User login
Take stronger steps to prevent staph infections and sepsis
according to data from a Vital Signs report issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The data include both methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA).
Although MRSA infections in health care settings declined by approximately 17% during 2005-2012, rates plateaued during 2012-2017, Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the CDC, said in a teleconference March 5 to present the findings. The report emphasizes the potential for serious illness and death with any staph infection and the need for ongoing vigilance on the part of clinicians, she said.
In addition, community-onset MSSA infections increased by 3.9%/year during 2012-2017. Data from previous studies suggest that this increase may be connected to the opioid epidemic, said Dr. Schuchat.
“People who inject drugs are 16% more likely to develop a staph infection” than are those who don’t inject drugs, she said.
Community-onset MRSA declined by 6.9% during 2001-2016, attributed to declines in health care–associated infections, according to Vital Signs author Athena P. Kourtis, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and her colleagues. Rates of hospital-associated MSSA infection remained essentially unchanged (P = .11). The overall unadjusted in-hospital mortality among patients with S. aureus bloodstream infections over the study period was 18%.
The data for the report were collected from electronic health records at more than 400 acute care hospitals, as well as population-based surveillance data from the CDC’s Emerging Infections Program.
Most people carry staph on their skin with no ill effects, but the bacteria become dangerous when they enter the bloodstream, Dr. Schuchat emphasized. “We hope the new data today will refocus the nation’s efforts to protect patients from staph infections,” she said.

Dr. Schuchat advised clinicians and hospital administrators to review their data and step up their safety protocols to prevent staph infections. Precautions include wearing gowns and gloves, following proper hand washing protocols, cautious use of antibiotics, and treating infections rapidly when they occur, she said. Dr. Schuchat noted that lack of adherence to these recommendations may have declined in recent years if clinicians and hospital administrators were wondering whether their protocols have an effect and have value. However, “this is a very serious infection, and we think it is very much worth preventing,” she emphasized.
Other strategies to prevent staph infections in health care settings include reviewing infection data regularly, exploring new approaches to prevent infections, and educating patients about when they may be at increased risk for infection, such as when invasive devices are in place or during surgical procedures. Also, clinicians should be aware of the increased risk for patients who inject drugs, Dr. Schuchat said.
Dr. Schuchat commended the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers (VAMC), which overall reduced their rate of staph infections by 43% during the period from 2005 through 2017 in contrast to the national trend. These findings also appeared in the MMWR on March 5. The VAMC implemented additional interventions and increased their adherence to CDC recommendations during this period, she noted.
The Vital Signs data were published March 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report; read the full report here.
The CDC researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kourtis AP et al. MMWR. 2019 Mar 5; 68:1-6.
according to data from a Vital Signs report issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The data include both methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA).
Although MRSA infections in health care settings declined by approximately 17% during 2005-2012, rates plateaued during 2012-2017, Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the CDC, said in a teleconference March 5 to present the findings. The report emphasizes the potential for serious illness and death with any staph infection and the need for ongoing vigilance on the part of clinicians, she said.
In addition, community-onset MSSA infections increased by 3.9%/year during 2012-2017. Data from previous studies suggest that this increase may be connected to the opioid epidemic, said Dr. Schuchat.
“People who inject drugs are 16% more likely to develop a staph infection” than are those who don’t inject drugs, she said.
Community-onset MRSA declined by 6.9% during 2001-2016, attributed to declines in health care–associated infections, according to Vital Signs author Athena P. Kourtis, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and her colleagues. Rates of hospital-associated MSSA infection remained essentially unchanged (P = .11). The overall unadjusted in-hospital mortality among patients with S. aureus bloodstream infections over the study period was 18%.
The data for the report were collected from electronic health records at more than 400 acute care hospitals, as well as population-based surveillance data from the CDC’s Emerging Infections Program.
Most people carry staph on their skin with no ill effects, but the bacteria become dangerous when they enter the bloodstream, Dr. Schuchat emphasized. “We hope the new data today will refocus the nation’s efforts to protect patients from staph infections,” she said.

Dr. Schuchat advised clinicians and hospital administrators to review their data and step up their safety protocols to prevent staph infections. Precautions include wearing gowns and gloves, following proper hand washing protocols, cautious use of antibiotics, and treating infections rapidly when they occur, she said. Dr. Schuchat noted that lack of adherence to these recommendations may have declined in recent years if clinicians and hospital administrators were wondering whether their protocols have an effect and have value. However, “this is a very serious infection, and we think it is very much worth preventing,” she emphasized.
Other strategies to prevent staph infections in health care settings include reviewing infection data regularly, exploring new approaches to prevent infections, and educating patients about when they may be at increased risk for infection, such as when invasive devices are in place or during surgical procedures. Also, clinicians should be aware of the increased risk for patients who inject drugs, Dr. Schuchat said.
Dr. Schuchat commended the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers (VAMC), which overall reduced their rate of staph infections by 43% during the period from 2005 through 2017 in contrast to the national trend. These findings also appeared in the MMWR on March 5. The VAMC implemented additional interventions and increased their adherence to CDC recommendations during this period, she noted.
The Vital Signs data were published March 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report; read the full report here.
The CDC researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kourtis AP et al. MMWR. 2019 Mar 5; 68:1-6.
according to data from a Vital Signs report issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The data include both methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA).
Although MRSA infections in health care settings declined by approximately 17% during 2005-2012, rates plateaued during 2012-2017, Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the CDC, said in a teleconference March 5 to present the findings. The report emphasizes the potential for serious illness and death with any staph infection and the need for ongoing vigilance on the part of clinicians, she said.
In addition, community-onset MSSA infections increased by 3.9%/year during 2012-2017. Data from previous studies suggest that this increase may be connected to the opioid epidemic, said Dr. Schuchat.
“People who inject drugs are 16% more likely to develop a staph infection” than are those who don’t inject drugs, she said.
Community-onset MRSA declined by 6.9% during 2001-2016, attributed to declines in health care–associated infections, according to Vital Signs author Athena P. Kourtis, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and her colleagues. Rates of hospital-associated MSSA infection remained essentially unchanged (P = .11). The overall unadjusted in-hospital mortality among patients with S. aureus bloodstream infections over the study period was 18%.
The data for the report were collected from electronic health records at more than 400 acute care hospitals, as well as population-based surveillance data from the CDC’s Emerging Infections Program.
Most people carry staph on their skin with no ill effects, but the bacteria become dangerous when they enter the bloodstream, Dr. Schuchat emphasized. “We hope the new data today will refocus the nation’s efforts to protect patients from staph infections,” she said.

Dr. Schuchat advised clinicians and hospital administrators to review their data and step up their safety protocols to prevent staph infections. Precautions include wearing gowns and gloves, following proper hand washing protocols, cautious use of antibiotics, and treating infections rapidly when they occur, she said. Dr. Schuchat noted that lack of adherence to these recommendations may have declined in recent years if clinicians and hospital administrators were wondering whether their protocols have an effect and have value. However, “this is a very serious infection, and we think it is very much worth preventing,” she emphasized.
Other strategies to prevent staph infections in health care settings include reviewing infection data regularly, exploring new approaches to prevent infections, and educating patients about when they may be at increased risk for infection, such as when invasive devices are in place or during surgical procedures. Also, clinicians should be aware of the increased risk for patients who inject drugs, Dr. Schuchat said.
Dr. Schuchat commended the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers (VAMC), which overall reduced their rate of staph infections by 43% during the period from 2005 through 2017 in contrast to the national trend. These findings also appeared in the MMWR on March 5. The VAMC implemented additional interventions and increased their adherence to CDC recommendations during this period, she noted.
The Vital Signs data were published March 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report; read the full report here.
The CDC researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kourtis AP et al. MMWR. 2019 Mar 5; 68:1-6.
FROM THE MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY WEEKLY REPORT
Don’t overlook this step in combatting the rise in STIs
Resources
1. Kuehn BM. A proactive approach needed to combat rising STIs. JAMA. 2019;321:330-332.
2. Screening Recommendations and Considerations Referenced in Treatment Guidelines and Original Sources. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/screening-recommendations.htm. Updated June 4, 2015. Accessed February 27, 2019.
3. STD Clinical Consultation Network. National STD Curriculum. https://www.std.uw.edu/page/site/clinical-consultation. Accessed February 27, 2019.
4. National STD Curriculum. https://www.std.uw.edu/. Accessed February 27, 2019.
5. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2017. Syphilis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/syphilis.htm. Reviewed July 24, 2018. Accessed February 27, 2019.
Resources
1. Kuehn BM. A proactive approach needed to combat rising STIs. JAMA. 2019;321:330-332.
2. Screening Recommendations and Considerations Referenced in Treatment Guidelines and Original Sources. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/screening-recommendations.htm. Updated June 4, 2015. Accessed February 27, 2019.
3. STD Clinical Consultation Network. National STD Curriculum. https://www.std.uw.edu/page/site/clinical-consultation. Accessed February 27, 2019.
4. National STD Curriculum. https://www.std.uw.edu/. Accessed February 27, 2019.
5. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2017. Syphilis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/syphilis.htm. Reviewed July 24, 2018. Accessed February 27, 2019.
Resources
1. Kuehn BM. A proactive approach needed to combat rising STIs. JAMA. 2019;321:330-332.
2. Screening Recommendations and Considerations Referenced in Treatment Guidelines and Original Sources. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/screening-recommendations.htm. Updated June 4, 2015. Accessed February 27, 2019.
3. STD Clinical Consultation Network. National STD Curriculum. https://www.std.uw.edu/page/site/clinical-consultation. Accessed February 27, 2019.
4. National STD Curriculum. https://www.std.uw.edu/. Accessed February 27, 2019.
5. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2017. Syphilis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/syphilis.htm. Reviewed July 24, 2018. Accessed February 27, 2019.
Drug pricing does not inspire Americans’ trust
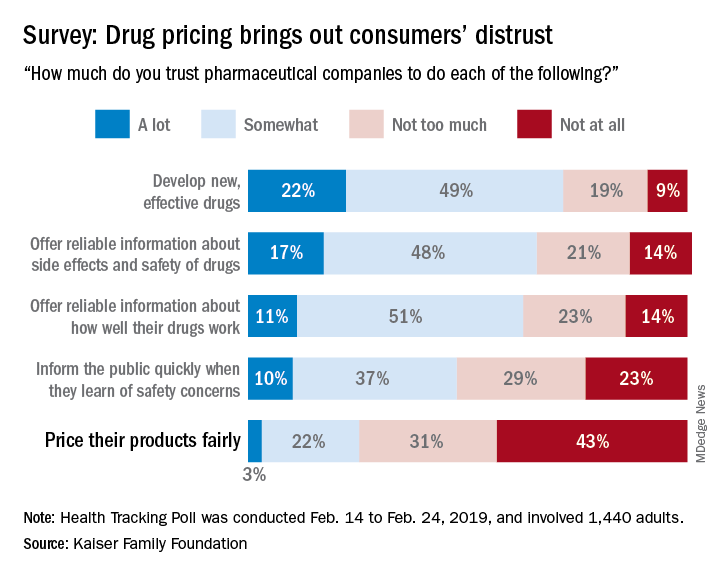
Only 25% of the respondents said that they currently trust drug companies “a lot” (3%) or “somewhat” (22%) when it comes to pricing their products fairly, which “is a significant decrease from 41% who said they trusted pharmaceutical companies to price their products fairly back in 2008,” Kaiser said in a recent Health Tracking Poll.
Safety issues were also a bit of a sore point in the current survey: Less than half of the 1,440 adults responding said that they trusted pharmaceutical companies a lot (10%) or somewhat (37%) regarding informing the public quickly when a safety concern is discovered.
Trust was more forthcoming when people were asked about the development of new, effective drugs – 71% expressed a favorable opinion – and companies’ offering “reliable information about side effects and safety of drugs,” which received a favorable response from 65% of those surveyed during Feb. 14 to Feb. 24, 2019.
A majority of respondents (61%) also thought that pharmaceutical companies could be trusted to “offer reliable information about how well their drugs work,” the report’s authors noted.
The lack of trust expressed regarding drug pricing also may explain why most consumers (80%) said that drug company profits were a major contributor to the cost of prescription drugs. The cost of research and development, at 69%, was the next most commonly mentioned factor, followed by profits made by pharmacy benefit managers at 63%, according to the report.

Only 25% of the respondents said that they currently trust drug companies “a lot” (3%) or “somewhat” (22%) when it comes to pricing their products fairly, which “is a significant decrease from 41% who said they trusted pharmaceutical companies to price their products fairly back in 2008,” Kaiser said in a recent Health Tracking Poll.
Safety issues were also a bit of a sore point in the current survey: Less than half of the 1,440 adults responding said that they trusted pharmaceutical companies a lot (10%) or somewhat (37%) regarding informing the public quickly when a safety concern is discovered.
Trust was more forthcoming when people were asked about the development of new, effective drugs – 71% expressed a favorable opinion – and companies’ offering “reliable information about side effects and safety of drugs,” which received a favorable response from 65% of those surveyed during Feb. 14 to Feb. 24, 2019.
A majority of respondents (61%) also thought that pharmaceutical companies could be trusted to “offer reliable information about how well their drugs work,” the report’s authors noted.
The lack of trust expressed regarding drug pricing also may explain why most consumers (80%) said that drug company profits were a major contributor to the cost of prescription drugs. The cost of research and development, at 69%, was the next most commonly mentioned factor, followed by profits made by pharmacy benefit managers at 63%, according to the report.

Only 25% of the respondents said that they currently trust drug companies “a lot” (3%) or “somewhat” (22%) when it comes to pricing their products fairly, which “is a significant decrease from 41% who said they trusted pharmaceutical companies to price their products fairly back in 2008,” Kaiser said in a recent Health Tracking Poll.
Safety issues were also a bit of a sore point in the current survey: Less than half of the 1,440 adults responding said that they trusted pharmaceutical companies a lot (10%) or somewhat (37%) regarding informing the public quickly when a safety concern is discovered.
Trust was more forthcoming when people were asked about the development of new, effective drugs – 71% expressed a favorable opinion – and companies’ offering “reliable information about side effects and safety of drugs,” which received a favorable response from 65% of those surveyed during Feb. 14 to Feb. 24, 2019.
A majority of respondents (61%) also thought that pharmaceutical companies could be trusted to “offer reliable information about how well their drugs work,” the report’s authors noted.
The lack of trust expressed regarding drug pricing also may explain why most consumers (80%) said that drug company profits were a major contributor to the cost of prescription drugs. The cost of research and development, at 69%, was the next most commonly mentioned factor, followed by profits made by pharmacy benefit managers at 63%, according to the report.
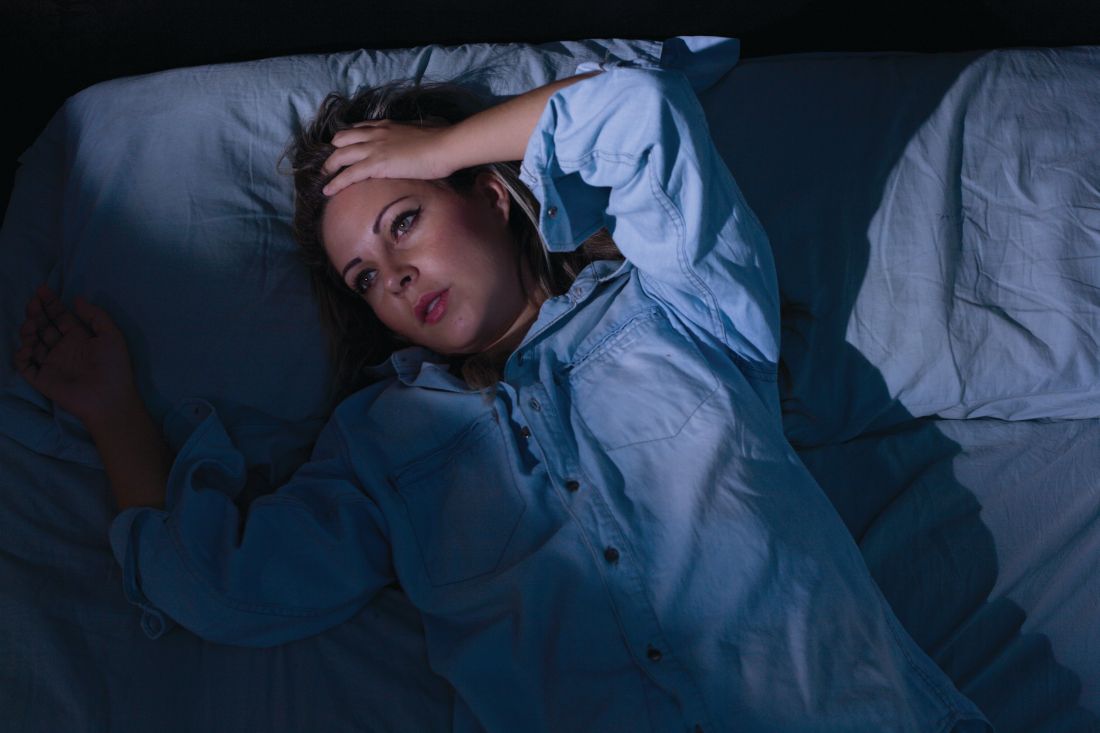
Try behavioral interventions for chronic insomnia
“The greatest medicine of all is teaching people how not to need it.” – Hippocrates
For many years, over-the-counter and prescription medications indicated for sleep problems/disorders have been available to patients. But the side effects associated with some of these medications are many. In light of the numerous nonpharmacologic interventions that are available to patients, they should be offered first when appropriate.
