User login
Haloperidol and delirium in critically ill patients
Clinical question: Does prophylactic use of haloperidol increase survival in critically ill adults with high risk of delirium?
Background: Delirium is common and associated with high mortality. Studies evaluating prophylactic use of haloperidol have been inconclusive.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, investigator-driven study.
Setting: ICUs at university hospitals and teaching and nonteaching hospitals in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: 1,789 adults with mean age 66.6 years were randomized to receive either 1 or 2 mg of haloperidol or placebo. The 1-mg haloperidol group was prematurely stopped because of futility.
There was no difference in the primary outcome of survival days within a 28-day period between the 2-mg haloperidol group and the placebo group (hazard ratio, 1.003; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-1.30; P = .93).
Secondary outcome of survival was also the same at 90 days. No significant difference was seen in the delirium incidence, delirium- and coma-free days, and the delirium-related outcome measures.
Patients were already undergoing nonpharmacologic interventions for delirium prevention, and this likely attenuated the effects of haloperidol. The dose and duration of haloperidol used might have also been too low and short to have an effect on the outcomes considering the severity of patient illness.
Bottom line: Haloperidol has no role in prophylactic use to increase survival among critically ill patients with a high risk of delirium.
Citation: van den Boogaard M et al. Effect of haloperidol on survival among critically ill adults with a high risk of delirium: The REDUCE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):680-90.
Dr. Chikkanna is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington.
Clinical question: Does prophylactic use of haloperidol increase survival in critically ill adults with high risk of delirium?
Background: Delirium is common and associated with high mortality. Studies evaluating prophylactic use of haloperidol have been inconclusive.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, investigator-driven study.
Setting: ICUs at university hospitals and teaching and nonteaching hospitals in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: 1,789 adults with mean age 66.6 years were randomized to receive either 1 or 2 mg of haloperidol or placebo. The 1-mg haloperidol group was prematurely stopped because of futility.
There was no difference in the primary outcome of survival days within a 28-day period between the 2-mg haloperidol group and the placebo group (hazard ratio, 1.003; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-1.30; P = .93).
Secondary outcome of survival was also the same at 90 days. No significant difference was seen in the delirium incidence, delirium- and coma-free days, and the delirium-related outcome measures.
Patients were already undergoing nonpharmacologic interventions for delirium prevention, and this likely attenuated the effects of haloperidol. The dose and duration of haloperidol used might have also been too low and short to have an effect on the outcomes considering the severity of patient illness.
Bottom line: Haloperidol has no role in prophylactic use to increase survival among critically ill patients with a high risk of delirium.
Citation: van den Boogaard M et al. Effect of haloperidol on survival among critically ill adults with a high risk of delirium: The REDUCE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):680-90.
Dr. Chikkanna is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington.
Clinical question: Does prophylactic use of haloperidol increase survival in critically ill adults with high risk of delirium?
Background: Delirium is common and associated with high mortality. Studies evaluating prophylactic use of haloperidol have been inconclusive.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, investigator-driven study.
Setting: ICUs at university hospitals and teaching and nonteaching hospitals in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: 1,789 adults with mean age 66.6 years were randomized to receive either 1 or 2 mg of haloperidol or placebo. The 1-mg haloperidol group was prematurely stopped because of futility.
There was no difference in the primary outcome of survival days within a 28-day period between the 2-mg haloperidol group and the placebo group (hazard ratio, 1.003; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-1.30; P = .93).
Secondary outcome of survival was also the same at 90 days. No significant difference was seen in the delirium incidence, delirium- and coma-free days, and the delirium-related outcome measures.
Patients were already undergoing nonpharmacologic interventions for delirium prevention, and this likely attenuated the effects of haloperidol. The dose and duration of haloperidol used might have also been too low and short to have an effect on the outcomes considering the severity of patient illness.
Bottom line: Haloperidol has no role in prophylactic use to increase survival among critically ill patients with a high risk of delirium.
Citation: van den Boogaard M et al. Effect of haloperidol on survival among critically ill adults with a high risk of delirium: The REDUCE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):680-90.
Dr. Chikkanna is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington.
Rivaroxaban beats aspirin for VTE
Also today, bone biopsy diagnostics for osteomyelitis vary widely, variation in bacterial drug susceptibility are tied to the risk of TB relapse, and CTA cuts MIs in patients with stable chest pain. Subscribe to the MDedge Daily News wherever you get your podcasts.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, bone biopsy diagnostics for osteomyelitis vary widely, variation in bacterial drug susceptibility are tied to the risk of TB relapse, and CTA cuts MIs in patients with stable chest pain. Subscribe to the MDedge Daily News wherever you get your podcasts.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, bone biopsy diagnostics for osteomyelitis vary widely, variation in bacterial drug susceptibility are tied to the risk of TB relapse, and CTA cuts MIs in patients with stable chest pain. Subscribe to the MDedge Daily News wherever you get your podcasts.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Spotify
ESC 2018 in review
Join MDedge reporters Bruce Jancin and Mitchel Zoler alongside MDedge Cardiology editor Catherine Hackett as they discuss practice changing data as well as what the world’s leading cardiologists are talking about.
Join MDedge reporters Bruce Jancin and Mitchel Zoler alongside MDedge Cardiology editor Catherine Hackett as they discuss practice changing data as well as what the world’s leading cardiologists are talking about.
Join MDedge reporters Bruce Jancin and Mitchel Zoler alongside MDedge Cardiology editor Catherine Hackett as they discuss practice changing data as well as what the world’s leading cardiologists are talking about.
Study examines POEM learning curve
Technical failures or adverse events complicated 4% of peroral endoscopic myotomies (POEMs) in a large single-center retrospective study.
Individual predictors of this composite negative outcome included case number, full-thickness myotomy, and procedure time, Zuqiang Liu, PhD, and his associates at Fudan University, Shanghai, China, wrote in the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
After controlling for these risk factors, the composite rate of adverse events and technical failures dropped gradually after an endoscopist had performed his or her first 100 cases, according to the researchers. “Technical proficiency, demonstrated by plateauing of the procedure time, could be achieved after 70 cases,” they wrote. “The volume of cases required to manage challenging situations and prevent adverse events was thus higher than that needed for simple technical proficiency.” The experience of the training surgeon helped trainees gain technical proficiency faster, they added.
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is minimally invasive and effectively treats spastic esophageal motility disorders. However, it is also a challenging procedure, and little is known about its learning curve. For the study, the researchers retrospectively reviewed technical failures and adverse events among 1,346 POEMs performed for achalasia at a single hospital in China between August 2010 and July 2015. They also assessed procedure time and a secondary composite outcome consisting of technical failure, adverse events, and clinical failure (further symptoms) for the first 192 cases performed by the original training surgeon.
There were 10 technical failures and 44 adverse events affecting a total of 54 patients (4%). Case number (P = .010), full-thickness myotomy (P = .002), and procedure time (P = .001) independently predicted this primary composite outcome. Adjusted cumulative sum analysis showed that the rate of this composite outcome decreased gradually after a surgeon had performed his or her first 100 cases. “The procedure time was high during the first few cases and decreased after endoscopists performed 70 cases,” indicating technical proficiency, the investigators wrote. The rate of the secondary composite outcome also fell gradually after the primary surgeon had performed between 90 and 100 cases.
