User login
Herpes simplex type 2 infection markedly increases HIV risk
The risk of contracting HIV was almost three to five times higher among people infected with herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), in a systematic review and meta-analysis.
The analysis of 57 longitudinal studies found that the adjusted relative risk (RR) of HIV incidence after exposure to HSV-2 infection at baseline (“prevalent infection”) was 2.7 and was 4.7 after exposure to HSV-2 infection during follow-up (“incident infection”). The studies, mostly conducted in Africa, were found in PubMed, MEDLINE, and Embase publications from Jan. 1, 2003, to May 25, 2017; the analysis was published online on Aug. 23 (Lancet Infect Dis. 2017. pii: S1473-3099[17]30405-X. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099[17]30405-X).
“The greater cofactor effect for incident HSV-2 infection than for prevalent HSV-2 infection might be because newly acquired HSV-2 infection is associated with an increased frequency and severity of genital ulceration, viral shedding, and inflammation in the genital tract, symptoms and manifestations that decrease with time after infection,” according to Katharine J. Looker, PhD, of the University of Bristol (England), and Jocelyn A.R. Elmes, PhD, of Imperial College London (England) and their coauthors.
Associations still were significant but lower in higher-risk populations, such as female sex workers and their clients, men who have sex with men, and serodiscordant couples, the researchers said. For those with prevalent HSV-2, the adjusted RR of contracting HIV was 1.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.4-2.1), compared with 2.9 for those with incident HSV-2 infection (95% CI, 1.7-5.0).
“Quantifying the effect of HSV-2 infection on HIV acquisition has important public health implications, particularly in high-prevalence settings where coinfection is common, because prevention of HSV-2 infection ... might indirectly prevent HIV infection,” the authors wrote. “Knowledge of this association informs the advice and information given to individuals diagnosed with genital herpes, who might be at increased risk of acquiring HIV.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization. Dr. Looker reported personal fees from the WHO. Dr. Elmes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Wellcome Trust outside of this study. Two authors reported financial support from Aquarius Population Health and other support from WHO and NIH; the three remaining authors had no disclosures.
The incidence of HIV infection has not changed in a decade. Development of successful strategies to prevent HIV acquisition might require more creative approaches to meet the needs of the most susceptible populations, including exploration of the role of sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), in HIV infection.
This study provides the first systematic review and meta-analysis in more than a decade to assess the effect of HSV-2 infection on subsequent HIV acquisition. There are some preventative treatments available for HIV and HSV-2, but they have poor availability in low-income regions that have the highest risk of infection. Therefore, other multipurpose prevention technologies for HSV-2 and HIV are needed to give individuals a broad range of prevention options and to target the lifestyles and preferences of the most susceptible populations, including young women in Africa who have the highest incidence of HIV and HSV-2 worldwide.
Thomas M. Zydowsky, PhD , is the director of biomedical research and pharmaceutical development in the HIV and AIDS program at the Population Council’s Center for Biomedical Research in New York. His commentary accompanied the Looker et al. study ( Lancet Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 23. pii: S1473-3099[17]30493-0. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099[17]30493-0 ). He reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The incidence of HIV infection has not changed in a decade. Development of successful strategies to prevent HIV acquisition might require more creative approaches to meet the needs of the most susceptible populations, including exploration of the role of sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), in HIV infection.
This study provides the first systematic review and meta-analysis in more than a decade to assess the effect of HSV-2 infection on subsequent HIV acquisition. There are some preventative treatments available for HIV and HSV-2, but they have poor availability in low-income regions that have the highest risk of infection. Therefore, other multipurpose prevention technologies for HSV-2 and HIV are needed to give individuals a broad range of prevention options and to target the lifestyles and preferences of the most susceptible populations, including young women in Africa who have the highest incidence of HIV and HSV-2 worldwide.
Thomas M. Zydowsky, PhD , is the director of biomedical research and pharmaceutical development in the HIV and AIDS program at the Population Council’s Center for Biomedical Research in New York. His commentary accompanied the Looker et al. study ( Lancet Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 23. pii: S1473-3099[17]30493-0. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099[17]30493-0 ). He reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The incidence of HIV infection has not changed in a decade. Development of successful strategies to prevent HIV acquisition might require more creative approaches to meet the needs of the most susceptible populations, including exploration of the role of sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), in HIV infection.
This study provides the first systematic review and meta-analysis in more than a decade to assess the effect of HSV-2 infection on subsequent HIV acquisition. There are some preventative treatments available for HIV and HSV-2, but they have poor availability in low-income regions that have the highest risk of infection. Therefore, other multipurpose prevention technologies for HSV-2 and HIV are needed to give individuals a broad range of prevention options and to target the lifestyles and preferences of the most susceptible populations, including young women in Africa who have the highest incidence of HIV and HSV-2 worldwide.
Thomas M. Zydowsky, PhD , is the director of biomedical research and pharmaceutical development in the HIV and AIDS program at the Population Council’s Center for Biomedical Research in New York. His commentary accompanied the Looker et al. study ( Lancet Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 23. pii: S1473-3099[17]30493-0. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099[17]30493-0 ). He reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The risk of contracting HIV was almost three to five times higher among people infected with herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), in a systematic review and meta-analysis.
The analysis of 57 longitudinal studies found that the adjusted relative risk (RR) of HIV incidence after exposure to HSV-2 infection at baseline (“prevalent infection”) was 2.7 and was 4.7 after exposure to HSV-2 infection during follow-up (“incident infection”). The studies, mostly conducted in Africa, were found in PubMed, MEDLINE, and Embase publications from Jan. 1, 2003, to May 25, 2017; the analysis was published online on Aug. 23 (Lancet Infect Dis. 2017. pii: S1473-3099[17]30405-X. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099[17]30405-X).
“The greater cofactor effect for incident HSV-2 infection than for prevalent HSV-2 infection might be because newly acquired HSV-2 infection is associated with an increased frequency and severity of genital ulceration, viral shedding, and inflammation in the genital tract, symptoms and manifestations that decrease with time after infection,” according to Katharine J. Looker, PhD, of the University of Bristol (England), and Jocelyn A.R. Elmes, PhD, of Imperial College London (England) and their coauthors.
Associations still were significant but lower in higher-risk populations, such as female sex workers and their clients, men who have sex with men, and serodiscordant couples, the researchers said. For those with prevalent HSV-2, the adjusted RR of contracting HIV was 1.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.4-2.1), compared with 2.9 for those with incident HSV-2 infection (95% CI, 1.7-5.0).
“Quantifying the effect of HSV-2 infection on HIV acquisition has important public health implications, particularly in high-prevalence settings where coinfection is common, because prevention of HSV-2 infection ... might indirectly prevent HIV infection,” the authors wrote. “Knowledge of this association informs the advice and information given to individuals diagnosed with genital herpes, who might be at increased risk of acquiring HIV.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization. Dr. Looker reported personal fees from the WHO. Dr. Elmes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Wellcome Trust outside of this study. Two authors reported financial support from Aquarius Population Health and other support from WHO and NIH; the three remaining authors had no disclosures.
The risk of contracting HIV was almost three to five times higher among people infected with herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), in a systematic review and meta-analysis.
The analysis of 57 longitudinal studies found that the adjusted relative risk (RR) of HIV incidence after exposure to HSV-2 infection at baseline (“prevalent infection”) was 2.7 and was 4.7 after exposure to HSV-2 infection during follow-up (“incident infection”). The studies, mostly conducted in Africa, were found in PubMed, MEDLINE, and Embase publications from Jan. 1, 2003, to May 25, 2017; the analysis was published online on Aug. 23 (Lancet Infect Dis. 2017. pii: S1473-3099[17]30405-X. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099[17]30405-X).
“The greater cofactor effect for incident HSV-2 infection than for prevalent HSV-2 infection might be because newly acquired HSV-2 infection is associated with an increased frequency and severity of genital ulceration, viral shedding, and inflammation in the genital tract, symptoms and manifestations that decrease with time after infection,” according to Katharine J. Looker, PhD, of the University of Bristol (England), and Jocelyn A.R. Elmes, PhD, of Imperial College London (England) and their coauthors.
Associations still were significant but lower in higher-risk populations, such as female sex workers and their clients, men who have sex with men, and serodiscordant couples, the researchers said. For those with prevalent HSV-2, the adjusted RR of contracting HIV was 1.7 (95% confidence interval, 1.4-2.1), compared with 2.9 for those with incident HSV-2 infection (95% CI, 1.7-5.0).
“Quantifying the effect of HSV-2 infection on HIV acquisition has important public health implications, particularly in high-prevalence settings where coinfection is common, because prevention of HSV-2 infection ... might indirectly prevent HIV infection,” the authors wrote. “Knowledge of this association informs the advice and information given to individuals diagnosed with genital herpes, who might be at increased risk of acquiring HIV.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization. Dr. Looker reported personal fees from the WHO. Dr. Elmes reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Wellcome Trust outside of this study. Two authors reported financial support from Aquarius Population Health and other support from WHO and NIH; the three remaining authors had no disclosures.
FROM THE LANCET: INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The adjusted relative risk of HIV incidence after exposure to prevalent HSV-2 was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.2-3.4) and was 4.7 after exposure to incident HSV-2 (95% CI, 2.2-10.1).
Data source: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 57 longitudinal studies on the risk of HIV acquisition associated with HSV-2 infection.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the World Health Organization. One lead author reported personal fees from the World Health Organization; the other reported grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Wellcome Trust outside of this study. Two authors reported financial support from Aquarius Population Health and other support from WHO and NIH; the three remaining authors had no disclosures.
TNF inhibitors associated with fewer side effects than methotrexate in children with psoriasis
Treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors was associated with fewer adverse events (AEs) than with methotrexate, in an international, retrospective study of children with psoriasis.
“Patients with pediatric psoriasis treated with methotrexate had a greater risk of having one or more AEs than those treated with TNF-I [tumor necrosis factor inhibitors], although fewer AEs occurred with methotrexate or TNF-I than with other drug classes,” Inge M.G.J. Bronckers, MD, of the department of dermatology at Radboud University, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, and his coauthors reported.
Among those treated with methotrexate, administration of folic acid six to seven times a week was more protective against methotrexate-associated gastrointestinal AEs, than when administered only once a week. The study was published on Sept. 13 in JAMA Dermatology (2017. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.3029).
The study evaluated 390 children with moderate to severe psoriasis, treated with at least one systemic medication at 20 centers in Canada, Europe, and the United States, during December 1990-September 2014. They were diagnosed at a mean age of about 8 years, and started systemic therapy a mean of 3 years later. Of the 390 children treated for psoriasis, 270 were treated with methotrexate and 106 were treated with biologics, most often the TNF inhibitor etanercept. The remaining treatments were acitretin, cyclosporine, and fumaric acid esters; almost 19% were treated with more than one medication.
