User login
Is our mental health system broken? If so, can it be fixed?
Numerous articles, books, and newspaper editorials have been written about the “crisis” in mental health care in our country from various perspectives, and the phrase is often used that the mental health system is “broken.” It seems that lately, this topic is often brought up after the most recent mass shooting.1
Philip T. Yanos, PhD, correctly asked recently whether we should be talking about a “broken” system, because implicit in the phrase is the assumption that the mental health system was once “whole,” and he has pointed out2 chronic deficiencies, such as the absence of affordable housing, and the availability of services to those with chronic mental illness.
In addition, many authors have asserted that, with deinstitutionalization – which occurred starting with the Community Mental Health Act of 1963 – homelessness also became a big problem for people in our prisons and jails, which became the default treatment providers for many of those with serious mental illness.Once authors make this point, they often offer up ways to start addressing various parts of the system, and it usually comes down to asking for more funding for more outpatient treatment and services as well as more inpatient beds. Some authors make the point3 that people with mental illness often lack insight into their illness and the need for treatment. Thus, we have the quandary of people with severe mental illness not believing that they need help, and thus not even trying to access services, which can lead to homelessness and jail time.
But what of those individuals with serious mental health problems who aren’t facing those obstacles and complications? What about individuals who aren’t facing homelessness, who haven’t gotten embroiled in the legal system, who do have insurance coverage, who live in areas with sufficient numbers of outpatient mental health centers to choose from, and who have no problems finding an inpatient bed when needed? Let’s suppose that we have an individual who does have insight into his mental illness and need for treatment, and is motivated to seek treatment. How responsive is the system to such individuals? That will be the focus on my article.
In a recent report,4 the author quotes American Psychiatric Association President Bruce J. Schwartz, MD, appealing to members of the U.S. Congress to step in. According to the author, Dr. Schwartz’s position is that the crisis in American mental health begins specifically with a drastic, and growing, shortage of psychiatric beds, especially in publicly funded state and county hospital beds. From there, the crisis spreads to the nation’s city streets, and its jails and prisons, where the largest number of people with serious mental illness now reside. He also talks about a shortage of psychiatrists and child psychiatrists, and says the shortage is likely to worsen. The proposed solution to this problem, of course, is more funding from Congress to open more psychiatric beds, as well as providing more funding for mental health in general and funding to residency programs to increase the numbers of psychiatrists.
I respect the opinions of Dr. Schwartz and that of the other authors who want to talk about lack of adequate beds, outpatient clinics and services, insufficient numbers of psychiatrists, and a lack of funding by Congress. However, I would like to provide further information, from a personal perspective, which causes me to believe that the problem is even more complex than that, and that the failures of the system are compounded by a dysfunctional culture within the ranks of professional caregivers. In other words, once the pieces are in place and assembled, the mental health system still seems to be “broken” but from within. I worry about apathy and an absence of motivation to provide good or even adequate services by the very people who are or should be aware of the problems and what it takes to help our vulnerable patients lead better lives.
I have practiced psychiatry for many years in various settings. I have spent many years working as an inpatient psychiatrist in a large state hospital. I have worked in community mental health outpatient settings. I have also worked in a private practice doing both inpatient and outpatient patient care as well as significant forensic work. At the hospitals, I have witnessed and prepared internal reports about patients who are “revolving doors.” Such patients often had more than 50 psychiatric hospitalizations and no apparent solution to keep them stable enough in the community.
But mental illness is not just a career for me. In addition to being psychiatrist, I am the father of a son with severe and persistent mental illness. I have watched him struggle to find stability. He, too, has been in and out of hospitals. My wife is also in the mental health field. She and I have endlessly tried to work with our son’s local community mental health center to provide them with feedback and to get them to respond to his needs – often with great frustration. It has been our impression that clinicians have difficulty listening to us and understanding the difficulties our son is having, from my son’s case manager to the treating psychiatrist, to the director of the agency. We have tried shifting him to other programs in a neighboring county, including one known to be a “model” program, but had the same issues.
Psychiatry is more of an art than science. Our other medical colleagues can try to resolve a clinical problem, no matter their rank, by ordering the right blood test or getting certain imaging. Psychiatry has no such biomarkers, or validated tests, to rely on to resolve disputes. We have only our training and experience and, unfortunately, our biases. If we don’t agree with a colleague, we often resort to rank and argument.
Psychiatrists (just as can colleagues in other specialties) can be insufferably arrogant.
My personal experience has been that the hospital and the community often don’t communicate well. This seems to be a systems problem, as is the case for many complex unsolvable problems. I have been to discharge meetings involving hospital staff and the receiving community system. The attitude of the inpatient psychiatrist is often: “If you guys only did your job better, this patient wouldn’t keep having to be admitted. It’s your job to keep him out of the hospital.”
Alternatively, the community rejects this attitude and points to the absence of resources that prevents them from seeing patients in a timely manner and from adequately monitoring them. They say they are shackled by their resource constraints and that the endless admissions are inevitable. Further, the outpatient psychiatrists complain bitterly that all the inpatient doctors do is make a bunch of useless medication changes and then don’t keep patients in long enough to make sure the patient stays well. And on and on the arguments go with no resolution.
Sadly, and confirmed by my personal experience, when well-meaning and knowledgeable family members try to communicate with the community mental health system about their son’s mental disintegration, the community agency often doesn’t welcome the feedback. They resort to “confidentiality” concerns, often ill advised. Their opinion seems to be that the patient, (i.e. the patient who is falling apart and is becoming psychotic), should be the one calling the agency, waiting on hold forever, and not getting a call back. When my son has been in this situation, he has hung up his telephone out of frustration, then headed off to the emergency room, where he knew he would be seen.
The other area of frustration is that of the ideal of recovery. Mental health programs love to tout that their mission is “recovery,” and they list it as one of their primary areas of vision and goals. Yet, when we tried to communicate with community clinicians, they usually ignored our request to assist our son with supported employment and to help him achieve independence and a social life. When we tried to convey our recovery concerns to the psychiatrist, the usual response was also to ignore it and focus on “meds, meds, meds,” which most psychiatrists seem to view as their mission and area of expertise. Many psychiatrists have embraced the “bio-bio-bio” model of evaluation and treatment5 with only lip service paid to the “biopsychosocial” theory they like to say they advocate. When we reached out to our son’s psychiatrists and could get through, we found that they mostly failed to display much interest in paying attention to broader areas of functioning, instead focusing on symptoms, which they could observe in person.
So, I add to the chorus complaining that our mental health system is broken. Broken not only in terms of adequate funding, but also broken from within. It would require much wisdom and self-examination to even begin to address the problem. Without a better plan, throwing money at this broken system won’t improve the lives of our seriously ill and vulnerable psychiatric patients.
Dr. Kausch is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist who is on the faculty at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland as an assistant clinical professor. He spends most of his time seeing patients through the Akron General/Cleveland Clinic health system. He has published in the area of forensic psychiatry, addictions, pathological gambling, and suicide. He has recently taken an interest in conducting marital therapy and is now publishing in that area as well.
References
1. Doroshow D. “We need to stop focusing on the mental health of mass shooters.” Washington Post. 2019 May 20.
2. Yanos P. “Is the mental health system ‘broken’?” Psychology Today. 2018 Oct 11.
3. Orenstein N. “How to fix a broken mental health system.” The Atlantic. 2016 Jun 8.
4. Moran M. APA rings alarm in nation’s capitol about crisis in mental health care. Psychiatr News. 2020 Jan 1.
5. Paris J. “Psychotherapy in an Age of Neuroscience.” New York: Oxford University Press, 2017.
Numerous articles, books, and newspaper editorials have been written about the “crisis” in mental health care in our country from various perspectives, and the phrase is often used that the mental health system is “broken.” It seems that lately, this topic is often brought up after the most recent mass shooting.1
Philip T. Yanos, PhD, correctly asked recently whether we should be talking about a “broken” system, because implicit in the phrase is the assumption that the mental health system was once “whole,” and he has pointed out2 chronic deficiencies, such as the absence of affordable housing, and the availability of services to those with chronic mental illness.
In addition, many authors have asserted that, with deinstitutionalization – which occurred starting with the Community Mental Health Act of 1963 – homelessness also became a big problem for people in our prisons and jails, which became the default treatment providers for many of those with serious mental illness.Once authors make this point, they often offer up ways to start addressing various parts of the system, and it usually comes down to asking for more funding for more outpatient treatment and services as well as more inpatient beds. Some authors make the point3 that people with mental illness often lack insight into their illness and the need for treatment. Thus, we have the quandary of people with severe mental illness not believing that they need help, and thus not even trying to access services, which can lead to homelessness and jail time.
But what of those individuals with serious mental health problems who aren’t facing those obstacles and complications? What about individuals who aren’t facing homelessness, who haven’t gotten embroiled in the legal system, who do have insurance coverage, who live in areas with sufficient numbers of outpatient mental health centers to choose from, and who have no problems finding an inpatient bed when needed? Let’s suppose that we have an individual who does have insight into his mental illness and need for treatment, and is motivated to seek treatment. How responsive is the system to such individuals? That will be the focus on my article.
In a recent report,4 the author quotes American Psychiatric Association President Bruce J. Schwartz, MD, appealing to members of the U.S. Congress to step in. According to the author, Dr. Schwartz’s position is that the crisis in American mental health begins specifically with a drastic, and growing, shortage of psychiatric beds, especially in publicly funded state and county hospital beds. From there, the crisis spreads to the nation’s city streets, and its jails and prisons, where the largest number of people with serious mental illness now reside. He also talks about a shortage of psychiatrists and child psychiatrists, and says the shortage is likely to worsen. The proposed solution to this problem, of course, is more funding from Congress to open more psychiatric beds, as well as providing more funding for mental health in general and funding to residency programs to increase the numbers of psychiatrists.
I respect the opinions of Dr. Schwartz and that of the other authors who want to talk about lack of adequate beds, outpatient clinics and services, insufficient numbers of psychiatrists, and a lack of funding by Congress. However, I would like to provide further information, from a personal perspective, which causes me to believe that the problem is even more complex than that, and that the failures of the system are compounded by a dysfunctional culture within the ranks of professional caregivers. In other words, once the pieces are in place and assembled, the mental health system still seems to be “broken” but from within. I worry about apathy and an absence of motivation to provide good or even adequate services by the very people who are or should be aware of the problems and what it takes to help our vulnerable patients lead better lives.
I have practiced psychiatry for many years in various settings. I have spent many years working as an inpatient psychiatrist in a large state hospital. I have worked in community mental health outpatient settings. I have also worked in a private practice doing both inpatient and outpatient patient care as well as significant forensic work. At the hospitals, I have witnessed and prepared internal reports about patients who are “revolving doors.” Such patients often had more than 50 psychiatric hospitalizations and no apparent solution to keep them stable enough in the community.
But mental illness is not just a career for me. In addition to being psychiatrist, I am the father of a son with severe and persistent mental illness. I have watched him struggle to find stability. He, too, has been in and out of hospitals. My wife is also in the mental health field. She and I have endlessly tried to work with our son’s local community mental health center to provide them with feedback and to get them to respond to his needs – often with great frustration. It has been our impression that clinicians have difficulty listening to us and understanding the difficulties our son is having, from my son’s case manager to the treating psychiatrist, to the director of the agency. We have tried shifting him to other programs in a neighboring county, including one known to be a “model” program, but had the same issues.
Psychiatry is more of an art than science. Our other medical colleagues can try to resolve a clinical problem, no matter their rank, by ordering the right blood test or getting certain imaging. Psychiatry has no such biomarkers, or validated tests, to rely on to resolve disputes. We have only our training and experience and, unfortunately, our biases. If we don’t agree with a colleague, we often resort to rank and argument.
Psychiatrists (just as can colleagues in other specialties) can be insufferably arrogant.
My personal experience has been that the hospital and the community often don’t communicate well. This seems to be a systems problem, as is the case for many complex unsolvable problems. I have been to discharge meetings involving hospital staff and the receiving community system. The attitude of the inpatient psychiatrist is often: “If you guys only did your job better, this patient wouldn’t keep having to be admitted. It’s your job to keep him out of the hospital.”
Alternatively, the community rejects this attitude and points to the absence of resources that prevents them from seeing patients in a timely manner and from adequately monitoring them. They say they are shackled by their resource constraints and that the endless admissions are inevitable. Further, the outpatient psychiatrists complain bitterly that all the inpatient doctors do is make a bunch of useless medication changes and then don’t keep patients in long enough to make sure the patient stays well. And on and on the arguments go with no resolution.
Sadly, and confirmed by my personal experience, when well-meaning and knowledgeable family members try to communicate with the community mental health system about their son’s mental disintegration, the community agency often doesn’t welcome the feedback. They resort to “confidentiality” concerns, often ill advised. Their opinion seems to be that the patient, (i.e. the patient who is falling apart and is becoming psychotic), should be the one calling the agency, waiting on hold forever, and not getting a call back. When my son has been in this situation, he has hung up his telephone out of frustration, then headed off to the emergency room, where he knew he would be seen.
The other area of frustration is that of the ideal of recovery. Mental health programs love to tout that their mission is “recovery,” and they list it as one of their primary areas of vision and goals. Yet, when we tried to communicate with community clinicians, they usually ignored our request to assist our son with supported employment and to help him achieve independence and a social life. When we tried to convey our recovery concerns to the psychiatrist, the usual response was also to ignore it and focus on “meds, meds, meds,” which most psychiatrists seem to view as their mission and area of expertise. Many psychiatrists have embraced the “bio-bio-bio” model of evaluation and treatment5 with only lip service paid to the “biopsychosocial” theory they like to say they advocate. When we reached out to our son’s psychiatrists and could get through, we found that they mostly failed to display much interest in paying attention to broader areas of functioning, instead focusing on symptoms, which they could observe in person.
So, I add to the chorus complaining that our mental health system is broken. Broken not only in terms of adequate funding, but also broken from within. It would require much wisdom and self-examination to even begin to address the problem. Without a better plan, throwing money at this broken system won’t improve the lives of our seriously ill and vulnerable psychiatric patients.
Dr. Kausch is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist who is on the faculty at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland as an assistant clinical professor. He spends most of his time seeing patients through the Akron General/Cleveland Clinic health system. He has published in the area of forensic psychiatry, addictions, pathological gambling, and suicide. He has recently taken an interest in conducting marital therapy and is now publishing in that area as well.
References
1. Doroshow D. “We need to stop focusing on the mental health of mass shooters.” Washington Post. 2019 May 20.
2. Yanos P. “Is the mental health system ‘broken’?” Psychology Today. 2018 Oct 11.
3. Orenstein N. “How to fix a broken mental health system.” The Atlantic. 2016 Jun 8.
4. Moran M. APA rings alarm in nation’s capitol about crisis in mental health care. Psychiatr News. 2020 Jan 1.
5. Paris J. “Psychotherapy in an Age of Neuroscience.” New York: Oxford University Press, 2017.
Numerous articles, books, and newspaper editorials have been written about the “crisis” in mental health care in our country from various perspectives, and the phrase is often used that the mental health system is “broken.” It seems that lately, this topic is often brought up after the most recent mass shooting.1
Philip T. Yanos, PhD, correctly asked recently whether we should be talking about a “broken” system, because implicit in the phrase is the assumption that the mental health system was once “whole,” and he has pointed out2 chronic deficiencies, such as the absence of affordable housing, and the availability of services to those with chronic mental illness.
In addition, many authors have asserted that, with deinstitutionalization – which occurred starting with the Community Mental Health Act of 1963 – homelessness also became a big problem for people in our prisons and jails, which became the default treatment providers for many of those with serious mental illness.Once authors make this point, they often offer up ways to start addressing various parts of the system, and it usually comes down to asking for more funding for more outpatient treatment and services as well as more inpatient beds. Some authors make the point3 that people with mental illness often lack insight into their illness and the need for treatment. Thus, we have the quandary of people with severe mental illness not believing that they need help, and thus not even trying to access services, which can lead to homelessness and jail time.