For the first 192 cases performed by the lead surgeon, postprocedural follow-up time was typically 59 months, with a range of 3-71 months. Clinical failures occurred in 20 cases (10%). Rates of clinical failure were 6% at 1 year, 8% at 2 years, and 10% at 3 years.
This is the first study and the largest POEM database so far to assess the learning curve for this procedure by evaluating adverse events and clinical and technical failure, said the researchers. Previous studies consisted of small cases, usually of less than 100 patients each, they added. Such studies would inherently be biased because the smaller the caseload, the longer it might take for the learning curves of surgeons to plateau, they added.
Funders included the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Major Project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Committee, the Chen Guang Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, and the Outstanding Young Doctor Training Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zuqiang L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Dec 5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.11.048.
Determining competency in endoscopic procedures has been a vexing challenge since the introduction of flexible endoscopy. Traditionally, procedure volume has been used as a surrogate for technical competence. However, each endoscopist has their own learning curve. Furthermore, that curve is influenced by both the endoscopist and the characteristics of each patient. Thus, relying on procedure volume or length of time are likely inadequate markers of the true learning process. It has become more important to rely on more sophisticated measurements of competence, as illustrated in this study by Liu et al.
By using a large database of patients undergoing POEM, the authors applied risk-adjusted cumulative sum and moving averages (CUSUM) analysis to develop individual learning curves of six training endoscopists. The primary outcomes used to develop the curve were technical failure and adverse effects (likely the two outcomes patients are most concerned about). The analysis was adjusted for case complexity as well, reflecting that not all training episodes are the same. The results reveal that, although trainee endoscopists were able to perform POEM “quickly” by 70 cases, they did not achieve the more important primary outcomes of technical success and low adverse events until at least 100 procedures. This is akin to the difference between getting to the cecum quickly and having a high adenoma detection rate in colonoscopy.
Moving forward, using sophisticated measurement of individual endoscopists’ learning curves will allow maximal effectiveness of routine procedures such as colonoscopy.
Kal Patel, MD, is associate professor of medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
Determining competency in endoscopic procedures has been a vexing challenge since the introduction of flexible endoscopy. Traditionally, procedure volume has been used as a surrogate for technical competence. However, each endoscopist has their own learning curve. Furthermore, that curve is influenced by both the endoscopist and the characteristics of each patient. Thus, relying on procedure volume or length of time are likely inadequate markers of the true learning process. It has become more important to rely on more sophisticated measurements of competence, as illustrated in this study by Liu et al.
By using a large database of patients undergoing POEM, the authors applied risk-adjusted cumulative sum and moving averages (CUSUM) analysis to develop individual learning curves of six training endoscopists. The primary outcomes used to develop the curve were technical failure and adverse effects (likely the two outcomes patients are most concerned about). The analysis was adjusted for case complexity as well, reflecting that not all training episodes are the same. The results reveal that, although trainee endoscopists were able to perform POEM “quickly” by 70 cases, they did not achieve the more important primary outcomes of technical success and low adverse events until at least 100 procedures. This is akin to the difference between getting to the cecum quickly and having a high adenoma detection rate in colonoscopy.
Moving forward, using sophisticated measurement of individual endoscopists’ learning curves will allow maximal effectiveness of routine procedures such as colonoscopy.
Kal Patel, MD, is associate professor of medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
Determining competency in endoscopic procedures has been a vexing challenge since the introduction of flexible endoscopy. Traditionally, procedure volume has been used as a surrogate for technical competence. However, each endoscopist has their own learning curve. Furthermore, that curve is influenced by both the endoscopist and the characteristics of each patient. Thus, relying on procedure volume or length of time are likely inadequate markers of the true learning process. It has become more important to rely on more sophisticated measurements of competence, as illustrated in this study by Liu et al.
By using a large database of patients undergoing POEM, the authors applied risk-adjusted cumulative sum and moving averages (CUSUM) analysis to develop individual learning curves of six training endoscopists. The primary outcomes used to develop the curve were technical failure and adverse effects (likely the two outcomes patients are most concerned about). The analysis was adjusted for case complexity as well, reflecting that not all training episodes are the same. The results reveal that, although trainee endoscopists were able to perform POEM “quickly” by 70 cases, they did not achieve the more important primary outcomes of technical success and low adverse events until at least 100 procedures. This is akin to the difference between getting to the cecum quickly and having a high adenoma detection rate in colonoscopy.
Moving forward, using sophisticated measurement of individual endoscopists’ learning curves will allow maximal effectiveness of routine procedures such as colonoscopy.
Kal Patel, MD, is associate professor of medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
Technical failures or adverse events complicated 4% of peroral endoscopic myotomies (POEMs) in a large single-center retrospective study.
Individual predictors of this composite negative outcome included case number, full-thickness myotomy, and procedure time, Zuqiang Liu, PhD, and his associates at Fudan University, Shanghai, China, wrote in the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
After controlling for these risk factors, the composite rate of adverse events and technical failures dropped gradually after an endoscopist had performed his or her first 100 cases, according to the researchers. “Technical proficiency, demonstrated by plateauing of the procedure time, could be achieved after 70 cases,” they wrote. “The volume of cases required to manage challenging situations and prevent adverse events was thus higher than that needed for simple technical proficiency.” The experience of the training surgeon helped trainees gain technical proficiency faster, they added.
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is minimally invasive and effectively treats spastic esophageal motility disorders. However, it is also a challenging procedure, and little is known about its learning curve. For the study, the researchers retrospectively reviewed technical failures and adverse events among 1,346 POEMs performed for achalasia at a single hospital in China between August 2010 and July 2015. They also assessed procedure time and a secondary composite outcome consisting of technical failure, adverse events, and clinical failure (further symptoms) for the first 192 cases performed by the original training surgeon.
There were 10 technical failures and 44 adverse events affecting a total of 54 patients (4%). Case number (P = .010), full-thickness myotomy (P = .002), and procedure time (P = .001) independently predicted this primary composite outcome. Adjusted cumulative sum analysis showed that the rate of this composite outcome decreased gradually after a surgeon had performed his or her first 100 cases. “The procedure time was high during the first few cases and decreased after endoscopists performed 70 cases,” indicating technical proficiency, the investigators wrote. The rate of the secondary composite outcome also fell gradually after the primary surgeon had performed between 90 and 100 cases.
For the first 192 cases performed by the lead surgeon, postprocedural follow-up time was typically 59 months, with a range of 3-71 months. Clinical failures occurred in 20 cases (10%). Rates of clinical failure were 6% at 1 year, 8% at 2 years, and 10% at 3 years.
This is the first study and the largest POEM database so far to assess the learning curve for this procedure by evaluating adverse events and clinical and technical failure, said the researchers. Previous studies consisted of small cases, usually of less than 100 patients each, they added. Such studies would inherently be biased because the smaller the caseload, the longer it might take for the learning curves of surgeons to plateau, they added.