Of those treated with methotrexate, 130 (48.1%) experienced one or more treatment-related AEs, compared with 41 (38.7%) of those treated with a biologic agent (odds ratio, 1.76; P = .03). Almost 25% of those on methotrexate had GI-related AEs, the most common AE; other AEs included elevated transaminase levels and fatigue. Among those on biologics, injection site reactions were the most common (in 18.9%); 12 patients (11.3%) of those on biologics had infections, primarily airway infections.
Compared with those on a TNF inhibitor, patients on methotrexate were more likely to experience GI-related AEs (OR, 11.49; P less than .001) or to discontinue treatment (OR, 5.69; P = .02), the investigators said. But associated infections were more common with TNF inhibitors (OR, 0.36; P = .03), compared with methotrexate. There were no cases of malignancies or tuberculosis.
Folic acid was prescribed to 239 patients receiving methotrexate in one of three regimens: once weekly; six times weekly, avoiding the methotrexate day; and seven times weekly, according to the investigators. Compared with once-weekly treatment, administration six or seven times weekly was associated with a lower probability of developing a GI-related AE (OR, 0.16; P less than .001; OR, 0.21; P = .003, respectively).
“Data are sparse on the relative use of systemic agents and their toxic effects in the pediatric population,” Dr. Bronckers and his coauthors wrote, adding that standardized guidelines and more data concerning children are needed. “Our data suggest that a weekly administration of folic acid could be replaced with a daily or six times weekly administration to reduce GI AEs, although the potential efficacy of six vs. seven times weekly dosing deserves further investigation,” they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from the International Psoriasis Council. Of the 23 authors, 11 had financial disclosures with various pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors was associated with fewer adverse events (AEs) than with methotrexate, in an international, retrospective study of children with psoriasis.
“Patients with pediatric psoriasis treated with methotrexate had a greater risk of having one or more AEs than those treated with TNF-I [tumor necrosis factor inhibitors], although fewer AEs occurred with methotrexate or TNF-I than with other drug classes,” Inge M.G.J. Bronckers, MD, of the department of dermatology at Radboud University, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, and his coauthors reported.
Among those treated with methotrexate, administration of folic acid six to seven times a week was more protective against methotrexate-associated gastrointestinal AEs, than when administered only once a week. The study was published on Sept. 13 in JAMA Dermatology (2017. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.3029).
The study evaluated 390 children with moderate to severe psoriasis, treated with at least one systemic medication at 20 centers in Canada, Europe, and the United States, during December 1990-September 2014. They were diagnosed at a mean age of about 8 years, and started systemic therapy a mean of 3 years later. Of the 390 children treated for psoriasis, 270 were treated with methotrexate and 106 were treated with biologics, most often the TNF inhibitor etanercept. The remaining treatments were acitretin, cyclosporine, and fumaric acid esters; almost 19% were treated with more than one medication.
Of those treated with methotrexate, 130 (48.1%) experienced one or more treatment-related AEs, compared with 41 (38.7%) of those treated with a biologic agent (odds ratio, 1.76; P = .03). Almost 25% of those on methotrexate had GI-related AEs, the most common AE; other AEs included elevated transaminase levels and fatigue. Among those on biologics, injection site reactions were the most common (in 18.9%); 12 patients (11.3%) of those on biologics had infections, primarily airway infections.
Compared with those on a TNF inhibitor, patients on methotrexate were more likely to experience GI-related AEs (OR, 11.49; P less than .001) or to discontinue treatment (OR, 5.69; P = .02), the investigators said. But associated infections were more common with TNF inhibitors (OR, 0.36; P = .03), compared with methotrexate. There were no cases of malignancies or tuberculosis.
Folic acid was prescribed to 239 patients receiving methotrexate in one of three regimens: once weekly; six times weekly, avoiding the methotrexate day; and seven times weekly, according to the investigators. Compared with once-weekly treatment, administration six or seven times weekly was associated with a lower probability of developing a GI-related AE (OR, 0.16; P less than .001; OR, 0.21; P = .003, respectively).
“Data are sparse on the relative use of systemic agents and their toxic effects in the pediatric population,” Dr. Bronckers and his coauthors wrote, adding that standardized guidelines and more data concerning children are needed. “Our data suggest that a weekly administration of folic acid could be replaced with a daily or six times weekly administration to reduce GI AEs, although the potential efficacy of six vs. seven times weekly dosing deserves further investigation,” they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from the International Psoriasis Council. Of the 23 authors, 11 had financial disclosures with various pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors was associated with fewer adverse events (AEs) than with methotrexate, in an international, retrospective study of children with psoriasis.
“Patients with pediatric psoriasis treated with methotrexate had a greater risk of having one or more AEs than those treated with TNF-I [tumor necrosis factor inhibitors], although fewer AEs occurred with methotrexate or TNF-I than with other drug classes,” Inge M.G.J. Bronckers, MD, of the department of dermatology at Radboud University, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, and his coauthors reported.
Among those treated with methotrexate, administration of folic acid six to seven times a week was more protective against methotrexate-associated gastrointestinal AEs, than when administered only once a week. The study was published on Sept. 13 in JAMA Dermatology (2017. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.3029).
The study evaluated 390 children with moderate to severe psoriasis, treated with at least one systemic medication at 20 centers in Canada, Europe, and the United States, during December 1990-September 2014. They were diagnosed at a mean age of about 8 years, and started systemic therapy a mean of 3 years later. Of the 390 children treated for psoriasis, 270 were treated with methotrexate and 106 were treated with biologics, most often the TNF inhibitor etanercept. The remaining treatments were acitretin, cyclosporine, and fumaric acid esters; almost 19% were treated with more than one medication.
Of those treated with methotrexate, 130 (48.1%) experienced one or more treatment-related AEs, compared with 41 (38.7%) of those treated with a biologic agent (odds ratio, 1.76; P = .03). Almost 25% of those on methotrexate had GI-related AEs, the most common AE; other AEs included elevated transaminase levels and fatigue. Among those on biologics, injection site reactions were the most common (in 18.9%); 12 patients (11.3%) of those on biologics had infections, primarily airway infections.
Compared with those on a TNF inhibitor, patients on methotrexate were more likely to experience GI-related AEs (OR, 11.49; P less than .001) or to discontinue treatment (OR, 5.69; P = .02), the investigators said. But associated infections were more common with TNF inhibitors (OR, 0.36; P = .03), compared with methotrexate. There were no cases of malignancies or tuberculosis.
Folic acid was prescribed to 239 patients receiving methotrexate in one of three regimens: once weekly; six times weekly, avoiding the methotrexate day; and seven times weekly, according to the investigators. Compared with once-weekly treatment, administration six or seven times weekly was associated with a lower probability of developing a GI-related AE (OR, 0.16; P less than .001; OR, 0.21; P = .003, respectively).
“Data are sparse on the relative use of systemic agents and their toxic effects in the pediatric population,” Dr. Bronckers and his coauthors wrote, adding that standardized guidelines and more data concerning children are needed. “Our data suggest that a weekly administration of folic acid could be replaced with a daily or six times weekly administration to reduce GI AEs, although the potential efficacy of six vs. seven times weekly dosing deserves further investigation,” they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from the International Psoriasis Council. Of the 23 authors, 11 had financial disclosures with various pharmaceutical manufacturers.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Almost half (48.1%) of the children treated with methotrexate experienced one or more treatment-related adverse events, compared with 41 (38.7%) of those treated with a biologic agent (OR, 1.76; P = .03).
Data source: An international, retrospective study of 390 children with moderate to severe psoriasis compared the adverse events associated with different systemic therapies.
Disclosures: The study was supported by a grant from the International Psoriasis Council.
The AHRQ Toolbox: Tools for negotiating shared decision making
This is the second in a series of articles from the National Center for Excellence in Primary Care Research (NCEPCR) in the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). This series introduces sets of tools and resources designed to help your practice.
Shared decision making means the decision takes into account evidence-based information about available options, the provider’s knowledge and experience, and the patient’s values and preferences. More and more patients and providers want to participate in shared decision making, but the “how” often is neglected in standard medical and graduate medical education. AHRQ provides two resources to assist in your practice’s use of shared decision making.
The SHARE Approach is a five-step process for shared decision making:
- Seek your patient’s participation.
- Help your patient explore & compare treatment options.
- Assess your patient’s values and preferences.
- Reach a decision with your patient.
- Evaluate your patient’s decision.
AHRQ’s SHARE Approach curriculum provides both a quick overview (for the busy clinician) and an extensive course (complete with slides and a trainer’s module). The website provides the clinician the opportunity to learn the key elements of the SHARE Approach, while providing the educator a full curriculum with slides, handouts, and a video in order to demonstrate the approach. Complementing the SHARE curriculum, AHRQ’s Effective Health Care Program offers excellent, easy-to-read summaries of evidence reports to help clinicians and consumers make informed health care decisions. AHRQ recently released Lung Cancer Screening Tools, including a decision aid, for patients and clinicians to facilitate discussions about lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography.
The SHARE Approach and other tools can be found at the NCEPCR website.
Dr. Bierman is the director of the Center for Evidence and Practice Improvement at AHRQ. Dr. Ganiats is the director for the National Center for Excellence in Primary Care Research at AHRQ.
This is the second in a series of articles from the National Center for Excellence in Primary Care Research (NCEPCR) in the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). This series introduces sets of tools and resources designed to help your practice.
Shared decision making means the decision takes into account evidence-based information about available options, the provider’s knowledge and experience, and the patient’s values and preferences. More and more patients and providers want to participate in shared decision making, but the “how” often is neglected in standard medical and graduate medical education. AHRQ provides two resources to assist in your practice’s use of shared decision making.
The SHARE Approach is a five-step process for shared decision making:
- Seek your patient’s participation.
- Help your patient explore & compare treatment options.
- Assess your patient’s values and preferences.
- Reach a decision with your patient.
- Evaluate your patient’s decision.
AHRQ’s SHARE Approach curriculum provides both a quick overview (for the busy clinician) and an extensive course (complete with slides and a trainer’s module). The website provides the clinician the opportunity to learn the key elements of the SHARE Approach, while providing the educator a full curriculum with slides, handouts, and a video in order to demonstrate the approach. Complementing the SHARE curriculum, AHRQ’s Effective Health Care Program offers excellent, easy-to-read summaries of evidence reports to help clinicians and consumers make informed health care decisions. AHRQ recently released Lung Cancer Screening Tools, including a decision aid, for patients and clinicians to facilitate discussions about lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography.
The SHARE Approach and other tools can be found at the NCEPCR website.
Dr. Bierman is the director of the Center for Evidence and Practice Improvement at AHRQ. Dr. Ganiats is the director for the National Center for Excellence in Primary Care Research at AHRQ.
This is the second in a series of articles from the National Center for Excellence in Primary Care Research (NCEPCR) in the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). This series introduces sets of tools and resources designed to help your practice.
Shared decision making means the decision takes into account evidence-based information about available options, the provider’s knowledge and experience, and the patient’s values and preferences. More and more patients and providers want to participate in shared decision making, but the “how” often is neglected in standard medical and graduate medical education. AHRQ provides two resources to assist in your practice’s use of shared decision making.