But what of those individuals with serious mental health problems who aren’t facing those obstacles and complications? What about individuals who aren’t facing homelessness, who haven’t gotten embroiled in the legal system, who do have insurance coverage, who live in areas with sufficient numbers of outpatient mental health centers to choose from, and who have no problems finding an inpatient bed when needed? Let’s suppose that we have an individual who does have insight into his mental illness and need for treatment, and is motivated to seek treatment. How responsive is the system to such individuals? That will be the focus on my article.
In a recent report,4 the author quotes American Psychiatric Association President Bruce J. Schwartz, MD, appealing to members of the U.S. Congress to step in. According to the author, Dr. Schwartz’s position is that the crisis in American mental health begins specifically with a drastic, and growing, shortage of psychiatric beds, especially in publicly funded state and county hospital beds. From there, the crisis spreads to the nation’s city streets, and its jails and prisons, where the largest number of people with serious mental illness now reside. He also talks about a shortage of psychiatrists and child psychiatrists, and says the shortage is likely to worsen. The proposed solution to this problem, of course, is more funding from Congress to open more psychiatric beds, as well as providing more funding for mental health in general and funding to residency programs to increase the numbers of psychiatrists.
I respect the opinions of Dr. Schwartz and that of the other authors who want to talk about lack of adequate beds, outpatient clinics and services, insufficient numbers of psychiatrists, and a lack of funding by Congress. However, I would like to provide further information, from a personal perspective, which causes me to believe that the problem is even more complex than that, and that the failures of the system are compounded by a dysfunctional culture within the ranks of professional caregivers. In other words, once the pieces are in place and assembled, the mental health system still seems to be “broken” but from within. I worry about apathy and an absence of motivation to provide good or even adequate services by the very people who are or should be aware of the problems and what it takes to help our vulnerable patients lead better lives.
I have practiced psychiatry for many years in various settings. I have spent many years working as an inpatient psychiatrist in a large state hospital. I have worked in community mental health outpatient settings. I have also worked in a private practice doing both inpatient and outpatient patient care as well as significant forensic work. At the hospitals, I have witnessed and prepared internal reports about patients who are “revolving doors.” Such patients often had more than 50 psychiatric hospitalizations and no apparent solution to keep them stable enough in the community.
But mental illness is not just a career for me. In addition to being psychiatrist, I am the father of a son with severe and persistent mental illness. I have watched him struggle to find stability. He, too, has been in and out of hospitals. My wife is also in the mental health field. She and I have endlessly tried to work with our son’s local community mental health center to provide them with feedback and to get them to respond to his needs – often with great frustration. It has been our impression that clinicians have difficulty listening to us and understanding the difficulties our son is having, from my son’s case manager to the treating psychiatrist, to the director of the agency. We have tried shifting him to other programs in a neighboring county, including one known to be a “model” program, but had the same issues.
Psychiatry is more of an art than science. Our other medical colleagues can try to resolve a clinical problem, no matter their rank, by ordering the right blood test or getting certain imaging. Psychiatry has no such biomarkers, or validated tests, to rely on to resolve disputes. We have only our training and experience and, unfortunately, our biases. If we don’t agree with a colleague, we often resort to rank and argument.
Psychiatrists (just as can colleagues in other specialties) can be insufferably arrogant.
My personal experience has been that the hospital and the community often don’t communicate well. This seems to be a systems problem, as is the case for many complex unsolvable problems. I have been to discharge meetings involving hospital staff and the receiving community system. The attitude of the inpatient psychiatrist is often: “If you guys only did your job better, this patient wouldn’t keep having to be admitted. It’s your job to keep him out of the hospital.”
Alternatively, the community rejects this attitude and points to the absence of resources that prevents them from seeing patients in a timely manner and from adequately monitoring them. They say they are shackled by their resource constraints and that the endless admissions are inevitable. Further, the outpatient psychiatrists complain bitterly that all the inpatient doctors do is make a bunch of useless medication changes and then don’t keep patients in long enough to make sure the patient stays well. And on and on the arguments go with no resolution.
Sadly, and confirmed by my personal experience, when well-meaning and knowledgeable family members try to communicate with the community mental health system about their son’s mental disintegration, the community agency often doesn’t welcome the feedback. They resort to “confidentiality” concerns, often ill advised. Their opinion seems to be that the patient, (i.e. the patient who is falling apart and is becoming psychotic), should be the one calling the agency, waiting on hold forever, and not getting a call back. When my son has been in this situation, he has hung up his telephone out of frustration, then headed off to the emergency room, where he knew he would be seen.
The other area of frustration is that of the ideal of recovery. Mental health programs love to tout that their mission is “recovery,” and they list it as one of their primary areas of vision and goals. Yet, when we tried to communicate with community clinicians, they usually ignored our request to assist our son with supported employment and to help him achieve independence and a social life. When we tried to convey our recovery concerns to the psychiatrist, the usual response was also to ignore it and focus on “meds, meds, meds,” which most psychiatrists seem to view as their mission and area of expertise. Many psychiatrists have embraced the “bio-bio-bio” model of evaluation and treatment5 with only lip service paid to the “biopsychosocial” theory they like to say they advocate. When we reached out to our son’s psychiatrists and could get through, we found that they mostly failed to display much interest in paying attention to broader areas of functioning, instead focusing on symptoms, which they could observe in person.
So, I add to the chorus complaining that our mental health system is broken. Broken not only in terms of adequate funding, but also broken from within. It would require much wisdom and self-examination to even begin to address the problem. Without a better plan, throwing money at this broken system won’t improve the lives of our seriously ill and vulnerable psychiatric patients.
Dr. Kausch is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist who is on the faculty at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland as an assistant clinical professor. He spends most of his time seeing patients through the Akron General/Cleveland Clinic health system. He has published in the area of forensic psychiatry, addictions, pathological gambling, and suicide. He has recently taken an interest in conducting marital therapy and is now publishing in that area as well.
References
1. Doroshow D. “We need to stop focusing on the mental health of mass shooters.” Washington Post. 2019 May 20.
2. Yanos P. “Is the mental health system ‘broken’?” Psychology Today. 2018 Oct 11.
3. Orenstein N. “How to fix a broken mental health system.” The Atlantic. 2016 Jun 8.
4. Moran M. APA rings alarm in nation’s capitol about crisis in mental health care. Psychiatr News. 2020 Jan 1.
5. Paris J. “Psychotherapy in an Age of Neuroscience.” New York: Oxford University Press, 2017.
FDA okays triple-combo pill for type 2 diabetes
Trijardy XR will be available in four different dosages and is indicated as a once-daily treatment, together with diet and exercise, for adults who are already on treatment for type 2 disease but require additional agents to attain healthy hemoglobin A1c targets, according to a statement released by Eli Lilly, which will market the newly approved treatment together with Boehringer Ingelheim.
“Type 2 diabetes is a complex disease that often requires the use of multiple antidiabetic medications to improve glycemic control. Having three different diabetes medications in a single tablet is an important advance in diabetes treatment,” Ralph DeFronzo, MD, professor and diabetes division chief at the University of Texas Health San Antonio, said in the release.
All three drugs are separately well-established therapies for type 2 diabetes. Metformin is the most commonly prescribed treatment for type 2. Empagliflozin, a sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor, and linagliptin, a single-dose dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor, are approved for the reduction of blood sugar in patients with type 2 disease, and empagliflozin is also approved for lowering the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 and established cardiovascular disease, according to the statement. (In 2015, the FDA approved a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin, Glyxambi, as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.)
The approval of the triple-combination treatment was based on findings from two randomized, open-label trials that assessed the bioequivalence of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and extended-release metformin hydrochloride fixed-dose combination tablets, as well as their individual components. In addition, the trials established that the safety profile of the combination therapy was similar to the safety profiles of the components, the statement said.
Lactic acidosis, pancreatitis, and heart failure are among the side effects associated with the combination therapy, with upper respiratory tract infection and gastroenteritis among the most common. Serious side effects include dehydration, ketoacidosis, kidney problems, urinary tract and vaginal yeast infections, and hypoglycemia.
As with empagliflozin and linagliptin alone, the combination therapy is not recommended for individuals with type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis, and it has not been tested in patients with a history of pancreatitis. The combination also has a warning for lactic acidosis, a rare, but serious, condition that can arise with metformin accumulation.
The combination product is contraindicated for people with kidney problems and end-stage renal disease or who are on dialysis; have metabolic acidosis or diabetic ketoacidosis; or are allergic to empagliflozin, linagliptin, or metformin.
Trijardy XR will be available in four different dosages and is indicated as a once-daily treatment, together with diet and exercise, for adults who are already on treatment for type 2 disease but require additional agents to attain healthy hemoglobin A1c targets, according to a statement released by Eli Lilly, which will market the newly approved treatment together with Boehringer Ingelheim.
“Type 2 diabetes is a complex disease that often requires the use of multiple antidiabetic medications to improve glycemic control. Having three different diabetes medications in a single tablet is an important advance in diabetes treatment,” Ralph DeFronzo, MD, professor and diabetes division chief at the University of Texas Health San Antonio, said in the release.
All three drugs are separately well-established therapies for type 2 diabetes. Metformin is the most commonly prescribed treatment for type 2. Empagliflozin, a sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor, and linagliptin, a single-dose dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor, are approved for the reduction of blood sugar in patients with type 2 disease, and empagliflozin is also approved for lowering the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 and established cardiovascular disease, according to the statement. (In 2015, the FDA approved a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin, Glyxambi, as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.)
The approval of the triple-combination treatment was based on findings from two randomized, open-label trials that assessed the bioequivalence of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and extended-release metformin hydrochloride fixed-dose combination tablets, as well as their individual components. In addition, the trials established that the safety profile of the combination therapy was similar to the safety profiles of the components, the statement said.
Lactic acidosis, pancreatitis, and heart failure are among the side effects associated with the combination therapy, with upper respiratory tract infection and gastroenteritis among the most common. Serious side effects include dehydration, ketoacidosis, kidney problems, urinary tract and vaginal yeast infections, and hypoglycemia.
As with empagliflozin and linagliptin alone, the combination therapy is not recommended for individuals with type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis, and it has not been tested in patients with a history of pancreatitis. The combination also has a warning for lactic acidosis, a rare, but serious, condition that can arise with metformin accumulation.
The combination product is contraindicated for people with kidney problems and end-stage renal disease or who are on dialysis; have metabolic acidosis or diabetic ketoacidosis; or are allergic to empagliflozin, linagliptin, or metformin.
Trijardy XR will be available in four different dosages and is indicated as a once-daily treatment, together with diet and exercise, for adults who are already on treatment for type 2 disease but require additional agents to attain healthy hemoglobin A1c targets, according to a statement released by Eli Lilly, which will market the newly approved treatment together with Boehringer Ingelheim.
“Type 2 diabetes is a complex disease that often requires the use of multiple antidiabetic medications to improve glycemic control. Having three different diabetes medications in a single tablet is an important advance in diabetes treatment,” Ralph DeFronzo, MD, professor and diabetes division chief at the University of Texas Health San Antonio, said in the release.
All three drugs are separately well-established therapies for type 2 diabetes. Metformin is the most commonly prescribed treatment for type 2. Empagliflozin, a sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor, and linagliptin, a single-dose dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor, are approved for the reduction of blood sugar in patients with type 2 disease, and empagliflozin is also approved for lowering the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 and established cardiovascular disease, according to the statement. (In 2015, the FDA approved a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin, Glyxambi, as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.)
The approval of the triple-combination treatment was based on findings from two randomized, open-label trials that assessed the bioequivalence of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and extended-release metformin hydrochloride fixed-dose combination tablets, as well as their individual components. In addition, the trials established that the safety profile of the combination therapy was similar to the safety profiles of the components, the statement said.
Lactic acidosis, pancreatitis, and heart failure are among the side effects associated with the combination therapy, with upper respiratory tract infection and gastroenteritis among the most common. Serious side effects include dehydration, ketoacidosis, kidney problems, urinary tract and vaginal yeast infections, and hypoglycemia.
As with empagliflozin and linagliptin alone, the combination therapy is not recommended for individuals with type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis, and it has not been tested in patients with a history of pancreatitis. The combination also has a warning for lactic acidosis, a rare, but serious, condition that can arise with metformin accumulation.
The combination product is contraindicated for people with kidney problems and end-stage renal disease or who are on dialysis; have metabolic acidosis or diabetic ketoacidosis; or are allergic to empagliflozin, linagliptin, or metformin.
In rheumatology, biosimilars are flatlining. Why?
Although biosimilar versions of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis) have been available to U.S. rheumatologists and their patients for over 3 years, uptake has thus far been slow.
In an analysis of data from a large commercial payer, the two available biosimilars for infliximab (Remicade) accounted for less than 1% of TNFi prescribing since the first biosimilar to infliximab was approved in 2016.
The study, published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, involved a total of 1.1 million TNFi prescriptions or infusions received by 95,906 patients from 2016 to 2019. Investigators found that uptake of biosimilar infliximab was essentially flat, standing at 0.1% of prescribing in the second quarter of 2017, and topping out at 0.9% in the first quarter of 2019. For branded infliximab, prescribing was also stable, but accounted for about 20% of overall biologic dispensing in each quarter of the period studied.
There are currently two biosimilar medications to the originator infliximab, which is one of five originator biologics available to treat rheumatic diseases in the United States: infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) and infliximab-abda (Renflexis). The former was approved in 2016 and the latter in 2017, said study author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, ScD, of the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and her coauthors.
“Our paper reports a disappointingly low uptake of biosimilar infliximab since the first quarter of 2017 using claims data from a large private health plan. The main and maybe the only reason to consider using a biosimilar is cost saving,” said Dr. Kim in an interview. “Our results suggest that current modest cost savings from infliximab biosimilars in the U.S. are not sufficient to promote their widespread use.”
In the payer database study conducted by Dr. Kim and colleagues, the insurer paid similar mean amounts per patient per quarter for originator and biosimilar infliximab in mid-2017 ($8,322 versus $8,656). By the end of 2018, a gap appeared, with the insurer paying a mean quarterly per-patient sum of $8,111 for biosimilar infliximab compared with $9,535 for the branded biologic.
“The lack of market penetration and very modest price reductions for biosimilars have left policymakers, payers, physicians, and the public frustrated, particularly because sales in Europe continue to rapidly expand and robust cost-savings have materialized,” wrote Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, in an editorial accompanying the study.
Dr. Yazdany, professor and chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, noted that increased spending on biologics in the United States – which increased by 50% from 2014 to 2018 – has been driven by rising prices as well as increased uptake of biologic therapies.
At least in part, Europe has been able to reap cost savings where the United States hasn’t because fundamental differences in health care reimbursement can ease sweeping biosimilar adoption, Dr. Yazdany noted. “Countries like Denmark and Sweden, using the negotiating and purchasing power of their single-payer systems have instituted a winner-takes-all bidding system,” with Denmark seeing cost savings of up to two-thirds when bidding was combined with mandatory switching, she said.
The continued market dominance of originator infliximab means that savings from biosimilars have thus far amounted to about $91 million, far short of the $1 billion that the Congressional Budget Office had projected for this date, Dr. Yazdany said.
One problem in the adoption of biosimilars by U.S. rheumatologists may have been uneven marketing and pricing across different types of practice, Colin C. Edgerton, MD, a rheumatologist at Low Country Rheumatology in South Carolina and chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care, said in an interview.
