User login
Accelerating the careers of future hospitalists
Grant program provides funding, research support
When it comes to what future hospitalists should be doing to accelerate their careers, is there such a thing as a “no-brainer” opportunity? Aram Namavar, MD, MS, thinks so.
Dr. Namavar is a first-year internal medicine resident at UC San Diego pursuing a career as an academic hospitalist. He is passionate about building interdisciplinary platforms for patient care enhancement and serving disadvantaged and underserved communities.
Membership in the Society of Hospital Medicine is free for medical students and offers a diverse array of resources specifically curated for the ever-expanding needs of the specialty and its aspiring leaders. An active member of SHM since 2015, Dr. Namavar has looked to the organization for leading career-enhancing opportunities and resources in hospital medicine to help him achieve his altruistic career goals.
For Dr. Namavar, a few of these professional development–focused opportunities include becoming an active member of the Physicians-in-Training Committee, a founding member of the Resident and Student Special Interest Group, and a recipient of the Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant.
“I applied for the Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant to have a dedicated summer of learning quality improvement through being in meetings with hospital medicine leaders and leading my research initiatives alongside my team,” Dr. Namavar said. He described the experience as pivotal to his growth within hospital medicine and as a medical student.
The key component to SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant opportunity is the ability for first- and second-year medical students to work alongside leading hospital medicine professionals in scholarly projects to help interested students gain perspective on working within the specialty.
“As a young, interested trainee in hospital medicine, working with a mentor who is established in the field allows one to learn what steps to take in the future to become a leader,” he said. “[It allowed me to] gain insight into leadership style and develop a strong network for the future.”
In addition to the program’s mentorship benefits, grant recipients also receive complimentary registration to SHM’s Annual Conference with the added perks of funding and research support, accommodation expenses, and acceptance into SHM’s RIV Poster Competition.
“I attended the SHM Annual Conference previously,” Dr. Namavar said. “However, as a grant recipient, you have the chance to connect with faculty who will come to your poster presentation and want to learn about your project. This platform allows you to meet individuals from across the nation and connect with those interested in helping trainees thrive within hospital medicine.”
With the grant funding, Dr. Namavar completed his project, “Evaluation of Decisional Conflict as a Simple Tool to Assess Risk of Readmission.” He described this endeavor as a multidimensional project that took on a holistic view of patient-centered readmissions. “We evaluated patient conflict in posthospitalization resources as a marker of readmission, social determinants of health, and health literacy as risk factors for hospital readmission.”
Described by Dr. Namavar as a “no-brainer” opportunity, SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant “offers some of the best benefits overall – funding for your project, automatic acceptance at the Annual Conference, the chance to have your work highlighted in blog posts, networking opportunities with faculty across the nation, and travel reimbursement for the conference.”
Building your networks or establishing your professional career path does not stop at individual networking events or scholarship programs, Dr. Namavar said. It’s about piecing together the building blocks to set yourself up for success.
“My long-term involvement in SHM through working on a committee, leading a special interest group, attending annual meetings, and receiving the grant from SHM has helped me to build new, long-lasting connections in the field,” he said. “Because of this, I plan to continue to serve within SHM in multiple capacities throughout my career in hospital medicine.”
Are you a first- or second-year medical student interested in taking the next step in your hospital medicine career? Apply to SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant program through late January 2020 at hospitalmedicine.org/scholargrant.
Ms. Cowan is a marketing communications specialist at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Grant program provides funding, research support
Grant program provides funding, research support
When it comes to what future hospitalists should be doing to accelerate their careers, is there such a thing as a “no-brainer” opportunity? Aram Namavar, MD, MS, thinks so.
Dr. Namavar is a first-year internal medicine resident at UC San Diego pursuing a career as an academic hospitalist. He is passionate about building interdisciplinary platforms for patient care enhancement and serving disadvantaged and underserved communities.
Membership in the Society of Hospital Medicine is free for medical students and offers a diverse array of resources specifically curated for the ever-expanding needs of the specialty and its aspiring leaders. An active member of SHM since 2015, Dr. Namavar has looked to the organization for leading career-enhancing opportunities and resources in hospital medicine to help him achieve his altruistic career goals.
For Dr. Namavar, a few of these professional development–focused opportunities include becoming an active member of the Physicians-in-Training Committee, a founding member of the Resident and Student Special Interest Group, and a recipient of the Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant.
“I applied for the Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant to have a dedicated summer of learning quality improvement through being in meetings with hospital medicine leaders and leading my research initiatives alongside my team,” Dr. Namavar said. He described the experience as pivotal to his growth within hospital medicine and as a medical student.
The key component to SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant opportunity is the ability for first- and second-year medical students to work alongside leading hospital medicine professionals in scholarly projects to help interested students gain perspective on working within the specialty.
“As a young, interested trainee in hospital medicine, working with a mentor who is established in the field allows one to learn what steps to take in the future to become a leader,” he said. “[It allowed me to] gain insight into leadership style and develop a strong network for the future.”
In addition to the program’s mentorship benefits, grant recipients also receive complimentary registration to SHM’s Annual Conference with the added perks of funding and research support, accommodation expenses, and acceptance into SHM’s RIV Poster Competition.
“I attended the SHM Annual Conference previously,” Dr. Namavar said. “However, as a grant recipient, you have the chance to connect with faculty who will come to your poster presentation and want to learn about your project. This platform allows you to meet individuals from across the nation and connect with those interested in helping trainees thrive within hospital medicine.”
With the grant funding, Dr. Namavar completed his project, “Evaluation of Decisional Conflict as a Simple Tool to Assess Risk of Readmission.” He described this endeavor as a multidimensional project that took on a holistic view of patient-centered readmissions. “We evaluated patient conflict in posthospitalization resources as a marker of readmission, social determinants of health, and health literacy as risk factors for hospital readmission.”
Described by Dr. Namavar as a “no-brainer” opportunity, SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant “offers some of the best benefits overall – funding for your project, automatic acceptance at the Annual Conference, the chance to have your work highlighted in blog posts, networking opportunities with faculty across the nation, and travel reimbursement for the conference.”
Building your networks or establishing your professional career path does not stop at individual networking events or scholarship programs, Dr. Namavar said. It’s about piecing together the building blocks to set yourself up for success.
“My long-term involvement in SHM through working on a committee, leading a special interest group, attending annual meetings, and receiving the grant from SHM has helped me to build new, long-lasting connections in the field,” he said. “Because of this, I plan to continue to serve within SHM in multiple capacities throughout my career in hospital medicine.”
Are you a first- or second-year medical student interested in taking the next step in your hospital medicine career? Apply to SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant program through late January 2020 at hospitalmedicine.org/scholargrant.
Ms. Cowan is a marketing communications specialist at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
When it comes to what future hospitalists should be doing to accelerate their careers, is there such a thing as a “no-brainer” opportunity? Aram Namavar, MD, MS, thinks so.
Dr. Namavar is a first-year internal medicine resident at UC San Diego pursuing a career as an academic hospitalist. He is passionate about building interdisciplinary platforms for patient care enhancement and serving disadvantaged and underserved communities.
Membership in the Society of Hospital Medicine is free for medical students and offers a diverse array of resources specifically curated for the ever-expanding needs of the specialty and its aspiring leaders. An active member of SHM since 2015, Dr. Namavar has looked to the organization for leading career-enhancing opportunities and resources in hospital medicine to help him achieve his altruistic career goals.
For Dr. Namavar, a few of these professional development–focused opportunities include becoming an active member of the Physicians-in-Training Committee, a founding member of the Resident and Student Special Interest Group, and a recipient of the Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant.
“I applied for the Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant to have a dedicated summer of learning quality improvement through being in meetings with hospital medicine leaders and leading my research initiatives alongside my team,” Dr. Namavar said. He described the experience as pivotal to his growth within hospital medicine and as a medical student.
The key component to SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant opportunity is the ability for first- and second-year medical students to work alongside leading hospital medicine professionals in scholarly projects to help interested students gain perspective on working within the specialty.
“As a young, interested trainee in hospital medicine, working with a mentor who is established in the field allows one to learn what steps to take in the future to become a leader,” he said. “[It allowed me to] gain insight into leadership style and develop a strong network for the future.”
In addition to the program’s mentorship benefits, grant recipients also receive complimentary registration to SHM’s Annual Conference with the added perks of funding and research support, accommodation expenses, and acceptance into SHM’s RIV Poster Competition.
“I attended the SHM Annual Conference previously,” Dr. Namavar said. “However, as a grant recipient, you have the chance to connect with faculty who will come to your poster presentation and want to learn about your project. This platform allows you to meet individuals from across the nation and connect with those interested in helping trainees thrive within hospital medicine.”
With the grant funding, Dr. Namavar completed his project, “Evaluation of Decisional Conflict as a Simple Tool to Assess Risk of Readmission.” He described this endeavor as a multidimensional project that took on a holistic view of patient-centered readmissions. “We evaluated patient conflict in posthospitalization resources as a marker of readmission, social determinants of health, and health literacy as risk factors for hospital readmission.”
Described by Dr. Namavar as a “no-brainer” opportunity, SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant “offers some of the best benefits overall – funding for your project, automatic acceptance at the Annual Conference, the chance to have your work highlighted in blog posts, networking opportunities with faculty across the nation, and travel reimbursement for the conference.”
Building your networks or establishing your professional career path does not stop at individual networking events or scholarship programs, Dr. Namavar said. It’s about piecing together the building blocks to set yourself up for success.
“My long-term involvement in SHM through working on a committee, leading a special interest group, attending annual meetings, and receiving the grant from SHM has helped me to build new, long-lasting connections in the field,” he said. “Because of this, I plan to continue to serve within SHM in multiple capacities throughout my career in hospital medicine.”
Are you a first- or second-year medical student interested in taking the next step in your hospital medicine career? Apply to SHM’s Student Hospitalist Scholar Grant program through late January 2020 at hospitalmedicine.org/scholargrant.
Ms. Cowan is a marketing communications specialist at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Letter to the Editor
Editor’s note: This is one of the many emails readers sent to Dermatology News in response to Dr. Alan Rockoff’s last “Under My Skin” column in the December issue.
Dr. Rockoff,
I was deeply heartbroken to read that this would be your last column in Dermatology News today. I am a medical dermatologist with 19 years of experience in a small town in North Carolina and have always looked forward to reading your columns. No matter what the topic for the article you chose, I would always glean something worthwhile from it, be it a poignant insight, a relevant practice tip on treatment or patient management, and nearly always a hearty laugh.
Being somewhat rural and without a lot of competition, my very busy practice consists mainly of salt of the earth patients needing straight dermatologic care, mostly skin cancer, psoriasis, acne, the general stuff. Your ability to capture the essence of what it is like to be one of us in the trenches, to expose and eloquently define the most common and frustrating issues we face, has been a source of pleasure for years. On more than one occasion, I put down the magazine and attempted to write a thank you letter for one article or another you wrote, to say that you are doing a great job and please continue to enlighten us with your insight and that your efforts are greatly valued. I am embarrassed to admit, I never could complete those emails, thinking “Why bother the man? He is clearly as busy as me, and why would he want to hear from me anyway?”
Well, at the risk of bothering you, sir, please do accept my apologies for not writing you before you retired your article, and please know that your articles have personally given me years of immense happiness. They will be sorely missed, and likely not ever replaced.