One of the top nonpharmacologic interventions is cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia, or CBT-I, which the American Academy of Sleep Medicine’s clinical guidelines say should be used as initial treatment if possible.1 Elements of CBT-I include cognitive therapy, which is aimed at reducing dysfunctional beliefs about sleep. Common distortions expressed by patients include: “I cannot sleep without medications” and “I must get 8 hours of sleep to feel refreshed and function well the next day.” It helps in dealing with anxiety and catastrophic thinking to establish realistic expectations and treatment related to insomnia.
CBT-I can be delivered in the form of monotherapy or in a combined manner. The individual components include psychoeducation, behavioral strategies, cognitive therapy, and relaxation training. CBT-I combines cognitive therapy with behavioral interventions. Behavioral elements include stimulus control therapy and sleep restriction therapy. Relaxation therapy might or might not be included. Sleep hygiene education usually is a part of it.2
Two other kinds of CBT that can be effective options are telephone-based CBT-I and Internet-based CBT-I.3,4 Meanwhile, among the disadvantages of CBT for insomnia are longer duration of therapy and lack of skilled clinicians.5
Many other kinds of behavioral interventions are available to patients with problems related to sleep, including stimulus control therapy, relaxation therapy, exercise therapy, and sleep restriction therapy.
Stimulus control therapy
This is a strategy aimed at strengthening the association of bed and bedroom to sleep, establishing a consistent sleep-wake rhythm, and reducing the activities that might interfere with sleep. This behavioral therapy is based on the idea that arousal occurs as a conditioned response to the stimulus of sleep environment, and it is among the most effective behavioral treatments.6,7 Strategies include the following:
1. Lie down with the intention of sleeping when sleepy.
2. Do not watch television, read, eat or worry while in bed. Use bed only for sleep and sex.
3. Get out of bed if unable to fall asleep within 10-15 minutes and go to another room. Return to bed only when sleepy. Do not watch the clock. Repeat this step as many times as necessary throughout the night.
4. Set an alarm clock to wake up at a fixed time each morning, including weekends, regardless of how much sleep you got during the night.
5. Do not take a nap during the day.
The goal of these strategies is to extinguish negative associations between bed and undesirable outcomes, such as wakefulness and frustration. One study showed that stimulus control participants, unlike control group participants, experienced significant improvement at follow-up for total sleep time, sleep efficiency, and sleep quality.8
Relaxation therapy
This encompasses different techniques that produce a relaxation response and reduce somatic arousal. It can be implemented before each sleep period. Progressive muscle relaxation, autogenic training, and biofeedback help reduce somatic arousal. Attention-focused procedures, such as imagery training and meditation, tend to lower presleep cognitive arousal (for example, intrusive thoughts, racing minds).9 Slow paced breathing prior to onset of sleep enhances vagal activity, which results in improved sleep parameters.10 One study showed improved quality of sleep and cognitive functions in the elderly by self-relaxation training.11
Exercise training
Participating in physical exercise can be useful in the treatment of insomnia.12 One randomized, controlled trial found that exercising regularly for at least 150 minutes per week was optimal.13 Another study found that, among overweight and obese men with insomnia, aerobic exercise over a 6-month period reduced difficulty in initiating and improving sleep.14
Sleep restriction therapy
The goal of this therapy is to increase the homeostatic drive to sleep. This is carried out by limiting the amount of time spent in bed to the same amount of time that the person reports sleeping. Naps are not allowed. Patients improve with increased drive to sleep in successive nights. In patients with bipolar disorder, however, sleep restriction should be used with caution as it can trigger manic episodes.15
Always ask about sleep
Clinicians should always ask patients about sleep during visits. Sleep duration and sleep quality should be assessed. Insomnia, which is an independent condition, may or may not coexist with other conditions. It is important to determine whether another sleep disorder, or a physical (such as pain, heart, or lung disease), neurological (such as Parkinson’s disease or cerebrovascular disease), or psychiatric disorder (such as depressive illness, anxiety disorder, or substance misuse) is the primary diagnosis. Treatment of insomnia can improve comorbidities.16
In addition, it is important to teach patients about basic sleep hygiene, which includes abiding by a consistent bedtime, and avoiding coffee, alcohol, and nicotine. Eliminating a bedroom clock, not exercising in the late afternoon/early evening, and consuming light bedtime snacks are other measures that can be taken. Avoiding the prolonged use of light-emitting screens before bedtime is another positive step.17
In conclusion, cognitive and behavioral methods are just as effective as prescription medications for short-term treatment of chronic insomnia and should be considered as first line before considering medications. The beneficial effects of CBT-I, in contrast to those produced by medication, might last well beyond the termination of active treatment.
References
1. J Clin Sleep Med. 2008 Oct 15;4(5):487-504.
2. J Clin Psychol. 2010;66(11):1148-60.
3. Sleep. 2013 Mar 1;36(3):353-62.
4. Sleep Med Rev. 2016 Dec;30:1-10.
5. BMC Family Prac. 2012;13:40.
6. Sleep. 2006 Nov;29(11):1398-414.
7. Behavioral Treatments for Sleep Disorders. 1991. doi: 10.1016/13978-0-12-381522-4.00002-X.
8. Behav Modif 1998 Jan;22(1):3-28.
9. Am Fam Physician. 1999 Jun;59(11):3029-38.
10. Psychophysiology. 2015 Mar;52(3):388-96.
11. J Clin Nursing. 2013 April 10. doi: 10.1111/jocn.12096.
12. J Physiother. 2012;58(3):157-63.
13. J Sleep Res. 2015 Oct;24(5):526-34.
14 Sleep Med. 2016 Sep;25:113-121.
15. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jul;170(7):716-20.
16. JAMA Intern Med. 2015 Sep;175(9):1461-72.
17. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(4):1232-7.
Dr. Lamba is a psychiatrist and medical director at Bayridge Hospital in Lynn, Mass. Dr. Rana is assistant professor of pediatrics at Boston University.
“The greatest medicine of all is teaching people how not to need it.” – Hippocrates
For many years, over-the-counter and prescription medications indicated for sleep problems/disorders have been available to patients. But the side effects associated with some of these medications are many. In light of the numerous nonpharmacologic interventions that are available to patients, they should be offered first when appropriate.
One of the top nonpharmacologic interventions is cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia, or CBT-I, which the American Academy of Sleep Medicine’s clinical guidelines say should be used as initial treatment if possible.1 Elements of CBT-I include cognitive therapy, which is aimed at reducing dysfunctional beliefs about sleep. Common distortions expressed by patients include: “I cannot sleep without medications” and “I must get 8 hours of sleep to feel refreshed and function well the next day.” It helps in dealing with anxiety and catastrophic thinking to establish realistic expectations and treatment related to insomnia.
CBT-I can be delivered in the form of monotherapy or in a combined manner. The individual components include psychoeducation, behavioral strategies, cognitive therapy, and relaxation training. CBT-I combines cognitive therapy with behavioral interventions. Behavioral elements include stimulus control therapy and sleep restriction therapy. Relaxation therapy might or might not be included. Sleep hygiene education usually is a part of it.2
Two other kinds of CBT that can be effective options are telephone-based CBT-I and Internet-based CBT-I.3,4 Meanwhile, among the disadvantages of CBT for insomnia are longer duration of therapy and lack of skilled clinicians.5
Many other kinds of behavioral interventions are available to patients with problems related to sleep, including stimulus control therapy, relaxation therapy, exercise therapy, and sleep restriction therapy.
Stimulus control therapy
This is a strategy aimed at strengthening the association of bed and bedroom to sleep, establishing a consistent sleep-wake rhythm, and reducing the activities that might interfere with sleep. This behavioral therapy is based on the idea that arousal occurs as a conditioned response to the stimulus of sleep environment, and it is among the most effective behavioral treatments.6,7 Strategies include the following:
1. Lie down with the intention of sleeping when sleepy.
2. Do not watch television, read, eat or worry while in bed. Use bed only for sleep and sex.
3. Get out of bed if unable to fall asleep within 10-15 minutes and go to another room. Return to bed only when sleepy. Do not watch the clock. Repeat this step as many times as necessary throughout the night.
4. Set an alarm clock to wake up at a fixed time each morning, including weekends, regardless of how much sleep you got during the night.
5. Do not take a nap during the day.
The goal of these strategies is to extinguish negative associations between bed and undesirable outcomes, such as wakefulness and frustration. One study showed that stimulus control participants, unlike control group participants, experienced significant improvement at follow-up for total sleep time, sleep efficiency, and sleep quality.8
Relaxation therapy
This encompasses different techniques that produce a relaxation response and reduce somatic arousal. It can be implemented before each sleep period. Progressive muscle relaxation, autogenic training, and biofeedback help reduce somatic arousal. Attention-focused procedures, such as imagery training and meditation, tend to lower presleep cognitive arousal (for example, intrusive thoughts, racing minds).9 Slow paced breathing prior to onset of sleep enhances vagal activity, which results in improved sleep parameters.10 One study showed improved quality of sleep and cognitive functions in the elderly by self-relaxation training.11
Exercise training
Participating in physical exercise can be useful in the treatment of insomnia.12 One randomized, controlled trial found that exercising regularly for at least 150 minutes per week was optimal.13 Another study found that, among overweight and obese men with insomnia, aerobic exercise over a 6-month period reduced difficulty in initiating and improving sleep.14
Sleep restriction therapy
The goal of this therapy is to increase the homeostatic drive to sleep. This is carried out by limiting the amount of time spent in bed to the same amount of time that the person reports sleeping. Naps are not allowed. Patients improve with increased drive to sleep in successive nights. In patients with bipolar disorder, however, sleep restriction should be used with caution as it can trigger manic episodes.15
Always ask about sleep
Clinicians should always ask patients about sleep during visits. Sleep duration and sleep quality should be assessed. Insomnia, which is an independent condition, may or may not coexist with other conditions. It is important to determine whether another sleep disorder, or a physical (such as pain, heart, or lung disease), neurological (such as Parkinson’s disease or cerebrovascular disease), or psychiatric disorder (such as depressive illness, anxiety disorder, or substance misuse) is the primary diagnosis. Treatment of insomnia can improve comorbidities.16
In addition, it is important to teach patients about basic sleep hygiene, which includes abiding by a consistent bedtime, and avoiding coffee, alcohol, and nicotine. Eliminating a bedroom clock, not exercising in the late afternoon/early evening, and consuming light bedtime snacks are other measures that can be taken. Avoiding the prolonged use of light-emitting screens before bedtime is another positive step.17
In conclusion, cognitive and behavioral methods are just as effective as prescription medications for short-term treatment of chronic insomnia and should be considered as first line before considering medications. The beneficial effects of CBT-I, in contrast to those produced by medication, might last well beyond the termination of active treatment.
References
1. J Clin Sleep Med. 2008 Oct 15;4(5):487-504.
2. J Clin Psychol. 2010;66(11):1148-60.
3. Sleep. 2013 Mar 1;36(3):353-62.
4. Sleep Med Rev. 2016 Dec;30:1-10.
5. BMC Family Prac. 2012;13:40.
6. Sleep. 2006 Nov;29(11):1398-414.
7. Behavioral Treatments for Sleep Disorders. 1991. doi: 10.1016/13978-0-12-381522-4.00002-X.
8. Behav Modif 1998 Jan;22(1):3-28.
9. Am Fam Physician. 1999 Jun;59(11):3029-38.
10. Psychophysiology. 2015 Mar;52(3):388-96.
11. J Clin Nursing. 2013 April 10. doi: 10.1111/jocn.12096.
12. J Physiother. 2012;58(3):157-63.
13. J Sleep Res. 2015 Oct;24(5):526-34.
14 Sleep Med. 2016 Sep;25:113-121.
15. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jul;170(7):716-20.
16. JAMA Intern Med. 2015 Sep;175(9):1461-72.
17. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(4):1232-7.
Dr. Lamba is a psychiatrist and medical director at Bayridge Hospital in Lynn, Mass. Dr. Rana is assistant professor of pediatrics at Boston University.
“The greatest medicine of all is teaching people how not to need it.” – Hippocrates
For many years, over-the-counter and prescription medications indicated for sleep problems/disorders have been available to patients. But the side effects associated with some of these medications are many. In light of the numerous nonpharmacologic interventions that are available to patients, they should be offered first when appropriate.
One of the top nonpharmacologic interventions is cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia, or CBT-I, which the American Academy of Sleep Medicine’s clinical guidelines say should be used as initial treatment if possible.1 Elements of CBT-I include cognitive therapy, which is aimed at reducing dysfunctional beliefs about sleep. Common distortions expressed by patients include: “I cannot sleep without medications” and “I must get 8 hours of sleep to feel refreshed and function well the next day.” It helps in dealing with anxiety and catastrophic thinking to establish realistic expectations and treatment related to insomnia.
CBT-I can be delivered in the form of monotherapy or in a combined manner. The individual components include psychoeducation, behavioral strategies, cognitive therapy, and relaxation training. CBT-I combines cognitive therapy with behavioral interventions. Behavioral elements include stimulus control therapy and sleep restriction therapy. Relaxation therapy might or might not be included. Sleep hygiene education usually is a part of it.2
Two other kinds of CBT that can be effective options are telephone-based CBT-I and Internet-based CBT-I.3,4 Meanwhile, among the disadvantages of CBT for insomnia are longer duration of therapy and lack of skilled clinicians.5
Many other kinds of behavioral interventions are available to patients with problems related to sleep, including stimulus control therapy, relaxation therapy, exercise therapy, and sleep restriction therapy.
Stimulus control therapy
This is a strategy aimed at strengthening the association of bed and bedroom to sleep, establishing a consistent sleep-wake rhythm, and reducing the activities that might interfere with sleep. This behavioral therapy is based on the idea that arousal occurs as a conditioned response to the stimulus of sleep environment, and it is among the most effective behavioral treatments.6,7 Strategies include the following:
1. Lie down with the intention of sleeping when sleepy.
2. Do not watch television, read, eat or worry while in bed. Use bed only for sleep and sex.
3. Get out of bed if unable to fall asleep within 10-15 minutes and go to another room. Return to bed only when sleepy. Do not watch the clock. Repeat this step as many times as necessary throughout the night.
4. Set an alarm clock to wake up at a fixed time each morning, including weekends, regardless of how much sleep you got during the night.
5. Do not take a nap during the day.
The goal of these strategies is to extinguish negative associations between bed and undesirable outcomes, such as wakefulness and frustration. One study showed that stimulus control participants, unlike control group participants, experienced significant improvement at follow-up for total sleep time, sleep efficiency, and sleep quality.8
Relaxation therapy
This encompasses different techniques that produce a relaxation response and reduce somatic arousal. It can be implemented before each sleep period. Progressive muscle relaxation, autogenic training, and biofeedback help reduce somatic arousal. Attention-focused procedures, such as imagery training and meditation, tend to lower presleep cognitive arousal (for example, intrusive thoughts, racing minds).9 Slow paced breathing prior to onset of sleep enhances vagal activity, which results in improved sleep parameters.10 One study showed improved quality of sleep and cognitive functions in the elderly by self-relaxation training.11
Exercise training
Participating in physical exercise can be useful in the treatment of insomnia.12 One randomized, controlled trial found that exercising regularly for at least 150 minutes per week was optimal.13 Another study found that, among overweight and obese men with insomnia, aerobic exercise over a 6-month period reduced difficulty in initiating and improving sleep.14
Sleep restriction therapy
The goal of this therapy is to increase the homeostatic drive to sleep. This is carried out by limiting the amount of time spent in bed to the same amount of time that the person reports sleeping. Naps are not allowed. Patients improve with increased drive to sleep in successive nights. In patients with bipolar disorder, however, sleep restriction should be used with caution as it can trigger manic episodes.15
Always ask about sleep
Clinicians should always ask patients about sleep during visits. Sleep duration and sleep quality should be assessed. Insomnia, which is an independent condition, may or may not coexist with other conditions. It is important to determine whether another sleep disorder, or a physical (such as pain, heart, or lung disease), neurological (such as Parkinson’s disease or cerebrovascular disease), or psychiatric disorder (such as depressive illness, anxiety disorder, or substance misuse) is the primary diagnosis. Treatment of insomnia can improve comorbidities.16
In addition, it is important to teach patients about basic sleep hygiene, which includes abiding by a consistent bedtime, and avoiding coffee, alcohol, and nicotine. Eliminating a bedroom clock, not exercising in the late afternoon/early evening, and consuming light bedtime snacks are other measures that can be taken. Avoiding the prolonged use of light-emitting screens before bedtime is another positive step.17
In conclusion, cognitive and behavioral methods are just as effective as prescription medications for short-term treatment of chronic insomnia and should be considered as first line before considering medications. The beneficial effects of CBT-I, in contrast to those produced by medication, might last well beyond the termination of active treatment.