“Rheumatologists have generally developed comfort with biosimilars, although this is not universal. The core message, that all biologics vary and that this is OK, is getting out. In general, rheumatologists also understand the problem with high drug prices and the threat to patient access,” Dr. Edgerton said. But “the early marketing and pricing focus for biosimilars seemed to be on hospitals and facilities, and this did not work effectively for community rheumatologists, where the majority of care is delivered. We have been pleased to see a manufacturer pivot toward community rheumatology where additional efforts need to be made to bend the curve on biosimilar adoption. It is critical for practices with experience using biosimilars to educate peers, and this is where networks of practicing rheumatologists are important.”
In Dr. Yazdany’s editorial, she cited four structural factors impeding biosimilar uptake and downstream savings.
First, she cites ongoing actions by pharmaceutical companies, which create a “patent thicket” that has the effect of fencing off originator biologics from biosimilars long beyond the original 12-year exclusivity period. Supporting the notion that “patent thickets” are a common strategy, Dr. Yazdany noted that almost half of the patent applications that AbbVie has filed for adalimumab (Humira) have come in after the original exclusivity period expired in 2014. Humira’s price has risen 18% yearly during this period.
The complicated role played by pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) is another factor in slow adoption, said Dr. Yazdany: When manufacturers offer rebates to PBMs, the price of the originator biologic may be less than its biosimilar. Further, manufacturers may sign multiyear rebate agreements just before a biosimilar launch; PBMs are also sometimes threatened with the withdrawal of rebates if they offer biosimilars, she noted.
Third, prescriber inertia may also be at play, Dr. Yazdany noted, not least because patients often see little difference in out-of-pocket costs when they make the switch to a biosimilar – PBM rebates are not necessarily passed on to patients. Payers may not reimburse a biosimilar, or formularies can be built without them, influencing prescribing, and there’s usually no reimbursement incentive for biosimilar prescribing in the nonpublic sector, she said. To the contrary, infusing a drug with a higher price often means higher reimbursement for the administering clinician, since commercial insurance reimbursement is often calculated as a percent of the charge for the drug.
Further contributing to inertia is the extra time required for patient education and writing a new set of orders – all work that can’t be captured for extra reimbursement. Dr. Edgerton said that rheumatologists can talk with patients about the “nocebo effect” relating to biosimilars. “This is a phenomenon in which patients are thought to experience worsening symptoms associated with negative beliefs about biosimilars. There has been a study in Arthritis Care & Research addressing this concern. The authors found that positive framing of biosimilars led to more participants being willing to switch than negative framing. This suggests that clinicians have an important role in informing patients about biosimilars, and addressing hesitancy.”
Finally, Dr. Yazdany pointed out that for a pharmaceutical company pursuing biosimilar approval, the regulatory pathway itself can provide its own set of complications and confusion. Biosimilars are not exact molecular replicas of the originator biologic, and these differences can change efficacy and immunogenicity, and also affect stability. Hence, a company wishing to market a biosimilar has to show the Food and Drug Administration that safety and efficacy aren’t affected by a switch to biosimilar from an originator biologic. Extrapolation from one indication to another can be made – with scientific justification.
Rheumatologists are mindful of the potential differences between biosimilars and the originator biologic, as evinced in a recent position statement from the American College of Rheumatology. The position statement advises that “extrapolation should be pursued with caution,” and asks for clear labeling when biosimilars have been designated “interchangeable” with their biosimilar. Interchangeability can clear the way for pharmacy substitution of a prescribed biologic, though Dr. Yazdany noted that 40 states have passed legislation requiring prescriber notification.
The FDA is currently using postmarketing pharmacovigilance to monitor biosimilar performance in the real world, and a recent systematic review “should provide some reassurance,” wrote Dr. Yazdany, citing the study, which looked at 14,000 patients who had a total of 14 disease indications for biosimilar use. The 90-article review largely found no differences in safety, efficacy, or immunogenicity between originators and their biosimilars. Dr. Yazdany recommended greater openness to incorporating the European experience in the FDA’s ongoing reassessment.
A further way forward can come through tackling the patent thicket with the proposed bipartisan Biologic Patent Transparency Act, which would require publication of biologic patents in a one-stop publicly searchable database. Going further with legislation to address anticompetitive activity by pharmaceutical companies could shorten the runway to biosimilar launching considerably, she noted.
The complicated landscape of PBMs and rebates affects many sectors of health care, and new policy efforts are needed here as well, she said. Reimbursement strategies – and much-needed continuing medical education – can both ease prescriber unfamiliarity with biosimilars and provide incentives for their use, she concluded.
Dr. Kim concurred that change is needed before the United States is likely to reap significant economic benefit from biosimilars. “The uptake of biosimilars and their impact on overall health care cost needs to be reevaluated when we have more biosimilars available in the next 3-4 years. However, for now, it appears that substantial savings achieved in some European countries – for example, Denmark – may not be possible without systemic reform of the U.S. pharmaceutical market,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany is supported by the Alice Betts Endowed Chair in Arthritis Research, the Russel/Engleman Research Center at the University of California, San Francisco, and the National Institutes of Health. She has received independent research grants from Pfizer and Genentech and research consulting fees from Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca.
Dr. Kim’s study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Arnold Ventures. Dr. Kim has received research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche.
SOURCES: Kim SC et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 13. doi: 10.1002/art.41201; Yazdany J. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 10. doi: 10.1002/art.41203.
Although biosimilar versions of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis) have been available to U.S. rheumatologists and their patients for over 3 years, uptake has thus far been slow.
In an analysis of data from a large commercial payer, the two available biosimilars for infliximab (Remicade) accounted for less than 1% of TNFi prescribing since the first biosimilar to infliximab was approved in 2016.
The study, published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, involved a total of 1.1 million TNFi prescriptions or infusions received by 95,906 patients from 2016 to 2019. Investigators found that uptake of biosimilar infliximab was essentially flat, standing at 0.1% of prescribing in the second quarter of 2017, and topping out at 0.9% in the first quarter of 2019. For branded infliximab, prescribing was also stable, but accounted for about 20% of overall biologic dispensing in each quarter of the period studied.
There are currently two biosimilar medications to the originator infliximab, which is one of five originator biologics available to treat rheumatic diseases in the United States: infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) and infliximab-abda (Renflexis). The former was approved in 2016 and the latter in 2017, said study author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, ScD, of the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and her coauthors.
“Our paper reports a disappointingly low uptake of biosimilar infliximab since the first quarter of 2017 using claims data from a large private health plan. The main and maybe the only reason to consider using a biosimilar is cost saving,” said Dr. Kim in an interview. “Our results suggest that current modest cost savings from infliximab biosimilars in the U.S. are not sufficient to promote their widespread use.”
In the payer database study conducted by Dr. Kim and colleagues, the insurer paid similar mean amounts per patient per quarter for originator and biosimilar infliximab in mid-2017 ($8,322 versus $8,656). By the end of 2018, a gap appeared, with the insurer paying a mean quarterly per-patient sum of $8,111 for biosimilar infliximab compared with $9,535 for the branded biologic.
“The lack of market penetration and very modest price reductions for biosimilars have left policymakers, payers, physicians, and the public frustrated, particularly because sales in Europe continue to rapidly expand and robust cost-savings have materialized,” wrote Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, in an editorial accompanying the study.
Dr. Yazdany, professor and chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, noted that increased spending on biologics in the United States – which increased by 50% from 2014 to 2018 – has been driven by rising prices as well as increased uptake of biologic therapies.
At least in part, Europe has been able to reap cost savings where the United States hasn’t because fundamental differences in health care reimbursement can ease sweeping biosimilar adoption, Dr. Yazdany noted. “Countries like Denmark and Sweden, using the negotiating and purchasing power of their single-payer systems have instituted a winner-takes-all bidding system,” with Denmark seeing cost savings of up to two-thirds when bidding was combined with mandatory switching, she said.
The continued market dominance of originator infliximab means that savings from biosimilars have thus far amounted to about $91 million, far short of the $1 billion that the Congressional Budget Office had projected for this date, Dr. Yazdany said.
One problem in the adoption of biosimilars by U.S. rheumatologists may have been uneven marketing and pricing across different types of practice, Colin C. Edgerton, MD, a rheumatologist at Low Country Rheumatology in South Carolina and chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care, said in an interview.
“Rheumatologists have generally developed comfort with biosimilars, although this is not universal. The core message, that all biologics vary and that this is OK, is getting out. In general, rheumatologists also understand the problem with high drug prices and the threat to patient access,” Dr. Edgerton said. But “the early marketing and pricing focus for biosimilars seemed to be on hospitals and facilities, and this did not work effectively for community rheumatologists, where the majority of care is delivered. We have been pleased to see a manufacturer pivot toward community rheumatology where additional efforts need to be made to bend the curve on biosimilar adoption. It is critical for practices with experience using biosimilars to educate peers, and this is where networks of practicing rheumatologists are important.”
In Dr. Yazdany’s editorial, she cited four structural factors impeding biosimilar uptake and downstream savings.
First, she cites ongoing actions by pharmaceutical companies, which create a “patent thicket” that has the effect of fencing off originator biologics from biosimilars long beyond the original 12-year exclusivity period. Supporting the notion that “patent thickets” are a common strategy, Dr. Yazdany noted that almost half of the patent applications that AbbVie has filed for adalimumab (Humira) have come in after the original exclusivity period expired in 2014. Humira’s price has risen 18% yearly during this period.
The complicated role played by pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) is another factor in slow adoption, said Dr. Yazdany: When manufacturers offer rebates to PBMs, the price of the originator biologic may be less than its biosimilar. Further, manufacturers may sign multiyear rebate agreements just before a biosimilar launch; PBMs are also sometimes threatened with the withdrawal of rebates if they offer biosimilars, she noted.
Third, prescriber inertia may also be at play, Dr. Yazdany noted, not least because patients often see little difference in out-of-pocket costs when they make the switch to a biosimilar – PBM rebates are not necessarily passed on to patients. Payers may not reimburse a biosimilar, or formularies can be built without them, influencing prescribing, and there’s usually no reimbursement incentive for biosimilar prescribing in the nonpublic sector, she said. To the contrary, infusing a drug with a higher price often means higher reimbursement for the administering clinician, since commercial insurance reimbursement is often calculated as a percent of the charge for the drug.
Further contributing to inertia is the extra time required for patient education and writing a new set of orders – all work that can’t be captured for extra reimbursement. Dr. Edgerton said that rheumatologists can talk with patients about the “nocebo effect” relating to biosimilars. “This is a phenomenon in which patients are thought to experience worsening symptoms associated with negative beliefs about biosimilars. There has been a study in Arthritis Care & Research addressing this concern. The authors found that positive framing of biosimilars led to more participants being willing to switch than negative framing. This suggests that clinicians have an important role in informing patients about biosimilars, and addressing hesitancy.”
Finally, Dr. Yazdany pointed out that for a pharmaceutical company pursuing biosimilar approval, the regulatory pathway itself can provide its own set of complications and confusion. Biosimilars are not exact molecular replicas of the originator biologic, and these differences can change efficacy and immunogenicity, and also affect stability. Hence, a company wishing to market a biosimilar has to show the Food and Drug Administration that safety and efficacy aren’t affected by a switch to biosimilar from an originator biologic. Extrapolation from one indication to another can be made – with scientific justification.
Rheumatologists are mindful of the potential differences between biosimilars and the originator biologic, as evinced in a recent position statement from the American College of Rheumatology. The position statement advises that “extrapolation should be pursued with caution,” and asks for clear labeling when biosimilars have been designated “interchangeable” with their biosimilar. Interchangeability can clear the way for pharmacy substitution of a prescribed biologic, though Dr. Yazdany noted that 40 states have passed legislation requiring prescriber notification.
The FDA is currently using postmarketing pharmacovigilance to monitor biosimilar performance in the real world, and a recent systematic review “should provide some reassurance,” wrote Dr. Yazdany, citing the study, which looked at 14,000 patients who had a total of 14 disease indications for biosimilar use. The 90-article review largely found no differences in safety, efficacy, or immunogenicity between originators and their biosimilars. Dr. Yazdany recommended greater openness to incorporating the European experience in the FDA’s ongoing reassessment.
A further way forward can come through tackling the patent thicket with the proposed bipartisan Biologic Patent Transparency Act, which would require publication of biologic patents in a one-stop publicly searchable database. Going further with legislation to address anticompetitive activity by pharmaceutical companies could shorten the runway to biosimilar launching considerably, she noted.
The complicated landscape of PBMs and rebates affects many sectors of health care, and new policy efforts are needed here as well, she said. Reimbursement strategies – and much-needed continuing medical education – can both ease prescriber unfamiliarity with biosimilars and provide incentives for their use, she concluded.
Dr. Kim concurred that change is needed before the United States is likely to reap significant economic benefit from biosimilars. “The uptake of biosimilars and their impact on overall health care cost needs to be reevaluated when we have more biosimilars available in the next 3-4 years. However, for now, it appears that substantial savings achieved in some European countries – for example, Denmark – may not be possible without systemic reform of the U.S. pharmaceutical market,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany is supported by the Alice Betts Endowed Chair in Arthritis Research, the Russel/Engleman Research Center at the University of California, San Francisco, and the National Institutes of Health. She has received independent research grants from Pfizer and Genentech and research consulting fees from Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca.
Dr. Kim’s study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Arnold Ventures. Dr. Kim has received research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche.
SOURCES: Kim SC et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 13. doi: 10.1002/art.41201; Yazdany J. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 10. doi: 10.1002/art.41203.
Although biosimilar versions of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis) have been available to U.S. rheumatologists and their patients for over 3 years, uptake has thus far been slow.
In an analysis of data from a large commercial payer, the two available biosimilars for infliximab (Remicade) accounted for less than 1% of TNFi prescribing since the first biosimilar to infliximab was approved in 2016.
The study, published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, involved a total of 1.1 million TNFi prescriptions or infusions received by 95,906 patients from 2016 to 2019. Investigators found that uptake of biosimilar infliximab was essentially flat, standing at 0.1% of prescribing in the second quarter of 2017, and topping out at 0.9% in the first quarter of 2019. For branded infliximab, prescribing was also stable, but accounted for about 20% of overall biologic dispensing in each quarter of the period studied.
There are currently two biosimilar medications to the originator infliximab, which is one of five originator biologics available to treat rheumatic diseases in the United States: infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) and infliximab-abda (Renflexis). The former was approved in 2016 and the latter in 2017, said study author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, ScD, of the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and her coauthors.
“Our paper reports a disappointingly low uptake of biosimilar infliximab since the first quarter of 2017 using claims data from a large private health plan. The main and maybe the only reason to consider using a biosimilar is cost saving,” said Dr. Kim in an interview. “Our results suggest that current modest cost savings from infliximab biosimilars in the U.S. are not sufficient to promote their widespread use.”
In the payer database study conducted by Dr. Kim and colleagues, the insurer paid similar mean amounts per patient per quarter for originator and biosimilar infliximab in mid-2017 ($8,322 versus $8,656). By the end of 2018, a gap appeared, with the insurer paying a mean quarterly per-patient sum of $8,111 for biosimilar infliximab compared with $9,535 for the branded biologic.
“The lack of market penetration and very modest price reductions for biosimilars have left policymakers, payers, physicians, and the public frustrated, particularly because sales in Europe continue to rapidly expand and robust cost-savings have materialized,” wrote Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, in an editorial accompanying the study.
Dr. Yazdany, professor and chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, noted that increased spending on biologics in the United States – which increased by 50% from 2014 to 2018 – has been driven by rising prices as well as increased uptake of biologic therapies.
At least in part, Europe has been able to reap cost savings where the United States hasn’t because fundamental differences in health care reimbursement can ease sweeping biosimilar adoption, Dr. Yazdany noted. “Countries like Denmark and Sweden, using the negotiating and purchasing power of their single-payer systems have instituted a winner-takes-all bidding system,” with Denmark seeing cost savings of up to two-thirds when bidding was combined with mandatory switching, she said.