With gratitude,
Jeff Suchniak, MD
Rocky Mount, N.C.
Editor’s note: This is one of the many emails readers sent to Dermatology News in response to Dr. Alan Rockoff’s last “Under My Skin” column in the December issue.
Dr. Rockoff,
I was deeply heartbroken to read that this would be your last column in Dermatology News today. I am a medical dermatologist with 19 years of experience in a small town in North Carolina and have always looked forward to reading your columns. No matter what the topic for the article you chose, I would always glean something worthwhile from it, be it a poignant insight, a relevant practice tip on treatment or patient management, and nearly always a hearty laugh.
Being somewhat rural and without a lot of competition, my very busy practice consists mainly of salt of the earth patients needing straight dermatologic care, mostly skin cancer, psoriasis, acne, the general stuff. Your ability to capture the essence of what it is like to be one of us in the trenches, to expose and eloquently define the most common and frustrating issues we face, has been a source of pleasure for years. On more than one occasion, I put down the magazine and attempted to write a thank you letter for one article or another you wrote, to say that you are doing a great job and please continue to enlighten us with your insight and that your efforts are greatly valued. I am embarrassed to admit, I never could complete those emails, thinking “Why bother the man? He is clearly as busy as me, and why would he want to hear from me anyway?”
Well, at the risk of bothering you, sir, please do accept my apologies for not writing you before you retired your article, and please know that your articles have personally given me years of immense happiness. They will be sorely missed, and likely not ever replaced.
With gratitude,
Jeff Suchniak, MD
Rocky Mount, N.C.
Editor’s note: This is one of the many emails readers sent to Dermatology News in response to Dr. Alan Rockoff’s last “Under My Skin” column in the December issue.
Dr. Rockoff,
I was deeply heartbroken to read that this would be your last column in Dermatology News today. I am a medical dermatologist with 19 years of experience in a small town in North Carolina and have always looked forward to reading your columns. No matter what the topic for the article you chose, I would always glean something worthwhile from it, be it a poignant insight, a relevant practice tip on treatment or patient management, and nearly always a hearty laugh.
Being somewhat rural and without a lot of competition, my very busy practice consists mainly of salt of the earth patients needing straight dermatologic care, mostly skin cancer, psoriasis, acne, the general stuff. Your ability to capture the essence of what it is like to be one of us in the trenches, to expose and eloquently define the most common and frustrating issues we face, has been a source of pleasure for years. On more than one occasion, I put down the magazine and attempted to write a thank you letter for one article or another you wrote, to say that you are doing a great job and please continue to enlighten us with your insight and that your efforts are greatly valued. I am embarrassed to admit, I never could complete those emails, thinking “Why bother the man? He is clearly as busy as me, and why would he want to hear from me anyway?”
Well, at the risk of bothering you, sir, please do accept my apologies for not writing you before you retired your article, and please know that your articles have personally given me years of immense happiness. They will be sorely missed, and likely not ever replaced.
With gratitude,
Jeff Suchniak, MD
Rocky Mount, N.C.
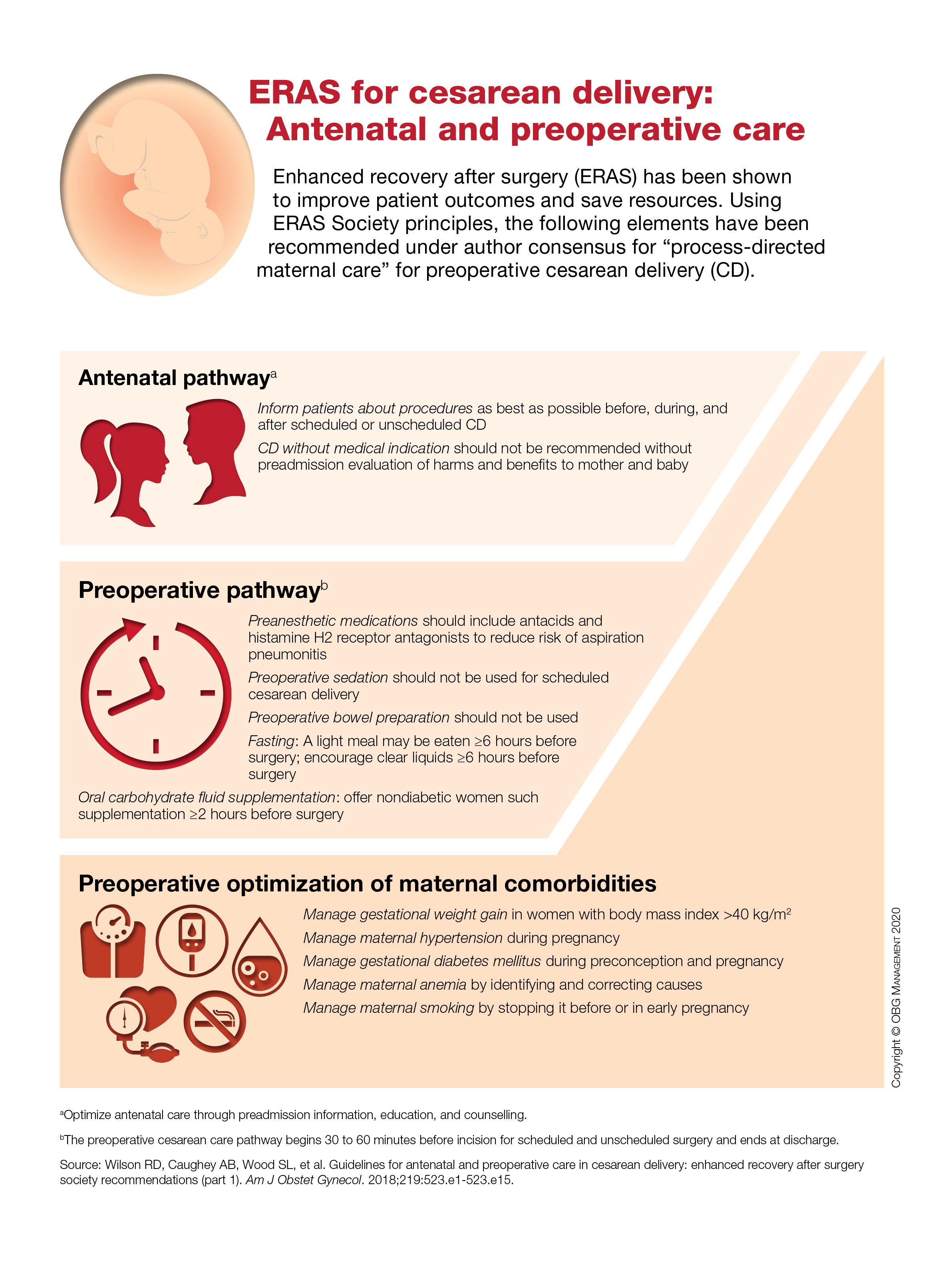
ERAS for cesarean delivery: Antenatal and preoperative care


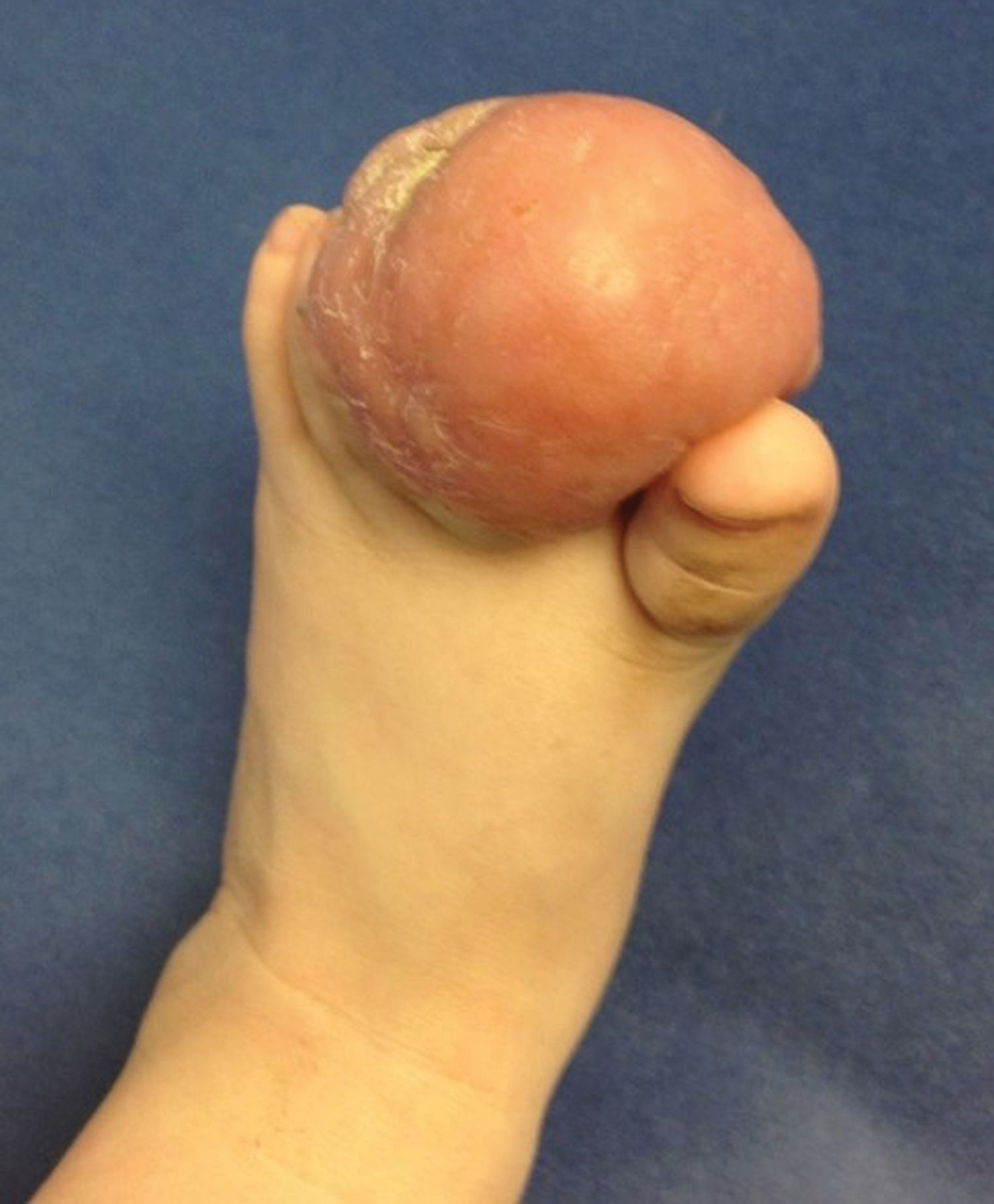
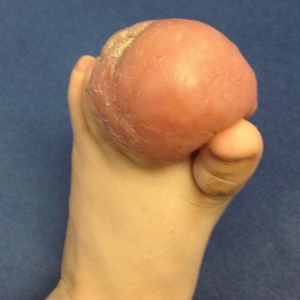
Firm Tumor Encasing the Left Second Toe of an Infant
The Diagnosis: Infantile Digital Fibromatosis
Infantile digital fibromatosis (IDF), or recurring digital fibrous tumor of childhood, is a benign juvenile myofibromatosis that presents as a firm, flesh-colored or slightly erythematous, dome-shaped papule or nodule on the dorsolateral aspects of the digits, usually sparing the thumbs and great toes.1 The tumor appears most commonly at birth and in infants younger than 1 year. It grows slowly over the first month, then rapidly over the next 10 to 14 months.1,2
Although lesions usually regress spontaneously within a few years, excision may be necessary when functional impairment and joint deformity occur. Tumors, however, may recur locally.1,2
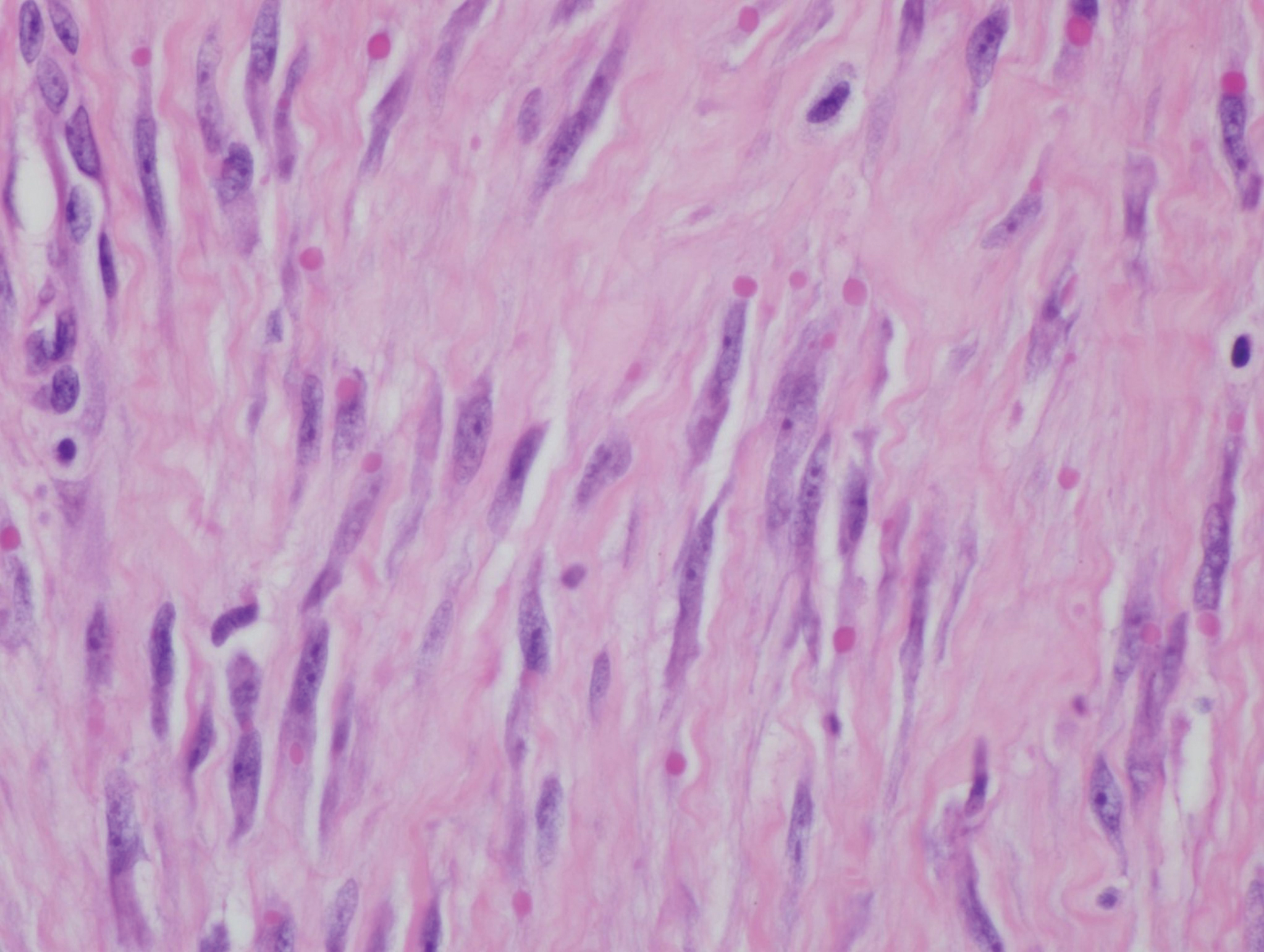
Histologically, IDFs are composed of spindled myofibroblasts with characteristic round eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies, which represent actin and vimentin filaments.1 In our case, histopathologic evaluation showed a proliferation of fibrous spindle cells with pathognomonic eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions consistent with IDF (Figure).
Fibrosarcomas are high-grade and low-grade soft-tissue neoplasms comprised of atypical spindle cells in a herringbone pattern with mitotic figures on pathology.3 They typically present as a slowly growing subcutaneous tumor on the lower extremities of young to middle-aged adults that may progress to become a palpable tender nodule. Infantile hemangiomas, the most common benign soft-tissue tumors of childhood, are vascular proliferations more commonly seen in low-birth-weight female white infants of multiple gestation pregnancies. Superficial hemangiomas present as bright red and lobular nodules or plaques. Deep hemangiomas present as ill-defined, blue-violaceous nodules with no overlying skin changes. Mixed hemangiomas present with features of both superficial and deep hemangiomas. Infantile hemangiomas experience a proliferative phase until 9 to 12 months of age, followed by a gradual involutional phase ending with possible residual telangiectases or fibrofatty change. Unlike IDFs, infantile hemangiomas favor the head and neck over other areas of the body. Keloids are firm, smooth, variably colored papules or plaques of haphazardly arranged thick dermal collagen bundles. They usually develop within a year of skin injury and extend beyond the original injury margin into normal tissue. Supernumerary digits present as small fleshy papules or larger nodules with a vestigial nail, most commonly on the ulnar side of the fifth finger or the radial side of the thumb. Histologically, they are composed of fascicles of nerve fibers.3
