represents a group of acquired and hereditary conditions that are characterized by excessive thickening of the palms and soles.5 Palmoplantar psoriasis is a variant of psoriasis that affects the palms and soles and can manifest as hyperkeratosis, pustular, or mixed morphology.7 Lichen amyloidosis is a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis that manifests as multiple pruritic, firm, hyperpigmented, hyperkeratotic papules on the shins that later coalesce in a rippled pattern.8,9
The first-line treatment for hypertrophic LP is topical corticosteroids. Alternative therapies include mycophenolate mofetil, acitretin, and intralesional corticosteroid injections.4 Treatment is similar for all of the LP variants.
- Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen planus. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Namazi MR, Bahmani M. Diagnosis: hypertrophic lichen planus. Ann Saudi Med. 2008;28:1-2. doi:10.5144/0256-4947.2008.222
- Riahi RR, Cohen PR. Hypertrophic lichen planus mimicking verrucous lupus erythematosus. Cureus. 2018;10:e3555. doi:10.7759 /cureus.3555
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149. doi:10.1016/j .ijwd.2015.04.001
- Has C, Technau-Hafsi K. Palmoplantar keratodermas: clinical and genetic aspects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:123-139; quiz 140. doi:10.1111/ddg.12930
- Konstantinov KN, Søndergaard J, Izuno G, et al. Keratosis lichenoides chronica. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38(2 Pt 2):306-309. doi:10.1016 /s0190-9622(98)70570-5
- Miceli A, Schmieder GJ. Palmoplantar psoriasis. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Tay CH, Dacosta JL. Lichen amyloidosis—clinical study of 40 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1970;82:129-136.
- Salim T, Shenoi SD, Balachandran C, et al. Lichen amyloidosis: a study of clinical, histopathologic and immunofluorescence findings in 30 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:166-169.
- Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen planus. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Namazi MR, Bahmani M. Diagnosis: hypertrophic lichen planus. Ann Saudi Med. 2008;28:1-2. doi:10.5144/0256-4947.2008.222
- Riahi RR, Cohen PR. Hypertrophic lichen planus mimicking verrucous lupus erythematosus. Cureus. 2018;10:e3555. doi:10.7759 /cureus.3555
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149. doi:10.1016/j .ijwd.2015.04.001
- Has C, Technau-Hafsi K. Palmoplantar keratodermas: clinical and genetic aspects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:123-139; quiz 140. doi:10.1111/ddg.12930
- Konstantinov KN, Søndergaard J, Izuno G, et al. Keratosis lichenoides chronica. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38(2 Pt 2):306-309. doi:10.1016 /s0190-9622(98)70570-5
- Miceli A, Schmieder GJ. Palmoplantar psoriasis. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Tay CH, Dacosta JL. Lichen amyloidosis—clinical study of 40 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1970;82:129-136.
- Salim T, Shenoi SD, Balachandran C, et al. Lichen amyloidosis: a study of clinical, histopathologic and immunofluorescence findings in 30 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:166-169.
An 83-year-old woman presented for evaluation of hyperkeratotic plaques on the medial and lateral aspects of the left heel (top). Physical examination also revealed onychodystrophy of the toenails on the halluces (bottom). A crusted friable plaque on the lower lip and white plaques with peripheral reticulation and erosions on the buccal mucosa also were present. The patient had a history of nummular eczema, stasis dermatitis, and hand dermatitis. She denied a history of cold sores.
Prevalence of Dementia in Homeless Twice That in Housed
, according to the results of a new study.
The findings suggested that dementia occurs earlier in homeless individuals, and that these patients could benefit from proactive screening and housing interventions.
“Whether dementia caused the homelessness or homelessness caused the dementia, it’s a bidirectional relationship,” said lead author Richard G. Booth, PhD, RN, adjunct scientist at ICES (formerly Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences) and associate professor of nursing at Western University in London, Ontario, Canada.
The study was published in the April issue of The Lancet Public Health.
Dementia at Early Ages
The investigators used health administrative data from Ontario to compare the prevalence of dementia among homeless people with that among housed individuals in the general population and those living in low-income neighborhoods.
They included individuals aged 45 years or older on January 1, 2019, who visited hospital-based ambulatory care (such as emergency departments), were hospitalized, or visited a community health center in 2019. The researchers identified people as experiencing homelessness if they had one or more healthcare records with an indication of homelessness or unstable housing. The prevalence of dementia was ascertained as of December 31, 2019.
Included in the population-based, cross-sectional comparative analysis were 12,863 homeless people, 475,544 people in the low-income group, and 2,273,068 people in the general population group.
Dementia prevalence was 68.7 per 1000 individuals among the homeless population, 62.6 per 1000 in the low-income group, and 51.0 per 1000 in the general population group.
After adjustments for age, sex, geographical location of residence (urban vs rural), and health conditions associated with dementia, the prevalence ratio of dementia among homeless people was 1.71, compared with the low-income group, and 1.90, compared with the general population group.
Dementia also was detected in the 45- to 55-year age group among homeless people. This age is much earlier than the age at which doctors start screening their patients for cognitive decline (65 years).
“The study was not designed to define the causality but consider: If you have early-stage dementia and you are not intact enough to do basic functions of life, the likelihood of you becoming homeless is definitely increased, and vice versa. If you are homeless and suffer significant environmental and physical traumas just living on the street, you age much quicker, and you will experience geriatric symptoms such as dementia earlier in your life trajectory,” said Dr. Booth.
“The main takeaway here is that if you don’t have housing, bad things are going to happen in life.”
Public Health Problem
In an accompanying editorial, William J. Panenka, MD, associate professor of psychiatry at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, and colleagues cited modifiable risk factors for dementia, including lower education, traumatic brain injury, substance use, smoking, mood disorders, and social isolation, many of which are disproportionately prevalent among homeless individuals.
“Ultimately, dementia could contribute to the cycle of homelessness, whereby housing instability increases the risk for brain impairment, and brain impairment makes breaking the cycle of homelessness progressively more challenging,” they wrote.
Dr. Panenka and colleagues also pointed out that the average age of homeless people is increasing. In the United States, it is now approximately 50 years. This fact underscores “the immediacy and gravity of the public health problem. A multifaceted approach that integrates healthcare, housing, and social services is needed to better understand and alleviate the health consequences of homelessness. A concerted effort at all levels is vital to inform future public health efforts and stem the tide of increasing morbidity, compromised function, and early mortality in homelessness,” they concluded.
Stephen Hwang, MD, director of the MAP Centre for Urban Health Solutions at St. Michael’s Hospital and Unity Health in Toronto, said that the study may underestimate the magnitude of the problem of dementia among homeless people.
“The methods used in this research study are very strong because they draw upon data for everyone living in the entire province of Ontario, and this is a very powerful way of looking at this challenging problem. The study probably underestimates the magnitude of the problem because to be diagnosed with dementia, patients have to have contact with healthcare providers that make that diagnosis. Often, people experiencing homelessness don’t have extensive contact with the healthcare system, and so their condition may go undiagnosed,” said Dr. Hwang.
A specialist in internal medicine, Dr. Hwang has provided healthcare for homeless people, and his research focuses on homelessness, housing, and health. He said that the findings from the Canadian study are applicable to the United States.
Forced clearances of homeless people and placing them in encampments, something that has been discussed in Florida, is unlikely to solve the problem, he said.
“The approach that has been shown to be beneficial is to engage with people and offer them housing and services that will allow them to exit homelessness without criminalizing the fact that they’re homeless. There really is no reason to think that this approach of forced clearances is going to help anyone.”
This study was supported by ICES (formerly the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences), which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ontario Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Booth and Dr. Hwang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Panenka reported receiving a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the results of a new study.
The findings suggested that dementia occurs earlier in homeless individuals, and that these patients could benefit from proactive screening and housing interventions.
“Whether dementia caused the homelessness or homelessness caused the dementia, it’s a bidirectional relationship,” said lead author Richard G. Booth, PhD, RN, adjunct scientist at ICES (formerly Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences) and associate professor of nursing at Western University in London, Ontario, Canada.
The study was published in the April issue of The Lancet Public Health.
Dementia at Early Ages
The investigators used health administrative data from Ontario to compare the prevalence of dementia among homeless people with that among housed individuals in the general population and those living in low-income neighborhoods.
They included individuals aged 45 years or older on January 1, 2019, who visited hospital-based ambulatory care (such as emergency departments), were hospitalized, or visited a community health center in 2019. The researchers identified people as experiencing homelessness if they had one or more healthcare records with an indication of homelessness or unstable housing. The prevalence of dementia was ascertained as of December 31, 2019.
Included in the population-based, cross-sectional comparative analysis were 12,863 homeless people, 475,544 people in the low-income group, and 2,273,068 people in the general population group.
Dementia prevalence was 68.7 per 1000 individuals among the homeless population, 62.6 per 1000 in the low-income group, and 51.0 per 1000 in the general population group.
After adjustments for age, sex, geographical location of residence (urban vs rural), and health conditions associated with dementia, the prevalence ratio of dementia among homeless people was 1.71, compared with the low-income group, and 1.90, compared with the general population group.
Dementia also was detected in the 45- to 55-year age group among homeless people. This age is much earlier than the age at which doctors start screening their patients for cognitive decline (65 years).
“The study was not designed to define the causality but consider: If you have early-stage dementia and you are not intact enough to do basic functions of life, the likelihood of you becoming homeless is definitely increased, and vice versa. If you are homeless and suffer significant environmental and physical traumas just living on the street, you age much quicker, and you will experience geriatric symptoms such as dementia earlier in your life trajectory,” said Dr. Booth.
“The main takeaway here is that if you don’t have housing, bad things are going to happen in life.”
Public Health Problem
In an accompanying editorial, William J. Panenka, MD, associate professor of psychiatry at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, and colleagues cited modifiable risk factors for dementia, including lower education, traumatic brain injury, substance use, smoking, mood disorders, and social isolation, many of which are disproportionately prevalent among homeless individuals.
“Ultimately, dementia could contribute to the cycle of homelessness, whereby housing instability increases the risk for brain impairment, and brain impairment makes breaking the cycle of homelessness progressively more challenging,” they wrote.
Dr. Panenka and colleagues also pointed out that the average age of homeless people is increasing. In the United States, it is now approximately 50 years. This fact underscores “the immediacy and gravity of the public health problem. A multifaceted approach that integrates healthcare, housing, and social services is needed to better understand and alleviate the health consequences of homelessness. A concerted effort at all levels is vital to inform future public health efforts and stem the tide of increasing morbidity, compromised function, and early mortality in homelessness,” they concluded.
Stephen Hwang, MD, director of the MAP Centre for Urban Health Solutions at St. Michael’s Hospital and Unity Health in Toronto, said that the study may underestimate the magnitude of the problem of dementia among homeless people.
“The methods used in this research study are very strong because they draw upon data for everyone living in the entire province of Ontario, and this is a very powerful way of looking at this challenging problem. The study probably underestimates the magnitude of the problem because to be diagnosed with dementia, patients have to have contact with healthcare providers that make that diagnosis. Often, people experiencing homelessness don’t have extensive contact with the healthcare system, and so their condition may go undiagnosed,” said Dr. Hwang.
A specialist in internal medicine, Dr. Hwang has provided healthcare for homeless people, and his research focuses on homelessness, housing, and health. He said that the findings from the Canadian study are applicable to the United States.
Forced clearances of homeless people and placing them in encampments, something that has been discussed in Florida, is unlikely to solve the problem, he said.
“The approach that has been shown to be beneficial is to engage with people and offer them housing and services that will allow them to exit homelessness without criminalizing the fact that they’re homeless. There really is no reason to think that this approach of forced clearances is going to help anyone.”
This study was supported by ICES (formerly the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences), which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ontario Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Booth and Dr. Hwang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Panenka reported receiving a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the results of a new study.
The findings suggested that dementia occurs earlier in homeless individuals, and that these patients could benefit from proactive screening and housing interventions.