The continued market dominance of originator infliximab means that savings from biosimilars have thus far amounted to about $91 million, far short of the $1 billion that the Congressional Budget Office had projected for this date, Dr. Yazdany said.
One problem in the adoption of biosimilars by U.S. rheumatologists may have been uneven marketing and pricing across different types of practice, Colin C. Edgerton, MD, a rheumatologist at Low Country Rheumatology in South Carolina and chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care, said in an interview.
“Rheumatologists have generally developed comfort with biosimilars, although this is not universal. The core message, that all biologics vary and that this is OK, is getting out. In general, rheumatologists also understand the problem with high drug prices and the threat to patient access,” Dr. Edgerton said. But “the early marketing and pricing focus for biosimilars seemed to be on hospitals and facilities, and this did not work effectively for community rheumatologists, where the majority of care is delivered. We have been pleased to see a manufacturer pivot toward community rheumatology where additional efforts need to be made to bend the curve on biosimilar adoption. It is critical for practices with experience using biosimilars to educate peers, and this is where networks of practicing rheumatologists are important.”
In Dr. Yazdany’s editorial, she cited four structural factors impeding biosimilar uptake and downstream savings.
First, she cites ongoing actions by pharmaceutical companies, which create a “patent thicket” that has the effect of fencing off originator biologics from biosimilars long beyond the original 12-year exclusivity period. Supporting the notion that “patent thickets” are a common strategy, Dr. Yazdany noted that almost half of the patent applications that AbbVie has filed for adalimumab (Humira) have come in after the original exclusivity period expired in 2014. Humira’s price has risen 18% yearly during this period.
The complicated role played by pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) is another factor in slow adoption, said Dr. Yazdany: When manufacturers offer rebates to PBMs, the price of the originator biologic may be less than its biosimilar. Further, manufacturers may sign multiyear rebate agreements just before a biosimilar launch; PBMs are also sometimes threatened with the withdrawal of rebates if they offer biosimilars, she noted.
Third, prescriber inertia may also be at play, Dr. Yazdany noted, not least because patients often see little difference in out-of-pocket costs when they make the switch to a biosimilar – PBM rebates are not necessarily passed on to patients. Payers may not reimburse a biosimilar, or formularies can be built without them, influencing prescribing, and there’s usually no reimbursement incentive for biosimilar prescribing in the nonpublic sector, she said. To the contrary, infusing a drug with a higher price often means higher reimbursement for the administering clinician, since commercial insurance reimbursement is often calculated as a percent of the charge for the drug.
Further contributing to inertia is the extra time required for patient education and writing a new set of orders – all work that can’t be captured for extra reimbursement. Dr. Edgerton said that rheumatologists can talk with patients about the “nocebo effect” relating to biosimilars. “This is a phenomenon in which patients are thought to experience worsening symptoms associated with negative beliefs about biosimilars. There has been a study in Arthritis Care & Research addressing this concern. The authors found that positive framing of biosimilars led to more participants being willing to switch than negative framing. This suggests that clinicians have an important role in informing patients about biosimilars, and addressing hesitancy.”
Finally, Dr. Yazdany pointed out that for a pharmaceutical company pursuing biosimilar approval, the regulatory pathway itself can provide its own set of complications and confusion. Biosimilars are not exact molecular replicas of the originator biologic, and these differences can change efficacy and immunogenicity, and also affect stability. Hence, a company wishing to market a biosimilar has to show the Food and Drug Administration that safety and efficacy aren’t affected by a switch to biosimilar from an originator biologic. Extrapolation from one indication to another can be made – with scientific justification.
Rheumatologists are mindful of the potential differences between biosimilars and the originator biologic, as evinced in a recent position statement from the American College of Rheumatology. The position statement advises that “extrapolation should be pursued with caution,” and asks for clear labeling when biosimilars have been designated “interchangeable” with their biosimilar. Interchangeability can clear the way for pharmacy substitution of a prescribed biologic, though Dr. Yazdany noted that 40 states have passed legislation requiring prescriber notification.
The FDA is currently using postmarketing pharmacovigilance to monitor biosimilar performance in the real world, and a recent systematic review “should provide some reassurance,” wrote Dr. Yazdany, citing the study, which looked at 14,000 patients who had a total of 14 disease indications for biosimilar use. The 90-article review largely found no differences in safety, efficacy, or immunogenicity between originators and their biosimilars. Dr. Yazdany recommended greater openness to incorporating the European experience in the FDA’s ongoing reassessment.
A further way forward can come through tackling the patent thicket with the proposed bipartisan Biologic Patent Transparency Act, which would require publication of biologic patents in a one-stop publicly searchable database. Going further with legislation to address anticompetitive activity by pharmaceutical companies could shorten the runway to biosimilar launching considerably, she noted.
The complicated landscape of PBMs and rebates affects many sectors of health care, and new policy efforts are needed here as well, she said. Reimbursement strategies – and much-needed continuing medical education – can both ease prescriber unfamiliarity with biosimilars and provide incentives for their use, she concluded.
Dr. Kim concurred that change is needed before the United States is likely to reap significant economic benefit from biosimilars. “The uptake of biosimilars and their impact on overall health care cost needs to be reevaluated when we have more biosimilars available in the next 3-4 years. However, for now, it appears that substantial savings achieved in some European countries – for example, Denmark – may not be possible without systemic reform of the U.S. pharmaceutical market,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany is supported by the Alice Betts Endowed Chair in Arthritis Research, the Russel/Engleman Research Center at the University of California, San Francisco, and the National Institutes of Health. She has received independent research grants from Pfizer and Genentech and research consulting fees from Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca.
Dr. Kim’s study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Arnold Ventures. Dr. Kim has received research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche.
SOURCES: Kim SC et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 13. doi: 10.1002/art.41201; Yazdany J. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 10. doi: 10.1002/art.41203.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Opioid deaths boost donor heart supply
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The tragic opioid epidemic has “one small bright spot”: an expanding pool of eligible donor hearts for transplantation, Akshay S. Desai, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
For decades, the annual volume of heart transplantations performed in the U.S. was static because of the huge mismatch between donor organ supply and demand. But heart transplant volume has increased steadily in the last few years – a result of the opioid epidemic.
Data from the U.S. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network show that the proportion of donor hearts obtained from individuals who died from drug intoxication climbed from a mere 1.5% in 1999 to 17.6% in 2017, the most recent year for which data are available. Meanwhile, the size of the heart transplant waiting list, which rose year after year in 2009-2015, has since declined (N Engl J Med. 2019 Feb 7;380[6]:597-9).
“What’s amazing is that, even though these patients might have historically been considered high risk in general, the organs recovered from these patients – and particularly the hearts – don’t seem to be any worse in terms of allograft survival than the organs recovered from patients who died from other causes, which are the traditional sources, like blunt head trauma, gunshot wounds, or stroke, that lead to brain death. In general, these organs are useful and do quite well,” according to Dr. Desai, medical director of the cardiomyopathy and heart failure program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
He highlighted several other recent developments in the field of cardiac transplantation that promise to further expand the donor heart pool, including acceptance of hepatitis C–infected donors and organ donation after circulatory rather than brain death. Dr. Desai also drew attention to the unintended perverse consequences of a recent redesign of the U.S. donor heart allocation system and discussed the impressive improvement in clinical outcomes with mechanical circulatory support. He noted that, while relatively few cardiologists practice in the highly specialized centers where heart transplants take place, virtually all cardiologists are affected by advances in heart transplantation since hundreds of thousands of the estimated 7 million Americans with heart failure have advanced disease.
Heart transplantation, he emphasized, is becoming increasingly complex. Recipients are on average older, sicker, and have more comorbidities than in times past. As a result, there is greater need for dual organ transplants: heart/lung, heart/liver, or heart/kidney. Plus, more patients come to transplantation after prior cardiac surgery for implantation of a ventricular assist device, so sensitization to blood products is a growing issue. And, of course, the pool of transplant candidates has expanded.
“We’re now forced to take patients previously considered to have contraindications to transplant; for example, diabetes was a contraindication to transplant in the early years, but now it’s the rule in 35%-40% of our patients who present with advanced heart failure,” the cardiologist noted.
Transplants from HCV-infected donors to uninfected recipients
Hearts and lungs from donors with hepatitis C viremia were traditionally deemed unsuitable for transplant. That’s all changed in the current era of highly effective direct-acting antiviral agents for the treatment of HCV infection.
In the DONATE HCV trial, Dr. Desai’s colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital showed that giving HCV-uninfected recipients of hearts or lungs from HCV-viremic donors a shortened 4-week course of treatment with sofosbuvir-velpatasvir (Epclusa) beginning within a few hours after transplantation uniformly blocked viral replication. Six months after transplantation, none of the study participants had a detectable HCV viral load, and all had excellent graft function (N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 25;380[17]:1606-17).
“This is effective prevention of HCV infection by aggressive upfront therapy,” Dr. Desai explained. “We can now take organs from HCV-viremic patients and use them in solid organ transplantation. This has led to a skyrocketing increase in donors with HCV infection, and those donations have helped us clear the waiting list.”
Donation after circulatory death
Australian transplant physicians have pioneered the use of donor hearts obtained after circulatory death in individuals with devastating neurologic injury who didn’t quite meet the criteria for brain death, which is the traditional prerequisite. In the new scenario, withdrawal of life-supporting therapy is followed by circulatory death, then the donor heart is procured and preserved via extracorporeal perfusion until transplantation.
The Australians report excellent outcomes, with rates of overall survival and rejection episodes similar to outcomes from brain-dead donors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Apr 2;73[12]:1447-59). The first U.S. heart transplant involving donation after circulatory death took place at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. A multicenter U.S. clinical trial of this practice is underway.
If the results are positive and the practice of donation after circulatory death becomes widely implemented, the U.S. heart donor pool could increase by 30%.
Recent overhaul of donor heart allocation system may have backfired
The U.S. donor heart allocation system was redesigned in the fall of 2018 in an effort to reduce waiting times. One of the biggest changes involved breaking down the category with the highest urgency status into three new subcategories based upon sickness. Now, the highest-urgency category is for patients in cardiogenic shock who are supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or other temporary mechanical circulatory support devices.
But an analysis of United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) data suggests this change has unintended adverse consequences for clinical outcomes.
Indeed, the investigators reported that the use of ECMO support is fourfold greater in the new system, the use of durable left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) as a bridge to transplant is down, and outcomes are worse. The 180-day rate of freedom from death or retransplantation was 77.9%, down significantly from 93.4% in the former system. In a multivariate analysis, patients transplanted in the new system had an adjusted 2.1-fold increased risk of death or retransplantation (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 Jan;39[1]:1-4).
“When you create a new listing system, you create new incentives, and people start to manage patients differently,” Dr. Desai observed. “Increasingly now, the path direct to transplant is through temporary mechanical circulatory support rather than durable mechanical circulatory support. Is that a good idea? We don’t know, but if you look at the best data, those on ECMO or percutaneous VADs have the worst outcomes. So the question of whether we should take the sickest of sick patients directly to transplant as a standard strategy has come under scrutiny.”
Improved durable LVAD technology brings impressive clinical outcomes
Results of the landmark MOMENTUM 3 randomized trial showed that 2-year clinical outcomes with the magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow HeartMate 3 LVAD now rival those of percutaneous mitral valve repair using the MitraClip device. Two-year all-cause mortality in the LVAD recipients was 22% versus 29.1% with the MitraClip in the COAPT trial and 34.9% in the MITRA-FR trial. The HeartMate 3 reduces the hemocompatibility issues that plagued earlier-generation durable LVADs, with resultant lower rates of pump thrombosis, stroke, and GI bleeding. Indeed, the outcomes in MOMENTUM 3 were so good – and so similar – with the HeartMate 3, regardless of whether the intended treatment goal was as a bridge to transplant or as lifelong destination therapy, that the investigators have recently proposed doing away with those distinctions.
“It is possible that use of arbitrary categorizations based on current or future transplant eligibility should be clinically abandoned in favor of a single preimplant strategy: to extend the survival and improve the quality of life of patients with medically refractory heart failure,” according to the investigators (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jan 15. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.5323).
The next step forward in LVAD technology is already on the horizon: a fully implantable device that eliminates the transcutaneous drive-line for the power supply, which is prone to infection and diminishes overall quality of life. This investigational device utilizes wireless coplanar energy transfer, with a coil ring placed around the lung and fixed to the chest wall. The implanted battery provides more than 6 hours of power without a recharge (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019 Apr;38[4]:339-43).
“The first LVAD patient has gone swimming in Kazakhstan,” according to Dr. Desai.
Myocardial recovery in LVAD recipients remains elusive
The initial hope for LVADs was that they would not only be able to serve as a bridge to transplantation or as lifetime therapy, but that the prolonged unloading of the ventricle would enable potent medical therapy to rescue myocardial function so that the device could eventually be explanted. That does happen, but only rarely. In a large registry study, myocardial recovery occurred in only about 1% of patients on mechanical circulatory support. Attempts to enhance the process by add-on stem cell therapy have thus far been ineffective.
“For the moment, recovery is still a hope, not a reality,” the cardiologist said.
He reported serving as a consultant to more than a dozen pharmaceutical or medical device companies and receiving research grants from Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, MyoKardia, and Novartis.
bjancin@mdedge.com
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The tragic opioid epidemic has “one small bright spot”: an expanding pool of eligible donor hearts for transplantation, Akshay S. Desai, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
For decades, the annual volume of heart transplantations performed in the U.S. was static because of the huge mismatch between donor organ supply and demand. But heart transplant volume has increased steadily in the last few years – a result of the opioid epidemic.
Data from the U.S. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network show that the proportion of donor hearts obtained from individuals who died from drug intoxication climbed from a mere 1.5% in 1999 to 17.6% in 2017, the most recent year for which data are available. Meanwhile, the size of the heart transplant waiting list, which rose year after year in 2009-2015, has since declined (N Engl J Med. 2019 Feb 7;380[6]:597-9).
“What’s amazing is that, even though these patients might have historically been considered high risk in general, the organs recovered from these patients – and particularly the hearts – don’t seem to be any worse in terms of allograft survival than the organs recovered from patients who died from other causes, which are the traditional sources, like blunt head trauma, gunshot wounds, or stroke, that lead to brain death. In general, these organs are useful and do quite well,” according to Dr. Desai, medical director of the cardiomyopathy and heart failure program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
He highlighted several other recent developments in the field of cardiac transplantation that promise to further expand the donor heart pool, including acceptance of hepatitis C–infected donors and organ donation after circulatory rather than brain death. Dr. Desai also drew attention to the unintended perverse consequences of a recent redesign of the U.S. donor heart allocation system and discussed the impressive improvement in clinical outcomes with mechanical circulatory support. He noted that, while relatively few cardiologists practice in the highly specialized centers where heart transplants take place, virtually all cardiologists are affected by advances in heart transplantation since hundreds of thousands of the estimated 7 million Americans with heart failure have advanced disease.
Heart transplantation, he emphasized, is becoming increasingly complex. Recipients are on average older, sicker, and have more comorbidities than in times past. As a result, there is greater need for dual organ transplants: heart/lung, heart/liver, or heart/kidney. Plus, more patients come to transplantation after prior cardiac surgery for implantation of a ventricular assist device, so sensitization to blood products is a growing issue. And, of course, the pool of transplant candidates has expanded.
“We’re now forced to take patients previously considered to have contraindications to transplant; for example, diabetes was a contraindication to transplant in the early years, but now it’s the rule in 35%-40% of our patients who present with advanced heart failure,” the cardiologist noted.
Transplants from HCV-infected donors to uninfected recipients
Hearts and lungs from donors with hepatitis C viremia were traditionally deemed unsuitable for transplant. That’s all changed in the current era of highly effective direct-acting antiviral agents for the treatment of HCV infection.
