User login
C-section linked to serious infection in preschoolers
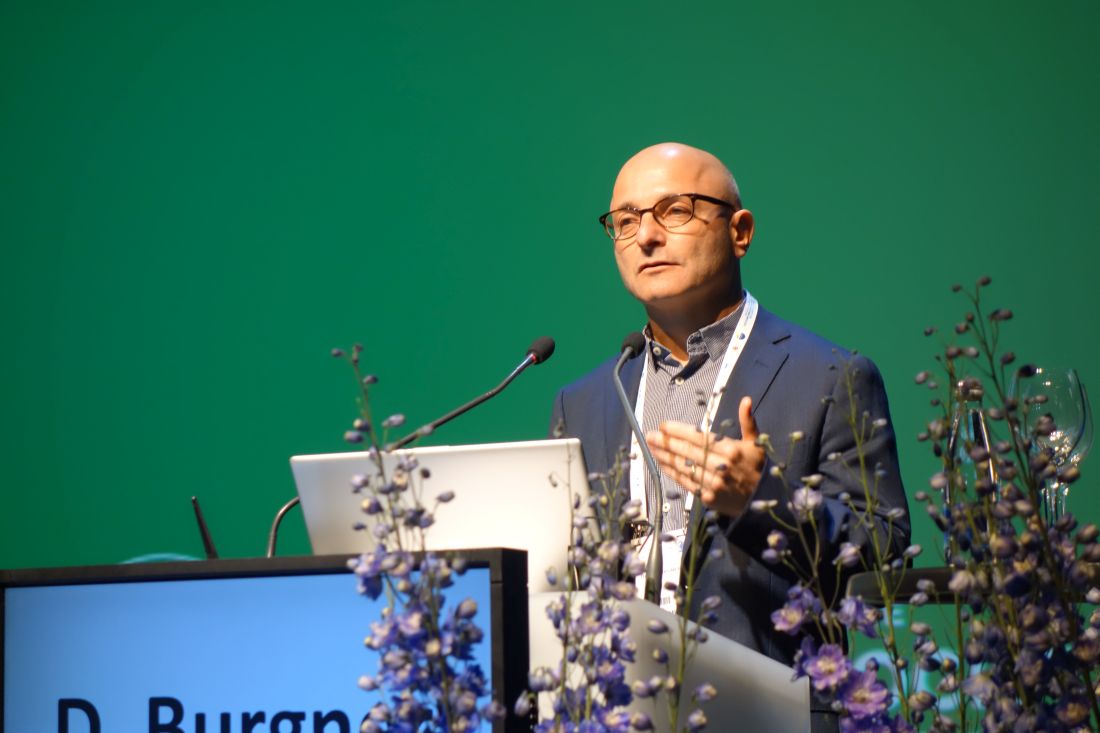
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – Delivery by C-section – especially when elective – carries a significantly higher hospitalization risk for severe infection in the first 5 years of life than vaginal delivery in a study of nearly 7.3 million singleton deliveries in four asset-rich countries, David Burgner, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“This is something that obstetricians might need to consider when discussing with the family the pros and cons for an elective C-section, particularly one that isn’t otherwise indicated for the baby or the mother,” said Dr. Burgner of the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Melbourne.
He presented an observational study of 7.29 million singleton births in Denmark, Great Britain, Scotland, and two Australian states during 1996-2015. C-section rates ranged from a low of 17.5% in Denmark to 29.4% in Western Australia, all of which are greater than the 10%-15% rate endorsed by the World Health Organization. Elective C-section rates varied by country from 39% to 57%. Of note, pediatric hospital care in all four countries is free, so economic considerations didn’t drive admission.
The impetus for this international collaboration was to gain new insight into the differential susceptibility to childhood infection, he explained.
“We know from our clinical practice that pretty much all of the children are exposed to pretty much all potentially serious pathogens during early life. And yet it’s only a minority that develop severe infection. It’s an extremely interesting scientific question and an extremely important clinical question as to what’s driving that differential susceptibility,” according to the pediatric infectious disease specialist.
There are a number of established risk factors for infection-related hospitalization in children, including parental smoking, maternal antibiotic exposure during pregnancy, and growth measurements at birth. Dr. Burgner and coinvestigators hypothesized that another important risk factor is the nature of the microbiome transmitted from mother to baby during delivery. This postnatal microbiome varies depending upon mode of delivery: Vaginal delivery transmits the maternal enteric microbiome, which they reasoned might be through direct immunomodulation that sets up protective immune responses early in life, especially against respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections. In contrast, delivery by C-section causes the baby to pick up the maternal skin and hospital environment microbiomes, but not the maternal enteric microbiome.
Thus, the investigators hypothesized that C-section poses a greater risk of infection-related hospitalization during the first 5 years of life than does vaginal delivery, and that elective C-section poses a higher risk than does emergency C-section because it is more likely to involve rupture of membranes.
The center-specific rates of C-section and infection-related pediatric infection, when combined into a meta-analysis, bore out the study hypothesis. Emergency C-section was associated with a 9% greater risk of infection-related hospitalization through 5 years of age than was vaginal delivery, while elective C-section was associated with a 13% increased risk, both of which were statistically significant and clinically important.
“We were quite taken with these results. We think they provide evidence that C-section is consistently associated with infection-related hospitalization. It’s an association study that can’t prove causality, but the results implicate the postnatal microbiome as the most plausible explanation in terms of what’s driving this association,” according to Dr. Burgner.
The association between C-section and infection-related hospitalization was persistent throughout the preschool years. For example, the increased risk associated with elective C-section was 16% during age 0-3 months, 20% during months 4-6, 14% in months 7-12, 13% during ages 1-2 years, and 11% among 2- to 5-year-olds, he continued.
The increased risk of severe preschool infection was highest for upper and lower respiratory tract and gastrointestinal infections, which involve the organ systems most likely to experience direct inoculation of the maternal microbiome, he noted.
Because the investigators recognized that the study results were potentially vulnerable to confounding by indication – that is, that the reason for doing a C-section might itself confer increased risk of subsequent preschool infection-related hospitalization – they repeated their analysis in a predefined low-risk subpopulation. The results closely mirrored those in the overall study population: an 8% increased risk in the emergency C-section group and a 14% increased risk with elective C-section.
Results of this large multinational study should provide further support for ongoing research aimed at supporting the infant microbiome after delivery by C-section via vaginal microbial transfer and other methods, he observed.
Dr. Burgner reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was cosponsored by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Danish Council for Independent Research, and nonprofit foundations.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – Delivery by C-section – especially when elective – carries a significantly higher hospitalization risk for severe infection in the first 5 years of life than vaginal delivery in a study of nearly 7.3 million singleton deliveries in four asset-rich countries, David Burgner, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“This is something that obstetricians might need to consider when discussing with the family the pros and cons for an elective C-section, particularly one that isn’t otherwise indicated for the baby or the mother,” said Dr. Burgner of the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Melbourne.
He presented an observational study of 7.29 million singleton births in Denmark, Great Britain, Scotland, and two Australian states during 1996-2015. C-section rates ranged from a low of 17.5% in Denmark to 29.4% in Western Australia, all of which are greater than the 10%-15% rate endorsed by the World Health Organization. Elective C-section rates varied by country from 39% to 57%. Of note, pediatric hospital care in all four countries is free, so economic considerations didn’t drive admission.
The impetus for this international collaboration was to gain new insight into the differential susceptibility to childhood infection, he explained.
“We know from our clinical practice that pretty much all of the children are exposed to pretty much all potentially serious pathogens during early life. And yet it’s only a minority that develop severe infection. It’s an extremely interesting scientific question and an extremely important clinical question as to what’s driving that differential susceptibility,” according to the pediatric infectious disease specialist.
There are a number of established risk factors for infection-related hospitalization in children, including parental smoking, maternal antibiotic exposure during pregnancy, and growth measurements at birth. Dr. Burgner and coinvestigators hypothesized that another important risk factor is the nature of the microbiome transmitted from mother to baby during delivery. This postnatal microbiome varies depending upon mode of delivery: Vaginal delivery transmits the maternal enteric microbiome, which they reasoned might be through direct immunomodulation that sets up protective immune responses early in life, especially against respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections. In contrast, delivery by C-section causes the baby to pick up the maternal skin and hospital environment microbiomes, but not the maternal enteric microbiome.
Thus, the investigators hypothesized that C-section poses a greater risk of infection-related hospitalization during the first 5 years of life than does vaginal delivery, and that elective C-section poses a higher risk than does emergency C-section because it is more likely to involve rupture of membranes.
The center-specific rates of C-section and infection-related pediatric infection, when combined into a meta-analysis, bore out the study hypothesis. Emergency C-section was associated with a 9% greater risk of infection-related hospitalization through 5 years of age than was vaginal delivery, while elective C-section was associated with a 13% increased risk, both of which were statistically significant and clinically important.
“We were quite taken with these results. We think they provide evidence that C-section is consistently associated with infection-related hospitalization. It’s an association study that can’t prove causality, but the results implicate the postnatal microbiome as the most plausible explanation in terms of what’s driving this association,” according to Dr. Burgner.
The association between C-section and infection-related hospitalization was persistent throughout the preschool years. For example, the increased risk associated with elective C-section was 16% during age 0-3 months, 20% during months 4-6, 14% in months 7-12, 13% during ages 1-2 years, and 11% among 2- to 5-year-olds, he continued.
The increased risk of severe preschool infection was highest for upper and lower respiratory tract and gastrointestinal infections, which involve the organ systems most likely to experience direct inoculation of the maternal microbiome, he noted.
Because the investigators recognized that the study results were potentially vulnerable to confounding by indication – that is, that the reason for doing a C-section might itself confer increased risk of subsequent preschool infection-related hospitalization – they repeated their analysis in a predefined low-risk subpopulation. The results closely mirrored those in the overall study population: an 8% increased risk in the emergency C-section group and a 14% increased risk with elective C-section.
Results of this large multinational study should provide further support for ongoing research aimed at supporting the infant microbiome after delivery by C-section via vaginal microbial transfer and other methods, he observed.
Dr. Burgner reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was cosponsored by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Danish Council for Independent Research, and nonprofit foundations.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – Delivery by C-section – especially when elective – carries a significantly higher hospitalization risk for severe infection in the first 5 years of life than vaginal delivery in a study of nearly 7.3 million singleton deliveries in four asset-rich countries, David Burgner, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“This is something that obstetricians might need to consider when discussing with the family the pros and cons for an elective C-section, particularly one that isn’t otherwise indicated for the baby or the mother,” said Dr. Burgner of the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Melbourne.
He presented an observational study of 7.29 million singleton births in Denmark, Great Britain, Scotland, and two Australian states during 1996-2015. C-section rates ranged from a low of 17.5% in Denmark to 29.4% in Western Australia, all of which are greater than the 10%-15% rate endorsed by the World Health Organization. Elective C-section rates varied by country from 39% to 57%. Of note, pediatric hospital care in all four countries is free, so economic considerations didn’t drive admission.
The impetus for this international collaboration was to gain new insight into the differential susceptibility to childhood infection, he explained.
“We know from our clinical practice that pretty much all of the children are exposed to pretty much all potentially serious pathogens during early life. And yet it’s only a minority that develop severe infection. It’s an extremely interesting scientific question and an extremely important clinical question as to what’s driving that differential susceptibility,” according to the pediatric infectious disease specialist.