Funders included the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Major Project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Committee, the Chen Guang Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, and the Outstanding Young Doctor Training Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zuqiang L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Dec 5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.11.048.
Technical failures or adverse events complicated 4% of peroral endoscopic myotomies (POEMs) in a large single-center retrospective study.
Individual predictors of this composite negative outcome included case number, full-thickness myotomy, and procedure time, Zuqiang Liu, PhD, and his associates at Fudan University, Shanghai, China, wrote in the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
After controlling for these risk factors, the composite rate of adverse events and technical failures dropped gradually after an endoscopist had performed his or her first 100 cases, according to the researchers. “Technical proficiency, demonstrated by plateauing of the procedure time, could be achieved after 70 cases,” they wrote. “The volume of cases required to manage challenging situations and prevent adverse events was thus higher than that needed for simple technical proficiency.” The experience of the training surgeon helped trainees gain technical proficiency faster, they added.
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is minimally invasive and effectively treats spastic esophageal motility disorders. However, it is also a challenging procedure, and little is known about its learning curve. For the study, the researchers retrospectively reviewed technical failures and adverse events among 1,346 POEMs performed for achalasia at a single hospital in China between August 2010 and July 2015. They also assessed procedure time and a secondary composite outcome consisting of technical failure, adverse events, and clinical failure (further symptoms) for the first 192 cases performed by the original training surgeon.
There were 10 technical failures and 44 adverse events affecting a total of 54 patients (4%). Case number (P = .010), full-thickness myotomy (P = .002), and procedure time (P = .001) independently predicted this primary composite outcome. Adjusted cumulative sum analysis showed that the rate of this composite outcome decreased gradually after a surgeon had performed his or her first 100 cases. “The procedure time was high during the first few cases and decreased after endoscopists performed 70 cases,” indicating technical proficiency, the investigators wrote. The rate of the secondary composite outcome also fell gradually after the primary surgeon had performed between 90 and 100 cases.
For the first 192 cases performed by the lead surgeon, postprocedural follow-up time was typically 59 months, with a range of 3-71 months. Clinical failures occurred in 20 cases (10%). Rates of clinical failure were 6% at 1 year, 8% at 2 years, and 10% at 3 years.
This is the first study and the largest POEM database so far to assess the learning curve for this procedure by evaluating adverse events and clinical and technical failure, said the researchers. Previous studies consisted of small cases, usually of less than 100 patients each, they added. Such studies would inherently be biased because the smaller the caseload, the longer it might take for the learning curves of surgeons to plateau, they added.
Funders included the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Major Project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Committee, the Chen Guang Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, and the Outstanding Young Doctor Training Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zuqiang L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Dec 5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.11.048.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Key clinical point: One hundred cases was the typical learning curve for peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM).
Major finding: The composite rate of technical failure or adverse events was 4%. An adjusted analysis showed that the rate of this negative composite outcome fell gradually after an endoscopist had performed his or her first 100 cases.
Study details: Single-center retrospective study of 1,346 patients undergoing POEM.
Disclosures: Funders included the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Major Project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Committee, the Chen Guang Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, and the Outstanding Young Doctor Training Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest..
Source: Zuqiang L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Dec 5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.11.048.
Even modest alcohol use may worsen NAFLD
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease who consumed modest quantities of alcohol had significantly less improvement in steatosis and significantly lower odds of resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, compared with nondrinkers, according to the results of a longitudinal cohort study published in the Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Modest drinkers also had significantly less improvement in their AST levels, compared with nondrinkers, said Veeral Ajmera, MD, of the University of California, San Diego, and his associates. “Importantly, our results suggest that cessation of alcohol use may mitigate these changes,” they wrote. Clinicians should consider the spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and especially nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), when making recommendations about alcohol use. “More advanced NAFLD severity may warrant counseling against [even] modest alcohol use.”
More than one in three adults in the United States has NAFLD and about two-thirds drink alcohol, almost always in moderation, the researchers noted. Modest alcohol use has been linked to decreased cardiovascular risk, which is particularly relevant because patients with NAFLD tend to have risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Results from at least two cross-sectional studies also suggest modest drinkers with NAFLD have less severe histology, including less NASH and fibrosis. However, modest drinkers tend to be more physically active, with lower body mass indices, higher physical activity levels, and less obesity, which are potential confounders. To better understand the effects of modest alcohol consumption on NAFLD, the researchers studied adults with NAFLD who participated in studies conducted by the multicenter NASH Clinical Research Network.
The 285 participants were typically aged in their late 40s, female, white, and obese, with an average body mass index of 34.7 kg/m2. In all, 168 participants (59%) reported consuming up to two drinks per day, while 41% abstained from alcohol use. During an average of 47 months between biopsies (standard deviation, 26 months), nondrinkers averaged a 0.49 reduction in steatosis grade, significantly more than that of modest drinkers (reduction, 0.30; P = .04). Nondrinkers also had a greater decrease in mean AST level (7 U/L), compared with drinkers (2 U/L; P = .04).
A total of 64% of patients were classified as having definite NASH, 19% had NAFLD without NASH, and 17% had borderline NASH. At baseline, 23% of patients did not have fibrosis, 32% had stage 1 fibrosis, 21% had stage 2, 21% had stage 3, and 3% had stage 4. Modest drinkers were more likely to be white and were less likely to be diagnosed with definitive NASH at baseline. After controlling for these potential confounders, modest drinkers had significantly lower odds of NASH resolution, compared with nondrinkers (adjusted odds ratio, 0.32; 95% confidence interval, 0.11-0.92; P = .04).
“[The] presence of NASH has consistently been shown to predict increased risk for fibrosis progression, and therefore, our finding of less NASH resolution among consistent modest drinkers is clinically relevant,” the investigators wrote. “Although we were unable to assess the association between modest alcohol consumption and cardiovascular risk, we did not see any significant changes in measured metabolic risk factors with known associations with cardiovascular disease including low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and insulin resistance.”
Funders of the study included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the Advanced/Transplant Hepatology Fellowship, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Foundation, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Ajmera V et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Mar 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.01.026.
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease who consumed modest quantities of alcohol had significantly less improvement in steatosis and significantly lower odds of resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, compared with nondrinkers, according to the results of a longitudinal cohort study published in the Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Modest drinkers also had significantly less improvement in their AST levels, compared with nondrinkers, said Veeral Ajmera, MD, of the University of California, San Diego, and his associates. “Importantly, our results suggest that cessation of alcohol use may mitigate these changes,” they wrote. Clinicians should consider the spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and especially nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), when making recommendations about alcohol use. “More advanced NAFLD severity may warrant counseling against [even] modest alcohol use.”
More than one in three adults in the United States has NAFLD and about two-thirds drink alcohol, almost always in moderation, the researchers noted. Modest alcohol use has been linked to decreased cardiovascular risk, which is particularly relevant because patients with NAFLD tend to have risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Results from at least two cross-sectional studies also suggest modest drinkers with NAFLD have less severe histology, including less NASH and fibrosis. However, modest drinkers tend to be more physically active, with lower body mass indices, higher physical activity levels, and less obesity, which are potential confounders. To better understand the effects of modest alcohol consumption on NAFLD, the researchers studied adults with NAFLD who participated in studies conducted by the multicenter NASH Clinical Research Network.