Treatment in our patient included partial amputation of the left second toe and excision with local tissue rearrangement by a plastic surgeon. His postoperative course was complicated by a minor wound infection, which resolved with a 7-day course of cephalexin. Since then, the patient has healed well, with gradual toe tissue and nail growth. No recurrence was reported 11 months after surgery.
- Heymann WR. Infantile digital fibromatosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:122-123.
- Niamba P, Léauté-Labrèze C, Boralevi F, et al. Further documentation of spontaneous regression of infantile digital fibromatosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:280-284.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2018.
The Diagnosis: Infantile Digital Fibromatosis
Infantile digital fibromatosis (IDF), or recurring digital fibrous tumor of childhood, is a benign juvenile myofibromatosis that presents as a firm, flesh-colored or slightly erythematous, dome-shaped papule or nodule on the dorsolateral aspects of the digits, usually sparing the thumbs and great toes.1 The tumor appears most commonly at birth and in infants younger than 1 year. It grows slowly over the first month, then rapidly over the next 10 to 14 months.1,2
Although lesions usually regress spontaneously within a few years, excision may be necessary when functional impairment and joint deformity occur. Tumors, however, may recur locally.1,2
Histologically, IDFs are composed of spindled myofibroblasts with characteristic round eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies, which represent actin and vimentin filaments.1 In our case, histopathologic evaluation showed a proliferation of fibrous spindle cells with pathognomonic eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions consistent with IDF (Figure).
Fibrosarcomas are high-grade and low-grade soft-tissue neoplasms comprised of atypical spindle cells in a herringbone pattern with mitotic figures on pathology.3 They typically present as a slowly growing subcutaneous tumor on the lower extremities of young to middle-aged adults that may progress to become a palpable tender nodule. Infantile hemangiomas, the most common benign soft-tissue tumors of childhood, are vascular proliferations more commonly seen in low-birth-weight female white infants of multiple gestation pregnancies. Superficial hemangiomas present as bright red and lobular nodules or plaques. Deep hemangiomas present as ill-defined, blue-violaceous nodules with no overlying skin changes. Mixed hemangiomas present with features of both superficial and deep hemangiomas. Infantile hemangiomas experience a proliferative phase until 9 to 12 months of age, followed by a gradual involutional phase ending with possible residual telangiectases or fibrofatty change. Unlike IDFs, infantile hemangiomas favor the head and neck over other areas of the body. Keloids are firm, smooth, variably colored papules or plaques of haphazardly arranged thick dermal collagen bundles. They usually develop within a year of skin injury and extend beyond the original injury margin into normal tissue. Supernumerary digits present as small fleshy papules or larger nodules with a vestigial nail, most commonly on the ulnar side of the fifth finger or the radial side of the thumb. Histologically, they are composed of fascicles of nerve fibers.3
Treatment in our patient included partial amputation of the left second toe and excision with local tissue rearrangement by a plastic surgeon. His postoperative course was complicated by a minor wound infection, which resolved with a 7-day course of cephalexin. Since then, the patient has healed well, with gradual toe tissue and nail growth. No recurrence was reported 11 months after surgery.
The Diagnosis: Infantile Digital Fibromatosis
Infantile digital fibromatosis (IDF), or recurring digital fibrous tumor of childhood, is a benign juvenile myofibromatosis that presents as a firm, flesh-colored or slightly erythematous, dome-shaped papule or nodule on the dorsolateral aspects of the digits, usually sparing the thumbs and great toes.1 The tumor appears most commonly at birth and in infants younger than 1 year. It grows slowly over the first month, then rapidly over the next 10 to 14 months.1,2
Although lesions usually regress spontaneously within a few years, excision may be necessary when functional impairment and joint deformity occur. Tumors, however, may recur locally.1,2
Histologically, IDFs are composed of spindled myofibroblasts with characteristic round eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies, which represent actin and vimentin filaments.1 In our case, histopathologic evaluation showed a proliferation of fibrous spindle cells with pathognomonic eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions consistent with IDF (Figure).
Fibrosarcomas are high-grade and low-grade soft-tissue neoplasms comprised of atypical spindle cells in a herringbone pattern with mitotic figures on pathology.3 They typically present as a slowly growing subcutaneous tumor on the lower extremities of young to middle-aged adults that may progress to become a palpable tender nodule. Infantile hemangiomas, the most common benign soft-tissue tumors of childhood, are vascular proliferations more commonly seen in low-birth-weight female white infants of multiple gestation pregnancies. Superficial hemangiomas present as bright red and lobular nodules or plaques. Deep hemangiomas present as ill-defined, blue-violaceous nodules with no overlying skin changes. Mixed hemangiomas present with features of both superficial and deep hemangiomas. Infantile hemangiomas experience a proliferative phase until 9 to 12 months of age, followed by a gradual involutional phase ending with possible residual telangiectases or fibrofatty change. Unlike IDFs, infantile hemangiomas favor the head and neck over other areas of the body. Keloids are firm, smooth, variably colored papules or plaques of haphazardly arranged thick dermal collagen bundles. They usually develop within a year of skin injury and extend beyond the original injury margin into normal tissue. Supernumerary digits present as small fleshy papules or larger nodules with a vestigial nail, most commonly on the ulnar side of the fifth finger or the radial side of the thumb. Histologically, they are composed of fascicles of nerve fibers.3
Treatment in our patient included partial amputation of the left second toe and excision with local tissue rearrangement by a plastic surgeon. His postoperative course was complicated by a minor wound infection, which resolved with a 7-day course of cephalexin. Since then, the patient has healed well, with gradual toe tissue and nail growth. No recurrence was reported 11 months after surgery.