References
1. J Clin Sleep Med. 2008 Oct 15;4(5):487-504.
2. J Clin Psychol. 2010;66(11):1148-60.
3. Sleep. 2013 Mar 1;36(3):353-62.
4. Sleep Med Rev. 2016 Dec;30:1-10.
5. BMC Family Prac. 2012;13:40.
6. Sleep. 2006 Nov;29(11):1398-414.
7. Behavioral Treatments for Sleep Disorders. 1991. doi: 10.1016/13978-0-12-381522-4.00002-X.
8. Behav Modif 1998 Jan;22(1):3-28.
9. Am Fam Physician. 1999 Jun;59(11):3029-38.
10. Psychophysiology. 2015 Mar;52(3):388-96.
11. J Clin Nursing. 2013 April 10. doi: 10.1111/jocn.12096.
12. J Physiother. 2012;58(3):157-63.
13. J Sleep Res. 2015 Oct;24(5):526-34.
14 Sleep Med. 2016 Sep;25:113-121.
15. Am J Psychiatry. 2013 Jul;170(7):716-20.
16. JAMA Intern Med. 2015 Sep;175(9):1461-72.
17. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(4):1232-7.
Dr. Lamba is a psychiatrist and medical director at Bayridge Hospital in Lynn, Mass. Dr. Rana is assistant professor of pediatrics at Boston University.
Genitourinary endometriosis: Diagnosis and management
Endometriosis is a benign disease characterized by endometrial glands and stroma outside of the uterine cavity. It is commonly associated with pelvic pain and infertility. Ectopic endometrial tissue is predominantly located in the pelvis, but it can appear anywhere in the body, where it is referred to as extragenital endometriosis. The bowel and urinary tract are the most common sites of extragenital endometriosis.1
Laparoscopic management of extragenital endometriosis has been described since the 1980s.2 However, laparoscopic management of genitourinary endometriosis is still not widespread.3,4 Physicians are often unfamiliar with the signs and symptoms of genitourinary endometriosis and fail to consider it when a patient presents with bladder pain or hematuria, which may or may not be cyclic. Furthermore, many gynecologists do not have the experience to correctly identify the various forms of endometriosis that may appear on the pelvic organ, including the serosa and peritoneum, as variable colored spots, blebs, lesions, or adhesions. Many surgeons are also not adequately trained in the advanced laparoscopic techniques required to treat genitourinary endometriosis.4
In this article, we describe the clinical presentation and diagnosis of genitourinary endometriosis and discuss laparoscopic management strategies with and without robotic assistance.
Clinical presentation and diagnosis of genitourinary endometriosis
While ureteral and bladder endometriosis are both diseases of the urinary tract, they are not always found together in the same patient. The bladder is the most commonly affected organ, followed by the ureter and kidney.3,5,6 Endometriosis of the bladder usually presents with significant lower urinary tract symptoms. In contrast, ureteral endometriosis is usually silent with no apparent urinary symptoms.
Ureteral endometriosis. Cyclic hematuria is present in less than 15% of patients with ureteral endometriosis. Some patients experience cyclic, nonspecific colicky flank pain.7-9 Otherwise, most patients present with the usual symptoms of endometriosis, such as pelvic pain and dysmenorrhea. In a systematic review, Cavaco-Gomes and colleagues described 700 patients with ureteral endometriosis; 81% reported dysmenorrhea, 70% had pelvic pain, and 66% had dyspareunia.10 Rarely, ureteral endometriosis can result in silent kidney loss if the ureter becomes severely obstructed without treatment.11,12
Continue to: The lack of symptoms makes...
The lack of symptoms makes the early diagnosis of ureteral endometriosis difficult. As with all types of endometriosis, histologic evaluation of a biopsy sample is diagnostic. Multiple imaging modalities have been used to preoperatively diagnose ureteral involvement, including computed tomography,13 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),14 intravenous pyelogram (IVP), and pelvic ultrasonography. However, each of these imaging modalities is limited in both sensitivity and the ability to characterize depth of tissue invasion.
In a study of 245 women undergoing pelvic ultrasonography, Pateman and colleagues reported that an experienced sonographer was able to visualize the bilateral ureters in 93% of cases.15 Renal ultrasonography is indicated in any woman suspected of having genitourinary tract involvement with the degree of hydroureter and level of obstruction noted during the exam.16
In our group, we perform renography to assess kidney function when hydroureter is noted preoperatively. Studies suggest that if greater than 10% of normal glomerular filtration rate remains, the kidney is considered salvageable, and near-normal function often returns following resection of disease. If preoperative kidney function is noted to be less than 10%, consultation with a nephrologist for possible nephrectomy is warranted.
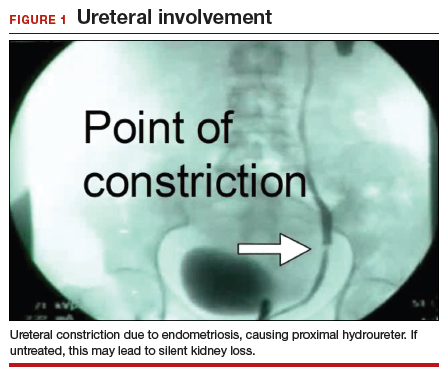
We find that IVP is often helpful for preoperatively identifying the level and degree of ureteral involvement, and it also can be used postoperatively to evaluate for ureteral continuity (FIGURE 1). Sillou and colleagues showed MRI to be adequately sensitive for the detection of intrinsic ureteral endometriosis, but they reported that MRI often overestimates the frequency of disease.17 Authors of a 2016 Cochrane review of imaging modalities for endometriosis, including 4,807 women in 49 studies, reported that no imaging test was superior to surgery for diagnosing endometriosis.18 However, the review notably excluded genitourinary tract endometriosis, as surgery is not an acceptable reference standard, given that many surgeons cannot reliably identify such lesions.18
Bladder endometriosis. Unlike patients with ureteral endometriosis, those with bladder endometriosis are typically symptomatic and experience dysuria, hematuria, urinary frequency, and suprapubic tenderness.7,19 Urinary tract infection, interstitial cystitis, and cancer must be considered in the differential diagnosis. Urinalysis and urine culture should be performed, and other diagnostic procedures such as ultrasonography, MRI, and cystoscopy should be considered to evaluate for endometriosis of the bladder.
Ultrasound and MRI of the bladder both demonstrate a high specificity for detecting bladder endometriosis, but they lack sensitivity for lesions less than 3 cm.20 Deep infiltrating endometriosis of the bladder can be identified at the time of cystoscopy, which can assist in determining the need for ureteroneocystostomy if lesions are within 2 cm of the urethral opening.20 Cystoscopy also allows for biopsy to be performed if underlying malignancy is of concern.19
In our group, when bladder endometriosis is suspected, we routinely perform preoperative bladder ultrasonography to identify the lesion and plan to perform intraoperative cystoscopy at the time of laparoscopic resection.19,21
Continue to: Treatment...
Treatment
Medical management
Empiric medical therapies for endometriosis are centered around the idea that ectopic endometrial tissue responds to treatment in a similar manner as normal eutopic endometrium. The goals of treatment are to reduce or eliminate cyclic menstruation, thereby decreasing peritoneal seeding and suppressing the growth and activity of established ectopic implants. Medical therapy commonly involves the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists or antagonists, danazol, combined oral contraceptives, progestins, and aromatase inhibitors.
Medical therapy is commonly employed for patients with mild or early-stage disease and in those who are poor surgical candidates or decline surgery. Medical management alone clearly is contraindicated in the setting of ureteral obstruction and—in our opinion—may not be a good option for those with endometriosis of the ureter, given the potential for recurrence and potential serious sequelae of reduced renal function.22 Therefore, surgery has become the standard approach to therapy for mild to moderate cases of ureteral endometriosis.3
Medical therapy for patients with endometriosis of the bladder is generally considered a temporary solution as hormonal suppression, with its associated adverse effects, must be maintained throughout menopause. However, if endometriosis lesions lie within close proximity to the trigone, medical management is preferred, as surgical excision in the area of the trigone may predispose patients to neurogenic bladder and retrograde bladder reflux.23,24
Surgical management
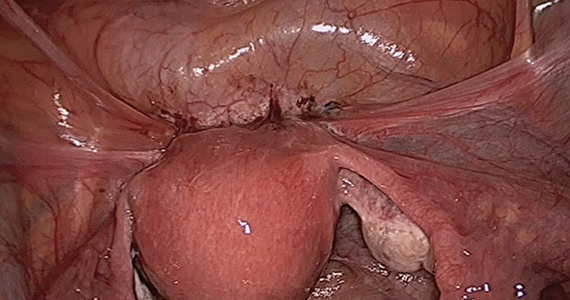
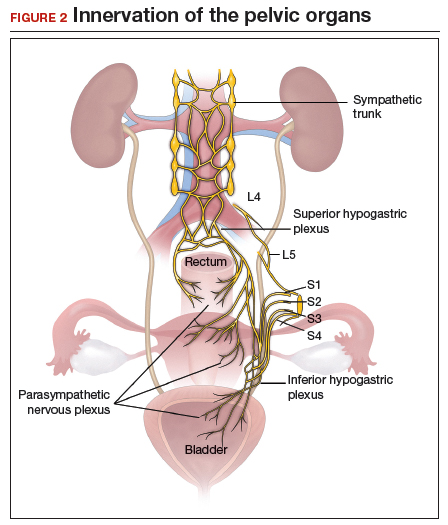
The objectives of surgical treatment for genitourinary tract endometriosis are to excise all visible disease, to prevent or delay recurrence of the disease to the extent possible, and to avoid any further morbidity—in particular, to preserve renal function in cases of ureteral endometriosis—and to avoid iatrogenic injury to surrounding pelvic nervous structures25-27 (FIGURE 2). The surgical approach depends on the technical expertise of the surgeon and the availability of necessary instrumentation. In our experience, laparoscopy with or without robotic assistance is the preferred surgical approach.3,4,6,11,28-32
Others have reported on the benefits of laparoscopy over laparotomy for the surgical management of genitourinary endometriosis. In a review of 61 patients who underwent either robot-assisted laparoscopic (n = 25) or open (n = 41) ureteroneocystostomy (n = 41), Isac and colleagues reported the procedure was longer in the laparoscopic group (279 min vs 200 min, P<.001), but the laparoscopic group had a shorter hospital stay (3 days vs 5 days, P<.001), used fewer narcotics postoperatively (P<.001), and had lower intraoperative blood loss (100 mL vs 150 mL, P<.001).32 No differences in long-term outcomes were observed in either cohort.
In a systematic review of 700 patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery for ureteral endometriosis, Cavaco-Gomes and colleagues reported that conversion to laparotomy occurred in only 3% to 7% of cases.10 In instances of ureteral endometriosis, laparoscopy provides greater visualization of the intraperitoneal contents over laparotomy, enabling better evaluation and treatment of lesions.3,29,33,34 Robot-assisted laparoscopy provides the additional advantages of 3D visualization, potential for an accelerated learning curve over traditional laparoscopy, improvement in dissection technique, and ease of suturing technique.6,35,36
Continue to: Extrinsic disease...
Extrinsic disease. In our group, we perform ureterolysis for extrinsic disease.25 The peritoneal incision is made in an area unaffected by endometriosis. Using the suction irrigator, a potential space is developed under the serosa of the ureter by injecting normal saline or lactated Ringer’s solution. By creating a fluid barrier between the serosa and underlying tissues, the depth of surgical incision and lateral thermal spread are minimized. Grasping forceps are used to peel the peritoneum away.25,37,38
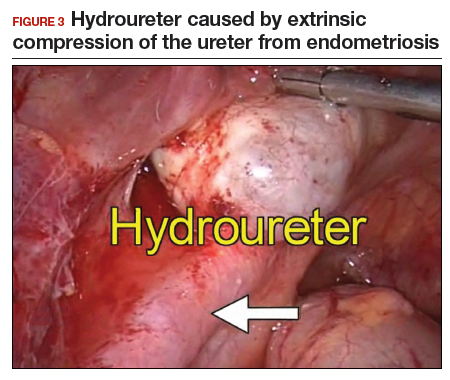
Intrinsic disease. Unlike extrinsic disease, intrinsic disease can infiltrate the muscularis, lamina propria, and ureteral lumen, resulting in proximal dilation of the ureter with strictures.8 In this situation, ureteral compromise is likely and resection of the ureter is indicated3,28 (FIGURE 3). Intrinsic disease can be suggested by preoperative imaging or when there is evidence of deep infiltrating disease on physical exam, such as rectovaginal nodularity.30,39 When intrinsic ureteral disease is known, consultation with a urologist to plan a joint procedure is advisable. The procedure chosen to re-establish a functional ureter following resection depends on the location and extent of the involved ureter. Resection in close proximity to the bladder may be repaired by ureteroneocystostomy with or without psoas hitch,30,39,40 whereas resection of more proximal ureter may be repaired using Boari flap, ileal interposition, or autotransplantation. Lesions in the upper third or middle ureter may be repaired using ureterouretral anastomosis.6,7,30,41-43
Continue to: Bladder endometriosis...
Bladder endometriosis. Surgical treatment for bladder endometriosis depends on the depth of invasion and the location of the lesion (FIGURE 4). Lesions of the superficial aspect of the bladder identified at the time of laparoscopy can be treated with either excision or fulguration28,35,44 In our group, we perform excision over fulguration to remove the entire lesion and obtain a pathologic diagnosis. Deeper lesions involving the detrusor muscle are likely to be an endometrioma of the bladder. In these cases, laparoscopic excision is recommended.7 Rarely, lesions close to the interureteric ridge may require ureteroneocystostomy.19,45
In our experience, laparoscopic resection of bladder endometriomas is associated with better results in terms of symptom relief, progression of disease, and recurrence risk compared with other approaches. When performing laparoscopic excision of bladder lesions, we concomitantly evaluate the bladder lesion via cystoscopy to ensure adequate margins are obtained. Double-J stent placement is advised when lesions are within 2 cm of the urethral meatus to ensure ureteral patency during the postoperative period.45 A postoperative cystogram routinely is performed 7 to 14 days after surgery to ensure adequate repair prior to removing the urinary catheter.9,25,46,47

Postsurgical follow-up
Follow-up after treatment of genitourinary tract endometriosis should include monitoring the patient for symptoms of recurrence. Regular history and physical examination, renal function testing, and, in some instances, pelvic ultrasonography, all have a role in surveillance for recurrent ureteric disease. IVP or MRI may be warranted if a recurrence is suspected. A high index of suspicion should be maintained on the part of the clinician to avoid the devastating consequences of silent kidney loss. Patients should be counseled about the risk of disease recurrence, especially in those not undergoing postoperative hormonal suppression.
In conclusion
While endometriosis of the genitourinary tract is rare, patients can experience significant morbidity. Medical management of the disease is often limited by substantial adverse effects that limit treatment duration and is best used postoperatively after excision. An adequate physical exam and preoperative diagnostic imaging can be employed to characterize the extent of disease. When extensive disease involving the ureter is suspected, preoperative consultation with a urologist is encouraged to plan a multidisciplinary approach to surgical resection.
The ideal approach to surgery is laparoscopic resection with or without robotic assistance. Treatment of ureteral disease most commonly involves ureterolysis for cases of extrinsic disease but may require total resection of the ureter with concurrent ureteral reconstruction when disease is intrinsic to the ureter. Surgery for bladder endometriosis depends on the depth of invasion and location of the lesion. Superficial bladder lesions can be treated with fulguration or excision, while deeper lesions involving the detrusor muscle require excision. Lesions in close proximity to the interureteric ridge may require ureteroneocystostomy. Follow-up after excisional procedures involves monitoring the patient for signs and symptoms of disease recurrence, especially in cases of ureteral involvement, to avoid the devastating consequences of silent kidney loss.
The definitive cause of endometriosis remains unknown, but several prominent theories have been proposed.
Sampson's theory of retrograde menstruation through the fallopian tubes is the most well-known theory,1 although Schron had acknowledged a similar thought 3 centuries before.2 This theory posits that refluxed endometrial cells enter the abdominal cavity and invade the peritoneum, developing a blood supply necessary for survival and growth. Early reports supported this theory by suggesting that women with genital tract obstruction have a higher incidence of endometriosis.3,4 However, it was later confirmed that women without genital tract obstruction have a similar incidence of retrograde menstruation. In fact, up to 90% of women are found to have retrograde menstruation, but only 10% develop endometriosis. This suggests that once endometrial cells have escaped the uterine cavity, other events are necessary for endometrial cells to implant and survive.3,5 Other evidence to support the theory of retrograde menstruation is the observation that endometriosis is most commonly observed in the dependent portions of the pelvis, on the ovaries, in the anterior and posterior cul-de-sacs, and on the uterosacral ligament.6
The coelomic metaplasia theory holds that endometriosis results from spontaneous metaplastic change to mesothelial cells derived from the coelomic epithelium (located in the peritoneum and the pleura) upon exposure to menstrual effluent or other stimuli.7 Evidence for this theory is supported by the observation that intact endometrial cells have no access to the thoracic cavity in the absence of anatomical defect; therefore, the implantation theory cannot explain cases of pleural or pulmonary endometriosis.
Immune dysregulation also has been invoked to explain endometriosis implants both inside and outside the genitourinary tract. Studies have shown a higher incidence of endometriosis in women with other autoimmune disorders, including hypothyroidism, chronic fatigue syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren syndrome, and multiple sclerosis as well as in women with allergies, asthma, and eczema.8 In such women, dysregulation of the innate and adaptive immune system might promote the disease by inhibiting apoptosis of ectopic endometrial cells and by promoting their attachment, invasion, and proliferation into healthy peritoneum through the secretion of various growth factors and cytokines.9,10
Other possible theories that might explain the pathogenesis of endometriosis exist.11-13 While each theory has documented supporting evidence, no single theory currently accounts for all cases of endometriosis. It is likely, then, that endometriosis is a multifactorial disease with a combination of immune dysregulation, molecular abnormalities, genetic and epigenetic factors, and environmental exposures involved in its pathogenesis.