In the DONATE HCV trial, Dr. Desai’s colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital showed that giving HCV-uninfected recipients of hearts or lungs from HCV-viremic donors a shortened 4-week course of treatment with sofosbuvir-velpatasvir (Epclusa) beginning within a few hours after transplantation uniformly blocked viral replication. Six months after transplantation, none of the study participants had a detectable HCV viral load, and all had excellent graft function (N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 25;380[17]:1606-17).
“This is effective prevention of HCV infection by aggressive upfront therapy,” Dr. Desai explained. “We can now take organs from HCV-viremic patients and use them in solid organ transplantation. This has led to a skyrocketing increase in donors with HCV infection, and those donations have helped us clear the waiting list.”
Donation after circulatory death
Australian transplant physicians have pioneered the use of donor hearts obtained after circulatory death in individuals with devastating neurologic injury who didn’t quite meet the criteria for brain death, which is the traditional prerequisite. In the new scenario, withdrawal of life-supporting therapy is followed by circulatory death, then the donor heart is procured and preserved via extracorporeal perfusion until transplantation.
The Australians report excellent outcomes, with rates of overall survival and rejection episodes similar to outcomes from brain-dead donors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Apr 2;73[12]:1447-59). The first U.S. heart transplant involving donation after circulatory death took place at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. A multicenter U.S. clinical trial of this practice is underway.
If the results are positive and the practice of donation after circulatory death becomes widely implemented, the U.S. heart donor pool could increase by 30%.
Recent overhaul of donor heart allocation system may have backfired
The U.S. donor heart allocation system was redesigned in the fall of 2018 in an effort to reduce waiting times. One of the biggest changes involved breaking down the category with the highest urgency status into three new subcategories based upon sickness. Now, the highest-urgency category is for patients in cardiogenic shock who are supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or other temporary mechanical circulatory support devices.
But an analysis of United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) data suggests this change has unintended adverse consequences for clinical outcomes.
Indeed, the investigators reported that the use of ECMO support is fourfold greater in the new system, the use of durable left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) as a bridge to transplant is down, and outcomes are worse. The 180-day rate of freedom from death or retransplantation was 77.9%, down significantly from 93.4% in the former system. In a multivariate analysis, patients transplanted in the new system had an adjusted 2.1-fold increased risk of death or retransplantation (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 Jan;39[1]:1-4).
“When you create a new listing system, you create new incentives, and people start to manage patients differently,” Dr. Desai observed. “Increasingly now, the path direct to transplant is through temporary mechanical circulatory support rather than durable mechanical circulatory support. Is that a good idea? We don’t know, but if you look at the best data, those on ECMO or percutaneous VADs have the worst outcomes. So the question of whether we should take the sickest of sick patients directly to transplant as a standard strategy has come under scrutiny.”
Improved durable LVAD technology brings impressive clinical outcomes
Results of the landmark MOMENTUM 3 randomized trial showed that 2-year clinical outcomes with the magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow HeartMate 3 LVAD now rival those of percutaneous mitral valve repair using the MitraClip device. Two-year all-cause mortality in the LVAD recipients was 22% versus 29.1% with the MitraClip in the COAPT trial and 34.9% in the MITRA-FR trial. The HeartMate 3 reduces the hemocompatibility issues that plagued earlier-generation durable LVADs, with resultant lower rates of pump thrombosis, stroke, and GI bleeding. Indeed, the outcomes in MOMENTUM 3 were so good – and so similar – with the HeartMate 3, regardless of whether the intended treatment goal was as a bridge to transplant or as lifelong destination therapy, that the investigators have recently proposed doing away with those distinctions.
“It is possible that use of arbitrary categorizations based on current or future transplant eligibility should be clinically abandoned in favor of a single preimplant strategy: to extend the survival and improve the quality of life of patients with medically refractory heart failure,” according to the investigators (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jan 15. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.5323).
The next step forward in LVAD technology is already on the horizon: a fully implantable device that eliminates the transcutaneous drive-line for the power supply, which is prone to infection and diminishes overall quality of life. This investigational device utilizes wireless coplanar energy transfer, with a coil ring placed around the lung and fixed to the chest wall. The implanted battery provides more than 6 hours of power without a recharge (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019 Apr;38[4]:339-43).
“The first LVAD patient has gone swimming in Kazakhstan,” according to Dr. Desai.
Myocardial recovery in LVAD recipients remains elusive
The initial hope for LVADs was that they would not only be able to serve as a bridge to transplantation or as lifetime therapy, but that the prolonged unloading of the ventricle would enable potent medical therapy to rescue myocardial function so that the device could eventually be explanted. That does happen, but only rarely. In a large registry study, myocardial recovery occurred in only about 1% of patients on mechanical circulatory support. Attempts to enhance the process by add-on stem cell therapy have thus far been ineffective.
“For the moment, recovery is still a hope, not a reality,” the cardiologist said.
He reported serving as a consultant to more than a dozen pharmaceutical or medical device companies and receiving research grants from Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, MyoKardia, and Novartis.
bjancin@mdedge.com
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The tragic opioid epidemic has “one small bright spot”: an expanding pool of eligible donor hearts for transplantation, Akshay S. Desai, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
For decades, the annual volume of heart transplantations performed in the U.S. was static because of the huge mismatch between donor organ supply and demand. But heart transplant volume has increased steadily in the last few years – a result of the opioid epidemic.
Data from the U.S. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network show that the proportion of donor hearts obtained from individuals who died from drug intoxication climbed from a mere 1.5% in 1999 to 17.6% in 2017, the most recent year for which data are available. Meanwhile, the size of the heart transplant waiting list, which rose year after year in 2009-2015, has since declined (N Engl J Med. 2019 Feb 7;380[6]:597-9).
“What’s amazing is that, even though these patients might have historically been considered high risk in general, the organs recovered from these patients – and particularly the hearts – don’t seem to be any worse in terms of allograft survival than the organs recovered from patients who died from other causes, which are the traditional sources, like blunt head trauma, gunshot wounds, or stroke, that lead to brain death. In general, these organs are useful and do quite well,” according to Dr. Desai, medical director of the cardiomyopathy and heart failure program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
He highlighted several other recent developments in the field of cardiac transplantation that promise to further expand the donor heart pool, including acceptance of hepatitis C–infected donors and organ donation after circulatory rather than brain death. Dr. Desai also drew attention to the unintended perverse consequences of a recent redesign of the U.S. donor heart allocation system and discussed the impressive improvement in clinical outcomes with mechanical circulatory support. He noted that, while relatively few cardiologists practice in the highly specialized centers where heart transplants take place, virtually all cardiologists are affected by advances in heart transplantation since hundreds of thousands of the estimated 7 million Americans with heart failure have advanced disease.
Heart transplantation, he emphasized, is becoming increasingly complex. Recipients are on average older, sicker, and have more comorbidities than in times past. As a result, there is greater need for dual organ transplants: heart/lung, heart/liver, or heart/kidney. Plus, more patients come to transplantation after prior cardiac surgery for implantation of a ventricular assist device, so sensitization to blood products is a growing issue. And, of course, the pool of transplant candidates has expanded.
“We’re now forced to take patients previously considered to have contraindications to transplant; for example, diabetes was a contraindication to transplant in the early years, but now it’s the rule in 35%-40% of our patients who present with advanced heart failure,” the cardiologist noted.
Transplants from HCV-infected donors to uninfected recipients
Hearts and lungs from donors with hepatitis C viremia were traditionally deemed unsuitable for transplant. That’s all changed in the current era of highly effective direct-acting antiviral agents for the treatment of HCV infection.
In the DONATE HCV trial, Dr. Desai’s colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital showed that giving HCV-uninfected recipients of hearts or lungs from HCV-viremic donors a shortened 4-week course of treatment with sofosbuvir-velpatasvir (Epclusa) beginning within a few hours after transplantation uniformly blocked viral replication. Six months after transplantation, none of the study participants had a detectable HCV viral load, and all had excellent graft function (N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 25;380[17]:1606-17).
“This is effective prevention of HCV infection by aggressive upfront therapy,” Dr. Desai explained. “We can now take organs from HCV-viremic patients and use them in solid organ transplantation. This has led to a skyrocketing increase in donors with HCV infection, and those donations have helped us clear the waiting list.”
Donation after circulatory death
Australian transplant physicians have pioneered the use of donor hearts obtained after circulatory death in individuals with devastating neurologic injury who didn’t quite meet the criteria for brain death, which is the traditional prerequisite. In the new scenario, withdrawal of life-supporting therapy is followed by circulatory death, then the donor heart is procured and preserved via extracorporeal perfusion until transplantation.
The Australians report excellent outcomes, with rates of overall survival and rejection episodes similar to outcomes from brain-dead donors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Apr 2;73[12]:1447-59). The first U.S. heart transplant involving donation after circulatory death took place at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. A multicenter U.S. clinical trial of this practice is underway.
If the results are positive and the practice of donation after circulatory death becomes widely implemented, the U.S. heart donor pool could increase by 30%.
Recent overhaul of donor heart allocation system may have backfired
The U.S. donor heart allocation system was redesigned in the fall of 2018 in an effort to reduce waiting times. One of the biggest changes involved breaking down the category with the highest urgency status into three new subcategories based upon sickness. Now, the highest-urgency category is for patients in cardiogenic shock who are supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or other temporary mechanical circulatory support devices.
But an analysis of United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) data suggests this change has unintended adverse consequences for clinical outcomes.
Indeed, the investigators reported that the use of ECMO support is fourfold greater in the new system, the use of durable left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) as a bridge to transplant is down, and outcomes are worse. The 180-day rate of freedom from death or retransplantation was 77.9%, down significantly from 93.4% in the former system. In a multivariate analysis, patients transplanted in the new system had an adjusted 2.1-fold increased risk of death or retransplantation (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 Jan;39[1]:1-4).
“When you create a new listing system, you create new incentives, and people start to manage patients differently,” Dr. Desai observed. “Increasingly now, the path direct to transplant is through temporary mechanical circulatory support rather than durable mechanical circulatory support. Is that a good idea? We don’t know, but if you look at the best data, those on ECMO or percutaneous VADs have the worst outcomes. So the question of whether we should take the sickest of sick patients directly to transplant as a standard strategy has come under scrutiny.”
Improved durable LVAD technology brings impressive clinical outcomes
Results of the landmark MOMENTUM 3 randomized trial showed that 2-year clinical outcomes with the magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow HeartMate 3 LVAD now rival those of percutaneous mitral valve repair using the MitraClip device. Two-year all-cause mortality in the LVAD recipients was 22% versus 29.1% with the MitraClip in the COAPT trial and 34.9% in the MITRA-FR trial. The HeartMate 3 reduces the hemocompatibility issues that plagued earlier-generation durable LVADs, with resultant lower rates of pump thrombosis, stroke, and GI bleeding. Indeed, the outcomes in MOMENTUM 3 were so good – and so similar – with the HeartMate 3, regardless of whether the intended treatment goal was as a bridge to transplant or as lifelong destination therapy, that the investigators have recently proposed doing away with those distinctions.
“It is possible that use of arbitrary categorizations based on current or future transplant eligibility should be clinically abandoned in favor of a single preimplant strategy: to extend the survival and improve the quality of life of patients with medically refractory heart failure,” according to the investigators (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jan 15. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.5323).
The next step forward in LVAD technology is already on the horizon: a fully implantable device that eliminates the transcutaneous drive-line for the power supply, which is prone to infection and diminishes overall quality of life. This investigational device utilizes wireless coplanar energy transfer, with a coil ring placed around the lung and fixed to the chest wall. The implanted battery provides more than 6 hours of power without a recharge (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019 Apr;38[4]:339-43).
“The first LVAD patient has gone swimming in Kazakhstan,” according to Dr. Desai.
Myocardial recovery in LVAD recipients remains elusive
The initial hope for LVADs was that they would not only be able to serve as a bridge to transplantation or as lifetime therapy, but that the prolonged unloading of the ventricle would enable potent medical therapy to rescue myocardial function so that the device could eventually be explanted. That does happen, but only rarely. In a large registry study, myocardial recovery occurred in only about 1% of patients on mechanical circulatory support. Attempts to enhance the process by add-on stem cell therapy have thus far been ineffective.
“For the moment, recovery is still a hope, not a reality,” the cardiologist said.
He reported serving as a consultant to more than a dozen pharmaceutical or medical device companies and receiving research grants from Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, MyoKardia, and Novartis.
bjancin@mdedge.com
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC SNOWMASS 2020
Cannabis use in pregnancy and lactation: A changing landscape
National survey data from 2007-2012 of more than 93,000 pregnant women suggest that around 7% of pregnant respondents reported any cannabis use in the last 2-12 months; of those, 16% reported daily or almost daily use. Among pregnant past-year users in the same survey, 70% perceived slight or no risk of harm from cannabis use 1-2 times a week in pregnancy.1
Data from the Kaiser Northern California health plan involving more than 279,000 pregnancies followed during 2009-2016 suggest that there has been a significant upward trend in use of cannabis during pregnancy, from 4% to 7%, as reported by the mother and/or identified by routine urine screening. The highest prevalence in that study was seen among 18- to 24-year-old pregnant women, increasing from 13% to 22% over the 7-year study period. Importantly, more than 50% of cannabis users in the sample were identified by toxicology screening alone.2,3 Common reasons given for use of cannabis in pregnancy include anxiety, pain, and nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.4
With respect to adverse perinatal outcomes, several case-control studies have examined risks for major birth defects with maternal self-report of cannabis use. Some have noted very modest increased risks for selected major birth defects (odds ratios less than 2); however, data still are very limited.5,6
A number of prospective studies have addressed risks of preterm birth and growth restriction, accounting for mother’s concomitant tobacco use.7-11 Some of these studies have suggested about a twofold to threefold increased risk for preterm delivery and an increased risk for reduced birth weight – particularly with heavier or regular cannabis use – but study findings have not been entirely consistent.
Given its psychoactive properties, there has been high interest in understanding whether there are any short- or long-term neurodevelopmental effects on children prenatally exposed to cannabis. These outcomes have been studied in two small older cohorts in the United States and Canada and one more recent cohort in the Netherlands.12-15 Deficits in several measures of cognition and behavior were noted in follow-up of those children from birth to adulthood. However, it is unclear to what extent these findings may have been influenced by heredity, environment, or other factors.
There have been limitations in almost all studies published to date, including small sample sizes, no biomarker validation of maternal report of dose and gestational timing of cannabis use, and lack of detailed data on common coexposures, such as alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs. In addition, newer studies of pregnancy outcomes in women who use currently available cannabis products are needed, given the substantial increase in the potency of cannabis used today, compared with that of 20 years ago. For example, the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentration in commonly cultivated marijuana plants has increased threefold from 4% to 12% between 1995 and 2014.16
There are very limited data on the presence of cannabis in breast milk and the potential effects of exposure to THC and other metabolites for breastfed infants. However, two recent studies have demonstrated there are low but measurable levels of some cannabis metabolites in breast milk.17-18 Further work is needed to determine if these metabolites accumulate in milk and if at a given dose and age of the breastfed infant, there are any growth, neurodevelopmental, or other clinically important adverse effects.
Related questions, such as potential differences in the effects of exposure during pregnancy or lactation based on the route of administration (edible vs. inhaled) and the use of cannabidiol (CBD) products, have not been studied.
At the present time, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women who are pregnant or contemplating pregnancy be encouraged to discontinue marijuana use. With respect to lactation and breastfeeding, ACOG concludes there are insufficient data to evaluate the effects on infants, and in the absence of such data, marijuana use is discouraged. Similarly, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends women of childbearing age abstain from marijuana use while pregnant or breastfeeding because of potential adverse consequences to the fetus, infant, or child.