The SHARE Approach is a five-step process for shared decision making:
- Seek your patient’s participation.
- Help your patient explore & compare treatment options.
- Assess your patient’s values and preferences.
- Reach a decision with your patient.
- Evaluate your patient’s decision.
AHRQ’s SHARE Approach curriculum provides both a quick overview (for the busy clinician) and an extensive course (complete with slides and a trainer’s module). The website provides the clinician the opportunity to learn the key elements of the SHARE Approach, while providing the educator a full curriculum with slides, handouts, and a video in order to demonstrate the approach. Complementing the SHARE curriculum, AHRQ’s Effective Health Care Program offers excellent, easy-to-read summaries of evidence reports to help clinicians and consumers make informed health care decisions. AHRQ recently released Lung Cancer Screening Tools, including a decision aid, for patients and clinicians to facilitate discussions about lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography.
The SHARE Approach and other tools can be found at the NCEPCR website.
Dr. Bierman is the director of the Center for Evidence and Practice Improvement at AHRQ. Dr. Ganiats is the director for the National Center for Excellence in Primary Care Research at AHRQ.
Ruling: Apologies can’t be used against doctors in court
The Ohio Supreme Court has ruled that apologies by physicians that include an admission of fault cannot be used against them in court, upholding a lower court decision that spared a doctor’s comments from being heard at trial.
In a Sept. 12 decision, state Supreme Court justices concluded that Ohio’s apology statute protects both expressions of regret for an unanticipated outcome and acknowledgments that the patient’s treatment fell below the standard of care. The decision resolves a split among Ohio appeals courts over whether expressions of fault are admissible.
The decision declaring Ohio’s apology statute “unambiguous” is an important and clarifying ruling for physicians and settles the differing opinions of some lower courts, said Reginald Fields, director of external and professional relations for the Ohio State Medical Association.
“We applaud the high court’s decision,” Mr. Fields said in an interview. “Even the two dissenting justices agreed that the apology law is clear; they just questioned whether it applied in this particular case. This ruling likely means pending legislation thought to be needed to clarify the law is now unnecessary. The OSMA will now focus on other aspects of tort reform, such as ‘loss of chance’ claims and further elimination of frivolous lawsuits.”
The Ohio Association for Justice, the state’s plaintiffs’ bar did not respond to a request for comment.
The case of Stewart v. Vivian resulted from a lawsuit filed by Dennis Stewart against Cincinnati psychiatrist Rodney Vivian, MD, after the death of Mr. Stewart’s wife by suicide. Michelle Stewart was admitted to the emergency department of Mt. Orab MediCenter in February 2010 after attempting suicide and was later transferred to the psychiatric unit at Mercy Hospital Clermont in Batavia, Ohio. After consulting with nurses, Dr. Vivian ordered that a staff member of the psychiatric unit visually observe Ms. Stewart every 15 minutes, according to court documents. The next evening, Mr. Stewart arrived at the psychiatric unit to visit his wife and found her unconscious as a result of hanging.
Two days later, Dr. Vivian went to Ms. Stewart’s room in the intensive care unit to speak with family members. The content of the conversation between Dr. Vivian and family members is disputed. Family members allege that Dr. Vivian expressed that it was a “terrible situation” and that the patient had told Dr. Vivian that she “wanted to be dead” would “keep trying” to kill herself. Dr. Vivian testified that he told the family he was “sorry this has happened.” Ms. Stewart was later taken off life support and died.
In 2011, Mr. Stewart sued Dr. Vivian and Mercy Hospital Clermont for medical malpractice, loss of spousal consortium, and wrongful death. Dr. Vivian argued that his statements to family members in the ICU room were inadmissible under the state’s apology law because they were “intended to express commiseration, condolence, or sympathy.” Mr. Stewart countered that Dr. Vivian’s statements were admissible because they were not “pure expressions of apology, sympathy, commiseration, condolence, compassion, or a general sense of benevolence.” The trial court sided with Dr. Vivian and his statements were kept from trial testimony. The jury returned a verdict in favor of Dr. Vivian, concluding that he was not negligent in his assessment, care, or treatment.
The 12th District Court of Appeals ruled that Dr. Vivian’s statements were properly excluded, finding that the Ohio’s apology law is ambiguous because according to the term’s dictionary definition, “apology” may or may not include an admission of fault. But the decision conflicted with the case of Davis v. Wooster Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine, Inc. in which the Court of Appeals for the 9th District in Ohio determined Ohio’s apology statute protects from admission “pure expressions of apology, sympathy, commiseration, condolence, compassion, or a general sense of benevolence,” but not “admission of fault.”
Resolving the split, the Ohio Supreme Court concluded that the state law is unambiguous and that its legislative intent is to shield expressions of regret for unexpected outcomes that may include acknowledgments that the patient’s medical care fell below the standard of care.
Ohio Supreme Court Chief Justice Maureen O’Connor and Justice William M. O’Neill partially dissented. While they agreed with the majority’s holding regarding the intent of Ohio’s apology law, Justice O’Connor wrote that the Dr. Vivian’s statements fell outside the law’s protection.
“Dr. Vivian’s statements were not an apology nor did they express regret or a type of shared sadness associated with sympathy or commiseration,” she wrote in her dissent.
At least 36 states have apology laws that shield against certain statements, expressions, or other evidence related to disclosures being used against physicians in court.
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
The Ohio Supreme Court has ruled that apologies by physicians that include an admission of fault cannot be used against them in court, upholding a lower court decision that spared a doctor’s comments from being heard at trial.
In a Sept. 12 decision, state Supreme Court justices concluded that Ohio’s apology statute protects both expressions of regret for an unanticipated outcome and acknowledgments that the patient’s treatment fell below the standard of care. The decision resolves a split among Ohio appeals courts over whether expressions of fault are admissible.
The decision declaring Ohio’s apology statute “unambiguous” is an important and clarifying ruling for physicians and settles the differing opinions of some lower courts, said Reginald Fields, director of external and professional relations for the Ohio State Medical Association.
“We applaud the high court’s decision,” Mr. Fields said in an interview. “Even the two dissenting justices agreed that the apology law is clear; they just questioned whether it applied in this particular case. This ruling likely means pending legislation thought to be needed to clarify the law is now unnecessary. The OSMA will now focus on other aspects of tort reform, such as ‘loss of chance’ claims and further elimination of frivolous lawsuits.”
The Ohio Association for Justice, the state’s plaintiffs’ bar did not respond to a request for comment.
The case of Stewart v. Vivian resulted from a lawsuit filed by Dennis Stewart against Cincinnati psychiatrist Rodney Vivian, MD, after the death of Mr. Stewart’s wife by suicide. Michelle Stewart was admitted to the emergency department of Mt. Orab MediCenter in February 2010 after attempting suicide and was later transferred to the psychiatric unit at Mercy Hospital Clermont in Batavia, Ohio. After consulting with nurses, Dr. Vivian ordered that a staff member of the psychiatric unit visually observe Ms. Stewart every 15 minutes, according to court documents. The next evening, Mr. Stewart arrived at the psychiatric unit to visit his wife and found her unconscious as a result of hanging.
Two days later, Dr. Vivian went to Ms. Stewart’s room in the intensive care unit to speak with family members. The content of the conversation between Dr. Vivian and family members is disputed. Family members allege that Dr. Vivian expressed that it was a “terrible situation” and that the patient had told Dr. Vivian that she “wanted to be dead” would “keep trying” to kill herself. Dr. Vivian testified that he told the family he was “sorry this has happened.” Ms. Stewart was later taken off life support and died.
In 2011, Mr. Stewart sued Dr. Vivian and Mercy Hospital Clermont for medical malpractice, loss of spousal consortium, and wrongful death. Dr. Vivian argued that his statements to family members in the ICU room were inadmissible under the state’s apology law because they were “intended to express commiseration, condolence, or sympathy.” Mr. Stewart countered that Dr. Vivian’s statements were admissible because they were not “pure expressions of apology, sympathy, commiseration, condolence, compassion, or a general sense of benevolence.” The trial court sided with Dr. Vivian and his statements were kept from trial testimony. The jury returned a verdict in favor of Dr. Vivian, concluding that he was not negligent in his assessment, care, or treatment.
The 12th District Court of Appeals ruled that Dr. Vivian’s statements were properly excluded, finding that the Ohio’s apology law is ambiguous because according to the term’s dictionary definition, “apology” may or may not include an admission of fault. But the decision conflicted with the case of Davis v. Wooster Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine, Inc. in which the Court of Appeals for the 9th District in Ohio determined Ohio’s apology statute protects from admission “pure expressions of apology, sympathy, commiseration, condolence, compassion, or a general sense of benevolence,” but not “admission of fault.”
Resolving the split, the Ohio Supreme Court concluded that the state law is unambiguous and that its legislative intent is to shield expressions of regret for unexpected outcomes that may include acknowledgments that the patient’s medical care fell below the standard of care.
Ohio Supreme Court Chief Justice Maureen O’Connor and Justice William M. O’Neill partially dissented. While they agreed with the majority’s holding regarding the intent of Ohio’s apology law, Justice O’Connor wrote that the Dr. Vivian’s statements fell outside the law’s protection.
“Dr. Vivian’s statements were not an apology nor did they express regret or a type of shared sadness associated with sympathy or commiseration,” she wrote in her dissent.
At least 36 states have apology laws that shield against certain statements, expressions, or other evidence related to disclosures being used against physicians in court.
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
The Ohio Supreme Court has ruled that apologies by physicians that include an admission of fault cannot be used against them in court, upholding a lower court decision that spared a doctor’s comments from being heard at trial.
In a Sept. 12 decision, state Supreme Court justices concluded that Ohio’s apology statute protects both expressions of regret for an unanticipated outcome and acknowledgments that the patient’s treatment fell below the standard of care. The decision resolves a split among Ohio appeals courts over whether expressions of fault are admissible.
The decision declaring Ohio’s apology statute “unambiguous” is an important and clarifying ruling for physicians and settles the differing opinions of some lower courts, said Reginald Fields, director of external and professional relations for the Ohio State Medical Association.
“We applaud the high court’s decision,” Mr. Fields said in an interview. “Even the two dissenting justices agreed that the apology law is clear; they just questioned whether it applied in this particular case. This ruling likely means pending legislation thought to be needed to clarify the law is now unnecessary. The OSMA will now focus on other aspects of tort reform, such as ‘loss of chance’ claims and further elimination of frivolous lawsuits.”
The Ohio Association for Justice, the state’s plaintiffs’ bar did not respond to a request for comment.
The case of Stewart v. Vivian resulted from a lawsuit filed by Dennis Stewart against Cincinnati psychiatrist Rodney Vivian, MD, after the death of Mr. Stewart’s wife by suicide. Michelle Stewart was admitted to the emergency department of Mt. Orab MediCenter in February 2010 after attempting suicide and was later transferred to the psychiatric unit at Mercy Hospital Clermont in Batavia, Ohio. After consulting with nurses, Dr. Vivian ordered that a staff member of the psychiatric unit visually observe Ms. Stewart every 15 minutes, according to court documents. The next evening, Mr. Stewart arrived at the psychiatric unit to visit his wife and found her unconscious as a result of hanging.