References
- Sampson J. Peritoneal endometriosis due to the menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the peritoneal cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1927;14:422-469.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C. Endometriosis: ancient disease, ancient treatments. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6 suppl):S1-62.
- Halme J, Hammond MG, Hulka JF, et al. Retrograde menstruation in healthy women and in patients with endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;64:151-154.
- Sanfilippo JS, Wakim NG, Schikler KN, et al. Endometriosis in association with uterine anomaly. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986;154:39-43.
- Burney RO, Giudice LC. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:511-519.
- Vercellini P, Chapron C, Fedele L, et al. Evidence for asymmetric distribution of lower intestinal tract endometriosis. BJOG. 2004;111:1213-1217.
- Sourial S, Tempest N, Hapangama DK. Theories on the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Int J Reprod Med. 2014;2014:179515.
- Sinaii N, Cleary SD, Ballweg ML, et al. High rates of autoimmune and endocrine disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome and atopic diseases among women with endometriosis: a survey analysis. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:2715-2724.
- Lebovic DI, Mueller MD, Taylor RN. Immunobiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2001;75:1-10.
- Sidell N, Han SW, Parthasarathy S. Regulation and modulation of abnormal immune responses in endometriosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;955: 159-173; discussion 199-200, 396-406.
- Burney RO, Giudice LC. The pathogenesis of endometriosis. In: Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013;252-258.
- Buka NJ. Vesical endometriosis after cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158:1117-1118.
- Price DT, Maloney KE, Ibrahim GK, et al. Vesical endometriosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Urology. 1996;48:639-643.
- Veeraswamy A, Lewis M, Mann A, et al. Extragenital endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:449-466.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison GP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1986;45:778-783.
- Bosev D, Nicoll LM, Bhagan L, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis: the Stanford University hospital experience with 96 consecutive cases. J Urol. 2009;182:2748-2752.
- Nezhat C, Falik R, McKinney S, et al. Pathophysiology and management of urinary tract endometriosis. Nat Rev Urol. 2017;14:359-372.
- Shook TE, Nyberg LM. Endometriosis of the urinary tract. Urology. 1988;31:1-6.
- Nezhat C, Modest AM, King LP. The role of the robot in treating urinary tract endometriosis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2013;25:308-311.
- Comiter CV. Endometriosis of the urinary tract. Urol Clin North Am. 2002;29:625-635.
- Gustilo-Ashby AM, Paraiso MF. Treatment of urinary tract endometriosis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2006;13:559-565.
- Berlanda N, Somigliana E, Frattaruolo MP, et al. Surgery versus hormonal therapy for deep endometriosis: is it a choice of the physician? Eur J Obstet Gyneocol Reprod Biol. 2017;209:67-71.
- Cavaco-Gomes J, Martinho M, Gilabert-Aguilar J, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017;210:94-101.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Green B. Laparoscopic treatment of obstructed ureter due to endometriosis by resection and ureteroureterostomy: a case report. J Urol. 1992;148:865-868.
- Nezhat C, Paka C, Gomaa M, et al. Silent loss of kidney secondary to ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2012;16:451-455.
- Iosca S, Lumia D, Bracchi E, et al. Multislice computed tomography with colon water distention (MSCT-c) in the study of intestinal and ureteral endometriosis. Clin Imaging. 2013;37(6):1061-1068.
- Medeiros LR, Rosa MI, Silva BR, et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance in deeply infiltrating endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015;291:611-621.
- Pateman K, Mavrelos D, Hoo WL, et al. Visualization of ureters on standard gynecological transvaginal scan: a feasibility study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013;41:696-701.
- Guerriero S, Condous G, van den Bosch T, et al. Systematic approach to sonographic evaluation of the pelvis in women with suspected endometriosis, including terms, definitions and measurements: a consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48:318-332.
- Sillou S, Poirée S, Millischer AE, et al. Urinary endometriosis: MR imaging appearance with surgical and histological correlations. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015;96:373-381.
- Nisenblat V, Bossuyt PM, Farquhar C, et al. Imaging modalities for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD009591.
- Nezhat CH, Malik S, Osias J, et al. Laparoscopic management of 15 patients with infiltrating endometriosis of the bladder and a case of primary intravesical endometrioid adenosarcoma. Fertil Steril. 2002;78:872-875.
- Kolodziej A, Krajewski W, Dolowy L, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis. Urol J. 2015;12:2213-2217.
- Nezhat C, Buescher E, Paka C, et al. Video-assisted laparoscopic treatment of endometriosis. In: Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013;265.
- Al-Fozan H, Tulandi T. Left lateral predisposition of endometriosis and endometrioma. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:164-166.
- Hastings JC, Van Winkle W, Barker E, et al. The effect of suture materials on healing wounds of the bladder. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975;140:933-937.
- Cornell KK. Cystotomy, partial cystectomy, and tube cystostomy. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2000;15:11-16.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013.
- Uccella S, Cromi A, Casarin J, et al. Laparoscopy for ureteral endometriosis: surgical details, long-term follow-up, and fertility outcomes. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:160-166.e2.
- Knabben L, Imboden S, Fellmann B, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis in patients with deep infiltrating endometriosis: prevalence, symptoms, management, and proposal for a new clinical classification. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:147-152.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat CH, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis treated by laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1996;66:920-924.
- Nezhat CH, Nezhat F, Seidman D, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroureterostomy: a prospective follow-up of 9 patients. Prim Care Update Ob Gyns. 1998;5:200.
- Nezhat CH, Bracale U, Scala A, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocystostomy and vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative endometriosis. JSLS. 2004;8:3-7.
- Nezhat C, Lewis M, Kotikela S, et al. Robotic versus standard laparoscopy for the treatment of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:2758-2760.
- Isac W, Kaouk J, Altunrende F, et al. Robotic-assisted ureteroneocytostomy: techniques and comparative outcomes. J Endourol. 2013;27:318-323.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F. Laparoscopic repair of ureter resected during operative laparoscopy. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;80(3 pt 2):543-544.
- De Cicco C, Ussia A, Koninckx PR. Laparoscopic ureteral repair in gynaecological surgery. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;23:296-300.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic treatment of bowel, bladder, and ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2011;15:387-392.
- Fadhlaoui A, Gillon T, Lebbi I, et al. Endometriosis and vesico-sphincteral disorders. Front Surg. 2015;2:23.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat FR. Safe laser endoscopic excision or vaporization of peritoneal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1989;52:149-151.
- Nezhat C, Winer W, Nezhat FA. Comparison of the CO2, argon, and KTP/532 lasers in the videolaseroscopic treatment of endometriosis. J Gynecol Surg. 2009;41-47.
- Azioni G, Bracale U, Scala A, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocytostomy and vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative ureteral endometriosis. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2010;19:292-297.
- Stepniewska A, Grosso G, Molon A, et al. Ureteral endometriosis: clinical and radiological follow-up after laparoscopic ureterocystoneostomy. Hum Reprod. 2011;26:112-116.
- Nezhat CH, Nezhat FR, Freiha F, et al. Laparoscopic vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative ureteral endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1999;71:376-379.
- Scioscia M, Molon A, Grosso G, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2009;21:325-328.
- Antonelli A. Urinary tract endometriosis. Urologia. 2012;79:167-170.
- Camanni M, Bonino L, Delpiano EM, et al. Laparoscopic conservative management of ureteral endometriosis: a survey of eighty patients submitted to ureterolysis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009;7:109.
- Chapron C, Bourret A, Chopin N, et al. Surgery for bladder endometriosis: long-term results and concomitant management of associated posterior deep lesions. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:884-889.
- Nezhat CR, Nezhat FR. Laparoscopic segmental bladder resection for endometriosis: a report of two cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1993;81(5 pt 2):882-884.
- Bourdel N, Cognet S, Canis M, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocystostomy: be prepared! J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:827-833.
- Page B. Camran Nezhat and the Advent of Advanced Operative Video-laparoscopy. In: Nezhat C, ed. Nezhat's History of Endoscopy. Tuttlingen, Germany: Endo Press; 2011:159-187.
- Podratz K. Degrees of Freedom: Advances in Gynecological and Obstetrical Surgery. Remembering Milestones and Achievements in Surgery: Inspiring Quality for a Hundred Years 1913-2012. Published by American College of Surgeons 2012. Tampa, FL: Faircount Media Group; 2013.
- Kelley WE. The evolution of laparoscopy and the revolution in surgery in the decade of the 1990s. JSLS: J Soc Laparoendoscopic Surgeons. 2008;12:351-357.
Endometriosis is a benign disease characterized by endometrial glands and stroma outside of the uterine cavity. It is commonly associated with pelvic pain and infertility. Ectopic endometrial tissue is predominantly located in the pelvis, but it can appear anywhere in the body, where it is referred to as extragenital endometriosis. The bowel and urinary tract are the most common sites of extragenital endometriosis.1
Laparoscopic management of extragenital endometriosis has been described since the 1980s.2 However, laparoscopic management of genitourinary endometriosis is still not widespread.3,4 Physicians are often unfamiliar with the signs and symptoms of genitourinary endometriosis and fail to consider it when a patient presents with bladder pain or hematuria, which may or may not be cyclic. Furthermore, many gynecologists do not have the experience to correctly identify the various forms of endometriosis that may appear on the pelvic organ, including the serosa and peritoneum, as variable colored spots, blebs, lesions, or adhesions. Many surgeons are also not adequately trained in the advanced laparoscopic techniques required to treat genitourinary endometriosis.4
In this article, we describe the clinical presentation and diagnosis of genitourinary endometriosis and discuss laparoscopic management strategies with and without robotic assistance.
Clinical presentation and diagnosis of genitourinary endometriosis
While ureteral and bladder endometriosis are both diseases of the urinary tract, they are not always found together in the same patient. The bladder is the most commonly affected organ, followed by the ureter and kidney.3,5,6 Endometriosis of the bladder usually presents with significant lower urinary tract symptoms. In contrast, ureteral endometriosis is usually silent with no apparent urinary symptoms.
Ureteral endometriosis. Cyclic hematuria is present in less than 15% of patients with ureteral endometriosis. Some patients experience cyclic, nonspecific colicky flank pain.7-9 Otherwise, most patients present with the usual symptoms of endometriosis, such as pelvic pain and dysmenorrhea. In a systematic review, Cavaco-Gomes and colleagues described 700 patients with ureteral endometriosis; 81% reported dysmenorrhea, 70% had pelvic pain, and 66% had dyspareunia.10 Rarely, ureteral endometriosis can result in silent kidney loss if the ureter becomes severely obstructed without treatment.11,12
Continue to: The lack of symptoms makes...
The lack of symptoms makes the early diagnosis of ureteral endometriosis difficult. As with all types of endometriosis, histologic evaluation of a biopsy sample is diagnostic. Multiple imaging modalities have been used to preoperatively diagnose ureteral involvement, including computed tomography,13 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),14 intravenous pyelogram (IVP), and pelvic ultrasonography. However, each of these imaging modalities is limited in both sensitivity and the ability to characterize depth of tissue invasion.
In a study of 245 women undergoing pelvic ultrasonography, Pateman and colleagues reported that an experienced sonographer was able to visualize the bilateral ureters in 93% of cases.15 Renal ultrasonography is indicated in any woman suspected of having genitourinary tract involvement with the degree of hydroureter and level of obstruction noted during the exam.16
In our group, we perform renography to assess kidney function when hydroureter is noted preoperatively. Studies suggest that if greater than 10% of normal glomerular filtration rate remains, the kidney is considered salvageable, and near-normal function often returns following resection of disease. If preoperative kidney function is noted to be less than 10%, consultation with a nephrologist for possible nephrectomy is warranted.
We find that IVP is often helpful for preoperatively identifying the level and degree of ureteral involvement, and it also can be used postoperatively to evaluate for ureteral continuity (FIGURE 1). Sillou and colleagues showed MRI to be adequately sensitive for the detection of intrinsic ureteral endometriosis, but they reported that MRI often overestimates the frequency of disease.17 Authors of a 2016 Cochrane review of imaging modalities for endometriosis, including 4,807 women in 49 studies, reported that no imaging test was superior to surgery for diagnosing endometriosis.18 However, the review notably excluded genitourinary tract endometriosis, as surgery is not an acceptable reference standard, given that many surgeons cannot reliably identify such lesions.18

Bladder endometriosis. Unlike patients with ureteral endometriosis, those with bladder endometriosis are typically symptomatic and experience dysuria, hematuria, urinary frequency, and suprapubic tenderness.7,19 Urinary tract infection, interstitial cystitis, and cancer must be considered in the differential diagnosis. Urinalysis and urine culture should be performed, and other diagnostic procedures such as ultrasonography, MRI, and cystoscopy should be considered to evaluate for endometriosis of the bladder.
Ultrasound and MRI of the bladder both demonstrate a high specificity for detecting bladder endometriosis, but they lack sensitivity for lesions less than 3 cm.20 Deep infiltrating endometriosis of the bladder can be identified at the time of cystoscopy, which can assist in determining the need for ureteroneocystostomy if lesions are within 2 cm of the urethral opening.20 Cystoscopy also allows for biopsy to be performed if underlying malignancy is of concern.19
In our group, when bladder endometriosis is suspected, we routinely perform preoperative bladder ultrasonography to identify the lesion and plan to perform intraoperative cystoscopy at the time of laparoscopic resection.19,21
Continue to: Treatment...
Treatment
Medical management
Empiric medical therapies for endometriosis are centered around the idea that ectopic endometrial tissue responds to treatment in a similar manner as normal eutopic endometrium. The goals of treatment are to reduce or eliminate cyclic menstruation, thereby decreasing peritoneal seeding and suppressing the growth and activity of established ectopic implants. Medical therapy commonly involves the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists or antagonists, danazol, combined oral contraceptives, progestins, and aromatase inhibitors.
Medical therapy is commonly employed for patients with mild or early-stage disease and in those who are poor surgical candidates or decline surgery. Medical management alone clearly is contraindicated in the setting of ureteral obstruction and—in our opinion—may not be a good option for those with endometriosis of the ureter, given the potential for recurrence and potential serious sequelae of reduced renal function.22 Therefore, surgery has become the standard approach to therapy for mild to moderate cases of ureteral endometriosis.3
Medical therapy for patients with endometriosis of the bladder is generally considered a temporary solution as hormonal suppression, with its associated adverse effects, must be maintained throughout menopause. However, if endometriosis lesions lie within close proximity to the trigone, medical management is preferred, as surgical excision in the area of the trigone may predispose patients to neurogenic bladder and retrograde bladder reflux.23,24
Surgical management
The objectives of surgical treatment for genitourinary tract endometriosis are to excise all visible disease, to prevent or delay recurrence of the disease to the extent possible, and to avoid any further morbidity—in particular, to preserve renal function in cases of ureteral endometriosis—and to avoid iatrogenic injury to surrounding pelvic nervous structures25-27 (FIGURE 2). The surgical approach depends on the technical expertise of the surgeon and the availability of necessary instrumentation. In our experience, laparoscopy with or without robotic assistance is the preferred surgical approach.3,4,6,11,28-32
Others have reported on the benefits of laparoscopy over laparotomy for the surgical management of genitourinary endometriosis. In a review of 61 patients who underwent either robot-assisted laparoscopic (n = 25) or open (n = 41) ureteroneocystostomy (n = 41), Isac and colleagues reported the procedure was longer in the laparoscopic group (279 min vs 200 min, P<.001), but the laparoscopic group had a shorter hospital stay (3 days vs 5 days, P<.001), used fewer narcotics postoperatively (P<.001), and had lower intraoperative blood loss (100 mL vs 150 mL, P<.001).32 No differences in long-term outcomes were observed in either cohort.
In a systematic review of 700 patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery for ureteral endometriosis, Cavaco-Gomes and colleagues reported that conversion to laparotomy occurred in only 3% to 7% of cases.10 In instances of ureteral endometriosis, laparoscopy provides greater visualization of the intraperitoneal contents over laparotomy, enabling better evaluation and treatment of lesions.3,29,33,34 Robot-assisted laparoscopy provides the additional advantages of 3D visualization, potential for an accelerated learning curve over traditional laparoscopy, improvement in dissection technique, and ease of suturing technique.6,35,36

Continue to: Extrinsic disease...
Extrinsic disease. In our group, we perform ureterolysis for extrinsic disease.25 The peritoneal incision is made in an area unaffected by endometriosis. Using the suction irrigator, a potential space is developed under the serosa of the ureter by injecting normal saline or lactated Ringer’s solution. By creating a fluid barrier between the serosa and underlying tissues, the depth of surgical incision and lateral thermal spread are minimized. Grasping forceps are used to peel the peritoneum away.25,37,38
Intrinsic disease. Unlike extrinsic disease, intrinsic disease can infiltrate the muscularis, lamina propria, and ureteral lumen, resulting in proximal dilation of the ureter with strictures.8 In this situation, ureteral compromise is likely and resection of the ureter is indicated3,28 (FIGURE 3). Intrinsic disease can be suggested by preoperative imaging or when there is evidence of deep infiltrating disease on physical exam, such as rectovaginal nodularity.30,39 When intrinsic ureteral disease is known, consultation with a urologist to plan a joint procedure is advisable. The procedure chosen to re-establish a functional ureter following resection depends on the location and extent of the involved ureter. Resection in close proximity to the bladder may be repaired by ureteroneocystostomy with or without psoas hitch,30,39,40 whereas resection of more proximal ureter may be repaired using Boari flap, ileal interposition, or autotransplantation. Lesions in the upper third or middle ureter may be repaired using ureterouretral anastomosis.6,7,30,41-43

Continue to: Bladder endometriosis...