There are a number of established risk factors for infection-related hospitalization in children, including parental smoking, maternal antibiotic exposure during pregnancy, and growth measurements at birth. Dr. Burgner and coinvestigators hypothesized that another important risk factor is the nature of the microbiome transmitted from mother to baby during delivery. This postnatal microbiome varies depending upon mode of delivery: Vaginal delivery transmits the maternal enteric microbiome, which they reasoned might be through direct immunomodulation that sets up protective immune responses early in life, especially against respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections. In contrast, delivery by C-section causes the baby to pick up the maternal skin and hospital environment microbiomes, but not the maternal enteric microbiome.
Thus, the investigators hypothesized that C-section poses a greater risk of infection-related hospitalization during the first 5 years of life than does vaginal delivery, and that elective C-section poses a higher risk than does emergency C-section because it is more likely to involve rupture of membranes.
The center-specific rates of C-section and infection-related pediatric infection, when combined into a meta-analysis, bore out the study hypothesis. Emergency C-section was associated with a 9% greater risk of infection-related hospitalization through 5 years of age than was vaginal delivery, while elective C-section was associated with a 13% increased risk, both of which were statistically significant and clinically important.
“We were quite taken with these results. We think they provide evidence that C-section is consistently associated with infection-related hospitalization. It’s an association study that can’t prove causality, but the results implicate the postnatal microbiome as the most plausible explanation in terms of what’s driving this association,” according to Dr. Burgner.
The association between C-section and infection-related hospitalization was persistent throughout the preschool years. For example, the increased risk associated with elective C-section was 16% during age 0-3 months, 20% during months 4-6, 14% in months 7-12, 13% during ages 1-2 years, and 11% among 2- to 5-year-olds, he continued.
The increased risk of severe preschool infection was highest for upper and lower respiratory tract and gastrointestinal infections, which involve the organ systems most likely to experience direct inoculation of the maternal microbiome, he noted.
Because the investigators recognized that the study results were potentially vulnerable to confounding by indication – that is, that the reason for doing a C-section might itself confer increased risk of subsequent preschool infection-related hospitalization – they repeated their analysis in a predefined low-risk subpopulation. The results closely mirrored those in the overall study population: an 8% increased risk in the emergency C-section group and a 14% increased risk with elective C-section.
Results of this large multinational study should provide further support for ongoing research aimed at supporting the infant microbiome after delivery by C-section via vaginal microbial transfer and other methods, he observed.
Dr. Burgner reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was cosponsored by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Danish Council for Independent Research, and nonprofit foundations.
REPORTING FROM ESPID 2019
Revision total joint replacements linked to higher infection risk
, according to the findings of a large cohort study.
In absolute terms, these rates were 15.6% after revision total knee replacement and 8.6% after revision total hip replacement, vs. 2.1% and 2.1% after the respective primary surgeries, wrote Charles E. Edmiston Jr., PhD, and associates. “This result is consistent with results from several other studies that have reported an increased risk after revision procedures,” they added. Such information is essential for developing care bundles based on presenting risk factors, they wrote in a report published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
Population aging and comorbidities are fueling the need for primary and revision joint replacement surgery. “Such trends highlight the need for solutions to cost-effectively prevent and treat surgical site infections, one of the common complications after total joint replacement procedures,” the researchers wrote. Using IBM MarketScan and Medicare data, they studied 335,134 total knee replacements and 163,547 total hip replacements performed in the United States between 2009 and 2015.
After adjustment for potential confounders, the comorbidities that were most strongly linked to surgical site infections during the 90 days after primary or revision joint replacement were AIDS, paralysis, coagulopathy, metastatic cancer, heart failure, alcohol use disorder, obesity, fluid electrolyte disorders, and chronic pulmonary disorders. The estimated odds ratios for these correlates ranged from 1.33 to 1.58, and all confidence intervals reached statistical significance.
In general, these findings reflect those of smaller studies, the researchers noted. “The challenge for the future will be the development of evidence-based surgical care bundles that focus on the peri-, intra-, and postoperative components of orthopedic patient care, especially in patients undergoing periprosthetic revision.”
Johnson & Johnson Medical Device Companies provided funding. Three coinvestigators reported employment and stockholder ties to the company. In addition, Dr. Edmiston and one coinvestigator reported speaker fees for Ethicon, a Johnson & Johnson company.
SOURCE: Edmiston CE et al. Am J Infect Control. 2019 May 6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.03.030.
, according to the findings of a large cohort study.
In absolute terms, these rates were 15.6% after revision total knee replacement and 8.6% after revision total hip replacement, vs. 2.1% and 2.1% after the respective primary surgeries, wrote Charles E. Edmiston Jr., PhD, and associates. “This result is consistent with results from several other studies that have reported an increased risk after revision procedures,” they added. Such information is essential for developing care bundles based on presenting risk factors, they wrote in a report published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
Population aging and comorbidities are fueling the need for primary and revision joint replacement surgery. “Such trends highlight the need for solutions to cost-effectively prevent and treat surgical site infections, one of the common complications after total joint replacement procedures,” the researchers wrote. Using IBM MarketScan and Medicare data, they studied 335,134 total knee replacements and 163,547 total hip replacements performed in the United States between 2009 and 2015.
After adjustment for potential confounders, the comorbidities that were most strongly linked to surgical site infections during the 90 days after primary or revision joint replacement were AIDS, paralysis, coagulopathy, metastatic cancer, heart failure, alcohol use disorder, obesity, fluid electrolyte disorders, and chronic pulmonary disorders. The estimated odds ratios for these correlates ranged from 1.33 to 1.58, and all confidence intervals reached statistical significance.
In general, these findings reflect those of smaller studies, the researchers noted. “The challenge for the future will be the development of evidence-based surgical care bundles that focus on the peri-, intra-, and postoperative components of orthopedic patient care, especially in patients undergoing periprosthetic revision.”
Johnson & Johnson Medical Device Companies provided funding. Three coinvestigators reported employment and stockholder ties to the company. In addition, Dr. Edmiston and one coinvestigator reported speaker fees for Ethicon, a Johnson & Johnson company.
SOURCE: Edmiston CE et al. Am J Infect Control. 2019 May 6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.03.030.
, according to the findings of a large cohort study.
In absolute terms, these rates were 15.6% after revision total knee replacement and 8.6% after revision total hip replacement, vs. 2.1% and 2.1% after the respective primary surgeries, wrote Charles E. Edmiston Jr., PhD, and associates. “This result is consistent with results from several other studies that have reported an increased risk after revision procedures,” they added. Such information is essential for developing care bundles based on presenting risk factors, they wrote in a report published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
Population aging and comorbidities are fueling the need for primary and revision joint replacement surgery. “Such trends highlight the need for solutions to cost-effectively prevent and treat surgical site infections, one of the common complications after total joint replacement procedures,” the researchers wrote. Using IBM MarketScan and Medicare data, they studied 335,134 total knee replacements and 163,547 total hip replacements performed in the United States between 2009 and 2015.
After adjustment for potential confounders, the comorbidities that were most strongly linked to surgical site infections during the 90 days after primary or revision joint replacement were AIDS, paralysis, coagulopathy, metastatic cancer, heart failure, alcohol use disorder, obesity, fluid electrolyte disorders, and chronic pulmonary disorders. The estimated odds ratios for these correlates ranged from 1.33 to 1.58, and all confidence intervals reached statistical significance.
In general, these findings reflect those of smaller studies, the researchers noted. “The challenge for the future will be the development of evidence-based surgical care bundles that focus on the peri-, intra-, and postoperative components of orthopedic patient care, especially in patients undergoing periprosthetic revision.”
Johnson & Johnson Medical Device Companies provided funding. Three coinvestigators reported employment and stockholder ties to the company. In addition, Dr. Edmiston and one coinvestigator reported speaker fees for Ethicon, a Johnson & Johnson company.
SOURCE: Edmiston CE et al. Am J Infect Control. 2019 May 6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.03.030.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF INFECTION CONTROL
Novel strategies may help curb bariatric SSI
BALTIMORE – While rates of surgical site infections after bariatric surgery have been reported in the low single digits, SSIs have continued to be a persistent complication.
At the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons, researchers reported on two strategies to reduce SSI in bariatric surgery: a predictive tool that identifies risk factors for wound infection, allowing surgeons to employ protective measures before and during surgery, and a change in surgical practice leading to a 78% reduction in wound infection rates that resulted from a single-center study.
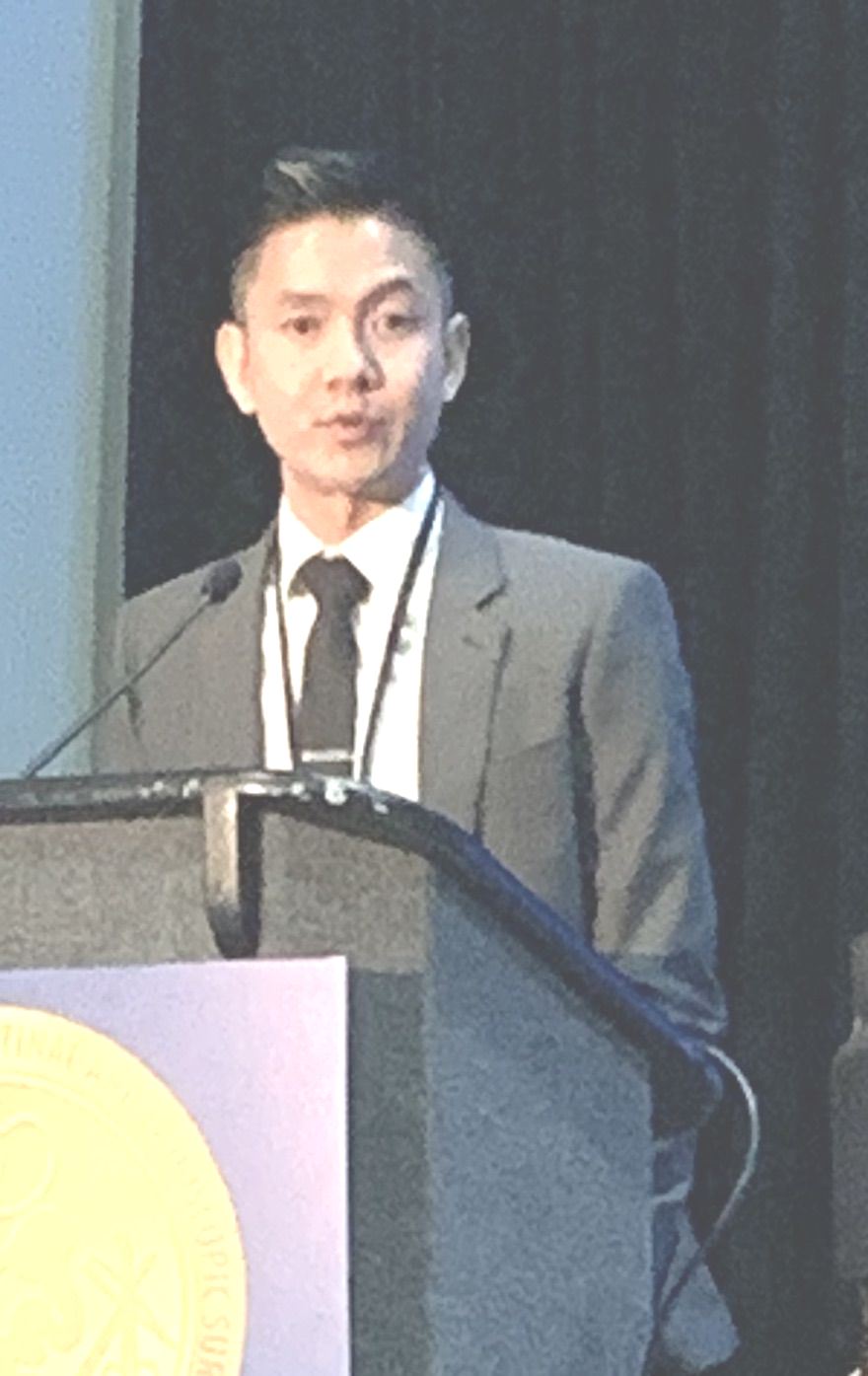
Jerry Dang, MD, of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, reported that the BariWound predictive tool designed to stratify patients into risk categories showed a high level of accuracy with an area under the curve of 0.73. Cynthia Weber, MD, of University Hospitals, Cleveland, reported that changing the method for performing circular-stapled gastrojejunostomy (GJ) from the transoral to the transabdominal approach along with more vigilant use of wound protection reduced wound infection rates from 6% to 1.3%.