Two days later, Dr. Vivian went to Ms. Stewart’s room in the intensive care unit to speak with family members. The content of the conversation between Dr. Vivian and family members is disputed. Family members allege that Dr. Vivian expressed that it was a “terrible situation” and that the patient had told Dr. Vivian that she “wanted to be dead” would “keep trying” to kill herself. Dr. Vivian testified that he told the family he was “sorry this has happened.” Ms. Stewart was later taken off life support and died.
In 2011, Mr. Stewart sued Dr. Vivian and Mercy Hospital Clermont for medical malpractice, loss of spousal consortium, and wrongful death. Dr. Vivian argued that his statements to family members in the ICU room were inadmissible under the state’s apology law because they were “intended to express commiseration, condolence, or sympathy.” Mr. Stewart countered that Dr. Vivian’s statements were admissible because they were not “pure expressions of apology, sympathy, commiseration, condolence, compassion, or a general sense of benevolence.” The trial court sided with Dr. Vivian and his statements were kept from trial testimony. The jury returned a verdict in favor of Dr. Vivian, concluding that he was not negligent in his assessment, care, or treatment.
The 12th District Court of Appeals ruled that Dr. Vivian’s statements were properly excluded, finding that the Ohio’s apology law is ambiguous because according to the term’s dictionary definition, “apology” may or may not include an admission of fault. But the decision conflicted with the case of Davis v. Wooster Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine, Inc. in which the Court of Appeals for the 9th District in Ohio determined Ohio’s apology statute protects from admission “pure expressions of apology, sympathy, commiseration, condolence, compassion, or a general sense of benevolence,” but not “admission of fault.”
Resolving the split, the Ohio Supreme Court concluded that the state law is unambiguous and that its legislative intent is to shield expressions of regret for unexpected outcomes that may include acknowledgments that the patient’s medical care fell below the standard of care.
Ohio Supreme Court Chief Justice Maureen O’Connor and Justice William M. O’Neill partially dissented. While they agreed with the majority’s holding regarding the intent of Ohio’s apology law, Justice O’Connor wrote that the Dr. Vivian’s statements fell outside the law’s protection.
“Dr. Vivian’s statements were not an apology nor did they express regret or a type of shared sadness associated with sympathy or commiseration,” she wrote in her dissent.
At least 36 states have apology laws that shield against certain statements, expressions, or other evidence related to disclosures being used against physicians in court.
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
FDA warns of endoleaks associated with endovascular grafts for AAA
The Food and Drug Administration has reported an apparent increase in device-related adverse events from the use of endovascular graft repair (EVAR) to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA).
In a Letter to Health Care Providers issued on Sept. 28, the FDA indicated that “recent information from several sources, including FDA’s Medical Device Reporting system and Annual Clinical Updates to Physicians by the manufacturers, suggests an increase in the occurrence of Type III endoleaks.”
A Type III endoleak is defined by the failure to completely exclude the AAA from blood flow, thereby allowing a systematic arterial pressurization of the aneurysm sac, increasing the risk of rupture, which is a life-threatening event.
The FDA stated that predictors of Type III endoleaks included treatment with early-generation graft materials, the presence of calcified plaque, and inadequate overlap between graft components.
Secondary interventions to treat Type III endoleaks carry their own risk of adverse events.
It is recommended that health care providers should do the following:
- Consider lifelong surveillance of patients who have been treated with EVAR.
- Consider type III endoleaks in the differential diagnosis of patients who present with symptoms of potential aneurysm expansion or rupture.
- Discuss all treatment options in depth with patients before deciding on the best treatment for Type III endoleaks.
- Report any early or late device-related adverse events, including Type IIIa and Type IIIb endoleaks, associated with EVAR, as well as any device-related adverse events that occur as the result of a secondary intervention to treat Type III endoleaks.
These events should be reported to MedWatch, using the FDA’s Safety Information and Adverse Event Reporting Program Online Voluntary Reporting Form. A form also can be requested by calling 800-332-1088.
The FDA stated that it “continues to work with all manufacturers of endovascular graft systems to better understand this issue,” and that the agency would keep the public informed when significant new information becomes available.
The Food and Drug Administration has reported an apparent increase in device-related adverse events from the use of endovascular graft repair (EVAR) to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA).
In a Letter to Health Care Providers issued on Sept. 28, the FDA indicated that “recent information from several sources, including FDA’s Medical Device Reporting system and Annual Clinical Updates to Physicians by the manufacturers, suggests an increase in the occurrence of Type III endoleaks.”
A Type III endoleak is defined by the failure to completely exclude the AAA from blood flow, thereby allowing a systematic arterial pressurization of the aneurysm sac, increasing the risk of rupture, which is a life-threatening event.
The FDA stated that predictors of Type III endoleaks included treatment with early-generation graft materials, the presence of calcified plaque, and inadequate overlap between graft components.
Secondary interventions to treat Type III endoleaks carry their own risk of adverse events.
It is recommended that health care providers should do the following:
- Consider lifelong surveillance of patients who have been treated with EVAR.
- Consider type III endoleaks in the differential diagnosis of patients who present with symptoms of potential aneurysm expansion or rupture.
- Discuss all treatment options in depth with patients before deciding on the best treatment for Type III endoleaks.
- Report any early or late device-related adverse events, including Type IIIa and Type IIIb endoleaks, associated with EVAR, as well as any device-related adverse events that occur as the result of a secondary intervention to treat Type III endoleaks.
These events should be reported to MedWatch, using the FDA’s Safety Information and Adverse Event Reporting Program Online Voluntary Reporting Form. A form also can be requested by calling 800-332-1088.
The FDA stated that it “continues to work with all manufacturers of endovascular graft systems to better understand this issue,” and that the agency would keep the public informed when significant new information becomes available.
The Food and Drug Administration has reported an apparent increase in device-related adverse events from the use of endovascular graft repair (EVAR) to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA).
In a Letter to Health Care Providers issued on Sept. 28, the FDA indicated that “recent information from several sources, including FDA’s Medical Device Reporting system and Annual Clinical Updates to Physicians by the manufacturers, suggests an increase in the occurrence of Type III endoleaks.”
A Type III endoleak is defined by the failure to completely exclude the AAA from blood flow, thereby allowing a systematic arterial pressurization of the aneurysm sac, increasing the risk of rupture, which is a life-threatening event.
The FDA stated that predictors of Type III endoleaks included treatment with early-generation graft materials, the presence of calcified plaque, and inadequate overlap between graft components.
Secondary interventions to treat Type III endoleaks carry their own risk of adverse events.
It is recommended that health care providers should do the following:
- Consider lifelong surveillance of patients who have been treated with EVAR.
- Consider type III endoleaks in the differential diagnosis of patients who present with symptoms of potential aneurysm expansion or rupture.
- Discuss all treatment options in depth with patients before deciding on the best treatment for Type III endoleaks.
- Report any early or late device-related adverse events, including Type IIIa and Type IIIb endoleaks, associated with EVAR, as well as any device-related adverse events that occur as the result of a secondary intervention to treat Type III endoleaks.
These events should be reported to MedWatch, using the FDA’s Safety Information and Adverse Event Reporting Program Online Voluntary Reporting Form. A form also can be requested by calling 800-332-1088.
The FDA stated that it “continues to work with all manufacturers of endovascular graft systems to better understand this issue,” and that the agency would keep the public informed when significant new information becomes available.
Key clinical point:
Major finding: FDA monitoring sources have detected an apparent increase in the occurrence of Type III endoleaks following EVAR.
Data source: FDA’s Medical Device Reporting System and the Annual Clinical Updates to Physicians by the manufacturers.
Disclosures: None.
HHS Secretary resigns amid flight criticism
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Secretary Tom Price, MD, has resigned from his post following furor over his use of private planes for government business paid for by taxpayers.
In a Sept. 29 press statement, White House press secretary Sarah Huckabee Sanders said Dr. Price offered his resignation early Sept. 29 and that President Trump accepted. Don J. Wright, deputy assistant secretary for health and director of the office of disease prevention and health promotion, will serve as Acting Secretary effective Sept. 30, according to the statement.
Dr. Price’s resignation comes after widespread criticism over his alleged repeated use of taxpayer-funded charter flights. Politico first broke the story, reporting that he has taken at least 24 flights on private charter planes at taxpayers’ expense since early May, costing an estimated $400,000-$500,000. After the reports, Dr. Price announced that he planned to write a personal check to the government for $60,000 to cover the cost of the flights.
During a press briefing on Sept. 29, President Trump said he was “disappointed” with Dr. Price’s actions, and that the White House was looking into the accusations.
“I felt very badly because Secretary Price is a good man, but we are looking into it, and we’re looking into it very strongly,” President Trump said at the briefing.
In his resignation letter, posted on Twitter, Dr. Price expressed remorse for having created a distraction for the administration and said he was grateful for the opportunity to have served as HHS Secretary.
“I have spent 40 years both as a doctor and public servant putting people first,” Dr. Price said in his resignation letter. “I regret that the recent events have created a distraction from these important objectives. Success on these issues is more important than any one person. In order for you to move forward without further disruption, I am officially tendering my resignation.”
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Secretary Tom Price, MD, has resigned from his post following furor over his use of private planes for government business paid for by taxpayers.
In a Sept. 29 press statement, White House press secretary Sarah Huckabee Sanders said Dr. Price offered his resignation early Sept. 29 and that President Trump accepted. Don J. Wright, deputy assistant secretary for health and director of the office of disease prevention and health promotion, will serve as Acting Secretary effective Sept. 30, according to the statement.
Dr. Price’s resignation comes after widespread criticism over his alleged repeated use of taxpayer-funded charter flights. Politico first broke the story, reporting that he has taken at least 24 flights on private charter planes at taxpayers’ expense since early May, costing an estimated $400,000-$500,000. After the reports, Dr. Price announced that he planned to write a personal check to the government for $60,000 to cover the cost of the flights.
During a press briefing on Sept. 29, President Trump said he was “disappointed” with Dr. Price’s actions, and that the White House was looking into the accusations.
“I felt very badly because Secretary Price is a good man, but we are looking into it, and we’re looking into it very strongly,” President Trump said at the briefing.
In his resignation letter, posted on Twitter, Dr. Price expressed remorse for having created a distraction for the administration and said he was grateful for the opportunity to have served as HHS Secretary.
“I have spent 40 years both as a doctor and public servant putting people first,” Dr. Price said in his resignation letter. “I regret that the recent events have created a distraction from these important objectives. Success on these issues is more important than any one person. In order for you to move forward without further disruption, I am officially tendering my resignation.”
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Secretary Tom Price, MD, has resigned from his post following furor over his use of private planes for government business paid for by taxpayers.