Bladder endometriosis. Surgical treatment for bladder endometriosis depends on the depth of invasion and the location of the lesion (FIGURE 4). Lesions of the superficial aspect of the bladder identified at the time of laparoscopy can be treated with either excision or fulguration28,35,44 In our group, we perform excision over fulguration to remove the entire lesion and obtain a pathologic diagnosis. Deeper lesions involving the detrusor muscle are likely to be an endometrioma of the bladder. In these cases, laparoscopic excision is recommended.7 Rarely, lesions close to the interureteric ridge may require ureteroneocystostomy.19,45
In our experience, laparoscopic resection of bladder endometriomas is associated with better results in terms of symptom relief, progression of disease, and recurrence risk compared with other approaches. When performing laparoscopic excision of bladder lesions, we concomitantly evaluate the bladder lesion via cystoscopy to ensure adequate margins are obtained. Double-J stent placement is advised when lesions are within 2 cm of the urethral meatus to ensure ureteral patency during the postoperative period.45 A postoperative cystogram routinely is performed 7 to 14 days after surgery to ensure adequate repair prior to removing the urinary catheter.9,25,46,47

Postsurgical follow-up
Follow-up after treatment of genitourinary tract endometriosis should include monitoring the patient for symptoms of recurrence. Regular history and physical examination, renal function testing, and, in some instances, pelvic ultrasonography, all have a role in surveillance for recurrent ureteric disease. IVP or MRI may be warranted if a recurrence is suspected. A high index of suspicion should be maintained on the part of the clinician to avoid the devastating consequences of silent kidney loss. Patients should be counseled about the risk of disease recurrence, especially in those not undergoing postoperative hormonal suppression.
In conclusion
While endometriosis of the genitourinary tract is rare, patients can experience significant morbidity. Medical management of the disease is often limited by substantial adverse effects that limit treatment duration and is best used postoperatively after excision. An adequate physical exam and preoperative diagnostic imaging can be employed to characterize the extent of disease. When extensive disease involving the ureter is suspected, preoperative consultation with a urologist is encouraged to plan a multidisciplinary approach to surgical resection.
The ideal approach to surgery is laparoscopic resection with or without robotic assistance. Treatment of ureteral disease most commonly involves ureterolysis for cases of extrinsic disease but may require total resection of the ureter with concurrent ureteral reconstruction when disease is intrinsic to the ureter. Surgery for bladder endometriosis depends on the depth of invasion and location of the lesion. Superficial bladder lesions can be treated with fulguration or excision, while deeper lesions involving the detrusor muscle require excision. Lesions in close proximity to the interureteric ridge may require ureteroneocystostomy. Follow-up after excisional procedures involves monitoring the patient for signs and symptoms of disease recurrence, especially in cases of ureteral involvement, to avoid the devastating consequences of silent kidney loss.
The definitive cause of endometriosis remains unknown, but several prominent theories have been proposed.
Sampson's theory of retrograde menstruation through the fallopian tubes is the most well-known theory,1 although Schron had acknowledged a similar thought 3 centuries before.2 This theory posits that refluxed endometrial cells enter the abdominal cavity and invade the peritoneum, developing a blood supply necessary for survival and growth. Early reports supported this theory by suggesting that women with genital tract obstruction have a higher incidence of endometriosis.3,4 However, it was later confirmed that women without genital tract obstruction have a similar incidence of retrograde menstruation. In fact, up to 90% of women are found to have retrograde menstruation, but only 10% develop endometriosis. This suggests that once endometrial cells have escaped the uterine cavity, other events are necessary for endometrial cells to implant and survive.3,5 Other evidence to support the theory of retrograde menstruation is the observation that endometriosis is most commonly observed in the dependent portions of the pelvis, on the ovaries, in the anterior and posterior cul-de-sacs, and on the uterosacral ligament.6
The coelomic metaplasia theory holds that endometriosis results from spontaneous metaplastic change to mesothelial cells derived from the coelomic epithelium (located in the peritoneum and the pleura) upon exposure to menstrual effluent or other stimuli.7 Evidence for this theory is supported by the observation that intact endometrial cells have no access to the thoracic cavity in the absence of anatomical defect; therefore, the implantation theory cannot explain cases of pleural or pulmonary endometriosis.
Immune dysregulation also has been invoked to explain endometriosis implants both inside and outside the genitourinary tract. Studies have shown a higher incidence of endometriosis in women with other autoimmune disorders, including hypothyroidism, chronic fatigue syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren syndrome, and multiple sclerosis as well as in women with allergies, asthma, and eczema.8 In such women, dysregulation of the innate and adaptive immune system might promote the disease by inhibiting apoptosis of ectopic endometrial cells and by promoting their attachment, invasion, and proliferation into healthy peritoneum through the secretion of various growth factors and cytokines.9,10
Other possible theories that might explain the pathogenesis of endometriosis exist.11-13 While each theory has documented supporting evidence, no single theory currently accounts for all cases of endometriosis. It is likely, then, that endometriosis is a multifactorial disease with a combination of immune dysregulation, molecular abnormalities, genetic and epigenetic factors, and environmental exposures involved in its pathogenesis.
References
- Sampson J. Peritoneal endometriosis due to the menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the peritoneal cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1927;14:422-469.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C. Endometriosis: ancient disease, ancient treatments. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6 suppl):S1-62.
- Halme J, Hammond MG, Hulka JF, et al. Retrograde menstruation in healthy women and in patients with endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;64:151-154.
- Sanfilippo JS, Wakim NG, Schikler KN, et al. Endometriosis in association with uterine anomaly. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986;154:39-43.
- Burney RO, Giudice LC. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:511-519.
- Vercellini P, Chapron C, Fedele L, et al. Evidence for asymmetric distribution of lower intestinal tract endometriosis. BJOG. 2004;111:1213-1217.
- Sourial S, Tempest N, Hapangama DK. Theories on the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Int J Reprod Med. 2014;2014:179515.
- Sinaii N, Cleary SD, Ballweg ML, et al. High rates of autoimmune and endocrine disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome and atopic diseases among women with endometriosis: a survey analysis. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:2715-2724.
- Lebovic DI, Mueller MD, Taylor RN. Immunobiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2001;75:1-10.
- Sidell N, Han SW, Parthasarathy S. Regulation and modulation of abnormal immune responses in endometriosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;955: 159-173; discussion 199-200, 396-406.
- Burney RO, Giudice LC. The pathogenesis of endometriosis. In: Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013;252-258.
- Buka NJ. Vesical endometriosis after cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158:1117-1118.
- Price DT, Maloney KE, Ibrahim GK, et al. Vesical endometriosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Urology. 1996;48:639-643.
Endometriosis is a benign disease characterized by endometrial glands and stroma outside of the uterine cavity. It is commonly associated with pelvic pain and infertility. Ectopic endometrial tissue is predominantly located in the pelvis, but it can appear anywhere in the body, where it is referred to as extragenital endometriosis. The bowel and urinary tract are the most common sites of extragenital endometriosis.1
Laparoscopic management of extragenital endometriosis has been described since the 1980s.2 However, laparoscopic management of genitourinary endometriosis is still not widespread.3,4 Physicians are often unfamiliar with the signs and symptoms of genitourinary endometriosis and fail to consider it when a patient presents with bladder pain or hematuria, which may or may not be cyclic. Furthermore, many gynecologists do not have the experience to correctly identify the various forms of endometriosis that may appear on the pelvic organ, including the serosa and peritoneum, as variable colored spots, blebs, lesions, or adhesions. Many surgeons are also not adequately trained in the advanced laparoscopic techniques required to treat genitourinary endometriosis.4
In this article, we describe the clinical presentation and diagnosis of genitourinary endometriosis and discuss laparoscopic management strategies with and without robotic assistance.
Clinical presentation and diagnosis of genitourinary endometriosis
While ureteral and bladder endometriosis are both diseases of the urinary tract, they are not always found together in the same patient. The bladder is the most commonly affected organ, followed by the ureter and kidney.3,5,6 Endometriosis of the bladder usually presents with significant lower urinary tract symptoms. In contrast, ureteral endometriosis is usually silent with no apparent urinary symptoms.
Ureteral endometriosis. Cyclic hematuria is present in less than 15% of patients with ureteral endometriosis. Some patients experience cyclic, nonspecific colicky flank pain.7-9 Otherwise, most patients present with the usual symptoms of endometriosis, such as pelvic pain and dysmenorrhea. In a systematic review, Cavaco-Gomes and colleagues described 700 patients with ureteral endometriosis; 81% reported dysmenorrhea, 70% had pelvic pain, and 66% had dyspareunia.10 Rarely, ureteral endometriosis can result in silent kidney loss if the ureter becomes severely obstructed without treatment.11,12
Continue to: The lack of symptoms makes...
The lack of symptoms makes the early diagnosis of ureteral endometriosis difficult. As with all types of endometriosis, histologic evaluation of a biopsy sample is diagnostic. Multiple imaging modalities have been used to preoperatively diagnose ureteral involvement, including computed tomography,13 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),14 intravenous pyelogram (IVP), and pelvic ultrasonography. However, each of these imaging modalities is limited in both sensitivity and the ability to characterize depth of tissue invasion.
In a study of 245 women undergoing pelvic ultrasonography, Pateman and colleagues reported that an experienced sonographer was able to visualize the bilateral ureters in 93% of cases.15 Renal ultrasonography is indicated in any woman suspected of having genitourinary tract involvement with the degree of hydroureter and level of obstruction noted during the exam.16
In our group, we perform renography to assess kidney function when hydroureter is noted preoperatively. Studies suggest that if greater than 10% of normal glomerular filtration rate remains, the kidney is considered salvageable, and near-normal function often returns following resection of disease. If preoperative kidney function is noted to be less than 10%, consultation with a nephrologist for possible nephrectomy is warranted.
We find that IVP is often helpful for preoperatively identifying the level and degree of ureteral involvement, and it also can be used postoperatively to evaluate for ureteral continuity (FIGURE 1). Sillou and colleagues showed MRI to be adequately sensitive for the detection of intrinsic ureteral endometriosis, but they reported that MRI often overestimates the frequency of disease.17 Authors of a 2016 Cochrane review of imaging modalities for endometriosis, including 4,807 women in 49 studies, reported that no imaging test was superior to surgery for diagnosing endometriosis.18 However, the review notably excluded genitourinary tract endometriosis, as surgery is not an acceptable reference standard, given that many surgeons cannot reliably identify such lesions.18

Bladder endometriosis. Unlike patients with ureteral endometriosis, those with bladder endometriosis are typically symptomatic and experience dysuria, hematuria, urinary frequency, and suprapubic tenderness.7,19 Urinary tract infection, interstitial cystitis, and cancer must be considered in the differential diagnosis. Urinalysis and urine culture should be performed, and other diagnostic procedures such as ultrasonography, MRI, and cystoscopy should be considered to evaluate for endometriosis of the bladder.
Ultrasound and MRI of the bladder both demonstrate a high specificity for detecting bladder endometriosis, but they lack sensitivity for lesions less than 3 cm.20 Deep infiltrating endometriosis of the bladder can be identified at the time of cystoscopy, which can assist in determining the need for ureteroneocystostomy if lesions are within 2 cm of the urethral opening.20 Cystoscopy also allows for biopsy to be performed if underlying malignancy is of concern.19
In our group, when bladder endometriosis is suspected, we routinely perform preoperative bladder ultrasonography to identify the lesion and plan to perform intraoperative cystoscopy at the time of laparoscopic resection.19,21
Continue to: Treatment...
Treatment
Medical management
Empiric medical therapies for endometriosis are centered around the idea that ectopic endometrial tissue responds to treatment in a similar manner as normal eutopic endometrium. The goals of treatment are to reduce or eliminate cyclic menstruation, thereby decreasing peritoneal seeding and suppressing the growth and activity of established ectopic implants. Medical therapy commonly involves the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists or antagonists, danazol, combined oral contraceptives, progestins, and aromatase inhibitors.
Medical therapy is commonly employed for patients with mild or early-stage disease and in those who are poor surgical candidates or decline surgery. Medical management alone clearly is contraindicated in the setting of ureteral obstruction and—in our opinion—may not be a good option for those with endometriosis of the ureter, given the potential for recurrence and potential serious sequelae of reduced renal function.22 Therefore, surgery has become the standard approach to therapy for mild to moderate cases of ureteral endometriosis.3
Medical therapy for patients with endometriosis of the bladder is generally considered a temporary solution as hormonal suppression, with its associated adverse effects, must be maintained throughout menopause. However, if endometriosis lesions lie within close proximity to the trigone, medical management is preferred, as surgical excision in the area of the trigone may predispose patients to neurogenic bladder and retrograde bladder reflux.23,24
Surgical management
The objectives of surgical treatment for genitourinary tract endometriosis are to excise all visible disease, to prevent or delay recurrence of the disease to the extent possible, and to avoid any further morbidity—in particular, to preserve renal function in cases of ureteral endometriosis—and to avoid iatrogenic injury to surrounding pelvic nervous structures25-27 (FIGURE 2). The surgical approach depends on the technical expertise of the surgeon and the availability of necessary instrumentation. In our experience, laparoscopy with or without robotic assistance is the preferred surgical approach.3,4,6,11,28-32
Others have reported on the benefits of laparoscopy over laparotomy for the surgical management of genitourinary endometriosis. In a review of 61 patients who underwent either robot-assisted laparoscopic (n = 25) or open (n = 41) ureteroneocystostomy (n = 41), Isac and colleagues reported the procedure was longer in the laparoscopic group (279 min vs 200 min, P<.001), but the laparoscopic group had a shorter hospital stay (3 days vs 5 days, P<.001), used fewer narcotics postoperatively (P<.001), and had lower intraoperative blood loss (100 mL vs 150 mL, P<.001).32 No differences in long-term outcomes were observed in either cohort.
In a systematic review of 700 patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery for ureteral endometriosis, Cavaco-Gomes and colleagues reported that conversion to laparotomy occurred in only 3% to 7% of cases.10 In instances of ureteral endometriosis, laparoscopy provides greater visualization of the intraperitoneal contents over laparotomy, enabling better evaluation and treatment of lesions.3,29,33,34 Robot-assisted laparoscopy provides the additional advantages of 3D visualization, potential for an accelerated learning curve over traditional laparoscopy, improvement in dissection technique, and ease of suturing technique.6,35,36

Continue to: Extrinsic disease...
Extrinsic disease. In our group, we perform ureterolysis for extrinsic disease.25 The peritoneal incision is made in an area unaffected by endometriosis. Using the suction irrigator, a potential space is developed under the serosa of the ureter by injecting normal saline or lactated Ringer’s solution. By creating a fluid barrier between the serosa and underlying tissues, the depth of surgical incision and lateral thermal spread are minimized. Grasping forceps are used to peel the peritoneum away.25,37,38
Intrinsic disease. Unlike extrinsic disease, intrinsic disease can infiltrate the muscularis, lamina propria, and ureteral lumen, resulting in proximal dilation of the ureter with strictures.8 In this situation, ureteral compromise is likely and resection of the ureter is indicated3,28 (FIGURE 3). Intrinsic disease can be suggested by preoperative imaging or when there is evidence of deep infiltrating disease on physical exam, such as rectovaginal nodularity.30,39 When intrinsic ureteral disease is known, consultation with a urologist to plan a joint procedure is advisable. The procedure chosen to re-establish a functional ureter following resection depends on the location and extent of the involved ureter. Resection in close proximity to the bladder may be repaired by ureteroneocystostomy with or without psoas hitch,30,39,40 whereas resection of more proximal ureter may be repaired using Boari flap, ileal interposition, or autotransplantation. Lesions in the upper third or middle ureter may be repaired using ureterouretral anastomosis.6,7,30,41-43

Continue to: Bladder endometriosis...
Bladder endometriosis. Surgical treatment for bladder endometriosis depends on the depth of invasion and the location of the lesion (FIGURE 4). Lesions of the superficial aspect of the bladder identified at the time of laparoscopy can be treated with either excision or fulguration28,35,44 In our group, we perform excision over fulguration to remove the entire lesion and obtain a pathologic diagnosis. Deeper lesions involving the detrusor muscle are likely to be an endometrioma of the bladder. In these cases, laparoscopic excision is recommended.7 Rarely, lesions close to the interureteric ridge may require ureteroneocystostomy.19,45
In our experience, laparoscopic resection of bladder endometriomas is associated with better results in terms of symptom relief, progression of disease, and recurrence risk compared with other approaches. When performing laparoscopic excision of bladder lesions, we concomitantly evaluate the bladder lesion via cystoscopy to ensure adequate margins are obtained. Double-J stent placement is advised when lesions are within 2 cm of the urethral meatus to ensure ureteral patency during the postoperative period.45 A postoperative cystogram routinely is performed 7 to 14 days after surgery to ensure adequate repair prior to removing the urinary catheter.9,25,46,47

Postsurgical follow-up
Follow-up after treatment of genitourinary tract endometriosis should include monitoring the patient for symptoms of recurrence. Regular history and physical examination, renal function testing, and, in some instances, pelvic ultrasonography, all have a role in surveillance for recurrent ureteric disease. IVP or MRI may be warranted if a recurrence is suspected. A high index of suspicion should be maintained on the part of the clinician to avoid the devastating consequences of silent kidney loss. Patients should be counseled about the risk of disease recurrence, especially in those not undergoing postoperative hormonal suppression.