In August 2019, the U.S. Surgeon General issued an advisory regarding potential harm to developing brains from the use of marijuana during pregnancy and lactation. The Food and Drug Administration issued a similar statement in October 2019 strongly advising against the use of CBD, THC, and marijuana in any form during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Dr. Chambers is professor of pediatrics and director of clinical research at Rady Children’s Hospital and associate director of the Clinical and Translational Research Institute at the University of California, San Diego. She is also director of MotherToBaby California, president of the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists, and past president of the Teratology Society.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Aug;213(2):201.e1-10.
2. JAMA. 2017 Dec 26;318(24):2490-1.
3. JAMA. 2017 Jan 10;317(2):207-9.
4. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2009 Nov;15(4)242-6.
5. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2014 Sep; 28(5): 424-33.
6. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2007 Jan;70(1):7-18.
7. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Aug 15;146(8):992-4.
8. Clin Perinatol. 1991 Mar;18(1):77-91.
9. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Dec;124(6):986-93.
10. Pediatr Res. 2012 Feb;71(2):215-9.
11. Reprod Toxicol. 2016;62:77-86.
12. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1-7.
13. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1994 Mar-Apr;16(2):169-75.
14. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Jun 15;79(12):971-9.
15. Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Feb;182:133-51.
16. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;79(7):613-9.
17. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 May;131(5):783-8.
18. Pediatrics. 2018 Sep;142(3):e20181076.
National survey data from 2007-2012 of more than 93,000 pregnant women suggest that around 7% of pregnant respondents reported any cannabis use in the last 2-12 months; of those, 16% reported daily or almost daily use. Among pregnant past-year users in the same survey, 70% perceived slight or no risk of harm from cannabis use 1-2 times a week in pregnancy.1
Data from the Kaiser Northern California health plan involving more than 279,000 pregnancies followed during 2009-2016 suggest that there has been a significant upward trend in use of cannabis during pregnancy, from 4% to 7%, as reported by the mother and/or identified by routine urine screening. The highest prevalence in that study was seen among 18- to 24-year-old pregnant women, increasing from 13% to 22% over the 7-year study period. Importantly, more than 50% of cannabis users in the sample were identified by toxicology screening alone.2,3 Common reasons given for use of cannabis in pregnancy include anxiety, pain, and nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.4
With respect to adverse perinatal outcomes, several case-control studies have examined risks for major birth defects with maternal self-report of cannabis use. Some have noted very modest increased risks for selected major birth defects (odds ratios less than 2); however, data still are very limited.5,6
A number of prospective studies have addressed risks of preterm birth and growth restriction, accounting for mother’s concomitant tobacco use.7-11 Some of these studies have suggested about a twofold to threefold increased risk for preterm delivery and an increased risk for reduced birth weight – particularly with heavier or regular cannabis use – but study findings have not been entirely consistent.
Given its psychoactive properties, there has been high interest in understanding whether there are any short- or long-term neurodevelopmental effects on children prenatally exposed to cannabis. These outcomes have been studied in two small older cohorts in the United States and Canada and one more recent cohort in the Netherlands.12-15 Deficits in several measures of cognition and behavior were noted in follow-up of those children from birth to adulthood. However, it is unclear to what extent these findings may have been influenced by heredity, environment, or other factors.
There have been limitations in almost all studies published to date, including small sample sizes, no biomarker validation of maternal report of dose and gestational timing of cannabis use, and lack of detailed data on common coexposures, such as alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs. In addition, newer studies of pregnancy outcomes in women who use currently available cannabis products are needed, given the substantial increase in the potency of cannabis used today, compared with that of 20 years ago. For example, the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentration in commonly cultivated marijuana plants has increased threefold from 4% to 12% between 1995 and 2014.16
There are very limited data on the presence of cannabis in breast milk and the potential effects of exposure to THC and other metabolites for breastfed infants. However, two recent studies have demonstrated there are low but measurable levels of some cannabis metabolites in breast milk.17-18 Further work is needed to determine if these metabolites accumulate in milk and if at a given dose and age of the breastfed infant, there are any growth, neurodevelopmental, or other clinically important adverse effects.
Related questions, such as potential differences in the effects of exposure during pregnancy or lactation based on the route of administration (edible vs. inhaled) and the use of cannabidiol (CBD) products, have not been studied.
At the present time, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women who are pregnant or contemplating pregnancy be encouraged to discontinue marijuana use. With respect to lactation and breastfeeding, ACOG concludes there are insufficient data to evaluate the effects on infants, and in the absence of such data, marijuana use is discouraged. Similarly, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends women of childbearing age abstain from marijuana use while pregnant or breastfeeding because of potential adverse consequences to the fetus, infant, or child.
In August 2019, the U.S. Surgeon General issued an advisory regarding potential harm to developing brains from the use of marijuana during pregnancy and lactation. The Food and Drug Administration issued a similar statement in October 2019 strongly advising against the use of CBD, THC, and marijuana in any form during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Dr. Chambers is professor of pediatrics and director of clinical research at Rady Children’s Hospital and associate director of the Clinical and Translational Research Institute at the University of California, San Diego. She is also director of MotherToBaby California, president of the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists, and past president of the Teratology Society.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Aug;213(2):201.e1-10.
2. JAMA. 2017 Dec 26;318(24):2490-1.
3. JAMA. 2017 Jan 10;317(2):207-9.
4. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2009 Nov;15(4)242-6.
5. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2014 Sep; 28(5): 424-33.
6. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2007 Jan;70(1):7-18.
7. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Aug 15;146(8):992-4.
8. Clin Perinatol. 1991 Mar;18(1):77-91.
9. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Dec;124(6):986-93.
10. Pediatr Res. 2012 Feb;71(2):215-9.
11. Reprod Toxicol. 2016;62:77-86.
12. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1-7.
13. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1994 Mar-Apr;16(2):169-75.
14. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Jun 15;79(12):971-9.
15. Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Feb;182:133-51.
16. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;79(7):613-9.
17. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 May;131(5):783-8.
18. Pediatrics. 2018 Sep;142(3):e20181076.
National survey data from 2007-2012 of more than 93,000 pregnant women suggest that around 7% of pregnant respondents reported any cannabis use in the last 2-12 months; of those, 16% reported daily or almost daily use. Among pregnant past-year users in the same survey, 70% perceived slight or no risk of harm from cannabis use 1-2 times a week in pregnancy.1
Data from the Kaiser Northern California health plan involving more than 279,000 pregnancies followed during 2009-2016 suggest that there has been a significant upward trend in use of cannabis during pregnancy, from 4% to 7%, as reported by the mother and/or identified by routine urine screening. The highest prevalence in that study was seen among 18- to 24-year-old pregnant women, increasing from 13% to 22% over the 7-year study period. Importantly, more than 50% of cannabis users in the sample were identified by toxicology screening alone.2,3 Common reasons given for use of cannabis in pregnancy include anxiety, pain, and nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.4
With respect to adverse perinatal outcomes, several case-control studies have examined risks for major birth defects with maternal self-report of cannabis use. Some have noted very modest increased risks for selected major birth defects (odds ratios less than 2); however, data still are very limited.5,6
A number of prospective studies have addressed risks of preterm birth and growth restriction, accounting for mother’s concomitant tobacco use.7-11 Some of these studies have suggested about a twofold to threefold increased risk for preterm delivery and an increased risk for reduced birth weight – particularly with heavier or regular cannabis use – but study findings have not been entirely consistent.
Given its psychoactive properties, there has been high interest in understanding whether there are any short- or long-term neurodevelopmental effects on children prenatally exposed to cannabis. These outcomes have been studied in two small older cohorts in the United States and Canada and one more recent cohort in the Netherlands.12-15 Deficits in several measures of cognition and behavior were noted in follow-up of those children from birth to adulthood. However, it is unclear to what extent these findings may have been influenced by heredity, environment, or other factors.
There have been limitations in almost all studies published to date, including small sample sizes, no biomarker validation of maternal report of dose and gestational timing of cannabis use, and lack of detailed data on common coexposures, such as alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs. In addition, newer studies of pregnancy outcomes in women who use currently available cannabis products are needed, given the substantial increase in the potency of cannabis used today, compared with that of 20 years ago. For example, the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentration in commonly cultivated marijuana plants has increased threefold from 4% to 12% between 1995 and 2014.16
There are very limited data on the presence of cannabis in breast milk and the potential effects of exposure to THC and other metabolites for breastfed infants. However, two recent studies have demonstrated there are low but measurable levels of some cannabis metabolites in breast milk.17-18 Further work is needed to determine if these metabolites accumulate in milk and if at a given dose and age of the breastfed infant, there are any growth, neurodevelopmental, or other clinically important adverse effects.
Related questions, such as potential differences in the effects of exposure during pregnancy or lactation based on the route of administration (edible vs. inhaled) and the use of cannabidiol (CBD) products, have not been studied.
At the present time, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women who are pregnant or contemplating pregnancy be encouraged to discontinue marijuana use. With respect to lactation and breastfeeding, ACOG concludes there are insufficient data to evaluate the effects on infants, and in the absence of such data, marijuana use is discouraged. Similarly, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends women of childbearing age abstain from marijuana use while pregnant or breastfeeding because of potential adverse consequences to the fetus, infant, or child.
In August 2019, the U.S. Surgeon General issued an advisory regarding potential harm to developing brains from the use of marijuana during pregnancy and lactation. The Food and Drug Administration issued a similar statement in October 2019 strongly advising against the use of CBD, THC, and marijuana in any form during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Dr. Chambers is professor of pediatrics and director of clinical research at Rady Children’s Hospital and associate director of the Clinical and Translational Research Institute at the University of California, San Diego. She is also director of MotherToBaby California, president of the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists, and past president of the Teratology Society.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Aug;213(2):201.e1-10.
2. JAMA. 2017 Dec 26;318(24):2490-1.
3. JAMA. 2017 Jan 10;317(2):207-9.
4. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2009 Nov;15(4)242-6.
5. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2014 Sep; 28(5): 424-33.
6. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2007 Jan;70(1):7-18.
7. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Aug 15;146(8):992-4.
8. Clin Perinatol. 1991 Mar;18(1):77-91.
9. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Dec;124(6):986-93.
10. Pediatr Res. 2012 Feb;71(2):215-9.
11. Reprod Toxicol. 2016;62:77-86.
12. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1-7.
13. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1994 Mar-Apr;16(2):169-75.
14. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Jun 15;79(12):971-9.
15. Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Feb;182:133-51.
16. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;79(7):613-9.
17. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 May;131(5):783-8.
18. Pediatrics. 2018 Sep;142(3):e20181076.
CDC: Five confirmed 2019-nCoV cases in the U.S.
Five cases of the new infectious coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, have been confirmed in the United States, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during a Jan. 27 press briefing.
A total of 110 individuals are under investigation in 26 states, she said. While five cases have been confirmed positive for the virus, 32 cases were confirmed negative. There have been no new cases overnight.
Last week, CDC scientists developed a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test that can diagnose the virus in respiratory and serum samples from clinical specimens. On Jan. 24, the protocol for this test was publicly posted. “This is essentially a blueprint to make the test,” Dr. Messonnier explained. “Currently, we are refining the use of the test so that it can provide optimal guidance to states and labs on how to use it. We are working on a plan so that priority states get these test kits as soon as possible. In the coming weeks, we will share these tests with domestic and international partners so they can test for this virus themselves.”
The CDC uploaded the entire genome of the virus from the first two cases in the United States to GenBank. It was similar to the one that China had previously posted. “Right now, based on CDC’s analysis of the available data, it doesn’t look like the virus has mutated,” she said. “And we are growing the virus in cell culture, which is necessary for further studies, including the additional genetic characterization.”
As of today, 16 international locations, including the United States, have identified cases of the virus. CDC officials are continuing to screen passengers from Wuhan, China, at five designated airports. “This serves two purposes: first to detect the illness and rapidly respond to [affected] people entering the country,” Dr. Messonnier said. “The second purpose is to educate travelers about the symptoms of this new virus, and what to do if they develop symptoms. I expect that in the coming days, our travel recommendations will change. Risk depends on exposure. Right now, we have an handful of new patients with this new virus here in the U.S. However, at this time in the U.S., this virus is not spreading in the community. For that reason, we believe that the immediate health risk of the new virus to the general American public is low.”
The CDC is asking its clinical lab partners to send virus samples to the CDC to ensure that results are analyzed as accurately as possible.
Five cases of the new infectious coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, have been confirmed in the United States, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during a Jan. 27 press briefing.
A total of 110 individuals are under investigation in 26 states, she said. While five cases have been confirmed positive for the virus, 32 cases were confirmed negative. There have been no new cases overnight.
Last week, CDC scientists developed a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test that can diagnose the virus in respiratory and serum samples from clinical specimens. On Jan. 24, the protocol for this test was publicly posted. “This is essentially a blueprint to make the test,” Dr. Messonnier explained. “Currently, we are refining the use of the test so that it can provide optimal guidance to states and labs on how to use it. We are working on a plan so that priority states get these test kits as soon as possible. In the coming weeks, we will share these tests with domestic and international partners so they can test for this virus themselves.”
The CDC uploaded the entire genome of the virus from the first two cases in the United States to GenBank. It was similar to the one that China had previously posted. “Right now, based on CDC’s analysis of the available data, it doesn’t look like the virus has mutated,” she said. “And we are growing the virus in cell culture, which is necessary for further studies, including the additional genetic characterization.”
As of today, 16 international locations, including the United States, have identified cases of the virus. CDC officials are continuing to screen passengers from Wuhan, China, at five designated airports. “This serves two purposes: first to detect the illness and rapidly respond to [affected] people entering the country,” Dr. Messonnier said. “The second purpose is to educate travelers about the symptoms of this new virus, and what to do if they develop symptoms. I expect that in the coming days, our travel recommendations will change. Risk depends on exposure. Right now, we have an handful of new patients with this new virus here in the U.S. However, at this time in the U.S., this virus is not spreading in the community. For that reason, we believe that the immediate health risk of the new virus to the general American public is low.”
The CDC is asking its clinical lab partners to send virus samples to the CDC to ensure that results are analyzed as accurately as possible.
Five cases of the new infectious coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, have been confirmed in the United States, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during a Jan. 27 press briefing.
A total of 110 individuals are under investigation in 26 states, she said. While five cases have been confirmed positive for the virus, 32 cases were confirmed negative. There have been no new cases overnight.
Last week, CDC scientists developed a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test that can diagnose the virus in respiratory and serum samples from clinical specimens. On Jan. 24, the protocol for this test was publicly posted. “This is essentially a blueprint to make the test,” Dr. Messonnier explained. “Currently, we are refining the use of the test so that it can provide optimal guidance to states and labs on how to use it. We are working on a plan so that priority states get these test kits as soon as possible. In the coming weeks, we will share these tests with domestic and international partners so they can test for this virus themselves.”
The CDC uploaded the entire genome of the virus from the first two cases in the United States to GenBank. It was similar to the one that China had previously posted. “Right now, based on CDC’s analysis of the available data, it doesn’t look like the virus has mutated,” she said. “And we are growing the virus in cell culture, which is necessary for further studies, including the additional genetic characterization.”
As of today, 16 international locations, including the United States, have identified cases of the virus. CDC officials are continuing to screen passengers from Wuhan, China, at five designated airports. “This serves two purposes: first to detect the illness and rapidly respond to [affected] people entering the country,” Dr. Messonnier said. “The second purpose is to educate travelers about the symptoms of this new virus, and what to do if they develop symptoms. I expect that in the coming days, our travel recommendations will change. Risk depends on exposure. Right now, we have an handful of new patients with this new virus here in the U.S. However, at this time in the U.S., this virus is not spreading in the community. For that reason, we believe that the immediate health risk of the new virus to the general American public is low.”
The CDC is asking its clinical lab partners to send virus samples to the CDC to ensure that results are analyzed as accurately as possible.
FFR use nearly halved 1-year mortality risk in ischemic heart disease
Use of fractional flow reserve significantly improved 1-year mortality rates in adults with stable ischemic heart disease, according to a review of 17,989 patients.