In a Sept. 29 press statement, White House press secretary Sarah Huckabee Sanders said Dr. Price offered his resignation early Sept. 29 and that President Trump accepted. Don J. Wright, deputy assistant secretary for health and director of the office of disease prevention and health promotion, will serve as Acting Secretary effective Sept. 30, according to the statement.
Dr. Price’s resignation comes after widespread criticism over his alleged repeated use of taxpayer-funded charter flights. Politico first broke the story, reporting that he has taken at least 24 flights on private charter planes at taxpayers’ expense since early May, costing an estimated $400,000-$500,000. After the reports, Dr. Price announced that he planned to write a personal check to the government for $60,000 to cover the cost of the flights.
During a press briefing on Sept. 29, President Trump said he was “disappointed” with Dr. Price’s actions, and that the White House was looking into the accusations.
“I felt very badly because Secretary Price is a good man, but we are looking into it, and we’re looking into it very strongly,” President Trump said at the briefing.
In his resignation letter, posted on Twitter, Dr. Price expressed remorse for having created a distraction for the administration and said he was grateful for the opportunity to have served as HHS Secretary.
“I have spent 40 years both as a doctor and public servant putting people first,” Dr. Price said in his resignation letter. “I regret that the recent events have created a distraction from these important objectives. Success on these issues is more important than any one person. In order for you to move forward without further disruption, I am officially tendering my resignation.”
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
Japan approves product for hemophilia A
Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare has approved lonoctocog alfa (AFSTYLA®), a recombinant single-chain coagulation factor VIII product, for use in patients with hemophilia A.
The product is approved for use as routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes, for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding, and for perioperative management.
Lonoctocog alfa is the first and only single-chain recombinant factor VIII product specifically designed to treat hemophilia A.
According to CSL Behring, the company developing lonoctocog alfa, the product was designed to provide greater molecular stability and longer duration of action. Lonoctocog alfa uses a covalent bond to form one structural entity, a single polypeptide chain, to improve the stability of factor VIII and provide factor VIII activity with the option of twice-weekly dosing.
Lonoctocog alfa is also approved in the European Union, US, Canada, Switzerland, and Australia.
AFFINITY trials
Japan’s approval of lonoctocog alfa is based on results from the AFFINITY clinical development program, which includes a trial of children (n=84) and a trial of adolescents and adults (n=175).
Among patients who received lonoctocog alfa prophylactically in these trials, the median annualized bleeding rate was 1.14 in the adults/adolescents and 3.69 in children younger than 12.
In all, there were 1195 bleeding events—848 in the adults/adolescents and 347 in the children.
Ninety-four percent of bleeds in adults/adolescents and 96% of bleeds in pediatric patients were effectively controlled with no more than 2 infusions of lonoctocog alfa weekly.
Eighty-one percent of bleeds in adults/adolescents and 86% of bleeds in pediatric patients were controlled by a single infusion.
Researchers assessed safety in 258 patients from both studies. Adverse reactions occurred in 14 patients and included hypersensitivity (n=4), dizziness (n=2), paresthesia (n=1), rash (n=1), erythema (n=1), pruritus (n=1), pyrexia (n=1), injection-site pain (n=1), chills (n=1), and feeling hot (n=1).
One patient withdrew from treatment due to hypersensitivity.
None of the patients developed neutralizing antibodies to factor VIII or antibodies to host cell proteins. There were no reports of anaphylaxis or thrombosis.
Results from the trial of adolescents/adults were published in Blood in August 2016. Results from the trial of children were published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis in March 2017. ![]()
Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare has approved lonoctocog alfa (AFSTYLA®), a recombinant single-chain coagulation factor VIII product, for use in patients with hemophilia A.
The product is approved for use as routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes, for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding, and for perioperative management.
Lonoctocog alfa is the first and only single-chain recombinant factor VIII product specifically designed to treat hemophilia A.
According to CSL Behring, the company developing lonoctocog alfa, the product was designed to provide greater molecular stability and longer duration of action. Lonoctocog alfa uses a covalent bond to form one structural entity, a single polypeptide chain, to improve the stability of factor VIII and provide factor VIII activity with the option of twice-weekly dosing.
Lonoctocog alfa is also approved in the European Union, US, Canada, Switzerland, and Australia.
AFFINITY trials
Japan’s approval of lonoctocog alfa is based on results from the AFFINITY clinical development program, which includes a trial of children (n=84) and a trial of adolescents and adults (n=175).
Among patients who received lonoctocog alfa prophylactically in these trials, the median annualized bleeding rate was 1.14 in the adults/adolescents and 3.69 in children younger than 12.
In all, there were 1195 bleeding events—848 in the adults/adolescents and 347 in the children.
Ninety-four percent of bleeds in adults/adolescents and 96% of bleeds in pediatric patients were effectively controlled with no more than 2 infusions of lonoctocog alfa weekly.
Eighty-one percent of bleeds in adults/adolescents and 86% of bleeds in pediatric patients were controlled by a single infusion.
Researchers assessed safety in 258 patients from both studies. Adverse reactions occurred in 14 patients and included hypersensitivity (n=4), dizziness (n=2), paresthesia (n=1), rash (n=1), erythema (n=1), pruritus (n=1), pyrexia (n=1), injection-site pain (n=1), chills (n=1), and feeling hot (n=1).
One patient withdrew from treatment due to hypersensitivity.
None of the patients developed neutralizing antibodies to factor VIII or antibodies to host cell proteins. There were no reports of anaphylaxis or thrombosis.
Results from the trial of adolescents/adults were published in Blood in August 2016. Results from the trial of children were published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis in March 2017. ![]()
Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare has approved lonoctocog alfa (AFSTYLA®), a recombinant single-chain coagulation factor VIII product, for use in patients with hemophilia A.
The product is approved for use as routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes, for on-demand treatment and control of bleeding, and for perioperative management.
Lonoctocog alfa is the first and only single-chain recombinant factor VIII product specifically designed to treat hemophilia A.
According to CSL Behring, the company developing lonoctocog alfa, the product was designed to provide greater molecular stability and longer duration of action. Lonoctocog alfa uses a covalent bond to form one structural entity, a single polypeptide chain, to improve the stability of factor VIII and provide factor VIII activity with the option of twice-weekly dosing.
Lonoctocog alfa is also approved in the European Union, US, Canada, Switzerland, and Australia.
AFFINITY trials
Japan’s approval of lonoctocog alfa is based on results from the AFFINITY clinical development program, which includes a trial of children (n=84) and a trial of adolescents and adults (n=175).
Among patients who received lonoctocog alfa prophylactically in these trials, the median annualized bleeding rate was 1.14 in the adults/adolescents and 3.69 in children younger than 12.
In all, there were 1195 bleeding events—848 in the adults/adolescents and 347 in the children.
Ninety-four percent of bleeds in adults/adolescents and 96% of bleeds in pediatric patients were effectively controlled with no more than 2 infusions of lonoctocog alfa weekly.
Eighty-one percent of bleeds in adults/adolescents and 86% of bleeds in pediatric patients were controlled by a single infusion.
Researchers assessed safety in 258 patients from both studies. Adverse reactions occurred in 14 patients and included hypersensitivity (n=4), dizziness (n=2), paresthesia (n=1), rash (n=1), erythema (n=1), pruritus (n=1), pyrexia (n=1), injection-site pain (n=1), chills (n=1), and feeling hot (n=1).
One patient withdrew from treatment due to hypersensitivity.
None of the patients developed neutralizing antibodies to factor VIII or antibodies to host cell proteins. There were no reports of anaphylaxis or thrombosis.
Results from the trial of adolescents/adults were published in Blood in August 2016. Results from the trial of children were published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis in March 2017. ![]()
Add aggressiveness to mixed features specifier for major depressive episode
PARIS – Aggressiveness deserves to be incorporated in the next Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders update as a new clinical criterion triggering application of the “with mixed features” specifier in patients diagnosed with a major depressive episode, Norma Verdolini, MD, said at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“Aggressiveness might be a trait component of bipolarity and a diagnostic indicator of ‘mixicity’ in patients with a major depressive episode. This has implications for the therapeutic strategy,” said Dr. Verdolini of the bipolar disorders unit at the University of Barcelona Institute of Neurosciences.
The BRIDGE-II-MIX study was a cross-sectional observational study of 2,811 adults with MDE at 239 centers in eight European countries (J Clin Psychiatry. 2015 Mar;76[3]:e351-8). Three hundred ninety-nine participants (14.2%) met the operational definition of physical or verbal aggressiveness used in Dr. Verdolini’s new post-hoc analysis.
Statistically significant and clinically meaningful differences were found between MDE patients with aggressiveness (MDE-aggro) and MDE without aggressiveness. For example, the MDE-aggro group was twice as likely to meet DSM-IV-TR criteria for bipolar disorder I. Twenty-seven percent of the MDE-aggro group met DSM-5 criteria for a mixed state, meaning both depressed mood and mania in the same episode, compared with just 4% of the MDE-no-aggro group.
The MDE-aggro patients also had a strikingly greater prevalence of comorbid borderline personality disorder, by a margin of 20% versus 4%. They had a younger mean age at their first depressive episode: 29.9 years old, compared with 36.1 in the MDE-no-aggro group. The MDE-aggro patients had more prior mood episodes and a greater number of lifetime suicide attempts. In addition, they had significantly more severe depression, mania, and bipolar disorder scores on the Clinical Global Impression Scale for Bipolar Disorder.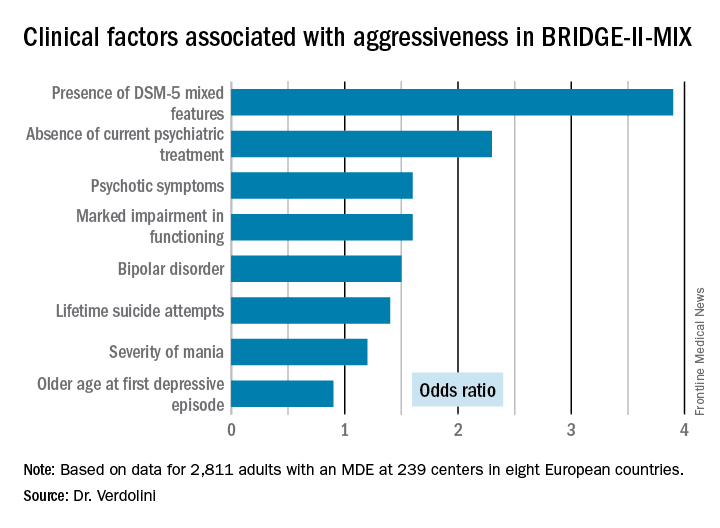
“Our results should prompt reconsideration of the diagnostic criteria for the mixed features specifier. The detection of aggression in MDE could represent a therapeutic target in personalized pharmacological treatment for bipolar disorder,” Dr. Verdolini concluded.
The BRIDGE-II-MIX study was sponsored by Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Verdolini reported receiving research funding from the company.