“Whether dementia caused the homelessness or homelessness caused the dementia, it’s a bidirectional relationship,” said lead author Richard G. Booth, PhD, RN, adjunct scientist at ICES (formerly Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences) and associate professor of nursing at Western University in London, Ontario, Canada.
The study was published in the April issue of The Lancet Public Health.
Dementia at Early Ages
The investigators used health administrative data from Ontario to compare the prevalence of dementia among homeless people with that among housed individuals in the general population and those living in low-income neighborhoods.
They included individuals aged 45 years or older on January 1, 2019, who visited hospital-based ambulatory care (such as emergency departments), were hospitalized, or visited a community health center in 2019. The researchers identified people as experiencing homelessness if they had one or more healthcare records with an indication of homelessness or unstable housing. The prevalence of dementia was ascertained as of December 31, 2019.
Included in the population-based, cross-sectional comparative analysis were 12,863 homeless people, 475,544 people in the low-income group, and 2,273,068 people in the general population group.
Dementia prevalence was 68.7 per 1000 individuals among the homeless population, 62.6 per 1000 in the low-income group, and 51.0 per 1000 in the general population group.
After adjustments for age, sex, geographical location of residence (urban vs rural), and health conditions associated with dementia, the prevalence ratio of dementia among homeless people was 1.71, compared with the low-income group, and 1.90, compared with the general population group.
Dementia also was detected in the 45- to 55-year age group among homeless people. This age is much earlier than the age at which doctors start screening their patients for cognitive decline (65 years).
“The study was not designed to define the causality but consider: If you have early-stage dementia and you are not intact enough to do basic functions of life, the likelihood of you becoming homeless is definitely increased, and vice versa. If you are homeless and suffer significant environmental and physical traumas just living on the street, you age much quicker, and you will experience geriatric symptoms such as dementia earlier in your life trajectory,” said Dr. Booth.
“The main takeaway here is that if you don’t have housing, bad things are going to happen in life.”
Public Health Problem
In an accompanying editorial, William J. Panenka, MD, associate professor of psychiatry at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, and colleagues cited modifiable risk factors for dementia, including lower education, traumatic brain injury, substance use, smoking, mood disorders, and social isolation, many of which are disproportionately prevalent among homeless individuals.
“Ultimately, dementia could contribute to the cycle of homelessness, whereby housing instability increases the risk for brain impairment, and brain impairment makes breaking the cycle of homelessness progressively more challenging,” they wrote.
Dr. Panenka and colleagues also pointed out that the average age of homeless people is increasing. In the United States, it is now approximately 50 years. This fact underscores “the immediacy and gravity of the public health problem. A multifaceted approach that integrates healthcare, housing, and social services is needed to better understand and alleviate the health consequences of homelessness. A concerted effort at all levels is vital to inform future public health efforts and stem the tide of increasing morbidity, compromised function, and early mortality in homelessness,” they concluded.
Stephen Hwang, MD, director of the MAP Centre for Urban Health Solutions at St. Michael’s Hospital and Unity Health in Toronto, said that the study may underestimate the magnitude of the problem of dementia among homeless people.
“The methods used in this research study are very strong because they draw upon data for everyone living in the entire province of Ontario, and this is a very powerful way of looking at this challenging problem. The study probably underestimates the magnitude of the problem because to be diagnosed with dementia, patients have to have contact with healthcare providers that make that diagnosis. Often, people experiencing homelessness don’t have extensive contact with the healthcare system, and so their condition may go undiagnosed,” said Dr. Hwang.
A specialist in internal medicine, Dr. Hwang has provided healthcare for homeless people, and his research focuses on homelessness, housing, and health. He said that the findings from the Canadian study are applicable to the United States.
Forced clearances of homeless people and placing them in encampments, something that has been discussed in Florida, is unlikely to solve the problem, he said.
“The approach that has been shown to be beneficial is to engage with people and offer them housing and services that will allow them to exit homelessness without criminalizing the fact that they’re homeless. There really is no reason to think that this approach of forced clearances is going to help anyone.”
This study was supported by ICES (formerly the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences), which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ontario Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Booth and Dr. Hwang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Panenka reported receiving a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
From Lancet Public Health
New Tool Helps Clinicians Detect Zoom Dysmorphia in Virtual Settings
SAN DIEGO — , according to George Kroumpouzos, MD, PhD, who, with colleagues, recently proposed a screening tool to help identify patients with zoom dysmorphia.
The term, coined in 2020 by dermatologist Shadi Kourosh, MD, MPH, and colleagues at Harvard Medical School, Boston, refers to an altered or skewed negative perception of one’s body image that results from spending extended amounts of time on video calls. Speaking at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Kroumpouzos, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Brown University, Providence Rhode Island, explained that most people believe that zoom dysmorphia falls within the spectrum of body dysmorphic disorder (BDD). He described zoom dysmorphia as “a facial dysmorphia triggered or aggravated by frequent virtual meetings. Frequent use of videoconferencing platforms is linked to a distorted perception of facial images, which leads to dysmorphic concerns.”
Individuals with zoom dysmorphia tend to scrutinize their facial features and fixate on what they think needs to improve, he continued. They experience anxiety about attending video conferences with the camera on and feel pressured to appear perfect before virtual meetings. “They find facial flaws during virtual meetings, and they believe others notice their perceived flaws,” he said. “This all has drastic effects on body dissatisfaction and self-esteem, which leads to a desire to seek cosmetic procedures. It interferes with an individual’s life and can trigger or aggravate body dysmorphic disorder.”
While several tools have been validated in cosmetic settings to screen for BDD, such as the 9-item Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Dermatology questionnaire, the 7-item Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Aesthetic Surgery questionnaire, the Cosmetic Procedure Screening Questionnaire, and the Body Dysmorphic Disorder Symptom Scale, no formal screening tools exist to identify zoom dysmorphia. To complicate matters, “identifying dysmorphic concerns in virtual settings can be challenging,” Dr. Kroumpouzos added. “This makes the recognition of zoom dysmorphia during telehealth visits even more difficult.”
Individuals who may have zoom dysmorphia may fear being misunderstood, judged, or ridiculed because of a perceived flaw in appearance, he said, making establishing rapport and eye contact difficult. “There’s a reticence and silence due to the individual’s avoidant characteristics,” he said. “Patients may become easily distracted or disengaged during telehealth visits in case of technical issues. Psychiatric comorbidities can mask symptoms related to dysmorphic concerns.”
To bridge this gap, Dr. Kroumpouzos and colleagues have proposed a screening tool, a questionnaire related to features of zoom dysmorphia, to facilitate recognition of zoom dysmorphia in virtual settings.
The first component consists of open-ended questions such as “Are you comfortable with being interviewed in a virtual appointment?” and “How do you feel about your appearance during virtual meetings?” Such questions “aim to start the dialogue, to facilitate the discussion with a patient who may be shy or avoidant,” Dr. Kroumpouzos explained.
The second component of the tool consists of questions more specific to screening for zoom dysmorphia, starting with “Are you concerned about facial flaws?” If the patient answers no, they don’t qualify for any others, he said. “But, if they answer yes to that question and yes to at least one more [question], they may have zoom dysmorphia.”
Other questions include, “Do you think that your face is not friendly to the camera?” “Do you hesitate to open the camera?” “Have you tried to hide or camouflage your flaw with your hands, hair, makeup, or clothing?” “Have you sought advice from others to improve your appearance or image?” “Do you often use the filter features of the video conferencing platform?” “Did you consider buying a new camera or equipment that helps improve your image?”
If the clinician deems the patient a candidate for the diagnosis of zoom dysmorphia, the tool recommends asking a BDD-focused question: “In the past month, have you been very concerned that there is something wrong with your physical appearance or the way one or more parts of your body look?” If the patient answers yes, “that individual should be invited to fill out a questionnaire specifically for BDD or come to the office for further evaluation,” Dr. Kroumpouzos said.
In his view, the brevity of the proposed screening tool makes it easy to incorporate into clinical practice, and the “yes or no” questions are practical. “It is crucial to elicit the presence of zoom dysmorphia in its early stage,” he said. “Zoom dysmorphia may trigger an increase in BDD, [so] it is essential to identify the presence of BDD in zoom dysmorphia sufferers and treat it appropriately.”
Dr. Kroumpouzos reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — , according to George Kroumpouzos, MD, PhD, who, with colleagues, recently proposed a screening tool to help identify patients with zoom dysmorphia.
The term, coined in 2020 by dermatologist Shadi Kourosh, MD, MPH, and colleagues at Harvard Medical School, Boston, refers to an altered or skewed negative perception of one’s body image that results from spending extended amounts of time on video calls. Speaking at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Kroumpouzos, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Brown University, Providence Rhode Island, explained that most people believe that zoom dysmorphia falls within the spectrum of body dysmorphic disorder (BDD). He described zoom dysmorphia as “a facial dysmorphia triggered or aggravated by frequent virtual meetings. Frequent use of videoconferencing platforms is linked to a distorted perception of facial images, which leads to dysmorphic concerns.”
Individuals with zoom dysmorphia tend to scrutinize their facial features and fixate on what they think needs to improve, he continued. They experience anxiety about attending video conferences with the camera on and feel pressured to appear perfect before virtual meetings. “They find facial flaws during virtual meetings, and they believe others notice their perceived flaws,” he said. “This all has drastic effects on body dissatisfaction and self-esteem, which leads to a desire to seek cosmetic procedures. It interferes with an individual’s life and can trigger or aggravate body dysmorphic disorder.”
While several tools have been validated in cosmetic settings to screen for BDD, such as the 9-item Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Dermatology questionnaire, the 7-item Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Aesthetic Surgery questionnaire, the Cosmetic Procedure Screening Questionnaire, and the Body Dysmorphic Disorder Symptom Scale, no formal screening tools exist to identify zoom dysmorphia. To complicate matters, “identifying dysmorphic concerns in virtual settings can be challenging,” Dr. Kroumpouzos added. “This makes the recognition of zoom dysmorphia during telehealth visits even more difficult.”
Individuals who may have zoom dysmorphia may fear being misunderstood, judged, or ridiculed because of a perceived flaw in appearance, he said, making establishing rapport and eye contact difficult. “There’s a reticence and silence due to the individual’s avoidant characteristics,” he said. “Patients may become easily distracted or disengaged during telehealth visits in case of technical issues. Psychiatric comorbidities can mask symptoms related to dysmorphic concerns.”
To bridge this gap, Dr. Kroumpouzos and colleagues have proposed a screening tool, a questionnaire related to features of zoom dysmorphia, to facilitate recognition of zoom dysmorphia in virtual settings.
The first component consists of open-ended questions such as “Are you comfortable with being interviewed in a virtual appointment?” and “How do you feel about your appearance during virtual meetings?” Such questions “aim to start the dialogue, to facilitate the discussion with a patient who may be shy or avoidant,” Dr. Kroumpouzos explained.
The second component of the tool consists of questions more specific to screening for zoom dysmorphia, starting with “Are you concerned about facial flaws?” If the patient answers no, they don’t qualify for any others, he said. “But, if they answer yes to that question and yes to at least one more [question], they may have zoom dysmorphia.”
Other questions include, “Do you think that your face is not friendly to the camera?” “Do you hesitate to open the camera?” “Have you tried to hide or camouflage your flaw with your hands, hair, makeup, or clothing?” “Have you sought advice from others to improve your appearance or image?” “Do you often use the filter features of the video conferencing platform?” “Did you consider buying a new camera or equipment that helps improve your image?”
If the clinician deems the patient a candidate for the diagnosis of zoom dysmorphia, the tool recommends asking a BDD-focused question: “In the past month, have you been very concerned that there is something wrong with your physical appearance or the way one or more parts of your body look?” If the patient answers yes, “that individual should be invited to fill out a questionnaire specifically for BDD or come to the office for further evaluation,” Dr. Kroumpouzos said.
In his view, the brevity of the proposed screening tool makes it easy to incorporate into clinical practice, and the “yes or no” questions are practical. “It is crucial to elicit the presence of zoom dysmorphia in its early stage,” he said. “Zoom dysmorphia may trigger an increase in BDD, [so] it is essential to identify the presence of BDD in zoom dysmorphia sufferers and treat it appropriately.”