The 285 participants were typically aged in their late 40s, female, white, and obese, with an average body mass index of 34.7 kg/m2. In all, 168 participants (59%) reported consuming up to two drinks per day, while 41% abstained from alcohol use. During an average of 47 months between biopsies (standard deviation, 26 months), nondrinkers averaged a 0.49 reduction in steatosis grade, significantly more than that of modest drinkers (reduction, 0.30; P = .04). Nondrinkers also had a greater decrease in mean AST level (7 U/L), compared with drinkers (2 U/L; P = .04).
A total of 64% of patients were classified as having definite NASH, 19% had NAFLD without NASH, and 17% had borderline NASH. At baseline, 23% of patients did not have fibrosis, 32% had stage 1 fibrosis, 21% had stage 2, 21% had stage 3, and 3% had stage 4. Modest drinkers were more likely to be white and were less likely to be diagnosed with definitive NASH at baseline. After controlling for these potential confounders, modest drinkers had significantly lower odds of NASH resolution, compared with nondrinkers (adjusted odds ratio, 0.32; 95% confidence interval, 0.11-0.92; P = .04).
“[The] presence of NASH has consistently been shown to predict increased risk for fibrosis progression, and therefore, our finding of less NASH resolution among consistent modest drinkers is clinically relevant,” the investigators wrote. “Although we were unable to assess the association between modest alcohol consumption and cardiovascular risk, we did not see any significant changes in measured metabolic risk factors with known associations with cardiovascular disease including low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and insulin resistance.”
Funders of the study included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the Advanced/Transplant Hepatology Fellowship, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Foundation, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Ajmera V et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Mar 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.01.026.
Patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease who consumed modest quantities of alcohol had significantly less improvement in steatosis and significantly lower odds of resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, compared with nondrinkers, according to the results of a longitudinal cohort study published in the Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Modest drinkers also had significantly less improvement in their AST levels, compared with nondrinkers, said Veeral Ajmera, MD, of the University of California, San Diego, and his associates. “Importantly, our results suggest that cessation of alcohol use may mitigate these changes,” they wrote. Clinicians should consider the spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and especially nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), when making recommendations about alcohol use. “More advanced NAFLD severity may warrant counseling against [even] modest alcohol use.”
More than one in three adults in the United States has NAFLD and about two-thirds drink alcohol, almost always in moderation, the researchers noted. Modest alcohol use has been linked to decreased cardiovascular risk, which is particularly relevant because patients with NAFLD tend to have risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Results from at least two cross-sectional studies also suggest modest drinkers with NAFLD have less severe histology, including less NASH and fibrosis. However, modest drinkers tend to be more physically active, with lower body mass indices, higher physical activity levels, and less obesity, which are potential confounders. To better understand the effects of modest alcohol consumption on NAFLD, the researchers studied adults with NAFLD who participated in studies conducted by the multicenter NASH Clinical Research Network.
The 285 participants were typically aged in their late 40s, female, white, and obese, with an average body mass index of 34.7 kg/m2. In all, 168 participants (59%) reported consuming up to two drinks per day, while 41% abstained from alcohol use. During an average of 47 months between biopsies (standard deviation, 26 months), nondrinkers averaged a 0.49 reduction in steatosis grade, significantly more than that of modest drinkers (reduction, 0.30; P = .04). Nondrinkers also had a greater decrease in mean AST level (7 U/L), compared with drinkers (2 U/L; P = .04).
A total of 64% of patients were classified as having definite NASH, 19% had NAFLD without NASH, and 17% had borderline NASH. At baseline, 23% of patients did not have fibrosis, 32% had stage 1 fibrosis, 21% had stage 2, 21% had stage 3, and 3% had stage 4. Modest drinkers were more likely to be white and were less likely to be diagnosed with definitive NASH at baseline. After controlling for these potential confounders, modest drinkers had significantly lower odds of NASH resolution, compared with nondrinkers (adjusted odds ratio, 0.32; 95% confidence interval, 0.11-0.92; P = .04).
“[The] presence of NASH has consistently been shown to predict increased risk for fibrosis progression, and therefore, our finding of less NASH resolution among consistent modest drinkers is clinically relevant,” the investigators wrote. “Although we were unable to assess the association between modest alcohol consumption and cardiovascular risk, we did not see any significant changes in measured metabolic risk factors with known associations with cardiovascular disease including low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and insulin resistance.”
Funders of the study included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the Advanced/Transplant Hepatology Fellowship, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Foundation, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Ajmera V et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Mar 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.01.026.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Consider counseling patients with more advanced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to avoid alcohol.
Major finding: Compared with nondrinkers, patients who reported modest alcohol use had significantly less improvement in steatosis and significantly lower odds of resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (P = .04 for both comparisons).
Study details: A longitudinal cohort study of 285 adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with paired biopsy specimens obtained an average of 4 years apart.
Disclosures: Funders of the study included the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the Advanced/Transplant Hepatology Fellowship, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Foundation, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health.
Source: Ajmera V et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Mar 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.01.026.
Pancreatic surveillance identified resectable cancers
Long-term pancreatic surveillance of high-risk patients identified cancers while they were still resectable, and 85% of such patients remained alive 3 years after diagnosis, researchers reported.
“Among individuals undergoing pancreatic surveillance, specific detectable lesions with worrisome features predicted neoplastic progression. The short-term outcomes of patients with screening-detected PDACs [pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas] improved,” wrote Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS, of the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, together with her associates in the September issue of Gastroenterology.
The lifetime risk of PDAC is about 1.5%, the researchers noted. Consequently, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force does not recommend pancreatic surveillance at a population level. However, pancreatic screening is being evaluated for individuals who are at significantly elevated risk of PDAC, including those with at least two first-degree relatives with PDAC or who have germline mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, PRSS1 (hereditary pancreatitis), CDKN2A, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 (Lynch syndrome), or STK11 (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome).
For the study, Dr. Canto and her associates analyzed data from 354 such high-risk individuals enrolled in the CAPS (Cancer of the Pancreas Screening) cohort studies, which were conducted at tertiary care academic centers during 1998-2014. All participants underwent endoscopic ultrasound at baseline, followed by surveillance with endoscopic ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, or some combination of these modalities. Patients who developed pancreatic cancer or high-grade dysplasia were offered surgery.
In all, 68 patients (19%) developed pancreatic lesions with worrisome features, such as solid masses, multiple cysts, mural nodules, thickened or enhancing walls, cysts exceeding 3 cm in size or that grew more than 4 mm annually, a greater than 5-mm dilation of the main pancreatic duct, or an abrupt change in duct caliber. The lesions developed over a median of 13.1 months (interquartile range, 0.2-52 months).
A total of 7% of patients had neoplastic progression, including 14 cases of PDAC and 10 cases of high-grade dysplasia. Median times from baseline to detection of PDAC were 4.8 years overall (IQR, 1.6-6.9 years), 1.7 years (IQR, 0.5-4.4 years) among patients aged at least 60 years at baseline, and 5.2 years among younger patients (IQR, 0.4-8 years). Patients developed PDAC at a median of 67 years old.