Dr. Dang noted that SSI has been reported as the most common hospital-acquired complication in bariatric surgery, with reported rates of between 1% and 10%. A 2014 analysis of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database reported an SSI rate of 1.8% (Surg Endosc. 2014;28:3285-92). Although these rates are low, Dr. Dang explained that his group wanted to identify factors associated with SSI within 30 days of bariatric surgery. They analyzed outcomes data of 274,187 patients in the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program database who had bariatric surgery in 2015 and 2016 (196,608 by laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy [SG] and 77,579 laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB]). Their analysis determined an incisional SSI rate of 0.47% (n = 1,291). “Incisional SSI rates were four times higher for laparoscopic RYGB: 1.04% vs. 0.25%,” Dr. Dang said.
On multivariable logistic regression, the adjusted odds ratio of SSI after RYGB vs. SG was 3.13 (P less than .001). Other significant risk factors were chronic steroid or immunosuppressant use (odds ratio, 1.75; P = .001), female sex (OR, 1.48; P less than .001) and history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (OR, 1.45; P less than .001). Other factors with a 21%-31% greater risk of SSI were white race (P = .002), history of diabetes (P less than .001), hypertension (P less than .001), obstructive sleep apnea (P = .001), and longer operation times (P less than .001). Each single-digit increase in body mass index increased risk by 3%, and older age actually had a protective effect for unknown reasons, Dr. Dang noted.
The BariWound tool assigns points to each risk factor. Each hour of operation time and each 10 kg/m2 of weight carry a value of 1 point, with partial points allowed. RYGB equals 5 points, and chronic steroid/immunosuppressant use, 4 points. The tool assigns risk to four categories based on score and 30-day SSI rate:
- Low, less than 15 (1% risk of SSI).
- Moderate, 15-21.9 (1%-5%).
- High, 22-26.9 (5%-10%).
- Very high, greater than 27 (greater than 10%).
“The BariWound tool can help to inform clinical decision making so patients can know they’re at higher risk, and this could allow for us to target high-risk patients with preventive packages, such as the Cleveland Clinic Technique of wound protection, wound irrigation, and wound packing as a resource-saving measure,” Dr. Dang said. “Targeting high-risk populations can reduce cost and operating time.”
Dr. Weber reported on her institution’s study of SSIs using two different methods for circular stapling of GJ that involved two different surgeons who performed 333 RYGB procedures from January 2016 to March 2018. Surgeon “A” had traditionally used the transoral technique without wound protection to insert the anvil of the stapler; surgeon “B” used wound protection and the transabdominal technique for stapler insertion. Wound protection involves draping of the stapler with sterile plastic.
“In a quarterly review, we detected a higher than expected wound complication rate of 6%,” Dr. Weber said. “Of particular concern was the development of five recent wound infection cases, which all occurred in the transoral group for a rate of 8.9% in that cohort.”
That left the quality team questioning the safety profile of the transoral technique, Dr. Weber said. “We wanted to know why and whether or not the main contributor to the development of a wound infection was the technique for the anvil introduction or was it the difference between surgeons using wound protection.”
Halfway through the study period, surgeon A made two modifications: He adopted the transabdominal technique for a subset of patients; and because of the surgeon’s comfort level and expertise with the transoral approach, he continued using that approach but added wound protection. Surgeon B continued with the transabdominal approach with wound protection. The share of transabdominal insertions in the study population increased from 69.2% before the change to 75% after. Demographics between the pre- and postchange patient populations were similar, as were the rates of revision surgery between the two groups.
“We noticed a significant reduction in total wound complications from 6% to 1.3%, and we noticed a complete elimination of surgical site infections after adding wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said.
Dr. Weber noted a number of limitations with the study: its retrospective nature; the lack of control for other intraoperative factors that contribute to SSIs; relatively low incidence of SSI; and surgeon’s choice to determine the technique of anvil insertion.
“We found that our quality improvement intervention was efficacious and decided that it was not the technique of anvil insertion, but it was the wound protection that was key to preventing wound infections, as we saw complete elimination after we added wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said. “Using proper precautions with the circular stapler and anastomosis can be done using either technique for anvil insertion. Overall self-assessment of outcomes leads to best practice.”
Dr. Dang had no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber’s coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
SOURCES: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
BALTIMORE – While rates of surgical site infections after bariatric surgery have been reported in the low single digits, SSIs have continued to be a persistent complication.
At the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons, researchers reported on two strategies to reduce SSI in bariatric surgery: a predictive tool that identifies risk factors for wound infection, allowing surgeons to employ protective measures before and during surgery, and a change in surgical practice leading to a 78% reduction in wound infection rates that resulted from a single-center study.
Jerry Dang, MD, of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, reported that the BariWound predictive tool designed to stratify patients into risk categories showed a high level of accuracy with an area under the curve of 0.73. Cynthia Weber, MD, of University Hospitals, Cleveland, reported that changing the method for performing circular-stapled gastrojejunostomy (GJ) from the transoral to the transabdominal approach along with more vigilant use of wound protection reduced wound infection rates from 6% to 1.3%.
Dr. Dang noted that SSI has been reported as the most common hospital-acquired complication in bariatric surgery, with reported rates of between 1% and 10%. A 2014 analysis of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database reported an SSI rate of 1.8% (Surg Endosc. 2014;28:3285-92). Although these rates are low, Dr. Dang explained that his group wanted to identify factors associated with SSI within 30 days of bariatric surgery. They analyzed outcomes data of 274,187 patients in the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program database who had bariatric surgery in 2015 and 2016 (196,608 by laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy [SG] and 77,579 laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB]). Their analysis determined an incisional SSI rate of 0.47% (n = 1,291). “Incisional SSI rates were four times higher for laparoscopic RYGB: 1.04% vs. 0.25%,” Dr. Dang said.
On multivariable logistic regression, the adjusted odds ratio of SSI after RYGB vs. SG was 3.13 (P less than .001). Other significant risk factors were chronic steroid or immunosuppressant use (odds ratio, 1.75; P = .001), female sex (OR, 1.48; P less than .001) and history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (OR, 1.45; P less than .001). Other factors with a 21%-31% greater risk of SSI were white race (P = .002), history of diabetes (P less than .001), hypertension (P less than .001), obstructive sleep apnea (P = .001), and longer operation times (P less than .001). Each single-digit increase in body mass index increased risk by 3%, and older age actually had a protective effect for unknown reasons, Dr. Dang noted.
The BariWound tool assigns points to each risk factor. Each hour of operation time and each 10 kg/m2 of weight carry a value of 1 point, with partial points allowed. RYGB equals 5 points, and chronic steroid/immunosuppressant use, 4 points. The tool assigns risk to four categories based on score and 30-day SSI rate:
- Low, less than 15 (1% risk of SSI).
- Moderate, 15-21.9 (1%-5%).
- High, 22-26.9 (5%-10%).
- Very high, greater than 27 (greater than 10%).
“The BariWound tool can help to inform clinical decision making so patients can know they’re at higher risk, and this could allow for us to target high-risk patients with preventive packages, such as the Cleveland Clinic Technique of wound protection, wound irrigation, and wound packing as a resource-saving measure,” Dr. Dang said. “Targeting high-risk populations can reduce cost and operating time.”
Dr. Weber reported on her institution’s study of SSIs using two different methods for circular stapling of GJ that involved two different surgeons who performed 333 RYGB procedures from January 2016 to March 2018. Surgeon “A” had traditionally used the transoral technique without wound protection to insert the anvil of the stapler; surgeon “B” used wound protection and the transabdominal technique for stapler insertion. Wound protection involves draping of the stapler with sterile plastic.
“In a quarterly review, we detected a higher than expected wound complication rate of 6%,” Dr. Weber said. “Of particular concern was the development of five recent wound infection cases, which all occurred in the transoral group for a rate of 8.9% in that cohort.”
That left the quality team questioning the safety profile of the transoral technique, Dr. Weber said. “We wanted to know why and whether or not the main contributor to the development of a wound infection was the technique for the anvil introduction or was it the difference between surgeons using wound protection.”
Halfway through the study period, surgeon A made two modifications: He adopted the transabdominal technique for a subset of patients; and because of the surgeon’s comfort level and expertise with the transoral approach, he continued using that approach but added wound protection. Surgeon B continued with the transabdominal approach with wound protection. The share of transabdominal insertions in the study population increased from 69.2% before the change to 75% after. Demographics between the pre- and postchange patient populations were similar, as were the rates of revision surgery between the two groups.
“We noticed a significant reduction in total wound complications from 6% to 1.3%, and we noticed a complete elimination of surgical site infections after adding wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said.
Dr. Weber noted a number of limitations with the study: its retrospective nature; the lack of control for other intraoperative factors that contribute to SSIs; relatively low incidence of SSI; and surgeon’s choice to determine the technique of anvil insertion.
“We found that our quality improvement intervention was efficacious and decided that it was not the technique of anvil insertion, but it was the wound protection that was key to preventing wound infections, as we saw complete elimination after we added wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said. “Using proper precautions with the circular stapler and anastomosis can be done using either technique for anvil insertion. Overall self-assessment of outcomes leads to best practice.”
Dr. Dang had no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber’s coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
SOURCES: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
BALTIMORE – While rates of surgical site infections after bariatric surgery have been reported in the low single digits, SSIs have continued to be a persistent complication.
At the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons, researchers reported on two strategies to reduce SSI in bariatric surgery: a predictive tool that identifies risk factors for wound infection, allowing surgeons to employ protective measures before and during surgery, and a change in surgical practice leading to a 78% reduction in wound infection rates that resulted from a single-center study.
Jerry Dang, MD, of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, reported that the BariWound predictive tool designed to stratify patients into risk categories showed a high level of accuracy with an area under the curve of 0.73. Cynthia Weber, MD, of University Hospitals, Cleveland, reported that changing the method for performing circular-stapled gastrojejunostomy (GJ) from the transoral to the transabdominal approach along with more vigilant use of wound protection reduced wound infection rates from 6% to 1.3%.
Dr. Dang noted that SSI has been reported as the most common hospital-acquired complication in bariatric surgery, with reported rates of between 1% and 10%. A 2014 analysis of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database reported an SSI rate of 1.8% (Surg Endosc. 2014;28:3285-92). Although these rates are low, Dr. Dang explained that his group wanted to identify factors associated with SSI within 30 days of bariatric surgery. They analyzed outcomes data of 274,187 patients in the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program database who had bariatric surgery in 2015 and 2016 (196,608 by laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy [SG] and 77,579 laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB]). Their analysis determined an incisional SSI rate of 0.47% (n = 1,291). “Incisional SSI rates were four times higher for laparoscopic RYGB: 1.04% vs. 0.25%,” Dr. Dang said.