Dr. Kroumpouzos reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — , according to George Kroumpouzos, MD, PhD, who, with colleagues, recently proposed a screening tool to help identify patients with zoom dysmorphia.
The term, coined in 2020 by dermatologist Shadi Kourosh, MD, MPH, and colleagues at Harvard Medical School, Boston, refers to an altered or skewed negative perception of one’s body image that results from spending extended amounts of time on video calls. Speaking at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Kroumpouzos, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Brown University, Providence Rhode Island, explained that most people believe that zoom dysmorphia falls within the spectrum of body dysmorphic disorder (BDD). He described zoom dysmorphia as “a facial dysmorphia triggered or aggravated by frequent virtual meetings. Frequent use of videoconferencing platforms is linked to a distorted perception of facial images, which leads to dysmorphic concerns.”
Individuals with zoom dysmorphia tend to scrutinize their facial features and fixate on what they think needs to improve, he continued. They experience anxiety about attending video conferences with the camera on and feel pressured to appear perfect before virtual meetings. “They find facial flaws during virtual meetings, and they believe others notice their perceived flaws,” he said. “This all has drastic effects on body dissatisfaction and self-esteem, which leads to a desire to seek cosmetic procedures. It interferes with an individual’s life and can trigger or aggravate body dysmorphic disorder.”
While several tools have been validated in cosmetic settings to screen for BDD, such as the 9-item Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Dermatology questionnaire, the 7-item Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Aesthetic Surgery questionnaire, the Cosmetic Procedure Screening Questionnaire, and the Body Dysmorphic Disorder Symptom Scale, no formal screening tools exist to identify zoom dysmorphia. To complicate matters, “identifying dysmorphic concerns in virtual settings can be challenging,” Dr. Kroumpouzos added. “This makes the recognition of zoom dysmorphia during telehealth visits even more difficult.”
Individuals who may have zoom dysmorphia may fear being misunderstood, judged, or ridiculed because of a perceived flaw in appearance, he said, making establishing rapport and eye contact difficult. “There’s a reticence and silence due to the individual’s avoidant characteristics,” he said. “Patients may become easily distracted or disengaged during telehealth visits in case of technical issues. Psychiatric comorbidities can mask symptoms related to dysmorphic concerns.”
To bridge this gap, Dr. Kroumpouzos and colleagues have proposed a screening tool, a questionnaire related to features of zoom dysmorphia, to facilitate recognition of zoom dysmorphia in virtual settings.
The first component consists of open-ended questions such as “Are you comfortable with being interviewed in a virtual appointment?” and “How do you feel about your appearance during virtual meetings?” Such questions “aim to start the dialogue, to facilitate the discussion with a patient who may be shy or avoidant,” Dr. Kroumpouzos explained.
The second component of the tool consists of questions more specific to screening for zoom dysmorphia, starting with “Are you concerned about facial flaws?” If the patient answers no, they don’t qualify for any others, he said. “But, if they answer yes to that question and yes to at least one more [question], they may have zoom dysmorphia.”
Other questions include, “Do you think that your face is not friendly to the camera?” “Do you hesitate to open the camera?” “Have you tried to hide or camouflage your flaw with your hands, hair, makeup, or clothing?” “Have you sought advice from others to improve your appearance or image?” “Do you often use the filter features of the video conferencing platform?” “Did you consider buying a new camera or equipment that helps improve your image?”
If the clinician deems the patient a candidate for the diagnosis of zoom dysmorphia, the tool recommends asking a BDD-focused question: “In the past month, have you been very concerned that there is something wrong with your physical appearance or the way one or more parts of your body look?” If the patient answers yes, “that individual should be invited to fill out a questionnaire specifically for BDD or come to the office for further evaluation,” Dr. Kroumpouzos said.
In his view, the brevity of the proposed screening tool makes it easy to incorporate into clinical practice, and the “yes or no” questions are practical. “It is crucial to elicit the presence of zoom dysmorphia in its early stage,” he said. “Zoom dysmorphia may trigger an increase in BDD, [so] it is essential to identify the presence of BDD in zoom dysmorphia sufferers and treat it appropriately.”
Dr. Kroumpouzos reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM AAD 2024
Real-World HDV Study Characterizes Responses to Bulevirtide
, based on real-world experience.
These findings suggest that longer follow-up is needed to determine the optimal treatment duration for bulevirtide monotherapy, reported lead author Alexander Killer, MD, of Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, Germany, and colleagues.
Bulevirtide was conditionally approved by the European Medicines Agency in 2020 and is on track for full marketing approval in Europe, but it remains unavailable in the United States, where Gilead, the manufacturer, has faced regulatory hurdles.
In the MYR202 and 301 clinical trials, bulevirtide significantly reduced HDV-RNA levels in 54% of patients after 24 weeks, and reduced viremia while normalizing ALT in 48% of patients after 48 weeks.
“Given its standalone status and good treatment tolerance even in patients with compensated cirrhosis, this represents a step change in the treatment of HDV-coinfected individuals,” Dr. Killer and colleagues wrote in Gastro Hep Advances.
Yet dynamics of response and clinical predictors of treatment outcome remain unclear, prompting Dr. Killer and colleagues to conduct the present retrospective study. The dataset included 15 patients who received bulevirtide for at least 1 year at a single center in Germany.
The analysis focused on monthly changes in biochemical and virologic parameters. The investigators also screened for clinical factors that might predict responses to therapy.
Treatment response rate and safety profile aligned with data from clinical trials, suggesting that bulevirtide is safe and effective in a real-world setting.
Patients typically achieved ALT normalization 2-6 months into therapy, followed by virologic response at least 6 months after starting treatment, with one-third of patients requiring at least 1 year to achieve HDV-RNA negativity.
“Of note, normalization of ALT under bulevirtide treatment occurs earlier than the decline of HDV-RNA levels, which contrasts with the response seen to nucleos(t)ide analog treatment in hepatitis B,” the investigators wrote. They suggested that this may be due to bulevirtide’s distinct mechanism of action.
Severe hepatitis was associated with lower response rates in the first year. Possible predictors of delayed response included low body mass index and high alpha-fetoprotein.
Of note, two patients had ALT normalization without virologic response.
“It is unclear whether these patients actually have worse outcomes in terms of overall success than patients with a combined response, especially since these patients experienced a decline of more than 1 log,” Dr. Killer and colleagues wrote, noting that a 1 log reduction is considered an intermediate virologic response, and hepatitis B virus (HBV) studies have shown that severe liver events are prevented by early ALT normalization. “Therefore, it does not seem appropriate to categorize patients with biochemical responses as ‘treatment nonresponders’ [according to FDA criteria].”
The investigators called for longer observational studies to determine the optimal duration of bulevirtide monotherapy.
This study was funded by the Ministry of Culture and Science of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia and the German Research Foundation. The investigators disclosed relationships with Novartis, GSK, AbbVie, and others.
, based on real-world experience.
These findings suggest that longer follow-up is needed to determine the optimal treatment duration for bulevirtide monotherapy, reported lead author Alexander Killer, MD, of Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, Germany, and colleagues.
Bulevirtide was conditionally approved by the European Medicines Agency in 2020 and is on track for full marketing approval in Europe, but it remains unavailable in the United States, where Gilead, the manufacturer, has faced regulatory hurdles.
In the MYR202 and 301 clinical trials, bulevirtide significantly reduced HDV-RNA levels in 54% of patients after 24 weeks, and reduced viremia while normalizing ALT in 48% of patients after 48 weeks.
“Given its standalone status and good treatment tolerance even in patients with compensated cirrhosis, this represents a step change in the treatment of HDV-coinfected individuals,” Dr. Killer and colleagues wrote in Gastro Hep Advances.
Yet dynamics of response and clinical predictors of treatment outcome remain unclear, prompting Dr. Killer and colleagues to conduct the present retrospective study. The dataset included 15 patients who received bulevirtide for at least 1 year at a single center in Germany.
The analysis focused on monthly changes in biochemical and virologic parameters. The investigators also screened for clinical factors that might predict responses to therapy.
Treatment response rate and safety profile aligned with data from clinical trials, suggesting that bulevirtide is safe and effective in a real-world setting.
Patients typically achieved ALT normalization 2-6 months into therapy, followed by virologic response at least 6 months after starting treatment, with one-third of patients requiring at least 1 year to achieve HDV-RNA negativity.
“Of note, normalization of ALT under bulevirtide treatment occurs earlier than the decline of HDV-RNA levels, which contrasts with the response seen to nucleos(t)ide analog treatment in hepatitis B,” the investigators wrote. They suggested that this may be due to bulevirtide’s distinct mechanism of action.
Severe hepatitis was associated with lower response rates in the first year. Possible predictors of delayed response included low body mass index and high alpha-fetoprotein.
Of note, two patients had ALT normalization without virologic response.
“It is unclear whether these patients actually have worse outcomes in terms of overall success than patients with a combined response, especially since these patients experienced a decline of more than 1 log,” Dr. Killer and colleagues wrote, noting that a 1 log reduction is considered an intermediate virologic response, and hepatitis B virus (HBV) studies have shown that severe liver events are prevented by early ALT normalization. “Therefore, it does not seem appropriate to categorize patients with biochemical responses as ‘treatment nonresponders’ [according to FDA criteria].”
The investigators called for longer observational studies to determine the optimal duration of bulevirtide monotherapy.
This study was funded by the Ministry of Culture and Science of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia and the German Research Foundation. The investigators disclosed relationships with Novartis, GSK, AbbVie, and others.
, based on real-world experience.
These findings suggest that longer follow-up is needed to determine the optimal treatment duration for bulevirtide monotherapy, reported lead author Alexander Killer, MD, of Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, Germany, and colleagues.
Bulevirtide was conditionally approved by the European Medicines Agency in 2020 and is on track for full marketing approval in Europe, but it remains unavailable in the United States, where Gilead, the manufacturer, has faced regulatory hurdles.
In the MYR202 and 301 clinical trials, bulevirtide significantly reduced HDV-RNA levels in 54% of patients after 24 weeks, and reduced viremia while normalizing ALT in 48% of patients after 48 weeks.
“Given its standalone status and good treatment tolerance even in patients with compensated cirrhosis, this represents a step change in the treatment of HDV-coinfected individuals,” Dr. Killer and colleagues wrote in Gastro Hep Advances.
Yet dynamics of response and clinical predictors of treatment outcome remain unclear, prompting Dr. Killer and colleagues to conduct the present retrospective study. The dataset included 15 patients who received bulevirtide for at least 1 year at a single center in Germany.
The analysis focused on monthly changes in biochemical and virologic parameters. The investigators also screened for clinical factors that might predict responses to therapy.
Treatment response rate and safety profile aligned with data from clinical trials, suggesting that bulevirtide is safe and effective in a real-world setting.
Patients typically achieved ALT normalization 2-6 months into therapy, followed by virologic response at least 6 months after starting treatment, with one-third of patients requiring at least 1 year to achieve HDV-RNA negativity.
“Of note, normalization of ALT under bulevirtide treatment occurs earlier than the decline of HDV-RNA levels, which contrasts with the response seen to nucleos(t)ide analog treatment in hepatitis B,” the investigators wrote. They suggested that this may be due to bulevirtide’s distinct mechanism of action.
Severe hepatitis was associated with lower response rates in the first year. Possible predictors of delayed response included low body mass index and high alpha-fetoprotein.
Of note, two patients had ALT normalization without virologic response.
“It is unclear whether these patients actually have worse outcomes in terms of overall success than patients with a combined response, especially since these patients experienced a decline of more than 1 log,” Dr. Killer and colleagues wrote, noting that a 1 log reduction is considered an intermediate virologic response, and hepatitis B virus (HBV) studies have shown that severe liver events are prevented by early ALT normalization. “Therefore, it does not seem appropriate to categorize patients with biochemical responses as ‘treatment nonresponders’ [according to FDA criteria].”
The investigators called for longer observational studies to determine the optimal duration of bulevirtide monotherapy.