In conclusion
While endometriosis of the genitourinary tract is rare, patients can experience significant morbidity. Medical management of the disease is often limited by substantial adverse effects that limit treatment duration and is best used postoperatively after excision. An adequate physical exam and preoperative diagnostic imaging can be employed to characterize the extent of disease. When extensive disease involving the ureter is suspected, preoperative consultation with a urologist is encouraged to plan a multidisciplinary approach to surgical resection.
The ideal approach to surgery is laparoscopic resection with or without robotic assistance. Treatment of ureteral disease most commonly involves ureterolysis for cases of extrinsic disease but may require total resection of the ureter with concurrent ureteral reconstruction when disease is intrinsic to the ureter. Surgery for bladder endometriosis depends on the depth of invasion and location of the lesion. Superficial bladder lesions can be treated with fulguration or excision, while deeper lesions involving the detrusor muscle require excision. Lesions in close proximity to the interureteric ridge may require ureteroneocystostomy. Follow-up after excisional procedures involves monitoring the patient for signs and symptoms of disease recurrence, especially in cases of ureteral involvement, to avoid the devastating consequences of silent kidney loss.
The definitive cause of endometriosis remains unknown, but several prominent theories have been proposed.
Sampson's theory of retrograde menstruation through the fallopian tubes is the most well-known theory,1 although Schron had acknowledged a similar thought 3 centuries before.2 This theory posits that refluxed endometrial cells enter the abdominal cavity and invade the peritoneum, developing a blood supply necessary for survival and growth. Early reports supported this theory by suggesting that women with genital tract obstruction have a higher incidence of endometriosis.3,4 However, it was later confirmed that women without genital tract obstruction have a similar incidence of retrograde menstruation. In fact, up to 90% of women are found to have retrograde menstruation, but only 10% develop endometriosis. This suggests that once endometrial cells have escaped the uterine cavity, other events are necessary for endometrial cells to implant and survive.3,5 Other evidence to support the theory of retrograde menstruation is the observation that endometriosis is most commonly observed in the dependent portions of the pelvis, on the ovaries, in the anterior and posterior cul-de-sacs, and on the uterosacral ligament.6
The coelomic metaplasia theory holds that endometriosis results from spontaneous metaplastic change to mesothelial cells derived from the coelomic epithelium (located in the peritoneum and the pleura) upon exposure to menstrual effluent or other stimuli.7 Evidence for this theory is supported by the observation that intact endometrial cells have no access to the thoracic cavity in the absence of anatomical defect; therefore, the implantation theory cannot explain cases of pleural or pulmonary endometriosis.
Immune dysregulation also has been invoked to explain endometriosis implants both inside and outside the genitourinary tract. Studies have shown a higher incidence of endometriosis in women with other autoimmune disorders, including hypothyroidism, chronic fatigue syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren syndrome, and multiple sclerosis as well as in women with allergies, asthma, and eczema.8 In such women, dysregulation of the innate and adaptive immune system might promote the disease by inhibiting apoptosis of ectopic endometrial cells and by promoting their attachment, invasion, and proliferation into healthy peritoneum through the secretion of various growth factors and cytokines.9,10
Other possible theories that might explain the pathogenesis of endometriosis exist.11-13 While each theory has documented supporting evidence, no single theory currently accounts for all cases of endometriosis. It is likely, then, that endometriosis is a multifactorial disease with a combination of immune dysregulation, molecular abnormalities, genetic and epigenetic factors, and environmental exposures involved in its pathogenesis.
References
- Sampson J. Peritoneal endometriosis due to the menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the peritoneal cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1927;14:422-469.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C. Endometriosis: ancient disease, ancient treatments. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6 suppl):S1-62.
- Halme J, Hammond MG, Hulka JF, et al. Retrograde menstruation in healthy women and in patients with endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;64:151-154.
- Sanfilippo JS, Wakim NG, Schikler KN, et al. Endometriosis in association with uterine anomaly. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986;154:39-43.
- Burney RO, Giudice LC. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:511-519.
- Vercellini P, Chapron C, Fedele L, et al. Evidence for asymmetric distribution of lower intestinal tract endometriosis. BJOG. 2004;111:1213-1217.
- Sourial S, Tempest N, Hapangama DK. Theories on the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Int J Reprod Med. 2014;2014:179515.
- Sinaii N, Cleary SD, Ballweg ML, et al. High rates of autoimmune and endocrine disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome and atopic diseases among women with endometriosis: a survey analysis. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:2715-2724.
- Lebovic DI, Mueller MD, Taylor RN. Immunobiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2001;75:1-10.
- Sidell N, Han SW, Parthasarathy S. Regulation and modulation of abnormal immune responses in endometriosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;955: 159-173; discussion 199-200, 396-406.
- Burney RO, Giudice LC. The pathogenesis of endometriosis. In: Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013;252-258.
- Buka NJ. Vesical endometriosis after cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158:1117-1118.
- Price DT, Maloney KE, Ibrahim GK, et al. Vesical endometriosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Urology. 1996;48:639-643.
- Veeraswamy A, Lewis M, Mann A, et al. Extragenital endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:449-466.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison GP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1986;45:778-783.
- Bosev D, Nicoll LM, Bhagan L, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis: the Stanford University hospital experience with 96 consecutive cases. J Urol. 2009;182:2748-2752.
- Nezhat C, Falik R, McKinney S, et al. Pathophysiology and management of urinary tract endometriosis. Nat Rev Urol. 2017;14:359-372.
- Shook TE, Nyberg LM. Endometriosis of the urinary tract. Urology. 1988;31:1-6.
- Nezhat C, Modest AM, King LP. The role of the robot in treating urinary tract endometriosis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2013;25:308-311.
- Comiter CV. Endometriosis of the urinary tract. Urol Clin North Am. 2002;29:625-635.
- Gustilo-Ashby AM, Paraiso MF. Treatment of urinary tract endometriosis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2006;13:559-565.
- Berlanda N, Somigliana E, Frattaruolo MP, et al. Surgery versus hormonal therapy for deep endometriosis: is it a choice of the physician? Eur J Obstet Gyneocol Reprod Biol. 2017;209:67-71.
- Cavaco-Gomes J, Martinho M, Gilabert-Aguilar J, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017;210:94-101.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Green B. Laparoscopic treatment of obstructed ureter due to endometriosis by resection and ureteroureterostomy: a case report. J Urol. 1992;148:865-868.
- Nezhat C, Paka C, Gomaa M, et al. Silent loss of kidney secondary to ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2012;16:451-455.
- Iosca S, Lumia D, Bracchi E, et al. Multislice computed tomography with colon water distention (MSCT-c) in the study of intestinal and ureteral endometriosis. Clin Imaging. 2013;37(6):1061-1068.
- Medeiros LR, Rosa MI, Silva BR, et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance in deeply infiltrating endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015;291:611-621.
- Pateman K, Mavrelos D, Hoo WL, et al. Visualization of ureters on standard gynecological transvaginal scan: a feasibility study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013;41:696-701.
- Guerriero S, Condous G, van den Bosch T, et al. Systematic approach to sonographic evaluation of the pelvis in women with suspected endometriosis, including terms, definitions and measurements: a consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48:318-332.
- Sillou S, Poirée S, Millischer AE, et al. Urinary endometriosis: MR imaging appearance with surgical and histological correlations. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015;96:373-381.
- Nisenblat V, Bossuyt PM, Farquhar C, et al. Imaging modalities for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD009591.
- Nezhat CH, Malik S, Osias J, et al. Laparoscopic management of 15 patients with infiltrating endometriosis of the bladder and a case of primary intravesical endometrioid adenosarcoma. Fertil Steril. 2002;78:872-875.
- Kolodziej A, Krajewski W, Dolowy L, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis. Urol J. 2015;12:2213-2217.
- Nezhat C, Buescher E, Paka C, et al. Video-assisted laparoscopic treatment of endometriosis. In: Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013;265.
- Al-Fozan H, Tulandi T. Left lateral predisposition of endometriosis and endometrioma. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:164-166.
- Hastings JC, Van Winkle W, Barker E, et al. The effect of suture materials on healing wounds of the bladder. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975;140:933-937.
- Cornell KK. Cystotomy, partial cystectomy, and tube cystostomy. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2000;15:11-16.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013.
- Uccella S, Cromi A, Casarin J, et al. Laparoscopy for ureteral endometriosis: surgical details, long-term follow-up, and fertility outcomes. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:160-166.e2.
- Knabben L, Imboden S, Fellmann B, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis in patients with deep infiltrating endometriosis: prevalence, symptoms, management, and proposal for a new clinical classification. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:147-152.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat CH, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis treated by laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1996;66:920-924.
- Nezhat CH, Nezhat F, Seidman D, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroureterostomy: a prospective follow-up of 9 patients. Prim Care Update Ob Gyns. 1998;5:200.
- Nezhat CH, Bracale U, Scala A, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocystostomy and vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative endometriosis. JSLS. 2004;8:3-7.
- Nezhat C, Lewis M, Kotikela S, et al. Robotic versus standard laparoscopy for the treatment of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:2758-2760.
- Isac W, Kaouk J, Altunrende F, et al. Robotic-assisted ureteroneocytostomy: techniques and comparative outcomes. J Endourol. 2013;27:318-323.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F. Laparoscopic repair of ureter resected during operative laparoscopy. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;80(3 pt 2):543-544.
- De Cicco C, Ussia A, Koninckx PR. Laparoscopic ureteral repair in gynaecological surgery. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;23:296-300.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic treatment of bowel, bladder, and ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2011;15:387-392.
- Fadhlaoui A, Gillon T, Lebbi I, et al. Endometriosis and vesico-sphincteral disorders. Front Surg. 2015;2:23.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat FR. Safe laser endoscopic excision or vaporization of peritoneal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1989;52:149-151.
- Nezhat C, Winer W, Nezhat FA. Comparison of the CO2, argon, and KTP/532 lasers in the videolaseroscopic treatment of endometriosis. J Gynecol Surg. 2009;41-47.
- Azioni G, Bracale U, Scala A, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocytostomy and vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative ureteral endometriosis. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2010;19:292-297.
- Stepniewska A, Grosso G, Molon A, et al. Ureteral endometriosis: clinical and radiological follow-up after laparoscopic ureterocystoneostomy. Hum Reprod. 2011;26:112-116.
- Nezhat CH, Nezhat FR, Freiha F, et al. Laparoscopic vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative ureteral endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1999;71:376-379.
- Scioscia M, Molon A, Grosso G, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2009;21:325-328.
- Antonelli A. Urinary tract endometriosis. Urologia. 2012;79:167-170.
- Camanni M, Bonino L, Delpiano EM, et al. Laparoscopic conservative management of ureteral endometriosis: a survey of eighty patients submitted to ureterolysis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009;7:109.
- Chapron C, Bourret A, Chopin N, et al. Surgery for bladder endometriosis: long-term results and concomitant management of associated posterior deep lesions. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:884-889.
- Nezhat CR, Nezhat FR. Laparoscopic segmental bladder resection for endometriosis: a report of two cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1993;81(5 pt 2):882-884.
- Bourdel N, Cognet S, Canis M, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocystostomy: be prepared! J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:827-833.
- Page B. Camran Nezhat and the Advent of Advanced Operative Video-laparoscopy. In: Nezhat C, ed. Nezhat's History of Endoscopy. Tuttlingen, Germany: Endo Press; 2011:159-187.
- Podratz K. Degrees of Freedom: Advances in Gynecological and Obstetrical Surgery. Remembering Milestones and Achievements in Surgery: Inspiring Quality for a Hundred Years 1913-2012. Published by American College of Surgeons 2012. Tampa, FL: Faircount Media Group; 2013.
- Kelley WE. The evolution of laparoscopy and the revolution in surgery in the decade of the 1990s. JSLS: J Soc Laparoendoscopic Surgeons. 2008;12:351-357.
- Veeraswamy A, Lewis M, Mann A, et al. Extragenital endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:449-466.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison GP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1986;45:778-783.
- Bosev D, Nicoll LM, Bhagan L, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis: the Stanford University hospital experience with 96 consecutive cases. J Urol. 2009;182:2748-2752.
- Nezhat C, Falik R, McKinney S, et al. Pathophysiology and management of urinary tract endometriosis. Nat Rev Urol. 2017;14:359-372.
- Shook TE, Nyberg LM. Endometriosis of the urinary tract. Urology. 1988;31:1-6.
- Nezhat C, Modest AM, King LP. The role of the robot in treating urinary tract endometriosis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2013;25:308-311.
- Comiter CV. Endometriosis of the urinary tract. Urol Clin North Am. 2002;29:625-635.
- Gustilo-Ashby AM, Paraiso MF. Treatment of urinary tract endometriosis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2006;13:559-565.
- Berlanda N, Somigliana E, Frattaruolo MP, et al. Surgery versus hormonal therapy for deep endometriosis: is it a choice of the physician? Eur J Obstet Gyneocol Reprod Biol. 2017;209:67-71.
- Cavaco-Gomes J, Martinho M, Gilabert-Aguilar J, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017;210:94-101.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Green B. Laparoscopic treatment of obstructed ureter due to endometriosis by resection and ureteroureterostomy: a case report. J Urol. 1992;148:865-868.
- Nezhat C, Paka C, Gomaa M, et al. Silent loss of kidney secondary to ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2012;16:451-455.
- Iosca S, Lumia D, Bracchi E, et al. Multislice computed tomography with colon water distention (MSCT-c) in the study of intestinal and ureteral endometriosis. Clin Imaging. 2013;37(6):1061-1068.
- Medeiros LR, Rosa MI, Silva BR, et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance in deeply infiltrating endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015;291:611-621.
- Pateman K, Mavrelos D, Hoo WL, et al. Visualization of ureters on standard gynecological transvaginal scan: a feasibility study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013;41:696-701.
- Guerriero S, Condous G, van den Bosch T, et al. Systematic approach to sonographic evaluation of the pelvis in women with suspected endometriosis, including terms, definitions and measurements: a consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48:318-332.
- Sillou S, Poirée S, Millischer AE, et al. Urinary endometriosis: MR imaging appearance with surgical and histological correlations. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015;96:373-381.
- Nisenblat V, Bossuyt PM, Farquhar C, et al. Imaging modalities for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD009591.
- Nezhat CH, Malik S, Osias J, et al. Laparoscopic management of 15 patients with infiltrating endometriosis of the bladder and a case of primary intravesical endometrioid adenosarcoma. Fertil Steril. 2002;78:872-875.
- Kolodziej A, Krajewski W, Dolowy L, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis. Urol J. 2015;12:2213-2217.
- Nezhat C, Buescher E, Paka C, et al. Video-assisted laparoscopic treatment of endometriosis. In: Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013;265.
- Al-Fozan H, Tulandi T. Left lateral predisposition of endometriosis and endometrioma. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:164-166.
- Hastings JC, Van Winkle W, Barker E, et al. The effect of suture materials on healing wounds of the bladder. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975;140:933-937.
- Cornell KK. Cystotomy, partial cystectomy, and tube cystostomy. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2000;15:11-16.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C, eds. Nezhat's Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy. 4th ed. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2013.
- Uccella S, Cromi A, Casarin J, et al. Laparoscopy for ureteral endometriosis: surgical details, long-term follow-up, and fertility outcomes. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:160-166.e2.
- Knabben L, Imboden S, Fellmann B, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis in patients with deep infiltrating endometriosis: prevalence, symptoms, management, and proposal for a new clinical classification. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:147-152.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat CH, et al. Urinary tract endometriosis treated by laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1996;66:920-924.
- Nezhat CH, Nezhat F, Seidman D, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroureterostomy: a prospective follow-up of 9 patients. Prim Care Update Ob Gyns. 1998;5:200.
- Nezhat CH, Bracale U, Scala A, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocystostomy and vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative endometriosis. JSLS. 2004;8:3-7.
- Nezhat C, Lewis M, Kotikela S, et al. Robotic versus standard laparoscopy for the treatment of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:2758-2760.
- Isac W, Kaouk J, Altunrende F, et al. Robotic-assisted ureteroneocytostomy: techniques and comparative outcomes. J Endourol. 2013;27:318-323.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F. Laparoscopic repair of ureter resected during operative laparoscopy. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;80(3 pt 2):543-544.
- De Cicco C, Ussia A, Koninckx PR. Laparoscopic ureteral repair in gynaecological surgery. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;23:296-300.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic treatment of bowel, bladder, and ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2011;15:387-392.
- Fadhlaoui A, Gillon T, Lebbi I, et al. Endometriosis and vesico-sphincteral disorders. Front Surg. 2015;2:23.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat FR. Safe laser endoscopic excision or vaporization of peritoneal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1989;52:149-151.