On multivariable logistic regression, the adjusted odds ratio of SSI after RYGB vs. SG was 3.13 (P less than .001). Other significant risk factors were chronic steroid or immunosuppressant use (odds ratio, 1.75; P = .001), female sex (OR, 1.48; P less than .001) and history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (OR, 1.45; P less than .001). Other factors with a 21%-31% greater risk of SSI were white race (P = .002), history of diabetes (P less than .001), hypertension (P less than .001), obstructive sleep apnea (P = .001), and longer operation times (P less than .001). Each single-digit increase in body mass index increased risk by 3%, and older age actually had a protective effect for unknown reasons, Dr. Dang noted.
The BariWound tool assigns points to each risk factor. Each hour of operation time and each 10 kg/m2 of weight carry a value of 1 point, with partial points allowed. RYGB equals 5 points, and chronic steroid/immunosuppressant use, 4 points. The tool assigns risk to four categories based on score and 30-day SSI rate:
- Low, less than 15 (1% risk of SSI).
- Moderate, 15-21.9 (1%-5%).
- High, 22-26.9 (5%-10%).
- Very high, greater than 27 (greater than 10%).
“The BariWound tool can help to inform clinical decision making so patients can know they’re at higher risk, and this could allow for us to target high-risk patients with preventive packages, such as the Cleveland Clinic Technique of wound protection, wound irrigation, and wound packing as a resource-saving measure,” Dr. Dang said. “Targeting high-risk populations can reduce cost and operating time.”
Dr. Weber reported on her institution’s study of SSIs using two different methods for circular stapling of GJ that involved two different surgeons who performed 333 RYGB procedures from January 2016 to March 2018. Surgeon “A” had traditionally used the transoral technique without wound protection to insert the anvil of the stapler; surgeon “B” used wound protection and the transabdominal technique for stapler insertion. Wound protection involves draping of the stapler with sterile plastic.
“In a quarterly review, we detected a higher than expected wound complication rate of 6%,” Dr. Weber said. “Of particular concern was the development of five recent wound infection cases, which all occurred in the transoral group for a rate of 8.9% in that cohort.”
That left the quality team questioning the safety profile of the transoral technique, Dr. Weber said. “We wanted to know why and whether or not the main contributor to the development of a wound infection was the technique for the anvil introduction or was it the difference between surgeons using wound protection.”
Halfway through the study period, surgeon A made two modifications: He adopted the transabdominal technique for a subset of patients; and because of the surgeon’s comfort level and expertise with the transoral approach, he continued using that approach but added wound protection. Surgeon B continued with the transabdominal approach with wound protection. The share of transabdominal insertions in the study population increased from 69.2% before the change to 75% after. Demographics between the pre- and postchange patient populations were similar, as were the rates of revision surgery between the two groups.
“We noticed a significant reduction in total wound complications from 6% to 1.3%, and we noticed a complete elimination of surgical site infections after adding wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said.
Dr. Weber noted a number of limitations with the study: its retrospective nature; the lack of control for other intraoperative factors that contribute to SSIs; relatively low incidence of SSI; and surgeon’s choice to determine the technique of anvil insertion.
“We found that our quality improvement intervention was efficacious and decided that it was not the technique of anvil insertion, but it was the wound protection that was key to preventing wound infections, as we saw complete elimination after we added wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said. “Using proper precautions with the circular stapler and anastomosis can be done using either technique for anvil insertion. Overall self-assessment of outcomes leads to best practice.”
Dr. Dang had no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber’s coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
SOURCES: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
REPORTING FROM SAGES 2019
Key clinical point: .
Major findings: The BariWound predictive model had an accuracy of area under the curve of 0.73; wound infection rates decreased from 6% to 1.3% after the change in practice.
Study details: Analysis of 274,187 cases from the 2015 MBSAQIP database; and a retrospective analysis of 333 bariatric cases performed from January 2016 to March 2018 at a single center.
Disclosures: Dr. Dang has no relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber has no disclosures, although coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
Sources: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
Antibiotic-eluting envelope reduces CIED infections
An absorbable, antibiotic-eluting envelope around cardiac implantable electronic devices could significantly reduce the incidence of infection, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
The WRAP-IT trial, which was simultaneously published online March 17 in the New England Journal of Medicine, involved 6,983 patients undergoing cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) implantation, replacement, revision, or upgrade. Patients were randomized either to receive the TYRX Absorbable Antibacterial Envelope or not.
After a mean follow-up of 20.7 months, there was a significant 40% lower rate of major infections in the envelope group compared to the control group, which met the efficacy objective of the study. Researchers saw 30 major infections in 25 patients in the envelope group; in the control group, there were 45 major infections in 42 patients (P = 0.04). The trial excluded patients at high risk of systemic infection due to other sources and patients with existing infection.
“CIED infection is a rare but serious event, and its management requires prolonged hospitalization, which involves device and lead extraction with adjunctive antibiotic therapy,” wrote Dr. Khaldoun G. Tarakji, from The Cleveland Clinic, and co-authors. “Despite proper management of CIED infection, both short- and long-term mortality remains high.”
One previous randomized study had shown that intravenous administration of antibiotics during CIED procedures can reduce the risk of infection, while a different study failed to find a benefit. The vast majority of patients in this study (98.7%) received periprocedural antibiotics, 74.5% received pocket wash and 29.6% received post-procedural antibiotics. These strategies were not controlled, but there is no clear evidence that any particular strategy influenced the infection rate, the authors wrote.
Patients in the envelope group experienced numerically fewer pocket infections but more endocarditis or bacteremia compared to those in the control group, a finding that the authors could not explain.
The most common pathogen responsible was staphylococcus, but data on antibiotic susceptibility was not collected. The authors stressed that this limited their ability to assess the risk of antibiotic resistance developing.
In this study, the researchers noted that the reduction in the risk of infection was greater among individuals who were implanted with higher-power devices, compared to those implanted with low-power devices or an initial cardiac resynchronization therapy device.
However, they said, the rate of infections was generally lower among those receiving low-power devices.
There was no increase in complications related to use of the envelope. The rate of complications occurring within 12 months of the procedure and relating to the CIED procedure or envelope was 6% in the envelope group and 6.9% in the control group.
When major infections were excluded, the rate of complications in each group was 5.7% and 5/9% respectively. There was also no significant difference in mortality rates between the two groups (17.4% and 17.8% respectively).
The authors wrote that while use of the envelope can require a slightly larger CIED dissection pocket, this was not associated with increased procedural time or complications. The envelope was successfully implanted in 99.7% of procedure attempts.
“There were fewer system revisions in the envelope group than in the control group and no complications due to allergy to the envelope mesh, polymer, or antibiotics,” they wrote.
The study was supported by Medtronic, the maker of the TYRX Absorbable Antibacterial Envelope. Twenty-four authors declared institutional funding or research grants from Medtronic, thirteen declared fees, consultancies and other support from private industry outside the submitted work. Three authors were employees of Medtronic.
SOURCE: Tarakji K et al. NEJM, 2019, March 17. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1901111
An absorbable, antibiotic-eluting envelope around cardiac implantable electronic devices could significantly reduce the incidence of infection, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
The WRAP-IT trial, which was simultaneously published online March 17 in the New England Journal of Medicine, involved 6,983 patients undergoing cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) implantation, replacement, revision, or upgrade. Patients were randomized either to receive the TYRX Absorbable Antibacterial Envelope or not.
After a mean follow-up of 20.7 months, there was a significant 40% lower rate of major infections in the envelope group compared to the control group, which met the efficacy objective of the study. Researchers saw 30 major infections in 25 patients in the envelope group; in the control group, there were 45 major infections in 42 patients (P = 0.04). The trial excluded patients at high risk of systemic infection due to other sources and patients with existing infection.
“CIED infection is a rare but serious event, and its management requires prolonged hospitalization, which involves device and lead extraction with adjunctive antibiotic therapy,” wrote Dr. Khaldoun G. Tarakji, from The Cleveland Clinic, and co-authors. “Despite proper management of CIED infection, both short- and long-term mortality remains high.”
One previous randomized study had shown that intravenous administration of antibiotics during CIED procedures can reduce the risk of infection, while a different study failed to find a benefit. The vast majority of patients in this study (98.7%) received periprocedural antibiotics, 74.5% received pocket wash and 29.6% received post-procedural antibiotics. These strategies were not controlled, but there is no clear evidence that any particular strategy influenced the infection rate, the authors wrote.
Patients in the envelope group experienced numerically fewer pocket infections but more endocarditis or bacteremia compared to those in the control group, a finding that the authors could not explain.
The most common pathogen responsible was staphylococcus, but data on antibiotic susceptibility was not collected. The authors stressed that this limited their ability to assess the risk of antibiotic resistance developing.
In this study, the researchers noted that the reduction in the risk of infection was greater among individuals who were implanted with higher-power devices, compared to those implanted with low-power devices or an initial cardiac resynchronization therapy device.
However, they said, the rate of infections was generally lower among those receiving low-power devices.
There was no increase in complications related to use of the envelope. The rate of complications occurring within 12 months of the procedure and relating to the CIED procedure or envelope was 6% in the envelope group and 6.9% in the control group.
When major infections were excluded, the rate of complications in each group was 5.7% and 5/9% respectively. There was also no significant difference in mortality rates between the two groups (17.4% and 17.8% respectively).
The authors wrote that while use of the envelope can require a slightly larger CIED dissection pocket, this was not associated with increased procedural time or complications. The envelope was successfully implanted in 99.7% of procedure attempts.
“There were fewer system revisions in the envelope group than in the control group and no complications due to allergy to the envelope mesh, polymer, or antibiotics,” they wrote.
The study was supported by Medtronic, the maker of the TYRX Absorbable Antibacterial Envelope. Twenty-four authors declared institutional funding or research grants from Medtronic, thirteen declared fees, consultancies and other support from private industry outside the submitted work. Three authors were employees of Medtronic.
SOURCE: Tarakji K et al. NEJM, 2019, March 17. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1901111
An absorbable, antibiotic-eluting envelope around cardiac implantable electronic devices could significantly reduce the incidence of infection, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
The WRAP-IT trial, which was simultaneously published online March 17 in the New England Journal of Medicine, involved 6,983 patients undergoing cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) implantation, replacement, revision, or upgrade. Patients were randomized either to receive the TYRX Absorbable Antibacterial Envelope or not.
After a mean follow-up of 20.7 months, there was a significant 40% lower rate of major infections in the envelope group compared to the control group, which met the efficacy objective of the study. Researchers saw 30 major infections in 25 patients in the envelope group; in the control group, there were 45 major infections in 42 patients (P = 0.04). The trial excluded patients at high risk of systemic infection due to other sources and patients with existing infection.
“CIED infection is a rare but serious event, and its management requires prolonged hospitalization, which involves device and lead extraction with adjunctive antibiotic therapy,” wrote Dr. Khaldoun G. Tarakji, from The Cleveland Clinic, and co-authors. “Despite proper management of CIED infection, both short- and long-term mortality remains high.”
One previous randomized study had shown that intravenous administration of antibiotics during CIED procedures can reduce the risk of infection, while a different study failed to find a benefit. The vast majority of patients in this study (98.7%) received periprocedural antibiotics, 74.5% received pocket wash and 29.6% received post-procedural antibiotics. These strategies were not controlled, but there is no clear evidence that any particular strategy influenced the infection rate, the authors wrote.
Patients in the envelope group experienced numerically fewer pocket infections but more endocarditis or bacteremia compared to those in the control group, a finding that the authors could not explain.
The most common pathogen responsible was staphylococcus, but data on antibiotic susceptibility was not collected. The authors stressed that this limited their ability to assess the risk of antibiotic resistance developing.
In this study, the researchers noted that the reduction in the risk of infection was greater among individuals who were implanted with higher-power devices, compared to those implanted with low-power devices or an initial cardiac resynchronization therapy device.
However, they said, the rate of infections was generally lower among those receiving low-power devices.
There was no increase in complications related to use of the envelope. The rate of complications occurring within 12 months of the procedure and relating to the CIED procedure or envelope was 6% in the envelope group and 6.9% in the control group.
When major infections were excluded, the rate of complications in each group was 5.7% and 5/9% respectively. There was also no significant difference in mortality rates between the two groups (17.4% and 17.8% respectively).
The authors wrote that while use of the envelope can require a slightly larger CIED dissection pocket, this was not associated with increased procedural time or complications. The envelope was successfully implanted in 99.7% of procedure attempts.
“There were fewer system revisions in the envelope group than in the control group and no complications due to allergy to the envelope mesh, polymer, or antibiotics,” they wrote.
The study was supported by Medtronic, the maker of the TYRX Absorbable Antibacterial Envelope. Twenty-four authors declared institutional funding or research grants from Medtronic, thirteen declared fees, consultancies and other support from private industry outside the submitted work. Three authors were employees of Medtronic.
SOURCE: Tarakji K et al. NEJM, 2019, March 17. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1901111
FROM ACC 19
Best practices lower postsepsis risk, but only if implemented
SAN DIEGO – North Carolina health care workers often failed to provide best-practice follow-up to patients who were released after hospitalization for sepsis, a small study has found. There may be a cost to this gap:
“It’s disappointing to see that we are not providing these seemingly common-sense care processes to our sepsis patients at discharge,” said study lead author Stephanie Parks Taylor, MD, of Atrium Health’s Carolinas Medical Center in Charlotte, in an interview following the presentation of the study findings at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. “We need to develop and implement strategies to improve outcomes for sepsis patients, not just while they are in the hospital, but after discharge as well.”
A 2017 report estimated that 1.7 million adults were hospitalized for sepsis in the United States in 2014, and 270,000 died (JAMA. 2017;318[13]:1241-9). Age-adjusted sepsis death rates in the United States are highest in states in the Eastern and Southern regions, a 2017 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggested; North Carolina has the 32nd-worst sepsis death rate in the country (12.4 deaths per 100,000 population).
Dr. Taylor said some recent news about sepsis is promising. “We’ve seen decreasing mortality rates from initiatives that improve the early detection of sepsis and rapid delivery of antibiotics, fluids, and other treatment. However, there is growing evidence that patients who survive an episode of sepsis face residual health deficits. Many sepsis survivors are left with new functional, cognitive, or mental health declines or worsening of their underlying comorbidities. Unfortunately, these patients have high rates of mortality and hospital readmission that persist for multiple years after hospitalization.”
Indeed, a 2013 report linked sepsis to significantly higher mortality risk over 5 years, after accounting for comorbidities. Postsepsis patients were 13 times more likely to die over the first year after hospitalization than counterparts who didn’t have sepsis (BMJ Open. 2014;4:e004283).
For the new study, Dr. Taylor said, “we aimed to evaluate current care practices with the hope to identify a postsepsis management strategy that could help nudge these patients towards a more meaningful recovery.”
The researchers retrospectively tracked a random sample of 100 patients (median age, 63 years), who were discharged following an admission for sepsis in 2017. They were treated at eight acute care hospitals in western and central North Carolina and hospitalized for a median of 5 days; 75 were discharged to home (17 received home health services there), 17 went to skilled nursing or long-term care facilities, and 8 went to hospice or another location.
The researchers analyzed whether the patients received four kinds of postsepsis care within 90 days, as recommended by a 2018 review: screening for common functional impairments (53/100 patients received this screening); adjustment of medications as needed following discharge (53/100 patients); monitoring for common and preventable causes for health deterioration, such as infection, chronic lung disease, or heart failure exacerbation (37/100); and assessment for palliative care (25/100 patients) (JAMA. 2018;319[1]:62-75).
Within 90 days of discharge, 34 patients were readmitted and 17 died. The 32 patients who received at least two recommended kinds of postsepsis care were less likely to be readmitted or die (9/32) than those who got zero or one recommended kind of care (34/68; odds ratio, 0.26; 95% confidence ratio, 0.09-0.82).
In an interview, study coauthor Marc Kowalkowski, PhD, associate professor with Atrium Health’s Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, said he was hesitant to only allocate blame to hospitals or outpatient providers. “Transition out of the hospital is an extremely complex event, involving often fragmented care settings, and sepsis patients tend to be more complicated than other patients. It probably makes sense to provide an added layer of support during the transition out of the hospital for patients who are at high risk for poor outcomes.”
Overall, the findings are “a call for clinicians to realize sepsis is more than just an acute illness. The combination of a growing number of sepsis survivors and the increased health problems following an episode of sepsis creates an urgent public health challenge,” Dr. Taylor said.
Is more home health an important part of a solution? It may be helpful, Dr. Taylor said, but “our data suggest that there really needs to be better coordination to bridge between the inpatient and outpatient transition. We are currently conducting a randomized study to investigate whether these types of care processes can be delivered effectively through a nurse navigator to improve patient outcomes.”
Fortunately, she said, the findings suggest “we don’t have to reinvent the wheel. We just have to work on implementation of strategies for care processes that we are already familiar with.”
No funding was reported. None of the study authors reported relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Taylor SP et al. CCC48, Abstract 1320.
SAN DIEGO – North Carolina health care workers often failed to provide best-practice follow-up to patients who were released after hospitalization for sepsis, a small study has found. There may be a cost to this gap:
“It’s disappointing to see that we are not providing these seemingly common-sense care processes to our sepsis patients at discharge,” said study lead author Stephanie Parks Taylor, MD, of Atrium Health’s Carolinas Medical Center in Charlotte, in an interview following the presentation of the study findings at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. “We need to develop and implement strategies to improve outcomes for sepsis patients, not just while they are in the hospital, but after discharge as well.”
A 2017 report estimated that 1.7 million adults were hospitalized for sepsis in the United States in 2014, and 270,000 died (JAMA. 2017;318[13]:1241-9). Age-adjusted sepsis death rates in the United States are highest in states in the Eastern and Southern regions, a 2017 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggested; North Carolina has the 32nd-worst sepsis death rate in the country (12.4 deaths per 100,000 population).
Dr. Taylor said some recent news about sepsis is promising. “We’ve seen decreasing mortality rates from initiatives that improve the early detection of sepsis and rapid delivery of antibiotics, fluids, and other treatment. However, there is growing evidence that patients who survive an episode of sepsis face residual health deficits. Many sepsis survivors are left with new functional, cognitive, or mental health declines or worsening of their underlying comorbidities. Unfortunately, these patients have high rates of mortality and hospital readmission that persist for multiple years after hospitalization.”
Indeed, a 2013 report linked sepsis to significantly higher mortality risk over 5 years, after accounting for comorbidities. Postsepsis patients were 13 times more likely to die over the first year after hospitalization than counterparts who didn’t have sepsis (BMJ Open. 2014;4:e004283).
For the new study, Dr. Taylor said, “we aimed to evaluate current care practices with the hope to identify a postsepsis management strategy that could help nudge these patients towards a more meaningful recovery.”
The researchers retrospectively tracked a random sample of 100 patients (median age, 63 years), who were discharged following an admission for sepsis in 2017. They were treated at eight acute care hospitals in western and central North Carolina and hospitalized for a median of 5 days; 75 were discharged to home (17 received home health services there), 17 went to skilled nursing or long-term care facilities, and 8 went to hospice or another location.
The researchers analyzed whether the patients received four kinds of postsepsis care within 90 days, as recommended by a 2018 review: screening for common functional impairments (53/100 patients received this screening); adjustment of medications as needed following discharge (53/100 patients); monitoring for common and preventable causes for health deterioration, such as infection, chronic lung disease, or heart failure exacerbation (37/100); and assessment for palliative care (25/100 patients) (JAMA. 2018;319[1]:62-75).
Within 90 days of discharge, 34 patients were readmitted and 17 died. The 32 patients who received at least two recommended kinds of postsepsis care were less likely to be readmitted or die (9/32) than those who got zero or one recommended kind of care (34/68; odds ratio, 0.26; 95% confidence ratio, 0.09-0.82).
In an interview, study coauthor Marc Kowalkowski, PhD, associate professor with Atrium Health’s Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, said he was hesitant to only allocate blame to hospitals or outpatient providers. “Transition out of the hospital is an extremely complex event, involving often fragmented care settings, and sepsis patients tend to be more complicated than other patients. It probably makes sense to provide an added layer of support during the transition out of the hospital for patients who are at high risk for poor outcomes.”
Overall, the findings are “a call for clinicians to realize sepsis is more than just an acute illness. The combination of a growing number of sepsis survivors and the increased health problems following an episode of sepsis creates an urgent public health challenge,” Dr. Taylor said.
Is more home health an important part of a solution? It may be helpful, Dr. Taylor said, but “our data suggest that there really needs to be better coordination to bridge between the inpatient and outpatient transition. We are currently conducting a randomized study to investigate whether these types of care processes can be delivered effectively through a nurse navigator to improve patient outcomes.”
Fortunately, she said, the findings suggest “we don’t have to reinvent the wheel. We just have to work on implementation of strategies for care processes that we are already familiar with.”
No funding was reported. None of the study authors reported relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Taylor SP et al. CCC48, Abstract 1320.
SAN DIEGO – North Carolina health care workers often failed to provide best-practice follow-up to patients who were released after hospitalization for sepsis, a small study has found. There may be a cost to this gap:
“It’s disappointing to see that we are not providing these seemingly common-sense care processes to our sepsis patients at discharge,” said study lead author Stephanie Parks Taylor, MD, of Atrium Health’s Carolinas Medical Center in Charlotte, in an interview following the presentation of the study findings at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. “We need to develop and implement strategies to improve outcomes for sepsis patients, not just while they are in the hospital, but after discharge as well.”
A 2017 report estimated that 1.7 million adults were hospitalized for sepsis in the United States in 2014, and 270,000 died (JAMA. 2017;318[13]:1241-9). Age-adjusted sepsis death rates in the United States are highest in states in the Eastern and Southern regions, a 2017 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggested; North Carolina has the 32nd-worst sepsis death rate in the country (12.4 deaths per 100,000 population).
Dr. Taylor said some recent news about sepsis is promising. “We’ve seen decreasing mortality rates from initiatives that improve the early detection of sepsis and rapid delivery of antibiotics, fluids, and other treatment. However, there is growing evidence that patients who survive an episode of sepsis face residual health deficits. Many sepsis survivors are left with new functional, cognitive, or mental health declines or worsening of their underlying comorbidities. Unfortunately, these patients have high rates of mortality and hospital readmission that persist for multiple years after hospitalization.”
Indeed, a 2013 report linked sepsis to significantly higher mortality risk over 5 years, after accounting for comorbidities. Postsepsis patients were 13 times more likely to die over the first year after hospitalization than counterparts who didn’t have sepsis (BMJ Open. 2014;4:e004283).
For the new study, Dr. Taylor said, “we aimed to evaluate current care practices with the hope to identify a postsepsis management strategy that could help nudge these patients towards a more meaningful recovery.”
The researchers retrospectively tracked a random sample of 100 patients (median age, 63 years), who were discharged following an admission for sepsis in 2017. They were treated at eight acute care hospitals in western and central North Carolina and hospitalized for a median of 5 days; 75 were discharged to home (17 received home health services there), 17 went to skilled nursing or long-term care facilities, and 8 went to hospice or another location.
The researchers analyzed whether the patients received four kinds of postsepsis care within 90 days, as recommended by a 2018 review: screening for common functional impairments (53/100 patients received this screening); adjustment of medications as needed following discharge (53/100 patients); monitoring for common and preventable causes for health deterioration, such as infection, chronic lung disease, or heart failure exacerbation (37/100); and assessment for palliative care (25/100 patients) (JAMA. 2018;319[1]:62-75).
Within 90 days of discharge, 34 patients were readmitted and 17 died. The 32 patients who received at least two recommended kinds of postsepsis care were less likely to be readmitted or die (9/32) than those who got zero or one recommended kind of care (34/68; odds ratio, 0.26; 95% confidence ratio, 0.09-0.82).
In an interview, study coauthor Marc Kowalkowski, PhD, associate professor with Atrium Health’s Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, said he was hesitant to only allocate blame to hospitals or outpatient providers. “Transition out of the hospital is an extremely complex event, involving often fragmented care settings, and sepsis patients tend to be more complicated than other patients. It probably makes sense to provide an added layer of support during the transition out of the hospital for patients who are at high risk for poor outcomes.”
Overall, the findings are “a call for clinicians to realize sepsis is more than just an acute illness. The combination of a growing number of sepsis survivors and the increased health problems following an episode of sepsis creates an urgent public health challenge,” Dr. Taylor said.
Is more home health an important part of a solution? It may be helpful, Dr. Taylor said, but “our data suggest that there really needs to be better coordination to bridge between the inpatient and outpatient transition. We are currently conducting a randomized study to investigate whether these types of care processes can be delivered effectively through a nurse navigator to improve patient outcomes.”
Fortunately, she said, the findings suggest “we don’t have to reinvent the wheel. We just have to work on implementation of strategies for care processes that we are already familiar with.”
No funding was reported. None of the study authors reported relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Taylor SP et al. CCC48, Abstract 1320.
REPORTING FROM CCC48
Take stronger steps to prevent staph infections and sepsis
according to data from a Vital Signs report issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The data include both methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA).
Although MRSA infections in health care settings declined by approximately 17% during 2005-2012, rates plateaued during 2012-2017, Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the CDC, said in a teleconference March 5 to present the findings. The report emphasizes the potential for serious illness and death with any staph infection and the need for ongoing vigilance on the part of clinicians, she said.
In addition, community-onset MSSA infections increased by 3.9%/year during 2012-2017. Data from previous studies suggest that this increase may be connected to the opioid epidemic, said Dr. Schuchat.
“People who inject drugs are 16% more likely to develop a staph infection” than are those who don’t inject drugs, she said.
Community-onset MRSA declined by 6.9% during 2001-2016, attributed to declines in health care–associated infections, according to Vital Signs author Athena P. Kourtis, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and her colleagues. Rates of hospital-associated MSSA infection remained essentially unchanged (P = .11). The overall unadjusted in-hospital mortality among patients with S. aureus bloodstream infections over the study period was 18%.
The data for the report were collected from electronic health records at more than 400 acute care hospitals, as well as population-based surveillance data from the CDC’s Emerging Infections Program.
Most people carry staph on their skin with no ill effects, but the bacteria become dangerous when they enter the bloodstream, Dr. Schuchat emphasized. “We hope the new data today will refocus the nation’s efforts to protect patients from staph infections,” she said.

Dr. Schuchat advised clinicians and hospital administrators to review their data and step up their safety protocols to prevent staph infections. Precautions include wearing gowns and gloves, following proper hand washing protocols, cautious use of antibiotics, and treating infections rapidly when they occur, she said. Dr. Schuchat noted that lack of adherence to these recommendations may have declined in recent years if clinicians and hospital administrators were wondering whether their protocols have an effect and have value. However, “this is a very serious infection, and we think it is very much worth preventing,” she emphasized.
Other strategies to prevent staph infections in health care settings include reviewing infection data regularly, exploring new approaches to prevent infections, and educating patients about when they may be at increased risk for infection, such as when invasive devices are in place or during surgical procedures. Also, clinicians should be aware of the increased risk for patients who inject drugs, Dr. Schuchat said.
Dr. Schuchat commended the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers (VAMC), which overall reduced their rate of staph infections by 43% during the period from 2005 through 2017 in contrast to the national trend. These findings also appeared in the MMWR on March 5. The VAMC implemented additional interventions and increased their adherence to CDC recommendations during this period, she noted.
The Vital Signs data were published March 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report; read the full report here.
The CDC researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kourtis AP et al. MMWR. 2019 Mar 5; 68:1-6.
according to data from a Vital Signs report issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The data include both methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA).
Although MRSA infections in health care settings declined by approximately 17% during 2005-2012, rates plateaued during 2012-2017, Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the CDC, said in a teleconference March 5 to present the findings. The report emphasizes the potential for serious illness and death with any staph infection and the need for ongoing vigilance on the part of clinicians, she said.
In addition, community-onset MSSA infections increased by 3.9%/year during 2012-2017. Data from previous studies suggest that this increase may be connected to the opioid epidemic, said Dr. Schuchat.
“People who inject drugs are 16% more likely to develop a staph infection” than are those who don’t inject drugs, she said.
Community-onset MRSA declined by 6.9% during 2001-2016, attributed to declines in health care–associated infections, according to Vital Signs author Athena P. Kourtis, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and her colleagues. Rates of hospital-associated MSSA infection remained essentially unchanged (P = .11). The overall unadjusted in-hospital mortality among patients with S. aureus bloodstream infections over the study period was 18%.
The data for the report were collected from electronic health records at more than 400 acute care hospitals, as well as population-based surveillance data from the CDC’s Emerging Infections Program.
Most people carry staph on their skin with no ill effects, but the bacteria become dangerous when they enter the bloodstream, Dr. Schuchat emphasized. “We hope the new data today will refocus the nation’s efforts to protect patients from staph infections,” she said.

Dr. Schuchat advised clinicians and hospital administrators to review their data and step up their safety protocols to prevent staph infections. Precautions include wearing gowns and gloves, following proper hand washing protocols, cautious use of antibiotics, and treating infections rapidly when they occur, she said. Dr. Schuchat noted that lack of adherence to these recommendations may have declined in recent years if clinicians and hospital administrators were wondering whether their protocols have an effect and have value. However, “this is a very serious infection, and we think it is very much worth preventing,” she emphasized.
Other strategies to prevent staph infections in health care settings include reviewing infection data regularly, exploring new approaches to prevent infections, and educating patients about when they may be at increased risk for infection, such as when invasive devices are in place or during surgical procedures. Also, clinicians should be aware of the increased risk for patients who inject drugs, Dr. Schuchat said.
Dr. Schuchat commended the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers (VAMC), which overall reduced their rate of staph infections by 43% during the period from 2005 through 2017 in contrast to the national trend. These findings also appeared in the MMWR on March 5. The VAMC implemented additional interventions and increased their adherence to CDC recommendations during this period, she noted.
The Vital Signs data were published March 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report; read the full report here.
The CDC researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kourtis AP et al. MMWR. 2019 Mar 5; 68:1-6.
according to data from a Vital Signs report issued by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The data include both methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA).
Although MRSA infections in health care settings declined by approximately 17% during 2005-2012, rates plateaued during 2012-2017, Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the CDC, said in a teleconference March 5 to present the findings. The report emphasizes the potential for serious illness and death with any staph infection and the need for ongoing vigilance on the part of clinicians, she said.
In addition, community-onset MSSA infections increased by 3.9%/year during 2012-2017. Data from previous studies suggest that this increase may be connected to the opioid epidemic, said Dr. Schuchat.
“People who inject drugs are 16% more likely to develop a staph infection” than are those who don’t inject drugs, she said.
Community-onset MRSA declined by 6.9% during 2001-2016, attributed to declines in health care–associated infections, according to Vital Signs author Athena P. Kourtis, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and her colleagues. Rates of hospital-associated MSSA infection remained essentially unchanged (P = .11). The overall unadjusted in-hospital mortality among patients with S. aureus bloodstream infections over the study period was 18%.
The data for the report were collected from electronic health records at more than 400 acute care hospitals, as well as population-based surveillance data from the CDC’s Emerging Infections Program.
Most people carry staph on their skin with no ill effects, but the bacteria become dangerous when they enter the bloodstream, Dr. Schuchat emphasized. “We hope the new data today will refocus the nation’s efforts to protect patients from staph infections,” she said.

Dr. Schuchat advised clinicians and hospital administrators to review their data and step up their safety protocols to prevent staph infections. Precautions include wearing gowns and gloves, following proper hand washing protocols, cautious use of antibiotics, and treating infections rapidly when they occur, she said. Dr. Schuchat noted that lack of adherence to these recommendations may have declined in recent years if clinicians and hospital administrators were wondering whether their protocols have an effect and have value. However, “this is a very serious infection, and we think it is very much worth preventing,” she emphasized.
Other strategies to prevent staph infections in health care settings include reviewing infection data regularly, exploring new approaches to prevent infections, and educating patients about when they may be at increased risk for infection, such as when invasive devices are in place or during surgical procedures. Also, clinicians should be aware of the increased risk for patients who inject drugs, Dr. Schuchat said.
Dr. Schuchat commended the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Centers (VAMC), which overall reduced their rate of staph infections by 43% during the period from 2005 through 2017 in contrast to the national trend. These findings also appeared in the MMWR on March 5. The VAMC implemented additional interventions and increased their adherence to CDC recommendations during this period, she noted.
The Vital Signs data were published March 5 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report; read the full report here.
The CDC researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kourtis AP et al. MMWR. 2019 Mar 5; 68:1-6.
FROM THE MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY WEEKLY REPORT
Duodenoscopes contain more bacteria than expected
Reprocessed duodenoscopes are more contaminated than expected, with up to 3% of samples testing positive for disease-causing bacteria including Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, according to an updated safety communication issued by the Food and Drug Administration on December 10.
“Because of the higher-than-expected contamination rates and to help protect patients from bacterial infections associated with the use of duodenoscopes, we have included in today’s safety communication updated recommendations regarding steps that health care providers can take to enhance duodenoscope reprocessing,” Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in the statement.
The FDA advised clinicians to follow additional cleaning measures including microbiological culturing, sterilization, use of a liquid chemical sterilant processing system, and repeated high-level disinfection beyond what is recommended by duodenoscope manufacturers.
The interim data cited in the safety communication come from postmarket surveillance studies conducted by duodenoscope manufacturers at the FDA’s request as part of the agency’s ongoing efforts to prevent patient infections caused by contaminated duodenoscopes. In addition to the positive tests for disease-causing bacteria, up to 3% of properly collected samples contained more than 100 colony-forming units of other organisms unlikely to cause infection. However, the presence of such organisms further highlights the failure of the current reprocessing protocol to adequately clean the devices, according to the FDA.
Dr. Shuren emphasized that the risk of infection from a duodenoscope for an individual patient remains low and that infection rates have declined in recent years in response to the FDA’s enhanced safety measures and stated that the agency remains “committed to enhancing the safety margin of procedures with reprocessed medical devices.”
Read the full safety communication here: https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm628020.htm.
Reprocessed duodenoscopes are more contaminated than expected, with up to 3% of samples testing positive for disease-causing bacteria including Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, according to an updated safety communication issued by the Food and Drug Administration on December 10.
“Because of the higher-than-expected contamination rates and to help protect patients from bacterial infections associated with the use of duodenoscopes, we have included in today’s safety communication updated recommendations regarding steps that health care providers can take to enhance duodenoscope reprocessing,” Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in the statement.
The FDA advised clinicians to follow additional cleaning measures including microbiological culturing, sterilization, use of a liquid chemical sterilant processing system, and repeated high-level disinfection beyond what is recommended by duodenoscope manufacturers.