This study was funded by the Ministry of Culture and Science of the State of North Rhine-Westphalia and the German Research Foundation. The investigators disclosed relationships with Novartis, GSK, AbbVie, and others.
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES
Less Than 50% of Accelerated Approvals Show Clinical Benefit
despite being on the US market for more than 5 years, according to a new study.
Under the program, drugs are approved for marketing if they show benefit in surrogate markers thought to indicate efficacy. Progression-free survival, tumor response, and duration of response are the most used surrogate markers for accelerated approvals of cancer drugs. These are based largely on imaging studies that show either a stop in growth in the case of progression-free survival or tumor shrinkage in the case of tumor response.
Following accelerated approvals, companies are then supposed to show actual clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The problem with relying on surrogate markers for drug approvals is that they don’t always correlate with longer survival or improved quality of life, said Edward Cliff, MBBS, who presented the findings at the American Association for Cancer Research 2024 annual meeting (abstract 918). The study was also published in JAMA to coincide with the meeting presentation.
In some cancers, these markers work well, but in others they don’t, said Dr. Cliff, a hematology trainee at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, when the work was conducted, and now a hematology fellow at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
To determine whether cancer drugs granted accelerated approval ultimately show an overall survival or quality of life benefit, researchers reviewed 46 cancer drugs granted accelerated approvals between 2013 and 2017. Twenty (43%) were granted full approval after demonstrating survival or quality-of-life benefits.
Nine, however, were converted to full approvals on the basis of surrogate markers. These include a full approval for pembrolizumab in previously treated recurrent or refractory head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and a full approval for nivolumab for refractory locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, both based on tumor response rate and duration of response.
Of the remaining 17 drugs evaluated in the trial, 10 have been withdrawn and seven do not yet have confirmatory trial results.
The reliance on surrogate markers means that these drugs are used for treatment, covered by insurance, and added to guidelines — all without solid evidence of real-world clinical benefit, said Dr. Cliff.
However, the goal should not be to do away with the accelerated approval process, because it sometimes does deliver powerful agents to patients quickly. Instead, Dr. Cliff told this news organization, the system needs to be improved so that “we keep the speed while getting certainty around clinical benefits” with robust and timely confirmatory trials.
In the meantime, “clinicians should communicate with patients about any residual uncertainty of clinical benefit when they offer novel therapies,” Dr. Cliff explained. “It’s important for them to have the information.”
There has been some progress on the issue. In December 2022, the US Congress passed the Food and Drug Administration Omnibus Reform Act. Among other things, the Act requires companies to have confirmation trials underway as a condition for accelerated approval, and to provide regular reports on their progress. The Act also expedites the withdrawal process for drugs that don’t show a benefit.
The Act has been put to the test twice recently. In February, FDA used the expedited process to remove the multiple myeloma drug melphalan flufenamide from the market. Melphalan flufenamide hadn’t been sold in the US for quite some time, so the process wasn’t contentious.
In March, Regeneron announced that accelerated approval for the follicular and diffuse B cell lymphoma drug odronextamab has been delayed pending enrollment in a confirmatory trial.
“There have been some promising steps,” Dr. Cliff said, but much work needs to be done.
Study moderator Shivaani Kummar, MD, agreed, noting that “the data is showing that the confirmatory trials aren’t happening at the pace which they should.”
But the solution is not to curtail approvals; it’s to make sure that accelerated approval commitments are met, said Dr. Kummar.
Still, “as a practicing oncologist, I welcome the accelerated pathway,” Dr. Kummar, a medical oncologist/hematologist at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “I want the availability to my patients.”
Having drugs approved on the basis of surrogate markers doesn’t necessarily mean patients are getting ineffective therapies, Dr. Kummar noted. For instance, if an agent just shrinks the tumor, it can sometimes still be “a huge clinical benefit because it can take the symptoms away.”
As for prescribing drugs based on accelerated approvals, she said she tells her patients that trials have been promising, but we don’t know what the long-term effects are. She and her patient then make a decision together.
The study was funded by Arnold Ventures. Dr. Kummar reported support from several companies, including Bayer, Gilead, and others. Dr. Cliff had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
despite being on the US market for more than 5 years, according to a new study.
Under the program, drugs are approved for marketing if they show benefit in surrogate markers thought to indicate efficacy. Progression-free survival, tumor response, and duration of response are the most used surrogate markers for accelerated approvals of cancer drugs. These are based largely on imaging studies that show either a stop in growth in the case of progression-free survival or tumor shrinkage in the case of tumor response.
Following accelerated approvals, companies are then supposed to show actual clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The problem with relying on surrogate markers for drug approvals is that they don’t always correlate with longer survival or improved quality of life, said Edward Cliff, MBBS, who presented the findings at the American Association for Cancer Research 2024 annual meeting (abstract 918). The study was also published in JAMA to coincide with the meeting presentation.
In some cancers, these markers work well, but in others they don’t, said Dr. Cliff, a hematology trainee at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, when the work was conducted, and now a hematology fellow at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
To determine whether cancer drugs granted accelerated approval ultimately show an overall survival or quality of life benefit, researchers reviewed 46 cancer drugs granted accelerated approvals between 2013 and 2017. Twenty (43%) were granted full approval after demonstrating survival or quality-of-life benefits.
Nine, however, were converted to full approvals on the basis of surrogate markers. These include a full approval for pembrolizumab in previously treated recurrent or refractory head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and a full approval for nivolumab for refractory locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, both based on tumor response rate and duration of response.
Of the remaining 17 drugs evaluated in the trial, 10 have been withdrawn and seven do not yet have confirmatory trial results.
The reliance on surrogate markers means that these drugs are used for treatment, covered by insurance, and added to guidelines — all without solid evidence of real-world clinical benefit, said Dr. Cliff.
However, the goal should not be to do away with the accelerated approval process, because it sometimes does deliver powerful agents to patients quickly. Instead, Dr. Cliff told this news organization, the system needs to be improved so that “we keep the speed while getting certainty around clinical benefits” with robust and timely confirmatory trials.
In the meantime, “clinicians should communicate with patients about any residual uncertainty of clinical benefit when they offer novel therapies,” Dr. Cliff explained. “It’s important for them to have the information.”
There has been some progress on the issue. In December 2022, the US Congress passed the Food and Drug Administration Omnibus Reform Act. Among other things, the Act requires companies to have confirmation trials underway as a condition for accelerated approval, and to provide regular reports on their progress. The Act also expedites the withdrawal process for drugs that don’t show a benefit.
The Act has been put to the test twice recently. In February, FDA used the expedited process to remove the multiple myeloma drug melphalan flufenamide from the market. Melphalan flufenamide hadn’t been sold in the US for quite some time, so the process wasn’t contentious.
In March, Regeneron announced that accelerated approval for the follicular and diffuse B cell lymphoma drug odronextamab has been delayed pending enrollment in a confirmatory trial.
“There have been some promising steps,” Dr. Cliff said, but much work needs to be done.
Study moderator Shivaani Kummar, MD, agreed, noting that “the data is showing that the confirmatory trials aren’t happening at the pace which they should.”
But the solution is not to curtail approvals; it’s to make sure that accelerated approval commitments are met, said Dr. Kummar.
Still, “as a practicing oncologist, I welcome the accelerated pathway,” Dr. Kummar, a medical oncologist/hematologist at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “I want the availability to my patients.”
Having drugs approved on the basis of surrogate markers doesn’t necessarily mean patients are getting ineffective therapies, Dr. Kummar noted. For instance, if an agent just shrinks the tumor, it can sometimes still be “a huge clinical benefit because it can take the symptoms away.”
As for prescribing drugs based on accelerated approvals, she said she tells her patients that trials have been promising, but we don’t know what the long-term effects are. She and her patient then make a decision together.
The study was funded by Arnold Ventures. Dr. Kummar reported support from several companies, including Bayer, Gilead, and others. Dr. Cliff had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
despite being on the US market for more than 5 years, according to a new study.
Under the program, drugs are approved for marketing if they show benefit in surrogate markers thought to indicate efficacy. Progression-free survival, tumor response, and duration of response are the most used surrogate markers for accelerated approvals of cancer drugs. These are based largely on imaging studies that show either a stop in growth in the case of progression-free survival or tumor shrinkage in the case of tumor response.
Following accelerated approvals, companies are then supposed to show actual clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The problem with relying on surrogate markers for drug approvals is that they don’t always correlate with longer survival or improved quality of life, said Edward Cliff, MBBS, who presented the findings at the American Association for Cancer Research 2024 annual meeting (abstract 918). The study was also published in JAMA to coincide with the meeting presentation.
In some cancers, these markers work well, but in others they don’t, said Dr. Cliff, a hematology trainee at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, when the work was conducted, and now a hematology fellow at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
To determine whether cancer drugs granted accelerated approval ultimately show an overall survival or quality of life benefit, researchers reviewed 46 cancer drugs granted accelerated approvals between 2013 and 2017. Twenty (43%) were granted full approval after demonstrating survival or quality-of-life benefits.
Nine, however, were converted to full approvals on the basis of surrogate markers. These include a full approval for pembrolizumab in previously treated recurrent or refractory head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and a full approval for nivolumab for refractory locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, both based on tumor response rate and duration of response.
Of the remaining 17 drugs evaluated in the trial, 10 have been withdrawn and seven do not yet have confirmatory trial results.
The reliance on surrogate markers means that these drugs are used for treatment, covered by insurance, and added to guidelines — all without solid evidence of real-world clinical benefit, said Dr. Cliff.
However, the goal should not be to do away with the accelerated approval process, because it sometimes does deliver powerful agents to patients quickly. Instead, Dr. Cliff told this news organization, the system needs to be improved so that “we keep the speed while getting certainty around clinical benefits” with robust and timely confirmatory trials.
In the meantime, “clinicians should communicate with patients about any residual uncertainty of clinical benefit when they offer novel therapies,” Dr. Cliff explained. “It’s important for them to have the information.”
There has been some progress on the issue. In December 2022, the US Congress passed the Food and Drug Administration Omnibus Reform Act. Among other things, the Act requires companies to have confirmation trials underway as a condition for accelerated approval, and to provide regular reports on their progress. The Act also expedites the withdrawal process for drugs that don’t show a benefit.
The Act has been put to the test twice recently. In February, FDA used the expedited process to remove the multiple myeloma drug melphalan flufenamide from the market. Melphalan flufenamide hadn’t been sold in the US for quite some time, so the process wasn’t contentious.
In March, Regeneron announced that accelerated approval for the follicular and diffuse B cell lymphoma drug odronextamab has been delayed pending enrollment in a confirmatory trial.
“There have been some promising steps,” Dr. Cliff said, but much work needs to be done.
Study moderator Shivaani Kummar, MD, agreed, noting that “the data is showing that the confirmatory trials aren’t happening at the pace which they should.”
But the solution is not to curtail approvals; it’s to make sure that accelerated approval commitments are met, said Dr. Kummar.
Still, “as a practicing oncologist, I welcome the accelerated pathway,” Dr. Kummar, a medical oncologist/hematologist at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, told this news organization. “I want the availability to my patients.”
Having drugs approved on the basis of surrogate markers doesn’t necessarily mean patients are getting ineffective therapies, Dr. Kummar noted. For instance, if an agent just shrinks the tumor, it can sometimes still be “a huge clinical benefit because it can take the symptoms away.”
As for prescribing drugs based on accelerated approvals, she said she tells her patients that trials have been promising, but we don’t know what the long-term effects are. She and her patient then make a decision together.
The study was funded by Arnold Ventures. Dr. Kummar reported support from several companies, including Bayer, Gilead, and others. Dr. Cliff had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Three Distinct MS Subtypes Identified
, a new study suggests.
With further validation, determining a patient’s blood “immune signature,” or endophenotype, before starting immunomodulatory therapy may help predict clinical disease trajectories and lead to more personalized treatment decisions, investigators said.
“The characterization of an endophenotype at timepoints of diagnosis will help to determine likely trajectory of the disease course but also will help to refine the chosen immune therapy,” said Heinz Wiendl, MD, professor and chair, Department of Neurology, University of Münster, Germany. “This is a rationale way of precision medicine for the future.”