- Nezhat C, Winer W, Nezhat FA. Comparison of the CO2, argon, and KTP/532 lasers in the videolaseroscopic treatment of endometriosis. J Gynecol Surg. 2009;41-47.
- Azioni G, Bracale U, Scala A, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocytostomy and vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative ureteral endometriosis. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2010;19:292-297.
- Stepniewska A, Grosso G, Molon A, et al. Ureteral endometriosis: clinical and radiological follow-up after laparoscopic ureterocystoneostomy. Hum Reprod. 2011;26:112-116.
- Nezhat CH, Nezhat FR, Freiha F, et al. Laparoscopic vesicopsoas hitch for infiltrative ureteral endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1999;71:376-379.
- Scioscia M, Molon A, Grosso G, et al. Laparoscopic management of ureteral endometriosis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2009;21:325-328.
- Antonelli A. Urinary tract endometriosis. Urologia. 2012;79:167-170.
- Camanni M, Bonino L, Delpiano EM, et al. Laparoscopic conservative management of ureteral endometriosis: a survey of eighty patients submitted to ureterolysis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009;7:109.
- Chapron C, Bourret A, Chopin N, et al. Surgery for bladder endometriosis: long-term results and concomitant management of associated posterior deep lesions. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:884-889.
- Nezhat CR, Nezhat FR. Laparoscopic segmental bladder resection for endometriosis: a report of two cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1993;81(5 pt 2):882-884.
- Bourdel N, Cognet S, Canis M, et al. Laparoscopic ureteroneocystostomy: be prepared! J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:827-833.
- Page B. Camran Nezhat and the Advent of Advanced Operative Video-laparoscopy. In: Nezhat C, ed. Nezhat's History of Endoscopy. Tuttlingen, Germany: Endo Press; 2011:159-187.
- Podratz K. Degrees of Freedom: Advances in Gynecological and Obstetrical Surgery. Remembering Milestones and Achievements in Surgery: Inspiring Quality for a Hundred Years 1913-2012. Published by American College of Surgeons 2012. Tampa, FL: Faircount Media Group; 2013.
- Kelley WE. The evolution of laparoscopy and the revolution in surgery in the decade of the 1990s. JSLS: J Soc Laparoendoscopic Surgeons. 2008;12:351-357.
Pregnancy after ventral hernia repair increased the risk for recurrence
concluded the authors of a systematic review of the literature on hernia and pregnancy.
Erling Omoa, MD, of Bispebjerg Hospital and the University of Copenhagen, and his colleagues surveyed 5,189 articles and chose four cohort studies, four case-control studies, and one case-series study that met their criteria of quality, comparability, and outcomes data. Only randomized, controlled trials, analytical observational studies, and large case series were included. The focus was primary ventral (umbilical and epigastric) and incisional hernia surgery before, during, and after pregnancy.
“The prevalence of clinically relevant primary ventral hernias is very low during pregnancy,” the investigators wrote, but there is a lack on consensus concerning the management of hernia repair in women of childbearing age. “The objective of this systematic review was to examine the risk of recurrence following prepregnancy ventral hernia repair, and secondly, to evaluate the prevalence of ventral hernia during pregnancy and the risk of surgical repair before and after childbirth,” they wrote.
The reviewers evaluated pregnancy following ventral hernia repair as a potential risk factor for hernia recurrence. One study found that subsequent pregnancy was associated with a 1.6-fold increased risk of recurrence. Another found that pregnancy was independently associated with a 73% raised risk of recurrence. The risk of recurrence was no different between mesh and suture repair.
The review found the prevalence of primary ventral and inguinal repair during pregnancy to be low. A single-center cohort study of 20,714 pregnant women of which 17 (0.08%) had umbilical hernias and none of these required repair before delivery. A case series of 126 women who underwent this surgery during pregnancy indicated that this procedure was associated with minimal 30-day morbidity and no deaths. No data was available on fetal morbidity or recurrence in this case series.
Case-control studies reporting on umbilical repair concomitant with elective C-section found that, although adding hernia repair to the procedure increased operative time in some studies, there was no additional complication risk.
Overall, the investigators found several areas in which evidence remains weak, such as the long-term risks for recurrence following pregnancy and long-term outcomes of mesh versus suture repairs. They recommended that patients be counseled on the risk of recurrence linked to subsequent pregnancies and that, if possible, ventral hernia repair should be postponed until after a last planned pregnancy. Watchful waiting until after a delivery was deemed safe in many cases.
The investigators reported no conflicts.
SOURCE: Oma E et al. Am J Surg. 2019 Jan;217:163-8.
concluded the authors of a systematic review of the literature on hernia and pregnancy.
Erling Omoa, MD, of Bispebjerg Hospital and the University of Copenhagen, and his colleagues surveyed 5,189 articles and chose four cohort studies, four case-control studies, and one case-series study that met their criteria of quality, comparability, and outcomes data. Only randomized, controlled trials, analytical observational studies, and large case series were included. The focus was primary ventral (umbilical and epigastric) and incisional hernia surgery before, during, and after pregnancy.
“The prevalence of clinically relevant primary ventral hernias is very low during pregnancy,” the investigators wrote, but there is a lack on consensus concerning the management of hernia repair in women of childbearing age. “The objective of this systematic review was to examine the risk of recurrence following prepregnancy ventral hernia repair, and secondly, to evaluate the prevalence of ventral hernia during pregnancy and the risk of surgical repair before and after childbirth,” they wrote.
The reviewers evaluated pregnancy following ventral hernia repair as a potential risk factor for hernia recurrence. One study found that subsequent pregnancy was associated with a 1.6-fold increased risk of recurrence. Another found that pregnancy was independently associated with a 73% raised risk of recurrence. The risk of recurrence was no different between mesh and suture repair.
The review found the prevalence of primary ventral and inguinal repair during pregnancy to be low. A single-center cohort study of 20,714 pregnant women of which 17 (0.08%) had umbilical hernias and none of these required repair before delivery. A case series of 126 women who underwent this surgery during pregnancy indicated that this procedure was associated with minimal 30-day morbidity and no deaths. No data was available on fetal morbidity or recurrence in this case series.
Case-control studies reporting on umbilical repair concomitant with elective C-section found that, although adding hernia repair to the procedure increased operative time in some studies, there was no additional complication risk.
Overall, the investigators found several areas in which evidence remains weak, such as the long-term risks for recurrence following pregnancy and long-term outcomes of mesh versus suture repairs. They recommended that patients be counseled on the risk of recurrence linked to subsequent pregnancies and that, if possible, ventral hernia repair should be postponed until after a last planned pregnancy. Watchful waiting until after a delivery was deemed safe in many cases.
The investigators reported no conflicts.
SOURCE: Oma E et al. Am J Surg. 2019 Jan;217:163-8.
concluded the authors of a systematic review of the literature on hernia and pregnancy.
Erling Omoa, MD, of Bispebjerg Hospital and the University of Copenhagen, and his colleagues surveyed 5,189 articles and chose four cohort studies, four case-control studies, and one case-series study that met their criteria of quality, comparability, and outcomes data. Only randomized, controlled trials, analytical observational studies, and large case series were included. The focus was primary ventral (umbilical and epigastric) and incisional hernia surgery before, during, and after pregnancy.
“The prevalence of clinically relevant primary ventral hernias is very low during pregnancy,” the investigators wrote, but there is a lack on consensus concerning the management of hernia repair in women of childbearing age. “The objective of this systematic review was to examine the risk of recurrence following prepregnancy ventral hernia repair, and secondly, to evaluate the prevalence of ventral hernia during pregnancy and the risk of surgical repair before and after childbirth,” they wrote.
The reviewers evaluated pregnancy following ventral hernia repair as a potential risk factor for hernia recurrence. One study found that subsequent pregnancy was associated with a 1.6-fold increased risk of recurrence. Another found that pregnancy was independently associated with a 73% raised risk of recurrence. The risk of recurrence was no different between mesh and suture repair.
The review found the prevalence of primary ventral and inguinal repair during pregnancy to be low. A single-center cohort study of 20,714 pregnant women of which 17 (0.08%) had umbilical hernias and none of these required repair before delivery. A case series of 126 women who underwent this surgery during pregnancy indicated that this procedure was associated with minimal 30-day morbidity and no deaths. No data was available on fetal morbidity or recurrence in this case series.
Case-control studies reporting on umbilical repair concomitant with elective C-section found that, although adding hernia repair to the procedure increased operative time in some studies, there was no additional complication risk.
Overall, the investigators found several areas in which evidence remains weak, such as the long-term risks for recurrence following pregnancy and long-term outcomes of mesh versus suture repairs. They recommended that patients be counseled on the risk of recurrence linked to subsequent pregnancies and that, if possible, ventral hernia repair should be postponed until after a last planned pregnancy. Watchful waiting until after a delivery was deemed safe in many cases.
The investigators reported no conflicts.
SOURCE: Oma E et al. Am J Surg. 2019 Jan;217:163-8.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SURGERY
Measles cases jumped 30% last week
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Those new cases represent a 30% increase in measles cases for the year, bringing the total to 206 reported to the CDC through Feb. 28. After just 2 months, 2019 has had more cases than all but 3 other years over the last decade, CDC data show.
The 11th state to report a case of measles this year is New Jersey, which joins California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Illinois (one outbreak), Kentucky, New York (three outbreaks), Oregon, Texas (one outbreak), and Washington (one outbreak), the CDC said.
The outbreak in Washington (4 new cases/70 for the year) had been the largest, but the majority of the new cases over the last 2 weeks have occurred in New York City, specifically Brooklyn, which reported 30 cases last week and 17 of the 32 new U.S. cases the week before.
Most of the 120 cases reported in the borough since the beginning of its outbreak in October of 2018 “have involved members of the Jewish Orthodox community. The initial child with measles was unvaccinated and acquired measles on a visit to Israel, where a large outbreak of the disease is occurring. Since then, there have been additional people from Brooklyn and Queens who were unvaccinated and acquired measles while in Israel. People who did not travel were also infected in Brooklyn or Rockland County,” the CDC said.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Those new cases represent a 30% increase in measles cases for the year, bringing the total to 206 reported to the CDC through Feb. 28. After just 2 months, 2019 has had more cases than all but 3 other years over the last decade, CDC data show.
The 11th state to report a case of measles this year is New Jersey, which joins California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Illinois (one outbreak), Kentucky, New York (three outbreaks), Oregon, Texas (one outbreak), and Washington (one outbreak), the CDC said.
The outbreak in Washington (4 new cases/70 for the year) had been the largest, but the majority of the new cases over the last 2 weeks have occurred in New York City, specifically Brooklyn, which reported 30 cases last week and 17 of the 32 new U.S. cases the week before.
Most of the 120 cases reported in the borough since the beginning of its outbreak in October of 2018 “have involved members of the Jewish Orthodox community. The initial child with measles was unvaccinated and acquired measles on a visit to Israel, where a large outbreak of the disease is occurring. Since then, there have been additional people from Brooklyn and Queens who were unvaccinated and acquired measles while in Israel. People who did not travel were also infected in Brooklyn or Rockland County,” the CDC said.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Those new cases represent a 30% increase in measles cases for the year, bringing the total to 206 reported to the CDC through Feb. 28. After just 2 months, 2019 has had more cases than all but 3 other years over the last decade, CDC data show.
The 11th state to report a case of measles this year is New Jersey, which joins California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Illinois (one outbreak), Kentucky, New York (three outbreaks), Oregon, Texas (one outbreak), and Washington (one outbreak), the CDC said.
The outbreak in Washington (4 new cases/70 for the year) had been the largest, but the majority of the new cases over the last 2 weeks have occurred in New York City, specifically Brooklyn, which reported 30 cases last week and 17 of the 32 new U.S. cases the week before.
Most of the 120 cases reported in the borough since the beginning of its outbreak in October of 2018 “have involved members of the Jewish Orthodox community. The initial child with measles was unvaccinated and acquired measles on a visit to Israel, where a large outbreak of the disease is occurring. Since then, there have been additional people from Brooklyn and Queens who were unvaccinated and acquired measles while in Israel. People who did not travel were also infected in Brooklyn or Rockland County,” the CDC said.
Point-of-care VL testing improves HIV suppression
SEATTLE – Point-of-care viral load testing improves HIV viral suppression and retention in care, according to a randomized trial of 390 subjects in South Africa.
Point-of-care (POC) testing delivers viral load results in about 2-3 hours, as opposed to the month or so patients wait to get results from a laboratory. The nearly instant turnaround gives clinicians the ability to identify patients who aren’t doing well – as indicated by high viral loads despite antiretroviral therapy (ART) – before they walk out the door, so immediate steps can be taken to address adherence or resistance problems.
However, POC viral load testing hasn’t really caught on in the United States, at least not yet, according to study leader Paul Drain, MD, assistant professor of global health at the University of Washington, Seattle.
To see if it would help, the team turned to a large public clinic in the city of Durban, and focused on adults who had been on ART for 6 months following HIV diagnosis. They randomized 195 to standard laboratory testing at study entrance, with a repeat at 6 months, at which point subjects had been on ART for 12 months; 195 others were randomized to POC testing with the Xpert HIV-1 Viral Load machine, from Cepheid, on the same schedule and with same-day counseling for those with high loads.
Treatment was otherwise similar between the groups, with clinic visits every 2 months and other measures as per South African HIV treatment guidelines.
POC testing made a difference. At study month 12,175 participants (89.7%) in the POC arm, but only 148 (75.9%) in the laboratory testing group, had reached the study’s primary endpoint: viral suppression with less than 200 copies/mL plus retention in care, meaning that subjects were still picking up their ART prescriptions.
Overall, POC testing increased viral load suppression by 10.3%, from 83.1% to 93.3% (P = .003) and retention by 7.7% from 84.6% to 92.3% (P = .03).
The investigators would like to evaluate the approach in the United States. Potentially, “POC testing will have a very important role in U.S. health care,” Dr. Drain said at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
It “helps us identify those who are having problems right away, before they leave the clinic, because whether it’s in South Africa or Seattle, as soon as they leave, it’s very hard to get them back. The more you can do POC testing, the better we can intervene and help these people,” he said.
“You don’t need POC testing for everybody; a lot of people do just fine. They take their medications reliably. They don’t need to get their results back right away ... But there are people who have challenges and would benefit from additional adherence counseling” or who might need help overcoming drug resistance. “We want to identify” them quickly; POC testing may be the answer, he said.
The mean age in the study was 33 years, and 60% of the subjects were women. The median CD4 count at baseline was 468 cells/mm3. POC was $22 per test, versus $25 for lab testing.
The National Institutes of Health funded the work. Dr. Drain had no disclosures. Cepheid donated the POC testing machines.
SOURCE: Drain PK et al. CROI 2019, Abstract 53LB.
SEATTLE – Point-of-care viral load testing improves HIV viral suppression and retention in care, according to a randomized trial of 390 subjects in South Africa.
Point-of-care (POC) testing delivers viral load results in about 2-3 hours, as opposed to the month or so patients wait to get results from a laboratory. The nearly instant turnaround gives clinicians the ability to identify patients who aren’t doing well – as indicated by high viral loads despite antiretroviral therapy (ART) – before they walk out the door, so immediate steps can be taken to address adherence or resistance problems.
However, POC viral load testing hasn’t really caught on in the United States, at least not yet, according to study leader Paul Drain, MD, assistant professor of global health at the University of Washington, Seattle.
To see if it would help, the team turned to a large public clinic in the city of Durban, and focused on adults who had been on ART for 6 months following HIV diagnosis. They randomized 195 to standard laboratory testing at study entrance, with a repeat at 6 months, at which point subjects had been on ART for 12 months; 195 others were randomized to POC testing with the Xpert HIV-1 Viral Load machine, from Cepheid, on the same schedule and with same-day counseling for those with high loads.
Treatment was otherwise similar between the groups, with clinic visits every 2 months and other measures as per South African HIV treatment guidelines.
POC testing made a difference. At study month 12,175 participants (89.7%) in the POC arm, but only 148 (75.9%) in the laboratory testing group, had reached the study’s primary endpoint: viral suppression with less than 200 copies/mL plus retention in care, meaning that subjects were still picking up their ART prescriptions.
Overall, POC testing increased viral load suppression by 10.3%, from 83.1% to 93.3% (P = .003) and retention by 7.7% from 84.6% to 92.3% (P = .03).
The investigators would like to evaluate the approach in the United States. Potentially, “POC testing will have a very important role in U.S. health care,” Dr. Drain said at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
It “helps us identify those who are having problems right away, before they leave the clinic, because whether it’s in South Africa or Seattle, as soon as they leave, it’s very hard to get them back. The more you can do POC testing, the better we can intervene and help these people,” he said.
“You don’t need POC testing for everybody; a lot of people do just fine. They take their medications reliably. They don’t need to get their results back right away ... But there are people who have challenges and would benefit from additional adherence counseling” or who might need help overcoming drug resistance. “We want to identify” them quickly; POC testing may be the answer, he said.
The mean age in the study was 33 years, and 60% of the subjects were women. The median CD4 count at baseline was 468 cells/mm3. POC was $22 per test, versus $25 for lab testing.
The National Institutes of Health funded the work. Dr. Drain had no disclosures. Cepheid donated the POC testing machines.
SOURCE: Drain PK et al. CROI 2019, Abstract 53LB.