PARIS – Aggressiveness deserves to be incorporated in the next Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders update as a new clinical criterion triggering application of the “with mixed features” specifier in patients diagnosed with a major depressive episode, Norma Verdolini, MD, said at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“Aggressiveness might be a trait component of bipolarity and a diagnostic indicator of ‘mixicity’ in patients with a major depressive episode. This has implications for the therapeutic strategy,” said Dr. Verdolini of the bipolar disorders unit at the University of Barcelona Institute of Neurosciences.
The BRIDGE-II-MIX study was a cross-sectional observational study of 2,811 adults with MDE at 239 centers in eight European countries (J Clin Psychiatry. 2015 Mar;76[3]:e351-8). Three hundred ninety-nine participants (14.2%) met the operational definition of physical or verbal aggressiveness used in Dr. Verdolini’s new post-hoc analysis.
Statistically significant and clinically meaningful differences were found between MDE patients with aggressiveness (MDE-aggro) and MDE without aggressiveness. For example, the MDE-aggro group was twice as likely to meet DSM-IV-TR criteria for bipolar disorder I. Twenty-seven percent of the MDE-aggro group met DSM-5 criteria for a mixed state, meaning both depressed mood and mania in the same episode, compared with just 4% of the MDE-no-aggro group.
The MDE-aggro patients also had a strikingly greater prevalence of comorbid borderline personality disorder, by a margin of 20% versus 4%. They had a younger mean age at their first depressive episode: 29.9 years old, compared with 36.1 in the MDE-no-aggro group. The MDE-aggro patients had more prior mood episodes and a greater number of lifetime suicide attempts. In addition, they had significantly more severe depression, mania, and bipolar disorder scores on the Clinical Global Impression Scale for Bipolar Disorder.
“Our results should prompt reconsideration of the diagnostic criteria for the mixed features specifier. The detection of aggression in MDE could represent a therapeutic target in personalized pharmacological treatment for bipolar disorder,” Dr. Verdolini concluded.
The BRIDGE-II-MIX study was sponsored by Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Verdolini reported receiving research funding from the company.
PARIS – Aggressiveness deserves to be incorporated in the next Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders update as a new clinical criterion triggering application of the “with mixed features” specifier in patients diagnosed with a major depressive episode, Norma Verdolini, MD, said at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“Aggressiveness might be a trait component of bipolarity and a diagnostic indicator of ‘mixicity’ in patients with a major depressive episode. This has implications for the therapeutic strategy,” said Dr. Verdolini of the bipolar disorders unit at the University of Barcelona Institute of Neurosciences.
The BRIDGE-II-MIX study was a cross-sectional observational study of 2,811 adults with MDE at 239 centers in eight European countries (J Clin Psychiatry. 2015 Mar;76[3]:e351-8). Three hundred ninety-nine participants (14.2%) met the operational definition of physical or verbal aggressiveness used in Dr. Verdolini’s new post-hoc analysis.
Statistically significant and clinically meaningful differences were found between MDE patients with aggressiveness (MDE-aggro) and MDE without aggressiveness. For example, the MDE-aggro group was twice as likely to meet DSM-IV-TR criteria for bipolar disorder I. Twenty-seven percent of the MDE-aggro group met DSM-5 criteria for a mixed state, meaning both depressed mood and mania in the same episode, compared with just 4% of the MDE-no-aggro group.
The MDE-aggro patients also had a strikingly greater prevalence of comorbid borderline personality disorder, by a margin of 20% versus 4%. They had a younger mean age at their first depressive episode: 29.9 years old, compared with 36.1 in the MDE-no-aggro group. The MDE-aggro patients had more prior mood episodes and a greater number of lifetime suicide attempts. In addition, they had significantly more severe depression, mania, and bipolar disorder scores on the Clinical Global Impression Scale for Bipolar Disorder.
“Our results should prompt reconsideration of the diagnostic criteria for the mixed features specifier. The detection of aggression in MDE could represent a therapeutic target in personalized pharmacological treatment for bipolar disorder,” Dr. Verdolini concluded.
The BRIDGE-II-MIX study was sponsored by Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Verdolini reported receiving research funding from the company.
AT THE ECNP CONGRESS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients who fulfilled the DSM-5 criteria for a major depressive episode with mixed features were 3.9-fold more likely to meet investigators’ operational definition of aggressiveness.
Data source: This was a post-hoc analysis of the BRIDGE-II-MIX study, an observational cross-sectional study of 2,811 adults experiencing a major depressive episode.
Disclosures: The BRIDGE-II-MIX study was sponsored by Sanofi-Aventis. The presenter reported receiving research funding from the company.
Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome
To the Editor:
A 55-year-old man presented with hyperpigmented brown macules on the lips, hands, and fingertips of 6 years’ duration. The spots were persistent, asymptomatic, and had not changed in size. The patient denied a history of alopecia or dystrophic nails. He also denied a family history of similar skin findings. He had no personal history of cancer and a colonoscopy performed 5 years prior revealed no notable abnormalities. His medications included amlodipine and hydrocodone-acetaminophen. His mother died of “abdominal bleeding” at 74 years of age and his father died of a brain tumor at 64 years of age. Physical examination demonstrated numerous well-defined, dark brown macules of variable size distributed on the lower and upper mucosal lips (Figure 1A), buccal mucosa, hard palate, and gingiva, as well as the dorsal aspect of the fingers (Figure 1B) and volar aspect of the fingertips (Figure 1C).

A shave biopsy of a dark brown macule from the lower lip (Figure 2) was performed. Histopathologic examination revealed pigmentation of the basal layer of the epidermis with pigment-laden cells in the dermis immediately deep to the surface epithelium. Immunoperoxidase stains showed a normal number and distribution of melanocytes.
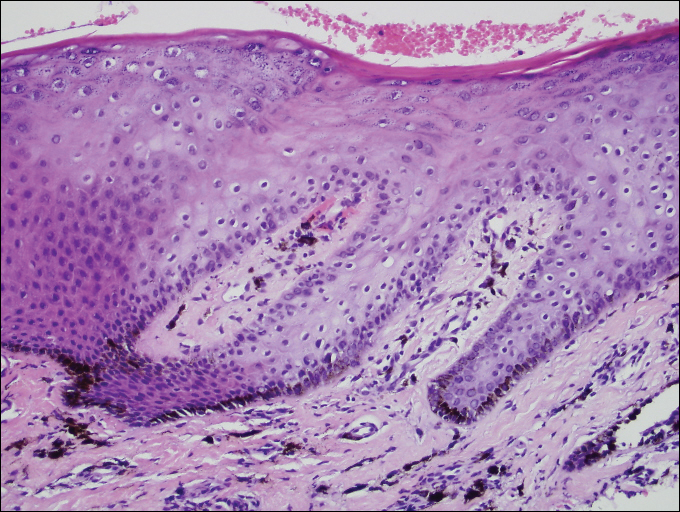
A diagnosis of Laugier-Hunziker syndrome (LHS) was made given the age of onset; distribution of pigmentation; and lack of pathologic colonoscopic findings, personal history of cancer, or gastrointestinal tract symptoms.
Benign hyperpigmentation of the lips and fingers has been reported.1 The average age of onset of LHS is 52 years, and it typically is diagnosed in white adults.1,2 In LHS, pigmentation is most commonly distributed on the lips, especially the lower lips and oral mucosa.2 Pigmentation of the nails in the form of longitudinal melanonychia is present in approximately half of cases.2,3 There also may be pigmentation of the neck; thorax; abdomen; and acral surfaces, especially the fingertips.1-3 Rarely, pigmented macules can occur on the genitalia or sclera.1,2 Unlike Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, the diagnosis of LHS does not result from a germline mutation and carries no risk of gastrointestinal polyposis or internal malignancy.3,4 The histopathology of a pigmented macule of LHS shows a normal number and morphology of melanocytes. Epidermal basement membrane pigmentation is common, with pigment-laden macrophages evident in the papillary dermis.3
RELATED ARTICLE: Asymptomatic Lower Lip Hyperpigmentation From Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome
The differential diagnosis of multiple lentigines is broad and includes Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; LEOPARD (lentigines, electrocardiographic conduction abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonary stenosis, abnormalities of genitalia, retardation of growth, deafness) syndrome; Carney complexes, including LAMB (lentigines, atrial myxoma, mucocutaneous myxoma, blue nevi) and NAME (nevi, atrial myxoma, myxoid neurofibroma, ephelide) syndromes5; primary adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison disease); and idiopathic melanoplakia.2 Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, an autosomal-dominant syndrome with mucocutaneous lentigines, has a similar clinical appearance to LHS; therefore, it is necessary to exclude this diagnosis due to its association with intestinal hamartomatous polyps and internal malignancies (Table).3,6,7
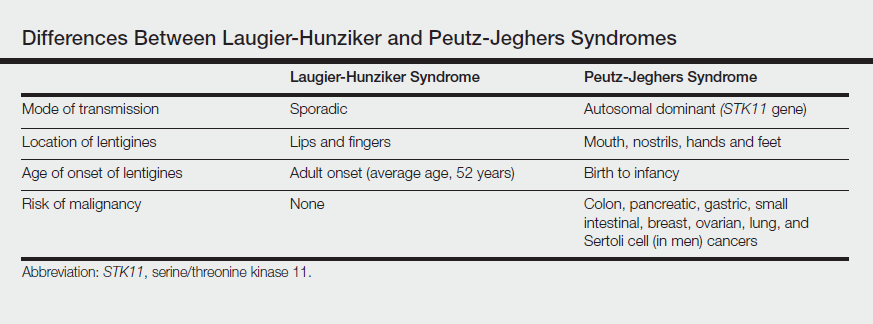
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is characterized by mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation and intestinal hamartomatous polyposis and is associated with internal malignancies of the colon, breast, pancreas, stomach, small intestines, ovaries, lung, and Sertoli cells in men.6,7 Associated gastrointestinal tract malignancies in descending order of frequency are colon (39%), pancreatic (36%), gastric (29%), and small intestine (13%).1 It is caused by a germ line mutation of the serine/threonine kinase 11 gene, STK11. Although the appearance and distribution of the mucocutaneous lentigines is similar to individuals with LHS, by contrast the lentiginosis in individuals with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is present from birth or develops during infancy.6 Aggressive cancer screening guidelines aid in early detection and begin at 8 years of age with a baseline colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy; future screening is dictated by the presence or absence of polyps. If no polyps are detected at 8 years of age, a colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy are repeated at 18 years of age and then every 3 years until 50 years of age.8
In an adult patient, the diagnosis of LHS can be made clinically and a correct diagnosis prevents frequent and unpleasant gastrointestinal tract cancer screening examinations. Lampe et al2 described a man with LHS who was incorrectly diagnosed with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and experienced a colonic perforation as a complication of a screening colonoscopy. Their case report underscores the importance of making the correct diagnosis of LHS to avoid undertaking unnecessary aggressive cancer screening regimens.2
Although LHS is a benign condition that does not require treatment, Q-switched alexandrite or erbium:YAG laser therapy has been shown to improve the pigmentary findings associated with LHS.9,10 It has been suggested that LHS should be renamed Laugier-Hunziker pigmentation2 or mucocutaneous lentiginosis of Laugier and Hunziker1 to differentiate LHS as simply a disorder of pigmentation rather than a potentially morbid genetic defect, as in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
- Moore RT, Chae KA, Rhodes AR. Laugier and Hunziker pigmentation: a lentiginous proliferation of melanocytes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl):S70-S74.