- Heymann WR. Infantile digital fibromatosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:122-123.
- Niamba P, Léauté-Labrèze C, Boralevi F, et al. Further documentation of spontaneous regression of infantile digital fibromatosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:280-284.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2018.
- Heymann WR. Infantile digital fibromatosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:122-123.
- Niamba P, Léauté-Labrèze C, Boralevi F, et al. Further documentation of spontaneous regression of infantile digital fibromatosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:280-284.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2018.
A 10-month-old infant boy presented to the dermatology clinic with a firm, nonpainful, 5.5.×5.6-cm tumor encasing the left second toe, with associated skin breakdown, gait impairment, and lateral displacement of the third toe. The lesion began as a small bump under the toenail at 2 months of age; it then grew rapidly without bleeding or ulceration. It was diagnosed as a hemangioma at 4 months of age, and oral propranolol was initiated for 3 months, without suppression of tumor growth. The patient was referred to the pediatric dermatology department where a clinical diagnosis was made, and the patient was subsequently referred to plastic surgery for excision.
Provide appropriate sexual, reproductive health care for transgender patients
I recently was on a panel of experts discussing how to prevent HIV among transgender youth. Preventing HIV among transgender youth, especially transgender youth of color, remains a challenge for multiple reasons – racism, poverty, stigma, marginalization, and discrimination play a role in the HIV epidemic. A barrier to preventing HIV infections among transgender youth is a lack of knowledge on how to provide them with comprehensive sexual and reproductive health care. Here are some tips and resources that can help you ensure that transgender youth are safe and healthy.
One of the challenges of obtaining a sexual history is asking the right questions For example, if you have a transgender male assigned female at birth, ask whether their partners produce sperm instead of asking about the sex of their partners. A transgender male’s partner may identify as female but is assigned male at birth and uses her penis during sex. Furthermore, a transgender male may be on testosterone, but he still can get pregnant. Asking how they use their organs is just as important. A transgender male who has condomless penile-vaginal sex with multiple partners is at a higher risk for HIV infection than is a transgender male who shares sex toys with his only partner.
Normalizing that you ask a comprehensive sexual history to all your patients regardless of gender identity may put the patient at ease. Many transgender people are reluctant to disclose their gender identity to their provider because they are afraid that the provider may fixate on their sexuality once they do. Stating that you ask sexual health questions to all your patients may prevent the transgender patient from feeling singled out.
Finally, you don’t have to ask a sexual history with every transgender patient, just as you wouldn’t for your cisgender patients. If a patient is complaining of a sprained ankle, a sexual history may not be helpful, compared with obtaining one when a patient comes in with pelvic pain. Many transgender patients avoid care because they are frequently asked about their sexual history or gender identity when these are not relevant to their chief complaint.
Here are some helpful questions to ask when taking a sexual history, according to the University of California, San Francisco, Transgender Care & Treatment Guidelines.1
- Are you having sex? How many sex partners have you had in the past year?
- Who are you having sex with? What types of sex are you having? What parts of your anatomy do you use for sex?
- How do you protect yourself from STIs?
- What STIs have you had in the past, if any? When were you last tested for STIs?
- Has your partner(s) ever been diagnosed with any STIs?
- Do you use alcohol or any drugs when you have sex?
- Do you exchange sex for money, drugs, or a place to stay?
Also, use a trauma-informed approach when working with transgender patients. Many have been victims of sexual trauma. Always have a chaperone accompany you during the exam, explain to the patient what you plan to do and why it is necessary, and allow them to decline (and document their declining the physical exam). Also consider having your patient self-swab for STI screening if appropriate.1
Like obtaining a sexual history, routine screenings for certain types of cancers will be based on the organs the patient has. For example, a transgender woman assigned male at birth will not need a cervical cancer screening, but a transgender man assigned female at birth may need one – if the patient still has a cervix. Cervical cancer screening guidelines are similar for transgender men as it is for nontransgender women, and one should use the same guidelines endorsed by the American Cancer Society, American Society of Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, American Society of Clinical Pathologists, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, and the World Health Organization.2-4
Cervical screenings should never be a requirement for testosterone therapy, and no transgender male under the age of 21 years will need cervical screening. The University of California guidelines offers tips on how to make transgender men more comfortable during cervical cancer screening.5
Contraception and menstrual management also are important for transgender patients. Testosterone can induce amenorrhea for transgender men, but it is not good birth control. If a transgender male patient has sex with partners that produce sperm, then the physician should discuss effective birth control options. There is no ideal birth control option for transgender men. One must consider multiple factors including the patient’s desire for pregnancy, desire to cease periods, ease of administration, and risk for thrombosis.
Most transgender men may balk at the idea of taking estrogen-containing contraception, but it is more effective than oral progestin-only pills. Intrauterine devices are highly effective in pregnancy prevention and can achieve amenorrhea in 50% of users within 1 year,but some transmen may become dysphoric with the procedure. 6 The etonogestrel implants also are highly effective birth control, but irregular periods are common, leading to discontinuation. Depot medroxyprogesterone is highly effective in preventing pregnancy and can induce amenorrhea in 70% of users within 1 year and 80% of users in 2 years, but also is associated with weight gain in one-third of users.7 Finally, pubertal blockers can rapidly stop periods for transmen who are severely dysphoric from their menses; however, before achieving amenorrhea, a flare bleed can occur 4-6 weeks after administration.8 Support from a mental health therapist during this time is critical. Pubertal blockers, nevertheless, are not suitable birth control.
When providing affirming sexual and reproductive health care for transgender patients, key principles include focusing on organs and activities over identity. Additionally, screening for certain types of cancers also is dependent on organs. Finally, do not neglect the importance of contraception among transgender men. Taking these principles in consideration will help you provide excellent care for transgender youth.
Dr. Montano is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Pittsburgh and an adolescent medicine physician at the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Transgender people and sexually transmitted infections (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/stis).
2. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012 May-Jun;62(3):147-72.
3. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(12):880-91.
4. Cervical cancer screening in developing countries: Report of a WHO consultation. 2002. World Health Organization, Geneva.
5. Screening for cervical cancer for transgender men (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/cervical-cancer).
6. Contraception. 2002 Feb;65(2):129-32.
7. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2011 Jun;12(2):93-106.
8. Int J Womens Health. 2014 Jun 23;6:631-7.
Resources
Breast cancer screening in transgender men. (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/breast-cancer-men).
Screening for breast cancer in transgender women. (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/breast-cancer-women).
Transgender health and HIV (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/hiv).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: HIV and Transgender People (https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/gender/transgender/index.html).
I recently was on a panel of experts discussing how to prevent HIV among transgender youth. Preventing HIV among transgender youth, especially transgender youth of color, remains a challenge for multiple reasons – racism, poverty, stigma, marginalization, and discrimination play a role in the HIV epidemic. A barrier to preventing HIV infections among transgender youth is a lack of knowledge on how to provide them with comprehensive sexual and reproductive health care. Here are some tips and resources that can help you ensure that transgender youth are safe and healthy.
One of the challenges of obtaining a sexual history is asking the right questions For example, if you have a transgender male assigned female at birth, ask whether their partners produce sperm instead of asking about the sex of their partners. A transgender male’s partner may identify as female but is assigned male at birth and uses her penis during sex. Furthermore, a transgender male may be on testosterone, but he still can get pregnant. Asking how they use their organs is just as important. A transgender male who has condomless penile-vaginal sex with multiple partners is at a higher risk for HIV infection than is a transgender male who shares sex toys with his only partner.
Normalizing that you ask a comprehensive sexual history to all your patients regardless of gender identity may put the patient at ease. Many transgender people are reluctant to disclose their gender identity to their provider because they are afraid that the provider may fixate on their sexuality once they do. Stating that you ask sexual health questions to all your patients may prevent the transgender patient from feeling singled out.
Finally, you don’t have to ask a sexual history with every transgender patient, just as you wouldn’t for your cisgender patients. If a patient is complaining of a sprained ankle, a sexual history may not be helpful, compared with obtaining one when a patient comes in with pelvic pain. Many transgender patients avoid care because they are frequently asked about their sexual history or gender identity when these are not relevant to their chief complaint.
Here are some helpful questions to ask when taking a sexual history, according to the University of California, San Francisco, Transgender Care & Treatment Guidelines.1
- Are you having sex? How many sex partners have you had in the past year?
- Who are you having sex with? What types of sex are you having? What parts of your anatomy do you use for sex?
- How do you protect yourself from STIs?
- What STIs have you had in the past, if any? When were you last tested for STIs?
- Has your partner(s) ever been diagnosed with any STIs?
- Do you use alcohol or any drugs when you have sex?
- Do you exchange sex for money, drugs, or a place to stay?
Also, use a trauma-informed approach when working with transgender patients. Many have been victims of sexual trauma. Always have a chaperone accompany you during the exam, explain to the patient what you plan to do and why it is necessary, and allow them to decline (and document their declining the physical exam). Also consider having your patient self-swab for STI screening if appropriate.1
Like obtaining a sexual history, routine screenings for certain types of cancers will be based on the organs the patient has. For example, a transgender woman assigned male at birth will not need a cervical cancer screening, but a transgender man assigned female at birth may need one – if the patient still has a cervix. Cervical cancer screening guidelines are similar for transgender men as it is for nontransgender women, and one should use the same guidelines endorsed by the American Cancer Society, American Society of Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, American Society of Clinical Pathologists, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, and the World Health Organization.2-4
Cervical screenings should never be a requirement for testosterone therapy, and no transgender male under the age of 21 years will need cervical screening. The University of California guidelines offers tips on how to make transgender men more comfortable during cervical cancer screening.5
Contraception and menstrual management also are important for transgender patients. Testosterone can induce amenorrhea for transgender men, but it is not good birth control. If a transgender male patient has sex with partners that produce sperm, then the physician should discuss effective birth control options. There is no ideal birth control option for transgender men. One must consider multiple factors including the patient’s desire for pregnancy, desire to cease periods, ease of administration, and risk for thrombosis.
Most transgender men may balk at the idea of taking estrogen-containing contraception, but it is more effective than oral progestin-only pills. Intrauterine devices are highly effective in pregnancy prevention and can achieve amenorrhea in 50% of users within 1 year,but some transmen may become dysphoric with the procedure. 6 The etonogestrel implants also are highly effective birth control, but irregular periods are common, leading to discontinuation. Depot medroxyprogesterone is highly effective in preventing pregnancy and can induce amenorrhea in 70% of users within 1 year and 80% of users in 2 years, but also is associated with weight gain in one-third of users.7 Finally, pubertal blockers can rapidly stop periods for transmen who are severely dysphoric from their menses; however, before achieving amenorrhea, a flare bleed can occur 4-6 weeks after administration.8 Support from a mental health therapist during this time is critical. Pubertal blockers, nevertheless, are not suitable birth control.
When providing affirming sexual and reproductive health care for transgender patients, key principles include focusing on organs and activities over identity. Additionally, screening for certain types of cancers also is dependent on organs. Finally, do not neglect the importance of contraception among transgender men. Taking these principles in consideration will help you provide excellent care for transgender youth.
Dr. Montano is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Pittsburgh and an adolescent medicine physician at the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Transgender people and sexually transmitted infections (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/stis).
2. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012 May-Jun;62(3):147-72.
3. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(12):880-91.
4. Cervical cancer screening in developing countries: Report of a WHO consultation. 2002. World Health Organization, Geneva.
5. Screening for cervical cancer for transgender men (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/cervical-cancer).
6. Contraception. 2002 Feb;65(2):129-32.
7. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2011 Jun;12(2):93-106.
8. Int J Womens Health. 2014 Jun 23;6:631-7.
Resources
Breast cancer screening in transgender men. (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/breast-cancer-men).
Screening for breast cancer in transgender women. (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/breast-cancer-women).
Transgender health and HIV (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/hiv).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: HIV and Transgender People (https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/gender/transgender/index.html).
I recently was on a panel of experts discussing how to prevent HIV among transgender youth. Preventing HIV among transgender youth, especially transgender youth of color, remains a challenge for multiple reasons – racism, poverty, stigma, marginalization, and discrimination play a role in the HIV epidemic. A barrier to preventing HIV infections among transgender youth is a lack of knowledge on how to provide them with comprehensive sexual and reproductive health care. Here are some tips and resources that can help you ensure that transgender youth are safe and healthy.
One of the challenges of obtaining a sexual history is asking the right questions For example, if you have a transgender male assigned female at birth, ask whether their partners produce sperm instead of asking about the sex of their partners. A transgender male’s partner may identify as female but is assigned male at birth and uses her penis during sex. Furthermore, a transgender male may be on testosterone, but he still can get pregnant. Asking how they use their organs is just as important. A transgender male who has condomless penile-vaginal sex with multiple partners is at a higher risk for HIV infection than is a transgender male who shares sex toys with his only partner.
Normalizing that you ask a comprehensive sexual history to all your patients regardless of gender identity may put the patient at ease. Many transgender people are reluctant to disclose their gender identity to their provider because they are afraid that the provider may fixate on their sexuality once they do. Stating that you ask sexual health questions to all your patients may prevent the transgender patient from feeling singled out.
Finally, you don’t have to ask a sexual history with every transgender patient, just as you wouldn’t for your cisgender patients. If a patient is complaining of a sprained ankle, a sexual history may not be helpful, compared with obtaining one when a patient comes in with pelvic pain. Many transgender patients avoid care because they are frequently asked about their sexual history or gender identity when these are not relevant to their chief complaint.
Here are some helpful questions to ask when taking a sexual history, according to the University of California, San Francisco, Transgender Care & Treatment Guidelines.1
- Are you having sex? How many sex partners have you had in the past year?
- Who are you having sex with? What types of sex are you having? What parts of your anatomy do you use for sex?
- How do you protect yourself from STIs?
- What STIs have you had in the past, if any? When were you last tested for STIs?
- Has your partner(s) ever been diagnosed with any STIs?
- Do you use alcohol or any drugs when you have sex?
- Do you exchange sex for money, drugs, or a place to stay?
Also, use a trauma-informed approach when working with transgender patients. Many have been victims of sexual trauma. Always have a chaperone accompany you during the exam, explain to the patient what you plan to do and why it is necessary, and allow them to decline (and document their declining the physical exam). Also consider having your patient self-swab for STI screening if appropriate.1
Like obtaining a sexual history, routine screenings for certain types of cancers will be based on the organs the patient has. For example, a transgender woman assigned male at birth will not need a cervical cancer screening, but a transgender man assigned female at birth may need one – if the patient still has a cervix. Cervical cancer screening guidelines are similar for transgender men as it is for nontransgender women, and one should use the same guidelines endorsed by the American Cancer Society, American Society of Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, American Society of Clinical Pathologists, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, and the World Health Organization.2-4
Cervical screenings should never be a requirement for testosterone therapy, and no transgender male under the age of 21 years will need cervical screening. The University of California guidelines offers tips on how to make transgender men more comfortable during cervical cancer screening.5
Contraception and menstrual management also are important for transgender patients. Testosterone can induce amenorrhea for transgender men, but it is not good birth control. If a transgender male patient has sex with partners that produce sperm, then the physician should discuss effective birth control options. There is no ideal birth control option for transgender men. One must consider multiple factors including the patient’s desire for pregnancy, desire to cease periods, ease of administration, and risk for thrombosis.
Most transgender men may balk at the idea of taking estrogen-containing contraception, but it is more effective than oral progestin-only pills. Intrauterine devices are highly effective in pregnancy prevention and can achieve amenorrhea in 50% of users within 1 year,but some transmen may become dysphoric with the procedure. 6 The etonogestrel implants also are highly effective birth control, but irregular periods are common, leading to discontinuation. Depot medroxyprogesterone is highly effective in preventing pregnancy and can induce amenorrhea in 70% of users within 1 year and 80% of users in 2 years, but also is associated with weight gain in one-third of users.7 Finally, pubertal blockers can rapidly stop periods for transmen who are severely dysphoric from their menses; however, before achieving amenorrhea, a flare bleed can occur 4-6 weeks after administration.8 Support from a mental health therapist during this time is critical. Pubertal blockers, nevertheless, are not suitable birth control.
When providing affirming sexual and reproductive health care for transgender patients, key principles include focusing on organs and activities over identity. Additionally, screening for certain types of cancers also is dependent on organs. Finally, do not neglect the importance of contraception among transgender men. Taking these principles in consideration will help you provide excellent care for transgender youth.
Dr. Montano is an assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Pittsburgh and an adolescent medicine physician at the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Transgender people and sexually transmitted infections (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/stis).
2. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012 May-Jun;62(3):147-72.
3. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(12):880-91.
4. Cervical cancer screening in developing countries: Report of a WHO consultation. 2002. World Health Organization, Geneva.
5. Screening for cervical cancer for transgender men (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/cervical-cancer).
6. Contraception. 2002 Feb;65(2):129-32.
7. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2011 Jun;12(2):93-106.
8. Int J Womens Health. 2014 Jun 23;6:631-7.
Resources
Breast cancer screening in transgender men. (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/breast-cancer-men).
Screening for breast cancer in transgender women. (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/breast-cancer-women).
Transgender health and HIV (https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/hiv).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: HIV and Transgender People (https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/gender/transgender/index.html).
FDA approves avapritinib for adults with GIST with PDGFRA mutation
The Food and Drug Administration has approved avapritinib (Ayvakit) for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) with a platelet-derived growth factor receptor–alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation.
Approval was based on results from a clinical trial of 43 patients with PDGFRA exon 18 mutations, including 38 patients with a PDGFRA D842V mutation, who received 300 mg avapritinib once daily, the FDA said in a statement.
The overall response rate was 84% (7% with complete response, 77% with partial response); the response rate in patients with a D842V mutation was 89% (8% with complete response, 82% with partial response). Median response duration was not reached, but 61% of patients had a response lasting longer than 6 months.
The most common adverse events associated with avapritinib include edema, nausea, fatigue/asthenia, cognitive impairment, vomiting, decreased appetite, diarrhea, hair color changes, increased lacrimation, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, and dizziness. The drug also can cause intracranial hemorrhage and have effects on the central nervous system.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies for GIST. However, today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved avapritinib (Ayvakit) for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) with a platelet-derived growth factor receptor–alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation.
Approval was based on results from a clinical trial of 43 patients with PDGFRA exon 18 mutations, including 38 patients with a PDGFRA D842V mutation, who received 300 mg avapritinib once daily, the FDA said in a statement.
The overall response rate was 84% (7% with complete response, 77% with partial response); the response rate in patients with a D842V mutation was 89% (8% with complete response, 82% with partial response). Median response duration was not reached, but 61% of patients had a response lasting longer than 6 months.
The most common adverse events associated with avapritinib include edema, nausea, fatigue/asthenia, cognitive impairment, vomiting, decreased appetite, diarrhea, hair color changes, increased lacrimation, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, and dizziness. The drug also can cause intracranial hemorrhage and have effects on the central nervous system.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies for GIST. However, today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved avapritinib (Ayvakit) for the treatment of adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) with a platelet-derived growth factor receptor–alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation.
Approval was based on results from a clinical trial of 43 patients with PDGFRA exon 18 mutations, including 38 patients with a PDGFRA D842V mutation, who received 300 mg avapritinib once daily, the FDA said in a statement.
The overall response rate was 84% (7% with complete response, 77% with partial response); the response rate in patients with a D842V mutation was 89% (8% with complete response, 82% with partial response). Median response duration was not reached, but 61% of patients had a response lasting longer than 6 months.
The most common adverse events associated with avapritinib include edema, nausea, fatigue/asthenia, cognitive impairment, vomiting, decreased appetite, diarrhea, hair color changes, increased lacrimation, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, and dizziness. The drug also can cause intracranial hemorrhage and have effects on the central nervous system.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies for GIST. However, today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the statement.
FUEL trial: Post-Fontan udenafil shows mixed results
PHILADELPHIA – In adolescents who have had a Fontan procedure for congenital heart disease, a randomized trial of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor udenafil showed that it achieved improved exercise performance but did not lead to significant improvement in oxygen levels or myocardial performance.
That’s according to results of the Pediatric Heart Network’s Fontan Udenafil Exercise Longitudinal Trial (FUEL) presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “Treatment with udenafil was not associated with a statistically significant improvement in oxygen consumption at peak exercise, but it was associated with statistically significant improvements in exercise performance at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold,” said David J. Goldberg, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in reporting the FUEL results. The results were published simultaneously in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044352).
“This is the first large clinical trial to show improvement in measures of clinically relevant exercise performance in those with single-ventricle heart disease after Fontan palliation,” he said.
FUEL enrolled 400 male and female adolescents with a single functional ventricle after Fontan surgical palliation. In these patients, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is critical for the efficient flow of blood through the lungs without the benefit of a ventricular pump. “While this circulation is typically stable through childhood, cardiovascular efficiency deteriorates over time, associated with a decline in exercise performance and the accrual of Fontan-associated morbidities,” Dr. Goldberg said. “Given the importance of pulmonary vascular resistance, modulators of PVR make sense as potential therapies.”
FUEL evaluated the effect of udenafil 87.5 mg twice daily versus placebo in post-Fontan patients who’d been on anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. The treatment group had a higher percentage of female patients (44% vs. 36% on placebo), but all other baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups.
While the trial found the drug was well tolerated and safe, with side effects typical of PDE5 inhibitors, it did not lead to changes in myocardial performance index, reactive hyperemia index, or log brain natriuretic peptide, Dr. Goldberg said.
At 6 months, both groups showed a decline in exercise data, “as expected,” Dr. Goldberg said. “But that decline was attenuated in the group receiving udenafil,” he said, with peak oxygen consumption declining an average of 0.23 and 0.89 mL/kg per minute in the treatment and placebo groups, respectively (P = 0.092).
Total oxygen consumption, however, actually improved in the udenafil group and declined in the placebo group, 44 mL/min on average versus –3.7 mL/min (P = 0.071).
“There was no significant difference in the change in peak heart rate or the change in peak oxygen saturation between the groups,” Dr. Goldberg said. But three measures at the ventilatory aerobic threshold (VAT) – oxygen consumption, work rate, and ventilation/carbon dioxide output – all showed statistically significant improvement in exercise performance.