SEATTLE – Point-of-care viral load testing improves HIV viral suppression and retention in care, according to a randomized trial of 390 subjects in South Africa.
Point-of-care (POC) testing delivers viral load results in about 2-3 hours, as opposed to the month or so patients wait to get results from a laboratory. The nearly instant turnaround gives clinicians the ability to identify patients who aren’t doing well – as indicated by high viral loads despite antiretroviral therapy (ART) – before they walk out the door, so immediate steps can be taken to address adherence or resistance problems.
However, POC viral load testing hasn’t really caught on in the United States, at least not yet, according to study leader Paul Drain, MD, assistant professor of global health at the University of Washington, Seattle.
To see if it would help, the team turned to a large public clinic in the city of Durban, and focused on adults who had been on ART for 6 months following HIV diagnosis. They randomized 195 to standard laboratory testing at study entrance, with a repeat at 6 months, at which point subjects had been on ART for 12 months; 195 others were randomized to POC testing with the Xpert HIV-1 Viral Load machine, from Cepheid, on the same schedule and with same-day counseling for those with high loads.
Treatment was otherwise similar between the groups, with clinic visits every 2 months and other measures as per South African HIV treatment guidelines.
POC testing made a difference. At study month 12,175 participants (89.7%) in the POC arm, but only 148 (75.9%) in the laboratory testing group, had reached the study’s primary endpoint: viral suppression with less than 200 copies/mL plus retention in care, meaning that subjects were still picking up their ART prescriptions.
Overall, POC testing increased viral load suppression by 10.3%, from 83.1% to 93.3% (P = .003) and retention by 7.7% from 84.6% to 92.3% (P = .03).
The investigators would like to evaluate the approach in the United States. Potentially, “POC testing will have a very important role in U.S. health care,” Dr. Drain said at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
It “helps us identify those who are having problems right away, before they leave the clinic, because whether it’s in South Africa or Seattle, as soon as they leave, it’s very hard to get them back. The more you can do POC testing, the better we can intervene and help these people,” he said.
“You don’t need POC testing for everybody; a lot of people do just fine. They take their medications reliably. They don’t need to get their results back right away ... But there are people who have challenges and would benefit from additional adherence counseling” or who might need help overcoming drug resistance. “We want to identify” them quickly; POC testing may be the answer, he said.
The mean age in the study was 33 years, and 60% of the subjects were women. The median CD4 count at baseline was 468 cells/mm3. POC was $22 per test, versus $25 for lab testing.
The National Institutes of Health funded the work. Dr. Drain had no disclosures. Cepheid donated the POC testing machines.
SOURCE: Drain PK et al. CROI 2019, Abstract 53LB.
REPORTING FROM CROI 2019
A couple of little known side effects of medications
A 46-year-old woman with diabetes and seizure disorder presents with nausea and fatigue. Her physical exam is unremarkable.
Meds: Glyburide 5 mg daily, metformin 850 mg b.i.d., phenytoin 300 mg daily, topiramate 400 mg daily, pantoprazole 40 mg daily.
Labs: Na 133, K 3.9, Cl 112, HCO3 13, Glu 158, Bun 18, Cr 1.0.
What is the most likely cause of this patient’s acidosis?
A. Phenytoin
B. Topiramate
C. Metformin
D. Pantoprazole
The correct answer to this question is topiramate.
Metformin has had warnings about risk of lactic acidosis occurring in patients with kidney disease, but there is no evidence that metformin is associated with lactic acidosis or raised serum lactate levels in patients with diabetes with normal renal function.1 and its use may decrease CV risk in patients with stage 3 CKD.2 This patient has a non–anion gap acidosis (anion gap is 8).
Topiramate acts as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, which causes impairment of both the normal reabsorption of filtered HCO3 by the proximal renal tubule and the excretion of hydrogen ion by the distal tubule.3 Acidosis occurs in most patients who are treated with topiramate. Dr. Ture and colleagues did a cross-sectional study to assess the frequency of metabolic acidosis in patients who were taking topiramate.4 Eighty patients who were on topiramate for seizure prevention prior to elective craniotomy were studied. Metabolic acidosis was present in 71% of the patients. Patients treated with topiramate also have a higher risk for kidney stones and uric acid elevation.
A 60-year-old patient presents with right great toe pain. On exam he has warmth and erythema of the 1st MTP joint. Aspiration of the joint shows uric acid crystals. He has had BP’s of 150-160 mm Hg systolic on his home BP monitoring over the past 6 months. In clinic today BP is 156/90 mm Hg. Labs: Bun 10, Cr 1.0, K 3.8, Uric acid 7.4.
Which blood pressure medication would you recommend?
A. Hydrochlorothiazide
B. Chlorthalidone
C. Lisinopril
D. Losartan
E. Irbesartan
In a patient with gout, diuretics should be avoided if possible, as they increase uric acid levels. Of the other three options, losartan offers the added benefit of lowering uric acid levels. Losartan has uricosuric effects and lowers uric acid levels, a property that is unique to losartan of the angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) that have been studied.5-6 The uric acid lowering appears to be a probenecid-like effect. Losartan has also been evaluated to see whether using it in combination with a thiazide diuretic can reduce the rise in uric acid that occurs with thiazides. Dr. Matsumura et al. looked at data from the COMFORT trial, focusing on the effect of combining losartan with hydrochlorothiazide on uric acid levels.7 They looked at a group of 118 patients on an ARB other than losartan plus a diuretic, who were then randomly assigned to losartan 50 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg or continuation of another ARB plus a diuretic. Blood pressure control was the same between groups, but the patients who received the losartan combination had lower uric acid levels (P = .01).
Pearls: Topiramate acts as a cerbonic anhydrase inhibitor and can cause a non–anion gap acidosis. Losartan has a modest uricosuric effect and can modestly lower uric acid levels. This is a unique property of losartan and is not shared by other ARBs.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Salpeter SR et al. Risk of fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis with metformin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;4:CD002967.
2. Charytan DM et al. Metformin use and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Jan 22. doi: 10.1111/dom.13642.
3. Mirza N et al. Effect of topiramate on acid-base balance: extent, mechanism and effects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;68(5):655-61.
4. Ture H et al. The frequency and severity of metabolic acidosis related to topiramate. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(6):1376-80.
5. Würzner G et al. Comparative effects of losartan and irbesartan on serum uric acid in hypertensive patients with hyperuricaemia and gout. J Hypertens. 2001 Oct;19(10):1855-60.
6. Puig JG et al. Effect of eprosartan and losartan on uric acid metabolism in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1999 Jul;17(7):1033-9.
7. Matsumura K et al. Effect of losartan on serum uric acid in hypertension treated with a diuretic: the COMFORT study. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2015;37(3):192-6.
A 46-year-old woman with diabetes and seizure disorder presents with nausea and fatigue. Her physical exam is unremarkable.
Meds: Glyburide 5 mg daily, metformin 850 mg b.i.d., phenytoin 300 mg daily, topiramate 400 mg daily, pantoprazole 40 mg daily.
Labs: Na 133, K 3.9, Cl 112, HCO3 13, Glu 158, Bun 18, Cr 1.0.
What is the most likely cause of this patient’s acidosis?
A. Phenytoin
B. Topiramate
C. Metformin
D. Pantoprazole
The correct answer to this question is topiramate.
Metformin has had warnings about risk of lactic acidosis occurring in patients with kidney disease, but there is no evidence that metformin is associated with lactic acidosis or raised serum lactate levels in patients with diabetes with normal renal function.1 and its use may decrease CV risk in patients with stage 3 CKD.2 This patient has a non–anion gap acidosis (anion gap is 8).
Topiramate acts as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, which causes impairment of both the normal reabsorption of filtered HCO3 by the proximal renal tubule and the excretion of hydrogen ion by the distal tubule.3 Acidosis occurs in most patients who are treated with topiramate. Dr. Ture and colleagues did a cross-sectional study to assess the frequency of metabolic acidosis in patients who were taking topiramate.4 Eighty patients who were on topiramate for seizure prevention prior to elective craniotomy were studied. Metabolic acidosis was present in 71% of the patients. Patients treated with topiramate also have a higher risk for kidney stones and uric acid elevation.
A 60-year-old patient presents with right great toe pain. On exam he has warmth and erythema of the 1st MTP joint. Aspiration of the joint shows uric acid crystals. He has had BP’s of 150-160 mm Hg systolic on his home BP monitoring over the past 6 months. In clinic today BP is 156/90 mm Hg. Labs: Bun 10, Cr 1.0, K 3.8, Uric acid 7.4.
Which blood pressure medication would you recommend?
A. Hydrochlorothiazide
B. Chlorthalidone
C. Lisinopril
D. Losartan
E. Irbesartan
In a patient with gout, diuretics should be avoided if possible, as they increase uric acid levels. Of the other three options, losartan offers the added benefit of lowering uric acid levels. Losartan has uricosuric effects and lowers uric acid levels, a property that is unique to losartan of the angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) that have been studied.5-6 The uric acid lowering appears to be a probenecid-like effect. Losartan has also been evaluated to see whether using it in combination with a thiazide diuretic can reduce the rise in uric acid that occurs with thiazides. Dr. Matsumura et al. looked at data from the COMFORT trial, focusing on the effect of combining losartan with hydrochlorothiazide on uric acid levels.7 They looked at a group of 118 patients on an ARB other than losartan plus a diuretic, who were then randomly assigned to losartan 50 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg or continuation of another ARB plus a diuretic. Blood pressure control was the same between groups, but the patients who received the losartan combination had lower uric acid levels (P = .01).
Pearls: Topiramate acts as a cerbonic anhydrase inhibitor and can cause a non–anion gap acidosis. Losartan has a modest uricosuric effect and can modestly lower uric acid levels. This is a unique property of losartan and is not shared by other ARBs.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Salpeter SR et al. Risk of fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis with metformin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;4:CD002967.
2. Charytan DM et al. Metformin use and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Jan 22. doi: 10.1111/dom.13642.
3. Mirza N et al. Effect of topiramate on acid-base balance: extent, mechanism and effects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;68(5):655-61.
4. Ture H et al. The frequency and severity of metabolic acidosis related to topiramate. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(6):1376-80.
5. Würzner G et al. Comparative effects of losartan and irbesartan on serum uric acid in hypertensive patients with hyperuricaemia and gout. J Hypertens. 2001 Oct;19(10):1855-60.
6. Puig JG et al. Effect of eprosartan and losartan on uric acid metabolism in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1999 Jul;17(7):1033-9.
7. Matsumura K et al. Effect of losartan on serum uric acid in hypertension treated with a diuretic: the COMFORT study. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2015;37(3):192-6.
A 46-year-old woman with diabetes and seizure disorder presents with nausea and fatigue. Her physical exam is unremarkable.
Meds: Glyburide 5 mg daily, metformin 850 mg b.i.d., phenytoin 300 mg daily, topiramate 400 mg daily, pantoprazole 40 mg daily.
Labs: Na 133, K 3.9, Cl 112, HCO3 13, Glu 158, Bun 18, Cr 1.0.
What is the most likely cause of this patient’s acidosis?
A. Phenytoin
B. Topiramate
C. Metformin
D. Pantoprazole
The correct answer to this question is topiramate.
Metformin has had warnings about risk of lactic acidosis occurring in patients with kidney disease, but there is no evidence that metformin is associated with lactic acidosis or raised serum lactate levels in patients with diabetes with normal renal function.1 and its use may decrease CV risk in patients with stage 3 CKD.2 This patient has a non–anion gap acidosis (anion gap is 8).
Topiramate acts as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, which causes impairment of both the normal reabsorption of filtered HCO3 by the proximal renal tubule and the excretion of hydrogen ion by the distal tubule.3 Acidosis occurs in most patients who are treated with topiramate. Dr. Ture and colleagues did a cross-sectional study to assess the frequency of metabolic acidosis in patients who were taking topiramate.4 Eighty patients who were on topiramate for seizure prevention prior to elective craniotomy were studied. Metabolic acidosis was present in 71% of the patients. Patients treated with topiramate also have a higher risk for kidney stones and uric acid elevation.
A 60-year-old patient presents with right great toe pain. On exam he has warmth and erythema of the 1st MTP joint. Aspiration of the joint shows uric acid crystals. He has had BP’s of 150-160 mm Hg systolic on his home BP monitoring over the past 6 months. In clinic today BP is 156/90 mm Hg. Labs: Bun 10, Cr 1.0, K 3.8, Uric acid 7.4.
Which blood pressure medication would you recommend?
A. Hydrochlorothiazide
B. Chlorthalidone
C. Lisinopril
D. Losartan
E. Irbesartan
In a patient with gout, diuretics should be avoided if possible, as they increase uric acid levels. Of the other three options, losartan offers the added benefit of lowering uric acid levels. Losartan has uricosuric effects and lowers uric acid levels, a property that is unique to losartan of the angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) that have been studied.5-6 The uric acid lowering appears to be a probenecid-like effect. Losartan has also been evaluated to see whether using it in combination with a thiazide diuretic can reduce the rise in uric acid that occurs with thiazides. Dr. Matsumura et al. looked at data from the COMFORT trial, focusing on the effect of combining losartan with hydrochlorothiazide on uric acid levels.7 They looked at a group of 118 patients on an ARB other than losartan plus a diuretic, who were then randomly assigned to losartan 50 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg or continuation of another ARB plus a diuretic. Blood pressure control was the same between groups, but the patients who received the losartan combination had lower uric acid levels (P = .01).
Pearls: Topiramate acts as a cerbonic anhydrase inhibitor and can cause a non–anion gap acidosis. Losartan has a modest uricosuric effect and can modestly lower uric acid levels. This is a unique property of losartan and is not shared by other ARBs.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Salpeter SR et al. Risk of fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis with metformin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;4:CD002967.
2. Charytan DM et al. Metformin use and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Jan 22. doi: 10.1111/dom.13642.
3. Mirza N et al. Effect of topiramate on acid-base balance: extent, mechanism and effects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;68(5):655-61.
4. Ture H et al. The frequency and severity of metabolic acidosis related to topiramate. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(6):1376-80.
5. Würzner G et al. Comparative effects of losartan and irbesartan on serum uric acid in hypertensive patients with hyperuricaemia and gout. J Hypertens. 2001 Oct;19(10):1855-60.
6. Puig JG et al. Effect of eprosartan and losartan on uric acid metabolism in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1999 Jul;17(7):1033-9.
7. Matsumura K et al. Effect of losartan on serum uric acid in hypertension treated with a diuretic: the COMFORT study. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2015;37(3):192-6.
SPD president discusses pediatric research, and more
WASHINGTON – in an interview at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Dr. Davis, a pediatric dermatologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the SPD had a strategic retreat prior to the AAD annual meeting to look at goals attained over the last 3 years “and where we’re going for the next 3 years.” Goals that have been accomplished “move us forward as a society for patient advocacy, specialty advocacy, workforce strengthening, research advancement, patient care, and education,” she noted. The education arena, for example, includes not only educating patients and their families, so they can get the best health care possible, “but we want to educate the pipeline of trainees coming through medical school so ... they have exposure to pediatric dermatology and they can hopefully develop an interest in pediatric dermatology as a future career.”
The SPD now has more than 1,200 members, and has a research arm, the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA), which has multiple projects, the largest of which is looking at the stigma of skin diseases, a study that involves patients with severe skin diseases and their families, said Dr. Davis. Watch the video above for more on PeDRA and SPD.
Dr. Davis disclosed that she is involved in a study for Regeneron but has not received any personal financial compensation.
WASHINGTON – in an interview at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Dr. Davis, a pediatric dermatologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the SPD had a strategic retreat prior to the AAD annual meeting to look at goals attained over the last 3 years “and where we’re going for the next 3 years.” Goals that have been accomplished “move us forward as a society for patient advocacy, specialty advocacy, workforce strengthening, research advancement, patient care, and education,” she noted. The education arena, for example, includes not only educating patients and their families, so they can get the best health care possible, “but we want to educate the pipeline of trainees coming through medical school so ... they have exposure to pediatric dermatology and they can hopefully develop an interest in pediatric dermatology as a future career.”
The SPD now has more than 1,200 members, and has a research arm, the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA), which has multiple projects, the largest of which is looking at the stigma of skin diseases, a study that involves patients with severe skin diseases and their families, said Dr. Davis. Watch the video above for more on PeDRA and SPD.
Dr. Davis disclosed that she is involved in a study for Regeneron but has not received any personal financial compensation.
WASHINGTON – in an interview at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Dr. Davis, a pediatric dermatologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the SPD had a strategic retreat prior to the AAD annual meeting to look at goals attained over the last 3 years “and where we’re going for the next 3 years.” Goals that have been accomplished “move us forward as a society for patient advocacy, specialty advocacy, workforce strengthening, research advancement, patient care, and education,” she noted. The education arena, for example, includes not only educating patients and their families, so they can get the best health care possible, “but we want to educate the pipeline of trainees coming through medical school so ... they have exposure to pediatric dermatology and they can hopefully develop an interest in pediatric dermatology as a future career.”
The SPD now has more than 1,200 members, and has a research arm, the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA), which has multiple projects, the largest of which is looking at the stigma of skin diseases, a study that involves patients with severe skin diseases and their families, said Dr. Davis. Watch the video above for more on PeDRA and SPD.
Dr. Davis disclosed that she is involved in a study for Regeneron but has not received any personal financial compensation.
REPORTING FROM AAD 2019