Although fractional flow reserve (FFR) has demonstrated value in guiding coronary revascularization, its impact on outcomes in patients with stable ischemic heart disease has not been well studied in a large population, wrote Rushi V. Parikh, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers analyzed data from the Veterans Affairs Clinical Assessment, Reporting, and Tracking Program for adults who underwent coronary angiography between January 2009 and September 2017. The study included patients with angiographically intermediate disease, defined as 40%-69% diameter stenosis on visual inspection.
The rate of FFR use increased from 14.8% to 18.5% during the study period for all patients with intermediate lesions, and from 44% to 75% for those who had percutaneous coronary intervention, the researchers wrote.
Overall, based on hazard models, 1-year mortality was significantly lower in patients who underwent FFR, compared with those who had angiography only (2.8% vs. 5.9%; P less than 0.001). In addition, FFR use in revascularization was associated with a 43% reduced 1-year mortality risk, compared with angiography only.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the observational nature of the study, inability to distinguish between cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality, lack of data on the technical performance of the FFR, and a relatively short follow-up period, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and support the use of FFR-guided revascularization in patients with angiographically intermediate stenosis, they wrote.
“Future registry-based studies accounting for all physiologic modalities are warranted to accurately quantify the landscape of coronary physiology-guided revascularization,” they added.
The study was supported in part by the Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center in Aurora, Colo. Lead author Dr. Parikh had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Parikh RV et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Feb 4;75:409-19.
Although the study suggests that the use of fractional flow reserve (FFR) has increased, it remains underused despite evidence and recommendations, wrote Julien Adjedj, MD, and Benoit Guillon, MD, in an accompanying editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Feb 4;75:420-1).
“Of course, time, cost, and need for hyperemia are often perceived as stumbling blocks. Yet, the real question is whether the cardiology community – not only interventional cardiologists – has truly adopted FFR (i.e., using it routinely and treating according to the results),” they wrote.
The editorialists noted that, in this study, typical predictors of FFR included younger age, multivessel or left main disease, previous history of percutaneous coronary intervention, no heart failure, and higher left ventricular ejection fraction.
“However, neither the absence of documented ischemia nor the presence of symptoms influenced the use of FFR. Significant site-level variation in FFR was observed,” they wrote. “This important finding suggests that the main reason for FFR underutilization in the contemporary era is operator belief regarding the utility of coronary physiology, and that revised reimbursement policies and additional education/training may not have a meaningful impact on FFR adoption.”
The editorialists emphasized that, although FFR use has increased, the findings of a significant decrease in mortality support additional use of FFR “and good reasons to do so.”
Dr. Adjedj is affiliated with the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois in Lausanne, Switzerland, and had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Guillon is affiliated with the University Hospital Jean Minjoz in Besançon, France, and disclosed a grant from Sanofi and participation in a conference for Abbott.
Although the study suggests that the use of fractional flow reserve (FFR) has increased, it remains underused despite evidence and recommendations, wrote Julien Adjedj, MD, and Benoit Guillon, MD, in an accompanying editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Feb 4;75:420-1).
“Of course, time, cost, and need for hyperemia are often perceived as stumbling blocks. Yet, the real question is whether the cardiology community – not only interventional cardiologists – has truly adopted FFR (i.e., using it routinely and treating according to the results),” they wrote.
The editorialists noted that, in this study, typical predictors of FFR included younger age, multivessel or left main disease, previous history of percutaneous coronary intervention, no heart failure, and higher left ventricular ejection fraction.
“However, neither the absence of documented ischemia nor the presence of symptoms influenced the use of FFR. Significant site-level variation in FFR was observed,” they wrote. “This important finding suggests that the main reason for FFR underutilization in the contemporary era is operator belief regarding the utility of coronary physiology, and that revised reimbursement policies and additional education/training may not have a meaningful impact on FFR adoption.”
The editorialists emphasized that, although FFR use has increased, the findings of a significant decrease in mortality support additional use of FFR “and good reasons to do so.”
Dr. Adjedj is affiliated with the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois in Lausanne, Switzerland, and had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Guillon is affiliated with the University Hospital Jean Minjoz in Besançon, France, and disclosed a grant from Sanofi and participation in a conference for Abbott.
Although the study suggests that the use of fractional flow reserve (FFR) has increased, it remains underused despite evidence and recommendations, wrote Julien Adjedj, MD, and Benoit Guillon, MD, in an accompanying editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Feb 4;75:420-1).
“Of course, time, cost, and need for hyperemia are often perceived as stumbling blocks. Yet, the real question is whether the cardiology community – not only interventional cardiologists – has truly adopted FFR (i.e., using it routinely and treating according to the results),” they wrote.
The editorialists noted that, in this study, typical predictors of FFR included younger age, multivessel or left main disease, previous history of percutaneous coronary intervention, no heart failure, and higher left ventricular ejection fraction.
“However, neither the absence of documented ischemia nor the presence of symptoms influenced the use of FFR. Significant site-level variation in FFR was observed,” they wrote. “This important finding suggests that the main reason for FFR underutilization in the contemporary era is operator belief regarding the utility of coronary physiology, and that revised reimbursement policies and additional education/training may not have a meaningful impact on FFR adoption.”
The editorialists emphasized that, although FFR use has increased, the findings of a significant decrease in mortality support additional use of FFR “and good reasons to do so.”
Dr. Adjedj is affiliated with the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois in Lausanne, Switzerland, and had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Guillon is affiliated with the University Hospital Jean Minjoz in Besançon, France, and disclosed a grant from Sanofi and participation in a conference for Abbott.
Use of fractional flow reserve significantly improved 1-year mortality rates in adults with stable ischemic heart disease, according to a review of 17,989 patients.
Although fractional flow reserve (FFR) has demonstrated value in guiding coronary revascularization, its impact on outcomes in patients with stable ischemic heart disease has not been well studied in a large population, wrote Rushi V. Parikh, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers analyzed data from the Veterans Affairs Clinical Assessment, Reporting, and Tracking Program for adults who underwent coronary angiography between January 2009 and September 2017. The study included patients with angiographically intermediate disease, defined as 40%-69% diameter stenosis on visual inspection.
The rate of FFR use increased from 14.8% to 18.5% during the study period for all patients with intermediate lesions, and from 44% to 75% for those who had percutaneous coronary intervention, the researchers wrote.
Overall, based on hazard models, 1-year mortality was significantly lower in patients who underwent FFR, compared with those who had angiography only (2.8% vs. 5.9%; P less than 0.001). In addition, FFR use in revascularization was associated with a 43% reduced 1-year mortality risk, compared with angiography only.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the observational nature of the study, inability to distinguish between cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality, lack of data on the technical performance of the FFR, and a relatively short follow-up period, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and support the use of FFR-guided revascularization in patients with angiographically intermediate stenosis, they wrote.
“Future registry-based studies accounting for all physiologic modalities are warranted to accurately quantify the landscape of coronary physiology-guided revascularization,” they added.
The study was supported in part by the Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center in Aurora, Colo. Lead author Dr. Parikh had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Parikh RV et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Feb 4;75:409-19.
Use of fractional flow reserve significantly improved 1-year mortality rates in adults with stable ischemic heart disease, according to a review of 17,989 patients.
Although fractional flow reserve (FFR) has demonstrated value in guiding coronary revascularization, its impact on outcomes in patients with stable ischemic heart disease has not been well studied in a large population, wrote Rushi V. Parikh, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the researchers analyzed data from the Veterans Affairs Clinical Assessment, Reporting, and Tracking Program for adults who underwent coronary angiography between January 2009 and September 2017. The study included patients with angiographically intermediate disease, defined as 40%-69% diameter stenosis on visual inspection.
The rate of FFR use increased from 14.8% to 18.5% during the study period for all patients with intermediate lesions, and from 44% to 75% for those who had percutaneous coronary intervention, the researchers wrote.
Overall, based on hazard models, 1-year mortality was significantly lower in patients who underwent FFR, compared with those who had angiography only (2.8% vs. 5.9%; P less than 0.001). In addition, FFR use in revascularization was associated with a 43% reduced 1-year mortality risk, compared with angiography only.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the observational nature of the study, inability to distinguish between cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality, lack of data on the technical performance of the FFR, and a relatively short follow-up period, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, and support the use of FFR-guided revascularization in patients with angiographically intermediate stenosis, they wrote.
“Future registry-based studies accounting for all physiologic modalities are warranted to accurately quantify the landscape of coronary physiology-guided revascularization,” they added.
The study was supported in part by the Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center in Aurora, Colo. Lead author Dr. Parikh had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Parikh RV et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Feb 4;75:409-19.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Key clinical point: Use of fractional flow reserve to assist in revascularization significantly reduced the 1-year mortality risk in patients with stable ischemic heart disease.
Major finding:
Study details: The data come from a review of 17,989 patients who underwent coronary angiography during 2009-2017.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by the Rocky Mountain Regional Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Aurora, Colo. Lead author Dr. Parikh had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Source: Parikh RV et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Feb 4;75:409-19.
Vigilance safely keeps AFib patients off anticoagulants post ablation
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – A pilot program of daily arrhythmia self-vigilance has allowed selected patients with no atrial fibrillation following a catheter ablation procedure to safely come off a regimen of daily oral anticoagulation despite having residual risk factors for ischemic stroke.
This program, which started several years ago at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, has now managed 190 patients and followed them for a median of just over 3 years, and during 576 patient-years of follow-up, just a single patient had an ischemic cerebrovascular event that occurred with no atrial fibrillation (AFib) recurrence and appeared to be caused by an atherosclerotic embolism, Francis E. Marchlinski, MD, said at the annual International AF Symposium.
Although this strategy has not yet been tested in a prospective, randomized trial, this anecdotal, single-center experience suggests that the approach is “safe and effective” for selected patients who are eager to come off of their anticoagulation regimen when they remain arrhythmia free following catheter ablation of their AFib, said Dr. Marchlinski, professor of medicine and director of electrophysiology at the University of Pennsylvania. He and his associates developed this strategy as a way to more safely allow these patients to stop taking a daily oral anticoagulant because he found that many patients were stopping on their own, with no safety strategy in place.
“Patients tell me they don’t want to be on an oral anticoagulant because a parent had a hemorrhagic stroke, and they say they’re willing to accept the risk” of having an ischemic stroke by coming off anticoagulation. “This is a way for them to do it safely,” Dr. Marchlinski said in an interview. He stressed that he only allows his patients to go this route if they understand the risk and accept their shared responsibility for vigilant, twice-daily pulse monitoring to detect resumption of an irregular heart beat.
Since 2011, Dr. Marchlinski’s program ablated 1,216 patients with AFib who then remained arrhythmia free during 3 weeks of continuous ECG monitoring following their procedure. Among these patients, 443 had a CHA2DS2-VAScscore of either 0 (men) or 1 (women) that indicated no ongoing need for oral anticoagulation according to current guidelines. Of the remaining 773 patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 1 in men and 2 in women, the clinicians determined 583 to be ineligible for the program because of their unwillingness to accept the risk, unwillingness to comply with daily pulse checks, a history of asymptomatic AFib, a CHA2DS2-VASc score greater than 4, or a resting pulse above 90 beats per minute, leaving 190 patients eligible to participate. Among these patients, 105 (55%) had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2-4, which should prompt anticoagulation according to current guidelines.Participating patients committed to check their resting pulse by palpation at least twice daily and to contacting the program immediately if their resting rate spiked by more than 20 beats per minutes or in another way seemed irregular. Patients were also instructed to restart their oral anticoagulation immediately if they experienced AFib symptoms that persisted for more than 5 minutes. Many patients in the program also use a wearable device (usually a watch) to monitor their resting pulse and to generate a 30-second ECG recording that they can send as an electronic file to the University of Pennsylvania staff. “We embrace wearables,” Dr. Marchlinski said. Those without a wearable can undergo transtelephonic EEG monitoring to document a suspected arrhythmia recurrence, and all patients undergo annual monitoring by continuous ECG for at least 2 weeks.During follow-up, in addition to the 1 patient free from recurrent AFib who had an atherosclerotic embolism, 34 patients resumed anticoagulant treatment because of AFib recurrence; 12 withdrew from the program because of noncompliance or preference, or because an exclusion appeared; 29 resumed oral anticoagulation transiently but then discontinued the drug a second time when their AFib recurrence resolved; and 114 patients (60% of the starting cohort of 190) remained completely off anticoagulation during a median of 37 months. These data updated a published report from Dr. Marchlinski and his associates on their first 99 patients followed for a median of 30 months (J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019 May;30[5]:631-8).
This experience underscored the need for ongoing rhythm monitoring even in the absence of AFib symptoms, as six patients developed asymptomatic AFib detected by monitoring, including one patient whose recurrence occurred 30 months after the ablation procedure.
Dr. Marchlinski stressed the stringent selection process he applies to limit this approach to patients who are willing to faithfully monitor their pulse and symptoms daily, and who accept the risk that this approach may pose and their responsibility to stay in contact with the clinical team. The program calls patients at the 6-month mark between annual monitoring to remind them of their need for daily attention.
“Being off anticoagulants is very important to these patients,” he explained, and he highlighted the added workload this strategy places on his staff. “I think this has legs” for adoption by other cardiac arrhythmia programs, “but it depends on the time the staff is willing to spend” monitoring and following these patients, some of whom regularly send in ECG traces from their wearable devices for assessment. “It takes a village” to make this program work, he said.
Dr. Marchlinski has been a consultant to or has received honoraria from Abbott EP/St. Jude, Biosense Webster, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – A pilot program of daily arrhythmia self-vigilance has allowed selected patients with no atrial fibrillation following a catheter ablation procedure to safely come off a regimen of daily oral anticoagulation despite having residual risk factors for ischemic stroke.
This program, which started several years ago at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, has now managed 190 patients and followed them for a median of just over 3 years, and during 576 patient-years of follow-up, just a single patient had an ischemic cerebrovascular event that occurred with no atrial fibrillation (AFib) recurrence and appeared to be caused by an atherosclerotic embolism, Francis E. Marchlinski, MD, said at the annual International AF Symposium.
Although this strategy has not yet been tested in a prospective, randomized trial, this anecdotal, single-center experience suggests that the approach is “safe and effective” for selected patients who are eager to come off of their anticoagulation regimen when they remain arrhythmia free following catheter ablation of their AFib, said Dr. Marchlinski, professor of medicine and director of electrophysiology at the University of Pennsylvania. He and his associates developed this strategy as a way to more safely allow these patients to stop taking a daily oral anticoagulant because he found that many patients were stopping on their own, with no safety strategy in place.
“Patients tell me they don’t want to be on an oral anticoagulant because a parent had a hemorrhagic stroke, and they say they’re willing to accept the risk” of having an ischemic stroke by coming off anticoagulation. “This is a way for them to do it safely,” Dr. Marchlinski said in an interview. He stressed that he only allows his patients to go this route if they understand the risk and accept their shared responsibility for vigilant, twice-daily pulse monitoring to detect resumption of an irregular heart beat.