Among 10 PDACs detected by surveillance, 9 were resectable. Three patients subsequently died of PDAC, while one patient died of complications of gastric cancer surgery. However, 85% of patients survived for at least 3 years after surgical resection of PDAC. The remaining four cases of PDAC were detected outside surveillance or after patients stopped surveillance.
The 10 cases of high-grade dysplasia consisted of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with high-grade dysplasia or high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Patients whose PDAC or high-grade dysplasia was detected by surveillance survived a median of 5.3 years, while patients whose surveillance was late or stopped and who subsequently developed neoplasia survived a median of only 1.4 years after diagnosis (P less than .0001).
Funders included the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, the John and Peter Hooven Memorial Endowment, Hugh and Rachel Victor, and ChiRhoClin. Dr. Canto had no disclosures. Three coinvestigators disclosed royalties for licensing of PALB2 as a pancreatic cancer susceptibility gene.
SOURCE: Canto MI et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 May 24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.035
Long-term pancreatic surveillance of high-risk patients identified cancers while they were still resectable, and 85% of such patients remained alive 3 years after diagnosis, researchers reported.
“Among individuals undergoing pancreatic surveillance, specific detectable lesions with worrisome features predicted neoplastic progression. The short-term outcomes of patients with screening-detected PDACs [pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas] improved,” wrote Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS, of the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, together with her associates in the September issue of Gastroenterology.
The lifetime risk of PDAC is about 1.5%, the researchers noted. Consequently, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force does not recommend pancreatic surveillance at a population level. However, pancreatic screening is being evaluated for individuals who are at significantly elevated risk of PDAC, including those with at least two first-degree relatives with PDAC or who have germline mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, PRSS1 (hereditary pancreatitis), CDKN2A, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 (Lynch syndrome), or STK11 (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome).
For the study, Dr. Canto and her associates analyzed data from 354 such high-risk individuals enrolled in the CAPS (Cancer of the Pancreas Screening) cohort studies, which were conducted at tertiary care academic centers during 1998-2014. All participants underwent endoscopic ultrasound at baseline, followed by surveillance with endoscopic ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, or some combination of these modalities. Patients who developed pancreatic cancer or high-grade dysplasia were offered surgery.
In all, 68 patients (19%) developed pancreatic lesions with worrisome features, such as solid masses, multiple cysts, mural nodules, thickened or enhancing walls, cysts exceeding 3 cm in size or that grew more than 4 mm annually, a greater than 5-mm dilation of the main pancreatic duct, or an abrupt change in duct caliber. The lesions developed over a median of 13.1 months (interquartile range, 0.2-52 months).
A total of 7% of patients had neoplastic progression, including 14 cases of PDAC and 10 cases of high-grade dysplasia. Median times from baseline to detection of PDAC were 4.8 years overall (IQR, 1.6-6.9 years), 1.7 years (IQR, 0.5-4.4 years) among patients aged at least 60 years at baseline, and 5.2 years among younger patients (IQR, 0.4-8 years). Patients developed PDAC at a median of 67 years old.
Among 10 PDACs detected by surveillance, 9 were resectable. Three patients subsequently died of PDAC, while one patient died of complications of gastric cancer surgery. However, 85% of patients survived for at least 3 years after surgical resection of PDAC. The remaining four cases of PDAC were detected outside surveillance or after patients stopped surveillance.
The 10 cases of high-grade dysplasia consisted of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with high-grade dysplasia or high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Patients whose PDAC or high-grade dysplasia was detected by surveillance survived a median of 5.3 years, while patients whose surveillance was late or stopped and who subsequently developed neoplasia survived a median of only 1.4 years after diagnosis (P less than .0001).
Funders included the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, the John and Peter Hooven Memorial Endowment, Hugh and Rachel Victor, and ChiRhoClin. Dr. Canto had no disclosures. Three coinvestigators disclosed royalties for licensing of PALB2 as a pancreatic cancer susceptibility gene.
SOURCE: Canto MI et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 May 24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.035
Long-term pancreatic surveillance of high-risk patients identified cancers while they were still resectable, and 85% of such patients remained alive 3 years after diagnosis, researchers reported.
“Among individuals undergoing pancreatic surveillance, specific detectable lesions with worrisome features predicted neoplastic progression. The short-term outcomes of patients with screening-detected PDACs [pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas] improved,” wrote Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS, of the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, together with her associates in the September issue of Gastroenterology.
The lifetime risk of PDAC is about 1.5%, the researchers noted. Consequently, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force does not recommend pancreatic surveillance at a population level. However, pancreatic screening is being evaluated for individuals who are at significantly elevated risk of PDAC, including those with at least two first-degree relatives with PDAC or who have germline mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, PRSS1 (hereditary pancreatitis), CDKN2A, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 (Lynch syndrome), or STK11 (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome).
For the study, Dr. Canto and her associates analyzed data from 354 such high-risk individuals enrolled in the CAPS (Cancer of the Pancreas Screening) cohort studies, which were conducted at tertiary care academic centers during 1998-2014. All participants underwent endoscopic ultrasound at baseline, followed by surveillance with endoscopic ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, or some combination of these modalities. Patients who developed pancreatic cancer or high-grade dysplasia were offered surgery.
In all, 68 patients (19%) developed pancreatic lesions with worrisome features, such as solid masses, multiple cysts, mural nodules, thickened or enhancing walls, cysts exceeding 3 cm in size or that grew more than 4 mm annually, a greater than 5-mm dilation of the main pancreatic duct, or an abrupt change in duct caliber. The lesions developed over a median of 13.1 months (interquartile range, 0.2-52 months).
A total of 7% of patients had neoplastic progression, including 14 cases of PDAC and 10 cases of high-grade dysplasia. Median times from baseline to detection of PDAC were 4.8 years overall (IQR, 1.6-6.9 years), 1.7 years (IQR, 0.5-4.4 years) among patients aged at least 60 years at baseline, and 5.2 years among younger patients (IQR, 0.4-8 years). Patients developed PDAC at a median of 67 years old.
Among 10 PDACs detected by surveillance, 9 were resectable. Three patients subsequently died of PDAC, while one patient died of complications of gastric cancer surgery. However, 85% of patients survived for at least 3 years after surgical resection of PDAC. The remaining four cases of PDAC were detected outside surveillance or after patients stopped surveillance.
The 10 cases of high-grade dysplasia consisted of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm with high-grade dysplasia or high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Patients whose PDAC or high-grade dysplasia was detected by surveillance survived a median of 5.3 years, while patients whose surveillance was late or stopped and who subsequently developed neoplasia survived a median of only 1.4 years after diagnosis (P less than .0001).
Funders included the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, the John and Peter Hooven Memorial Endowment, Hugh and Rachel Victor, and ChiRhoClin. Dr. Canto had no disclosures. Three coinvestigators disclosed royalties for licensing of PALB2 as a pancreatic cancer susceptibility gene.