- Lampe AK, Hampton PJ, Woodford-Richens K, et al. Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome: an important differential diagnosis for Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. J Med Genet. 2003;40:E77.
- Baran R. Longitudinal melanotic streaks as a clue for Laugier-Hunziker syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1148-1149.
- Grimes P, Nordlund JJ, Pandya AG, et al. Increasing our understanding of pigmentary disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(5 suppl 2):S255-S261.
- Bertherat J. Carney complex (CNC). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006;1:21.
- Giardiello FM, Brensinger JD, Tersemette AC, et al. Very high risk of cancer in Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:1447-1453.
- Brosens LA, van Hattem WA, Jansen M, et al. Gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes. Curr Mol Med. 2007;7:29-46.
- Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010;59:975-986.
- Zuo YG, Ma DL, Jin HZ, et al. Treatment of Laugier-Hunziker syndrome with the Q-switched alexandrite laser in 22 Chinese patients. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010;302:125-130.
- Ergun S, Saruhanog˘lu A, Migliari DA, et al. Refractory pigmentation associated with Laugier-Hunziker syndrome following Er:YAG laser treatment [published online December 3, 2013]. Case Rep Dent. 2013;2013:561040.
To the Editor:
A 55-year-old man presented with hyperpigmented brown macules on the lips, hands, and fingertips of 6 years’ duration. The spots were persistent, asymptomatic, and had not changed in size. The patient denied a history of alopecia or dystrophic nails. He also denied a family history of similar skin findings. He had no personal history of cancer and a colonoscopy performed 5 years prior revealed no notable abnormalities. His medications included amlodipine and hydrocodone-acetaminophen. His mother died of “abdominal bleeding” at 74 years of age and his father died of a brain tumor at 64 years of age. Physical examination demonstrated numerous well-defined, dark brown macules of variable size distributed on the lower and upper mucosal lips (Figure 1A), buccal mucosa, hard palate, and gingiva, as well as the dorsal aspect of the fingers (Figure 1B) and volar aspect of the fingertips (Figure 1C).

A shave biopsy of a dark brown macule from the lower lip (Figure 2) was performed. Histopathologic examination revealed pigmentation of the basal layer of the epidermis with pigment-laden cells in the dermis immediately deep to the surface epithelium. Immunoperoxidase stains showed a normal number and distribution of melanocytes.

A diagnosis of Laugier-Hunziker syndrome (LHS) was made given the age of onset; distribution of pigmentation; and lack of pathologic colonoscopic findings, personal history of cancer, or gastrointestinal tract symptoms.
Benign hyperpigmentation of the lips and fingers has been reported.1 The average age of onset of LHS is 52 years, and it typically is diagnosed in white adults.1,2 In LHS, pigmentation is most commonly distributed on the lips, especially the lower lips and oral mucosa.2 Pigmentation of the nails in the form of longitudinal melanonychia is present in approximately half of cases.2,3 There also may be pigmentation of the neck; thorax; abdomen; and acral surfaces, especially the fingertips.1-3 Rarely, pigmented macules can occur on the genitalia or sclera.1,2 Unlike Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, the diagnosis of LHS does not result from a germline mutation and carries no risk of gastrointestinal polyposis or internal malignancy.3,4 The histopathology of a pigmented macule of LHS shows a normal number and morphology of melanocytes. Epidermal basement membrane pigmentation is common, with pigment-laden macrophages evident in the papillary dermis.3
RELATED ARTICLE: Asymptomatic Lower Lip Hyperpigmentation From Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome
The differential diagnosis of multiple lentigines is broad and includes Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; LEOPARD (lentigines, electrocardiographic conduction abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonary stenosis, abnormalities of genitalia, retardation of growth, deafness) syndrome; Carney complexes, including LAMB (lentigines, atrial myxoma, mucocutaneous myxoma, blue nevi) and NAME (nevi, atrial myxoma, myxoid neurofibroma, ephelide) syndromes5; primary adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison disease); and idiopathic melanoplakia.2 Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, an autosomal-dominant syndrome with mucocutaneous lentigines, has a similar clinical appearance to LHS; therefore, it is necessary to exclude this diagnosis due to its association with intestinal hamartomatous polyps and internal malignancies (Table).3,6,7

Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is characterized by mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation and intestinal hamartomatous polyposis and is associated with internal malignancies of the colon, breast, pancreas, stomach, small intestines, ovaries, lung, and Sertoli cells in men.6,7 Associated gastrointestinal tract malignancies in descending order of frequency are colon (39%), pancreatic (36%), gastric (29%), and small intestine (13%).1 It is caused by a germ line mutation of the serine/threonine kinase 11 gene, STK11. Although the appearance and distribution of the mucocutaneous lentigines is similar to individuals with LHS, by contrast the lentiginosis in individuals with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is present from birth or develops during infancy.6 Aggressive cancer screening guidelines aid in early detection and begin at 8 years of age with a baseline colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy; future screening is dictated by the presence or absence of polyps. If no polyps are detected at 8 years of age, a colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy are repeated at 18 years of age and then every 3 years until 50 years of age.8
In an adult patient, the diagnosis of LHS can be made clinically and a correct diagnosis prevents frequent and unpleasant gastrointestinal tract cancer screening examinations. Lampe et al2 described a man with LHS who was incorrectly diagnosed with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and experienced a colonic perforation as a complication of a screening colonoscopy. Their case report underscores the importance of making the correct diagnosis of LHS to avoid undertaking unnecessary aggressive cancer screening regimens.2
Although LHS is a benign condition that does not require treatment, Q-switched alexandrite or erbium:YAG laser therapy has been shown to improve the pigmentary findings associated with LHS.9,10 It has been suggested that LHS should be renamed Laugier-Hunziker pigmentation2 or mucocutaneous lentiginosis of Laugier and Hunziker1 to differentiate LHS as simply a disorder of pigmentation rather than a potentially morbid genetic defect, as in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
To the Editor:
A 55-year-old man presented with hyperpigmented brown macules on the lips, hands, and fingertips of 6 years’ duration. The spots were persistent, asymptomatic, and had not changed in size. The patient denied a history of alopecia or dystrophic nails. He also denied a family history of similar skin findings. He had no personal history of cancer and a colonoscopy performed 5 years prior revealed no notable abnormalities. His medications included amlodipine and hydrocodone-acetaminophen. His mother died of “abdominal bleeding” at 74 years of age and his father died of a brain tumor at 64 years of age. Physical examination demonstrated numerous well-defined, dark brown macules of variable size distributed on the lower and upper mucosal lips (Figure 1A), buccal mucosa, hard palate, and gingiva, as well as the dorsal aspect of the fingers (Figure 1B) and volar aspect of the fingertips (Figure 1C).

A shave biopsy of a dark brown macule from the lower lip (Figure 2) was performed. Histopathologic examination revealed pigmentation of the basal layer of the epidermis with pigment-laden cells in the dermis immediately deep to the surface epithelium. Immunoperoxidase stains showed a normal number and distribution of melanocytes.

A diagnosis of Laugier-Hunziker syndrome (LHS) was made given the age of onset; distribution of pigmentation; and lack of pathologic colonoscopic findings, personal history of cancer, or gastrointestinal tract symptoms.
Benign hyperpigmentation of the lips and fingers has been reported.1 The average age of onset of LHS is 52 years, and it typically is diagnosed in white adults.1,2 In LHS, pigmentation is most commonly distributed on the lips, especially the lower lips and oral mucosa.2 Pigmentation of the nails in the form of longitudinal melanonychia is present in approximately half of cases.2,3 There also may be pigmentation of the neck; thorax; abdomen; and acral surfaces, especially the fingertips.1-3 Rarely, pigmented macules can occur on the genitalia or sclera.1,2 Unlike Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, the diagnosis of LHS does not result from a germline mutation and carries no risk of gastrointestinal polyposis or internal malignancy.3,4 The histopathology of a pigmented macule of LHS shows a normal number and morphology of melanocytes. Epidermal basement membrane pigmentation is common, with pigment-laden macrophages evident in the papillary dermis.3
RELATED ARTICLE: Asymptomatic Lower Lip Hyperpigmentation From Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome
The differential diagnosis of multiple lentigines is broad and includes Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; LEOPARD (lentigines, electrocardiographic conduction abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonary stenosis, abnormalities of genitalia, retardation of growth, deafness) syndrome; Carney complexes, including LAMB (lentigines, atrial myxoma, mucocutaneous myxoma, blue nevi) and NAME (nevi, atrial myxoma, myxoid neurofibroma, ephelide) syndromes5; primary adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison disease); and idiopathic melanoplakia.2 Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, an autosomal-dominant syndrome with mucocutaneous lentigines, has a similar clinical appearance to LHS; therefore, it is necessary to exclude this diagnosis due to its association with intestinal hamartomatous polyps and internal malignancies (Table).3,6,7

Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is characterized by mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation and intestinal hamartomatous polyposis and is associated with internal malignancies of the colon, breast, pancreas, stomach, small intestines, ovaries, lung, and Sertoli cells in men.6,7 Associated gastrointestinal tract malignancies in descending order of frequency are colon (39%), pancreatic (36%), gastric (29%), and small intestine (13%).1 It is caused by a germ line mutation of the serine/threonine kinase 11 gene, STK11. Although the appearance and distribution of the mucocutaneous lentigines is similar to individuals with LHS, by contrast the lentiginosis in individuals with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is present from birth or develops during infancy.6 Aggressive cancer screening guidelines aid in early detection and begin at 8 years of age with a baseline colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy; future screening is dictated by the presence or absence of polyps. If no polyps are detected at 8 years of age, a colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy are repeated at 18 years of age and then every 3 years until 50 years of age.8
In an adult patient, the diagnosis of LHS can be made clinically and a correct diagnosis prevents frequent and unpleasant gastrointestinal tract cancer screening examinations. Lampe et al2 described a man with LHS who was incorrectly diagnosed with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and experienced a colonic perforation as a complication of a screening colonoscopy. Their case report underscores the importance of making the correct diagnosis of LHS to avoid undertaking unnecessary aggressive cancer screening regimens.2
Although LHS is a benign condition that does not require treatment, Q-switched alexandrite or erbium:YAG laser therapy has been shown to improve the pigmentary findings associated with LHS.9,10 It has been suggested that LHS should be renamed Laugier-Hunziker pigmentation2 or mucocutaneous lentiginosis of Laugier and Hunziker1 to differentiate LHS as simply a disorder of pigmentation rather than a potentially morbid genetic defect, as in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
- Moore RT, Chae KA, Rhodes AR. Laugier and Hunziker pigmentation: a lentiginous proliferation of melanocytes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl):S70-S74.