The interim data cited in the safety communication come from postmarket surveillance studies conducted by duodenoscope manufacturers at the FDA’s request as part of the agency’s ongoing efforts to prevent patient infections caused by contaminated duodenoscopes. In addition to the positive tests for disease-causing bacteria, up to 3% of properly collected samples contained more than 100 colony-forming units of other organisms unlikely to cause infection. However, the presence of such organisms further highlights the failure of the current reprocessing protocol to adequately clean the devices, according to the FDA.
Dr. Shuren emphasized that the risk of infection from a duodenoscope for an individual patient remains low and that infection rates have declined in recent years in response to the FDA’s enhanced safety measures and stated that the agency remains “committed to enhancing the safety margin of procedures with reprocessed medical devices.”
Read the full safety communication here: https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm628020.htm.
Reprocessed duodenoscopes are more contaminated than expected, with up to 3% of samples testing positive for disease-causing bacteria including Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, according to an updated safety communication issued by the Food and Drug Administration on December 10.
“Because of the higher-than-expected contamination rates and to help protect patients from bacterial infections associated with the use of duodenoscopes, we have included in today’s safety communication updated recommendations regarding steps that health care providers can take to enhance duodenoscope reprocessing,” Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in the statement.
The FDA advised clinicians to follow additional cleaning measures including microbiological culturing, sterilization, use of a liquid chemical sterilant processing system, and repeated high-level disinfection beyond what is recommended by duodenoscope manufacturers.
The interim data cited in the safety communication come from postmarket surveillance studies conducted by duodenoscope manufacturers at the FDA’s request as part of the agency’s ongoing efforts to prevent patient infections caused by contaminated duodenoscopes. In addition to the positive tests for disease-causing bacteria, up to 3% of properly collected samples contained more than 100 colony-forming units of other organisms unlikely to cause infection. However, the presence of such organisms further highlights the failure of the current reprocessing protocol to adequately clean the devices, according to the FDA.
Dr. Shuren emphasized that the risk of infection from a duodenoscope for an individual patient remains low and that infection rates have declined in recent years in response to the FDA’s enhanced safety measures and stated that the agency remains “committed to enhancing the safety margin of procedures with reprocessed medical devices.”
Read the full safety communication here: https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm628020.htm.
Antibiotics backed as standard of care for myomectomies
LAS VEGAS – The surgical site infection rate was 2.9% among women who received perioperative antibiotics for fibroid surgery, but 7.8% among those who did not, in a review of 1,433 cases at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
That is despite the fact that antibiotic cases were longer – 155 minutes vs. 89 minutes – and had more blood loss, 200 ml vs. 117 ml. Antibiotic cases also had larger specimen weights – 346 g vs. 176 g – and were more likely to have the uterine cavity entered, 30.2% vs. 14.4%.
“Surgical site infections were more common in the no-antibiotics group despite these being less complex cases.” There was “nearly a fivefold increased odds of surgical site infection or any infectious complication when no antibiotics were given,” after controlling for infection risk factors, including smoking and diabetes, said investigator Nisse V. Clark, MD, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon affiliated with Massachusetts General Hospital.
There are no perioperative antibiotic guidelines for myomectomies; maybe there should be. Almost 94% of the women in the review did receive antibiotics at the Harvard-affiliated hospitals, but the nationwide average has been pegged at about two-thirds, she said at the meeting, sponsored by the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists.
The antibiotic cases usually received a cephalosporin before surgery, and were about evenly about evenly split between abdominal, robotic, and laparoscopic approaches.
About one-third of the 90 women (6.3%) who did not get antibiotics had hysteroscopic procedures in which antibiotics usually are not given because the peritoneal cavity is not breeched. Most of the rest, however, were laparoscopic cases. It’s unknown why they weren’t given antibiotics. In her own practice, Dr. Clark said preop antibiotics are the rule for laparoscopic myomectomies.
The surgical site infection difference was driven largely by higher incidences of pelvic abscesses and other organ space infections in the no-antibiotic group.
The only significant demographic difference between the two groups was that women who received antibiotics were slightly younger (mean 38 versus 39.7 years).
In addition to diabetes and smoking, the team adjusted for age, surgery route, body mass index, uterine entry, intraoperative complications, and myoma weight in their multivariate analysis. Still, women in the no-antibiotic group were 4.59 times more likely to have a surgical site infection, 4.76 more likely to have any infectious complication, and almost 8 times more likely to have a major infectious complication. All of the findings were statistically significant.
The study had no industry funding, and Dr. Clark had no disclosures.
aotto@mdedge.com
LAS VEGAS – The surgical site infection rate was 2.9% among women who received perioperative antibiotics for fibroid surgery, but 7.8% among those who did not, in a review of 1,433 cases at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
That is despite the fact that antibiotic cases were longer – 155 minutes vs. 89 minutes – and had more blood loss, 200 ml vs. 117 ml. Antibiotic cases also had larger specimen weights – 346 g vs. 176 g – and were more likely to have the uterine cavity entered, 30.2% vs. 14.4%.
“Surgical site infections were more common in the no-antibiotics group despite these being less complex cases.” There was “nearly a fivefold increased odds of surgical site infection or any infectious complication when no antibiotics were given,” after controlling for infection risk factors, including smoking and diabetes, said investigator Nisse V. Clark, MD, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon affiliated with Massachusetts General Hospital.
There are no perioperative antibiotic guidelines for myomectomies; maybe there should be. Almost 94% of the women in the review did receive antibiotics at the Harvard-affiliated hospitals, but the nationwide average has been pegged at about two-thirds, she said at the meeting, sponsored by the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists.
The antibiotic cases usually received a cephalosporin before surgery, and were about evenly about evenly split between abdominal, robotic, and laparoscopic approaches.
About one-third of the 90 women (6.3%) who did not get antibiotics had hysteroscopic procedures in which antibiotics usually are not given because the peritoneal cavity is not breeched. Most of the rest, however, were laparoscopic cases. It’s unknown why they weren’t given antibiotics. In her own practice, Dr. Clark said preop antibiotics are the rule for laparoscopic myomectomies.
The surgical site infection difference was driven largely by higher incidences of pelvic abscesses and other organ space infections in the no-antibiotic group.
The only significant demographic difference between the two groups was that women who received antibiotics were slightly younger (mean 38 versus 39.7 years).
In addition to diabetes and smoking, the team adjusted for age, surgery route, body mass index, uterine entry, intraoperative complications, and myoma weight in their multivariate analysis. Still, women in the no-antibiotic group were 4.59 times more likely to have a surgical site infection, 4.76 more likely to have any infectious complication, and almost 8 times more likely to have a major infectious complication. All of the findings were statistically significant.
The study had no industry funding, and Dr. Clark had no disclosures.
aotto@mdedge.com
LAS VEGAS – The surgical site infection rate was 2.9% among women who received perioperative antibiotics for fibroid surgery, but 7.8% among those who did not, in a review of 1,433 cases at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
That is despite the fact that antibiotic cases were longer – 155 minutes vs. 89 minutes – and had more blood loss, 200 ml vs. 117 ml. Antibiotic cases also had larger specimen weights – 346 g vs. 176 g – and were more likely to have the uterine cavity entered, 30.2% vs. 14.4%.
“Surgical site infections were more common in the no-antibiotics group despite these being less complex cases.” There was “nearly a fivefold increased odds of surgical site infection or any infectious complication when no antibiotics were given,” after controlling for infection risk factors, including smoking and diabetes, said investigator Nisse V. Clark, MD, a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon affiliated with Massachusetts General Hospital.
There are no perioperative antibiotic guidelines for myomectomies; maybe there should be. Almost 94% of the women in the review did receive antibiotics at the Harvard-affiliated hospitals, but the nationwide average has been pegged at about two-thirds, she said at the meeting, sponsored by the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists.
The antibiotic cases usually received a cephalosporin before surgery, and were about evenly about evenly split between abdominal, robotic, and laparoscopic approaches.
About one-third of the 90 women (6.3%) who did not get antibiotics had hysteroscopic procedures in which antibiotics usually are not given because the peritoneal cavity is not breeched. Most of the rest, however, were laparoscopic cases. It’s unknown why they weren’t given antibiotics. In her own practice, Dr. Clark said preop antibiotics are the rule for laparoscopic myomectomies.
The surgical site infection difference was driven largely by higher incidences of pelvic abscesses and other organ space infections in the no-antibiotic group.
The only significant demographic difference between the two groups was that women who received antibiotics were slightly younger (mean 38 versus 39.7 years).
In addition to diabetes and smoking, the team adjusted for age, surgery route, body mass index, uterine entry, intraoperative complications, and myoma weight in their multivariate analysis. Still, women in the no-antibiotic group were 4.59 times more likely to have a surgical site infection, 4.76 more likely to have any infectious complication, and almost 8 times more likely to have a major infectious complication. All of the findings were statistically significant.
The study had no industry funding, and Dr. Clark had no disclosures.
aotto@mdedge.com
REPORTING FROM THE AAGL GLOBAL CONGRESS
Key clinical point: A Boston study suggests that even low-risk cases benefit from antibiotics.
Major finding: The surgical site infection rate was 2.9% among women who received perioperative antibiotics for fibroid surgery, but 7.8% among those who did not.
Study details: Review of 1,433 myomectomies at two academic medical centers.
Disclosures: The study had no industry funding, and Dr. Clark had no disclosures.
How to slash colorectal surgery infection rates
BOSTON – driven mostly by a reduction in deep organ space infections from 5.5% to 1.7%.
It was a remarkable finding that got the attention of attendees at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgeons. The Cleveland Clinic had been an outlier, in the wrong direction, compared with other centers, and administrators wanted a solution.
I. Emre Gorgun, MD, FACS, a colorectal surgeon and quality improvement officer at Cleveland Clinic, led the search for evidence-based interventions. Eventually, big changes were made to perioperative antibiotics, mechanical bowel prep, preop shower routines, and intraoperative procedures. The efforts paid off (Dis Colon Rectum. 2018 Jan;61[1]:89-98).
To help surgeons lower their own infection rates, Dr. Gorgun agreed to an interview at the meeting to explain exactly what was done.
There was resistance at first from surgeons who wanted to stick with their routines, but they came around once they were shown the data backing the changes. Eventually, “everyone was on board. We believe in this,” Dr. Gorgun said.
BOSTON – driven mostly by a reduction in deep organ space infections from 5.5% to 1.7%.
It was a remarkable finding that got the attention of attendees at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgeons. The Cleveland Clinic had been an outlier, in the wrong direction, compared with other centers, and administrators wanted a solution.
I. Emre Gorgun, MD, FACS, a colorectal surgeon and quality improvement officer at Cleveland Clinic, led the search for evidence-based interventions. Eventually, big changes were made to perioperative antibiotics, mechanical bowel prep, preop shower routines, and intraoperative procedures. The efforts paid off (Dis Colon Rectum. 2018 Jan;61[1]:89-98).
To help surgeons lower their own infection rates, Dr. Gorgun agreed to an interview at the meeting to explain exactly what was done.
There was resistance at first from surgeons who wanted to stick with their routines, but they came around once they were shown the data backing the changes. Eventually, “everyone was on board. We believe in this,” Dr. Gorgun said.
BOSTON – driven mostly by a reduction in deep organ space infections from 5.5% to 1.7%.
It was a remarkable finding that got the attention of attendees at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgeons. The Cleveland Clinic had been an outlier, in the wrong direction, compared with other centers, and administrators wanted a solution.
I. Emre Gorgun, MD, FACS, a colorectal surgeon and quality improvement officer at Cleveland Clinic, led the search for evidence-based interventions. Eventually, big changes were made to perioperative antibiotics, mechanical bowel prep, preop shower routines, and intraoperative procedures. The efforts paid off (Dis Colon Rectum. 2018 Jan;61[1]:89-98).
To help surgeons lower their own infection rates, Dr. Gorgun agreed to an interview at the meeting to explain exactly what was done.
There was resistance at first from surgeons who wanted to stick with their routines, but they came around once they were shown the data backing the changes. Eventually, “everyone was on board. We believe in this,” Dr. Gorgun said.
REPORTING FROM THE ACS CLINICAL CONGRESS
Two novel approaches for infected ventral hernia mesh
BOSTON – Deep according to Cleveland Clinic investigators.
When infected mesh is removed, however, there’s a novel approach that avoids the pitfalls of both immediate and staged abdominal wall reconstruction, according to a second team from the Georgetown University, Washington.
The two approaches were offered at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgery as alternatives to usual care. Infected ventral hernia mesh is a well-known headache for general surgeons, and management isn’t standardized. Surgeons are keenly alert for new approaches to improve outcomes; the presenters said they hoped their talks would help.
The work “is really pushing this forward, and giving us new data to manage a really vexing problem,” said an audience member.
Almost 80% salvageable
Infected meshes are usually removed, but the Cleveland Clinic investigators found that that’s often not necessary.
They reviewed 905 elective ventral hernia repairs at the clinic with synthetic sublay mesh in the retrorectus space. The median hernia width was about 15 cm, and the implanted mesh – usually medium- or heavy-weight polypropylene – had a mean area of 900 cm2, “so these were big hernias with a lot of mesh. [Patients] often come to us as a last resort because they’ve been told no elsewhere,” said lead investigator Dominykas Burneikis, MD.
Twenty-four patients (2.7%) developed deep surgical site infections below the anterior rectus fascia. Instead of returning to the OR for new mesh, the team opened, drained, and debrided the wounds, and patients received antibiotics plus negative pressure wound therapy.
Those measures were enough for all but one patient. Mesh was generally found to be granulating well into surrounding tissue, so it was left completely intact in 19 cases (79%), and just trimmed a bit in four others. One man had an excision after his skin flap died and the hernia recurred. At 8 months, 11 patients were completely healed, and 12 had granulating wounds with no visible mesh. There were no cutaneous fistulas.
In short, “we had an 80% mesh salvage rate at 8 months, [which] led us to conclude that most synthetic mesh infections after retrorectus sublay repair do not require explanation,” Dr. Burneikis said.
A hybrid approach
When infected mesh does need to come out, abdominal wall reconstruction is either done in the same procedure or months later. Immediate reconstruction generally means operating in a contaminated field, with subsequent rates of wound infection of up to 48%. Delayed closure, meanwhile, means long-term wound care and temporary hernia recurrence, among other problems.
The Georgetown team reported good outcomes with a hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both procedures while avoiding their pitfalls. In the first step, mesh is removed, the abdominal wall debrided, fistulas taken down, and cultures obtained, explained lead investigator and surgery resident Kieranjeet Nijhar, MD.
The wound is temporarily closed with a sterile plastic liner under negative pressure, and patients are taken to the floor for IV antibiotics based on culture results. Three days later, after the infection has been knocked down, the patient is returned to the OR for debridement to healthy tissue and definitive reconstruction with biologic mesh. It’s all done during the same hospitalization.
Dr. Nijhar reviewed 53 cases at Georgetown since 2009. Patients were a mean age of 58 years, with an average body mass index of 35.1 kg/m2. Infected mesh was most commonly underlain or retrorectus; mean defect size was 206 cm2. Patients spent an average of 11 days in the hospital.
During a mean follow-up of about 9 months, 17 patients (32%) had surgical site problems – infection, dehiscence, hematoma, or seroma – and hernia recurred in six (11.3%); the results compare favorably with especially immediate reconstruction. As in prior studies, higher age and bridge repair were associated with recurrence and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection with surgical site problems.
“We propose this as a potential alternative for” repairs of ventral hernias with infected mesh, Dr. Nijhar said.
Dr. Nijhar and Dr. Burneikis had no relevant disclosures. There was no external funding for the work.
BOSTON – Deep according to Cleveland Clinic investigators.
When infected mesh is removed, however, there’s a novel approach that avoids the pitfalls of both immediate and staged abdominal wall reconstruction, according to a second team from the Georgetown University, Washington.
The two approaches were offered at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgery as alternatives to usual care. Infected ventral hernia mesh is a well-known headache for general surgeons, and management isn’t standardized. Surgeons are keenly alert for new approaches to improve outcomes; the presenters said they hoped their talks would help.
The work “is really pushing this forward, and giving us new data to manage a really vexing problem,” said an audience member.
Almost 80% salvageable
Infected meshes are usually removed, but the Cleveland Clinic investigators found that that’s often not necessary.
They reviewed 905 elective ventral hernia repairs at the clinic with synthetic sublay mesh in the retrorectus space. The median hernia width was about 15 cm, and the implanted mesh – usually medium- or heavy-weight polypropylene – had a mean area of 900 cm2, “so these were big hernias with a lot of mesh. [Patients] often come to us as a last resort because they’ve been told no elsewhere,” said lead investigator Dominykas Burneikis, MD.
Twenty-four patients (2.7%) developed deep surgical site infections below the anterior rectus fascia. Instead of returning to the OR for new mesh, the team opened, drained, and debrided the wounds, and patients received antibiotics plus negative pressure wound therapy.
Those measures were enough for all but one patient. Mesh was generally found to be granulating well into surrounding tissue, so it was left completely intact in 19 cases (79%), and just trimmed a bit in four others. One man had an excision after his skin flap died and the hernia recurred. At 8 months, 11 patients were completely healed, and 12 had granulating wounds with no visible mesh. There were no cutaneous fistulas.
In short, “we had an 80% mesh salvage rate at 8 months, [which] led us to conclude that most synthetic mesh infections after retrorectus sublay repair do not require explanation,” Dr. Burneikis said.
A hybrid approach
When infected mesh does need to come out, abdominal wall reconstruction is either done in the same procedure or months later. Immediate reconstruction generally means operating in a contaminated field, with subsequent rates of wound infection of up to 48%. Delayed closure, meanwhile, means long-term wound care and temporary hernia recurrence, among other problems.
The Georgetown team reported good outcomes with a hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both procedures while avoiding their pitfalls. In the first step, mesh is removed, the abdominal wall debrided, fistulas taken down, and cultures obtained, explained lead investigator and surgery resident Kieranjeet Nijhar, MD.
The wound is temporarily closed with a sterile plastic liner under negative pressure, and patients are taken to the floor for IV antibiotics based on culture results. Three days later, after the infection has been knocked down, the patient is returned to the OR for debridement to healthy tissue and definitive reconstruction with biologic mesh. It’s all done during the same hospitalization.
Dr. Nijhar reviewed 53 cases at Georgetown since 2009. Patients were a mean age of 58 years, with an average body mass index of 35.1 kg/m2. Infected mesh was most commonly underlain or retrorectus; mean defect size was 206 cm2. Patients spent an average of 11 days in the hospital.
During a mean follow-up of about 9 months, 17 patients (32%) had surgical site problems – infection, dehiscence, hematoma, or seroma – and hernia recurred in six (11.3%); the results compare favorably with especially immediate reconstruction. As in prior studies, higher age and bridge repair were associated with recurrence and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection with surgical site problems.
“We propose this as a potential alternative for” repairs of ventral hernias with infected mesh, Dr. Nijhar said.
Dr. Nijhar and Dr. Burneikis had no relevant disclosures. There was no external funding for the work.
BOSTON – Deep according to Cleveland Clinic investigators.
When infected mesh is removed, however, there’s a novel approach that avoids the pitfalls of both immediate and staged abdominal wall reconstruction, according to a second team from the Georgetown University, Washington.
The two approaches were offered at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgery as alternatives to usual care. Infected ventral hernia mesh is a well-known headache for general surgeons, and management isn’t standardized. Surgeons are keenly alert for new approaches to improve outcomes; the presenters said they hoped their talks would help.
The work “is really pushing this forward, and giving us new data to manage a really vexing problem,” said an audience member.
Almost 80% salvageable
Infected meshes are usually removed, but the Cleveland Clinic investigators found that that’s often not necessary.
They reviewed 905 elective ventral hernia repairs at the clinic with synthetic sublay mesh in the retrorectus space. The median hernia width was about 15 cm, and the implanted mesh – usually medium- or heavy-weight polypropylene – had a mean area of 900 cm2, “so these were big hernias with a lot of mesh. [Patients] often come to us as a last resort because they’ve been told no elsewhere,” said lead investigator Dominykas Burneikis, MD.
Twenty-four patients (2.7%) developed deep surgical site infections below the anterior rectus fascia. Instead of returning to the OR for new mesh, the team opened, drained, and debrided the wounds, and patients received antibiotics plus negative pressure wound therapy.
Those measures were enough for all but one patient. Mesh was generally found to be granulating well into surrounding tissue, so it was left completely intact in 19 cases (79%), and just trimmed a bit in four others. One man had an excision after his skin flap died and the hernia recurred. At 8 months, 11 patients were completely healed, and 12 had granulating wounds with no visible mesh. There were no cutaneous fistulas.
In short, “we had an 80% mesh salvage rate at 8 months, [which] led us to conclude that most synthetic mesh infections after retrorectus sublay repair do not require explanation,” Dr. Burneikis said.
A hybrid approach
When infected mesh does need to come out, abdominal wall reconstruction is either done in the same procedure or months later. Immediate reconstruction generally means operating in a contaminated field, with subsequent rates of wound infection of up to 48%. Delayed closure, meanwhile, means long-term wound care and temporary hernia recurrence, among other problems.
The Georgetown team reported good outcomes with a hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both procedures while avoiding their pitfalls. In the first step, mesh is removed, the abdominal wall debrided, fistulas taken down, and cultures obtained, explained lead investigator and surgery resident Kieranjeet Nijhar, MD.
The wound is temporarily closed with a sterile plastic liner under negative pressure, and patients are taken to the floor for IV antibiotics based on culture results. Three days later, after the infection has been knocked down, the patient is returned to the OR for debridement to healthy tissue and definitive reconstruction with biologic mesh. It’s all done during the same hospitalization.
Dr. Nijhar reviewed 53 cases at Georgetown since 2009. Patients were a mean age of 58 years, with an average body mass index of 35.1 kg/m2. Infected mesh was most commonly underlain or retrorectus; mean defect size was 206 cm2. Patients spent an average of 11 days in the hospital.
During a mean follow-up of about 9 months, 17 patients (32%) had surgical site problems – infection, dehiscence, hematoma, or seroma – and hernia recurred in six (11.3%); the results compare favorably with especially immediate reconstruction. As in prior studies, higher age and bridge repair were associated with recurrence and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection with surgical site problems.
“We propose this as a potential alternative for” repairs of ventral hernias with infected mesh, Dr. Nijhar said.
Dr. Nijhar and Dr. Burneikis had no relevant disclosures. There was no external funding for the work.
REPORTING FROM THE ACS CLINICAL CONGRESS
Key clinical point: Infected mesh can sometimes be left in place, and a new surgical approach splits the difference between immediate and staged reconstruction.
Major finding: The salvage rate for infected ventral hernia mesh was almost 80% at 8 months, and the recurrence rate was 11.3% with hybrid reconstruction at 9 months.
Study details: Reviews of 24 infected mesh cases and 53 hybrid repairs
Disclosures: The study leads didn’t have any disclosures, and there was no external funding.