SOURCE: Canto MI et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 May 24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.035
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Key clinical point: Pancreatic surveillance of high-risk individuals identified neoplasias when they were still resectable.
Major finding: Nine of ten tumors detected by surveillance were resectable, and 85% of patients remained alive 3 years after surgery, versus 25% of patients who were diagnosed after stopping or delaying surveillance (P less than .001).
Study details: Prospective cohort study of 354 high-risk individuals with 16 years of follow-up.
Disclosures: Funders included the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, the John and Peter Hooven Memorial Endowment, Hugh and Rachel Victor, and ChiRhoClin. Dr. Canto had no disclosures. Three coinvestigators disclosed royalties for licensing of PALB2 as a pancreatic cancer susceptibility gene.
Source: Canto MI et al. Gastroenterology. 2018 May 24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.05.035.
Questions About Herbal Supplements? There’s An App for That
To help, the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health has turned its “Herbs at a Glance” webpage into an app: HerbList™. The app gives research-based information on safety, effectiveness, and side effects of kava, açai, ginkgo, turmeric, and > 50 other herbs and herbal supplements marketed for health purposes.
HerbList is available to download from Apple App Store and Google Play.
To help, the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health has turned its “Herbs at a Glance” webpage into an app: HerbList™. The app gives research-based information on safety, effectiveness, and side effects of kava, açai, ginkgo, turmeric, and > 50 other herbs and herbal supplements marketed for health purposes.
HerbList is available to download from Apple App Store and Google Play.
To help, the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health has turned its “Herbs at a Glance” webpage into an app: HerbList™. The app gives research-based information on safety, effectiveness, and side effects of kava, açai, ginkgo, turmeric, and > 50 other herbs and herbal supplements marketed for health purposes.
HerbList is available to download from Apple App Store and Google Play.
Factor VIII product approved for hemophilia A
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Jivi® (antihemophilic factor [recombinant] PEGylated-aucl) for the treatment of hemophilia A.
Jivi (formerly BAY94-9027) is a DNA-derived, factor VIII concentrate approved for use in previously treated adults and adolescents (age 12 and older) with hemophilia A.
The product is approved for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding episodes, for perioperative management of bleeding, and as routine prophylaxis to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes.
The initial recommended prophylactic regimen is dosing twice weekly (30-40 IU/kg) with the ability to dose every 5 days (45-60 IU/kg) and further individually adjust to less or more frequent dosing based on bleeding episodes.
The FDA’s approval of Jivi is based on results from the phase 2/3 PROTECT VIII trial. Some results from this trial were published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis in 2016. Additional results are available in the prescribing information for Jivi.
PROTECT VIII enrolled previously treated adults and adolescents (ages 12 to 65) with severe hemophilia A.
In part A, researchers evaluated different dosing regimens for Jivi used as prophylaxis and on-demand treatment. An optional extension study was available to patients who completed part A.
In part B, researchers evaluated Jivi for perioperative management.
Efficacy
In part A, there were 132 patients in the intent‐to‐treat population—112 in the prophylaxis group and 20 in the on-demand group.
Patients received Jivi for 36 weeks. For the first 10 weeks, patients in the prophylaxis group received twice-weekly dosing at 25 IU/kg.
Patients with more than one bleed during this time went on to receive 30–40 IU/kg twice weekly. Patients with one or fewer bleeds were eligible for randomization to dosing every 5 days (45–60 IU/kg) or every 7 days (60 IU/kg).
The median annualized bleeding rate (ABR) was 4.1 for the patients who were treated twice weekly and were not eligible for randomization (n=13) and 1.9 for patients who were eligible for randomization but continued on twice-weekly treatment (n=11).
The median ABR was 1.9 for patients who were randomized to treatment every 5 days (n=43) and 0.96 for patients who completed prophylaxis with dosing every 7 days (32/43).
The median ABR for patients treated on demand was 24.1.
There were 388 treated bleeds in the on-demand group and 317 treated bleeds in the prophylaxis group. Overall, 73.3% of responses to treatment were considered “excellent” or “good,” 23.3% were considered “moderate,” and 3.3% were considered “poor.”
There were 17 patients who underwent 20 major surgeries in part B or the extension study and 10 patients who underwent minor surgeries in part A. Jivi provided “good” or “excellent” hemostatic control during all surgeries.
Safety
Safety data are available for 148 patients age 12 and older.
Adverse events in these patients included abdominal pain (3%), nausea (5%), vomiting (3%), injection site reactions (1%), pyrexia (5%), hypersensitivity (2%), dizziness (2%), headache (14%), insomnia (3%), cough (7%), erythema (1%), pruritus (1%), rash (2%), and flushing (1%).
A factor VIII inhibitor was reported in one adult patient, but repeat testing did not confirm the report.
One adult with asthma had a clinical hypersensitivity reaction and a transient increase of IgM anti-PEG antibody titer, which was negative upon retesting.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Jivi® (antihemophilic factor [recombinant] PEGylated-aucl) for the treatment of hemophilia A.
Jivi (formerly BAY94-9027) is a DNA-derived, factor VIII concentrate approved for use in previously treated adults and adolescents (age 12 and older) with hemophilia A.
The product is approved for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding episodes, for perioperative management of bleeding, and as routine prophylaxis to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes.
The initial recommended prophylactic regimen is dosing twice weekly (30-40 IU/kg) with the ability to dose every 5 days (45-60 IU/kg) and further individually adjust to less or more frequent dosing based on bleeding episodes.
The FDA’s approval of Jivi is based on results from the phase 2/3 PROTECT VIII trial. Some results from this trial were published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis in 2016. Additional results are available in the prescribing information for Jivi.
PROTECT VIII enrolled previously treated adults and adolescents (ages 12 to 65) with severe hemophilia A.
In part A, researchers evaluated different dosing regimens for Jivi used as prophylaxis and on-demand treatment. An optional extension study was available to patients who completed part A.
In part B, researchers evaluated Jivi for perioperative management.
Efficacy
In part A, there were 132 patients in the intent‐to‐treat population—112 in the prophylaxis group and 20 in the on-demand group.
Patients received Jivi for 36 weeks. For the first 10 weeks, patients in the prophylaxis group received twice-weekly dosing at 25 IU/kg.
Patients with more than one bleed during this time went on to receive 30–40 IU/kg twice weekly. Patients with one or fewer bleeds were eligible for randomization to dosing every 5 days (45–60 IU/kg) or every 7 days (60 IU/kg).
The median annualized bleeding rate (ABR) was 4.1 for the patients who were treated twice weekly and were not eligible for randomization (n=13) and 1.9 for patients who were eligible for randomization but continued on twice-weekly treatment (n=11).
The median ABR was 1.9 for patients who were randomized to treatment every 5 days (n=43) and 0.96 for patients who completed prophylaxis with dosing every 7 days (32/43).
The median ABR for patients treated on demand was 24.1.
There were 388 treated bleeds in the on-demand group and 317 treated bleeds in the prophylaxis group. Overall, 73.3% of responses to treatment were considered “excellent” or “good,” 23.3% were considered “moderate,” and 3.3% were considered “poor.”