Since 2011, Dr. Marchlinski’s program ablated 1,216 patients with AFib who then remained arrhythmia free during 3 weeks of continuous ECG monitoring following their procedure. Among these patients, 443 had a CHA2DS2-VAScscore of either 0 (men) or 1 (women) that indicated no ongoing need for oral anticoagulation according to current guidelines. Of the remaining 773 patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 1 in men and 2 in women, the clinicians determined 583 to be ineligible for the program because of their unwillingness to accept the risk, unwillingness to comply with daily pulse checks, a history of asymptomatic AFib, a CHA2DS2-VASc score greater than 4, or a resting pulse above 90 beats per minute, leaving 190 patients eligible to participate. Among these patients, 105 (55%) had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2-4, which should prompt anticoagulation according to current guidelines.Participating patients committed to check their resting pulse by palpation at least twice daily and to contacting the program immediately if their resting rate spiked by more than 20 beats per minutes or in another way seemed irregular. Patients were also instructed to restart their oral anticoagulation immediately if they experienced AFib symptoms that persisted for more than 5 minutes. Many patients in the program also use a wearable device (usually a watch) to monitor their resting pulse and to generate a 30-second ECG recording that they can send as an electronic file to the University of Pennsylvania staff. “We embrace wearables,” Dr. Marchlinski said. Those without a wearable can undergo transtelephonic EEG monitoring to document a suspected arrhythmia recurrence, and all patients undergo annual monitoring by continuous ECG for at least 2 weeks.During follow-up, in addition to the 1 patient free from recurrent AFib who had an atherosclerotic embolism, 34 patients resumed anticoagulant treatment because of AFib recurrence; 12 withdrew from the program because of noncompliance or preference, or because an exclusion appeared; 29 resumed oral anticoagulation transiently but then discontinued the drug a second time when their AFib recurrence resolved; and 114 patients (60% of the starting cohort of 190) remained completely off anticoagulation during a median of 37 months. These data updated a published report from Dr. Marchlinski and his associates on their first 99 patients followed for a median of 30 months (J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019 May;30[5]:631-8).
This experience underscored the need for ongoing rhythm monitoring even in the absence of AFib symptoms, as six patients developed asymptomatic AFib detected by monitoring, including one patient whose recurrence occurred 30 months after the ablation procedure.
Dr. Marchlinski stressed the stringent selection process he applies to limit this approach to patients who are willing to faithfully monitor their pulse and symptoms daily, and who accept the risk that this approach may pose and their responsibility to stay in contact with the clinical team. The program calls patients at the 6-month mark between annual monitoring to remind them of their need for daily attention.
“Being off anticoagulants is very important to these patients,” he explained, and he highlighted the added workload this strategy places on his staff. “I think this has legs” for adoption by other cardiac arrhythmia programs, “but it depends on the time the staff is willing to spend” monitoring and following these patients, some of whom regularly send in ECG traces from their wearable devices for assessment. “It takes a village” to make this program work, he said.
Dr. Marchlinski has been a consultant to or has received honoraria from Abbott EP/St. Jude, Biosense Webster, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – A pilot program of daily arrhythmia self-vigilance has allowed selected patients with no atrial fibrillation following a catheter ablation procedure to safely come off a regimen of daily oral anticoagulation despite having residual risk factors for ischemic stroke.
This program, which started several years ago at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, has now managed 190 patients and followed them for a median of just over 3 years, and during 576 patient-years of follow-up, just a single patient had an ischemic cerebrovascular event that occurred with no atrial fibrillation (AFib) recurrence and appeared to be caused by an atherosclerotic embolism, Francis E. Marchlinski, MD, said at the annual International AF Symposium.
Although this strategy has not yet been tested in a prospective, randomized trial, this anecdotal, single-center experience suggests that the approach is “safe and effective” for selected patients who are eager to come off of their anticoagulation regimen when they remain arrhythmia free following catheter ablation of their AFib, said Dr. Marchlinski, professor of medicine and director of electrophysiology at the University of Pennsylvania. He and his associates developed this strategy as a way to more safely allow these patients to stop taking a daily oral anticoagulant because he found that many patients were stopping on their own, with no safety strategy in place.
“Patients tell me they don’t want to be on an oral anticoagulant because a parent had a hemorrhagic stroke, and they say they’re willing to accept the risk” of having an ischemic stroke by coming off anticoagulation. “This is a way for them to do it safely,” Dr. Marchlinski said in an interview. He stressed that he only allows his patients to go this route if they understand the risk and accept their shared responsibility for vigilant, twice-daily pulse monitoring to detect resumption of an irregular heart beat.
Since 2011, Dr. Marchlinski’s program ablated 1,216 patients with AFib who then remained arrhythmia free during 3 weeks of continuous ECG monitoring following their procedure. Among these patients, 443 had a CHA2DS2-VAScscore of either 0 (men) or 1 (women) that indicated no ongoing need for oral anticoagulation according to current guidelines. Of the remaining 773 patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 1 in men and 2 in women, the clinicians determined 583 to be ineligible for the program because of their unwillingness to accept the risk, unwillingness to comply with daily pulse checks, a history of asymptomatic AFib, a CHA2DS2-VASc score greater than 4, or a resting pulse above 90 beats per minute, leaving 190 patients eligible to participate. Among these patients, 105 (55%) had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2-4, which should prompt anticoagulation according to current guidelines.Participating patients committed to check their resting pulse by palpation at least twice daily and to contacting the program immediately if their resting rate spiked by more than 20 beats per minutes or in another way seemed irregular. Patients were also instructed to restart their oral anticoagulation immediately if they experienced AFib symptoms that persisted for more than 5 minutes. Many patients in the program also use a wearable device (usually a watch) to monitor their resting pulse and to generate a 30-second ECG recording that they can send as an electronic file to the University of Pennsylvania staff. “We embrace wearables,” Dr. Marchlinski said. Those without a wearable can undergo transtelephonic EEG monitoring to document a suspected arrhythmia recurrence, and all patients undergo annual monitoring by continuous ECG for at least 2 weeks.During follow-up, in addition to the 1 patient free from recurrent AFib who had an atherosclerotic embolism, 34 patients resumed anticoagulant treatment because of AFib recurrence; 12 withdrew from the program because of noncompliance or preference, or because an exclusion appeared; 29 resumed oral anticoagulation transiently but then discontinued the drug a second time when their AFib recurrence resolved; and 114 patients (60% of the starting cohort of 190) remained completely off anticoagulation during a median of 37 months. These data updated a published report from Dr. Marchlinski and his associates on their first 99 patients followed for a median of 30 months (J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019 May;30[5]:631-8).
This experience underscored the need for ongoing rhythm monitoring even in the absence of AFib symptoms, as six patients developed asymptomatic AFib detected by monitoring, including one patient whose recurrence occurred 30 months after the ablation procedure.
Dr. Marchlinski stressed the stringent selection process he applies to limit this approach to patients who are willing to faithfully monitor their pulse and symptoms daily, and who accept the risk that this approach may pose and their responsibility to stay in contact with the clinical team. The program calls patients at the 6-month mark between annual monitoring to remind them of their need for daily attention.
“Being off anticoagulants is very important to these patients,” he explained, and he highlighted the added workload this strategy places on his staff. “I think this has legs” for adoption by other cardiac arrhythmia programs, “but it depends on the time the staff is willing to spend” monitoring and following these patients, some of whom regularly send in ECG traces from their wearable devices for assessment. “It takes a village” to make this program work, he said.
Dr. Marchlinski has been a consultant to or has received honoraria from Abbott EP/St. Jude, Biosense Webster, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
REPORTING FROM THE AF SYMPOSIUM 2020
FDA approves fidaxomicin for treatment of C. difficile–associated diarrhea
The Food and Drug Administration has approved fidaxomicin (Dificid) for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile–associated diarrhea in children aged 6 months and older.
Approval was based on results from SUNSHINE, a phase 3, multicenter, investigator-blind, randomized, parallel-group study in 142 pediatric patients aged between 6 months and 18 years with confirmed C. difficile infection who received either fidaxomicin or vancomycin for 10 days. Clinical response 2 days after the conclusion of treatment was similar in both groups (77.6% for fidaxomicin vs. 70.5% for vancomycin), and fidaxomicin had a superior sustained response 30 days after the conclusion of treatment (68.4% vs. 50.0%).
The safety of fidaxomicin was assessed in a pair of clinical trials involving 136 patients; the most common adverse events were pyrexia, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, increased aminotransferases, and rash. Four patients discontinued fidaxomicin treatment because of adverse events, and four patients died during the trials, though all deaths were in patients aged younger than 2 years and seemed to be related to other comorbidities.
“C. difficile is an important cause of health care– and community-associated diarrheal illness in children, and sustained cure is difficult to achieve in some patients. The fidaxomicin pediatric trial was the first randomized, controlled trial of C. difficile infection treatment in children,” Larry K. Kociolek, MD, associate medical director of infection prevention and control at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, said in the press release from Merck, manufacturer of fidaxomicin.
*This story was updated on 1/27/2020.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved fidaxomicin (Dificid) for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile–associated diarrhea in children aged 6 months and older.
Approval was based on results from SUNSHINE, a phase 3, multicenter, investigator-blind, randomized, parallel-group study in 142 pediatric patients aged between 6 months and 18 years with confirmed C. difficile infection who received either fidaxomicin or vancomycin for 10 days. Clinical response 2 days after the conclusion of treatment was similar in both groups (77.6% for fidaxomicin vs. 70.5% for vancomycin), and fidaxomicin had a superior sustained response 30 days after the conclusion of treatment (68.4% vs. 50.0%).
The safety of fidaxomicin was assessed in a pair of clinical trials involving 136 patients; the most common adverse events were pyrexia, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, increased aminotransferases, and rash. Four patients discontinued fidaxomicin treatment because of adverse events, and four patients died during the trials, though all deaths were in patients aged younger than 2 years and seemed to be related to other comorbidities.
“C. difficile is an important cause of health care– and community-associated diarrheal illness in children, and sustained cure is difficult to achieve in some patients. The fidaxomicin pediatric trial was the first randomized, controlled trial of C. difficile infection treatment in children,” Larry K. Kociolek, MD, associate medical director of infection prevention and control at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, said in the press release from Merck, manufacturer of fidaxomicin.
*This story was updated on 1/27/2020.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved fidaxomicin (Dificid) for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile–associated diarrhea in children aged 6 months and older.
Approval was based on results from SUNSHINE, a phase 3, multicenter, investigator-blind, randomized, parallel-group study in 142 pediatric patients aged between 6 months and 18 years with confirmed C. difficile infection who received either fidaxomicin or vancomycin for 10 days. Clinical response 2 days after the conclusion of treatment was similar in both groups (77.6% for fidaxomicin vs. 70.5% for vancomycin), and fidaxomicin had a superior sustained response 30 days after the conclusion of treatment (68.4% vs. 50.0%).
The safety of fidaxomicin was assessed in a pair of clinical trials involving 136 patients; the most common adverse events were pyrexia, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, increased aminotransferases, and rash. Four patients discontinued fidaxomicin treatment because of adverse events, and four patients died during the trials, though all deaths were in patients aged younger than 2 years and seemed to be related to other comorbidities.
“C. difficile is an important cause of health care– and community-associated diarrheal illness in children, and sustained cure is difficult to achieve in some patients. The fidaxomicin pediatric trial was the first randomized, controlled trial of C. difficile infection treatment in children,” Larry K. Kociolek, MD, associate medical director of infection prevention and control at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, said in the press release from Merck, manufacturer of fidaxomicin.
*This story was updated on 1/27/2020.
Zika virus: Birth defects rose fourfold in U.S. hardest-hit areas
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
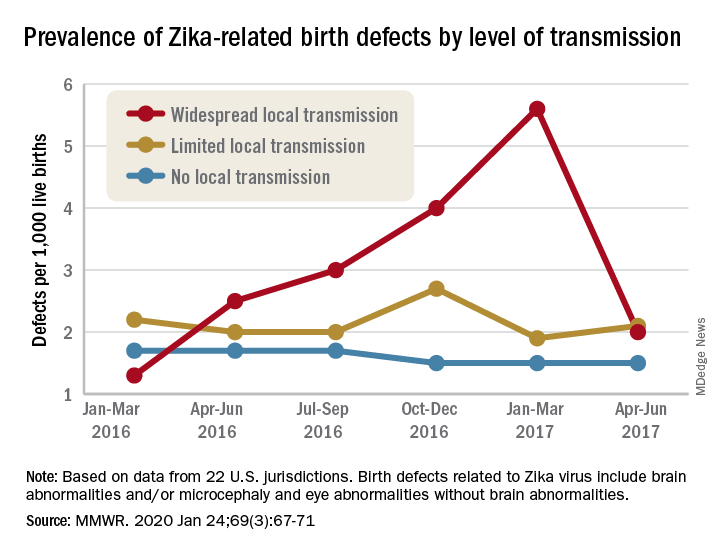
That spike in the prevalence of brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly or eye abnormalities without brain abnormalities came during January through March 2017, about 6 months after the Zika outbreak’s reported peak in the jurisdictions with widespread local transmission, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, wrote Ashley N. Smoots, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities and associates in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In those two territories, the prevalence of birth defects potentially related to Zika virus infection was 5.6 per 1,000 live births during January through March 2017, compared with 1.3 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, they reported.
In the southern areas of Florida and Texas, where there was limited local Zika transmission, the highest prevalence of birth defects, 2.7 per 1,000, occurred during October through December 2016, and was only slightly greater than the baseline rate of 2.2 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, the investigators reported.
Among the other 19 jurisdictions (including Illinois, Louisiana, New Jersey, South Carolina, and Virginia) involved in the analysis, the rate of Zika virus–related birth defects never reached any higher than the 1.7 per 1,000 recorded at the start of the study period in January through March 2016, they said.
“Population-based birth defects surveillance is critical for identifying infants and fetuses with birth defects potentially related to Zika virus regardless of whether Zika virus testing was conducted, especially given the high prevalence of asymptomatic disease. These data can be used to inform follow-up care and services as well as strengthen surveillance,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Smoots AN et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):67-71.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

That spike in the prevalence of brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly or eye abnormalities without brain abnormalities came during January through March 2017, about 6 months after the Zika outbreak’s reported peak in the jurisdictions with widespread local transmission, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, wrote Ashley N. Smoots, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities and associates in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In those two territories, the prevalence of birth defects potentially related to Zika virus infection was 5.6 per 1,000 live births during January through March 2017, compared with 1.3 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, they reported.
In the southern areas of Florida and Texas, where there was limited local Zika transmission, the highest prevalence of birth defects, 2.7 per 1,000, occurred during October through December 2016, and was only slightly greater than the baseline rate of 2.2 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, the investigators reported.
Among the other 19 jurisdictions (including Illinois, Louisiana, New Jersey, South Carolina, and Virginia) involved in the analysis, the rate of Zika virus–related birth defects never reached any higher than the 1.7 per 1,000 recorded at the start of the study period in January through March 2016, they said.
“Population-based birth defects surveillance is critical for identifying infants and fetuses with birth defects potentially related to Zika virus regardless of whether Zika virus testing was conducted, especially given the high prevalence of asymptomatic disease. These data can be used to inform follow-up care and services as well as strengthen surveillance,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Smoots AN et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):67-71.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

That spike in the prevalence of brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly or eye abnormalities without brain abnormalities came during January through March 2017, about 6 months after the Zika outbreak’s reported peak in the jurisdictions with widespread local transmission, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, wrote Ashley N. Smoots, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities and associates in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In those two territories, the prevalence of birth defects potentially related to Zika virus infection was 5.6 per 1,000 live births during January through March 2017, compared with 1.3 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, they reported.
In the southern areas of Florida and Texas, where there was limited local Zika transmission, the highest prevalence of birth defects, 2.7 per 1,000, occurred during October through December 2016, and was only slightly greater than the baseline rate of 2.2 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, the investigators reported.
Among the other 19 jurisdictions (including Illinois, Louisiana, New Jersey, South Carolina, and Virginia) involved in the analysis, the rate of Zika virus–related birth defects never reached any higher than the 1.7 per 1,000 recorded at the start of the study period in January through March 2016, they said.
“Population-based birth defects surveillance is critical for identifying infants and fetuses with birth defects potentially related to Zika virus regardless of whether Zika virus testing was conducted, especially given the high prevalence of asymptomatic disease. These data can be used to inform follow-up care and services as well as strengthen surveillance,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Smoots AN et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):67-71.
FROM MMWR