The study was published online in Science Translational Medicine.
Degenerative and Inflammatory Subtypes
MS is a highly heterogeneous disorder with different clinical manifestations and disease trajectories, making it a challenge to manage. Whether this heterogeneity is reflected by discrete immune signatures in the blood has been unclear.
To investigate, Dr. Wiendl and a multicenter team comprehensively analyzed the immunological properties of blood samples collected from 309 patients with early MS and an independent validation cohort of 232 patients with early MS.
In both cohorts, they found that cellular immune signatures split into three distinct immunological endophenotypes, dubbed E1, E2, and E3.
E1 is characterized by alterations in the CD4 T-cell compartment, with increases in inflammatory cytokines, namely interleukin-17A (IL-17A), IL-22, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, as well as earlier structural brain damage, more severe disease, and higher disability.
Alterations in natural killer cells are a hallmark of the E2 subtype, while alterations in the CD8 T cells dominate the E3 subtype.
The different subtypes were associated with distinct clinical disease trajectories. E3 patients displayed a pattern reflecting higher inflammatory disease activity, as illustrated by a higher relapse rate (≥ 2) within the first year from baseline and more frequent use of highly active disease-modifying therapies as first immunomodulatory treatment.
E3 patients also had higher numbers of gadolinium-enhancing lesions at baseline, a higher conversion rate from clinically isolated syndrome to relapsing-remitting MS, and rapid disability accrual within 2 years after baseline.
This endophenotype was also associated with an increase in total cell numbers within the cerebrospinal fluid and intrathecal immunoglobulin (Ig) G synthesis at baseline.
E1 patients had a higher degree of early structural brain damage and disease severity, including disability and impaired evident at baseline, and increased serum neurofilament light and increased intrathecal IgM synthesis at baseline.
“According to these different patterns of disease trajectories, we therefore termed these subsets degenerative E1 and inflammatory E3. Overall, although some of the clinical and paraclinical parameters partially overlapped, our analysis reveals that distinct immunological endophenotypes might have predictive value with regard to clinically relevant disease trajectories,” the researchers wrote.
Toward Personalized Care
In addition, during up to 4-year follow-up of some patients, they observed that patients with the inflammatory E3 endophenotype treated with interferon-beta exhibited higher disease progression and MRI activity relative to E3 patients receiving other therapies. These differential effects of interferon-beta were not observed in the other endophenotypes.
With further study and refinement, the hope is to make this test a “clinical reality,” Dr. Wiendl said.
Commenting on the findings, Kimberly O’Neill, MD, clinical instructor, Department of Neurology, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York City, noted that people with MS can have “a broad variety of disease course and outcomes ranging from mild to a very severe and life-altering disease course. At this point, we are not great at predicting who is going to be on which path and also which medication is right for each patient.
“Research like this gives us hope for a more personalized precision medicine in MS,” said Dr. O’Neill, who was not part of the study. “The ideal world would be to have a blood test that could tell their disease course and which treatments will work for an individual patient, but we are certainly not there yet.”
Also providing an outside perspective, Mary Rensel, MD, director of wellness and pediatric MS at the Cleveland Clinic Mellen Center for MS, Cleveland, said, “Precision medicine is our goal and dream in MS care — to be able to do a blood test and know what medicine a patient may or may not respond to and save them years of ongoing symptoms or the risk of disability. This study is a great start.”
Support for this research was provided by grants from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the German Research Council, and the Hermann and Lilly Schilling Foundation. Disclosures for study authors are listed with the original article. Dr. O’Neill and Dr. Rensel had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
With further validation, determining a patient’s blood “immune signature,” or endophenotype, before starting immunomodulatory therapy may help predict clinical disease trajectories and lead to more personalized treatment decisions, investigators said.
“The characterization of an endophenotype at timepoints of diagnosis will help to determine likely trajectory of the disease course but also will help to refine the chosen immune therapy,” said Heinz Wiendl, MD, professor and chair, Department of Neurology, University of Münster, Germany. “This is a rationale way of precision medicine for the future.”
The study was published online in Science Translational Medicine.
Degenerative and Inflammatory Subtypes
MS is a highly heterogeneous disorder with different clinical manifestations and disease trajectories, making it a challenge to manage. Whether this heterogeneity is reflected by discrete immune signatures in the blood has been unclear.
To investigate, Dr. Wiendl and a multicenter team comprehensively analyzed the immunological properties of blood samples collected from 309 patients with early MS and an independent validation cohort of 232 patients with early MS.
In both cohorts, they found that cellular immune signatures split into three distinct immunological endophenotypes, dubbed E1, E2, and E3.
E1 is characterized by alterations in the CD4 T-cell compartment, with increases in inflammatory cytokines, namely interleukin-17A (IL-17A), IL-22, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, as well as earlier structural brain damage, more severe disease, and higher disability.
Alterations in natural killer cells are a hallmark of the E2 subtype, while alterations in the CD8 T cells dominate the E3 subtype.
The different subtypes were associated with distinct clinical disease trajectories. E3 patients displayed a pattern reflecting higher inflammatory disease activity, as illustrated by a higher relapse rate (≥ 2) within the first year from baseline and more frequent use of highly active disease-modifying therapies as first immunomodulatory treatment.
E3 patients also had higher numbers of gadolinium-enhancing lesions at baseline, a higher conversion rate from clinically isolated syndrome to relapsing-remitting MS, and rapid disability accrual within 2 years after baseline.
This endophenotype was also associated with an increase in total cell numbers within the cerebrospinal fluid and intrathecal immunoglobulin (Ig) G synthesis at baseline.
E1 patients had a higher degree of early structural brain damage and disease severity, including disability and impaired evident at baseline, and increased serum neurofilament light and increased intrathecal IgM synthesis at baseline.
“According to these different patterns of disease trajectories, we therefore termed these subsets degenerative E1 and inflammatory E3. Overall, although some of the clinical and paraclinical parameters partially overlapped, our analysis reveals that distinct immunological endophenotypes might have predictive value with regard to clinically relevant disease trajectories,” the researchers wrote.
Toward Personalized Care
In addition, during up to 4-year follow-up of some patients, they observed that patients with the inflammatory E3 endophenotype treated with interferon-beta exhibited higher disease progression and MRI activity relative to E3 patients receiving other therapies. These differential effects of interferon-beta were not observed in the other endophenotypes.
With further study and refinement, the hope is to make this test a “clinical reality,” Dr. Wiendl said.
Commenting on the findings, Kimberly O’Neill, MD, clinical instructor, Department of Neurology, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York City, noted that people with MS can have “a broad variety of disease course and outcomes ranging from mild to a very severe and life-altering disease course. At this point, we are not great at predicting who is going to be on which path and also which medication is right for each patient.
“Research like this gives us hope for a more personalized precision medicine in MS,” said Dr. O’Neill, who was not part of the study. “The ideal world would be to have a blood test that could tell their disease course and which treatments will work for an individual patient, but we are certainly not there yet.”
Also providing an outside perspective, Mary Rensel, MD, director of wellness and pediatric MS at the Cleveland Clinic Mellen Center for MS, Cleveland, said, “Precision medicine is our goal and dream in MS care — to be able to do a blood test and know what medicine a patient may or may not respond to and save them years of ongoing symptoms or the risk of disability. This study is a great start.”
Support for this research was provided by grants from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the German Research Council, and the Hermann and Lilly Schilling Foundation. Disclosures for study authors are listed with the original article. Dr. O’Neill and Dr. Rensel had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
With further validation, determining a patient’s blood “immune signature,” or endophenotype, before starting immunomodulatory therapy may help predict clinical disease trajectories and lead to more personalized treatment decisions, investigators said.
“The characterization of an endophenotype at timepoints of diagnosis will help to determine likely trajectory of the disease course but also will help to refine the chosen immune therapy,” said Heinz Wiendl, MD, professor and chair, Department of Neurology, University of Münster, Germany. “This is a rationale way of precision medicine for the future.”
The study was published online in Science Translational Medicine.
Degenerative and Inflammatory Subtypes
MS is a highly heterogeneous disorder with different clinical manifestations and disease trajectories, making it a challenge to manage. Whether this heterogeneity is reflected by discrete immune signatures in the blood has been unclear.
To investigate, Dr. Wiendl and a multicenter team comprehensively analyzed the immunological properties of blood samples collected from 309 patients with early MS and an independent validation cohort of 232 patients with early MS.
In both cohorts, they found that cellular immune signatures split into three distinct immunological endophenotypes, dubbed E1, E2, and E3.
E1 is characterized by alterations in the CD4 T-cell compartment, with increases in inflammatory cytokines, namely interleukin-17A (IL-17A), IL-22, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, as well as earlier structural brain damage, more severe disease, and higher disability.
Alterations in natural killer cells are a hallmark of the E2 subtype, while alterations in the CD8 T cells dominate the E3 subtype.
The different subtypes were associated with distinct clinical disease trajectories. E3 patients displayed a pattern reflecting higher inflammatory disease activity, as illustrated by a higher relapse rate (≥ 2) within the first year from baseline and more frequent use of highly active disease-modifying therapies as first immunomodulatory treatment.
E3 patients also had higher numbers of gadolinium-enhancing lesions at baseline, a higher conversion rate from clinically isolated syndrome to relapsing-remitting MS, and rapid disability accrual within 2 years after baseline.
This endophenotype was also associated with an increase in total cell numbers within the cerebrospinal fluid and intrathecal immunoglobulin (Ig) G synthesis at baseline.
E1 patients had a higher degree of early structural brain damage and disease severity, including disability and impaired evident at baseline, and increased serum neurofilament light and increased intrathecal IgM synthesis at baseline.
“According to these different patterns of disease trajectories, we therefore termed these subsets degenerative E1 and inflammatory E3. Overall, although some of the clinical and paraclinical parameters partially overlapped, our analysis reveals that distinct immunological endophenotypes might have predictive value with regard to clinically relevant disease trajectories,” the researchers wrote.
Toward Personalized Care
In addition, during up to 4-year follow-up of some patients, they observed that patients with the inflammatory E3 endophenotype treated with interferon-beta exhibited higher disease progression and MRI activity relative to E3 patients receiving other therapies. These differential effects of interferon-beta were not observed in the other endophenotypes.
With further study and refinement, the hope is to make this test a “clinical reality,” Dr. Wiendl said.
Commenting on the findings, Kimberly O’Neill, MD, clinical instructor, Department of Neurology, NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York City, noted that people with MS can have “a broad variety of disease course and outcomes ranging from mild to a very severe and life-altering disease course. At this point, we are not great at predicting who is going to be on which path and also which medication is right for each patient.
“Research like this gives us hope for a more personalized precision medicine in MS,” said Dr. O’Neill, who was not part of the study. “The ideal world would be to have a blood test that could tell their disease course and which treatments will work for an individual patient, but we are certainly not there yet.”
Also providing an outside perspective, Mary Rensel, MD, director of wellness and pediatric MS at the Cleveland Clinic Mellen Center for MS, Cleveland, said, “Precision medicine is our goal and dream in MS care — to be able to do a blood test and know what medicine a patient may or may not respond to and save them years of ongoing symptoms or the risk of disability. This study is a great start.”
Support for this research was provided by grants from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the German Research Council, and the Hermann and Lilly Schilling Foundation. Disclosures for study authors are listed with the original article. Dr. O’Neill and Dr. Rensel had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
Combo Therapy Prolongs Survival in Gastric Cancer Patients, Regardless of PD-L1 Expression
, according to a new study.
Jiafu Ji, MD, PhD, presented this and other findings of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 COMPASSION-15 trial at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
“The consistent survival benefits across all prespecified PD-L1 expression cutoffs, particularly in patients with low PD-L1 expression, have significant implications for clinical practice by expanding treatment options, improving outcomes for patients with PD-L1–low tumors, influencing guidelines, and stimulating further research in advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma treatment,” said Dr. Ji, a principal investigator of this trial, in an interview.