There were 17 patients who underwent 20 major surgeries in part B or the extension study and 10 patients who underwent minor surgeries in part A. Jivi provided “good” or “excellent” hemostatic control during all surgeries.
Safety
Safety data are available for 148 patients age 12 and older.
Adverse events in these patients included abdominal pain (3%), nausea (5%), vomiting (3%), injection site reactions (1%), pyrexia (5%), hypersensitivity (2%), dizziness (2%), headache (14%), insomnia (3%), cough (7%), erythema (1%), pruritus (1%), rash (2%), and flushing (1%).
A factor VIII inhibitor was reported in one adult patient, but repeat testing did not confirm the report.
One adult with asthma had a clinical hypersensitivity reaction and a transient increase of IgM anti-PEG antibody titer, which was negative upon retesting.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Jivi® (antihemophilic factor [recombinant] PEGylated-aucl) for the treatment of hemophilia A.
Jivi (formerly BAY94-9027) is a DNA-derived, factor VIII concentrate approved for use in previously treated adults and adolescents (age 12 and older) with hemophilia A.
The product is approved for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding episodes, for perioperative management of bleeding, and as routine prophylaxis to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes.
The initial recommended prophylactic regimen is dosing twice weekly (30-40 IU/kg) with the ability to dose every 5 days (45-60 IU/kg) and further individually adjust to less or more frequent dosing based on bleeding episodes.
The FDA’s approval of Jivi is based on results from the phase 2/3 PROTECT VIII trial. Some results from this trial were published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis in 2016. Additional results are available in the prescribing information for Jivi.
PROTECT VIII enrolled previously treated adults and adolescents (ages 12 to 65) with severe hemophilia A.
In part A, researchers evaluated different dosing regimens for Jivi used as prophylaxis and on-demand treatment. An optional extension study was available to patients who completed part A.
In part B, researchers evaluated Jivi for perioperative management.
Efficacy
In part A, there were 132 patients in the intent‐to‐treat population—112 in the prophylaxis group and 20 in the on-demand group.
Patients received Jivi for 36 weeks. For the first 10 weeks, patients in the prophylaxis group received twice-weekly dosing at 25 IU/kg.
Patients with more than one bleed during this time went on to receive 30–40 IU/kg twice weekly. Patients with one or fewer bleeds were eligible for randomization to dosing every 5 days (45–60 IU/kg) or every 7 days (60 IU/kg).
The median annualized bleeding rate (ABR) was 4.1 for the patients who were treated twice weekly and were not eligible for randomization (n=13) and 1.9 for patients who were eligible for randomization but continued on twice-weekly treatment (n=11).
The median ABR was 1.9 for patients who were randomized to treatment every 5 days (n=43) and 0.96 for patients who completed prophylaxis with dosing every 7 days (32/43).
The median ABR for patients treated on demand was 24.1.
There were 388 treated bleeds in the on-demand group and 317 treated bleeds in the prophylaxis group. Overall, 73.3% of responses to treatment were considered “excellent” or “good,” 23.3% were considered “moderate,” and 3.3% were considered “poor.”
There were 17 patients who underwent 20 major surgeries in part B or the extension study and 10 patients who underwent minor surgeries in part A. Jivi provided “good” or “excellent” hemostatic control during all surgeries.
Safety
Safety data are available for 148 patients age 12 and older.
Adverse events in these patients included abdominal pain (3%), nausea (5%), vomiting (3%), injection site reactions (1%), pyrexia (5%), hypersensitivity (2%), dizziness (2%), headache (14%), insomnia (3%), cough (7%), erythema (1%), pruritus (1%), rash (2%), and flushing (1%).
A factor VIII inhibitor was reported in one adult patient, but repeat testing did not confirm the report.
One adult with asthma had a clinical hypersensitivity reaction and a transient increase of IgM anti-PEG antibody titer, which was negative upon retesting.
PLK1 inhibitor receives orphan designation for AML
The European Commission has granted orphan drug designation to onvansertib for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Onvansertib (formerly PCM-075) is an oral adenosine triphosphate competitive inhibitor of the serine/threonine Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) enzyme, which is overexpressed in hematologic and solid tumor malignancies.
Trovagene, Inc., the company developing onvansertib, said the drug has a 24-hour half-life with reversible, on-target hematologic activity.
These factors, combined with an improved dose/scheduling protocol, could mean onvansertib will improve upon long-term outcomes observed in previous studies with a PLK inhibitor in AML.
This includes a phase 2 study in which AML patients who received a PLK inhibitor plus low-dose cytarabine (LDAC) had a higher response rate than patients who received LDAC alone—31% and 13.3%, respectively.
Trovagene said preclinical studies have shown that onvansertib synergizes with more than 10 drugs used to treat hematologic and solid tumor malignancies. This includes FLT3 and HDAC inhibitors, taxanes, and cytotoxins.
Trovagene is now conducting a phase 1b/2 trial of onvansertib in combination with standard care (LDAC or decitabine) in patients with AML (NCT03303339).
The company has already completed a phase 1 dose-escalation study of onvansertib in patients with advanced metastatic solid tumor malignancies. Results from this study were published in Investigational New Drugs.
About orphan designation
Orphan drug designation in Europe is available to companies developing products intended to treat a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition that affects fewer than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union (EU).
The designation allows for financial and regulatory incentives that include 10 years of marketing exclusivity in the EU after product approval, eligibility for conditional marketing authorization, protocol assistance from the European Medicines Agency at reduced fees during the product development phase, and direct access to centralized marketing authorization in the EU.
The European Commission has granted orphan drug designation to onvansertib for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Onvansertib (formerly PCM-075) is an oral adenosine triphosphate competitive inhibitor of the serine/threonine Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) enzyme, which is overexpressed in hematologic and solid tumor malignancies.
Trovagene, Inc., the company developing onvansertib, said the drug has a 24-hour half-life with reversible, on-target hematologic activity.
These factors, combined with an improved dose/scheduling protocol, could mean onvansertib will improve upon long-term outcomes observed in previous studies with a PLK inhibitor in AML.
This includes a phase 2 study in which AML patients who received a PLK inhibitor plus low-dose cytarabine (LDAC) had a higher response rate than patients who received LDAC alone—31% and 13.3%, respectively.
Trovagene said preclinical studies have shown that onvansertib synergizes with more than 10 drugs used to treat hematologic and solid tumor malignancies. This includes FLT3 and HDAC inhibitors, taxanes, and cytotoxins.
Trovagene is now conducting a phase 1b/2 trial of onvansertib in combination with standard care (LDAC or decitabine) in patients with AML (NCT03303339).
The company has already completed a phase 1 dose-escalation study of onvansertib in patients with advanced metastatic solid tumor malignancies. Results from this study were published in Investigational New Drugs.
About orphan designation
Orphan drug designation in Europe is available to companies developing products intended to treat a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition that affects fewer than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union (EU).
The designation allows for financial and regulatory incentives that include 10 years of marketing exclusivity in the EU after product approval, eligibility for conditional marketing authorization, protocol assistance from the European Medicines Agency at reduced fees during the product development phase, and direct access to centralized marketing authorization in the EU.