- Lampe AK, Hampton PJ, Woodford-Richens K, et al. Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome: an important differential diagnosis for Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. J Med Genet. 2003;40:E77.
- Baran R. Longitudinal melanotic streaks as a clue for Laugier-Hunziker syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1148-1149.
- Grimes P, Nordlund JJ, Pandya AG, et al. Increasing our understanding of pigmentary disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(5 suppl 2):S255-S261.
- Bertherat J. Carney complex (CNC). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006;1:21.
- Giardiello FM, Brensinger JD, Tersemette AC, et al. Very high risk of cancer in Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:1447-1453.
- Brosens LA, van Hattem WA, Jansen M, et al. Gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes. Curr Mol Med. 2007;7:29-46.
- Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010;59:975-986.
- Zuo YG, Ma DL, Jin HZ, et al. Treatment of Laugier-Hunziker syndrome with the Q-switched alexandrite laser in 22 Chinese patients. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010;302:125-130.
- Ergun S, Saruhanog˘lu A, Migliari DA, et al. Refractory pigmentation associated with Laugier-Hunziker syndrome following Er:YAG laser treatment [published online December 3, 2013]. Case Rep Dent. 2013;2013:561040.
- Moore RT, Chae KA, Rhodes AR. Laugier and Hunziker pigmentation: a lentiginous proliferation of melanocytes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl):S70-S74.
- Lampe AK, Hampton PJ, Woodford-Richens K, et al. Laugier-Hunziker Syndrome: an important differential diagnosis for Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. J Med Genet. 2003;40:E77.
- Baran R. Longitudinal melanotic streaks as a clue for Laugier-Hunziker syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1148-1149.
- Grimes P, Nordlund JJ, Pandya AG, et al. Increasing our understanding of pigmentary disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(5 suppl 2):S255-S261.
- Bertherat J. Carney complex (CNC). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006;1:21.
- Giardiello FM, Brensinger JD, Tersemette AC, et al. Very high risk of cancer in Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:1447-1453.
- Brosens LA, van Hattem WA, Jansen M, et al. Gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes. Curr Mol Med. 2007;7:29-46.
- Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010;59:975-986.
- Zuo YG, Ma DL, Jin HZ, et al. Treatment of Laugier-Hunziker syndrome with the Q-switched alexandrite laser in 22 Chinese patients. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010;302:125-130.
- Ergun S, Saruhanog˘lu A, Migliari DA, et al. Refractory pigmentation associated with Laugier-Hunziker syndrome following Er:YAG laser treatment [published online December 3, 2013]. Case Rep Dent. 2013;2013:561040.
Practice Points
- Laugier-Hunziker syndrome (LHS) comprises benign mucosal pigmentation in the absence of gastrointestinal pathology.
- Differentiating LHS from Peutz-Jeghers syndrome can prevent unnecessary aggressive cancer screening protocols.
- The average age of onset of LHS is 52 years and typically occurs in white adults.
- Pigmentation in LHS is most commonly distributed on the lower lips and oral mucosa.
Robot-assisted abdominoperineal resection outperforms open or laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancers
MADRID – The automaton uprising continues: Robot-assisted abdominoperineal resection (APR) can be safely performed in patients with rectal cancers within 5 cm of the anal verge, with surgical results equivalent to those seen with open or laparoscopic APR, investigators say.
Robot-assisted procedures were associated with a significantly lower rate of postoperative complications and with faster functional recovery than either laparoscopic or open surgery in a randomized trial, reported Jianmin Xu, MD, PhD., from Fudan University in Shanghai, China, and colleagues in a scientific poster presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“Retrospective studies have showed that robotic surgery was better than laparoscopic surgery in ensuring radical resection, reducing complications, and promoting recovery. However, there is no clinical trial reported for robotic surgery for rectal cancer. Thus, we conduct this randomized controlled trial to compare the safety and efficacy of robotic, laparoscopic, and open surgery for low rectal cancer,” they wrote.
Dr. Xu and colleagues enrolled 506 patients from 18 to 75 years of age with clinical stage T1 to T3 cancers within 5 cm of the anal verge and no distant metastases and randomly assigned them to resection with either a robot-assisted, laparoscopic, or open APR technique. Three of the 506 patients randomized did not undergo resection, leaving 503 for the per-protocol analysis presented here.
For the primary endpoint of complications rates within 30 days following surgery, the investigators found that patients assigned to robotic-assisted surgery (173 patients) had a total complication rate of 10.4%, compared with 18.8% for 176 patients assigned to laparoscopy (P = .027), and 26% for 154 assigned to open APR (P less than .001). The latter group included four patients assigned to laparoscopy whose procedures were converted to open surgery.
Among patients without complications, robot-assisted procedures were also associated with faster recovery, as measured by days to first flatus, at a median of 1 vs. 2 for laparoscopy and 3 for open procedures (P less than .001 for robots vs. each other surgery type). The robotic surgery was also significantly associated with fewer days to first automatic urination (median 2 vs. 4 for each of the other procedures; P less than .001), and with fewer days to discharge (median 5 vs. 7 for the other procedures; P less than .001).
"These are excellent postoperative complication rates reported, especially for the robotic treatment group, commented Thomas Gruenberger, MD, an oncologic surgeon at Rudolf Hospital in Vienna, in a poster discussion session.
“We all are now favoring laparoscopic surgery for these kinds of patients. The robot is a nice thing to have; however, we cannot use it in every hospital because it’s still quite expensive,” he said.
“We require – and this is a secondary endpoint of the study – long-term follow-up for local and distant outcomes,” he added,
The investigators did not report a funding source. All authors declared having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gruenberger disclosed research funding, speakers bureau participation, and/or advisory roles with several companies.
MADRID – The automaton uprising continues: Robot-assisted abdominoperineal resection (APR) can be safely performed in patients with rectal cancers within 5 cm of the anal verge, with surgical results equivalent to those seen with open or laparoscopic APR, investigators say.
Robot-assisted procedures were associated with a significantly lower rate of postoperative complications and with faster functional recovery than either laparoscopic or open surgery in a randomized trial, reported Jianmin Xu, MD, PhD., from Fudan University in Shanghai, China, and colleagues in a scientific poster presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“Retrospective studies have showed that robotic surgery was better than laparoscopic surgery in ensuring radical resection, reducing complications, and promoting recovery. However, there is no clinical trial reported for robotic surgery for rectal cancer. Thus, we conduct this randomized controlled trial to compare the safety and efficacy of robotic, laparoscopic, and open surgery for low rectal cancer,” they wrote.
Dr. Xu and colleagues enrolled 506 patients from 18 to 75 years of age with clinical stage T1 to T3 cancers within 5 cm of the anal verge and no distant metastases and randomly assigned them to resection with either a robot-assisted, laparoscopic, or open APR technique. Three of the 506 patients randomized did not undergo resection, leaving 503 for the per-protocol analysis presented here.
For the primary endpoint of complications rates within 30 days following surgery, the investigators found that patients assigned to robotic-assisted surgery (173 patients) had a total complication rate of 10.4%, compared with 18.8% for 176 patients assigned to laparoscopy (P = .027), and 26% for 154 assigned to open APR (P less than .001). The latter group included four patients assigned to laparoscopy whose procedures were converted to open surgery.
Among patients without complications, robot-assisted procedures were also associated with faster recovery, as measured by days to first flatus, at a median of 1 vs. 2 for laparoscopy and 3 for open procedures (P less than .001 for robots vs. each other surgery type). The robotic surgery was also significantly associated with fewer days to first automatic urination (median 2 vs. 4 for each of the other procedures; P less than .001), and with fewer days to discharge (median 5 vs. 7 for the other procedures; P less than .001).
"These are excellent postoperative complication rates reported, especially for the robotic treatment group, commented Thomas Gruenberger, MD, an oncologic surgeon at Rudolf Hospital in Vienna, in a poster discussion session.
“We all are now favoring laparoscopic surgery for these kinds of patients. The robot is a nice thing to have; however, we cannot use it in every hospital because it’s still quite expensive,” he said.
“We require – and this is a secondary endpoint of the study – long-term follow-up for local and distant outcomes,” he added,
The investigators did not report a funding source. All authors declared having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gruenberger disclosed research funding, speakers bureau participation, and/or advisory roles with several companies.
MADRID – The automaton uprising continues: Robot-assisted abdominoperineal resection (APR) can be safely performed in patients with rectal cancers within 5 cm of the anal verge, with surgical results equivalent to those seen with open or laparoscopic APR, investigators say.
Robot-assisted procedures were associated with a significantly lower rate of postoperative complications and with faster functional recovery than either laparoscopic or open surgery in a randomized trial, reported Jianmin Xu, MD, PhD., from Fudan University in Shanghai, China, and colleagues in a scientific poster presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“Retrospective studies have showed that robotic surgery was better than laparoscopic surgery in ensuring radical resection, reducing complications, and promoting recovery. However, there is no clinical trial reported for robotic surgery for rectal cancer. Thus, we conduct this randomized controlled trial to compare the safety and efficacy of robotic, laparoscopic, and open surgery for low rectal cancer,” they wrote.
Dr. Xu and colleagues enrolled 506 patients from 18 to 75 years of age with clinical stage T1 to T3 cancers within 5 cm of the anal verge and no distant metastases and randomly assigned them to resection with either a robot-assisted, laparoscopic, or open APR technique. Three of the 506 patients randomized did not undergo resection, leaving 503 for the per-protocol analysis presented here.
For the primary endpoint of complications rates within 30 days following surgery, the investigators found that patients assigned to robotic-assisted surgery (173 patients) had a total complication rate of 10.4%, compared with 18.8% for 176 patients assigned to laparoscopy (P = .027), and 26% for 154 assigned to open APR (P less than .001). The latter group included four patients assigned to laparoscopy whose procedures were converted to open surgery.
Among patients without complications, robot-assisted procedures were also associated with faster recovery, as measured by days to first flatus, at a median of 1 vs. 2 for laparoscopy and 3 for open procedures (P less than .001 for robots vs. each other surgery type). The robotic surgery was also significantly associated with fewer days to first automatic urination (median 2 vs. 4 for each of the other procedures; P less than .001), and with fewer days to discharge (median 5 vs. 7 for the other procedures; P less than .001).
"These are excellent postoperative complication rates reported, especially for the robotic treatment group, commented Thomas Gruenberger, MD, an oncologic surgeon at Rudolf Hospital in Vienna, in a poster discussion session.
“We all are now favoring laparoscopic surgery for these kinds of patients. The robot is a nice thing to have; however, we cannot use it in every hospital because it’s still quite expensive,” he said.
“We require – and this is a secondary endpoint of the study – long-term follow-up for local and distant outcomes,” he added,
The investigators did not report a funding source. All authors declared having no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gruenberger disclosed research funding, speakers bureau participation, and/or advisory roles with several companies.
AT ESMO 2017