“This has important clinical implications,” Dr. Goldberg said of the study findings. “Our study extends recent findings in highlighting the importance of submaximal exercise in the understanding of Fontan physiology. And unlike peak oxygen consumption, submaximal exercise is not constrained by the physiologic ceiling of central venous pressure inherent in exercise physiology after Fontan palliation.”
Maximum oxygen consumption at VAT is likely a more relevant measure after Fontan palliation than is central venous pressure, discussant Craig A. Sable, MD, a pediatric cardiologist in Potomac, Md., noted in his comments. “This is because VAT occurs at about 70% of maximum VO2 [oxygen consumption] in Fontan as opposed to 55% in two-ventricle physiology,” Dr. Sable said.
In adults with congenital heart disease, maximal VO2 of 45%-50% of predicted levels portends increased risk of heart failure and death. “Therefore, a medication that addresses the central deficiencies of Fontan physiology and results in improved exercise performance may allow for a longer period of symptom-free survival,” he said.
In an invited commentary in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044512), Marc Gewillig, MD, and Alexander van de Bruaene, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) said that the findings of FUEL and other trials of pulmonary vasodilators after Fontan leave “open for debate” whether the treatment effects of a 3%-5% improvement in oxygen consumption is clinically meaningful for adolescents. “For failing Fontan patients (not studied in FUEL), these improvements are minimal but maybe relevant,” the commentators wrote. But the studies do not resolve whether that’s enough to prevent further decline.
Dr. Goldberg disclosed receiving research grants from trial sponsor Mezzion Pharmaceuticals and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Sable, Dr. Gewillig, and Dr. van de Bruaene have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldberg D. AHA 2019, Late Breaking Science Session 5.
PHILADELPHIA – In adolescents who have had a Fontan procedure for congenital heart disease, a randomized trial of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor udenafil showed that it achieved improved exercise performance but did not lead to significant improvement in oxygen levels or myocardial performance.
That’s according to results of the Pediatric Heart Network’s Fontan Udenafil Exercise Longitudinal Trial (FUEL) presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “Treatment with udenafil was not associated with a statistically significant improvement in oxygen consumption at peak exercise, but it was associated with statistically significant improvements in exercise performance at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold,” said David J. Goldberg, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in reporting the FUEL results. The results were published simultaneously in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044352).
“This is the first large clinical trial to show improvement in measures of clinically relevant exercise performance in those with single-ventricle heart disease after Fontan palliation,” he said.
FUEL enrolled 400 male and female adolescents with a single functional ventricle after Fontan surgical palliation. In these patients, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is critical for the efficient flow of blood through the lungs without the benefit of a ventricular pump. “While this circulation is typically stable through childhood, cardiovascular efficiency deteriorates over time, associated with a decline in exercise performance and the accrual of Fontan-associated morbidities,” Dr. Goldberg said. “Given the importance of pulmonary vascular resistance, modulators of PVR make sense as potential therapies.”
FUEL evaluated the effect of udenafil 87.5 mg twice daily versus placebo in post-Fontan patients who’d been on anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. The treatment group had a higher percentage of female patients (44% vs. 36% on placebo), but all other baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups.
While the trial found the drug was well tolerated and safe, with side effects typical of PDE5 inhibitors, it did not lead to changes in myocardial performance index, reactive hyperemia index, or log brain natriuretic peptide, Dr. Goldberg said.
At 6 months, both groups showed a decline in exercise data, “as expected,” Dr. Goldberg said. “But that decline was attenuated in the group receiving udenafil,” he said, with peak oxygen consumption declining an average of 0.23 and 0.89 mL/kg per minute in the treatment and placebo groups, respectively (P = 0.092).
Total oxygen consumption, however, actually improved in the udenafil group and declined in the placebo group, 44 mL/min on average versus –3.7 mL/min (P = 0.071).
“There was no significant difference in the change in peak heart rate or the change in peak oxygen saturation between the groups,” Dr. Goldberg said. But three measures at the ventilatory aerobic threshold (VAT) – oxygen consumption, work rate, and ventilation/carbon dioxide output – all showed statistically significant improvement in exercise performance.
“This has important clinical implications,” Dr. Goldberg said of the study findings. “Our study extends recent findings in highlighting the importance of submaximal exercise in the understanding of Fontan physiology. And unlike peak oxygen consumption, submaximal exercise is not constrained by the physiologic ceiling of central venous pressure inherent in exercise physiology after Fontan palliation.”
Maximum oxygen consumption at VAT is likely a more relevant measure after Fontan palliation than is central venous pressure, discussant Craig A. Sable, MD, a pediatric cardiologist in Potomac, Md., noted in his comments. “This is because VAT occurs at about 70% of maximum VO2 [oxygen consumption] in Fontan as opposed to 55% in two-ventricle physiology,” Dr. Sable said.
In adults with congenital heart disease, maximal VO2 of 45%-50% of predicted levels portends increased risk of heart failure and death. “Therefore, a medication that addresses the central deficiencies of Fontan physiology and results in improved exercise performance may allow for a longer period of symptom-free survival,” he said.
In an invited commentary in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044512), Marc Gewillig, MD, and Alexander van de Bruaene, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) said that the findings of FUEL and other trials of pulmonary vasodilators after Fontan leave “open for debate” whether the treatment effects of a 3%-5% improvement in oxygen consumption is clinically meaningful for adolescents. “For failing Fontan patients (not studied in FUEL), these improvements are minimal but maybe relevant,” the commentators wrote. But the studies do not resolve whether that’s enough to prevent further decline.
Dr. Goldberg disclosed receiving research grants from trial sponsor Mezzion Pharmaceuticals and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Sable, Dr. Gewillig, and Dr. van de Bruaene have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldberg D. AHA 2019, Late Breaking Science Session 5.
PHILADELPHIA – In adolescents who have had a Fontan procedure for congenital heart disease, a randomized trial of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor udenafil showed that it achieved improved exercise performance but did not lead to significant improvement in oxygen levels or myocardial performance.
That’s according to results of the Pediatric Heart Network’s Fontan Udenafil Exercise Longitudinal Trial (FUEL) presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “Treatment with udenafil was not associated with a statistically significant improvement in oxygen consumption at peak exercise, but it was associated with statistically significant improvements in exercise performance at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold,” said David J. Goldberg, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in reporting the FUEL results. The results were published simultaneously in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044352).
“This is the first large clinical trial to show improvement in measures of clinically relevant exercise performance in those with single-ventricle heart disease after Fontan palliation,” he said.
FUEL enrolled 400 male and female adolescents with a single functional ventricle after Fontan surgical palliation. In these patients, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is critical for the efficient flow of blood through the lungs without the benefit of a ventricular pump. “While this circulation is typically stable through childhood, cardiovascular efficiency deteriorates over time, associated with a decline in exercise performance and the accrual of Fontan-associated morbidities,” Dr. Goldberg said. “Given the importance of pulmonary vascular resistance, modulators of PVR make sense as potential therapies.”
FUEL evaluated the effect of udenafil 87.5 mg twice daily versus placebo in post-Fontan patients who’d been on anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. The treatment group had a higher percentage of female patients (44% vs. 36% on placebo), but all other baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups.
While the trial found the drug was well tolerated and safe, with side effects typical of PDE5 inhibitors, it did not lead to changes in myocardial performance index, reactive hyperemia index, or log brain natriuretic peptide, Dr. Goldberg said.
At 6 months, both groups showed a decline in exercise data, “as expected,” Dr. Goldberg said. “But that decline was attenuated in the group receiving udenafil,” he said, with peak oxygen consumption declining an average of 0.23 and 0.89 mL/kg per minute in the treatment and placebo groups, respectively (P = 0.092).
Total oxygen consumption, however, actually improved in the udenafil group and declined in the placebo group, 44 mL/min on average versus –3.7 mL/min (P = 0.071).
“There was no significant difference in the change in peak heart rate or the change in peak oxygen saturation between the groups,” Dr. Goldberg said. But three measures at the ventilatory aerobic threshold (VAT) – oxygen consumption, work rate, and ventilation/carbon dioxide output – all showed statistically significant improvement in exercise performance.
“This has important clinical implications,” Dr. Goldberg said of the study findings. “Our study extends recent findings in highlighting the importance of submaximal exercise in the understanding of Fontan physiology. And unlike peak oxygen consumption, submaximal exercise is not constrained by the physiologic ceiling of central venous pressure inherent in exercise physiology after Fontan palliation.”
Maximum oxygen consumption at VAT is likely a more relevant measure after Fontan palliation than is central venous pressure, discussant Craig A. Sable, MD, a pediatric cardiologist in Potomac, Md., noted in his comments. “This is because VAT occurs at about 70% of maximum VO2 [oxygen consumption] in Fontan as opposed to 55% in two-ventricle physiology,” Dr. Sable said.
In adults with congenital heart disease, maximal VO2 of 45%-50% of predicted levels portends increased risk of heart failure and death. “Therefore, a medication that addresses the central deficiencies of Fontan physiology and results in improved exercise performance may allow for a longer period of symptom-free survival,” he said.
In an invited commentary in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044512), Marc Gewillig, MD, and Alexander van de Bruaene, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) said that the findings of FUEL and other trials of pulmonary vasodilators after Fontan leave “open for debate” whether the treatment effects of a 3%-5% improvement in oxygen consumption is clinically meaningful for adolescents. “For failing Fontan patients (not studied in FUEL), these improvements are minimal but maybe relevant,” the commentators wrote. But the studies do not resolve whether that’s enough to prevent further decline.
Dr. Goldberg disclosed receiving research grants from trial sponsor Mezzion Pharmaceuticals and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Sable, Dr. Gewillig, and Dr. van de Bruaene have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldberg D. AHA 2019, Late Breaking Science Session 5.
REPORTING FROM AHA 2019
Cognitive problems after extremely preterm birth persist
Cognitive and neuropsychological impairment associated with extremely preterm (EP) birth persists into young adulthood, according to findings from the 1995 EPICure cohort.
Of note, intellectual impairment increased significantly after the age of 11 years among 19-year-olds in the cohort of individuals born EP, Helen O’Reilly, PhD, of the Institute for Women’s Health at University College London and colleagues reported in Pediatrics.
Neuropsychological assessment to examine general cognitive abilities, visuomotor abilities, prospective memory, and certain aspects of executive functioning and language in 127 cases and 64 term-born controls showed significantly lower scores across all tests in those born EP.
Impairment in at least one neuropsychological domain was present in 60% of EP birth cases (compared with 21% of controls), with 35% having impairment in at least four domains. Most deficits occurred in general cognitive function and/or visuomotor abilities.
Further, and those with cognitive impairment at 11 years were at increased risk of deficit at 19 years (RR, 3.56), even after adjustment for sex and socioeconomic status, the authors wrote.
None of the term-born controls had a cognitive impairment at 11 years, and two (3%) had impairment at 19 years.
Studies of adults born very preterm have revealed that these individuals are at risk for neuropsychological impairment, but the extent of such impairment in individuals with EP birth, defined as birth before 26 weeks’ gestation, had not previously been studied in the long term.
Assessments in the EPICure cohort of individuals born EP in 1995 previously showed scores at 1.1-1.6 standard deviations lower on measures of general cognitive function, compared with standardized norms and/or term-born controls, at age 2.5, 6, and 11 years, Dr. O’Reilly and colleagues explained.