The European Commission has granted orphan drug designation to onvansertib for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Onvansertib (formerly PCM-075) is an oral adenosine triphosphate competitive inhibitor of the serine/threonine Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) enzyme, which is overexpressed in hematologic and solid tumor malignancies.
Trovagene, Inc., the company developing onvansertib, said the drug has a 24-hour half-life with reversible, on-target hematologic activity.
These factors, combined with an improved dose/scheduling protocol, could mean onvansertib will improve upon long-term outcomes observed in previous studies with a PLK inhibitor in AML.
This includes a phase 2 study in which AML patients who received a PLK inhibitor plus low-dose cytarabine (LDAC) had a higher response rate than patients who received LDAC alone—31% and 13.3%, respectively.
Trovagene said preclinical studies have shown that onvansertib synergizes with more than 10 drugs used to treat hematologic and solid tumor malignancies. This includes FLT3 and HDAC inhibitors, taxanes, and cytotoxins.
Trovagene is now conducting a phase 1b/2 trial of onvansertib in combination with standard care (LDAC or decitabine) in patients with AML (NCT03303339).
The company has already completed a phase 1 dose-escalation study of onvansertib in patients with advanced metastatic solid tumor malignancies. Results from this study were published in Investigational New Drugs.
About orphan designation
Orphan drug designation in Europe is available to companies developing products intended to treat a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition that affects fewer than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union (EU).
The designation allows for financial and regulatory incentives that include 10 years of marketing exclusivity in the EU after product approval, eligibility for conditional marketing authorization, protocol assistance from the European Medicines Agency at reduced fees during the product development phase, and direct access to centralized marketing authorization in the EU.
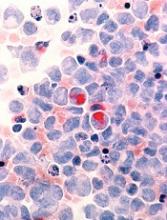
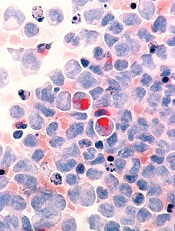
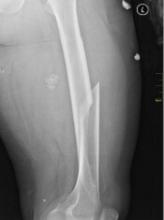
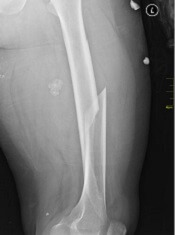
Fracture risk tied to death in women with MM
Preexisting osteoporosis is an important risk factor for mortality in postmenopausal women who develop multiple myeloma (MM), according to researchers.
They found that high fracture risk was associated with an increased risk of death in postmenopausal females with MM, independent of other clinical risk factors.
Ashley E. Rosko, MD, of Ohio State University in Columbus, and her colleagues reported these findings in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The researchers studied 362 subjects in the Women’s Health Initiative data set who developed MM but had no history of any cancer at baseline. The women were between 50 and 79 years of age and postmenopausal when they were originally recruited at 40 US centers between 1993 and 1998.
Dr. Rosko and her colleagues calculated bone health for the women using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), a web-based tool that calculates 10-year probability of hip and other major osteoporotic fractures.
Ninety-eight of the subjects were classified as having high FRAX scores, defined as a 10-year probability of 3% or greater for hip fracture or 20% or greater for other major osteoporosis-related fractures.
With a median follow-up of 10.5 years, the adjusted risk of death was elevated in women with high FRAX scores, with a covariate-adjusted hazard ratio of 1.51 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.25; P=0.044) versus women with low FRAX scores.
Of the 362 patients, 226 died during the follow-up period. That included 72% (n=71) of women with high FRAX scores and 59% (n=155) of women with low FRAX scores.
These findings suggest osteoporosis is an “important comorbidity” in women who develop MM, according to Dr. Rosko and her coauthors.
“Recognizing osteoporosis as a risk factor associated with multiple myeloma mortality is an important prognostic factor in postmenopausal women,” the researchers wrote.
This work was supported, in part, by the National Cancer Institute. The researchers reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Preexisting osteoporosis is an important risk factor for mortality in postmenopausal women who develop multiple myeloma (MM), according to researchers.
They found that high fracture risk was associated with an increased risk of death in postmenopausal females with MM, independent of other clinical risk factors.
Ashley E. Rosko, MD, of Ohio State University in Columbus, and her colleagues reported these findings in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The researchers studied 362 subjects in the Women’s Health Initiative data set who developed MM but had no history of any cancer at baseline. The women were between 50 and 79 years of age and postmenopausal when they were originally recruited at 40 US centers between 1993 and 1998.
Dr. Rosko and her colleagues calculated bone health for the women using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), a web-based tool that calculates 10-year probability of hip and other major osteoporotic fractures.
Ninety-eight of the subjects were classified as having high FRAX scores, defined as a 10-year probability of 3% or greater for hip fracture or 20% or greater for other major osteoporosis-related fractures.
With a median follow-up of 10.5 years, the adjusted risk of death was elevated in women with high FRAX scores, with a covariate-adjusted hazard ratio of 1.51 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.25; P=0.044) versus women with low FRAX scores.
Of the 362 patients, 226 died during the follow-up period. That included 72% (n=71) of women with high FRAX scores and 59% (n=155) of women with low FRAX scores.
These findings suggest osteoporosis is an “important comorbidity” in women who develop MM, according to Dr. Rosko and her coauthors.
“Recognizing osteoporosis as a risk factor associated with multiple myeloma mortality is an important prognostic factor in postmenopausal women,” the researchers wrote.
This work was supported, in part, by the National Cancer Institute. The researchers reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Preexisting osteoporosis is an important risk factor for mortality in postmenopausal women who develop multiple myeloma (MM), according to researchers.
They found that high fracture risk was associated with an increased risk of death in postmenopausal females with MM, independent of other clinical risk factors.
Ashley E. Rosko, MD, of Ohio State University in Columbus, and her colleagues reported these findings in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The researchers studied 362 subjects in the Women’s Health Initiative data set who developed MM but had no history of any cancer at baseline. The women were between 50 and 79 years of age and postmenopausal when they were originally recruited at 40 US centers between 1993 and 1998.
Dr. Rosko and her colleagues calculated bone health for the women using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), a web-based tool that calculates 10-year probability of hip and other major osteoporotic fractures.
Ninety-eight of the subjects were classified as having high FRAX scores, defined as a 10-year probability of 3% or greater for hip fracture or 20% or greater for other major osteoporosis-related fractures.
With a median follow-up of 10.5 years, the adjusted risk of death was elevated in women with high FRAX scores, with a covariate-adjusted hazard ratio of 1.51 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.25; P=0.044) versus women with low FRAX scores.
Of the 362 patients, 226 died during the follow-up period. That included 72% (n=71) of women with high FRAX scores and 59% (n=155) of women with low FRAX scores.
These findings suggest osteoporosis is an “important comorbidity” in women who develop MM, according to Dr. Rosko and her coauthors.
“Recognizing osteoporosis as a risk factor associated with multiple myeloma mortality is an important prognostic factor in postmenopausal women,” the researchers wrote.
This work was supported, in part, by the National Cancer Institute. The researchers reported no relevant financial disclosures.