Unmet Need
The incidence of gastric cancer is particularly high in China, but as Dr. Ji discussed in his talk, the treatment options for patients with advanced disease remain limited. Although the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the combination of PD-L1 inhibitors with chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer, not all patients respond to the treatment, explained Dr. Ji, who is a professor of gastrointestinal surgery and president of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Beijing Institute for Cancer Research in China.
He added that the combination of PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy has not yet been approved for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer in China, leaving chemotherapy as the only treatment option for Chinese patients.
Study Design
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of first-line cadonilimab plus standard chemotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, the authors of the COMPASSION-15 trial enrolled 610 patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic G/GEJ adenocarcinoma who had not received any prior treatments. PD-L1 expression status was not used to exclude patients from the trial.
In a press conference held at AACR 2024, Dr. Ji explained the study rationale, design, and endpoints. He said that patients with tumors without PD-L1 expression typically show little to no benefit from anti–PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and their treatment options are limited to chemotherapy.
“Testing the efficacy of this bispecific antibody in this patient population could provide an alternative treatment approach for them,” he added.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either cadonilimab (10 mg/kg every 3 weeks) plus chemotherapy or placebo plus chemotherapy. The primary endpoint of the study was overall survival (OS) in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, and secondary efficacy endpoints included OS, progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) in the ITT population, as well as in patients stratified by PD-L1 expression.
Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Improves OS
Interim analysis, conducted with a median follow-up of 18.69 months, showed a significant improvement in OS for the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy group compared with the chemotherapy-alone group, according to data presented at the press conference. The median OS was 15.0 months in the cadonilimab group versus 10.8 months in the placebo group, representing a 38% reduction in the risk of death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.62; 95% CI, 0.50-0.78, P < .001).
Yelena Y. Janjigian, MD, who not involved in COMPASSION-15, provided critique of the study, during another session at the meeting, in which she discussed the CheckMate 649 trial. She noted that, although the median OS of 15 months in the COMPASSION-15 study was slightly higher than the OS in the CheckMate 649 trial (approximately 14 months), comparing the results of two studies is challenging.
“In the COMPASSION-15 trial, chemotherapy was stopped after [4.5 months], and only 50% of patients received chemotherapy with subsequent treatment — this is not standard and may limit the comparison with other immunotherapy trials,” explained Dr. Janjigian, who is a gastrointestinal oncologist and was a principal investigator in the phase 3 CheckMate 649 immunotherapy trial for advanced gastric cancer.
Importantly, survival benefit with cadonilimab plus chemotherapy was observed across all prespecified PD-L1 expression levels, including in patients with low PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 combined positive score [CPS] less than 5%). In the low PD-L1 expression group (CPS less than 5%), the median OS was 14.8 months in the cadonilimab group compared with 11.8 months in the placebo group (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.95; P = .011).
“These positive survival outcomes when cadonilimab was combined with chemotherapy may be attributed to synergistic mechanisms of action, enhanced immune responses, modulation of the tumor microenvironment, and careful patient selection based on biomarker assessments,” noted Dr. Ji, during an interview. “Targeting multiple pathways using bispecific antibodies provides potential synergistic effects, enhancing anti-tumor activity and improving treatment outcomes.”
Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Reduces the Risk of Tumor Progression
In addition to prolonging OS, cadonilimab plus chemotherapy also provided superior PFS and ORR compared to placebo plus chemotherapy.
The median PFS was 7.0 months in the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy group, versus 5.3 months in the chemotherapy-only group (HR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.44-0.65, P < .001), and the ORR was 65.2% versus 48.9%, respectively. Furthermore, the duration of response was longer with cadonilimab plus chemotherapy than with placebo plus chemotherapy (8.8 versus 4.4 months, respectively).
Toxicities Associated With Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Are Manageable
The safety profile of the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy regimen was manageable, with grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events occurring in 71.8% of patients in the cadonilimab group and 60.5% of patients in the placebo group. No new safety signals were observed.
During an interview, Dr. Ji said that the most common adverse events were endocrine toxicity, skin toxicity, and lung toxicity. “These adverse events were managed through close monitoring, symptom management, and appropriate interventions based on the severity and nature of the toxicity experienced by patients,” he explained. He added that this toxicity profile of cadonilimab is similar to the toxicity profiles of approved PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors.
Implications — A New Treatment Paradigm for Advanced Gastric Cancer?
According to Dr. Ji, the interim results from the cadonilimab study suggest that this novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody, in combination with chemotherapy, could become a new standard first-line treatment option for patients with advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma, offering a significant survival advantage over chemotherapy alone, regardless of PD-L1 status.
“The ability of cadonilimab to improve survival outcomes, regardless of PD-L1 status, is a significant advancement, as we have struggled to find effective treatments for patients with low PD-L1 expression in this setting,” he said, during the interview.
Despite these promising findings, Dr. Janjigian highlighted that patient stratification in the COMPASSION-15 study is currently lacking. She explained that biomarkers such as MSI status, T-reg signatures, and HER-2 are important to consider according to data from the CheckMate 649 trial.
“Hazard ratios for patients with T-reg–high tumors were almost 0.6, independent of inflammatory status. These data suggest that we can maybe even cure some patients with PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibitors,” she noted.
She added that knowing the status of MSI and HER-2 is clinically important as it can inform clinicians whether they can avoid chemotherapy or add trastuzumab.
“Despite the suboptimal comparator arm, the study is very important and offers a rationale for dual PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade,” Dr. Janjigian concluded.
COMPASSION-15 was funded by Akeso Biopharma, Inc. Dr. Ji reported no relationships with entities whose primary business is producing, marketing, selling, reselling, or distributing healthcare products used by or on patients. Dr. Janjigian lists relationships with AbbVie, AmerisourceBergen Drug Corporation, Arcus Biosciences, Ask-Gene Pharma, Inc., Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd., Bayer, Bristol Myers, Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Pfizer, and many other companies, as well as the U.S. Department of Defense, National Cancer Institute, and others.
, according to a new study.
Jiafu Ji, MD, PhD, presented this and other findings of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 COMPASSION-15 trial at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
“The consistent survival benefits across all prespecified PD-L1 expression cutoffs, particularly in patients with low PD-L1 expression, have significant implications for clinical practice by expanding treatment options, improving outcomes for patients with PD-L1–low tumors, influencing guidelines, and stimulating further research in advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma treatment,” said Dr. Ji, a principal investigator of this trial, in an interview.
Unmet Need
The incidence of gastric cancer is particularly high in China, but as Dr. Ji discussed in his talk, the treatment options for patients with advanced disease remain limited. Although the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the combination of PD-L1 inhibitors with chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer, not all patients respond to the treatment, explained Dr. Ji, who is a professor of gastrointestinal surgery and president of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Beijing Institute for Cancer Research in China.
He added that the combination of PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy has not yet been approved for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer in China, leaving chemotherapy as the only treatment option for Chinese patients.
Study Design
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of first-line cadonilimab plus standard chemotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, the authors of the COMPASSION-15 trial enrolled 610 patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic G/GEJ adenocarcinoma who had not received any prior treatments. PD-L1 expression status was not used to exclude patients from the trial.
In a press conference held at AACR 2024, Dr. Ji explained the study rationale, design, and endpoints. He said that patients with tumors without PD-L1 expression typically show little to no benefit from anti–PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and their treatment options are limited to chemotherapy.
“Testing the efficacy of this bispecific antibody in this patient population could provide an alternative treatment approach for them,” he added.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either cadonilimab (10 mg/kg every 3 weeks) plus chemotherapy or placebo plus chemotherapy. The primary endpoint of the study was overall survival (OS) in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, and secondary efficacy endpoints included OS, progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) in the ITT population, as well as in patients stratified by PD-L1 expression.
Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Improves OS
Interim analysis, conducted with a median follow-up of 18.69 months, showed a significant improvement in OS for the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy group compared with the chemotherapy-alone group, according to data presented at the press conference. The median OS was 15.0 months in the cadonilimab group versus 10.8 months in the placebo group, representing a 38% reduction in the risk of death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.62; 95% CI, 0.50-0.78, P < .001).
Yelena Y. Janjigian, MD, who not involved in COMPASSION-15, provided critique of the study, during another session at the meeting, in which she discussed the CheckMate 649 trial. She noted that, although the median OS of 15 months in the COMPASSION-15 study was slightly higher than the OS in the CheckMate 649 trial (approximately 14 months), comparing the results of two studies is challenging.
“In the COMPASSION-15 trial, chemotherapy was stopped after [4.5 months], and only 50% of patients received chemotherapy with subsequent treatment — this is not standard and may limit the comparison with other immunotherapy trials,” explained Dr. Janjigian, who is a gastrointestinal oncologist and was a principal investigator in the phase 3 CheckMate 649 immunotherapy trial for advanced gastric cancer.
Importantly, survival benefit with cadonilimab plus chemotherapy was observed across all prespecified PD-L1 expression levels, including in patients with low PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 combined positive score [CPS] less than 5%). In the low PD-L1 expression group (CPS less than 5%), the median OS was 14.8 months in the cadonilimab group compared with 11.8 months in the placebo group (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.95; P = .011).
“These positive survival outcomes when cadonilimab was combined with chemotherapy may be attributed to synergistic mechanisms of action, enhanced immune responses, modulation of the tumor microenvironment, and careful patient selection based on biomarker assessments,” noted Dr. Ji, during an interview. “Targeting multiple pathways using bispecific antibodies provides potential synergistic effects, enhancing anti-tumor activity and improving treatment outcomes.”
Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Reduces the Risk of Tumor Progression
In addition to prolonging OS, cadonilimab plus chemotherapy also provided superior PFS and ORR compared to placebo plus chemotherapy.
The median PFS was 7.0 months in the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy group, versus 5.3 months in the chemotherapy-only group (HR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.44-0.65, P < .001), and the ORR was 65.2% versus 48.9%, respectively. Furthermore, the duration of response was longer with cadonilimab plus chemotherapy than with placebo plus chemotherapy (8.8 versus 4.4 months, respectively).
Toxicities Associated With Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Are Manageable
The safety profile of the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy regimen was manageable, with grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events occurring in 71.8% of patients in the cadonilimab group and 60.5% of patients in the placebo group. No new safety signals were observed.
During an interview, Dr. Ji said that the most common adverse events were endocrine toxicity, skin toxicity, and lung toxicity. “These adverse events were managed through close monitoring, symptom management, and appropriate interventions based on the severity and nature of the toxicity experienced by patients,” he explained. He added that this toxicity profile of cadonilimab is similar to the toxicity profiles of approved PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors.
Implications — A New Treatment Paradigm for Advanced Gastric Cancer?
According to Dr. Ji, the interim results from the cadonilimab study suggest that this novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody, in combination with chemotherapy, could become a new standard first-line treatment option for patients with advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma, offering a significant survival advantage over chemotherapy alone, regardless of PD-L1 status.
“The ability of cadonilimab to improve survival outcomes, regardless of PD-L1 status, is a significant advancement, as we have struggled to find effective treatments for patients with low PD-L1 expression in this setting,” he said, during the interview.
Despite these promising findings, Dr. Janjigian highlighted that patient stratification in the COMPASSION-15 study is currently lacking. She explained that biomarkers such as MSI status, T-reg signatures, and HER-2 are important to consider according to data from the CheckMate 649 trial.
“Hazard ratios for patients with T-reg–high tumors were almost 0.6, independent of inflammatory status. These data suggest that we can maybe even cure some patients with PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibitors,” she noted.
She added that knowing the status of MSI and HER-2 is clinically important as it can inform clinicians whether they can avoid chemotherapy or add trastuzumab.
“Despite the suboptimal comparator arm, the study is very important and offers a rationale for dual PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade,” Dr. Janjigian concluded.
COMPASSION-15 was funded by Akeso Biopharma, Inc. Dr. Ji reported no relationships with entities whose primary business is producing, marketing, selling, reselling, or distributing healthcare products used by or on patients. Dr. Janjigian lists relationships with AbbVie, AmerisourceBergen Drug Corporation, Arcus Biosciences, Ask-Gene Pharma, Inc., Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd., Bayer, Bristol Myers, Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Pfizer, and many other companies, as well as the U.S. Department of Defense, National Cancer Institute, and others.
, according to a new study.
Jiafu Ji, MD, PhD, presented this and other findings of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 COMPASSION-15 trial at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
“The consistent survival benefits across all prespecified PD-L1 expression cutoffs, particularly in patients with low PD-L1 expression, have significant implications for clinical practice by expanding treatment options, improving outcomes for patients with PD-L1–low tumors, influencing guidelines, and stimulating further research in advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma treatment,” said Dr. Ji, a principal investigator of this trial, in an interview.
Unmet Need
The incidence of gastric cancer is particularly high in China, but as Dr. Ji discussed in his talk, the treatment options for patients with advanced disease remain limited. Although the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the combination of PD-L1 inhibitors with chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer, not all patients respond to the treatment, explained Dr. Ji, who is a professor of gastrointestinal surgery and president of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Beijing Institute for Cancer Research in China.
He added that the combination of PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy has not yet been approved for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer in China, leaving chemotherapy as the only treatment option for Chinese patients.
Study Design
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of first-line cadonilimab plus standard chemotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, the authors of the COMPASSION-15 trial enrolled 610 patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic G/GEJ adenocarcinoma who had not received any prior treatments. PD-L1 expression status was not used to exclude patients from the trial.
In a press conference held at AACR 2024, Dr. Ji explained the study rationale, design, and endpoints. He said that patients with tumors without PD-L1 expression typically show little to no benefit from anti–PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and their treatment options are limited to chemotherapy.
“Testing the efficacy of this bispecific antibody in this patient population could provide an alternative treatment approach for them,” he added.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either cadonilimab (10 mg/kg every 3 weeks) plus chemotherapy or placebo plus chemotherapy. The primary endpoint of the study was overall survival (OS) in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population, and secondary efficacy endpoints included OS, progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) in the ITT population, as well as in patients stratified by PD-L1 expression.
Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Improves OS
Interim analysis, conducted with a median follow-up of 18.69 months, showed a significant improvement in OS for the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy group compared with the chemotherapy-alone group, according to data presented at the press conference. The median OS was 15.0 months in the cadonilimab group versus 10.8 months in the placebo group, representing a 38% reduction in the risk of death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.62; 95% CI, 0.50-0.78, P < .001).
Yelena Y. Janjigian, MD, who not involved in COMPASSION-15, provided critique of the study, during another session at the meeting, in which she discussed the CheckMate 649 trial. She noted that, although the median OS of 15 months in the COMPASSION-15 study was slightly higher than the OS in the CheckMate 649 trial (approximately 14 months), comparing the results of two studies is challenging.
“In the COMPASSION-15 trial, chemotherapy was stopped after [4.5 months], and only 50% of patients received chemotherapy with subsequent treatment — this is not standard and may limit the comparison with other immunotherapy trials,” explained Dr. Janjigian, who is a gastrointestinal oncologist and was a principal investigator in the phase 3 CheckMate 649 immunotherapy trial for advanced gastric cancer.
Importantly, survival benefit with cadonilimab plus chemotherapy was observed across all prespecified PD-L1 expression levels, including in patients with low PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 combined positive score [CPS] less than 5%). In the low PD-L1 expression group (CPS less than 5%), the median OS was 14.8 months in the cadonilimab group compared with 11.8 months in the placebo group (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.95; P = .011).
“These positive survival outcomes when cadonilimab was combined with chemotherapy may be attributed to synergistic mechanisms of action, enhanced immune responses, modulation of the tumor microenvironment, and careful patient selection based on biomarker assessments,” noted Dr. Ji, during an interview. “Targeting multiple pathways using bispecific antibodies provides potential synergistic effects, enhancing anti-tumor activity and improving treatment outcomes.”
Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Reduces the Risk of Tumor Progression
In addition to prolonging OS, cadonilimab plus chemotherapy also provided superior PFS and ORR compared to placebo plus chemotherapy.
The median PFS was 7.0 months in the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy group, versus 5.3 months in the chemotherapy-only group (HR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.44-0.65, P < .001), and the ORR was 65.2% versus 48.9%, respectively. Furthermore, the duration of response was longer with cadonilimab plus chemotherapy than with placebo plus chemotherapy (8.8 versus 4.4 months, respectively).
Toxicities Associated With Cadonilimab Plus Standard Chemotherapy Are Manageable
The safety profile of the cadonilimab plus chemotherapy regimen was manageable, with grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events occurring in 71.8% of patients in the cadonilimab group and 60.5% of patients in the placebo group. No new safety signals were observed.
During an interview, Dr. Ji said that the most common adverse events were endocrine toxicity, skin toxicity, and lung toxicity. “These adverse events were managed through close monitoring, symptom management, and appropriate interventions based on the severity and nature of the toxicity experienced by patients,” he explained. He added that this toxicity profile of cadonilimab is similar to the toxicity profiles of approved PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors.
Implications — A New Treatment Paradigm for Advanced Gastric Cancer?
According to Dr. Ji, the interim results from the cadonilimab study suggest that this novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody, in combination with chemotherapy, could become a new standard first-line treatment option for patients with advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma, offering a significant survival advantage over chemotherapy alone, regardless of PD-L1 status.
“The ability of cadonilimab to improve survival outcomes, regardless of PD-L1 status, is a significant advancement, as we have struggled to find effective treatments for patients with low PD-L1 expression in this setting,” he said, during the interview.
Despite these promising findings, Dr. Janjigian highlighted that patient stratification in the COMPASSION-15 study is currently lacking. She explained that biomarkers such as MSI status, T-reg signatures, and HER-2 are important to consider according to data from the CheckMate 649 trial.
“Hazard ratios for patients with T-reg–high tumors were almost 0.6, independent of inflammatory status. These data suggest that we can maybe even cure some patients with PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibitors,” she noted.
She added that knowing the status of MSI and HER-2 is clinically important as it can inform clinicians whether they can avoid chemotherapy or add trastuzumab.
“Despite the suboptimal comparator arm, the study is very important and offers a rationale for dual PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade,” Dr. Janjigian concluded.
COMPASSION-15 was funded by Akeso Biopharma, Inc. Dr. Ji reported no relationships with entities whose primary business is producing, marketing, selling, reselling, or distributing healthcare products used by or on patients. Dr. Janjigian lists relationships with AbbVie, AmerisourceBergen Drug Corporation, Arcus Biosciences, Ask-Gene Pharma, Inc., Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd., Bayer, Bristol Myers, Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Pfizer, and many other companies, as well as the U.S. Department of Defense, National Cancer Institute, and others.
FROM AACR 2024
Is A Patient Getting Under Your Skin? A Dermatologist Shares Tips for Coping
SAN DIEGO — In his role as chief medical officer for Ascension Medical Group–Texas, which employs about 1,000 physicians across every medical specialty,
At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Reichenberg, professor of dermatology at the University of Texas at Austin, shared several tips for managing such difficult patients:
Look for ‘red flags’ that raise concerns. This may include patients’ unrealistic expectations for a cure, “which could be because of their cultural or educational background,” he said. Difficult patients also may view physicians as enemies.
“They may quote legal jargon or threaten consequences if there is a bad outcome,” he explained. “They may say, ‘I’m a great reviewer on Yelp and I look forward to giving you a great Yelp review when we finish today.’ They may also have previously sued physicians, or they may tell you that their last physician was horrible.”
Shift into robot mode. In other words, don’t stray from your practice’s protocol by offering special treatment to difficult patients. For example, if a difficult patient shows up 15 minutes late and the office has a policy that patients should be rescheduled if they arrive 10 minutes late, “do not break that policy no matter what, because that’s your protocol,” he advised. “You also do not promise anything you don’t know or that nobody could know. If a difficult patient asks, ‘what is the statistical chance that I’ll get better with this treatment,’ you either say, ‘studies have shown that this is the exact percentage,’ or ‘I don’t know. We’re going to do our best.’”
Set expectations at the outset. “If I walk into the room and the nurse has been in there for 25 minutes doing the intake and I know it’s going to be a long visit, I’ll start by saying, ‘I have 8 minutes to see you today,’ ” Dr. Reichenberg said. “ ‘Whatever we don’t finish today we’ll have to do during a follow-up visit, so let’s please prioritize what we need to do.’ ” Sometimes he sets his smartphone alarm to 8 minutes and when the timer goes off, he’ll say, “I’m so sorry, but I have to go.” For talkative patients, he continued, “I’ll ask, ‘is it okay if I interrupt you if I have a clarifying question?’ That gives you permission to interrupt.”
Blame a third “party” or policy. When patients express anger, find an “enemy” that you can be angry at together. “You might say something like, ‘I’m as frustrated as you are; I can’t believe how broken our health care system is that I have only 8 minutes with you today,’ ” he advised. “Show that you’re on the same side as them.” You could also blame a policy by saying something like, “I’m sorry; I can’t do that for you. My practice has strict rules about that. I’m as frustrated as you are.”
Practice self-regulation. Here, the goal is to delay the time between being triggered by the patient who gets under your skin and your response to that person, such as saying you received “a page or an important text before you walk out of the exam room,” he said. This principle also applies to messages that unreasonable individuals send by e-mail or through messages on their patient portal. “Probably the biggest mistakes I’ve seen from physicians is when they get really angry and they write an angry portal message or e-mail and send it out,” Dr. Reichenberg said. “If I feel triggered, I wait to respond. I’ll sometimes forward [the response] it to my nurse and request that person to send it out the next morning, so the reply reads, ‘Dr. Reichenberg said…’ That gives me the chance to calm down. It also gives the patient a chance to calm down.”
Never worry alone. When struggling to communicate effectively with a difficult patient, he recommends seeking input from a trusted physician colleague. “Better yet, pick up the phone and call the patient’s primary care doctor or another specialist who takes care of that person, and talk about it,” he said. “Figure out if this is your problem or the patient’s problem. They may offer advice on how to handle that person.”
Know when the conflict is untenable. Sometimes it’s best to resign from providing care to difficult patients. “I might write or say something like, ‘I resign from your care. I do not have any expertise to help you with your problem,’ ” Dr. Reichenberg said. “Or, ‘I don’t know that I have the infrastructure to handle the kind of problems you have. I’m not sure we’re the best fit.’ I would suggest that you not give every single detail about why you’re firing them, because the patients could write a step-by-step response, arguing against that.” If you decide to terminate the relationship with a patient, make sure that he or she is not in an acute phase of their illness. “You do not want to get sued for patient abandonment,” he said. “Know your state laws. In general, you’re going to give them a statement of intent to terminate — usually in 30 days — but you have to agree to treat them emergently.” Dr. Reichenberg also provides them with a referral source so they can find a new physician and waives the fee for sending medical records to the new provider. “Also, though it’s not required, I’ll include a statement about the consequences of not receiving care, if I think that they’re [neglecting] their own care,” he said.
Dr. Reichenberg reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — In his role as chief medical officer for Ascension Medical Group–Texas, which employs about 1,000 physicians across every medical specialty,
At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Reichenberg, professor of dermatology at the University of Texas at Austin, shared several tips for managing such difficult patients:
Look for ‘red flags’ that raise concerns. This may include patients’ unrealistic expectations for a cure, “which could be because of their cultural or educational background,” he said. Difficult patients also may view physicians as enemies.
“They may quote legal jargon or threaten consequences if there is a bad outcome,” he explained. “They may say, ‘I’m a great reviewer on Yelp and I look forward to giving you a great Yelp review when we finish today.’ They may also have previously sued physicians, or they may tell you that their last physician was horrible.”
Shift into robot mode. In other words, don’t stray from your practice’s protocol by offering special treatment to difficult patients. For example, if a difficult patient shows up 15 minutes late and the office has a policy that patients should be rescheduled if they arrive 10 minutes late, “do not break that policy no matter what, because that’s your protocol,” he advised. “You also do not promise anything you don’t know or that nobody could know. If a difficult patient asks, ‘what is the statistical chance that I’ll get better with this treatment,’ you either say, ‘studies have shown that this is the exact percentage,’ or ‘I don’t know. We’re going to do our best.’”
Set expectations at the outset. “If I walk into the room and the nurse has been in there for 25 minutes doing the intake and I know it’s going to be a long visit, I’ll start by saying, ‘I have 8 minutes to see you today,’ ” Dr. Reichenberg said. “ ‘Whatever we don’t finish today we’ll have to do during a follow-up visit, so let’s please prioritize what we need to do.’ ” Sometimes he sets his smartphone alarm to 8 minutes and when the timer goes off, he’ll say, “I’m so sorry, but I have to go.” For talkative patients, he continued, “I’ll ask, ‘is it okay if I interrupt you if I have a clarifying question?’ That gives you permission to interrupt.”
Blame a third “party” or policy. When patients express anger, find an “enemy” that you can be angry at together. “You might say something like, ‘I’m as frustrated as you are; I can’t believe how broken our health care system is that I have only 8 minutes with you today,’ ” he advised. “Show that you’re on the same side as them.” You could also blame a policy by saying something like, “I’m sorry; I can’t do that for you. My practice has strict rules about that. I’m as frustrated as you are.”
Practice self-regulation. Here, the goal is to delay the time between being triggered by the patient who gets under your skin and your response to that person, such as saying you received “a page or an important text before you walk out of the exam room,” he said. This principle also applies to messages that unreasonable individuals send by e-mail or through messages on their patient portal. “Probably the biggest mistakes I’ve seen from physicians is when they get really angry and they write an angry portal message or e-mail and send it out,” Dr. Reichenberg said. “If I feel triggered, I wait to respond. I’ll sometimes forward [the response] it to my nurse and request that person to send it out the next morning, so the reply reads, ‘Dr. Reichenberg said…’ That gives me the chance to calm down. It also gives the patient a chance to calm down.”
Never worry alone. When struggling to communicate effectively with a difficult patient, he recommends seeking input from a trusted physician colleague. “Better yet, pick up the phone and call the patient’s primary care doctor or another specialist who takes care of that person, and talk about it,” he said. “Figure out if this is your problem or the patient’s problem. They may offer advice on how to handle that person.”
Know when the conflict is untenable. Sometimes it’s best to resign from providing care to difficult patients. “I might write or say something like, ‘I resign from your care. I do not have any expertise to help you with your problem,’ ” Dr. Reichenberg said. “Or, ‘I don’t know that I have the infrastructure to handle the kind of problems you have. I’m not sure we’re the best fit.’ I would suggest that you not give every single detail about why you’re firing them, because the patients could write a step-by-step response, arguing against that.” If you decide to terminate the relationship with a patient, make sure that he or she is not in an acute phase of their illness. “You do not want to get sued for patient abandonment,” he said. “Know your state laws. In general, you’re going to give them a statement of intent to terminate — usually in 30 days — but you have to agree to treat them emergently.” Dr. Reichenberg also provides them with a referral source so they can find a new physician and waives the fee for sending medical records to the new provider. “Also, though it’s not required, I’ll include a statement about the consequences of not receiving care, if I think that they’re [neglecting] their own care,” he said.
Dr. Reichenberg reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — In his role as chief medical officer for Ascension Medical Group–Texas, which employs about 1,000 physicians across every medical specialty,
At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Reichenberg, professor of dermatology at the University of Texas at Austin, shared several tips for managing such difficult patients:
Look for ‘red flags’ that raise concerns. This may include patients’ unrealistic expectations for a cure, “which could be because of their cultural or educational background,” he said. Difficult patients also may view physicians as enemies.
“They may quote legal jargon or threaten consequences if there is a bad outcome,” he explained. “They may say, ‘I’m a great reviewer on Yelp and I look forward to giving you a great Yelp review when we finish today.’ They may also have previously sued physicians, or they may tell you that their last physician was horrible.”
Shift into robot mode. In other words, don’t stray from your practice’s protocol by offering special treatment to difficult patients. For example, if a difficult patient shows up 15 minutes late and the office has a policy that patients should be rescheduled if they arrive 10 minutes late, “do not break that policy no matter what, because that’s your protocol,” he advised. “You also do not promise anything you don’t know or that nobody could know. If a difficult patient asks, ‘what is the statistical chance that I’ll get better with this treatment,’ you either say, ‘studies have shown that this is the exact percentage,’ or ‘I don’t know. We’re going to do our best.’”
Set expectations at the outset. “If I walk into the room and the nurse has been in there for 25 minutes doing the intake and I know it’s going to be a long visit, I’ll start by saying, ‘I have 8 minutes to see you today,’ ” Dr. Reichenberg said. “ ‘Whatever we don’t finish today we’ll have to do during a follow-up visit, so let’s please prioritize what we need to do.’ ” Sometimes he sets his smartphone alarm to 8 minutes and when the timer goes off, he’ll say, “I’m so sorry, but I have to go.” For talkative patients, he continued, “I’ll ask, ‘is it okay if I interrupt you if I have a clarifying question?’ That gives you permission to interrupt.”
Blame a third “party” or policy. When patients express anger, find an “enemy” that you can be angry at together. “You might say something like, ‘I’m as frustrated as you are; I can’t believe how broken our health care system is that I have only 8 minutes with you today,’ ” he advised. “Show that you’re on the same side as them.” You could also blame a policy by saying something like, “I’m sorry; I can’t do that for you. My practice has strict rules about that. I’m as frustrated as you are.”
Practice self-regulation. Here, the goal is to delay the time between being triggered by the patient who gets under your skin and your response to that person, such as saying you received “a page or an important text before you walk out of the exam room,” he said. This principle also applies to messages that unreasonable individuals send by e-mail or through messages on their patient portal. “Probably the biggest mistakes I’ve seen from physicians is when they get really angry and they write an angry portal message or e-mail and send it out,” Dr. Reichenberg said. “If I feel triggered, I wait to respond. I’ll sometimes forward [the response] it to my nurse and request that person to send it out the next morning, so the reply reads, ‘Dr. Reichenberg said…’ That gives me the chance to calm down. It also gives the patient a chance to calm down.”
Never worry alone. When struggling to communicate effectively with a difficult patient, he recommends seeking input from a trusted physician colleague. “Better yet, pick up the phone and call the patient’s primary care doctor or another specialist who takes care of that person, and talk about it,” he said. “Figure out if this is your problem or the patient’s problem. They may offer advice on how to handle that person.”
Know when the conflict is untenable. Sometimes it’s best to resign from providing care to difficult patients. “I might write or say something like, ‘I resign from your care. I do not have any expertise to help you with your problem,’ ” Dr. Reichenberg said. “Or, ‘I don’t know that I have the infrastructure to handle the kind of problems you have. I’m not sure we’re the best fit.’ I would suggest that you not give every single detail about why you’re firing them, because the patients could write a step-by-step response, arguing against that.” If you decide to terminate the relationship with a patient, make sure that he or she is not in an acute phase of their illness. “You do not want to get sued for patient abandonment,” he said. “Know your state laws. In general, you’re going to give them a statement of intent to terminate — usually in 30 days — but you have to agree to treat them emergently.” Dr. Reichenberg also provides them with a referral source so they can find a new physician and waives the fee for sending medical records to the new provider. “Also, though it’s not required, I’ll include a statement about the consequences of not receiving care, if I think that they’re [neglecting] their own care,” he said.
Dr. Reichenberg reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM AAD 2024
Ultraprocessed Food May Increase Long-Term Risk for IBS
TOPLINE:
Higher consumption of ultraprocessed food (UPF) is associated with an increased risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), with a significant dose-response relationship.
METHODOLOGY:
- The simultaneous rise in UPF consumption and IBS in recent years is concerning, but there is a lack of epidemiologic evidence regarding the link between UPF consumption and the risk of developing IBS.
- This study included 178,711 participants without IBS, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, or cancer (mean age, 55.8 years; 53.1% women) from the UK Biobank who had completed a 24-hour diet recall questionnaire over five cycles.
- The researchers used the NOVA system to categorize food into four groups, ranging from unprocessed or minimally processed food to UPF. They calculated consumption of food in each group on the basis of portion sizes and UPF consumption as a percentage of total diet intake (as grams per day) using data from participants who completed at least two dietary cycles.
- The primary outcome was incident IBS.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median of 11.3 years of follow-up, 2690 incident IBS cases were reported.
- The mean UPF consumption was 21% of the total diet.
- For every 10% increase in UPF consumption, the risk for IBS also increased by 8%.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that avoiding or lowering UPF consumption could be considered as a potential strategy to help reduce the increasing burden of IBS,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Shanshan Wu, PhD, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Disease, Beijing, China, was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Questionnaire-based data could introduce misclassification and recall bias. Lifestyle factors (eg, smoking) or nutritional factors (eg, total intake of protein, fat, and carbohydrates) that may confound the association were not considered. The observational study design has inherent bias.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the Beijing Nova Program, National Key Research and Development Program of China, and Beijing Science and Technology Project. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher consumption of ultraprocessed food (UPF) is associated with an increased risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), with a significant dose-response relationship.
METHODOLOGY:
- The simultaneous rise in UPF consumption and IBS in recent years is concerning, but there is a lack of epidemiologic evidence regarding the link between UPF consumption and the risk of developing IBS.
- This study included 178,711 participants without IBS, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, or cancer (mean age, 55.8 years; 53.1% women) from the UK Biobank who had completed a 24-hour diet recall questionnaire over five cycles.
- The researchers used the NOVA system to categorize food into four groups, ranging from unprocessed or minimally processed food to UPF. They calculated consumption of food in each group on the basis of portion sizes and UPF consumption as a percentage of total diet intake (as grams per day) using data from participants who completed at least two dietary cycles.
- The primary outcome was incident IBS.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median of 11.3 years of follow-up, 2690 incident IBS cases were reported.
- The mean UPF consumption was 21% of the total diet.
- For every 10% increase in UPF consumption, the risk for IBS also increased by 8%.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that avoiding or lowering UPF consumption could be considered as a potential strategy to help reduce the increasing burden of IBS,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Shanshan Wu, PhD, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Disease, Beijing, China, was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Questionnaire-based data could introduce misclassification and recall bias. Lifestyle factors (eg, smoking) or nutritional factors (eg, total intake of protein, fat, and carbohydrates) that may confound the association were not considered. The observational study design has inherent bias.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the Beijing Nova Program, National Key Research and Development Program of China, and Beijing Science and Technology Project. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher consumption of ultraprocessed food (UPF) is associated with an increased risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), with a significant dose-response relationship.
METHODOLOGY:
- The simultaneous rise in UPF consumption and IBS in recent years is concerning, but there is a lack of epidemiologic evidence regarding the link between UPF consumption and the risk of developing IBS.
- This study included 178,711 participants without IBS, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, or cancer (mean age, 55.8 years; 53.1% women) from the UK Biobank who had completed a 24-hour diet recall questionnaire over five cycles.
- The researchers used the NOVA system to categorize food into four groups, ranging from unprocessed or minimally processed food to UPF. They calculated consumption of food in each group on the basis of portion sizes and UPF consumption as a percentage of total diet intake (as grams per day) using data from participants who completed at least two dietary cycles.
- The primary outcome was incident IBS.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median of 11.3 years of follow-up, 2690 incident IBS cases were reported.
- The mean UPF consumption was 21% of the total diet.
- For every 10% increase in UPF consumption, the risk for IBS also increased by 8%.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that avoiding or lowering UPF consumption could be considered as a potential strategy to help reduce the increasing burden of IBS,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Shanshan Wu, PhD, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Disease, Beijing, China, was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Questionnaire-based data could introduce misclassification and recall bias. Lifestyle factors (eg, smoking) or nutritional factors (eg, total intake of protein, fat, and carbohydrates) that may confound the association were not considered. The observational study design has inherent bias.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the Beijing Nova Program, National Key Research and Development Program of China, and Beijing Science and Technology Project. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.