The current findings indicate that general cognitive and neuropsychological functioning problems associated with EP birth persist and can increase into early adulthood, and they “highlight the need for early and ongoing neuropsychological and educational assessment in EP children to ensure these children receive appropriate support in school and for planned educational pathways,” the investigators concluded.
In an accompanying editorial, Louis A. Schmidt, PhD, and Saroj Saigal, MD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., wrote that these findings “provide compelling evidence for persistent effects of cognitive impairments” in individuals born EP.
They highlighted three lessons from the study:
- It is important to control for anxiety in future studies like this “to eliminate potential confounding influences of anxiety when examining performance-based measures in the laboratory setting,” as individuals born EP are known to exhibit anxiety.
- Group heterogeneity also should be considered, as all survivors of prematurity are not alike.
- Measurement equivalency should be established between groups.
With respect to the latter, “although many of the measures used by O’Reilly et al. have been normed, issues of measurement invariance have not been established between EP and control groups on some of the measures reported,” Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal wrote, noting that “many other studies [also] fail to consider this fundamental measurement property.”
“Considering issues of measurement equivalency is of critical importance to ensuring unbiased interpretations of findings,” they added, concluding that the findings by O’Reilly et al. represent an important contribution and confirm findings from many prior studies of extreme prematurity, which “informs how we effectively manage these problems.”
“As the percentage of preterm birth continues to rise worldwide, coupled with reduced morbidity and mortality, and with more EP infants reaching adulthood, there is a need for prospective, long-term outcome studies of extreme prematurity,” Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal added.
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council United Kingdom. The authors reported having no relevant financial disclosures. The editorial by Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal, who also reported having no relevant financial disclosures, was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
SOURCES: O’Reilly H et al. Pediatrics. 2020;145(2):e20192087; Schmidt LA, Saigal S. Pediatrics. 2020;145(2):e20193359.
Cognitive and neuropsychological impairment associated with extremely preterm (EP) birth persists into young adulthood, according to findings from the 1995 EPICure cohort.
Of note, intellectual impairment increased significantly after the age of 11 years among 19-year-olds in the cohort of individuals born EP, Helen O’Reilly, PhD, of the Institute for Women’s Health at University College London and colleagues reported in Pediatrics.
Neuropsychological assessment to examine general cognitive abilities, visuomotor abilities, prospective memory, and certain aspects of executive functioning and language in 127 cases and 64 term-born controls showed significantly lower scores across all tests in those born EP.
Impairment in at least one neuropsychological domain was present in 60% of EP birth cases (compared with 21% of controls), with 35% having impairment in at least four domains. Most deficits occurred in general cognitive function and/or visuomotor abilities.
Further, and those with cognitive impairment at 11 years were at increased risk of deficit at 19 years (RR, 3.56), even after adjustment for sex and socioeconomic status, the authors wrote.
None of the term-born controls had a cognitive impairment at 11 years, and two (3%) had impairment at 19 years.
Studies of adults born very preterm have revealed that these individuals are at risk for neuropsychological impairment, but the extent of such impairment in individuals with EP birth, defined as birth before 26 weeks’ gestation, had not previously been studied in the long term.
Assessments in the EPICure cohort of individuals born EP in 1995 previously showed scores at 1.1-1.6 standard deviations lower on measures of general cognitive function, compared with standardized norms and/or term-born controls, at age 2.5, 6, and 11 years, Dr. O’Reilly and colleagues explained.
The current findings indicate that general cognitive and neuropsychological functioning problems associated with EP birth persist and can increase into early adulthood, and they “highlight the need for early and ongoing neuropsychological and educational assessment in EP children to ensure these children receive appropriate support in school and for planned educational pathways,” the investigators concluded.
In an accompanying editorial, Louis A. Schmidt, PhD, and Saroj Saigal, MD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., wrote that these findings “provide compelling evidence for persistent effects of cognitive impairments” in individuals born EP.
They highlighted three lessons from the study:
- It is important to control for anxiety in future studies like this “to eliminate potential confounding influences of anxiety when examining performance-based measures in the laboratory setting,” as individuals born EP are known to exhibit anxiety.
- Group heterogeneity also should be considered, as all survivors of prematurity are not alike.
- Measurement equivalency should be established between groups.
With respect to the latter, “although many of the measures used by O’Reilly et al. have been normed, issues of measurement invariance have not been established between EP and control groups on some of the measures reported,” Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal wrote, noting that “many other studies [also] fail to consider this fundamental measurement property.”
“Considering issues of measurement equivalency is of critical importance to ensuring unbiased interpretations of findings,” they added, concluding that the findings by O’Reilly et al. represent an important contribution and confirm findings from many prior studies of extreme prematurity, which “informs how we effectively manage these problems.”
“As the percentage of preterm birth continues to rise worldwide, coupled with reduced morbidity and mortality, and with more EP infants reaching adulthood, there is a need for prospective, long-term outcome studies of extreme prematurity,” Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal added.
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council United Kingdom. The authors reported having no relevant financial disclosures. The editorial by Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal, who also reported having no relevant financial disclosures, was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
SOURCES: O’Reilly H et al. Pediatrics. 2020;145(2):e20192087; Schmidt LA, Saigal S. Pediatrics. 2020;145(2):e20193359.
Cognitive and neuropsychological impairment associated with extremely preterm (EP) birth persists into young adulthood, according to findings from the 1995 EPICure cohort.
Of note, intellectual impairment increased significantly after the age of 11 years among 19-year-olds in the cohort of individuals born EP, Helen O’Reilly, PhD, of the Institute for Women’s Health at University College London and colleagues reported in Pediatrics.
Neuropsychological assessment to examine general cognitive abilities, visuomotor abilities, prospective memory, and certain aspects of executive functioning and language in 127 cases and 64 term-born controls showed significantly lower scores across all tests in those born EP.
Impairment in at least one neuropsychological domain was present in 60% of EP birth cases (compared with 21% of controls), with 35% having impairment in at least four domains. Most deficits occurred in general cognitive function and/or visuomotor abilities.
Further, and those with cognitive impairment at 11 years were at increased risk of deficit at 19 years (RR, 3.56), even after adjustment for sex and socioeconomic status, the authors wrote.
None of the term-born controls had a cognitive impairment at 11 years, and two (3%) had impairment at 19 years.
Studies of adults born very preterm have revealed that these individuals are at risk for neuropsychological impairment, but the extent of such impairment in individuals with EP birth, defined as birth before 26 weeks’ gestation, had not previously been studied in the long term.
Assessments in the EPICure cohort of individuals born EP in 1995 previously showed scores at 1.1-1.6 standard deviations lower on measures of general cognitive function, compared with standardized norms and/or term-born controls, at age 2.5, 6, and 11 years, Dr. O’Reilly and colleagues explained.
The current findings indicate that general cognitive and neuropsychological functioning problems associated with EP birth persist and can increase into early adulthood, and they “highlight the need for early and ongoing neuropsychological and educational assessment in EP children to ensure these children receive appropriate support in school and for planned educational pathways,” the investigators concluded.
In an accompanying editorial, Louis A. Schmidt, PhD, and Saroj Saigal, MD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., wrote that these findings “provide compelling evidence for persistent effects of cognitive impairments” in individuals born EP.
They highlighted three lessons from the study:
- It is important to control for anxiety in future studies like this “to eliminate potential confounding influences of anxiety when examining performance-based measures in the laboratory setting,” as individuals born EP are known to exhibit anxiety.
- Group heterogeneity also should be considered, as all survivors of prematurity are not alike.
- Measurement equivalency should be established between groups.
With respect to the latter, “although many of the measures used by O’Reilly et al. have been normed, issues of measurement invariance have not been established between EP and control groups on some of the measures reported,” Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal wrote, noting that “many other studies [also] fail to consider this fundamental measurement property.”
“Considering issues of measurement equivalency is of critical importance to ensuring unbiased interpretations of findings,” they added, concluding that the findings by O’Reilly et al. represent an important contribution and confirm findings from many prior studies of extreme prematurity, which “informs how we effectively manage these problems.”
“As the percentage of preterm birth continues to rise worldwide, coupled with reduced morbidity and mortality, and with more EP infants reaching adulthood, there is a need for prospective, long-term outcome studies of extreme prematurity,” Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal added.
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council United Kingdom. The authors reported having no relevant financial disclosures. The editorial by Dr. Schmidt and Dr. Saigal, who also reported having no relevant financial disclosures, was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
SOURCES: O’Reilly H et al. Pediatrics. 2020;145(2):e20192087; Schmidt LA, Saigal S. Pediatrics. 2020;145(2):e20193359.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Oral lichen planus prevalence estimates go global
for the general population and 0.98% among clinical patients.
Globally, oral lichen planus (OLP) appears to be more prevalent in women than men (1.55% vs. 1.11% in population-based studies; 1.69% vs. 1.09% in clinic-based), in those aged 40 years and older (1.90% vs. 0.62% in clinic-based studies), and in non-Asian countries (see graph), Changchang Li, MD, and associates reported in JAMA Dermatology.
Of the 25 countries represented among the 46 included studies, Brazil had the highest OLP prevalence at 6.04% and India had the lowest at 0.02%. “Smokers and patients who abuse alcohol have a higher prevalence of OLP. This factor may explain why the highest prevalence … was found in Brazil, where 18.18% of residents report being smokers and 29.09% report consumption of alcoholic beverages,” wrote Dr. Li of the department of dermatology at Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wenzhou, China, and associates.
The difference in OLP prevalence by sex may be related to fluctuating female hormone levels, “especially during menstruation or menopause, and that different social roles may lead to the body being in a state of stress,” the investigators suggested.
The age-related difference in OLP could be the result of “longstanding oral habits” or changes to the oral mucosa over time, such as mucosal thinning, decreased elasticity, less saliva secretion, and greater tissue permeability. The higher prevalence among those aged 40 years and older also may be “associated with metabolic changes during aging or with decreased immunity, nutritional deficiencies, medication use, or denture wear,” they wrote.
The review and meta-analysis involved 15 studies (n = 462,993) that included general population data and 31 (n = 191,963) that used information from clinical patients. Sample sizes for those studies ranged from 308 to 402,669.
Statistically significant publication bias was seen among the clinic-based studies but not those that were population based, Dr. Li and associates wrote, adding that “our findings should be considered with caution because of the high heterogeneity of the included studies.”
The study was funded by the First-Class Discipline Construction Foundation of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, the Young Top Talent Project of Scientific and Technological Innovation in Special Support Plan for Training High-level Talents, and the Youth Research and Cultivation Project of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. The investigators did not report any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: C Li et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jan 2. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3797.
for the general population and 0.98% among clinical patients.

Globally, oral lichen planus (OLP) appears to be more prevalent in women than men (1.55% vs. 1.11% in population-based studies; 1.69% vs. 1.09% in clinic-based), in those aged 40 years and older (1.90% vs. 0.62% in clinic-based studies), and in non-Asian countries (see graph), Changchang Li, MD, and associates reported in JAMA Dermatology.
Of the 25 countries represented among the 46 included studies, Brazil had the highest OLP prevalence at 6.04% and India had the lowest at 0.02%. “Smokers and patients who abuse alcohol have a higher prevalence of OLP. This factor may explain why the highest prevalence … was found in Brazil, where 18.18% of residents report being smokers and 29.09% report consumption of alcoholic beverages,” wrote Dr. Li of the department of dermatology at Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wenzhou, China, and associates.
The difference in OLP prevalence by sex may be related to fluctuating female hormone levels, “especially during menstruation or menopause, and that different social roles may lead to the body being in a state of stress,” the investigators suggested.
The age-related difference in OLP could be the result of “longstanding oral habits” or changes to the oral mucosa over time, such as mucosal thinning, decreased elasticity, less saliva secretion, and greater tissue permeability. The higher prevalence among those aged 40 years and older also may be “associated with metabolic changes during aging or with decreased immunity, nutritional deficiencies, medication use, or denture wear,” they wrote.
The review and meta-analysis involved 15 studies (n = 462,993) that included general population data and 31 (n = 191,963) that used information from clinical patients. Sample sizes for those studies ranged from 308 to 402,669.
Statistically significant publication bias was seen among the clinic-based studies but not those that were population based, Dr. Li and associates wrote, adding that “our findings should be considered with caution because of the high heterogeneity of the included studies.”
The study was funded by the First-Class Discipline Construction Foundation of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, the Young Top Talent Project of Scientific and Technological Innovation in Special Support Plan for Training High-level Talents, and the Youth Research and Cultivation Project of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. The investigators did not report any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: C Li et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jan 2. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3797.
for the general population and 0.98% among clinical patients.

Globally, oral lichen planus (OLP) appears to be more prevalent in women than men (1.55% vs. 1.11% in population-based studies; 1.69% vs. 1.09% in clinic-based), in those aged 40 years and older (1.90% vs. 0.62% in clinic-based studies), and in non-Asian countries (see graph), Changchang Li, MD, and associates reported in JAMA Dermatology.
Of the 25 countries represented among the 46 included studies, Brazil had the highest OLP prevalence at 6.04% and India had the lowest at 0.02%. “Smokers and patients who abuse alcohol have a higher prevalence of OLP. This factor may explain why the highest prevalence … was found in Brazil, where 18.18% of residents report being smokers and 29.09% report consumption of alcoholic beverages,” wrote Dr. Li of the department of dermatology at Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wenzhou, China, and associates.
The difference in OLP prevalence by sex may be related to fluctuating female hormone levels, “especially during menstruation or menopause, and that different social roles may lead to the body being in a state of stress,” the investigators suggested.
The age-related difference in OLP could be the result of “longstanding oral habits” or changes to the oral mucosa over time, such as mucosal thinning, decreased elasticity, less saliva secretion, and greater tissue permeability. The higher prevalence among those aged 40 years and older also may be “associated with metabolic changes during aging or with decreased immunity, nutritional deficiencies, medication use, or denture wear,” they wrote.
The review and meta-analysis involved 15 studies (n = 462,993) that included general population data and 31 (n = 191,963) that used information from clinical patients. Sample sizes for those studies ranged from 308 to 402,669.
Statistically significant publication bias was seen among the clinic-based studies but not those that were population based, Dr. Li and associates wrote, adding that “our findings should be considered with caution because of the high heterogeneity of the included studies.”
The study was funded by the First-Class Discipline Construction Foundation of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, the Young Top Talent Project of Scientific and Technological Innovation in Special Support Plan for Training High-level Talents, and the Youth Research and Cultivation Project of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. The investigators did not report any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: C Li et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jan 2. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3797.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Long-term entecavir looks safe, effective in HBV
For patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, up to 10 years of treatment with entecavir was safe and produced a superior rate of sustained virologic response, compared with other HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogues in a global randomized clinical trial.
Virologic responses were confirmed and maintained in 80% of entecavir patients and 61% of patients who received other therapies, said Jin-Lin Hou, MD, of Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, China, and associates. Regardless of which treatment patients received, a sustained virologic response was associated with a significantly lower rate of liver-related hepatitis B virus (HBV) disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Rates of serious treatment-related adverse events were 0.2% in the entecavir arm and 0.8% in the nonentecavir arm. Moreover, the primary outcome of time-to-adjudicated clinical outcome events “showed that entecavir treatment, compared with nonentecavir, was not associated with an increased risk of malignant neoplasms, including hepatocellular carcinoma, nonhepatocellular carcinoma malignancies, and overall malignancies,” they wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Entecavir is approved for the treatment of adults with chronic HBV infection, and its long-term use has been linked to the regression of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. In treatment-naive patients, genotypic resistance and virologic breakthrough are rare even after up to 5 years of entecavir therapy. Although human studies have not linked this treatment duration with an increased risk of adverse events, murine studies have identified benign and malignant tumors of the brain, lung, and liver in entecavir-treated mice and rats. “With the exception of lung tumors, which were limited to male mice, rodent tumors occurred only at entecavir exposures [that were] significantly higher than those achieved in human beings with standard approved doses,” the researchers wrote.
For the trial, they assigned more than 12,000 patients with chronic HBV infection to receive long-term treatment with entecavir or investigators’ choice of another HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogue. Patients were from 229 centers in Asia, Europe, and North and South America, and a total of 6,216 received entecavir, while 6,162 received another therapy.
Compared with other HBV nucleoside and nucleotide analogues, long-term treatment with entecavir “provided a high margin of safety” and was not tied to higher rates of liver or nonliver malignancies, the researchers found. The carcinogenicity of entecavir in rodents did not appear to extend to humans. Furthermore, among 5,305 trial participants in China, a sustained virologic response was associated with a clinically and statistically significant reduction in the risk of liver-related HBV disease progression (hazard ratio, 0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.22) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.009-0.113).
The results confirm the appropriateness of long-term entecavir therapy for chronic HBV infection, as recommended by current guidelines, Dr. Hou and associates concluded. However, patients in this trial were relatively young, with a median age of only 39 years. Therefore, the risk of entecavir-associated malignancies in older age cohorts could not be evaluated.
Bristol-Myers Squibb designed the study, performed statistical analyses, and funded the study and manuscript preparation. The Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program provided partial support. Dr. Hou disclosed grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis. Several coinvestigators also disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and to several other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Hou J-L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul 12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.010.
For patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, up to 10 years of treatment with entecavir was safe and produced a superior rate of sustained virologic response, compared with other HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogues in a global randomized clinical trial.
Virologic responses were confirmed and maintained in 80% of entecavir patients and 61% of patients who received other therapies, said Jin-Lin Hou, MD, of Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, China, and associates. Regardless of which treatment patients received, a sustained virologic response was associated with a significantly lower rate of liver-related hepatitis B virus (HBV) disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Rates of serious treatment-related adverse events were 0.2% in the entecavir arm and 0.8% in the nonentecavir arm. Moreover, the primary outcome of time-to-adjudicated clinical outcome events “showed that entecavir treatment, compared with nonentecavir, was not associated with an increased risk of malignant neoplasms, including hepatocellular carcinoma, nonhepatocellular carcinoma malignancies, and overall malignancies,” they wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Entecavir is approved for the treatment of adults with chronic HBV infection, and its long-term use has been linked to the regression of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. In treatment-naive patients, genotypic resistance and virologic breakthrough are rare even after up to 5 years of entecavir therapy. Although human studies have not linked this treatment duration with an increased risk of adverse events, murine studies have identified benign and malignant tumors of the brain, lung, and liver in entecavir-treated mice and rats. “With the exception of lung tumors, which were limited to male mice, rodent tumors occurred only at entecavir exposures [that were] significantly higher than those achieved in human beings with standard approved doses,” the researchers wrote.
For the trial, they assigned more than 12,000 patients with chronic HBV infection to receive long-term treatment with entecavir or investigators’ choice of another HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogue. Patients were from 229 centers in Asia, Europe, and North and South America, and a total of 6,216 received entecavir, while 6,162 received another therapy.
Compared with other HBV nucleoside and nucleotide analogues, long-term treatment with entecavir “provided a high margin of safety” and was not tied to higher rates of liver or nonliver malignancies, the researchers found. The carcinogenicity of entecavir in rodents did not appear to extend to humans. Furthermore, among 5,305 trial participants in China, a sustained virologic response was associated with a clinically and statistically significant reduction in the risk of liver-related HBV disease progression (hazard ratio, 0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.22) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.009-0.113).
The results confirm the appropriateness of long-term entecavir therapy for chronic HBV infection, as recommended by current guidelines, Dr. Hou and associates concluded. However, patients in this trial were relatively young, with a median age of only 39 years. Therefore, the risk of entecavir-associated malignancies in older age cohorts could not be evaluated.
Bristol-Myers Squibb designed the study, performed statistical analyses, and funded the study and manuscript preparation. The Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program provided partial support. Dr. Hou disclosed grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis. Several coinvestigators also disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and to several other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Hou J-L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul 12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.010.
For patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, up to 10 years of treatment with entecavir was safe and produced a superior rate of sustained virologic response, compared with other HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogues in a global randomized clinical trial.
Virologic responses were confirmed and maintained in 80% of entecavir patients and 61% of patients who received other therapies, said Jin-Lin Hou, MD, of Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, China, and associates. Regardless of which treatment patients received, a sustained virologic response was associated with a significantly lower rate of liver-related hepatitis B virus (HBV) disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Rates of serious treatment-related adverse events were 0.2% in the entecavir arm and 0.8% in the nonentecavir arm. Moreover, the primary outcome of time-to-adjudicated clinical outcome events “showed that entecavir treatment, compared with nonentecavir, was not associated with an increased risk of malignant neoplasms, including hepatocellular carcinoma, nonhepatocellular carcinoma malignancies, and overall malignancies,” they wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Entecavir is approved for the treatment of adults with chronic HBV infection, and its long-term use has been linked to the regression of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. In treatment-naive patients, genotypic resistance and virologic breakthrough are rare even after up to 5 years of entecavir therapy. Although human studies have not linked this treatment duration with an increased risk of adverse events, murine studies have identified benign and malignant tumors of the brain, lung, and liver in entecavir-treated mice and rats. “With the exception of lung tumors, which were limited to male mice, rodent tumors occurred only at entecavir exposures [that were] significantly higher than those achieved in human beings with standard approved doses,” the researchers wrote.
For the trial, they assigned more than 12,000 patients with chronic HBV infection to receive long-term treatment with entecavir or investigators’ choice of another HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogue. Patients were from 229 centers in Asia, Europe, and North and South America, and a total of 6,216 received entecavir, while 6,162 received another therapy.
Compared with other HBV nucleoside and nucleotide analogues, long-term treatment with entecavir “provided a high margin of safety” and was not tied to higher rates of liver or nonliver malignancies, the researchers found. The carcinogenicity of entecavir in rodents did not appear to extend to humans. Furthermore, among 5,305 trial participants in China, a sustained virologic response was associated with a clinically and statistically significant reduction in the risk of liver-related HBV disease progression (hazard ratio, 0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.22) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.009-0.113).
The results confirm the appropriateness of long-term entecavir therapy for chronic HBV infection, as recommended by current guidelines, Dr. Hou and associates concluded. However, patients in this trial were relatively young, with a median age of only 39 years. Therefore, the risk of entecavir-associated malignancies in older age cohorts could not be evaluated.
Bristol-Myers Squibb designed the study, performed statistical analyses, and funded the study and manuscript preparation. The Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program provided partial support. Dr. Hou disclosed grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis. Several coinvestigators also disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and to several other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Hou J-L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul 12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.010.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY